Thomas Vanhoutte
Personal website and blog

Submit academic research paper to Google Scholar
You have worked many months to complete your thesis or academic paper and you have relied on existing knowledge to finalize your research. Now you want to make your work available to the public. Here is how to properly include your academic research (journal article, thesis, book, ) in the Google Scholar search engine.
Create your Google Scholar profile
From this page, you can create your Google Scholar profile page. Include as much information as possible, such as a profile picture, your website, affiliation and areas of interest. I would also recommend you to make your profile public.
Once your profile looks good, we can move on to actually adding your academic writings. From here on, you have two options:
- You have only one or a few documents you want to submit, go for option 1
- You have many articles you want to add and are planning on writing even more in the future, go for option 2
Option 1 – Adding one by one
If you only want to include one document (let’s say, your master’s thesis), you can do so manually. Here are the steps:
- Go to this page to start adding a document manually.
- Choose the type of document (journal, conference, chapter, book, thesis, patent, court case or other).
- Fill in all the details about your article (title, author(s), publication date(s), volume, publisher, institution).
Click save and if you filled in everything correctly, you will see the message ‘Added article to your profile’. Congratulations!
Option 2 – Submit a website with all your work
In case you have an academic career and you have a list of work on your (academic or personal) website, option 2 is more suitable for you.
Google has guidelines to help you index your website that contains your academic work. Here are the steps you should follow to successfully include all of your work at once:
- Go to this page and pick the type of website you are submitting. In my case, I choose ‘Personal publications’.
- Read and check the check-boxes that apply to you, such as ‘My inclusion request is for my personal publications’.
- Fill in the requested details, whereby the your webpage with academic articles should be filled in by ‘List of publications page’.
- Lastly, you are asked to include one or more article examples. So, paste the direct link to on or more of your PDFs there.
click submit and you are greeted with this message
Thanks for submitting your website to Google Scholar. Our crawl team is working hard to add new content as quickly as possible, and we appreciate your assistance. Please keep in mind that bibliographic data is extracted from your pages by automatic software. If you aren’t satisfied with the accuracy of your listings, please refer to our technical guidelines at http://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/inclusion.html for ways to provide more accurate bibliographic data. An email detailing your submission has been sent to [email protected] . If your content meets our guidelines, you can generally expect to find it included within the Google Scholar results within 4-6 weeks.
Be patient, because as the message says, it can take up to a month or more before your articles are indexed. You will also receive an e-mail from [email protected] with the data you just submitted.
Follow your own profile
Here is a great tip: follow your own Google Scholar profile!
Go to your own profile and at the top right, choose ‘follow’. Enter your e-mail and create the alert. If Google adds a new article to your profile, or a new citation, you will receive an e-mail alert.
This is an excellent way to receive a heads up if another researcher or student has cited your work in their academic writings. Maybe you can even reach out to the author(s) and talk about their research; a great way to expand your network.
Join the conversation
17 Comments
What are good open alternatives or extensions for Google Scholar and Microsoft Academic Search?
Mate is it equivalent to journal publishings.
Thanks a lot Mr. Thomas. I am much benefited by your informative article. The way and simplicity gave me enourament to read all and actually helped me to solve my problem. God bless you.
I like to add my journal in indexing of google scholar
Thanks Thomas for the link to “Submit a website with all your work”, that was a great tip.
I am genuinely happy to read this webpage posts which carries lots of valuable information, thanks for providing such statistics.
RESPECTED SIR, HOW CAN I UPLOAD MY ARTICLE WHICH IS NOT PUBLISHED ANYWHERE TO GOOGLE SCHOLAR, AS I AM A PHD SCHOLAR, THERE IS NO PROVISION TO UPLOAD AND SAVE OPTION IN MY SCHOLAR ACCOUNT. I JUST OPENED AN ACCOUNT SIR. PLS GUIDE ME IN THIS REGARD. THANK YOU SIR
how to add pdf file to google scholars?
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Name Course Professor Institution City and State location The Date
TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Introduction…………………………………………………..4 1.1 Background Information………………………………….4 1.2 Definition of Corporate Governance……………………4 1.3 Importance of Corporate Governance…………………..4 1.4 Corporate Governance Theories………………………….5 1.5 Corporate Governance Codes……………………………5 2. Corporate Governance Mechanism………………………….6 2.1 Corporate boards………………………………………….7 2.1.1 Corporate board Structure……………………………7 2.1.2 Role of corporate board……………………………..8 2.2 Institutional Investors……………………………………9 2.2.1 Role of Institutional Investors ……………………..9 2.3 Other Corporate Governance Mechanisms……………10 3. Case Studies…………………………………………………10 3.1 Enron…………………………………………………….10 3.1.1 Background………………………………………..10 3.1.2 Enron’s Failure of Corporate Governance………..11 3.2 Reckitt Benckiser………………………………………12 3.2.1 Background………………………………………..12 3.2.2 Failure of Corporate Governance…………………12 3.3 Satyam………………………………………………….13 3.3.1 Background………………………………………..13 3.3.2 Failure of Corporate Governance ………………..13 3.4 WorldCom……………………………………………..14 3.4.1 Background……………………………………….14 3.4.2 Failure of Corporate Governance…………………14
4 Recommendations…………………………………………15 5 Conclusion…………………………………………………17 6 References…………………………………………………18 Introduction 1.1 Background Many scholars, economists, and other professions consider 2007- 2009 global financial crisis as the worst financial crisis ever since the great depression of 1930. The period characterized by the collapse of many financial institutions, massive bailouts, the economic downturn and finally the great recession was primarily attributed to the failure of corporate governance. As much as this was a low point in corporate governance, it also showed its importance not only to individual firms but to the world economy as a whole (Tricker & Tricker 2015). Never before has the notion that corporate boards and institutional investors are the most important corporate governance mechanisms in the firms with important implications for the sustainable long-term success of the firm been so vividly seen. From time immemorial as humans, we have always learned from our mistakes and the 2007-2009 was an eye opener especially to corporate governance. Before I can explain further on the notion, it is important to learn the basic aspects of corporate governance. 1.2 Definition of Corporate Governance Corporate governance in simple terms refers to the set of rules, processes, and practice through which a company is controlled and directed with (Solomon 2007). It involves balancing the interests of the organization with the interests of other parties such as the government, investors, lenders, suppliers, the community etc. 1.3 Importance of Corporate Governance When executed properly, corporate governance can help a company avoid certain risks such as lawsuits, fraud, and misappropriation of funds. In addition to that, good corporate governance helps in boosting the organization’s brand and reputation to the media, investors, suppliers, customers and the society as the whole. Furthermore, cooperate governance protects the financial interests of the individuals involved with the company such as the shareholders and the employees as explained by (Vitez, 2017).
1.4 Theories of Corporate Governance Corporate governance can be defined in many ways but when it comes to analyzing it, we do it through a framework of different theories. One of those theories is the agency theory which looks at the shareholders as the principals and the executives that have been hired to run the business as their agents. Another theory is the stewardship theory which looks at the executive as the stewards of the shareholders with both parties sharing the same goals. In addition to that, we have the resource dependent theory which considers the board as to be in existence so as to provide resources to the management with the aim of achieving the overall objectives of the business. Stakeholder theory comes from the assumptions that it is not just the shareholders who have an interest in the company but other parties too such as suppliers, the government, creditors among others (Farrar 2008). This means that this parties too can be affected by the success or failure of the business. Other theories of cooperate governance include transaction cost theory, political theory, and ethical related theories. 1.5 Corporate Governance Codes Introduction The code of governance over the years have originated for various reasons or in response to various circumstances. The first major release was in 1992 by Sir Adrian Cadbury popularly referred to ‘Cadbury Code’ titled “the Financial Aspects of Corporate Governance”. Following serious revisions over the years, the code is nowadays administered by the Financial Reporting Council. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) developed the first internationally influential codes back in 1999 following a business advisory committee that was led by Irra Milstein. Boards that govern companies are influenced by several documents which include but not limited to articles of incorporation, by-laws, corporate governance guidelines, committee charters, and codes of conduct. When it comes to the United States, various federals laws such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Act, federal laws as well as federal security laws in addition to regulations, rules, and guidance from SEC are used. These documents are meant to be used for the purpose of best practices and flexible working standards to safeguard the various parties that have an interest in the organization. In short, they basically outline the interaction between the board and management outlining the structure and the behavior of the board. The codes are normally contributed to by various individuals including investors, accounting firms, regulators, banks, corporate governance interest organizations, academics, and stock exchanges, among others.
Corporate Governance Mechanism Policies, control, and guidelines are vital for an adequate corporate governance mechanisms. An effective corporate governance mechanism will consist of a number of various mechanisms. The first level consists of internal mechanisms which monitor the business from within and take corrective measures when the business stray away from its set objectives. They include reporting lines that are clearly defined, systems that measure performance and systems for the smooth operation of the business. The next level is the external mechanisms which are controlled by those outside the business and serve the objectives of outsiders such as the regulators, government, financial institutions, and trade unions among others. The objectives of the external mechanism include proper debt management and legal compliance by the company in question. The last level consists of an audit of the entity’s financial statements by an independent auditor who generally works to serve both the internal and external parties that are involved with an organization to ensure that their interests are guided and that the management is doing everything properly. They also act as a second opinion to back up what the management is saying. 2.1 Corporate Boards The board generally consist of groups of individuals elected or nominated by shareholders in the annual general meeting. The board of directors normally act as a bridge between the company and the shareholders -it decides as a fiduciary with the aim of protecting the latter’s interests. This is the norm with a Public company even though nowadays most non-profit making organizations and private companies also have a board. Their main mandate is to make policies for corporate management and also to make decisions on major issues that affect the company. 2.1.1 Corporate Board Structure The structure of the board of directors is mainly guided by the company’s bylaws which sets out the structure, number of members, how often they meet etc. The most important element is that it should be able to balance both the interests of the management and Shareholders. The duties are regulated by the statutory laws, federal statutory laws, listing standards, common law and shareholder activism and litigation. The membership of the board normally constitutes independent directors, senior company executives, non-independent directors such as former senior executives of the company among others. Nasdaq rules require the majority of the board members to be independent and in they constitute up to 75% or more of the boards in 93 of the top 100 US companies. Most boards consist of 8 to 15 members. There are no age and nationality restrictions although in recent years gender balance has been emphasized. 2.1.2 Roles of the Corporate Boards The board’s primary role as discussed earlier is the fiduciary duty to safeguard the finances and the legal requirements of the entity. They do this by ensuring that the entity in questions does all that is required of it by the law, and the funds are properly used. Another role of the board of directors is setting up the mission and vision of the organization. In addition to that, they ensure that the management adheres and work towards achieving them. Over sighting the activities of members of the organization such as executives is another role of the corporate board. The board ensures that the management adheres to rules and regulations and do their work as prescribed. Other roles of the board of directors come up in the annual meetings where-by, they announce the annual dividends, oversee the appointment of key executives and amend the by-laws where it is necessary (Dimopoulos & Wagner, 2016). Other roles of the corporate board include setting up the strategy for the company for long-term survival, short-term gains and future exploration of opportunities that are likely to arise. This might also include setting up the structure of the company to ensure efficiency. The board, however, does not take part in the day to day running of the organization and thus serve another role of delegating the duties to the management. The board should also monitor, control functions and set up compensation plans for the executives. Last but definitely not least, the board helps in acquiring resources for the organization while ensuring continuity. With great power comes great responsibilities. The board must always use their powers for the right reason and do what is required of them by the shareholders of the company. The board must always carry out whatever they do in the full interest of the company, and in case there is a conflict of interest then the interests of the company should always come first. They must also carry out their task with due care minding the interests of both the shareholders and that of the employees. Other responsibilities of the board include acting as the court of appeal in case there are disputes, accessing the performance of the firm and enhancing the organization’s overall public image and brand name. 2.2 Institutional Investors An institutional investor is a person, persons or organization that pools money or provides funds to purchase securities, other investment assets, property or originate loans. They include financial institutions such as banks, Insurance companies, pension and hedge firms, investment advisors, commercial trusts and mutual funds. For a firm to grow, it requires resources inform of money which is provided by these institutional investors who get profits and interests as compensation for their troubles in taking the risk. The returns should exceed the fees and expenses of the investments and is compared against treasury bills which are considered to be risk-free. 2.2.1 Roles and Responsibilities of Institutional investors The best thing about institutional investors is the fact that they have expertise and knowledge to monitor the health and progress of the business. With this knowledge, they can provide the best advice the organization and also control the tendency of the management to put their interests first as opposed to the interests of the company. This active monitoring helps reduce misappropriation of funds and other forms of fraud (Gillan & Starks 2002, pp. 275-305) The institutional investors can act as a source of stability in hard times as was the case in the coal crisis in India recently. By offering additional funds, the institutional investors increase their stake and say in the company thus can push for better corporate governance. Another aspect related to this is the fact the institutional investors have a louder voice compared to minority investors. Most of the time when minority shareholders raise their concerns on corporate governance, they will rarely get addressed or at times get thwarted by the minorities which are not the case with institutional investors. 