Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to's, java reference, java examples, java operators.
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values.
In the example below, we use the + operator to add together two values:
Try it Yourself »
Although the + operator is often used to add together two values, like in the example above, it can also be used to add together a variable and a value, or a variable and another variable:
Java divides the operators into the following groups:
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators

Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform common mathematical operations.
| Operator | Name | Description | Example | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | Adds together two values | x + y | |
| - | Subtraction | Subtracts one value from another | x - y | |
| * | Multiplication | Multiplies two values | x * y | |
| / | Division | Divides one value by another | x / y | |
| % | Modulus | Returns the division remainder | x % y | |
| ++ | Increment | Increases the value of a variable by 1 | ++x | |
| -- | Decrement | Decreases the value of a variable by 1 | --x |
Advertisement
Java Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
In the example below, we use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x :
The addition assignment operator ( += ) adds a value to a variable:
A list of all assignment operators:
| Operator | Example | Same As | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 | |
| += | x += 3 | x = x + 3 | |
| -= | x -= 3 | x = x - 3 | |
| *= | x *= 3 | x = x * 3 | |
| /= | x /= 3 | x = x / 3 | |
| %= | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 | |
| &= | x &= 3 | x = x & 3 | |
| |= | x |= 3 | x = x | 3 | |
| ^= | x ^= 3 | x = x ^ 3 | |
| >>= | x >>= 3 | x = x >> 3 | |
| <<= | x <<= 3 | x = x << 3 |
Java Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions.
The return value of a comparison is either true or false . These values are known as Boolean values , and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If..Else chapter.
In the following example, we use the greater than operator ( > ) to find out if 5 is greater than 3:
| Operator | Name | Example | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal to | x == y | |
| != | Not equal | x != y | |
| > | Greater than | x > y | |
| < | Less than | x < y | |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y | |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x <= y |
Java Logical Operators
You can also test for true or false values with logical operators.
Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values:
| Operator | Name | Description | Example | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| && | Logical and | Returns true if both statements are true | x < 5 && x < 10 | |
| || | Logical or | Returns true if one of the statements is true | x < 5 || x < 4 | |
| ! | Logical not | Reverse the result, returns false if the result is true | !(x < 5 && x < 10) |
Java Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators are used to perform binary logic with the bits of an integer or long integer.
| Operator | Description | Example | Same as | Result | Decimal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| & | AND - Sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1 | 5 & 1 | 0101 & 0001 | 0001 | 1 |
| | | OR - Sets each bit to 1 if any of the two bits is 1 | 5 | 1 | 0101 | 0001 | 0101 | 5 |
| ~ | NOT - Inverts all the bits | ~ 5 | ~0101 | 1010 | 10 |
| ^ | XOR - Sets each bit to 1 if only one of the two bits is 1 | 5 ^ 1 | 0101 ^ 0001 | 0100 | 4 |
| << | Zero-fill left shift - Shift left by pushing zeroes in from the right and letting the leftmost bits fall off | 9 << 1 | 1001 << 1 | 0010 | 2 |
| >> | Signed right shift - Shift right by pushing copies of the leftmost bit in from the left and letting the rightmost bits fall off | 9 >> 1 | 1001 >> 1 | 1100 | 12 |
| >>> | Zero-fill right shift - Shift right by pushing zeroes in from the left and letting the rightmost bits fall off | 9 >>> 1 | 1001 >>> 1 | 0100 | 4 |
Note: The Bitwise examples above use 4-bit unsigned examples, but Java uses 32-bit signed integers and 64-bit signed long integers. Because of this, in Java, ~5 will not return 10. It will return -6. ~00000000000000000000000000000101 will return 11111111111111111111111111111010
In Java, 9 >> 1 will not return 12. It will return 4. 00000000000000000000000000001001 >> 1 will return 00000000000000000000000000000100
Test Yourself With Exercises
Multiply 10 with 5 , and print the result.
Start the Exercise

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

Java Tutorial
Control statements, java object class, java inheritance, java polymorphism, java abstraction, java encapsulation, java oops misc.
| Java is a popular programming language that software developers use to construct a wide range of applications. It is a simple, robust, and platform-independent object-oriented language. There are various types of assignment operators in Java, each with its own function. In this section, we will look at Java's many types of assignment operators, how they function, and how they are utilized. To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side.
In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10. To add a value to a variable and subsequently assign the new value to the same variable, use the addition assignment operator (+=). It takes the value on the right side of the operator, adds it to the variable's existing value on the left side, and then assigns the new value to the variable.
To subtract one numeric number from another, use the subtraction operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we create two integer variables, a and b, subtract b from a, and then assign the result to the variable c. To combine two numerical numbers, use the multiplication operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we declare two integer variables, a and b, multiply their values using the multiplication operator, and then assign the outcome to the third variable, c. To divide one numerical number by another, use the division operator. All numeric data types, including integers and floating-point values, can be utilised with it. Here's an illustration:
In this example, we declare two integer variables, a and b, divide them by one another using the division operator, and then assign the outcome to the variable c. It's vital to remember that when two numbers are divided, the outcome will also be an integer, and any residual will be thrown away. For instance: The modulus assignment operator (%=) computes the remainder of a variable divided by a value and then assigns the resulting value to the same variable. It takes the value on the right side of the operator, divides it by the current value of the variable on the left side, and then assigns the new value to the variable on the left side.
|

- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

Java Assignment Operators
Java programming tutorial index.
