Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper

Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![how to prepare an abstract for a research paper “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![how to prepare an abstract for a research paper “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![how to prepare an abstract for a research paper “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write an Abstract (With Examples)

Sarah Oakley

Table of Contents
What is an abstract in a paper, how long should an abstract be, 5 steps for writing an abstract, examples of an abstract, how prowritingaid can help you write an abstract.
If you are writing a scientific research paper or a book proposal, you need to know how to write an abstract, which summarizes the contents of the paper or book.
When researchers are looking for peer-reviewed papers to use in their studies, the first place they will check is the abstract to see if it applies to their work. Therefore, your abstract is one of the most important parts of your entire paper.
In this article, we’ll explain what an abstract is, what it should include, and how to write one.
An abstract is a concise summary of the details within a report. Some abstracts give more details than others, but the main things you’ll be talking about are why you conducted the research, what you did, and what the results show.
When a reader is deciding whether to read your paper completely, they will first look at the abstract. You need to be concise in your abstract and give the reader the most important information so they can determine if they want to read the whole paper.
Remember that an abstract is the last thing you’ll want to write for the research paper because it directly references parts of the report. If you haven’t written the report, you won’t know what to include in your abstract.
If you are writing a paper for a journal or an assignment, the publication or academic institution might have specific formatting rules for how long your abstract should be. However, if they don’t, most abstracts are between 150 and 300 words long.
A short word count means your writing has to be precise and without filler words or phrases. Once you’ve written a first draft, you can always use an editing tool, such as ProWritingAid, to identify areas where you can reduce words and increase readability.
If your abstract is over the word limit, and you’ve edited it but still can’t figure out how to reduce it further, your abstract might include some things that aren’t needed. Here’s a list of three elements you can remove from your abstract:
Discussion : You don’t need to go into detail about the findings of your research because your reader will find your discussion within the paper.
Definition of terms : Your readers are interested the field you are writing about, so they are likely to understand the terms you are using. If not, they can always look them up. Your readers do not expect you to give a definition of terms in your abstract.
References and citations : You can mention there have been studies that support or have inspired your research, but you do not need to give details as the reader will find them in your bibliography.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
If you’ve never written an abstract before, and you’re wondering how to write an abstract, we’ve got some steps for you to follow. It’s best to start with planning your abstract, so we’ve outlined the details you need to include in your plan before you write.
Remember to consider your audience when you’re planning and writing your abstract. They are likely to skim read your abstract, so you want to be sure your abstract delivers all the information they’re expecting to see at key points.
1. What Should an Abstract Include?
Abstracts have a lot of information to cover in a short number of words, so it’s important to know what to include. There are three elements that need to be present in your abstract:
Your context is the background for where your research sits within your field of study. You should briefly mention any previous scientific papers or experiments that have led to your hypothesis and how research develops in those studies.
Your hypothesis is your prediction of what your study will show. As you are writing your abstract after you have conducted your research, you should still include your hypothesis in your abstract because it shows the motivation for your paper.
Throughout your abstract, you also need to include keywords and phrases that will help researchers to find your article in the databases they’re searching. Make sure the keywords are specific to your field of study and the subject you’re reporting on, otherwise your article might not reach the relevant audience.
2. Can You Use First Person in an Abstract?
You might think that first person is too informal for a research paper, but it’s not. Historically, writers of academic reports avoided writing in first person to uphold the formality standards of the time. However, first person is more accepted in research papers in modern times.
If you’re still unsure whether to write in first person for your abstract, refer to any style guide rules imposed by the journal you’re writing for or your teachers if you are writing an assignment.
3. Abstract Structure
Some scientific journals have strict rules on how to structure an abstract, so it’s best to check those first. If you don’t have any style rules to follow, try using the IMRaD structure, which stands for Introduction, Methodology, Results, and Discussion.

Following the IMRaD structure, start with an introduction. The amount of background information you should include depends on your specific research area. Adding a broad overview gives you less room to include other details. Remember to include your hypothesis in this section.
The next part of your abstract should cover your methodology. Try to include the following details if they apply to your study:
What type of research was conducted?
How were the test subjects sampled?
What were the sample sizes?
What was done to each group?
How long was the experiment?
How was data recorded and interpreted?
Following the methodology, include a sentence or two about the results, which is where your reader will determine if your research supports or contradicts their own investigations.
The results are also where most people will want to find out what your outcomes were, even if they are just mildly interested in your research area. You should be specific about all the details but as concise as possible.
The last few sentences are your conclusion. It needs to explain how your findings affect the context and whether your hypothesis was correct. Include the primary take-home message, additional findings of importance, and perspective. Also explain whether there is scope for further research into the subject of your report.
Your conclusion should be honest and give the reader the ultimate message that your research shows. Readers trust the conclusion, so make sure you’re not fabricating the results of your research. Some readers won’t read your entire paper, but this section will tell them if it’s worth them referencing it in their own study.
4. How to Start an Abstract
The first line of your abstract should give your reader the context of your report by providing background information. You can use this sentence to imply the motivation for your research.
You don’t need to use a hook phrase or device in your first sentence to grab the reader’s attention. Your reader will look to establish relevance quickly, so readability and clarity are more important than trying to persuade the reader to read on.
5. How to Format an Abstract
Most abstracts use the same formatting rules, which help the reader identify the abstract so they know where to look for it.
Here’s a list of formatting guidelines for writing an abstract:
Stick to one paragraph
Use block formatting with no indentation at the beginning
Put your abstract straight after the title and acknowledgements pages
Use present or past tense, not future tense
There are two primary types of abstract you could write for your paper—descriptive and informative.
An informative abstract is the most common, and they follow the structure mentioned previously. They are longer than descriptive abstracts because they cover more details.
Descriptive abstracts differ from informative abstracts, as they don’t include as much discussion or detail. The word count for a descriptive abstract is between 50 and 150 words.
Here is an example of an informative abstract:
A growing trend exists for authors to employ a more informal writing style that uses “we” in academic writing to acknowledge one’s stance and engagement. However, few studies have compared the ways in which the first-person pronoun “we” is used in the abstracts and conclusions of empirical papers. To address this lacuna in the literature, this study conducted a systematic corpus analysis of the use of “we” in the abstracts and conclusions of 400 articles collected from eight leading electrical and electronic (EE) engineering journals. The abstracts and conclusions were extracted to form two subcorpora, and an integrated framework was applied to analyze and seek to explain how we-clusters and we-collocations were employed. Results revealed whether authors’ use of first-person pronouns partially depends on a journal policy. The trend of using “we” showed that a yearly increase occurred in the frequency of “we” in EE journal papers, as well as the existence of three “we-use” types in the article conclusions and abstracts: exclusive, inclusive, and ambiguous. Other possible “we-use” alternatives such as “I” and other personal pronouns were used very rarely—if at all—in either section. These findings also suggest that the present tense was used more in article abstracts, but the present perfect tense was the most preferred tense in article conclusions. Both research and pedagogical implications are proffered and critically discussed.
Wang, S., Tseng, W.-T., & Johanson, R. (2021). To We or Not to We: Corpus-Based Research on First-Person Pronoun Use in Abstracts and Conclusions. SAGE Open, 11(2).
Here is an example of a descriptive abstract:
From the 1850s to the present, considerable criminological attention has focused on the development of theoretically-significant systems for classifying crime. This article reviews and attempts to evaluate a number of these efforts, and we conclude that further work on this basic task is needed. The latter part of the article explicates a conceptual foundation for a crime pattern classification system, and offers a preliminary taxonomy of crime.
Farr, K. A., & Gibbons, D. C. (1990). Observations on the Development of Crime Categories. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 34(3), 223–237.
If you want to ensure your abstract is grammatically correct and easy to read, you can use ProWritingAid to edit it. The software integrates with Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and most web browsers, so you can make the most of it wherever you’re writing your paper.
Before you edit with ProWritingAid, make sure the suggestions you are seeing are relevant for your document by changing the document type to “Abstract” within the Academic writing style section.
You can use the Readability report to check your abstract for places to improve the clarity of your writing. Some suggestions might show you where to remove words, which is great if you’re over your word count.
We hope the five steps and examples we’ve provided help you write a great abstract for your research paper.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- How to write and format an APA abstract
APA Abstract (2020) | Formatting, Length, and Keywords
Published on November 6, 2020 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on January 17, 2024.
An APA abstract is a comprehensive summary of your paper in which you briefly address the research problem , hypotheses , methods , results , and implications of your research. It’s placed on a separate page right after the title page and is usually no longer than 250 words.
Most professional papers that are submitted for publication require an abstract. Student papers typically don’t need an abstract, unless instructed otherwise.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to format the abstract, how to write an apa abstract, which keywords to use, frequently asked questions, apa abstract example.
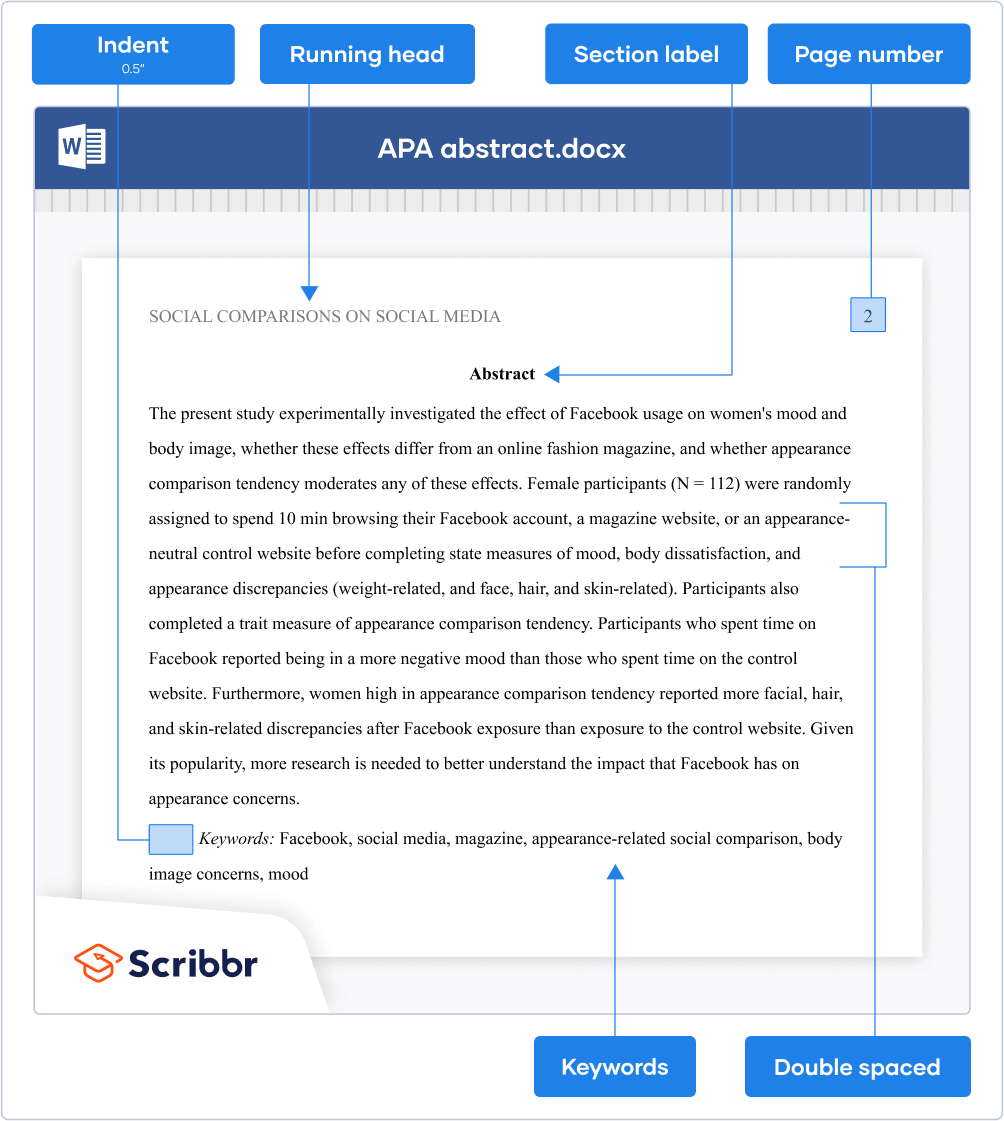
Formatting instructions
Follow these five steps to format your abstract in APA Style:
- Insert a running head (for a professional paper—not needed for a student paper) and page number.
- Set page margins to 1 inch (2.54 cm).
- Write “Abstract” (bold and centered) at the top of the page.
- Do not indent the first line.
- Double-space the text.
- Use a legible font like Times New Roman (12 pt.).
- Limit the length to 250 words.
- Indent the first line 0.5 inches.
- Write the label “Keywords:” (italicized).
- Write keywords in lowercase letters.
- Separate keywords with commas.
- Do not use a period after the keywords.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The abstract is a self-contained piece of text that informs the reader what your research is about. It’s best to write the abstract after you’re finished with the rest of your paper.
The questions below may help structure your abstract. Try answering them in one to three sentences each.
- What is the problem? Outline the objective, research questions , and/or hypotheses .
- What has been done? Explain your research methods .
- What did you discover? Summarize the key findings and conclusions .
- What do the findings mean? Summarize the discussion and recommendations .
Check out our guide on how to write an abstract for more guidance and an annotated example.
Guide: writing an abstract
At the end of the abstract, you may include a few keywords that will be used for indexing if your paper is published on a database. Listing your keywords will help other researchers find your work.
Choosing relevant keywords is essential. Try to identify keywords that address your topic, method, or population. APA recommends including three to five keywords.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of your paper.
An APA abstract is around 150–250 words long. However, always check your target journal’s guidelines and don’t exceed the specified word count.
In an APA Style paper , the abstract is placed on a separate page after the title page (page 2).
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). APA Abstract (2020) | Formatting, Length, and Keywords. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, apa headings and subheadings, apa running head, apa title page (7th edition) | template for students & professionals, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write an Abstract in Research Papers (with Examples)

An abstract in research papers is a keyword-rich summary usually not exceeding 200-350 words. It can be considered the “face” of research papers because it creates an initial impression on the readers. While searching databases (such as PubMed) for research papers, a title is usually the first selection criterion for readers. If the title matches their search criteria, then the readers read the abstract, which sets the tone of the paper. Titles and abstracts are often the only freely available parts of research papers on journal websites. The pdf versions of full articles need to be purchased. Journal reviewers are often provided with only the title and abstract before they agree to review the complete paper. [ 1]
Abstracts in research papers provide readers with a quick insight into what the paper is about to help them decide whether they want to read it further or not. Abstracts are the main selling points of articles and therefore should be carefully drafted, accurately highlighting the important aspects. [ 2]
This article will help you identify the important components and provide tips on how to write an abstract in research papers effectively
What is an Abstract?
An abstract in research papers can be defined as a synopsis of the paper. It should be clear, direct, self-contained, specific, unbiased, and concise. These summaries are published along with the complete research paper and are also submitted to conferences for consideration for presentation.
Abstracts are of four types and journals can follow any of these formats: [ 2]
- Structured
- Unstructured
- Descriptive
- Informative
Structured abstracts are used by most journals because they are more organized and have clear sections, usually including introduction/background; objective; design, settings, and participants (or materials and methods); outcomes and measures; results; and conclusion. These headings may differ based on the journal or the type of paper. Clinical trial abstracts should include the essential items mentioned in the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) guidelines.

Figure 1. Structured abstract example [3]
Unstructured abstracts are common in social science, humanities, and physical science journals. They usually have one paragraph and no specific structure or subheadings. These abstracts are commonly used for research papers that don’t report original work and therefore have a more flexible and narrative style.

Figure 2. Unstructured abstract example [3]
Descriptive abstracts are short (75–150 words) and provide an outline with only the most important points of research papers. They are used for shorter articles such as case reports, reviews, and opinions where space is at a premium, and rarely for original investigations. These abstracts don’t present the results but mainly list the topics covered.
Here’s a sample abstract . [ 4]
“Design of a Radio-Based System for Distribution Automation”
A new survey by the Maryland Public Utilities Commission suggests that utilities have not effectively explained to consumers the benefits of smart meters. The two-year study of 86,000 consumers concludes that the long-term benefits of smart meters will not be realized until consumers understand the benefits of shifting some of their power usage to off-peak hours in response to the data they receive from their meters. The study presents recommendations for utilities and municipal governments to improve customer understanding of how to use the smart meters effectively.
Keywords: smart meters, distribution systems, load, customer attitudes, power consumption, utilities
Informative abstracts (structured or unstructured) give a complete detailed summary, including the main results, of the research paper and may or may not have subsections.

Figure 3. Informative abstract example [5]
Purpose of Abstracts in Research
Abstracts in research have two main purposes—selection and indexing. [ 6,7]
- Selection : Abstracts allow interested readers to quickly decide the relevance of a paper to gauge if they should read it completely.
- Indexing : Most academic journal databases accessed through libraries enable you to search abstracts, allowing for quick retrieval of relevant articles and avoiding unnecessary search results. Therefore, abstracts must necessarily include the keywords that researchers may use to search for articles.
Thus, a well-written, keyword-rich abstract can p ique readers’ interest and curiosity and help them decide whether they want to read the complete paper. It can also direct readers to articles of potential clinical and research interest during an online search.

