Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Diversity — Promoting the Diversity and Inclusion within the Workplace

Promoting Diversity and Inclusion Within The Workplace
- Categories: Diversity Workplace
About this sample

Words: 904 |
Published: Nov 15, 2018
Words: 904 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
- being aware of our own beliefs and behaviors and how this may influence the way we treat others
- listening with an open mind to understand different points of view
- being proactive in offering support to others
- encourage team members and help each other
- regularly reinforcing behaviors (e.g. as a part of team meetings)
- providing feedback on employee behaviors in relation to inclusivity as a part of performance reviews
- ensuring that teams are not overly influenced by a small number of individuals by seeking out perspectives of all team members and encouraging full participation
- treating women equally at par and not trying to belittle them (e.g. not automatically making an assumption that a woman in the team should be taking the meeting minutes)
- creating opportunities for team members to get to know each other beyond their job roles.
- Promptly addressing misunderstandings, such as providing feedback when the impact of their actions inadvertently differ from their intent
- Taking prompt action when disrespectful incidents occur, such as inappropriate jokes or language, or when people are excluded
- Ensuring consequences are in place for repeated inappropriate behavior.
- Maintaining a culture that embraces gender equality
- Undertaking a culture survey
- Raising awareness of the detrimental effects of gender stereotypes and areas of unconscious bias
- Including the expectation of equitable and inclusive behaviors as a part of the induction for all new employees and a compulsory part of ongoing employee performance review discussions.
- Commit to boosting our own cultural competency.
- Cross cultural communication.
- Having seminars to educate about other cultural traditions.
- Actively seek out new perspectives and ideas for any problems globally across the team (People from different cultures and background may take a different approach to issues).
- Creating a workplace where different perspectives are valued and embraced can go a long way and take the hospital to even greater heights.
- Treat others how they want to be treated and not to “treat others how you want to be treated”
- Always be considerate and sensitive to the boundaries and expectations of others. For example, understanding how different cultures perceive a handshake, maintaining eye contact or the boundaries of personal space can help to avert misunderstandings.
- Very important when in doubt, ask if you accidentally caused offense, apologize. This will be appreciated.
- Being respectful of personal and cultural boundaries, and encouraging your colleagues to do the same through your example, will make the workplace more welcoming and productive for everyone.
- Observe diverse traditions, celebrations, and holidays from other culture.
Works Cited
- Bell, M. P. (2012). Diversity in organizations. Cengage Learning.
- Cox, T. (1994). Cultural diversity in organizations: Theory, research and practice. Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
- Deane, B. R., & Stokols, D. (2018). Community interventions for health and wellbeing: Theory, practice, and outcomes. Routledge.
- Harvard Business Review. (2013). Diversity & Inclusion. Harvard Business School Publishing.
- Herring, C. (2009). Does diversity pay?: Race, gender, and the business case for diversity. American Sociological Review, 74(2), 208-224.
- Madsen, S. R., & Shafritz, J. M. (2010). Essentials of business ethics. Penguin.
- Pless, N. M., & Maak, T. (2004). Building an inclusive diversity culture: Principles, processes and practice. Journal of Business Ethics, 54(2), 129-147.
- Roberson, Q. M., & Park, H. J. (2007). Examining the link between diversity and firm performance: The effects of diversity reputation and leader racial diversity. Group & Organization Management, 32(5), 548-568.
- Robinson, V. M., & Hayday, S. (2015). The positive effects of diversity management on innovation: An empirical study in the UK hospitality industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 27(2), 168-182.
- Thomas, R. R., & Ely, R. J. (1996). Making differences matter: A new paradigm for managing diversity. Harvard Business Review, 74(5), 79-90.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1064 words
2 pages / 774 words
5 pages / 2323 words
1 pages / 1265 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Diversity
The differences between traditional and modern families are vast and reflect the changing values and norms of society. Shifting gender roles, embracing diversity and inclusivity, prioritizing open communication and emotional [...]
Diversity in the classroom refers to the variety of differences that exist among students, including but not limited to race, ethnicity, gender, socioeconomic status, language, culture, and learning styles. In today's globalized [...]
The future can be both exciting and daunting. The constant barrage of questions about what we plan on doing next can be overwhelming, but it is an important aspect of growing up. The question of where we see ourselves in the [...]
Imagine a workplace where every employee brings a unique set of skills, perspectives, and experiences to the table. A place where diversity is not just tolerated, but celebrated. This is precisely the world that "The Office" [...]
In a rapidly growing globalised economy, workforces that are culturally diverse can help organisations expand their business in global markets. Being able to communicate effectively in different parts of the world is a crucial [...]
In conclusion, Bronx Masquerade by Nikki Grimes offers a powerful exploration of the themes of self-expression and diversity. Through the analysis of the themes, characters, and literary devices used in the novel, it becomes [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
DEI: What It Is & How to Champion It in the Workplace

- 03 Oct 2023
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives are essential to fostering a positive work culture. Through exposure to diverse perspectives, you can improve employee morale, promote business ethics , and drive creative problem-solving and innovation .
According to a LinkedIn survey , 69 percent of recruiters and human resources professionals believe their organizations commit to diverse hiring practices. Yet, only 47 percent think they hold hiring managers to those standards.
If you want to champion diversity, equity, and inclusion at your organization, here's an overview of DEI’s goals, why it’s important in business, and how you can implement it.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion?
According to the online course Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability , DEI comprises:
- Diversity: The presence and participation of individuals with varying backgrounds and perspectives, including those who have been traditionally underrepresented
- Equity: Equal access to opportunities and fair, just, and impartial treatment
- Inclusion: A sense of belonging in an environment where all feel welcomed, accepted, and respected
To better understand DEI, here’s a breakdown of its components and benefits.
Your organization can achieve workplace diversity by employing people from various backgrounds based on:
- Sexual orientation
Doing so can produce several benefits for your company's bottom line. For example, research shows that businesses with diverse teams experience more than twice as much cash flow per employee .
Employees can also file charges against your organization if they've been discriminated against. According to a Good Jobs First report , 99 percent of Fortune 500 companies have been involved in at least one lawsuit related to discrimination or sexual harassment since 2000.
Such conflict resolution can be costly, but workplace diversity involves more than difficult conversations with employees .
“I don’t want diversity to be about policing people,” says Oona King, vice president of diversity, equity, and inclusion at Snap Inc., in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability . “I want diversity to be about unleashing innovation and having more diverse perspectives in the room to come up with solutions to the most pressing problems of our day.”
Equity in the workplace requires treating all employees fairly and justly—regardless of their backgrounds—and ensuring equal opportunities for growth, development, and success.
While diversity provides financial benefits, equity ensures all employees feel valued. Yet, this isn’t always the case. According to a Gallup poll , 24 percent of Black and Hispanic employees experienced workplace discrimination between 2019 and 2020.
Since people often hire or promote individuals who share similar characteristics as themselves , proactively combatting influences—such as unconscious bias —can lead to workplace equity in the form of:
- Equal opportunities
- Fair compensation
- Balanced training and educational opportunities
“What you have to do around equity is tell people there are a lot of biases we’ve built up since we were kids that have been reinforced repeatedly,” King says in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability . “And you need more awareness around them if you want to do well in a forward-thinking company.”
Inclusion extends beyond diversity and refers to employees’ workplace experiences.
It involves creating an environment where all employees feel valued, respected, and fully integrated into your organization's culture and operations.
According to Forrester , 60 percent of sales teams believe inclusion in the workplace has contributed to their success, while a Pew Research study indicates that over half of employees value DEI initiatives at work.
If you hope to make your organization more inclusive, consider your role as an ethical leader . According to Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability , thinking about the biases and concepts that influence your decision-making is essential to creating an inclusive workplace.
Related: The Importance of Reflective Leadership in Business
How to Implement DEI Within Your Organization
DEI is only effective when you implement it into your overall business strategy .
“You cannot have a diversity, equity, and inclusion strategy as a separate strategy,” King says in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability . “It's not going to work. You have to tie it into the heart of your business strategy because separate is never equal.”
Here are four tips for implementing DEI effectively.
1. Invest in Diversity Initiatives
Investing in DEI initiatives can take several forms in business.
For example, Walmart invests in DEI by offering a Supplier Inclusion Program that supports businesses and suppliers from communities often underrepresented in large-scale retail.
Companies like Salesforce also emphasize DEI education . Through its partnership with professional skills-based platform Trailhead , employees can take courses and earn certifications in subjects such as inclusion guidelines for data visualization and inclusive content creation. According to the company’s Annual Equality Update , its commitment to DEI education and inclusive hiring tactics has resulted in nearly 51 percent of U.S. employees coming from underrepresented groups.

2. Offer Bias Training Sessions
Stereotypes—whether blatant or unconscious—can negatively impact your organization and result in decreased motivation and employee engagement.
One way to overcome workplace stereotypes is by offering unconscious bias training sessions to increase employees’ awareness of implicit biases. For example, the Implicit Association Test (IAT) —developed by professors from Harvard University, the University of Washington, and the University of Virginia—helps identify implicit associations or stereotypes you might be unaware of.
You can also provide employees the opportunity to earn a business ethics certificate to gain skills to identify and surmount biases.
Don’t be afraid to make training mandatory. According to Pew Research , approximately 53 percent of employees find DEI training helpful, with only 13 percent finding it unhelpful.
In addition, companies like Google provide this type of training through workshops that more than half of its employees participate in.
Related: Leadership in Big Tech: How to Make Ethical Decisions
3. Promote Pay Equity
Ensuring employees earn equitable salaries is crucial to championing DEI.
“When you measure objectives for metrics in corporate America, you’ll see very clear differences for different groups,” King says in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability . “That's the data; we know it's a fact. So our job is to change those objectives in the workplace.”
One of those data points is pay equity. In the U.S., women earn approximately 82 percent of what men do—a figure that's only increased two percent since 2002. While various factors impact that statistic, it's critical for your organization to offer equitable compensation, regardless of gender.
“That's where today's diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts really come in,” King says. “What levers and tools do we have to change, so that whoever walks through the door has the same chance as anyone else of success?”
4. Prioritize Developing Talent from Underrepresented Groups
Developing talent from underrepresented groups is crucial to fostering diversity and inclusion. By providing opportunities for personal and professional growth, your organization can help address historical workplace disparities.
For example, Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability highlights Google’s push for DEI initiatives, including:
- Funding research on why fewer students who identify as female or are from underrepresented groups enroll in computer science programs
- Offering financial support to science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) programs in underrepresented communities
- Forming recruiting teams that establish a “pipeline program” with universities that have large populations of underrepresented students
These align with what Harvard Business School Professor Nien-hê Hsieh calls “the pipeline problem” in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability .
“There simply aren’t enough qualified members of underrepresented groups available to hire for these jobs,” Hsieh says. “In the United States, this theory points to patterns like fewer women and Black people receiving degrees in science, technology, engineering, or math than their male, white, or Asian counterparts.”

Make Your Organization More Equitable
When implemented properly, DEI’s benefits can't be overstated.
“The underlying point of DEI is to understand the impact of culture and the way we do things in business strategy,” King says.
If you want to promote DEI, Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability can help you learn how to make ethical leadership decisions and create a fair workplace culture through interactive learning activities and real-world business examples.
Ready to champion DEI at your organization? Enroll in Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability —one of our online leadership and management courses —and download our free leadership e-book on how to become a more effective leader.

About the Author
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- College essay
- How to Write a Diversity Essay | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Diversity Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on November 1, 2021 by Kirsten Courault . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Table of contents
What is a diversity essay, identify how you will enrich the campus community, share stories about your lived experience, explain how your background or identity has affected your life, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about college application essays.
Diversity essays ask students to highlight an important aspect of their identity, background, culture, experience, viewpoints, beliefs, skills, passions, goals, etc.
Diversity essays can come in many forms. Some scholarships are offered specifically for students who come from an underrepresented background or identity in higher education. At highly competitive schools, supplemental diversity essays require students to address how they will enhance the student body with a unique perspective, identity, or background.
In the Common Application and applications for several other colleges, some main essay prompts ask about how your background, identity, or experience has affected you.
Why schools want a diversity essay
Many universities believe a student body representing different perspectives, beliefs, identities, and backgrounds will enhance the campus learning and community experience.
Admissions officers are interested in hearing about how your unique background, identity, beliefs, culture, or characteristics will enrich the campus community.
Through the diversity essay, admissions officers want students to articulate the following:
- What makes them different from other applicants
- Stories related to their background, identity, or experience
- How their unique lived experience has affected their outlook, activities, and goals
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Think about what aspects of your identity or background make you unique, and choose one that has significantly impacted your life.
For some students, it may be easy to identify what sets them apart from their peers. But if you’re having trouble identifying what makes you different from other applicants, consider your life from an outsider’s perspective. Don’t presume your lived experiences are normal or boring just because you’re used to them.
Some examples of identities or experiences that you might write about include the following:
- Race/ethnicity
- Gender identity
- Sexual orientation
- Nationality
- Socioeconomic status
- Immigration background
- Religion/belief system
- Place of residence
- Family circumstances
- Extracurricular activities related to diversity
Include vulnerable, authentic stories about your lived experiences. Maintain focus on your experience rather than going into too much detail comparing yourself to others or describing their experiences.
Keep the focus on you
Tell a story about how your background, identity, or experience has impacted you. While you can briefly mention another person’s experience to provide context, be sure to keep the essay focused on you. Admissions officers are mostly interested in learning about your lived experience, not anyone else’s.
When I was a baby, my grandmother took me in, even though that meant postponing her retirement and continuing to work full-time at the local hairdresser. Even working every shift she could, she never missed a single school play or soccer game.
She and I had a really special bond, even creating our own special language to leave each other secret notes and messages. She always pushed me to succeed in school, and celebrated every academic achievement like it was worthy of a Nobel Prize. Every month, any leftover tip money she received at work went to a special 509 savings plan for my college education.
When I was in the 10th grade, my grandmother was diagnosed with ALS. We didn’t have health insurance, and what began with quitting soccer eventually led to dropping out of school as her condition worsened. In between her doctor’s appointments, keeping the house tidy, and keeping her comfortable, I took advantage of those few free moments to study for the GED.
In school pictures at Raleigh Elementary School, you could immediately spot me as “that Asian girl.” At lunch, I used to bring leftover fun see noodles, but after my classmates remarked how they smelled disgusting, I begged my mom to make a “regular” lunch of sliced bread, mayonnaise, and deli meat.
Although born and raised in North Carolina, I felt a cultural obligation to learn my “mother tongue” and reconnect with my “homeland.” After two years of all-day Saturday Chinese school, I finally visited Beijing for the first time, expecting I would finally belong. While my face initially assured locals of my Chinese identity, the moment I spoke, my cover was blown. My Chinese was littered with tonal errors, and I was instantly labeled as an “ABC,” American-born Chinese.
I felt culturally homeless.
Speak from your own experience
Highlight your actions, difficulties, and feelings rather than comparing yourself to others. While it may be tempting to write about how you have been more or less fortunate than those around you, keep the focus on you and your unique experiences, as shown below.
I began to despair when the FAFSA website once again filled with red error messages.
I had been at the local library for hours and hadn’t even been able to finish the form, much less the other to-do items for my application.
I am the first person in my family to even consider going to college. My parents work two jobs each, but even then, it’s sometimes very hard to make ends meet. Rather than playing soccer or competing in speech and debate, I help my family by taking care of my younger siblings after school and on the weekends.
“We only speak one language here. Speak proper English!” roared a store owner when I had attempted to buy bread and accidentally used the wrong preposition.
In middle school, I had relentlessly studied English grammar textbooks and received the highest marks.
Leaving Seoul was hard, but living in West Orange, New Jersey was much harder一especially navigating everyday communication with Americans.
After sharing relevant personal stories, make sure to provide insight into how your lived experience has influenced your perspective, activities, and goals. You should also explain how your background led you to apply to this university and why you’re a good fit.
Include your outlook, actions, and goals
Conclude your essay with an insight about how your background or identity has affected your outlook, actions, and goals. You should include specific actions and activities that you have done as a result of your insight.
One night, before the midnight premiere of Avengers: Endgame , I stopped by my best friend Maria’s house. Her mother prepared tamales, churros, and Mexican hot chocolate, packing them all neatly in an Igloo lunch box. As we sat in the line snaking around the AMC theater, I thought back to when Maria and I took salsa classes together and when we belted out Selena’s “Bidi Bidi Bom Bom” at karaoke. In that moment, as I munched on a chicken tamale, I realized how much I admired the beauty, complexity, and joy in Maria’s culture but had suppressed and devalued my own.
The following semester, I joined Model UN. Since then, I have learned how to proudly represent other countries and have gained cultural perspectives other than my own. I now understand that all cultures, including my own, are equal. I still struggle with small triggers, like when I go through airport security and feel a suspicious glance toward me, or when I feel self-conscious for bringing kabsa to school lunch. But in the future, I hope to study and work in international relations to continue learning about other cultures and impart a positive impression of Saudi culture to the world.
The smell of the early morning dew and the welcoming whinnies of my family’s horses are some of my most treasured childhood memories. To this day, our farm remains so rural that we do not have broadband access, and we’re too far away from the closest town for the postal service to reach us.
Going to school regularly was always a struggle: between the unceasing demands of the farm and our lack of connectivity, it was hard to keep up with my studies. Despite being a voracious reader, avid amateur chemist, and active participant in the classroom, emergencies and unforeseen events at the farm meant that I had a lot of unexcused absences.
Although it had challenges, my upbringing taught me resilience, the value of hard work, and the importance of family. Staying up all night to watch a foal being born, successfully saving the animals from a minor fire, and finding ways to soothe a nervous mare afraid of thunder have led to an unbreakable family bond.
Our farm is my family’s birthright and our livelihood, and I am eager to learn how to ensure the farm’s financial and technological success for future generations. In college, I am looking forward to joining a chapter of Future Farmers of America and studying agricultural business to carry my family’s legacy forward.
Tailor your answer to the university
After explaining how your identity or background will enrich the university’s existing student body, you can mention the university organizations, groups, or courses in which you’re interested.
Maybe a larger public school setting will allow you to broaden your community, or a small liberal arts college has a specialized program that will give you space to discover your voice and identity. Perhaps this particular university has an active affinity group you’d like to join.
Demonstrating how a university’s specific programs or clubs are relevant to you can show that you’ve done your research and would be a great addition to the university.
At the University of Michigan Engineering, I want to study engineering not only to emulate my mother’s achievements and strength, but also to forge my own path as an engineer with disabilities. I appreciate the University of Michigan’s long-standing dedication to supporting students with disabilities in ways ranging from accessible housing to assistive technology. At the University of Michigan Engineering, I want to receive a top-notch education and use it to inspire others to strive for their best, regardless of their circumstances.
If you want to know more about academic writing , effective communication , or parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Transition words
- Passive voice
- Paraphrasing
Communication
- How to end an email
- Ms, mrs, miss
- How to start an email
- I hope this email finds you well
- Hope you are doing well
Parts of speech
- Personal pronouns
- Conjunctions
In addition to your main college essay , some schools and scholarships may ask for a supplementary essay focused on an aspect of your identity or background. This is sometimes called a diversity essay .
Many universities believe a student body composed of different perspectives, beliefs, identities, and backgrounds will enhance the campus learning and community experience.
Admissions officers are interested in hearing about how your unique background, identity, beliefs, culture, or characteristics will enrich the campus community, which is why they assign a diversity essay .
To write an effective diversity essay , include vulnerable, authentic stories about your unique identity, background, or perspective. Provide insight into how your lived experience has influenced your outlook, activities, and goals. If relevant, you should also mention how your background has led you to apply for this university and why you’re a good fit.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Courault, K. (2023, May 31). How to Write a Diversity Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/college-essay/diversity-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Kirsten Courault
Other students also liked, how to write about yourself in a college essay | examples, what do colleges look for in an essay | examples & tips, how to write a scholarship essay | template & example, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Diversity, Equity and Inclusion in the Workplace
A majority of u.s. workers say focusing on dei at work is a good thing, but relatively small shares place great importance on diversity in their own workplace, table of contents.
- The value of DEI efforts at work
- The importance of a diverse workforce
- DEI measures and their impact
- How gender, race and ethnicity impact success in the workplace
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand how adults in the United States think about diversity, equity and inclusion efforts in the workplace. This analysis is based on survey responses from 4,744 U.S. adults who are working part time or full time, are not self-employed, have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job, and whose company or organization has 10 or more people. The data was collected as part of a larger survey of workers conducted Feb. 6-12, 2023. Everyone who took part is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Read more about the questions used for this report and the report’s methodology .
References to workers or employed adults include those who are employed part time or full time, are not self-employed, have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job, and whose company or organization has 10 or more people.
References to White, Black and Asian adults include those who are not Hispanic and identify as only one race. Hispanics are of any race.
References to college graduates or people with a college degree comprise those with a bachelor’s degree or more. “Some college” includes those with an associate degree and those who attended college but did not obtain a degree.
References to disabled workers include those who say a disability or handicap keeps them from fully participating in work, school, housework or other activities.
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and those who say they lean toward the Republican Party. Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and those who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
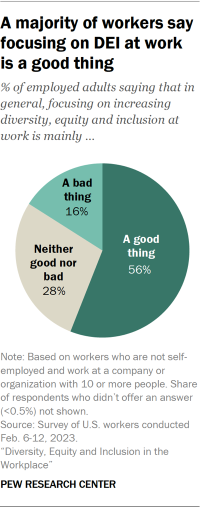
Workplace diversity, equity and inclusion efforts, or DEI, are increasingly becoming part of national political debates . For a majority of employed U.S. adults (56%), focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. But opinions about DEI vary considerably along demographic and political lines.
Most workers have some experience with DEI measures at their workplace. About six-in-ten (61%) say their company or organization has policies that ensure fairness in hiring, pay or promotions, and 52% say they have trainings or meetings on DEI at work. Smaller shares say their workplace has a staff member who promotes DEI (33%), that their workplace offers salary transparency (30%), and that it has affinity groups or employee resource groups based on a shared identity (26%). Majorities of those who have access to these measures say each has had a positive impact where they work.
Related : How Americans View Their Jobs
This nationally representative survey of 5,902 U.S. workers, including 4,744 who are not self-employed, was conducted Feb. 6-12, 2023, using the Center’s American Trends Panel . 1 The survey comes at a time when DEI efforts are facing some backlash and many major companies are laying off their DEI professionals .
Some key findings from the survey:
- Relatively small shares of workers place a lot of importance on diversity at their workplace. About three-in-ten say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (32%) or ages (28%). Roughly a quarter say the same about having a workplace with about an equal mix of men and women (26%) and 18% say this about a mix of employees of different sexual orientations.
- More than half of workers (54%) say their company or organization pays about the right amount of attention to increasing DEI. Smaller shares say their company or organization pays too much (14%) or too little attention (15%), and 17% say they’re not sure. Black workers are more likely than those in other racial and ethnic groups to say their employer pays too little attention to increasing DEI. They’re also among the most likely to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing (78% of Black workers say this), while White workers are the least likely to express this view (47%).
- Women are more likely than men to value DEI at work. About six-in-ten women (61%) say focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, compared with half of men. And larger shares of women than men say it’s extremely or very important to them to work at a place that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation.
- There are wide partisan differences in views of workplace DEI. Most Democratic and Democratic-leaning workers (78%) say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, compared with 30% of Republicans and Republican leaners. Democrats are also far more likely than Republicans to value different aspects of diversity. And by wide margins, higher shares of Democrats than Republicans say the policies and resources related to DEI available at their workplace have had a positive impact.
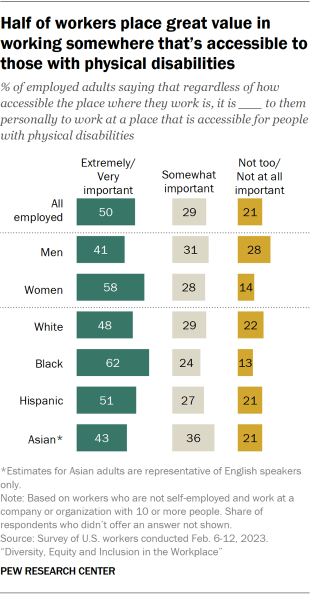
- Half of workers say it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities. About three-in-ten workers (29%) say this is somewhat important to them, and 21% say it’s not too or not at all important. A majority of workers (76% among those who do not work fully remotely) say their workplace is at least somewhat accessible for people with physical disabilities.
- Many say being a man or being White is an advantage where they work. The survey asked respondents whether a person’s gender, race or ethnicity makes it easier or harder to be successful where they work. Shares ranging from 45% to 57% say these traits make it neither easier nor harder. But far more say being a man and being White makes it easier than say it makes it harder for someone to be successful. Conversely, by double-digit margins, more say being a woman, being Black or being Hispanic makes it harder than say it makes it easier to be successful where they work.
A majority of workers (56%) say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is mainly a good thing; 28% say it is neither good nor bad, and 16% say it is a bad thing. Views on this vary along key demographic and partisan lines.

