- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

COVID‑19 Pandemic
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 11, 2024 | Original: April 25, 2023
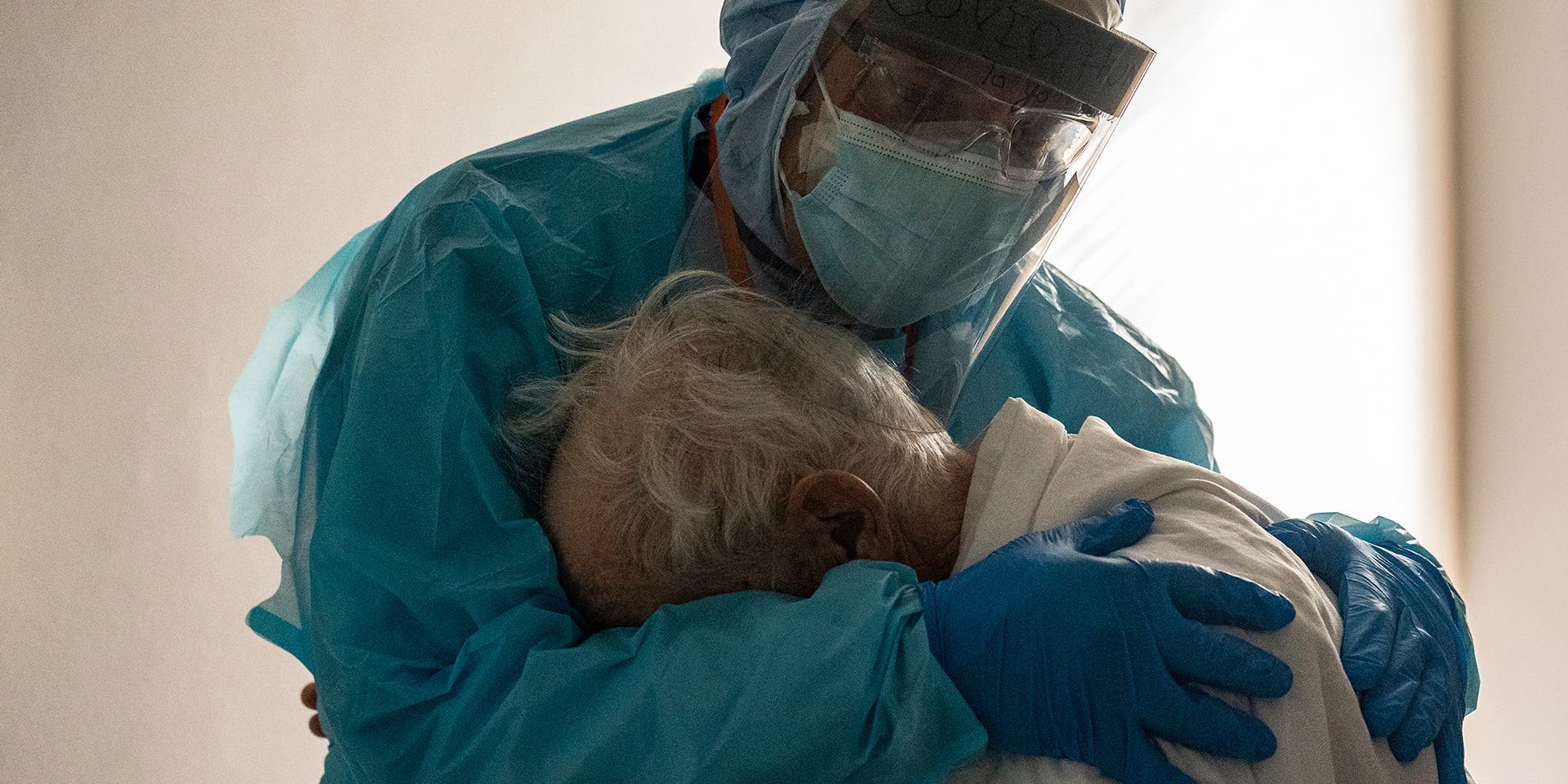
The outbreak of the infectious respiratory disease known as COVID-19 triggered one of the deadliest pandemics in modern history. COVID-19 claimed nearly 7 million lives worldwide. In the United States, deaths from COVID-19 exceeded 1.1 million, nearly twice the American death toll from the 1918 flu pandemic . The COVID-19 pandemic also took a heavy toll economically, politically and psychologically, revealing deep divisions in the way that Americans viewed the role of government in a public health crisis, particularly vaccine mandates. While the United States downgraded its “national emergency” status over the pandemic on May 11, 2023, the full effects of the COVID-19 pandemic will reverberate for decades.
A New Virus Breaks Out in Wuhan, China
In December 2019, the China office of the World Health Organization (WHO) received news of an isolated outbreak of a pneumonia-like virus in the city of Wuhan. The virus caused high fevers and shortness of breath, and the cases seemed connected to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, which was closed by an emergency order on January 1, 2020.
After testing samples of the unknown virus, the WHO identified it as a novel type of coronavirus similar to the deadly SARS virus that swept through Asia from 2002-2004. The WHO named this new strain SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2). The first Chinese victim of SARS-CoV-2 died on January 11, 2020.
Where, exactly, the novel virus originated has been hotly debated. There are two leading theories. One is that the virus jumped from animals to humans, possibly carried by infected animals sold at the Wuhan market in late 2019. A second theory claims the virus escaped from the Wuhan Institute of Virology, a research lab that was studying coronaviruses. U.S. intelligence agencies maintain that both origin stories are “plausible.”
The First COVID-19 Cases in America
The WHO hoped that the virus outbreak would be contained to Wuhan, but by mid-January 2020, infections were reported in Thailand, Japan and Korea, all from people who had traveled to China.
On January 18, 2020, a 35-year-old man checked into an urgent care center near Seattle, Washington. He had just returned from Wuhan and was experiencing a fever, nausea and vomiting. On January 21, he was identified as the first American infected with SARS-CoV-2.
In reality, dozens of Americans had contracted SARS-CoV-2 weeks earlier, but doctors didn’t think to test for a new type of virus. One of those unknowingly infected patients died on February 6, 2020, but her death wasn’t confirmed as the first American casualty until April 21.
On February 11, 2020, the WHO released a new name for the disease causing the deadly outbreak: Coronavirus Disease 2019 or COVID-19. By mid-March 2020, all 50 U.S. states had reported at least one positive case of COVID-19, and nearly all of the new infections were caused by “community spread,” not by people who contracted the disease while traveling abroad.
At the same time, COVID-19 had spread to 114 countries worldwide, killing more than 4,000 people and infecting hundreds of thousands more. On March 11, the WHO made it official and declared COVID-19 a pandemic.
The World Shuts Down

