
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7


Top 10 Elements of Creative Writing: All you Need to Know
Learn the art of storytelling with our comprehensive blog on the Elements of Creative Writing. Discover the vital components that transform ordinary words into extraordinary tales. Dive into character development, plot intricacies, and more as we cover the core aspects of crafting captivating narratives. Read more to find out!

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Whether you're an aspiring novelist, a poet, or simply someone who loves to pen down your ideas, understanding the key Elements of Creative Writing can significantly enhance your skills. In this blog, we will explore the top 10 Elements of Creative Writing that are essential for creating compelling and impactful written works, along with tips.
Table of Contents
1) The i mportance of Creative Writing elements
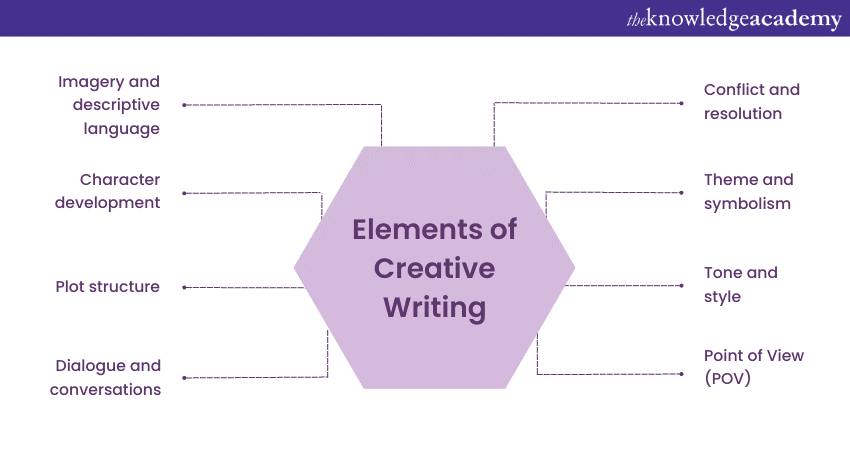
2) Top 10 Elements of Creative Writing
a) Imagery and descriptive language
b) Character development
c) Plot structure
d) Dialogue and conversations
e) Point of View (POV)
f) Setting and world-building
g) Tone and Style
h) Conflict and resolution
i) Theme and symbolism
j) Editing and revision
3) Conclusion
The importance of Creative Writing elements
Creative writing isn't confined to the pages of novels or the lines of poetry; it's a fundamental human expression that predates recorded history. It has been a conduit for cultural preservation, knowledge transfer, and emotional catharsis. But how exactly mastering these elements can improve your writing?
Every art has its tools, and Creative Writing is no different. The elements we'll delve into aren't just guidelines; they're the building blocks that transform your words from ordinary to extraordinary. By understanding and mastering these Creative Writing elements, you'll be equipped to craft narratives that draw readers in, keep them engaged, and leave an indelible mark on their minds and hearts.
Unlock your creative potential with our expert-led Creative Writing Training – Register now to ignite your imagination!
Top 10 Elements of Creative Writing
Generally, there are various Elements of Creative Writing, each possessing its own unique features. However, many forms of Creative Writing also share some common features. Here’s a detailed explanation of each element every Writer must follow:
1) Imagery and d escriptive l anguage
Imagery and descriptive language are the brushes with which writers paint vivid mental pictures for their readers. By skillfully weaving sensory details, you bring scenes to life and evoke emotions. The rustling leaves, the scent of freshly baked bread, the gritty texture of sand beneath one's feet—these details create a sensory symphony that immerses readers in your world.
Metaphors, similes, and analogies act as bridges, connecting the familiar with the unfamiliar. Through them, you can compare the indescribable to the known, enriching your narrative with layers of meaning. Mastery of imagery and descriptive language transforms passive reading into an active experience where readers can taste, smell, hear, see, and feel the world you've created.
Tips :
a) When selecting details, focus on the ones that have the most impact and avoid including unnecessary clutter.
b) Use metaphors and similes sparingly, making them truly resonate.
c) T ailor your descriptions to the tone and mood of the scene or story.
2) Character d evelopment
Character development is the art of breathing life into your fictional personas. Well-crafted characters are not only relatable but also complex, with layers of personality, desires, flaws, and history. They drive the plot forward, compelling readers to invest emotionally in their journeys. Backstories provide context, explaining why characters behave the way they do.
Effective character development allows readers to understand, empathise, and even dislike characters. The key lies in making them authentic and evolving. Just as people change, so should your characters. They learn, grow, and adapt, making their arcs believable and satisfying. The beauty of character development is in its ability to mirror the human experience, forging connections between fictional worlds and real hearts.
a) Explore your characters' pasts to understand their motivations and fears.
b) Create a character profile detailing their appearance, background, and personality traits.
c) Show character development through actions and decisions rather than telling.

