

Business Plans

In this post
Business plans are used to outline the industry in which a business is working in as well as the economic structure of a company to give an idea of the financial prospects of a business. They are used primarily to organise the routes to market that a company will take and give projections on earnings and target dates for when the company expects to have a certain income.
Writing a strong business plan is important for any business, whether large or small, and is the perfect way to map out your route to success. Not only will the plan contain your aims and plans to attract new customers but it can also act as a strong tool for financial projections and help you to set out goals for your company. Throughout the units that we have already covered on this course we have seen a lot of aspects that could be included in a business plan, and including as much information as possible is key.
A lot of entrepreneurs fail to produce a clear business plan when they set up a new company and this can be a big issue further down the line. By not outlining your company and its operations you may affect the business in a negative way and be unable to keep track on the progress and route the business is taking. If you are seeking finance to launch your company it is more than likely that you will need to create a business plan to secure a loan, but this should not be thrown away once you have started the business. Your plan can be updated and adapted at any time and you must try to keep things relevant and up to date so you know the long-term aims of your company.
Why create a business plan?
Some entrepreneurs fail to create a business plan before starting a company because they feel it is a waste of time. They know what they want to do, how they want to do it and everything that is needed has been formulated in their heads. This is a very good skill to have, but without your thoughts and projections down on paper it can be very easy for them to become misinterpreted, forgotten or skewed. Simply having things thought out in your mind is not enough to convince others or explain your strategies to those you are working with. Business plans are used to organise your approach and produce a strategy that allows you the best possible chance of success. They should include:
- Information about your company so that you can plan the structure and objectives which you have
- Your relationships with others and how these can be used (e.g. banks, lenders and accountants)
- To find weaknesses in your plans and areas where you must improve
- Areas for discussion so that you can find out other people’s opinions and include them in the planning process
Some people start a business and want everything to be done immediately. With great confidence that they can do it all alone and have no input from experts, they may not stop and think about forming a clear plan that includes facts and figures to help them along the way. Doing this can be of massive detriment to any business and you need to gather as many opinions, facts and ideas as possible from those around you.
What to avoid
A business plan should include lots of information but there are a few things that should be avoided. You should put some restrictions on the long-term (over 1 year) predictions of your finances. A long-range prediction on the amount of money you will have coming into the business can be completely meaningless because it is very hard to predict how a business will perform far into the future.
Very few business plans get the figures projected spot on, so remember to give a good indication of what you expect to earn but try to be conservative with this. By exaggerating the earning potential of the company you will not be impressing anyone and this will make it difficult for you to plan your spending. Outline clear time frames and indicate your aims during these periods. Try to show what you will be working on at any time, for example if your business will take quite a lot of setting up then the first 6 months may be devoted solely to this and you should outline this in your plans and projections. Try to correctly anticipate the money and time that will be required for processes to be completed and always factor in a margin of error. By slightly exaggerating the money that will be required when completing a stage of expansion or setting more time than is needed, you will be well prepared if some unforeseen issue crops up.
Don’t just use the business plan to explain how great your product or service is. This alone will not turn your business into a big success (although it is very important). Identifying areas to improve and how you will market your company is much more important than simply relying on the uniqueness of your product.