2.3 Other Corporate Governance Mechanism Other parties that are involved in corporate governance include the shareholders themselves who have the biggest interests as the main contributors of capital, the employees who get their incomes and job security from the good governance of the company, the government which gets taxes from the organization and the society as a whole which benefits from job creation, income distribution, corporate social responsibility activities of the firm among other benefits. Case Studies 3.1 Enron 3.1.1 Background The story of Enron was not only the largest bankruptcy case at the time but also the biggest audit failure. This was cited by many as the biggest corporate governance failure especially on the part of corporate boards and institutional investors. Enron was founded in 1985 by Kenneth Lay who also triples up as the chairman and chief executive officer. This was after merging Houston Natural gas and Intermonth. Other key people involved with Enron included: Jeffrey Skiing who was the C.O.O, Andrew Fastow who was the CFO and Rebecca Mark-Jusbasche who was the once a vice chairman. From 1995 to 2000 Enron was in fact named America most innovative company by Fortune. In the mid-2000s at its peak, the shares of Enron were trading at $90.75 per share. By the end of November 2001, they were trading at less than $1 per share. This was when the shareholders filed a $40 billion lawsuit. Enron filed for bankruptcy on December second, 2001 with assets worth $63.4 billion making it the biggest bankruptcy scandal ever in American history at the time. At this stage, the shares were going at $0.26 per share. 3.1.2 Failure of Corporate Governance in Enron Lack of due care and skill from the board was one of the reasons why Enron failed. As submitted by S.Watkins, Kenneth Lay who was Enron’s chair, could not get what was being said to him in regards to the company having questionable accounting practices. This also showed lack of proper communication between the board and the executives. This was further elaborated by Jeffrey McMahon, the new Enron’s president who said it was virtually impossible to challenge the authorities at Enron. A culture of intimidation had also developed at the company with the likes of Ms. Watkins fearing to lose their jobs. The board literally failed in its role of directing. This showed some sort of conflict of interests where they were more than happy to receive high compensations without asking serious questions which would have led to a decrease in their personal bonuses. The management who carried out the day to running of the Enron misrepresented information by allocating Enron’s debts to its dubious partners. This also showed the lack of proper internal controls at Enron (Carberry & Zajac 2017, p.15134). The corporate investors also failed to properly supervise the company and advice accordingly. For example, according to an economist at Enron, it was important it was all mind games as it was important for the employees, investors, and analysts to believe that the stock will bounce back. Other corporate investors such as the two trustees of Enron’s 401(k) plan failed in their duties as they did not warn the plan participants despite a memo detailing the accounting malpractices. The institutional investors also had all the knowledge and expertise but failed to utilize them- they just sat back and believed whatever they were told. 3.2 Reckitt Benckiser 3.2.1 Background Reckitt Benckiser is a British multinational that produces consumer goods to do with hygien, health, and home products. The name comes from the merging of a United Kingdom company Reckitt & Coleman and Benckiser NV that was based in the Netherlands back in 1999. The most well-known products worldwide include Dettol and Strepsil. Reckitt Benckiser acquired Korean Oxy brand in 2001 which had been using polyhexamethathylene guanidine (PHMG) in a product since 1996. In 2011, PHMG was banned by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and prevention after a published report showed a link to lung damage and report. Several reports also came out supporting the Korean report, and at the height of this in 2016 a coalition of consumer groups came out for the total boycott of Reckitt Benckiser products after it had been linked to more than 500 deaths from a BBC report. 3.2.1 Failure of Corporate Governance Mechanism in Reckitt Benckiser In the case of corporate governance, the management and directors fail as a whole in doing their duty of due care and skill when acquiring the Korean Oxy brand. They had a duty to investigate and know what is in the product. They put the company’s financial interests before the safety of the consumers. In addition to that, several attempts were made by the board and management to suppress investigations instead of taking corrective measures. Even though this was mostly a failure by the management and board, institutional investors also had the power to ask questions. Despite the various reports, they were silent till there was outrage in the mass media. 3.3 Satyam 3.3.1 Background Satyam was India’s fourth largest computer service company in India which has a population of over 1 billion. It was even listed on New York Stock exchange in 2001 with revenues exceeding $1 billion. The founder, M. Raju Ramalinga who was also the chair was a highly regarded person in the business often gracing all the major corporate events. In 2008 Satyam won the coveted prize of the Golden Peacock Award for compliance issues and Risk Management in corporate governance. In 2009, M. Raju confessed that the company’s accounts had been falsified by a massive $1.47 billion (Bhasin 2005). In the same year, Satyam stock was banned from trading on the New York Stock Exchange, and the Golden Peacock Award stripped off. Mr. Raju was later convicted together with other senior members. 3.3.2 Failure of Corporate Governance Mechanisms The board at Satyam failed in their primary duty of due care and monitoring the activity of the business as they did not notice the discrepancy. This was so evident that the first order was to appoint a temporary board. The board also put their interests first at the expense of the company for financial gains as confessed by their chairman. Despite the amount that falsified being that large, the auditors who were Price Water House Coopers failed in their auditing duties as they did not report anything amiss despite having all the expertise and experience. They were even fined $6 million by the US stock exchange for not following the code of conduct and auditing standards in when offering their services to Satyam. Institutional investors also failed to raise questions or properly examine the financial statements. Furthermore, with their expertise, they should have pushed for compliance with the corporate code of governance. 3.4 Worldcom 3.4.1 Background Before filing for bankruptcy protection in 2002, WorldCom was the second largest long distance phone company in the United States. With assets totaling over $104 billion, $30 billion in revenues and over 60,000 employees WorldCom filed for bankruptcy protection on July 1, 2002. The company later wrote down more than 75% of the total assets with over 17,000 of the workers losing their jobs. Over the period between 1999-2002, WorldCom had deliberately overstated their income before tax by over $7 billion which was the main reason behind the falling from grace to grass. It is currently known as Verizon business or Verizon enterprise solution after being acquired by Verizon Communications and is slowly rebuilding and being integrated into the parent company. 3.4.2 Failure of corporate Mechanism in WorldCom The biggest failure of WorldCom was the fact that the board had failed in its structuring role. Over the years, it had acquired a lot of companies with even one accountant confessing that they would get calls from people they did not even know existed. The departments were also not even properly structured for efficient working and were very decentralized. For example, the finance department was in Mississippi; the network operations were in Texas, the human resource in Florida and the legal department in Washington DC. This provided a challenge of communication as each department developed their ways of doing things. Apart from that, the difference in management style and the culture that was developed of not questioning seniors was a discouragement for employees who wanted to correct any issues that arose. In fact, there was a deliberate attempt by the management to hide vital financial issues as explained by Buddy Yates, the director of general accounting who was told he would be thrown outside the window in case he had shown the numbers to the auditors by Gene Morse, a senior manager. The employees also put their self-interests above the interest of the company as loyal employees were often compensated above the company’s approved salaries and bonus packages by Ebbers and Sullivan. The biggest failure was the board however as they failed terribly in all their roles and responsibilities including due care, supervision, bridging the gap between management and shareholder among others. In the case of institutional investors, they also failed terribly. No one raised a question on the structure of the firm or why the firm was highly decentralized. The increase in the salaries and compensation for the ‘loyal’ employees in the finance and accounting department should also have raised questions. Institutional investors should have also used their expertise to confirm the information that was being provided to them. Recommendations on Improving the Quality Of Corporate Governance Corporates Boards Should Meet Regularly: The corporates boards do not take part in the day to day running of the business, but they have a supervisory role. To carry out the tasks effectively, they need to meet more often (Christensen et al 2015, pp.133-164) Division of Responsibilities: The duties and responsibilities of a firm should be properly defined and allocated within an organization. This will help in reducing conflicts and also knowing who is liable and for what. This will also help enhance effective communication within an organization. Stronger Internal Controls: Controls in an organization should start from within for effective corporate governance. The controls include the supervision of seniors, physical controls, controls among others. Transparency: Corporate governance is all about transparency. Transparency does not mean revealing the companies but being honest in its activities. In case there is a loss it should be stated and corrective measures to correct it taken, Proper succession planning: One of the best attributes is that its life is not limited to that of the owners or directors. A proper succession plan should, therefore, be set in place to ensure that the values of the company that encourages proper corporate governance are passed from one generation to the other within the company Proper training of directors: The directors of the company are the eyes of the society and shareholders in the business. They need to be properly trained to carry out their tasks effectively as is required of them. Another option is to select a board of directors that is highly qualified in the different fields that the business is engaged in. Independent members increase: Any organization that is interested in improving its corporate governance should try as much as possible to increase the list of independent parties in its running. The independent parties with no direct relation can view the business from a better neutral point (Klapper & Love 2002, pp.703-728) Conclusion It is crystal clear from the discussions above that the corporate governance mechanisms such as corporate boards and institutional boards are the backbone for the survival of any company. From the cases discussed above, we can see the consequences of bad corporate governance and the fact that it does not matter how big the company is. In addition to that, there is a failure the many bodies that are meant to supervise corporate governance. Corporate governance board needs to do more than just take the words of corporations. It is an understatement to say that corporate governance should be a priority, it should actually be a prerequisite (Lebedeva et al 2016).
References Bhasin, M.L., 2015. Corporate accounting fraud: A case study of Satyam Computers Limited. Carberry, E. and Zajac, E., 2017, January. How US Corporations Changed Executive Compensation after Enron: Substance and Symbol. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2017, No. 1, p. 15134). Academy of Management Christensen, J., Kent, P., Routledge, J. and Stewart, J., 2015. Do corporate governance recommendations improve the performance and accountability of small listed companies?. Accounting & Finance, 55(1), pp.133-164. Dimopoulos, T. and Wagner, H.F., 2016. Corporate Governance and CEO Turnover Decisions. Farrar, J., 2008. Corporate governance: theories, principles and practice. Oxford University Press Gillan, S.L. and Starks, L.T., 2000. Corporate governance proposals and shareholder activism: The role of institutional investors. Journal of financial Economics, 57(2), pp.275-305. Ilya, P., 2015. inc. [Online] Available at: http://www.inc.com/ilya-pozin/14-highly-effective-ways-to-motivate-employees.html [Accessed 27 January 2018].
Klapper, L.F. and Love, I., 2004. Corporate governance, investor protection, and performance in emerging markets. Journal of corporate Finance, 10(5), pp.703-728. Lebedeva, T.E., Akhmetshin, E.M., Dzagoyeva, M.R., Kobersy, I.S. and Ikoev, S.K., 2016. Corporate governance issues and control in conditions of unstable capital risk. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(1S). Solomon, J., 2007. Corporate governance and accountability. John Wiley & Sons. Tricker, R.B. and Tricker, R.I., 2015. Corporate governance: Principles, policies, and practices. Oxford University Press, USA. Vitez, O., 2017. Bizfluent. [Online] Available at: https://bizfluent.com/facts-6884459-importance-corporate governance.html [Accessed 21 February 2018].
Hi, we have the scientific journal: https://journal.scsa.ge/
we are submitting it to google scholar manually already for one year, but it is not indexed still in scholar.
What can we do?
Hi, how to upload my thesis into google or share
hello, how to upload my thesis into google or share .
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who was doing a little research on this. And he actually bought me breakfast simply because I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to discuss this subject here on your web site.
I am interested to publish my articles on Goodle scholar but I have know clear idea about the steps to follow. Please link me
Thanks, Thomas your article help me to explore google scholar differently thanks a lots.
Thanks, friend. I wanted to publish my marketing papers over there. Your article helped. Thanks again.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Leave a comment