The Java Assignment Operators are used when you want to assign a value to the expression. The assignment operator denoted by the single equal sign = .
In a Java assignment statement, any expression can be on the right side and the left side must be a variable name. For example, this does not mean that "a" is equal to "b", instead, it means assigning the value of 'b' to 'a'. It is as follows:
Java also has the facility of chain assignment operators, where we can specify a single value for multiple variables.
- Java Operators
Last updated: January 8, 2024
Get non-trivial analysis (and trivial, too!) suggested right inside your IDE or Git platform so you can code smart, create more value, and stay confident when you push.
Get CodiumAI for free and become part of a community of over 280,000 developers who are already experiencing improved and quicker coding.
Write code that works the way you meant it to:
>> CodiumAI. Meaningful Code Tests for Busy Devs
Java applications have a notoriously slow startup and a long warmup time. The CRaC (Coordinated Restore at Checkpoint) project from OpenJDK can help improve these issues by creating a checkpoint with an application's peak performance and restoring an instance of the JVM to that point.
To take full advantage of this feature, BellSoft provides containers that are highly optimized for Java applications. These package Alpaquita Linux (a full-featured OS optimized for Java and cloud environment) and Liberica JDK (an open-source Java runtime based on OpenJDK).
These ready-to-use images allow us to easily integrate CRaC in a Spring Boot application:
Improve Java application performance with CRaC support
Modern software architecture is often broken. Slow delivery leads to missed opportunities, innovation is stalled due to architectural complexities, and engineering resources are exceedingly expensive.
Orkes is the leading workflow orchestration platform built to enable teams to transform the way they develop, connect, and deploy applications, microservices, AI agents, and more.
With Orkes Conductor managed through Orkes Cloud, developers can focus on building mission critical applications without worrying about infrastructure maintenance to meet goals and, simply put, taking new products live faster and reducing total cost of ownership.
Try a 14-Day Free Trial of Orkes Conductor today.
Azure Container Apps is a fully managed serverless container service that enables you to build and deploy modern, cloud-native Java applications and microservices at scale. It offers a simplified developer experience while providing the flexibility and portability of containers.
Of course, Azure Container Apps has really solid support for our ecosystem, from a number of build options, managed Java components, native metrics, dynamic logger, and quite a bit more.
To learn more about Java features on Azure Container Apps, you can get started over on the documentation page .
And, you can also ask questions and leave feedback on the Azure Container Apps GitHub page .
Whether you're just starting out or have years of experience, Spring Boot is obviously a great choice for building a web application.
Jmix builds on this highly powerful and mature Boot stack, allowing devs to build and deliver full-stack web applications without having to code the frontend. Quite flexibly as well, from simple web GUI CRUD applications to complex enterprise solutions.
Concretely, The Jmix Platform includes a framework built on top of Spring Boot, JPA, and Vaadin , and comes with Jmix Studio, an IntelliJ IDEA plugin equipped with a suite of developer productivity tools.
The platform comes with interconnected out-of-the-box add-ons for report generation, BPM, maps, instant web app generation from a DB, and quite a bit more:
>> Become an efficient full-stack developer with Jmix
DbSchema is a super-flexible database designer, which can take you from designing the DB with your team all the way to safely deploying the schema .
The way it does all of that is by using a design model , a database-independent image of the schema, which can be shared in a team using GIT and compared or deployed on to any database.
And, of course, it can be heavily visual, allowing you to interact with the database using diagrams, visually compose queries, explore the data, generate random data, import data or build HTML5 database reports.
>> Take a look at DBSchema
Do JSON right with Jackson
Download the E-book
Get the most out of the Apache HTTP Client
Get Started with Apache Maven:
Working on getting your persistence layer right with Spring?
Explore the eBook
Building a REST API with Spring?
We’ve opened a new Java/Spring Course Team Lead position. Part-time and entirely remote, of course: Read More
Get started with Spring and Spring Boot, through the Learn Spring course:
Explore Spring Boot 3 and Spring 6 in-depth through building a full REST API with the framework:
>> The New “REST With Spring Boot”
Get started with Spring and Spring Boot, through the reference Learn Spring course:
>> LEARN SPRING
The AI Assistant to boost Boost your productivity writing unit tests - Machinet AI .
AI is all the rage these days, but for very good reason. The highly practical coding companion, you'll get the power of AI-assisted coding and automated unit test generation . Machinet's Unit Test AI Agent utilizes your own project context to create meaningful unit tests that intelligently aligns with the behavior of the code. And, the AI Chat crafts code and fixes errors with ease, like a helpful sidekick.
Simplify Your Coding Journey with Machinet AI :
>> Install Machinet AI in your IntelliJ
Yes, Spring Security can be complex, from the more advanced functionality within the Core to the deep OAuth support in the framework.
I built the security material as two full courses - Core and OAuth , to get practical with these more complex scenarios. We explore when and how to use each feature and code through it on the backing project .
You can explore the course here:
>> Learn Spring Security
Spring Data JPA is a great way to handle the complexity of JPA with the powerful simplicity of Spring Boot .
Get started with Spring Data JPA through the guided reference course:
>> CHECK OUT THE COURSE
1. Overview
Operators are a fundamental building block of any programming language. We use operators to perform operations on values and variables.
Java provides many groups of operators. They are categorized by their functionalities.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk through all Java operators to understand their functionalities and how to use them.
2. Arithmetic Operators
We use arithmetic operators to perform simple mathematical operations. We should note that arithmetic operators only work with primitive number types and their boxed types , such as int and Integer .