The purpose of a business plan
Business plans are used for a variety of different reasons and the importance of these should not be underestimated. Creating a plan that is precise and includes information that is relevant to the new or existing business will ensure that ideas are implemented quickly. Without a solid business plan it will be much more difficult to judge the success of the new venture and the direction of the company will be hard for everyone to see.
Minimising risk
The risks when starting a new business can be huge. Money is invested into new businesses and time will also be spent on getting a company off the ground. Without a business plan in place, owners and employees could end up wasting their time in certain areas. Using resources inefficiently and having no clear direction for a business can lead to disaster very quickly. The best way to avoid this is with a clear outline of what the business needs to work on and what resources will be needed in order to make the venture work. A business plan will be used to set goals and objectives while losing no time in areas that do not see a large enough return on the investment.
Securing finance
Many people use business plans to secure finance for a new venture. This finance can come from several different sources such as banks, investors and start-up funds. Having a business plan that shows exactly how the business will operate and where money will be made will act as a way to convince potential investors to finance the company. With clear profits to be made and a route to market mapped clearly, investing in a business will be a much more desirable prospect for a potential investor.
Formats of business plans
There are many different formats which a business plan can be created in but the main areas to cover are:
Executive summary
Company summary, products and services, market analysis, strategy and implementation, management and personnel, financial plan.
Any business plan should include an executive summary which gives an outline of the business and the vision of the owners. Here you should briefly explain the business and its activities as well as the key areas that will help the company to succeed. A mission statement can be included to explain why your company will be unique in the market and what will give you the edge over your competitors.
You should also include some information about the financial aspirations of the company here to show the economic aims over the first few years in operation. Remember, these do not need to be hugely accurate and taking a realistic look at what can be earned is essential. It is usually best to complete the executive summary of the company last as you can include information from other sections in this part of the plan to give a good overview and concise insight into the business and your plans.
The company summary will explain key aspects of the operation of the company. This includes the owners of the business as well as where the business is located. Information about all directors must be included in this area of the plan and you should summarise their roles within the organisation. If you have any other personnel that will be involved at a senior level then they should be included also. In this part of the business plan you need to outline the funds required to set up and maintain the business also. By including information about the company’s location and operations you will be able to forecast the money required to get the company started and any investment that will be needed. Try to include a spreadsheet showing where the initial funding will come from and how much is being put into the business to start with. Remember, most new businesses make a loss in their first year due to the expenses involved in starting a new company, so be realistic. Plan the initial outlays and costs carefully and make sure you know the limits to how much you can put into the company to get started.
The location of the business can also be included here and any rent that you will be required to pay can be outlined and the costs per square foot for the company premises. Then you can go on to make projections about the sales required to cover all of your fixed costs such as office and equipment rentals.
Next we move on to explaining the things which will earn your business money – the goods and services that you have to offer. In this section you must include descriptions of what you can offer your customers and the prices you will be charging. Outline what makes your goods and services special and the key aspects that will influence potential clients and convert them into paying customers. It is also a good idea to compare your pricing structure to your competitors. It may be that you offer the same products but cheaper, or with any additional features to make your products more appealing. You should explore the need for your products and services to be better than any of the competition. As a new business you may struggle to compete unless you have something that nobody else has. By bringing to the market something which is already selling well with another company that has established its brand in the marketplace, you might struggle to take a large enough section of the market to warrant starting a whole new company. If this is the case then you must compare your pricing to your biggest competitors and ensure that you are competitive.
In this section you can also include any products and services that you may offer in the future. Explain your product development processes and how you will be able to innovate and bring new products or services to the marketplace.
Next you need to carry out some market analysis to identify your potential customers . In this section of the business plan you need to include information about your ideal customers and what sort of people they will be. Think about the earnings of your potential clients, the type of lifestyles they will live and the products and services they expect from a business. This part of your plan is great for you to use figures about your market and show any growth projections for the sector in the future.