Pandemics are expected in a globally interconnected world, so emergency plans were in place. In the United States, health officials at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) set in motion a national response plan developed for flu pandemics.
State by state and city by city, government officials took emergency measures to encourage “ social distancing ,” one of the many new terms that became part of the COVID-19 vocabulary. Travel was restricted. Schools and churches were closed. With the exception of “essential workers,” all offices and businesses were shuttered. By early April 2020, more than 316 million Americans were under a shelter-in-place or stay-at-home order.
With more than 1,000 deaths and nearly 100,000 cases, it was clear by April 2020 that COVID-19 was highly contagious and virulent. What wasn’t clear, even to public health officials, was how individuals could best protect themselves from COVID-19. In the early weeks of the outbreak, the CDC discouraged people from buying face masks, because officials feared a shortage of masks for doctors and hospital workers.
By April 2020, the CDC revised its recommendations, encouraging people to wear masks in public, to socially distance and to wash hands frequently. President Donald Trump undercut the CDC recommendations by emphasizing that masking was voluntary and vowing not to wear a mask himself. This was just the beginning of the political divisions that hobbled the COVID-19 response in America.

When WWI, Pandemic and Slump Ended, Americans Sprang Into the Roaring Twenties
After enduring dark times, Americans were eager for a comeback.
Why the 1918 Flu Pandemic Never Really Ended
After infecting millions of people worldwide, the 1918 flu strain shifted—and then stuck around.
When Mask‑Wearing Rules in the 1918 Pandemic Faced Resistance
Most people complied, but some resisted (or poked holes in their masks to smoke).
Global Financial Markets Collapse
In the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, with billions of people worldwide out of work, stuck at home, and fretting over shortages of essential items like toilet paper , global financial markets went into a tailspin.
In the United States, share prices on the New York Stock Exchange plummeted so quickly that the exchange had to shut down trading three separate times. The Dow Jones Industrial Average eventually lost 37 percent of its value, and the S&P 500 was down 34 percent.
Business closures and stay-at-home orders gutted the U.S. economy. The unemployment rate skyrocketed, particularly in the service sector (restaurant and other retail workers). By May 2020, the U.S. unemployment rate reached 14.7 percent, the highest jobless rate since the Great Depression .
All across America, households felt the pinch of lost jobs and lower wages. Food insecurity reached a peak by December 2020 with 30 million American adults—a full 14 percent—reporting that their families didn’t get enough to eat in the past week.
The economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, like its health effects, weren’t experienced equally. Black, Hispanic and Native Americans suffered from unemployment and food insecurity at significantly higher rates than white Americans.
Congress tried to avoid a complete economic collapse by authorizing a series of COVID-19 relief packages in 2020 and 2021, which included direct stimulus checks for all American families.