How to Publish in Google Scholar?
When searching for academic information or articles, there are several ways to do it. You can use Internet search engines, but the results of this search may come from unreliable sources ; or you can approach virtual libraries or academic search engines. Among all the academic search engines and databases that we can currently find, Google Scholar stands out.
Google Scholar is a search engine specialized in academic documents, whether they are articles, books, theses, etc. This documentation can come from different sources, whether publishers, universities, or journals. Google Scholar works in a very similar way to Google's own search engine, performing a search in the search bar and displaying the results following an algorithm similar to the one used in the browser.
In this article, we will explain the steps to get your article published in Google Scholar, how to perform searches and the benefits of this academic search engine.
How Do I Publish My Article in Google Scholar?
First of all, you need to access Google Scholar and log in. Generally, like with the Google browser, Google Scholar will log in with the email account that you have by default in the search engine.

If you are using Google Scholar for the first time, My profile section will appear at the top left. This section will look like this:

If you enter with your institution's email, Google will most likely give you a warning and recommend you enter a personal email, to ensure that you will always have access to your Scholar account. In the sections that appear you will be able to enter your institution's email if you want to.
Once you have filled in the required fields, you will arrive at a new section where you will have the option to search for your academic articles, so that you can easily add them to your profile.

You can select from the articles shown or search by a different name in the search bar above. It also allows you to search for articles individually or by groups of articles. To do this, select Groups or Articles at the top.
When you have selected your articles, you can move on to the next step, where you will have the option of modifying some features regarding your account.
By following these steps, you will now be able to view your articles from your own profile. Once here, you will also be able to modify your profile data, add a visible photo and specify the fields you are interested in.
Add Articles Manually
To add publications that do not appear in Google Scholar, you can go to the add article manually option in your profile.

Once you have clicked here, a window will appear where you can enter the information to use as a bibliographic reference, as it is not possible to enter the whole article.

Tip : Be sure to keep your profile updated and confirm that the articles displayed are yours and remove those that are not. In case any article is detected that is not of your authorship, penalties may be applied.
How to Search in Google Scholar?
Similar to how the Google search engine works, Google Scholar has a search bar to enter the terms you are interested in. Once you have entered them, a series of results will appear, sorted in a similar way to how the browser's algorithm does.

In this search screen, you will see different options. In the left bar, you will have the option to filter the articles by year. You will also find the option to sort the articles by relevance or by date. In addition, like Google alerts, you will be able to create your own alerts, that will notify you in case there are new articles published on a specific topic that may be of your interest.
Under each article, you can also find several options:

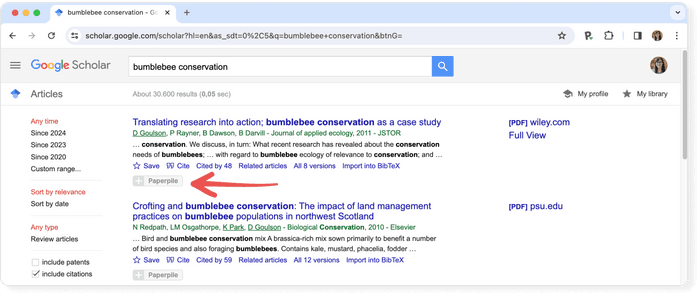
- Save : With this option, you can save the article in your own library to read it later or to have quicker access in case you need to come back to it.
- Cite : this option takes you to the section where you will be able to cite the specific article and in which format you want the citation. The options given are BibTex , EndNote , RefMan, and RefWorks . Right next to it, it also shows you the number of citations that the article you are consulting has and the access to those same citations.
- Related articles : related academic articles.
- Versions : not all articles have this section. In case it does, it shows you all the versions that can be found of the article.
Benefits of Google Scholar
Having explained how Google Scholar works, the question is: what advantages can we extract from its use?
- It allows you to search a wide variety of academic documentation , from scientific articles to theses, including conference papers. This gives you access to a wide range of information that can support your research.
- When using a search engine, it allows us to enter the search terms of what we are looking for. Not only that, but it also allows us to find related material that may be useful with the search engine's own suggestions.
- It shows us how many times an article has been cited (either our own or someone else's) as well as where it has been cited and the citation style that has been used for it. It can also be used to cite an article ourselves.
- You can easily save articles for later access.
- You can find documents in different languages.
- It's a very complete tool to find Open Access documentation on the Internet , without necessarily having to search for it on a specific site.
- Anyone can access this search engine and find articles on any academic topic in which they may be interested, whether they are related to the academic field or not.
Orvium Connects You to Google Scholar
Now that you know better what Google Scholar is and how it works, you can see how important it is that your article is correctly indexed and that it shows up in this search engine easily. Google Scholar is a tool that promotes Open Access to different articles and helps your document to have more reach and visibility.
Therefore, at Orvium we are indexed with both Google Scholar and OpenAire , ensuring that all articles displayed on our platform can be easily found in this search engine.
If you want to know more about how we work, do not hesitate to visit our website and get more information.
- Academic Resources
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox.

Now check your inbox and click the link to confirm your subscription.
Please enter a valid email address
Oops! There was an error sending the email, please try later.
Leyre Martínez
Recommended for you.