Next, let’s see what operators we have in the arithmetic operator group.
2.1. The Addition Operator
The addition operator (+) allows us to add two values or concatenate two strings:
2.2. The Subtraction Operator
Usually, we use the subtraction operator (-) to subtract one value from another:
2.3. The Multiplication Operator
The multiplication operator (*) is used to multiply two values or variables:
2.4. The Division Operator
The division operator (/) allows us to divide the left-hand value by the right-hand one:
When we use the division operator on two integer values ( byte , short , int , and long ), we should note that the result is the quotient value. The remainder is not included .
As the example above shows, if we calculate 15 / 2 , the quotient is 7, and the remainder is 1 . Therefore, we have 15 / 2 = 7 .
2.5. The Modulo Operator
We can get the quotient using the division operator. However, if we just want to get the remainder of a division calculation, we can use the modulo operator (%):
3. Unary Operators
As the name implies, unary operators only require one single operand . For example, we usually use unary operators to increment, decrement, or negate a variable or value.
Now, let’s see the details of unary operators in Java.
3.1. The Unary Plus Operator
The unary plus operator (+) indicates a positive value. If the number is positive, we can omit the ‘+’ operator:
3.2. The Unary Minus Operator
Opposite to the unary plus operator, the unary minus operator (-) negates a value or an expression:
3.3. The Logical Complement Operator
The logical complement operator (!) is also known as the “NOT” operator . We can use it to invert the value of a boolean variable or value:
3.4. The Increment Operator
The increment operator (++) allows us to increase the value of a variable by 1:
3.5. The Decrement Opeartor
The decrement operator (–) does the opposite of the increment operator. It decreases the value of a variable by 1:
We should keep in mind that the increment and decrement operators can only be used on a variable . For example, “ int a = 5; a++; ” is fine. However, the expression “ 5++ ” won’t be compiled.
4. Relational Operators
Relational operators can be called “comparison operators” as well. Basically, we use these operators to compare two values or variables.
4.1. The “Equal To” Operator
We use the “equal to” operator (==) to compare the values on both sides. If they’re equal, the operation returns true :
The “equal to” operator is pretty straightforward. On the other hand, the Object class has provided the equals() method. As the Object class is the superclass of all Java classes, all Java objects can use the equals() method to compare each other.
When we want to compare two objects – for instance, when we compare Long objects or compare String s – we should choose between the comparison method from the equals() method and that of the “equal to” operator wisely .
4.2. The “Not Equal To” Operator
The “not equal to” operator (!=) does the opposite of the ‘==’ operator. If the values on both sides are not equal, the operation returns true :
4.3. The “Greater Than” Operator
When we compare two values with the “greater than” operator (>), it returns true if the value on the left-hand side is greater than the value on the right-hand side:
4.4. The “Greater Than or Equal To” Operator
The “greater than or equal to” operator (>=) compares the values on both sides and returns true if the left-hand side operand is greater than or equal to the right-hand side operand:
4.5. The “Less Than” Operator
The “less than” operator (<) compares two values on both sides and returns true if the value on the left-hand side is less than the value on the right-hand side:
4.6. The “Less Than or Equal To” Operator
Similarly, the “less than or equal to” operator (<=) compares the values on both sides and returns true if the left-hand side operand is less than or equal to the right-hand side:
5. Logical Operators
We have two logical operators in Java: the logical AND and OR operators. Basically, their function is pretty similar to the AND gate and the OR gate in digital electronics.
Usually, we use a logical operator with two operands, which are variables or expressions that can be evaluated as boolean .
Next, let’s take a closer look at them.
5.1. The Logical AND Operator
The logical AND operator ( && ) returns true only if both operands are true :
5.2. The Logical OR Operator
Unlike the ‘ && ‘ operator, the logical OR operator ( || ) returns true if at least one operand is true :
We should note that the logical OR operator has the short-circuiting effect : It returns true as soon as one of the operands is evaluated as true, without evaluating the remaining operands.
6. Ternary Operator
A ternary operator is a short form of the if-then-else statement. It has the name ternary as it has three operands. First, let’s have a look at the standard if-then-else statement syntax:
We can convert the above if-then-else statement into a compact version using the ternary operator:
Let’s look at its syntax:
Next, let’s understand how the ternary operator works through a simple example:
7. Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators
As the article “ Java bitwise operators ” covers the details of bitwise and bit shift operators, we’ll briefly summarize these operators in this tutorial.
7.1. The Bitwise AND Operator
The bitwise AND operator (&) returns the bit-by-bit AND of input values:
7.2. The Bitwise OR Operator
The bitwise OR operator (|) returns the bit-by-bit OR of input values:

7.3. The Bitwise XOR Operator
The bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) operator (^) returns the bit-by-bit XOR of input values:
7.4. The Bitwise Complement Operator
The bitwise complement operator (~) is a unary operator. It returns the value’s complement representation, which inverts all bits from the input value:
7.5. The Left Shift Operator
Shift operators shift the bits to the left or right by the given number of times.
The left shift operator (<<) shifts the bits to the left by the number of times defined by the right-hand side operand. After the left shift, the empty space in the right is filled with 0.
Next, let’s left shift the number 12 twice:
n << x has the same effect of multiplying the number n with x power of two.
7.6. The Signed Right Shift Operator
The signed right shift operator (>>) shifts the bits to the right by the number of times defined by the right-hand side operand and fills 0 on voids left as a result.
