How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: July 18, 2024
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a major challenge. Before you can expect to earn their business, you’ll need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on the promises of your product or service. The best way to win new business is with cold, hard proof.

A great way to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. HubSpot’s 2024 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so captivating that they were the fifth most commonly used type of content that marketers relied on.
That statistic still holds true in Forbes Advisor’s 2024 study, which adds that 78% of B2B businesses report using case studies and customer stories because they are “ crucial for demonstrating real-world value. ”
Having written these ever more frequently over the past ten years, I hope to serve as your guide through a process that can feel daunting, but I promise is worth the effort. Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic.
Table of Contents

Case Study Definition
- Why Write a Case Study?
- How Long Should a Case Study Be?
Case Study Templates
How to write a case study, case study format, business case study examples.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A case study is coverage of a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it‘s common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client.
Perhaps the success you’re highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers, helping you attract new clients.
Why write a case study?
I know, it sounds like a huge endeavor — is it really worth it?
The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples.
Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain complex topics or concepts.
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies, showing how they can be applied in a practical way.
You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that demonstrates how your product solved their issue. Most importantly, it explains how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar, successful results.
2. Show expertise.
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build trust and credibility.
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework.
A robust case study instills confidence in the solutions you present because the reader has now vicariously experienced the problem — and they followed, step-by-step, what it took to solve it. These elements work together, enabling you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create social proof.
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof .
People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — put your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes play together like an orchestra to help you gain more clients. Afterward, the case study acts as a reference. You can pull quotes from customers that were featured in these studies to repurpose them in other marketing content.
How long should a case study be?
Now that you’re more acquainted with the benefits of producing a case study, let’s explore how long these documents should be.
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved.
This may be easier said than done, but it‘s important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader’s interest.
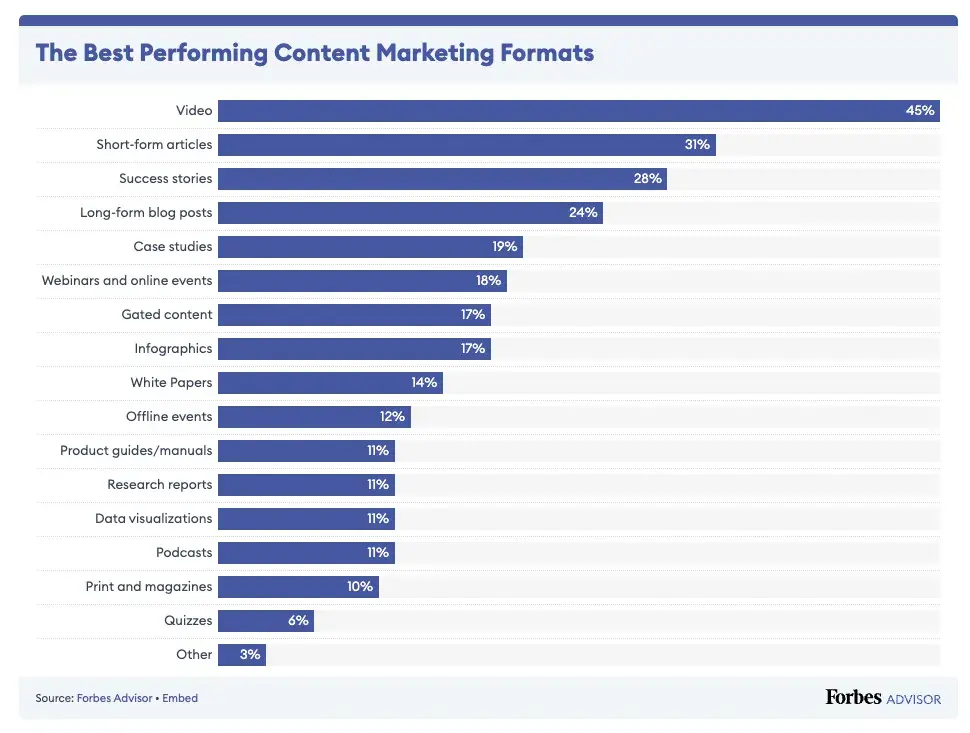
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Make it attractive to dive into by using headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers.
I’ve also seen more and more brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience, which is highly recommended given that video is currently the best performing marketing content format.
In terms of the interview structure, I recommend categorizing the questions in a way that the answers flow into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, plus how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context that helps match the customer's needs with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes.
Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
It’s a smart idea to send a copy of your interview questions to your subject ahead of time so they can prepare strong answers and collect the numerical data you need from them.
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you‘ve collected and actually turn it into something useful, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. I always do, but I also know that it works out in the end, so I just jump on in and work it through.
So where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
It‘s important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study.
They can be very visual, which you’ll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated through video or photos with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections I’d suggest, and I'll cover these in more detail after #11 below:
- Title. Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle. Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary . A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject. An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives. A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped. A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results. A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes. Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans. Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call-to-Action (CTA). Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible.
Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you‘ve completed your case study, it’s time to publish and promote it.
Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas.
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF.
To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client‘s success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they’d like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people to it from your homepage with a “Case Studies” or “Testimonials” button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

23 Pro Tips for Running a Successful Business — From Building Your Company Benefits to Leading a Team (+ Expert Insights)
![what is com case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![what is com case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![what is com case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved September 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Sales CRM Terms
What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into various data sources, Case Study Analysis provides valuable insights and knowledge that can be used to inform decision-making and problem-solving strategies.
1°) What is Case Study Analysis?
Case Study Analysis is a research methodology that involves the systematic investigation of a specific case or cases to gain a deep understanding of the subject matter. This analysis encompasses collecting and analyzing various types of data, including qualitative and quantitative information. By examining multiple aspects of the case, such as its context, background, influences, and outcomes, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions and provide valuable insights for various fields of study.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers typically begin by selecting a case or multiple cases that are relevant to their research question or area of interest. This can involve choosing a specific organization, individual, event, or phenomenon to study. Once the case is selected, researchers gather relevant data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and artifact examination.
The data collected during a Case Study Analysis is then carefully analyzed and interpreted. Researchers use different analytical frameworks and techniques to make sense of the information and identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the data. This process involves coding and categorizing the data, conducting comparative analysis, and drawing conclusions based on the findings.
One of the key strengths of Case Study Analysis is its ability to provide a rich and detailed understanding of a specific case. This method allows researchers to delve deep into the complexities and nuances of the subject matter, uncovering insights that may not be captured through other research methods. By examining the case in its natural context, researchers can gain a holistic perspective and explore the various factors and variables that contribute to the case.
1.1 - Definition of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis can be defined as an in-depth examination and exploration of a particular case or cases to unravel relevant details and complexities associated with the subject being studied. It involves a comprehensive and detailed analysis of various factors and variables that contribute to the case, aiming to answer research questions and uncover insights that can be applied in real-world scenarios.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers employ a range of research methods and techniques to collect and analyze data. These methods can include interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis, and experiments, among others. By using multiple sources of data, researchers can triangulate their findings and ensure the validity and reliability of their analysis.
Furthermore, Case Study Analysis often involves the use of theoretical frameworks and models to guide the research process. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing the case and help researchers make sense of the data collected. By applying relevant theories and concepts, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors and dynamics at play in the case.
1.2 - Advantages of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis offers numerous advantages that make it a popular research method across different disciplines. One significant advantage is its ability to provide rich and detailed information about a specific case, allowing researchers to gain a holistic understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, Case Study Analysis enables researchers to explore complex issues and phenomena in their natural context, capturing the intricacies and nuances that may not be captured through other research methods.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis allows researchers to investigate rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated or studied through experimental methods. This method is particularly useful when studying phenomena that are complex, multifaceted, or involve multiple variables. By examining real-world cases, researchers can gain insights that can be applied to similar situations or inform future research and practice.
Furthermore, this research method allows for the analysis of multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which can contribute to a comprehensive and well-rounded examination of the case. Case Study Analysis also facilitates the exploration and identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, generating valuable insights and knowledge for future reference and application.
1.3 - Disadvantages of Case Study Analysis
While Case Study Analysis offers various advantages, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. One major limitation is the potential for researcher bias, as the interpretation of data and findings can be influenced by preconceived notions and personal perspectives. Researchers must be aware of their own biases and take steps to minimize their impact on the analysis.
Additionally, Case Study Analysis may suffer from limited generalizability, as it focuses on specific cases and contexts, which might not be applicable or representative of broader populations or situations. The findings of a case study may not be easily generalized to other settings or individuals, and caution should be exercised when applying the results to different contexts.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis can require significant time and resources due to its in-depth nature and the need for meticulous data collection and analysis. This can pose challenges for researchers working with limited budgets or tight deadlines. However, the thoroughness and depth of the analysis often outweigh the resource constraints, as the insights gained from a well-conducted case study can be highly valuable.
Finally, ethical considerations also play a crucial role in Case Study Analysis, as researchers must ensure the protection of participant confidentiality and privacy. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants and take measures to safeguard their identities and personal information. Ethical guidelines and protocols should be followed to ensure the rights and well-being of the individuals involved in the case study.
2°) Examples of Case Study Analysis
Real-world examples of Case Study Analysis demonstrate the method's practical application and showcase its usefulness across various fields. The following examples provide insights into different scenarios where Case Study Analysis has been employed successfully.
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In a startup context, a Case Study Analysis might explore the factors that contributed to the success of a particular startup company. It would involve examining the organization's background, strategies, market conditions, and key decision-making processes. This analysis could reveal valuable lessons and insights for aspiring entrepreneurs and those interested in understanding the intricacies of startup success.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, Case Study Analysis is often utilized to understand and develop solutions for complex business problems. For instance, a consulting firm might conduct a Case Study Analysis on a company facing challenges in its supply chain management. This analysis would involve identifying the underlying issues, evaluating different options, and proposing recommendations based on the findings. This approach enables consultants to apply their expertise and provide practical solutions to their clients.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
Within a digital marketing agency, Case Study Analysis can be used to examine successful marketing campaigns. By analyzing various factors such as target audience, message effectiveness, channel selection, and campaign metrics, this analysis can provide valuable insights into the strategies and tactics that contribute to successful marketing initiatives. Digital marketers can then apply these insights to optimize future campaigns and drive better results for their clients.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
Case Study Analysis can also be utilized with analogies to investigate specific scenarios and draw parallels to similar situations. For instance, a Case Study Analysis could explore the response of different countries to natural disasters and draw analogies to inform disaster management strategies in other regions. These analogies can help policymakers and researchers develop more effective approaches to mitigate the impact of disasters and protect vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, Case Study Analysis is a powerful research method that provides a comprehensive understanding of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. By analyzing real-life cases and exploring various data sources, researchers can unravel complexities, generate valuable insights, and inform decision-making processes. With its advantages and limitations, Case Study Analysis offers a unique approach to gaining in-depth knowledge and practical application across numerous fields.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

"i wrote this article"
Try my sales crm software (people love it) 👇.
DISCOVER BREAKCOLD CRM
Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)


What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales CRM Software
Sales Pipeline
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Seminal Authors
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

| Descriptive | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How has the implementation and use of the instructional coaching intervention for elementary teachers impacted students’ attitudes toward reading? |
| Explanatory | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | Why do differences exist when implementing the same online reading curriculum in three elementary classrooms? |
| Exploratory | This type of case study allows the researcher to:
| What are potential barriers to student’s reading success when middle school teachers implement the Ready Reader curriculum online? |
| Multiple Case Studies or Collective Case Study | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How are individual school districts addressing student engagement in an online classroom? |
| Intrinsic | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How does a student’s familial background influence a teacher’s ability to provide meaningful instruction? |
| Instrumental | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How a rural school district’s integration of a reward system maximized student engagement? |
Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

|
|
This type of study is implemented to understand an individual by developing a detailed explanation of the individual’s lived experiences or perceptions.
|
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore a particular group of people’s perceptions. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore the perspectives of people who work for or had interaction with a specific organization or company. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore participant’s perceptions of an event. |
What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

|
|
|
|
|
|

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 8:27 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Transformative Design – Methods, Types, Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Case Study in Research? Definition, Methods, and Examples
Case study methodology offers researchers an exciting opportunity to explore intricate phenomena within specific contexts using a wide range of data sources and collection methods. It is highly pertinent in health and social sciences, environmental studies, social work, education, and business studies. Its diverse applications, such as advancing theory, program evaluation, and intervention development, make it an invaluable tool for driving meaningful research and fostering positive change.[ 1]
Table of Contents
What is a Case Study?
A case study method involves a detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or community, to explore and understand complex issues in real-life contexts. By focusing on one specific case, researchers can gain a deep understanding of the factors and dynamics at play, understanding their complex relationships, which might be missed in broader, more quantitative studies.
When to do a Case Study?
A case study design is useful when you want to explore a phenomenon in-depth and in its natural context. Here are some examples of when to use a case study :[ 2]
- Exploratory Research: When you want to explore a new topic or phenomenon, a case study can help you understand the subject deeply. For example , a researcher studying a newly discovered plant species might use a case study to document its characteristics and behavior.
- Descriptive Research: If you want to describe a complex phenomenon or process, a case study can provide a detailed and comprehensive description. For instance, a case study design could describe the experiences of a group of individuals living with a rare disease.
- Explanatory Research: When you want to understand why a particular phenomenon occurs, a case study can help you identify causal relationships. A case study design could investigate the reasons behind the success or failure of a particular business strategy.
- Theory Building: Case studies can also be used to develop or refine theories. By systematically analyzing a series of cases, researchers can identify patterns and relationships that can contribute to developing new theories or refining existing ones.
- Critical Instance: Sometimes, a single case can be used to study a rare or unusual phenomenon, but it is important for theoretical or practical reasons. For example , the case of Phineas Gage, a man who survived a severe brain injury, has been widely studied to understand the relationship between the brain and behavior.
- Comparative Analysis: Case studies can also compare different cases or contexts. A case study example involves comparing the implementation of a particular policy in different countries to understand its effectiveness and identifying best practices.

How to Create a Case Study – Step by Step
Step 1: select a case .
Careful case selection ensures relevance, insight, and meaningful contribution to existing knowledge in your field. Here’s how you can choose a case study design :[ 3]
- Define Your Objectives: Clarify the purpose of your case study and what you hope to achieve. Do you want to provide new insights, challenge existing theories, propose solutions to a problem, or explore new research directions?
- Consider Unusual or Outlying Cases: Focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases that can provide unique insights.
- Choose a Representative Case: Alternatively, select a common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
- Avoid Bias: Ensure your selection process is unbiased using random or criteria-based selection.
- Be Clear and Specific: Clearly define the boundaries of your study design , including the scope, timeframe, and key stakeholders.
- Ethical Considerations: Consider ethical issues, such as confidentiality and informed consent.
Step 2: Build a Theoretical Framework
To ensure your case study has a solid academic foundation, it’s important to build a theoretical framework:
- Conduct a Literature Review: Identify key concepts and theories relevant to your case study .
- Establish Connections with Theory: Connect your case study with existing theories in the field.
- Guide Your Analysis and Interpretation: Use your theoretical framework to guide your analysis, ensuring your findings are grounded in established theories and concepts.
Step 3: Collect Your Data
To conduct a comprehensive case study , you can use various research methods. These include interviews, observations, primary and secondary sources analysis, surveys, and a mixed methods approach. The aim is to gather rich and diverse data to enable a detailed analysis of your case study .
Step 4: Describe and Analyze the Case
How you report your findings will depend on the type of research you’re conducting. Here are two approaches:
- Structured Approach: Follows a scientific paper format, making it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Narrative Approach: A more exploratory style aiming to analyze meanings and implications.
Regardless of the approach you choose, it’s important to include the following elements in your case study :
- Contextual Details: Provide background information about the case, including relevant historical, cultural, and social factors that may have influenced the outcome.
- Literature and Theory: Connect your case study to existing literature and theory in the field. Discuss how your findings contribute to or challenge existing knowledge.
- Wider Patterns or Debates: Consider how your case study fits into wider patterns or debates within the field. Discuss any implications your findings may have for future research or practice.