Contents of Abstracts in Research
Abstracts in research papers summarize the main points of an article and are broadly categorized into four or five sections. Here are some details on how to write an abstract .
Introduction/Background and/or Objectives
This section should provide the following information:
- What is already known about the subject?
- What is not known about the subject or what does the study aim to investigate?
The hypothesis or research question and objectives should be mentioned here. The Background sets the context for the rest of the paper and its length should be short so that the word count could be saved for the Results or other information directly pertaining to the study. The objective should be written in present or past simple tense.
Examples:
The antidepressant efficacy of desvenlafaxine (DV) has been established in 8-week, randomized controlled trials. The present study examined the continued efficacy of DV across 6 months of maintenance treatment . [ 1]
Objective: To describe gastric and breast cancer risk estimates for individuals with CDH1 variants.
Design, Setting, and Participants (or Materials and Methods)
This section should provide information on the processes used and should be written in past simple tense because the process is already completed.
A few important questions to be answered include:
- What was the research design and setting?
- What was the sample size and how were the participants sampled?
- What treatments did the participants receive?
- What were the data collection and data analysis dates?
- What was the primary outcome measure?
Hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated for each cancer type and used to calculate cumulative risks and risks per decade of life up to age 80 years.

This section, written in either present or past simple tense, should be the longest and should describe the main findings of the study. Here’s an example of how descriptive the sentences should be:
Avoid: Response rates differed significantly between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.
Better: The response rate was higher in nondiabetic than in diabetic patients (49% vs 30%, respectively; P<0.01).
This section should include the following information:
- Total number of patients (included, excluded [exclusion criteria])
- Primary and secondary outcomes, expressed in words, and supported by numerical data
- Data on adverse outcomes
Example: [ 8]
In total, 10.9% of students were reported to have favorable study skills. The minimum score was found for preparation for examination domain. Also, a significantly positive correlation was observed between students’ study skills and their Grade Point Average (GPA) of previous term (P=0.001, r=0.269) and satisfaction with study skills (P=0.001, r=0.493).
Conclusions
Here, authors should mention the importance of their findings and also the practical and theoretical implications, which would benefit readers referring to this paper for their own research. Present simple tense should be used here.
Examples: [ 1,8]
The 9.3% prevalence of bipolar spectrum disorders in students at an arts university is substantially higher than general population estimates. These findings strengthen the oft-expressed hypothesis linking creativity with affective psychopathology.
The findings indicated that students’ study skills need to be improved. Given the significant relationship between study skills and GPA, as an index of academic achievement, and satisfaction, it is necessary to promote the students’ study skills. These skills are suggested to be reinforced, with more emphasis on weaker domains.

When to Write an Abstract
In addition to knowing how to write an abstract , you should also know when to write an abstract . It’s best to write abstracts once the paper is completed because this would make it easier for authors to extract relevant parts from every section.
Abstracts are usually required for: [ 7]
- submitting articles to journals
- applying for research grants
- writing book proposals
- completing and submitting dissertations
- submitting proposals for conference papers
Mostly, the author of the entire work writes the abstract (the first author, in works with multiple authors). However, there are professional abstracting services that hire writers to draft abstracts of other people’s work.
How to Write an Abstract (Step-by-Step Process)
Here are some key steps on how to write an abstract in research papers: [ 9]
- Write the abstract after you’ve finished writing your paper.
- Select the major objectives/hypotheses and conclusions from your Introduction and Conclusion sections.
- Select key sentences from your Methods section.
- Identify the major results from the Results section.
- Paraphrase or re-write the sentences selected in steps 2, 3, and 4 in your own words into one or two paragraphs in the following sequence: Introduction/Objective, Methods, Results, and Conclusions. The headings may differ among journals, but the content remains the same.
- Ensure that this draft does not contain: a. new information that is not present in the paper b. undefined abbreviations c. a discussion of previous literature or reference citations d. unnecessary details about the methods used
- Remove all extra information and connect your sentences to ensure that the information flows well, preferably in the following order: purpose; basic study design, methodology and techniques used; major findings; summary of your interpretations, conclusions, and implications. Use section headings for structured abstracts.
- Ensure consistency between the information presented in the abstract and the paper.
- Check to see if the final abstract meets the guidelines of the target journal (word limit, type of abstract, recommended subheadings, etc.) and if all the required information has been included.
Choosing Keywords for Abstracts
Keywords [ 2] are the important and repeatedly used words and phrases in research papers and can help indexers and search engines find papers relevant to your requirements. Easy retrieval would help in reaching a wider audience and eventually gain more citations. In the fields of medicine and health, keywords should preferably be chosen from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list of the US National Library of Medicine because they are used for indexing. These keywords need to be different from the words in the main title (automatically used for indexing) but can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, abstract, and the main text. Keywords should represent the content of your manuscript and be specific to your subject area.
Basic tips for authors [ 10,11]
- Read through your paper and highlight key terms or phrases that are most relevant and frequently used in your field, to ensure familiarity.
- Several journals provide instructions about the length (eg, 3 words in a keyword) and maximum number of keywords allowed and other related rules. Create a list of keywords based on these instructions and include specific phrases containing 2 to 4 words. A longer string of words would yield generic results irrelevant to your field.
- Use abbreviations, acronyms, and initializations if these would be more familiar.
- Search with your keywords to ensure the results fit with your article and assess how helpful they would be to readers.
- Narrow down your keywords to about five to ten, to ensure accuracy.
- Finalize your list based on the maximum number allowed.
Few examples: [ 12]
| Direct observation of nonlinear optics in an isolated carbon nanotube | molecule, optics, lasers, energy lifetime | single-molecule interaction, Kerr effect, carbon nanotube, energy level |
| Region-specific neuronal degeneration after okadaic acid administration | neuron, brain, regional-specific neuronal degeneration, signaling | neurodegenerative diseases; CA1 region, hippocampal; okadaic acid; neurotoxins; MAP kinase signaling system; cell death |
| Increases in levels of sediment transport at former glacial-interglacial transitions | climate change, erosion, plant effects | quaternary climate change, soil erosion, bioturbation |
Important Tips for Writing an Abstract
Here are a few tips on how to write an abstract to ensure that your abstract is complete, concise, and accurate. [ 1,2]
- Write the abstract last.
- Follow journal-specific formatting guidelines or Instructions to Authors strictly to ensure acceptance for publication.
- Proofread the final draft meticulously to avoid grammatical or typographical errors.
- Ensure that the terms or data mentioned in the abstract are consistent with the main text.
- Include appropriate keywords at the end.
Do not include:
- New information
- Text citations to references
- Citations to tables and figures
- Generic statements
- Abbreviations unless necessary, like a trial or study name

Key Takeaways
Here’s a quick snapshot of all the important aspects of how to write an abstract . [2]
- An abstract in research is a summary of the paper and describes only the main aspects. Typically, abstracts are about 200-350 words long.
- Abstracts are of four types—structured, unstructured, descriptive, and informative.
- Abstracts should be simple, clear, concise, independent, and unbiased (present both favorable and adverse outcomes).
- They should adhere to the prescribed journal format, including word limits, section headings, number of keywords, fonts used, etc.
- The terminology should be consistent with the main text.
- Although the section heading names may differ for journals, every abstract should include a background and objective, analysis methods, primary results, and conclusions.
- Nonstandard abbreviations, references, and URLs shouldn’t be included.
- Only relevant and specific keywords should be used to ensure focused searches and higher citation frequency.
- Abstracts should be written last after completing the main paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Do all journals have different guidelines for abstracts?
A1. Yes, all journals have their own specific guidelines for writing abstracts; a few examples are given in the following table. [ 6,13,14,15]
| American Psychological Association | |
| American Society for Microbiology | |
| The Lancet | |
| Journal of the American Medical Association |
Q2. What are the common mistakes to avoid when writing an abstract?
A2. Listed below are a few mistakes that authors may make inadvertently while writing abstracts.
- Copying sentences from the paper verbatim
An abstract is a summary, which should be created by paraphrasing your own work or writing in your own words. Extracting sentences from every section and combining them into one paragraph cannot be considered summarizing.
- Not adhering to the formatting guidelines
Journals have special instructions for writing abstracts, such as word limits and section headings. These should be followed strictly to avoid rejections.
- Not including the right amount of details in every section
Both too little and too much information could discourage readers. For instance, if the Background has very little information, the readers may not get sufficient context to appreciate your research. Similarly, incomplete information in the Methods and a text-heavy Results section without supporting numerical data may affect the credibility of your research.
- Including citations, standard abbreviations, and detailed measurements
Typically, abstracts shouldn’t include these elements—citations, URLs, and abbreviations. Only nonstandard abbreviations are allowed or those that would be more familiar to readers than the expansions.
- Including new information
Abstracts should strictly include only the same information mentioned in the main text. Any new information should first be added to the text and then to the abstract only if necessary or if permitted by the word limit.
- Not including keywords
Keywords are essential for indexing and searching and should be included to increase the frequency of retrieval and citation.
Q3. What is the difference between abstracts in research papers and conference abstracts? [16]
A3. The table summarizes the main differences between research and conference abstracts.
| Context | Concise summary of ongoing or completed research presented at conferences | Summary of full research paper published in a journal |
| Length | Shorter (150-250 words) | Longer (150-350 words) |
| Audience | Diverse conference attendees (both experts & people with general interest) | People or other researchers specifically interested in the subject |
| Focus | Intended to quickly attract interest; provides just enough information to highlight the significance, objectives, and impact; may briefly state methods and results | Deeper insight into the study; more detailed sections on methodology, results, and broader implications |
| Publication venue | Not published independently but included in conference schedules, booklets, etc. | Published with the full research paper in academic journals, conference proceedings, research databases, etc. |
| Citations | Allowed | Not allowed |
Thus, abstracts are essential “trailers” that can market your research to a wide audience. The better and more complete the abstract the more are the chances of your paper being read and cited. By following our checklist and ensuring that all key elements are included, you can create a well-structured abstract that summarizes your paper accurately.
References
- Andrade C. How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation. Indian J Psychiatry . 2011; 53(2):172-175. Accessed June 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136027/
- Tullu MS. Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key. 2019; 13(Suppl 1): S12-S17. Accessed June 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6398294/
- Zawia J. Writing an Academic Paper? Get to know Abstracts vs. Structured Abstracts. Medium. Published October 16, 2023. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://medium.com/@jamala.zawia/writing-an-academic-paper-get-to-know-abstracts-vs-structured-abstracts-11ed86888367
- Markel M and Selber S. Technical Communication, 12 th edition. 2018; pp. 482. Bedford/St Martin’s.
- Abstracts. Arkansas State University. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.astate.edu/a/global-initiatives/online/a-state-online-services/online-writing-center/resources/How%20to%20Write%20an%20Abstract1.pdf
- AMA Manual of Style. 11 th edition. Oxford University Press.
- Writing an Abstract. The University of Melbourne. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://services.unimelb.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/471274/Writing_an_Abstract_Update_051112.pdf
- 10 Good Abstract Examples that will Kickstart Your Brain. Kibin Essay Writing Blog. Published April 5, 2017. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.kibin.com/essay-writing-blog/10-good-abstract-examples/
- A 10-step guide to make your research paper abstract more effective. Editage Insights. Published October 16, 2013. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.editage.com/insights/a-10-step-guide-to-make-your-research-paper-abstract-more-effective
- Using keywords to write your title and abstract. Taylor & Francis Author Services. Accessed June 15, 2024. https://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com/publishing-your-research/writing-your-paper/using-keywords-to-write-title-and-abstract/
- How to choose and use keywords in research papers. Paperpal by Editage blog. Published March 10, 2023. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://paperpal.com/blog/researcher-resources/phd-pointers/how-to-choose-and-use-keywords-in-research-papers
- Title, abstract and keywords. Springer. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://www.springer.com/it/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/writing-a-journal-manuscript/title-abstract-and-keywords/10285522
- Abstract and keywords guide. APA Style, 7 th edition. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/abstract-keywords-guide.pdf
- Abstract guidelines. American Society for Microbiology. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://asm.org/events/asm-microbe/present/abstract-guidelines
- Guidelines for conference abstracts. The Lancet. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://www.thelancet.com/pb/assets/raw/Lancet/pdfs/Abstract_Guidelines_2013.pdf
- Is a conference abstract the same as a paper abstract? Global Conference Alliance, Inc. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://globalconference.ca/is-a-conference-abstract-the-same-as-a-paper-abstract/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
- How to Write a High-Quality Conference Paper
How to Write Dissertation Acknowledgements?
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
Top 7 AI Tools for Research 2024
You may also like, maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a....
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Abstract Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide With Tips & Examples