We should note that the leftmost position after the shifting depends on the sign extension .
Next, let’s do “signed right shift” twice on the numbers 12 and -12 to see the difference:
As the second example above shows, if the number is negative, the leftmost position after each shift will be set by the sign extension.
n >> x has the same effect of dividing the number n by x power of two.
7.7. The Unsigned Right Shift Operator
The unsigned right shift operator (>>>) works in a similar way as the ‘>>’ operator. The only difference is that after a shift, the leftmost bit is set to 0 .
Next, let’s unsigned right shift twice on the numbers 12 and -12 to see the difference:
As we can see in the second example above, the >>> operator fills voids on the left with 0 irrespective of whether the number is positive or negative .
8. The “ instanceof ” Operator
Sometimes, when we have an object, we would like to test if it’s an instance of a given type . The “ instanceof ” operator can help us to do it:
9. Assignment Operators
We use assignment operators to assign values to variables. Next, let’s see which assignment operators we can use in Java.
9.1. The Simple Assignment Operator
The simple assignment operator (=) is a straightforward but important operator in Java. Actually, we’ve used it many times in previous examples. It assigns the value on its right to the operand on its left:
9.2. Compound Assignments
We’ve learned arithmetic operators. We can combine the arithmetic operators with the simple assignment operator to create compound assignments.
For example, we can write “ a = a + 5 ” in a compound way: “ a += 5 “.
Finally, let’s walk through all supported compound assignments in Java through examples:
10. Conclusion
Java provides many groups of operators for different functionalities. In this article, we’ve passed through the operators in Java.
Looking for the ideal Linux distro for running modern Spring apps in the cloud?
Meet Alpaquita Linux : lightweight, secure, and powerful enough to handle heavy workloads.
This distro is specifically designed for running Java apps . It builds upon Alpine and features significant enhancements to excel in high-density container environments while meeting enterprise-grade security standards.
Specifically, the container image size is ~30% smaller than standard options, and it consumes up to 30% less RAM:
>> Try Alpaquita Containers now.
Just published a new writeup on how to run a standard Java/Boot application as a Docker container, using the Liberica JDK on top of Alpaquita Linux:
>> Spring Boot Application on Liberica Runtime Container.
Explore the secure, reliable, and high-performance Test Execution Cloud built for scale. Right in your IDE:
Basically, write code that works the way you meant it to.
AI is all the rage these days, but for very good reason. The highly practical coding companion, you'll get the power of AI-assisted coding and automated unit test generation . Machinet's Unit Test AI Agent utilizes your own project context to create meaningful unit tests that intelligently aligns with the behavior of the code.
Get started with Spring Boot and with core Spring, through the Learn Spring course:

- Enterprise Java
- Web-based Java
- Data & Java
- Project Management
- Visual Basic
- Ruby / Rails
- Java Mobile
- Architecture & Design
- Open Source
- Web Services

Java provides many types of operators to perform a variety of calculations and functions, such as logical , arithmetic , relational , and others. With so many operators to choose from, it helps to group them based on the type of functionality they provide. This programming tutorial will focus on Java’s numerous a ssignment operators.
Before we begin, however, you may want to bookmark our other tutorials on Java operators, which include:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise and Shift Operators
Assignment Operators in Java
As the name conveys, assignment operators are used to assign values to a variable using the following syntax:
The left side operand of the assignment operator must be a variable, whereas the right side operand of the assignment operator may be a literal value or another variable. Moreover, the value or variable on the right side must be of the same data type of the operand on the left side. Otherwise, the compiler will raise an error. Assignment operators have a right to left associativity in that the value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left. Therefore, the right-hand side variable must be declared before assignment.
You can learn more about variables in our programming tutorial: Working with Java Variables .
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound .
The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( = ) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left.
Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator in addition to the equals ( = ) sign.
Equals Operator (=) Java Example
First, let’s learn to use the one-and-only simple assignment operator – the Equals ( = ) operator – with the help of a Java program. It includes two assignments: a literal value to num1 and the num1 variable to num2 , after which both are printed to the console to show that the values have been assigned to the numbers:
The += Operator Java Example
A compound of the + and = operators, the += adds the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right before assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here is some sample code to demonstrate how to use the += operator in Java:
The -= Operator Java Example
Made up of the – and = operators, the -= first subtracts the variable’s value on the right from the current value of the variable on the left before assigning the result to the operand on the left. We can see it at work below in the following code example showing how to decrement in Java using the -= operator:
The *= Operator Java Example
This Java operator is comprised of the * and = operators. It operates by multiplying the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here’s a program that shows the *= operator in action:
The /= Operator Java Example
A combination of the / and = operators, the /= Operator divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the quotient to the operand on the left. Here is some example code showing how to use the /= operator in Java:
%= Operator Java Example
The %= operator includes both the % and = operators. As seen in the program below, it divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the remainder to the operand on the left:
Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators in Java
The Bitwise and Shift Operators that we just recently covered can also be utilized in compound form as seen in the list below:
- &= – Compound bitwise Assignment operator.
- ^= – Compound bitwise ^ assignment operator.
- >>= – Compound right shift assignment operator.
- >>>= – Compound right shift filled 0 assignment operator.
- <<= – Compound left shift assignment operator.
The following program demonstrates the working of all the Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators :
Final Thoughts on Java Assignment Operators
This programming tutorial presented an overview of Java’s simple and compound assignment Operators. An essential building block to any programming language, developers would be unable to store any data in their programs without them. Though not quite as indispensable as the equals operator, compound operators are great time savers, allowing you to perform arithmetic and bitwise operations and assignment in a single line of code.