3) Plot s tructure
Plot structure is the architecture that holds your narrative together. Think of it as a roller coaster, with highs and lows that keep readers engaged. The introduction sets the stage, introducing characters, settings, and the initial conflict. Rising action builds tension, propelling the story forward. At its peak is the climax, the turning point that determines the characters' fate.
Falling action allows for a gradual untwisting of events, leading to the resolution. Effective plot structure balances pacing, ensuring readers remain intrigued without feeling rushed. Twists and turns add surprise, while cause-and-effect relationships maintain coherence. A well-structured plot keeps readers invested, eagerly flipping pages to discover what happens next.
a) Introduce the main conflict early to hook readers' curiosity.
b) Use cliffhangers and unexpected twists to maintain suspense.
c) Ensure each scene contributes to character development or plot progression.
4) Dialogue and c onversations
Dialogue and conversations are windows into your characters' minds and hearts. Natural and dynamic dialogue conveys information and reveals personalities and relationships. Each character's speech patterns, vocabulary, and tone should be distinct, reflecting their backgrounds and emotions .
Through dialogue, conflicts can be ignited, alliances forged, and secrets unveiled. Subtext—the unspoken thoughts beneath the spoken words—adds depth and intrigue. Conversations can quicken the story's pace, providing relief from dense narrative passages. Dialogue-driven scenes foster engagement, inviting readers to eavesdrop on captivating interactions that fuel the narrative's fire.
a) Listen to real conversations to capture natural rhythms and speech patterns.
b) Use interruptions and nonverbal cues to make dialogue dynamic.
c) Balance dialogue with narrative to avoid overwhelming the reader.
5) Point of View (POV)
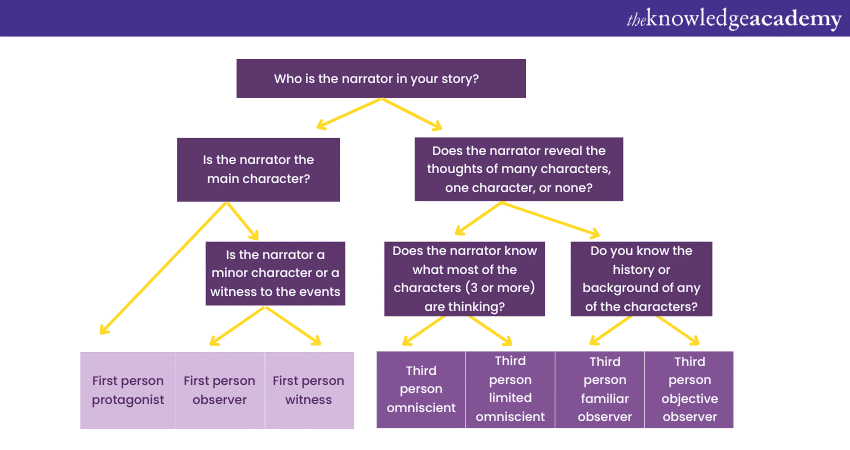
Point of view (POV) is the lens through which your story is perceived. The choice of POV shapes the reader's relationship with characters and events. First-person offers intimacy, allowing readers to see the world through a character's eyes. Second person immerses readers directly into the narrative. Third person limited provides insight into a character's thoughts, while third-person omniscient offers a broader perspective.
Consistency in POV is vital; changing viewpoints can confuse readers. The chosen POV influences what readers know and when they know it. It also affects emotional connection and empathy. Selecting the appropriate POV requires consideration of the story's needs and the desired reader experience.
a) Experiment with different POVs to find the best fit for your story.
b) Consider the level of intimacy and distance you want between characters and readers.
c) Be aware of the limitations and advantages of each POV.
6) Setting and w orld- b uilding
The setting isn't just a backdrop; it's a dynamic element that influences mood and plot. A well-defined setting isn't merely a stage but an active participant, influencing characters and events. You transport readers to a different reality through meticulous detail, allowing them to immerse themselves fully.
Effective world-building extends beyond the physical, encompassing societal norms, rules, and even magic systems in speculative fiction. The environment can reflect themes and impact mood. Whether in a fantasy realm or a contemporary city, the authenticity of the setting enhances the reader's experience.
a) Research settings thoroughly to ensure accuracy and authenticity.
b) Show how characters interact with their environment to convey their experiences.
c) Create a sense of place by using unique and specific details.
7) Tone and style
Tone and style are the fingerprints that make your writing uniquely yours. The tone is the distinctive way you express yourself through words—a combination of tone, diction, and syntax. It reflects your personality as an author. Style encompasses sentence structure, pacing, and word choice, influencing the overall feel of your work .
A comedic style might employ wordplay and witty dialogue, while a dramatic style could use evocative descriptions and emotional introspection. Finding your voice and style involves self-discovery and experimenting with different approaches until you uncover what feels authentic. A strong voice and style leave an indelible mark on readers, making your work instantly recognisable
a) Read more to familiarise yourself with different writing styles.
b) Practice writing in different tones to discover your preferred voice.
c) Revise with a focus on refining your voice; eliminate elements that don't align.
8) Conflict and r esolution
Conflict and resolution are the engine that drives your narrative forward. Conflict introduces challenges that characters must overcome, making their journeys compelling and relatable. There are various types of conflict—internal struggles within characters, external conflicts with other characters or nature, and interpersonal conflicts between characters. Conflict creates tension, propelling the story toward its climax.
The resolution, whether happy or bittersweet, provides closure and offers insights into the characters' growth. Well-crafted conflicts test characters' limits, forcing them to confront their fears, flaws, and desires. Through the resolution, readers witness the transformation and the culmination of the character's arcs.
a) Vary the types of conflict to maintain reader engagement.
b) Build tension gradually; escalate the stakes as the story progresses.
c) Avoid convenient solutions; resolutions should arise from the characters' choices and actions.
Supercharge your writing skills with our Speedwriting Masterclass – Register now and amplify your productivity!
9) Theme and symbolism
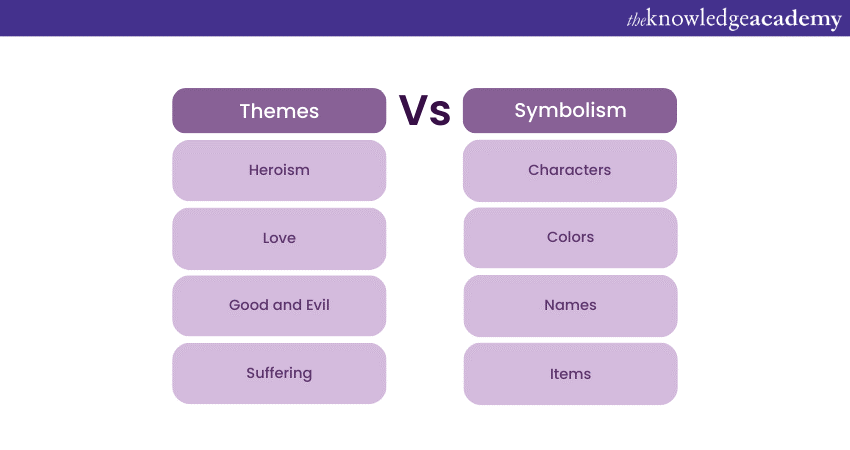
Theme and symbolism lend depth and layers to your writing. Themes are the underlying ideas, beliefs, or messages that resonate with readers. They can explore love, friendship, power, or mortality, connecting the narrative to universal human experiences. Symbolism employs objects, actions, or concepts to convey abstract ideas, often adding an element of intrigue.
A red rose might symbolize love or passion, while a broken mirror could represent self-perception. Themes and symbols intertwine, enriching the story's interpretation and emotional impact. Skilful use of theme and symbolism transforms a tale into an exploration of human nature and society.
Tips:
a) Reflect on the themes that resonate with you and explore them in your writing.
b) Use recurring symbols to reinforce thematic elements.
c) Allow themes to emerge naturally from the characters' struggles and growth.
10) Editing and r evisi on
Editing and revising are the crucial phases that turn your initial draft into a polished masterpiece. Writing is rewriting; the initial draft is a raw exploration of ideas. Editing involves refining sentences for clarity, coherence, and flow. It ensures grammar and punctuation are correct. Revising delves deeper, examining plot holes, character consistency, and thematic resonance.
Seeking feedback from peers or professionals is invaluable, offering fresh perspectives. The revision process is where your story truly comes to life. It's an opportunity to tighten narrative threads, enhance descriptions, and amplify emotions. Embrace the iterative nature of editing and revising; each pass brings your writing closer to its full potential.
a) Revise in multiple passes, focusing on different aspects in each round.
b) Cut unnecessary details or scenes that don't contribute to the narrative.
c) Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling to ensure a polished final product.
Conclusion
Creative Writing is a journey of discovery, both for the Writer and the reader. In this blog post, we've explored the essential elements that constitute effective Creative Writing. From the foundation of imagination to the nuances of dialogue, style, and conflict, each element plays a pivotal role in crafting a compelling narrative. By mastering these top 10 Elements of Creative Writing, you'll be equipped to create stories that resonate, inspire, and captivate audiences.
Elevate your Copywriting skills to new heights with our Copywriting Masterclass – Join today and craft compelling content that captivates your audience!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 3rd Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
| Recommended Tools | Learn More |
|---|---|
| Jasper AI | |
| Show Not Tell GPT | |
| Dragon Professional Speech Dictation and Voice Recognition | |
| Surface Laptop | |
| Bluehost | |
| Sqribble (eBook maker) |
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
7 Elements of Fiction: ProWritingAid's Expert Guide

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Elements of fiction: definition, the 7 elements of fiction, examples of the most famous elements of fiction in literature, elements of fiction: conclusion.
We live in a world full of stories. Novels, short stories, myths, and even plays are all forms of fiction.
All works of fiction are built using the same blocks. So what exactly are those building blocks, and how do they work?
This article will explain the seven elements of fiction and show you examples of what they look like in famous novels.
There are seven elements of fiction that can be found in any story, regardless of the form the narrative takes. These elements are character , plot , setting , theme , point of view , conflict , and tone.