What Are the Benefits of a Case Study
Case studies offer a range of benefits , making them a powerful tool in research.
1. In-Depth Analysis
- Comprehensive Understanding: Case studies allow researchers to thoroughly explore a subject, understanding the complexities and nuances involved.
- Rich Data: They offer rich qualitative and sometimes quantitative data, capturing the intricacies of real-life contexts.
2. Contextual Insight
- Real-World Application: Case studies provide insights into real-world applications, making the findings highly relevant and practical.
- Context-Specific: They highlight how various factors interact within a specific context, offering a detailed picture of the situation.
3. Flexibility
- Methodological Diversity: Case studies can use various data collection methods, including interviews, observations, document analysis, and surveys.
- Adaptability: Researchers can adapt the case study approach to fit the specific needs and circumstances of the research.
4. Practical Solutions
- Actionable Insights: The detailed findings from case studies can inform practical solutions and recommendations for practitioners and policymakers.
- Problem-Solving: They help understand the root causes of problems and devise effective strategies to address them.
5. Unique Cases
- Rare Phenomena: Case studies are particularly valuable for studying rare or unique cases that other research methods may not capture.
- Detailed Documentation: They document and preserve detailed information about specific instances that might otherwise be overlooked.
What Are the Limitations of a Case Study
While case studies offer valuable insights and a detailed understanding of complex issues, they have several limitations .
1. Limited Generalizability
- Specific Context: Case studies often focus on a single case or a small number of cases, which may limit the generalization of findings to broader populations or different contexts.
- Unique Situations: The unique characteristics of the case may not be representative of other situations, reducing the applicability of the results.
2. Subjectivity
- Researcher Bias: The researcher’s perspectives and interpretations can influence the analysis and conclusions, potentially introducing bias.
- Participant Bias: Participants’ responses and behaviors may be influenced by their awareness of being studied, known as the Hawthorne effect.
3. Time-Consuming
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering detailed, in-depth data requires significant time and effort, making case studies more time-consuming than other research methods.
- Longitudinal Studies: If the case study observes changes over time, it can become even more prolonged.
4. Resource Intensive
- Financial and Human Resources: Conducting comprehensive case studies may require significant financial investment and human resources, including trained researchers and participant access.
- Access to Data: Accessing relevant and reliable data sources can be challenging, particularly in sensitive or proprietary contexts.
5. Replication Difficulties
- Unique Contexts: A case study’s specific and detailed context makes it difficult to replicate the study exactly, limiting the ability to validate findings through repetition.
- Variability: Differences in contexts, researchers, and methodologies can lead to variations in findings, complicating efforts to achieve consistent results.
By acknowledging and addressing these limitations , researchers can enhance the rigor and reliability of their case study findings.
Key Takeaways
Case studies are valuable in research because they provide an in-depth, contextual analysis of a single subject, event, or organization. They allow researchers to explore complex issues in real-world settings, capturing detailed qualitative and quantitative data. This method is useful for generating insights, developing theories, and offering practical solutions to problems. They are versatile, applicable in diverse fields such as business, education, and health, and can complement other research methods by providing rich, contextual evidence. However, their findings may have limited generalizability due to the focus on a specific case.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a case study in research?
A case study in research is an impactful tool for gaining a deep understanding of complex issues within their real-life context. It combines various data collection methods and provides rich, detailed insights that can inform theory development and practical applications.
Q: What are the advantages of using case studies in research?
Case studies are a powerful research method, offering advantages such as in-depth analysis, contextual insights, flexibility, rich data, and the ability to handle complex issues. They are particularly valuable for exploring new areas, generating hypotheses, and providing detailed, illustrative examples that can inform theory and practice.
Q: Can case studies be used in quantitative research?
While case studies are predominantly associated with qualitative research, they can effectively incorporate quantitative methods to provide a more comprehensive analysis. A mixed-methods approach leverages qualitative and quantitative research strengths, offering a powerful tool for exploring complex issues in a real-world context. For example , a new medical treatment case study can incorporate quantitative clinical outcomes (e.g., patient recovery rates and dosage levels) along with qualitative patient interviews.
Q: What are the key components of a case study?
A case study typically includes several key components:
- Introductio n, which provides an overview and sets the context by presenting the problem statement and research objectives;
- Literature review , which connects the study to existing theories and prior research;
- Methodology , which details the case study design , data collection methods, and analysis techniques;
- Findings , which present the data and results, including descriptions, patterns, and themes;
- Discussion and conclusion , which interpret the findings, discuss their implications, and offer conclusions, practical applications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Together, these components ensure a comprehensive, systematic, and insightful exploration of the case.
References
- de Vries, K. (2020). Case study methodology. In Critical qualitative health research (pp. 41-52). Routledge.
- Fidel, R. (1984). The case study method: A case study. Library and Information Science Research , 6 (3), 273-288.
- Thomas, G. (2021). How to do your case study. How to do your case study , 1-320.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Journal Turnaround Time: Researcher.Life and Scholarly Intelligence Join Hands to Empower Researchers with Publication Time Insights
- All Categories
- Marketing Analytics Software
What Is a Case Study? How to Write, Examples, and Template

In this post
How to write a case study
Case study template, case study examples, types of case studies, what are the benefits of case studies , what are the limitations of case studies , case study vs. testimonial.
In today's marketplace, conveying your product's value through a compelling narrative is crucial to genuinely connecting with your customers.
Your business can use marketing analytics tools to understand what customers want to know about your product. Once you have this information, the next step is to showcase your product and its benefits to your target audience. This strategy involves a mix of data, analysis, and storytelling. Combining these elements allows you to create a narrative that engages your audience. So, how can you do this effectively?
What is a case study?
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing a business's success in helping clients achieve their goals. It's a form of storytelling that details real-world scenarios where a business implemented its solutions to deliver positive results for a client.
In this article, we explore the concept of a case study , including its writing process, benefits, various types, challenges, and more.
Understanding how to write a case study is an invaluable skill. You'll need to embrace decision-making – from deciding which customers to feature to designing the best format to make them as engaging as possible. This can feel overwhelming in a hurry, so let's break it down.
Step 1: Reach out to the target persona
If you've been in business for a while, you have no shortage of happy customers. But w ith limited time and resources, you can't choose everyone. So, take some time beforehand to flesh out your target buyer personas.
Once you know precisely who you're targeting, go through your stable of happy customers to find a buyer representative of the audience you're trying to reach. The closer their problems, goals, and industries align, the more your case study will resonate.
What if you have more than one buyer persona? No problem. This is a common situation for companies because buyers comprise an entire committee. You might be marketing to procurement experts, executives, engineers, etc. Try to develop a case study tailored to each key persona. This might be a long-term goal, and that's fine. The better you can personalize the experience for each stakeholder, the easier it is to keep their attention.
Here are a few considerations to think about before research:
- Products/services of yours the customer uses (and how familiar they are with them)
- The customer's brand recognition in the industry
- Whether the results they've achieved are specific and remarkable
- Whether they've switched from a competitor's product/service
- How closely aligned they are with your target audience
These items are just a jumping-off point as you develop your criteria. Once you have a list, run each customer through it to determine your top targets. Approach the ones on the top (your "dream" case study subjects) and work your way down as needed.
Who to interview
You should consider interviewing top-level managers or executives because those are high-profile positions. But consider how close they are to your product and its results.
Focusing on an office manager or engineer who uses your product daily would be better. Look for someone with a courtside view of the effects.
The ways to request customer participation in case studies can vary, but certain principles can improve your chances:
- Make it easy for customers to work with you, respecting their valuable time. Be well-prepared and minimize their involvement.
- Emphasize how customers will benefit through increased publicity, revenue opportunities, or recognition for their success.
- Acknowledge their contributions and showcase their achievements.
- Standardizing the request process with a script incorporating these principles can help your team consistently secure case study approvals and track performance.
Step 2: Prepare for the interview
Case study interviews are like school exams. The more prepared you are for them, the better they turn out. Preparing thoroughly also shows participants that you value their time. You don't waste precious minutes rehashing things you should have already known. You focus on getting the information you need as efficiently as possible.
You can conduct your case study interview in multiple formats, from exchanging emails to in-person interviews. This isn't a trivial decision. As you'll see in the chart below, each format has its unique advantages and disadvantages.
| Seeing each other's facial expressions puts everyone at ease and encourages case study participants to open up. It's a good format if you're simultaneously conferencing with several people from the customer's team. | Always be on guard for connection issues; not every customer knows the technology. Audio quality will probably be less good than on the phone. When multiple people are talking, pieces of conversation can be lost. | |
| It is a more personal than email because you can hear someone's tone. You can encourage them to continue if they get really excited about certain answers. Convenient and immediate. Dial a number and start interviewing without ever leaving the office. | It isn't as personal as a video chat or an in-person interview because you can't see the customer's face, and nonverbal cues might be missed. Don't get direct quotes like you would with email responses. The only way to preserve the interview is to remember to have it recorded. | |
| The most personal interview style. It feels like an informal conversation, making it easier to tell stories and switch seamlessly between topics. Humanizes the customer's experience and allows you to put a face to the incredible results. | Puts a lot of pressure on customers who are shy or introverted – especially if they're being recorded. Requires the most commitment for the participant – travel, dressing up, dealing with audiovisual equipment, etc. | |
| Gives customers the most flexibility with respect to scheduling. They can answer a few questions, see to their obligations, and return to them at their convenience. No coordination of schedules is needed. Each party can fulfill their obligations whenever they're able to. | There is less opportunity for customers to go “off script” and tell compelling anecdotes that your questions might have overlooked. Some of the study participant's personalities might be lost in their typed responses. It's harder to sense their enthusiasm or frustration. |
You'll also have to consider who will ask and answer the questions during your case study interview. It's wise to consider this while considering the case study format. The number of participants factors into which format will work best. Pulling off an in-person interview becomes much harder if you're trying to juggle four or five people's busy schedules. Try a video conference instead.
Before interviewing your case study participant, it is crucial to identify the specific questions that need to be asked. It's essential to thoroughly evaluate your collaboration with the client and understand how your product's contributions impact the company.
Remember that structuring your case study is akin to crafting a compelling narrative. To achieve this, follow a structured approach:
- Beginning of your story. Delve into the customer's challenge that ultimately led them to do business with you. What were their problems like? What drove them to make a decision finally? Why did they choose you?
- The middle of the case study. Your audience also wants to know about the experience of working with you. Your customer has taken action to address their problems. What happened once you got on board?
- An ending that makes you the hero. Describe the specific results your company produced for the customer. How has the customer's business (and life) changed once they implemented your solution?
Sample questions for the case study interview
If you're preparing for a case study interview, here are some sample case study research questions to help you get started:
- What challenges led you to seek a solution?
- When did you realize the need for immediate action? Was there a tipping point?
- How did you decide on the criteria for choosing a B2B solution, and who was involved?
- What set our product or service apart from others you considered?
- How was your experience working with us post-purchase?
- Were there any pleasant surprises or exceeded expectations during our collaboration?
- How smoothly did your team integrate our solution into their workflows?
- How long before you started seeing positive results?
- How have you benefited from our products or services?
- How do you measure the value our product or service provides?
Step 3: Conduct the interview
Preparing for case study interviews can be different from everyday conversations. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Create a comfortable atmosphere. Before diving into the discussion, talk about their business and personal interests. Ensure everyone is at ease, and address any questions or concerns.
- Prioritize key questions. Lead with your most crucial questions to respect your customer's time. Interview lengths can vary, so starting with the essentials ensures you get the vital information.
- Be flexible. Case study interviews don't have to be rigid. If your interviewee goes "off script," embrace it. Their spontaneous responses often provide valuable insights.
- Record the interview. If not conducted via email, ask for permission to record the interview. This lets you focus on the conversation and capture valuable quotes without distractions.
Step 4: Figure out who will create the case study
When creating written case studies for your business, deciding who should handle the writing depends on cost, perspective, and revisions.
Outsourcing might be pricier, but it ensures a professionally crafted outcome. On the other hand, in-house writing has its considerations, including understanding your customers and products.
Technical expertise and equipment are needed for video case studies, which often leads companies to consider outsourcing due to production and editing costs.
Tip: When outsourcing work, it's essential to clearly understand pricing details to avoid surprises and unexpected charges during payment.
Step 5: Utilize storytelling
Understanding and applying storytelling elements can make your case studies unforgettable, offering a competitive edge.

Source: The Framework Bank
Every great study follows a narrative arc (also called a "story arc"). This arc represents how a character faces challenges, struggles against raising stakes, and encounters a formidable obstacle before the tension resolves.
In a case study narrative, consider:
- Exposition. Provide background information about the company, revealing their "old life" before becoming your customer.
- Inciting incident. Highlight the problem that drove the customer to seek a solution, creating a sense of urgency.
- Obstacles (rising action). Describe the customer's journey in researching and evaluating solutions, building tension as they explore options.
- Midpoint. Explain what made the business choose your product or service and what set you apart.
- Climax. Showcase the success achieved with your product.
- Denouement. Describe the customer's transformed business and end with a call-to-action for the reader to take the next step.
Step 6: Design the case study
The adage "Don't judge a book by its cover" is familiar, but people tend to do just that quite often!
A poor layout can deter readers even if you have an outstanding case study. To create an engaging case study, follow these steps:
- Craft a compelling title. Just like you wouldn't read a newspaper article without an eye-catching headline, the same goes for case studies. Start with a title that grabs attention.
- Organize your content. Break down your content into different sections, such as challenges, results, etc. Each section can also include subsections. This case study approach divides the content into manageable portions, preventing readers from feeling overwhelmed by lengthy blocks of text.
- Conciseness is key. Keep your case study as concise as possible. The most compelling case studies are precisely long enough to introduce the customer's challenge, experience with your solution, and outstanding results. Prioritize clarity and omit any sections that may detract from the main storyline.
- Utilize visual elements. To break up text and maintain reader interest, incorporate visual elements like callout boxes, bulleted lists, and sidebars.
- Include charts and images. Summarize results and simplify complex topics by including pictures and charts. Visual aids enhance the overall appeal of your case study.
- Embrace white space. Avoid overwhelming walls of text to prevent reader fatigue. Opt for plenty of white space, use shorter paragraphs, and employ subsections to ensure easy readability and navigation.
- Enhance video case studies. In video case studies, elements like music, fonts, and color grading are pivotal in setting the right tone. Choose music that complements your message and use it strategically throughout your story. Carefully select fonts to convey the desired style, and consider how lighting and color grading can influence the mood. These elements collectively help create the desired tone for your video case study.
Step 7: Edits and revisions
Once you've finished the interview and created your case study, the hardest part is over. Now's the time for editing and revision. This might feel frustrating for impatient B2B marketers, but it can turn good stories into great ones.
Ideally, you'll want to submit your case study through two different rounds of editing and revisions:
- Internal review. Seek feedback from various team members to ensure your case study is captivating and error-free. Gather perspectives from marketing, sales, and those in close contact with customers for well-rounded insights. Use patterns from this feedback to guide revisions and apply lessons to future case studies.
- Customer feedback. Share the case study with customers to make them feel valued and ensure accuracy. Let them review quotes and data points, as they are the "heroes" of the story, and their logos will be prominently featured. This step maintains positive customer relationships.
Case study mistakes to avoid
- Ensure easy access to case studies on your website.
- Spotlight the customer, not just your business.
- Tailor each case study to a specific audience.
- Avoid excessive industry jargon in your content.
Step 8: Publishing
Take a moment to proofread your case study one more time carefully. Even if you're reasonably confident you've caught all the errors, it's always a good idea to check. Your case study will be a valuable marketing tool for years, so it's worth the investment to ensure it's flawless. Once done, your case study is all set to go!
Consider sharing a copy of the completed case study with your customer as a thoughtful gesture. They'll likely appreciate it; some may want to keep it for their records. After all, your case study wouldn't have been possible without their help, and they deserve to see the final product.
Where you publish your case study depends on its role in your overall marketing strategy. If you want to reach as many people as possible with your case study, consider publishing it on your website and social media platforms.
Tip: Some companies prefer to keep their case studies exclusive, making them available only to those who request them. This approach is often taken to control access to valuable information and to engage more deeply with potential customers who express specific interests. It can create a sense of exclusivity and encourage interested parties to engage directly with the company.
Step 9: Case study distribution
When sharing individual case studies, concentrate on reaching the audience with the most influence on purchasing decisions
Here are some common distribution channels to consider:
- Sales teams. Share case studies to enhance customer interactions, retention , and upselling among your sales and customer success teams. Keep them updated on new studies and offer easily accessible formats like PDFs or landing page links.
- Company website. Feature case studies on your website to establish authority and provide valuable information to potential buyers. Organize them by categories such as location, size, industry, challenges, and products or services used for effective presentation.
- Events. Use live events like conferences and webinars to distribute printed case study copies, showcase video case studies at trade show booths, and conclude webinars with links to your case study library. This creative approach blends personal interactions with compelling content.
- Industry journalists. Engage relevant industry journalists to gain media coverage by identifying suitable publications and journalists covering related topics. Building relationships is vital, and platforms like HARO (Help A Reporter Out) can facilitate connections, especially if your competitors have received coverage before.
Want to learn more about Marketing Analytics Software? Explore Marketing Analytics products.
It can seem daunting to transform the information you've gathered into a cohesive narrative. We’ve created a versatile case study template that can serve as a solid starting point for your case study.
With this template, your business can explore any solutions offered to satisfied customers, covering their background, the factors that led them to choose your services, and their outcomes.