Table of Contents

Introduction
Abstracts of research papers have always played an essential role in describing your research concisely and clearly to researchers and editors of journals, enticing them to continue reading. However, with the widespread availability of scientific databases, the need to write a convincing abstract is more crucial now than during the time of paper-bound manuscripts.
Abstracts serve to "sell" your research and can be compared with your "executive outline" of a resume or, rather, a formal summary of the critical aspects of your work. Also, it can be the "gist" of your study. Since most educational research is done online, it's a sign that you have a shorter time for impressing your readers, and have more competition from other abstracts that are available to be read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) articulates 12 issues or points considered during the final approval process for conferences & journals and emphasises the importance of writing an abstract that checks all these boxes (12 points). Since it's the only opportunity you have to captivate your readers, you must invest time and effort in creating an abstract that accurately reflects the critical points of your research.
With that in mind, let’s head over to understand and discover the core concept and guidelines to create a substantial abstract. Also, learn how to organise the ideas or plots into an effective abstract that will be awe-inspiring to the readers you want to reach.
What is Abstract? Definition and Overview
The word "Abstract' is derived from Latin abstractus meaning "drawn off." This etymological meaning also applies to art movements as well as music, like abstract expressionism. In this context, it refers to the revealing of the artist's intention.
Based on this, you can determine the meaning of an abstract: A condensed research summary. It must be self-contained and independent of the body of the research. However, it should outline the subject, the strategies used to study the problem, and the methods implemented to attain the outcomes. The specific elements of the study differ based on the area of study; however, together, it must be a succinct summary of the entire research paper.
Abstracts are typically written at the end of the paper, even though it serves as a prologue. In general, the abstract must be in a position to:
- Describe the paper.
- Identify the problem or the issue at hand.
- Explain to the reader the research process, the results you came up with, and what conclusion you've reached using these results.
- Include keywords to guide your strategy and the content.
Furthermore, the abstract you submit should not reflect upon any of the following elements:
- Examine, analyse or defend the paper or your opinion.
- What you want to study, achieve or discover.
- Be redundant or irrelevant.
After reading an abstract, your audience should understand the reason - what the research was about in the first place, what the study has revealed and how it can be utilised or can be used to benefit others. You can understand the importance of abstract by knowing the fact that the abstract is the most frequently read portion of any research paper. In simpler terms, it should contain all the main points of the research paper.
What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
Abstracts are typically an essential requirement for research papers; however, it's not an obligation to preserve traditional reasons without any purpose. Abstracts allow readers to scan the text to determine whether it is relevant to their research or studies. The abstract allows other researchers to decide if your research paper can provide them with some additional information. A good abstract paves the interest of the audience to pore through your entire paper to find the content or context they're searching for.
Abstract writing is essential for indexing, as well. The Digital Repository of academic papers makes use of abstracts to index the entire content of academic research papers. Like meta descriptions in the regular Google outcomes, abstracts must include keywords that help researchers locate what they seek.
Types of Abstract
Informative and Descriptive are two kinds of abstracts often used in scientific writing.
A descriptive abstract gives readers an outline of the author's main points in their study. The reader can determine if they want to stick to the research work, based on their interest in the topic. An abstract that is descriptive is similar to the contents table of books, however, the format of an abstract depicts complete sentences encapsulated in one paragraph. It is unfortunate that the abstract can't be used as a substitute for reading a piece of writing because it's just an overview, which omits readers from getting an entire view. Also, it cannot be a way to fill in the gaps the reader may have after reading this kind of abstract since it does not contain crucial information needed to evaluate the article.
To conclude, a descriptive abstract is:
- A simple summary of the task, just summarises the work, but some researchers think it is much more of an outline
- Typically, the length is approximately 100 words. It is too short when compared to an informative abstract.
- A brief explanation but doesn't provide the reader with the complete information they need;
- An overview that omits conclusions and results
An informative abstract is a comprehensive outline of the research. There are times when people rely on the abstract as an information source. And the reason is why it is crucial to provide entire data of particular research. A well-written, informative abstract could be a good substitute for the remainder of the paper on its own.
A well-written abstract typically follows a particular style. The author begins by providing the identifying information, backed by citations and other identifiers of the papers. Then, the major elements are summarised to make the reader aware of the study. It is followed by the methodology and all-important findings from the study. The conclusion then presents study results and ends the abstract with a comprehensive summary.
In a nutshell, an informative abstract:
- Has a length that can vary, based on the subject, but is not longer than 300 words.
- Contains all the content-like methods and intentions
- Offers evidence and possible recommendations.
Informative Abstracts are more frequent than descriptive abstracts because of their extensive content and linkage to the topic specifically. You should select different types of abstracts to papers based on their length: informative abstracts for extended and more complex abstracts and descriptive ones for simpler and shorter research papers.
What are the Characteristics of a Good Abstract?
- A good abstract clearly defines the goals and purposes of the study.
- It should clearly describe the research methodology with a primary focus on data gathering, processing, and subsequent analysis.
- A good abstract should provide specific research findings.
- It presents the principal conclusions of the systematic study.
- It should be concise, clear, and relevant to the field of study.
- A well-designed abstract should be unifying and coherent.
- It is easy to grasp and free of technical jargon.
- It is written impartially and objectively.
What are the various sections of an ideal Abstract?
By now, you must have gained some concrete idea of the essential elements that your abstract needs to convey . Accordingly, the information is broken down into six key sections of the abstract, which include:
An Introduction or Background
Research methodology, objectives and goals, limitations.
Let's go over them in detail.
The introduction, also known as background, is the most concise part of your abstract. Ideally, it comprises a couple of sentences. Some researchers only write one sentence to introduce their abstract. The idea behind this is to guide readers through the key factors that led to your study.
It's understandable that this information might seem difficult to explain in a couple of sentences. For example, think about the following two questions like the background of your study:
- What is currently available about the subject with respect to the paper being discussed?
- What isn't understood about this issue? (This is the subject of your research)
While writing the abstract’s introduction, make sure that it is not lengthy. Because if it crosses the word limit, it may eat up the words meant to be used for providing other key information.
Research methodology is where you describe the theories and techniques you used in your research. It is recommended that you describe what you have done and the method you used to get your thorough investigation results. Certainly, it is the second-longest paragraph in the abstract.
In the research methodology section, it is essential to mention the kind of research you conducted; for instance, qualitative research or quantitative research (this will guide your research methodology too) . If you've conducted quantitative research, your abstract should contain information like the sample size, data collection method, sampling techniques, and duration of the study. Likewise, your abstract should reflect observational data, opinions, questionnaires (especially the non-numerical data) if you work on qualitative research.
The research objectives and goals speak about what you intend to accomplish with your research. The majority of research projects focus on the long-term effects of a project, and the goals focus on the immediate, short-term outcomes of the research. It is possible to summarise both in just multiple sentences.
In stating your objectives and goals, you give readers a picture of the scope of the study, its depth and the direction your research ultimately follows. Your readers can evaluate the results of your research against the goals and stated objectives to determine if you have achieved the goal of your research.
In the end, your readers are more attracted by the results you've obtained through your study. Therefore, you must take the time to explain each relevant result and explain how they impact your research. The results section exists as the longest in your abstract, and nothing should diminish its reach or quality.
One of the most important things you should adhere to is to spell out details and figures on the results of your research.
Instead of making a vague assertion such as, "We noticed that response rates varied greatly between respondents with high incomes and those with low incomes", Try these: "The response rate was higher for high-income respondents than those with lower incomes (59 30 percent vs. 30 percent in both cases; P<0.01)."
You're likely to encounter certain obstacles during your research. It could have been during data collection or even during conducting the sample . Whatever the issue, it's essential to inform your readers about them and their effects on the research.
Research limitations offer an opportunity to suggest further and deep research. If, for instance, you were forced to change for convenient sampling and snowball samples because of difficulties in reaching well-suited research participants, then you should mention this reason when you write your research abstract. In addition, a lack of prior studies on the subject could hinder your research.
Your conclusion should include the same number of sentences to wrap the abstract as the introduction. The majority of researchers offer an idea of the consequences of their research in this case.
Your conclusion should include three essential components:
- A significant take-home message.
- Corresponding important findings.
- The Interpretation.
Even though the conclusion of your abstract needs to be brief, it can have an enormous influence on the way that readers view your research. Therefore, make use of this section to reinforce the central message from your research. Be sure that your statements reflect the actual results and the methods you used to conduct your research.
Good Abstract Examples
Abstract example #1.
Children’s consumption behavior in response to food product placements in movies.
The abstract:
"Almost all research into the effects of brand placements on children has focused on the brand's attitudes or behavior intentions. Based on the significant differences between attitudes and behavioral intentions on one hand and actual behavior on the other hand, this study examines the impact of placements by brands on children's eating habits. Children aged 6-14 years old were shown an excerpt from the popular film Alvin and the Chipmunks and were shown places for the item Cheese Balls. Three different versions were developed with no placements, one with moderately frequent placements and the third with the highest frequency of placement. The results revealed that exposure to high-frequency places had a profound effect on snack consumption, however, there was no impact on consumer attitudes towards brands or products. The effects were not dependent on the age of the children. These findings are of major importance to researchers studying consumer behavior as well as nutrition experts as well as policy regulators."
Abstract Example #2
Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. The abstract:
"The research conducted in this study investigated the effects of Facebook use on women's moods and body image if the effects are different from an internet-based fashion journal and if the appearance comparison tendencies moderate one or more of these effects. Participants who were female ( N = 112) were randomly allocated to spend 10 minutes exploring their Facebook account or a magazine's website or an appearance neutral control website prior to completing state assessments of body dissatisfaction, mood, and differences in appearance (weight-related and facial hair, face, and skin). Participants also completed a test of the tendency to compare appearances. The participants who used Facebook were reported to be more depressed than those who stayed on the control site. In addition, women who have the tendency to compare appearances reported more facial, hair and skin-related issues following Facebook exposure than when they were exposed to the control site. Due to its popularity it is imperative to conduct more research to understand the effect that Facebook affects the way people view themselves."
Abstract Example #3
The Relationship Between Cell Phone Use and Academic Performance in a Sample of U.S. College Students
"The cellphone is always present on campuses of colleges and is often utilised in situations in which learning takes place. The study examined the connection between the use of cell phones and the actual grades point average (GPA) after adjusting for predictors that are known to be a factor. In the end 536 students in the undergraduate program from 82 self-reported majors of an enormous, public institution were studied. Hierarchical analysis ( R 2 = .449) showed that use of mobile phones is significantly ( p < .001) and negative (b equal to -.164) connected to the actual college GPA, after taking into account factors such as demographics, self-efficacy in self-regulated learning, self-efficacy to improve academic performance, and the actual high school GPA that were all important predictors ( p < .05). Therefore, after adjusting for other known predictors increasing cell phone usage was associated with lower academic performance. While more research is required to determine the mechanisms behind these results, they suggest the need to educate teachers and students to the possible academic risks that are associated with high-frequency mobile phone usage."
Quick tips on writing a good abstract
There exists a common dilemma among early age researchers whether to write the abstract at first or last? However, it's recommended to compose your abstract when you've completed the research since you'll have all the information to give to your readers. You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later.
If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it:
1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract
Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract. Divide it into sections and draw the primary and supporting elements in each one. You can include keywords and a few sentences that convey the essence of your message.
2. Review Other Abstracts
Abstracts are among the most frequently used research documents, and thousands of them were written in the past. Therefore, prior to writing yours, take a look at some examples from other abstracts. There are plenty of examples of abstracts for dissertations in the dissertation and thesis databases.
3. Avoid Jargon To the Maximum
When you write your abstract, focus on simplicity over formality. You should write in simple language, and avoid excessive filler words or ambiguous sentences. Keep in mind that your abstract must be readable to those who aren't acquainted with your subject.
4. Focus on Your Research
It's a given fact that the abstract you write should be about your research and the findings you've made. It is not the right time to mention secondary and primary data sources unless it's absolutely required.
Conclusion: How to Structure an Interesting Abstract?
Abstracts are a short outline of your essay. However, it's among the most important, if not the most important. The process of writing an abstract is not straightforward. A few early-age researchers tend to begin by writing it, thinking they are doing it to "tease" the next step (the document itself). However, it is better to treat it as a spoiler.
The simple, concise style of the abstract lends itself to a well-written and well-investigated study. If your research paper doesn't provide definitive results, or the goal of your research is questioned, so will the abstract. Thus, only write your abstract after witnessing your findings and put your findings in the context of a larger scenario.
The process of writing an abstract can be daunting, but with these guidelines, you will succeed. The most efficient method of writing an excellent abstract is to centre the primary points of your abstract, including the research question and goals methods, as well as key results.
Interested in learning more about dedicated research solutions? Go to the SciSpace product page to find out how our suite of products can help you simplify your research workflows so you can focus on advancing science.

The best-in-class solution is equipped with features such as literature search and discovery, profile management, research writing and formatting, and so much more.
But before you go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write an Abstract

Expedite peer review, increase search-ability, and set the tone for your study
The abstract is your chance to let your readers know what they can expect from your article. Learn how to write a clear, and concise abstract that will keep your audience reading.
How your abstract impacts editorial evaluation and future readership
After the title , the abstract is the second-most-read part of your article. A good abstract can help to expedite peer review and, if your article is accepted for publication, it’s an important tool for readers to find and evaluate your work. Editors use your abstract when they first assess your article. Prospective reviewers see it when they decide whether to accept an invitation to review. Once published, the abstract gets indexed in PubMed and Google Scholar , as well as library systems and other popular databases. Like the title, your abstract influences keyword search results. Readers will use it to decide whether to read the rest of your article. Other researchers will use it to evaluate your work for inclusion in systematic reviews and meta-analysis. It should be a concise standalone piece that accurately represents your research.
What to include in an abstract
The main challenge you’ll face when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND fitting in all the information you need. Depending on your subject area the journal may require a structured abstract following specific headings. A structured abstract helps your readers understand your study more easily. If your journal doesn’t require a structured abstract it’s still a good idea to follow a similar format, just present the abstract as one paragraph without headings.
Background or Introduction – What is currently known? Start with a brief, 2 or 3 sentence, introduction to the research area.
Objectives or Aims – What is the study and why did you do it? Clearly state the research question you’re trying to answer.
Methods – What did you do? Explain what you did and how you did it. Include important information about your methods, but avoid the low-level specifics. Some disciplines have specific requirements for abstract methods.
- CONSORT for randomized trials.
- STROBE for observational studies
- PRISMA for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Results – What did you find? Briefly give the key findings of your study. Include key numeric data (including confidence intervals or p values), where possible.
Conclusions – What did you conclude? Tell the reader why your findings matter, and what this could mean for the ‘bigger picture’ of this area of research.
Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND convering all the information you need to.

- Keep it concise and to the point. Most journals have a maximum word count, so check guidelines before you write the abstract to save time editing it later.
- Write for your audience. Are they specialists in your specific field? Are they cross-disciplinary? Are they non-specialists? If you’re writing for a general audience, or your research could be of interest to the public keep your language as straightforward as possible. If you’re writing in English, do remember that not all of your readers will necessarily be native English speakers.
- Focus on key results, conclusions and take home messages.
- Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary.
- Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings.
- Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar.
- Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors. These kind of errors can give potential reviewers the impression that your research isn’t sound, and can make it easier to find reviewers who accept the invitation to review your manuscript. Your abstract should be a taste of what is to come in the rest of your article.

Don’t
- Sensationalize your research.
- Speculate about where this research might lead in the future.
- Use abbreviations or acronyms (unless absolutely necessary or unless they’re widely known, eg. DNA).
- Repeat yourself unnecessarily, eg. “Methods: We used X technique. Results: Using X technique, we found…”
- Contradict anything in the rest of your manuscript.
- Include content that isn’t also covered in the main manuscript.
- Include citations or references.
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Abstract
Research Paper Abstract is a brief summary of a research pape r that describes the study’s purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions . It is often the first section of the paper that readers encounter, and its purpose is to provide a concise and accurate overview of the paper’s content. The typical length of an abstract is usually around 150-250 words, and it should be written in a concise and clear manner.
Research Paper Abstract Structure
The structure of a research paper abstract usually includes the following elements:
- Background or Introduction: Briefly describe the problem or research question that the study addresses.
- Methods : Explain the methodology used to conduct the study, including the participants, materials, and procedures.
- Results : Summarize the main findings of the study, including statistical analyses and key outcomes.
- Conclusions : Discuss the implications of the study’s findings and their significance for the field, as well as any limitations or future directions for research.
- Keywords : List a few keywords that describe the main topics or themes of the research.
How to Write Research Paper Abstract
Here are the steps to follow when writing a research paper abstract:
- Start by reading your paper: Before you write an abstract, you should have a complete understanding of your paper. Read through the paper carefully, making sure you understand the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the key components : Identify the key components of your paper, such as the research question, methods used, results obtained, and conclusion reached.
- Write a draft: Write a draft of your abstract, using concise and clear language. Make sure to include all the important information, but keep it short and to the point. A good rule of thumb is to keep your abstract between 150-250 words.
- Use clear and concise language : Use clear and concise language to explain the purpose of your study, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn.
- Emphasize your findings: Emphasize your findings in the abstract, highlighting the key results and the significance of your study.
- Revise and edit: Once you have a draft, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free from errors.
- Check the formatting: Finally, check the formatting of your abstract to make sure it meets the requirements of the journal or conference where you plan to submit it.
Research Paper Abstract Examples
Research Paper Abstract Examples could be following:
Title : “The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Treating Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This meta-analysis examines the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating anxiety disorders. Through the analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials, we found that CBT is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders, with large effect sizes across a range of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Our findings support the use of CBT as a first-line treatment for anxiety disorders and highlight the importance of further research to identify the mechanisms underlying its effectiveness.
Title : “Exploring the Role of Parental Involvement in Children’s Education: A Qualitative Study”
Abstract : This qualitative study explores the role of parental involvement in children’s education. Through in-depth interviews with 20 parents of children in elementary school, we found that parental involvement takes many forms, including volunteering in the classroom, helping with homework, and communicating with teachers. We also found that parental involvement is influenced by a range of factors, including parent and child characteristics, school culture, and socio-economic status. Our findings suggest that schools and educators should prioritize building strong partnerships with parents to support children’s academic success.
Title : “The Impact of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This paper presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of the existing literature on the impact of exercise on cognitive function in older adults. Through the analysis of 25 randomized controlled trials, we found that exercise is associated with significant improvements in cognitive function, particularly in the domains of executive function and attention. Our findings highlight the potential of exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to support cognitive health in older adults.
When to Write Research Paper Abstract
The abstract of a research paper should typically be written after you have completed the main body of the paper. This is because the abstract is intended to provide a brief summary of the key points and findings of the research, and you can’t do that until you have completed the research and written about it in detail.
Once you have completed your research paper, you can begin writing your abstract. It is important to remember that the abstract should be a concise summary of your research paper, and should be written in a way that is easy to understand for readers who may not have expertise in your specific area of research.
Purpose of Research Paper Abstract
The purpose of a research paper abstract is to provide a concise summary of the key points and findings of a research paper. It is typically a brief paragraph or two that appears at the beginning of the paper, before the introduction, and is intended to give readers a quick overview of the paper’s content.
The abstract should include a brief statement of the research problem, the methods used to investigate the problem, the key results and findings, and the main conclusions and implications of the research. It should be written in a clear and concise manner, avoiding jargon and technical language, and should be understandable to a broad audience.
The abstract serves as a way to quickly and easily communicate the main points of a research paper to potential readers, such as academics, researchers, and students, who may be looking for information on a particular topic. It can also help researchers determine whether a paper is relevant to their own research interests and whether they should read the full paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step...