The Race for a Vaccine
A new vaccine typically takes 10 to 15 years to develop and test, but the world couldn’t wait that long for a COVID-19 vaccine. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under the Trump administration launched “ Operation Warp Speed ,” a public-private partnership which provided billions of dollars in upfront funding to pharmaceutical companies to rapidly develop vaccines and conduct clinical trials.
The first clinical trial for a COVID-19 vaccine was announced on March 16, 2020, only days after the WHO officially classified COVID-19 as a pandemic. The vaccines developed by Moderna and Pfizer were the first ever to employ messenger RNA, a breakthrough technology. After large-scale clinical trials, both vaccines were found to be greater than 95 percent effective against infection with COVID-19.
A nurse from New York officially became the first American to receive a COVID-19 vaccine on December 14, 2020. Ten days later, more than 1 million vaccines had been administered, starting with healthcare workers and elderly residents of nursing homes. As the months rolled on, vaccine availability was expanded to all American adults, and then to teenagers and all school-age children.
By the end of the pandemic in early 2023, more than 670 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines had been administered in the United States at a rate of 203 doses per 100 people. Approximately 80 percent of the U.S. population received at least one COVID-19 shot, but vaccination rates were markedly lower among Black, Hispanic and Native Americans.
The First ‘Vaccine Passports’ Were Scars from Smallpox Vaccinations
When smallpox ravaged the United States at the turn of the 20th century, many public spaces required people to show their vaccine scars for entry.
When the Supreme Court Ruled a Vaccine Could Be Mandatory
A 1905 decision provided a powerful and controversial precedent for the flexing of government authority.
4 Diseases You’ve Probably Forgotten About Because of Vaccines
Vaccines are so effective at fighting disease that sometimes it’s easy to forget their impact.
COVID-19 Deaths Heaviest Among Elderly and People of Color
In America, the COVID-19 pandemic impacted everyone’s lives, but those who died from the disease were far more likely to be older and people of color.
Of the more than 1.1 million COVID deaths in the United States, 75 percent were individuals who were 65 or older. A full 93 percent of American COVID-19 victims were 50 or older. Throughout the emergence of COVID-19 variants and the vaccine rollouts, older Americans remained the most at-risk for being hospitalized and ultimately dying from the disease.
Black, Hispanic and Native Americans were also at a statistically higher risk of developing life-threatening COVID-19 systems and succumbing to the disease. For example, Black and Hispanic Americans were twice as likely to be hospitalized from COVID-19 than white Americans. The COVID-19 pandemic shined light on the health disparities between racial and ethnic groups driven by systemic racism and lower access to healthcare.
Mental health also worsened during the COVID-19 pandemic. The anxiety of contracting the disease, and the stresses of being unemployed or confined at home, led to unprecedented numbers of Americans reporting feelings of depression and suicidal ideation.
A Time of Social & Political Upheaval
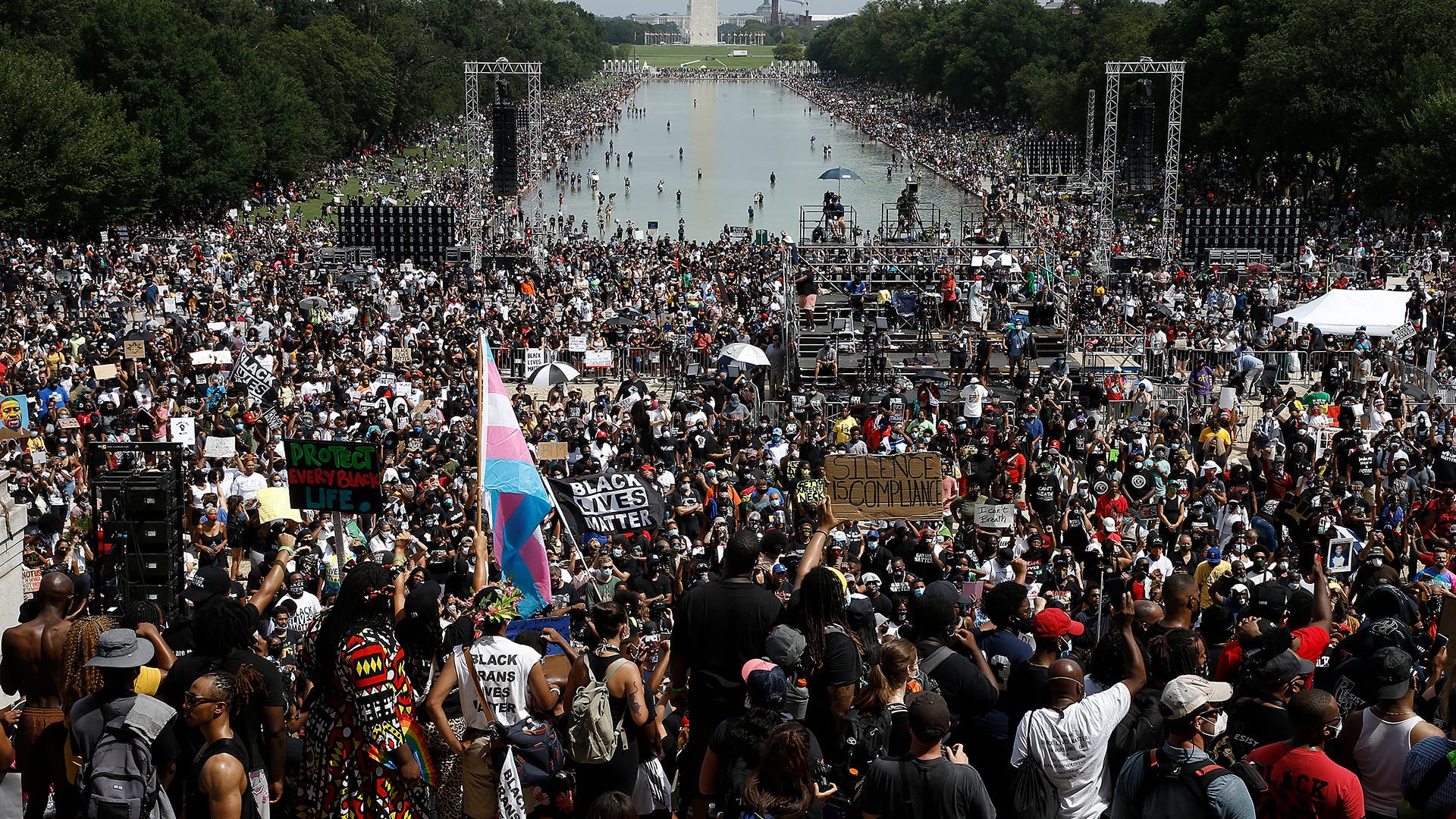