The template boasts a straightforward design, featuring distinct sections that guide you in effectively narrating your and your customer's story. However, remember that limitless ways to showcase your business's accomplishments exist.
To assist you in this process, here's a breakdown of the recommended sections to include in a case study:
- Title. Keep it concise. Create a brief yet engaging project title summarizing your work with your subject. Consider your title like a newspaper headline; do it well, and readers will want to learn more.
- Subtitle . Use this section to elaborate on the achievement briefly. Make it creative and catchy to engage your audience.
- Executive summary. Use this as an overview of the story, followed by 2-3 bullet points highlighting key success metrics.
- Challenges and objectives. This section describes the customer's challenges before adopting your product or service, along with the goals or objectives they sought to achieve.
- How product/service helped. A paragraph explaining how your product or service addressed their problem.
- Testimonials. Incorporate short quotes or statements from the individuals involved in the case study, sharing their perspectives and experiences.
- Supporting visuals. Include one or two impactful visuals, such as graphs, infographics, or highlighted metrics, that reinforce the narrative.
- Call to action (CTA). If you do your job well, your audience will read (or watch) your case studies from beginning to end. They are interested in everything you've said. Now, what's the next step they should take to continue their relationship with you? Give people a simple action they can complete.
Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study:
- Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced using AWS.
- LinkedIn Marketing Solutions combines captivating visuals with measurable results in the case study created for BlackRock. This case study illustrates how LinkedIn has contributed to the growth of BlackRock's brand awareness over the years.
- Salesforce , a sales and marketing automation SaaS solutions provider, seamlessly integrates written and visual elements to convey its success stories with Pepe Jeans. This case study effectively demonstrates how Pepe Jeans is captivating online shoppers with immersive and context-driven e-commerce experiences through Salesforce.
- HubSpot offers a combination of sales and marketing tools. Their case study demonstrates the effectiveness of its all-in-one solutions. These typically focus on a particular client's journey and how HubSpot helped them achieve significant results.
There are two different types of case studies that businesses might utilize:
Written case studies
Written case studies offer readers a clear visual representation of data, which helps them quickly identify and focus on the information that matters most.
Printed versions of case studies find their place at events like trade shows, where they serve as valuable sales collateral to engage prospective clients. Even in the digital age, many businesses provide case studies in PDF format or as web-based landing pages, improving accessibility for their audience.
Note: Landing pages , in particular, offer the flexibility to incorporate rich multimedia content, including images, charts, and videos. This flexibility in design makes landing pages an attractive choice for presenting detailed content to the audience.
Written case study advantages
Here are several significant advantages to leveraging case studies for your company:
- Hyperlink accessibility. Whether in PDF or landing page format, written case studies allow for embedded hyperlinks, offering prospects easy access to additional information and contact forms.
- Flexible engagement. Unlike video case studies, which may demand in-person arrangements, written case studies can be conducted via phone or video streaming, reducing customer commitment and simplifying scheduling.
- Efficient scanning . Well-structured written case studies with a scannable format cater to time-strapped professionals. Charts and callout boxes with key statistics enhance the ease of information retrieval.
- Printable for offline use. Written case studies can be effortlessly printed and distributed at trade shows, sales meetings, and live events. This tangible format accommodates those who prefer physical materials and provides versatility in outreach, unlike video content, which is less portable.
Written case study disadvantages
Here are some drawbacks associated with the use of case studies:
- Reduced emotional impact. Written content lacks the emotional punch of live video testimonials, which engage more senses and emotions, making a stronger connection.
- Consider time investment. Creating a compelling case study involves editing, proofreading, and design collaboration, with multiple revisions commonly required before publication.
- Challenges in maintaining attention. Attention spans are short in today's ad-saturated world. Using graphics, infographics, and videos more often is more powerful to incite the right emotions in customers.
Video case studies
Video case studies are the latest marketing trend. Unlike in the past, when video production was costly, today's tools make it more accessible for users to create and edit their videos. However, specific technical requirements still apply.
Like written case studies, video case studies delve into a specific customer's challenges and how your business provides solutions. Yet, the video offers a more profound connection by showcasing the person who faced and conquered the problem.
Video case studies can boost brand exposure when shared on platforms like YouTube. For example, Slack's engaging case study video with Sandwich Video illustrates how Slack transformed its workflow and adds humor, which can be challenging in written case studies focused on factual evidence.
Source : YouTube
This video case study has garnered nearly a million views on YouTube.
Video case study advantages
Here are some of the top advantages of video case studies. While video testimonials take more time, the payoff can be worth it.
- Humanization and authenticity. Video case studies connect viewers with real people, adding authenticity and fostering a stronger emotional connection.
- Engaging multiple senses. They engage both auditory and visual senses, enhancing credibility and emotional impact. Charts, statistics, and images can also be incorporated.
- Broad distribution. Videos can be shared on websites, YouTube, social media, and more, reaching diverse audiences and boosting engagement, especially on social platforms.
Video case study disadvantages
Before fully committing to video testimonials, consider the following:
- Technical expertise and equipment. Video production requires technical know-how and equipment, which can be costly. Skilled video editing is essential to maintain a professional image. While technology advances, producing amateurish videos may harm your brand's perception.
- Viewer convenience. Some prospects prefer written formats due to faster reading and ease of navigation. Video typically requires sound, which can be inconvenient for viewers in specific settings. Many people may not have headphones readily available to watch your content.
- Demand on case study participants. On-camera interviews can be time-consuming and location-dependent, making scheduling challenging for case study participants. Additionally, being on screen for a global audience may create insecurities and performance pressure.
- Comfort on camera. Not everyone feels at ease on camera. Nervousness or a different on-screen persona can impact the effectiveness of the testimonial, and discovering this late in the process can be problematic.
Written or video case studies: Which is right for you?
Now that you know the pros and cons of each, how do you choose which is right for you?
One of the most significant factors in doing video case studies can be the technical expertise and equipment required for a high level of production quality. Whether you have the budget to do this in-house or hire a production company can be one of the major deciding factors.
Still, written or video doesn't have to be an either-or decision. Some B2B companies are using both formats. They can complement each other nicely, minimizing the downsides mentioned above and reaching your potential customers where they prefer.
Let's say you're selling IT network security. What you offer is invaluable but complicated. You could create a short (three- or four-minute) video case study to get attention and touch on the significant benefits of your services. This whets the viewer's appetite for more information, which they could find in a written case study that supplements the video.
Should you decide to test the water in video case studies, test their effectiveness among your target audience. See how well they work for your company and sales team. And, just like a written case study, you can always find ways to improve your process as you continue exploring video case studies.
Case studies offer several distinctive advantages, making them an ideal tool for businesses to market their products to customers. However, their benefits extend beyond these qualities.
Here's an overview of all the advantages of case studies:
Valuable sales support
Case studies serve as a valuable resource for your sales endeavors. Buyers frequently require additional information before finalizing a purchase decision. These studies provide concrete evidence of your product or service's effectiveness, assisting your sales representatives in closing deals more efficiently, especially with customers with lingering uncertainties.
Validating your value
Case studies serve as evidence of your product or service's worth or value proposition , playing a role in building trust with potential customers. By showcasing successful partnerships, you make it easier for prospects to place trust in your offerings. This effect is particularly notable when the featured customer holds a reputable status.
Unique and engaging content
By working closely with your customer success teams, you can uncover various customer stories that resonate with different prospects. Case studies allow marketers to shape product features and benefits into compelling narratives.
Each case study's distinctiveness, mirroring the uniqueness of every customer's journey, makes them a valuable source of relatable and engaging content. Storytelling possesses the unique ability to connect with audiences on an emotional level, a dimension that statistics alone often cannot achieve.
Spotlighting valuable customers
Case studies provide a valuable platform for showcasing your esteemed customers. Featuring them in these studies offers a chance to give them visibility and express your gratitude for the partnership, which can enhance customer loyalty . Depending on the company you are writing about, it can also demonstrate the caliber of your business.
Now is the time to get SaaS-y news and entertainment with our 5-minute newsletter, G2 Tea , featuring inspiring leaders, hot takes, and bold predictions. Subscribe below!

It's important to consider limitations when designing and interpreting the results of case studies. Here's an overview of the limitations of case studies:
Challenges in replication
Case studies often focus on specific individuals, organizations, or situations, making generalizing their findings to broader populations or contexts challenging.
Time-intensive process
Case studies require a significant time investment. The extensive data collection process and the need for comprehensive analysis can be demanding, especially for researchers who are new to this method.
Potential for errors
Case studies can be influenced by memory and judgment, potentially leading to inaccuracies. Depending on human memory to reconstruct a case's history may result in variations and potential inconsistencies in how individuals recall past events. Additionally, bias may emerge, as individuals tend to prioritize what they consider most significant, which could limit their consideration of alternative perspectives.
Challenges in verification
Confirming results through additional research can present difficulties. This complexity arises from the need for detailed and extensive data in the initial creation of a case study. Consequently, this process requires significant effort and a substantial amount of time.
While looking at case studies, you may have noticed a quote. This type of quote is considered a testimonial, a key element of case studies.
If a customer's quote proves that your brand does what it says it will or performs as expected, you may wonder: 'Aren't customer testimonials and case studies the same thing?' Not exactly.

Testimonials are brief endorsements designed to establish trust on a broad scale. In contrast, case studies are detailed narratives that offer a comprehensive understanding of how a product or service addresses a specific problem, targeting a more focused audience.
Crafting case studies requires more resources and a structured approach than testimonials. Your selection between the two depends on your marketing objectives and the complexity of your product or service.
Case in point!
Case studies are among a company's most effective tools. You're well on your way to mastering them.
Today's buyers are tackling much of the case study research methodology independently. Many are understandably skeptical before making a buying decision. By connecting them with multiple case studies, you can prove you've gotten the results you say you can. There's hardly a better way to boost your credibility and persuade them to consider your solution.
Case study formats and distribution methods might change as technology evolves. However, the fundamentals that make them effective—knowing how to choose subjects, conduct interviews, and structure everything to get attention—will serve you for as long as you're in business.
We covered a ton of concepts and resources, so go ahead and bookmark this page. You can refer to it whenever you have questions or need a refresher.
Dive into market research to uncover customer preferences and spending habits.
Kristen McCabe
Kristen’s is a former senior content marketing specialist at G2. Her global marketing experience extends from Australia to Chicago, with expertise in B2B and B2C industries. Specializing in content, conversions, and events, Kristen spends her time outside of work time acting, learning nature photography, and joining in the #instadog fun with her Pug/Jack Russell, Bella. (she/her/hers)
Explore More G2 Articles
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 6 Types of Case Studies to Inspire Your Research and Analysis
6 Types of Case Studies to Inspire Your Research and Analysis
Written by: Ronita Mohan Sep 20, 2021

Case studies have become powerful business tools. But what is a case study? What are the benefits of creating one? Are there limitations to the format?
If you’ve asked yourself these questions, our helpful guide will clear things up. Learn how to use a case study for business. Find out how cases analysis works in psychology and research.
We’ve also got examples of case studies to inspire you.
Haven’t made a case study before? You can easily create a case study with Venngage’s customizable case study templates .
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study?
6 types of case studies, what is a business case study, what is a case study in research, what is a case study in psychology, what is the case study method, benefits of case studies, limitations of case studies, faqs about case studies.
A case study is a research process aimed at learning about a subject, an event or an organization. Case studies are use in business, the social sciences and healthcare.
A case study may focus on one observation or many. It can also examine a series of events or a single case. An effective case study tells a story and provides a conclusion.

Healthcare industries write reports on patients and diagnoses. Marketing case study examples , like the one below, highlight the benefits of a business product.

Now that you know what a case study is, let’s look at the six different types of case studies next.
There are six common types of case reports. Depending on your industry, you might use one of these types.
Descriptive case studies
Explanatory case studies, exploratory case reports, intrinsic case studies, instrumental case studies, collective case reports.

We go into more detail about each type of study in the guide below.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
When you have an existing hypothesis, you can design a descriptive study. This type of report starts with a description. The aim is to find connections between the subject being studied and a theory.
Once these connections are found, the study can conclude. The results of this type of study will usually suggest how to develop a theory further.
A study like the one below has concrete results. A descriptive report would use the quantitative data as a suggestion for researching the subject deeply.

When an incident occurs in a field, an explanation is required. An explanatory report investigates the cause of the event. It will include explanations for that cause.
The study will also share details about the impact of the event. In most cases, this report will use evidence to predict future occurrences. The results of explanatory reports are definitive.
Note that there is no room for interpretation here. The results are absolute.
The study below is a good example. It explains how one brand used the services of another. It concludes by showing definitive proof that the collaboration was successful.

Another example of this study would be in the automotive industry. If a vehicle fails a test, an explanatory study will examine why. The results could show that the failure was because of a particular part.
Related: How to Write a Case Study [+ Design Tips]
An explanatory report is a self-contained document. An exploratory one is only the beginning of an investigation.
Exploratory cases act as the starting point of studies. This is usually conducted as a precursor to large-scale investigations. The research is used to suggest why further investigations are needed.
An exploratory study can also be used to suggest methods for further examination.
For example, the below analysis could have found inconclusive results. In that situation, it would be the basis for an in-depth study.

Intrinsic studies are more common in the field of psychology. These reports can also be conducted in healthcare or social work.
These types of studies focus on a unique subject, such as a patient. They can sometimes study groups close to the researcher.
The aim of such studies is to understand the subject better. This requires learning their history. The researcher will also examine how they interact with their environment.
For instance, if the case study below was about a unique brand, it could be an intrinsic study.

Once the study is complete, the researcher will have developed a better understanding of a phenomenon. This phenomenon will likely not have been studied or theorized about before.
Examples of intrinsic case analysis can be found across psychology. For example, Jean Piaget’s theories on cognitive development. He established the theory from intrinsic studies into his own children.
Related: What Disney Villains Can Tell Us About Color Psychology [Infographic]
This is another type of study seen in medical and psychology fields. Instrumental reports are created to examine more than just the primary subject.
When research is conducted for an instrumental study, it is to provide the basis for a larger phenomenon. The subject matter is usually the best example of the phenomenon. This is why it is being studied.
Take the example of the fictional brand below.

Assume it’s examining lead generation strategies. It may want to show that visual marketing is the definitive lead generation tool. The brand can conduct an instrumental case study to examine this phenomenon.
Collective studies are based on instrumental case reports. These types of studies examine multiple reports.
There are a number of reasons why collective reports are created:
- To provide evidence for starting a new study
- To find pattens between multiple instrumental reports
- To find differences in similar types of cases
- Gain a deeper understanding of a complex phenomenon
- Understand a phenomenon from diverse contexts
A researcher could use multiple reports, like the one below, to build a collective case report.

Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
A business or marketing case study aims at showcasing a successful partnership. This can be between a brand and a client. Or the case study can examine a brand’s project.
There is a perception that case studies are used to advertise a brand. But effective reports, like the one below, can show clients how a brand can support them.

Hubspot created a case study on a customer that successfully scaled its business. The report outlines the various Hubspot tools used to achieve these results.

Hubspot also added a video with testimonials from the client company’s employees.
So, what is the purpose of a case study for businesses? There is a lot of competition in the corporate world. Companies are run by people. They can be on the fence about which brand to work with.
Business reports stand out aesthetically, as well. They use brand colors and brand fonts . Usually, a combination of the client’s and the brand’s.
With the Venngage My Brand Kit feature, businesses can automatically apply their brand to designs.
A business case study, like the one below, acts as social proof. This helps customers decide between your brand and your competitors.

Don’t know how to design a report? You can learn how to write a case study with Venngage’s guide. We also share design tips and examples that will help you convert.
Related: 55+ Annual Report Design Templates, Inspirational Examples & Tips [Updated]
Research is a necessary part of every case study. But specific research fields are required to create studies. These fields include user research, healthcare, education, or social work.
For example, this UX Design report examined the public perception of a client. The brand researched and implemented new visuals to improve it. The study breaks down this research through lessons learned.

Clinical reports are a necessity in the medical field. These documents are used to share knowledge with other professionals. They also help examine new or unusual diseases or symptoms.
The pandemic has led to a significant increase in research. For example, Spectrum Health studied the value of health systems in the pandemic. They created the study by examining community outreach.

The pandemic has significantly impacted the field of education. This has led to numerous examinations on remote studying. There have also been studies on how students react to decreased peer communication.
Social work case reports often have a community focus. They can also examine public health responses. In certain regions, social workers study disaster responses.
You now know what case studies in various fields are. In the next step of our guide, we explain the case study method.
In the field of psychology, case studies focus on a particular subject. Psychology case histories also examine human behaviors.
Case reports search for commonalities between humans. They are also used to prescribe further research. Or these studies can elaborate on a solution for a behavioral ailment.
The American Psychology Association has a number of case studies on real-life clients. Note how the reports are more text-heavy than a business case study.

Famous psychologists such as Sigmund Freud and Anna O popularised the use of case studies in the field. They did so by regularly interviewing subjects. Their detailed observations build the field of psychology.
It is important to note that psychological studies must be conducted by professionals. Psychologists, psychiatrists and therapists should be the researchers in these cases.
Related: What Netflix’s Top 50 Shows Can Teach Us About Font Psychology [Infographic]
The case study method, or case method, is a learning technique where you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it.
After working through it independently and with peers, you learn how the actual scenario unfolded. This approach helps develop problem-solving skills and practical knowledge.
This method often uses various data sources like interviews, observations, and documents to provide comprehensive insights. The below example would have been created after numerous interviews.
Case studies are largely qualitative. They analyze and describe phenomena. While some data is included, a case analysis is not quantitative.
There are a few steps in the case method. You have to start by identifying the subject of your study. Then determine what kind of research is required.
In natural sciences, case studies can take years to complete. Business reports, like this one, don’t take that long. A few weeks of interviews should be enough.