Half or more of both men and women say focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, but women are more likely than men to offer this view (61% vs. 50%). In turn, men are more than twice as likely as women to say it is a bad thing (23% vs. 9%).
About two-thirds or more of Black (78%), Asian (72%) and Hispanic (65%) workers say that focusing on DEI at work is a good thing. Among White workers, however, fewer than half (47%) say it’s a good thing; in fact, 21% say it’s a bad thing. But there are wide partisan, gender and age gaps among White workers, with majorities of White Democrats, women and those under age 30 saying focusing on DEI at work is a good thing.
Workers under 30 are the most likely age group to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing. About two-thirds (68%) of workers ages 18 to 29 say this, compared with 56% of workers 30 to 49, 46% of those 50 to 64, and 52% of those 65 and older.
Views also differ by educational attainment, with 68% of workers with a postgraduate degree saying focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, compared with 59% of those with a bachelor’s degree only and 50% of those with some college or less education.
Democratic and Democratic-leaning workers are much more likely to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing (78%) than to say it is a bad thing (4%) or that it is neither good nor bad (18%). Views among Republican and Republican-leaning workers are more mixed: Some 30% say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, while the same share (30%) say it’s a bad thing, and 39% say it’s neither good nor bad.
A majority of workers say their employer pays the right amount of attention to DEI
When it comes to the focus of their own employer, 54% of workers say their company or organization pays about the right amount of attention to increasing diversity, equity and inclusion. The remainder are divided between saying their employer pays too much (14%) or too little attention (15%), or that they’re not sure (17%).
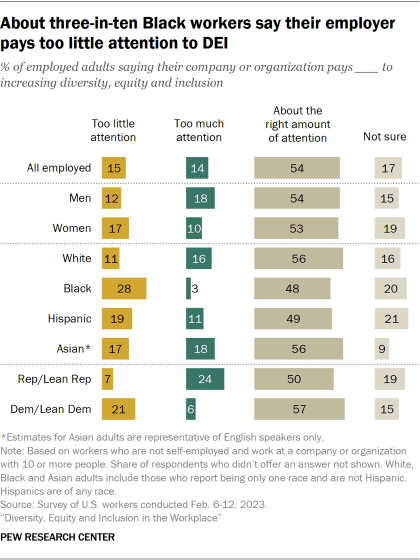
Women are more likely than men to say their employer pays too little attention to increasing DEI (17% vs. 12%). In turn, men are more likely than women to say too much attention is paid to this where they work (18% vs. 10%).
Black workers (28%) are the most likely to say their company or organization pays too little attention to increasing DEI, compared with smaller shares of White (11%), Hispanic (19%) and Asian (17%) workers who say the same.
Views on this question also differ by party. While half or more of both Republican and Democratic workers say their company or organization pays the right amount of attention to DEI, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say their employer pays too little attention to it (21% vs. 7%). In turn, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say their employer pays too much attention to DEI (24% vs. 6%).
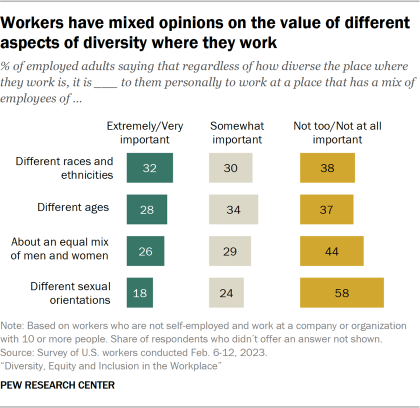
While a majority of workers say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is a good thing, relatively small shares place great importance on working at a place that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation. About three-in-ten workers say it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (32%) and ages (28%), while 26% say the same about having about an equal mix of men and women. And 18% say this about having a mix of employees of different sexual orientations at their workplace.
Women are more likely than men to say it’s extremely or very important to them to work at a place that is diverse across all measures asked about in the survey. For example, there are 11 percentage point differences in the shares of women compared with men saying it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that has a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (37% vs. 26%) and about an equal mix of men and women (31% vs. 20%).
Black workers are among the most likely to value racial, ethnic and age diversity in the workplace. Some 53% of Black workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities, compared with 39% of Hispanic workers and 25% of White workers who say the same; 43% of Asian workers say this is important to them. (There is no statistically significant difference between the share of Asian workers and the shares of Black and Hispanic workers who hold this view.) And while 42% of Black workers highly value working somewhere with a mix of employees of different ages, smaller shares of Hispanic (33%), Asian (30%) and White (24%) workers say the same.
When it comes to diversity of sexual orientation, 28% of Black workers and 22% of Hispanic workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is diverse in this way; 15% each among White and Asian workers say the same.
Workers under age 50 are more likely than those 50 and older to say racial and ethnic diversity in their workplace is extremely or very important to them (35% vs. 26%). Workers younger than 50 are also more likely to say having about an equal mix of men and women is important to them, with workers ages 18 t0 29 the most likely to say this (34% vs. 26% of workers 30 to 49, and 20% each among those 50 to 64 and 65 and older).
There are also differences by educational attainment, with larger shares of workers with a postgraduate degree than those with less education saying it’s extremely or very important to them that their workplace is diverse across all measures asked about in the survey. For example, 44% of workers with a postgraduate degree say having a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities is extremely or very important to them, compared with 34% of those with a bachelor’s degree only and 27% of those with some college or less.
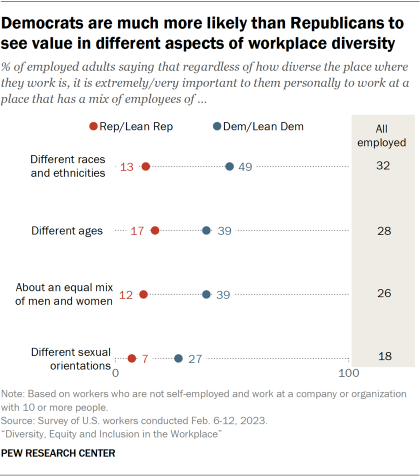
Democratic workers are much more likely than Republican workers to say working somewhere that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation is extremely or very important to them. In fact, about half of Democrats (49%) place great importance on having a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities where they work, compared with 13% of Republicans. And there are differences of at least 20 points between the shares of Democrats and Republicans saying it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that has about an equal mix of men and women (39% of Democrats say this vs. 12% of Republicans) and a mix of employees of different ages (39% vs. 17%) and sexual orientations (27% vs. 7%).
Overall, a majority of workers say their workplace has a mix of employees of different ages (58% say this describes their current workplace extremely or very well). Smaller shares say their workplace has about an equal mix of men and women (38%) and a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (46%) and sexual orientations (28%). These assessments do not vary much across demographic groups.
Half of workers place great importance on working at a place that is accessible for people with physical disabilities
Half of workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities; 29% say it is somewhat important and 21% say it is not too or not at all important to them.
Highly valuing an accessible workplace varies by gender, race and ethnicity, and party, but there is no significant difference in responses between those who do and don’t report having a disability.
About six-in-ten women (58%) say it is extremely or very important to them that their workplace is accessible, compared with 41% of men.
Black workers are more likely than workers of other racial and ethnic groups to place great importance on their workplace being accessible: 62% of Black workers say this is extremely or very important, compared with 51% of Hispanic, 48% of White and 43% of Asian workers.
A majority of Democrats (59%) say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities; 40% of Republican say the same. Some 27% of Republicans say this is not too or not at all important to them, compared with 15% of Democrats.
There is no statistically significant difference in the shares of workers who have a disability and those who do not saying it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities. But workers who do not have a disability are more likely than those who do to say this is not too or not at all important to them (21% vs. 15%).
Among those who don’t work fully remotely, about three-quarters of workers (76%) say their workplace is at least somewhat accessible for people with physical disabilities, with 51% saying it is extremely or very accessible. Some 17% say their workplace is not too or not at all accessible, and 8% are not sure.
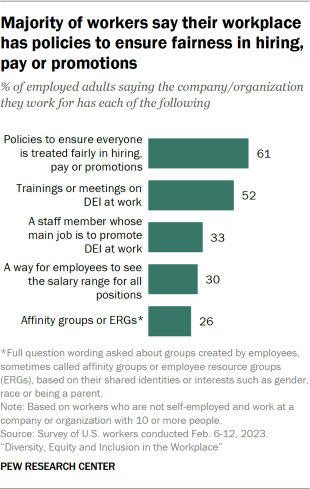
When asked whether the company or organization they work for has a series of measures that are typically associated with diversity, equity and inclusion efforts, a majority of workers say their employer has policies that ensure everyone is treated fairly in hiring, pay or promotions (61%), and 52% say there are trainings or meetings on DEI where they work.
Smaller shares say their workplace has a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work (33%), a way for employees to see the salary range for all positions (30%), and groups created by employees sometimes known as affinity groups or employee resource groups (ERGs) based on shared identities such as gender, race or being a parent (26%).
Responses do not vary much by most demographic characteristics. However, workers with at least a bachelor’s degree are consistently more likely than those with less education to say each of these five measures is available where they work.
Workers tend to see positive impact from policies and resources associated with DEI where they work
Among those whose workplace offers each policy or resource, a majority of workers say each measure has had a somewhat or very positive impact where they work. About a third or fewer workers say each resource has had neither a positive nor negative impact, and about one-in-ten or fewer say each of these has had a somewhat or very negative impact.
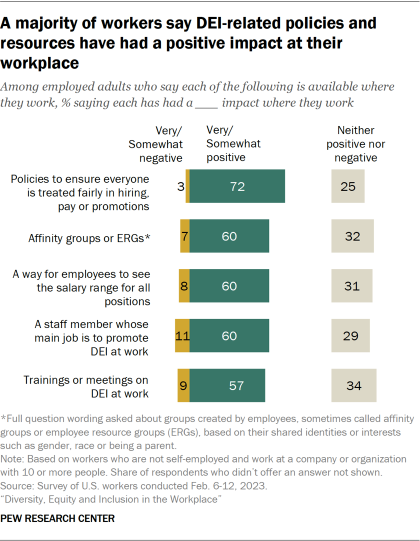
Democrats and Republicans are about equally likely to say their workplace has these measures in place, but Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say the impact of each has been positive by margins ranging from 10 to 32 points (among those who say their workplace has these measures). For example, 66% of Democrats who say their workplace has a way for employees to see the salary range for all positions say this has had a somewhat or very positive impact, compared with 56% of Republicans who say this. And while about three-quarters of Democrats (74%) say having a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work has had a positive impact, fewer than half of Republicans (42%) say the same.
Women are more likely than men to say each of these policies and resources has had a very or somewhat positive impact where they work. This is mainly driven by gender differences among Republicans: There are double-digit differences in the shares of Republican women and Republican men who say many of these resources have had a positive impact. For example, 58% of Republican women say having a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work has had at least a somewhat positive impact where they work, compared with 31% of Republican men who hold this view. The same share of Republican women (58%) say having affinity groups or ERGs has had a positive impact, compared with 38% of Republican men who say the same.
Among Democrats, majorities of both men and women offer positive assessments of these resources in their workplace, but Democratic women are more likely than Democratic men to say having trainings or meetings on DEI at work have had a positive impact (72% vs. 65%).
While there are differences by race, ethnicity and age on overall attitudes about DEI in the workplace, there are no consistent differences along these dimensions in how workers with access to these policies and resources at their workplace assess their impact.
About half of workers who have participated in DEI trainings in the last year say they’ve been helpful
Out of all workers, about four-in-ten (38%) have participated in a DEI training in the last year. A similar share (40%) did not participate or say their workplace does not offer these trainings, and 21% are not sure if their employer offers these trainings.
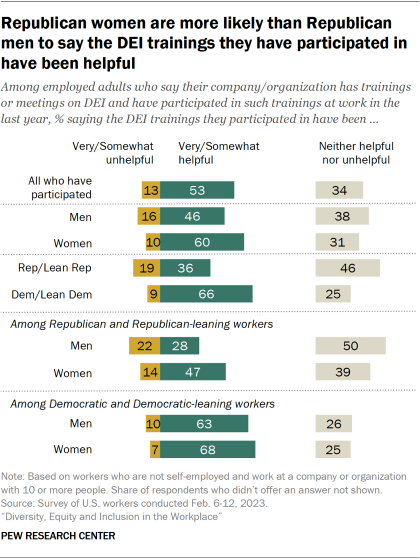
Looking only at those whose company or organization has trainings or meetings on DEI, about three-quarters (73%) say they have participated in such trainings in the past year. And assessments of these trainings tend to be positive, with 53% of workers who’ve participated saying they were very or somewhat helpful. About a third (34%) give a more neutral assessment, saying the trainings were neither helpful nor unhelpful, and 13% say they were very or somewhat unhelpful.
While men and women are about equally likely to have participated in trainings on DEI in the past year, women are more likely than men to say the trainings have been at least somewhat helpful (60% vs. 46%).
Republicans and Democrats are also equally likely to say they’ve participated in these trainings in the past year, but Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to say the trainings have been helpful (66% vs. 36%). About one-in-five Republicans say they’ve been unhelpful (19%), compared with 9% of Democrats.
While both Democratic men and women offer similar assessments of the DEI trainings they’ve participated in, there are gender differences among Republican workers. Republican women are more likely than Republican men to say the trainings they’ve participated in have been helpful (47% vs. 28%). Conversely, 22% of Republican men, compared with 14% of Republican women, say the trainings have been unhelpful.
Few workers are members of affinity groups or ERGs at work
While 26% of workers say there are affinity groups or employee resource groups (ERGs) where they work, members of these groups account for a very small share of workers overall. Just 6% of workers say they are members of an affinity group or ERG, with 58% of workers saying these groups are either not available at their workplace or that they aren’t a member. Another 37% say they are not sure if their workplace offers these groups.
Among workers who say there are affinity groups or ERGs at their workplace, 22% say they are personally a member. Women are more likely than men to be members of these groups (28% vs. 16%). And 28% of non-White workers say they are a member of an affinity group or ERG, compared with 18% of White workers. 2
When asked about the impact a person’s gender, race or ethnicity has on their ability to succeed at work, workers tend to say these characteristics neither make it easier nor harder to be successful at their workplace.
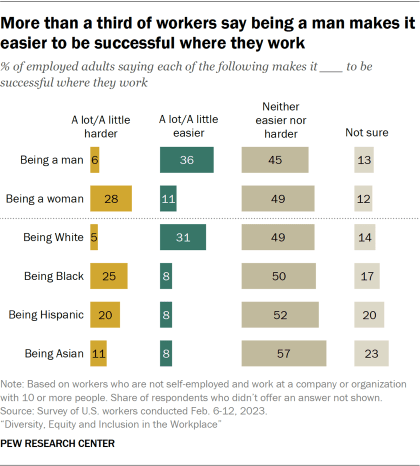
Still, when it comes to gender, workers are more likely to say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work than to say it makes it harder (36% vs. 6%). In contrast, a larger share says being a woman makes it harder to be successful than say it makes it easier (28% vs. 11%).
Men and women have different views on the impact gender has on a person’s ability to succeed where they work. Some 44% of women say being a man makes it at least a little easier to be successful, including 24% who say it makes it a lot easier. This compares with 29% of men who say being a man makes it at least a little easier to be successful.
Similarly, 34% of women say being a woman makes it harder to be successful where they work, compared with 21% of men.
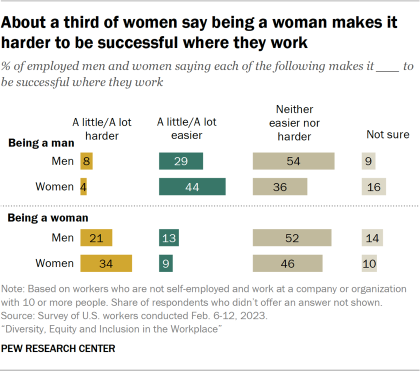
Women under age 50 are especially likely – more so than women ages 50 and older or men in either age group – to say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work and that being a woman makes it harder. For example, 38% of women ages 18 to 49 say being a woman makes it harder to be successful where they work. This compares with 29% of women 50 and older, 25% of men younger than 50, and an even smaller share of men 50 and older (13%).
When it comes to views about how race or ethnicity affects people’s ability to succeed at work, 51% of Black workers say being Black makes it harder to be successful where they work. This is significantly higher than the shares of Asian (41%), Hispanic (23%) and White (18%) workers who say the same about the impact of being Black.
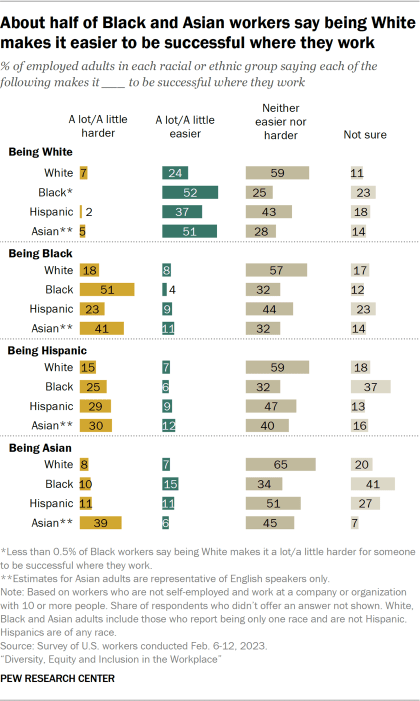
Similarly, about four-in-ten Asian workers (39%) say being Asian makes it harder to be successful in their workplace, a higher share than workers of other racial and ethnic groups who say the same about being Asian.
Hispanic, Black and Asian workers are about equally likely to say being Hispanic makes it harder to be successful where they work. A smaller share of White workers say the same about being Hispanic.
When asked about the impact of being White in their workplace, workers across racial and ethnic groups are more likely to say it makes it easier than to say it makes it harder to be successful. This is especially the case among Black and Asian workers. About half of Black (52%) and Asian (51%) workers say being White makes it easier to be successful where they work, compared with 37% of Hispanic and 24% of White workers who say the same about being White.
Previously released findings from this survey found that Black workers are more likely than White, Hispanic and Asian workers to report that they have experienced discrimination or have been treated unfairly by an employer in hiring, pay or promotions because of their race or ethnicity at some point in their careers (though not necessarily where they currently work). Women are also more likely than men to say they’ve experienced such discrimination because of their gender.
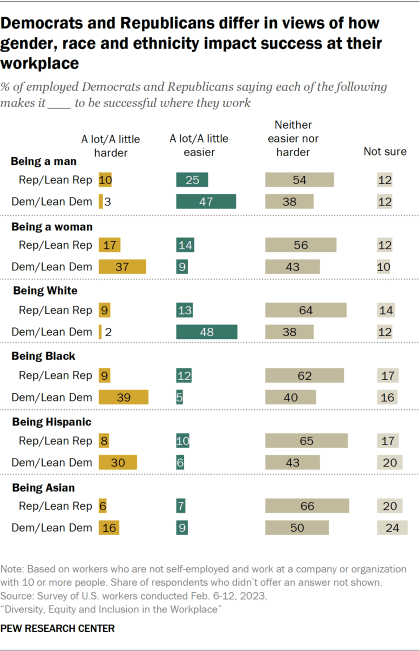
There are large partisan gaps in views of whether gender, race or ethnicity make it easier or harder to be successful at work. Some 47% of Democratic workers say being a man makes it at least somewhat easier to be successful at their workplace, compared with 25% of Republican workers. Democrats are also more likely than Republicans to say being a woman makes it harder to succeed (37% vs. 17%).
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts to say being a woman makes it harder – and being a man makes it easier – to be successful where they work. The differences between Republican women and Republican men are particularly striking. About a quarter of Republican women (26%) say being a woman makes it harder to be successful, compared with 10% of Republican men. And while 36% of Republican women say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work, just 16% of Republican men say the same.
Democratic workers are more than three times as likely as Republican workers to say being White makes it easier to succeed where they work (48% vs. 13%), and they are also more likely than Republicans to say being Black, Hispanic or Asian makes it harder. About four-in-ten Democrats (39%) say being Black makes it harder for someone to succeed at their workplace, compared with just 9% of Republicans. Similarly, 30% of Democrats say being Hispanic makes it harder to succeed, compared with 8% of Republicans. And while smaller shares in both parties say being Asian makes it harder to succeed, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say this (16% vs. 6%). These partisan differences remain when looking only at Democrats and Republicans who are White.
- For details, see the Methodology section of the report. The analysis in this report is based on U.S. workers who are employed full time or part time, who are not self-employed, and who have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job (99% of workers who are not self-employed have one job or a primary job). Additionally, the analysis is restricted to workers at companies or organizations with at least 10 employees as certain federal requirements such as non-discrimination mandates apply to larger workplaces. ↩
- Non-White adults include Black, Hispanic, Asian and other races besides White, as well as people who identify as more than one race. The sample sizes among Black, Hispanic and Asian workers who have affinity groups or ERGs at work are too small to analyze separately. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Asian Americans
- Black Americans
- Business & Workplace
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Economics, Work & Gender
- Economy & Work
- Gender & Work
- Happiness & Life Satisfaction
- Hispanics/Latinos
- Partisanship & Issues
- Race & Ethnicity
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
