
Complete Guide on Article Analysis (with 1 Analysis Example)
In this dynamic guide, we will help you to understand what is a critical analysis writing and how to write a good critical analysis paper that fits news articles and research journals.
Here is a flow of our guide:
- What is Critical Analysis Writing?
How to Analyze an Article
How to write a critical analysis, how to analyze a news article, how to analyze research articles, article analysis template: follow for a better writing, example of an article critical analysis, what is a critical analysis writing.
Critical analysis writing means evaluation of author’s work where it can be a news article analysis, a research journal article, a book, transcript of a conference or even a movie.
In most cases, it has an aim to increase reader’s understanding of an article’s thesis and the contents. A critical analysis article writing is subjective because it expresses writer’s opinion, analysis or evaluation of a given text. In order to understand that you are working with a critical analysis, you have to remember that analysis means breaking down and studying of the parts. As already mentioned, there can be many types of articles to analyze. You have to understand what type of an article you are going to work with, so you can come up with a right tone and format of your future essay.
Remember that when you analyze your paper, your main task is to make sure that your audience understands the major points without much difficulty. You have to show your critical thinking skills and make judgments about the subject as you analyze an article, so you can come up with clear opinion and conclusions.
When you read an article or a news report, find and identify author’s main points and the thesis. Analyze the structure of the article step-by-step as you read. Always give yourself enough time to read through the article. If writing is “ a must ” for you as you read, you can start with an outline draft first where you mention the most important points. In most cases, look for a purpose of author’s written work. There can be several purposes of writing:
- Inform the reader: look if the article has a clear structure and whether it provides sufficient evidence supported by facts and additional research.
- Persuade the reader: look to find if the author has presented logical reasoning and counter-arguments, opposite opinions to persuade someone about particular opinion.
- Entertain the reader: see what emotions are caused by the article and how does it personally influence and inspire you.
At the end of the day, Linda resolves her Chicago citation problems — being mentored by a Professional Nerd. Let Nerdify find your perfect match using AI! 🤖
Start with reading an article in question to help yourself understand author’s opinion and a purpose. Next, start working with an outline that will guide you through the main ideas as you prepare to write a critical analysis. Make sure to:
- Try to avoid speaking of your ideas by starting with “ I think ”, “ I believe ” and “ In my opinion ” as the subject of your critical analysis is a subject, not your personality.
- Always make sure to introduce the subject in your paper, as the audience may not be aware of what you are writing of.
- Focus on both strengths and weaknesses of the author by trying to follow the same structure used.
- Always use evidence and the facts to support your claims and presented ideas.
- Use critical analysis writing to tell of article’s value and relevance.
- Always remain open-minded and unbiased as you analyze, read, and write your paper.
Since the news article has a purpose to inform the audience, it is important to understand that the news reports are time-sensitive and usually relate to particular events and incidents. When working with the news article critical analysis, look out for the following:
- Check the headline of the news article and include it in your thesis
- Focus on structure, voice of the article, tone, and rhetoric
- Examine the structure of the news report to see how much of a personal opinion is included
- Look for metaphors, alliterations, and allegories to understand author’s true opinion.
- Determine the tone of the article by trying to identify the news report with one word. It can be critical, angry, passionate, satirical or even neutral.
When you have to analyze research articles, you should make sure that you:
- Describe the article briefly and explain it to the reader what the article is about. While you are reading the article, you have to look for details that identify the topic of the article.
- Identify the purpose of the author or a reason why the author believes that a topic of research is relevant and important.
- Identify the research methods and try to identify whether they appear to be suitable or not.
- Check and provide evidence and facts as you speak of a research article and back it up with your own examples.
- Check (and state, if applicable) whether the author refers to other research articles and if similar studies have been done. If yes, it should be mentioned and explained in your work as you speak of research methods and evidence.
- Analyze the sources that were used by the author to get a better idea of how the author has formed his or her thoughts. It will help you to analyze research articles with greater professional competence and a higher level of confidence.
To make it easier for you to write a critical analysis essay, we have a helpful analysis writing template that will guide you through the most critical points. This helpful writing template will make sure that you are following the right format, structure, and do not miss anything important!
Introduction
- State the title of the work that you analyze, specify author’s name and the date of publication, if available.
- Outline the main ideas of a news report or a research journal article to identify the author’s thesis.
- Come up with your own thesis statement and talk briefly of your main vision and ideas related to original paper.
- Keep it short! After all, it is an introduction!
Examples to Follow : The “Things They Carried” by Tim O’Brien is an educational and a self-critical story because the author makes a point about… The article “Racial Prejudice in Pretoria, South Africa” by Joost Van Der Graaf provides an unbiased insight on racial relationships in South Africa in a unique manner because the author has studied…
- Provide a brief outline of the main ideas presented in your research article, news report, book or a movie.
- This is an actual part that should answer to the questions what, why, who, when and how exactly .
- Discuss the structure of an article that you are working with, talk about the style and the point of view presented by the author.
Examples to Follow: This article tells about… An academic environment where the research has taken place is… The main subject in the news report is telling a story of his own vision of a financial crisis… The theme of a research article focuses on… The author clearly argues that… The research makes an important point of a difference between home-schooling and public education through the lens of … The authors conclude that…
- State what you like and what you do not like about the article or a news report in a critical way.
- Explain your own ideas by offering specific examples from an actual article, a news report or a book.
- Next, you have to state and explain whether the author has achieved his or her intentions and goals or not.
You have to use analysis to see whether an original journal article or a paper is focused, clear, unbiased, informative, and persuasive enough. Another important point to check is whether an article directs to appropriate and specific audience and if it really meets intentions and a purpose. Check for correct conclusions and summing up of a research being done.
a) Restate your thesis in a different way, using new words. b) Summarize your main thesis and ideas presented, using core points in a different tone. c) If necessary and if appropriate, you should make a call to action for your target audience.
Examples to follow:
This article is important because it provides a unique… This article has a biased attitude because the author only focuses on… Instead of turning to real-life examples and the actual statistics, the author of the news report only makes assumptions…
Now let us move on to an actual critical analysis writing example of a research article, so you can learn and start with your own work!
We want to offer you a real-life critical analysis example of a research article. Therefore, we did an actual work for you, based on an important topic of virtue ethics approach and morals in the field of healthcare.
An original article can be accessed here .
“A Virtue Ethics Approach to Moral Dilemmas in Medicine” Critical Analysis
“A Virtue Ethics Approach to Moral Dilemmas in Medicine” article by Patricia Gardiner, published in 2003 in Journal of Medical Ethics, is an example of innovative study of the role and place of morals and the virtue ethics in medicine and nursing practices. While majority of complex moral dilemmas are analyzed through the lens of consequences and the facts, the author takes a different approach where the virtue ethics play a key role in analysis and strategic thinking. In other words, the author tries to make it clear to the audience that once the principles of a person or an organization enter a conflict stage, there is always bias that forces an individual to choose the factors that should or should not dominate. Considering emotional and moral elements of an equation, Gardiner turns to virtue ethics as to a framework that focuses on the character of a moral agent itself instead of being limited by studying the rightfulness of an action alone.
Turning to analysis of two different moral dilemmas, the author walks an extra mile to illustrate the ways how different scenarios can be enhanced by the virtue ethics in such complex environments as healthcare. While the subject may appear to be philosophical to general audience, Gardiner approaches moral dilemmas as a general practitioner, which makes her opinion less biased from practical perspective. Still, turning to philosophy, the research article studies the place of a reason and analyzes the role of emotion on a daily basis. It allows the audience to see diverse circumstances and apply their emotions in practice. An important role is given to motivation because a virtuous person approaches a situation where internal attitudes, professional skills, and a reasoning should come in balance. The cases presented by the author, while familiar to most of us, speak of moral dilemmas in healthcare from a different point. Even though Jehovah’s Witness case has legislation’s element, the author speaks of a moral side and the virtue ethics. The same relates to the case of a doctor where professional judgment collides with anxiety, stress, and personal experiences. What kind of a moral choice should be made? The article helps a reader to understand decency and professionalism from a moral point that replaces consequentialism and deontology.
It is important to understand that Gardiner does not try to persuade a reader that virtue ethics is a superior solution or an only way to deal with moral dilemmas. One of the differences with the virtue ethics is that it recognizes emotional constituent as an integral and an important element of moral perceptions. It considers the role of motivation as important to provide a space for unbiased human interactions. Finally, it provides additional flexibility and allows a person to look for creative solutions in moral and ethically-complex situations where not all the parties involved can be satisfied. The article makes an important call for every professional in the field of healthcare to look beyond usual solutions used on a daily basis and implement such virtuous personal and professional characteristics as honesty, courage, empathy, integrity, and an ability to follow one’s obligations and responsibilities in a natural way.
If you enjoyed this article, please, 👏 — it’s free. Share it so that others can find it too.
Study smarter, not harder. Learn more from Nerdify today:
Learn How to Quote a Quote (Lots of Examples)
Hey there, dear reader you might be here right now because you need help in learning how to quote., 3 definition essay examples and 50 topics to choose from, besides 3 excellent definition essay examples, you’ll find extremely helpful tips and tricks for writing definition…, on how i nailed chi-square test with my nerd | nerdify blog, we've got a feedback story from our grateful customer who decided to share his success story and help students who….
gonerdify.com

Written by Nerdify
Articles, guidelines, examples and samples to improve your writing skills. We share — you learn. https://gonerdify.com/
Text to speech
ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
How To Critically Analyse An Article – Become A Savvy Reader
By Laura Brown on 22nd September 2023
In the current academic scenario, knowing how to analyse an article critically is essential to attain stability and strength. It’s about reading between the lines, questioning what you encounter, and forming informed opinions based on evidence and sound reasoning.
- To critically analyse an article, read it thoroughly to grasp the author’s main points.
- Evaluate the evidence and arguments presented, checking for credibility and logical consistency.
- Consider the article’s structure, tone, and style while also assessing its sources.
- Formulate your critical response by synthesising your analysis and constructing a well-supported argument.
Have you ever wondered how to tell if an article is good or not? It’s important when it comes to your academic superiority. Critical analysis of an article is like being a detective. You check the article closely to see if it makes sense, if the facts are correct, and if the writer is trying to trick you.
But it’s not just something for school, college or university; it’s a superpower for everyday life. It helps you find the important stuff in an article, spot when someone is trying to persuade you and understand what the writer really thinks.
Think of it as a special skill that lets you dig deep into an article, like a treasure hunt. You uncover hidden biases, find the truth, and see how the writer tries to convince you. It’s a bit like being a detective and a wizard at the same time.
Get ready to become a smart reader. This guide will show you how to use this superpower to make sense of the information around us in just 8 simple steps.
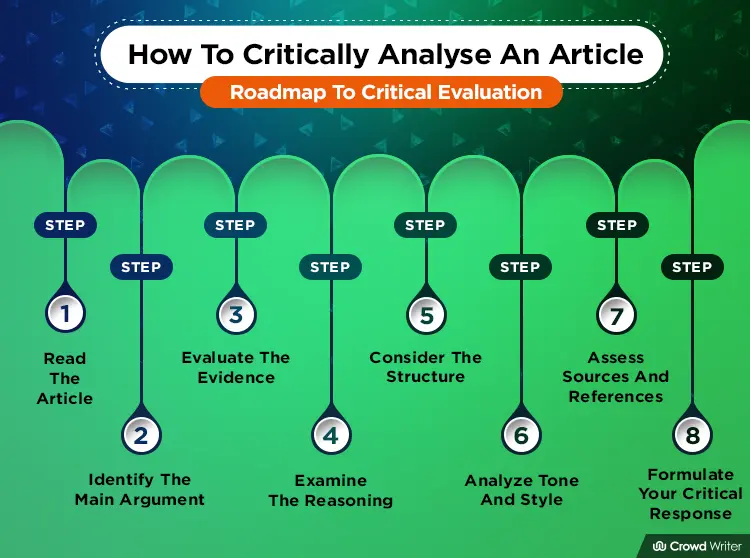
Step 1: Read the Article
Before embarking on the journey to analyse an article critically, it is paramount to begin with the foundational step of reading the article itself. This step lays the groundwork for a comprehensive understanding of the material, enabling you to effectively evaluate its merits and demerits.
Reading an article critically starts with setting aside distractions and immersing yourself in the text. Instead of skimming through it hurriedly, take the time to read it meticulously.
To truly grasp the article’s essence, you must consider both its content and context. Content refers to the information and ideas presented within the article, while context encompasses the circumstances in which it was written.
- Why was this article written?
- Who is the intended audience?
- When was it published, and what was happening in the world at that time?
- What is the author’s background or expertise in the subject matter?
As you read, do not rely solely on your memory to retain key points and insights. Taking notes is an invaluable practice during this phase. Record significant ideas, quotes, and statistics that catch your attention.
Your initial impressions of the article can offer valuable insights into your subjective response. If a particular passage elicits a strong emotional reaction, make a note of it. Identifying your emotional responses can help you later in the analysis process when considering your own biases and reactions to the author’s arguments.
Step 2: Identify the Main Argument
While you are up to critically analyse an article, pinpointing the central argument is akin to finding the North Star guiding you through the article’s content. Every well-crafted article should possess a clear and concise main argument or thesis, which serves as the nucleus of the author’s message. Typically situated in the article’s introduction or abstract , this argument not only encapsulates the author’s viewpoint but also functions as a roadmap for the reader, outlining what to expect in the subsequent sections.
Identifying the main argument necessitates a discerning eye. Delve into the introductory paragraphs, abstract, or the initial sections of the article to locate this pivotal statement. This argument may be explicit, explicitly stated by the author, or implicit, inferred through careful examination of the content. Once you’ve grasped the main argument, keep it at the forefront of your mind as you proceed with your analysis, it will serve as the cornerstone against which all other elements are evaluated.
Step 3: Evaluate the Evidence
In order to solely understand how to analyse an article critically, it is imperative to know that an article’s persuasive power hinges on the quality of evidence presented to substantiate its main argument. In this critical step, it’s imperative to scrutinise the evidence with a discerning eye. Look beyond the surface to assess the data, statistics, examples, and citations provided by the author. You can run it through Turnitin for a plagiarism check. These elements serve as the pillars upon which the argument stands or crumbles.
Begin by evaluating the credibility and relevance of the sources used to support the argument. Are they authoritative and trustworthy? Are they current and pertinent to the subject matter? Assess the quality of evidence by considering the reliability of the data, the objectivity of the sources, and the breadth of examples. Moreover, consider the quantity of evidence; is there enough to convincingly underpin the thesis, or does it appear lacking or selective? A well-supported argument should be built upon a solid foundation of robust evidence.
Step 4: Examine the Reasoning
Critical analysis doesn’t stop at identifying the argument and assessing the evidence; it extends to examining the underlying reasoning that connects these elements. In this step, delve deeper into the author’s logic and the structure of the argument. The goal is to identify any logical fallacies or weak assumptions that might undermine the article’s credibility.
Scrutinise the coherence and consistency of the author’s reasoning. Are there any gaps in the argument, or does it flow logically from point to point? Identify any potential biases, emotional appeals, or rhetorical strategies employed by the author. Assess whether the argument is grounded in sound principles and reasoning.
Be on the lookout for flawed deductive or inductive reasoning, and question whether the evidence truly supports the conclusions drawn . Critical thinking is pivotal here, as it allows you to gauge the strength of the article’s argumentation and identify areas where it may be lacking or vulnerable to critique.
Step 5: Consider the Structure
The structure of an article is not merely a cosmetic feature but a fundamental aspect that can profoundly influence its overall effectiveness in conveying its message. A well-organised article possesses the power to captivate readers, enhance comprehension, and amplify its impact. To harness this power effectively, it’s crucial to pay close attention to various structural elements.
- Headings and Subheadings: Examine headings and subheadings to understand the article’s structure and main themes.
- Transitions Between Sections: Observe how transitions between sections maintain or disrupt the flow of ideas.
- Logical Progression: Assess if the article logically builds upon concepts or feels disjointed.
- Use of Visual Aids: Evaluate the integration and effectiveness of visual aids like graphs and charts.
- Paragraph Organisation: Analyse paragraph structure, including clear topic sentences.
- Conclusion and Summary: Review the conclusion for a strong reiteration of the main argument and key takeaways.
In essence, the structure of an article serves as the blueprint that shapes the reader’s journey. A thoughtfully organised article not only makes it easier for readers to navigate the content but also enhances their overall comprehension and retention. By paying attention to these structural elements, you can gain a deeper understanding of the author’s message and how it is effectively conveyed to the audience.
Step 6: Analyse Tone and Style
Exploring the tone and style of an article is like deciphering the author’s hidden intentions and underlying biases. It involves looking closely at how the author has crafted their words, examining their choice of language, tone, and use of rhetorical devices . Is the tone even-handed and impartial, or can you detect signs of favouritism or prejudice? Understanding the author’s perspective in this way allows you to place their argument within a broader context, helping you see beyond the surface of the text.
When you analyse tone, consider whether the author’s language carries any emotional weight. Are they using words that evoke strong feelings, or do they maintain an objective and rational tone throughout? Furthermore, observe how the author addresses counterarguments. Are they respectful and considerate, or do they employ ad hominem attacks? Evaluating tone and style can offer valuable insights into the author’s intentions and their ability to construct a persuasive argument.
Step 7: Assess Sources and References
A critical analysis wouldn’t be complete without examining the sources and references cited within the article. These citations form the foundation upon which the author’s arguments rest. To assess the credibility of the author’s research, it’s essential to scrutinise the origins of these sources. Are they drawn from reputable, well-established journals, books, or widely recognised and trusted websites? High-quality sources reflect positively on the author’s research and strengthen the overall validity of the argument.
While staying on the journey of how to critically analyse an article, be vigilant when encountering articles that heavily rely on sources that might be considered unreliable or biased. Investigate whether the author has balanced their sources and considered diverse perspectives. A well-researched article should draw upon a variety of reputable sources to provide a well-rounded view of the topic. By assessing the sources and references, you can gauge the robustness of the author’s supporting evidence.
Step 8: Formulate Your Critical Response
Having navigated through the previous steps, it’s now your turn to construct a critical response to the article. This step involves summarising your analysis by identifying the strengths and weaknesses within the article. Do you find yourself in agreement with the main argument, or do you have reservations? Highlight the evidence that you found compelling and areas where you believe the article falls short. Your critical response serves as a valuable contribution to the ongoing discourse surrounding the topic, adding your unique perspective to the conversation. Remember that constructive criticism can lead to deeper understanding and improved future discourse.
Now, let’s be specific on two of the most analysed articles, i.e. research articles and journal articles.
How To Critically Analyse A Research Article?
A research article is a scholarly document that presents the findings of original research conducted by the author(s) and is typically published in academic journals. It follows a structured format, including sections such as an abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and references. To critically analyse a research article, you may go through the following six steps.
- Scrutinise the research question’s clarity and significance.
- Examine the appropriateness of research methods.
- Assess sample quality and data reliability.
- Evaluate the accuracy and significance of results.
- Review the discussion for supported conclusions.
- Check references for relevant and high-quality sources.
Never hesitate to ask our customer support for examples and relevant guides as you face any challenges while critically analysing a research paper .
How To Critically Analyse A Journal Article?
A journal article is a scholarly publication that presents research findings, analyses, or discussions within a specific academic or scientific field. These articles typically follow a structured format and are subject to peer review before publication. In order to critically analyse a journal article, take the following steps.
- Evaluate the article’s clarity and relevance.
- Examine the research methods and their suitability.
- Assess the credibility of data and sources.
- Scrutinise the presentation of results.
- Analyse the conclusions drawn.
- Consider the quality of references and citations.
If you have any difficulty conducting a good critical analysis, you can always ask our research paper service for help and relevant examples.
Concluding Upon How To Analyse An Article Critically
Mastering the art of analysing an article critically is a valuable skill that empowers you to navigate the vast sea of information with confidence. By following these eight steps, you can dissect articles effectively, separating reliable information from biased or poorly supported claims. Remember, critical analysis is not about tearing an article apart but understanding it deeply and thoughtfully. With practice, you’ll become a more discerning and informed reader, researcher, or student.

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.

Writing a Critical Analysis
What is in this guide, definitions, putting it together, tips and examples of critques.
- Background Information
- Cite Sources
Library Links
- Ask a Librarian
- Library Tutorials
- The Research Process
- Library Hours
- Online Databases (A-Z)
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Reserve a Study Room
- Report a Problem
This guide is meant to help you understand the basics of writing a critical analysis. A critical analysis is an argument about a particular piece of media. There are typically two parts: (1) identify and explain the argument the author is making, and (2), provide your own argument about that argument. Your instructor may have very specific requirements on how you are to write your critical analysis, so make sure you read your assignment carefully.