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write an abstract

What is an abstract?
General format of an abstract, the content of an abstract, abstract example, abstract style guides, frequently asked questions about writing an abstract, related articles.
An abstract is a summary of the main contents of a paper.
The abstract is the first glimpse that readers get of the content of a research paper. It can influence the popularity of a paper, as a well-written one will attract readers, and a poorly-written one will drive them away.
➡️ Different types of papers may require distinct abstract styles. Visit our guide on the different types of research papers to learn more.
Tip: Always wait until you’ve written your entire paper before you write the abstract.
Before you actually start writing an abstract, make sure to follow these steps:
- Read other papers : find papers with similar topics, or similar methodologies, simply to have an idea of how others have written their abstracts. Notice which points they decided to include, and how in depth they described them.
- Double check the journal requirements : always make sure to review the journal guidelines to format your paper accordingly. Usually, they also specify abstract's formats.
- Write the abstract after you finish writing the paper : you can only write an abstract once you finish writing the whole paper. This way you can include all important aspects, such as scope, methodology, and conclusion.
➡️ Read more about what is a research methodology?
The general format of an abstract includes the following features:
- Between 150-300 words .
- An independent page , after the title page and before the table of contents.
- Concise summary including the aim of the research, methodology , and conclusion .
- Keywords describing the content.
As mentioned before, an abstract is a text that summarizes the main points of a research. Here is a break down of each element that should be included in an abstract:
- Purpose : every abstract should start by describing the main purpose or aim of the research.
- Methods : as a second point, the methodology carried out should be explained.
- Results : then, a concise summary of the results should be included.
- Conclusion : finally, a short outline of the general outcome of the research should be given.
- Keywords : along with the abstract, specific words and phrases related to the topics discussed in the research should be added. These words are usually around five, but the number can vary depending on the journal's guidelines.
This abstract, taken from ScienceDirect , illustrates the ideal structure of an abstract. It has 155 words, it's concise, and it clearly shows the division of elements necessary to write a successful abstract.
This paper explores the implicit assumption in the growing body of literature that social media usage is fundamentally different in business-to-business (B2B) companies than in the extant business-to-consumer (B2C) literature. Sashi's (2012) customer engagement cycle is utilized to compare organizational practices in relation to social media marketing in B2B, B2C, Mixed B2B/B2C and B2B2C business models. Utilizing 449 responses to an exploratory panel based survey instrument, we clearly identify differences in social media usage and its perceived importance as a communications channel. In particular we identify distinct differences in the relationship between social media importance and the perceived effectiveness of social media marketing across business models. Our results indicate that B2B social media usage is distinct from B2C, Mixed and B2B2C business model approaches. Specifically B2B organizational members perceive social media to have a lower overall effectiveness as a channel and identify it as less important for relationship oriented usage than other business models.
The exact format of an abstract depends on the citation style you implement. Whether it’s a well-known style (like APA, IEEE, etc.) or a journal's style, each format has its own guidelines, so make sure you know which style you are using before writing your abstract.
APA is one of the most commonly used styles to format an abstract. Therefore, we created a guide with exact instructions on how to write an abstract in APA style, and a template to download:
📕 APA abstract page: format and template
Additionally, you will find below an IEEE and ASA abstract guide by Purdue Online Writing Lab :
📗 IEEE General Format - Abstract
📘 ASA Manuscript Formatting - Abstract
No. You should always write an abstract once you finish writing the whole paper. This way you can include all important aspects of the paper, such as scope, methodology, and conclusion.
The length of an abstract depends on the formatting style of the paper. For example, APA style calls for 150 to 250 words. Generally, you need between 150-300 words.
No. An abstract has an independent section after the title page and before the table of contents, and should not be included in the table of contents.
Take a look at APA abstract page: format and template for exact details on how to format an abstract in APA style.
You can access any paper through Google Scholar or any other search engine; pick a paper and read the abstract. Abstracts are always freely available to read.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
Published on 1 March 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022 by Eoghan Ryan.
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a dissertation or research paper ). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
- Introduction
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis , include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Abstract example, when to write an abstract, step 1: introduction, step 2: methods, step 3: results, step 4: discussion, tips for writing an abstract, frequently asked questions about abstracts.
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the UK during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your topic, but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialised terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyse,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here — the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Next, summarise the main research results . This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research : what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalisability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style , have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review —try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases .
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarise the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services .
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format .
Checklist: Abstract
The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page.
The abstract appears after the title page and acknowledgements and before the table of contents .
I have clearly stated my research problem and objectives.
I have briefly described my methodology .
I have summarized the most important results .
I have stated my main conclusions .
I have mentioned any important limitations and recommendations.
The abstract can be understood by someone without prior knowledge of the topic.
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarises the contents of your paper.
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 150–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis or paper.
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 10 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation title page.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper | Examples
What is a research paper abstract?
Research paper abstracts summarize your study quickly and succinctly to journal editors and researchers and prompt them to read further. But with the ubiquity of online publication databases, writing a compelling abstract is even more important today than it was in the days of bound paper manuscripts.
Abstracts exist to “sell” your work, and they could thus be compared to the “executive summary” of a business resume: an official briefing on what is most important about your research. Or the “gist” of your research. With the majority of academic transactions being conducted online, this means that you have even less time to impress readers–and increased competition in terms of other abstracts out there to read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) notes that there are 12 questions or “points” considered in the selection process for journals and conferences and stresses the importance of having an abstract that ticks all of these boxes. Because it is often the ONLY chance you have to convince readers to keep reading, it is important that you spend time and energy crafting an abstract that faithfully represents the central parts of your study and captivates your audience.
With that in mind, follow these suggestions when structuring and writing your abstract, and learn how exactly to put these ideas into a solid abstract that will captivate your target readers.
Before Writing Your Abstract
How long should an abstract be.
All abstracts are written with the same essential objective: to give a summary of your study. But there are two basic styles of abstract: descriptive and informative . Here is a brief delineation of the two:
| Around 100-200 words (or shorter) in length; indicates the type of information found in the paper; briefly explains the background, purpose, and objective of the paper but omits the results, often the methods, and sometimes also the conclusion | |
| One paragraph to one page in length; a truncated version of your paper that summarizes every aspect of the study, including the results; acts as a “surrogate” for the research itself, standing in for the larger paper |
Of the two types of abstracts, informative abstracts are much more common, and they are widely used for submission to journals and conferences. Informative abstracts apply to lengthier and more technical research and are common in the sciences, engineering, and psychology, while descriptive abstracts are more likely used in humanities and social science papers. The best method of determining which abstract type you need to use is to follow the instructions for journal submissions and to read as many other published articles in those journals as possible.
Research Abstract Guidelines and Requirements
As any article about research writing will tell you, authors must always closely follow the specific guidelines and requirements indicated in the Guide for Authors section of their target journal’s website. The same kind of adherence to conventions should be applied to journal publications, for consideration at a conference, and even when completing a class assignment.
Each publisher has particular demands when it comes to formatting and structure. Here are some common questions addressed in the journal guidelines:
- Is there a maximum or minimum word/character length?
- What are the style and formatting requirements?
- What is the appropriate abstract type?
- Are there any specific content or organization rules that apply?
There are of course other rules to consider when composing a research paper abstract. But if you follow the stated rules the first time you submit your manuscript, you can avoid your work being thrown in the “circular file” right off the bat.
Identify Your Target Readership
The main purpose of your abstract is to lead researchers to the full text of your research paper. In scientific journals, abstracts let readers decide whether the research discussed is relevant to their own interests or study. Abstracts also help readers understand your main argument quickly. Consider these questions as you write your abstract:
- Are other academics in your field the main target of your study?
- Will your study perhaps be useful to members of the general public?
- Do your study results include the wider implications presented in the abstract?
Outlining and Writing Your Abstract
What to include in an abstract.
Just as your research paper title should cover as much ground as possible in a few short words, your abstract must cover all parts of your study in order to fully explain your paper and research. Because it must accomplish this task in the space of only a few hundred words, it is important not to include ambiguous references or phrases that will confuse the reader or mislead them about the content and objectives of your research. Follow these dos and don’ts when it comes to what kind of writing to include:
- Avoid acronyms or abbreviations since these will need to be explained in order to make sense to the reader, which takes up valuable abstract space. Instead, explain these terms in the Introduction section of the main text.
- Only use references to people or other works if they are well-known. Otherwise, avoid referencing anything outside of your study in the abstract.
- Never include tables, figures, sources, or long quotations in your abstract; you will have plenty of time to present and refer to these in the body of your paper.
Use keywords in your abstract to focus your topic
A vital search tool is the research paper keywords section, which lists the most relevant terms directly underneath the abstract. Think of these keywords as the “tubes” that readers will seek and enter—via queries on databases and search engines—to ultimately land at their destination, which is your paper. Your abstract keywords should thus be words that are commonly used in searches but should also be highly relevant to your work and found in the text of your abstract. Include 5 to 10 important words or short phrases central to your research in both the abstract and the keywords section.
For example, if you are writing a paper on the prevalence of obesity among lower classes that crosses international boundaries, you should include terms like “obesity,” “prevalence,” “international,” “lower classes,” and “cross-cultural.” These are terms that should net a wide array of people interested in your topic of study. Look at our nine rules for choosing keywords for your research paper if you need more input on this.
Research Paper Abstract Structure
As mentioned above, the abstract (especially the informative abstract) acts as a surrogate or synopsis of your research paper, doing almost as much work as the thousands of words that follow it in the body of the main text. In the hard sciences and most social sciences, the abstract includes the following sections and organizational schema.
Each section is quite compact—only a single sentence or two, although there is room for expansion if one element or statement is particularly interesting or compelling. As the abstract is almost always one long paragraph, the individual sections should naturally merge into one another to create a holistic effect. Use the following as a checklist to ensure that you have included all of the necessary content in your abstract.

1) Identify your purpose and motivation
So your research is about rabies in Brazilian squirrels. Why is this important? You should start your abstract by explaining why people should care about this study—why is it significant to your field and perhaps to the wider world? And what is the exact purpose of your study; what are you trying to achieve? Start by answering the following questions:
- What made you decide to do this study or project?
- Why is this study important to your field or to the lay reader?
- Why should someone read your entire article?
In summary, the first section of your abstract should include the importance of the research and its impact on related research fields or on the wider scientific domain.
2) Explain the research problem you are addressing
Stating the research problem that your study addresses is the corollary to why your specific study is important and necessary. For instance, even if the issue of “rabies in Brazilian squirrels” is important, what is the problem—the “missing piece of the puzzle”—that your study helps resolve?
You can combine the problem with the motivation section, but from a perspective of organization and clarity, it is best to separate the two. Here are some precise questions to address:
- What is your research trying to better understand or what problem is it trying to solve?
- What is the scope of your study—does it try to explain something general or specific?
- What is your central claim or argument?
3) Discuss your research approach
Your specific study approach is detailed in the Methods and Materials section . You have already established the importance of the research, your motivation for studying this issue, and the specific problem your paper addresses. Now you need to discuss how you solved or made progress on this problem—how you conducted your research. If your study includes your own work or that of your team, describe that here. If in your paper you reviewed the work of others, explain this here. Did you use analytic models? A simulation? A double-blind study? A case study? You are basically showing the reader the internal engine of your research machine and how it functioned in the study. Be sure to:
- Detail your research—include methods/type of the study, your variables, and the extent of the work
- Briefly present evidence to support your claim
- Highlight your most important sources
4) Briefly summarize your results
Here you will give an overview of the outcome of your study. Avoid using too many vague qualitative terms (e.g, “very,” “small,” or “tremendous”) and try to use at least some quantitative terms (i.e., percentages, figures, numbers). Save your qualitative language for the conclusion statement. Answer questions like these:
- What did your study yield in concrete terms (e.g., trends, figures, correlation between phenomena)?
- How did your results compare to your hypothesis? Was the study successful?
- Where there any highly unexpected outcomes or were they all largely predicted?
5) State your conclusion
In the last section of your abstract, you will give a statement about the implications and limitations of the study . Be sure to connect this statement closely to your results and not the area of study in general. Are the results of this study going to shake up the scientific world? Will they impact how people see “Brazilian squirrels”? Or are the implications minor? Try not to boast about your study or present its impact as too far-reaching, as researchers and journals will tend to be skeptical of bold claims in scientific papers. Answer one of these questions:
- What are the exact effects of these results on my field? On the wider world?
- What other kind of study would yield further solutions to problems?
- What other information is needed to expand knowledge in this area?
After Completing the First Draft of Your Abstract
Revise your abstract.
The abstract, like any piece of academic writing, should be revised before being considered complete. Check it for grammatical and spelling errors and make sure it is formatted properly.
Get feedback from a peer
Getting a fresh set of eyes to review your abstract is a great way to find out whether you’ve summarized your research well. Find a reader who understands research papers but is not an expert in this field or is not affiliated with your study. Ask your reader to summarize what your study is about (including all key points of each section). This should tell you if you have communicated your key points clearly.
In addition to research peers, consider consulting with a professor or even a specialist or generalist writing center consultant about your abstract. Use any resource that helps you see your work from another perspective.
Consider getting professional editing and proofreading
While peer feedback is quite important to ensure the effectiveness of your abstract content, it may be a good idea to find an academic editor to fix mistakes in grammar, spelling, mechanics, style, or formatting. The presence of basic errors in the abstract may not affect your content, but it might dissuade someone from reading your entire study. Wordvice provides English editing services that both correct objective errors and enhance the readability and impact of your work.
Additional Abstract Rules and Guidelines
Write your abstract after completing your paper.
Although the abstract goes at the beginning of your manuscript, it does not merely introduce your research topic (that is the job of the title), but rather summarizes your entire paper. Writing the abstract last will ensure that it is complete and consistent with the findings and statements in your paper.
Keep your content in the correct order
Both questions and answers should be organized in a standard and familiar way to make the content easier for readers to absorb. Ideally, it should mimic the overall format of your essay and the classic “introduction,” “body,” and “conclusion” form, even if the parts are not neatly divided as such.
Write the abstract from scratch
Because the abstract is a self-contained piece of writing viewed separately from the body of the paper, you should write it separately as well. Never copy and paste direct quotes from the paper and avoid paraphrasing sentences in the paper. Using new vocabulary and phrases will keep your abstract interesting and free of redundancies while conserving space.
Don’t include too many details in the abstract
Again, the density of your abstract makes it incompatible with including specific points other than possibly names or locations. You can make references to terms, but do not explain or define them in the abstract. Try to strike a balance between being specific to your study and presenting a relatively broad overview of your work.
Wordvice Resources
If you think your abstract is fine now but you need input on abstract writing or require English editing services (including paper editing ), then head over to the Wordvice academic resources page, where you will find many more articles, for example on writing the Results , Methods , and Discussion sections of your manuscript, on choosing a title for your paper , or on how to finalize your journal submission with a strong cover letter .
How to Write an Abstract
- Research Process
Abstracts are the first thing people read when they come across your manuscript on online databases. It's also a deciding factor in peer reviews. Do not overlook its importance.
Updated on March 24, 2022

You've finished your entire paper. All those hours put into your research have finally paid off. Research writing can be tough .
But hold on; you're not quite finished yet. You forgot to write your abstract!
The abstract can sometimes be overlooked, but that does not mean it's unimportant. In fact, some researchers argue that the abstract is the most important part of your manuscript. It's the first thing people read when they come across your manuscript on online databases. Depending on how well written it is, it could also be the first and last thing your audience reads.
It's also what publications and journals use to determine whether they want to publish your research. Continue reading to learn how to write an abstract and how AJE can help you with your writing.
What is an abstract?
An abstract is a concise summary of the major findings in your research paper. It is usually found at the beginning of your research paper. A good abstract should be able to give the average lay reader a strong sense of the main findings within your full-text paper.
Abstracts are typically one paragraph depending on how you decide to structure it. Your target publication could have specific guidelines that determine the structure of your abstract. However, all abstracts have the commonality of being brief summaries of your longer research.
Types of abstracts
Informative abstracts.
A good informative abstract acts as a thorough summary for your full paper. It should be a structured abstract. It includes sections for the introduction, methods, results, discussion and conclusion. Each section should only be a couple sentences each. The total number of words should typically be around 250, but they can be longer, too.
Informative abstracts are typically meant for psychology, science, and engineering papers.
Components of an informative abstract
Introduction.
The introduction should only be one or two sentences. This is where you state your thesis and why your research is important. The introduction should state:
- Your paper's purpose
- The problems your research solves
- Historical references
Start writing your methods sections by explaining what you did in the experiment. Begin by setting the scene. The methods section should only be a couple sentences long.
Who/what was involved in the study?
- State who or what was used in the experiment. Include the population studied; mention any plants, animals, or humans and how many were involved.
When did the experiment take place?
- State the time frame or duration of the experiment.
Where did the experiment take place?
- Give the geographical location of the experiment.
Tips for writing the methods section
- Write your research methods section as you are doing your experimentation. Some details of your experiment could be left out if you wait too long between the experiment and writing an abstract.
- If you're having trouble structuring your methods, look at what others have done. Look at an abstract from a study in your target publication.
The results section should describe your most important findings with the data to back it up. Write this section in the past tense.
Conclusions
Your conclusions section should only be two to three sentences. In this short amount of space, you should include your interpretation of the experiment to answer the main question of your research. It should answer this question: How do these results have an effect on my area of study or the wider population?
Descriptive abstracts
A descriptive abstract is also called a limited abstract for a good reason. It's much shorter than an informative abstract - about half the size. It's a very brief summary.
It should include background information, the study's purpose, the focus of the paper, and an optional overview of the contents.
A descriptive abstract is generally used for psychology, social sciences, and humanities papers.
Tip for writing a descriptive abstract
If you're having trouble writing a descriptive abstract, take your main headings from your table of contents and write them into a paragraph format.
Critical abstracts
A critical abstract is less common than the other abstracts, but it's still worth knowing. It still includes your general findings, but it also has a section devoted to the completeness, validity, and readability of your paper. In a critical abstract, your work is compared with other studies on your subject matter.
Incorporate keywords found in your research paper
It is wise to list the key phrases and words in your research paper for Search Engine Optimization (SEO) purposes. Your key terms section helps search engines like Google and Bing direct readers and other researchers to your work. The key words section comes at the bottom of your abstract. It can be formatted as follows:
Keywords: example 1, example 2, example 3
How to format the abstract
Some researchers make their abstract a single paragraph that looks like one giant block of text. If you wish to make it easier on your readers, you can break your abstract into sections depending on your target journal's specifications.
It should immediately follow the title page. There should be no page number on the abstract page.
When should you write your abstract?
Since the abstract is the first thing your audience reads, it would make sense to write an abstract first, right?
Not exactly.
Trying to summarize your research before you've written your research paper can be incredibly challenging.
Instead, the abstract should be the last thing you write. Your research should still be fresh in your mind and you should have no problem summarizing the important findings.
There are plenty of other tips for writing your abstract as well.