Explain market trends and analyse the need for your goods/services in this sector. Attempt to find some facts about the disposable income of your potential customers and target certain people who will be interested in what your company offers. Think about how you will be attracting your customers and the potential for growth over the first 3 years in operation. Make estimations about the number of people in the area where you will be offering your products and services to get a good idea of how many different potential clients you can attract. Having a good understanding of your target market will give you the tools to design marketing strategies and techniques to attract the maximum number of customers to your business.
Having outlined your market and explained who your products/services will attract, it is time to explain your techniques when doing this and show how you are going to market your company. Explain the key aspects of what you offer and the main selling points that should be tailored to suit the target clients that you have in mind. Products designed for the more affluent will need to be luxurious and have an exclusivity about them, whereas items that are for people with limited incomes will need to offer greater value for money. Try to understand a clear link between the market in which you will be operating, your potential clients and the main aspects of your business which you should focus on.
Ensuring that your business suits the needs of customers is essential to getting the most customers. For example, opening up a luxury spa in an area where there is high unemployment and typically lower incomes will encounter lots of issues as the potential customers (those within a 15-mile radius) will have no need for this service and may not be able to afford what you have to offer. You will need to come up with at least five ways of promoting your business that will appeal to your target market and attract clients. Remember all of the techniques and skills we discussed on marketing and try to link what you know about your potential clients to the advertising methods you will use.
Here you can also outline the potential sales forecasts and investments which you will make when promoting your goods and services. Come up with some realistic projections about the money to be spent on advertising and increasing awareness of your brand as well as any sales targets you may wish to set. Be conservative with your sales projections as it takes time for any business to get a good level of customers and building brand awareness does not happen overnight. Your sales in year 1 will normally be fairly low and you need to take this into account when projecting your income and the amount it will cost to set up your company.
The next thing to plan is the personnel involved in your business. This will include the owners and directors as well as any senior managers that are to be involved in the company. Explain the team structure and hierarchy of your new company and the number of employees you will be hiring. Knowing the team behind the company and their individual duties will let you outline the various skills that your team possesses and establish each person’s duties within the organisation.
Outlining the duties of each person and giving a brief job description is a good way for you to understand the team dynamic and responsibilities of each member. Most new companies make the mistake of hiring too soon, but with a clear plan of the business personnel that will be involved in your company you will be able to ensure each person is needed for the business to operate. Establishing a business will require you to be frugal in your approach and employing staff that are not needed can have a terrible impact on your profits and end up costing you tens of thousands of pounds a year.
Outline the wages of your employees and then come up with some totals for staffing costs that can be used when writing your executive summary.
Your financial plan will provide a clear breakdown of all the income and outgoings of the business that you expect. These will only be projected figures so will be likely to change in reality, but you should be able to predict fairly accurately using your knowledge of costs incurred and the pricing and potential customer base for your products/services.
Make projected figures for your fixed and variable costs as well as the profits you expect to earn from sales. This will then help you to create a break-even analysis for your company that will show the amount of money required to cover all of your outgoings. Remember that your first year will have fixed and variable costs as well as additional outgoings which come from setting up your company. You will also have a limited number of sales during the first 12 months as you build up your customer base, so the projected net profit for year 1 will be lower than any other year. Try to think about the most popular goods/services you offer and come up with an average sale price for your customers. This will then help you to identify the number of customers you need in your first year to break even.
Come up with some cash flow and profit and loss charts (look over our work in Unit 1.3 to help) to project how much money you can expect to see in the business each year. This will help you to come up with clear and concise predictions for how much money you will be making in your first three years.
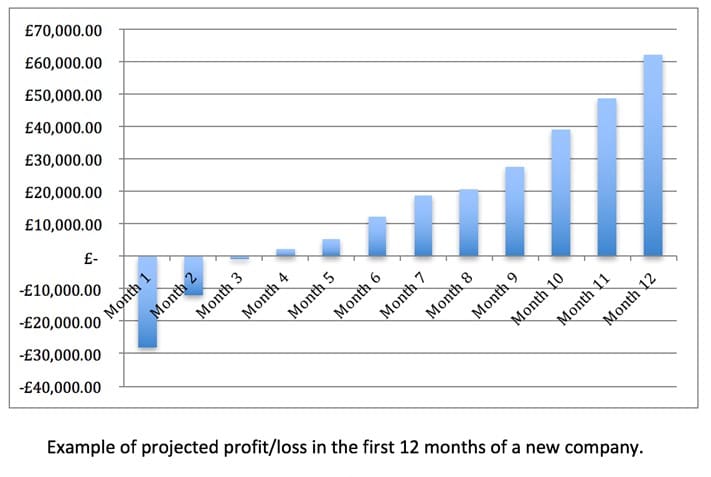
Reformulating a business plan
If you do ever happen to make a slight error in judgement on your initial business plan this can always be altered and the plan changed as required. The chances of figures being completely correct in your first projections are very slim and there will be certain things that you miss or random payments to be made when setting up your business which you did not account for. This is the main reason why being conservative with your income projections and adding in a ‘safety net’ figure to your costings will help you to deal with these circumstances. Business plans should be flexible and are a working document, so chopping and changing them is fine. When doing this try to use what you already have to create a new plan for the next few years rather than just altering figures to make it look like you got the initial plan correct.
Business plans are working documents, so they should be altered and added to as time goes by to determine where your company is heading and how it will get there. Being understanding of the nature of business and the fact that you will not be able to predict certain outcomes will give you an edge and allow you to put in place certain measures to help if you ever do come up against any problems.