Critical Analysis
A deep approach to your understanding of a piece of media by relating new knowledge to what you already know.
Part 1: Introduction
- Identify the work being criticized.
- Present thesis - argument about the work.
- Preview your argument - what are the steps you will take to prove your argument.
Part 2: Summarize
- Provide a short summary of the work.
- Present only what is needed to know to understand your argument.
Part 3: Your Argument
- This is the bulk of your paper.
- Provide "sub-arguments" to prove your main argument.
- Use scholarly articles to back up your argument(s).
Part 4: Conclusion
- Reflect on how you have proven your argument.
- Point out the importance of your argument.
- Comment on the potential for further research or analysis.
- Cornell University Library Tips for writing a critical appraisal and analysis of a scholarly article.
- Queen's University Library How to Critique an Article (Psychology)
- University of Illinois, Springfield An example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article
- Next: Background Information >>
- Last Updated: Aug 23, 2024 11:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.pittcc.edu/critical_analysis
- Privacy Policy

Home » Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Critical Analysis
Definition:
Critical analysis is a process of examining a piece of work or an idea in a systematic, objective, and analytical way. It involves breaking down complex ideas, concepts, or arguments into smaller, more manageable parts to understand them better.
Types of Critical Analysis
Types of Critical Analysis are as follows:
Literary Analysis
This type of analysis focuses on analyzing and interpreting works of literature , such as novels, poetry, plays, etc. The analysis involves examining the literary devices used in the work, such as symbolism, imagery, and metaphor, and how they contribute to the overall meaning of the work.
Film Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting films, including their themes, cinematography, editing, and sound. Film analysis can also include evaluating the director’s style and how it contributes to the overall message of the film.
Art Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting works of art , such as paintings, sculptures, and installations. The analysis involves examining the elements of the artwork, such as color, composition, and technique, and how they contribute to the overall meaning of the work.
Cultural Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting cultural artifacts , such as advertisements, popular music, and social media posts. The analysis involves examining the cultural context of the artifact and how it reflects and shapes cultural values, beliefs, and norms.
Historical Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting historical documents , such as diaries, letters, and government records. The analysis involves examining the historical context of the document and how it reflects the social, political, and cultural attitudes of the time.
Philosophical Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting philosophical texts and ideas, such as the works of philosophers and their arguments. The analysis involves evaluating the logical consistency of the arguments and assessing the validity and soundness of the conclusions.
Scientific Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting scientific research studies and their findings. The analysis involves evaluating the methods used in the study, the data collected, and the conclusions drawn, and assessing their reliability and validity.
Critical Discourse Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting language use in social and political contexts. The analysis involves evaluating the power dynamics and social relationships conveyed through language use and how they shape discourse and social reality.
Comparative Analysis
This type of analysis involves examining and interpreting multiple texts or works of art and comparing them to each other. The analysis involves evaluating the similarities and differences between the texts and how they contribute to understanding the themes and meanings conveyed.
Critical Analysis Format
Critical Analysis Format is as follows:
I. Introduction
- Provide a brief overview of the text, object, or event being analyzed
- Explain the purpose of the analysis and its significance
- Provide background information on the context and relevant historical or cultural factors
II. Description
- Provide a detailed description of the text, object, or event being analyzed
- Identify key themes, ideas, and arguments presented
- Describe the author or creator’s style, tone, and use of language or visual elements
III. Analysis
- Analyze the text, object, or event using critical thinking skills
- Identify the main strengths and weaknesses of the argument or presentation
- Evaluate the reliability and validity of the evidence presented
- Assess any assumptions or biases that may be present in the text, object, or event
- Consider the implications of the argument or presentation for different audiences and contexts
IV. Evaluation
- Provide an overall evaluation of the text, object, or event based on the analysis
- Assess the effectiveness of the argument or presentation in achieving its intended purpose
- Identify any limitations or gaps in the argument or presentation
- Consider any alternative viewpoints or interpretations that could be presented
- Summarize the main points of the analysis and evaluation
- Reiterate the significance of the text, object, or event and its relevance to broader issues or debates
- Provide any recommendations for further research or future developments in the field.
VI. Example
- Provide an example or two to support your analysis and evaluation
- Use quotes or specific details from the text, object, or event to support your claims
- Analyze the example(s) using critical thinking skills and explain how they relate to your overall argument
VII. Conclusion
- Reiterate your thesis statement and summarize your main points
- Provide a final evaluation of the text, object, or event based on your analysis
- Offer recommendations for future research or further developments in the field
- End with a thought-provoking statement or question that encourages the reader to think more deeply about the topic
How to Write Critical Analysis
Writing a critical analysis involves evaluating and interpreting a text, such as a book, article, or film, and expressing your opinion about its quality and significance. Here are some steps you can follow to write a critical analysis:
- Read and re-read the text: Before you begin writing, make sure you have a good understanding of the text. Read it several times and take notes on the key points, themes, and arguments.
- Identify the author’s purpose and audience: Consider why the author wrote the text and who the intended audience is. This can help you evaluate whether the author achieved their goals and whether the text is effective in reaching its audience.
- Analyze the structure and style: Look at the organization of the text and the author’s writing style. Consider how these elements contribute to the overall meaning of the text.
- Evaluate the content : Analyze the author’s arguments, evidence, and conclusions. Consider whether they are logical, convincing, and supported by the evidence presented in the text.
- Consider the context: Think about the historical, cultural, and social context in which the text was written. This can help you understand the author’s perspective and the significance of the text.
- Develop your thesis statement : Based on your analysis, develop a clear and concise thesis statement that summarizes your overall evaluation of the text.
- Support your thesis: Use evidence from the text to support your thesis statement. This can include direct quotes, paraphrases, and examples from the text.
- Write the introduction, body, and conclusion : Organize your analysis into an introduction that provides context and presents your thesis, a body that presents your evidence and analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes your main points and restates your thesis.
- Revise and edit: After you have written your analysis, revise and edit it to ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and well-organized. Check for spelling and grammar errors, and make sure that your analysis is logically sound and supported by evidence.
When to Write Critical Analysis
You may want to write a critical analysis in the following situations:
- Academic Assignments: If you are a student, you may be assigned to write a critical analysis as a part of your coursework. This could include analyzing a piece of literature, a historical event, or a scientific paper.
- Journalism and Media: As a journalist or media person, you may need to write a critical analysis of current events, political speeches, or media coverage.
- Personal Interest: If you are interested in a particular topic, you may want to write a critical analysis to gain a deeper understanding of it. For example, you may want to analyze the themes and motifs in a novel or film that you enjoyed.
- Professional Development : Professionals such as writers, scholars, and researchers often write critical analyses to gain insights into their field of study or work.
Critical Analysis Example
An Example of Critical Analysis Could be as follow:
Research Topic:
The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance
Introduction:
The introduction of the research topic is clear and provides an overview of the issue. However, it could benefit from providing more background information on the prevalence of online learning and its potential impact on student performance.
Literature Review:
The literature review is comprehensive and well-structured. It covers a broad range of studies that have examined the relationship between online learning and student performance. However, it could benefit from including more recent studies and providing a more critical analysis of the existing literature.
Research Methods:
The research methods are clearly described and appropriate for the research question. The study uses a quasi-experimental design to compare the performance of students who took an online course with those who took the same course in a traditional classroom setting. However, the study may benefit from using a randomized controlled trial design to reduce potential confounding factors.
The results are presented in a clear and concise manner. The study finds that students who took the online course performed similarly to those who took the traditional course. However, the study only measures performance on one course and may not be generalizable to other courses or contexts.
Discussion :
The discussion section provides a thorough analysis of the study’s findings. The authors acknowledge the limitations of the study and provide suggestions for future research. However, they could benefit from discussing potential mechanisms underlying the relationship between online learning and student performance.
Conclusion :
The conclusion summarizes the main findings of the study and provides some implications for future research and practice. However, it could benefit from providing more specific recommendations for implementing online learning programs in educational settings.
Purpose of Critical Analysis
There are several purposes of critical analysis, including:
- To identify and evaluate arguments : Critical analysis helps to identify the main arguments in a piece of writing or speech and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. This enables the reader to form their own opinion and make informed decisions.
- To assess evidence : Critical analysis involves examining the evidence presented in a text or speech and evaluating its quality and relevance to the argument. This helps to determine the credibility of the claims being made.
- To recognize biases and assumptions : Critical analysis helps to identify any biases or assumptions that may be present in the argument, and evaluate how these affect the credibility of the argument.
- To develop critical thinking skills: Critical analysis helps to develop the ability to think critically, evaluate information objectively, and make reasoned judgments based on evidence.
- To improve communication skills: Critical analysis involves carefully reading and listening to information, evaluating it, and expressing one’s own opinion in a clear and concise manner. This helps to improve communication skills and the ability to express ideas effectively.
Importance of Critical Analysis
Here are some specific reasons why critical analysis is important:
- Helps to identify biases: Critical analysis helps individuals to recognize their own biases and assumptions, as well as the biases of others. By being aware of biases, individuals can better evaluate the credibility and reliability of information.
- Enhances problem-solving skills : Critical analysis encourages individuals to question assumptions and consider multiple perspectives, which can lead to creative problem-solving and innovation.
- Promotes better decision-making: By carefully evaluating evidence and arguments, critical analysis can help individuals make more informed and effective decisions.
- Facilitates understanding: Critical analysis helps individuals to understand complex issues and ideas by breaking them down into smaller parts and evaluating them separately.
- Fosters intellectual growth : Engaging in critical analysis challenges individuals to think deeply and critically, which can lead to intellectual growth and development.
Advantages of Critical Analysis
Some advantages of critical analysis include:
- Improved decision-making: Critical analysis helps individuals make informed decisions by evaluating all available information and considering various perspectives.
- Enhanced problem-solving skills : Critical analysis requires individuals to identify and analyze the root cause of a problem, which can help develop effective solutions.
- Increased creativity : Critical analysis encourages individuals to think outside the box and consider alternative solutions to problems, which can lead to more creative and innovative ideas.
- Improved communication : Critical analysis helps individuals communicate their ideas and opinions more effectively by providing logical and coherent arguments.
- Reduced bias: Critical analysis requires individuals to evaluate information objectively, which can help reduce personal biases and subjective opinions.
- Better understanding of complex issues : Critical analysis helps individuals to understand complex issues by breaking them down into smaller parts, examining each part and understanding how they fit together.
- Greater self-awareness: Critical analysis helps individuals to recognize their own biases, assumptions, and limitations, which can lead to personal growth and development.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Correlation Analysis – Types, Methods and...

Descriptive Statistics – Types, Methods and...

References in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples
33 Critical Analysis Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Critical analysis refers to the ability to examine something in detail in preparation to make an evaluation or judgment.
It will involve exploring underlying assumptions, theories, arguments, evidence, logic, biases, contextual factors, and so forth, that could help shed more light on the topic.
In essay writing, a critical analysis essay will involve using a range of analytical skills to explore a topic, such as:
- Evaluating sources
- Exploring strengths and weaknesses
- Exploring pros and cons
- Questioning and challenging ideas
- Comparing and contrasting ideas
If you’re writing an essay, you could also watch my guide on how to write a critical analysis essay below, and don’t forget to grab your worksheets and critical analysis essay plan to save yourself a ton of time:
Grab your Critical Analysis Worksheets and Essay Plan Here

Critical Analysis Examples
1. exploring strengths and weaknesses.
Perhaps the first and most straightforward method of critical analysis is to create a simple strengths-vs-weaknesses comparison.
Most things have both strengths and weaknesses – you could even do this for yourself! What are your strengths? Maybe you’re kind or good at sports or good with children. What are your weaknesses? Maybe you struggle with essay writing or concentration.
If you can analyze your own strengths and weaknesses, then you understand the concept. What might be the strengths and weaknesses of the idea you’re hoping to critically analyze?
Strengths and weaknesses could include:
- Does it seem highly ethical (strength) or could it be more ethical (weakness)?
- Is it clearly explained (strength) or complex and lacking logical structure (weakness)?
- Does it seem balanced (strength) or biased (weakness)?
You may consider using a SWOT analysis for this step. I’ve provided a SWOT analysis guide here .
2. Evaluating Sources
Evaluation of sources refers to looking at whether a source is reliable or unreliable.
This is a fundamental media literacy skill .
Steps involved in evaluating sources include asking questions like:
- Who is the author and are they trustworthy?
- Is this written by an expert?
- Is this sufficiently reviewed by an expert?
- Is this published in a trustworthy publication?
- Are the arguments sound or common sense?
For more on this topic, I’d recommend my detailed guide on digital literacy .
3. Identifying Similarities
Identifying similarities encompasses the act of drawing parallels between elements, concepts, or issues.
In critical analysis, it’s common to compare a given article, idea, or theory to another one. In this way, you can identify areas in which they are alike.
Determining similarities can be a challenge, but it’s an intellectual exercise that fosters a greater understanding of the aspects you’re studying. This step often calls for a careful reading and note-taking to highlight matching information, points of view, arguments or even suggested solutions.
Similarities might be found in:
- The key themes or topics discussed
- The theories or principles used
- The demographic the work is written for or about
- The solutions or recommendations proposed
Remember, the intention of identifying similarities is not to prove one right or wrong. Rather, it sets the foundation for understanding the larger context of your analysis, anchoring your arguments in a broader spectrum of ideas.
Your critical analysis strengthens when you can see the patterns and connections across different works or topics. It fosters a more comprehensive, insightful perspective. And importantly, it is a stepping stone in your analysis journey towards evaluating differences, which is equally imperative and insightful in any analysis.
4. Identifying Differences
Identifying differences involves pinpointing the unique aspects, viewpoints or solutions introduced by the text you’re analyzing. How does it stand out as different from other texts?
To do this, you’ll need to compare this text to another text.
Differences can be revealed in:
- The potential applications of each idea
- The time, context, or place in which the elements were conceived or implemented
- The available evidence each element uses to support its ideas
- The perspectives of authors
- The conclusions reached
Identifying differences helps to reveal the multiplicity of perspectives and approaches on a given topic. Doing so provides a more in-depth, nuanced understanding of the field or issue you’re exploring.
This deeper understanding can greatly enhance your overall critique of the text you’re looking at. As such, learning to identify both similarities and differences is an essential skill for effective critical analysis.
My favorite tool for identifying similarities and differences is a Venn Diagram:

To use a venn diagram, title each circle for two different texts. Then, place similarities in the overlapping area of the circles, while unique characteristics (differences) of each text in the non-overlapping parts.
6. Identifying Oversights
Identifying oversights entails pointing out what the author missed, overlooked, or neglected in their work.
Almost every written work, no matter the expertise or meticulousness of the author, contains oversights. These omissions can be absent-minded mistakes or gaps in the argument, stemming from a lack of knowledge, foresight, or attentiveness.
Such gaps can be found in:
- Missed opportunities to counter or address opposing views
- Failure to consider certain relevant aspects or perspectives
- Incomplete or insufficient data that leaves the argument weak
- Failing to address potential criticism or counter-arguments
By shining a light on these weaknesses, you increase the depth and breadth of your critical analysis. It helps you to estimate the full worth of the text, understand its limitations, and contextualize it within the broader landscape of related work. Ultimately, noticing these oversights helps to make your analysis more balanced and considerate of the full complexity of the topic at hand.
You may notice here that identifying oversights requires you to already have a broad understanding and knowledge of the topic in the first place – so, study up!
7. Fact Checking
Fact-checking refers to the process of meticulously verifying the truth and accuracy of the data, statements, or claims put forward in a text.
Fact-checking serves as the bulwark against misinformation, bias, and unsubstantiated claims. It demands thorough research, resourcefulness, and a keen eye for detail.
Fact-checking goes beyond surface-level assertions:
- Examining the validity of the data given
- Cross-referencing information with other reliable sources
- Scrutinizing references, citations, and sources utilized in the article
- Distinguishing between opinion and objectively verifiable truths
- Checking for outdated, biased, or unbalanced information
If you identify factual errors, it’s vital to highlight them when critically analyzing the text. But remember, you could also (after careful scrutiny) also highlight that the text appears to be factually correct – that, too, is critical analysis.
8. Exploring Counterexamples
Exploring counterexamples involves searching and presenting instances or cases which contradict the arguments or conclusions presented in a text.
Counterexamples are an effective way to challenge the generalizations, assumptions or conclusions made in an article or theory. They can reveal weaknesses or oversights in the logic or validity of the author’s perspective.
Considerations in counterexample analysis are:
- Identifying generalizations made in the text
- Seeking examples in academic literature or real-world instances that contradict these generalizations
- Assessing the impact of these counterexamples on the validity of the text’s argument or conclusion
Exploring counterexamples enriches your critical analysis by injecting an extra layer of scrutiny, and even doubt, in the text.
By presenting counterexamples, you not only test the resilience and validity of the text but also open up new avenues of discussion and investigation that can further your understanding of the topic.
See Also: Counterargument Examples
9. Assessing Methodologies
Assessing methodologies entails examining the techniques, tools, or procedures employed by the author to collect, analyze and present their information.
The accuracy and validity of a text’s conclusions often depend on the credibility and appropriateness of the methodologies used.
Aspects to inspect include:
- The appropriateness of the research method for the research question
- The adequacy of the sample size
- The validity and reliability of data collection instruments
- The application of statistical tests and evaluations
- The implementation of controls to prevent bias or mitigate its impact
One strategy you could implement here is to consider a range of other methodologies the author could have used. If the author conducted interviews, consider questioning why they didn’t use broad surveys that could have presented more quantitative findings. If they only interviewed people with one perspective, consider questioning why they didn’t interview a wider variety of people, etc.
See Also: A List of Research Methodologies
10. Exploring Alternative Explanations
Exploring alternative explanations refers to the practice of proposing differing or opposing ideas to those put forward in the text.
An underlying assumption in any analysis is that there may be multiple valid perspectives on a single topic. The text you’re analyzing might provide one perspective, but your job is to bring into the light other reasonable explanations or interpretations.
Cultivating alternative explanations often involves:
- Formulating hypotheses or theories that differ from those presented in the text
- Referring to other established ideas or models that offer a differing viewpoint
- Suggesting a new or unique angle to interpret the data or phenomenon discussed in the text
Searching for alternative explanations challenges the authority of a singular narrative or perspective, fostering an environment ripe for intellectual discourse and critical thinking . It nudges you to examine the topic from multiple angles, enhancing your understanding and appreciation of the complexity inherent in the field.
A Full List of Critical Analysis Skills
- Exploring Strengths and Weaknesses
- Evaluating Sources
- Identifying Similarities
- Identifying Differences
- Identifying Biases
- Hypothesis Testing
- Fact-Checking
- Exploring Counterexamples
- Assessing Methodologies
- Exploring Alternative Explanations
- Pointing Out Contradictions
- Challenging the Significance
- Cause-And-Effect Analysis
- Assessing Generalizability
- Highlighting Inconsistencies
- Reductio ad Absurdum
- Comparing to Expert Testimony
- Comparing to Precedent
- Reframing the Argument
- Pointing Out Fallacies
- Questioning the Ethics
- Clarifying Definitions
- Challenging Assumptions
- Exposing Oversimplifications
- Highlighting Missing Information
- Demonstrating Irrelevance
- Assessing Effectiveness
- Assessing Trustworthiness
- Recognizing Patterns
- Differentiating Facts from Opinions
- Analyzing Perspectives
- Prioritization
- Making Predictions
- Conducting a SWOT Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Asking the Five Whys
- Correlating Data Points
- Finding Anomalies Or Outliers
- Comparing to Expert Literature
- Drawing Inferences
- Assessing Validity & Reliability
Analysis and Bloom’s Taxonomy
Benjamin Bloom placed analysis as the third-highest form of thinking on his ladder of cognitive skills called Bloom’s Taxonomy .
This taxonomy starts with the lowest levels of thinking – remembering and understanding. The further we go up the ladder, the more we reach higher-order thinking skills that demonstrate depth of understanding and knowledge, as outlined below:

Here’s a full outline of the taxonomy in a table format:
| Level (Shallow to Deep) | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Retain and recall information | Reiterate, memorize, duplicate, repeat, identify | |
| Grasp the meaning of something | Explain, paraphrase, report, describe, summarize | |
| Use existing knowledge in new contexts | Practice, calculate, implement, operate, use, illustrate | |
| Explore relationships, causes, and connections | Compare, contrast, categorize, organize, distinguish | |
| Make judgments based on sound analysis | Assess, judge, defend, prioritize, , recommend | |
| Use existing information to make something new | Invent, develop, design, compose, generate, construct |

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
2 thoughts on “33 Critical Analysis Examples”
THANK YOU, THANK YOU, THANK YOU! – I cannot even being to explain how hard it has been to find a simple but in-depth understanding of what ‘Critical Analysis’ is. I have looked at over 10 different pages and went down so many rabbit holes but this is brilliant! I only skimmed through the article but it was already promising, I then went back and read it more in-depth, it just all clicked into place. So thank you again!

You’re welcome – so glad it was helpful.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Critical Analysis and Essay Formatting: How to Structure Your Thinking
This blog will outline the nine steps you should follow when using critical analysis in either an academic essay or any other type of analytical writing. The value of critical analysis extends beyond essay writing. It’s a skill that enhances all written work, from in-depth research papers to creative stories and even business proposals. It allows us to break down complex ideas, evaluate their merits and drawbacks, and then build strong, logical conclusions. This rigorous approach to thinking and writing brings clarity and richness to our arguments, leading to more persuasive and insightful communication – limiting bias. The skills you gain from writing critical analysis essays, such as reading with a discerning eye, constructing clear arguments, supporting claims with evidence, and refining through revision, are versatile and invaluable. They not only elevate academic writing but also enrich literature and strengthen professional documents.