- Sexual Misconduct & Harassment
Among young U.S. workers without a college degree, men and women hold very different types of jobs
Is college worth it, half of latinas say hispanic women’s situation has improved in the past decade and expect more gains, a majority of latinas feel pressure to support their families or to succeed at work, a look at small businesses in the u.s., most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
May 8, 2023
Celebrating Our Differences: Inspiring Essays on Diversity and Inclusion
Ready to celebrate diversity and inclusion? Discover how to craft an exceptional essay on this important topic with our expert tips and real-world examples. Join us as we explore the power of diversity and its impact on individuals and communities alike.
Imagine yourself walking into a room full of people, each with their own stories to tell. What makes your story stand out? What makes your voice unique? This is the essence of a good diversity essay .
In your essay, you have the opportunity to show the admissions committee how your life experiences have shaped your perspective, identity, and aspirations. Through sharing personal stories, you can paint a picture of who you are and how you will contribute to the vibrant tapestry of the campus community.
Maybe it's growing up in a multicultural household that has taught you to value different perspectives and ways of life. Or, perhaps it's overcoming adversity and facing challenges that have made you a more empathetic and resilient person. Whatever your story may be, your diversity essay is a chance to showcase the richness and depth of your lived experiences.
As you craft your essay, think about how your unique background has informed your actions, beliefs, and goals. Share specific examples and anecdotes that bring your story to life, and make sure to emphasize how you will use your diverse perspective to contribute positively to the campus community. With a well-written diversity essay, you can show the admissions committee that you are more than just a set of grades and test scores - you are a unique and valuable addition to their community.
We have provided a guide as well as some essay examples to assist you in writing your essay about diversity. If you need inspiration for an essay, read them till last. But before we dig into the specifics, a basic understanding of diversity is necessary.
What is Diversity in actuality?
institutions. By recognizing and celebrating the unique experiences, viewpoints, and identities of students from diverse backgrounds, schools can create a more inclusive and welcoming environment that benefits everyone. Through diversity essays, students have the opportunity to showcase the strength of diversity and how it can contribute to the greater community.
Scholarship options designed for historically underserved communities also demonstrate the importance of diversity in leveling the playing field and creating opportunities for all. Therefore, embracing diversity can lead to a stronger and more vibrant academic community.
What is Inclusion?
Inclusion is the practice of making a place where everyone, despite their differences, is treated with dignity and respect . It's the act of making sure nobody is held back from contributing to a group or community because of their identity or background.
Each person's race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, financial background, ability, religion, and other characteristics are valued and celebrated through the practice of inclusion. It's not enough to just tolerate differences; we need to celebrate them and foster communities where everyone can feel safe and included.
To advance social justice and equity, inclusion is crucial. It allows people from all walks of life to meet one another, learn from one another, and work together towards a shared objective. Positive results for individuals and communities can result from their inclusion in more open, welcoming, and supportive settings.
Step-by-Step guide on how to write an essay on diversity and inclusion
Writing an essay on diversity and inclusion is an important task that requires careful planning and execution. In this step-by-step guide, we will provide you with a roadmap on how to write a compelling essay on this topic.
Here are seven suggestions to consider as you write your diversity statement.
Tell your story
Highlight any challenges you had to overcome while writing an essay. Tell the world about how you used to have to lug two 20-pound sacks of rice uphill to school every day. Recognize your privilege if you were born into affluence. Either way, you can utilize your experience to demonstrate your ability to empathize with kids who struggle to complete their education.
Focus on commonly accepted understandings of diversity and inclusiveness
Issues of race, gender, class, and sexual orientation should be given special attention. Don't try to soften your stance by mentioning, for example, how challenging it is to be a Kansan in Missouri. Write about racism, sexism, homophobia, transphobia, ableism, or another form of oppression that is well-known instead.
Avoid false parallels
When writing a diversity essay, it is important to avoid false parallels. False parallels are when two things appear to be similar, but in reality, they are different. To avoid false parallels, you must carefully examine the similarities and differences between the two things you are comparing. This will help you to make accurate and meaningful comparisons, which will ultimately strengthen your diversity essay.
Write about specific things you have done to help students from underrepresented backgrounds succeed
If you've never helped anybody before, now is the time to start. Become involved as a tutor at a low-performing school, help Habitat for Humanity construct homes, or adopt an antiracist pedagogical approach in your classroom. Not only will you gain valuable experience, but you can also use it to strengthen your diversity statement.
Highlight any programs for underrepresented students you’ve participated in
If you have participated in any programs for underrepresented students, be sure to highlight them in your essay on diversity. This could include programs focused on increasing access to education for students from disadvantaged backgrounds, mentorship or internship programs for underrepresented groups, or community service initiatives aimed at promoting diversity and inclusion.
By highlighting these programs, you can showcase your commitment to diversity and demonstrate how you have taken active steps to promote equity and inclusion in your community.
Write about your commitment to working toward achieving equity and enhancing diversity
Provide details on what you can bring to the table. You might express your desire to help existing programmes on campus or to start something brand new inspired by what you've seen elsewhere.
Modify your statement based on where you are sending it
When writing an essay on diversity, it's important to tailor your statement to the specific institution or audience you are addressing. Modifying your statement based on where you are sending it shows that you have taken the time to research the institution and understand its values and priorities. This can increase the likelihood of your statement resonating with the reader and ultimately being successful in achieving your goals.
3 Example essays on Diversity and Inclusion
The importance of diversity workforce, introduction.
Workforce diversity is a critical aspect of modern-day organizations. It involves hiring individuals from different backgrounds, cultures, ethnicities, genders, and ages. The concept of workforce diversity is gaining prominence as organizations are increasingly recognizing the benefits of having a diverse workforce. In this essay, we will explore the importance of workforce diversity, the challenges associated with it, and the benefits it offers.
Encourages Innovation and Creativity
Diversity brings together a wide range of perspectives and ideas that can help drive innovation and creativity. When people from diverse backgrounds come together, they can offer different viewpoints and ideas, leading to new solutions to problems.
Enhances Employee Engagement and Retention
Employees who feel included and valued are more engaged and motivated, leading to higher retention rates. When employees feel they belong and are appreciated, they are more likely to stay with the organization, reducing turnover costs.
Increases Global Competitiveness
Diversity in the workforce is crucial for organizations looking to expand globally. Organizations with a diverse workforce are better equipped to understand and navigate the cultural nuances of different countries and regions, making them more competitive in the global marketplace.
Promotes a Positive Image
Organizations that embrace diversity are viewed positively by the public, customers, and employees. A diverse workforce demonstrates that the organization values and respects individuals from all backgrounds, contributing to a positive brand image.
Resistance to Change
Implementing diversity initiatives can be met with resistance, particularly from those who believe that the traditional way of doing things is the best. It is essential to educate and raise awareness about the benefits of diversity to overcome this challenge.
Communication Barriers
When individuals from different backgrounds come together, there may be communication barriers due to language or cultural differences. It is essential to provide training and resources to overcome these barriers and foster effective communication.
Stereotyping and Bias
Stereotyping and bias can negatively impact diversity initiatives. It is essential to establish a culture of inclusivity and respect, where individuals feel valued and appreciated for their unique contributions.
Improved Decision-Making
A diverse workforce can provide a range of perspectives, leading to better decision-making. When individuals with different backgrounds come together, they can offer different viewpoints, leading to a more comprehensive and well-rounded decision-making process.
Increased Creativity and Innovation
Diversity can lead to new ideas and perspectives that can drive innovation and creativity. A diverse workforce can bring together different viewpoints and experiences, leading to new solutions to problems.
Enhanced Reputation
Improved Employee Engagement and Retention
When employees feel included and valued, they are more engaged and motivated, leading to higher retention rates. A diverse workforce can help create a sense of belonging, leading to improved employee engagement and retention.
Workforce diversity is crucial for modern-day organizations. It can lead to improved decision-making, increased creativity and innovation, and enhanced reputation. However, diversity initiatives can be met with resistance, communication barriers, stereotyping, and bias. It is essential to establish a culture of inclusivity and respect, where individuals feel valued and appreciated for their unique contributions. By embracing diversity, organizations can create a more productive, engaged, and innovative workforce.
2. The challenges of diversity in different institutions
Diversity is a term that describes the differences among people, whether they are cultural, ethnic, racial, linguistic, gender, or sexual orientation differences. While diversity is often celebrated, it can also pose challenges, especially in institutions such as schools, workplaces, and governments. This essay will explore the challenges of diversity in different institutions and how they can be addressed.
Challenges of Diversity in Schools
Schools are meant to be places where students can learn and grow, but diversity can sometimes be a challenge. Students who come from different backgrounds may face discrimination and exclusion from their peers, which can affect their ability to learn and thrive.
Teachers may also struggle to provide a curriculum that is inclusive of all students experiences and perspectives. Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to creating an inclusive environment where all students feel valued and respected.
Challenges of Diversity in the Workplace
Workplaces are becoming increasingly diverse, but this diversity can pose challenges. Employees from different cultural backgrounds may struggle to communicate effectively or may feel excluded from the workplace culture. Discrimination and bias can also be a problem, as can the assumption that everyone shares the same experiences and perspectives. To address these challenges, employers need to be proactive in creating a workplace culture that values diversity and promotes inclusivity. This can involve training and education for employees, as well as policies and procedures that support diversity and inclusion.
Challenges of Diversity in Government
Governments are responsible for serving diverse populations, but this can be a challenge. Members of different cultural and linguistic groups may have different needs and expectations from their government, and some groups may face discrimination or exclusion.
To address these challenges, governments need to be proactive in engaging with diverse communities and ensuring that their policies and programs are inclusive. This can involve outreach and consultation with community groups, as well as the development of policies that reflect the needs and perspectives of diverse communities.
Ways to Address the Challenges of Diversity
Addressing the challenges of diversity requires a commitment to creating inclusive environments where all individuals feel valued and respected. This can involve several strategies, including education and training, policies and procedures, and community engagement.
Education and training can help individuals better understand the experiences and perspectives of those from different backgrounds. This can involve training programs for employees or professional development opportunities for teachers. It can also involve curriculum changes in schools that better reflect the experiences and perspectives of diverse students.
Policies and procedures can also play a role in promoting diversity and inclusion. This can involve policies that prohibit discrimination and harassment in the workplace or schools. It can also involve policies that promote diversity in hiring or that ensure that government programs and services are inclusive of all members of the community.
Community engagement is also an important strategy for promoting diversity and inclusion. This can involve outreach to community groups and the development of partnerships with organizations that serve diverse communities. It can also involve the creation of advisory committees or other mechanisms for engaging with diverse populations.
In conclusion, diversity is an important aspect of our society, but it can also pose challenges in different institutions. Schools, workplaces, and governments need to be proactive in creating inclusive environments where all individuals feel valued and respected. This requires a commitment to education and training, policies and procedures that promote diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. By addressing the challenges of diversity, we can create a more equitable and inclusive society for all.
3. Ideas on how to Reduce Discrimination in Society
Racial discrimination is a pervasive issue that has plagued society for centuries. It is a problem that continues to affect individuals and communities around the world. Discrimination is an act that denies individuals equal rights, opportunities, and treatment based on their race or ethnicity. The impacts of racism are far-reaching, and it affects individuals' economic, social, and emotional well-being. Therefore, there is a need for collective efforts to reduce racial discrimination and promote social justice. This essay discusses some of the best ways to reduce racial discrimination in society.
Education and Awareness
Education is a powerful tool that can help reduce racial discrimination. Education is essential in teaching individuals about diversity, equity, and inclusion. When people understand the impact of racism, they are more likely to become allies and advocates for change. Education can take many forms, such as books, documentaries, and workshops.
Institutions can also incorporate cultural competency training into their curriculum to educate students and faculty members about the impact of discrimination. It is essential to recognize the different forms of discrimination, including implicit bias, microaggressions, and institutional racism, to address them appropriately.
Political Action
Political action is another way to reduce racial discrimination in society. Leaders at the local, state, and federal levels can enact policies that promote equality and diversity. Policies such as affirmative action and diversity initiatives can promote inclusion in the workforce and educational institutions.
Politicians can also pass laws that make racial discrimination illegal and provide support to victims of discrimination. It is essential to recognize that racism is a systemic issue that requires political action to address.
Community Engagement
Community engagement is an important way to reduce racial discrimination. Building strong communities that are inclusive and diverse can help reduce racism. Communities can engage in activities that promote diversity, such as cultural festivals, food fairs, and art exhibits.
These events can help build bridges between different communities and promote understanding. Community members can also engage in conversations about racism and work together to address it. This can create a sense of belonging and unity that can help reduce discrimination.
Diversity in Institutions
Institutions play a significant role in reducing racial discrimination. Institutions such as schools, businesses, and government agencies can promote diversity by recruiting and retaining individuals from diverse backgrounds. A diverse workforce or student body can help reduce discrimination by promoting inclusion and understanding.
Institutions can also create policies that promote equality and diversity, such as flexible work arrangements, diversity training, and bias reporting systems. It is important to ensure that institutions are representative of the communities they serve to reduce discrimination.
In conclusion, reducing racial discrimination requires a collective effort from individuals, institutions, and political leaders. Education and awareness, political action, community engagement, and diversity in institutions are all effective ways to address discrimination. It is important to recognize that reducing discrimination is a long-term effort that requires commitment and perseverance. By working together, we can create a more inclusive and equitable society that values diversity and promotes social justice.
Final Words
In conclusion, embracing diversity and inclusion is crucial for creating a more equitable and harmonious society. Whether it's through recognizing and celebrating racial diversity and cultural diversity, fostering a sense of belonging for all individuals, or actively working to combat discrimination and prejudice, we must prioritize these values in all aspects of our lives. By championing diversity and inclusion, we can cultivate a richer, more vibrant world that values the unique perspectives and experiences of all people. By embracing diversity and inclusion, we can build a better future for ourselves and for generations to come.
If you are tired of struggling to write essays on diversity and inclusion and find yourself running short on time and needing assistance to meet your deadline then go for Jenni.ai! This powerful AI tool can help you write an essay in a matter of minutes. Jenni.ai eliminates the stress and pressure of essay writing, allowing you to produce high-quality content quickly and efficiently. With its innovative technology, you can enjoy originality and coherence in your writing without spending hours of writer’s block. Sign up for Jenni.ai today and take your writing to the next level!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
Need to start saving with a new ATS? Learn how to calculate the return on investment of your ATS Calculate ROI now
- Inside HR |
- Stories & Insights |
- Diversity & Inclusion |
Diversity in the workplace: why it matters and how to increase inclusion
Diversity in the workplace refers to the coexistence of individuals with varying characteristics, skills, and traits. It's crucial to pair diversity with inclusion, ensuring equal opportunities throughout the employee lifecycle. A diverse workforce brings unique perspectives, fostering creativity, innovation, and better product development.