The case method will vary depending on the industry. Reports will also look different once produced.
As you will have seen, business reports are more colorful. The design is also more accessible . Healthcare and psychology reports are more text-heavy.
Designing case reports takes time and energy. So, is it worth taking the time to write them? Here are the benefits of creating case studies.
- Collects large amounts of information
- Helps formulate hypotheses
- Builds the case for further research
- Discovers new insights into a subject
- Builds brand trust and loyalty
- Engages customers through stories
For example, the business study below creates a story around a brand partnership. It makes for engaging reading. The study also shows evidence backing up the information.

We’ve shared the benefits of why studies are needed. We will also look at the limitations of creating them.
Related: How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
There are a few disadvantages to conducting a case analysis. The limitations will vary according to the industry.
- Responses from interviews are subjective
- Subjects may tailor responses to the researcher
- Studies can’t always be replicated
- In certain industries, analyses can take time and be expensive
- Risk of generalizing the results among a larger population
These are some of the common weaknesses of creating case reports. If you’re on the fence, look at the competition in your industry.
Other brands or professionals are building reports, like this example. In that case, you may want to do the same.

What makes a case study a case study?
A case study has a very particular research methodology. They are an in-depth study of a person or a group of individuals. They can also study a community or an organization. Case reports examine real-world phenomena within a set context.
How long should a case study be?
The length of studies depends on the industry. It also depends on the story you’re telling. Most case studies should be at least 500-1500 words long. But you can increase the length if you have more details to share.
What should you ask in a case study?
The one thing you shouldn’t ask is ‘yes’ or ‘no’ questions. Case studies are qualitative. These questions won’t give you the information you need.
Ask your client about the problems they faced. Ask them about solutions they found. Or what they think is the ideal solution. Leave room to ask them follow-up questions. This will help build out the study.
How to present a case study?
When you’re ready to present a case study, begin by providing a summary of the problem or challenge you were addressing. Follow this with an outline of the solution you implemented, and support this with the results you achieved, backed by relevant data. Incorporate visual aids like slides, graphs, and images to make your case study presentation more engaging and impactful.
Now you know what a case study means, you can begin creating one. These reports are a great tool for analyzing brands. They are also useful in a variety of other fields.
Use a visual communication platform like Venngage to design case studies. With Venngage’s templates, you can design easily. Create branded, engaging reports, all without design experience.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Text for Mobile
What Is a Case Study? Definition, Examples, Types & Methods
What is the definition of a case study.
A case study is typically a research paper to generate an in-depth and multi-faced understanding of any complicated issue in a life scenario. It is a well-written research design that is very commonly used in a wide range of disciplines.
Looking for fast and professional case study assignment help online ? Choose Casestudyhelp.com and enjoy high-quality case study assistance and the lowest rate!
Also Read: A Complete Guide to Writing an Effective Case Study
Case Study Examples
- Marketing case study examples: Case studies in marketing are written to show your success, and you must always prominently showcase your buoyant suits. You can use bright, bold colours with many contesting fonts, shapes, and simple icons to highlight your case study.
- You need to highlight your big win on the 2nd page with a bright orange colour with highlighted circles.
- Make the essential data stand out exceptionally to track your prospective customers.
- Marketing all the critical data is very important in your marketing case study.
Use a straightforward and crystal clear layout of the case study.
- Using a straightforward layout in any case study is very effective. For example, keeping a spotless white background and drawing slim lines helps to separate these sections in a specific way for formatting the case study.
- Making the information clear helps draw attention to the results and helps to improve the accessibility of the design.
- The case study examples must sit nicely with more extended reports and a consistent layout.
Need Help with Writing a Case Study?
Casestudyhelp.com is the right place that can help you.
What Are the Types of Case Studies?
Case studies can be categorized into several types based on their focus and purpose. Here are some common types of case studies:
- Collective Case Studies : These types of case studies involve investigating any group of individuals. Here, the researchers need to study a group of people in a specific setting or any community. Ex: Psychologists must explore how access to the resources in any society can affect people’s mental wellness.
- Descriptive Case Studies: These involve starting with any descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the gathered information is compared to the preexisting approaches.
- Explanatory Case Studies: These types of case studies are primarily used to conduct any casual investigation. Here, the researchers are more interested in looking for the factors that caused specific results.
- Exploratory Case Studies : These case studies are conducted when researchers want to explore a new or relatively unexplored topic. They are more open-ended and aim to generate hypotheses and ideas for further research.
- Instrumental Case Studies : These case studies are selected because they provide insights into a broader issue or theory. The case is used as a means to investigate a more general phenomenon.
- Intrinsic Case Studies : In these case studies, the case itself is of particular interest due to its uniqueness or rarity. The goal is not to generalize findings to a larger population but to understand the specific case deeply.
- Pilot Case Studies : Pilot case studies are conducted as a preliminary investigation before launching a larger study. They help researchers refine their research questions, methods, and procedures.
- Problem-Oriented Case Studies : These case studies focus on solving a specific problem or addressing a particular issue. Researchers aim to provide practical solutions based on their analysis of the case.
- Ethnographic Case Studies : Ethnographic case studies involve immersing the researcher in the subject’s environment to gain an in-depth cultural understanding. This is often used in anthropology and sociology.
- Longitudinal Case Studies : Longitudinal studies involve observing and analyzing a case over an extended period of time. This allows researchers to track changes, developments, and trends that occur over time.
- Comparative Case Studies : Comparative case studies involve comparing two or more cases to draw similarities, differences, and patterns between them. This type of study is often used to test hypotheses or theories.
- Critical Instance Case Studies : Critical instance cases are chosen because they represent a crucial or pivotal event that can provide insights into a larger issue or theory.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and is designed to answer specific research questions. Researchers choose the type of case study that best aligns with their objectives and the nature of the phenomenon they are investigating.
Also, Check Out – Why Is Everyone Talking About Case Study Help?
What Are the Methods of a Case Study?
A case study research is a qualitative research design. It is often used in the social sciences since it involves observing the cases or subjects in their settings with the most minor interference from the researcher.
In the case study method, the researchers pose a definite question raging any individual or group for testing their hypotheses or theories. This is done by gathering data from the interviews with the essential data.
Case study research is a perfect way to understand the nuances of any matter often neglected in quantitative research methods. A case study is distinct from any other qualitative study in the following ways:
- Focused on the effect of any set of circumstances in any group or any individual
- It mostly begins with any specific question regarding one or more cases
- It usually focuses on the individual accounts and its experiences
The primary features of case study research methods are as follows:
- The case study methods must involve the researcher asking a few questions of one person or a small group of people who are known as the respondents for testing the survey.
- The case study in the research mythology might apply triangulation to collect data. It is then analyzed and interpreted to form a hypothesis to be tested through further research or validated by other researchers.
- Concepts are defined using objective language with references to the Preconceived Notions. These individuals may have about them. A researcher sets out to discover by asking any specific question on how people think about their findings.
- The case study method needs a clear concept and theory to guide the processes. A well-organized research question is fundamental while conducting any case study since its results depend on it. The best approach for answering the research questions is challenging the preexisting theories, assumptions or hypotheses.

Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies
The benefits of case studies are as follows:
- Case studies give many details to be collected and will be easily obtained by the other research designs. The collected data is mostly richer than that can be funded via different experimental methods.
- Case studies are primarily conducted on the rare cases where more extensive samples of similar participants are unavailable.
- Within certain case studies, scientific experiments can also be conducted.
- The case studies can also help the experimenters adapt the ideas and produce novel hypotheses for later testing.
Disadvantages of Case Studies
- One of the main criticisms in case studies is that the collected data cannot necessarily be generated for any broader population. This can lead to data being collected over any case study that is only sometimes relevant or useful.
- Some of the case studies still need to be scientific. Many scientists used case studies for conducting several experiments, the results of which were only sometimes very successful.
- Case studies are primarily based on one person, so it can be only one experimenter who is collecting the data. This can lead to a bias in data collection that can influence the results in frequent designs.
- Drawing any definite cause or effect from many case studies is sometimes challenging.
Importance of Case Study
- A case study is a particular research h method involving an up-close and in-depth investigation of any subject, and it is related to a contextual position. These are produced by following a research form. The case study helps in bringing the understanding of any complex issue. This can extend experience or add strength to the already existing knowledge via the previous research. The contextual analysis revolves around a small number of events or situations.
- Researchers have used case studies for an extended period, and they have been successfully applied in various disciplines like social sciences.
Writing the best case study paper on any subject is a challenging task. Thus, you will always need the best service provider in this regard. The CaseStudyHelp.com is the top choice for you.
A Word from CaseStudyHelp
- We are the top choice for you to write a case study . Always provide the best case study examples for students
- 24×7 hours of support are available via our website
- Our experts always assure you of the top grades
- The service charges are also quite reasonable
Thus, could you register with us soon?
11 Inspiring UX Case Studies That Every Designer Should Study

A UX case study is a sort of detailed overview of a designer's work. They are often part of a UX designer's portfolio and showcase the designer's skill in managing tasks and problems. From a recruiter's perspective, such a UX portfolio shows the skill, insights, knowledge, and talent of the designer.
Therefore, UX case studies play an important role in the recruitment and demand for designers.
What Makes a Powerful Case Study
Building a UX case study includes showing the design process through compelling stories. They will use plain language to demonstrate how they handled key design issues, offering a comprehensive view of their process. Well done case studies often include:
- A problem statement and solutions with real applications.
- Relevant numbers, data, or testimonials to demonstrate the work and efforts.
- A story that directly connects the problem to the solution.
Any competent UX professional will know that creating a stunning UX case study is about the little details.
11 Best UX Case Studies for Designers
The best way to understand what a good case study looks like is to go over other examples. Each of these UX case study examples shows a designer's insights, basic skills, and other designers' lessons learned through their experience.
1. Promo.com web editor

For this video-creation platform , UX designer Sascha was brought on to revamp v2.0, adding new features that could work alongside the existing UX design. The point was to work on interface details that would help create a user friendly platform, and that users could find simple enough to use.
User personas mapped by the UX designer revealed the most common confusion to be the process of inserting particular features into the video, such as subtitles. The designer's goal, therefore, was to create a platform with improved editor controls.
The designer then used a common text-editor layout to include top and side navigation bars that made it easy to access and implement text editing.
Key Learnings from Promo.com
This case study focuses on addressing a particular problem that customers were currently facing. Its main theme is to show a problem, and how the product designer addressed this problem. Its strength points include:
- clearly highlighting the problem (i.e. inaccessible and limited video-text editor options)
- conduction research to understand the nature of the problem and the kind of solutions customers want
- implementing research insights into the redesign to create a platform that actively served customer needs
2. Productivity tracker app
The main concept behind this UX case study is to address a pre-existing problem through the design of the app. Immediately from the start, the study highlights a common pain point among users: that of a lack of productivity due to device usage.
This UX case study example addressed some of the main problems within existing productivity apps included:a poor UI and UX that made navigation difficult
- a poorly-built information architecture
- limited functions on the mobile application
Key Learnings from the Productivity app case study
The case study highlights the simple design process that was then used to build the app. Wireframes were created, a moldboard developed, and finally, individual pages of the app were designed in line with the initial goals.
3. Postmates Unlimited

This case study clearly identifies the improvements made to the Postmates app in a simple overview before jumping into greater detail. The redesign goal, which it achieved, was to improve the experience and other interface details of the app.
The problems identified included:
- usability that led to high support ticket volume.
- technical app infrastructure issues that prevented scalability.
- lack of efficient product management, such as batching orders.
A UX research course can help understand the kind of research needed for a case study. The app redesign involved bringing couriers in and running usability testing on improvements. The final model, therefore, had input from real users on what worked and what caused issues.
Key Learnings from Postmates
The Postmates redesign works as a great UX case study for the simple way it approaches problem-solving. Following an overview of the work, it addresses the problems faced by users of the app. It then establishes research processes and highlights how changes were made to reduce these issues.
4. TV Guide

Addressing the fragmentation of content across channels, this case study sought to redesign how people consume media. The key problems identified included:
- the overabundance of content across various TV and streaming platforms
- the difficulty in discovering and managing content across all platforms
To deliver on the key goals of content personalization, smart recommendations, and offering cross-platform content search, the design process included conducting interviews, surveys, and checking customer reviews.
The design of TV Guide enables users to get custom recommendations sourced from friends' and family's watchlists.
Key Learnings from TV Guide
Like previous UX design case studies, this one tackled the issue head-on. Describing the research process, it goes into detail regarding the approach used by the UX designers to create the app. It takes readers on a journey, from identifying pain points, to testing solutions, and implementing the final version.
5. The FlexBox Inspector

Designer Victoria discusses how she developed the investigator tool for the Mozilla Firefox browser. Surveys into understanding the problems with the existing CSS Flexbox tool revealed a need for a user-friendly design. Interviews with a senior designer and other designers helped developers understand the features design-focused tools ought to have. A feature analysis revealed what most users look for in such tools.
The final result of the development process was a design that incorporated several new features, including:
- a new layout
- color-coded design
- multiple entry points to make workflow management efficient
Key Learnings from the Flexbox
This UX design case study starts with a clear goal, then addresses multiple user needs. It clearly defines the design process behind each feature developed by the time, and the reasoning for including that feature. To give a complete picture, it also discusses why certain features or processes were excluded.
6. The Current State of Checkouts

This Baymard UX design case study looks into the checkout process in over 70 e-commerce websites. Through competitive analysis, it isolates problem points in the UX design, which, if addressed, could improve the customer's checkout process.
The study found at least 31 common issues that were easily preventable. The study was designed and conducted on a large scale, over 12 years, to incorporate changing design patterns into the review.
Recommendations based on findings include:
- prominent guest checkout option
- simple password requirements
- specific delivery period
- price comparison tool for shipping vs store pickup
Key Learnings from Checkout Case Study
Each identified issue is backed up by data and research to highlight its importance. Further research backs up each recommendation made within the case study, with usability testing to support the idea. As far as UX case studies go, this one provides practical insight into an existing, widely used e-commerce feature, and offers practical solutions.
7. New York Times App

Using a creative illustration website, the designers proposed a landing page feature "Timely" that could counter the problems faced by the NYT app . Its major issues included too much irrelevant content, low usage, and undesirable coverage of content.
The goal behind Timely was to improve user incentives, build long-term loyalty, and encourage reading. Design mapping for the app covered:
- identifying the problem
- understanding audience needs
- creating wireframes
- designing and prototyping
The end result was an app that could help readers get notifications regarding news of interest at convenient moments (at breakfast, before bed). This encouraged interaction and improved readability with short-form articles.
Key Learnings from NYT App
The UX case study proposes a problem solution that works with an existing information architecture, instead adding custom graphics to the mobile app. It leads from a simple problem statement to discuss the project that could address these issues without changing was customers already loved.

UX case studies focused on redesign include the FitBit redesign, which started off by understanding personas and what users expect from a fitness tracker. Developing use cases and personas, Guerilla usability testing was employed to assess pain points.
These pain points were then ranked based on their importance to users and to app performance. They were addressed through:
- Highlighting essential parts and features of the app
- Changing easily missed icons to more recognizable icons
- relabelling tracking options to guide users better to its usage
Key Learnings from Fitbit
While the case study maps user experiences and offers solutions, it does not begin with an intensive research-based approach. The prototype is successful in testing, but problem factors are not identified with research-based statistics, meaning key factors could have been ignored.
9. Rating System UX

The designer behind the rating system UX redesign sought to solve issues with the 5-star rating system. Highlighted issues included:
- the lack of subjective accuracy of a 5-point rating system
- the issue of calculating the average of a zero-star rating
- average ratings are misleading
Better alternatives include:
- 5-star emoticon rating that relates the user experience
- Like/dislike buttons that make approval/disapproval simple
The final design incorporated both these styles to make full use of the rating system.
Key Learnings from Rating System UX
The UX case study stemmed from insight into the limitations of the existing rating system. The new design addressed old issues and incorporated better efficiencies.

The Intuit redesign was focused on making content readable, more engaging, and accessible. Looking into product personalization, the content was found to be lacking aesthetic value, as well as being hard to find. The goal was to create content that was easy to find, clear, and consistent.
The implemented solutions included:
- increased readability with increased body text and header spacing
- table of contents on the sidebar for easier navigation
- visible and prominent search bar
- illustrations and designs for pretty visuals
Key Learnings from Intuit
The Intuit case study approaches the problem from a practical point of view. It begins with isolating problems with the interface, in particular with the content. This is an example of a case study that breaks down problems into broader categories, and solves each problem with a practical solution.