1. Comprehensive Reading
The first step towards a successful critical analysis essay is in-depth engagement with the text you’ll analyse. If you are working with a single text, that means understanding the author’s point of view to form the foundation of your essay. Take your time and delve into the text to explore its deeper meanings and intentions. Critical analysis is best performed in conjunction with a wide scope of literature containing different points of view to ensure a thorough and unbiased understanding of the topic at hand.
2. Formulating a Clear Thesis
Your thesis statement serves as the core of your essay — it should argue a particular perspective about the author’s approach and use of literary devices. Make sure this statement is strong and arguable, offering an insight that you’ll further develop and prove with evidence from the text. For other types of writing where a thesis is not required – having concise summary sentence in your writing will still help guide the development of strong arguments and keep the writing focused. You can adjust your thesis to be more accurate after the body paragraphs have been written – if you approach it with an open mind, your research will often take you in unexpected directions which require tweaking.
3. Structuring the Essay’s Body
The body of your essay should unpack your thesis in distinct paragraphs, each focusing on a separate aspect of your argument. We have reached the “Tell them” section of this writing journey. Whether they provide background information, explore specific details, or discuss alternate interpretations, all paragraphs should contribute towards affirming your thesis. It is important to build your arguments with a critical guise – do not be afraid to challenge even established author’s assertions. Organize your paragraphs logically for a seamless reading experience – you can play around with paragraph ordering to see what feels best, removing any sections which are not compelling arguments or irrelevant to the writing’s purpose.
4. Creating Effective Topic Sentences
Each paragraph within the body of your essay should begin with a concise topic sentence. This sentence previews the paragraph’s content and ties it back to your overarching thesis, maintaining a clear link between the two and ensuring coherence in your argument.
5. Using Evidence to Support Your Claims
Support your claims with solid evidence from the text to make your essay more convincing. Examples, quotations, and references to the source material can all serve as proof of your argument, adding weight to your analysis and strengthening your reader’s confidence in your conclusions. Ensure your citation style is accurate and consistent throughout your essay. Click here to check out our citations guide for in depth guidance on citation quality, frequency and formatting.
6. Developing a Strong Introduction
That’s right, only now that your essay is finished is it time to begin writing your Grab your reader’s attention right from the start with an engaging introduction. “Tell them what you are going to tell them”. Begin with an interesting hook, like a relevant question, a statistic or a bold claim. If you are writing an essay specific to one text or author, you can introduce the text you’ll analyze, including the author’s name and the title. Round off your introduction by clearly stating your thesis, setting the stage for your analysis.
7. Wrapping up with a Conclusion
Your essay should end with a clear and compelling conclusion that summarises your argument and reaffirms your thesis – “Tell them what you told them, why its significant and what’s next”. This is not the place to introduce new information—instead, use your conclusion to consolidate your analysis, leaving the reader with your most critical insights.
8. Thorough Revision
Once you’ve completed your draft, take some time away from it before starting the revision process. Re-read your essay critically, asking yourself whether your interpretations are unbiased, your evidence is strong, and your writing is clear. Sometimes reading out loud can help identify clunky or run on sentences. Revising multiple times can help you refine your essay to a polished final draft.
9. The Final Draft
After a careful self-review, make necessary changes to your essay. This is the stage where your rough draft transforms into a polished academic essay. Do not hesitate to seek external feedback from peers or a mentor — they might offer fresh insights and helpful suggestions to improve your essay further.
By following these steps, you can strengthen your critical analysis skills and write essays that are not only academically sound but also engaging and insightful. Remember that the key to a strong critical analysis essay lies in a deep understanding of multiple perspectives of an issue, a compelling argument, and dedication to revision and improvement.

Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay

What is a Critical Analysis Essay?
A critical analysis essay is one that focuses on a work produced by another author or artist, such as a book, an article, or a movie. It critiques the work in a manner that is guided by the thesis. In general, the subject of the analysis in such essays is the message contained in the text and/or its style. Sometimes, the analysis can also be directed at the text’s plot or a specific character.
Critical analysis essays help readers understand the work they focus on. They also demonstrate the writer’s grasp of it. Before they can be written, the writer should read, watch, or otherwise consume the work of focus carefully and critically. If needed, this can be done multiple times as it is imperative for the writer to have an in-depth comprehension of what they are writing about.
Parts of a Critical Analysis Essay
Like all essays, critical analysis essays are also divided into three distinct parts. The content each part conveys is as follows.
1. Introduction
The essay begins with an introduction to the piece of work it is going to critically analyze. Information pertinent to the analysis is provided. This can include a summary of the work, its context, themes, message, and/or details about the author/artist.
A hook is often incorporated into the first sentence to capture and hold the reader’s attention. Typically, the paragraph is finished with the thesis statement.
Thesis statement: This is the guiding star of the whole essay and determines everything that will be included in it. It should be arrived at before the essay writing process begins, after several examinations of the text to be analyzed. The thesis could be based on the writer’s personal opinion of the text too. It should, however, be substantiated through the analysis that follows.
The body of the essay is divided into multiple paragraphs , each one analyzing a sub topic derived from the thesis. All paragraphs should be organized in a logical manner to flow from topic to topic. And using the right transition words or phrases ensures a smooth shift between paragraphs.
The number of paragraphs in the body of the essay is variable, depending on the sub topics being discussed. If required, the first body paragraph can be a summary of the focus text. While a summary is generally a needed element in critical analyses, it can sometimes be skipped, especially if the work being analyzed is a well-known one. Summaries are usually included in the introduction; when they are not, they can form a part of the body of the essay.
Each paragraph ought to begin with a topic sentence that states the topic it will discuss. However, if the paragraph is the summary of the text being analyzed, it does not need a topic sentence.
3. Conclusion
The final section of the essay concludes it by summing up the analysis. The thesis is also reiterated here with an added comment. No new points should be introduced in the essay’s conclusion.
Outline for Critical Analysis Essays
- Introduction:
- The work being critically analyzed is identified and contextualized.
- If a very brief summary serves the purpose, it can be included here.
- The thesis statement marks the focus and nature of the analysis being conducted in the essay.
- If a more detailed summary is needed, it should be placed here rather than in the introduction. The summary then forms the first body paragraph.
- The rest of the body too is divided into multiple paragraphs.
- The topic sentence of each paragraph succinctly states the topic or point of analysis it will focus on.
- The rest of the paragraph then discusses and explores the topic while also providing evidence, which serves to support the paragraph’s individual focus, and through it, the thesis. Very often, the evidence is in the form of quotations from the text itself.
- Conclusion:
- The results of the analysis are summarized.
- Their implications on the thesis are stated.
- A comment can be included.
Example of a Critical Analysis Essay
The following is an example of a critical analysis essay looking at Arthur Miller’s most renowned play, Death of a Salesman.
The writer begins with an eye-catching question that works as a hook while effectively setting up the essay’s premise. They then proceed to provide the background leading up to the thesis statement.
“How can two people watch or read the same story and yet, interpret it completely differently? Does it have to do with the author’s intentions, or with the viewers’ own backgrounds and ideologies? Whatever the case may be, viewing one piece of work can lead to a wide array of opinions and critiques. It is through the diversity of such lenses that Death of a Salesman by Arthur Miller has become one of the most well-known plays in modern history.”
Here, the writer has chosen to locate their thesis in the middle of the introductory paragraph rather than at the end as is common with most essays.
“There are many different ways in which a play can be criticized. However, criticisms from Marxist and reader-response approaches will be utilized to further dissect Death of a Salesman.”
Further information leading from the thesis statement is then given.
“Marxist criticism sees work as a struggle between different socioeconomic classes; what better way to see Miller’s play than for what it is at face value, the struggle of a middle-class man trying to achieve the American dream. On the other hand, a reader-response criticism comes from either an objective or subjective view; in this case, Death of a Salesman will be viewed with a subjective lens based on Willy’s deteriorating mental health.”
Given that the text being analyzed is a widely known classic, the writer has chosen not to include a summary, assuming that most readers will already be familiar with it. This choice could also work to push those who haven’t read the original text to do so if they’ve been made curious enough by the essay.
The topic sentence of the first body paragraph states the first point to be discussed.
“Through a Marxist’s eyes, Death of a Salesman represents the struggle of middle-class families in a capitalistic world.”
The aspects of the play that lend themselves to Marxist analysis are then enumerated.
“From an early age, kids are taught to do well in school, be involved with sports and activities, and to go on to college; all in the hopes of achieving the American Dream. This dream of obtaining success through hard work leads many into the rat race of life. Early on, Willy encourages Biff to do well in sports and be popular in order to succeed; however, Willy’s inability to realize his own status and abilities leads him to instill the wrong work ethics in his sons. In his flashbacks of interactions with his sons, Biff and Happy, Willy tells them to be well-liked over well-educated, and to find jobs that pay nicely, not jobs that they will enjoy doing. When Biff steals a football from school, Willy rationalizes it by saying it is ok because he is popular. When Bernard gets on Biff for not studying with him, Willy reiterates that education is secondary to being popular in order to be successful in life. This illusion of popularity and success that Willy is fixated on leads him to believe the American Dream comes by way of having a lot of money, something he feels his brother and his father have achieved. Social and economic forces have a stronghold on Willy as he continues to defend the capitalistic economy that surrounds him. When he is offered a job by Charley, Willy scoffs at the idea and is insulted by it, too proud and lost in the rat race to accept outside help.”
The topic sentence of the third paragraph states another point of analysis for the essay.
“As a reader-response critique based on a subjective view of mental health disorders, Death of a Salesman is about a man becoming senile and exhibiting signs of dementia.”
More examples from the play are cited to corroborate this declaration.
“Willy is a typical middle-class salesman chasing the American Dream. His marriage, lifestyle, and family all resemble the lives of many in America, yet he is delusional. He fails to see the loving wife and sons that need him most as he falls in and out of hallucinations and mood swings. He experiences mood swings early on in the play when he is talking about Biff’s lack of success. He starts off by telling Linda, “The trouble is he’s lazy, goddammit!”, followed by, “Biff is a lazy bum!”. Then, realizing that Biff was home, he says, “There’s one thing about Biff-he’s not lazy.” Signs of dementia also are shown when Willy is seen talking to himself in the kitchen. As Biff and Happy are talking in their bedroom upstairs, Willy is talking and laughing to himself in the kitchen. After talking to himself, he starts to hallucinate about a time in the past. The hallucinations Willy has throughout the play question his mental health. His reliving of the past and oppression of certain memories are also reflective of dementia or Alzheimer’s. His suicide is justified yet again with the hallucination of a conversation with Ben.”
The final paragraph restates the thesis with the detail accrued from the analysis that supports it.
“There are many different ways in which a piece of work can be critiqued and analyzed. Whether through Marxist, reader-response, or any other type of criticism, there is no doubt they all bring something new and different to the piece of work. At face value, Death of a Salesman is about a man and his family chasing the American Dream. Marxists see the capitalistic and socio-economic forces tying down Willy and keeping him from achieving his goals. The unrealistic social standards thrust upon him lead him to suicide in order to finally realize a false sense of reality. From a reader-response standpoint, Willy is slowly falling apart and experiencing mental health issues such as dementia and Alzheimer’s. Thoughts and attempts of suicide often lead back to mental health issues that need to be addressed professionally. The anxieties and stresses of life can sometimes weigh down individuals so much that they feel death is the only way out. Had Willy or his family members recognized his mental health disorders, they might have been able to save him.”

BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a critical analysis

Unlike the name implies a critical analysis does not necessarily mean that you are only exploring what is wrong with a piece of work. Instead, the purpose of this type of essay is to interact with and understand a text. Here’s what you need to know to create a well-written critical analysis essay.
What is a critical analysis?
A critical analysis examines and evaluates someone else’s work, such as a book, an essay, or an article. It requires two steps: a careful reading of the work and thoughtful analysis of the information presented in the work.
Although this may sound complicated, all you are doing in a critical essay is closely reading an author’s work and providing your opinion on how well the author accomplished their purpose.
Critical analyses are most frequently done in academic settings (such as a class assignment). Writing a critical analysis demonstrates that you are able to read a text and think deeply about it. However, critical thinking skills are vital outside of an educational context as well. You just don’t always have to demonstrate them in essay form.
How to outline and write a critical analysis essay
Writing a critical analysis essay involves two main chunks of work: reading the text you are going to write about and writing an analysis of that text. Both are equally important when writing a critical analysis essay.
Step one: Reading critically
The first step in writing a critical analysis is to carefully study the source you plan to analyze.
If you are writing for a class assignment, your professor may have already given you the topic to analyze in an article, short story, book, or other work. If so, you can focus your note-taking on that topic while reading.
Other times, you may have to develop your own topic to analyze within a piece of work. In this case, you should focus on a few key areas as you read:
- What is the author’s intended purpose for the work?
- What techniques and language does the author use to achieve this purpose?
- How does the author support the thesis?
- Who is the author writing for?
- Is the author effective at achieving the intended purpose?
Once you have carefully examined the source material, then you are ready to begin planning your critical analysis essay.
Step two: Writing the critical analysis essay
Taking time to organize your ideas before you begin writing can shorten the amount of time that you spend working on your critical analysis essay. As an added bonus, the quality of your essay will likely be higher if you have a plan before writing.
Here’s a rough outline of what should be in your essay. Of course, if your instructor gives you a sample essay or outline, refer to the sample first.
- Background Information
Critical Analysis
Here is some additional information on what needs to go into each section:
Background information
In the first paragraph of your essay, include background information on the material that you are critiquing. Include context that helps the reader understand the piece you are analyzing. Be sure to include the title of the piece, the author’s name, and information about when and where it was published.
“Success is counted sweetest” is a poem by Emily Dickinson published in 1864. Dickinson was not widely known as a poet during her lifetime, and this poem is one of the first published while she was alive.
After you have provided background information, state your thesis. The thesis should be your reaction to the work. It also lets your reader know what to expect from the rest of your essay. The points you make in the critical analysis should support the thesis.
Dickinson’s use of metaphor in the poem is unexpected but works well to convey the paradoxical theme that success is most valued by those who never experience success.
The next section should include a summary of the work that you are analyzing. Do not assume that the reader is familiar with the source material. Your summary should show that you understood the text, but it should not include the arguments that you will discuss later in the essay.
Dickinson introduces the theme of success in the first line of the poem. She begins by comparing success to nectar. Then, she uses the extended metaphor of a battle in order to demonstrate that the winner has less understanding of success than the loser.
The next paragraphs will contain your critical analysis. Use as many paragraphs as necessary to support your thesis.
Discuss the areas that you took notes on as you were reading. While a critical analysis should include your opinion, it needs to have evidence from the source material in order to be credible to readers. Be sure to use textual evidence to support your claims, and remember to explain your reasoning.
Dickinson’s comparison of success to nectar seems strange at first. However the first line “success is counted sweetest” brings to mind that this nectar could be bees searching for nectar to make honey. In this first stanza, Dickinson seems to imply that success requires work because bees are usually considered to be hard-working and industrious.
In the next two stanzas, Dickinson expands on the meaning of success. This time she uses the image of a victorious army and a dying man on the vanquished side. Now the idea of success is more than something you value because you have worked hard for it. Dickinson states that the dying man values success even more than the victors because he has given everything and still has not achieved success.
This last section is where you remind the readers of your thesis and make closing remarks to wrap up your essay. Avoid summarizing the main points of your critical analysis unless your essay is so long that readers might have forgotten parts of it.
In “Success is counted sweetest” Dickinson cleverly upends the reader’s usual thoughts about success through her unexpected use of metaphors. The poem may be short, but Dickinson conveys a serious theme in just a few carefully chosen words.
What type of language should be used in a critical analysis essay?
Because critical analysis papers are written in an academic setting, you should use formal language, which means:
- No contractions
- Avoid first-person pronouns (I, we, me)
Do not include phrases such as “in my opinion” or “I think”. In a critical analysis, the reader already assumes that the claims are your opinions.
Your instructor may have specific guidelines for the writing style to use. If the instructor assigns a style guide for the class, be sure to use the guidelines in the style manual in your writing.
Additional t ips for writing a critical analysis essay
To conclude this article, here are some additional tips for writing a critical analysis essay:
- Give yourself plenty of time to read the source material. If you have time, read through the text once to get the gist and a second time to take notes.
- Outlining your essay can help you save time. You don’t have to stick exactly to the outline though. You can change it as needed once you start writing.
- Spend the bulk of your writing time working on your thesis and critical analysis. The introduction and conclusion are important, but these sections cannot make up for a weak thesis or critical analysis.
- Give yourself time between your first draft and your second draft. A day or two away from your essay can make it easier to see what you need to improve.
Frequently Asked Questions about critical analyses
In the introduction of a critical analysis essay, you should give background information on the source that you are analyzing. Be sure to include the author’s name and the title of the work. Your thesis normally goes in the introduction as well.
A critical analysis has four main parts.
- Introduction
The focus of a critical analysis should be on the work being analyzed rather than on you. This means that you should avoid using first person unless your instructor tells you to do otherwise. Most formal academic writing is written in third person.
How many paragraphs your critical analysis should have depends on the assignment and will most likely be determined by your instructor. However, in general, your critical analysis paper should have three to six paragraphs, unless otherwise stated.
Your critical analysis ends with your conclusion. You should restate the thesis and make closing remarks, but avoid summarizing the main points of your critical analysis unless your essay is so long that readers might have forgotten parts of it.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
What Is a Critical Analysis Essay? Simple Guide With Examples

- DESCRIPTION Woman writing on laptop with critical analysis essay definition
- SOURCE fizkes / iStock / Getty Images Plus / via Getty created by YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Used under Getty Images license
You’ve already written a basic essay of some kind, so you’ve already performed a bit of analysis. Really, you already have all the tools and know-how to tackle a critical analysis essay. Unlike other essays, critical analysis essays ask that you go a little deeper into other people’s ideas to build your own responses to art, media, and the world at large. Simple, right?
What Is a Critical Analysis Essay?
Okay, there’s admittedly maybe a little more to it than just that. A critical analysis essay is a form of writing that asks you to:
- Analyze a subject, which may include a historical document, a scientific theory, or a piece of art or media (books, poems, movies, even other essays)
- Determine what the author of that piece is trying to say
- Respond with ideas of your own, backed up with evidence from other texts or media
Critical analysis branches out into things like literary criticism , genre studies, and editorial journalism. If you want to think about it on a smaller scale: Have you read a tweet thread or blog post and thought, “Hey, I have a differing opinion!” or “I agree with this”? Have you then responded to that post or thread with your own opinion? Congrats! You did a little critical analysis!
General Structure and Format of a Critical Analysis Essay
You’ll find some variations in form and structure with the critical analysis essay. As you get more comfortable with it, you can absolutely change things around and get creative. Otherwise, don’t overthink the format too much.
Your typical critical analysis essay is made up of:
- An introduction paragraph, including your opinion about the piece you're analyzing
- A paragraph (potentially more) summarizing the thing that you’re analyzing
- the actual analysis of the piece, which will usually include your opinion about that piece
- an evaluation of the author’s success in achieving their intended goal
- a larger idea or argument within the text that you can elaborate on
- A concluding paragraph that sums up your analysis and relates it to your audience
Sometimes, the summary paragraph is shortened and folded into the introduction.
Critical Analysis Essay Example
Seeing is believing (and understanding). We can’t help you with your actual critical analyzing, but we can at least give you an example of a critical analysis essay to show you how it might look. Note that we’re not in the business of giving away free essays, and that this is purely to help you see a (fairly incomplete) critical analysis essay in the works.