Interested in business?
We offer a GCSE Business course that covers information on Business plans.
Learn more about our GCSE business course
Read another one of our posts
Essential skills every babysitter should master.

Community Health Initiatives – Promoting Wellness Locally

Enhancing Language Development in Early Years

GCSE Maths in Everyday Life: Practical Applications You Never Knew
Acing A-Level Exams- Revision and Exam Preparation Tips

Balancing Work and Personal Life in Home-based Childcare

Managing Stress and Anxiety in Parenthood

The Impact of Social Media on Youth Mental Health


Save your cart?
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Business news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Business Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes
Business Planning - Introduction
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
The business plan sets out how the owners/managers of a business intend to realise its objectives. Without such a plan a business is likely to drift.
The business plan serves several purposes:it
(1) enables management to think through the business in a logical and structured way and to set out the stages in the achievement of the business objectives.
(2) enables management to plot progress against the plan (through the management accounts)
(3) ensures that both the resources needed to carry out the strategy and the time when they are required are identified.
(4) is a means for making all employees aware of the business's direction (assuming the key features of the business plan are communicated to employees)
(5) is an important document for for discussion with prospective investors and lenders of finance (e.g. banks and venture capitalists).
(6) links into the detailed, short-term, one-year budget.
The Link Between the Business Plan and the Budget
A budget can be defined as "a financial or quantitative statement", prepared for a specific accounting period (typically a year), containing the plans and policies to be pursued during that period.
The main purposes of a budget are:
(1) to monitor business unit and managerial performance (the latter possibly linking into bonus arrangements)
(2 )to forecast the out-turn of the period's trading (through the use of flexed budgets and based on variance analyses)
(3 )to assist with cost control.
Generally, a functional budget is prepared for each functional area within a business (e.g. call-centre, marketing, production, research and development, finance and administration). In addition, it is also normal to produce a "capital budget" detailing the capital investment required for the period, a "cash flow budget", a "stock budget" and a "master budget", which includes the budgeted profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Preparing a Business Plan
A business plan has to be particular to the organisation in question, its situation and time. However, a business plan is not just a document, to be produced and filed. Business planning is a continuous process. The business plan has to be a living document, constantly in use to monitor, control and guide the progress of a business. That means it should be under regular review and will need to be amended in line with changing circumstances.
Before preparing the plan management should: - review previous business plans (if any) and their outcome. This review will help highlight which areas of the business have proved difficult to forecast historically. For example, are sales difficult to estimate? If so why? - be very clear as to their objectives - a business plan must have a purpose - set out the key business assumptions on which their plans will be based (e.g. inflation, exchange rates, market growth, competitive pressures, etc.) - take a critical look at their business. The classical way is by means of the strengths-weaknesses-opportunities-threats (SWOT) analysis, which identifies the business's situation from four key angles. The strategies adopted by a business will be largely based on the outcome of this analysis.
Preparing the Budget
A typical business plan looks up to three years forward and it is normal for the first year of the plan to be set out in considerable detail. This one-year plan, or budget, will be prepared in such a way that progress can be regularly monitored (usually monthly) by checking the variance between the actual performance and the budget, which will be phased to take account of seasonal variations.
The budget will show financial figures (cash, profit/loss working capital, etc) and also non-financial items such as personnel numbers, output, order book, etc. Budgets can be produced for units, departments and products as well as for the total organisation. Budgets for the forthcoming period are usually produced before the end of the current period. While it is not usual for budgets to be changed during the period to which they relate (apart from the most extraordinary circumstances) it is common practice for revised forecasts to be produced during the year as circumstances change.
A further refinement is to flex the budgets, i.e. to show performance at different levels of business. This makes comparisons with actual outcomes more meaningful in cases where activity levels differ from those included in the budget.
What Providers of Finance Want from a Business Plan
Almost invariably bank managers and other providers of finance will want to see a business plan before agreeing to provide finance. Not to have a business plan will be regarded as a bad sign. They will be looking not only at the plan, but at the persons behind it. They will want details of the owner/managers of the business, their background and experience, other activities, etc. They will be looking for management commitment, with enthusiasm tempered by realism. The plan must be thought through and not be a skimpy piece of work. A few figures on a spreadsheet are not enough.
The plan must be used to run the business and there must be a means for checking progress against the plan. An information system must be in place to provide regular details of progress against plan. Bank managers are particularly wary of businesses that are slow in producing internal performance figures. Lenders will want to guard against risk. In particular they will be looking for two assurances:
(1) that the business has the means of making regular payment of interest on the amount loaned, and
(2) that if everything goes wrong the bank can still get its money back (i.e. by having a debenture over the business's assets). Forward-looking financial statements, particularly the cash flow forecast, are therefore of critical importance. The bank wants openness and no surprises. If something is going wrong it does not want this covered up, it wants to be informed - quickly.
- Strategic planning
- Marketing planning
- Corporate planning
- Business plan
You might also like
Corporate objectives, marketing objectives (revision presentation).
Teaching PowerPoints
Why is market research needed?
The role of competitor analysis, the mckinsey / general electric growth share matrix, 3.3 decision making to improve marketing performance - impossible 5 revision activity.
Quizzes & Activities
Marketing Objectives (Introduction)
Topic Videos
Internal and External Influences on Marketing Objectives
Our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
Trump's tough trade stance could undercut his plans for a weaker dollar
- Donald Trump wants a weaker dollar in order to boost exports for US manufacturers.
- But his tariff proposals would cause the opposite: a stronger greenback, a Barclays analyst said.
- Other ways Trump could weaken the dollar would also risk raising US debt or inflation, Barclays said.