This UX case study about a social platform tackles a commonly-faced problem from existing platforms. It addresses the issue of recognizing non-monetary user engagement, to help creators identify their user base.
The case study addresses the problem statement and establishes the design process (building wireframes and prototypes) as well as conducting user testing. The final result is to develop "Discover" pages, engaging layouts, and animated interactions to increase usability.
Key Learnings from Jambb
The study goes into detail regarding problem identification, then moves on to propose solutions that take into account the perspective of all stakeholders involved. It then explains why each design decision was made, and proves its efficacy through testing and prototyping.
Key Takeaways
Developing good UX case studies examples is as much about the details you include as the ones you leave out. Going over UX courses can give you a better understanding of what your case study should look like. A good case study should provide an overview of the problem, include numbers and statistics, and offer practical solutions that directly address the problem. The above-discussed UX case studies provide a good example of the dos and don'ts of a well-structured UX design case study that should be part of every UX portfolio .
Additional Resources
Check out these resources to learn more about UX case studies:
8 UX Case Studies to Read
UX Design Case Study
Frequently Asked Questions
Upskill your design team effectively.
Equip your design team with the best-in-class design training that sticks.
Do you know your design team skill level? Send them this quick test & see where their skills stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Level up your design career
Get step-by-step guide how to build or advance your UX design career.
Do you know your design skills level? Take a quick test & see where you stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Continue reading
How famous cartoons use colors for storytelling, top 7 resources for ux/ui designers for meaningful design inspiration, how to write a ux case study in 10 steps, cookie settings 🍪.
- Interactive UX learning for all levels
- 20+ UX courses and career paths
- Personalized learning & practice
Design-first companies are training their design teams. Are you?
- Measure & identify team skill gaps
- Tailor learning for your team’s needs
- Unlock extensive learning library
- Visualize team growth over time
- Retain your designers

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

Case Study Research Design
The case study research design have evolved over the past few years as a useful tool for investigating trends and specific situations in many scientific disciplines.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Research Designs
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- Literature Review
- Quantitative Research Design
- Descriptive Research
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Research Designs
- 2.1 Pilot Study
- 2.2 Quantitative Research Design
- 2.3 Qualitative Research Design
- 2.4 Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- 3.1 Case Study
- 3.2 Naturalistic Observation
- 3.3 Survey Research Design
- 3.4 Observational Study
- 4.1 Case-Control Study
- 4.2 Cohort Study
- 4.3 Longitudinal Study
- 4.4 Cross Sectional Study
- 4.5 Correlational Study
- 5.1 Field Experiments
- 5.2 Quasi-Experimental Design
- 5.3 Identical Twins Study
- 6.1 Experimental Design
- 6.2 True Experimental Design
- 6.3 Double Blind Experiment
- 6.4 Factorial Design
- 7.1 Literature Review
- 7.2 Systematic Reviews
- 7.3 Meta Analysis
The case study has been especially used in social science, psychology, anthropology and ecology.
This method of study is especially useful for trying to test theoretical models by using them in real world situations. For example, if an anthropologist were to live amongst a remote tribe, whilst their observations might produce no quantitative data, they are still useful to science.

What is a Case Study?
Basically, a case study is an in depth study of a particular situation rather than a sweeping statistical survey . It is a method used to narrow down a very broad field of research into one easily researchable topic.
Whilst it will not answer a question completely, it will give some indications and allow further elaboration and hypothesis creation on a subject.
The case study research design is also useful for testing whether scientific theories and models actually work in the real world. You may come out with a great computer model for describing how the ecosystem of a rock pool works but it is only by trying it out on a real life pool that you can see if it is a realistic simulation.
For psychologists, anthropologists and social scientists they have been regarded as a valid method of research for many years. Scientists are sometimes guilty of becoming bogged down in the general picture and it is sometimes important to understand specific cases and ensure a more holistic approach to research .
H.M.: An example of a study using the case study research design.

The Argument for and Against the Case Study Research Design
Some argue that because a case study is such a narrow field that its results cannot be extrapolated to fit an entire question and that they show only one narrow example. On the other hand, it is argued that a case study provides more realistic responses than a purely statistical survey.
The truth probably lies between the two and it is probably best to try and synergize the two approaches. It is valid to conduct case studies but they should be tied in with more general statistical processes.
For example, a statistical survey might show how much time people spend talking on mobile phones, but it is case studies of a narrow group that will determine why this is so.
The other main thing to remember during case studies is their flexibility. Whilst a pure scientist is trying to prove or disprove a hypothesis , a case study might introduce new and unexpected results during its course, and lead to research taking new directions.
The argument between case study and statistical method also appears to be one of scale. Whilst many 'physical' scientists avoid case studies, for psychology, anthropology and ecology they are an essential tool. It is important to ensure that you realize that a case study cannot be generalized to fit a whole population or ecosystem.
Finally, one peripheral point is that, when informing others of your results, case studies make more interesting topics than purely statistical surveys, something that has been realized by teachers and magazine editors for many years. The general public has little interest in pages of statistical calculations but some well placed case studies can have a strong impact.
How to Design and Conduct a Case Study
The advantage of the case study research design is that you can focus on specific and interesting cases. This may be an attempt to test a theory with a typical case or it can be a specific topic that is of interest. Research should be thorough and note taking should be meticulous and systematic.
The first foundation of the case study is the subject and relevance. In a case study, you are deliberately trying to isolate a small study group, one individual case or one particular population.
For example, statistical analysis may have shown that birthrates in African countries are increasing. A case study on one or two specific countries becomes a powerful and focused tool for determining the social and economic pressures driving this.
In the design of a case study, it is important to plan and design how you are going to address the study and make sure that all collected data is relevant. Unlike a scientific report, there is no strict set of rules so the most important part is making sure that the study is focused and concise; otherwise you will end up having to wade through a lot of irrelevant information.
It is best if you make yourself a short list of 4 or 5 bullet points that you are going to try and address during the study. If you make sure that all research refers back to these then you will not be far wrong.
With a case study, even more than a questionnaire or survey , it is important to be passive in your research. You are much more of an observer than an experimenter and you must remember that, even in a multi-subject case, each case must be treated individually and then cross case conclusions can be drawn .
How to Analyze the Results
Analyzing results for a case study tends to be more opinion based than statistical methods. The usual idea is to try and collate your data into a manageable form and construct a narrative around it.
Use examples in your narrative whilst keeping things concise and interesting. It is useful to show some numerical data but remember that you are only trying to judge trends and not analyze every last piece of data. Constantly refer back to your bullet points so that you do not lose focus.
It is always a good idea to assume that a person reading your research may not possess a lot of knowledge of the subject so try to write accordingly.
In addition, unlike a scientific study which deals with facts, a case study is based on opinion and is very much designed to provoke reasoned debate. There really is no right or wrong answer in a case study.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Apr 1, 2008). Case Study Research Design. Retrieved Sep 05, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/case-study-research-design
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Get all these articles in 1 guide.
Want the full version to study at home, take to school or just scribble on?
Whether you are an academic novice, or you simply want to brush up your skills, this book will take your academic writing skills to the next level.

Download electronic versions: - Epub for mobiles and tablets - PDF version here
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Memberships
Case Study explained including an example

Case study: This article explains the concept of case study in a practical way. The article starts with the definition and meaning. You will then read all about the usefulness of the results in these studies and an example of a very remarkable case study. Enjoy reading!
What is a Case Study?
A case study (CS) is an in-depth study of a particular case, such as a person, group, or event, within a real life context. Nearly every aspect of the subject’s life is analyzed to identify patterns and causes of behavior. These studies are used in various fields such as education, medicine, political science, social studies, psychology, marketing ( Market Research ) and business administration ( business case ).
It does not necessarily have to highlight one observation or subject. In that case N=1 applies. It is common for multiple individuals or entities to be included within the same study over one or more time periods. Studies where multiple cases are combined are also referred to as cross-case studies, as opposed to single case studies for individual cases.

Case Study definition
It is defined by John Gerring as an “intensive study of a single unit or small number of units, with the aim of understanding a larger class of similar units” .
Advantages and Disadvantages of conducting a Case Study
The use of this research method has both strengths and weaknesses. The researchers conducting the research should carefully consider these advantages and disadvantages before deciding whether the CS is indeed the best form of research for their particular task.
One of the greatest benefits of this research method is that it allows researchers to investigate cases that would be impossible to replicate in a laboratory or other setting.
Other benefits are:
- Researchers can collect a lot of information
- Provides the opportunity to collect information on rare or unusual items
- Offers the opportunity to develop hypotheses that can be tested in experimental research
There are also disadvantages to using this research method.
Examples of this are:
- It is sometimes difficult to generalize the results to a larger population
- Demonstrating a cause-effect relationship is in many cases impossible
- Scientifically, the case study is not waterproof
Researchers can choose to conduct case studies for unique or recently discovered phenomena. The results they obtain can help them develop follow-up research questions . These will be investigated in future studies.
Case Study Example
In the field of psychology in particular, there have been remarkable case studies, including studies by Sigmund Freud . Many of his theories have been developed through the use of these studies.
A well-known example of this is the study of Little Hans.
Little Hans was the son of a friend of Sigmund, Max Graf. This little boy witnessed a serious accident in the street, where a horse collapsed with a cart that was overloaded. The five-year-old boy developed a great fear of horses and other animals, so he did not dare to leave the house for fear of encountering animals. The father wrote letters to Sigmund, describing his son’s behavior. The therapist and client met only once, but Freud published the case as “Analysis of a Phobia in a Five-Year-Old Boy” , in 1909.
Among other things, the father wrote about the development of the boy and his interest in the male genitalia. The therapist attributed this behavior to the phallic phase of psychosexual development. During this phase, the erogenous zone switches to the genitals.
Signs of the Oedipus complex can also be observed at this stage. A child then competes with his father for his position as the central focus of his mother’s affections.
Freud believed that this idea was supported by the fantasy described by Little Hans, in which a giraffe and another disheveled giraffe entered the room.
When the boy took the last giraffe away, the other giraffe protested. Sigmund believed the giraffes represented his parents. The crumpled giraffe represented his mother, with whom he shared a bed when the father was absent. The other giraffe represented his father.
Children can also develop castration anxiety as a result of their fear of the threat they pose to their parents’ relationship.
According to Freud , the boy’s fear of horses was the cause of his fear of his father. The fear therefore shifted to animals, whose blinkers resembled the man with his glasses. The little boy’s fear of horses disappeared, according to Freud , when his fantasies indicated the resolution of his castration anxiety and the acceptance of his love for his mother.
Various types of Case Studies
There are different types that are used by psychologists and other researchers. The three main types are collective case studies, instrumental case studies and intrinsic case studies. The type used by a researcher depends on the characteristics of the case.
Collective case studies
In this form of research, a group of people is studied. For example, researchers look at a group of people in a certain setting, or at an entire community. An example would be psychologists examining how access to a particular drug affects the collective mental well-being of the people in that group.
Instrumental studies
An instrumental study is used to gain insight into a particular phenomenon. For example, a researcher interested in children with diabetes could start a study in a high school through an exercise program. The focus in this case is not on the children or the program, but on the link between children and exercise and why some children become obese.
Intrinsic studies
Intrinsic studies are those case studies where the researcher has a personal interest in conducting them. Jean Piaget , a well-known Swiss psychologist, studied his own children. This is a good example of how intrinsic studies can contribute to the development of a theory.
Exploratory studies
Exploratory studies can be used as a prelude to more in-depth research. This form allows researchers to collect more information so that they can better formulate their research questions and hypotheses.
Descriptive studies
Descriptive studies start with a theory. Subjects are then observed in a setting and the information gained is compared with an existing theory.
Explanatory studies
Explanatory studies are used to conduct causal investigations. That means that researchers are mainly interested in certain factors that cause other things. Although it is difficult to confirm a direct cause-and-effect relationship with these studies, it is possible to discover a possible relationship. However, it cannot then be declared irrefutable.
How Do I Write it: a Step-by-Step Plan
Do you want to get started writing one? Follow the steps below for an effective approach.
Step 1: Select a case
Once a problem definition and research question have been established in the research design, the researcher is ready to choose a specific case to focus on.
A good take away will at least produce the following:
- Offers new or unexpected insights into the chosen topic
- Challenges existing views or makes them more complex
- Suggests practical actions to solve a problem
- Opens new avenues for future case study research
Step 2: Build a theoretical framework
The second step is to develop a theoretical framework. Studies focus more on concrete details and specific issues than on a general theory. Still, they must have some connection to theory in a particular field. In this way, it is not just an isolated description, but is related to existing knowledge on a subject.
The study may focus on:
- Expanding a theory by discovering new concepts and ideas
- Challenging a theory by exploring outliers and exceptions that are inconsistent with existing assumptions
- Ensuring that an analysis has a solid academic basis through a literature study, which means identifying concepts and theories to guide and support their analysis and interpretation
Step 3: Collect data
There are many different research methods that can be used to collect data on a topic. Researchers tend to focus on qualitative data and collect it through methods such as interviews, observations, and the analysis of primary and secondary sources. It is of course also possible that quantitative data is collected, or a combination of the two.
An example of a mixed methods is a study on the development of wind farms in a rural area. Quantitative data can then be focused on employment and business income figures. Qualitative data then concerns, for example, the perceptions and experiences of the population and the media attention for the development of the parks.
The aim is to get as complete a picture as possible of the case and the context.
Step 4: Describe and analyze the case
The last step is to bring together all relevant aspects to form the most complete picture possible about the subject. How the findings are presented depends on the type of research involved. Some studies are prepared as a scientific article with separate chapters for methods, results and discussions. Others are written in a narrative style, with the aim of looking at the case from different angles.

Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation in this blog post about the case study? Do you have experience conducting this research method, or multiple case studies? Or have you perhaps been the subject of such a study? Are you still missing information about a certain related topic? Let us know in the comments or fill out the contact form.
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Kitchenham, B., Pickard, L., & Pfleeger, S. L. (1995). Case studies for method and tool evaluation . IEEE software, 12(4), 52-62.
- Stake, R. E. (2008). Qualitative case studies .
- Yin, R. K. (2009). How to do better case studies . The SAGE handbook of applied social research methods, 2(254-282).
- Yin, R. K. (2003). Designing case studies . Qualitative research methods, 5(14), 359-386.
How to cite this article: Janse, B. (2023). Case Study . Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/case-study/
Published on: 01/30/2023 | Last update: 08/21/2023
Add a link to this page on your website: <a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/case-study/”>Toolshero: Case Study</a>
Did you find this article interesting?
Your rating is more than welcome or share this article via Social media!
Average rating 4 / 5. Vote count: 4
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Ben Janse is a young professional working at ToolsHero as Content Manager. He is also an International Business student at Rotterdam Business School where he focusses on analyzing and developing management models. Thanks to his theoretical and practical knowledge, he knows how to distinguish main- and side issues and to make the essence of each article clearly visible.
Related ARTICLES

Univariate Analysis: basic theory and example

Contingency Table: the Theory and an Example

Research questions explained plus examples

Research Proposal explained and guide

Research Ethics in Research: the Definition and Principles

Observational Research Method explained
Also interesting.

System Dynamics and Control by Jay Forrester

Strategic Planning: the Basics, Process and Tools

Business Transformation Strategy and Model
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
BOOST YOUR SKILLS
Toolshero supports people worldwide ( 10+ million visitors from 100+ countries ) to empower themselves through an easily accessible and high-quality learning platform for personal and professional development.
By making access to scientific knowledge simple and affordable, self-development becomes attainable for everyone, including you! Join our learning platform and boost your skills with Toolshero.

POPULAR TOPICS
- Change Management
- Marketing Theories
- Problem Solving Theories
- Psychology Theories
ABOUT TOOLSHERO
- Free Toolshero e-book
- Memberships & Pricing
What is the Case Study Method?
Simply put, the case method is a discussion of real-life situations that business executives have faced.
On average, you'll attend three to four different classes a day, for a total of about six hours of class time (schedules vary). To prepare, you'll work through problems with your peers.
How the Case Method Creates Value
Often, executives are surprised to discover that the objective of the case study is not to reach consensus, but to understand how different people use the same information to arrive at diverse conclusions. When you begin to understand the context, you can appreciate the reasons why those decisions were made. You can prepare for case discussions in several ways.
Case Discussion Preparation Details
In self-reflection.
The time you spend here is deeply introspective. You're not only working with case materials and assignments, but also taking on the role of the case protagonist—the person who's supposed to make those tough decisions. How would you react in those situations? We put people in a variety of contexts, and they start by addressing that specific problem.
In a small group setting
The discussion group is a critical component of the HBS experience. You're working in close quarters with a group of seven or eight very accomplished peers in diverse functions, industries, and geographies. Because they bring unique experience to play you begin to see that there are many different ways to wrestle with a problem—and that’s very enriching.
In the classroom
The faculty guides you in examining and resolving the issues—but the beauty here is that they don't provide you with the answers. You're interacting in the classroom with other executives—debating the issue, presenting new viewpoints, countering positions, and building on one another's ideas. And that leads to the next stage of learning.
Beyond the classroom
Once you leave the classroom, the learning continues and amplifies as you get to know people in different settings—over meals, at social gatherings, in the fitness center, or as you are walking to class. You begin to distill the takeaways that you want to bring back and apply in your organization to ensure that the decisions you make will create more value for your firm.
How Cases Unfold In the Classroom
Pioneered by HBS faculty, the case method puts you in the role of the chief decision maker as you explore the challenges facing leading companies across the globe. Learning to think fast on your feet with limited information sharpens your analytical skills and empowers you to make critical decisions in real time.
To get the most out of each case, it's important to read and reflect, and then meet with your discussion group to share your insights. You and your peers will explore the underlying issues, compare alternatives, and suggest various ways of resolving the problem.
How to Prepare for Case Discussions
There's more than one way to prepare for a case discussion, but these general guidelines can help you develop a method that works for you.
Preparation Guidelines
Read the professor's assignment or discussion questions.
The assignment and discussion questions help you focus on the key aspects of the case. Ask yourself: What are the most important issues being raised?
Read the first few paragraphs and then skim the case
Each case begins with a text description followed by exhibits. Ask yourself: What is the case generally about, and what information do I need to analyze?
Reread the case, underline text, and make margin notes
Put yourself in the shoes of the case protagonist, and own that person's problems. Ask yourself: What basic problem is this executive trying to resolve?
Note the key problems on a pad of paper and go through the case again
Sort out relevant considerations and do the quantitative or qualitative analysis. Ask yourself: What recommendations should I make based on my case data analysis?
Case Study Best Practices
The key to being an active listener and participant in case discussions—and to getting the most out of the learning experience—is thorough individual preparation.
We've set aside formal time for you to discuss the case with your group. These sessions will help you to become more confident about sharing your views in the classroom discussion.
Participate
Actively express your views and challenge others. Don't be afraid to share related "war stories" that will heighten the relevance and enrich the discussion.
If the content doesn't seem to relate to your business, don't tune out. You can learn a lot about marketing insurance from a case on marketing razor blades!
Actively apply what you're learning to your own specific management situations, both past and future. This will magnify the relevance to your business.
People with diverse backgrounds, experiences, skills, and styles will take away different things. Be sure to note what resonates with you, not your peers.
Being exposed to so many different approaches to a given situation will put you in a better position to enhance your management style.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can i expect on the first day, what happens in class if nobody talks, does everyone take part in "role-playing".
How to Write a Case Study: A Step-by-Step Guide (+ Examples)
by Todd Brehe
on Jan 3, 2024
If you want to learn how to write a case study that engages prospective clients, demonstrates that you can solve real business problems, and showcases the results you deliver, this guide will help.
We’ll give you a proven template to follow, show you how to conduct an engaging interview, and give you several examples and tips for best practices.
Let’s start with the basics.