- DESCRIPTION critical analysis example essay with comments
- SOURCE Created by Karina Goto for YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Owned by YourDictionary, Copyright YourDictionary
The Introduction Paragraph
With your introduction , you want to hook readers, broadly introduce the ideas that you’ll talk about, and give readers a reason to read the essay in its entirety. The most important part of the intro is the thesis , which states your central argument. In its most general sense, that includes what you think about the piece and the larger idea you think it might present.
The party is one of the most well-known social events across all cultures. Once reserved for celebrating birthdays, holidays, and other specific occasions, the modern party has grown beyond those limits, often sprouting up without singular intent or reason. Parties are a hub for social interaction among youths and have naturally been a space of uncertainty as attendees attempt to both “have fun” and “be cool.” While the instructional video Show Off! How To Be Cool At Parties engages with some decidedly uncool ideas, it presents the idea of “coolness” as attainable, and grounds the archetype of the “Cool Person at the Party” within historical contexts.
The Summary Paragraph(s)
Following the introduction, you have your summary of the piece or object that you are critically analyzing. Depending on the work and the requirements of the assignment, this might expand to more than one paragraph. Some classes may also do without it completely (your professor, who has read The Great Gatsby , probably doesn’t need you and the 15 other students in the class to summarize it.)
The summary generally shouldn’t be an in-depth, beat-by-beat retelling of the thing that you’re analyzing. You want to give enough details that your reader knows what you’re talking about without having to necessarily read or watch what you’re analyzing.
Show Off! How To Be Cool At Parties (Stunts, Tricks and Gags to Amaze Your Friends) is an instructional video released on VHS in 1986. Nearly a half-hour long, the video stars Malcolm-Jamal Warner, best known for his role on The Cosby Show, and a cast of relatively unknown actors and comedians as they attempt to instruct the viewer on the fine art of being cool around other people. Despite the central thesis of the video, much of its material is uncool, impractical, or downright strange. For example, there is some suspension of disbelief that even young children of the 1980s would find coolness in pretending to be attacked by a dog or playing the air piano.
The Analysis Paragraphs
This is where you’ll really get into your critical analysis. Along with presenting your own opinions and engaging with the chosen text, you should draw evidence from other authoritative sources, which can support your argument and present new ideas that you can build off of.
Through a modern lens, Show Off! possesses a toothlessness, but this may be a direct response to the events of its time. According to Haynes Johnson of the Washington Post, 1986 was “A Year of National Shocks,” a time when “events seemed out of control.” In the waning years of the Cold War, 1986 was underlined by two major disasters: the failed launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger in January and the nuclear explosion at Chernobyl in April. These events sowed doubt about global technologies and fear in the systems and infrastructure designed to care for us. Retreating to the mundanities of nose whistling and “catching” an invisible ball in a paper bag were as much about staying grounded as they were maintaining a sense of control. Much of Show Off! is built on the archetype of the “Cool Person at the Party.” This archetype is largely left to the imagination of the viewer as funny, dexterous, readily armed with props and parlor tricks, and attainable by anyone. In the essay “Myth and Archetype in Science Fiction,” author Ursula K. Le Guin states that “nobody can invent an archetype by taking thought, any more than he can invent a new organ in his body.” She goes on to say that myth and archetypes are a means of communication and that “alienation isn’t the final human condition, since there is a vast human ground on which we can meet, not only rationally, but aesthetically, intuitively, emotionally.” Given global uncertainties, the process of becoming a cool person at a party is equivalent to reaching for connection, familiarity, and communication.
The Concluding Paragraph
Your conclusion should restate the thesis, act as a general wrap-up for your essay, and consider questions or ideas beyond what you discussed in the body paragraphs. A critical analysis essay can also end with a call to action about engaging with the analyzed piece, but this isn’t a requirement.
In conclusion, Show Off! How To Be Cool At Parties is an instructional video that acts as a direct response to politics and trauma of the time through the social archetype of the cool person at a party. Although it presents a hazy idea of what “coolness” could look like, the video begs the opposite question: How does one become uncool at parties? Warner’s introduction to the video includes the rule of having fun, not for one’s own sake, but to ensure that one’s friends are having fun. Perhaps the true turning point of “cool” is thinking outward.
Let’s Get Critical!
Critical analysis essays can be difficult for people of all education levels. Learning to think (and write) critically comes with practice, so don’t be afraid to play around with your language. Discover new ways to engage with what you read, watch, experience, or listen to using our helpful tips for writing a critical analysis essay.
Writing Academically
Proofreading, other editing & coaching for highly successful academic writing
- Editing & coaching pricing
- Academic coaching
- How to conduct a targeted literature search
How to write a successful critical analysis
- How to write a strong literature review
- Cautious in tone
- Formal English
- Precise and concise English
- Impartial and objective English
- Substantiate your claims
- The academic team

For further queries or assistance in writing a critical analysis email Bill Wrigley .
What do you critically analyse?
In a critical analysis you do not express your own opinion or views on the topic. You need to develop your thesis, position or stance on the topic from the views and research of others . In academic writing you critically analyse other researchers’:
- concepts, terms
- viewpoints, arguments, positions
- methodologies, approaches
- research results and conclusions
This means weighing up the strength of the arguments or research support on the topic, and deciding who or what has the more or stronger weight of evidence or support.
Therefore, your thesis argues, with evidence, why a particular theory, concept, viewpoint, methodology, or research result(s) is/are stronger, more sound, or more advantageous than others.
What does ‘analysis’ mean?
A critical analysis means analysing or breaking down the parts of the literature and grouping these into themes, patterns or trends.
In an analysis you need to:
1. Identify and separate out the parts of the topic by grouping the various key theories, main concepts, the main arguments or ideas, and the key research results and conclusions on the topic into themes, patterns or trends of agreement , dispute and omission .
2. Discuss each of these parts by explaining:
i. the areas of agreement/consensus, or similarity
ii. the issues or controversies: in dispute or debate, areas of difference
ii. the omissions, gaps, or areas that are under-researched
3. Discuss the relationship between these parts
4. Examine how each contributes to the whole topic
5. Make conclusions about their significance or importance in the topic
What does ‘critical’ mean?
A critical analysis does not mean writing angry, rude or disrespectful comments, or expressing your views in judgmental terms of black and white, good and bad, or right and wrong.
To be critical, or to critique, means to evaluate . Therefore, to write critically in an academic analysis means to:
- judge the quality, significance or worth of the theories, concepts, viewpoints, methodologies, and research results
- evaluate in a fair and balanced manner
- avoid extreme or emotional language

- strengths, advantages, benefits, gains, or improvements
- disadvantages, weaknesses, shortcomings, limitations, or drawbacks
How to critically analyse a theory, model or framework
The evaluative words used most often to refer to theory, model or framework are a sound theory or a strong theory.
The table below summarizes the criteria for judging the strengths and weaknesses of a theory:
- comprehensive
- empirically supported
- parsimonious
Evaluating a Theory, Model or Framework
The table below lists the criteria for the strengths and their corresponding weaknesses that are usually considered in a theory.
| Comprehensively accounts for main phenomena | overlooks or omits important features or concepts |
| Clear, detailed | vague, unexplained, ill-defined, misconceived |
| Main tenets or concepts are logical and consistent | concepts or tenets are inconsistent or contradictory |
| Practical, useful | impractical, unuseful |
| Applicable across a range of settings, contexts, groups and conditions | limited or narrow applicability |
| Empirically supported by a large body of evidence propositions and predictions are supported by evidence | supported by small or no body of evidence insufficient empirical support for the propositions and predictions |
| Up-to-date, accounts for new developments | outdated |
| Parsimonius (not excessive): simple, clear, with few variables | excessive, overly complex or complicated |
Critical analysis examples of theories
The following sentences are examples of the phrases used to explain strengths and weaknesses.
Smith’s (2005) theory appears up to date, practical and applicable across many divergent settings.
Brown’s (2010) theory, although parsimonious and logical, lacks a sufficient body of evidence to support its propositions and predictions
Little scientific evidence has been presented to support the premises of this theory.
One of the limitations with this theory is that it does not explain why…
A significant strength of this model is that it takes into account …
The propositions of this model appear unambiguous and logical.
A key problem with this framework is the conceptual inconsistency between ….
How to critically analyse a concept
The table below summarizes the criteria for judging the strengths and weaknesses of a concept:
- key variables identified
- clear and well-defined
Evaluating Concepts
| Key variables or constructs identified | key variables or constructs omitted or missed |
| Clear, well-defined, specific, precise | ambiguous, vague, ill-defined, overly general, imprecise, not sufficiently distinctive overinclusive, too broad, or narrowly defined |
| Meaningful, useful | conceptually flawed |
| Logical | contradictory |
| Relevant | questionable relevance |
| Up-to-date | out of date |
Critical analysis examples of concepts
Many researchers have used the concept of control in different ways.
There is little consensus about what constitutes automaticity.
Putting forth a very general definition of motivation means that it is possible that any behaviour could be included.
The concept of global education lacks clarity, is imprecisely defined and is overly complex.
Some have questioned the usefulness of resilience as a concept because it has been used so often and in so many contexts.
Research suggests that the concept of preoperative fasting is an outdated clinical approach.
How to critically analyse arguments, viewpoints or ideas
The table below summarizes the criteria for judging the strengths and weaknesses of an argument, viewpoint or idea:
- reasons support the argument
- argument is substantiated by evidence
- evidence for the argument is relevant
- evidence for the argument is unbiased, sufficient and important
- evidence is reputable
Evaluating Arguments, Views or Ideas
| Reasons and evidence provided support the argument | the reasons or evidence do not support the argument - overgeneralization |
| Substantiated (supported) by factual evidence | insufficient substantiation (support) |
| Evidence is relevant and believable | Based on peripheral or irrelevant evidence |
| Unbiased: sufficient or important evidence or ideas included and considered. | biased: overlooks, omits, disregards, or is selective with important or relevant evidence or ideas. |
| Evidence from reputable or authoritative sources | evidence relies on non reputable or unrecognized sources |
| Balanced: considers opposing views | unbalanced: does not consider opposing views |
| Clear, not confused, unambiguous | confused, ambiguous |
| Logical, consistent | the reasons do not follow logically from and support the arguments; arguments or ideas are inconsistent |
| Convincing | unconvincing |
Critical analysis examples of arguments, viewpoints or ideas
The validity of this argument is questionable as there is insufficient evidence to support it.
Many writers have challenged Jones’ claim on the grounds that …….
This argument fails to draw on the evidence of others in the field.
This explanation is incomplete because it does not explain why…
The key problem with this explanation is that ……
The existing accounts fail to resolve the contradiction between …
However, there is an inconsistency with this argument. The inconsistency lies in…
Although this argument has been proposed by some, it lacks justification.
However, the body of evidence showing that… contradicts this argument.
How to critically analyse a methodology
The table below provides the criteria for judging the strengths and weaknesses of methodology.
An evaluation of a methodology usually involves a critical analysis of its main sections:
design; sampling (participants); measurement tools and materials; procedure
- design tests the hypotheses or research questions
- method valid and reliable
- potential bias or measurement error, and confounding variables addressed
- method allows results to be generalized
- representative sampling of cohort and phenomena; sufficient response rate
- valid and reliable measurement tools
- valid and reliable procedure
- method clear and detailed to allow replication
Evaluating a Methodology
| Research design tests the hypotheses or research questions | research design is inappropriate for the hypotheses or research questions |
| Valid and reliable method | dubious, questionable validity |
| The method addresses potential sources of bias or measurement error. confounding variables were identified | insufficiently rigorous measurement error produces questionable or unreliable confounding variables not identified or addressed |
| The method (sample, measurement tools, procedure) allows results to be generalized or transferred. Sampling was representative to enable generalization | generalizability of the results is limited due to an unrepresentative sample: small sample size or limited sample range |
| Sampling of cohort was representative to enable generalization sampling of phenomena under investigation sufficiently wide and representative sampling response rate was sufficiently high | limited generalizability of results due to unrepresentative sample: small sample size or limited sample range of cohort or phenomena under investigation sampling response rate was too low |
| Measurement tool(s) / instrument(s), appropriate, reliable and valid measurements were accurate | inappropriate measurement tools; incomplete or ambiguous scale items inaccurate measurement reliability statistics from previous research for measurement tool not reported measurement instrument items are ambiguous, unclear, contradictory |
| Procedure reliable and valid | Measurement error from administration of the measurement tool(s) |
| Method was clearly explained and sufficiently detailed to allow replication | Explanation of the methodology (or parts of it, for example the Procedure) is unclear, confused, imprecise, ambiguous, inconsistent or contradictory |
Critical analysis examples of a methodology
The unrepresentativeness of the sample makes these results misleading.
The presence of unmeasured variables in this study limits the interpretation of the results.
Other, unmeasured confounding variables may be influencing this association.
The interpretation of the data requires caution because the effect of confounding variables was not taken into account.
The insufficient control of several response biases in this study means the results are likely to be unreliable.
Although this correlational study shows association between the variables, it does not establish a causal relationship.
Taken together, the methodological shortcomings of this study suggest the need for serious caution in the meaningful interpretation of the study’s results.
How to critically analyse research results and conclusions
The table below provides the criteria for judging the strengths and weaknesses of research results and conclusions:
- appropriate choice and use of statistics
- correct interpretation of results
- all results explained
- alternative explanations considered
- significance of all results discussed
- consistency of results with previous research discussed
- results add to existing understanding or knowledge
- limitations discussed
- results clearly explained
- conclusions consistent with results
Evaluating the Results and Conclusions
| Chose and used appropriate statistics | inappropriate choice or use of statistics |
| Results interpreted correctly or accurately | incorrect interpretation of results the results have been over-interpreted For example: correlation measures have been incorrectly interpreted to suggest causation rather than association |
| All results were explained, including inconsistent or misleading results | inconsistent or misleading results not explained |
| Alternative explanations for results were considered | unbalanced explanations: alternative explanations for results not explored |
| Significance of all results were considered | incomplete consideration of results |
| Results considered according to consistency with other research or viewpoints Results are conclusive because they have been replicated by other studies | consistency of results with other research not considered results are suggestive rather than conclusive because they have not been replicated by other studies |
| Results add significantly to existing understanding or knowledge | results do not significantly add to existing understanding knowledge |
| Limitations of the research design or method are acknowledged | limitations of the research design or method not considered |
| Results were clearly explained, sufficiently detailed, consistent | results were unclear, insufficiently detailed, inconsistent, confusing, ambiguous, contradictory |
| Conclusions were consistent with and supported by the results | conclusions were not consistent with or not supported by the results |
Leave a Reply
Click here to cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
WRITING FORMATS FOR EDITING OR COACHING
- Essay or assignment
- Thesis or dissertation
- Proposal for PhD or Masters research
- Literature review
- Journal article or book chapter
- IELTS writing tasks 1 & 2 for general and academic writing
- Resumes & cover letters
- Presentations
- Applications & submissions
Do you have a question?
- Academic writing skills
- Academic English skills
- The Academic team
- Privacy policy
- Terms and conditions
- ABN: 15796080518
- 66 Mungarie Street, Keperra, Qld 4054 Australia
- Email: [email protected]
Website design and development by Caboodle Web
How To Write A Critical Analysis Essay With Examples
Declan Gessel
May 4, 2024

A Critical Analysis Essay is a form of academic writing that requires students to extract information and critically analyze a specific topic. The task may seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can become an exciting task.
Critical Analysis Essays help students improve their analytical skills and foster principles of logic. In this article, we are going to discuss how to write an essay and break it down for you. So sit back, relax, and enjoy the ride!
Table Of Content
What is a critical analysis essay, why the subject of your critical analysis essay is important, 5 reading strategies for critical analysis essay, building the body of your analysis, 5 things to avoid when writing your critical analysis essay, write smarter critical analysis essay with jotbot — start writing for free today.

When you write a critical analysis essay, you move beyond recounting the subject's main points and delve into examining it with a discerning eye. The goal? To form your own insights about the subject, based on the evidence you gather.
This involves dissecting and contemplating the author's arguments , techniques, and themes while also developing your own critical response. While forming your own conclusions may sound intimidating, it's a key aspect of fine-tuning your critical thinking skills and organizing your thoughts into a cohesive, argumentative response.
Key Skills in the Craft
This process consists of two key elements: understanding the core components of the subject and forming your own critical response, both supported by evidence. The first part involves grasping the subject's main arguments, techniques, and themes. The second part entails taking that knowledge and constructing your analytical and evaluative response.
Deconstructing the Subject
In other words, roll up your sleeves and get deep into the subject matter. Start by identifying the author's main point, deconstructing their arguments, examining the structure and techniques they use, and exploring the underlying themes and messages. By engaging with the subject on this level, you'll have a thorough understanding of it and be better prepared to develop your own response.
The Power of Evidence
Remember that evidence is your secret weapon for crafting a convincing analysis. This means going beyond summarizing the content and instead using specific examples from the subject to support your own arguments and interpretations. Evidence isn't just about facts, either; it can also be used to address the effectiveness of the subject, highlighting both its strengths and weaknesses.
The Art of Evaluation
Lastly, put your evaluation skills to work. Critically assess the subject's effectiveness, pinpointing its strengths and potential shortcomings. From there, you can offer your own interpretation, supported by evidence from the subject itself. This is where you put everything you've learned about the subject to the test, showcasing your analytical skills and proving your point.
Related Reading
• Argumentative Essay • Essay Format • Expository Essay • Essay Outline • How To Write A Conclusion For An Essay • Transition Sentences • Narrative Essay • Rhetorical Analysis Essay • Persuasive Essay

Let’s delve on the importance of understanding the Work you'll be analyzing:
Main Argument
When diving into a work, one must unravel the central point or message the author is conveying. All other analyses stem from this fundamental point. By identifying and comprehending the main argument, one can dissect the various elements that support it, revealing the author's stance or point of view.
Themes are the underlying concepts and messages explored in the subject matter. By venturing into the depths of themes, one can unravel the layers of meaning within the work. Understanding these underlying ideas not only enriches the analysis but also sheds light on the author's intentions and insights.
Structure & Techniques
Understanding how the work is built - be it a chronological story, persuasive arguments, or the use of figurative language - provides insight into the author's craft. Structure and techniques can influence the way the work is perceived, and by dissecting them, one can appreciate the intricacies of the author's style and the impact it has on the audience.
In critical analysis, understanding the context can add an extra layer of depth to the analysis. Considering the historical, social, or cultural context in which the work was created can provide valuable insights into the author's influences, intentions, and the reception of the work. While not always necessary, contextual analysis can elucidate aspects of the work that might otherwise go unnoticed.
To conduct a comprehensive critical analysis , understanding the work you'll be analyzing is the foundation on which all other interpretations rely. By identifying the main argument, themes, structure, techniques, and context, a nuanced and insightful analysis can be crafted. This step sets the stage for a thorough examination of the work, bringing to light the nuances and complexities that make critical analysis a valuable tool in literary and artistic exploration.

1. Close Reading: Go Deeper Than Skimming
Close reading is a focused approach to reading where you don't just skim the text. Instead, you pay close attention to every word, sentence, and detail. By doing this, you can uncover hidden meanings, themes, and literary devices that you might miss if you were reading too quickly. I recommend underlining or annotating key passages, literary devices, or recurring ideas. This helps you remember these important details later on when you're writing your critical analysis essay.
2. Active Note-Taking to Capture Important Points
When reading a text for a critical analysis essay, it's important to take active notes that go beyond summarizing the plot or main points. Instead, try jotting down the author's arguments, interesting details, confusing sections, and potential evidence for your analysis. These notes will give you a solid foundation to build your essay upon and will help you keep track of all the important elements of the text.
3. Identify Recurring Ideas: Look for Patterns
In a critical analysis essay, it's crucial to recognize recurring ideas, themes, motifs, or symbols that might hold deeper meaning. By looking for patterns in the text, you can uncover hidden messages or themes that the author might be trying to convey. Ask yourself why these elements are used repeatedly and how they contribute to the overall message of the text. By identifying these patterns, you can craft a more nuanced analysis of the text.
4. Consider the Author's Purpose
Authorial intent is an essential concept to consider when writing a critical analysis essay. Think about the author's goals: are they trying to inform, persuade, entertain, or something else entirely? Understanding the author's purpose can help you interpret the text more accurately and can give you insight into the author's motivations for writing the text in the first place.
5. Question and Analyze your Arguments
In a critical analysis essay, it's important to take a critical approach to the text. Question the author's ideas, analyze the effectiveness of their arguments, and consider different interpretations. By approaching the text with a critical eye, you can craft a more thorough and nuanced analysis that goes beyond a surface-level reading of the text.
Jotbot is your personal document assistant. Jotbot does AI note taking, AI video summarizing, AI citation/source finder, it writes AI outlines for essays, and even writes entire essays with Jotbot’s AI essay writer. Join 500,000+ writers, students, teams, and researchers around the world to write more, write better, and write faster with Jotbot. Write smarter, not harder with Jotbot. Start writing for free with Jotbot today — sign in with Google and get started in seconds.

Let’s delve on the essentials of building the body of your analysis:
Topic Sentence Breakdown: The Purpose of a Strong Topic Sentence
A powerful topic sentence in each paragraph of your critical analysis essay serves as a roadmap for your reader. It tells them the focus of the paragraph, introducing the main point you will explore and tying it back to your thesis. For instance, in an essay about the role of symbolism in "The Great Gatsby," a topic sentence might read, "Fitzgerald's use of the green light symbolizes Gatsby's unattainable dreams, highlighting the theme of the American Dream's illusion."
Evidence Integration: The Significance of Evidence from the Subject
To bolster your arguments, you need to use evidence from the subject you are analyzing. For example, in "To Kill a Mockingbird," when explaining Atticus Finch's moral compass, using a quote like, "You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view - until you climb into his skin and walk around in it," can back up your analysis. It proves that the character values empathy and understanding.
Textual Evidence: Integrating Quotes, Paraphrases, or Specific Details
When you quote or paraphrase text, ensure it directly relates to your analysis. For example, when discussing Sylvia Plath's use of imagery in "The Bell Jar," quote, "I saw my life branching out before me like the green fig tree in the story." This paints a vivid picture for readers and helps solidify your point about the protagonist's feelings of entrapment.
Visual Evidence: Analyzing Specific Elements in the Artwork
If you are analyzing a painting, you can use visual details like color, lines, or symbolism as evidence. For instance, if exploring Van Gogh's "Starry Night," you could delve into the calming effect of the swirls in the sky or the stark contrast between the bright stars and the dark village below. This visual evidence helps explain the painting's emotional impact on viewers.
Analysis & Explanation: The Importance of Going Beyond Evidence Presentation
When examining evidence, don't stop at merely presenting it. Analyze how it supports your thesis. For instance, when exploring the role of the conch in "Lord of the Flies," after showing how it represents order, explain how its loss signals the boys' descent into savagery. By unpacking the evidence's meaning, you help readers understand why it matters and how it connects to your overall argument.
• Words To Start A Paragraph • Essay Structure • Types Of Essays • How To Write A Narrative Essay • Synthesis Essay • Descriptive Essay • How To Start Off An Essay • How To Write An Analytical Essay • Write Me A Paragraph • How To Write A Synthesis Essay

1. Avoiding Summary vs. Analysis Pitfalls
When crafting a critical analysis essay, it's crucial not to fall into the trap of merely summarizing the subject without offering your own critical analysis. A summary merely recaps the content, while an analysis breaks down and interprets the subject. If you overlook this vital distinction, your essay will lack the depth and insight that characterize a strong critical analysis. Ensure your critical analysis essay doesn't read like an extended book report.
2. Steering Clear of Weak Thesis Statements
A critical analysis essay lives and dies on the strength of its thesis statement, the central argument that guides your analysis. A weak or vague thesis statement will result in an unfocused essay devoid of direction, leaving readers unclear about your point of view. It's essential to craft a thesis statement that is specific, arguable, and concise, setting the tone for a thoughtful and illuminating analysis.
3. Using Evidence is Key
The use of evidence from the subject matter under analysis is instrumental in substantiating your critical claims. Without evidence to back up your assertions, your analysis will appear unsubstantiated and unconvincing. Be sure to provide detailed examples, quotes, or data from the text under scrutiny to support your analysis. Evidence adds credibility, depth, and weight to your critical analysis essay.