Final Thoughts
Abstract writing can be difficult. Luckily, AJE's editing staff can edit your abstract . If your target journal requests a graphic abstract, our Figure Formatting team can make you one for you.

Jonny Rhein, BA
See our "Privacy Policy"
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The Title Page of a Dissertation
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic , Research , Research Paper
In academic writing, learning how to create a brief and informative abstract for your research paper is really important. An abstract serves as a sneak peek into your research, giving readers a quick look to decide if they want to read more.
But what exactly is an abstract in a research paper, and how to write an abstract for a research paper that captures the essence of your study effectively? Let’s dive into the nuances of writing a standout research paper abstract!
Improve your paper’s quality with top-notch editing! Get started
Let’s start by understanding what is an abstract in a research paper:
What is an abstract in a research paper?
A research paper abstract is a summary that outlines the key points of your research paper. It serves as a condensed version of your work, allowing readers to quickly grasp the purpose, methodology , results, implications, and conclusion of your study. Think of it as a mini-version of your paper, where you highlight the most critical information to entice further reading.
What is the purpose of an abstract in a research paper?
The primary purpose of an abstract in a research paper is to inform potential readers about the essential contents of the document. It will help them decide whether it aligns with their own research interests or objectives. Also, it’s important because it helps your paper show up in academic databases, making it easier for people to find and read.
Where does the abstract go in a research paper?
Typically, the abstract is placed right after the title page and before the main body of the research paper . This arrangement guarantees that it is the first in-depth synopsis of your work that readers will come across.
How long should an abstract be for a research paper?
The length of an abstract for a research paper typically ranges from 150 to 250 words. This short length summarizes the research’s main aspects clearly and briefly. Sticking within this word range is important to maintain clarity and brevity so that readers can quickly grasp the important information. You can use academic ChatGPT prompts to reduce your abstract’s length if it exceeds the word count.
What does the abstract of a research paper contain?
A research paper abstract usually contains the following key elements:
- Purpose of the study: Clearly states the main goal or issue addressed by the research, providing insight into its importance.
- Methodology: Concisely explains the methods or approaches employed in the research, including the type of study conducted (e.g., experimental, observational, qualitative) and specific techniques or tools utilized.
- Results: Summarizes the primary findings or outcomes of the research, highlighting key data points, trends, or discoveries relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Conclusions: Outlines the implications of the findings. This could involve discussing the significance of the results in the context of the field, potential applications, or future research directions. If your study has significant limitations, it’s advisable to briefly note them in the abstract.
- Keywords: Often, research paper abstracts include a list of keywords that help categorize the paper and make it easier for others to find through searches. Select words that are directly related to your research topic. Typically, 5-7 keywords are sufficient. Check the journal’s guidelines for specific requirements.
How to write an abstract for a research paper?
Use the following steps to write your research paper abstract perfectly:
1. Start with clarity and precision
Begin your abstract by clearly stating the research problem or the main objective of the study. This should address the ‘what’ of your study—what was your research trying to find or prove?
- Avoid vague phrases and focus on delivering a specific and concise statement that encapsulates the essence of your research .
- Use active voice and confident language to state your research aim. For example, instead of saying “This research attempts to explore,” you could say, “This research explores.”
- Ensure that the first one or two sentences encapsulate the critical motivation behind the study.
Poor example: “This paper looks at climate change.”
Improved example: “This study quantifies the impact of industrial emissions on urban air quality, addressing a critical gap in environmental policy formulation.”
- Avoid filler words or overly complex sentences that do not add value to the core understanding of your research.
2. Describe your methodology
Provide a concise overview of the methods you employed for your research. This part should give readers a clear understanding of your approach and techniques. The goal is to provide enough information to understand the foundation of your findings.
- Focus on including only the most crucial methods used in your research. Typically, this would be the overall approach (e.g., qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods), significant techniques or instruments used, and the type of analysis conducted.
- Avoid jargon or overly technical terms that might be unfamiliar to a broader audience, aiming instead for clear, accessible language.
- If specific tools, software, or technologies are central to the results, mention them by name.
Example: “Data was analyzed using SPSS software.”
- Abstracts do not allow for extensive methodological descriptions. Provide enough detail to understand the framework briefly.
For example: Instead of saying, “We conducted several tests to analyze the samples,” specify briefly, “Samples were analyzed using X-ray diffraction and gas chromatography.”
3. Highlight key findings
Briefly summarize the most significant results of your study . Make sure to capture the importance and implications of your results. This part typically grabs the most attention from readers.
- Focus on mentioning quantifiable results if applicable, as these often convey the impact of your findings more powerfully.
- Use phrases that summarize significant trends rather than complex data details. For example, “Results show a 50% increase in efficiency” or “Findings indicate a significant reduction in incidence rates.”
- Use strong, positive adjectives to describe your findings, such as “significant,” “substantial,” “robust,” etc., where appropriate and accurate.
- Include critical statistics such as p-values or confidence intervals to support the significance of your findings.
4. Discuss the implications
In a few sentences, describe the broader implications of your findings. How does your research contribute to the field? What are the practical or theoretical implications?
- Consider questions like, “Why does this matter?” and “Who will benefit from this research?”
- This can be framed as, “These findings suggest new pathways for clinical treatment,” or “This research informs policy by demonstrating…”
- Clearly state how your findings contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field. Do they extend, contradict, or refine previous theories?
Example: “These findings challenge the conventional understanding of X, suggesting a revised model for Y.”
- Use strong action verbs to describe the effect of your research, such as “transforms,” “enables,” “revolutionizes,” or “underscores.”
5. Keep it concise
Focus on writing within the word limit and keeping the information that is required to be showcased or highlighted.
- After drafting your abstract, review it specifically for redundancy and verbosity. You can edit your research paper abstract using content editors and grammar checker tools to ensure an error-free research paper abstract.
- Word counter tools like QuillBot, Semrush, Word Count, etc. can help ensure you stay within the typical 150-250 word range.
- Additionally, asking a colleague to review your abstract format can provide insights into any unnecessary details or unclear wording. Proofreading your research paper abstract is a crucial step.
Research paper abstract example
To solidify your understanding, let’s look at a research paper abstract example:
In this study, we explored the impact of climate change on Arctic marine life. Using a combination of satellite imagery and direct observation methods over five years, we observed a significant decrease in sea ice coverage and its direct effects on the indigenous marine populations. Notably, the reduction in ice has led to altered migration patterns and decreased population stability in polar bears and seals. These findings highlight the urgent need for policies aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change in polar regions.
Creating a strong research paper abstract goes beyond simply summarizing your work. It involves offering a clear, concise, and captivating overview that sparks interest and showcases the significance of your research. By adhering to these tips, you can develop an abstract that meets academic requirements while also engaging your target audience effectively.
To refine your abstract, consider PaperTrue’s expert editing and proofreading services . Our team of professionals can help ensure that your abstract—and your entire research paper—meets the highest standards of academic excellence and is ready to make a lasting impression in the scholarly community!
Here are some more research-related articles for you:
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
What should be included in a research paper abstract, how does one write an effective research paper abstract, can a research paper abstract include citations.
Found this article helpful?
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
What is an abstract?
What is a "good" abstract, techniques to write an abstract, "abstract checklist" from: how to write a good scientific paper. chris a. mack. spie. 2018..
- INTRODUCTION
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
There are as many kinds as abstracts as there are types of research papers. The classic abstract is usually a "Informative" abstract. This kind of abstract communicates compressed information and include the purpose, methods, and scope of the article. They are usually short (250 words or less) and allow the reader to decide whether they want to read the article.
The goal is to communicate:
- What was done?
- Why was it done?
- How was it done?
- What was found?
- What is the significance of the findings?
- Self contained. Uses 1 or more well developed paragraphs
- Uses introduction/body/conclusion structure
- Presents purpose, results, conclusions and recommendations in that order
- Adds no new information
- Is understandable to a wide audience
- Write the abstract last
- Reread the article looking specifically for the main parts: Purpose, methods, scope, results, conclusions, and recommendations
- Write a first rough draft without looking at the original article
- Edit your draft by correcting organization, improving transitions, dropping unnecessary information and words, and adding important information you left out
The abstract should be a concise (200 words or less), standalone summary of the paper, with 1–2 sentences on each of these topics:
- Background: What issues led to this work? What is the environment that makes this work interesting or important?
- Aim: What were the goals of this work? What gap is being filled?
- Approach: What went into trying to achieve the aims (e.g., experimental method, simulation approach, theoretical approach, combinations of these, etc.)? What was actually done?
- Results: What were the main results of the study (including numbers, if appropriate)?
- Conclusions: What were the main conclusions? Why are the results important? Where will they lead?
The abstract should be written for the audience of this journal: do not assume too much or too little background with the topic.
Ensure that all of the information found in the abstract also can be found in the body of the paper.
Ensure that the important information of the paper is found in the abstract.
Avoid: using the first paragraph of the introduction as an abstract; citations in the abstract; acronyms (but if used, spell them out); referring to figures or tables from the body of the paper; use of the first person; use of words like “new” or “novel,” or phrases like “in this paper,” “we report,” or “will be discussed.”
- << Previous: TITLE
- Next: INTRODUCTION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.

How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper

The abstract is the most important piece of your scientific article. In this post, you’ll get your hands on the scientific abstract template that normally only members of our scientific writing program , the Researchers’ Writing Academy, get access to! Writing a scientific abstract according to the suggested scientific abstract structure will make your paper more likely to get accepted, read and cited.
Take a few seconds and think how you read other researchers’ papers. Let me guess… You first read the title and then you read the abstract , right? This means the scientific abstract is the second impression you will make on your editor and peer-reviewers too. Therefore, it’s worthwhile to tweak the abstract for a research paper until it is, oh yes, perfect.
WRITING A SCIENTIFIC ABSTRACT – THE READER’S PERSPECTIVE
So, what would you like to know when you read the abstract of a scientific paper? I’m guessing you would either like to understand whether the scientific paper reports a specific finding you are looking for or you are just generally curious what the paper is about. This is why a scientific abstract should make sense on its own — the reader shouldn’t be required to read the whole scientific article to understand the context, main result or conclusion of the study.
Instead, it’s helpful for the reader when the scientific abstract is told as a story. Identifying the story of the scientific paper we are writing is the first step in the writing process that I guide researchers through inside the Researchers’ Writing Academy . Telling a story in your scientific paper will make it easier for your reader to understand the results you are communicating AND their significance.

HOW TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC ABSTRACT
So, how do we write a research abstract that tells a story? Here are the components your scientific abstract needs to include so that it tells a story:
- Context to your research topic
- Context to your particular study
- The specific problem you solve
- The central message of your paper
- A summary of your main results
- The broader perspective that put your results into context
Ideally, you are already super clear on each component before you start writing a scientific abstract. Once your paper is written, you can then just put these story components together in a single paragraph, and voilà, the abstract of your scientific paper is ready.
SCIENTIFIC ABSTRACT TEMPLATE
You’re going to like what’s coming because I’m giving you the exact template that I teach our Researchers’ Writing Academy members. This scientific abstract template works for many journals. However, some journals specify a scientific abstract structure. In this case, I recommend to allocate the components described above to the prompts you are being given by the journal.
Here’s how you write an abstract for a research paper:
1. PROVIDE CONTEXT TO YOUR RESEARCH TOPIC
The first one or two sentences create the setting and provide an introduction to the topic of your study. As a rule of thumb, every reader of the journal should understand this first part of your scientific abstract. This means that for a journal with a broad readership, the introduction is ideally quite general. Use the present tense.
2. PROVIDE CONTEXT TO YOUR PARTICULAR STUDY
You can use the next one or two sentences of your scientific abstract to delve deeper into the introduction to your scientific study. Provide the background that your reader will need to understand what context your study is situated in. This is written in present tense too.
3. DESCRIBE THE SPECIFIC PROBLEM YOU SOLVE
Now it’s time to introduce tension! State the problem in the research field that your study addresses — in one concise sentence. Here it’s important to be as specific as possible. Present tense for this one too.
4. STATE YOUR CENTRAL MESSAGE
Then you summarise the central message of your research starting with phrases such as “Here, we show”, “In this article, we demonstrate” or similar. Ideally, this sentence is the exact answer to the problem stated in step 3. Still present tense.
5. SUMMARISE YOUR RESULTS
It’s finally time to talk about your findings in two or three sentences. Here it is important to focus on the most important results. Don’t make the mistake of describing several results in one sentence. When it comes to the methods you used, only mention them if they are central to the central message you described in step 4. Write these sentences in the past tense.
6. STATE THE BROAD PERSPECTIVE
In the last one or two sentences of your scientific abstract, put your results in a broader perspective. Explain why your findings are significant and what impact your findings are likely or possibly going to make in your field of research or for an application – be as specific as possible here. Use the present and/or future tense here.
WRITING A SCIENTIFIC ABSTRACT – NEXT STEPS
If you use the above scientific abstract template, your abstract will make sense on its own, present a concise summary of your scientific paper and tell a compelling story.
But I know from experience how hard it can be to nail each component of the scientific abstract. The prompts are relatively simple but it pays off to nail each one of them!
The good news is that this is exactly what we help you with inside the Researchers’ Writing Academy. If you want us to coach you through defining the scientific story of your paper and writing a concise, coherent and compelling abstract, I recommend watching our free training class! It’s only an hour long, and by clicking the orange button below you can get immediate access or save it for later. So, click the button now!

Share article
© Copyright 2018-2024 by Anna Clemens. All Rights Reserved.
Photography by Alice Dix
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper

Writing Informative Abstracts
Informative abstracts state in one paragraph the essence of a whole paper about a study or a research project. That one paragraph must mention all the main points or parts of the paper: a description of the study or project, its methods, the results, and the conclusions. Here is an example of the abstract accompanying a seven-page essay that appeared in 2002 in The Journal of Clinical Psychology :
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
The relationship between boredom proneness and health-symptom reporting was examined. Undergraduate students (N = 200) completed the Boredom Proneness Scale and the Hopkins Symptom Checklist. A multiple analysis of covariance indicated that individuals with high boredom-proneness total scores reported significantly higher ratings on all five sub-scales of the Hopkins Symptom Checklist (Obsessive–Compulsive, Somatization, Anxiety, Interpersonal Sensitivity, and Depression). The results suggest that boredom proneness may be an important element to consider when assessing symptom reporting. Implications for determining the effects of boredom proneness on psychological- and physical-health symptoms, as well as the application in clinical settings, are discussed. —Jennifer Sommers and Stephen J. Vodanovich, (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); “Boredom Proneness”
The first sentence states the nature of the study being reported. The next summarizes the method used to investigate the problem, and the following one gives the results: students who, according to specific tests, are more likely to be bored are also more likely to have certain medical or psychological symptoms. The last two sentences indicate that the paper discusses those results and examines the conclusion and its implications.
Writing Descriptive Abstracts
Descriptive abstracts are usually much briefer than informative abstracts and provide much less information. Rather than summarizing the entire paper, a descriptive abstract functions more as a teaser, providing a quick overview that invites the reader to read the whole. Descriptive abstracts usually do not give or discuss results or set out the conclusion or its implications. A descriptive abstract of the boredom-proneness essay might simply include the first sentence from the informative abstract plus a final sentence of its own:
The relationship between boredom proneness and health-symptom reporting was examined. The findings and their application in clinical settings are discussed.
Writing Proposal Abstracts
Proposal abstracts contain the same basic information as informative abstracts, but their purpose is very different. You prepare proposal abstracts to persuade someone to let you write on a topic, pursue a project, conduct an experiment, or present a paper at a scholarly conference. This kind of abstract is not written to introduce a longer piece but rather to stand alone, and often the abstract is written before the paper itself. Titles and other aspects of the proposal deliberately reflect the theme of the proposed work, and you may use the future tense, rather than the past, to describe work not yet completed. Here is a possible proposal for doing research on boredom:
Undergraduate students will complete the Boredom Proneness Scale and the Hopkins Symptom Checklist. A multiple analysis of covariance will be performed to determine the relationship between boredom-proneness total scores and ratings on the five sub-scales of the Hopkins Symptom Checklist (Obsessive–Compulsive, Somatization, Anxiety, Interpersonal Sensitivity, and Depression).
Key Features of a Research Paper Abstract
- A summary of basic information . An informative abstract includes enough information to substitute for the report itself, a descriptive abstract offers only enough information to let the audience decide whether to read further, and a proposal abstract gives an overview of the planned work.
- Objective description . Abstracts present information on the contents of a report or a proposed study; they do not present arguments about or personal perspectives on those contents. The informative abstract on boredom proneness, for example, offers only a tentative conclusion: “The results suggest that boredom proneness may be an important element to consider.”
- Brevity . Although the length of abstracts may vary, journals and organizations often restrict them to 120–200 words—meaning you must carefully select and edit your words.
A Brief Guide to Writing Abstracts
Consider the rhetorical situation.
- Purpose : Are you giving a brief but thorough overview of a completed study? Only enough information to create interest? Or a proposal for a planned study or presentation?
- Audience : For whom are you writing this abstract? What information about your project will your readers need?
- Stance : Whatever your stance in the longer work, your abstract must be objective.
- Media/Design : How will you set your abstract off from the rest of the text? If you are publishing it online, will you devote a single page to it? What format does your audience require?
Generating Ideas and Text
Write the paper first, the abstract last. You can then use the finished work as the guide for the abstract, which should follow the same basic structure. Exception: You may need to write a proposal abstract months before the work it describes will be complete.
Copy and paste key statements. If you’ve already written the work, highlight your thesis, objective, or purpose; basic information on your methods; your results; and your conclusion. Copy and paste those sentences into a new document to create a rough version of your abstract.
Pare down the information to key ideas. Summarize the report, editing out any nonessential words and details. In your first sentence, introduce the overall scope of your study. Also include any other information that seems crucial to understanding your paper. Avoid phrases that add unnecessary words, such as “It is concluded that.” In general, you probably won’t want to use “I”; an abstract should cover ideas, not say what you think or will do.
Conform to any requirements. In general, an informative abstract should be at most 10 percent as long as the original and no longer than the maximum length allowed. Descriptive abstracts should be shorter still, and proposal abstracts should conform to the requirements of the organization calling for the proposal.
By now your writing is almost complete; you’ve come a long way, but you’re not finished yet! Now it’s time to revise the research paper.
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- How to Order
Research Paper Guide
How To Write An Abstract
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Have you ever wondered why writing an abstract matters? It might seem like a small part of your research paper or project, but it plays a big role.
Picture this: You've worked hard on your research, and you want people to read it. But if your abstract isn't well-written, they might just skip it and miss all your great ideas.
Don't worry!
In this easy-to-follow guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a clear and attention-grabbing abstract step-by-step.
By the end, you'll be able to write abstracts that make your work stand out and get the attention it deserves.
Let's get started!
- 1. What is an Abstract?
- 3. Steps to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- 4. Abstract Page Template and Examples
- 5. Tips to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
What is an Abstract?
An abstract is a short summary of your research. It tells the readers what the central point of your paper is and also describes the aims and outcomes.
A strong abstract further allows the audience to decide whether they want to continue with your paper or not. It is a vital component of a research paper and a thesis, and no paper is considered complete without it.
What Goes into an Abstract?
An abstract typically includes:
- The Purpose: Why was the research or document created?
- Methods: How was the research conducted or the document prepared?
- Results: What did the research find, or what does the document discuss?
- Conclusions: What are the main takeaways or implications?
Below is an example of a research paper abstract, with each section highlighted for clarity.