In the United States, the three long years of the COVID-19 pandemic paralleled a time of heightened political contention and social upheaval.
When George Floyd was killed by Minneapolis police on May 25, 2020, it sparked nationwide protests against police brutality and energized the Black Lives Matter movement. Because so many Americans were out of work or home from school due to COVID-19 shutdowns, unprecedented numbers of people from all walks of life took to the streets to demand reforms.
Instead of banding together to slow the spread of the disease, Americans became sharply divided along political lines in their opinions of masking requirements, vaccines and social distancing.
By March 2024, in signs that the pandemic was waning, the CDC issued new guidelines for people who were recovering from COVID-19. The agency said those infected with the virus no longer needed to remain isolated for five days after symptoms. And on March 10, 2024, the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center stopped collecting data for its highly referenced COVID-19 dashboard.
Still, an estimated 17 percent of U.S. adults reported having experienced symptoms of long COVID, according to the Household Pulse Survey. The medical community is still working to understand the causes behind long COVID, which can afflict a patient for weeks, months or even years.

HISTORY Vault
Stream thousands of hours of acclaimed series, probing documentaries and captivating specials commercial-free in HISTORY Vault
“CDC Museum COVID Timeline.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . “Coronavirus: Timeline.” U.S. Department of Defense . “COVID-19 and Related Vaccine Development and Research.” Mayo Clinic . “COVID-19 Cases and Deaths by Race/Ethnicity: Current Data and Changes Over Time.” Kaiser Family Foundation . “Number of COVID-19 Deaths in the U.S. by Age.” Statista . “The Pandemic Deepened Fault Lines in American Society.” Scientific American . “Tracking the COVID-19 Economy’s Effects on Food, Housing, and Employment Hardships.” Center on Budget and Policy Priorities . “U.S. Confirmed Country’s First Case of COVID-19 3 Years Ago.” CNN .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately
Due to the downward trend in respiratory viruses in Maryland, masking is no longer required but remains strongly recommended in Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. Read more .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines
What Is Coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a type of virus. There are many different kinds, and some cause disease. A coronavirus identified in 2019, SARS-CoV-2, has caused a pandemic of respiratory illness, called COVID-19.
What You Need to Know COVID-19
- COVID-19 is the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that emerged in December 2019.
- COVID-19 can be severe, and has caused millions of deaths around the world as well as lasting health problems in some who have survived the illness.
- The coronavirus can be spread from person to person. It is diagnosed with a test.
- The best way to protect yourself is to get vaccinated and boosted when you are eligible, follow testing guidelines, wear a mask, wash your hands and practice physical distancing.
How does the coronavirus spread?
As of now, researchers know that the coronavirus is spread through droplets and virus particles released into the air when an infected person breathes, talks, laughs, sings, coughs or sneezes. Larger droplets may fall to the ground in a few seconds, but tiny infectious particles can linger in the air and accumulate in indoor places, especially where many people are gathered and there is poor ventilation. This is why mask-wearing, hand hygiene and physical distancing are essential to preventing COVID-19.

How did the coronavirus start?
The first case of COVID-19 was reported Dec. 1, 2019, and the cause was a then-new coronavirus later named SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 may have originated in an animal and changed (mutated) so it could cause illness in humans. In the past, several infectious disease outbreaks have been traced to viruses originating in birds, pigs, bats and other animals that mutated to become dangerous to humans. Research continues, and more study may reveal how and why the coronavirus evolved to cause pandemic disease.
What is the incubation period for COVID-19?
Symptoms show up in people within two to 14 days of exposure to the virus. A person infected with the coronavirus is contagious to others for up to two days before symptoms appear, and they remain contagious to others for 10 to 20 days, depending upon their immune system and the severity of their illness.
What have you learned about coronavirus in the last six months?