4. The Importance of Clear and Supported Analysis
A successful critical analysis essay goes beyond simply presenting evidence to analyzing its significance and connecting it to your central argument. If your essay lacks clear analysis, readers won't understand the relevance of the evidence you present. Go beyond description to interpret the evidence, explaining its implications and how it supports your thesis. Without this analysis, your essay will lack depth and will not persuade your audience.
5. Addressing Counter Arguments
In a critical analysis essay, it's vital to acknowledge and engage with potential counterarguments. Ignoring opposing viewpoints undermines the credibility of your essay, presenting a one-sided argument that lacks nuance. Addressing counter arguments demonstrates that you understand the complexity of the issue and can anticipate and respond to objections.
By incorporating counterarguments, you strengthen your analysis and enhance the overall persuasiveness of your critical essay.

Jotbot is an AI-powered writing tool that offers a wide range of features to assist writers in producing high-quality written content efficiently. These features include AI note-taking, video summarization, citation and source finding, generating essay outlines, and even writing complete essays. Jotbot is designed to streamline the writing process, enabling writers to create content more effectively and quickly than traditional methods.
AI Note-Taking
Jotbot's AI note-taking feature helps writers collect and organize information in a structured manner. By enabling writers to jot down key points and ideas during research or brainstorming sessions, Jotbot ensures that important details are not missed and can be easily accessed during the writing process.
AI Video Summarization
The AI video summarization feature of Jotbot allows writers to input videos for summarization and analysis. Jotbot’s AI engine processes the content of the video and provides a concise summary. This feature is particularly useful for writers who need to reference video content in their work but may not have the time to watch the entire video.
AI Citation/Source Finder
Jotbot's AI citation and source finding feature helps writers accurately reference and cite sources in their work. By analyzing the text and identifying key information, Jotbot streamlines the citation process, reducing the time and effort involved in finding and citing sources manually.
AI Outlines for Essays
Jotbot generates AI outlines for essays based on the writer's input. These outlines provide a structured framework that writers can use to organize their thoughts and ideas before beginning the writing process. By creating a roadmap for the essay, Jotbot helps writers maintain focus and coherence throughout their work.
AI Essay Writer
Jotbot's AI essay writer feature can generate complete essays based on the writer's input and preferences. By analyzing the given information, Jotbot constructs an essay that meets the writer's criteria, enabling users to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently. With its advanced AI capabilities, Jotbot helps writers write more, write better, and write faster.
• How To Write A Personal Essay • Chat Gpt Essay Writer • How To Write An Outline For An Essay • What Makes A Good Thesis Statement • Essay Writing Tools • How To Write A 5 Paragraph Essay • How To Write A Rhetorical Analysis Essay • First Person Essay • How To Write A Header For An Essay • Memoir Essay • Formula For A Thesis Statement
Trusted by top universities and businesses

Loved by 1,000,000+
Write more, better, faster..
Your personal AI document assistant
Start writing — it's free
Your personal document assistant.
Start for free
Press enquiries
Influencer Program
Affiliate Program
Terms & Conditions
Privacy policy
AI Source Finder
AI Outline Generator
How to Use JotBot AI
© 2023 JotBot AI by SLAM Ventures, LLC all rights reserved
© 2023 SLAM Ventures, LLC
How to Critically Analyse an Article
Critical analysis refers to the skill required to evaluate an author’s work. Students are frequently asked to critically analyse a particular journal. The analysis is designed to enhance the reader’s understanding of the thesis and content of the article, and crucially is subjective, because a piece of critical analysis writing is a way for the writer to express their opinions, analysis, and evaluation of the article in question. In essence, the article needs to be broken down into parts, each one analysed separately and then brought together as one piece of critical analysis of the whole.
Key point: you need to be aware that when you are analysing an article your goal is to ensure that your readers understand the main points of the paper with ease. This means demonstrating critical thinking skills, judgement, and evaluation to illustrate how you came to your conclusions and opinions on the work. This might sound simple, and it can be, if you follow our guide to critically analyse an article:
- Before you start your essay, you should read through the paper at least three times.
- The first time ensures you understand, the second allows you to examine the structure of the work and the third enables you to pick out the key points and focus of the thesis statement given by the author (if there is one of course!). During these reads and re-reads you can set down bullet points which will eventually frame your outline and draft for the final work.
- Look for the purpose of the article – is the writer trying to inform through facts and research, are they trying to persuade through logical argument, or are they simply trying to entertain and create an emotional response. Examine your own responses to the article and this will guide to the purpose.
- When you start writing your analysis, avoid phrases such as “I think/believe”, “In my opinion”. The analysis is of the paper, not your views and perspectives.
- Ensure you have clearly indicated the subject of the article so that is evident to the reader.
- Look for both strengths and weaknesses in the work – and always support your assertions with credible, viable sources that are clearly referenced at the end of your work.
- Be open-minded and objective, rely on facts and evidence as you pull your work together.
Structure for Critical Analysis of an Article
Remember, your essay should be in three mains sections: the introduction, the main body, and a conclusion.
Introduction
Your introduction should commence by indicating the title of the work being analysed, including author and date of publication. This should be followed by an indication of the main themes in the thesis statement. Once you have provided the information about the author’s paper, you should then develop your thesis statement which sets out what you intend to achieve or prove with your critical analysis of the article.
Key point: your introduction should be short, succinct and draw your readers in. Keep it simple and concise but interesting enough to encourage further reading.
Overview of the paper
This is an important section to include when writing a critical analysis of an article because it answers the four “w’s”, of what, why, who, when and also the how. This section should include a brief overview of the key ideas in the article, along with the structure, style and dominant point of view expressed. For example,
“The focus of this article is… based on work undertaken… The main thrust of the thesis is that… which is the foundation for an argument which suggests. The conclusion from the authors is that…. However, it can be argued that…
Once you have given the overview and outline, you can then move onto the more detailed analysis.
For each point you make about the article, you should contain this in a separate paragraph. Introduce the point you wish to make, regarding what you see as a strength or weakness of the work, provide evidence for your perspective from reliable and credible sources, and indicate how the authors have achieved, or not their goal in relation to the points made. For each point, you should identify whether the paper is objective, informative, persuasive, and sufficiently unbiased. In addition, identify whether the target audience for the work has been correctly addressed, the survey instruments used are appropriate and the results are presented in a clear and concise way.
If the authors have used tables, figures or graphs do they back up the conclusions made? If not, why not? Again, back up your statements with reliable hard evidence and credible sources, fully referenced at the end of your work.
In the same way that an introduction opens up the analysis to readers, the conclusion should close it. Clearly, concisely and without the addition of any new information not included in the body paragraph.
Key points for a strong conclusion include restating your thesis statement, paraphrased, with a summary of the evidence for the accuracy of your views, combined with identification of how the article could have been improved – in other words, asking the reader to take action.
Key phrases for Critical Analysis of an article
- This article has value because it…
- There is a clear bias within this article based on the focus on…
- It appears that the assumptions made do not correlate with the information presented…
- Aspects of the work suggest that…
- The proposal is therefore that…
- The evidence presented supports the view that…
- The evidence presented however overlooks…
- Whilst the author’s view is generally accurate, it can also be indicated that…
- Closer examination suggests there is an omission in relation to
How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay: Examples & Guide
A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases.
Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you have the right approach. In this guide by our custom writing team, you will find:
- Different types of critical analysis;
- Best ways to structure your essay;
- Two excellent critical analysis essay examples.
- 📝 Critical Analysis Definition
- ✍️ Writing Guide
- ✅ Critical Analysis Types
- 📑 Examples & Tips
📝 What Is a Critical Analysis?
Criticism is the process of appraising things such as works of art and literature. It comes from the word meaning “able to make judgments”. A critical analysis essay is often referred to as a critical thinking essay, critical response paper, critical evaluation essay, and summary and response essay.
When we hear the word “criticism,” we often associate it with negative judgments. However, to criticize doesn’t necessarily mean to find faults. Even though criticism involves active disagreement, it strives to understand the meaning further and evaluate its efficiency. We call it constructive criticism .
In other words, critical analysis is an evaluation of a piece of work that promotes its better understanding . Have a look at this comparison and see what critical analysis is and what it isn’t:
| Critical analysis is: | Critical analysis is not: |
|---|---|
Aside from art and literature, critical analysis is often used in theoretical research, nursing, and social work. In any of these areas, you have an opportunity to exercise your critical faculties.
Analysis in Writing: Definition & Examples
Analysis is a step you take before writing any paper. It’s aimed at evaluating and interpreting the sources. To do it, you break them down and study them in detail. You can learn more from this article on critical analysis by Southeastern Louisiana University .
In the following table, we’ve compiled several forms of analysis in writing and illustrated each type with a topic example:
| Type of Analysis | Explanation | Topic example |
|---|---|---|
| Rhetorical Analysis | The purpose of this analysis type is to discover how a text persuades its readers. It can help you develop an ability to detect manipulations. | Techniques that Sir Ken Robinson to emotionally appeal to the viewer in his TED talk |
| Process Analysis | This form of analysis divides a business, social, or political process into several steps. There are two distinct types of process analysis: | How to purify water using carbon filtering. |
| Causal Analysis | This type of analysis focuses on the events that already happened and may try to predict what will happen in the future. Counter-arguments are a crucial part of the causal analysis. | Causes and effects of internet addiction among younger generations. |
| Critical analysis | This type of analysis aims to evaluate a work and to promote its better understanding. | The role of Zen Buddhism in JD Salinger’s . |
What Is the Difference between Summary and Analysis?
Students often confuse analysis with summary and get a lower grade as a result. Here is how two notions differ. A summary is a brief restatement of the text’s main points that involves paraphrasing. An analysis is a detailed examination of the evidence that uncovers something new.
Check out this comparison to understand the difference better:
| Summary | Analysis |
|---|---|
✍️ How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay
Now, we will show you the steps to writing a critical analysis with examples to guide you through this process. Keep in mind that the purpose of your critical analysis paper is to help readers understand a subject to a full extent.

Critical analysis consists of two stages: critical reading and critical writing. Read on to learn more about them.
Critical Reading Examples & Definition
Critical reading a technique that involves discovering and evaluating the text’s meaning and incorporating it into what you already know. It’s the first stage of critical analysis.
According to Cleveland State University, critical reading occurs after you’ve skimmed the research material and decided where to focus your efforts. While you are reading, use the following techniques to stay on track:
- Determine the central claim and identify how it is argued;
- Look for the large patterns that give purpose, order, and meaning to arguments;
- Contextualize the text within an original historical, political, or religious context;
- Distinguish the kinds of reasoning and methodology the text employs;
- Examine the evidence;
- Recognize manipulations.
When it comes to recognizing manipulations, authors use three persuasive appeals to convince their readers of something: ethos , pathos , and logos .
| Ethos, or the appeal to ethics, refers to the author’s effort to convince you of their credibility through appropriate language. It refers to the author’s reputation and the reader’s trust. | |
| Pathos, or the appeal to feelings, refers to the effort to persuade a reader by making them feel a particular emotion. It is achieved through language, tone of voice, use of anecdotes, and metaphors. | |
| Logos, or the appeal to rationality, is persuasion through logic and reason. Storytelling, historical facts, recorded evidence, and exceptional arguments are the authors’ tools to convince you. |
Now, let’s apply the critical reading techniques to an actual text:
The death estimates during the US invasions of Tokyo were exaggerated by a factor of ten to twenty. The wartime casualty estimates were based on inaccurate assumptions. The data was not updated to exclude the civilians’ deaths and justify the strategic decision to drop off an atomic bomb.
- What is the text saying? US bombs killed up to two million people.
- What is the text doing? The death estimates were exaggerated to downplay the casualties and emphasize the importance of dropping the atomic bomb.
When you are able to recognize these persuasive modes in your reading, you can master them in writing.
What Is Critical Writing: Definition & Techniques
Critical writing is a process of commenting on another piece of work using several writing strategies. It is the second stage of critical analysis.
Want to know how to write critically? Have a look at the following tips:
- Take a critical stance: recognize that every text comes from a perspective and is subject to interpretation.
- Pay close attention: look not only for the facts but also for explanations.
- Think big picture : put your sources in context with the time it was written.
- Bring yourself in: consider the connections between several texts and add your own perspective.
When it comes to the critical writing, certain strategies can be beneficial. Yet, others are better to avoid. We’ve compiled the most important dos and don’ts in the table below:
| ✔️ Dos | ❌ Don’ts |
|---|---|
| . The more thorough you are with your primary and additional sources, the stronger your argument will be. . Credible sources and strong arguments will help you to prove your point. . The way you communicate your point and structure your paper will determine how confident your writing sounds. . Present the reader not only with facts and quotes but also with in-depth research and thorough analysis. | . The only essay part where you can take advantage of descriptive writing is the summary. . Question your sources and always back up your arguments. . Instead of drawing attention to yourself, focus on the strengths or weaknesses of the piece you are analyzing. . Always use proper citation style and have works cited page at the end of your paper. . Instead, re-read it out loud. Look for mistakes and missing information. |
Want to learn more? Check out our article on critical writing .
Critical Analysis Essay Topics: How to Choose
Now that you’ve learned about critical analysis, there is a big question to answer: how do you choose the topic for your essay? It might require using a specific strategy to make the right choice.
Many students find it helpful to have a list of critical thinking questions to answer while brainstorming. We’ve prepared them for you:
- Theme : How well does the author approach the central theme? Are the arguments strong enough?
- Organization : Is this piece of work well-structured and easy to follow?
- Audience : Who is the audience? Are there any manipulations the author is using to persuade the reader?
- Tone : Is there a specific tone used by the author throughout their work? How does it affect the reader?
- Bias and informational gaps : Does the author look at their work from several angles? Are there any contradicting arguments or missing information?
- Word choice : Does the author invent new words? Is the vocabulary serious or silly, casual or technical? How does it affect the overall writing?
- Logos : Does the author use logic to prove their point?
- Ethos : Does the author have any proof of their credibility? Do they claim to be an expert? In what ways is the reader’s trust gained?
- Pathos : Does the author use emotion to connect with the reader? Does the writing appeal to common beliefs and values?
Answering these questions will help you with deciding on critical thinking essay topics. If you want some additional inspiration, feel free to use our topic generator .
Critical Analysis Template
After carefully analyzing all of your sources, you can start writing your first draft using our critical analysis template. Use this outline to structure your essay and to ensure your arguments are related to your thesis.
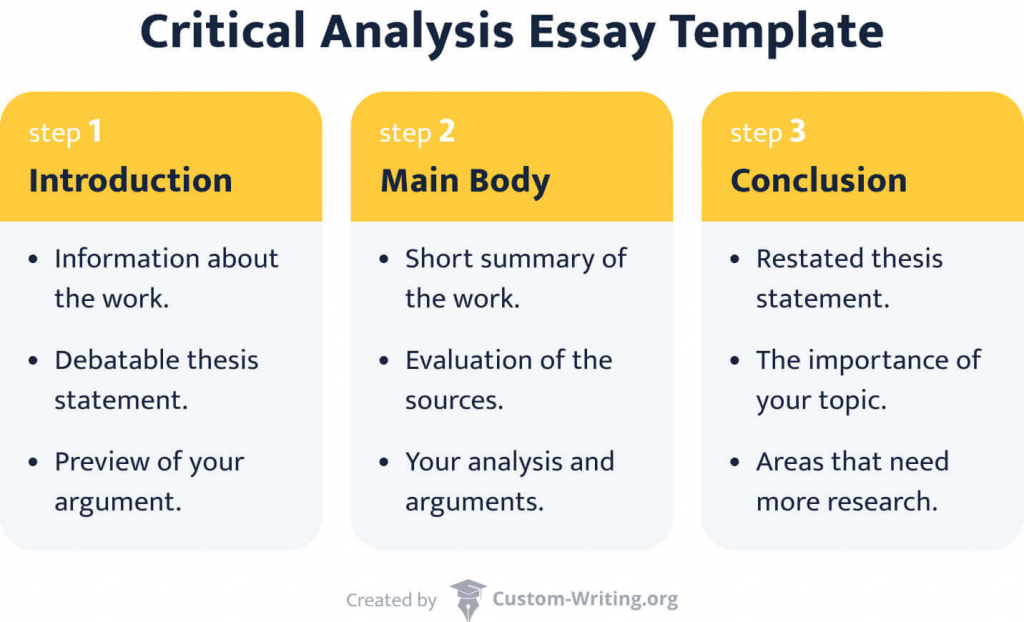
How to Start a Critical Analysis Essay
To create an outstanding opening paragraph, you may want to start it with a hook. It can be a quote from your source or a rhetorical question. Be sure to make it catchy so that it will grab your reader’s attention.
After you’re done with the hook, write the following:
- the work’s title and some background information,
- an outline of the main ideas from your sources,
- your thesis statement.
Here are two introduction examples for your inspiration:
What happens when there is a considerable wage gap between the upper and middle classes? The unsurprising reality forces poor people to use credit cards to pay off their debt. Credit card industries collect interest from those who can’t pay off their debt right away.
A romantic novel Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen is about overcoming social stereotypes in the name of love. Its main character, Elizabeth Bennet, has to fight against her discrimination against wealthy men like Mr. Darcy to find love and be happy.
Critical Analysis Essay: Thesis
A thesis statement is what you are aiming to prove. Ideally, it should be the first thing you write because every other part of your critical analysis paper will be connected to it.
To create a strong thesis statement, you want to start with a broader idea of what you would like to critique. Then, you narrow it down. Choose a debatable thesis so you can back it up with evidence from your sources and anchor your entire paper around it.
The examples below will help you write your essay’s thesis:
People in positions of power are less likely to recognize the social injustice than marginalized groups of the civilian population.
In a 1989 American superhero film Batman, Tim Burton subverts the concept of heroism by refraining Batman from murder and making him morally ambiguous.
Critical Analysis Essays: Summary and Response
The body paragraphs of a critical essay consist of your source’s summary and a response with arguments.

