| | Broccoli is the healthiest food. It has many vitamins and minerals for health. | | | Broccoli has vitamin C, which helps the immune system. It fights colds and infections. Just one cup of broccoli covers your whole day's vitamin C needs. | | | Broccoli also provides vitamin K, which is good for bone health. It helps build strong bones that don't break easily as you get older. | | | Some people don't like broccoli because of the taste. It can be bitter and hard to chew. But adding cheese sauce or roasting it makes broccoli taste better. | Differences between Paragraph & Essay
Purpose | | | | Gives one main point | Discusses a whole topic | | Scope | Focuses on one piece of a topic | Covers a topic fully and deeply | | Components
| - Topic Sentence | - Introduction | | - Supporting Sentences | - Body Paragraphs (Multiple) | | - Transitions (Optional) | - Conclusion | | - Closing Sentence (Optional) | - Transitions | | - References or Citations (if applicable) | | | 3-5 sentences usually | It varies a lot depending on the topic | | | Used in longer writings | Narrative, descriptive, persuasive, etc. | | | Provides focused information | Explores and analyzes a whole topic | Paragraphs and essays have different purposes. Knowing when and how to use each one improves writing. Concise, focused paragraphs help with writing. Thorough, organized essays help too. Together, they let writers express ideas powerfully. Understanding the structures matters. Utilizing them well is key. It makes writing stronger overall. Frequently Asked Questions1. what is the main purpose of a paragraph. The main purpose of a paragraph is to explain one central idea. Paragraphs expand on one main point or topic. They let the writer give details before moving on. All the sentences work together. They expand on one point. 2. What makes a good essay?A strong essay has an engaging introduction. The introduction previews the topic. The body paragraphs are smoothly ordered. There are transitions between ideas. The essay has solid research and facts. These support the claims. There is a memorable conclusion. The conclusion summarizes the main points. A thoughtful structure helps create a quality essay. Strong analysis also helps. Good grammar helps too. 3. Can an essay have only one body paragraph?It is possible for an essay to have just one body paragraph. This is more common in short essays or types like narrative or descriptive essays. But most essays with a full exploration of a topic have multiple body paragraphs. Each body paragraph addresses different aspects. 4. Is it necessary to include references or citations in a paragraph?Usually, citations are not needed in a paragraph. But if the information comes from other sources, you should give credit. This matters most within the full essay or document. Proper attribution there is important. 5. When should I start a new paragraph?Start a new paragraph when you are moving from discussing one main idea to another. For example, each body paragraph of an essay focuses on a distinct main point, so a new paragraph is needed when shifting gears to a new sub-topic or example. New paragraphs help organize information. Unlock FeaturesUnleash creativity, precision, and excellence in every word. Upgrade now for limitless potential. Enjoy this post? Rate it!  Paragraph and essay are not the same; here’s whyStudents often get confused between paragraphs and essays. however, although they share a few similarities, the differences are far more significant. this makes it even more crucial for you to understand the differences well, especially if you are to give an english language test like ielts or toefl. moreover, understanding the main differences will help you answer the questions better., table of contents, let’s understand the difference between a paragraph and an essay. . - What makes a good paragraph and essay?
Key takeawaysThe difference between a paragraph and an essay is far too significant to get confused. Yes, both indeed share many similarities. This makes it easy for one to get confused when comparing the two. However, you must understand the difference between an essay and a paragraph to avoid getting mixed up. Understanding the differences will be especially handy if you plan to attempt any English language exam like IELTS or TOEFL. They often include questions related to both a paragraph and an essay. If you understand the difference between paragraph and essay, you are better equipped to provide efficient responses. We have highlighted the following key difference between a paragraph and an essay – A paragraph is usually short. It may include 4 to 6 sentences. The paragraph will address a specific topic or theme, but that is about it. On the other hand, an essay will include 4 to 6 paragraphs. The main idea will be discussed throughout these paragraphs. Since the word limit is higher, it takes more time to think about the topic and provide appropriate responses. Due to how limited the wordings are, the main point of the topic or theme is generally explained within the first two sentences. The supporting information, as well as the concluding sentence, is included in the last few lines. The standard structure of the essay is where an individual uses the first paragraph to introduce the topic. The following two or three paragraphs provide supporting information (including examples), and the last paragraph provides any concluding sentences. The paragraph and essay make good points. They follow entirely different structures to serve their respective purposes. If you wish to talk about a topic in length, the best way to go about it is by writing an essay. However, a paragraph should suffice if you want to discuss a topic briefly. The essay addresses the topic from a broad perspective. In contrast, a paragraph will concisely explain the same topic.  A good paragraph uses simple and brief sentences to explain the point. The paragraph is generally limited to a single topic, which should follow a decent structure. A good essay will consist of the main statement that is then expanded and explained clearly and smoothly. Interestingly, if you wish to write a good essay, you have to get better at forming a paragraph. Straightforward and well-structured paragraphs will help you write good essays. In addition, your thoughts should be clearly communicated in each paragraph. - Understanding the differences will be especially handy if you plan to attempt any English language exam like IELTS or TOEFL.