All seven elements work together to create a coherent story. When you’re writing a story, these are the fundamental building blocks you should use.
You can approach the seven elements in any order. For example, you can start with tone—you might know you want to write a funny story, or a scary story. Or you can start with setting—you might decide you want to set the story in your own hometown.
Eventually though, you’ll need all seven elements to make your story complete.
Here’s an in-depth guide to the seven elements of fiction that every fiction writer and reader should know.
Element 1: Character
Characters are the players within a story. They can be human beings, animals, aliens, or even sentient objects. As long as they make decisions within the story, they’re characters.
Most stories have a main character , or multiple main characters. Some have antagonists who prevent the main characters from achieving their goals. There are also side characters , romantic interests, and many other roles that fictional characters can take in a story.
In a well-written story, each character has a distinct appearance, personality, and motivation. They should be rounded characters who drive the story forward by pursuing their individual goals rather than flat characters who behave like cardboard cut-outs.
Element 2: Plot
Plot refers to the events that happen within the story. It includes every major turning point that the characters experience.
In general, every story has a beginning , middle, and end.
The beginning is the exposition, where the key events of the story are set into action. The middle is the rising action, where progressive complications raise the stakes. And finally, the end is the resolution, where the story gets wrapped up.
Element 3: Setting
Setting is a broad term for the world the story takes place in.
On a macro level, setting might include the country the characters live in and the climate of that country. On a micro level, setting can include the room the characters are standing in, the time of day a scene takes place, or even the day-to-day weather.
Settings can sometimes take on symbolic meanings. For example, the never-ending winter in Narnia in C.S. Lewis’s The Lion, The Witch and the Wardrobe represents the tyranny of the White Witch’s rule.
Setting includes time as well as place. A story might take place over the span of a single night, like in A Christmas Carol by Charles Dickens, or an entire lifetime, like in A Man Called Ove by Fredrik Backman.
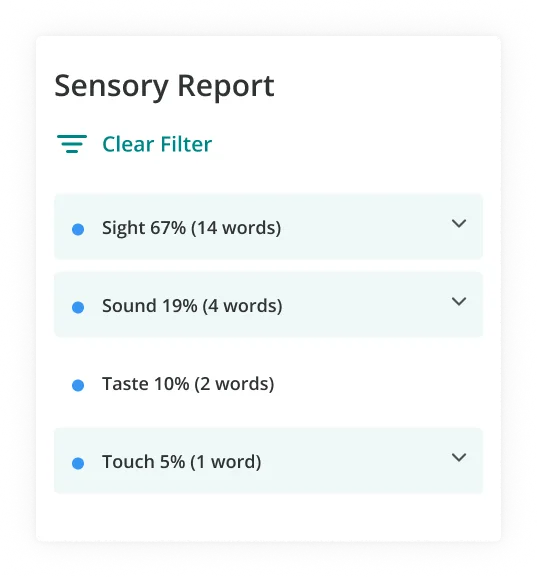
You can use ProWritingAid’s Sensory Report to make sure you’re using all five sense to describe the setting in your story. The more sensory descriptions you use, the more your setting will come to life.
Element 4: Theme
Theme refers to the philosophical questions your story explores.
Often, theme is revealed in the lesson the protagonist needs to learn. For example, one of the themes of Shelley’s science fiction book Frankenstein is that scientists shouldn’t use their powers to create new beings without considering the consequences.
Theme can also be revealed through the core conflict between the protagonist and the antagonist.
For example, in the Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling, the antagonist, Voldemort, doesn’t love anybody, while the protagonist, Harry, is protected by the love of his family and friends. Thus, the power of love is a major theme in the series.
Element 5: Point of View
Point of view (POV) is the perspective from which a story is told.
In English class, you might have learned about the four basic POVs:
First person (“I”)
Second person (“you”)
Limited third person (“he, she, they” in one character’s head)
Omniscient third person (“he, she, they” from an all-seeing perspective)
POV is closely intertwined with form and structure. For example, if your story takes the form of advice offered to someone else, second person makes sense. On the other hand, if your story takes the form of a diary entry, first person makes sense.
Element 6: Conflict
Conflict is what prevents the protagonist from achieving their goals. All fiction writing requires conflict because otherwise there would be no story, just a happy ending.
For example, imagine your protagonist’s goal is to get back home as quickly as possible. The conflict can be as small as a late bus that delays their return, or as large as an earthquake that tears their hometown apart.
There are seven types of conflict: character vs character , character vs self , character vs society , character vs fate , character vs nature , and character vs technology .
Conflict is important because it’s what makes the story interesting. There would be no story if everyone could easily achieve everything they wanted. Adding meaningful obstacles for the characters to overcome is key for creating a compelling story.
Element 7: Tone
Tone helps the author evoke emotion.
When you’re reading or writing, ask yourself: What feeling is this story meant to evoke in the reader? Fear? Amusement? Thoughtfulness? Dread?
Tone is closely related to genre. If you’re writing a thriller, you might want to go for a scary and suspenseful tone. If you’re writing a romantic comedy, you might lean toward a lighter and more humorous tone.
Stories can vary their tones on a scene level. Even a thriller should have lighthearted scenes, and romantic comedies should have serious scenes.
(SPOILER ALERT: There are minor spoilers ahead for The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins and The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald.)
Let’s look at the seven elements of fiction in The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins, a young adult (YA) dystopian novel.
Character : The protagonist is Katniss Everdeen, who competes in the Hunger Games. Other major characters include her love interest Peeta Mellark, her younger sister Primrose Everdeen, and the other contestants in the Hunger Games.
Plot : The plot kicks off when Katniss volunteers for the Hunger Games to protect her sister. The rest of the plot follows Katniss training for and competing in the Games.
Setting : The setting is the nation of Panem. Specific settings include District 12, the impoverished district where Katniss grew up; the glittering Capitol, where the rich citizens live in blissful ignorance; and the arena, where the Games take place.
Theme : The themes of the story include power and oppression, suffering as entertainment, and inequality.
Point of View : Katniss is the first-person narrator.
Conflict : The primary conflict is character vs character when Katniss and the other tributes battle one another. Other forms of conflict are present as well, such as the character vs society conflict when Katniss confronts the dystopian society she lives in.
Tone : The writing style of the book is fast-paced and suspenseful, often evoking fear and excitement, as Katniss tells the reader about the life-and-death situations she’s experiencing.
Now let’s look at the seven elements of fiction in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald, a classic work of literary fiction.
Character : The protagonist is Jay Gatsby, the Great Gatsby himself. Other key characters include his friend Nick Carraway, his love interest Daisy Buchanan, and Daisy’s husband Tom Buchanan.
Plot : The plot follows Jay Gatsby as he throws lavish parties in an attempt to win back Daisy, the love of his life. Over the course of the story, he courts her and nearly convinces her to leave her husband for him, but ultimately loses his life as a result of his efforts.
Setting : The setting is New York in the 1920s during the Jazz Age. Specific settings include West Egg, East Egg, the valley of ashes, and New York City.
Theme : The themes of the story include the American Dream, love and marriage, and dissatisfaction with life in spite of wealth and status.
Point of View : The book is written in the first person from Nick’s point of view. This POV is sometimes called first-person witness, since the narrator isn’t the same person as the protagonist.
Conflict : The primary conflict is character vs self conflict as Gatsby tries to achieve the American Dream and prove to Daisy he’s a great man. There’s also character vs character conflict between Gatsby and the other characters.
Tone : The tone of the book is serious and reflective while Nick reflects on Gatsby’s story and relays it to the reader.
Now you know the key elements that make a story work! Here’s a quick recap:
Point of view
What do these elements look like in your favorite stories? Let us know in the comments.

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Elements of Creative Writing
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review , the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. We’ve selected nearly all of our readings and examples from writing that has appeared in our pages over the years. Because we had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, our perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, we hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of our magazine as we analyze and discuss some reasons we think this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable.

Cover image credit: Hannah Olinger, https://unsplash.com/photos/8eSrC43qdro Used under Unsplash license: https://unsplash.com/license Background image credit: Copyright University of Northern Iowa. All rights reserved.

Introduction
- 0 This text has 0 annotations
- 0 This text has 0 highlights
Chapter One One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- 18 This text has 18 annotations
- 160 This text has 160 highlights
Chapter Two Plotting
- 8 This text has 8 annotations
- 156 This text has 156 highlights
Chapter Three Counterpointed Plotting
- 14 This text has 14 annotations
- 122 This text has 122 highlights
Chapter Four Show and Tell
- 19 This text has 19 annotations
- 222 This text has 222 highlights
Chapter Five Characterization and Method Writing
- 5 This text has 5 annotations
- 194 This text has 194 highlights
Chapter Six Character and Dialogue
- 11 This text has 11 annotations
- 184 This text has 184 highlights
Chapter Seven Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- 3 This text has 3 annotations
- 85 This text has 85 highlights
Chapter Eight Point of View
- 16 This text has 16 annotations
- 165 This text has 165 highlights
Chapter Nine Learning the Unwritten Rules
- 13 This text has 13 annotations
- 120 This text has 120 highlights
Chapter One A Poetry State of Mind
- 97 This text has 97 highlights
Chapter Two The Architecture of a Poem
- 12 This text has 12 annotations
- 117 This text has 117 highlights
Chapter Three Sound
- 107 This text has 107 highlights
Chapter Four Inspiration and Risk
- 136 This text has 136 highlights
Chapter Five Endings and Beginnings
- 67 This text has 67 highlights
Chapter Six Figurative Language
- 7 This text has 7 annotations
- 114 This text has 114 highlights