An experienced recruiter and HR professional who has transferred her expertise to insightful content to support others in HR.

We live in interesting times. The Black Lives Matter and #MeToo movements, the global rise of immigration, and large-scale political changes such as Brexit and the election of Trump, shed light on – previously overlooked – minority groups and draw our attention toward equal rights, racism, feminism and socio-economic disparities.
The workplace is not unaffected by all this. Calls for greater diversity in the workplace have increased exponentially. Now is the time for HR professionals to focus on diversity in the workplace and reinforcing inclusion not just in words, but in practice. Many are expecting to see results.
But what exactly is diversity in the workplace?
Diversity is the coexistence of people with different characteristics (e.g. race, age, gender, sexual orientation), skills and personality traits. For example, at work, we can talk about a diverse team when employees come from various cultural, academic and professional backgrounds and when there’s a balance in gender, age and race. You can find more examples in our diversity in the workplace definition .
You can’t build diverse teams, though, without pairing diversity with inclusion . Nor have you “won” if you now have a diverse team, because equity and inclusion are where the real work begins. Employees feel included in their workplace when they have equal opportunities during the entire employee lifecycle: from the way they’re treated during the hiring process to how they’re being managed, trained, evaluated and promoted.
But this can’t happen automatically. To build an inclusive workplace, employers must provide those equal opportunities to all potential and existing employees. They should also revisit and improve their procedures as needed to ensure they’re respectful to all people regardless of protected characteristics.
For an inclusive workplace, employers must provide equal opportunities to all potential & existing employees. They should also improve procedures as needed to ensure they’re respectful to all regardless of protected characteristics.
Build inclusive hiring practices
Creating a safe and equitable workplace starts with hiring. That's why we've developed solutions to cultivate inclusivity and support diversity at every stage of the hiring process.
The importance of diversity and inclusion
Why do we care so much about DEI in the workplace, though? And why should we care? Is it simply the right thing to do or are there business gains associated with diversity?
It’s both. When you try to build diverse teams, you fight discrimination in the workplace. You aim to give equal opportunities to all employees – even those (or especially those) in underrepresented groups.
We can better understand the value of diversity in the workplace with some examples of what happens when companies don’t take into account diverse voices. Two diversity in the workplace articles talk about the importance of a diverse workforce when building and testing products:
- a Black person struggles to use an automatic soap dispenser because the light sensor doesn’t detect a dark-skinned hand
- Black women speak up about the extensive hair searches they have to undertake at airports, as body scanners give false alarms due to their natural Afro.
These examples prove that diversity, equity and inclusion is not just about the moral aspect of it; when you add diverse voices in your teams, you learn things you wouldn’t have known otherwise, you build better products and you increase equity in the workplace and beyond.
There are financial benefits, too, that motivate employers to boost their DEI efforts . Diverse companies:
- Reflect societies more accurately. Societies are by default diverse in age, race, gender and socio-economic class. Therefore, organizations with diverse employees are better aligned with the demographics of the area (or areas) where they operate. On a macroeconomics scope, this means that they can better predict – and adjust to – changes in the market and local consumer behavior.
- Speak to a broader audience. People usually relate to those from a similar background. So, when your employees come from various backgrounds, they can understand the needs, interests and pain points of diverse audiences, too. This gives you the opportunity to expand your messaging and promote your products and services to a larger customer base.
- Get more creative and profitable. Diversity doesn’t only refer to protected characteristics. There’s also diversity of thought – that may or may not be a result of different protected characteristics. Employees with different experiences and perspectives can bring fresh ideas and innovative solutions to the table which, in turn, benefit the entire organization.
You can start building a business case for diverse teams for your organization with studies and interesting stats.
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion in action
A quick online search will give you lots of studies and articles on the benefits of diversity in the workplace. And while talking about diversity is a good thing, because it means we’re paying attention, it’s not enough. Let’s take a deeper look at how companies, and particularly HR departments, can actively foster diversity in the workplace.
The legal aspect of diversity in the workplace
To promote diversity at work, there is legislation that protects minority or underrepresented groups from discrimination. There are also regulations that reinforce human rights in the workplace. For example, in many countries, employers can’t fire a pregnant employee and they can’t include age and gender requirements in their job ads unless it’s absolutely necessary or relevant for the role. It’s best to consult a lawyer to ensure that your company complies with all relevant legislation that applies in your specific location.
In the United States, Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is the regulatory body that enforces diversity in every work situation; for example, when employers hire, terminate, compensate, promote, and train employees. For more details, check our guides and learn what you need to do to comply with the law:
- What is Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO)
- EEO guidelines for employers
- How to follow EEOC regulations
- How to file an EEO-1 report
- Why EEO statements fall short
In Canada, the Human Rights Act includes a number of laws and regulations that protect people against discriminatory practices. There are also specific regulations about equal pay and the Canadian Human Rights Commission where employees can file complaints when treated unfairly.
The UK has established a similar commission, the Equality and Human Rights Commission , that provides guidance for employees and employers regarding the Equality Act 2010 .
Finally, the European Union has implemented a series of non-discriminatory directives to reinforce equity across the EU. For example, the Directive 2000/78/EC is about discrimination at work on grounds of religion or belief, disability, age or sexual orientation and the Directive 2006/54/EC provides the framework of equal treatment for men and women in matters of employment and occupation.
Anti-discrimination laws are not here to pose limitations to employers. They exist so that all people have equal opportunities at work. It’s important to have an official, legal context that ensures that companies treat employees objectively and respectfully, because we are all prone to unconscious bias . Also, sometimes for the sake of faster hiring, it’s common to pick candidates based on convenience, i.e. based on arbitrary or even superficial hiring criteria .
In this case, diversity regulations can serve as guidelines for employers who don’t just need or want to be compliant with the law, but try to actively fight all types of discrimination in the workplace. For example, take a look at these illegal interview questions – even if it’s not legally forbidden to ask them in your area, it’s still a good idea to avoid them so that you hire candidates using objective, job-related criteria.
The role of recruiters and HR
While increasing DEI is not one person’s (or one department’s) responsibility, the HR experts can take many actions to build a truly inclusive workplace. That’s because they’re in charge of everything that has to do with the human aspect of the company: from attracting and recruiting diverse candidates to setting the guidelines for fair treatment, management and compensation of all employees to ensure a fully inclusive workplace.
Here’s how recruiters and HR professionals can foster workplace diversity:
- Remove biases from hiring. From gender-neutral job descriptions to targeted, skill-based interview questions, your hiring process should be built in a way that helps you find the best people for the job – not the ones you like the most. Here are some examples from companies that are taking actions to reduce bias in recruiting , plus a few tips to get you started when you aim to create an inclusive work environment .
- Look for areas of improvement. Diversity might not always be tangible, but you can still set some goals and track your progress. For example, what’s the gender ratio at your company and by department? How many of your female employees have a leadership role ? If those numbers are not close to your goals, you might want to invest your energy into increasing diversity specifically in these areas. Rachel Bates, who was SVP of Sales & Marketing at Workable until spring 2020, describes how she successfully built a more gender-balanced sales team , while recruitment expert Matt Buckland, at one point Workable’s VP of Customer Advocacy, advises on how to hire more women in tech , a traditionally male-dominated field.
- Consider the overlooked types of diversity. When we talk about diversity, we mostly refer to race and gender. But there’s more than that. Some examples include age discrimination , bias against employees with disabilities , and rejection of candidates with non-traditional career paths . You should also keep in mind that there’s intersectionality in the workplace, i.e. overlapping biases such as age and gender discrimination . Your DEI efforts should take into account all different types of diversity that exist in your workplace – or that you’d like them to exist.
- Involve all of your team members. A recruiter alone can’t build a diverse company. Picture this: As a recruiter at your company, you might be diversifying your candidate sources and screening resumes with strictly job-related criteria. But if those who’re making the final hiring decision are biased, they could still reject good candidates because, for example, some candidates don’t have a degree from a prestigious school. It’s essential that all employees, no matter their seniority level, understand the importance of diversity in the workplace. Whether it’s through bias trainings or official anti-discrimination company policies , everyone should be aware of expectations, values and appropriate behaviors in terms of mutual respect and acceptance. For example, those who’re involved in recruiting should know how to document interview feedback to help their teams make well-rounded hiring decisions and all colleagues should know what constitutes unacceptable work behavior .
Why oppose diversity in the workplace?
“ I want to hire people I get along with because I know we’ll collaborate better. ”
“ When I’m actively looking to increase the number of female employees at my company, don’t I discriminate against male candidates? ”
“ Things like religious beliefs and sexual preferences have no place in a professional setting – they only bring controversy and distractions from work. ”
These are valid concerns, but not strong enough to dismiss DEI efforts from the workplace. In fact, it’s quite the opposite; it goes back to building an inclusive environment where all employees feel safe and respected no matter their protected characteristics, personal opinions, backgrounds, etc.
You fight the challenges of diversity in the workplace by structuring your interview process in a way that helps you hire on merit (rather than make decisions that lead to homogenous teams) by implementing affirmative action programs to support underrepresented groups when needed, and by setting the framework for approaching controversial topics at work .
Ultimately, you want to create a place where employees are treated equally and there are no privileged and underprivileged groups, and everyone feels included.
Frequently asked questions
Need action and results in your dei initiative.
Find diverse candidates, eliminate unconscious bias while hiring, and measure your impact.
Improve DEI
Related topics
Inside HR | Stories & Insights | Trends |
Exploring the future of jobs and the positive impact of ai.

Inside HR | Stories & Insights | Ask an Expert |
Ai in finance could free up at least four hours per week.
Inside HR | Stories & Insights | Tech & Data |
Anxiety in the workplace: it’s affecting everyone in different ways.

Inside HR | Stories & Insights | Workplace |
6 workplace changes we can expect in the 2020s, new guide: calculate the roi of an ats.
Need to start saving with a new ATS? Calculate the ROI of your ATS with our template.
Popular topics
- Candidate sourcing and attraction
- Working together with others
- Maximizing candidate & employee experience
- Finding & attracting people
- Digitizing work processes
- Ensuring compliance best practices
Let's grow together
Explore our full platform with a 15-day free trial. Post jobs, get candidates and onboard employees all in one place.
Share on Mastodon
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Implementing Inclusive Policies Across a Global Organization
- Nataly Kelly

Three strategies for multinational companies.
As more and more U.S. companies commit to supporting diversity, inclusion, and belonging in the workplace, one component that often gets left behind is the extension of those initiatives across an organization’s global offices. On the one hand, policies informed by the American cultural and political context aren’t necessarily effective when applied wholesale in other environments. At the same time, it’s essential for organizations to demonstrate a consistent commitment to their stated values, no matter where in the world they may operate. To address these challenges, the author identifies three tactical opportunities for companies to step up and ensure their inclusion policies are upheld globally: choosing international office locations that align with the company’s values, helping international teams to understand and contextualize U.S.-driven initiatives, and pursuing inclusive language policies in any foreign languages in which the company operates.
While issues surrounding diversity, inclusion, and belonging (DI&B) have increasingly taken center stage in corporate America, many U.S.-based companies struggle to extend new policies across their global teams. That’s no surprise. Their DI&B initiatives are often largely informed by American social, legal, and political considerations — and that context seldom maps perfectly to every country in which a company operates. Given these challenges, what does it take for multinational companies to stay true to their DI&B values around the world while acknowledging differences in local cultural contexts?
- Nataly Kelly is the chief marketing officer at Zappi . Her latest book is Take Your Company Global and her blog is Born to Be Global .
Partner Center
- Home >
- Insights >

Why Is Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace Important?

DEIB , Diversity & Inclusion , Leadership & Management
Here's why diversity and inclusion in the workplace is important. More than policies, programs, or headcounts, equitable employers outpace their competitors by respecting the unique needs, perspectives, and potential of their diverse workforce. As a result, diverse and inclusive workplaces earn deeper trust and more commitment from their employees.
What is the difference between diversity and inclusion?
Diversity and inclusion are two interconnected concepts—but they are far from interchangeable. Diversity focuses on representation or the make-up of an entity. Inclusion is about how well the contributions, presence, and perspectives of different groups of people are valued and integrated into an environment.
An environment where many different genders, races, nationalities, and sexual orientations and identities are present but only the perspectives of certain groups are valued or carry any authority or influence, may be diverse, but it is not inclusive.
What is diversity and inclusion in the workplace?
A diverse and inclusive workplace is one that makes everyone, regardless of who they are or what they do for the business, feel equally involved in and supported in all areas of the workplace. The “all areas” part is important.
Do you have diversity in your recruiting , in each of your departments, and in your leadership? Or do you have a diverse workplace where 50% of your employees are women but 0% of your women are managers? Do you have a good representation of employees of color overall, but all of them are in the same department?
These telling questions reveal true diversity and inclusion in the workplace.
Why is diversity and inclusion in the workplace important?
Research has shown many benefits of a diverse and inclusive workplace:
- Higher revenue growth
- Greater readiness to innovate
- Increased ability to recruit a diverse talent pool
- 5.4 times higher employee retention
Inclusion in the workplace is one of the most important keys to retention
When employees don’t feel that their ideas, presence or contributions are truly valued or taken seriously by their organization, they will eventually leave.
Our research on company culture shows that when employees trust that they, and their colleagues, will be treated fairly regardless of race, gender, sexual orientation or age, they are.