A summary should present specific facts from your source to help your reader understand your arguments better. You can use these sentence starters to structure a summary:
- The book is about…
- The theme of the article is…
- The author argues that…
- The author concludes…
- The main character is…
- The main points are…
The main plot of Elizabeth Bennet’s plan to save her family from poverty intersects with stereotypes that romantic love and marriage don’t go together. She does not accept a marriage proposal from Mr. Darcy because she does not want to be walking proof that women marry for money. The rejected proposal leads Darcy to open up and change Elizabeth’s perception of him.
A response should present your main arguments that support your thesis statement. Each argument is a sub-thesis that connects to your central thesis. It’s crucial to discuss each point in detail and prove it with strong evidence.
Your arguments should be:
- clear, informative, and persuasive;
- well-researched and backed up with solid evidence;
- connected to your thesis.
At first, Elizabeth Bennet sees Mr. Darcy only as a powerful man with wealth and high social status. For her, he represents a marriage of convenience that she is so desperately trying to fight against. After Mr. Darcy attempts to separate Jane and Bingley, Elizabeth gets proof for her ideas about powerful men who do everything in their power to destroy a loving relationship for a better financial suit.
Critical Essay Outline: Conclusion
The final stage of essay writing is to ensure you have proven your arguments. The goal of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your thesis and the essay’s main points. You may also want to leave them with some final statements for consideration.
Keep in mind that the concluding paragraph is not a place to introduce new evidence. Instead, you can do the following:
- Restate your thesis;
- Summarize your main ideas;
- Talk about the work’s overall performance or outcome;
- Identify potential opportunities for further research or investigation.
Elizabeth Bennet struggles with the societal association of marriage with financial stability. Eventually, she marries a rich man, Mr. Darcy, but she marries him for love rather than his money and social status. Her pride and prejudice towards him were destroyed by his acts of kindness and true love. Their relationship had a rough start, but both of them could get their happy ending by breaking out of old beliefs and habits.
✅ Types of Critical Analysis
Choosing the correct type of analysis will help you stay on track with your research objectives. It will give you the anchor to develop your essay around in a systematic manner.
Critical analysis can be categorized into 4 main types:
- Literary analysis gives a critical evaluation of a literary text.
- Article analysis reflects upon arguments presented in an article.
- Media analysis essay interprets messages conveyed through visual media, music, or radio.
- Cultural analysis interprets cultural phenomena and practices.
Literary Analysis: Definition & Characteristics
Literary analysis is an argument that expresses one’s critical evaluation of a poem, novel, short story, or play. A critique of literature has the same characteristics as other types of critical essays. The difference is the kind of information you can include in this type of essay.
Here’s how to analyze literature:
You will find more interesting info in our article on literary analysis essays .
How to Write an Analysis of an Article
Critical analysis of an article aims to analyze the writing strategies and techniques an author uses to develop their argument. The process is a little different than persuading the reader to accept a particular point of view. Here is a sample outline:
Critical Film Analysis: Types & How to Write
Film analysis goes beyond the plot structure and includes composition elements such as camera work, lighting, costume choices, etc. After watching the film at least twice, you can select what type of film analysis you will be performing. Check out the types and see what they’re about:
- Semiotic analysis involves interpretation of signs and symbols within a film.
- Narrative analysis examines the story the film seeks to tell.
- Historical analysis is an examination of a film’s relationship to a cultural or historical context.
- Mise-en-scène analysis is an analysis of compositional elements used in a scene or a single shot.
Once you’ve chosen a topic, use this outline to guide you through the writing process:
You can learn more from our article on film analysis .
How to Write a Cultural Analysis Essay
Critical analysis essay refers to your comment upon one specific cultural aspect that works or doesn’t work in a society. After you’ve chosen a topic for your cultural analysis paper, you can start drafting your outline. Here is how the structure of this kind of paper differs from others:
Critical Analysis Essay Topics
- Critical analysis of qualitative research article.
- Rhetorical analysis of articles on qualitative studies in healthcare.
- American Exodus by James N. Gregory: Rhetorical Analysis.
- Critical analysis of religion and faith .
- Analyze the sonnet My Mistress’ Eyes by W. Shakespeare .
- Critical essay on issues of cognitive neuroscience.
- A Doll House as an example of feminist literature: rhetorical analysis.
- Conduct a comparative critical analysis of Judaism and Christianity.
- Rhetorical analysis of an Anglo-Saxon poem Beowulf .
- Semantic meaning of The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath .
- Critical evaluation of Seligman articles.
- Analyze psychological literature based on A Clean, Well-Lighted Place by E. Hemingway.
- Rhetorical analysis of literary devices and expressive means in A Good Man Is Hard to Find .
- Analyze the characteristic features of drama using the example of Death of a Salesman .
- Critical analysis of the most popular business strategies .
- Discuss the problem of childhood obesity in Active Living by Van Kann.
- Analyze IT strategies and planning.
- Critical analysis of a controversial art using the example of Home by Yann Arthus-Bertrand.
- Emotional impact of comedy films.
- Rhetorical analysis of Sophocles’ Antigone as an example of Greek drama.
- Influence of Socrate’s philosophy on the ancient Greek playwrights.
- Critical analysis of Sophocles’ plays.
- Different sets of values in Everyday Use by A. Walker .
- Analysis of corporate crimes using the example of Lehman Brothers’ scandal.
- Critical analysis of a scientific article based on Nursing Pain Management .
- Different interpretations of A Good Man Is Hard to Find by Flannery O’Connor.
- Critical analysis of Longinus’ idea of sublime .
- The importance of a teacher’s role in Freedom Writers .
- Critical analysis of the efficiency of CBT.
- Rhetorical analysis of an article on a proactive care program.
- The concept of emotional intelligence: critical analysis.
- Evaluate implementation of Windsome’s risk management strategy to enhance the company’s response to stress.
- The importance of symbolism in Truman Capote’s Breakfast at Tiffany’s .
- Critical analysis of Thomas Paine’s pamphlets.
- Rhetorical techniques used in Hamlet by W. Shakespeare .
- In-depth analysis of the modern world’s social issues in The Handmaid’s Tale .
- Social messages in Robinson’s and Kincaid’s stories.
- Analysis of rhetorical strategies used in Dwellings by Linda Hogan.
- Critical analysis of issues elucidated in A Loss for Words by J. Thurman.
- Discuss the problems of alienation and perception in The Things They Carried .
📑 Critical Analysis Essay Examples & Bonus Tips
The following writing tips will help you understand how to apply your critical thinking skills in practice and write an excellent critical essay on your own.
Critical Essay Format & Free Samples
Looking for some tips on how to format your paper? This section reflects the latest guidelines for citing your sources with the latest APA 7th and MLA 9th publication manuals.
| APA format | MLA format | |
|---|---|---|
| Not required. | ||
| Sources in alphabetical order. | Sources in alphabetical order. |
Before you dive into writing your critical analysis paper, get inspired with some compelling essay examples. The first is a film analysis example. You can download the PDF file below:
The Birds by Alfred Hitchcock is a thriller that derives its suspense from the violence which stands on the borderline with divine retribution. The birds of the film are the symbol of the said violence and primary actors that contribute to the semiotic revelations of the film.
The following critical analysis essay is concerned with a literary work. You can download it below:
Feminism has been influential in various aspects of society for many decades. With the beginning of women’s emancipation, humanity has progressed not only in political and social life but also in science, culture, and literary studies. A feminist standpoint in literature research points to the limited portrayal of the characters in literary works, which showed the world mainly from a patriarchal perspective.
Here’s the list of critical analysis essay examples. You can check them out to get a better understanding of critical analysis and to gain some inspiration.
- Managing Business Risks: A Critical Analysis
- Nursing Skills for Palliative Care: A Critical Analysis
- Critical Analysis of Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
- Nighthawks by Edward Hopper: Critical Analysis
- Roosevelt and Obama: Critical Analysis of Two Speeches
- “The Love of My Life” by T. C. Boyle Critical Analysis
- Nursing Education-Practice Gap: Critical Analysis
- Affordable Care Act: A Critical Analysis
- Mother Tongue by Amy Tan: Critical Analysis
Bonus Tips: Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the process of conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information. It is about careful reasoning directed to a goal. The main components of this process include observing, wondering, imagining, experimenting, judging, and deciding.
This type of thinking is instrumental in conducting a critical analysis. To succeed at it, you need to be attentive, confident, and open-minded. Below are some questions that you can ask yourself while thinking critically:
- Why are you being told this?
- What are you not being told?
- Who is telling you this?
- How reliable is this information?
- Are there any manipulations involved?
- How else can you analyze the same material?
Critical thinking is a skill that develops with time and effort. However, you may encounter barriers that can prevent you from making accurate judgments. The following tips will help you overcome them:
- Step back from your personal feelings and biases
- Look for different ways to examine the data
- Check your sources for reliability
- Do your best to detect manipulations in arguments
- Always conceptualize what you are reading
- Challenge your worldview
Want to learn more? Feel free to check out our article on critical thinking essays .
Now you know everything necessary to write a perfect critical analysis essay. Feel free to share this article or leave a comment!
Further reading
- How to Write a Critique Paper: Tips + Critique Essay Examples
- How to Write an Art Critique: Examples & Strategies
- How to Write an Analysis Essay: Examples + Writing Guide
- How to Write a Book Review: Format, Outline, & Example
- How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Outline, Steps, & Examples
❓ Critical Analysis Essay FAQs
When analyzing any literary text, it is essential to evaluate the work and use the theme to support your opinion. The response’s goal is to show the reader what the selection of the source and the theme means to you personally.
The purpose of a response to a literature essay is to inform your reader about something interesting and insightful you found in a literary work. It may focus on the characters, plot, or theme of the story.
In a critical essay, choose the formal language and avoid using “I” statements. Focus on the piece you are analyzing, its strengths, and weaknesses. Using the first-person singular will take away the reader’s attention from your argument to you.
A critical source is a source that interprets, analyzes, critiques, and adds to the discussion of the primary source. It is then integrated into critical writing. The best critical sources can be found through library catalogs and scholarly databases.
🔍 References
- Critical Analysis: University of Wollongong
- Some Suggestions on Critically Evaluating Your Reading in History: Carleton College
- Criticism and Critical Analysis: Kansas State University
- Resources for Writers: Analytical Writing: Drew University
- Critical Thinking and Writing: University of Kent
- Writing Critical Essays about Literature: Gallaudet University
- Film Analysis: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Cultural Critique: Southern Illinois University Edwardsville
- Writing a Critical or Rhetorical Analysis: Bellevue College
- Writing Critical Analysis Papers: University of Washington
- Critical Analysis Template: Thompson Rivers University
- Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays: Colorado State University
- Rhetorical/Critical Analysis: Houston Community College
- Writing Critical Reviews: Queen’s University
- General APA Guidelines: Purdue University
- Using MLA Format: MLA.org
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![critical analysis essay on newspaper article How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![critical analysis essay on newspaper article How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![critical analysis essay on newspaper article How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
Critically Analyzing Information Sources: Critical Appraisal and Analysis
- Critical Appraisal and Analysis
Initial Appraisal : Reviewing the source
- What are the author's credentials--institutional affiliation (where he or she works), educational background, past writings, or experience? Is the book or article written on a topic in the author's area of expertise? You can use the various Who's Who publications for the U.S. and other countries and for specific subjects and the biographical information located in the publication itself to help determine the author's affiliation and credentials.
- Has your instructor mentioned this author? Have you seen the author's name cited in other sources or bibliographies? Respected authors are cited frequently by other scholars. For this reason, always note those names that appear in many different sources.
- Is the author associated with a reputable institution or organization? What are the basic values or goals of the organization or institution?
B. Date of Publication
- When was the source published? This date is often located on the face of the title page below the name of the publisher. If it is not there, look for the copyright date on the reverse of the title page. On Web pages, the date of the last revision is usually at the bottom of the home page, sometimes every page.
- Is the source current or out-of-date for your topic? Topic areas of continuing and rapid development, such as the sciences, demand more current information. On the other hand, topics in the humanities often require material that was written many years ago. At the other extreme, some news sources on the Web now note the hour and minute that articles are posted on their site.
C. Edition or Revision
Is this a first edition of this publication or not? Further editions indicate a source has been revised and updated to reflect changes in knowledge, include omissions, and harmonize with its intended reader's needs. Also, many printings or editions may indicate that the work has become a standard source in the area and is reliable. If you are using a Web source, do the pages indicate revision dates?
D. Publisher
Note the publisher. If the source is published by a university press, it is likely to be scholarly. Although the fact that the publisher is reputable does not necessarily guarantee quality, it does show that the publisher may have high regard for the source being published.
E. Title of Journal
Is this a scholarly or a popular journal? This distinction is important because it indicates different levels of complexity in conveying ideas. If you need help in determining the type of journal, see Distinguishing Scholarly from Non-Scholarly Periodicals . Or you may wish to check your journal title in the latest edition of Katz's Magazines for Libraries (Olin Reference Z 6941 .K21, shelved at the reference desk) for a brief evaluative description.
Critical Analysis of the Content
Having made an initial appraisal, you should now examine the body of the source. Read the preface to determine the author's intentions for the book. Scan the table of contents and the index to get a broad overview of the material it covers. Note whether bibliographies are included. Read the chapters that specifically address your topic. Reading the article abstract and scanning the table of contents of a journal or magazine issue is also useful. As with books, the presence and quality of a bibliography at the end of the article may reflect the care with which the authors have prepared their work.
A. Intended Audience
What type of audience is the author addressing? Is the publication aimed at a specialized or a general audience? Is this source too elementary, too technical, too advanced, or just right for your needs?
B. Objective Reasoning
- Is the information covered fact, opinion, or propaganda? It is not always easy to separate fact from opinion. Facts can usually be verified; opinions, though they may be based on factual information, evolve from the interpretation of facts. Skilled writers can make you think their interpretations are facts.
- Does the information appear to be valid and well-researched, or is it questionable and unsupported by evidence? Assumptions should be reasonable. Note errors or omissions.
- Are the ideas and arguments advanced more or less in line with other works you have read on the same topic? The more radically an author departs from the views of others in the same field, the more carefully and critically you should scrutinize his or her ideas.
- Is the author's point of view objective and impartial? Is the language free of emotion-arousing words and bias?
C. Coverage
- Does the work update other sources, substantiate other materials you have read, or add new information? Does it extensively or marginally cover your topic? You should explore enough sources to obtain a variety of viewpoints.
- Is the material primary or secondary in nature? Primary sources are the raw material of the research process. Secondary sources are based on primary sources. For example, if you were researching Konrad Adenauer's role in rebuilding West Germany after World War II, Adenauer's own writings would be one of many primary sources available on this topic. Others might include relevant government documents and contemporary German newspaper articles. Scholars use this primary material to help generate historical interpretations--a secondary source. Books, encyclopedia articles, and scholarly journal articles about Adenauer's role are considered secondary sources. In the sciences, journal articles and conference proceedings written by experimenters reporting the results of their research are primary documents. Choose both primary and secondary sources when you have the opportunity.
D. Writing Style
Is the publication organized logically? Are the main points clearly presented? Do you find the text easy to read, or is it stilted or choppy? Is the author's argument repetitive?
E. Evaluative Reviews
- Locate critical reviews of books in a reviewing source , such as the Articles & Full Text , Book Review Index , Book Review Digest, and ProQuest Research Library . Is the review positive? Is the book under review considered a valuable contribution to the field? Does the reviewer mention other books that might be better? If so, locate these sources for more information on your topic.
- Do the various reviewers agree on the value or attributes of the book or has it aroused controversy among the critics?
- For Web sites, consider consulting this evaluation source from UC Berkeley .
Permissions Information
If you wish to use or adapt any or all of the content of this Guide go to Cornell Library's Research Guides Use Conditions to review our use permissions and our Creative Commons license.
- Next: Tips >>
- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2024 3:08 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/critically_analyzing
- Scholarships
- Student Guide
- Study Abroad
- Advertise With Us
- Contact Us for Expert Assistance: Unlock Your Academic Success with Scholar Ace – 24/7 Support

10 Military Spouse Scholarships to Help You Achieve Your Education Goals:…

Applying for the Prestigious NHS Scholarship: Step-by-Step

The HPRA National Scholarship – Empowering Future Leaders

Unlocking Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide to the Knight-Hennessy Scholarship

Top Ten Best International Scholarships to Look for this Fall- January…

Top Ranked Apple and Android Tablets For Students in 2024

5 Must-have Tech Accessories For Students Below $50

5 Gadgets College Students Think They Need But Don’t

What Clever Electronics Do University Students Really Need?

IXL for Parents: How to Monitor and Support Your Child’s Learning

Unlocking Opportunities: How to Apply for the US Bank Scholarship Program

160 Top English-Taught Masters Programs in Asia For International Students

Navigating The Crucial Role of CDR Report for Engineers: How to…

Countries Where International Students Can Earn Money While Studying Abroad

Know Everything About Studying Abroad In Russia As An International Student

Top Budget Friendly Countries To Learn French Abroad

Best Summer And Winter Break Study Abroad Programs

A 101 Guide To Dell Scholarship: Exploring The Application Process And…

IFMA FMP Certification: Everything You Need to Know

The Ultimate Guide To Passing A CFE Examination

Competency Demonstration Report (CDR) Writing For Engineers Australia | Everything That…

A Guide To Kick-Starting Your Essay With A Quote

How To Write A Process Analysis Essay?

INFANT MORTALITY

“WOMEN, MARRIAGE AND TABOOS”

A Girl In The Cage Of Insecurities
How to write an analysis of a newspaper article.

Newspapers and other new sources provide valuable information and updates about current events and ongoing issues. They keep the audience updated about the latest updates and trends in the world. They benefit a variety of audiences. They are a great resource for students and researchers, helping them gain insight into various perspectives on their topics of interest and also help them analyze the topics of their interest.
Why Analyze a News Paper Article?
Analyzing a newspaper article is vital for gaining a deeper understanding of current events and issues. It allows the readers to identify the purpose of the article and also identify the intended audience of the article. Analyzing the newspaper also involves summarizing its key points and arguments, analyzing the language and style, and evaluating the credibility of the article, writer, and information written. It also involves considering its overall effectiveness and relevance. Using these steps, you can develop a well-informed and clear perspective on the topic of interest.

In order to write an excellent, well-organized and well-researched analysis of a newspaper article. you first need to understand how the information is put forth in the article that you’ve chosen and wish to undertake the analysis of. Most newspapers, however, get their articles written in what is called in technical jargon- “The Inverted Pyramid ”. The inverted pyramid is where the meatiest part of the information or piece of news is mentioned at the commencement of the article and the news with lesser degrees of importance is mentioned gradually.
Also Learn: How To Write College Application Essay
This is done in order to assist the process where a certain new piece of information is found out or got released and you have to add it to the pre-existing structure . This is done by employing the editing style where you go from the bottom of the article to the very top.
Newspaper articles aim to bring answers to six main issues regarding any news . These are:
- The ‘who’ of the news
- The ‘what’ of the news
- The ‘when’ of the news
- The ‘where’ of the news
- The ‘why’ of the news
- The ‘how’ of the news
The “inverted pyramid” structure came about as a result of old media technology – the telegraph. When news information was telegraphed over the wires, the most crucial information was transmitted first. If the connection was lost, the story could still be printed with the essential facts.
Therefore, this method is also suitable for the editors, where they can choose to cut the bottom part to adjust the length of the news. Same way, for analysis purposes, the information structure helps you figure out important aspects of the newspaper article and overall structure.

Criticism of The Inverted Pyramid
While it is a common way to present information in a newspaper article, this method is also criticized often. Few in the media critique the inverted pyramid is not the right fit for every news story, as it may also lead to a decline in the reader’s attention. With the ending being told at the beginning of the story, most of the readers may not read it till the end.
However, this organized method of information is still beneficial in presenting you with structured information.
How to Analyze a Newspaper Article
Now that we have established the fact that newspaper articles are of utmost importance in the modern narrative of affairs , we shall now move onto explaining how one can evaluate these articles. Analyses of a newspaper articles can easily by written by making sure the following steps are well taken care of:
Finding the article that you would like to comment on is quite obviously the very first step. It should be a topic that you are interested in, well-rehearsed in, have some knowledge about and are even passionate about.
Summarizing the Article
To begin with, make a summary of the key points the article is trying to convey. Make sure they are concise and don’t stretch farther than three or five sentences.
To summarize the article, you should consider answering the following questions:
- What is the main topic the author is covering?
- What are the main arguments made by the author?
- What are the pieces of evidence used by the author to support these arguments?
- What is the conclusion?
With this, you will get a clear picture of the article’s content. This summary will also help you in the following steps when it comes to analyzing the tone and style and evaluating the credibility.
Identifying the Purpose and the Audience
Once you have the summary of key points in place, the first step in analyzing the newspaper article is to identify its purpose and the target audience for whom this article was intended. While a summary will provide you with a brief understanding of the key points, this step will help you thoroughly understand the main message and how it is conveyed.
To figure out the audience and its purpose, consider answering the following questions:
- What is the main idea that the article is about?
- What is the author’s main argument about the point or their main point of view?
- Who is this article written for i.e. who is the intended audience ?
- What is the author trying to accomplish i.e. his/her main goal ?
Figure out and denote the intention the article was written for, whether it has some purpose and make a note of that. It’s entirely possible for a newspaper article to have more than b to achieve for example a piece of news can be influencing and entertaining, both for its cause. You must make the critical choice of opting for one main objective of your chosen article and go further enough to provide valid justifications for your choice.
While you have already explained your choice of the article’s purpose initially, you must also go into further detail regarding this by having direct quotations from the article as a part of your analysis.
Moreover, by answering the question mentioned above, you will be able to gain a better understanding of the article’s context and the underlying message as well.
Analyzing Tone and Style
Once you have identified the purpose and the intended audience, you can focus on analyzing its tone and style. Both, the tone and style, can influence the impact and effectiveness of the article greatly. An article writer can use various techniques to convey their message. It can involve the use of persuasive techniques and rhetorical elements to convey the message as well as engage the reader. For analysis purposes, you will be focusing on identifying the use of these techniques and evaluating their impact on the article.
When you are trying to identify the tone, the article just might be trying to convey different tones as well as perspectives. You must make the critical choice of identifying the one major tone that can easily be seen as being the predominant tone of your article.
Again, you must then provide the reader of your newspaper article analysis with valid justifications for your choice of tone as well as provide them with the context by selecting some quotations from the article and making them a part of your analysis.
To identify tone and style, you should consider the following elements:
- Language Use: Is the author conveying his/her point clearly and concisely? Are the terms used right for the target audience? Is the writer using complex or too many technical terms? Are they difficult for the reader to understand?
- Tone: Is the author using a formal tone or being informal? Is it persuasive or informative?
- Style: Is the author’s writing descriptive or analytical? Is the writer using metaphors? How is the writer providing supporting evidence?
When you analyze these elements, you will be able to gain a better understanding of how the author is using various language and writing techniques to convey their message. You’ll also be able to understand how successfully these techniques are contributing to the author’s objective.
Analyzing the Language
After analyzing the tone and style, you should focus on analyzing the language used by the author. This will further help you gain a better understanding of how the author is trying to get their point across and how are they engaging the reader.
To analyze the language, determine the techniques and expressions used by the writer of your article and pick the major three techniques that you think have much more impact than any other. These techniques must each be explained and alluded to separately- not to forget that their objective and function must be established as well so that the use of these by the author of your newspaper article is justified.
This is a great way to make your analysis seem professional and organized. Some examples of techniques you could easily identify and use are the choice of certain words as being appropriate or not for the topic of the article, any wordplay that might cater to the entertainment of the audience, structures that the sentences are put in and whether or not they effectively convey the idea the article is trying to pertain to.
Another golden method to give your newspaper article analysis an upper hand is by picking up words or even writing techniques from the article that you have found unfamiliar to your previous knowledge. These are then to be explained and alluded to in succinct detail and must connect to the context of your article.
If such a thing cannot be identified in your chosen article, another way to ace your analysis is by pointing out certain words, sentences, or approaches that you have found particularly well employed and refined and going into detail about THEIR significance.
In general, try to focus on the following areas to help you follow a more structured approach:
- Use of Persuasive Language: Is the author using any persuasive techniques such as emotional appeals?
- Information Analysis : Is the author giving the information or also challenging any narratives?
- Use of Words: Is the author using simple language for a mass audience or using technical terms? Can the target audience understand the concept clearly?

Last but not the least, comment in detail about any particular ideas or perspectives that the article is trying to convey or perhaps the problems it has tried to address or the solutions provided .
This can be made even more sophisticated if the writer, that is, you give your personal opinion about all of the above. Stating whether you are in agreement or not or have found it helpful or perhaps disturbing can bring a refined edge to your analysis as well.