Chapter Seven Forms, Forms, Forms
- 52 This text has 52 highlights
Chapter Eight Go to the Image
- 4 This text has 4 annotations
- 40 This text has 40 highlights
Chapter Nine The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
- 68 This text has 68 highlights
Creative Nonfiction
Chapter one creative nonfiction and the essay.
- 1 This text has 1 annotation
Chapter Two Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- 70 This text has 70 highlights
Chapter Three Research and History
- 2 This text has 2 annotations
- 49 This text has 49 highlights
Chapter Four Writing Environments
- 42 This text has 42 highlights
Chapter Five Notes on Style
- 81 This text has 81 highlights
- 51 This text has 51 highlights
Chapter Seven Imagery and the Senses
Chapter eight writing the body.
- 34 This text has 34 highlights
Chapter Nine Forms
- 54 This text has 54 highlights
Back Matter
Contributors, north american review staff, resource collections, single resources, creative nonfiction: alison alstrom, "good morning, heartache", creative nonfiction: lucienne bloch, "365 new words a year: october", creative nonfiction: traci brimhall, "philematophilia", creative nonfiction: taylor brorby, "confluence", creative nonfiction: lee ann roripaugh, "notes on beauty", creative nonfiction: paul crenshaw, "fire", fiction: sarah cypher, "ghost town", fiction: marc dickinson, "three days discovered", fiction: frannie dove, "a twister on stage 14", creative nonfiction: samantha edmonds, "an incomplete list of sad beautiful things...".
- isbn 978-0-915996-17-9
- publisher Rod Library, University of Northern Iowa with support from North American Review Press. Funding for this project was provided through the University of Northern Iowa Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
- publisher place Cedar Falls, IA
- rights Original textbook content (Introduction, Fiction, Poetry, & Creative Non-Fiction sections) is CC BY-NC 4.0. Readings and examples in Resources section are used with author permission; all rights reserved.
- rights holder Jeremy Schraffenberger, Rachel Morgan, & Grant Tracey except where noted.
We use cookies to analyze our traffic. Please decide if you are willing to accept cookies from our website. You can change this setting anytime in Privacy Settings .

- WRITING SKILLS
Creative Writing
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Writing Skills:
- A - Z List of Writing Skills
The Essentials of Writing
- Common Mistakes in Writing
- Introduction to Grammar
- Improving Your Grammar
- Active and Passive Voice
- Punctuation
- Clarity in Writing
- Writing Concisely
- Coherence in Writing
- Gender Neutral Language
- Figurative Language
- When to Use Capital Letters
- Using Plain English
- Writing in UK and US English
- Understanding (and Avoiding) Clichés
- The Importance of Structure
- Know Your Audience
- Know Your Medium
- Formal and Informal Writing Styles
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Top Tips for Writing Fiction
- Writer's Voice
- Writing for Children
- Writing for Pleasure
- Writing for the Internet
- Journalistic Writing
- Technical Writing
- Academic Writing
- Editing and Proofreading
Writing Specific Documents
- Writing a CV or Résumé
- Writing a Covering Letter
- Writing a Personal Statement
- Writing Reviews
- Using LinkedIn Effectively
- Business Writing
- Study Skills
- Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Creative writing is loosely defined as more or less any form of original writing: anything that involves creativity and ‘making things up’. It can therefore be defined simply as writing that falls outside the usual bounds of journalistic, academic, technical or professional writing.
Creative writing is generally considered to encompass all fiction writing, as well as poetry, and many people also include writing plays and screenplays.
The focus of creative writing is generally, but not invariably, on the narrative arc and character development. It is therefore very different from writing such as journalistic writing , which may aim to tell stories, but is focused on facts.
Elements of Creative Writing
There are many different forms of creative writing, and they all have their own features. However, many types of creative writing also share some common features. These include:
1. A strong plot or narrative arc
The plot, also known as the ‘narrative arc’, is the unique ‘story’ of your writing. It describes what happens to your characters.
It is fair to say that this is a feature of all creative writing, and is effectively what distinguishes it from other forms of writing. Without a story, you are simply providing facts. There is a place for that—but it is not creative writing.
A plot does not have to cover a long period of time, or even have a clear ending. If you consider many short stories, they are very much a snapshot in time. You enter the characters’ lives at a particular point, and often leave them shortly afterwards. You do not necessarily know what happens next. Some of the most frightening stories are those where your imagination fills in the gaps (a good example of this is Daphne Du Maurier’s short story The Birds , later made into a film by Alfred Hitchcock).
Even a poem has a story (see box).
Narrative arc in poetry
It is possible to suggest that much poetry, especially more modern poetry is not a ‘story’, but is about feelings and emotions. However, that does not mean that it has no narrative arc.
Consider Robert Frost’s poem The Road Not Taken, which ends
“Two roads diverged in a wood, and I— / I took the one less traveled by, / And that has made all the difference.”
Most people are only aware of these last few couplets. However, the poem has four verses, setting out the poet’s situation (standing in a wood, having to choose between two possible roads), and his feelings about that. He then looks ahead to the future, and how he will one day look back on this and recognise the importance of the moment.
The road is undoubtedly metaphorical. However, there is still a clear plot and story to the poem.
2. Character development
The second feature of creative writing is the creation of characters, and their development over the course of the writing.
In this context, ‘development’ can describe either changes in the character themselves, or a change in the reader’s understanding of the character.
For example, in Charles Dickens’ A Christmas Carol , Ebenezer Scrooge, the main character, undergoes an epiphany in the course of the book, and his character completely changes.
However, by contrast, in Daphne Du Maurier’s Rebecca , the unnamed heroine—and by extension, the reader—learns more and more about her husband’s former wife over the course of the book, and comes to appreciate that all is not what it seemed on the surface.
3. A characteristic use of language
One of the features that distinguishes creative writing is the wide diversity of language use.
Creative writers often, if not always, provide visual descriptions of locations and people. This is because their readers need to be able to imagine the characters and scenes—and providing more descriptions makes this process easier.
Writers like J.R.R. Tolkien spent years creating imaginary worlds. They wanted their readers to share their vision of these worlds in as much detail as possible.
Creative writing also often features a more vivid use of language. Metaphors, similes, adjectives and adverbs abound. Unlike business writing, it is not a matter of ‘more concise often equals better’. In creative writing, more can definitely be more.
4. An underlying theme or message
Some people suggest that every piece of creative writing has an underlying theme or message.
It is certainly true that there can be some very strong underlying themes, especially in certain types of writing. For example, many fantasy novels are very much ‘good vs. evil’, usually with a strong undertone of ‘coming of age’ of characters. Journeys within books are often metaphors for a character’s own journey of development, with a sense of ‘homecoming’ or ‘journey’s end’ towards the end of the story.
This idea of an underlying theme is interesting, because it is arguable that it is not always intentional.
In other words, it is not clear whether writers sit down and decide on this underlying theme, or whether it develops with the writing. It certainly does not seem to be necessary to have a clear ‘message’ in mind in writing—and certainly not a moral one. However, there is also something intensely human about wanting to draw lessons from experience.
The real question is: does the writer do this, or is this part of what happens during the reading process?
5. An emotional appeal
Creative writing has to appeal to our emotions. Otherwise, we might as well read non-fiction.
Writers have to create this emotional appeal, but it is often part of the other aspects of a piece of creative writing. For example, writers develop strong characters, with an appealing story arc. Readers empathise with those characters, and care what happens to them. If the writer does not create interesting characters, the reader loses interest.
It therefore seems likely that the most important aspect of creating emotional appeal is that you, the writer, care about your characters and what happens to them.
After all, if you don’t care, why would anyone else?
Developing Creative Writing Skills
Creative writing is a skill like any other form of writing. It therefore follows that you can develop that skill.
However, it can be much harder to do that than with many other forms of writing. It is, for example, harder to get external opinions about your writing without going on a course (see box).
Creative writing courses and teaching
Many universities and schools offer courses in creative writing. Some of these may be general, and others may have a more specific focus, such as writing for films or screen.
If you want to pursue an interest in creative writing, but you are struggling to get started, one of these courses may be right for you.
However, as with any other course, it is worth doing your research to ensure that you will get value for money.
You can also find plenty of advice and creative writing exercises online, some of which are free. It may be worth trying some of these first, to see if they are sufficient to get you started.
A final thought
Writing is a very personal process.
Nobody can tell you how writing ‘should’ be for you, especially creative writing. Everyone works differently, and the process of developing characters and stories is different for every writer.
Probably the best advice is simply to start writing, keeping in mind the elements listed here, and then seek feedback from those around you.
Continue to: Top Tips for Writing Fiction Storytelling in Business
See also: Writing for Children Writing for Pleasure Common Mistakes in Writing
10 Impactful Elements of Creative Writing