- A paragraph is usually short. It may include 4 to 6 sentences. The paragraph will address a specific topic or theme. On the other hand, an essay will include 4 to 6 paragraphs. The main idea will be discussed throughout these paragraphs.
- Interestingly, if you wish to write a good essay, you have to get better at forming a paragraph. Straightforward and well-structured paragraphs will help you write good essays.
- What is the difference between a paragraph and an essay?
The difference between a paragraph and an essay is that a paragraph consists of 4-6 sentences while an essay consists of 4-6 paragraphs. - What is required to write a good essay?
You need to be able to form a good paragraph to write a good essay. A good paragraph and essay is the kind that uses simple and brief sentences to explain the point. How useful was this post? Click on a star to rate it! Average rating 4 / 5. Vote count: 27 No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.  People also liked IELTS success| Tips to master each section Importance of IELTS grammar | Tips and tricks TOEFL and IELTS | Role of contextual & academic words Simulated tests | Opportunity to overcome challenges TOEFL, IELTS, & GRE exam structure | Key differences 2024! Ace the GMAT exam | Navigate quant & verbal difficulties!Leave a reply cancel reply. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked * Start your journey with iSchoolPrepNeed help with your Test Preparations? Contact Us for more details  Inquire NowGet e-books, expert guidance, live classes and more.... Pasco-Hernando State College Paragraphs and Essays- The Writing Process
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Sentences are a basic structure of language. They convey the action or existence of a person, place, or thing. Sentences are combined to form paragraphs to form longer written documents. This may sound simplistic, but to build effective written communication, sentences have to be combined in certain ways to form the paragraphs which in turn can be combined to write longer works. Even the longest novel is made up of sentences which are organized into paragraphs except for dialogue. An essay is a special type of writing focused on proving a point called the thesis. Essays are composed of special types of paragraphs with very particular content. The rules for punctuation and sentence structure are covered in the Grammar section. This section will cover how to compose paragraphs and an academic essay which is also, generally, the way beginning level research papers are organized. Research papers are also called research essays.  Academic Editing and Proofreading- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment Add Comment Checklist: Dissertation ProposalEnter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox! Examples: Edited PapersNeed editing and proofreading services.  - Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
Writing an effective and impactful essay is crucial to your academic or professional success. Whether it’s getting into the college of your dreams or scoring high on a major assignment, writing a well-structured essay will help you achieve it all. But before you learn how to write an essay , you need to know its basic components. In this article, we will understand what an essay is, how long it should be, and its different parts and types. We will also take a detailed look at relevant examples to better understand the essay structure. Get an A+ with our essay editing and proofreading services! Learn more What is an essay?An essay is a concise piece of nonfiction writing that aims to either inform the reader about a topic or argue a particular perspective. It can either be formal or informal in nature. Most academic essays are highly formal, whereas informal essays are commonly found in journal entries, social media, or even blog posts. As we can see from this essay definition, the beauty of essays lies in their versatility. From the exploration of complex scientific concepts to the history and evolution of everyday objects, they can cover a vast range of topics. How long is an essay?The length of an essay can vary from a few hundred to several thousand words but typically falls between 500–5,000 words. However, there are exceptions to this norm, such as Joan Didion and David Sedaris who have written entire books of essays. Let’s take a look at the different types of essays and their lengths with the help of the following table: How many paragraphs are in an essay?Typically, an essay has five paragraphs: an introduction, a conclusion, and three body paragraphs. However, there is no set rule about the number of paragraphs in an essay. The number of paragraphs can vary depending on the type and scope of your essay. An expository or argumentative essay may require more body paragraphs to include all the necessary information, whereas a narrative essay may need fewer. Structure of an essayTo enhance the coherence and readability of your essay, it’s important to follow certain rules regarding the structure. Take a look: 1. Arrange your information from the most simple to the most complex bits. You can start the body paragraph off with a general statement and then move on to specifics. 2. Provide the necessary background information at the beginning of your essay to give the reader the context behind your thesis statement. 3. Select topic statements that provide value, more information, or evidence for your thesis statement. There are also various essay structures , such as the compare and contrast structure, chronological structure, problem method solution structure, and signposting structure that you can follow to create an organized and impactful essay. Parts of an essayAn impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. 1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader’s attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about. 2. The body is where you dive deeper into your topic and present your arguments and evidence. It usually consists of two paragraphs, but this can vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing. 3. The conclusion brings your essay to a close and is typically one paragraph long. It should summarize the main points of the essay and leave the reader with something to think about. The length of your paragraphs can vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing. So, make sure you take the time to plan out your essay structure so each section flows smoothly into the next. IntroductionWhen it comes to writing an essay, the introduction is a critical component that sets the tone for the entire piece. A well-crafted introduction not only grabs the reader’s attention but also provides them with a clear understanding of what the essay is all about. An essay editor can help you achieve this, but it’s best to know the brief yourself! Let’s take a look at how to write an attractive and informative introductory paragraph. 