Read more Java programming tutorials and guides to software development .
Get the Free Newsletter!
Subscribe to Developer Insider for top news, trends & analysis
Latest Posts
What is the role of a project manager in software development, how to use optional in java, overview of the jad methodology, microsoft project tips and tricks, how to become a project manager in 2023, related stories, understanding types of thread synchronization errors in java, understanding memory consistency in java threads.

In general-purpose programming, certain operators tend to appear more frequently than others; for example, the assignment operator " = " is far more common than the unsigned right shift operator " >>> ". With that in mind, the following discussion focuses first on the operators that you're most likely to use on a regular basis, and ends focusing on those that are less common. Each discussion is accompanied by sample code that you can compile and run. Studying its output will help reinforce what you've just learned.
About Oracle | Contact Us | Legal Notices | Terms of Use | Your Privacy Rights
Copyright © 1995, 2022 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
01 Career Opportunities
02 beginner, 03 intermediate, 04 questions, 05 training programs, assignment operator in java, java online course free with certificate (2024), assignment operators in java: an overview, what are the assignment operators in java, types of assignment operators in java, 1. simple assignment operator (=):, explanation, 2. addition assignment operator (+=) :, 3. subtraction operator (-=):, 4. multiplication operator (*=):, 5. division operator (/=):, 6. modulus assignment operator (%=):, example of assignment operator in java, q1. can i use multiple assignment operators in a single statement, q2. are there any other compound assignment operators in java, q3. how many types of assignment operators, live classes schedule.
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast | |
| Filling Fast |
About Author
- ▼Java Tutorial
- Introduction
- Java Program Structure
- Java Primitive data type
- ▼Development environment setup
- Download and Install JDK, Eclipse (IDE)
- Compiling, running and debugging Java programs
- ▼Declaration and Access control
- Class, methods, instance variables
- Java Packages
- ▼OOPS Concepts
- Java Object Oriented Programming concepts
- Is-A and Has-A relationship
- ▼Assignments
- Arrays - 2D array and Multi dimension array
- Wrapper classes
- ▼Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Arithmetic Operator
- Conditional Operator
- Logical Operator
- ▼Flow Control
- Switch Satement
- While and Do loop
- Java Branching Statements
- ▼Exceptions
- Handling Exceptions
- Checked and unchecked
- Custom Exception
- Try with resource feature of Java 7
- ▼String Class
- String Class
- Important methods of String class with example
- String buffer class and string builder class
- ▼File I/O and serialization
- File Input and Output
- Reading file
- Writing file
- Java Property File Processing
- Java Serialization
- ▼Java Collection
- Java Collection Framework
- Java ArrayList and Vector
- Java LinkedList Class
- Java HashSet
- Java TreeSet
- Java Linked HashSet
- Java Utility Class
- ▼Java Thread
- Java Defining, Instantiating and Starting Thread
- Java Thread States and Transitions
- Java Thread Interaction
- Java Code Synchronization
- ▼Java Package
- ▼Miscellaneous
- Garbage Collection in Java
- BigDecimal Method
Java Assignment Operators
Description.
Assigning a value to a variable seems straightforward enough; you simply assign the stuff on the right side of the '= 'to the variable on the left. Below statement 1 assigning value 10 to variable x and statement 2 is creating String object called name and assigning value "Amit" to it.
Assignment can be of various types. Let’s discuss each in detail.
Primitive Assignment:
The equal (=) sign is used for assigning a value to a variable. We can assign a primitive variable using a literal or the result of an expression.
Primitive Casting
Casting lets you convert primitive values from one type to another. We need to provide casting when we are trying to assign higher precision primitive to lower precision primitive for example If we try to assign int variable (which is in the range of byte variable) to byte variable then the compiler will throw an exception called "possible loss of precision". Eclipse IDE will suggest the solution as well as shown below. To avoid such problem we should use type casting which will instruct compiler for type conversion.
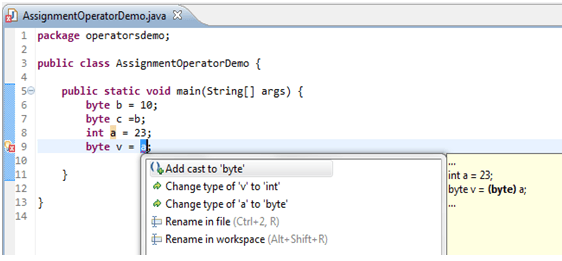
For cases where we try to assign smaller container variable to larger container variables we do not need of explicit casting. The compiler will take care of those type conversions. For example, we can assign byte variable or short variable to an int without any explicit casting.
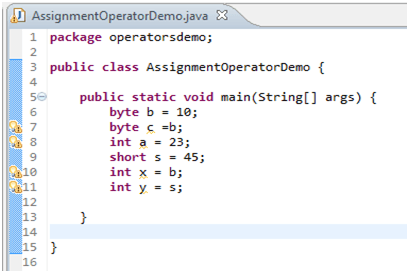
Assigning Literal that is too large for a variable
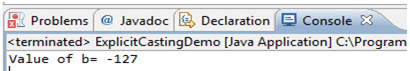
When we try to assign a variable value which is too large (or out of range ) for a primitive variable then the compiler will throw exception “possible loss of precision” if we try to provide explicit cast then the compiler will accept it but narrowed down the value using two’s complement method. Let’s take an example of the byte which has 8-bit storage space and range -128 to 127. In below program we are trying to assign 129 literal value to byte primitive type which is out of range for byte so compiler converted it to -127 using two’s complement method. Refer link for two’s complement calculation (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two's_complement)
Java Code: Go to the editor
Reference variable assignment
We can assign newly created object to object reference variable as below
First line will do following things,
- Makes a reference variable named s of type String
- Creates a new String object on the heap memory
- Assigns the newly created String object to the reference variables
You can also assign null to an object reference variable, which simply means the variable is not referring to any object. The below statement creates space for the Employee reference variable (the bit holder for a reference value) but doesn't create an actual Employee object.