Are you beginning to get a better understanding of how to write an analysis of a newspaper article ? Let us know in the comment sections below!
About Post Author
Scholar Ace
See author's posts
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Recent posts, college essay: top 10 critical mistakes to avoid when writing your college essay, 10 military spouse scholarships to help you achieve your education goals: a comprehensive guide.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
Privacy Overview

What Is a Critical Analysis Essay: Definition

Have you ever had to read a book or watch a movie for school and then write an essay about it? Well, a critical analysis essay is a type of essay where you do just that! So, when wondering what is a critical analysis essay, know that it's a fancy way of saying that you're going to take a closer look at something and analyze it.
So, let's say you're assigned to read a novel for your literature class. A critical analysis essay would require you to examine the characters, plot, themes, and writing style of the book. You would need to evaluate its strengths and weaknesses and provide your own thoughts and opinions on the text.
Similarly, if you're tasked with writing a critical analysis essay on a scientific article, you would need to analyze the methodology, results, and conclusions presented in the article and evaluate its significance and potential impact on the field.
The key to a successful critical analysis essay is to approach the subject matter with an open mind and a willingness to engage with it on a deeper level. By doing so, you can gain a greater appreciation and understanding of the subject matter and develop your own informed opinions and perspectives. Considering this, we bet you want to learn how to write critical analysis essay easily and efficiently, so keep on reading to find out more!
Meanwhile, if you'd rather have your own sample critical analysis essay crafted by professionals from our custom writings , contact us to buy essays online .

Need a CRITICAL ANALYSIS Essay Written?
Simply pick a topic, send us your requirements and choose a writer. That’s all we need to write you an original paper.
Critical Analysis Essay Topics by Category
If you're looking for an interesting and thought-provoking topic for your critical analysis essay, you've come to the right place! Critical analysis essays can cover many subjects and topics, with endless possibilities. To help you get started, we've compiled a list of critical analysis essay topics by category. We've got you covered whether you're interested in literature, science, social issues, or something else. So, grab a notebook and pen, and get ready to dive deep into your chosen topic. In the following sections, we will provide you with various good critical analysis paper topics to choose from, each with its unique angle and approach.
Critical Analysis Essay Topics on Mass Media
From television and radio to social media and advertising, mass media is everywhere, shaping our perceptions of the world around us. As a result, it's no surprise that critical analysis essays on mass media are a popular choice for students and scholars alike. To help you get started, here are ten critical essay example topics on mass media:
- The Influence of Viral Memes on Pop Culture: An In-Depth Analysis.
- The Portrayal of Mental Health in Television: Examining Stigmatization and Advocacy.
- The Power of Satirical News Shows: Analyzing the Impact of Political Commentary.
- Mass Media and Consumer Behavior: Investigating Advertising and Persuasion Techniques.
- The Ethics of Deepfake Technology: Implications for Trust and Authenticity in Media.
- Media Framing and Public Perception: A Critical Analysis of News Coverage.
- The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Discourse and Activism.
- Fake News in the Digital Age: Identifying Disinformation and Its Effects.
- The Representation of Gender and Diversity in Hollywood Films: A Critical Examination.
- Media Ownership and Its Impact on Journalism and News Reporting: A Comprehensive Study.
Critical Analysis Essay Topics on Sports
Sports are a ubiquitous aspect of our culture, and they have the power to unite and inspire people from all walks of life. Whether you're an athlete, a fan, or just someone who appreciates the beauty of competition, there's no denying the significance of sports in our society. If you're looking for an engaging and thought-provoking topic for your critical analysis essay, sports offer a wealth of possibilities:
- The Role of Sports in Diplomacy: Examining International Relations Through Athletic Events.
- Sports and Identity: How Athletic Success Shapes National and Cultural Pride.
- The Business of Sports: Analyzing the Economics and Commercialization of Athletics.
- Athlete Activism: Exploring the Impact of Athletes' Social and Political Engagement.
- Sports Fandom and Online Communities: The Impact of Social Media on Fan Engagement.
- The Representation of Athletes in the Media: Gender, Race, and Stereotypes.
- The Psychology of Sports: Exploring Mental Toughness, Motivation, and Peak Performance.
- The Evolution of Sports Equipment and Technology: From Innovation to Regulation.
- The Legacy of Sports Legends: Analyzing Their Impact Beyond Athletic Achievement.
- Sports and Social Change: How Athletic Movements Shape Societal Attitudes and Policies.
Critical Analysis Essay Topics on Literature and Arts
Literature and arts can inspire, challenge, and transform our perceptions of the world around us. From classic novels to contemporary art, the realm of literature and arts offers many possibilities for critical analysis essays. Here are ten original critic essay example topics on literature and arts:
- The Use of Symbolism in Contemporary Poetry: Analyzing Hidden Meanings and Significance.
- The Intersection of Art and Identity: How Self-Expression Shapes Artists' Works.
- The Role of Nonlinear Narrative in Postmodern Novels: Techniques and Interpretation.
- The Influence of Jazz on African American Literature: A Comparative Study.
- The Complexity of Visual Storytelling: Graphic Novels and Their Narrative Power.
- The Art of Literary Translation: Challenges, Impact, and Interpretation.
- The Evolution of Music Videos: From Promotional Tools to a Unique Art Form.
- The Literary Techniques of Magical Realism: Exploring Reality and Fantasy.
- The Impact of Visual Arts in Advertising: Analyzing the Connection Between Art and Commerce.
- Art in Times of Crisis: How Artists Respond to Societal and Political Challenges.
Critical Analysis Essay Topics on Culture
Culture is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect of our society, encompassing everything from language and religion to art and music. As a result, there are countless possibilities for critical analysis essays on culture. Whether you're interested in exploring the complexities of globalization or delving into the nuances of cultural identity, there's a wealth of topics to choose from:
- The Influence of K-Pop on Global Youth Culture: A Comparative Study.
- Cultural Significance of Street Art in Urban Spaces: Beyond Vandalism.
- The Role of Mythology in Shaping Indigenous Cultures and Belief Systems.
- Nollywood: Analyzing the Cultural Impact of Nigerian Cinema on the African Diaspora.
- The Language of Hip-Hop Lyrics: A Semiotic Analysis of Cultural Expression.
- Digital Nomads and Cultural Adaptation: Examining the Subculture of Remote Work.
- The Cultural Significance of Tattooing Among Indigenous Tribes in Oceania.
- The Art of Culinary Fusion: Analyzing Cross-Cultural Food Trends and Innovation.
- The Impact of Cultural Festivals on Local Identity and Economy.
- The Influence of Internet Memes on Language and Cultural Evolution.
How to Write a Critical Analysis: Easy Steps
When wondering how to write a critical analysis essay, remember that it can be a challenging but rewarding process. Crafting a critical analysis example requires a careful and thoughtful examination of a text or artwork to assess its strengths and weaknesses and broader implications. The key to success is to approach the task in a systematic and organized manner, breaking it down into two distinct steps: critical reading and critical writing. Here are some tips for each step of the process to help you write a critical essay.
Step 1: Critical Reading
Here are some tips for critical reading that can help you with your critical analysis paper:
- Read actively : Don't just read the text passively, but actively engage with it by highlighting or underlining important points, taking notes, and asking questions.
- Identify the author's main argument: Figure out what the author is trying to say and what evidence they use to support their argument.
- Evaluate the evidence: Determine whether the evidence is reliable, relevant, and sufficient to support the author's argument.
- Analyze the author's tone and style: Consider the author's tone and style and how it affects the reader's interpretation of the text.
- Identify assumptions: Identify any underlying assumptions the author makes and consider whether they are valid or questionable.
- Consider alternative perspectives: Consider alternative perspectives or interpretations of the text and consider how they might affect the author's argument.
- Assess the author's credibility : Evaluate the author's credibility by considering their expertise, biases, and motivations.
- Consider the context: Consider the historical, social, cultural, and political context in which the text was written and how it affects its meaning.
- Pay attention to language: Pay attention to the author's language, including metaphors, symbolism, and other literary devices.
- Synthesize your analysis: Use your analysis of the text to develop a well-supported argument in your critical analysis essay.
Step 2: Critical Analysis Writing
Here are some tips for critical analysis writing, with examples:

- Start with a strong thesis statement: A strong critical analysis thesis is the foundation of any critical analysis essay. It should clearly state your argument or interpretation of the text. You can also consult us on how to write a thesis statement . Meanwhile, here is a clear example:
- Weak thesis statement: 'The author of this article is wrong.'
- Strong thesis statement: 'In this article, the author's argument fails to consider the socio-economic factors that contributed to the issue, rendering their analysis incomplete.'
- Use evidence to support your argument: Use evidence from the text to support your thesis statement, and make sure to explain how the evidence supports your argument. For example:
- Weak argument: 'The author of this article is biased.'
- Strong argument: 'The author's use of emotional language and selective evidence suggests a bias towards one particular viewpoint, as they fail to consider counterarguments and present a balanced analysis.'
- Analyze the evidence : Analyze the evidence you use by considering its relevance, reliability, and sufficiency. For example:
- Weak analysis: 'The author mentions statistics in their argument.'
- Strong analysis: 'The author uses statistics to support their argument, but it is important to note that these statistics are outdated and do not take into account recent developments in the field.'
- Use quotes and paraphrases effectively: Use quotes and paraphrases to support your argument and properly cite your sources. For example:
- Weak use of quotes: 'The author said, 'This is important.'
- Strong use of quotes: 'As the author points out, 'This issue is of utmost importance in shaping our understanding of the problem' (p. 25).'
- Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to make your argument easy to understand, and avoid jargon or overly complicated language. For example:
- Weak language: 'The author's rhetorical devices obfuscate the issue.'
- Strong language: 'The author's use of rhetorical devices such as metaphor and hyperbole obscures the key issues at play.'
- Address counterarguments: Address potential counterarguments to your argument and explain why your interpretation is more convincing. For example:
- Weak argument: 'The author is wrong because they did not consider X.'
- Strong argument: 'While the author's analysis is thorough, it overlooks the role of X in shaping the issue. However, by considering this factor, a more nuanced understanding of the problem emerges.'
- Consider the audience: Consider your audience during your writing process. Your language and tone should be appropriate for your audience and should reflect the level of knowledge they have about the topic. For example:
- Weak language: 'As any knowledgeable reader can see, the author's argument is flawed.'
- Strong language: 'Through a critical analysis of the author's argument, it becomes clear that there are gaps in their analysis that require further consideration.'
Master the art of critical analysis with EssayPro . Our team is ready to guide you in dissecting texts, theories, or artworks with depth and sophistication. Let us help you deliver a critical analysis essay that showcases your analytical prowess.

Creating a Detailed Critical Analysis Essay Outline
Creating a detailed outline is essential when writing a critical analysis essay. It helps you organize your thoughts and arguments, ensuring your essay flows logically and coherently. Here is a detailed critical analysis outline from our dissertation writers :
I. Introduction
A. Background information about the text and its author
B. Brief summary of the text
C. Thesis statement that clearly states your argument
II. Analysis of the Text
A. Overview of the text's main themes and ideas
B. Examination of the author's writing style and techniques
C. Analysis of the text's structure and organization
III. Evaluation of the Text
A. Evaluation of the author's argument and evidence
B. Analysis of the author's use of language and rhetorical strategies
C. Assessment of the text's effectiveness and relevance to the topic
IV. Discussion of the Context
A. Exploration of the historical, cultural, and social context of the text
B. Examination of the text's influence on its audience and society
C. Analysis of the text's significance and relevance to the present day
V. Counter Arguments and Responses
A. Identification of potential counterarguments to your argument
B. Refutation of counterarguments and defense of your position
C. Acknowledgement of the limitations and weaknesses of your argument
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of your argument and main points
B. Evaluation of the text's significance and relevance
C. Final thoughts and recommendations for further research or analysis.
This outline can be adjusted to fit the specific requirements of your essay. Still, it should give you a solid foundation for creating a detailed and well-organized critical analysis essay.
Useful Techniques Used in Literary Criticism
There are several techniques used in literary criticism to analyze and evaluate a work of literature. Here are some of the most common techniques:

- Close reading: This technique involves carefully analyzing a text to identify its literary devices, themes, and meanings.
- Historical and cultural context: This technique involves examining the historical and cultural context of a work of literature to understand the social, political, and cultural influences that shaped it.
- Structural analysis: This technique involves analyzing the structure of a text, including its plot, characters, and narrative techniques, to identify patterns and themes.
- Formalism: This technique focuses on the literary elements of a text, such as its language, imagery, and symbolism, to analyze its meaning and significance.
- Psychological analysis: This technique examines the psychological and emotional aspects of a text, including the motivations and desires of its characters, to understand the deeper meanings and themes.
- Feminist and gender analysis: This technique focuses on the representation of gender and sexuality in a text, including how gender roles and stereotypes are reinforced or challenged.
- Marxist and social analysis: This technique examines the social and economic structures portrayed in a text, including issues of class, power, and inequality.
By using these and other techniques, literary critics can offer insightful and nuanced analyses of works of literature, helping readers to understand and appreciate the complexity and richness of the texts.
Sample Critical Analysis Essay
Now that you know how to write a critical analysis, take a look at the critical analysis essay sample provided by our research paper writers and better understand this kind of paper!
Final Words
At our professional writing services, we understand the challenges and pressures that students face regarding academic writing. That's why we offer high-quality, custom-written essays for sale designed to meet each student's specific needs and requirements.
By using our essay writing service , you can save time and energy while also learning from our expert writers and improving your own writing skills. We take pride in our work and are dedicated to providing friendly and responsive customer support to ensure your satisfaction with every order. So why struggle with difficult assignments when you can trust our professional writing services to deliver the quality and originality you need? Place your order today and experience the benefits of working with our team of skilled and dedicated writers.
If you need help with any of the STEPS ABOVE
Feel free to use EssayPro Outline Help
What Type Of Language Should Be Used In A Critical Analysis Essay?
How to write a critical analysis essay, what is a critical analysis essay.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Definition and Introduction
Journal article analysis assignments require you to summarize and critically assess the quality of an empirical research study published in a scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer-reviewed] journal. The article may be assigned by the professor, chosen from course readings listed in the syllabus, or you must locate an article on your own, usually with the requirement that you search using a reputable library database, such as, JSTOR or ProQuest . The article chosen is expected to relate to the overall discipline of the course, specific course content, or key concepts discussed in class. In some cases, the purpose of the assignment is to analyze an article that is part of the literature review for a future research project.
Analysis of an article can be assigned to students individually or as part of a small group project. The final product is usually in the form of a short paper [typically 1- 6 double-spaced pages] that addresses key questions the professor uses to guide your analysis or that assesses specific parts of a scholarly research study [e.g., the research problem, methodology, discussion, conclusions or findings]. The analysis paper may be shared on a digital course management platform and/or presented to the class for the purpose of promoting a wider discussion about the topic of the study. Although assigned in any level of undergraduate and graduate coursework in the social and behavioral sciences, professors frequently include this assignment in upper division courses to help students learn how to effectively identify, read, and analyze empirical research within their major.
Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students make the most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535.
Benefits of Journal Article Analysis Assignments
Analyzing and synthesizing a scholarly journal article is intended to help students obtain the reading and critical thinking skills needed to develop and write their own research papers. This assignment also supports workplace skills where you could be asked to summarize a report or other type of document and report it, for example, during a staff meeting or for a presentation.
There are two broadly defined ways that analyzing a scholarly journal article supports student learning:
Improve Reading Skills
Conducting research requires an ability to review, evaluate, and synthesize prior research studies. Reading prior research requires an understanding of the academic writing style , the type of epistemological beliefs or practices underpinning the research design, and the specific vocabulary and technical terminology [i.e., jargon] used within a discipline. Reading scholarly articles is important because academic writing is unfamiliar to most students; they have had limited exposure to using peer-reviewed journal articles prior to entering college or students have yet to gain exposure to the specific academic writing style of their disciplinary major. Learning how to read scholarly articles also requires careful and deliberate concentration on how authors use specific language and phrasing to convey their research, the problem it addresses, its relationship to prior research, its significance, its limitations, and how authors connect methods of data gathering to the results so as to develop recommended solutions derived from the overall research process.
Improve Comprehension Skills
In addition to knowing how to read scholarly journals articles, students must learn how to effectively interpret what the scholar(s) are trying to convey. Academic writing can be dense, multi-layered, and non-linear in how information is presented. In addition, scholarly articles contain footnotes or endnotes, references to sources, multiple appendices, and, in some cases, non-textual elements [e.g., graphs, charts] that can break-up the reader’s experience with the narrative flow of the study. Analyzing articles helps students practice comprehending these elements of writing, critiquing the arguments being made, reflecting upon the significance of the research, and how it relates to building new knowledge and understanding or applying new approaches to practice. Comprehending scholarly writing also involves thinking critically about where you fit within the overall dialogue among scholars concerning the research problem, finding possible gaps in the research that require further analysis, or identifying where the author(s) has failed to examine fully any specific elements of the study.
In addition, journal article analysis assignments are used by professors to strengthen discipline-specific information literacy skills, either alone or in relation to other tasks, such as, giving a class presentation or participating in a group project. These benefits can include the ability to:
- Effectively paraphrase text, which leads to a more thorough understanding of the overall study;
- Identify and describe strengths and weaknesses of the study and their implications;
- Relate the article to other course readings and in relation to particular research concepts or ideas discussed during class;
- Think critically about the research and summarize complex ideas contained within;
- Plan, organize, and write an effective inquiry-based paper that investigates a research study, evaluates evidence, expounds on the author’s main ideas, and presents an argument concerning the significance and impact of the research in a clear and concise manner;
- Model the type of source summary and critique you should do for any college-level research paper; and,
- Increase interest and engagement with the research problem of the study as well as with the discipline.
Kershaw, Trina C., Jennifer Fugate, and Aminda J. O'Hare. "Teaching Undergraduates to Understand Published Research through Structured Practice in Identifying Key Research Concepts." Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology . Advance online publication, 2020; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students make the most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946.
Structure and Organization
A journal article analysis paper should be written in paragraph format and include an instruction to the study, your analysis of the research, and a conclusion that provides an overall assessment of the author's work, along with an explanation of what you believe is the study's overall impact and significance. Unless the purpose of the assignment is to examine foundational studies published many years ago, you should select articles that have been published relatively recently [e.g., within the past few years].
Since the research has been completed, reference to the study in your paper should be written in the past tense, with your analysis stated in the present tense [e.g., “The author portrayed access to health care services in rural areas as primarily a problem of having reliable transportation. However, I believe the author is overgeneralizing this issue because...”].
Introduction Section
The first section of a journal analysis paper should describe the topic of the article and highlight the author’s main points. This includes describing the research problem and theoretical framework, the rationale for the research, the methods of data gathering and analysis, the key findings, and the author’s final conclusions and recommendations. The narrative should focus on the act of describing rather than analyzing. Think of the introduction as a more comprehensive and detailed descriptive abstract of the study.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the introduction section may include:
- Who are the authors and what credentials do they hold that contributes to the validity of the study?
- What was the research problem being investigated?
- What type of research design was used to investigate the research problem?
- What theoretical idea(s) and/or research questions were used to address the problem?
- What was the source of the data or information used as evidence for analysis?
- What methods were applied to investigate this evidence?
- What were the author's overall conclusions and key findings?
Critical Analysis Section
The second section of a journal analysis paper should describe the strengths and weaknesses of the study and analyze its significance and impact. This section is where you shift the narrative from describing to analyzing. Think critically about the research in relation to other course readings, what has been discussed in class, or based on your own life experiences. If you are struggling to identify any weaknesses, explain why you believe this to be true. However, no study is perfect, regardless of how laudable its design may be. Given this, think about the repercussions of the choices made by the author(s) and how you might have conducted the study differently. Examples can include contemplating the choice of what sources were included or excluded in support of examining the research problem, the choice of the method used to analyze the data, or the choice to highlight specific recommended courses of action and/or implications for practice over others. Another strategy is to place yourself within the research study itself by thinking reflectively about what may be missing if you had been a participant in the study or if the recommended courses of action specifically targeted you or your community.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the analysis section may include:
Introduction
- Did the author clearly state the problem being investigated?
- What was your reaction to and perspective on the research problem?
- Was the study’s objective clearly stated? Did the author clearly explain why the study was necessary?
- How well did the introduction frame the scope of the study?
- Did the introduction conclude with a clear purpose statement?
Literature Review
- Did the literature review lay a foundation for understanding the significance of the research problem?
- Did the literature review provide enough background information to understand the problem in relation to relevant contexts [e.g., historical, economic, social, cultural, etc.].
- Did literature review effectively place the study within the domain of prior research? Is anything missing?
- Was the literature review organized by conceptual categories or did the author simply list and describe sources?
- Did the author accurately explain how the data or information were collected?
- Was the data used sufficient in supporting the study of the research problem?
- Was there another methodological approach that could have been more illuminating?
- Give your overall evaluation of the methods used in this article. How much trust would you put in generating relevant findings?
Results and Discussion
- Were the results clearly presented?
- Did you feel that the results support the theoretical and interpretive claims of the author? Why?
- What did the author(s) do especially well in describing or analyzing their results?
- Was the author's evaluation of the findings clearly stated?
- How well did the discussion of the results relate to what is already known about the research problem?
- Was the discussion of the results free of repetition and redundancies?
- What interpretations did the authors make that you think are in incomplete, unwarranted, or overstated?
- Did the conclusion effectively capture the main points of study?
- Did the conclusion address the research questions posed? Do they seem reasonable?
- Were the author’s conclusions consistent with the evidence and arguments presented?
- Has the author explained how the research added new knowledge or understanding?
Overall Writing Style
- If the article included tables, figures, or other non-textual elements, did they contribute to understanding the study?
- Were ideas developed and related in a logical sequence?
- Were transitions between sections of the article smooth and easy to follow?
Overall Evaluation Section
The final section of a journal analysis paper should bring your thoughts together into a coherent assessment of the value of the research study . This section is where the narrative flow transitions from analyzing specific elements of the article to critically evaluating the overall study. Explain what you view as the significance of the research in relation to the overall course content and any relevant discussions that occurred during class. Think about how the article contributes to understanding the overall research problem, how it fits within existing literature on the topic, how it relates to the course, and what it means to you as a student researcher. In some cases, your professor will also ask you to describe your experiences writing the journal article analysis paper as part of a reflective learning exercise.
Possible questions to help guide your writing of the conclusion and evaluation section may include:
- Was the structure of the article clear and well organized?
- Was the topic of current or enduring interest to you?
- What were the main weaknesses of the article? [this does not refer to limitations stated by the author, but what you believe are potential flaws]
- Was any of the information in the article unclear or ambiguous?
- What did you learn from the research? If nothing stood out to you, explain why.
- Assess the originality of the research. Did you believe it contributed new understanding of the research problem?
- Were you persuaded by the author’s arguments?
- If the author made any final recommendations, will they be impactful if applied to practice?
- In what ways could future research build off of this study?
- What implications does the study have for daily life?
- Was the use of non-textual elements, footnotes or endnotes, and/or appendices helpful in understanding the research?
- What lingering questions do you have after analyzing the article?
NOTE: Avoid using quotes. One of the main purposes of writing an article analysis paper is to learn how to effectively paraphrase and use your own words to summarize a scholarly research study and to explain what the research means to you. Using and citing a direct quote from the article should only be done to help emphasize a key point or to underscore an important concept or idea.
Business: The Article Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing, Grand Valley State University; Bachiochi, Peter et al. "Using Empirical Article Analysis to Assess Research Methods Courses." Teaching of Psychology 38 (2011): 5-9; Brosowsky, Nicholaus P. et al. “Teaching Undergraduate Students to Read Empirical Articles: An Evaluation and Revision of the QALMRI Method.” PsyArXi Preprints , 2020; Holster, Kristin. “Article Evaluation Assignment”. TRAILS: Teaching Resources and Innovations Library for Sociology . Washington DC: American Sociological Association, 2016; Kershaw, Trina C., Jennifer Fugate, and Aminda J. O'Hare. "Teaching Undergraduates to Understand Published Research through Structured Practice in Identifying Key Research Concepts." Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology . Advance online publication, 2020; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Reviewer's Guide . SAGE Reviewer Gateway, SAGE Journals; Sego, Sandra A. and Anne E. Stuart. "Learning to Read Empirical Articles in General Psychology." Teaching of Psychology 43 (2016): 38-42; Kershaw, Trina C., Jordan P. Lippman, and Jennifer Fugate. "Practice Makes Proficient: Teaching Undergraduate Students to Understand Published Research." Instructional Science 46 (2018): 921-946; Gyuris, Emma, and Laura Castell. "To Tell Them or Show Them? How to Improve Science Students’ Skills of Critical Reading." International Journal of Innovation in Science and Mathematics Education 21 (2013): 70-80; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36; MacMillan, Margy and Allison MacKenzie. "Strategies for Integrating Information Literacy and Academic Literacy: Helping Undergraduate Students Make the Most of Scholarly Articles." Library Management 33 (2012): 525-535.
Writing Tip
Not All Scholarly Journal Articles Can Be Critically Analyzed
There are a variety of articles published in scholarly journals that do not fit within the guidelines of an article analysis assignment. This is because the work cannot be empirically examined or it does not generate new knowledge in a way which can be critically analyzed.
If you are required to locate a research study on your own, avoid selecting these types of journal articles:
- Theoretical essays which discuss concepts, assumptions, and propositions, but report no empirical research;
- Statistical or methodological papers that may analyze data, but the bulk of the work is devoted to refining a new measurement, statistical technique, or modeling procedure;
- Articles that review, analyze, critique, and synthesize prior research, but do not report any original research;
- Brief essays devoted to research methods and findings;
- Articles written by scholars in popular magazines or industry trade journals;
- Academic commentary that discusses research trends or emerging concepts and ideas, but does not contain citations to sources; and
- Pre-print articles that have been posted online, but may undergo further editing and revision by the journal's editorial staff before final publication. An indication that an article is a pre-print is that it has no volume, issue, or page numbers assigned to it.
Journal Analysis Assignment - Myers . Writing@CSU, Colorado State University; Franco, Josue. “Introducing the Analysis of Journal Articles.” Prepared for presentation at the American Political Science Association’s 2020 Teaching and Learning Conference, February 7-9, 2020, Albuquerque, New Mexico; Woodward-Kron, Robyn. "Critical Analysis and the Journal Article Review Assignment." Prospect 18 (August 2003): 20-36.
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Giving an Oral Presentation >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Exploring Female Narratives of Sexual Intimacy and the Social Suppression of Desire
- Published: 04 September 2024
Cite this article