Donald Trump's proposed policies run counter to one another, with his plan to increase trade tariffs complicating his intent to weaken the dollar, Ajay Rajadhyaksha of Barclays wrote in the Financial Times.
In a Bloomberg interview last week, the Republican presidential candidate explained that the dollar's recent strength has hampered US businesses and made exports more expensive.
"That's a tremendous burden on our companies that try and sell tractors and other things to other places outside of this country. It's a tremendous burden," Trump told Bloomberg.
Since March 2020, the greenback is 5% stronger than the Chinese yuan, 15% higher than the Indian rupee, and 50% above the Japanese yen, according to Barclays.
Meanwhile, Trump has has frequently touted plans to implement universal tariffs on all US imports in an attempt to make America more competitive on trade.
But when tariffs are raised, they actually usually cheapen the currency of impacted countries, Rajadhyaksha cautioned:
"The reality is that weakening the dollar runs counter to many of the Trump campaign's other goals, such as tariffs and cutting taxes (tax cuts should push up growth, which is normally dollar — positive)," he said.
Other options for weakening the dollar exist, but none come without consequences, the strategist noted.
For instance, the Federal Reserve could buy sovereign bonds from other nations, adding dollars into global circulation. But increasing the central bank's balance sheet risks inflation, and is not something the Fed is likely to go along with, Rajadhyaksha said.
He cited alternative plans: raising US debt could help, at the cost of Treasury market volatility and more inflation pressure.
Otherwise, enlisting other countries to help devalue the dollar is unlikely to gain much support. The last time the US did so under the 1985 Plaza Accords, it created decades of stagflation for Japan, Rajadhyaksha said.
- Main content
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Business Plans - GCSE Business Studies - PPT & Create Your Own Business Plan Task
Subject: Business and finance
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
14 June 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A bumper lesson on a business plans. The presentation looks at what a business plan is and how it helps a business reduce risk. The lesson covers the main pros and cons of developing a business plan and the most important headings of a business plan. There are a number of tasks throughout the lesson to help keep students engaged. The lesson finishes with students asked to fill in a business plan template of their own business idea (this has been included). I have also included a simple worksheet on the various headings in a typical business plan. This lesson is perfect for GCSE Business Studies and Setting up a New Business unit. This lesson could easily stretched across a few periods as it will take time for students to complete their own business plans plus they could also present their idea and plan to the class.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Exam-Style Questions - Business Plans
Test yourself on this topic.
This topic is designed as an interactive quiz.
Test yourself in an adaptive quiz or answer open-ended exam questions for free, by signing in to Seneca.
Jump to other topics
1 Enterprise & Entrepreneurship
1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.2 Risk & Reward
1.1.3 The Role of Business Enterprise
1.1.4 The Role of Business Enterprise 2
1.1.5 The Role of the Entrepreneur
1.1.6 End of Topic Test - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.1.7 Grade 9 - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.2 Spotting a Business Opportunity
1.2.1 Customer Needs
1.2.2 Market Research
1.2.3 Market Segmentation
1.2.4 The Competitive Environment
1.2.5 Primary & Secondary Market Research
1.2.6 End of Topic Test - Business Opportunities
1.2.7 Application Questions - Business Opportunities
1.2.8 Exam-Style Questions - Market Segmentation
1.3 Putting a Business Idea into Practice
1.3.1 Business Aims
1.3.2 Business Objectives
1.3.3 Business Revenues & Costs
1.3.4 Costs - Calculations
1.3.5 Revenue - Calculations
1.3.6 Business Profits & Break-Even Analysis
1.3.7 Profits & Losses - Calculations
1.3.8 Interest - Calculations
1.3.9 Cash & Cash Flow
1.3.10 Cash & Cash Flow 2
1.3.11 Cash Flow - Calculations
1.3.12 Sources of Business Finance
1.3.13 End of Topic Test - Business in Practice
1.3.14 Grade 9 - Business in Practice
1.3.15 Exam-Style Questions - Business in Practice
1.4 Making the Business Effective
1.4.1 The Options for Start-Up & Small Businesses
1.4.2 Limited Liability
1.4.3 Franchising & Not-For-Profits
1.4.4 Business Location
1.4.5 The Marketing Mix
1.4.6 Business Plans
1.4.7 End of Topic Test - Effective Business
1.4.8 Application Questions - Effective Business
1.4.9 Exam-Style Questions - Business Plans
1.5 Business Stakeholders
1.5.1 Business Stakeholders
1.5.2 Technology & Business
1.5.3 Legislation & Business
1.5.4 Legislation & Business 2
1.5.5 The Economy & Business
1.5.6 External Influences
1.5.7 End of Topic Test - Business Stakeholders
1.5.8 Grade 9 - Business Stakeholders
2 Building a Business
2.1 Growing the Business
2.1.1 Business Growth
2.1.2 Finance
2.1.3 Changes in Business Aims & Globalisation
2.1.4 Ethics & Business
2.1.5 The Environment & Business
2.1.6 End of Topic Test - Growing a Business
2.1.7 Application Questions - Growing a Business
2.1.8 Exam-Style Questions - Business Growth
2.2 Making Marketing Decisions
2.2.1 Product
2.2.2 Product Life Cycle
2.2.3 Price
2.2.4 Pricing Methods
2.2.5 End of Topic Test - Product & Price
2.2.6 Grade 9 - Product & Price
2.2.7 Promotion & Advertising
2.2.8 PR & Sales Promotions
2.2.9 Sponsorship & Product Placement
2.2.10 Promotional Mix
2.2.11 End of Topic Test - Promotion
2.2.12 Application Questions - Promotion
2.2.13 Exam-Style Questions - Promotional Mix
2.2.14 Place & Wholesalers
2.2.15 Direct to Consumer
2.2.16 E-commerce & M-commerce
2.3 Making Operational Decisions
2.3.1 Job Production
2.3.2 Batch & Flow Production
2.3.3 Working with Suppliers
2.3.4 Effective Supply Chains
2.3.5 Just In Time & Just In Case
2.3.6 Managing Quality
2.3.7 Total Quality Management
2.3.8 The Sales Process
2.3.9 End of Topic Test - Operational Decisions
2.3.10 Grade 9 - Operational Decisions
2.3.11 Exam-Style Questions - Managing Stock
2.4 Making Financial Decisions
2.4.1 Gross Profit & Net Profit - Definitions
2.4.2 Gross Profit - Calculations
2.4.3 Net Profit - Calculations
2.4.4 Rate of Return
2.4.5 Rate of Return - Calculations
2.4.6 Research & Financial Data
2.4.7 Marketing Data
2.4.8 Percentage Change - Calculations
2.5 Making Human Resource Decisions
2.5.1 Organisational Structures
2.5.2 Organisational Structures 2
2.5.3 Recruitment
2.5.4 Effective Recruitment
2.5.5 Training a Workforce
2.5.6 Motivating a Workforce
2.5.7 End of Topic Tests - Human Resources
2.5.8 Application Questions - Human Resources
2.5.9 Exam-Style Questions - Human Resources
Application Questions - Effective Business
Business Stakeholders
Business Plans & Government Support ( CIE IGCSE Business )
Revision note.