Compound Assignment Operators
Sometime we need to modify the same variable value and reassigned it to a same reference variable. Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as:
The += is called the addition assignment operator. Other shorthand operators are shown below table
| Operator | Name | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| += | Addition assignment | i+=5; | i=i+5 |
| -= | Subtraction assignment | j-=10; | j=j-10; |
| *= | Multiplication assignment | k*=2; | k=k*2; |
| /= | Division assignment | x/=10; | x=x/10; |
| %= | Remainder assignment | a%=4; | a=a%4; |
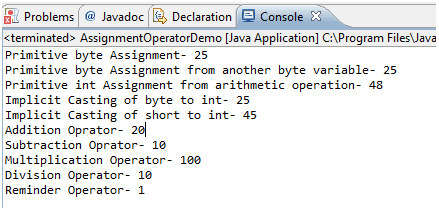
Below is the sample program explaining assignment operators:
- Assigning a value to can be straight forward or casting.
- If we assign the value which is out of range of variable type then 2’s complement is assigned.
- Java supports shortcut/compound assignment operator.
Java Code Editor:
Previous: Wrapper classes Next: Arithmetic Operator
Follow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics

- Basics of Java
- ➤ Java Introduction
- ➤ History of Java
- ➤ Getting started with Java
- ➤ What is Path and Classpath
- ➤ Checking Java installation and Version
- ➤ Syntax in Java
- ➤ My First Java Program
- ➤ Basic terms in Java Program
- ➤ Runtime and Compile time
- ➤ What is Bytecode
- ➤ Features of Java
- ➤ What is JDK JRE and JVM
- ➤ Basic Program Examples
- Variables and Data Types
- ➤ What is Variable
- ➤ Types of Java Variables
- ➤ Naming conventions for Identifiers
- ➤ Data Type in Java
- ➤ Mathematical operators in Java
- ➤ Assignment operator in Java
- ➤ Arithmetic operators in Java
- ➤ Unary operators in Java
- ➤ Conditional and Relational Operators
- ➤ Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators
- ➤ Operator Precedence
- ➤ Overflow Underflow Widening Narrowing
- ➤ Variable and Data Type Programs
- Control flow Statements
- ➤ Java if and if else Statement
- ➤ else if and nested if else Statement
- ➤ Java for Loop
- ➤ Java while and do-while Loop
- ➤ Nested loops
- ➤ Java break Statement
- ➤ Java continue and return Statement
- ➤ Java switch Statement
- ➤ Control Flow Program Examples
- Array and String in Java
- ➤ Array in Java
- ➤ Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- ➤ for-each loop in java
- ➤ Java String
- ➤ Useful Methods of String Class
- ➤ StringBuffer and StringBuilder
- ➤ Array and String Program Examples
- Classes and Objects
- ➤ Classes in Java
- ➤ Objects in Java
- ➤ Methods in Java
- ➤ Constructors in Java
- ➤ static keyword in Java
- ➤ Call By Value
- ➤ Inner/nested classes in Java
- ➤ Wrapper Classes
- ➤ Enum in Java
- ➤ Initializer blocks
- ➤ Method Chaining and Recursion
- Packages and Interfaces
- ➤ What is package
- ➤ Sub packages in java
- ➤ built-in packages in java
- ➤ Import packages
- ➤ Access modifiers
- ➤ Interfaces in Java
- ➤ Key points about Interfaces
- ➤ New features in Interfaces
- ➤ Nested Interfaces
- ➤ Structure of Java Program
- OOPS Concepts
- ➤ What is OOPS
- ➤ Inheritance in Java
- ➤ Inheritance types in Java
- ➤ Abstraction in Java
- ➤ Encapsulation in Java
- ➤ Polymorphism in Java
- ➤ Runtime and Compile-time Polymorphism
- ➤ Method Overloading
- ➤ Method Overriding
- ➤ Overloading and Overriding Differences
- ➤ Overriding using Covariant Return Type
- ➤ this keyword in Java
- ➤ super keyword in Java
- ➤ final keyword in Java
Assignment Operator in Java with Example
Assignment operator is one of the simplest and most used operator in java programming language. As the name itself suggests, the assignment operator is used to assign value inside a variable. In java we can divide assignment operator in two types :
- Assignment operator or simple assignment operator
- Compound assignment operators
What is assignment operator in java
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand(variable) on its left side. For example :
The left-hand side of an assignment operator must be a variable while the right side of it should be a value which can be in the form of a constant value, a variable name, an expression, a method call returning a compatible value or a combination of these.
The value at right side of assignment operator must be compatible with the data type of left side variable, otherwise compiler will throw compilation error. Following are incorrect assignment :
Another important thing about assignment operator is that, it is evaluated from right to left . If there is an expression at right side of assignment operator, it is evaluated first then the resulted value is assigned in left side variable.