Wondering how can you think like J.K. Rowling and craft a creative masterpiece like Harry Potter? Is that even possible for you? Of course, it is quite doable for anyone having a flair for creative writing. But only a passion would not be enough as you need to know how things work in creative writing.
It means you must be aware of the elements of creative writing. Speaking of which, this exciting blog post sheds light on each of these elements in detail for you to form a good base for such writing. So, without further ado, let’s get to read them all.
Table of Contents
The Elements of Creative WritingYou Should Know
Characterization.
Development: Characters with a range of features including emotions, depth, and complexity can capture readers’ attention and propel the story along. Character development is an important element of creative writing!
Arcs and Growth: The development of characters throughout the narrative can create an interesting journey that viewers can relate to.
Plot and Structure
Engaging Plot: A series of occurrences that intrigue readers, containing components such as suspense, opposition, and resolution.
Structure: A structure that is carefully constructed either to adhere to conventional formats or to attempt unconventional storytelling for a stronger effect.
Setting and Atmosphere
Vivid Settings: Writing that creates vivid imagery and allows readers to experience the story’s environment.
Atmospheric Elements: Creating an atmosphere with vivid descriptions of the setting to add to the emotion of the story.
Dialogue and Voice
Authentic Dialogue: Discussions that expose personality attributes, propel the storyline forward, and sound realistic.
Distinctive Voice: The writer’s style and character are expressed through the storytelling.
Theme and Symbolism
Exploration of Themes: Implicit ideas or themes that give the story more substance and significance.
Symbolic Elements: Employment of symbols or figures of speech to express additional layers of meaning and interpretation.
Emotional Resonance
Eliciting Emotions: Evoking feelings in readers, encouraging understanding, bonding, and making a lasting impression.
Authenticity of Emotions: Depiction of real feelings and events that are true to life.
Language and Style
Vivid Language: Employing vivid language, figurative comparisons, and sensory details to form pictures in the mind and to stimulate the senses.
Narrative Style: Developing a distinctive writing style to establish the mood and pacing of the narrative.
Foreshadowing and Pacing
Foreshadowing: Scattered hints and clues placed throughout the story, sparking curiosity and suspense.
Pacing: Varying the pace of the story to keep the reader engaged and emotionally invested.
Suspense and Tension
Suspenseful Elements: Creating excitement about what will happen next in the narrative.
Tension Creation: Factors that create suspense and keep readers interested in the conclusion.
Originality and Innovation
Innovative Storytelling: Trying out different ways of telling a story, such as different narrative forms, genres, and perspectives, which can result in interesting and original stories.
Unexpected Twists: Unanticipated features that defy expectations and draw in viewers.
Understanding Elements with the Help of a Creative Writing Example
Going through creative writing examples is often a good way to adapt the right technique for tackling this task. Here you go with an example.
The Creative Writing Piece
In a peaceful spot in the city, surrounded by towering skyscrapers, was an old house. Its worn-out exterior didn’t give away the secrets inside, especially in the attic, where forgotten gems were collecting dust.
Anna, once full of life as a cellist, now found comfort in the peace and quiet of her home. Her music stopped playing after a heartbreaking incident that took away her brother, Daniel, leaving her with a deep sadness in her heart.
On a stormy afternoon, Anna was trying to avoid thinking about painful memories, so she went into her attic. She found an old music box, with tarnished edges, and she nervously wound it up. A sad melody filled the quiet room.
Anna’s body shuddered as the melancholic tune filled her soul, bringing up memories she had wanted to forget. Daniel’s favorite song was playing, the song they’d shared during their happiest times together. Her eyes blurred with tears as a mix of nostalgia and pain overwhelmed her.
Anna ran her fingers over the detailed carvings on the music box in a trance. The grooves reminded her of all the good times she had with Daniel – his wide grin, and the bond they had. She was filled with emotion as she remembered it all, tears streaming down her face.
As the music tapered off, Anna’s determination increased. She held onto the music box tightly, dead set on figuring out what it meant. She stayed up all night and kept searching, and eventually found hints – a worn-out photo, an outdated show ticket – each one being a small lead to a song that had been forgotten.
Anna had a moment of self-reflection and remembered how much she loved music. She carefully picked up her cello and slowly plucked at the strings, feeling the music stir up her emotions. Gradually, the forgotten melody came back to her and filled the house, blending with the pitter-patter of rain hitting the windows.
Anna used music to find her way to recovery. Every tune she played was a step towards accepting her situation, a reminder of Daniel’s presence. The attic, which had once been a place of grief, now filled with the bittersweet sound of reflection and optimism.
In her music, Anna found that even when she had forgotten certain melodies, they still had the power to bring healing and renewal.
Breaking Down Elements of Creative Writing from the Story
You can get all the ideas about composition and more about creative writing in the comprehensive guide to master creative writing by experts.
Element 1: Idea Generation
Anna, a disheartened cellist who can’t stop thinking about the awful accident that involved her brother, finds comfort in a dusty attic. There she finds an old music box that plays a sorrowful tune, and it brings back memories, causing her to go on a mission to understand its importance.
Element 2: Character Development
Anna: A once-passionate cellist now withdrawn, struggling with unresolved emotions stemming from her brother’s accident.
Brother: A pivotal character in flashbacks, portrayed as a source of inspiration and unresolved grief in Anna’s life.
Element 3: Plot and Structure
The narrative alternates between the present, where Anna discovers the music box, and poignant flashbacks revealing her relationship with her brother and the accident’s aftermath. The structure slowly unravels the emotional layers of Anna’s journey.
Element 4: Setting and Atmosphere
The attic serves as a metaphorical space for introspection, filled with forgotten relics that evoke nostalgia and pain. The contrast between the melancholic tune of the music box and the present silence heightens the emotional atmosphere.
Element 5: Dialogue and Voice
Conversations between Anna and her brother in flashbacks reveal their bond, regrets, and unspoken emotions. Anna’s internal monologue and interactions reflect her inner turmoil and gradual emotional healing.
Element 6: Theme and Symbolism
Themes of loss, healing, and the restorative power of music are explored. The music box symbolizes Anna’s unresolved emotions and her quest to rediscover joy amidst grief.
Element 7: Emotional Resonance
Readers empathize with Anna’s grief and find hope in her journey toward healing. Authentic emotions and gradual healing resonate throughout the narrative, evoking a range of emotions in the audience.
Element 8: Language and Style
Descriptive prose paints vivid images of both physical and emotional landscapes, evoking nostalgia and heartache. The narrative style, with its lyrical prose and introspective reflections, establishes a poignant and contemplative tone.
Element 9: Foreshadowing and Pacing
Clues within the narrative hint at the music box’s significance, building anticipation. Alternating between reflective moments and revelations maintains a pace that allows emotions to linger while propelling the story forward.
Element 10: Originality and Innovation
The blend of music, memories, and emotional introspection creates a narrative that resonates uniquely. Unexpected revelations within Anna’s journey offer hope amidst sorrow, adding depth to the story. The expert writers working with professional paper writing service providers also vouch this element to be very important for the effectiveness of creative writing.
Creative writing is like painting with words! You create characters, plots, and settings and inject emotions to make stories come alive. With interesting characters, emotional appeal, an exciting story, and vivid descriptions, you can draw readers in and make them feel like they’re right there in the adventure. It’s a great way to evoke emotion and fire up imaginations!
This blog post was all about helping you get better with creative writing with knowing the elements of creative writing in good detail.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Lesson 3: Elements of Fiction
What Is Fiction?
Fiction is make-believe, invented stories. They may be short stories, fables, vignettes, plays, novellas, or novels. Although writers may base a character on people they have met in real life, the characters and the experiences that the character faces in the story are not real.
So, how does a writer write fiction? Characters, setting, plot, conflict, point of view, and theme are six key elements for writing fiction.
Characters are the people, animals, or aliens in the story. Readers come to know the characters through what they say, what they think, and how they act.
E. M. Forster, an English novelist, identified that characters are either flat or round. Flat characters do not play important roles in the stories. They often have only one or two traits with little description about them. A flat character may even be a stock character, which is a stereotypical figure that is easily recognized by readers, for example, the mad scientist or the evil stepmother.
On the other hand, the round characters play an important role, often the lead roles in stories. They are complex, dimensional, and well-developed. The stories are about them; therefore, pages of writing will be about them. They often change by going through a life-changing experience as the story unfolds.
When discussing stories with other readers and writers or when writing an analysis of a story, fictional characters can be described as static or developing. Static means the character stays the same throughout the story. They do not change. Developing, also called dynamic, means the character changes. The change may impact the character’s beliefs, attitudes, or actions. The change may be small or large. This change occurs because the character experiences an epiphany, an insight about life.
If writers write about characters outside their own culture, they need to do research so as not to misrepresent a particular culture. The same is also true of characters, who have illnesses. The writer may need to research the illness and treatment for it in order to be accurate about it.
Setting is where and when the story takes place. It includes the following:
- The immediate surroundings of the characters such as props in a scene: trees, furniture, food, inside of a house or car, etc.
- The time of day such as morning, afternoon, or night.
- The weather such as cloudy, sunny, windy, snow, or rain, etc.
- The time of year, particularly the seasons: fall, winter, summer, spring.
- The historical period such as what century or decade the story takes place.
- The geographical location including the city, state, country, and possibly even the universe, if the writer is writing science fiction.
Setting can function as a main force that the characters encounter, such as a tornado or flood, or a setting can play a minor role such as setting the mood. Often times, the setting can reveal something about the main character as he/she functions in that place and time period.
Writers write about places they are familiar with. If they aren’t familiar with the place, then they need to research it in order to be accurate about the place.
Plot is the order of events in the story. The plot usually follows a particular structure called Freytag’s Pyramid. Gustav Freytag, a German playwright who lived during the 1800s, identified this structure.
Freytag’s Pyramid has five parts: exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and denouement, also known as resolution. See Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1: Freytag’s Pyramid