Types of an Abstract
The use of different types of abstracts depends on the document you're summarising and the audience you're targeting.
Let's explore the common types of abstracts:
Critical Abstracts
Critical abstracts not only summarize but also offer a thoughtful evaluation or analysis of the research paper. They cover the paper’s methods and main findings and assess the quality and importance of the work.
Descriptive Abstracts
Descriptive abstracts give a clear overview of what's in the research paper. They are the most basic type. They describe the main topic, purpose, and scope of the paper without giving away specific details, conclusions, or results.
Informative Abstracts
Informative abstracts go a step further than descriptive ones. They not only describe the paper’s content but also provide key results, findings, and conclusions. They include essential details about the paper, such as the research methodology , results, and conclusions, allowing readers to understand its significance.
Highlight Abstracts
Highlight abstracts emphasize the most critical points of a paper. They aim to grab the reader's attention and highlight its most significant contributions. These abstracts focus on the most important findings, key conclusions, and their broader implications, often showcasing why the research paper is worth reading.
Steps to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
Whether you're a student working on a research paper or a researcher aiming to publish your work, writing an effective abstract follows a structured process.
Here are the key steps to help you write a compelling abstract:
Step 1: Follow Instructions Closely
When tackling a research paper abstract, always begin by thoroughly reviewing the provided instructions. These guidelines act as your roadmap, ensuring you stay on the right track. Look out for:
- Abstract Type: Your teacher may specify the type, such as descriptive or informative.
- Structure: Note any recommended sections or organization rules.
- Word Count: Stick to the prescribed word limit diligently.
- Style and Formatting: Adhere to style and formatting requirements.
Step 2: Include Relevant Background
Incorporate concise background information into your abstract to provide context. Focus on why your study's expected outcomes matter in addressing the main research question. Avoid lengthy or irrelevant details.
Step 3: Define the Research Problem and Objectives
Begin your abstract by clearly outlining the research's purpose and objectives. Make the case for its significance to individuals and society. Specify the research question(s) you aim to address.
- Use Action Words: Employ terms like "evaluate," "analyze," and "investigate" to describe your research's purpose.
- Past or Present Tense: Write this section in simple past or present tense; avoid the future tense.
- Address Key Questions: Answer these vital questions:
- Why conduct this research?
- How does it contribute to the field?
- Why should readers delve into the full paper?
- What central problem does your research solve?
- What's the study's scope, specific or general?
- What's the primary argument?
Step 4: Describe the Research Methods
In your abstract, briefly touch on the research methods employed to address your research question. Use 1 to 2 concise, past-tense sentences.
- Concise Overview: Offer a high-level view of the approaches, procedures, and sources utilized in your research.
- Methodology Type: Mention whether your methods were qualitative , quantitative , case study , or another type.
- Explain Method Choice: State why you selected a specific method and how it benefits your research.
Step 5: Highlight Previous Research
Incorporate a brief mention of relevant previous research on your chosen topic in your abstract. Emphasize the unique perspective of your research without delving into excessive detail.
- Concise Overview: Provide a brief overview of previous research, highlighting its relevance to your work.
- Uniqueness: Mention how your research offers a distinct perspective or contribution to the existing body of knowledge.
- Engaging Content: Keep the reader engaged by including enough information to convey the importance of your research within the context of prior studies.
Step 6: Summarize Key Findings and Results
Summarize the major findings and results of your study using simple past and present tense. Avoid vague qualitative terms and instead focus on concrete details.
- Clarity is Key: Ensure clarity in your summary, using concrete measures such as percentages, trends, figures, or specific outcomes.
- Evaluate Against Hypothesis: State whether your study aligns with the initial hypothesis, highlighting the success or divergence of your findings.
Step 7: Present Your Conclusion
In the final section of your abstract, provide a clear and concise conclusion to your research. Explain how your study addresses the research question and problem.
- Answer the Question: Articulate the answer to your research question and problem.
- Acknowledge Limitations: Mention any limitations related to sample size or methodology. This transparency helps readers assess the research's credibility and context.
- Future Research and Recommendations: Consider offering suggestions and recommendations for future research or a call to action. Ensure your results contribute value to the field of knowledge.
Abstract Page Template and Examples
The following are the abstract examples and a template. Read them if you want to know more.
Abstract Template
Sample Research Paper Abstract APA
Sample Research Paper Abstract MLA
Abstract Example
Scientific Research Paper Abstract
Abstract for Thesis
Abstract of a Report
Abstract for research paper proposal
Abstract for a presentation
Abstract for a book chapter
Abstract For A Research Paper APA
How to Write An Abstract For A Research Paper
Tips to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
Follow these tips to ensure your abstract is concise, engaging, and accurately represents your work:
- Revise Your Abstract
Revision is a crucial step in crafting an effective abstract. Once you've drafted your initial version, go back and carefully review it. Check for clarity, coherence, and alignment with the main paper. Look for opportunities to improve conciseness without sacrificing essential information.
- Get Feedback from a Peer
Seeking feedback from a peer provides an external perspective on your abstract. Another person can offer valuable insights into the clarity and effectiveness of your communication.
- Consider Getting Professional Editing and Proofreading
An experienced editor can help refine your language, ensure proper grammar and syntax, and enhance overall readability. This step is especially important when aiming for publication in academic journals or presenting your research to a wider audience.
- Write Your Abstract After Completing Your Paper
Crafting the abstract after completing the paper allows for a comprehensive overview of your research. It ensures that the abstract accurately reflects the main points, key findings, and conclusions of your work. This approach contributes to a more cohesive and aligned representation of your research.
- Keep Your Content in the Correct Order
Maintain the proper sequence of information in your abstract. Follow the structure outlined in the earlier steps: purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. This logical flow helps readers navigate through your abstract effortlessly, enhancing comprehension and engagement.
- Write the Abstract from Scratch
Avoid copying and pasting sentences directly from your paper into the abstract. Instead, write the abstract from scratch, ensuring that it is a standalone piece that effectively encapsulates the essence of your research. This approach fosters clarity and ensures that the abstract serves its purpose of providing a concise summary.
- Don’t Include Too Many Details in the Abstract
Resist the temptation to include excessive details in the abstract. Focus on the essential aspects of your research, emphasizing key findings and conclusions. A concise abstract maintains reader interest and encourages them to delve into the full paper for a more in-depth understanding.
In summary, this guide will help you write a perfect abstract for your paper if you follow it closely.
However, not everyone possesses the knack for creating a stellar abstract. In such cases, seek essay help online from MyPerfectWords.com .
For all your academic writing requirements, MyPerfectWords.com is your ultimate choice. Simply make an order for a meticulously crafted abstract from our expert writers.
Feel free to reach out to our customer service now for your " write my research paper " needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an abstract and an introduction.
The difference between an abstract and an introduction lies in their respective scopes and content. An abstract condenses your larger work into a concise paragraph, whereas the introduction encompasses some but not all elements found in an abstract.
How long should an abstract be?
The length of an abstract can vary depending on the specific requirements of the journal article, or academic institution you are submitting to. However, a typical length falls in the range of 150 to 250 words.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper (Example and Tips)
Understand the structure of an abstract and learn technical tips on writing a proper abstract for a research paper.
Publishing an article is a very prestigious moment in a researcher’s life. Thus, it is pretty common that you might want to know how to make everything flawless, from abstract to conclusion.
Nowadays the internet has a huge influence on abstract writing, mostly because the readers use it to search for methodologies, results and references, considering that titles can be misleading and sometimes don’t go to specifics.
This article is here to help you understand the structure of an abstract, know the difference between its types and how to write a proper abstract for a research paper.
What is an abstract?
An abstract is a short summary of a larger work, such as academic, scientific or general research papers. Its purpose is to give the readers a glance at what comes next and convince them to keep reading. Therefore, it is usually situated at the beginning of such works.
The size of an abstract is around 100-300 words including one or two paragraphs, but that might depend on the requirements of the journal you choose to publish on.
Abstract example
Have a look at an abstract published in Elsevier by Fabricio Pamplona, pharmacist, PhD in Pharmacology and co-founder of Mind The Graph.
N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) administered at subtoxic dose plays a protective role against neuronal excitotoxicity, a mechanism described as preconditioning. Since the activation of adenosinergic receptors influences the achievement of NMDA preconditioning in the hippocampus, we evaluated the potential functional interplay between adenosine A1 and A2A receptors (A1R and A2AR) activities and NMDA preconditioning. Adult male Swiss mice received saline (NaCl 0.9 g%, i.p.) or a nonconvulsant dose of NMDA (75 mg/kg, i.p.) and 24 h later they were treated with the one of the ligands: A1R agonist (CCPA, 0.2 mg/kg, i.p.) or antagonist (DPCPX, 3 mg/kg, i.p.), A2AR agonist (CGS21680, 0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) or antagonist (ZM241385, 0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) and subjected to contextual fear conditioning task. Binding properties and content of A2AR and glutamate uptake were assessed in the hippocampus of mice subjected to NMDA preconditioning. Treatment with CGS21680 increased the time of freezing during the exposure of animals to the new environment. NMDA preconditioning did not affect the freezing time of mice per se, but it prevented the response observed after the activation of A2AR. Furthermore, the activation of A2AR by CGS21680 after the preconditioning blocked the increase of glutamate uptake induced by NMDA preconditioning. The immunodetection of A2AR in total hippocampal homogenates showed no significant differences evoked by NMDA preconditioning and did not alter A2AR maximum binding for the selective ligand [3H]CGS21680. These results demonstrate changes in A2AR functionality in mice following NMDA preconditioning.
Reference: Functional interplay between adenosine A2A receptor and NMDA preconditioning in fear memory and glutamate uptake in the mice hippocampus. PMID: 33691195 DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107422
What’s the purpose of an abstract?
In addition to attracting readers and helping them index specific points in your work, abstracts are also very good to encourage financial support. If potential investors could understand your research’s details right away, the financial support for grant proposals and the fundraising process would be a lot faster, right?
Knowing how to write an abstract for a research paper is also important for search engine optimization (SEO). If anyone searches the words used in your abstract, the link of your publication will appear in the search results, raising the chances of getting clicks and visualization of your work.
Types of abstracts
There are three most used types of abstracts: descriptive , informative and visual . Descriptive abstracts are usually applied for less formal documents, whereas informative and visual abstracts are most used in research papers.
Descriptive
Descriptive abstracts are considered more friendly than others. They are brief and don’t bring much data and details, focusing on overviews, and leaving aside results and conclusions. It demands you to read the whole paper to get to the main point.
To clarify ideas, you can think of it as a synopsis of a movie or the back cover of a book.
Informative
Informative abstracts are more complete, containing all you need to know about the paper before reading it completely: introduction, research significance, methodology, results and conclusion. That’s why informative abstracts are the best choice for research papers.
Their main goal is to be used as a quick reference, lacking personality but full of relevant data.
Visual Abstract
Also known as graphical abstract, this type is not very popular among academics yet, but it has a bright future ahead. That is due to some publishers requiring visual abstracts as mandatory for science papers.
Using science figures, infographics and illustrations, graphical abstracts are great at making your work much more accessible for everyone. A study done by Cactus Communications indicates that articles with Graphical Abstracts have 3x more downloads and 8x more shares on social media.