Here in statement int x = a + b + c; the expression a + b + c is evaluated first, then the resulted value( 60 ) is assigned into x . Similarly in statement a = b = c , first the value of c which is 30 is assigned into b and then the value of b which is now 30 is assigned into a .
The variable at left side of an assignment operator can also be a non-primitive variable. For example if we have a class MyFirstProgram , we can assign object of MyFirstProgram class using = operator in MyFirstProgram type variable.
Is == an assignment operator ?
No , it's not an assignment operator, it's a relational operator used to compare two values.
Is assignment operator a binary operator
Yes , as it requires two operands.
Assignment operator program in Java
a = 2 b = 2 c = 4 d = 4 e = false
Java compound assignment operators
The assignment operator can be mixed or compound with other operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication etc. We call such assignment operators as compound assignment operator. For example :
Here the statement a += 10; is the short version of a = a + 10; the operator += is basically addition compound assignment operator. Similarly b *= 5; is short version of b = b * 5; the operator *= is multiplication compound assignment operator. The compound assignment can be in more complex form as well, like below :
List of all assignment operators in Java
The table below shows the list of all possible assignment(simple and compound) operators in java. Consider a is an integer variable for this table.
| Operator | Example | Same As |
|---|---|---|
| = | a = 10 | a = 10 |
| += | a += 5 | a = a + 5 |
| -= | a -= 3 | a = a - 3 |
| *= | a *= 6 | a = a * 6 |
| /= | a /= 5 | a = a / 5 |
| %= | a %= 7 | a = a % 7 |
| &= | a &= 3 | a = a & 3 |
| |= | a |= 3 | a = a | 3 |
| ^= | a ^= 2 | a = a ^ 2 |
| >>= | a >>= 3 | a = a >> 3 |
| >>>= | a >>>= 3 | a = a >>> 3 |
| <<= | a <<= 2 | a = a << 2 |
How many assignment operators are there in Java ?
Including simple and compound assignment we have total 12 assignment operators in java as given in above table.
What is shorthand operator in Java ?
Shorthand operators are nothing new they are just a shorter way to write something that is already available in java language. For example the code a += 5 is shorter way to write a = a + 5 , so += is a shorthand operator. In java all the compound assignment operator(given above) and the increment/decrement operators are basically shorthand operators.
Compound assignment operator program in Java
a = 20 b = 80 c = 30 s = 64 s2 = 110 b2 = 15
What is the difference between += and =+ in Java?
An expression a += 1 will result as a = a + 1 while the expression a =+ 1 will result as a = +1 . The correct compound statement is += , not =+ , so do not use the later one.

- Java Arrays
- Java Strings
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
- Java Multithreading
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
- Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
Compound assignment operators in Java
Compound-assignment operators provide a shorter syntax for assigning the result of an arithmetic or bitwise operator. They perform the operation on the two operands before assigning the result to the first operand. The following are all possible assignment operator in java:
Implementation of all compound assignment operator
Rules for resolving the Compound assignment operators
At run time, the expression is evaluated in one of two ways.Depending upon the programming conditions:
- First, the left-hand operand is evaluated to produce a variable. If this evaluation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason; the right-hand operand is not evaluated and no assignment occurs.
- Otherwise, the value of the left-hand operand is saved and then the right-hand operand is evaluated. If this evaluation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason and no assignment occurs.
- Otherwise, the saved value of the left-hand variable and the value of the right-hand operand are used to perform the binary operation indicated by the compound assignment operator. If this operation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason and no assignment occurs.
- Otherwise, the result of the binary operation is converted to the type of the left-hand variable, subjected to value set conversion to the appropriate standard value set, and the result of the conversion is stored into the variable.
- First, the array reference sub-expression of the left-hand operand array access expression is evaluated. If this evaluation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason; the index sub-expression (of the left-hand operand array access expression) and the right-hand operand are not evaluated and no assignment occurs.
- Otherwise, the index sub-expression of the left-hand operand array access expression is evaluated. If this evaluation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason and the right-hand operand is not evaluated and no assignment occurs.
- Otherwise, if the value of the array reference sub-expression is null, then no assignment occurs and a NullPointerException is thrown.
- Otherwise, the value of the array reference sub-expression indeed refers to an array. If the value of the index sub-expression is less than zero, or greater than or equal to the length of the array, then no assignment occurs and an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown.
- Otherwise, the value of the index sub-expression is used to select a component of the array referred to by the value of the array reference sub-expression. The value of this component is saved and then the right-hand operand is evaluated. If this evaluation completes abruptly, then the assignment expression completes abruptly for the same reason and no assignment occurs.
Examples : Resolving the statements with Compound assignment operators
We all know that whenever we are assigning a bigger value to a smaller data type variable then we have to perform explicit type casting to get the result without any compile-time error. If we did not perform explicit type-casting then we will get compile time error. But in the case of compound assignment operators internally type-casting will be performed automatically, even we are assigning a bigger value to a smaller data-type variable but there may be a chance of loss of data information. The programmer will not responsible to perform explicit type-casting. Let’s see the below example to find the difference between normal assignment operator and compound assignment operator. A compound assignment expression of the form E1 op= E2 is equivalent to E1 = (T) ((E1) op (E2)), where T is the type of E1, except that E1 is evaluated only once.
For example, the following code is correct:
and results in x having the value 7 because it is equivalent to:
Because here 6.6 which is double is automatically converted to short type without explicit type-casting.