Infectious disease expert Lisa Maragakis explains the advances in COVID-19 treatments and how knowledge of COVID-19 can assist in preventing further spread of the virus.
What are symptoms of coronavirus?
COVID-19 symptoms include:
- Fever or chills
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Muscle or body aches
- Sore throat
- New loss of taste or smell
- New fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Congestion or runny nose
Some people infected with the coronavirus have mild COVID-19 illness, and others have no symptoms at all. In some cases, however, COVID-19 can lead to respiratory failure, lasting lung and heart muscle damage , nervous system problems , kidney failure or death.
If you have a fever or any of the symptoms listed above, call your doctor or a health care provider and explain your symptoms over the phone before going to the doctor’s office, urgent care facility or emergency room. Here are suggestions if you feel sick and are concerned you might have COVID-19 .
CALL 911 if you have a medical emergency such as severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Learn more about COVID-19 symptoms .
How is COVID-19 diagnosed?
COVID-19 is diagnosed through a test. Diagnosis by examination alone is difficult since many COVID-19 signs and symptoms can be caused by other illnesses. Some people with the coronavirus do not have symptoms at all. Learn more about COVID-19 testing .
How is COVID-19 treated?
Treatment for COVID-19 depends on the severity of the infection. For milder illness, resting at home and taking medicine to reduce fever is often sufficient. More severe cases may require hospitalization, with treatment that might include intravenous medications, supplemental oxygen, assisted ventilation and other supportive measures
How do you protect yourself from this?
There are several COVID-19 vaccines recommended by the CDC . It is also important to receive a booster when you are eligible .
In addition, it helps to keep up with other safety precautions, such as following testing guidelines, wearing a mask, washing your hands and practicing physical distancing.
Does COVID-19 cause death?
Yes, severe COVID-19 can be fatal. For updates of coronavirus infections, deaths and vaccinations worldwide, see the Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases map developed by the Johns Hopkins Center for Systems Science and Engineering.
Two COVID-19 vaccines – Pfizer and Moderna - have been fully approved by the FDA and recommended by the CDC as highly effective in preventing serious disease, hospitalization and death from COVID-19.
The CDC notes that in most situations the two mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna are preferred over the Johnson & Johnson vaccine due to a risk of serious adverse events .
It is also important to receive a booster when eligible. You can get any of these three authorized or approved vaccines, but the CDC explains that Pfizer and Moderna are preferred in most situations.
Why is it called coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are named for their appearance: “corona” means “crown.” The virus’s outer layers are covered with spike proteins that surround them like a crown.
Is this coronavirus different from SARS?
SARS stands for severe acute respiratory syndrome. In 2003, an outbreak of SARS affected people in several countries before ending in 2004. The coronavirus that causes COVID-19 is similar to the one that caused the 2003 SARS outbreak.
Since the 2019 coronavirus is related to the original coronavirus that caused SARS and can also cause severe acute respiratory syndrome, there is “SARS” in its name: SARS-CoV-2. Much is still unknown about these viruses, but SARS-CoV-2 spreads faster and farther than the 2003 SARS-CoV-1 virus. This is likely because of how easily it is transmitted person to person, even from asymptomatic carriers of the virus.
Are there different variants of this coronavirus?
Yes, there are different variants of this coronavirus. Like other viruses, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 can change (mutate). Mutations may enable the coronavirus to spread faster from person to person as in the case of the delta and omicron variants. More infections can result in more people getting very sick and also create more opportunity for the virus to develop further mutations. Read more about coronavirus variants .
Coronavirus: What do I do if I Feel Sick?

If you are concerned that you may have COVID-19, follow these steps to help protect your health and the health of others.
About Coronaviruses