- 9.8 times more likely to look forward to going to work
- 6.3 times more likely to have pride in their work
- 5.4 times more likely to want to stay a long time at their company
Having an inclusive workplace culture will not only help you attract a diverse set of talent but also help you retain the diverse talent you attracted in the first place. In other words, diversity and inclusion is critical to a strong employee retention strategy.
What is an inclusive workplace?
The diversity that lacks genuine inclusion is often called “tokenism.” A genuinely inclusive workplace doesn’t just have a diversity of people present, it has a diversity of people involved, developed, empowered, and trusted by the business. Diversity efforts need to go beyond a pretty companywide memo.
What is the difference between diversity, inclusion and belonging?
The difference between diversity, inclusion and belonging is that diversity is the representation of different people in an organization, inclusion is ensuring that everyone has an equal opportunity to contribute to and influence every part and level of a workplace, and belonging is ensuring that everyone feels safe and can bring their full, unique selves to work. It can be confusing and many companies are guilty of making simple mistakes when it comes to diversity or inclusion efforts. Thankfully, they can be corrected - if workplaces know what they're doing wrong. Unfortunately, many companies won't recognize what's 'right' and 'wrong' when it comes to diversity and inclusion in the workplace unless they're seeking it out.
What is the Great Place To Work For All™ definition?
For All™ is Great Place To Work’s definition of a workplace culture that has evolved beyond “Diversity and Inclusion.”
The goal of the For All approach is to create a consistently high-trust workplace experience for everyone, no matter who they are or what they do for the organization. It's being able to create spaces that celebrate diverse backgrounds and inclusive cultures.
Everyone matters in a For All workplace
For All is the accumulation of day-to-day experiences that fuel a thriving company culture. They are the leaders who push to overcome challenges and create a workplace where employees feel they belong, that their unique talents matter, and that their individual needs are cared for by their colleagues and leaders. When companies experience the very human acts of acknowledgment, inclusion, dignity, and compassion, that is when they can achieve For All.
For All is critical for success. Workplaces today are more diverse and globally connected than ever before. With the complexities of today’s work environment, leaders must tap into collective intelligence to maximize the potential of every person.
Technological and social changes continue to alter the landscape in every industry. Organizations will need the human judgment, empathy, passion and creativity of all their people to realize the full promise of the era’s new technologies, increase agility and inventiveness and address the challenges of an increasingly demanding, vocal marketplace.
Why it can't be For Some, but For All
Organizations that remain “For Some” workplaces will risk losing money, earning less and falling behind their competitors in this disruptive climate. However, the companies that succeed with For All will cultivate tremendous value from their people’s differences and will thrive.
If you’re ready to create a great place to work For All™ – contact us about our solutions today.
Learn how to create the kind of culture that makes people excited to come to work.
Matt Bush is the Culture Coaching Lead at Great Place to Work®. With a background in both quantitative and qualitative research and analysis methods, Matt helps leaders gain insight into how to build great workplaces for all, while simultaneously achieving their business goals and fueling new and innovative practices.
Latest Articles

Written by Ted Kitterman

Written by Roula Amire

Get fresh culture insights straight to your inbox!
- A-Z Publications
Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior
Volume 6, 2019, review article, diversity in the workplace: a review, synthesis, and future research agenda.
- Quinetta M. Roberson 1
- View Affiliations Hide Affiliations Affiliations: Villanova School of Business, Villanova University, Villanova, Pennsylvania 19085, USA; email: [email protected]
- Vol. 6:69-88 (Volume publication date January 2019) https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-012218-015243
- First published as a Review in Advance on October 31, 2018
- Copyright © 2019 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved
Fueled by socioeconomic trends that changed the composition of organizational workforces, the term workforce diversity was coined in the 1990s. Since then, both researchers and practitioners have strived (and struggled) to understand the concept, its effects in and on organizations, and strategies for managing such effects. In this article, I provide an overview and interpretation of the current literature to examine its purpose, progress, and direction. Highlighting key conceptualizations of the construct, theoretical foundations, and empirical findings on diversity and diversity management, I discuss the evolution and current state of the field and synthesize this information to propose a future research agenda. In doing so, I seek to identify theoretical, empirical, and practice areas of opportunity for advancing scientific knowledge about the meaning, substance, and outcomes of diversity as well as the implementation of diversity science in organizations.
Article metrics loading...
Full text loading...
Literature Cited
- Allen TD , Aby LT , Poteet ML , Lentz E , Lima L 2004 . Career benefits associated with mentoring for protégés: a meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 89 : 1 127– 36 [Google Scholar]
- Allen TD , Herst DEL , Bruck CS , Sutton M 2000 . Consequences associated with work-to-family conflict: a review and agenda for future research. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 5 : 278– 308 [Google Scholar]
- Ancona DG , Caldwell DF 1992 . Demography and design: predictors of new product design team performance. Org. Sci. 3 : 321– 39 [Google Scholar]
- Avery DR , McKay PF 2006 . Target practice: an organizational impression management approach to attracting minority and female job applicants. Pers. Psychol. 59 : 157– 87 [Google Scholar]
- Avery DR , McKay PF , Volpone SD 2013 . Diversity staffing: Inclusive personnel recruitment and selection practices. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 282– 99 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Berscheid E 1985 . Interpersonal attraction. Handbook of Social Psychology G Lindzey, E Aronson 2 413– 84 New York: Random House [Google Scholar]
- Berscheid E , Walster EH 1978 . Interpersonal Attraction Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley [Google Scholar]
- Bezrukova K , Thatcher SMB , Jehn K 2007 . Group heterogeneity and faultlines: comparing alignment and dispersion theories of group composition. Conflict in Organizational Groups: New Directions in Theory and Practice KJ Behfar, LL Thompson 57– 92 Evanston, IL: Northwestern Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Blake-Beard SD , Murrell AJ , Thomas DA 2007 . Unfinished business: the impact of race on understanding mentoring relationships. The Handbook of Mentoring . BR Ragins, KE Kram 223– 48 Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage
- Blau PM 1977 . Inequality and Heterogeneity New York: Free Press [Google Scholar]
- Bowers C , Pharmer J , Salas E 2000 . When member homogeneity is needed in work teams: a meta-analysis. Small Group Res. 31 : 305– 27 [Google Scholar]
- Byrne D 1971 . The Attraction Paradigm New York: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Cantor N , Mischel W 1979 . Prototypes in person perception. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 12 : 3– 52 [Google Scholar]
- Chao GT , Moon H 2005 . The cultural mosaic: a meta-theory for understanding the complexity of culture. J. Appl. Psychol. 90 : 1128– 40 [Google Scholar]
- Cole ER 2009 . Intersectionality and research in psychology. Am. Psychol. 64 : 170– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Cox TH Jr. , Blake S 1991 . Managing cultural diversity: implications for organizational competitiveness. Acad. Manag. Exec. 5 : 45– 56 [Google Scholar]
- Creary SJ , Roberts LM 2017 . G.I.V.E.-based mentoring in diverse organizations. Mentoring Diversity Leaders: Creating Change for People, Process, and Paradigms AJ Murrell, SD Blake-Beard 3– 24 New York: Routledge [Google Scholar]
- De Dreu CKW , Weingart LR 2003 . Task versus relationship conflict, team performance, and team member satisfaction: a meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 88 : 741– 49 [Google Scholar]
- Dobbin F , Kalev A 2013 . The origins and effects of corporate diversity programs. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 253– 81 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Dobbin F , Kalev A , Kelly E 2007 . Diversity management in corporate America. Contexts 6 : 21– 28 [Google Scholar]
- Dreher GF , Cox TH 1996 . Race, gender and opportunity: a study of compensation attainment and the establishment of mentoring relationships. J. Appl. Psychol. 81 : 297– 308 [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M , Porter SC 2013 . An examination of categorization processes in organizations: the root of intergroup bias and a route to prejudice reduction. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 98– 114 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Frone MR , Russell M , Cooper ML 1992 . Antecedents and outcomes of work-family conflict: testing a model of the work-family interface. J. Appl. Psychol. 77 : 65– 78 [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg C 2005 . Relational demography and similarity-attraction in interview assessment and subsequent offer decisions. Group Org. Manag. 30 : 597– 624 [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald AG , McGhee DE , Schwartz JLK 1998 . Measuring individual differences in implicit cognition: the implicit association test. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 74 : 1464– 80 [Google Scholar]
- Harrison DA , Klein KJ 2007 . What's the difference? Diversity constructs as separation, variety, or disparity in organizations. Acad. Manag. Rev. 32 : 1199– 228 [Google Scholar]
- Harrison DA , Price KH , Bell MP 1998 . Beyond relational demography: time and the effects of surface- and deep-level diversity on work group cohesion. Acad. Manag. J. 41 : 96– 107 [Google Scholar]
- Harrison DA , Price KH , Gavin JH , Florey AT 2002 . Time, teams, and task performance: changing effects of surface- and deep-level diversity on group functioning. Acad. Manag. J. 45 : 1029– 45 [Google Scholar]
- Hebl MR , King EB 2013 . The social and psychological experience of stigma. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 115– 31 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Hite LM , McDonald KS 2006 . Diversity training pitfalls and possibilities: an exploration of small and mid-size US organizations. Hum. Res. Dev. Internat. 9 : 365– 77 [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz SK , Horwitz IB 2007 . The effects of team diversity on team outcomes: a meta-analytic review of team demography. J. Manag. 33 : 987– 1015 [Google Scholar]
- Jackson SE , Joshi A , Erhardt NL 2003 . Recent research on team and organizational diversity: SWOT analysis and implications. J. Manag. 29 : 801– 30 [Google Scholar]
- Jackson SE , May KA , Whitney K 1995 . Understanding the dynamics of diversity in decision making teams. Team Decision Making Effectiveness in Organizations RA Guzzo, E Salas 204– 61 San Francisco: Jossey-Bass [Google Scholar]
- Jehn KA 1995 . A multi-method examination of the benefits and detriments of intragroup conflicts. Admin. Sci. Quart. 40 : 256– 82 [Google Scholar]
- Jehn KA 1997 . Qualitative analysis of conflict types and dimensions in organizational groups. Admin. Sci. Quart. 42 : 530– 57 [Google Scholar]
- Jehn KA , Greer LL 2013 . Diversity as disagreement: the role of group conflict. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 179– 91 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Jehn KA , Greer LL , Rupert J 2008 . Diversity and conflict. Diversity at Work ed. A Brief 166– 219 Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Jehn KA , Rispens S , Thatcher SMB 2010 . The effects of conflict asymmetry on work group and individual outcomes. Acad. Manag. J. 53 : 596– 616 [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A , Liao H , Roh H 2011 . Bridging domains in workplace demography research: a review and conceptualization. J. Manag. 37 : 521– 52 [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A , Roh H 2009 . The role of context in work team diversity research: a meta-analytic review. Acad. Manag. J. 52 : 599– 627 [Google Scholar]
- Kalev A , Dobbin F , Kelly E 2006 . Best practices or best guesses? Diversity management and the remediation of inequality. Am. Soc. Rev. 71 : 589– 617 [Google Scholar]
- Kanter R 1977 . Men and Women of the Organization . New York: Basic Books
- Konrad AM 2013 . Work-life interface and flexibility: impacts on women, men, families and employers. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 366– 90 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Kossek EE , Ozeki C 1998 . Work-family conflict, policies, and the job-life satisfaction relationship: a review and directions for organizational behavior-human resources research. J. Appl. Psychol. 83 : 139– 49 [Google Scholar]
- Kram KE 1988 . Mentoring at Work: Developmental Relationships in Organizational Life Lanham, MD: Univ. Press Am. [Google Scholar]
- Kulik CT , Roberson L 2008 . Common goals and golden opportunities: evaluations of diversity education in academic and organizational settings. Acad. Manag. Learn. Edu. 73 : 309– 31 [Google Scholar]
- Lau DC , Murnighan JK 1998 . Demographic diversity and faultlines: the compositional dynamics of organizational groups. Acad. Manag. Rev. 23 : 325– 40 [Google Scholar]
- Lau DC , Murnighan JK 2005 . Interactions within groups and subgroups: the effects of demographic faultlines. Acad. Manag. J. 48 : 645– 59 [Google Scholar]
- Mannix E , Neale MA 2005 . What differences make a difference? The promise and reality of diverse teams in organizations. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 6 : 31– 55 [Google Scholar]
- McMahon AM 2010 . Does workplace diversity matter? A survey of empirical studies on diversity and firm performance, 2000–09. J. Divers. Manag. 5 : 37– 48 [Google Scholar]
- McNall LA , Nicklin JM , Masuda AD 2010 . A meta-analytic review of the consequences associated with work-family enrichment. J. Bus. Psychol. 25 : 381– 96 [Google Scholar]
- Milliken F , Martins L 1996 . Searching for common threads: understanding the multiple effects of diversity in organizational groups. Acad. Manag. Rev. 21 : 402– 33 [Google Scholar]
- Mor Barak ME 2000 . The inclusive workplace: an ecosystems approach to diversity management. Social Work 45 : 339– 53 [Google Scholar]
- Mor Barak ME , Cherin DA 1998 . A tool to expand organizational understanding of workforce diversity. Admin. Soc. Work 22 : 47– 64 [Google Scholar]
- Mor Barak ME , Travis DJ 2013 . Socioeconomic trends: broadening the diversity ecosystem. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 393– 418 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Nishii LH 2013 . The benefits of climate for inclusion for gender-diverse groups. Acad. Manag. J. 56 : 1754– 74 [Google Scholar]
- Ng ESW , Burke RJ 2005 . Person-organization fit and the war for talent: Does diversity management make a difference?. Internat. J. Hum. Res. Manag. 16 : 1195– 210 [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly C , Caldwell D , Barnett W 1989 . Work group demography, social integration, and turnover. Admin. Sci. Q. 34 : 21– 37 [Google Scholar]
- Ozbilgin M , Jonsen J , Tatli A , Vassilopoulou J , Surgevil O 2013 . Global diversity management. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 419– 41 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Pelled L 1996 . Demographic diversity, conflict, and work group outcomes: an intervening process theory. Org. Sci. 7 : 615– 31 [Google Scholar]
- Pelled LH , Eisenhardt KM , Xin KR 1999 . Exploring the black box: an analysis of work group diversity, conflict and performance. Admin. Sci. Q. 44 : 1– 28 [Google Scholar]
- Pendry LF , Driscoll DM , Field SCT 2007 . Diversity training: putting theory into practice. J. Occup. Org. Psychol. 80 : 27– 50 [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer J 1983 . Organizational demography. Research in Organizational Behavior LL Cummings, BM Staw 5 299– 357 Greenwich, CT: JAI Press [Google Scholar]
- Ployhart RE , Holtz BC 2008 . The diversity-validity dilemma: Strategies for reducing racioethnic and sex subgroup differences and adverse impact in selection. Pers. Psychol. 61 : 153– 72 [Google Scholar]
- Reis CR , Castillo MAS , Dobon SR 2007 . Diversity and business performance: 50 years of research. Serv. Bus. 1 : 257– 74 [Google Scholar]
- Richard OC , Miller CD 2013 . Considering diversity as a source of competitive advantage. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 239– 50 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Roberson QM 2006 . Disentangling the meanings of diversity and inclusion in organizations. Group Org. Manag. 31 : 212– 36 [Google Scholar]
- Roberson QM , Holmes OH , Perry JL 2017 . a Transforming research on diversity and firm performance: a dynamic capabilities perspective. Acad. Manag. Ann. 11 : 189– 216 [Google Scholar]
- Roberson L , Kulik CT , Pepper MB 2003 . Using needs assessment to resolve controversies in diversity training design. Group Org. Manag. 28 : 148– 74 [Google Scholar]
- Roberson L , Kulik CT , Tan RY 2013 . Effective diversity training. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 341– 65 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Roberson QM , Ryan AM , Ragins BR 2017 . b The evolution and future of diversity at work. J. Appl. Psychol. 102 : 483– 99 [Google Scholar]
- Rosch E 1977 . Human categorization. Studies in Cross-Cultural Psychology N Warren, 1– 49 London: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Rosch E 1978 . Principles of categorization. Cognition and Categorization E Roach, B Lloyd 27– 48 New York: Wiley [Google Scholar]
- Shore LM , Randel AE , Chung BG , Dean MA , Ehrhart KH , Singh G 2011 . Inclusion and diversity in work groups: a review and model for future research. J. Manag. 37 : 1262– 89 [Google Scholar]
- Simons T , Pelled LH , Smith KA 1999 . Making use of difference: diversity, debate, and decision comprehensiveness in top management teams. Acad. Manag. J. 42 : 662– 73 [Google Scholar]
- Smith KG , Smith KA , Olian JD , Sims HP Jr. , O'Bannon DP , Scully JA 1994 . Top management team demography and process: the role of social integration and communication. Admin. Sci. Q. 39 : 412– 38 [Google Scholar]
- Tajfel H 1978 . Differentiation Between Social Groups London: Academic [Google Scholar]
- Tajfel H , Turner JC 1986 . The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. The Psychology of Intergroup Relations S Worchel, WG Austin 7– 24 Chicago: Nelson-Hall [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher SMB 2013 . Moving beyond a categorical approach to diversity: the role of demographic faultlines. The Oxford Handbook of Diversity and Work Q Roberson 52– 70 New York: Oxford Univ. Press [Google Scholar]
- Tsui AS , Egan TD , O'Reilly CA 1992 . Being different: Relational demography and organizational attachment. Admin. Sci. Q. 37 : 549– 79 [Google Scholar]
- Tsui AS , Gutek BA 1999 . Demographic Differences in Organizations: Current Research and Future Directions New York: Lexington Press [Google Scholar]
- Turner JC 1985 . Social categorization and the self-concept: a social cognitive theory of group behavior. Advances in Group Processes EE Lawler III 2 77– 121 Greenwich, CT: JAI Press [Google Scholar]
- Turner JC 1987 . A self-categorization theory. See Turner et al. 1987, pp. 42–67 [Google Scholar]
- Turner JC , Hogg MA , Oakes PJ , Reicher SD , Wetherell MS 1987 . Rediscovering the Social Group: A Self-Categorization Theory Oxford, UK: Blackwell [Google Scholar]
- van Knippenberg D , De Dreu CKW , Homan AC 2004 . Work group diversity and group performance: an integrative model and research agenda. J. Appl. Psychol. 89 : 1008– 22 [Google Scholar]
- Watson W , Kumar K , Michaelsen LK 1993 . Cultural diversity's impact on interaction process and performance: comparing homogeneous and diverse task groups. Acad. Manag. J. 36 : 590– 602 [Google Scholar]
- Webber SS , Donahue LM 2001 . Impact of highly and less job-related diversity on work group cohesion and performance: a meta-analysis. J. Manag. 27 : 141– 62 [Google Scholar]
- Wentling RM , Palma-Rivas N 2000 . Current status of diversity initiatives in selected multinational corporations. Hum. Res. Dev. Q. 11 : 35– 60 [Google Scholar]
- Williams K , O'Reilly C 1998 . The complexity of diversity: a review of forty years of research. Research on Managing in Groups and Teams D Gruenfeld, M Neale 20 77– 140 Greenwich, CT: JAI Press [Google Scholar]
- Williamson IO , Slay HS , Shapiro DL , Shivers-Blackwell SL 2008 . The effect of explanations on prospective applicants’ reaction to firm diversity practices. Hum. Res. Manag. 47 : 311– 30 [Google Scholar]
Data & Media loading...
- Article Type: Review Article
Most Read This Month
Most cited most cited rss feed, conservation of resources in the organizational context: the reality of resources and their consequences, self-determination theory in work organizations: the state of a science, burnout and work engagement: the jd–r approach, psychological safety: the history, renaissance, and future of an interpersonal construct, employee voice and silence, psychological capital: an evidence-based positive approach, how technology is changing work and organizations, research on workplace creativity: a review and redirection, abusive supervision, the psychology of entrepreneurship.
Creating an Inclusive Workplace: The Effectiveness of Diversity Training
- September 2021

- Austin Peay State University

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Kwaku Asiedu-Nketiah
- Yakubu Yakubu
- Dennis Yao Dzansi

- Muhammad Irfan
- Syed Muhammad Abbas Shah
- Lisa Stewart

- Nadira Dewanto
- Adita Pritasari
- Rashida Jabeen

- Dev Learn Org Int J

- Juan Ganaza-Vargas

- Akon E. Ekpo
- Oluwatoniloba “Toni” Abiru

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
What is diversity and inclusion in the workplace?
Foster an inclusive work environment and you empower people to be their authentic selves.