What are the 5 parts of an abstract?
The 5 parts of an abstract are: introduction , research significance , methodology , results and conclusion . They are all stated below so you can get a better understanding:
Introduction
The first part of the abstract is a brief and enticing text that aims to capture the reader’s attention. A well-written intro can really persuade the reader to dive into your abstract.
Research significance
Usually, this is the answer to the question: “Why did you do this research?”.
Methodology
A short space for explaining what you did during your analysis and the methods you used to get the proper results.
You may use this part to share a glance of your discoveries or clarify the advantages of your method based on the results.
Finally, the part where you put a short description of the meaning and the impact of your data and how it contributes to the actual findings.
Expert tips to write an abstract for a research paper
- Write the abstract last : Save time and write the abstract for last. Since the abstract contains a small part of every research’s main topics, it’ll be better if you focus on it when everything else is almost done.
- Don’t forget about the keywords : If you have an interest in optimizing your paper for SEO (explained above in What’s the purpose of an abstract? section), you may also include keywords. Working just like hashtags in social media, they list out the topics discussed in your paper so interested people can easily find them online.
- Follow the publisher’s instructions: Stay tuned to the publisher’s requirements. To ensure the success of your publication, always follow the publisher’s instructions before submitting.
- State your conclusion: Another thing you have to keep in mind when writing an abstract is that you need to set up a connection between the paper’s abstract and conclusion. It is fundamental that a reader can understand the research’s idea if they only read the abstract and the conclusion.
How do you write a good abstract for a research paper?
After all, let’s go through some easy steps on how to write a good abstract for a research paper.
Step 1: Introduce your work to the audience
Start with the contextualization of your research. Don’t forget to mention the general topic under study and also the specific topic of your research.
Step 2: The Problem Statement
Every research aims to solve some questions. Make sure yours are clearly identified in this section. You may also add what’s already known about the subject, including previous research.
Step 3: Support your research
That’s the point where you support your reasons and goals. For example, “Why is that topic relevant? Are those questions worth addressing? Did you apply any new method?” and so on.
Step 4: New discoveries
Share your main findings and results, presenting them whether they are satisfactory or not. Select only the necessary so that the abstract doesn’t be too long.
Step 5: The si g nificance of your findings
Last but not least, in this part, you may explain the impact of the results of your research and how they influence the actual knowledge. You may use data and plead to support your findings.
Improve your papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual abstracts
Imagine your audience getting your whole purpose just by looking at an infographic for a few minutes. Use the Mind The Graph tool to create amazing graphical abstracts and take your research paper to another level.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Content tags
Five Steps to a Brilliant Abstract
by Dr. Jo Koster, Winthrop University
Humanities scholars and students aren’t usually taught to write abstracts like our friends in the natural and social sciences are. That’s because in the humanities, full pieces of discourse are preferred to short, condensed summaries. But in many cases you will NEED to write an abstract for your work—and a lot of what your colleagues in other disciplines know can help you.
Let’s start with the basic questions.
What is a descriptive abstract?
A descriptive abstract is the summary of work you have already completed or work you are proposing. It is not the same thing as the introduction to your work. The abstract should give readers a short, concise snapshot of the work as a whole—not just how it starts. Remember that the readers of your abstract will sometimes not read the paper as a whole, so in this short document you need to give them an overall picture of your work. If you are writing an abstract as a proposal for your research—in other words, as a request for permission to write a paper—the abstract serves to predict the kind of paper you hope to write.
What’s different about a conference paper (or informative) abstract?
A conference abstract is one you submit to have your paper considered for presentation at a professional conference (CURAH maintains a growing list of these opportunities ). The conference organizers will specify the length — rarely be more than 500 words (just short of two double-spaced pages). In an ideal world, you write your abstract after the actual paper is completed, but in some cases you may write an abstract for a paper you haven’t yet written—especially if the conference is some time away. Because the conference review committee will usually read the abstract and not your actual paper, you need to think of it as an independent document, aimed at that specific committee and connecting solidly with the theme of the conference. You may want to pick up phrasing from the conference title or call for papers in the abstract to reinforce this connection. Examine the call for papers carefully; it will specify the length of the abstract, special formatting requirements, whether the abstract will be published in the conference bulletin or proceedings, etc. Abstracts that do not meet the specified format are usually rejected early in the proceedings, so pay attention to each conference’s rules!
How wedded are you to the abstract you submit?
An abstract is a promissory note. That is, you are promising that you can and will produce the goods in the paper. Particularly in the case of a conference abstract, the organizers will make up a session based on the contents of the abstract. If you propose a paper that says you will use Foucault to comment on post-colonialism in Heat and Dust” and then show up with a paper on “Metaphors for Spring in A Bend in the River,” your paper may not fit the session where it was slotted, and you’ll look silly—and those organizers may not ask you back. While some divergence from the promised topic is acceptable (and probably inevitable if you haven’t written the paper when you submit the abstract), you need to produce a paper that’s within shouting distance of your original topic for the sake of keeping your promise.
The Five Step Process
Descriptive abstracts are usually only 100-250 words, so they must be pared down to the essentials. Typically, a descriptive abstract answers these questions:
Why did you choose this study or project? What did/will you do and how? What did you/do you hope to find? (For a completed work) What do your findings mean?
Step 1: A catchy title
Which paper would you rather go hear at a conference? ‘Issues of Heteronormativity and Gender Performance In Twain’s Novels” or “Come Back to the Raft, Huck Honey”?
Your title should be informative and focused, indicating the problem and your general approach. It’s very fashionable in the humanities to have titles featuring a catchy phrase, a colon, and then an explanation of the title. While snappy titles may help your abstract be noticed, it’s really what comes after the colon that sells the abstract, so pay attention to it. “All the World’s a Ship: Race and Ethnicity in Moby Dick” catches the eye, but “Melville’s Deconstruction of Ethnicity in the ‘Midnight, Forecastle’ Episode of Moby Dick” tells readers much more specifically what you’re promising to deliver.
Step 2: A snappy context sentence (or sentences)
The abstract should begin with a clear sense of the research question you have framed. Often writers set this up as a problem: “Although some recent scholars claim to have identified Shakespeare’s lost play Cardenio, that attribution is still not accepted.
Step 3: Introduce your argument (don’t just copy your thesis statement).
If you began with a problem, you can pose your argument as the solution: “In this paper I use the records of the Worshipful Company of Stationers, London’s chief publishing organization, to show that the play identified by Charles Hamilton in 1990 is not actually the play Shakespeare’s company mounted in 1613.” It’s perfectly legit to use “I” in sentences referring to your argument.
Step 4: Add some sentences describing how you make your argument.
It always helps when you identify the theoretical or methodological school that you are using to approach your question or position yourself within an ongoing debate. This helps readers situate your ideas in the larger conversations of your discipline. For instance, “The debate among Folsom, McGann, and Stallybrass over the notion of database as a genre (PMLA 122.5, Fall 2007) suggests that….” or “Using the definition of dataclouds proposed by Johnson-Eilola (2005), I will argue that…”
Finally, briefly state your conclusion.
“ Through analyzing Dickinson’s use of metaphor, I demonstrate that she systematically transformed Watt’s hymnal tropes as a way of asserting her own doctrinal truths. This transformation…”
Not everyone agrees how much jargon should be included in an abstract. My best advice is to add any technical terms you need, but don’t put in jargon for jargon’s sake or just to make it look like you are an expert (this especially extends to (post)modernizing your words or other typographical excrescences).
Special for conference papers:
To the basic requirements of the descriptive abstract, a conference paper abstract should also include a few sentences about how the proposed paper fits in the theme of the conference. For instance, a call for papers for a session on “Science and Literature in the 19th Century” at a conference entitled “(Dis)Junctions” requested “critical works on the interaction between scientific writing and literature in the 19th century. How did scientific discoveries, theories and assumptions (for example, in medicine and psychology, but not limited to these) influence contemporaneous fiction?” If you were submitting a paper to this session, you would want to have a sentence or two about the theories you were discussing and name the particular works where you would identify their influence. If you can work the words “join” or “junction” (or “disjunction”) into your title or abstract, you’ll increase your chance of having the paper accepted, since you’re showing clearly how the paper fits the theme of the session.
Step 5: Show the conference organizers or editors that you’re a pro.
Tell them your essay is a finished work (even if it’s only complete in your head!). It’s also considered good in a conference abstract to conclude with a sentence about your presentation, since the great horror of session chairs is the paper that runs far too long (or embarrassingly too short). Organizers also need to know if you need any special technology to present the paper. So a a much-appreciated professional touch is concluding passage such as, “My paper is complete and can be presented in 20 minutes. I will bring bring video clips on a portable drive but will need a computer, projector, and Internet access to show all my materials.”
Be professional!
Double-check your abstract to make sure it meets the length requirements. Make sure it’s edited and documented. And above all, make sure it’s submitted on time.
Here is a video version of this page, taking you from the call for papers to the finished abstract.
Check out these other guides from CURAH:
- How to write a proposal
- How to make a poster
- A list of regional and national conferences where you can present your work
Acknowledgements:
Illustrated by Ian MacInnes Thanks to Dr. Leslie Bickford for her sample abstract
I consulted and borrowed material from the following websites in preparing these suggestions:
www.unc.edu/depts/wcweb/handouts/abstracts.html www.linguistics.ucsb.edu/faculty/bucholtz/sociocultural/abstracttips.html www.academic-conferences.org/abstract-guidelines.htm ceca.icom.museum/ dbase upl/writinganabstract.pdf ling.wisc.edu/macaulay/800.abstracts.html writingcenter.unlv.edu/writing/abstract.html www.lightbluetouchpaper.org/2007/03/14/how-not-to-write-an-abstract/ webapp.comcol.umass.edu/msc/absGuidelines.aspx www.oberlin.edu/history/Honors/prospectus.html www.english.eku.edu/ma/scholarlythesis.php
The Arts and Humanities Division of the Council on Undergraduate Research
University of Missouri
- Bias Hotline: Report bias incidents
Undergraduate Research
- How to Write An Abstract
Think of your abstract or artist statement like a movie trailer: it should leave the reader eager to learn more but knowledgeable enough to grasp the scope of your work. Although abstracts and artist statements need to contain key information on your project, your title and summary should be understandable to a lay audience.

Please remember that you can seek assistance with any of your writing needs at the MU Writing Center . Their tutors work with students from all disciplines on a wide variety of documents. And they are specially trained to use the Abstract Review Rubric that will be used on the abstracts reviewed at the Spring Forum.
Types of Research Summaries
Students should submit artist statements as their abstracts. Artist statements should introduce to the art, performance, or creative work and include information on media and methods in creating the pieces. The statements should also include a description of the inspiration for the work, the meaning the work signifies to the artist, the artistic influences, and any unique methods used to create the pieces. Students are encouraged to explain the connections of the work with their inspirations or themes. The statements should be specific to the work presented and not a general statements about the students’ artistic philosophies and approaches. Effective artist statements should provide the viewer with information to better understand the work of the artists. If presentations are based on previous performances, then students may include reflections on the performance experiences and audience reactions.
Abstracts should describe the nature of the project or piece (ex: architectural images used for a charrette, fashion plates, advertising campaign story boards) and its intended purpose. Students should describe the project or problem that they addressed and limitations and challenges that impact the design process. Students may wish to include research conducted to provide context for the project and inform the design process. A description of the clients/end users may be included. Information on inspirations, motivations, and influences may also be included as appropriate to the discipline and project. A description of the project outcome should be included.
Abstracts should include a short introduction or background to put the research into context; purpose of the research project; a problem statement or thesis; a brief description of materials, methods, or subjects (as appropriate for the discipline); results and analysis; conclusions and implications; and recommendations. For research projects still in progress at the time of abstract submission, students may opt to indicate that results and conclusions will be presented [at the Forum].
Tips for writing a clear and concise abstract
The title of your abstract/statement/poster should include some language that the lay person can understand. When someone reads your title they should have SOME idea of the nature of your work and your discipline.
Ask a peer unfamiliar with your research to read your abstract. If they’re confused by it, others will be too.
Keep it short and sweet.
- Interesting eye-catching title
- Introduction: 1-3 sentences
- What you did: 1 sentence
- Why you did it: 1 sentence
- How you did it: 1 sentence
- Results or when they are expected: 2 sentences
- Conclusion: 1-3 sentences
Ideas to Address:
- The big picture your project helps tackle
- The problem motivating your work on this particular project
- General methods you used
- Results and/or conclusions
- The next steps for the project
Things to Avoid:
- A long and confusing title
- Jargon or complicated industry terms
- Long description of methods/procedures
- Exaggerating your results
- Exceeding the allowable word limit
- Forgetting to tell people why to care
- References that keep the abstract from being a “stand alone” document
- Being boring, confusing, or unintelligible!
Artist Statement
The artist statement should be an introduction to the art and include information on media and methods in creating the piece(s). It should include a description of the inspiration for the work, what the work signifies to the artist, the artistic influences, and any unique methods used to create the work. Students are encouraged to explain the connections of the work with their inspiration or theme. The artist statement (up to 300 words) should be written in plain language to invite viewers to learn more about the artist’s work and make their own interpretations. The statement should be specific to the piece(s) that will be on display, and not a general statement about the student’s artistic philosophy and approach. An effective artist statement should provide the viewer with information to better understand and experience viewing the work on display.
Research/Applied Design Abstract
The project abstract (up to 300 words) should describe the nature of the project or piece (ex: architectural images used for a charrette, fashion plates, small scale model of a theater set) and its intended purpose. Students should describe the project or problem that was addressed and limitations and challenges that impact the design process. Students may wish to include research conducted to provide context for the project and inform the design process. A description of the clients/end users may be included. Information on inspirations, motivations, and influences may also be included as appropriate to the discipline and project.
Key Considerations
- What is the problem/ big picture that your project helps to address?
- What is the appropriate background to put your project into context? What do we know? What don’t we know? (informed rationale)
- What is YOUR project? What are you seeking to answer?
- How do you DO your research? What kind of data do you collect? How do you collect it?
- What is the experimental design? Number of subjects or tests run? (quantify if you can!)
- Provide some data (not raw, but analyzed)
- What have you found? What are your results? How do you KNOW this – how did you analyze this?
- What does this mean?
- What are the next steps? What don’t we know still?
- How does this relate (again) to the bigger picture. Who should care and why? (what is your audience?)
More Resources
- Abstract Writing Presentation from University of Illinois – Chicago
- Sample Abstracts
- A 10-Step Guide to Make Your Research Paper More Effective
- Your Artist Statement: Explaining the Unexplainable
- How to Write an Artist Statement

Here is the Forum Abstract Review Rubric for you and your mentor to use when writing your abstract to submit to the Spring Research & Creative Achievements Forum.

Magnum Proofreading Services
- Jake Magnum
- Feb 19, 2021
How to Write an Abstract Before You Have Obtained Your Results
Updated: Jun 25
When you need to produce an abstract for research that has not yet been carried out, you should write what is known as a descriptive abstract . In this type of abstract, you explain the background, purpose, and focus of your paper but not the results or conclusion.
Obviously, it is preferable to write the abstract for your research after you have obtained your results. While you might be under pressure to submit an abstract months before your research has been completed, it is still best to postpone writing your abstract until you have your results if this is at all possible. The advice given in this article is intended for authors who have no choice but to submit an abstract before they have their results.
Guidelines and Tips for Writing an Abstract without Results
When you need to write an abstract but haven’t yet gathered your results, you can write a descriptive abstract . While these are typically used for papers written in the humanities and social sciences, you may adapt them to a scientific work if you have no other option — for example, if you need to submit an abstract eight months before your research is scheduled to be completed.
A typical descriptive abstract accomplishes three things — namely, it (1) provides background information about your study topic, (2) expresses the purpose of your study, and (3) explains what you will do to accomplish your study’s purpose. Descriptive abstracts do not usually make any mention of a study’s results. However, if a description of the results is a general requirement for your abstract, you can briefly state that you intend to express your results at a later time (after you have gathered your data).
This article will guide you through writing all three parts of a descriptive abstract for a scientific paper. Afterward, examples of full abstracts written in this style are provided.
1. Background: Give general information about your topic.
The background section of a descriptive abstract is longer than that of an informative abstract (which is the abstract style used in most scientific works). The background information provided in an informative abstract is often restricted to two sentences, one mentioning the study topic and the other introducing the general problem to be addressed. A further discussion of these kinds of abstracts can be found here . In a descriptive abstract, you can use two sentences for each of these purposes, which allows you to give more detailed background information.
The background section of an informative abstract might read as follows:
Body dissatisfaction has adverse effects on women of all ages. However, research suggests that women can apply self-compassion to reduce body dissatisfaction and create a positive body image instead. This paper aims to…
In this example, the author very quickly lets the reader know the overall topic of their paper (body dissatisfaction among women) and what avenue of this topic they will explore. They then immediately transition into discussing the purpose of their paper.
If the author had written a descriptive abstract instead, the background section might look like this:
Body dissatisfaction has adverse effects on women of all ages. It has been linked to low self-esteem, depression, social anxiety, and eating disorders. These problems can be made worse when a woman criticizes herself because of her body. Conversely, practicing self-compassion, which entails being warm towards oneself when recognizing one’s failures or inadequacies, can reduce body dissatisfaction and help to create a positive body image. This paper aims to…
In this second example, the author uses an extra sentence to list some of the specific adverse effects of body dissatisfaction. The author also defines the key term of “self-compassion” to give non-experts of the subject a better understanding of the topic.
2. Purpose: Describe the general problem that your research aims to explore.
This part of a descriptive abstract is typically made up of a single sentence. Here, you should describe your purpose for conducting your research work. This sentence should be more specific than the preceding sentences, as it should describe the specific constructs that the study will investigate. Unlike the other parts of a descriptive abstract, the sentence describing the study’s purpose should be the same as it would appear if you were writing an informative abstract.
This paper aims to explore sources of positive and negative body image by investigating whether the association between self-esteem and body image avoidance behaviors is mediated by self-compassion and appearance contingent self-worth.
This example was taken from an informative abstract but could just as well be included in a descriptive abstract.
3. Focus: Explain what you intend to do to solve the problem.
Normally, you would now describe what you did to accomplish your research goal. However, if you have not yet carried out your research, you have nothing to report. As such, you should instead explain what you intend to do to accomplish your goal. It is best to be specific regarding what tools you will use and what parameters you will measure.
In an informative abstract, the author could express the focus of their research as follows:
Using a multiple mediation model, we assessed the responses of 222 female participants who completed the Body Image Avoidance Questionnaire.
Here, the author quickly explains who the participants were, what the researchers measured, and what tool they used.
If you are writing a descriptive abstract because you do not yet have your results, then this part of your abstract will be different in two ways. First, you will have to leave out information that you do not have (e.g., the number of participants). Second, you cannot write this sentence in the past tense since you haven’t done anything yet. If the example sentence above were part of a descriptive abstract, it might read as follows:
We will employ a multiple mediation model to assess the responses given by a group of females to the Body Image Avoidance Questionnaire.
Here, the author has not included the number of participants, and they have stated what they will do rather than what they have done.
Do not in any way express what you expect or hope to find.
If you were writing an informative abstract, the next step would be to describe your results. If you are writing a descriptive abstract instead, you might be tempted to describe what you expect or hope to find. However, this should be avoided, as it reflects a lack of scientific integrity and will be perceived as misleading if you do not obtain the expected results.
On this note, you must be very careful about how you express the purpose of your study. To clarify this, I will revisit a previous example.
The use of the word “whether” is crucial in this sentence, as it expresses doubt. That is, it indicates that you don’t know what you will find. Therefore, no matter what results you obtain, this sentence cannot be considered misleading.
The following example includes a subtle change in wording, but it changes the implied meaning of the sentence:
This paper aims to explore sources of positive and negative body image by showing that the association between self-esteem and body image avoidance behaviors is mediated by self-compassion and appearance contingent self-worth.
“Investigating whether” has been changed to “showing that.” Because of this change, the author is now claiming that they will obtain a certain result (i.e., that self-compassion and appearance contingent self-worth mediate the relationship in question). This statement will be considered misleading if either variable does not turn out to be a mediating factor.
Examples of Abstracts without Results
I will begin with an abstract from the field of English literature, where descriptive abstracts are common. Afterward, I will provide a second example that shows how you can adapt this style to an abstract written in a scientific field.
(1) Revolutions are considered as a way to replace a situation or system of government with a better one. (2) However, many writers have addressed the question of whether revolution really is the right way to improve people’s lives or if it merely changes the faces of rulers or the names of governments. (3) George Orwell, who was considered an apolitical writer, is one of the writers who tackled this issue. (4) His novella Animal Farm is an allegorical story of some animals living on a farm who successfully revolt against their owner, only to create a dystopia in the end. (5) This paper aims to explore the nature of revolution throughout human history in general and how this phenomenon is treated by Orwell in his novella. (6) Specifically, we intend to use examples from Animal Farm to investigate whether we should consider revolution as an appropriate way to generate a true change in a political system and in the way people think.
The above abstract is a modified version of the abstract from “The Nature of Revolution on Animal Farm.” It contains the three main parts that have been described in this article:
First, Sentences 1–4 provide background information for the present study. In Sentence 1, the author makes a very broad statement about a widespread topic (i.e., revolutions). Sentence 2 describes the general problem that the paper addresses. The author then gets more specific in Sentences 3 and 4, mentioning a specific writer and a specific novella.
Second, the author states their purpose for writing the paper in Sentence 5, indicated by the introductory phrase “this paper aims to.” Notice that the purpose stated in this sentence is quite general, though it is more specific than the problem described in Sentence 2.
Third, in Sentence 6, the author explains what particular question they intend to answer (i.e., “Should we consider revolution as an appropriate way to generate a true change in a political system?”), and they mention what tools they will use to do this (i.e., examples from Animal Farm ).
(1) The physical self has been considered one of the most important factors impacting global self-esteem. (2) Moreover, the physical self has recently become widely accepted as a multidimensional construct that contains several specific perceptions across various domains. (3) However, limited research has examined the physical self of athletes with physical disabilities, especially in Middle-Eastern countries. (4) Therefore, the purpose of this study is to explore the physical self-esteem and global self-esteem of wheelchair basketball players from Middle-Eastern countries. (5) Using the Physical Self-Description Questionnaire (PSDQ) as a measurement tool, this study aims to determine (i) whether there is a correlation between physical self-esteem and global self-esteem and (ii) which of the nine domains of the PSDQ (Health, Coordination, Activity, Body Fat, Sport Competence, Appearance, Strength, Flexibility, and Endurance) are correlated with physical self-esteem.
The above abstract is a modified version of the abstract of the article entitled “Physical self-esteem of wheelchair basketball players.” It has the same three main parts as the first example:
First, Sentences 1–3 are devoted to providing the background of the study. Specifically, Sentences 1 and 2 describe the general topic that will be investigated, while Sentence 3 states the general problem that the author intends to explore.
Second, in Sentence 4, the author states the overall purpose of their study by explaining what aspect of the issue mentioned in Sentence 3 they will be tackling.
Third, Sentence 5 describes the specific questions that the study will address (i.e., “Is there a correlation between physical self-esteem and global self-esteem, and which of the nine domains of the PSDQ are correlated with physical self-esteem?”). It also lets the reader know what kind of data will be used to answer these questions (i.e., PDSQ scores). Notice that the authors do not state that they expect to find any correlations.
- How to Write an Abstract
Related Posts
How to Write a Research Paper in English: A Guide for Non-native Speakers
How to Write an Abstract Quickly
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
Center for Undergraduate Research and Engaged Learning
Distinguish Yourself
How to Submit An Abstract
Students should consult with their faculty mentor(s) to determine the most appropriate presentation format to present their work prior to submission:
- Poster Presentations concisely communicate research using graphics/images/figures with minimal text. A 5-7 minute explanation guides the audience through the research topic, methodology, preliminary/expected results, and conclusion/next steps.
- Emerging Research presentations represent research projects that are not completed, but might be of significant interest to the research community. Both conceptually- and empirically-based papers on "work-in-progress" projects would fall into this category.
- Completed Research presentations represent fully developed empirical research. This is open to papers based on completed research studies. Students clearly present their research question, outline the research methodology and assessment, and present clear outcomes.
- Creative Activities and performances can be either in-person poster or online oral presentation and represent the final product of scholarly creative activity. These projects include, but are not limited to, submissions from Dance, Art, Music, Creative Writing, Media and Cultural Studies, and Theatre, Film, and Digital Production. Students discuss the research/inspiration behind the final product. Performing and visual arts projects may be presented in the traditional oral or poster format, or as exhibits, displays, performances, readings, and viewings.
Next, please watch this video (24:28) about abstract expectations. Students are expected to consult with their faculty mentor(s) to develop their abstract, which must meet the following format requirements:
- Abstract is no more than 250 words
- Microsoft Word document (.DOC or .DOCX)
- Document size cannot exceed 3 MB
- 12-point font size
- Times New Roman font face
- Single space (no double-spacing)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
Ensure your document has all the following information to identify you and your project, in the upper TOP-LEFT of your document:
- Lead Presenter: Name (First Last) and Major (lead presenter submits the abstract)
- Faculty Mentor: Name (first, last), Department
- Secondary Presenters or Contributing Members: Name(s) (First Last). In order of contribution credit.
- Project Title (case-sensitive)
- 250-word abstract
Here is a sample abstract for your reference. Abstracts not following the required formatting guidelines will NOT be considered.
2025 Symposium Dates
Coinciding with National Undergraduate Research Week #URW2025 April 21-23 Oral Presentations April 24-25 Poster Presentations
Submit an abstraCT
Table of Contents
Presentation Schedule & Registration
Virtual Oral Presenter Resources
Poster Presenter Resources
Moderator Resources
Evaluator Resources
Leverage Your Research
Upcoming Events
Connect with the center for undergraduate research and engaged learning.
Crack the Code: A Simple Guide to Reading Scientific Articles