What is a Case Study?
A business case study is simply a story about how you successfully delivered a solution to your client.
Case studies start with background information about the customer, describe problems they were facing, present the solutions you developed, and explain how those solutions positively impacted the customer’s business.
Do Marketing Case Studies Really Work?
Absolutely. A well-written case study puts prospective clients into the shoes of your paying clients, encouraging them to engage with you. Plus, they:
- Get shared “behind the lines” with decision makers you may not know;
- Leverage the power of “social proof” to encourage a prospective client to take a chance with your company;
- Build trust and foster likeability;
- Lessen the perceived risk of doing business with you and offer proof that your business can deliver results;
- Help prospects become aware of unrecognized problems;
- Show prospects experiencing similar problems that possible solutions are available (and you can provide said solutions);
- Make it easier for your target audience to find you when using Google and other search engines.
Case studies serve your clients too. For example, they can generate positive publicity and highlight the accomplishments of line staff to the management team. Your company might even throw in a new product/service discount, or a gift as an added bonus.
But don’t just take my word for it. Let’s look at a few statistics and success stories:
5 Winning Case Study Examples to Model
Before we get into the nuts and bolts of how to write a case study, let’s go over a few examples of what an excellent one looks like.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure.
1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory

This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable.
2. WalkMe Mobile and Hulyo
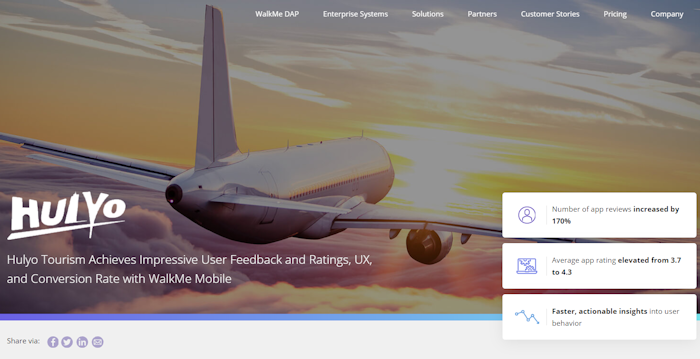
This case study from WalkMe Mobile leads with an engaging headline and the three most important results the client was able to generate.
In the first paragraph, the writer expands the list of accomplishments encouraging readers to learn more.
3. CurationSuite Listening Engine

This is an example of a well-designed printable case study . The client, specific problem, and solution are called out in the left column and summarized succinctly.
4. Brain Traffic and ASAE

This long format case study (6 pages) from Brain Traffic summarizes the challenges, solutions, and results prominently in the left column. It uses testimonials and headshots of the case study participants very effectively.
5. Adobe and Home Depot

This case study from Adobe and Home Depot is a great example of combining video, attention-getting graphics, and long form writing. It also uses testimonials and headshots well.
Now that we’ve gone over the basics and showed a few great case study examples you can use as inspiration, let’s roll up our sleeves and get to work.
A Case Study Structure That Pros Use
Let’s break down the structure of a compelling case study:
Choose Your Case Study Format
In this guide, we focus on written case studies. They’re affordable to create, and they have a proven track record. However, written case studies are just one of four case study formats to consider:
- Infographic
If you have the resources, video (like the Adobe and Home Depot example above) and podcast case studies can be very compelling. Hearing a client discuss in his or her own words how your company helped is an effective content marketing strategy
Infographic case studies are usually one-page images that summarize the challenge, proposed solution, and results. They tend to work well on social media.
Follow a Tried-and-True Case Study Template
The success story structure we’re using incorporates a “narrative” or “story arc” designed to suck readers in and captivate their interest.
Note: I recommend creating a blog post or landing page on your website that includes the text from your case study, along with a downloadable PDF. Doing so helps people find your content when they perform Google and other web searches.
There are a few simple SEO strategies that you can apply to your blog post that will optimize your chances of being found. I’ll include those tips below.
Craft a Compelling Headline
The headline should capture your audience’s attention quickly. Include the most important result you achieved, the client’s name, and your company’s name. Create several examples, mull them over a bit, then pick the best one. And, yes, this means writing the headline is done at the very end.
SEO Tip: Let’s say your firm provided “video editing services” and you want to target this primary keyword. Include it, your company name, and your client’s name in the case study title.
Write the Executive Summary
This is a mini-narrative using an abbreviated version of the Challenge + Solution + Results model (3-4 short paragraphs). Write this after you complete the case study.
SEO Tip: Include your primary keyword in the first paragraph of the Executive Summary.
Provide the Client’s Background
Introduce your client to the reader and create context for the story.
List the Customer’s Challenges and Problems
Vividly describe the situation and problems the customer was dealing with, before working with you.
SEO Tip: To rank on page one of Google for our target keyword, review the questions listed in the “People also ask” section at the top of Google’s search results. If you can include some of these questions and their answers into your case study, do so. Just make sure they fit with the flow of your narrative.
Detail Your Solutions
Explain the product or service your company provided, and spell out how it alleviated the client’s problems. Recap how the solution was delivered and implemented. Describe any training needed and the customer’s work effort.
Show Your Results
Detail what you accomplished for the customer and the impact your product/service made. Objective, measurable results that resonate with your target audience are best.
List Future Plans
Share how your client might work with your company in the future.
Give a Call-to-Action
Clearly detail what you want the reader to do at the end of your case study.
Talk About You
Include a “press release-like” description of your client’s organization, with a link to their website. For your printable document, add an “About” section with your contact information.
And that’s it. That’s the basic structure of any good case study.
Now, let’s go over how to get the information you’ll use in your case study.
How to Conduct an Engaging Case Study Interview
One of the best parts of creating a case study is talking with your client about the experience. This is a fun and productive way to learn what your company did well, and what it can improve on, directly from your customer’s perspective.
Here are some suggestions for conducting great case study interviews:
When Choosing a Case Study Subject, Pick a Raving Fan
Your sales and marketing team should know which clients are vocal advocates willing to talk about their experiences. Your customer service and technical support teams should be able to contribute suggestions.
Clients who are experts with your product/service make solid case study candidates. If you sponsor an online community, look for product champions who post consistently and help others.
When selecting a candidate, think about customer stories that would appeal to your target audience. For example, let’s say your sales team is consistently bumping into prospects who are excited about your solution, but are slow to pull the trigger and do business with you.
In this instance, finding a client who felt the same way, but overcame their reluctance and contracted with you anyway, would be a compelling story to capture and share.
Prepping for the Interview
If you’ve ever seen an Oprah interview, you’ve seen a master who can get almost anyone to open up and talk. Part of the reason is that she and her team are disciplined about planning.
Before conducting a case study interview, talk to your own team about the following:
- What’s unique about the client (location, size, industry, etc.) that will resonate with our prospects?
- Why did the customer select us?
- How did we help the client?
- What’s unique about this customer’s experience?
- What problems did we solve?
- Were any measurable, objective results generated?
- What do we want readers to do after reading this case study analysis?
Pro Tip: Tee up your client. Send them the questions in advance.
Providing questions to clients before the interview helps them prepare, gather input from other colleagues if needed, and feel more comfortable because they know what to expect.
In a moment, I’ll give you an exhaustive list of interview questions. But don’t send them all. Instead, pare the list down to one or two questions in each section and personalize them for your customer.
Nailing the Client Interview
Decide how you’ll conduct the interview. Will you call the client, use Skype or Facetime, or meet in person? Whatever mode you choose, plan the process in advance.
Make sure you record the conversation. It’s tough to lead an interview, listen to your contact’s responses, keep the conversation flowing, write notes, and capture all that the person is saying.
A recording will make it easier to write the client’s story later. It’s also useful for other departments in your company (management, sales, development, etc.) to hear real customer feedback.
Use open-ended questions that spur your contact to talk and share. Here are some real-life examples:
Introduction
- Recap the purpose of the call. Confirm how much time your contact has to talk (30-45 minutes is preferable).
- Confirm the company’s location, number of employees, years in business, industry, etc.
- What’s the contact’s background, title, time with the company, primary responsibilities, and so on?
Initial Challenges
- Describe the situation at your company before engaging with us?
- What were the initial problems you wanted to solve?
- What was the impact of those problems?
- When did you realize you had to take some action?
- What solutions did you try?
- What solutions did you implement?
- What process did you go through to make a purchase?
- How did the implementation go?
- How would you describe the work effort required of your team?
- If training was involved, how did that go?
Results, Improvements, Progress
- When did you start seeing improvements?
- What were the most valuable results?
- What did your team like best about working with us?
- Would you recommend our solution/company? Why?
Future Plans
- How do you see our companies working together in the future?
Honest Feedback
- Our company is very focused on continual improvement. What could we have done differently to make this an even better experience?
- What would you like us to add or change in our product/service?
During the interview, use your contact’s responses to guide the conversation.
Once the interview is complete, it’s time to write your case study.
How to Write a Case Study… Effortlessly
Case study writing is not nearly as difficult as many people make it out to be. And you don’t have to be Stephen King to do professional work. Here are a few tips:
- Use the case study structure that we outlined earlier, but write these sections first: company background, challenges, solutions, and results.
- Write the headline, executive summary, future plans, and call-to-action (CTA) last.
- In each section, include as much content from your interview as you can. Don’t worry about editing at this point
- Tell the story by discussing their trials and tribulations.
- Stay focused on the client and the results they achieved.
- Make their organization and employees shine.
- When including information about your company, frame your efforts in a supporting role.
Also, make sure to do the following:
Add Testimonials, Quotes, and Visuals
The more you can use your contact’s words to describe the engagement, the better. Weave direct quotes throughout your narrative.
Strive to be conversational when you’re writing case studies, as if you’re talking to a peer.
Include images in your case study that visually represent the content and break up the text. Photos of the company, your contact, and other employees are ideal.
If you need to incorporate stock photos, here are three resources:
- Deposit p hotos
And if you need more, check out Smart Blogger’s excellent resource: 17 Sites with High-Quality, Royalty-Free Stock Photos .
Proofread and Tighten Your Writing
Make sure there are no grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors. If you need help, consider using a grammar checker tool like Grammarly .
My high school English teacher’s mantra was “tighten your writing.” She taught that impactful writing is concise and free of weak, unnecessary words . This takes effort and discipline, but will make your writing stronger.
Also, keep in mind that we live in an attention-diverted society. Before your audience will dive in and read each paragraph, they’ll first scan your work. Use subheadings to summarize information, convey meaning quickly, and pull the reader in.
Be Sure to Use Best Practices
Consider applying the following best practices to your case study:
- Stay laser-focused on your client and the results they were able to achieve.
- Even if your audience is technical, minimize the use of industry jargon . If you use acronyms, explain them.
- Leave out the selling and advertising.
- Don’t write like a Shakespearean wannabe. Write how people speak. Write to be understood.
- Clear and concise writing is not only more understandable, it inspires trust. Don’t ramble.
- Weave your paragraphs together so that each sentence is dependent on the one before and after it.
- Include a specific case study call-to-action (CTA).
- A recommended case study length is 2-4 pages.
- Commit to building a library of case studies.
Get Client Approval
After you have a final draft, send it to the client for review and approval. Incorporate any edits they suggest.
Use or modify the following “Consent to Publish” form to get the client’s written sign-off:
Consent to Publish
Case Study Title:
I hereby confirm that I have reviewed the case study listed above and on behalf of the [Company Name], I provide full permission for the work to be published, in whole or in part, for the life of the work, in all languages and all formats by [Company publishing the case study].
By signing this form, I affirm that I am authorized to grant full permission.
Company Name:
E-mail Address:
Common Case Study Questions (& Answers)
We’ll wrap things up with a quick Q&A. If you have a question I didn’t answer, be sure to leave it in a blog comment below.
Should I worry about print versions of my case studies?
Absolutely.
As we saw in the CurationSuite and Brain Traffic examples earlier, case studies get downloaded, printed, and shared. Prospects can and will judge your book by its cover.
So, make sure your printed case study is eye-catching and professionally designed. Hire a designer if necessary.
Why are good case studies so effective?
Case studies work because people trust them.
They’re not ads, they’re not press releases, and they’re not about how stellar your company is.
Plus, everyone likes spellbinding stories with a hero [your client], a conflict [challenges], and a riveting resolution [best solution and results].
How do I promote my case study?
After you’ve written your case study and received the client’s approval to use it, you’ll want to get it in front of as many eyes as possible.
Try the following:
- Make sure your case studies can be easily found on your company’s homepage.
- Tweet and share the case study on your various social media accounts.
- Have your sales team use the case study as a reason to call on potential customers. For example: “Hi [prospect], we just published a case study on Company A. They were facing some of the same challenges I believe your firm is dealing with. I’m going to e-mail you a copy. Let me know what you think.”
- Distribute printed copies at trade shows, seminars, or during sales presentations.
- If you’re bidding on a job and have to submit a quote or a Request for Proposal (RFP), include relevant case studies as supporting documents.
Ready to Write a Case Study That Converts?
If you want to stand out and you want to win business, case studies should be an integral part of your sales and marketing efforts.
Hopefully, this guide answered some of your questions and laid out a path that will make it faster and easier for your team to create professional, sales-generating content.
Now it’s time to take action and get started. Gather your staff, select a client, and ask a contact to participate. Plan your interview and lead an engaging conversation. Write up your client’s story, make them shine, and then share it.
Get better at the case study process by doing it more frequently. Challenge yourself to write at least one case study every two months.
As you do, you’ll be building a valuable repository of meaningful, powerful content. These success stories will serve your business in countless ways, and for years to come.
Content Marketing
The ultimate toolkit for becoming one of the highest-paid writers online. Premium training. Yours for free.
Written by todd brehe, latest from the blog.