How to Write a Research Funding Application | Orvium

Increasing Representation and Diversity in Research with Open Science | Orvium

Your Guide to Open Access Week 2023

Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- Starting your Dissertation/Thesis
- Dissertation/Thesis Resources
- Books That May Help
- Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliography
- We Don't Have It? / Interlibrary Loan
- Online Learning Study Tips
- Search Strategy
- Advanced Search Techniques
- Kemp Library Video Tutorials
- Find Articles / Journals / Databases
- What are...
- Database Video Tutorials
- Peer Reviewed
- How to confirm and cite peer review
- Primary/Secondary Sources
- Other Types of Sources (i.e. Newspapers)
- Legal Research Resources
- Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
Google Scholar
- Website Evaluation
- Internet Searching
- Apps You Didn't Know You Needed
- Who is citing me?
- Questions After Hours
- ESU Thesis Submission
- ESU Dissertation Submission
- How to Integrate
- How to Use It
What is Google Scholar and Why Should You Care?
Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it's available for free.
Below are a few videos on how to use Google Scholar (you can skip the intros if you want) that will show you tips and tricks on how to best use Google Scholar.

Did you know that you can use Google Scholar in addition to Primo to help search Kemp library materials? You just have to add us to your Google Scholar and our results will show up in your searches showing you what you have access to as an ESU community member!
- Go to Google Scholar
- Make sure you're logged into your Google Account - you'll see your initials or your icon in the top right hand corner of the screen if you're logged in.
- Click on Settings (either from the top of the Scholar home page, or from the drop-down on the right hand side of the results page).
Choose Library Links .
Type ‘East Stroudsburg University’ into the search box.
Click the boxes next to “ESU” and "Kemp Library"
Click Save .
If you have other institutions you're affilitated with, or ResearchGate, you can add them too!
Getting to Google Scholar Settings:

The Library Link Screen: Search, Select and Save!

What your search results will look like:

Add / Reorder
Databases have more sophisticated search features than Google Scholar , but if you have a one or two word topic Google Scholar can be useful. You can also try using the Advanced Search in Google Scholar (see the first video below).
However, if you're having trouble finding something specific, i.e. a specific article, try Google Scholar. For example you want " Game of Thrones and Graffiti" and you don't see it in a database, search the title of the article in Google Scholar (here you'd search "Game of Thrones and Graffiti"). You may find it freely available OR discover it is available through the library, but in a database you didn't look at.
If we don't have it and you can't access it on Google Scholar, you can always request it via interlibrary loan .
"If Google Scholar isn’t turning up what you need, try an open Google search with the article title in quotes, and type the added filter “filetype:pdf”. This scours the open web for papers hosted somewhere, by someone, in PDF format. Google Books provides limited preview access to many copyrighted books. Other alternate services include SemanticScholar , Microsoft Academic , Dimensions , or GetTheResearch . Here too there are subject-specific portals like EconBiz or the Virtual Health Library , some of which offer multilingual search options." - Paragraph taken from A Wikipedia Librarian.
The other services like Microsoft Academic mentioned above are also useful when looking for freely available journal article and research! Don't forget to cite everything you use in your paper/project/presentation/etc.
Google Scholar Videos
- << Previous: Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
- Next: Website Evaluation >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://esu.libguides.com/thesis
Lydon and O'Leary libraries will be closing at 2:00pm on Wednesday, July 3rd , and will be closed on Thursday, July 4th . If you have any questions, please contact [email protected] .

- University of Massachusetts Lowell
- University Libraries
Google Scholar Search Strategies
- Add Articles Manually
- About Google Scholar
- Manage Settings
- Enable My Library
- Google Scholar Library
- Cite from Google Scholar
- Tracking Citations
- Refine your Profile Settings

How do I manually add articles?
When adding articles after Google Scholar profile set-up, you have the option to add articles manually. Select the third option on the left navigation panel "Add article manually". You will see a screen similar to this.

relevant information and select save on the bottom right hand corner to add the article to your citations.
- << Previous: Tracking Citations
- Next: Refine your Profile Settings >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 2:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uml.edu/googlescholar
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Google Scholar: the ultimate guide


What is Google Scholar?
Why is google scholar better than google for finding research papers, the google scholar search results page, the first two lines: core bibliographic information, quick full text-access options, "cited by" count and other useful links, tips for searching google scholar, 1. google scholar searches are not case sensitive, 2. use keywords instead of full sentences, 3. use quotes to search for an exact match, 3. add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year, 4. use the side bar controls to adjust your search result, 5. use boolean operator to better control your searches, google scholar advanced search interface, customizing search preferences and options, using the "my library" feature in google scholar, the scope and limitations of google scholar, alternatives to google scholar, country-specific google scholar sites, frequently asked questions about google scholar, related articles.
Google Scholar (GS) is a free academic search engine that can be thought of as the academic version of Google. Rather than searching all of the indexed information on the web, it searches repositories of:
- universities
- scholarly websites
This is generally a smaller subset of the pool that Google searches. It's all done automatically, but most of the search results tend to be reliable scholarly sources.
However, Google is typically less careful about what it includes in search results than more curated, subscription-based academic databases like Scopus and Web of Science . As a result, it is important to take some time to assess the credibility of the resources linked through Google Scholar.
➡️ Take a look at our guide on the best academic databases .
One advantage of using Google Scholar is that the interface is comforting and familiar to anyone who uses Google. This lowers the learning curve of finding scholarly information .
There are a number of useful differences from a regular Google search. Google Scholar allows you to:
- copy a formatted citation in different styles including MLA and APA
- export bibliographic data (BibTeX, RIS) to use with reference management software
- explore other works have cited the listed work
- easily find full text versions of the article
Although it is free to search in Google Scholar, most of the content is not freely available. Google does its best to find copies of restricted articles in public repositories. If you are at an academic or research institution, you can also set up a library connection that allows you to see items that are available through your institution.
The Google Scholar results page differs from the Google results page in a few key ways. The search result page is, however, different and it is worth being familiar with the different pieces of information that are shown. Let's have a look at the results for the search term "machine learning.”
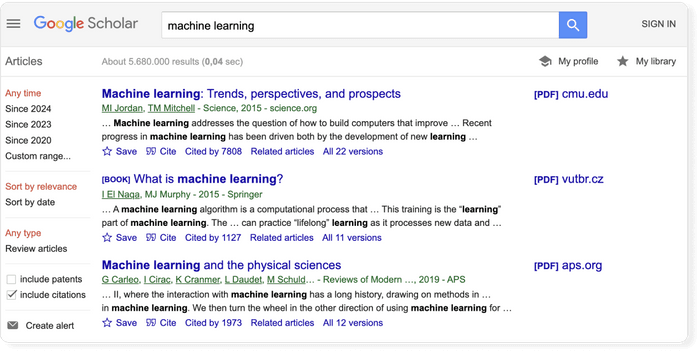
- The first line of each result provides the title of the document (e.g. of an article, book, chapter, or report).
- The second line provides the bibliographic information about the document, in order: the author(s), the journal or book it appears in, the year of publication, and the publisher.
Clicking on the title link will bring you to the publisher’s page where you may be able to access more information about the document. This includes the abstract and options to download the PDF.

To the far right of the entry are more direct options for obtaining the full text of the document. In this example, Google has also located a publicly available PDF of the document hosted at umich.edu . Note, that it's not guaranteed that it is the version of the article that was finally published in the journal.
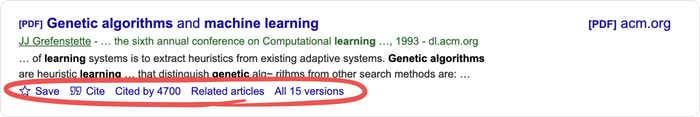
Below the text snippet/abstract you can find a number of useful links.
- Cited by : the cited by link will show other articles that have cited this resource. That is a super useful feature that can help you in many ways. First, it is a good way to track the more recent research that has referenced this article, and second the fact that other researches cited this document lends greater credibility to it. But be aware that there is a lag in publication type. Therefore, an article published in 2017 will not have an extensive number of cited by results. It takes a minimum of 6 months for most articles to get published, so even if an article was using the source, the more recent article has not been published yet.
- Versions : this link will display other versions of the article or other databases where the article may be found, some of which may offer free access to the article.
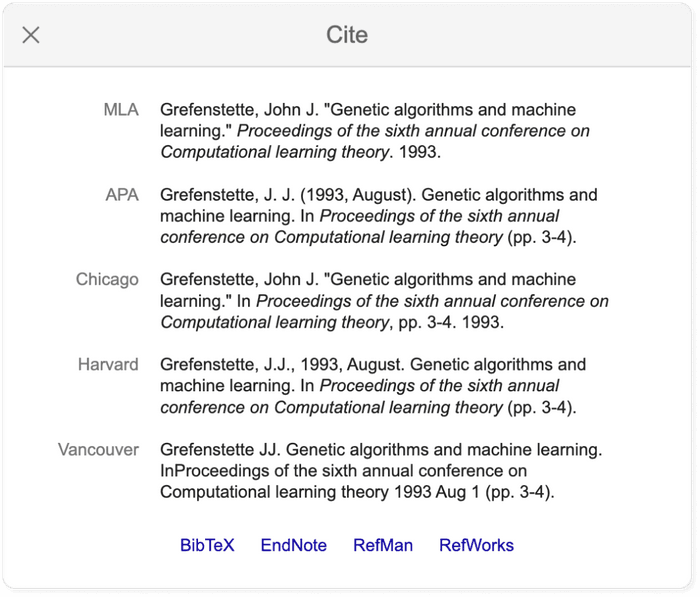
- Quotation mark icon : this will display a popup with commonly used citation formats such as MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and Vancouver that may be copied and pasted. Note, however, that the Google Scholar citation data is sometimes incomplete and so it is often a good idea to check this data at the source. The "cite" popup also includes links for exporting the citation data as BibTeX or RIS files that any major reference manager can import.
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular academic research engines and databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
Although Google Scholar limits each search to a maximum of 1,000 results , it's still too much to explore, and you need an effective way of locating the relevant articles. Here’s a list of pro tips that will help you save time and search more effectively.
You don’t need to worry about case sensitivity when you’re using Google scholar. In other words, a search for "Machine Learning" will produce the same results as a search for "machine learning.”
Let's say your research topic is about self driving cars. For a regular Google search we might enter something like " what is the current state of the technology used for self driving cars ". In Google Scholar, you will see less than ideal results for this query .
The trick is to build a list of keywords and perform searches for them like self-driving cars, autonomous vehicles, or driverless cars. Google Scholar will assist you on that: if you start typing in the search field you will see related queries suggested by Scholar!
If you put your search phrase into quotes you can search for exact matches of that phrase in the title and the body text of the document. Without quotes, Google Scholar will treat each word separately.
This means that if you search national parks , the words will not necessarily appear together. Grouped words and exact phrases should be enclosed in quotation marks.
A search using “self-driving cars 2015,” for example, will return articles or books published in 2015.
Using the options in the left hand panel you can further restrict the search results by limiting the years covered by the search, the inclusion or exclude of patents, and you can sort the results by relevance or by date.
Searches are not case sensitive, however, there are a number of Boolean operators you can use to control the search and these must be capitalized.
- AND requires both of the words or phrases on either side to be somewhere in the record.
- NOT can be placed in front of a word or phrases to exclude results which include them.
- OR will give equal weight to results which match just one of the words or phrases on either side.
➡️ Read more about how to efficiently search online databases for academic research .
In case you got overwhelmed by the above options, here’s some illustrative examples:
| Example queries | When to use and what will it do? |
|---|---|
"alternative medicine" | Multiword concepts like are best searched as an exact phrase match. Otherwise, Google Scholar will display results that contain and/or . |
"The wisdom of the hive: the social physiology of honey bee colonies" | If you are looking for a particular article and know the title, it is best to put it into quotes to look for an exact match. |
author:"Jane Goodall" | A query for a particular author, e.g., Jane Goodall. "J Goodall" or "Goodall" will also work, but will be less restrictive. |
"self-driving cars" AND "autonomous vehicles" | Only results will be shown that contain both the phrases "self-driving cars" and "autonomous vehicles" |
dinosaur 2014 | Limits search results about dinosaurs to articles that were published in 2014 |
Tip: Use the advanced search features in Google Scholar to narrow down your search results.
You can gain even more fine-grained control over your search by using the advanced search feature. This feature is available by clicking on the hamburger menu in the upper left and selecting the "Advanced search" menu item.