Business Content Creator
Contents of a Business Plan
- The main aim of producing a business plan is to reduce the risk associated with starting a new business
- A business plan is a document produced by the owner at start-up, which provides forecasts of items such as sales, costs and cash flow
Diagram to show the Elements of a Business Plan

The main elements included in a business plan, although some differ slightly depending on the nature of the business
- Producing a business plan forces the owner to think about every aspect of the business before they start which should reduce the risk of failure
Explaining the Main Elements of a Business Plan
|
| provided by the business which will help to attract investors |
|
| in the medium and long term |
|
| e.g. age, gender, income and will form part of the firms marketing strategy |
|
| through sales |
|
| , variable and total costs in order to manage their spending |
|
| to see whether the e.g. bank |
|
| which will outline how the |
|
| of cash on a monthly basis in order to avoid liquidity problems |
|
| e.g. loans, owners funds or venture capital |
|
| including a map along with an explanation of potential advantages such as transport links or proximity to customers |
How Business Plans help Entrepreneurs
- The main aim of producing a business plan is to reduce the risk associated with starting a new business and help the owners to raise finance
- Having carried out research to support the plan, the business will be well-informed about the potential problems and chance of success and can select the most appropriate source of finance based on this information
- Lenders (e.g. banks) and other investors will be able to explore the plan and make an informed decision about whether the business is credible and worth the financial risk
- Investors (e.g. venture capitalists ) will use the business plan to explore whether there is an opportunity to increase the value of their investment and make a worthwhile profit
- The business, having carried out research to support the plan, will be well-informed about the potential problems and chance of success and can select the most appropriate source of finance based on this information
- A clear action plan provides direction for the business and helps lenders and investors to have confidence in the future success of the business
- Most high street banks can provide a detailed template for business owners to complete when applying for finance
Government Support of Business Start-ups
- Governments often provide support to entrepreneurs so as to encourage them to set up new businesses or take steps to grow their business
- Increase the country's level of output to achieve economic growth
- Reduce the level of unemployment as new or growing businesses create jobs
- Improve choice for consumers by providing competition for existing businesses
- Encourage entrepreneurs to set up social enterprises which may support disadvantaged groups or improve communities
How Governments Support Business Start-ups
|
| can often be accessed through local authorities offered by business mentors allow entrepreneurs to ask specific questions related to their business |
|
| and incentives such as reduced business rates who share expertise and facilities, especially in less economically-developed regions |
|
| and grants for new or growing businesses that create jobs or invest in training workers |
You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access.
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Join the 100,000 + Students that ❤️ Save My Exams
the (exam) results speak for themselves:
Did this page help you?
Author: Danielle Maguire
Danielle is an experienced Business and Economics teacher who has taught GCSE, A-Level, BTEC and IB for 15 years. Danielle's career has taken her from across various parts of the UK including Liverpool and Yorkshire, along with teaching at a renowned international school in Dubai for 3 years. Danielle loves to engage students with real life examples and creative resources which allow students to put topics in a context they understand.
A federal court has now blocked Biden's new student-loan repayment plan in full, prohibiting borrowers from getting cheaper payments and debt cancellation
- The 8th Circuit on Thursday blocked the SAVE student-loan repayment plan in full.
- This means debt cancellation and cheaper payments through the plan cannot be implemented.
- This also reverses the 10th Circuit's decision that allowed some of SAVE's provisions to continue.