- Coronaviruses are common in different animals. Rarely, an animal coronavirus can infect humans.
- There are many different kinds of coronaviruses. Some of them can cause colds or other mild respiratory (nose, throat, lung) illnesses.
- Other coronaviruses can cause serious diseases, including severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
Coronavirus (COVID-19)

What you need to know from Johns Hopkins Medicine.

Trauma Team Puts an Athlete Back in the Saddle

Patient Safety Infographic

Comparación entre la COVID-19 y la gripe
Related Topics
- Infectious Diseases
I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .
More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- Heman Bekele Is TIME’s 2024 Kid of the Year
- The Reintroduction of Kamala Harris
- A Battle Over Fertility Law in China
- For the Love of Savoring Sandwiches : Column
- The 1 Heart-Health Habit You Should Start When You’re Young
- Cuddling Might Help You Get Better Sleep
- The 50 Best Romance Novels to Read Right Now
Contact us at [email protected]

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
Horrific history
The early days, health and medicine.

What was the impact of COVID-19?
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Table Of Contents

On February 25, 2020, a top official at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention decided it was time to level with the U.S. public about the COVID-19 outbreak. At the time, there were just 57 people in the country confirmed to have the infection, all but 14 having been repatriated from Hubei province in China and the Diamond Princess cruise ship , docked off Yokohama , Japan .
The infected were in quarantine. But Nancy Messonnier, then head of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, knew what was coming. “It’s not so much a question of if this will happen anymore but rather more a question of exactly when this will happen and how many people in this country will have severe illness,” Messonnier said at a news briefing.
“I understand this whole situation may seem overwhelming and that disruption to everyday life may be severe,” she continued. “But these are things that people need to start thinking about now.”
Looking back, the COVID-19 pandemic stands as arguably the most disruptive event of the 21st century, surpassing wars, the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks , the effects of climate change , and the Great Recession . It has killed more than seven million people to date and reshaped the world economy, public health , education, work, social interaction, family life, medicine, and mental health—leaving no corner of the globe untouched in some way. Now endemic in many societies, the consistently mutating virus remains one of the leading annual causes of death, especially among people older than 65 and the immunosuppressed.
“The coronavirus outbreak, historically, beyond a doubt, has been the most devastating pandemic of an infectious disease that global society has experienced in well over 100 years, since the 1918 influenza pandemic ,” Anthony Fauci , who helped lead the U.S. government’s health response to the pandemic under Pres. Donald Trump and became Pres. Joe Biden ’s chief medical adviser, told Encyclopædia Britannica in 2024.
“I think the impact of this outbreak on the world in general, on the United States, is really historic. Fifty years from now, 100 years from now, when they talk about the history of what we’ve been through, this is going to go down equally with the 1918 influenza pandemic , with the stock market crash of 1929 , with World War II —all the things that were profoundly disruptive of the social order.”
What few could imagine in the first days of the pandemic was the extent of the disruption the disease would bring to the everyday lives of just about everyone around the globe.
Within weeks, schools and child-care centers began shuttering, businesses sent their workforces home, public gatherings were canceled, stores and restaurants closed, and cruise ships were barred from sailing. On March 11, actor Tom Hanks announced that he had COVID-19, and the NBA suspended its season. (It was ultimately completed in a closed “bubble” at Walt Disney World .) On March 12, as college basketball players left courts mid-game during conference tournaments, the NCAA announced that it would not hold its wildly popular season-ending national competition, known as March Madness , for the first time since 1939. Three days later, the New York City public school system, the country’s largest, with 1.1 million students, closed. On March 19, all 40 million Californians were placed under a stay-at-home order.