Refer: When is the Type-conversion required?
Explanation: In the above example, we are using normal assignment operator. Here we are assigning an int (b+1=20) value to byte variable (i.e. b) that’s results in compile time error. Here we have to do type-casting to get the result.
Explanation: In the above example, we are using compound assignment operator. Here we are assigning an int (b+1=20) value to byte variable (i.e. b) apart from that we get the result as 20 because In compound assignment operator type-casting is automatically done by compile. Here we don’t have to do type-casting to get the result.
Reference: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se7/html/jls-15.html#jls-15.26.2
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Java-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
variable operator value; Types of Assignment Operators in Java. The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are: 1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
Java Comparison Operators. Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. The return value of a comparison is either true or false. These values are known as Boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If ...
The Simple Assignment Operator. One of the most common operators that you'll encounter is the simple assignment operator "=". You saw this operator in the Bicycle class; it assigns the value on its right to the operand on its left: ... The Java programming language provides operators that perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and ...
To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side. Example: int x = 10; int x = 10; In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10.
Java Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used in Java to assign values to variables. For example, int age; age = 5; Here, = is the assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left. ... 6. Java Bitwise Operators. Bitwise operators in Java are used to perform operations on individual bits. For example,
Java Assignment Operators. The Java Assignment Operators are used when you want to assign a value to the expression. The assignment operator denoted by the single equal sign =. In a Java assignment statement, any expression can be on the right side and the left side must be a variable name. For example, this does not mean that "a" is equal to ...
The simple assignment operator (=) is a straightforward but important operator in Java. Actually, we've used it many times in previous examples. It assigns the value on its right to the operand on its left: int seven = 7; 9.2. Compound Assignments
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound. The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( =) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left. Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator ...
The Java Assignment operators are used to assign the values to the declared variables. The equals ( = ) operator is the most commonly used Java assignment operator. For example: int i = 25; The table below displays all the assignment operators in the Java programming language. Operators.
Java's basic assignment operator is a single equals-to (=) sign that assigns the right-hand side value to the left-hand side operand. On left side of the assignment operator there must be a variable that can hold the value assigned to it. Assignment operator operates on both primitive and reference types. It has the following syntax: var ...
Learning the operators of the Java programming language is a good place to start. Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result. As we explore the operators of the Java programming language, it may be helpful for you to know ahead of time which operators have the highest ...
3. Assignment Operator '=' Assignment operator is used to assign a value to any variable. It has right-to-left associativity, i.e. value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left, and therefore right-hand side value must be declared before using it or should be a constant.
There are mainly two types of assignment operators in Java, which are as follows: Simple Assignment Operator ; We use the simple assignment operator with the "=" sign, where the left side consists of an operand and the right side is a value. The value of the operand on the right side must be of the same data type defined on the left side.
Assignment Operators in Java: An Overview. We already discussed the Types of Operators in the previous tutorial Java. In this Java tutorial, we will delve into the different types of assignment operators in Java, and their syntax, and provide examples for better understanding.Because Java is a flexible and widely used programming language. Assignment operators play a crucial role in ...
Compound Assignment Operators. Sometime we need to modify the same variable value and reassigned it to a same reference variable. Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as: i +=8; //This is same as i = i+8; The += is called the addition ...
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand (variable) on its left side. For example : int a = 10; // value 10 is assigned in variable a double d = 20.25; // value 20.25 is assigned in variable d char c = 'A'; // Character A is assigned in variable c. a = 20 ...
Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to ...
The compound assignment operators are right to left associated. We might expect the result to be 1. But the actual result is 0. Because of the associativity. The expression on the right is evaluated first and then the compound assignment operator is applied. $ java Associativity.java 0 0 0 0 0 Java ternary operator
5. Because your sec statement will be evaluated as x = x * (2+5); x = 10; x *= 2+5; x = x * (2+5); While in the first case, its normal left to right precedence.Java guarantees that all operands of an operator are fully evaluated before the operator is applied. A compound assignment operator has the following syntax: <variable> <op>= <expression>.
Let's look at the various operators that Java has to provide under the arithmetic operators. Now let's look at each one of the arithmetic operators in Java: 1. Addition (+): This operator is a binary operator and is used to add two operands. Syntax: num1 + num2. Example: num1 = 10, num2 = 20. sum = num1 + num2 = 30.
a |= b; is the same as. a = (a | b); It calculates the bitwise OR of the two operands, and assigns the result to the left operand. To explain your example code: for (String search : textSearch.getValue()) matches |= field.contains(search); I presume matches is a boolean; this means that the bitwise operators behave the same as logical operators.
The |= is a compound assignment operator ( JLS 15.26.2) for the boolean logical operator | ( JLS 15.22.2 ); not to be confused with the conditional-or || ( JLS 15.24 ). There are also &= and ^= corresponding to the compound assignment version of the boolean logical & and ^ respectively. In other words, for boolean b1, b2, these two are ...
Compound-assignment operators provide a shorter syntax for assigning the result of an arithmetic or bitwise operator. They perform the operation on the two operands before assigning the result to the first operand. The following are all possible assignment operator in java: 1. += (compound addition assignment operator) 2.
JavaScript (JS) is a lightweight interpreted (or just-in-time compiled) programming language with first-class functions. While it is most well-known as the scripting language for Web pages, many non-browser environments also use it, such as Node.js, Apache CouchDB and Adobe Acrobat. JavaScript is a prototype-based, multi-paradigm, single-threaded, dynamic language, supporting object-oriented ...