Adjusting the Google Scholar settings is not necessary for getting good results, but offers some additional customization, including the ability to enable the above-mentioned library integrations.
The settings menu is found in the hamburger menu located in the top left of the Google Scholar page. The settings are divided into five sections:
- Collections to search: by default Google scholar searches articles and includes patents, but this default can be changed if you are not interested in patents or if you wish to search case law instead.
- Bibliographic manager: you can export relevant citation data via the “Bibliography manager” subsection.
- Languages: if you wish for results to return only articles written in a specific subset of languages, you can define that here.
- Library links: as noted, Google Scholar allows you to get the Full Text of articles through your institution’s subscriptions, where available. Search for, and add, your institution here to have the relevant link included in your search results.
- Button: the Scholar Button is a Chrome extension which adds a dropdown search box to your toolbar. This allows you to search Google Scholar from any website. Moreover, if you have any text selected on the page and then click the button it will display results from a search on those words when clicked.
When signed in, Google Scholar adds some simple tools for keeping track of and organizing the articles you find. These can be useful if you are not using a full academic reference manager.
All the search results include a “save” button at the end of the bottom row of links, clicking this will add it to your "My Library".
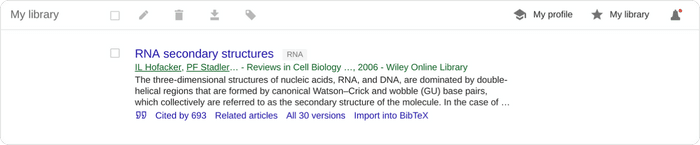
To help you provide some structure, you can create and apply labels to the items in your library. Appended labels will appear at the end of the article titles. For example, the following article has been assigned a “RNA” label:
Within your Google Scholar library, you can also edit the metadata associated with titles. This will often be necessary as Google Scholar citation data is often faulty.
There is no official statement about how big the Scholar search index is, but unofficial estimates are in the range of about 160 million , and it is supposed to continue to grow by several million each year.
Yet, Google Scholar does not return all resources that you may get in search at you local library catalog. For example, a library database could return podcasts, videos, articles, statistics, or special collections. For now, Google Scholar has only the following publication types:
- Journal articles : articles published in journals. It's a mixture of articles from peer reviewed journals, predatory journals and pre-print archives.
- Books : links to the Google limited version of the text, when possible.
- Book chapters : chapters within a book, sometimes they are also electronically available.
- Book reviews : reviews of books, but it is not always apparent that it is a review from the search result.
- Conference proceedings : papers written as part of a conference, typically used as part of presentation at the conference.
- Court opinions .
- Patents : Google Scholar only searches patents if the option is selected in the search settings described above.
The information in Google Scholar is not cataloged by professionals. The quality of the metadata will depend heavily on the source that Google Scholar is pulling the information from. This is a much different process to how information is collected and indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus or Web of Science .
➡️ Visit our list of the best academic databases .
Google Scholar is by far the most frequently used academic search engine , but it is not the only one. Other academic search engines include:
- Science.gov
- Semantic Scholar
- scholar.google.fr : Sur les épaules d'un géant
- scholar.google.es (Google Académico): A hombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.pt (Google Académico): Sobre os ombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.de : Auf den Schultern von Riesen
➡️ Once you’ve found some research, it’s time to read it. Take a look at our guide on how to read a scientific paper .
No. Google Scholar is a bibliographic search engine rather than a bibliographic database. In order to qualify as a database Google Scholar would need to have stable identifiers for its records.
No. Google Scholar is an academic search engine, but the records found in Google Scholar are scholarly sources.
No. Google Scholar collects research papers from all over the web, including grey literature and non-peer reviewed papers and reports.
Google Scholar does not provide any full text content itself, but links to the full text article on the publisher page, which can either be open access or paywalled content. Google Scholar tries to provide links to free versions, when possible.
The easiest way to access Google scholar is by using The Google Scholar Button. This is a browser extension that allows you easily access Google Scholar from any web page. You can install it from the Chrome Webstore .

- Library FAQs
Q. How can I add my publications to my Google Scholar profile?
- 9 Academic Integrity Module
- 19 Borrowing
- 27 Copyright licensing
- 9 Creative Commons Licence
- 4 Document Delivery
- 6 e-journal
- 58 General Library
- 32 Higher Degree Research (HDR)
- 23 Information
- 2 Library fees
- 3 My Library and Off Campus Access Login
- 5 Newspapers
- 15 Off-Campus Access
- 8 Open Access
- 33 Open Educational Resources (OER)
- 28 Open Scholarship
- 32 Open Textbooks
- 1 Peer Review
- 7 Printing and Photocopying
- 11 Publications
- 2 Reading Lists
- 24 Referencing
- 104 Research
- 10 Research Data Management
- 6 Research Metrics
- 18 Researcher Profiles
- 39 Resources
- 3 Studiosity
- 2 Study Smart
- 3 Study Smart Librarian
- 13 Textbooks
- 30 Turnitin for students
- 25 Western Open Books
- 8 Western Sydney University Digital Theses
Answered By: The Library Last Updated: Aug 02, 2022 Views: 58478
- 'SIGN IN' to your Google Scholar profile
- Click on 'My profile'
- To add publications, click on the + button and select from the list of the following options:
a) Add article groups : Articles will be grouped together by name. Use the check box to select and add a group of articles under your name
b) Add articles : Lists articles individually. Tick the check box to select and add the articles you have authored
c) Add article manually : If the article cannot be found you can create an entry manually. First choose the publication type at the top of the form then fill in as many fields as possible
NOTE: Archiving your publication to ResearchDirect (Western’s Institutional Repository) or personal web page will help Google Scholar find your publication. Remember to check which version of your paper you are permitted to archive and always link to an Open Access URL if available.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 56 No 117
Comments (0)
Related topics.
- Researcher Profiles
- Interlibrary Loan and Scan & Deliver
- Course Reserves
- Purchase Request
- Collection Development & Maintenance
- Current Negotiations
- Ask a Librarian
- Instructor Support
- Library How-To
- Research Guides
- Research Support
- Study Rooms
- Research Rooms
- Partner Spaces
- Loanable Equipment
- Print, Scan, Copy
- 3D Printers
- Poster Printing
- OSULP Leadership
- Strategic Plan
PH 403: Thesis
- Finding Articles
- Use Web of Science
Don't Pay for Articles in Google Scholar!
Set up your google scholar preferences, google scholar and find it at osu, accessing paid content from off-campus.
- Theses & Dissertations
- Staying Organized
Google Scholar is a great place to scan across a lot of sources at once, but if it doesn't know that you have rights to access online articles and other sources from a library, it might send you to a page like this - which asks you to pay for the article you want:
The journal in this example is in the OSU Libraries' collection, and OSU students, staff and faculty have the right to access it (and articles in lots of other journals) from any computer with an Internet connection. With a few adjustments to your preferences, you can tell Google Scholar to point you to the resources that the library provides for the OSU community.
Step 1: To make Google Scholar talk to the OSU Libraries collection, go to the Settings link, located on the top left corner of the page:

Step 2: On the left-hand side of the Scholar Settings page, choose Library links :
Step 3: Next either search for Oregon State University in the search box or simply use the checkbox next to Oregon State University .