By mid-April, with hospital beds and ventilators in critically short supply, workers were burying the coffins of COVID-19 victims in mass graves on Hart Island, off the Bronx . At first, the public embraced caregivers. New Yorkers applauded them from windows and balconies, and individuals sewed masks for them. But that spirit soon gave way to the crushing long-term reality of the pandemic and the national division that followed.
Around the world, it was worse. On the day Messonnier spoke, the virus had spread from its origin point in Wuhan , China, to at least two dozen countries, sickening thousands and killing dozens. By April 4, more than one million cases had been confirmed worldwide. Some countries, including China and Italy, imposed strict lockdowns on their citizens. Paris restricted movement, with certain exceptions, including an hour a day for exercise, within 1 km (0.62 mile) of home.
In the United States , the threat posed by the virus did not keep large crowds from gathering to protest the May 25 slaying of George Floyd , a 46-year-old Black man, by a white police officer, Derek Chauvin. The murder, taped by a bystander in Minneapolis , Minnesota , sparked raucous and sometimes violent street protests for racial justice around the world that contributed to an overall sense of societal instability.
The official World Health Organization total of more than seven million deaths as of March 2024 is widely considered a serious undercount of the actual toll. In some countries there was limited testing for the virus and difficulty attributing fatalities to it. Others suppressed total counts or were not able to devote resources to compiling their totals. In May 2021, a panel of experts consulted by The New York Times estimated that India ’s actual COVID-19 death toll was likely 1.6 million, more than five times the reported total of 307,231.
An average of 3,100 people—one every 28 seconds—died of COVID-19 every day in the United States in January 2021.
When “ excess mortality”—COVID and non-COVID deaths that likely would not have occurred under normal, pre-outbreak conditions—are included in the worldwide tally, the number of pandemic victims was about 15 million by the end of 2021, WHO estimated.
Not long after the pandemic took hold, the United States, which spends more per capita on medical care than any other country, became the epicenter of COVID-19 fatalities. The country fell victim to a fractured health care system that is inequitable to poor and rural patients and people of color, as well as a deep ideological divide over its political leadership and public health policies, such as wearing protective face masks. By early 2024, the U.S. had recorded nearly 1.2 million COVID-19 deaths.
Life expectancy at birth plunged from 78.8 years in 2019 to 76.4 in 2021, a staggering decline in a barometer of a country’s health that typically changes by only a tenth or two annually. An average of 3,100 people—one every 28 seconds—died of COVID-19 every day in the United States in January 2021, before vaccines for the virus became widely available, The Washington Post reported.
The impact on those caring for the sick and dying was profound. “The second week of December [2020] was probably the worst week of my career,” said Brad Butcher, director of the medical-surgical intensive care unit at UPMC Mercy hospital in Pittsburgh , Pennsylvania. “The first day I was on service, five patients died in a shift. And then I came back the next day, and three patients died. And I came back the next day, and three more patients died. And it was completely defeating,” he told The Washington Post on January 11, 2021.
“We can’t get the graves dug fast enough,” a Maryland funeral home operator told The Washington Post that same day.
As the pandemic surged in waves around the world, country after country was plunged into economic recession , the inevitable damage caused by layoffs, business closures, lockdowns, deaths, reduced trade, debt repayment moratoriums , the cost to governments of responding to the crisis, and other factors. Overall, the virus triggered the greatest economic calamity in more than a century, according to a 2022 report by the World Bank .
“Economic activity contracted in 2020 in about 90 percent of countries, exceeding the number of countries seeing such declines during two world wars, the Great Depression of the 1930s, the emerging economy debt crises of the 1980s, and the 2007–09 global financial crisis,” the report noted. “In 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the global economy shrank by approximately 3 percent, and global poverty increased for the first time in a generation.”
A 2020 study that attempted to aggregate the costs of lost gross domestic product (GDP) estimated that premature deaths and health-related losses in the United States totaled more than $16 trillion, or roughly “90% of the annual GDP of the United States. For a family of 4, the estimated loss would be nearly $200,000.”
In April 2020, the U.S. unemployment rate stood at 14.7 percent, higher than at any point since the Great Depression. There were 23.1 million people out of work. The hospitality, leisure, and health care industries were especially hard hit. Consumer spending, which accounts for about two-thirds of the U.S. economy, plunged.
With workers at home, many businesses turned to telework, a development that would persist beyond the pandemic and radically change working conditions for millions. In 2023, 12.7 percent of full-time U.S. employees worked from home and 28.2 percent worked a hybrid office-home schedule, according to Forbes Advisor . Urban centers accustomed to large daily influxes of workers have suffered. Office vacancies are up, and small businesses have closed. The national office vacancy rate rose to a record 19.6 percent in the fourth quarter of 2023, according to Moody’s Analytics , which has been tracking the statistic since 1979.
Many hospitals were overwhelmed during COVID-19 surges, with too few beds for the flood of patients. But many also demonstrated their resilience and “surge capacity,” dramatically expanding bed counts in very short periods of time and finding other ways to treat patients in swamped medical centers. Triage units and COVID-19 wards were hastily erected in temporary structures on hospital grounds.
Still, U.S. hospitals suffered severe shortages of nurses and found themselves lacking basic necessities such as N95 masks and personal protective garb for the doctors, nurses, and other workers who risked their lives against the new pathogen at the start of the outbreak. Mortuaries and first responders were overwhelmed as well. The dead were kept in refrigerated trucks outside hospitals.
The country’s fragmented public health system proved inadequate to the task of coping with the outbreak, sparking calls for major reform of the CDC and other agencies. The CDC botched its initial attempt to create tests for the virus, leaving the United States almost blind to its spread during the early stages of the pandemic.
Beyond the physical dangers, mental health became a serious issue for overburdened health care personnel, other “essential” workers who continued to labor in crucial jobs, and many millions of isolated, stressed, fearful, locked-down people in the United States and elsewhere. Parents struggled to care for children kept at home by the pandemic while also attending to their jobs.
In a June 2020 survey, the CDC found that 41 percent of respondents said they were struggling with mental health and 11 percent had seriously considered suicide recently. Essential workers, unpaid caregivers , young adults, and members of racial and ethnic minority groups were found to be at a higher risk for experiencing mental health struggles, with 31 percent of unpaid caregivers reporting that they were considering suicide. WHO reported two years later that the pandemic had caused a 25 percent increase in anxiety and depression worldwide, young people and women being at the highest risk.
The rate of homicides by firearm in the United States rose by 35 percent during the pandemic to the highest rate in more than a quarter century.
A silver lining in the chaos of the pandemic’s opening year was the development in just 11 months of highly effective vaccines for the virus, a process that normally had taken 7–10 years. The U.S. government’s bet on unproven messenger RNA technology under the Trump administration’s Operation Warp Speed paid off, and the result validated the billions of dollars that the government pours into basic research every year.
On December 14, 2020, New York nurse Sandra Lindsay capped the tumultuous year by receiving the first shot of the vaccine that eventually would help end the public health crisis caused by COVID-19 pandemic.
Advertisement
Supported by
W.H.O. Declares Global Emergency Over New Mpox Outbreak
The epidemic is concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo, but the virus has now appeared in a dozen other African countries.
- Share full article