A major repayment plan for millions of student-loan borrowers is once again blocked.
On Thursday, the 8th Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the SAVE plan, intended to lower borrowers' monthly payments and give many of them a shorter timeline for loan forgiveness, cannot be implemented as the legal process continues.
It follows a series of legal challenges to the plan. Earlier this year, two separate groups of GOP state attorneys general filed lawsuits to block the SAVE plan, and at the end of June, two federal courts placed preliminary injunctions on the plan .
Just days later, however, the 10th Circuit appeals court granted the Biden administration's request to stay one of the rulings, allowing provisions that were set to go into effect in July — including cheaper payments — to move forward.
Thursday's ruling from the 8th Circuit blocked all provisions of SAVE in a one-sentence ruling: "Appellants' emergency motion for an administrative stay prohibiting the appellees from implementing or acting pursuant to the Final Rule until this Court rules on the appellants' motion for an injunction pending appeal is granted."
An Education Department spokesperson told Business Insider, "We are assessing the impacts of this ruling and will be in touch directly with borrowers with any impacts that affect them."
Related stories
"Our Administration will continue to aggressively defend the SAVE Plan — which has been helping over 8 million borrowers access lower monthly payments, including 4.5 million borrowers who have had a zero dollar payment each month," the spokesperson said. "And, we won't stop fighting against Republican elected officials' efforts to raise costs on millions of their own constituents' student loan payments."
Thursday's ruling was in response to the lawsuit led by Missouri's attorney general. Kansas is leading the other lawsuit to block SAVE, which it has requested the Supreme Court take on. SCOTUS hasn't yet said whether it will.
But the Education Department recently filed a response to the Supreme Court detailing the steps the department and borrowers would be forced to take should the SAVE plan be blocked. Solicitor General Elizabeth Prelogar wrote that if the plan couldn't be carried out, the department must put borrowers on forbearance as they recalculate new payments.
"Many have already received bills that reflect the decrease in monthly payments to 5% of their discretionary income," she wrote. "Many would experience intense confusion when they are told that their payments must be recalculated and that they must be placed in forbearance -- which would delay any eventual loan forgiveness."
The back-and-forth rulings have already prompted payment delays and confusion among borrowers. After the 10th circuit allowed SAVE's June provisions to move forward, the Education Department moved to direct servicers to begin processing the new, lower payments for borrowers. The department also clarified at the time that because of the lawsuits, payments wouldn't become due until July or August.
That timeline is now in flux, and borrowers will once again be waiting for clarity on the status of their payments and what will happen to their SAVE benefits now that the plan is blocked.
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is a document produced by the owner at start-up, which provides forecasts of items such as:. The business idea (sub-topic 1.1.1)The business aims and objectives (sub-topic 1.3.1)The target market (sub-topic 1.2.2)The forecast revenues, costs and profits (sub-topic 1.3.2)The cash-flow forecast (sub-topic 1.3.5)The sources of finance (sub-topic 1.3.6)
Business plans provide parameters for setting targets. Management can check staffing, incomes, product ranges and lots of other things against previous business plans and expansion plans. A business plan can be used as a benchmark against outcomes like cashflow, production outcomes or service delivery. The plan can also be compared to the ...
Reasons for Developing a Business Plan. A business plan sets out key aspects of a business and how the owners intend it to develop. Producing a business plan helps reduce the risk associated with starting a new business and can help the owners raise finance. A business plan forces the owner to think about every aspect of the business and ...
A business plan is a written document that describes a business, its objectives, its strategies, the market it is in and its financial forecasts. The business plan has many functions, from securing external funding to measuring success within the business. Benefits of business planning to a start-up. The main reasons why a start-up should ...
Business Plans Explained - GCSE and A Level Business Revision 📝 This video explains what a business plan is, includes the contents of a business plan as we...
The lesson outlines all the specification points of Business Plans within the GCSE (9-1) Edexcel Business Studies course (useful for other exam boards too) This lesson teaches the following content: The role and importance of a business plan: to identify:the business idea; business aims and objectives; target market (market research); forecast ...