Now, when you do a search, your results list will look like this. Click on the Find it at OSU link to get to either the full-text of the article or an easy option for requesting the article through interlibrary loan . Notice that if the article doesn't have a Find it at OSU link, you can click on the More link to Check Library Holdings .
Clicking on these Find it at OSU links will now take you to the library's collections. If you are in the library, or at an IP address recognized as an OSU address, this process will usually be immediate. If you are not on campus, you will need to prove that you have access to the sources the library has paid for. You do this by entering your ONID login and password after this sign in prompt:

This process works well, but it doesn't work perfectly. If there is an article you want, and you can't get it this way, ask a librarian how you can get it.
- << Previous: Use Web of Science
- Next: Theses & Dissertations >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 12:59 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.oregonstate.edu/PH403
Contact Info
121 The Valley Library Corvallis OR 97331–4501
Phone: 541-737-3331
Services for Persons with Disabilities
In the Valley Library
- Oregon State University Press
- Special Collections and Archives Research Center
- Undergrad Research & Writing Studio
- Graduate Student Commons
- Tutoring Services
- Northwest Art Collection
Digital Projects
- Oregon Explorer
- Oregon Digital
- ScholarsArchive@OSU
- Digital Publishing Initiatives
- Atlas of the Pacific Northwest
- Marilyn Potts Guin Library
- Cascades Campus Library
- McDowell Library of Vet Medicine
Indexing Policies
- Other Policies
Publisher Support
Google Scholar can boost the worldwide visibility and accessibility of your content. We work with publishers of scholarly information to index peer-reviewed papers, theses, preprints, abstracts, and technical reports from all disciplines of research and make them searchable on Google and Google Scholar.
This section provides policy and technical information for scholarly publishers and societies. Detailed technical inclusion guidelines for webmasters can be found here .
Multiple versions of a work are grouped to improve its ranking
In many research areas versions of a work may appear as preprints and conference papers before being published as a journal article. These preliminary versions of a work are often cited in addition to the authoritative journal version. The number of citations to a particular work is an important part of determining its rank in the Google Scholar search results. Grouping versions allows us to collect all citations to all versions of a work. In practice, this can significantly improve the position of an article in the search results.
Publisher's full-text, if indexed, is the primary version
When multiple versions of a work are indexed, we select the full and authoritative text from the publisher as the primary version. We can only do this if we are able to successfully identify, crawl and process the full text of the publisher's version.
Publishers have control over access to their articles
We work with publishers to preserve their control over access to their content and only cache articles and papers that don't have access restrictions. Publishers can help us by identifying the regions of their sites that have access restrictions.
Google users must see at least the complete abstract or the first full page
This is a necessary component of our indexing program. For papers with access restrictions, all users clicking on search results must see at least the full author-written abstract or the first full page of the article without requiring to login or click on additional links.
We will respond to complaints regarding copyright infringement
Our policy is to respond to all notices of alleged copyright infringement that comply with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. For directions and more information, please click here .
Subscriber Links Policies
Google's use of electronic holdings information
We will use electronic holdings information for generating per article links in our search results to publisher servers. We will not share this information with third parties or use it for marketing purposes.
Electronic holdings usage information
We will not share information with third parties on the usage of your electronic holdings or on aggregate usage based on institutional characteristics or profiles.
Publishers can withdraw electronic holdings information
Once the electronic holdings information is no longer available to our search robots, we will stop using it within 30 days.
General Questions
We would love to work with you. As noted in the policies, an abstract (at least) of each work must be available to non-subscribers who come from Google and Google Scholar. Please configure your website according to our technical inclusion guidelines .
Maybe. Google Scholar indexes mostly scholarly articles. For textbooks and monographs, we recommend Google Book Search. Google Scholar automatically includes scholarly works from Google Book Search.
Since users click through to your website, your web server logs should have all the usage statistics.
It is our policy to respond to notices of alleged infringement that comply with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. For directions and more information, please click here .
Technical Questions
Yes. We can index PDF articles as long as they're searchable and as long as their size doesn't exceed 5MB. For larger documents and for scanned images that require OCR, we recommend Google Book Search.
Open the file in Adobe Acrobat Reader. Click 'Find' (look for the binocular icon), and confirm that you can search for and find several words on the page.
Alas, we can't. We can index only one file per article at the moment.
Refer to Google webmaster help .
Add the following robots meta-tag to the <head> section of your webpage:
If we're showing 'Cached' links for your restricted-access content, please email us specific examples of where the links appear. Display of cached links for restricted-access content isn't intentional, but may happen if our methodical crawlers accidentally discover a forgotten alternative interface to your content. You'll need to tell us of all such interfaces, because crawlers can go places where you least expect them. Please email us and we'll look into it.
If you believe another site is infringing your copyright, please see our directions on the DMCA process .
If we're showing unwanted Quick Abstracts for your restricted-access content, please email us specific examples of where the abstracts appear. Display of unwanted Quick Abstracts for restricted-access content isn't intentional, but may happen if our methodical crawlers accidentally discover a forgotten alternative interface to your content. You'll need to tell us of all such interfaces, because crawlers can go places where you least expect them. Please email us and we'll look into it.
Indeed you can. Our indexing algorithms automatically extract bibliographic data, citations and other information from articles and use it for ranking purposes. Providing authoritative metadata about your articles can help facilitate this and can increase the likelihood of identifying all the citations to your articles. We strongly recommend this approach. Please refer to the following technical inclusion guidelines for the details of how to implement it.
Yes. Gaps in coverage are certainly not intentional; but they could be caused by a number of different technical issues in the automatic processing of your website by our search robots. The troubleshooting section in our technical inclusion guidelines describes ways to identify and fix common coverage issues. We encourage you to take a look.
- Privacy & Terms
SOCY 391: Sociological Research Methods
- Tips for Beginning Your Search
- Sociological Abstracts
- Web of Science
- Find It @ USC
Google Scholar
Search Tip: Connect USC Library to Google Scholar
Search tip: advanced search, how do i....
- Find a Known Item
- LibKey Nomad
Find peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, pre-prints, abstracts, and technical reports.
To access Full Text via the library, update your personal settings in Google Scholar
- On the Google Scholar site, click on the Menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top left of the screen.
- Select Settings
- Click on Library links in the left column
- Type University of South Carolina
- Check the box next to UofSC University Libraries - ViewIt@UofSC
- Click Save
**Never purchase an article! Check the library's resources or make a free ILL request.**
You can use the Google search operators in Google Scholar, plus some other search techniques
Searching for papers by a specific author?
author: finds papers written by
- returns papers written by people with the name Washington)
- finds the word washington, but excludes papers written by people named Washington
Other Helpful Information
- Learn what other sources in Google Scholar have cited it
- Google has its own algorithm for determining similar articles
- Especially helpful if your initial result doesn’t link to the full-text. Maybe another version will.
- Learn what other sources from the Web of Science database (a library subscription) have cited it.
- Shows the format for MLA, APA and Chicago styles.
To get to the Advanced search in Google Scholar, after doing a search click on the 3 lines on the top left of the screen

- Request Materials through Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- << Previous: Find It @ USC
- Next: Find a Known Item >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2024 11:59 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.sc.edu/socy391
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Publication Research Help
Google Scholar Profile
Publication research help: google scholar profile.
- Peer Reviewed Architecture Journals
- Peer Reviewed Planning Journals
- Creating an ORCID iD
- Research Rabbit & Elicit
Creating a profile in Google Scholar is a popular way to highlight your articles, books, and book chapters. Google Scholar will generate an H index based on your cited works. Google Scholar counts citations from any online source: articles, white papers, slides, etc.
H-index in Google Scholar : The h-index of a publication is the largest number h such that at least h articles in that publication were cited at least h times each. For example, a publication with five articles cited by, respectively, 17, 9, 6, 3, and 2, has the h-index of 3.
Google Scholar Profile set-up help: https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/citations.html#setup
Create a basic profile
Step 1: Create a Google account or sign in if you already have an account.
Step 2: Go to Google Scholar's home page and click on My Profile in the upper left corner of the page.
Step 3: Follow the instructions, add in your affiliation information and your email address. (Validate the email address, an email will be sent to you asking for validation).
Step 4: Add in any keywords that is related to your research and add a link from the SAP faculty page .
Step 5: Add a photo to personalize your profile. Check box to make profile public.
Adding in Publications
Google Scholar will present a list of publications that may be yours. Check the box that are your publications.
If you don't have a common name, click the box for Google Scholar to automatically update your profile.
To add articles and books:
Click the + button below your photo to add articles to your profile in the grey toolbar. By clicking on the Add Articles , Google Scholar will create a list of articles that you may have published. By clicking, Add Articles Manually, you can chose to add articles, conference proceedings, chapters, books, thesis, patents, court case, and other.
If you have duplicate citations, check the box and then click on Merge in the grey toolbar.
To delete a citation, check the box and click on Delete in the grey toolbar.
Add any co-authors by clicking on the Edit link on the right side and search for co-authors.
Exporting citations
Step 1: Check the box of the citations you want to export
Step 2: Click on Export in the grey toolbar. Export to: BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, CSV
- << Previous: Creating an ORCID iD
- Next: Research Rabbit & Elicit >>