By Apoorva Mandavilli
The rapid spread of mpox, formerly called monkeypox, in African countries constitutes a global health emergency, the World Health Organization declared on Wednesday.
This is the second time in three years that the W.H.O. has designated an mpox epidemic as a global emergency. It previously did so in July 2022. That outbreak went on to affect nearly 100,000 people , primarily gay and bisexual men, in 116 countries, and killed about 200 people.
The threat this time is deadlier. Since the beginning of this year, the Democratic Republic of Congo alone has reported 15,600 mpox cases and 537 deaths. Those most at risk include women and children under 15.
“The detection and rapid spread of a new clade of mpox in eastern D.R.C., its detection in neighboring countries that had not previously reported mpox, and the potential for further spread within Africa and beyond is very worrying,” said Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the W.H.O.’s director general.
The outbreak has spread through 13 countries in Africa, including a few that had never reported mpox cases before. On Tuesday, the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention declared a “public health emergency of continental security,” the first time the organization has taken that step since the African Union granted it the power to do so last year.
“It’s in the interests of the countries, of the continent and of the world to get our arms around this and stop transmission as soon as we can,” said Dr. Nicole Lurie, the executive director for preparedness and response at the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, a nonprofit that finances vaccine development.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. [7] Most scientists believe the SARS-CoV-2 virus entered into human populations through natural zoonosis, similar to the SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV outbreaks, and consistent with other pandemics in human history.
COVID-19 is the deadliest pandemic in US history; [359] it was the third-leading cause of death in the US in 2020, behind heart disease and cancer. [360] From 2019 to 2020, US life expectancy dropped by 3 years for Hispanic Americans, 2.9 years for African Americans, and 1.2 years for white Americans. [361]
How COVID‑19 vaccines work. The video shows the process of vaccination, from injection with RNA or viral vector vaccines, to uptake and translation, and on to immune system stimulation and effect. Part of a series on the COVID-19 pandemic Scientifically accurate atomic model of the external structure of SARS-CoV-2. Each "ball" is an atom. COVID-19 (disease) SARS-CoV-2 (virus) Cases Deaths ...
The name "coronavirus" is derived from Latin corona, meaning "crown" or "wreath", itself a borrowing from Greek κορώνη korṓnē, "garland, wreath". [8] [9] The name was coined by June Almeida and David Tyrrell who first observed and studied human coronaviruses. [10]The word was first used in print in 1968 by an informal group of virologists in the journal Nature to designate the new ...
SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh known coronavirus to infect people, after 229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1, MERS-CoV, and the original SARS-CoV. [105] Like the SARS-related coronavirus implicated in the 2003 SARS outbreak, SARS‑CoV‑2 is a member of the subgenus Sarbecovirus (beta-CoV lineage B). [106] [107] Coronaviruses undergo frequent recombination. [108]
The COVID-19 pandemic, also called the coronavirus pandemic, was a world-wide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). It is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). [1] [7] [b]The disease was first found in Wuhan, Hubei, China, in December 2019.On 31 December, Chinese health authorities told the World Health Organization (WHO) about a group of viral ...
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention.
The default answer for most scientists has been that the virus, SARS-CoV-2, probably made the jump to humans from bats, if it was a direct spillover — or, more likely, through one or more intermediate mammals. MCKEEVER A (6 April 2021). "We still don't know the origins of the coronavirus. Here are 4 scenarios".
COVID-19 is a disease caused by a virus. The most common symptoms are fever, chills, and sore throat, but there are a range of others. Most people make a full recovery without needing hospital treatment. People with severe symptoms should seek medical care as soon as possible. Over 760 million cases and 6.9 million deaths have been recorded ...
Key Events in the Effort to Determine the Origins of the Covid-19 Pandemic. The joint WHO-China technical report published in March 2021 rated a zoonotic spillover as a "likely to very likely ...
Abstract. The novel coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) outbreak that emerged at the end of 2019 has now swept the world for more than 2 years, causing immeasurable damage to the lives and economies of the world. It has drawn so much attention to discovering how the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) originated and ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a considerable impact on female education. Female education relates to the unequal social norms and the specific forms of discrimination that girls face. In 2018, 130 million girls worldwide were out of school, and only two out of three girls were enrolled in secondary education.
In America, the COVID-19 pandemic impacted everyone's lives, but those who died from the disease were far more likely to be older and people of color. Of the more than 1.1 million COVID deaths ...
The COVID-19 pandemic swept the world in the early months of 2020, causing massive economic and social disruption. ... Italian physicist and award-winning author of the Premio Strega, published his thoughts about the virus outbreak in an essay entitled How Contagion Works in March 2020. It was quickly translated into more than 20 languages.
What You Need to Know COVID-19. COVID-19 is the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that emerged in December 2019. COVID-19 can be severe, and has caused millions of deaths around the world as well as lasting health problems in some who have survived the illness. The coronavirus can be spread from person to person.
The Origin of COVID-19 and Why It Matters. The COVID-19 pandemic is among the deadliest infectious diseases to have emerged in recent history. As with all past pandemics, the specific mechanism of its emergence in humans remains unknown. Nevertheless, a large body of virologic, epidemiologic, veterinary, and ecologic data establishes that the ...
Abstract. The SARS-CoV-2 virus of the COVID-19 pandemic, that is presently devastating the entire world, had been active well before January of this year, when its pathogenic potential exploded full force in Wuhan. It had caused the onset of small disease outbreaks in China, and probably elsewhere as well, which failed to reach epidemic potential.
Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. "The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry ...
Abstract. The coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a highly transmittable and pathogenic viral infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which emerged in Wuhan, China and spread around the world. Genomic analysis revealed that SARS-CoV-2 is phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome ...
With these new freely-licensed resources, Wikipedia's more than 250,000 volunteer editors can also build on and expand the site's COVID-19 coverage, which currently offers more than 5,200 coronavirus-related articles in 175 languages. This WHO content will also be translated across national and regional languages through Wikipedia's vast ...
Horrific history. Looking back, the COVID-19 pandemic stands as arguably the most disruptive event of the 21st century, surpassing wars, the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, the effects of climate change, and the Great Recession. It has killed more than seven million people to date and reshaped the world economy, public health, education ...
Chester city centre during the first lockdown in April 2020 New COVID-19 cases and deaths in the UK, with the dates of lockdown and its partial lifting. This shows both the COVID-19 death figures confirmed by tests and the figures registered by three authorities. The initial announcement was made by Boris Johnson, with agreement from the other three heads of government.
From January to March 2020, US President Donald Trump repeatedly described the virus as the "Chinese virus". [14] In March 2020, the president claimed to have abandoned the term, telling Fox News "we shouldn't make any more of a big deal out of it". [15] On March 18 and 19, 2020, Trump twice defended using the term "Chinese virus" amid instances of bigotry against Asians in the United States. [16]
করোনাভাইরাস বলতে এআরএনএ ভাইরাসের একটি শ্রেণিকে বোঝায় যেগুলি ...
The outbreak that year stayed mostly within tight sexual networks, among gay and bisexual men. A combination of behavioral changes and vaccination tamped down the spread.. In the United States ...