By Jin Chow
Co-founder of Polygence, Forbes 30 Under 30 for Education
6 minute read
Science articles and research papers might seem like a maze of complicated words and confusing graphs, especially when you’re new to them, but fear not! We're here to help you decode these treasure troves of knowledge and learn how to read a scientific article. Initially, it’s important not to approach a scientific article or scientific literature like a textbook, where you read without pause for reflection.
It’s highly recommended that you highlight and jot down notes as you navigate the scientific research article. Taking notes while you read scientific papers keeps you on track and enhances comprehension. Now, let’s dive into the exciting world of reading scientific articles step by step as well as make it easier to decide if you are going to use scientific journals in your research.
Do your own research through Polygence!
Polygence pairs you with an expert mentor in your area of passion. Together, you work to create a high quality research project that is uniquely your own.
1. Unveil the Mystery: Title & Abstract
Imagine you're about to embark on an adventure. Start by reading the title and abstract of the scientific research paper – they're like your treasure map! The title gives you a sneak peek of the scientific paper, while the abstract sums up the whole journey in a few sentences. The abstract of the journal article is like the trailer for a movie, giving you an idea of what to expect without revealing all the details.
When reading an abstract, focus on the main objective of the study, the key findings, and any major implications as well as limitations. Skimming articles for research also helps you determine if the article aligns with your interests or research, especially when dealing with multiple lengthy articles.
2. Connect the Dots: Discussion or Conclusion
Now, let’s dive into the deep waters of either the discussion or the conclusion section. If the article is about a topic you know, head straight to the discussion to find out what all the fuss is about. Scientists chat about their findings and what they mean for the world. It’s like getting to the end of a mystery novel and revealing the solution!
If the topic is new to you, follow the path of the conclusion. Think of it as the last chapter of a fantastic story. Scientists sum up their journey, tell you what they learned, and suggest where the adventure might lead next. It’s your chance to grasp the big picture without delving into all
the scientific jargon. Pay attention to any limitations the scientists mention; this shows their honesty and helps you understand the study’s scope.
3. The Recipe of Discovery: Methods
If you’re diving into a topic you’re familiar with, start with the methods section. Imagine this as your secret recipe for a scientific experiment. Scientists spill the beans on how they conducted their research – what tools they used, how they gathered data, and more. It’s like peeking into a magician’s hat to learn their tricks! Don’t worry if you don’t understand every technical term; the goal is to get a general idea of how the study was conducted.
4. The Opening Act: Introduction
But if the topic is new, begin with the introduction. This is like the opening act of a play. Scientists tell you what they’re exploring and why it matters. It’s your chance to understand the questions they’re trying to answer and why those questions are exciting. Pay attention to any prior research they reference, as this will help you understand the foundation of their study.
Tip: As you read the introduction, jot down key points, questions, and any connections you make with your existing knowledge. Seek definitions for pivotal concepts. If the study involves specialized terms, the introduction might provide definitions or explanations to ensure readers understand them. Maintain these on sticky notes or separate paper for reference, aiding your assimilation of the article’s contents as these words will often appear throughout the article.
5. The Heart of the Journey: Results
The results section is where the heart of the journey lies. Scientists unveil what they found, often using graphs, charts, or tables. These are like the clues in a treasure hunt – they show you the evidence behind the discoveries. Look for patterns, trends, and any significant differences. Remember, it’s okay to take your time and go back to the methods section if you need to clarify how the data was collected. Don’t worry if you’re not sure about everything – even scientists take time to piece it all together!
A proven college admissions edge
Polygence alumni had a 90% admissions rate to R1 universities in 2023. Polygence provides high schoolers a personalized, flexible research experience proven to boost your admission odds. Get matched to a mentor now!"
6. Deciding to Use the Article
After reading through these sections, you’ll have a better understanding of the study. Now, it’s time to decide whether the article is useful for your needs. Ask yourself if the research addresses your questions or supports your ideas. Consider whether the methods used are appropriate and if the conclusions are supported by the evidence presented. Remember, not all articles will be a perfect fit, and that’s okay. Each piece of the puzzle you encounter adds to your knowledge and critical thinking skills.
7. Embrace the Adventure: Take Your Time
Remember, you're not racing against time. Take your time to absorb the information. If you find unfamiliar words, don't worry. Use a dictionary or ask your teacher for help. Like any great adventure, understanding comes with practice.
8. Join the Scientific Expedition: Ask Questions
Are questions popping up? Don’t hesitate to ask! Talk to your teachers, classmates, or even online communities. Science is all about curiosity, and questions are your superpower. Or you can use those questions for your research – they might lead you to a new adventure!
9. Verify the Sources: Check Citations
Examine references to see if the authors are building upon previous work and how their study fits into the broader scientific context.
10. Take Notes
Summarize key points and your understanding of the article. Note any questions or areas that need further exploration.
Next Steps with Polygence
Congratulations! You’ve just uncovered the secrets of reading scientific articles, one step at a time. So, dear explorers, arm yourself with curiosity and embark on the journey of reading scientific articles. Reading top neuroscience journals , medical journals , and scientific articles might feel like a journey into the unknown, but with the right approach, it becomes an exciting adventure.
Start with the abstract to get a sense of the study’s purpose, then dive into the discussion or conclusion. Then uncover the methods or introduction depending on your familiarity with the topic. Explore the results and graphs like a treasure map.
As you read more articles, you’ll become more skilled at deciphering their secrets and unlocking the wealth of knowledge they hold. From there, you can explore how to potentially publish and showcase your own research article . Happy reading, intrepid young scientists!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It's easiest to write your abstract last, right before the proofreading stage, because it's a summary of the work you've already done. Your abstract should: ... For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format. Checklist: Abstract 0 / 8. The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page. ...
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
5. How to Format an Abstract. Most abstracts use the same formatting rules, which help the reader identify the abstract so they know where to look for it. Here's a list of formatting guidelines for writing an abstract: Stick to one paragraph. Use block formatting with no indentation at the beginning.
Follow these five steps to format your abstract in APA Style: Insert a running head (for a professional paper—not needed for a student paper) and page number. Set page margins to 1 inch (2.54 cm). Write "Abstract" (bold and centered) at the top of the page. Place the contents of your abstract on the next line.
An abstract in research papers is a keyword-rich summary usually not exceeding 200-350 words. It can be considered the "face" of research papers because it creates an initial impression on the readers. While searching databases (such as PubMed) for research papers, a title is usually the first selection criterion for readers.
Abstracts of research papers have always played an essential role in describing your research concisely and clearly to researchers and editors of journals, enticing them to continue reading. However, with the widespread availability of scientific databases, the need to write a convincing abstract is more crucial now than during the time of ...
Focus on key results, conclusions and take home messages. Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary. Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings. Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar.
How to Write Research Paper Abstract. Here are the steps to follow when writing a research paper abstract: Start by reading your paper: Before you write an abstract, you should have a complete understanding of your paper. Read through the paper carefully, making sure you understand the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. ...
How to write an abstract. Tip: Always wait until you've written your entire paper before you write the abstract. Before you actually start writing an abstract, make sure to follow these steps: Read other papers: find papers with similar topics, or similar methodologies, simply to have an idea of how others have written their abstracts.
You will almost always have to include an abstract when: Completing a thesis or dissertation. Submitting a research paper to an academic journal. Writing a book proposal. Applying for research grants. It's easiest to write your abstract last, because it's a summary of the work you've already done.
Include 5 to 10 important words or short phrases central to your research in both the abstract and the keywords section. For example, if you are writing a paper on the prevalence of obesity among lower classes that crosses international boundaries, you should include terms like "obesity," "prevalence," "international," "lower ...
Set a 1-inch (2.54 centimeter) margin on all sides. The running head should be aligned to the left at the top of the page. The abstract should be on the second page of the paper (the first one is reserved for the title). Avoid indentations, unless you must include a keywords section at the end of the abstract.
An abstract is a concise summary of the major findings in your research paper. It is usually found at the beginning of your research paper. A good abstract should be able to give the average lay reader a strong sense of the main findings within your full-text paper. Abstracts are typically one paragraph depending on how you decide to structure it.
Here are the basic steps to follow when writing an abstract: 1. Write your paper. Since the abstract is a summary of a research paper, the first step is to write your paper. Even if you know what you will be including in your paper, it's always best to save your abstract for the end so you can accurately summarize the findings you describe in ...
To write an effective research paper abstract, start by clearly stating the research problem and objectives, followed by a concise explanation of the methodology. Then, summarize the key findings and conclude with the implications or contributions of the research, ensuring all information is relevant and brief. ...
The abstract should be written for the audience of this journal: do not assume too much or too little background with the topic. Ensure that all of the information found in the abstract also can be found in the body of the paper. Ensure that the important information of the paper is found in the abstract. Avoid: using the first paragraph of the ...
In this case, I recommend to allocate the components described above to the prompts you are being given by the journal. Here's how you write an abstract for a research paper: 1. PROVIDE CONTEXT TO YOUR RESEARCH TOPIC. The first one or two sentences create the setting and provide an introduction to the topic of your study.
Generating Ideas and Text. Write the paper first, the abstract last. You can then use the finished work as the guide for the abstract, which should follow the same basic structure. Exception: You may need to write a proposal abstract months before the work it describes will be complete. Copy and paste key statements.
Step 3: Define the Research Problem and Objectives. Begin your abstract by clearly outlining the research's purpose and objectives. Make the case for its significance to individuals and society. Specify the research question (s) you aim to address.
Informative Abstract Example 1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) has been correlated with leadership effectiveness in organizations. Using a mixed-methods approach, this study assesses the importance of emotional intelligence on academic performance at the high school level. The Emotional Intelligence rating scale was used, as well as semi ...
An abstract is a short summary of a larger work, such as academic, scientific or general research papers. Its purpose is to give the readers a glance at what comes next and convince them to keep reading. Therefore, it is usually situated at the beginning of such works. The size of an abstract is around 100-300 words including one or two ...
Step 4: Add some sentences describing how you make your argument. It always helps when you identify the theoretical or methodological school that you are using to approach your question or position yourself within an ongoing debate. This helps readers situate your ideas in the larger conversations of your discipline.
How to Write An Abstract. Think of your abstract or artist statement like a movie trailer: it should leave the reader eager to learn more but knowledgeable enough to grasp the scope of your work. Although abstracts and artist statements need to contain key information on your project, your title and summary should be understandable to a lay ...
How to Prepare Your Abstract. Write your abstract Review it Ask a peer to read it Send your abstract to your co-authors with time for them to review and provide edits/feedback to you. Track changes in Word works great. For "Co-Authors," include those you've worked with closely, who've been directly involved in your work.
3. Focus: Explain what you intend to do to solve the problem. Normally, you would now describe what you did to accomplish your research goal. However, if you have not yet carried out your research, you have nothing to report. As such, you should instead explain what you intend to do to accomplish your goal.
Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper. APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper. APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information. In APA papers, in-text ...
How to Submit An Abstract. Students should consult with their faculty mentor(s) to determine the most appropriate presentation format to present their work prior to submission:. Poster Presentations concisely communicate research using graphics/images/figures with minimal text.A 5-7 minute explanation guides the audience through the research topic, methodology, preliminary/expected results ...
Abstracts have always served the function of "selling" your work. But now, instead of merely convincing the reader to keep reading the rest of the attached paper, an abstract must convince the reader to leave the comfort of an office and go hunt down a copy of the article from a library (or worse, obtain one after a long wait through inter ...
1. Unveil the Mystery: Title & Abstract Imagine you're about to embark on an adventure. Start by reading the title and abstract of the scientific research paper - they're like your treasure map! The title gives you a sneak peek of the scientific paper, while the abstract sums up the whole journey in a few sentences.
Steps to write a research paper introduction. By following the steps below, you can learn how to write an introduction for a research paper that helps readers "shake hands" with your topic. In each step, thinking about the answers to key questions can help you reach your readers. 1. Get your readers' attention