The mission to ensure that every employee feels safe and supported in the workplace is a never-ending one, but in recent years many strides have been made in making diversity and inclusion a core part of doing business.
Large global corporations are often the most visible in this respect, as they tend to lead the way in flagship diversity and inclusion policies. These policies not only allow them to foster a healthy and happy workforce, but to conduct business internationally and attract the most qualified applicants from all backgrounds.
Small- to medium-sized companies have an even more important role to play when it comes to fairness and equity in the office. To begin, it’s the right thing to do; but implementing a diversity and inclusion policy can also help a company become more adaptable, more creative, and more competitive.
What is meant by diversity and inclusion in the workplace?
The term “ diversity and inclusion ” describes both the makeup of a workforce, as well as the policies and processes used to remove barriers and ensure that every employee has equal access to opportunities and support at a company.
The ultimate goal is to ensure fairness and equity for all employees, regardless of characteristics like gender, ethnicity, nationality, sexual orientation, and age; however, diversity and inclusion is an ongoing process rather than a destination. With a well-designed diversity and inclusion policy, a company can not only make better and fairer decisions at the recruitment stage but also foster a healthier workplace where employees feel heard and supported.
What’s the difference between diversity and inclusion?
While the terms are usually bundled together as one, there’s a big difference between diversity and inclusion. Diversity describes the ways in which we are different. A diverse workplace will be made up of people from a wide variety of backgrounds at every level of the business, from entry-level roles all the way up to management.

But just because a workplace is diverse doesn’t necessarily mean it’s also inclusive. Inclusion describes the power employees have to make decisions and hold influence. A company focused on being inclusive will make sure that every employee can participate fully in the organization; in other words, workers should feel that their voices are being heard, and that they have the same access as their colleagues to opportunities for success.
Diversity and inclusion in the workplace
Diversity and inclusion should naturally reflect a company’s greater mission to strive for fairness and equality in every sphere of business . This is more than just in the office—it’s in how the company communicates with customers, how it chooses the clients it works with, and how it creates products and services .
But beyond simply being the greater good, there are direct and immediate benefits for any employer that pursues a diverse and inclusive work environment. In this article, we’re going to take a look at some of the advantages offered by recruiting diversely and striving toward inclusivity.
Benefits of having a diverse and inclusive environment in the workplace
Diverse and fresh points of view.
A diverse and inclusive workplace comprised of people from many different backgrounds will tend to have a wider variety of perspectives and ideas to draw from. Problems can be framed in different ways that lead to creative solutions across every department of the business.
A better understanding of customer needs
The company gains a greater understanding of the needs of its customers when its own workplace reflects the very people who use its products and services every day. By hiring thoughtfully from a broader pool of potential employees and retaining a diverse workforce, a company can reach a much wider customer base.
Better decision-making
With a greater variety of perspectives as well as a work environment that encourages communication, companies will experience improved decision-making. This benefits everything from day-to-day actions to long-term planning for the future of the business.
Access to more qualified potential employees
A well-structured diversity and inclusion policy ensures that the recruitment process isn’t simply open to all potential employees, but actively seeks out and encourages applicants who might be less visible in their industry or who are hesitant to apply. A wider applicant pool means more qualified hires. When a company has a reputation for hiring diversely and fostering an inclusive work environment, it will more easily attract and retain the best and most qualified candidates in the future.
How can diversity and inclusion be promoted in the workplace?
Choose leaders who promote this idea.
Take into account a candidate’s commitment to diversity and inclusion when hiring, but also when promoting team leaders from within. By elevating employees who champion these values, a company can improve equity among staff and create a self-sustaining push toward fairness in the business.

Use appropriate internal and external communication
Diversity training courses can improve communication at all levels—between teams, with customers, and with people outside the company as well. Small changes to how we write and speak to one another, such as avoiding gendered language in emails, can have a big impact on overall inclusivity.
Give support to those who need it
Equity is about more than simply ensuring equal access and treatment for all—it’s also about raising up and supporting those employees who have particular needs. Every company is required by law to make reasonable adjustments so that no worker is disadvantaged in the workplace, but this is a baseline rather than a target. Discuss individual workers’ needs with them, and make changes to ensure they’re met or even exceeded.
Have a clear recruiting plan for it
Recruitment is the biggest driver of diversity in the workplace. For a recruitment plan to reach the most varied pool of potential applicants, it should consider every aspect of the process: from how and where your vacancies are advertised to how accessible the application and interview process is to interested parties.
Equal access to opportunities
When evaluating and considering employees for promotions and other opportunities, be aware of unconscious bias at every stage. Even well-intentioned managers are prone to discriminatory behavior, whether they realize it or not. Bias training helps to alleviate this, as do systems like blind recruitment, in which identifying characteristics such as gender and applicant names are removed from résumés.
Educate about diversity
Education is a key part of fostering a sense of inclusion and fairness in business. A company should publicize its diversity goals, update employees on the progress being made, and strive to help everybody understand why diversity in the workplace is important. This might mean taking steps such as opening a dialogue about things like gender pay imbalance, or bridging a skill gap by offering training courses.
Examples of companies that promote diversity and inclusion
Mastercard .
The global financial services firm is regularly recognized for its diversity and inclusion initiatives. As well as sponsoring STEM mentorship programs such as Girls4Tech, the company offers a range of employee benefits such as coverage for gender-affirming surgery, fertility treatment, and adoption assistance.
The cosmetics company consistently scores highly in corporate equality benchmarks, thanks to a diversity and inclusion strategy designed to span the 130 countries in which L’Oréal operates. Women make up 69 percent of the workforce, and the company offers multicultural mentorship courses and on-the-ground job training for young people in some of the poorest nations in the world.
This biotech research organization in San Francisco works to make genetic information more affordable to those who need it. In 2020, it launched a suite of diversity and inclusion initiatives centered on a set of seven employee resource groups, which include Women in Tech, Pride, and Black Genetics. These ERGs host regular community table talks where employees can openly and informally discuss issues affecting them.
Related articles

Fair treatment to all: The key to diversity and inclusion at work
Diversity and inclusion can’t be easily summarized, mainly because it’s a catchall term consisting of unrelated challenges. For example: A goal of hiring more women into management positions will require a different approach than ensuring that LGBTQ+ employees feel welcome in the workplace, or that workers of different ethnicities have a voice.

But the basis for these ideas is a commitment to fair treatment for all and consideration of the unique perspectives of every employee. That mindset will lead to the creation of an equitable workplace that accepts, appreciates, and values differences. This is the key point to keep in mind when designing a diversity and inclusion initiative for your own company.
Steve Hogarty is a writer and journalist based in London. He is the travel editor of City AM newspaper and the deputy editor of City AM Magazine , where his work focuses on technology, travel, and entertainment.
Rethinking your workspace?

From watercooler chats to crisis communication, the way companies share information can make or break them

Millennials now make up most of the workforce, and it’s changing how we communicate at the office
Managing Diversity in the Workplace Problem Solution Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Globalization and advancements in information and communication technology have caused tremendous changes in various sectors of the economy, especially, the hospitality industry. Many businesses in the hospitality industry have joined the global market in the last decade.
This move has been informed by high competition in the domestic market, globalization and improvements in the exportation and importation of services. Consequently, most businesses serve customers from diverse socio-economic backgrounds. Furthermore, most organizations have had to employ people from different social and cultural backgrounds.
This has led to the emergence of a diverse workforce in the modern workplace. Diversity refers to the “variety of experiences and perspectives which arise from differences in race, culture, religion, mental/ physical ability and gender”. Thus, diversity refers to the human characteristics which are significantly different from our own attributes.
Diversity also includes differences in work experience, educational achievements, as well as, geographical location. These differences affect how people interact at the workplace. They also affect employees’ performance, motivation, as well as, career development.
Through diversity management, businesses can understand how socio-cultural differences affect the performance of their employees. Diversity management refers to the process of bringing together individuals with different social, economic and cultural backgrounds into a cohesive, harmonious and productive unit.
It involves examining and reforming organizational structures that prevent inclusivity at the workplace. Empirical studies show that effective diversity programs are beneficial to the organization. Concisely, they facilitate high productivity, motivation and innovation among employees.
Ignoring diversity, on the other hand, is likely to cause low morale, discrimination and poor performance in the organization. Thus, every organization should focus on effective diversity management in order to improve its competitiveness in the industry. This paper will shed light on the concept of diversity in the context of the hospitality industry. Additionally, my human resource functions in the industry will be presented.
Causes of Diversity
Diversity at the workplace has been caused by the following factors. To begin with, the number of immigrants has increased in the country. Immigrants usually come from different cultures. Thus, hiring immigrants results into a multi-cultural workforce. Enforcement of antidiscrimination laws has also forced many employers and citizens to be tolerant to people who come from different cultures and social orientations.
Most labor unions advocate for equal employment opportunities to all citizens irrespective of their social backgrounds. Thus, employers have embarked on improving diversity in their organizations in order to avert any opposition from labor unions.
Demographic shift is another factor that has contributed to diversity at the workplace. Many businesses in the hospitality industry have had to employ individuals who understand the needs of the most important generations. For instance, hotels and restaurants that target the youth normally include youthful employees in their management teams in order to enhance product development.
As competition increase in the domestic market, most companies have had to join international markets. Due to legal and political issues, multinational companies have been forced to recruit employees in the overseas markets. Additionally, sending expatriates to work in overseas subsidiaries tend to be expensive. Thus, most multinationals have employees from different socio-cultural backgrounds.
The Benefits of Diversity Management
Human resource managers need to focus on diversity management due to the following reasons. First, diversity management enables businesses to attract, hire and retain the best talent in the market. Research shows that jobseekers prefer to work for companies that are tolerant to cultural, racial and ethnic diversity.
In this regard, a firm that promotes diversity is likely to attract the best talent. In the hospitality industry, the success of product differentiation and customer service improvement efforts depends on the competencies of the employees.
Consequently, demand for highly talented employees has been on the rise. However, businesses can still access the best talent by incorporating diversity management initiatives in their human resource policies.
Second, diversity management helps in reducing the costs associated with labor turnover and absenteeism. Labor turnover and absenteeism tends to be high in organizations whose managers pay little or no attention to employees’ feelings, perceptions and differences.
Such organizations are also characterized by cases of discrimination and low staff morale. These factors normally precipitate mass exodus of employees from organizations. Third, high commitment among employees can be achieved through diversity management.
In this case, managing diversity helps managers to create a sense of belonging among employees. It also helps in improving interactions/ relationships in the organization, as well as, building cohesion and tolerance among staff members.
Fourth, diversity management enables companies to improve their reputation and to develop a positive rapport with local communities. Organizations with weak diversity management structures tend to have poor reputation and financial performance. Last and most importantly, managing diversity is one of the best ways of improving the performance of the business.
Focusing on diversity enables managers to acquire knowledge on the best strategies for operating in different cultures. In the hospitality industry, high customer satisfaction can be achieved if the customers’ cultural orientations are taken into account during product development.
In this regard, it is important to hire people who understand the customers’ culture in order to develop the right product. Furthermore, the best marketing strategies can be developed if the process is led by people who understand the market.
For instance, most multinational hotels usually recruit their marketing executives from the markets in which they operate. The rationale of this strategy is that locals have a better understanding of the market. Consequently, they are likely to develop marketing plans and policies that reflect the needs of the market.
Negativity of Diversity
The benefits of diversity can only be realized if it is well managed. Diversity can also be a major source of poor financial performance, especially, if it occurs in a clandestine manner. Generally, large organizations tend to take deliberate measures to hire a diverse workforce. Consequently, they are ready to manage the challenges associated with diversity.
However, small organizations tend to recruit people from different social backgrounds without realizing that they are creating diversity in their workforce. In this case, diversity is likely to have negative effects in the organization. Some of these effects include the following.
To begin with, diversity is likely to cause communication problems. It is apparent that people from different cultures are not likely to speak the same language. This leads to communication barriers in the organization. Communication barriers have both internal and external impacts.
At the internal level, it hampers coordination of work and relationships among employees. Work coordination becomes difficult if the employees are not able to understand each other. Additionally, instructions from managers and supervisors can be misinterpreted due to poor understanding of the language that is being used at the workplace.
Companies whose employees have a low command of the national language are likely to offer poor customer service. In order to address the problem of language barriers, most organizations usually employ interpreters to facilitate communication among employees. However, employing interpreters involve high costs which reduce the business’ ability to expand.
At the external level, communication barriers can lead to misunderstanding between the company and the public. For instance, incorrect use of a local language in an advert can cause public outrage and loss of customers. Additionally, communication barriers hamper effective exchange of feedbacks between the organization and the public or customers.
Diversity is one of the major causes of cultural resistance at the workplace. It changes the nature of relationships and interactions at the workplace. Employees who lack training on diversity are likely to be intolerant to foreign cultures.
Consequently, they will tend to interact only with people from their cultures. This leads to poor cooperation and teamwork. Additionally, cases of discrimination and low morale tend to be high in organizations in which employees resist foreign cultures. The tensions associated with cultural resistance eventually results into low productivity.
Diversity Management Strategies
Effective diversity management involves “planning and implementing organizational systems and practices to manage people so that the potential advantages of diversity are maximized while its potential disadvantages are minimized”. As a result, the organization will be flexible and adaptable to emerging market needs. The process of managing diversity must be led by individuals who possess the right skills and knowledge.
In general, the following skills are required for effective management of diversity. The manager should have a good understanding of diversity concepts and how to apply them within the organization.
Consequently, the process should be led by a person who has undergone training about diversity and has experience in applying the acquired knowledge. The manager should recognize that diversity is embedded in all aspects of management. This means that the manager should be able to incorporate diversity management initiatives in every role or duty that he performs at the workplace.
Self-awareness is also important in diversity management. The manager should understand his own culture and learn to make decisions that are free from cultural bias. It is also important to understand the cultures of other employees in order to avoid making decisions based on stereotypes and assumptions.
In a multicultural workforce, understanding the culture of every employee can be very difficult. However, the manager should be willing and able to learn the cultures of his employees. Finally, the manager should be willing to challenge organizational practices that encourage intolerance at the workplace. The specific strategies for managing diversity include the following.
Ensure Management Commitment
Diversity management is likely to be effective if the process is supported by the company’s top leadership. In this regard, the management plays the following roles. First, the management is expected to demonstrate commitment, as well as, accountability. The management should be able to indentify the most appropriate performance measures to be used in diversity management.
The measures must be relevant and acceptable in the organization. Additionally, the management should set specific performance targets to facilitate effective management. In a nutshell, the targets should be used as benchmarks for monitoring the progress of diversity management programs on a regular basis.
The management should also allocate adequate resources to support the implementation of diversity management initiatives. The required resources include personnel, funds, technology, as well as, training facilities.
Second, the company’s management should clearly communicate the importance of diversity. This will enable all members to understand the value of an inclusive and harmonious work environment. Additionally, clear communication will enable the management to win the support of junior employees in its quest for cohesion at the workplace. Management meetings can be used to articulate the importance of diversity.
However, management meetings are likely to lockout junior employees in the discussions concerning diversity. Consequently, the management can take advantage of company events such as end of year parties to engage employees in discussions about diversity. Additionally, line managers can use informal sessions to discuss various aspects of diversity with the junior employees.
Finally, the company’s leaders should be role models to all employees. They should actively participate in the implementation of diversity management initiatives. For example, managers should participate in diversity training programs in order to encourage other employees to do the same.
Similarly, managers should be part of employee network groups in order to strengthen their relationships with junior staff members. The behavior of top managers should be informed by the organization’s values that promote diversity. For instance, managers should avoid behaviors such as favoritism.
Reform Human Resource Functions
Diversity management initiatives should be incorporated in human resource functions. Concisely, the initiatives must be reflected in activities such as staff recruitment, staff compensation, performance appraisals and dispute resolution. During staff selection, human resource managers should accept applications from a diverse applicant pool.
Affirmative action can be used to ensure that applications are received from all groups of potential employees. During interviews, specific skills and personal attributes must be identified and used to select the employees. For instance, the company can focus on recruiting people who are able to tolerate cultural differences.
Similarly, people who can speak different languages can be hired in order to minimize the conflicts caused by language barriers. The interviews should be conducted by a panel that consists of people from diverse socio-cultural backgrounds.
Applicants should be hired based on academic qualifications, leadership skills and work experience rather than personal attributes such as race, age or gender. Staff performance appraisals should be based on productivity and work related variables such as leadership skills and relationships with other employees. Similarly, promotions and pay rises should be based on performance.
Adequate training is an important aspect of diversity management. In a multicultural workforce, employees must be trained on the importance of diversity. Such training will enable employees to appreciate their differences and focus on cohesion. Through training, employees will acquire skills for managing disputes that might arise due to their cultural differences.
The training process should be led by qualified personnel. Outsiders can be invited to provide expert advice in the training sessions. Since cultural change takes place over a long period of time, training on diversity should be offered on a continuous basis. Furthermore, the training should be incorporated in the employee orientation programs. This will help new recruits to understand the importance of diversity and how to achieve it.
My Human Resource Management Functions
The human resource manager plays an important role in the hospitality industry, especially, in hotels and restaurants. Human resource management in the hospitality industry tends to be different as compared to other industries. The industry provides a series of services whose quality depends on the employees’ competencies, motivation and attitude towards work. Besides, the industry primarily serves tourists from different cultures and social backgrounds.
Thus, the individual tastes and preferences of each customer must be considered in all operations in the industry. Employees play a fundamental role in the provision of excellent services to customers. However, this can only be achieved if the employees are well managed.
Hence, the importance of human resource department in the hospitality industry becomes apparent. The responsibilities of human resource executives include staffing, training employees and designing job descriptions. They also formulate and implement policies that guide staff compensation and employee retention. These functions are applied as follows in the hospitality industry.
Recruitment
Success in the hospitality industry begins with the hiring of the right employees. In this regard, the recruitment process must help businesses to hire people with the right attitude, as well as, behavioral attributes. During the selection and recruitment process, several assessments are often used to determine the work orientations of potential employees.
These assessments include the applicants’ work values, personality, as well as, interpersonal skills. The applicants’ problem solving abilities should also be taken into account. These attributes help human resource specialists to determine the applicants’ ability to offer services in the hospitality industry.
High labor turnover is one of the major challenges in the hospitality industry. Many employees usually quit within their first year of employment in hotels and restaurants. The main causes of high turnover in the industry include poor pay, lack of growth opportunities, unfavorable work conditions and inability to cope with workload.
High turnover is costly to businesses in terms of lost productivity, high cost of replacing employees and loss of talented staff. Consequently, reducing turnover helps in saving time, money and increasing productivity. This can be achieved through employee retention policies such as introducing flexible work schedules in order to prevent fatigue.
Obtaining feedback from the employees concerning work processes and organizational policies help in understanding workers’ concerns. Turnover can be reduced significantly if the grievances of the employees are addressed in time. Additionally, promoting cultural tolerance helps in retaining employees in a diverse workforce.
Training and Development
Training and development is one of the most important human resource functions in the hospitality industry. Training helps in imparting knowledge, skills and abilities to workers. Consequently, it contributes to innovation, product development and improvement of customer care services.
However, most businesses in the industry are yet to realize these benefits since their investments in staff training tend to be a reactive process. Such businesses use training as a means of coping with immediate problems such as poor service quality.
Staff training and development can be beneficial if it is conducted in a proactive manner. In this regard, the role of a human resource specialist is to identify employees’ training needs. He is also responsible for developing a suitable training program in order to bridge the identified skill gaps among employees. Training and development can be done on-the-job or off-the-job.
On-the-job training is the most suitable for hotels and restaurants since it involves learning by doing. It enables employees to acquire practical skills as they also create value to the organization. However, on-the-job training can be abused if its implementation is not well planned.
Hence, its implementation requires proper planning, structure, as well as, supervision. Off-the-job training is often done in a learning institution through lectures, discussions and practical sessions. It helps employees to acquire conceptual skills on various aspects of their jobs.
Performance Appraisal
It is important to evaluate employees’ performance in order to determine their strengths and weaknesses. Empirical studies have shown that most employees often quit their jobs due to biased or unfair performance appraisals. A fair appraisal system can help in reducing biases in performance evaluations. Businesses such as hotels should adopt a 360 degrees appraisal system to evaluate their employees.
The evaluation system should focus on productivity and the behaviors of the employees. Feedback or information about productivity and behavior should be obtained from various stakeholders such as customers, managers, colleagues and suppliers. Additionally, the managers should be evaluated by their juniors in order to provide a balanced view on their performance.
Facilitating inclusiveness
Providing services in the hospitality industry requires effective coordination among employees. Effective coordination and interaction among employees is often achieved by creating a work environment that is not only inclusive, but also harmonious. Promoting inclusivity is also one of the best ways of managing diversity in the hospitality industry.
Strategies for promoting inclusivity include the following. Formal and informal activities such as sports can be organized to promote teamwork among workers. Workplace designs should facilitate interaction at the workplace.
For example, hotels usually design their kitchens in a manner that facilitates sharing of equipment among cooks. Additionally, locating cooking stations in a central place facilitates consultations among cooks and other kitchen staff members.
Some hotels and restaurants have buddy systems in which new recruits are assigned to the incumbents to foster relationships and interactions. Similarly, employee networks have been used successfully to promote inclusivity in most hotels. These networks usually consist of employees who share some work attributes such as being members of the same department.
Mentorship programs are often provided through these networks in order to promote productivity and tolerance among employees. Large organizations often use employee networks to involve workers in decision making processes.
In this context, employee networks are used to enhance autonomy, creativity, as well as, cooperation among workers. For example, cooks in a hotel can use informal meetings to discuss alternative cooking methods. Their conclusions can then be forwarded to the management for consideration and approval.
Rewarding Employees
Employees’ compensation packages should reflect the value of their effort at the workplace. It is the responsibility of the human resource manager to ensure that employees are adequately compensated. An effective compensation system helps in reducing labor turnover, as well as, improving motivation and productivity.
Employees whose shifts are longer than 8 hours should be compensated for the extra time. The compensation system should also promote productivity by rewarding employees for attaining or exceeding quality targets. In general, the compensation system should be fair and acceptable to all employees.
Diversity refers to the human characteristics that differentiate people from different socio-cultural backgrounds. These characteristics include race, religion, gender, work experience and academic achievements. These attributes affect interactions and employees’ performance.
Hence, appropriate diversity management systems must be put in place in order to maximize the benefits of diversity and to reduce its disadvantages. The benefits of diversity management include high productivity, recruiting the best talent, reducing labor turnover and improving the reputation of the company.
However, poor management of diversity can lead to discrimination, low morale and dismal performance at the workplace. The most important human resource functions in the hospitality industry include staff recruitment, retention, compensation, training, performance appraisal and promoting inclusiveness. Staff recruitment, training and promoting inclusiveness facilitate diversity management.
Staff retention and compensation policies help in improving staff motivation and commitment. Fair performance appraisal and appropriate staff training and development facilitate high productivity. Businesses in the hospitality industry should incorporate their diversity management initiatives in human resource management functions in order to succeed.
Alleyne, P., Doherty, L., & Greenidge, D. (2006). Approaches to HRM in the Barbados Hotel Industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Industry Management, 18(1) , 34-40.
Amirthaj, D., Kalist, R., & Vembar, V. (2011). HR Concepts in Hotel Industry Towards Employee Training and Development. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 1(1) , 44-56.
Bendl, R., Fleischmann, A., & Walenta, C. (2008). Diversity Management Discourse Meets Queer Theory. International Journal of Gender in Management, 23(6) , 382-394.
Cooke, L., & Saini, D. (2012). Managing Diversity in Chinese and Indian Organizations. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 3(1) , 16-32.
Friday, E., & Shawnta, F. (2003). Managing Diversity Using a Strategic Planned Change Approach. Journal of Management Development, 22(10) , 863-880.
Groschl, S. (2011). Diversity Management Strategies of Global Hotel Groups. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 23(2) , 224-240.
Kapoor, C., & Madera, J. (2011). Industry Perspective on Diversity Research. World Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 23(1) , 45-48.
Madera, J. (2011). Removing Communication Barriers at Work: What Workforce Diversity Means for the Hospitality Industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 3(1) , 56-60.
Nicole, S., & Kapoor, C. (2011). Understanding and Managing Generational Differences in the Workplace. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 3(2) , 308-318.
Seymen, O. (2006). The Cultural Diversity Phenomenon in Organizations and Different Approaches for Effective Cultural Diversity Management. International Journal of Cross-Cultural Management, 13(4) , 296-315.
- Teamwork's Achievements and Challenges
- Concepts of Leadership Styles
- Labor Turnover in Hotels
- Managing Culture Diversity
- Managing Cultural Diversity: Sustain and Respect Cultural Identities
- Human Resource Management: Tourism and Hospitality Industry
- Recruitment Practices: Different Levels of Qualifications
- The Question of the Distributed Workforce under the Impact of Globalization Tendencies
- Training Evaluation: New Techniques and Strategies
- Finding a suitable consultant for BBB
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 12). Managing Diversity in the Workplace. https://ivypanda.com/essays/managing-diversity-in-the-workplace/
"Managing Diversity in the Workplace." IvyPanda , 12 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/managing-diversity-in-the-workplace/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Managing Diversity in the Workplace'. 12 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Managing Diversity in the Workplace." April 12, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/managing-diversity-in-the-workplace/.
1. IvyPanda . "Managing Diversity in the Workplace." April 12, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/managing-diversity-in-the-workplace/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Managing Diversity in the Workplace." April 12, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/managing-diversity-in-the-workplace/.
Which program are you applying to?

Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted

May 8, 2024
The Diversity Essay: How to Write an Excellent Diversity Essay

What is a diversity essay in a school application? And why does it matter when applying to leading programs and universities? Most importantly, how should you go about writing such an essay?
Diversity is of supreme value in higher education, and schools want to know how every student will contribute to the diversity on their campus. A diversity essay gives applicants with disadvantaged or underrepresented backgrounds, an unusual education, a distinctive experience, or a unique family history an opportunity to write about how these elements of their background have prepared them to play a useful role in increasing and encouraging diversity among their target program’s student body and broader community.
The purpose of all application essays is to help the adcom better understand who an applicant is and what they care about. Your essays are your chance to share your voice and humanize your application. This is especially true for the diversity essay, which aims to reveal your unique perspectives and experiences, as well as the ways in which you might contribute to a college community.
In this post, we’ll discuss what exactly a diversity essay is, look at examples of actual prompts and a sample essay, and offer tips for writing a standout essay.
In this post, you’ll find the following:
What a diversity essay covers
How to show you can add to a school’s diversity, why diversity matters to schools.
- Seven examples that reveal diversity
Sample diversity essay prompts
How to write about your diversity.
- A diversity essay example
Upon hearing the word “diversity” in relation to an application essay, many people assume that they will have to write about gender, sexuality, class, or race. To many, this can feel overly personal or irrelevant, and some students might worry that their identity isn’t unique or interesting enough. In reality, the diversity essay is much broader than many people realize.
Identity means different things to different people. The important thing is that you demonstrate your uniqueness and what matters to you. In addition to writing about one of the traditional identity features we just mentioned (gender, sexuality, class, race), you could consider writing about a more unusual feature of yourself or your life – or even the intersection of two or more identities.
Consider these questions as you think about what to include in your diversity essay:
- Do you have a unique or unusual talent or skill?
- Do you have beliefs or values that are markedly different from those of the people around you?
- Do you have a hobby or interest that sets you apart from your peers?
- Have you done or experienced something that few people have? Note that if you choose to write about a single event as a diverse identity feature, that event needs to have had a pretty substantial impact on you and your life. For example, perhaps you’re part of the 0.2% of the world’s population that has run a marathon, or you’ve had the chance to watch wolves hunt in the wild.
- Do you have a role in life that gives you a special outlook on the world? For example, maybe one of your siblings has a rare disability, or you grew up in a town with fewer than 500 inhabitants.

If you are an immigrant to the United States, the child of immigrants, or someone whose ethnicity is underrepresented in the States, your response to “How will you add to the diversity of our class/community?” and similar questions might help your application efforts. Why? Because you have the opportunity to show the adcom how your background will contribute a distinctive perspective to the program you are applying to.
Of course, if you’re not underrepresented in your field or part of a disadvantaged group, that doesn’t mean that you don’t have anything to write about in a diversity essay.
For example, you might have an unusual or special experience to share, such as serving in the military, being a member of a dance troupe, or caring for a disabled relative. These and other distinctive experiences can convey how you will contribute to the diversity of the school’s campus.
Maybe you are the first member of your family to apply to college or the first person in your household to learn English. Perhaps you have worked your way through college or helped raise your siblings. You might also have been an ally to those who are underrepresented, disadvantaged, or marginalized in your community, at your school, or in a work setting.
As you can see, diversity is not limited to one’s religion, ethnicity, culture, language, or sexual orientation. It refers to whatever element of your identity distinguishes you from others and shows that you, too, value diversity.
The diversity essay provides colleges the chance to build a student body that includes different ethnicities, religions, sexual orientations, backgrounds, interests, and so on. Applicants are asked to illuminate what sets them apart so that the adcoms can see what kind of diverse views and opinions they can bring to the campus.
Admissions officers believe that diversity in the classroom improves the educational experience of all the students involved. They also believe that having a diverse workforce better serves society as a whole.
The more diverse perspectives found in the classroom, throughout the dorms, in the dining halls, and mixed into study groups, the richer people’s discussions will be.
Plus, learning and growing in this kind of multicultural environment will prepare students for working in our increasingly multicultural and global world.
In medicine, for example, a heterogeneous workforce benefits people from previously underrepresented cultures. Businesses realize that they will market more effectively if they can speak to different audiences, which is possible when members of their workforce come from various backgrounds and cultures. Schools simply want to prepare graduates for the 21st century job market.
Seven examples that reveal diversity
Adcoms want to know about the diverse elements of your character and how these have helped you develop particular personality traits , as well as about any unusual experiences that have shaped you.
Here are seven examples an applicant could write about:
1. They grew up in an environment with a strong emphasis on respecting their elders, attending family events, and/or learning their parents’ native language and culture.
2. They are close to their grandparents and extended family members who have taught them how teamwork can help everyone thrive.
3. They have had to face difficulties that stem from their parents’ values being in conflict with theirs or those of their peers.
4. Teachers have not always understood the elements of their culture or lifestyle and how those elements influence their performance.
5. They have suffered discrimination and succeeded despite it because of their grit, values, and character.
6. They learned skills from a lifestyle that is outside the norm (e.g., living in foreign countries as the child of a diplomat or contractor; performing professionally in theater, dance, music, or sports; having a deaf sibling).
7. They’ve encountered racism or other prejudice (either toward themselves or others) and responded by actively promoting diverse, tolerant values.
And remember, diversity is not about who your parents are. It’s about who you are – at the core.
Your background, influences, religious observances, native language, ideas, work environment, community experiences – all these factors come together to create a unique individual, one who will contribute to a varied class of distinct individuals taking their place in a diverse world.
The best-known diversity essay prompt is from the Common App . It states:
“Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.”
Some schools have individual diversity essay prompts. For example, this one is from Duke University :
“We believe a wide range of personal perspectives, beliefs, and lived experiences are essential to making Duke a vibrant and meaningful living and learning community. Feel free to share with us anything in this context that might help us better understand you and what you might bring to our community.”
And the Rice University application includes the following prompt:
“Rice is strengthened by its diverse community of learning and discovery that produces leaders and change agents across the spectrum of human endeavor. What perspectives shaped by your background, experiences, upbringing, and/or racial identity inspire you to join our community of change agents at Rice?”
In all instances, colleges want you to demonstrate how and what you’ll contribute to their communities.
Your answer to a school’s diversity essay question should focus on how your experiences have built your empathy for others, your embrace of differences, your resilience, your character, and your perspective.
The school might ask how you think of diversity or how you will bring or add to the diversity of the school, your chosen profession, or your community. Make sure you answer the specific question posed by highlighting distinctive elements of your profile that will add to the class mosaic every adcom is trying to create. You don’t want to blend in; you want to stand out in a positive way while also complementing the school’s canvas.
Here’s a simple, three-part framework that will help you think of diversity more broadly:
Who are you? What has contributed to your identity? How do you distinguish yourself? Your identity can include any of the following: gender, sexual orientation, ethnicity, disability, religion, nontraditional work experience, nontraditional educational background, multicultural background, and family’s educational level.
What have you done? What have you accomplished? This could include any of the following: achievements inside and/or outside your field of study, leadership opportunities, community service, internship or professional experience, research opportunities, hobbies, and travel. Any or all of these could be unique. Also, what life-derailing, throw-you-for-a-loop challenges have you faced and overcome?
How do you think? How do you approach things? What drives you? What influences you? Are you the person who can break up a tense meeting with some well-timed humor? Are you the one who intuitively sees how to bring people together?
Read more about this three-part framework in Episode 193 of Accepted’s Admissions Straight Talk podcast or listen wherever you get your favorite podcast s.

Think about each question within this framework and how you could apply your diversity elements to your target school’s classroom or community. Any of these elements can serve as the framework for your essay.
Don’t worry if you can’t think of something totally “out there.” You don’t need to be a tightrope walker living in the Andes or a Buddhist monk from Japan to be able to contribute to a school’s diversity!
And please remember, the examples we have offered here are not exhaustive. There are many other ways to show diversity!
All you need to do to be able to write successfully about how you will contribute to the diversity of your target school’s community is examine your identity, deeds, and ideas, with an eye toward your personal distinctiveness and individuality. There is only one you .
Take a look at the sample diversity essay in the next section of this post, and pay attention to how the writer underscores their appreciation for, and experience with, diversity.
A diversity essay sample
When I was starting 11th grade, my dad, an agricultural scientist, was assigned to a 3-month research project in a farm village in Niigata (northwest Honshu in Japan). Rather than stay behind with my mom and siblings, I begged to go with him. As a straight-A student, I convinced my parents and the principal that I could handle my schoolwork remotely (pre-COVID) for that stretch. It was time to leap beyond my comfortable suburban Wisconsin life—and my Western orientation, reinforced by travel to Europe the year before.
We roomed in a sprawling farmhouse with a family participating in my dad’s study. I thought I’d experience an “English-free zone,” but the high school students all studied and wanted to practice English, so I did meet peers even though I didn’t attend their school. Of the many eye-opening, influential, cultural experiences, the one that resonates most powerfully to me is experiencing their community. It was a living, organic whole. Elementary school kids spent time helping with the rice harvest. People who foraged for seasonal wild edibles gave them to acquaintances throughout the town. In fact, there was a constant sharing of food among residents—garden veggies carried in straw baskets, fish or meat in coolers. The pharmacist would drive prescriptions to people who couldn’t easily get out—new mothers, the elderly—not as a business service but as a good neighbor. If rain suddenly threatened, neighbors would bring in each other’s drying laundry. When an empty-nest 50-year-old woman had to be hospitalized suddenly for a near-fatal snakebite, neighbors maintained her veggie patch until she returned. The community embodied constant awareness of others’ needs and circumstances. The community flowed!
Yet, people there lamented that this lifestyle was vanishing; more young people left than stayed or came. And it wasn’t idyllic: I heard about ubiquitous gossip, long-standing personal enmities, busybody-ness. But these very human foibles didn’t dam the flow. This dynamic community organism couldn’t have been more different from my suburban life back home, with its insular nuclear families. We nod hello to neighbors in passing.
This wonderful experience contained a personal challenge. Blond and blue-eyed, I became “the other” for the first time. Except for my dad, I saw no Westerner there. Curious eyes followed me. Stepping into a market or walking down the street, I drew gazes. People swiftly looked away if they accidentally caught my eye. It was not at all hostile, I knew, but I felt like an object. I began making extra sure to appear “presentable” before going outside. The sense of being watched sometimes generated mild stress or resentment. Returning to my lovely tatami room, I would decompress, grateful to be alone. I realized this challenge was a minute fraction of what others experience in my own country. The toll that feeling—and being— “other” takes on non-white and visibly different people in the US can be extremely painful. Experiencing it firsthand, albeit briefly, benignly, and in relative comfort, I got it.
Unlike the organic Niigata community, work teams, and the workplace itself, have externally driven purposes. Within this different environment, I will strive to exemplify the ongoing mutual awareness that fueled the community life in Niigata. Does it benefit the bottom line, improve the results? I don’t know. But it helps me be the mature, engaged person I want to be, and to appreciate the individuals who are my colleagues and who comprise my professional community. I am now far more conscious of people feeling their “otherness”—even when it’s not in response to negative treatment, it can arise simply from awareness of being in some way different.
What did you think of this essay? Does this middle class Midwesterner have the unique experience of being different from the surrounding majority, something she had not experienced in the United States? Did she encounter diversity from the perspective of “the other”?
Here a few things to note about why this diversity essay works so well:
1. The writer comes from “a comfortable, suburban, Wisconsin life,” suggesting that her background might not be ethnically, racially, or in any other way diverse.
2. The diversity “points” scored all come from her fascinating experience of having lived in a Japanese farm village, where she immersed herself in a totally different culture.
3. The lessons learned about the meaning of community are what broaden and deepen the writer’s perspective about life, about a purpose-driven life, and about the concept of “otherness.”
By writing about a time when you experienced diversity in one of its many forms, you can write a memorable and meaningful diversity essay.
Working on your diversity essay?
Want to ensure that your application demonstrates the diversity that your dream school is seeking? Work with one of our admissions experts . This checklist includes more than 30 different ways to think about diversity to jump-start your creative engine.