- Shivani Rajan ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-3470-9241 1 &
- Swati Pathak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1189-1457 1
Exploring the construction of sexual identities by women, this research attempts to provide an experiential understanding of sexual intimacy in young adulthood through critical narrative analysis of the accounts of ten unmarried cis-gender women, located in the postmodern feminist paradigm and drawing from contemporary psychoanalytic tradition. The study highlighted the lack of discourse on female desire and pleasure (that is not fetishised, penalised, or ostracised) in the hetero-patriarchal socio-cultural fabric of India and how it manifests in the sense of shame, guilt, and self-doubt in the navigation of sexual intimacy. The social matrix, including the influence of family and partner dynamics and cultural and generational differences, was observed to play a prominent role in the evolution of individual perceptions of sexual intimacy. Analysing the narratives through a feminist lens foregrounded the predominance of male satisfaction and pleasure, the sense of obligation towards male partners, the infringement of boundaries and compromise, and the performativity in sexual experiences, thus calling attention to the female struggle of realising and practising sexual agency. The research indicates the need to critically examine the pervasive phallocentrism in the experience of sexual intimacy and the marginalisation of female sexual desire due to the suppression of female sexuality in the patriarchal hierarchy of power distribution.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Atallah, S., & Redón, A. M. (2023). Relevant (sexual) aspects of Cultural differences. In S. Geuens, A. Polona Mivšek, & W. Gianotten (Eds.), Midwifery and sexuality . Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18432-1_23
Bell, E. (2005). Sex acts beyond boundaries and binaries: A feminist challenge for self care in performance studies. Text and Performance Quarterly , 25 (3), 187–219.
Article Google Scholar
Butler, J. (1990). Gender trouble: Feminism and the subversion of identity. Routledge.
Cash, T. F., Maikkula, C. L., & Yamamiya, Y. (2004). Baring the body in the bedroom: Body image, sexual self-schemas, and sexual functioning among college women and men. Electronic Journal of Human Sexuality , 7 , 1–9.
Google Scholar
Chakraborty, K., & Thakurata, R. G. (2013). Indian concepts on sexuality. Indian Journal of Psychiatry , 55 (Suppl 2), S250–S255.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chasseguet-Smirgel, J. (1976). Freud and female sexuality: The consideration of some blind spots in the exploration of the Dark Continent. The International Journal of Psychoanalysis .
Crooks, R. L., Baur, K., & Widman, L. (2020). Our sexuality . Cengage Learning.
Dion, K. K., & Dion, K. L. (1993). Individualistic and collectivistic perspectives on gender and the cultural context of love and intimacy. Journal of Social Issues , 49 (3), 53–69.
Easteal, P., Holland, K., & Judd, K. (2015). Enduring themes and silences in media portrayals of violence against women. Women’s Studies International Forum (Vol. 48, pp. 103–113). Pergamon.
Emerson, P., & Frosh, S. (2004). Critical narrative analysis in psychology: A guide to practice. Springer.
Elise, D. (2008). Sex and shame: The inhibition of female desires. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association , 56 (1), 73–98.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Faustino, M. J., & Gavey, N. (2024). The failed promise of consent in women’s experiences of coercive and unwanted anal sex with men. Feminism & Psychology , 09593535241234429.
Fazli Khalaf, Z., Liow, J. W., Low, W. Y., Ghorbani, B., & Merghati-Khoei, E. (2018). Young women’s experience of sexuality: A battle of pleasure and sexual purity in the context of Malaysian society. Sexuality & Culture , 22, 849–864.
Freud, S. (1920). Introductory lectures on psychoanalysis (A. A. Brill, Trans) . Hogarth. (Originally published, 1916-17).
Freud, S. (1905). Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality. In J. Strachy, & A. Freud (Eds.), The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud, Volume VII (1901-1905): A Case of Hysteria, Three Essays on Sexuality and Other Works (pp. 123–246). London: Hogarth Press.
Friedman, J., & Valenti, J. (Eds.). (2019). Yes means yes! Visions of female sexual power and a world without rape . Seal.
Gavin, J. (2000). Arousing suspicion and violating trust: The lived ideology of safe sex talk. Culture Health & Sexuality . https://doi.org/10.1080/136910500300750
Gill, R. (2009). Mediated intimacy and postfeminism: A discourse analytic examination of sex and relationships advice in a women’s magazine . Discourse & Communication. https://doi.org/10.1177/1750481309343870
Guba, E. G., & Lincoln Y. S. (1994). Competing paradigms in qualitative research. Handbook of qualitative research . Sage.
Haberland, N., & Rogow, D. (2015). Sexuality education: Emerging trends in evidence and practice. Journal of Adolescent Health , 56 (1), S15–S21.
Hawkes, G. (1996). Sociology of sex and sexuality . McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
Impett, E. A., & Peplau, L. A. (2002). Why some women consent to unwanted sex with a dating partner: Insights from attachment theory. Psychology of Women Quarterly , 26 (4), 360–370.
Jackson, A., & Guerra, N. S. (2011). Cultural Difference. In: Goldstein, S., Naglieri, J.A. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9_752
Kulwicki, C. (2008). Real sex education. Yes Means yes , 305–312.
McAdams, D. P. (1988). Biography, narrative, and lives: An introduction. Journal of Personality , 56 (1), 1–18.
Mitchell, J. (2000). Psychoanalysis and feminism: A radical reassessment of Freudian psychoanalysis . Basic Books.
Mitra, D. (2020). Indian sex life: Sexuality and the colonial origins of modern social thought . Princeton University Press.
Olamijuwon, E., & Odimegwu, C. (2022). Saving sex for marriage: An analysis of lay attitudes towards virginity and its perceived benefit for marriage. Sexuality & Culture , 26 (2), 568–594.
Rahmani, A., Merghati-Khoei, E., Moghaddam-Banaem, L., Hajizadeh, E., & Montazeri, A. (2016). The viewpoints of sexually active single women about premarital sexual relationships: A qualitative study in the Iranian context. International journal of high risk behaviors & addiction , 5(1).
Özcan, Ö., Cumurcu, B. E., Karlidag, R., Ünal, S., Mutlu, E. A., & Kartalci, S. (2015). Attachment styles in women with vaginismus/Vaginismusu olan kadinlarda baglanma stilleri. Anadolu Psikiyatri Dergisi , 16 (1), 37.
Sanchez, D. T., Fetterolf, J. C., & Rudman, L. A. (2012). Eroticizing Inequality in the United States: The Consequences and Determinants of Traditional Gender Role Adherence in Intimate Relationships. Journal of Sex Research, 49(2–3), 168–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224499.2011.653699
Simon-Kumar, R. (2014). Sexual violence in India: The discourses of rape and the discourses of justice. Indian Journal of Gender Studies , 21 (3), 451–460.
Sprecher, S., & Sedikides, C. (1993). Gender differences in perceptions of emotionality: The case of close heterosexual relationships. Sex Roles , 28 (9–10), 511–530.
Srivastava, S. (2020). Passionate modernity: Sexuality, class, and consumption in India . Taylor & Francis.
Szymanski, D. M., & Carr, E. R. (2008). The roles of gender role conflict and internalized heterosexism in gay and bisexual men’s psychological distress: Testing two mediation models. Psychology of Men & Masculinity , 9 (1), 40.
Tangney, J. P., & Dearing, R. L. (2003). Shame and guilt . Guilford Press.
Techasrivichien, T., Darawuttimaprakorn, N., Punpuing, S., Musumari, P. M., Lukhele, B. W., El-Saaidi, C., & Kihara, M. (2016). Changes in sexual behavior and attitudes across generations and gender among a population-based probability sample from an urbanizing province in Thailand. Archives of Sexual Behavior , 45 , 367–382.
Tillman, L. (2021). The influence of parent-child relationships on female sexual functioning . A Review Of The Literature.
Tolman, D. L. (2005). Dilemmas of desire: Teenage girls talk about sexuality . Harvard University Press.
Tolman, D. L., & McClelland, S. I. (2011). Normative sexuality development in adolescence: A decade in review, 2000–2009. Journal of Research on Adolescence , 21 (1), 242–255.
Twenge, J. M., Sherman, R. A., & Wells, B. E. (2015). Changes in American adults’ sexual behavior and attitudes, 1972–2012. Archives of Sexual Behavior , 44 , 2273–2285.
Wagner, B. (2009). Becoming a sexual being: Overcoming constraints on female sexuality. Sexualities , 12 (3), 289–311.
Wallwiener, S., Strohmaier, J., Wallwiener, L. M., Schönfisch, B., Zipfel, S., Brucker, S. Y., Rietschel, M., & Wallwiener, C. W. (2016). Sexual function is correlated with body image and partnership quality in female university students. The Journal of Sexual Medicine , 13 (10), 1530–1538.
Willoughby, B. J., Busby, D. M., & Young-Petersen, B. (2018). Understanding associations between Personal definitions of Pornography, using pornography, and Depression. Sexuality Research and Social Policy . https://doi.org/10.1007/s13178-018-0345-x
Witting, K., Santtila, P., Varjonen, M., Jern, P., Johansson, A., Von Der Pahlen, B., & Sandnabba, K. (2008). Female sexual dysfunction, sexual distress, and compatibility with partner. The Journal of Sexual Medicine , 5 (11), 2587–2599.
Yasmine, R., El Salibi, N., El Kak, F., & Ghandour, L. (2015). Postponing sexual debut among university youth: How do men and women differ in their perceptions, values and non-penetrative sexual practices? Culture Health & Sexuality , 17 (5), 555–575.
Download references
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, CHRIST University, Delhi NCR, India
Shivani Rajan & Swati Pathak
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.R. drafted the research idea, conducted the interview with the participants and prepared the initial draft of the manuscript.S.P the research supervisor who directly monitored the research and reviewed the progress of changes in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Swati Pathak .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study has been approved by the Research Conduct Ethics Committee (RCEC) at CHRIST University. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Rajan, S., Pathak, S. Exploring Female Narratives of Sexual Intimacy and the Social Suppression of Desire. Hu Arenas (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-024-00441-2
Download citation
Received : 02 February 2024
Revised : 20 August 2024
Accepted : 21 August 2024
Published : 04 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-024-00441-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Female sexuality
- Sexual intimacy
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

OXY Crosses Critical Technical Indicator
September 04, 2024 — 04:00 pm EDT
Written by BNK Invest for BNK Invest ->
In the case of Occidental Petroleum Corp, the RSI reading has hit 29.3 — by comparison, the universe of energy stocks covered by Energy Stock Channel currently has an average RSI of 47.7, the RSI of WTI Crude Oil is at 33.3, the RSI of Henry Hub Natural Gas is presently 51.8, and the 3-2-1 Crack Spread RSI is 60.3. A bullish investor could look at OXY's 29.3 reading as a sign that the recent heavy selling is in the process of exhausting itself, and begin to look for entry point opportunities on the buy side.
Looking at a chart of one year performance (below), OXY's low point in its 52 week range is $54.82 per share, with $71.185 as the 52 week high point — that compares with a last trade of $54.85. Occidental Petroleum Corp shares are currently trading down about 0.9% on the day.
The OXY RSI information above was sourced from Technical Analysis Channel .com
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

Stocks mentioned
More related articles.
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Instructions for Comparative Newspaper Analysis. Choose a news story which has been reported in both the Daily Mail and The Guardian. Provide a link to each. Write a brief summary (4-6 sentences) of the incident/topic both articles are reporting on. Write a short analysis of the difference in the two headlines.
When working with the news article critical analysis, look out for the following: Check the headline of the news article and include it in your thesis; Focus on structure, voice of the article, tone, and rhetoric; ... To make it easier for you to write a critical analysis essay, we have a helpful analysis writing template that will guide you ...
Step 3: Evaluate the Evidence. In order to solely understand how to analyse an article critically, it is imperative to know that an article's persuasive power hinges on the quality of evidence presented to substantiate its main argument. In this critical step, it's imperative to scrutinise the evidence with a discerning eye.
A critical analysis is an argument about a particular piece of media. There are typically two parts: (1) identify and explain the argument the author is making, and (2), provide your own argument about that argument. Your instructor may have very specific requirements on how you are to write your critical analysis, so make sure you read your ...
Critical Analysis Format is as follows: I. Introduction. Provide a brief overview of the text, object, or event being analyzed. Explain the purpose of the analysis and its significance. Provide background information on the context and relevant historical or cultural factors. II.
33 Critical Analysis Examples. Critical analysis refers to the ability to examine something in detail in preparation to make an evaluation or judgment. It will involve exploring underlying assumptions, theories, arguments, evidence, logic, biases, contextual factors, and so forth, that could help shed more light on the topic.
Writing Critical Analysis Papers1. A critical analysis paper asks the writer to make an argument about a particular book, essay, movie, etc. The goal is two fold: one, identify and explain the argument that the author is making, and two, provide your own argument about that argument. One of the key directions of these assignments is often to ...
How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Critical analysis essays can be a daunting form of academic writing, but crafting a good critical analysis paper can be straightforward if you have the right approach.
1. Comprehensive Reading. The first step towards a successful critical analysis essay is in-depth engagement with the text you'll analyse. If you are working with a single text, that means understanding the author's point of view to form the foundation of your essay. Take your time and delve into the text to explore its deeper meanings and ...
The content each part conveys is as follows. 1. Introduction. The essay begins with an introduction to the piece of work it is going to critically analyze. Information pertinent to the analysis is provided. This can include a summary of the work, its context, themes, message, and/or details about the author/artist.
Step one: Reading critically. The first step in writing a critical analysis is to carefully study the source you plan to analyze. If you are writing for a class assignment, your professor may have already given you the topic to analyze in an article, short story, book, or other work.
A critical analysis essay requires you to analyze a subject and determine its meaning, backing it with evidence and ideas of your own. We've got examples to help you write one. ... Retreating to the mundanities of nose whistling and "catching" an invisible ball in a paper bag were as much about staying grounded as they were maintaining a ...
In this article, we discuss what critical analysis is, the process for writing one and offer some writing tips and an example of a well-written critical analysis. Read more: ... Critical analysis, which draws upon your critical thinking skills, is usually presented as a written essay or paper, but may also be presented as an oral report. Good ...
To be critical, or to critique, means to evaluate. Therefore, to write critically in an academic analysis means to: judge the quality, significance or worth of the theories, concepts, viewpoints, methodologies, and research results. evaluate in a fair and balanced manner. avoid extreme or emotional language. You evaluate or judge the quality ...
s made. Critical vs DescriptiveA critical review or analysis is characterised by two main types of writing: (i) writing descriptively to summarise the particular arguments or concepts of a text, and (ii) writing critically to evaluate and/or an. lyse these arguments and concepts. It is necessary for a critical review to contain some descriptive ...
May 4, 2024. A Critical Analysis Essay is a form of academic writing that requires students to extract information and critically analyze a specific topic. The task may seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can become an exciting task. Critical Analysis Essays help students improve their analytical skills and foster principles of logic.
Overview of the paper. This is an important section to include when writing a critical analysis of an article because it answers the four "w's", of what, why, who, when and also the how. This section should include a brief overview of the key ideas in the article, along with the structure, style and dominant point of view expressed.
Critical analysis of an article aims to analyze the writing strategies and techniques an author uses to develop their argument. The process is a little different than persuading the reader to accept a particular point of view. Here is a sample outline: Introduction. Introduce the author and the work under analysis.
Read the chapters that specifically address your topic. Reading the article abstract and scanning the table of contents of a journal or magazine issue is also useful. As with books, the presence and quality of a bibliography at the end of the article may reflect the care with which the authors have prepared their work. A. Intended Audience
This is done by employing the editing style where you go from the bottom of the article to the very top. Newspaper articles aim to bring answers to six main issues regarding any news. These are: The 'who' of the news. The 'what' of the news. The 'when' of the news. The 'where' of the news. The 'why' of the news. The 'how ...
A collection of our critical analysis' focusing on effect of nuclear for our Environmental Politics and Policy class. Group members: Julianna, Ky, and Meredith. The newspaper article "The ...
To help you get started, here are ten critical essay example topics on mass media: The Influence of Viral Memes on Pop Culture: An In-Depth Analysis. The Portrayal of Mental Health in Television: Examining Stigmatization and Advocacy. The Power of Satirical News Shows: Analyzing the Impact of Political Commentary.
A journal article analysis paper should be written in paragraph format and include an instruction to the study, your analysis of the research, and a conclusion that provides an overall assessment of the author's work, along with an explanation of what you believe is the study's overall impact and significance.
Exploring the construction of sexual identities by women, this research attempts to provide an experiential understanding of sexual intimacy in young adulthood through critical narrative analysis of the accounts of ten unmarried cis-gender women, located in the postmodern feminist paradigm and drawing from contemporary psychoanalytic tradition. The study highlighted the lack of discourse on ...
In the assessment of 12-month price targets, analysts unveil insights for Jabil, presenting an average target of $134.17, a high estimate of $145.00, and a low estimate of $120.00.
OXY Crosses Critical Technical Indicator September 04, 2024 — 04:00 pm EDT Written by BNK Invest for BNK Invest ->