Freytag’s Pyramid by Gustav Freytag, a German playwright
Exposition is an introduction to the characters, time, and the problem. At the point where exposition moves into rising action a problem, sometimes called an inciting incident, occurs for the main character to handle or solve. This creates the beginning of the story.
Rising action includes the events that the main character encounters. Each event, developed in separate scenes, makes the problem more complex.
Climax is the turning point in the story. Usually, it is a single event with the greatest intensity and uncertainty. The main character must contend with the problem at this point.
Falling action includes the events that unfold after the climax. This usually creates an emotional response from the reader.
Denouement or resolution provides closure to the story. It ties up loose ends in the story.
Do writers plan out their stories? Some do, especially if they are an extreme think-write writer. Some don’t. They have a story idea, begin it, and watch it unfold as they write.
Conflict is the struggle between two entities. In story writing the main character, also known as the protagonist, encounters a conflict with the antagonist, which is an adversary. The conflict may be one of six kinds:
- Character vs. character
- Character vs. nature or natural forces
- Character vs. society or culture
- Character vs. machine or technology
- Character vs. God
- Character vs himself or herself
Point of View
Stories are generally told in one of two points of views:
- First-person point of view
- Third-person point of view
First-person point of view means that one of the characters in the story will narrate–give an account–of the story. The narrator may be the protagonist, the main character. Writing in first-person point of view brings the readers closer to the story. They can read it as if they are the character because personal pronouns like I, me, my, we, us, and our are used.
Third-person point of view means that the narrator is not in the story. The third-person narrator is not a character. Third-person point of view can be done two ways:
- Third-person limited
- Third-person omniscient
Third-person limited means that the narrator limits him/herself by being able to be in one character’s thoughts. Whereas, third-person omniscient means the narrator has unlimited ability to be in various character’s thoughts. Writing in third-person point of view removes readers from the story because of the pronouns he, she, it, him, her, his, hers, they, them , and theirs .
A theme is not the plot of the story. It is the underlying truth that is being conveyed in the story. Themes can be universal, meaning they are understood by readers no matter what culture or country the readers are in. Common themes include coming of age, circle of life, prejudice, greed, good vs. evil, beating the odds, etc.
Introduction to Creative Writing Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Writers' Treasure
Effective writing advice for aspiring writers
- Fiction Writing 101: The Elements of Stories
- Fiction Writing
You guessed it: fiction writing. Novels are written every month and every year. The vast majority don’t see the light of day (a fancy expression meaning getting published). Some do. Some become bestsellers. Some don’t even sell a few copies.
What makes the difference between writing a really good story that people read with pleasure and a boring one that makes readers throw it across the room?
Mastering the art of writing great fiction is called fiction writing.
Just in case you missed the earlier instalments of this series, here they are for you. Enjoy:
1. An Introduction to Creative Writing 2. How to Get Started in Creative Writing in Just Three Steps 3. Creative Writing vs. Technical Writing
Now, there are a few fiction writing elements which you should know. This isn’t one of those “which you can’t live without” lists. You can live without this one. But you wouldn’t want to. Once you know all the elements, you only have to perfect them and there you have it, a masterpiece in your hands…
Only there’s nothing “only” about perfecting elements. But that’s another post. Below are the fiction writing elements found in all the novels, novelettes, novellas and short stories:
1. Character
Every story has a main character. If you don’t have any characters, you don’t have any story. You might have the most exciting plot in the history of the universe, but if you don’t have characters that make the reader care about them, you might just as well throw out your story.
There is a whole art to character writing. Sure, you can slap up a name on a caricature, give it a few clichés (qualities so well known that there’s nothing caring about them) and call it a character. But that doesn’t make it a believable and real character… and I’m not talking just about cardboard cut-outs here. Unbelievable characters are… well there’s no strong enough word in English to describe them. Don’t waste your ink making them up.
Every story has a main character. But does every story have a plot? The answer is not every story… but all the good ones have them. If a story does not have a plot, you can conclude it’s a bad story, not publishable at all, because there’s nothing happening within it.
Yes, the question you can ask to yourself if you want to know whether your story has a plot or not (what a mouthful) is: what happens in it?
Action is not plot . Plot is something different. Whether you want to write a detailed plot outline or just start your story, you must take care of plot. Without characters there is no story even if you have plot, and vice versa. Without plot there is no story even if you have the best characters in the world. Both are necessary. Omission of any one can seriously hinder your story.
Your plot can be anything in the world. It can be happy, it can be sad, it can be serious, it can be funny, it can be realistic and it can be fantastical. Its only function is to draw the reader in.
If you write a plot that makes your readers bored, then you can conclude that it was a failure. Many plots are failures. Far more are failures than successes. It can be bitter to realize that your plot is not holding the reader’s attention, but it happens to all of us and it is the way of the world.
a. Subplots
If you include subplots in your story, you can increase interest in your novel. But that’s only if you carry it off well. What are subplots? From Wikipedia:
A subplot is a secondary plot strand that is a supporting side story for any story or the main plot. Subplots may connect to main plots, in either time and place or in thematic significance. Subplots often involve supporting characters, those besides the protagonist or antagonist.
That defines it succinctly.
b. Conflict
In your plot, you must introduce conflict between the main character and his surroundings. Conflict is necessary to make your novel spicy. Conflict between the protagonist (hero) and antagonist (villain), conflict between the protagonist and the side characters and so on. Without conflict there is no excitement in a story. People hate to see everyone agreeing with each other. Introduce some conflict.
Where is your novel set? It might be set in modern age India, it might be set in ancient Europe, it might be set in a fantasy world such as Middle Earth. Wherever, it doesn’t matter. But it must be believable.
What is your novel about? Is it about crime, about politics, about realism or about fantasy? What is the theme of the story? How will readers feel after reading it? If you answer these questions, you have a theme.
5. Style and Grammar
Writing voice, point of view, style and grammar matter. If you break the rules, sometimes it’s for the better. But it’s always better to know them before breaking them. If you make a spelling mistake, be sure to correct it with proof-reading. Nothing gives away the amateurishness of a writer more than a spelling mistake.
That’s it for Fiction Writing Elements. Over to you.
I’m sure I missed some of them out. What are your experiences in fiction writing elements? Have you found the explanation easy to follow, or was it rambling and not succinct enough? Feel free to give feedback in the comments.
This is the fourth instalment in the eight part series “Creative Writing 101.”
Share this:
Further reading:.
- What Should Be Told and Shown in the Opening Chapter?
- How to pick out a character for your novel
- Conflict is Necessary to Make it Spicy
- Why Hunting for Plots is Worthless
- The Best Way of Writing a Compelling Opening Chapter
19 thoughts on “Fiction Writing 101: The Elements of Stories”
I just updated this post to include more fiction writing elements. Please share feedback about the site.
It was interesting to read. I have a question ! can I write stories in English even I am not a native speaker ? and do you think that my story could be published ?
- Pingback: Creative Non-Fiction: What is it? | Writers Treasure
Not easily.You’ll only ever rellay make a living off your writing if you hit it big, say work for a newspaper or become a top-selling author. You likely won’t make a lot of money off of stories on a website.If you want to try though, look into publishers that sell eBooks, or try self-publishing on sites like Lulu.com.
True words. But who said anything about writing stories on a website? This is a how-to blog, not a blog to showcase stories.
- Pingback: Why Hunting for Plots is Worthless
- Pingback: Finding the Balance between Narrative and Dialogue | Writing Tip
- Pingback: POV: What it is and how it matters
- Pingback: Pen and Paper vs. Computer – Which Do You Use?
- Pingback: Web Writing vs. Print Writing
- Pingback: Creating Writing | Creative Writing Tips
- Pingback: Links on Writing « amiecus curiae
I enjoy reading and writing but since I began to write namely fiction stories which is the field I seem to feel in my own element I don’t quite seem to build up the entire storyline from start to finish for I seem to build it all like an essay meaning introduction and body of the storyline and conclusion yet what is the proper formula how to blend all the ideas into a story book from begining to the end.
THANKS PATEL I HAVE GAINED A LOT WHAT I READ ON YOUR SITE WILL HELP IN MY NOVEL WRITING.
I like this post and find it really helpful.
Love this blog! Have a young family member who talks endlessly about characters he has built and all the things that each character does. We want to try to get him to write his story. THESE tips are what I’m looking for in an audio book or written book!! Any suggestions on what are good?
I love your article! Thank you very much for taking the time to share your helpful insights!
I agree with those words at the same time they are all true. That is the thing that fiction is for. It’s for getting at reality when the fact of the matter isn’t adequate for reality.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Related Post
How to create characters readers really care about how to create characters readers really care about.
This is a guest article by Alex Limberg. If you want to write a guest article of your own be sure to read the guest article guidelines .
Some writers claim they know their characters even better than their spouses. It’s great when your spouse doesn’t just exist on paper, and even greater when you can create real, three-dimensional characters. The more real your character seems, the more your audience will root for him. Your readers will be more involved in the story emotionally and live with him through his fears and joys. This makes for a much more rewarding reading experience.
This post will show you how to make your characters come alive. Also, because it’s easy to overlook when your figures lack depth, you can download a free goodie below the post to help you discover any problems with your characters and pretty much any other aspect of your story (it uses test questions).
(more…)
- POV: What it is and how it matters
Writing Tip: Finding the Balance of Narrative and Dialogue Writing Tip: Finding the Balance of Narrative and Dialogue
In the world of fiction writing, there are many things to explore. Subplots, conflict, POV , characters, you name it. But have you heard of narrative and dialogue? If you’ve got a story, you’ve got to narrate it. If you’ve got a set of characters, they have to converse, i.e., talk. Talking in fiction writing is known as dialogue, and narrating or describing anything is known as narrative.
Now where’s the problem in that?
Too much of a good thing is usually a bad thing, and it applies here. Some writers use narrative a lot. Their characters aren’t talkers. It’s just page after page of narrative, how they did this, their journey, their perils, the people they met, the surroundings, and so on. All description. At which point your story looks like an essay which no one wants to read, rather than an amazing novel.
- Compelling Opening Chapters Written — Then What?
- An Introduction to Academic Writing – Part II
- 100 Writing Mistakes to Avoid: A Review
Conflict is Necessary to Make it Spicy Conflict is Necessary to Make it Spicy
Get ready for some more writing advice. Today’s post is an important one — for me at least! — and I hope it will be interesting for you.
When you are writing a novel, what is the important thing to consider? Of course there are many important things. I wrote the wrong words. To correct it, I’ll write it again: What is ONE of the most important things to consider when you are writing a novel? (more…)
- Writing Tip: Finding the Balance of Narrative and Dialogue
Last updated 10th July 2024: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > The Cambridge Introduction to Creative Writing
- > Creative nonfiction

Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1 Introducing creative writing
- Chapter 2 Creative writing in the world
- Chapter 3 Challenges of creative writing
- Chapter 4 Composition and creative writing
- Chapter 5 Processes of creative writing
- Chapter 6 The practice of fiction
- Chapter 7 Creative nonfiction
- Chapter 8 Writing poetry
- Chapter 9 Performing writing
- Chapter 10 Writing in the community and academy
- Illustrative bibliography
Chapter 7 - Creative nonfiction
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2012
the permanent importance … lies in its being the meeting point of an impersonal art and a very personal life story … Obviously Nabokov's method would lose all sense unless the material were as true an account of personal experience as memory could possibly make it. The selective apparatus pertains to art; but the parts selected belong to unadulterated life.
A story grows from real and imagined experience. Creative nonfiction usually takes reality as its origin, but that does not mean we dispense with the mind's natural skill for story. Creative nonfiction deals with realities truthfully – experiences, events, facts – yet the drive of the writing is the author's involvement in the story, and writers use every literary device in the book to tell that story well. Carol Bly offers a precis in Beyond the Writers' Workshop : ‘All you have to do is be truthful, tell things in your personal voice, and have your modus operandi be revealing your own life circumstances through anecdote or narrative and revealing the meanings you attach to those circumstances, rather than arguing the point’ (2001: xvii). Readers are drawn in by this personal engagement, the author's literary style and passion for the telling. This chapter introduces some of the introductory elements of creative nonfiction, and some basic literary tools.
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- Creative nonfiction
- David Morley , University of Warwick
- Book: The Cambridge Introduction to Creative Writing
- Online publication: 05 June 2012
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511803024.008
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .

Writing Creatively to Make Sense of the Times We Live In
Journalist katrin schumann talks about why she writes fiction..
Updated July 12, 2024 | Reviewed by Davia Sills
- Studies show that the act of all kinds of writing hones our reflective abilities.
- Creative writing stretches our imagination, increases emotional resilience, and alleviates stress.
- Writers of nonfiction examine complex issues that are relevant to our times.
- Novelists examine the issues using characters as a vehicle for empathy.
Studies show that the act of writing hones our reflective abilities, stretches our imagination , increases emotional resilience , and alleviates stress . In my conversation with journalist-turned-novelist Katrin Schumann, we discuss how creative writing, in particular, is a worthy pursuit to understand the issues of our time. Schumann is the author of the nonfiction books Mothers Need Time Outs Too and The Secret Life of Middle Children, as well as the novels The Forgotten Hours and This Terrible Beauty .
You’re a trained journalist and the author of nonfiction books. Why, in the last few years, have you focused on writing fiction?
Writing nonfiction has been a way for me to examine complex issues that are relevant to our times, including psychological ones, but I’ve found that in recent years, I’ve been drawn to fiction because it allows me to get closer to the subject. In exploring thorny issues like loyalty and trust or co-dependency , I’m able to do more of a deep dive in fiction. The form allows me to sit with the complexities, to live in the gray areas with my characters.
I can’t always do this with nonfiction, where I’m approaching the topic from a specific angle, seeking solutions. In fiction, I have space to explore nuances that fascinate and confuse me and try to make sense of the inevitable contradictions. It’s messier and more delicate than nonfiction. For me, this feels more true to the human experience.
All writing involves deep reflection. Do you find the act of writing fiction to be a different kind of therapy?
Yes. Spending years creating characters and situations that grapple with serious, real-world problems lets me explore my own difficult experiences. For instance, I’d been wrestling with the aftermath of dealing with a narcissist when I started writing my first novel. By fictionalizing those challenges, I was able to find the courage to linger in the dark areas, examining them from all angles in order to find where the light might get in.
I discovered greater empathy and resilience in myself while also being able to acknowledge the trauma I’d been through. It’s using my imagination, combined with researching some very real and current psychological challenges, that ultimately feels most powerful to me and an effective way to reach readers.
How does fictionalizing the story give you more latitude or depth in exploring topics? You write about things like self-reliance and depression, and I’m wondering why not just write articles about it.
I write to figure out my own issues and to learn, but also to share. For me, fiction writing makes me work harder and go deeper. I’m trying to change people’s minds and hearts in subtler ways. I’m reflecting on experiences I’ve had, wrestling with what they mean, and how we can all learn from them and come out the better for it.
Yet, I don’t want to be prescriptive; I want people to draw their own conclusions. I research deeply about whatever topic I’m tackling.
To write my last novel, I studied the history of neuropsychology, dissecting studies on substance abuse . I conducted interviews. For all my books, I gather and study facts and figures, but with novels, I take that a step further. I put those facts and figures into play with my imagined characters to explore what happens. I imbue the impersonal with empathy and allow readers to try to figure out how they feel about how the characters contend with the issue. This approach leads me to meaningful personal discoveries while also taking the reader along on the emotional journey.
How do you decide whether to approach a topic in a nonfiction book or in a novel?
The more I’m personally involved with the topic, the more I want to explore it in fictional form. Ironically, for fiction, I feel like I should have an even better understanding of some of these psychological challenges than if I were covering them through straight nonfiction reportage. I first have to understand the topic and its history so my story is not only realistic but feels authentic.
I want readers to trust me, which means I have to be thorough. It’s my aim to take them on a ride that’s compelling as well as informative. And I love learning something new when I’m immersed in researching and writing fiction.
If writing fiction is about wrestling with your own demons, why not simply journal?

Journaling is, without question, a beneficial reflective activity. Yet what differentiates this kind of work from journaling about our problems or writing blog posts is that novelists are committing more time and energy to the deep dive on a specific topic. My last novel took almost three years to write, and during that time, I was reading everything I could get my hands on about the topic in order to distill it so that readers might find it relevant to their own lives.
At that stage, it’s not really about me anymore; it’s about the human condition. And in the end, that’s what readers relate to, I think. It’s what makes them call their friends and say, “I just finished this great book. You’ve got to read it.”
More about Katrin Schumann 's work

Lynne Griffin, R.N., M.Ed. , researches family life and is a novelist.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

COMMENTS
2) Top 10 Elements of Creative Writing. a) Imagery and descriptive language. b) Character development. c) Plot structure. d) Dialogue and conversations. e) Point of View (POV) f) Setting and world-building. g) Tone and Style. h) Conflict and resolution.
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
Literary techniques are specific aspects of literature used to deliver a message of any written work more effectively. The difference between literary elements and techniques is that these techniques are only found in written works. Also, stories can exist without them. Furthermore, think of literary techniques as clues to a deeper meaning.
Elements of Fiction: Definition. There are seven elements of fiction that can be found in any story, regardless of the form the narrative takes. These elements are character, plot, setting, theme, point of view, conflict, and tone. All seven elements work together to create a coherent story. When you're writing a story, these are the ...
How To Write Dialogue That Sounds Natural. Dialogue is a huge part of writing, and it can be difficult to make it sound natural. There are a few things to keep in mind: 1. Make sure your dialogue ...
Elements of Creative Writing. This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Creative writing is any writing that falls outside of technical, journalistic, or academic writing. It can be fiction or nonfiction, and it can use various techniques to tell stories and evoke emotions.
Creative writing is writing meant to evoke emotion in a reader by communicating a theme. In storytelling (including literature, movies, graphic novels, creative nonfiction, and many video games), the theme is the central meaning the work communicates. Take the movie (and the novel upon which it's based) Jaws, for instance.
Lesson 3: Elements of Fiction. What Is Fiction? Fiction is make-believe, invented stories. They may be short stories, fables, vignettes, plays, novellas, or novels. Although writers may base a character on people they have met in real life, the characters and the experiences that the character faces in the story are not real.
Elements of Creative Writing. There are many different forms of creative writing, and they all have their own features. However, many types of creative writing also share some common features. These include: 1. A strong plot or narrative arc. The plot, also known as the 'narrative arc', is the unique 'story' of your writing.
Literary elements are essential components that build a story, such as plot, narrator, point of view, and setting. Think of literary elements as answering the who, what, where, when, why, and how of a story. If the story lacks an answer to one of these questions, it's an incomplete story. There are endless variations within each element, and ...
Characters, setting, plot, conflict, point of view, and theme are six key elements for writing fiction. Characters. Characters are the people, animals, or aliens in the story. Readers come to know the characters through what they say, what they think, and how they act. E. M. Forster, an English novelist, identified that characters are either ...
Creative Writing Definition of genre Creative writing, a form of artistic expression, draws on the imagination to convey meaning through the use of imagery, narrative, and drama. This is in contrast to analytic or pragmatic forms of writing. This genre includes poetry, fiction (novels, short stories), scripts, screenplays, and creative non-fiction.
Contributors and Attributions. The main elements of creative nonfiction are setting, descriptive imagery, figurative language, plot, and character. The overarching element or requirement that distinguishes creative nonfiction from any other genre of writing is that while other literary genres can spring from the imagination, creative nonfiction ...
The Elements of Creative WritingYou Should Know Characterization. Development: Characters with a range of features including emotions, depth, and complexity can capture readers' attention and propel the story along.Character development is an important element of creative writing! Arcs and Growth: The development of characters throughout the narrative can create an interesting journey that ...
Characters, setting, plot, conflict, point of view, and theme are six key elements for writing fiction. Characters. Characters are the people, animals, or aliens in the story. Readers come to know the characters through what they say, what they think, and how they act. E. M. Forster, an English novelist, identified that characters are either ...
Creative nonfiction is a genre of writing that combines factual accounts found in nonfiction with literary techniques found in fiction and poetry. In other words, it's a true story with a touch of literary flair. Certain genres of nonfiction are often written as creative nonfiction, such as memoir, personal essays, literary journalism, and ...
Below are the fiction writing elements found in all the novels, novelettes, novellas and short stories: 1. Character. Every story has a main character. If you don't have any characters, you don't have any story. You might have the most exciting plot in the history of the universe, but if you don't have characters that make the reader care ...
Creative nonfiction deals with realities truthfully - experiences, events, facts - yet the drive of the writing is the author's involvement in the story, and writers use every literary device in the book to tell that story well. Carol Bly offers a precis in Beyond the Writers' Workshop: 'All you have to do is be truthful, tell things in ...
Creative writing, such as poems, short stories, or novels, focuses more on elements like imagery (A), which uses descriptive language to create vivid mental pictures for the reader. Setting (C) refers to the time and place where a story takes place and is an important element in creative writing. Figurative language (D) involves the use of ...
Find an answer to your question What is an element NOT found in creative writing? A. conflict B. plot C. works cited D. description
Creative writing stretches our imagination, increases emotional resilience, and alleviates stress. Writers of nonfiction examine complex issues that are relevant to our times.
Similarity Report and AI Writing guidance: Academic integrity tools: Creating PeerMark assignments guidance: Class and assignment management: Creating and managing QuickMarks, rubrics and grading PeerMark assignments guidance: Grading and feedback: User profile guidance for administrators and instructors: User profile settings
The main elements of creative nonfiction are setting, descriptive imagery, figurative language, plot, and character.The overarching element or requirement that distinguishes creative nonfiction from any other genre of writing is that while other literary genres can spring from the imagination, creative nonfiction is, by definition, true. As you complete the assigned readings in this chapter ...