How to Increase Website Traffic (& Get 200+ Million Visitors)

Copywriter Salary: Hourly, Daily, Weekly, & Monthly Rates (2024)

10 Social Media Campaigns to Inspire Your Own in 2024

With over 300k subscribers and 4 million readers, Smart Blogger is one of the world's largest websites dedicated to writing and blogging.
Best of the Blog
© 2012-2024 Smart Blogger — Boost Blog Traffic, Inc.
Terms | Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Affiliate Disclosure
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
UX Case Studies
What are ux case studies.
A UX case study is a detailed analysis and narrative of a user experience (UX) design project . It illustrates a designer's process and solution to a specific UX challenge. A UX case study encompasses an explanation of the challenge, the designer’s research, design decisions and the impact of their work. UX designers include these case studies in their portfolios to demonstrate their experience, skills, approach and value to potential employers and clients.
“ Every great design begins with an even better story.” — Lorinda Mamo, Designer and creative director
Why UX Case Studies are Essential for a Successful Design Career
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
UX case studies are more than just documentation—they are powerful tools that advance a designer’s career and are integral to their success. They provide concrete evidence of a designer’s ability to tackle complex challenges from the initial user research to the final implementation of their solution. This transparency—a clear explanation and examination of the approach, thinking and methods—builds trust and credibility with potential clients and employers.
Beyond showcasing expertise, case studies encourage personal and professional growth . Through reflection and analysis, designers identify areas for improvement that hone their skills and deepen their understanding of user-centered design principles. What’s more, when designers compile and refine their case studies, they strengthen communication skills which allows them to articulate, rationalize and present data effectively.
For potential employers and clients, case studies give insight into a designer’s thought process and problem-solving approach . They reveal how designers gather and analyze user data, iterate on designs, and ultimately deliver solutions. This level of insight goes beyond resumes and qualifications as they provide tangible evidence of a designer's ability to research, reason and create user-centered products that meet business objectives. Ultimately, UX case studies empower designers to tell their unique story, stand out in a competitive market and forge a successful career in the evolving field of UX design.
How to Approach UX Case Studies
Recruiters want candidates who can communicate through designs and explain themselves clearly and appealingly. Recruiters will typically decide within five minutes of skimming UX portfolios whether a candidate is a good fit. Quantity over quality is the best approach to selecting case studies for a portfolio. The case studies should represent the designer accurately and positively. So, they should illustrate a designer’s entire process and contain clear, engaging, error-free copywriting and compelling visual aids. Designers can convince recruiters they’re the right candidate when they portray their skills, thought processes, choices and actions in context through engaging, image-supported stories.
- Transcript loading…
Content strategy, too, is a fundamental aspect of UX design case studies and portfolios. In the next video, Morgane Peng talks about content strategy in the context of case studies and design portfolios.
How to Build Successful UX Case Studies
Case studies should have an active story with a beginning, middle and end—never a flat report. So, a designer would write, e.g., “We found…”, not “It was found…”. Designers must always get their employer’s/client’s permission when they select case studies for their portfolios. Important information should be anonymized to protect your employer’s/client’s confidential data (by changing figures to percentages, removing unnecessary details, etc.). What is anonymized or omitted depends on whether a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is involved.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Create a UX Case Study
1. Choose the right project: Whether this is for a web-based portfolio or one created for a specific job, choose a project that showcases the best, most relevant work and skills. Make sure permission is granted to share the project, especially if it involves client work.
2. Define the problem: Clearly articulate the problem addressed in the project. Explain its significance and why it was worth solving. Provide context and background information about the project, including the target audience and stakeholders.
3. Establish your role and contribution: Detail specific responsibilities and contributions to the project. Highlight collaboration with team members to showcase teamwork and communication too.
4. Describe the process: Include research methods used (e.g., user interviews, surveys) and the insights gained. Use quotes , anecdotes and even photographs and artifacts from user research to bring the story to life. Introduce user personas developed from the research to add depth to the narrative. Insert user journey maps to visualize the user experience and identify pain points.
5. Illustrate the design and development journey: Show the initial wireframes and prototypes . Explain the iteration process and how feedback was incorporated. Explain the reasons behind design choices , supported by visuals like sketches, wireframes, and prototypes. Mention the tools and techniques used during the design process.
6. Highlight the testing and iteration phase: Detail the usability tests conducted and key findings. Use real user feedback to add authenticity to the story. Describe how feedback was used to make iterations to demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement.
7. Showcase the final solution: Present high-fidelity mockups of the final design. Highlight key features and functionalities. Discuss final product’s visual and functional aspects with the use of visuals to enhance the narrative.
8. Conclude with results and impact: Describe the results, including metrics and data that demonstrate the impact (e.g., increased user engagement, improved usability). Reflect on the lessons learned during the project—mention any challenges faced and how they were overcome.
9. Present the story: Make sure the case study tells a compelling story with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Check to see where images, charts, and other visuals can be added to further support the story. Ensure visuals are well-integrated and enhance the narrative. Keep the narrative concise and focused—always avoid unnecessary details and jargon.
10. Final review and polishing: Reread, edit and proofread—the case study should be clear, well-written, free of errors, and professional. It’s always advisable to get feedback from peers or mentors to refine the case study.
In this video, Michal Malewicz, Creative Director and CEO of Hype4, has some tips for writing great case studies.
Storytelling for Case Studies: How to Hook Hiring Managers and Clients
Consider Greek philosopher Aristotle’s storytelling elements and work with these in mind when getting started on a case study:
Plot : The career- or job-related aspect the designer wants to highlight. This should be consistent across case studies for the specific role for which they’re applying. So, if they want to land a job as a UX researcher, they must focus on the relevant skills—user research methods—in their case studies.
Character : A designer’s expertise in applying industry standards and working in teams.
Theme : Goals, motivations and obstacles of their project.
Diction : A friendly, professional tone in jargon-free language.
Melody : Your passion—for instance, where a designer proves that design is a lifelong interest as opposed to just a job.
Décor : A balance of engaging text and images.
Spectacle : The plot twist/wow factor—e.g., a surprise discovery. Naturally this can only be included if there was a surprise discovery in the case study.
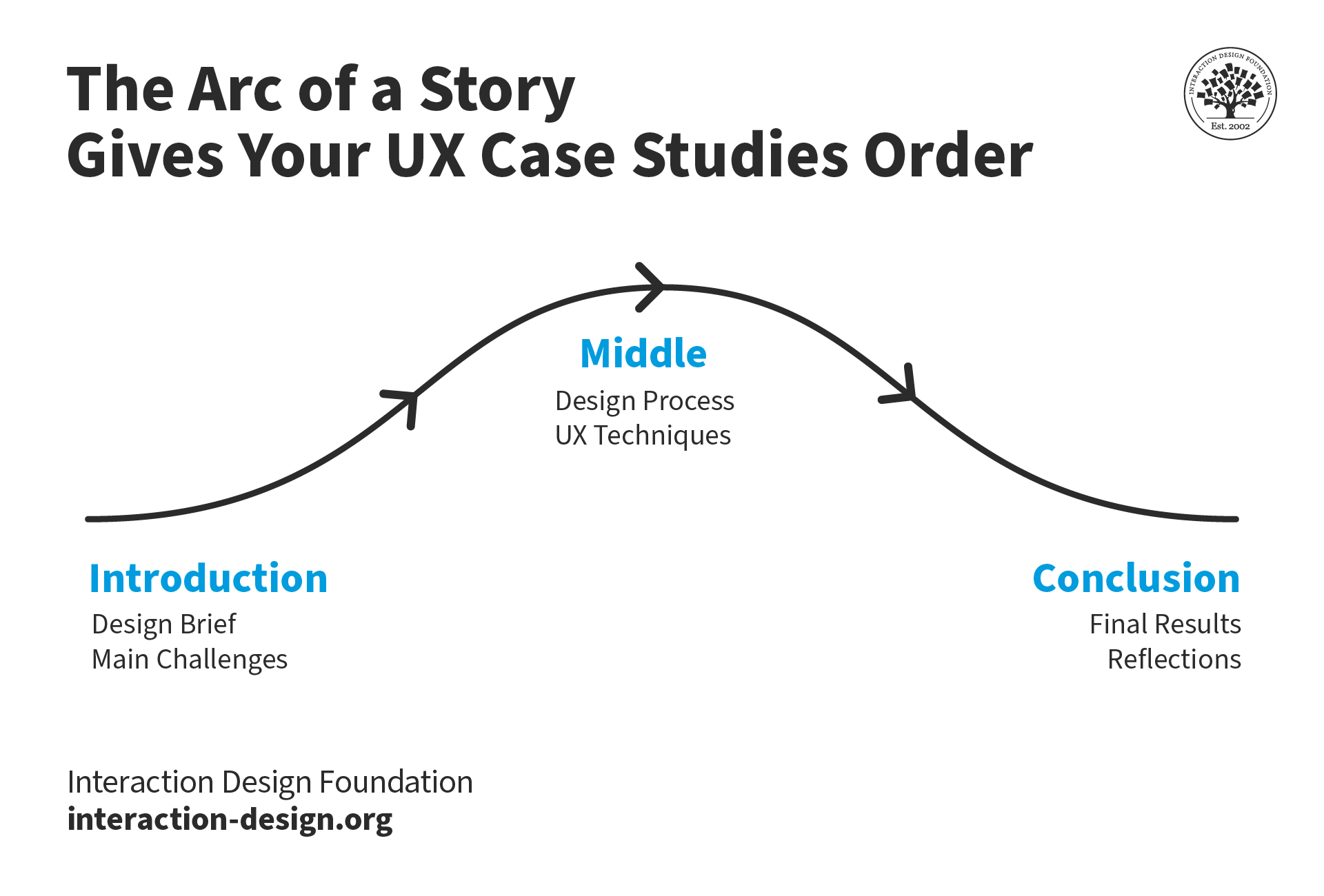
All good stories have a beginning, a middle and an end.
© Interaction Design Foundation. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Designers can also take inspiration from German novelist-playwright Gustav Freytag’s 5-part pyramid to structure their case studies and add a narrative flow:
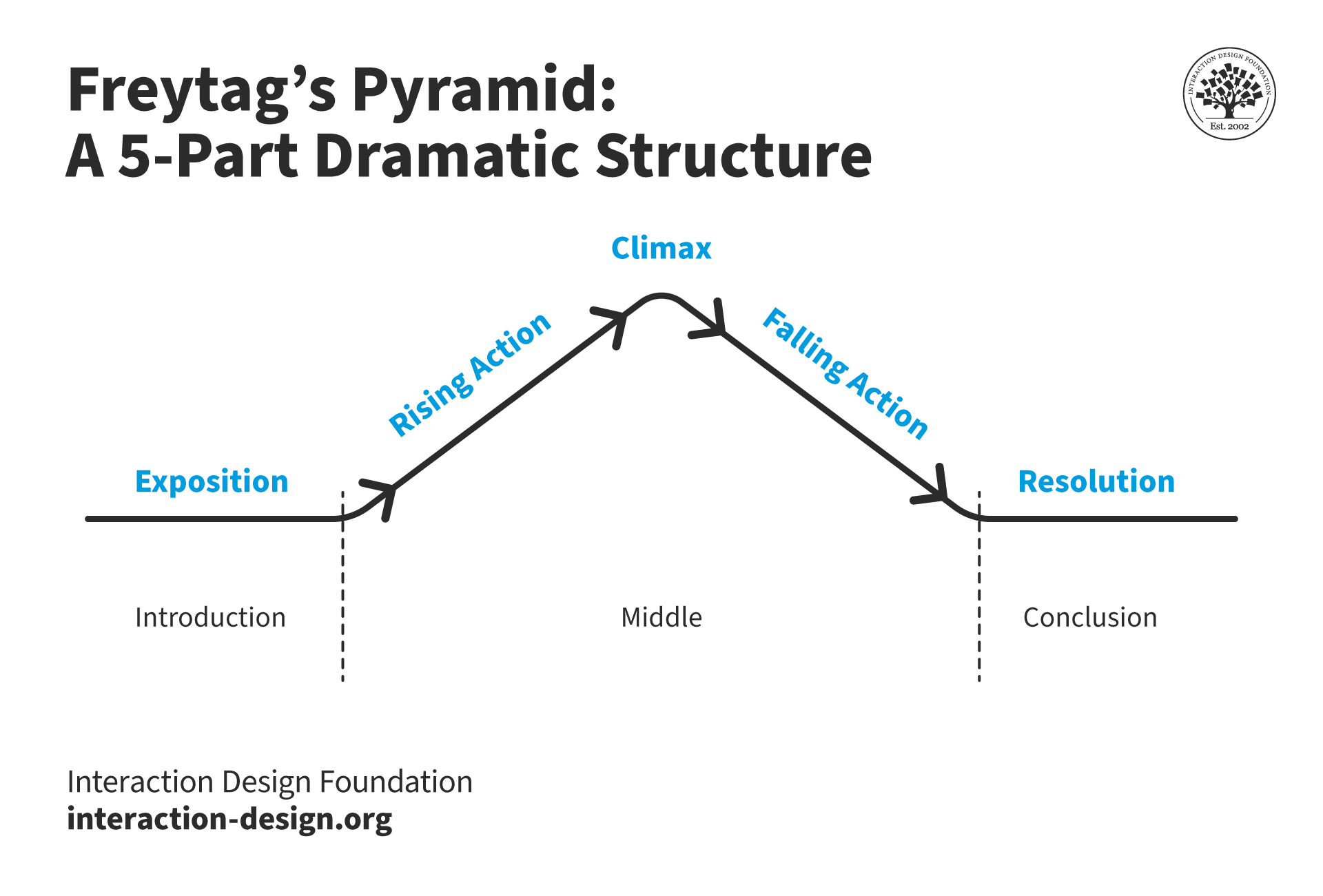
Typical dramatic structure consists of an exposition and resolution with rising action, climax and falling action in between.
Exposition — the introduction or hook (4–5 sentences) . This should describe the:
Problem statement : Include the motivations and thoughts/feelings about the problem.
The solution : Outline the approach. Hint at the outcome by describing the deliverables/final output.
The role: What role was played, what contribution was made.
Stages 2-4 form the middle (more than 5 sentences). Summarize the process and highlight the decisions:
Rising action : Outline some obstacles/constraints (e.g., budget) to build conflict and explain the design process (e.g., design thinking ). Describe how certain methods were used, e.g., qualitative research to progress to one or two key moments of climax.
Climax : Highlight this, the story’s apex, with an intriguing factor (e.g., unexpected challenges). Choose only the most important information and insights to tighten the narrative and build intrigue.
Falling action: Show how the combination of user insights, ideas and decisions guided the project’s final iterations. Explain how, e.g., usability testing helped shape the final product.
Stage 5 is the conclusion:
Resolution (4–5 sentences) : Showcase the end results as how the work achieved its business-oriented goal and what was learned. Refer to the motivations and problems described earlier to bring the story to an impressive close.
Overall, the case study should:
Tell a design story that progresses meaningfully and smoothly.
Tighten/rearrange the account into a linear, straightforward narrative .
Reinforce each “what” that’s introduced with a “how” and “why”.
Support text with the most appropriate visuals (e.g., screenshots of the final product, wireframing , user personas , flowcharts , customer journey maps , Post-it notes from brainstorming ). Use software (e.g., Canva, Illustrator) to customize visually appealing graphics that help tell a story.
Balance “I” with “we” to acknowledge team members’ contributions and shared victories/setbacks.
Make the case study scannable , e.g., Use headings, subheadings etc.
Remove anything that doesn’t help explain the thought process or advance the story.
Learn More about UX Case Studies
Take our course Build a Standout UX/UI Portfolio: Land Your Dream Job .
Read our article Turn Your Non-Design Experience into Design Portfolio Gold .
Read our article 7 Design Portfolio Mistakes That Are Costing You Jobs! And How to Fix Them .
UX designer and entrepreneur Sarah Doody offers advice in How to write a UX case study .
Learn what can go wrong in UX case studies in the article 7 Case Study Mistakes You Are Making in Your UX Portfolio .
Questions related to UX Case Studies
A UX case study showcases a designer's process in solving a specific design problem. It includes a problem statement, the designer's role, and the solution approach. The case study details the challenges and methods used to overcome them. It highlights critical decisions and their impact on the project.
The narrative often contains visuals like wireframes or user flowcharts. These elements demonstrate the designer's skills and thought process. The goal is to show potential employers or clients the value the designer can bring to a team or project. This storytelling approach helps the designer stand out in the industry.
To further illustrate this, consider watching this insightful video on the role of UX design in AI projects. It emphasizes the importance of credibility and user trust in technology.
Consider these three detailed UX/UI case studies:
Travel UX & UI Case Study : This case study examines a travel-related project. It emphasizes user experience and interface design. It also provides insights into the practical application of UX/UI design in the travel industry.
HAVEN — UX/UI Case Study : This explores the design of a fictional safety and emergency assistance app, HAVEN. The study highlights user empowerment, interaction, and interface design. It also talks about the importance of accessibility and inclusivity.
UX Case Study — Whiskers : This case study discusses a fictional pet care mobile app, Whiskers. It focuses on the unique needs of pet care users. It shows the user journey, visual design, and integration of community and social features.
Writing a UX case study involves several key steps:
Identify a project you have worked on. Describe the problem you addressed.
Detail your role in the project and the specific actions you took.
Explain your design process, including research , ideation , and user testing.
Highlight key challenges and how you overcame them.
Showcase the final design through visuals like screenshots or prototypes . This video discusses why you should include visuals in your UX case study/portfolio.
Reflect on the project's impact and any lessons learned.
Conclude with the outcomes. Showcase the value you provided.
A well-written case study tells a compelling story of your design journey. It shows your skills and thought process.
A case study in UI/UX is a detailed account of a design project. It describes a designer's process to solve a user interface or user experience problem. The case study includes
The project's background and the problem it addresses.
The designer's role and the steps they took.
Methods used for research and testing.
Challenges faced and how the designer overcame them.
The final design solutions with visual examples.
Results and impact of the design on users or the business.
This case study showcases a designer’s skills, decision-making process, and ability to solve real-world problems.
A UX writing case study focuses on the role of language in user experience design. It includes:
The project's background and the specific language-related challenges.
The UX writer's role and the strategies they employed.
How did they create the text for interfaces, like buttons or error messages?
Research and testing methods used to refine the language.
Challenges encountered and solutions developed.
The final text and its impact on user experience and engagement.
Outcomes that show how the right words improved the product's usability.
You can find professionals with diverse backgrounds in this field and their unique approaches to UX writing. Torrey Podmakersky discusses varied paths into UX writing careers through his video.
Planning a case study for UX involves several steps:
First, select a meaningful project that showcases your skills and problem-solving abilities. Gather all relevant information, including project goals, user research data, and design processes used.
Next, outline the structure of your case study. This should include the problem you addressed, your role, the design process, and the outcomes.
Ensure to detail the challenges faced and how you overcame them.
To strengthen your narrative, incorporate visuals like wireframes, prototypes, and user feedback .
Finally, reflect on the project's impact and what you learned.
This careful planning helps you create a comprehensive and engaging case study.
Presenting a UX research case study involves clear organization and storytelling.
Here are eight guidelines:
Introduction: Start with a brief overview of the project, including its objectives and the key research question.
Background: Provide context about the company, product, or service. Explain why you did the research.
Methodology: Detail the research methods, like surveys, interviews, or usability testing.
Findings: Present the key findings from your research. Use visuals like charts or user quotes to better present the data.
Challenges and Solutions: Discuss any obstacles encountered during the research and how you addressed them.
Implications: Explain how your findings impacted the design or product strategy.
Conclusion: Summarize the main points and reflect on what you learned from the project.
Appendix (if necessary): Include any additional data or materials that support your case study.
UX case studies for beginners demonstrate the fundamentals of user experience design. They include:
A defined problem statement to clarify the user experience issue.
Descriptions of research methods used for understanding user needs and behaviors.
Steps of the design process, showing solution development. The 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process illustrate these steps in detail.
Visual elements, such as sketches, wireframes, or prototypes, illustrate the design stages.
The final design solution emphasizes its impact on user experience.
Reflections on the project's outcomes and lessons learned.
These case studies guide beginners through the essential steps and considerations in UX design projects. Consider watching this video on How to Write Great Case Studies for Your UX Design Portfolio to improve your case studies.
To learn more about UX case studies, two excellent resources are available:
Article on Structuring a UX Case Study : This insightful article explains how to craft a compelling case study. It emphasizes storytelling and the strategic thinking behind UX design, guided by expert opinions and industry insights.
User Experience: The Beginner's Guide Course by the Interaction Design Foundation: This comprehensive course offers a broad introduction to UX design. It covers UX principles, tools, and methods. The course provides practical exercises and industry-recognized certification. This course is valuable for aspiring designers and professionals transitioning to UX.
These resources provide both theoretical knowledge and practical application in UX design.
Literature on UX Case Studies
Here’s the entire UX literature on UX Case Studies by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about UX Case Studies
Take a deep dive into UX Case Studies with our course Build a Standout UX/UI Portfolio: Land Your Dream Job .
“Your portfolio is your best advocate in showing your work, your skills and your personality. It also shows not only the final outcomes but the process you took to get there and how you aligned your design decisions with the business and user needs.”
— Morgane Peng, Design Director, Societe Generale CIB
In many industries, your education, certifications and previous job roles help you get a foot in the door in the hiring process. However, in the design world, this is often not the case. Potential employers and clients want to see evidence of your skills and work and assess if they fit the job or design project in question. This is where portfolios come in.
Your portfolio is your first impression, your foot in the door—it must engage your audience and stand out against the hundreds of others they might be reviewing. Join us as we equip you with the skills and knowledge to create a portfolio that takes you one step closer to your dream career.
Build Your Portfolio is taught by Morgane Peng, a designer, speaker, mentor and writer who serves as Director of Experience Design at Societe Generale CIB. With over 12 years of experience in management roles, she has reviewed thousands of design portfolios and conducted hundreds of interviews with designers. She has collated her extensive real-world knowledge into this course to teach you how to build a compelling portfolio that hiring managers will want to explore.
In lesson 1, you’ll learn the importance of portfolios and which type of portfolio you should create based on your career stage and background. You’ll discover the most significant mistakes designers make in their portfolios, the importance of content over aesthetics and why today is the best day to start documenting your design processes. This knowledge will serve as your foundation as you build your portfolio.
In lesson 2, you’ll grasp the importance of hooks in your portfolio, how to write them, and the best practices based on your career stage and target audience. You’ll learn how and why to balance your professional and personal biographies in your about me section, how to talk about your life before design and how to use tools and resources in conjunction with your creativity to create a unique and distinctive portfolio.
In lesson 3, you’ll dive into case studies—the backbone of your portfolio. You’ll learn how to plan your case studies for success and hook your reader in to learn more about your design research, sketches, prototypes and outcomes. An attractive and attention-grabbing portfolio is nothing without solid and engaging case studies that effectively communicate who you are as a designer and why employers and clients should hire you.
In lesson 4, you’ll understand the industry expectations for your portfolio and how to apply the finishing touches that illustrate your attention to detail. You’ll explore how visual design, menus and structure, landing pages, visualizations and interactive elements make your portfolio accessible, engaging and compelling. Finally, you’ll learn the tips and best practices to follow when you convert your portfolio into a presentation for interviews and pitches.
Throughout the course, you'll get practical tips to apply to your portfolio. In the " Build Your Portfolio" project, you'll create your portfolio strategy, write and test your hook, build a case study and prepare your portfolio presentation. You’ll be able to share your progress, tips and reflections with your coursemates, gain insights from the community and elevate each other’s portfolios.
All open-source articles on UX Case Studies
How to write the conclusion of your case study.