- Become Involved |
- Give to the Library |
- Staff Directory |
- UNF Library
- Thomas G. Carpenter Library
Faculty Resources
How to set up your google scholar profile.
- Databases and Database Trials This link opens in a new window
- eBook Collections This link opens in a new window
- Streaming Videos This link opens in a new window
- Special Collections & Archives This link opens in a new window
- Digital Commons This link opens in a new window
- SelectedWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Instruction
- Course Reserves
- Request Forms This link opens in a new window
- Policies and Guidelines This link opens in a new window
- Citation Management
- Remote Access
- OER This link opens in a new window
- Enhancing the Visibilty of Your Research Profile
- Author Impact Beamplots
- Impact Factors for P&T This link opens in a new window
- Determining Your Research Impact
- Predatory vs Professional Journals
Connect to the Library
Creating your profile (for authors), editing your profile, managing your publications - add a publication, managing your publications - merge duplicates, managing your publications - delete publications, managing your publications - exporting data.
- Library Liaisons
For UNF-authenticated users, Google Scholar search results contain links to full text from UNF-subscribed content,
Connecting Google Scholar to the library will add "Full Text@UNF" links to your search results. If the Library subscribes to the item you are looking for, click on Full Text@UNF to be directed to the service that will let you access it. (Off-campus users will be prompted to sign in to the Library with their N# and password.)
- Go to https://scholar.google.com
- Click on the icon showing three horizontal bars on the top left of the webpage.
- From this menu, click Settings
- From the navigation on the left, click Library Links .
- In the search box on the Library links page, enter University of North Florida .
- Note: If University of North Florida - Full Text @ UNF (there are spaces on either side of the @) is selected, you should unmark it. This link resolver is being retired and will no longer work.
- Click Save.
- Sign in to Google Scholar using your Google account.
- Click My Profile at the top of the page, on the left side, to enter your profile.
- Set up your initial profile.
- Edit your profile information, including where you work, name, photo, and research interests.
- Manage your publications.
You can also view the profiles of other UNF faculty on Google Scholar.
- Starting from Google Scholar , you can access and edit your profile by clicking on My Profile in the top left corner.
- Click the pencil icon next to your photo to enter edit mode.
- Add a photo by clicking on the placeholder profile picture and then uploading a photo from your computer.
- Fill out your university affiliation and add your UNF email address (this will verify your scholar profile.
- Making your profile public makes it easier for people to locate, read, and use your scholarship.
Click the + button below your photo to add articles to your profile. You can locate articles to add three different ways.
- Add article groups : This option shows you groups of articles that may all be yours (or not). This method doesn't always work well but it does let you add multiple articles to your profile at once.
- Add articles : This option allows you to select individual articles to add to your profile. Change the search terms if the suggestions don't include the article you are looking for.
- Add articles manually : This option allows you to enter individual works that have not been indexed by Google Scholar. You can add many different types of publications of publications using this form, including:
- Check the box next to the duplicate publications, one set at a time.
- Click the MERGE button in the toolbar.
- Choose the record with the most accurate information. Click MERGE .
- Repeat as needed.
- Check the box next to the publication(s) you want to delete.
- Click the DELETE button in the toolbar.
- The publications are immediately removed.
There are two options for retrieving publications from the trash:
- Immediately after clicking DELETE a yellow box appears at the top of the screen offering an UNDO option.
- Select View Trash,
- Select the publications to be restored.
- Click on the Restore button.
- Click on the arrow in the upper left corner to leave the trash.
Publication data can be downloaded for import into other programs. This feature only exports publication information, it does not include citation counts.
- You can select all by checking the box on the far left in the gray bar under your photo.
- Click EXPORT and choose a file type. The available file types are:
- << Previous: Predatory vs Professional Journals
- Next: Library Liaisons >>
- Last Updated: Aug 16, 2024 7:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.unf.edu/faculty
Scholar Blog
- Save papers to read later
Found an interesting paper and don’t have time to read it right now? Today we are adding a reading list to your Scholar Library to help you save papers and read them later.
You can also use it to save papers you find off-campus but want to read on-campus where you have access to the full text, or papers you find on your smartphone but want to read on a larger screen.
To add a paper to your reading list, click “Save” and add the “Reading list” label. To use this feature, you need to be signed in to your Google account.

To get to your reading list, click “My library”:
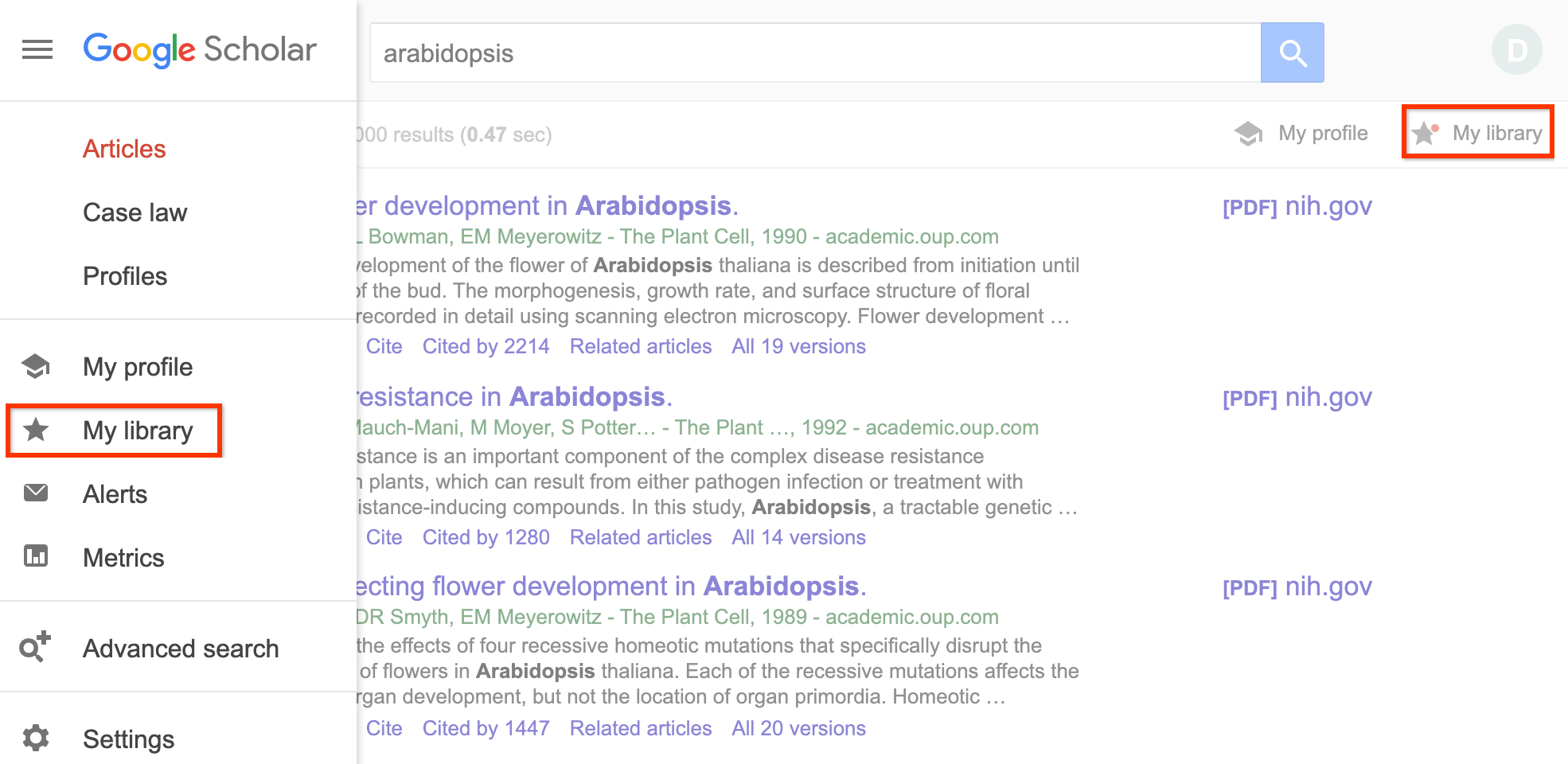
…and select “Reading list” in the sidebar.
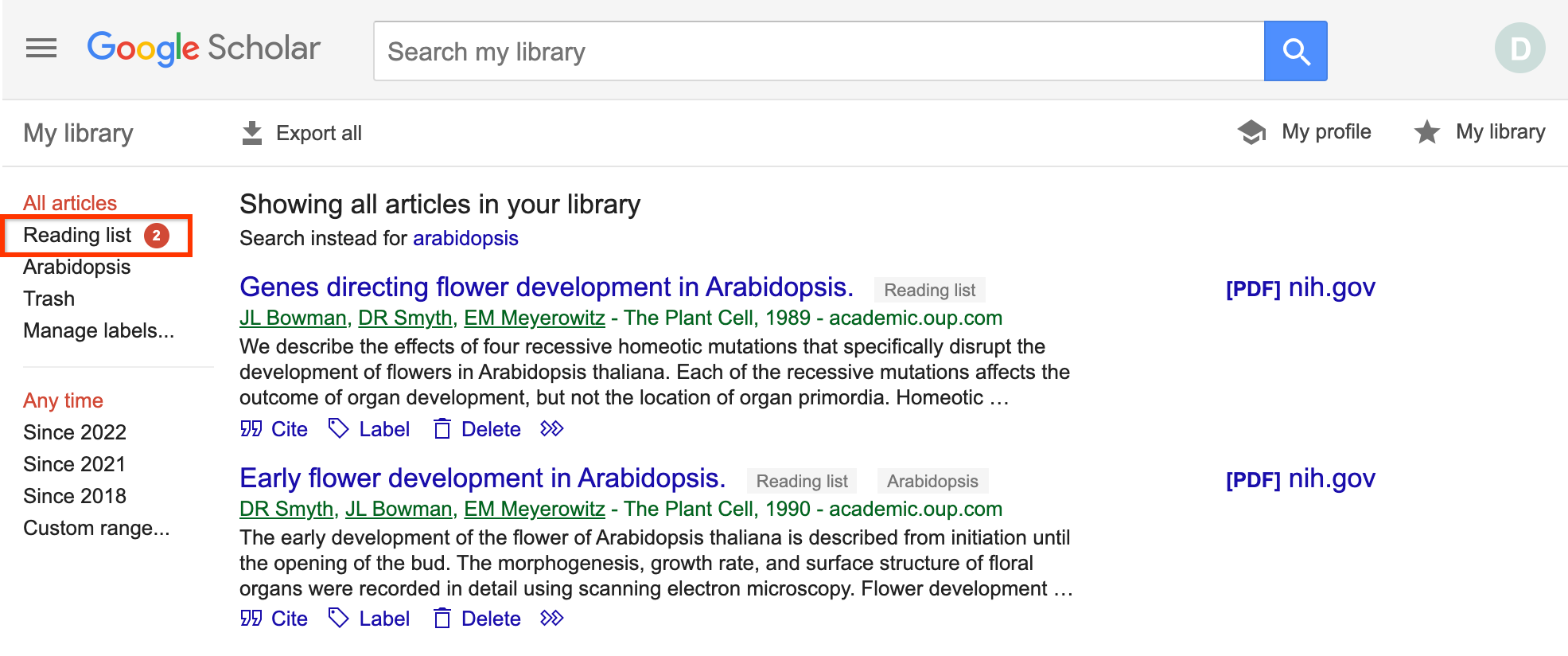
To read the paper, click the [PDF] or [HTML] link next to its title.