Dr. Sundas Ali has more than 15 years of experience teaching and advising students, providing career and admissions advice, reviewing applications, and conducting interviews for the University of Oxford’s undergraduate and graduate programs. In addition, Sundas has worked with students from a wide range of countries, including the United Kingdom, the United States, India, Pakistan, China, Japan, and the Middle East. Want Sundas to help you get Accepted? Click here to get in touch!
Related Resources:
- Different Dimensions of Diversity , podcast Episode 193
- What Should You Do If You Belong to an Overrepresented MBA Applicant Group?
- Fitting In & Standing Out: The Paradox at the Heart of Admissions , a free guide
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted

More From Forbes
Inclusion in the workplace and 6 reasons why it matters.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Senior Vice President & Chief People Officer at CNFA overseeing the culture of positive engagement with its employees globally.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the modern workplace, the importance of fostering a diverse, inclusive environment is often understated and overlooked—consciously or unconsciously. Now more than ever, we must underscore that inclusion isn't just a buzzword or an action item to check off a list. It's a fundamental driver for achieving success.
As HR leaders, it's imperative to show your workforce that true inclusion is about a "one human being" experience, irrespective of race, gender, ethnicity, sexual orientation and other identifiers. It goes beyond mere representation, encompassing a commitment to embracing differences and ensuring everyone feels valued and respected.
Here are six impactful areas that highlight the compelling significance of inclusion in the workplace and how prioritizing it can contribute to overall organizational success.
1. Talent Attraction And Retention
When organizations prioritize inclusion and flexibility, they're more likely to attract top talent. Jobseekers will be drawn to your company if they know it celebrates diversity and provides equal access to opportunities. Moreover, inclusive workplaces tend to retain talent more effectively because employees are more likely to stay in environments where they feel supported and respected .
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
As an HR leader, there are a few strategies you can use to center inclusivity in your recruitment and talent management efforts. Consider implementing unbiased hiring practices, promoting equal opportunities for growth and fostering a workplace culture that embraces diversity.
2. Employee Engagement And Satisfaction
Connection is one of five workplace essentials when it comes to workers' psychological health and well-being. When you prioritize inclusion, you help cultivate a sense of belonging and community among employees. When people feel their unique perspectives are being honored, they're more engaged in their work. This enhances job satisfaction, morale and overall well-being because everyone feels they can contribute meaningfully toward your organization's goals.
3. Innovation And Creativity
Businesses must generate groundbreaking solutions if they want to stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing business landscape. When they have diverse teams, they're more able to tap into new ways of thinking. But this requires an environment where employees know their creativity and innovation will be nurtured.
Try leveraging cross-functional teams so employees from all over your company can collaborate on projects and find innovative solutions by combining their diverse perspectives. At my organization, CNFA, we decided to embrace collaborative problem-solving when we were reevaluating our office space needs. We interviewed a sampling of our employee population and learned that they wanted dedicated thinking rooms or focus areas, as well as open communal areas, to be included in the redesign. Many felt this would help encourage spontaneous interactions and idea exchanges.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making
Having a diverse group involved in your organization's decision-making processes can encourage more extensive discussion and consideration of potential outcomes. This helps decision-makers avoid the pitfalls of groupthink . This kind of homogenous mindset increases the risk of biased decisions, potentially leading to suboptimal decision-making because people might hesitate to voice dissenting opinions or concerns out of fear of disrupting the group's harmony. While teams engaged in groupthink may make quick decisions, the speed doesn't guarantee the best choice.
It's crucial to promote diversity of thought and ensure open communication within your workplace. By creating inclusive teams, everyone can benefit from a range of perspectives, mitigate knee-jerk reactions and foster more well-rounded, thoughtful decision-making.
5. Improved Customer And Client Relationships
In a globalized marketplace, inclusive organizations are able to better understand and relate to the needs of a diverse clientele. By bringing a range of cultural insights and communication skills, you can see positive results like improved customer satisfaction and stronger business relationships .
When your organization incorporates diverse perspectives, it can develop inclusive marketing strategies that resonate with a broad audience. This will help position you as a socially responsible brand that appeals to all customers. Recognizing the varied backgrounds of customers and clients may enable you to expand your customer base, enhance loyalty and foster a positive reputation.
6. Regulatory Considerations
Beyond the moral imperative, there are legal and ethical reasons for prioritizing inclusion in the workplace. Discrimination and exclusion issues can lead to legal consequences that pose reputational risks—some of which are irreparable. By fostering an inclusive culture, you can ensure you're complying with anti-discrimination laws, as well as demonstrating your commitment to good governance and ethical business practices. To stay abreast of DEI-related changes in law, I highly recommend joining industry associations so you can take advantage of the vast resources on all things work, including up-to-date news.
When your organization prioritizes diversity and inclusion, you can tap into your workforce's full potential and be better positioned to thrive in a competitive environment. Beyond benefitting from enhanced innovation, employee engagement and talent retention, you'll also contribute to a more equitable, harmonious society. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st-century workplace, embracing inclusion is not a choice; it's a strategic imperative for sustained business success.
Forbes Human Resources Council is an invitation-only organization for HR executives across all industries. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
Explore the latest in efforts to advance equity in health care access and outcomes, expand diversity in medicine, and create an inclusive work and care environment for all people.
Publication
Article type.
This cohort study assesses the association of poststroke disability with risk of recurrent stroke and major cardiovascular events among participants in 2 randomized clinical trials of secondary stroke prevention.
This cohort study assesses trends and disparities in next-generation sequencing testing among US patients with metastatic prostate cancer and advanced urothelial carcinoma.
This narrative review identifies current racial disparities in sports cardiology and proposes strategies to address these disparities and advance the sports cardiology field as a race-conscious, rather than race-based, practice.
This cross-sectional study evaluates how primary care physicians rate draft responses to patient inbox messages written by generative artificial intelligence compared with those written by health care professionals.
- Randomized Clinical Trials That Advance Health and Health Equity: JAMA Internal Medicine Call for Papers JAMA Internal Medicine Opinion July 15, 2024 Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Health Disparities Ethics Full Text | pdf link PDF
This population-based observational study assesses disparities in mortality risk between American Indian/Alaska Native and White arrestees in South Dakota from 2000 to 2016.
This cross-sectional study evaluates whether there is an association between neighborhood disadvantage and the tumor RNA expression of stress-related genes in African American and White men with prostate cancer.
This meta-analysis of phase 1 trial data from a single institution assesses whether Asian, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Black trial participants with advanced cancer experience similar response outcomes as non-Hispanic White trial participants.
This cohort study investigates the longitudinal changes in workforce diversity of US full-time academic ophthalmology faculty and department chairs from 1966 to 2021.
This cohort study evaluates whether racial bias exists in a machine learning model that identifies cancer mortality risk among patients with solid malignant tumors.
This cross-sectional study investigates if there are racial, ethnic, or gender disparities in the length of boarding in emergency departments for youth awaiting inpatient psychiatric care.
This qualitative study examines factors associated with differences in the leadership development experiences, including organizational support, sponsorship, and cultivation of leadership potential, between women and men in their ascent to medical school deanship.
This cohort study examines whether household socioeconomic status is associated with mental health outcomes among youths during the COVID-19 pandemic.
This cross-sectional study of US adults compares rates of injuries related to firearm use vs motor vehicles crashes relative to community-level social determinants of health.
This cohort study identifies the factors associated with likelihood of microsatellite instability and KRAS biomarker testing among patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
This cross-sectional study assesses the association of Medicare with disparities in health insurance coverage, access to care, and self-reported health status among individuals by sexual orientation and by gender identity.
- NIH Introduces National Primary Care Research Network in US JAMA News July 5, 2024 Medical Education and Training Research, Methods, Statistics Ethics Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Full Text | pdf link PDF free
- Opportunities for Improving System-Level Barriers to Biomarker Testing for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer JAMA Network Open Opinion July 5, 2024 Cancer Biomarkers Health Disparities Oncology Health Policy Health Inequities Full Text | pdf link PDF open access
- Creating Equitable Paths to Medical School Deanship JAMA Network Open Opinion July 5, 2024 Medical Education Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Medical Education and Training Academic Medicine Full Text | pdf link PDF open access
This cohort study examines housing status and acute care use after a cancer diagnosis among individuals treated at a public hospital in San Francisco, California.
Select Your Interests
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Can CRT Save DEI?: Workplace Diversity, Equity & Inclusion in the Shadow of Anti-Affirmative Action
71 UCLA Law Review Discourse 282 (2024)
Fordham Law Legal Studies Research Paper No. 4897843
35 Pages Posted: 18 Jul 2024
Tanya Kateri Hernandez
Fordham University School of Law
Date Written: July 17, 2024
Just four years after the nation's summer of 2020 protests-sparked by the murder of George Floyd-culminated in a racial reckoning in which many organizations across the country instituted racial equity measures and policies, legislators across the nation are enacting anti-Critical Race Theory (CRT) bans in a seeming backlash to this advocacy for racial justice. The bans simultaneously mischaracterize CRT as anti-White discrimination while strategically conflating it with workplace diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives. Further inflaming the racially hostile public discourse is the U.S. Supreme Court's recent decision in Students for Fair Admissions v. Harvard (2023), which greatly narrows the constitutional grounds for race-based affirmative action by questioning the coherence of diversity as a goal for race-conscious, inclusive university admissions policies. As a result, corporate actors are apprehensive about the continued viability of their multibillion dollar investment in workplace DEI trainings. Moreover, given the significant role of DEI training as a remedy for antidiscrimination law violations, it is important for legal scholars to analyze the animating factors of the legal movement to outlaw workplace DEI trainings. This Article details how the worker frustration with individual bias-focused DEI trainings has dovetailed with the wrongful depiction of CRT, in ways that threaten the pursuit of racial equality. The Article then explores a counterintuitive path forward of proposing a wholesale shift to CRT framed DEI trainings as a defense against the attacks on individual bias-focused trainings. Social science research suggests that programs focused on systemic and structural issues make the difference between well-received and poorly received DEI interventions, yielding better results in increasing workplace diversity, retaining employees of color, and addressing harmful, racially disparate systemic policies. The focus on systemic and structural aspects of racism is the very heart of what CRT concerns itself with. Put together, what this means is what DEI actually needs is an infusion of CRT. Ironically, thanks to the legislative and political attacks on CRT, there is now greater public interest in learning what CRT is and what it has to offer. This Article concludes by providing concrete, evidence-based examples of what CRT DEI workplace training can be for antidiscrimination law remedies and beyond.
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Tanya Kateri Hernandez (Contact Author)
Fordham university school of law ( email ).
150 West 62nd Street New York, NY 10023 United States
HOME PAGE: http://https://www.professortkh.com/
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, fordham law school legal studies research paper series.
Subscribe to this free journal for more curated articles on this topic
Discrimination, Law & Justice eJournal
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Employment Law eJournal
Human rights & the global economy ejournal, legal anthropology: laws & constitutions ejournal, anthropology of race, ethnicity & indigenous people ejournal.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Promoting Diversity and Inclusion Within The Workplace. To discuss the importance of diversity and inclusion this essay will first define these two concepts. Firstly, diversity is a concept that considers the many ways we are alike while respecting the ways we are different. When we value diversity we do not try to make all of us the same ...
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives are essential to fostering a positive work culture. Through exposure to diverse perspectives, you can improve employee morale, promote business ethics, and drive creative problem-solving and innovation. According to a LinkedIn survey, 69 percent of recruiters and human resources professionals ...
Workplace inclusion, diversity, and belonging have developed into crucial components of a philosophy that permeates all enterprises. Due to the value they provide, hose concepts swiftly ascend to the forefront of enterprises' priorities. They not only help to create more content, open-minded, and productive staff, but they also enhance the ...
Diversity and inclusion is an important recipe of a long lasting successful organisation. In an organisation, diversity comprises many dimensions outside gender and race. Therefore, age, disability, ethnicity, religion and sexual orientation cover diversity. Secondary, the aspects of diversity include work and communication style, economic ...
simply wish to be allowed to be themselves. The purpose of this chapter is to. provide a broad discussion of the con cepts of diversity and inclusion in the. workplace to assist the reader with ...
Tell a story about how your background, identity, or experience has impacted you. While you can briefly mention another person's experience to provide context, be sure to keep the essay focused on you. Admissions officers are mostly interested in learning about your lived experience, not anyone else's. Example.
Diversity and Inclusion Efforts That Really Work. Five best practices. by. David Pedulla. May 12, 2020. Rusty Hill/Getty Images. Summary. A Stanford and Harvard professor convened a symposium on ...
A literature review analysis was commissioned to focus on diversity and inclusion at workplace and its research trends from 2010 to 2017. The varied meanings and interpretations of the terms 'diversity and inclusion' make it ripe for examining the literature on diversity and that of inclusion to offer a deeper and nuanced understanding of their meanings and conceptualizations.
The value of DEI efforts at work. A majority of workers (56%) say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is mainly a good thing; 28% say it is neither good nor bad, and 16% say it is a bad thing. Views on this vary along key demographic and partisan lines. Half or more of both men and women say focusing on increasing DEI ...
Introduction. Diversity is a term that describes the differences among people, whether they are cultural, ethnic, racial, linguistic, gender, or sexual orientation differences. While diversity is often celebrated, it can also pose challenges, especially in institutions such as schools, workplaces, and governments.
Diversity is the coexistence of people with different characteristics (e.g. race, age, gender, sexual orientation), skills and personality traits. For example, at work, we can talk about a diverse team when employees come from various cultural, academic and professional backgrounds and when there's a balance in gender, age and race.
First, ensure the CEO positions themselves as the top champion for D&I efforts. Second, center D&I in your business strategy. Third, hold executive leaders accountable for D&I outcomes. Fourth ...
This research paper explores the critical issue of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in the workplace and the strategies that can be employed to achieve and sustain a diverse workforce. The research paper is based on a comprehensive review of relevant literature, including peer-reviewed articles, reports, and other relevant documents.
As more and more U.S. companies commit to supporting diversity, inclusion, and belonging in the workplace, one component that often gets left behind is the extension of those initiatives across an ...
The difference between diversity, inclusion and belonging is that diversity is the representation of different people in an organization, inclusion is ensuring that everyone has an equal opportunity to contribute to and influence every part and level of a workplace, and belonging is ensuring that everyone feels safe and can bring their full ...
Fueled by socioeconomic trends that changed the composition of organizational workforces, the term workforce diversity was coined in the 1990s. Since then, both researchers and practitioners have strived (and struggled) to understand the concept, its effects in and on organizations, and strategies for managing such effects. In this article, I provide an overview and interpretation of the ...
By defining inclusion and differentiating between diversity and inclusion, we argue for a contemporary approach to developing diversity training in the workplace for creating an inclusive environment.
The term " diversity and inclusion " describes both the makeup of a workforce, as well as the policies and processes used to remove barriers and ensure that every employee has equal access to opportunities and support at a company. The ultimate goal is to ensure fairness and equity for all employees, regardless of characteristics like ...
Human resource managers need to focus on diversity management due to the following reasons. First, diversity management enables businesses to attract, hire and retain the best talent in the market. Research shows that jobseekers prefer to work for companies that are tolerant to cultural, racial and ethnic diversity.
How to write about your diversity. Your answer to a school's diversity essay question should focus on how your experiences have built your empathy for others, your embrace of differences, your resilience, your character, and your perspective. The school might ask how you think of diversity or how you will bring or add to the diversity of the ...
In contemporary society, the idea of diversity has come to the forefront of workplace culture. Diversity by definition is the existence of multiple different and complex social identities and issues in society or a space (Woodson). In simple terms, people self-identify or are identified as belonging to a specific group based on background ...
2. Employee Engagement And Satisfaction. Connection is one of five workplace essentials when it comes to workers' psychological health and well-being. When you prioritize inclusion, you help ...
As much as the company asserts diversity in its workplace and that inclusion is a priority management policy, it should follow its objectives to achieve them. The dangers of empty discourse, and inconsistency between words and reality, have to be avoided when designing a diversity statement. ... Diversity and Inclusion Essay. (2022, September ...
Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Explore the latest in efforts to advance equity in health care access and outcomes, expand diversity in medicine, and create an inclusive work and care environment for all people.
The bans simultaneously mischaracterize CRT as anti-White discrimination while strategically conflating it with workplace diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives. Further inflaming the racially hostile public discourse is the U.S. Supreme Court's recent decision in Students for Fair Admissions v.