- 6 years ago
How to create the perfect structure for a UX case study

How to Create a PDF UX Design Portfolio
- 4 years ago
How to Write the Perfect Introduction to Your UX Case Study
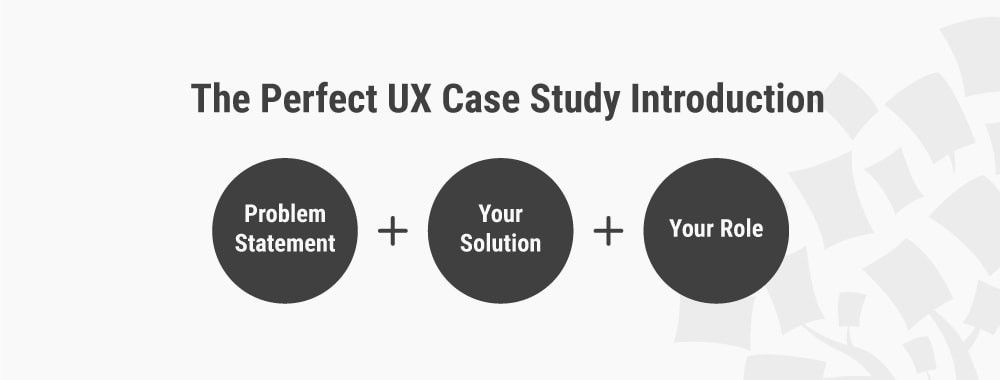
- 3 years ago
How to Write the Perfect Conclusion to Your UX Case Study
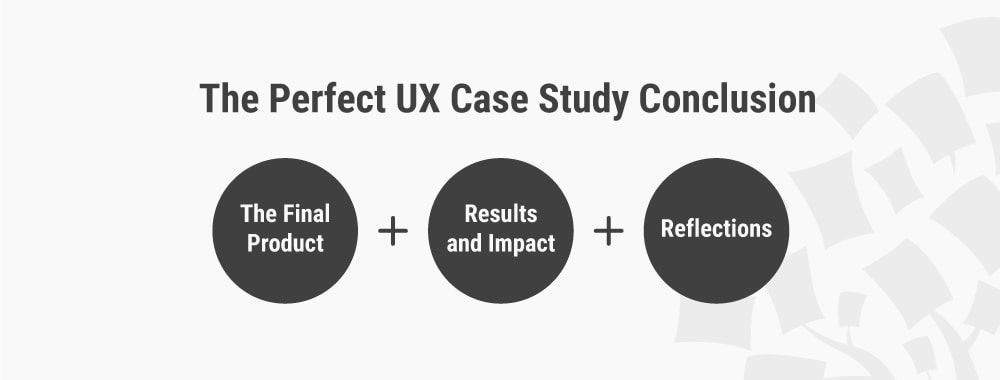
What Should a UX Design Portfolio Contain?
How to Write Great Case Studies for Your UX Design Portfolio
- 11 mths ago
No Experience? No Problem! 3 Ways to Find Projects for Your UX/UI Design Portfolio Case Studies
Should You Create an Online or PDF UX Design Portfolio?
How to write the beginning of your UX case study

- 5 years ago
What is a UX Portfolio?
3 Reasons Why You Should Have a UX Design Portfolio
How to Write the Perfect Middle Part of Your UX Case Study
4 Tips to Amplify the Potential of Your UX/UI Design Portfolio
How to write the middle or “process” part of your case study

Turn Your Non-Design Experience into Design Portfolio Gold
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Jack Smith seeks to streamline Trump's appeals in election interference case amid delays
WASHINGTON — No date has yet been set for former President Donald Trump's federal trial over his scheme to overturn his 2020 presidential loss by spreading what an indictment called his " unsupported, objectively unreasonable, and ever-changing " claims of mass voter fraud.
U.S. District Judge Tanya Chutkan held a status hearing in the case in a federal courtroom in Washington on Thursday, nine days after a new federal grand jury returned a superseding indictment against Trump charging him with the same four felonies he first faced in his original indictment last August : conspiracy to defraud the United States, conspiracy to obstruct an official proceeding, obstruction of and attempt to obstruct an official proceeding and conspiracy against rights.
Chutkan acknowledged that the case has not moved forward quickly due to Trump's appeal to the Supreme Court, which ruled that Trump has some presidential immunity and returned the issue to the lower court.
Chutkan said Thursday that she would not let the 2024 election determine the schedule of the case, saying that Trump attorney John Lauro seemed to be arguing that the November election should impact the pre-trial briefing schedule.
"It strikes me that what you're trying to do is affect the presentation of evidence in this case so as to not impinge on a presidential election," Chutkan said.
"I understand there is an election pending," she said. "This court is not concerned with the electoral schedule. ... That’s nothing I’m going to consider."
Pointing out that the case has been "pending for a year," Chutkan said that the court "can’t even really contemplate a trial date" yet because of pending appellate issues.
"We’re hardly sprinting towards the finish line here," Chutkan said, saying it would be "an exercise in futility" to set a trial date at this point given the appellate issues.
Chutkan said she would take all arguments into consideration before issuing a schedule in the case.
Chutkan on Thursday also accepted Trump’s not guilty plea for the superseding indictment, which Lauro entered on Trump’s behalf after the former president signed paperwork authorizing Lauro to do so. Trump was not present in the courtroom.
The latest indictment against Trump removed references to some evidence from his initial indictment following the Supreme Court's immunity ruling : chiefly, the government's claim that Trump attempted to weaponize the Justice Department on behalf of his presidential campaign, including by enlisting a right-wing civil environmental lawyer and election denier, Jeffrey Clark , to potentially take over the DOJ just days before the Jan. 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol .
A lawyer with Smith’s office told Chutkan Thursday that prosecutors know that Trump’s team plans to bring another appeal all the way up to the Supreme Court and that Smith's office is seeking to streamline the process.
“We should structure a schedule that leads to only one additional interlocutory appeal,” said federal prosecutor Thomas Windom, who works for Smith's office. “We think all immunity determinations should be held at the same time, simultaneous.”
Lauro, Trump's lawyer, noted that the defense plans on not only challenging the indictment itself but also Smith's appointment.
“We have an illegitimate prosecutor, we have an illegitimate indictment,” Lauro said, arguing that Smith's appointment as special counsel wasn’t authorized by the law and describing Smith as a "private citizen."
A Trump-appointed federal judge in Florida ruled that Smith was illegitimately appointed in dismissing a separate classified documents case against Trump in July. That ruling would impact many of the special counsels that have been appointed for decades. The Justice Department is appealing, and Attorney General Merrick Garland told NBC News that U.S. District Judge Aileen Cannon's ruling was mistaken.
“Do I look like somebody who would make that basic mistake about the law?" Garland, who appointed Smith, said . "I don’t think so.”
Chutkan said in court Thursday that she didn't find the ruling from the Florida judge persuasive.
After the hearing, Chutkan released a scheduling order making clear that additional pre-trial briefing in the case will go well past Election Day. She gave Smith’s office a Sept. 26 deadline to file its opening brief on the presidential immunity issue. The briefing process will run through Oct. 29, after which Chutkan “will determine whether further proceedings are necessary.” Both sides will also produce briefings on the Trump team’s contention that the case must be dismissed because Smith was improperly appointed, with a final reply from the former president due on Nov. 7, two days after the election.
After Trump's initial indictment last August, Chutkan set a trial date for March 2024, meaning that a verdict would very likely have been returned at this point and, if convicted, Trump would likely be facing sentencing.
While numerous Jan. 6 defendants have told federal courts that they regret being gullible enough to be duped and manipulated by Trump's false election claims — some of them even describing themselves as "idiots" — Trump has continued to spread false information about the election, even as Fox News and his lawyer Rudy Giuliani have settled and lost civil cases, respectively, over their false 2020 election claims, resulting in findings totaling in hundreds of millions of dollars.
Trump recently told a podcaster that he lost the last election “ by a whisker “ — he actually lost the popular vote by seven million and the Electoral College count by a significant margin — before adding that he still thinks “the election was a fraud, and many people felt it was.”
Federal prosecutors have charged more than 1,400 defendants in connection with the Jan. 6 attack and secured more than 1,000 convictions. Hundreds of rioters have received probationary sentences, but more than 500 have been sentenced to periods of incarceration ranging from a few days behind bars to 22 years in federal prison for former Proud Boy chairman Enrique Tarrio, who was convicted of seditious conspiracy.
Ryan J. Reilly is a justice reporter for NBC News.
Daniel Barnes reports for NBC News, based in Washington.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
Written Case Study. Consider writing your case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form that your readers fill out before downloading the piece. This enables your case study to generate leads for your business.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
A case study method involves a detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or community, to explore and understand complex issues in real-life contexts. By focusing on one specific case, researchers can gain a deep understanding of the factors and dynamics at play, understanding their complex ...
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced ...
A case study is a research process aimed at learning about a subject, an event or an organization. Case studies are use in business, the social sciences and healthcare. A case study may focus on one observation or many. It can also examine a series of events or a single case. An effective case study tells a story and provides a conclusion.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Résumé. Case study is a common methodology in the social sciences (management, psychology, science of education, political science, sociology). A lot of methodological papers have been dedicated to case study but, paradoxically, the question "what is a case?" has been less studied.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
A case study is a particular research h method involving an up-close and in-depth investigation of any subject, and it is related to a contextual position. These are produced by following a research form. The case study helps in bringing the understanding of any complex issue. This can extend experience or add strength to the already existing ...
A case study is a method that investigates an occurrence, or case, in a real-life setting. The purpose of conducting a case study is to understand the participant's experience or to examine ...
A case study is an in-depth analysis of specific, real-world situations or the scenarios inspired by them. Both teachers and professionals use them as training tools. They're used to present a problem, allowing individuals to interpret it and provide a solution. In the business world, organizations of many sizes use case studies to train ...
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. [1] [2] For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a ...
11 Best UX Case Studies for Designers. The best way to understand what a good case study looks like is to go over other examples. Each of these UX case study examples shows a designer's insights, basic skills, and other designers' lessons learned through their experience. 1. Promo.com web editor.
How to Design and Conduct a Case Study. The advantage of the case study research design is that you can focus on specific and interesting cases. This may be an attempt to test a theory with a typical case or it can be a specific topic that is of interest. Research should be thorough and note taking should be meticulous and systematic.
A case study (CS) is an in-depth study of a particular case, such as a person, group, or event, within a real life context. Nearly every aspect of the subject's life is analyzed to identify patterns and causes of behavior. These studies are used in various fields such as education, medicine, political science, social studies, psychology ...
Simply put, the case method is a discussion of real-life situations that business executives have faced. Harvard Business School. The Learning Experience. The Case Study Method. On average, you'll attend three to four different classes a day, for a total of about six hours of class time (schedules vary). To prepare, you'll work through problems ...
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
The case can refer to a real-life or hypothetical event, organisation, individual or group of people and/or issue. Depending upon your assignment, you will be asked to develop solutions to problems or recommendations for future action. Generally, a case study is either formatted as an essay or a report. If it is the latter, your assignment is ...
A UX case study is a detailed analysis and narrative of a user experience (UX) design project. It illustrates a designer's process and solution to a specific UX challenge. A UX case study encompasses an explanation of the challenge, the designer's research, design decisions and the impact of their work. UX designers include these case studies ...
Judge Tanya Chutkan has set a schedule in the federal election subversion case against Donald Trump that will allow prosecutors to release never-before-seen evidence, such as grand jury ...
The study found contaminants with potential health risks across all three sources, with the highest prevalence in tap water and the lowest in bottled water. Lead was detected in 51 percent of tap ...
Hunter Biden pleaded guilty Thursday to all nine charges in his federal tax case, in a surprise move on the day that an agonizing weekslong trial was supposed to begin.
Trump faces four felonies in the Washington, D.C., case related to his attempts to overturn his 2020 election loss. No trial date has been set.
In the past, the judge has shown a desire to push the case forward as quickly as possible. Chutkan has ruled on issues several times without holding in-person hearings, and before the case was ...
Hunter Biden is set to go on trial Thursday for alleged tax crimes, in a case that was once seen as a potential political liability for President Joe Biden, but is now a sordid closing chapter to ...