After reading a paper, click "Archive" or "Delete" to remove it from your reading list. Archived papers are kept in your library for later reference; deleted papers are removed from your library.

Now you can gather papers as you go, block off a good chunk of time, and dig into the details.
Posted by: Danni Chen, Kyu Jin Hwang, and Alex Verstak
- July
- March
- April
- June
- February
- September
- August
- October
- January
- November
- May
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How can I create a google scholar profile without publicaitons?
I'm currently doing my master's in physics. I have written a few articles which are yet to be communicated. But I'm graduating within 3 months due to which I will lose my institute email ID. And since the creation of a profile on google scholar mandates an institution ID as well as articles, Im at a loss. I have done a minor project due to which I have a minor thesis document at hand and I have seen scholar profiles where the first publication kept on it is not published in any journal but instead was a thesis report. Is there anyway I could use my minor thesis to open a google scholar profile? It would be nice if I could know where to upload my thesis so that it would be searchable on google scholar.
Thanks in advance!
- publications
- google-scholar
- 1 The google scholar help page says that you can change your institutional id. So set it up now and change it later. I think google scholar searches arXiv; if so posting your thesis there will work. – Ethan Bolker Commented Jan 8, 2021 at 17:50
You must log in to answer this question.
Browse other questions tagged publications google-scholar ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- "We take these items to be …" VS "These items we take to be …" — How natural to put "these items" forward?
- Lore reasons for being faithless
- Do passengers transiting in YVR (Vancouver) from international to US go through Canadian immigration?
- How can moral disagreements be resolved when the conflicting parties are guided by fundamentally different value systems?
- Fast algorithm to obtain an orthogonal vector to a set of vectors
- How to frame certain cells with tabular?
- Why is Namibia killing game animals for food rather than allowing more big game hunting?
- Where did I go wrong in using Kirchhoff's Voltage Law for this circuit?
- A SF novel where one character makes a "light portrait" of another one, with huge consequences
- How do I backup only changed files on an external hard drive?
- Is a company liable for "potential" harms?
- In 1982 Admiral Grace Hopper said "I still haven't found out why helicopter rotors go the way they do". If she were here today, how might one answer?
- What is the difference between "Hubiera" and "Habría"?
- If Starliner returns safely on autopilot, can this still prove that it's safe? Could it be launched back up to the ISS again to complete its mission?
- What is a "hard-boiled turtle-slapper"?
- Krasner–Kaloujnine universal embedding theorem for finitely generated groups?
- Why didn't Cuddy appear at the House funerals?
- Explain how π – 1 + 50 + ⅔ × 1000 is PLONK
- Which Mosaic law was in the backdrop of ceremonial hand-washing in Mark 7?
- Replacing aircon capacitor, using off brand same spec vs lower/higher spec from correct brand?
- Doesn't counting hole and electron current lead to double-counting of actual current?
- Barnum Effectus
- Can an international student email a professor at a foreign university for an internship opportunity?
- Functor composition rule necessary?

Technology Resources
- Microsoft Teams
Google accounts
Google chrome.
- Google Drive
Google Scholar
- Adobe Softwares
- Technology in the Library
- Other Resources
- Technology Help

What started as a humble search engine has now become a huge collection of services, from email, to video sharing, to web browsing, to word processing and more. Google has become more and more utilized in our daily internet routines, so here are websites and tips on the most major resources provided by Google.
- Google Account Help From Google
- Manage third party logins through Google An FAQ on linking third party sites (so, non-Google sites) to your Google account.
- Common Google Chrome issues A list of common Google Chrome issues and how to solve them from LinkedIn
- Google Chrome Help Center Customer support, FAQs, and community posts from Google.
- What is "website not secure" and how do I fix it? Why an old website you're trying to visit might be giving you error messages.
- Manage warnings about insecure sites Information about Secure Sites from Google Support
- Google Chrome and privacy Tips for increasing privacy for your information when using Google Chrome, from Consumer Reports.

- Google Drive Help
- Useful features of Google Drive 35 useful features of Google Drive and its related apps, from PCMag.

- Gmail Help Center

- YouTube Help Center
- 25 channels for higher education A list of useful YouTube Channels for universities, from Academic Influence.
- Webster University's YouTube Channel Webster's Official YouTube Channel
- Webster Univeristy Library Our channel, with how-to videos on researching, writing, and using the library's resources.
Google Scholar is a simple tool to search for scholarly (peer-reviewed) articles, and see how many times an article has been cited in other research. And when you hit a paywall, it can connect to Webster University Library's resources. If you are using a computer with an off-campus IP address, follow these instructions to connect Google Scholar to library resources:
- Go to Google Scholar
- Click on Settings.

- Connect Google Scholar to Webster University Library
- Using Google Scholar for Research (Recorded on September 15, 2016. 22 minutes.) Learn how to use both Google and Google Scholar more effectively for research. Connect Google Scholar to library resources and get tips and tricks to make your searches more efficient. Click here to watch specific parts of this video.
- << Previous: Canvas
- Next: Adobe Softwares >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2024 6:37 PM
- URL: https://library.webster.edu/tech-resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are the steps: Go to this page to start adding a document manually. Choose the type of document (journal, conference, chapter, book, thesis, patent, court case or other). Fill in all the details about your article (title, author (s), publication date (s), volume, publisher, institution). Click save and if you filled in everything correctly ...
5. Log in, go to your profile, click the "+" icon, and select "Add article manually". Then fill in the details and it will appear on your profile immediately. However you cannot upload a pdf to Google Scholar or anything like that. Google Scholar is not a repository. And the citations will only appear after the crawler finds it on the internet.
First of all, you need to access Google Scholar and log in. Generally, like with the. Google browser, Google Scholar will log in with the email account that you have by. default in the search engine. If you are using Google Scholar for the first time, My profile section will. appear at the top left.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it's available for free.
Uploading your papers in Researchgate is (often) a way to get your papers in Google Scholar. In my own experience some papers (or documents like preprints, master thesis, method etc.) are picked ...
In this video, i will share how add or update articles. You can't upload articles in google scholar as like academia or research gate, SSRN ...etc. Must watc...
When adding articles after Google Scholar profile set-up, you have the option to add articles manually. ... Start by selecting the type of resource first (journal, conference, book, thesis, etc). Continue with adding the. relevant information and select save on the bottom right hand corner to add the article to your citations. << Previous ...
Questions. Google Scholar Profiles. Google Scholar Profiles provide a simple way for authors to showcase their academic publications. You can check who is citing your articles, graph citations over time, and compute several citation metrics. You can also make your profile public, so that it may appear in Google Scholar results when people ...
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
To add publications, click on the + button and select from the list of the following options: a) Add article groups: Articles will be grouped together by name. Use the check box to select and add a group of articles under your name. b) Add articles: Lists articles individually. Tick the check box to select and add the articles you have authored.
Set Up Your Google Scholar Preferences. Step 1: To make Google Scholar talk to the OSU Libraries collection, go to the Settings link, located on the top left corner of the page: Step 2: On the left-hand side of the Scholar Settings page, choose Library links: Step 3: Next either search for Oregon State University in the search box or simply use ...
Questions. Publisher Support. Google Scholar can boost the worldwide visibility and accessibility of your content. We work with publishers of scholarly information to index peer-reviewed papers, theses, preprints, abstracts, and technical reports from all disciplines of research and make them searchable on Google and Google Scholar. This ...
The Neotia University. Open google scholar and then login with your ID and password. There is a option with + symbol. Click on that and then click on add mannually and then fill about your ...
The google scholar help documentation states: Documents larger than 5MB, such as books and long dissertations, should be uploaded to Google Book Search; Google Scholar automatically includes scholarly works from Google Book Search. What is implied by "uploading to Google Book Search"? I see no way to upload to the search.
Google Books does not seem to have more than Google Scholar, but it provides links to WorldCat on the left side for each item. I often use both Google Books and WorldCat to do full text searches of books, and I sometimes find dissertations this way. ProQuest is also a good source of digitized dissertations and theses. The service requires a ...
On the Google Scholar site, click on the Menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top left of the screen.; Select Settings; Click on Library links in the left column; Type University of South Carolina; Check the box next to UofSC University Libraries - ViewIt@UofSC; Click Save **Never purchase an article! Check the library's resources or make a free ILL request.**
Create a basic profile. Step 1: Create a Google account or sign in if you already have an account. Step 2: Go to Google Scholar's home page and click on My Profile in the upper left corner of the page. Step 3: Follow the instructions, add in your affiliation information and your email address. (Validate the email address, an email will be sent ...
Starting from Google Scholar, you can access and edit your profile by clicking on My Profile in the top left corner.; Click the pencil icon next to your photo to enter edit mode.; Add a photo by clicking on the placeholder profile picture and then uploading a photo from your computer. Fill out your university affiliation and add your UNF email address (this will verify your scholar profile.
To add a paper to your reading list, click "Save" and add the "Reading list" label. To use this feature, you need to be signed in to your Google account. To get to your reading list, click "My library": …and select "Reading list" in the sidebar. To read the paper, click the [PDF] or [HTML] link next to its title.
Before uploading your complete, formatted document to the LSU Scholarly Repository (formerly Digital Commons), consult the Final Thesis and Dissertation Checklist (see p. 22 herein) and then follow these steps: • Convert your document to an Adobe pdf. • Create an account in the LSU Scholarly Repository (formerly Digital Commons). •
And since the creation of a profile on google scholar mandates an institution ID as well as articles, Im at a loss. I have done a minor project due to which I have a minor thesis document at hand and I have seen scholar profiles where the first publication kept on it is not published in any journal but instead was a thesis report.
And when you hit a paywall, it can connect to Webster University Library's resources. If you are using a computer with an off-campus IP address, follow these instructions to connect Google Scholar to library resources: Go to Google Scholar; Click on Settings. Click on Library Links and connect with Webster University Library resources as shown ...