zip, 914 Bytes. pdf, 59.95 KB. pptx, 1.99 MB. This lesson / resource is from Unit 1 - Understanding Business Activity and looks specifically at Business Plans . I normally teach this in Year 10 and it has been designed for GCSE with the following learning objectives: Know what a Business Plan is and why a person might write one.
Business Plans - Topic 1.4 - Edexcel GCSE Business - Theme 1. This sequence of lessons (roughly two) focuses upon business plans and includes an evaluate exam question. Resource includes one Dragons' Den video activity, application activities and worksheet activities. Plenty of videos and activities for you to choose from - allowing you to ...
Reformulating a business plan. Business plans are used to outline the industry in which a business is working in as well as the economic structure of a company to give an idea of the financial prospects of a business. They are used primarily to organise the routes to market that a company will take and give projections on earnings and target ...
Setting Business Aims & Objectives | AQA GCSE Business Quizzes & Activities. The McKinsey / General Electric Growth Share Matrix Study Notes. Business Planning for a New Business (Revision Presentation) ... Starting a Business: Contents of a Startup Business Plan (GCSE) Study Notes. How to start an airline 1st March 2021 ...
The business plan sets out how the owners/managers of a business intend to realise its objectives. Without such a plan a business is likely to drift. The business plan serves several purposes:it. (1) enables management to think through the business in a logical and structured way and to set out the stages in the achievement of the business ...
Building a Business. 2.1 Growing the Business. 2.2 Making Marketing Decisions. 2.3 Making Operational Decisions. 2.4 Making Financial Decisions. 2.5 Making Human Resource Decisions. Revision notes for the Edexcel GCSE Business syllabus, written by the Business experts at Save My Exams.
Use Quizlet for GCSE Business Studies revision to learn about everything from business operations to influences on business. Discover curriculum-aligned study sets and learning activities for the exam board specifications below.
Trump wants both trade barriers and a weaker dollar. But raising tariffs typically creates a stronger greenback, Barclays Ajay Rajadhyaksha said.
Chinese electric truck startup Windrose plans to set up a U.S. assembly plant for its semi-trucks for delivery there from 2025, directly challenging Tesla in its home market, founder and Chief ...
The plan will still need voter approval before it can get final approval. Sramek said in the statement that California Forever still plans to submit the full package for approval in 2026.
China has announced plans to raise some of the world's lowest statutory retirement ages as it tries to cope with the consequences of a rapidly ageing population and a pensions funding crisis.
A bumper lesson on a business plans. The presentation looks at what a business plan is and how it helps a business reduce risk. The lesson covers the main pros and cons of developing a business plan and the most important headings of a business plan. There are a number of tasks throughout the lesson to help keep students engaged.
The East Solano Plan, ... CSG raised its offer for the Vista ammo business once more, announcing on Monday that it would now pay $2.15 billion. (It had originally agreed to buy the division, known ...
This topic is designed as an interactive quiz. Test yourself in an adaptive quiz or answer open-ended exam questions for free, by signing in to Seneca. Test yourself. Jump to other topics. Application Questions - Effective Business. Business Stakeholders. Seneca Learning Exam-Style Questions - Business Plans revision content.
Silicon Valley's plans for a start-up city are on hold. The East Solano Plan — a proposal backed by a roster of technology billionaires to build a city of up to 400,000 people on farmland ...
Author: Danielle Maguire Danielle is an experienced Business and Economics teacher who has taught GCSE, A-Level, BTEC and IB for 15 years. Danielle's career has taken her from across various parts of the UK including Liverpool and Yorkshire, along with teaching at a renowned international school in Dubai for 3 years.
Dunn hopes the upcoming 5,500-square-foot building being built by Harvey Construction will open later this year or early 2025. The current 547-square-foot liquor store will remain open throughout ...
The 8th Circuit Appeals Court blocked the SAVE student-loan repayment plan in its entirety, forcing borrowers to once again wait on cheaper payments. Menu icon A vertical stack of three evenly ...
Ford Motor on Thursday outlined plans to use a Canadian plant it had earmarked for a future electric vehicle to instead build larger, gasoline-powered versions of its flagship F-Series pickup truck.
We are all about to be given a crash course in GCSE economics. The only trouble is that it will be a very expensive one. At the higher levels, economics is a complex subject involving a deep ...
Last week, Ms. Harris echoed her earlier criticism of Mr. Trump when discussing his plan to impose 10 percent tariffs on all imports into the United States. She said such a policy would inflate ...