1. Construct an attractive hook To grab the reader’s attention, an opening statement or hook is crucial. This can be achieved by incorporating a surprising statistic, a shocking fact, or an interesting anecdote into the beginning of your piece. For example, if you’re writing an essay about water conservation you can begin your essay with, “Clean drinking water, a fundamental human need, remains out of reach for more than one billion people worldwide. It deprives them of a basic human right and jeopardizes their health and wellbeing.” 2. Provide sufficient context or background information An effective introduction should begin with a brief description or background of your topic. This will help provide context and set the stage for your discussion. For example, if you’re writing an essay about climate change, you start by describing the current state of the planet and the impact that human activity is having on it. 3. Construct a well-rounded and comprehensive thesis statement A good introduction should also include the main message or thesis statement of your essay. This is the central argument that you’ll be making throughout the piece. It should be clear, concise, and ideally placed toward the end of the introduction. By including these elements in your introduction, you’ll be setting yourself up for success in the rest of your essay. Let’s take a look at an example. Essay introduction example- Background information
- Thesis statement
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane in 1903 revolutionized the way humans travel and explore the world. Prior to this invention, transportation relied on trains, boats, and cars, which limited the distance and speed of travel. However, the airplane made air travel a reality, allowing people to reach far-off destinations in mere hours. This breakthrough paved the way for modern-day air travel, transforming the world into a smaller, more connected place. In this essay, we will explore the impact of the Wright Brothers’ invention on modern-day travel, including the growth of the aviation industry, increased accessibility of air travel to the general public, and the economic and cultural benefits of air travel. Body paragraphsYou can persuade your readers and make your thesis statement compelling by providing evidence, examples, and logical reasoning. To write a fool-proof and authoritative essay, you need to provide multiple well-structured, substantial arguments. Let’s take a look at how this can be done: 1. Write a topic sentence for each paragraph The beginning of each of your body paragraphs should contain the main arguments that you’d like to address. They should provide ground for your thesis statement and make it well-rounded. You can arrange these arguments in several formats depending on the type of essay you’re writing. 2. Provide the supporting information The next point of your body paragraph should provide supporting information to back up your main argument. Depending on the type of essay, you can elaborate on your main argument with the help of relevant statistics, key information, examples, or even personal anecdotes. 3. Analyze the supporting information After providing relevant details and supporting information, it is important to analyze it and link it back to your main argument. 4. Create a smooth transition to the next paragraphEnd one body paragraph with a smooth transition to the next. There are many ways in which this can be done, but the most common way is to give a gist of your main argument along with the supporting information with transitory words such as “however” “in addition to” “therefore”. Here’s an example of a body paragraph. Essay body paragraph example- Topic sentence
- Supporting information
- Analysis of the information
- Smooth transition to the next paragraph
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane revolutionized air travel. They achieved the first-ever successful powered flight with the Wright Flyer in 1903, after years of conducting experiments and studying flight principles. Despite their first flight lasting only 12 seconds, it was a significant milestone that paved the way for modern aviation. The Wright Brothers’ success can be attributed to their systematic approach to problem-solving, which included numerous experiments with gliders, the development of a wind tunnel to test their designs, and meticulous analysis and recording of their results. Their dedication and ingenuity forever changed the way we travel, making modern aviation possible. A powerful concluding statement separates a good essay from a brilliant one. To create a powerful conclusion, you need to start with a strong foundation. Let’s take a look at how to construct an impactful concluding statement. 1. Restructure your thesis statement To conclude your essay effectively, don’t just restate your thesis statement. Instead, use what you’ve learned throughout your essay and modify your thesis statement accordingly. This will help you create a conclusion that ties together all of the arguments you’ve presented. 2. Summarize the main points of your essay The next point of your conclusion consists of a summary of the main arguments of your essay. It is crucial to effectively summarize the gist of your essay into one, well-structured paragraph. 3. Create a lasting impression with your concluding statement Conclude your essay by including a key takeaway, or a powerful statement that creates a lasting impression on the reader. This can include the broader implications or consequences of your essay topic. Here’s an example of a concluding paragraph. Essay conclusion example- Restated thesis statement
- Summary of the main points
- Broader implications of the thesis statement
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane forever changed history by paving the way for modern aviation and countless aerospace advancements. Their persistence, innovation, and dedication to problem-solving led to the first successful powered flight in 1903, sparking a revolution in transportation that transformed the world. Today, air travel remains an integral part of our globalized society, highlighting the undeniable impact of the Wright Brothers’ contribution to human civilization. Types of essaysMost essays are derived from the combination or variation of these four main types of essays . let’s take a closer look at these types. 1. Narrative essay A narrative essay is a type of writing that involves telling a story, often based on personal experiences. It is a form of creative nonfiction that allows you to use storytelling techniques to convey a message or a theme. 2. Descriptive essay A descriptive essay aims to provide an immersive experience for the reader by using sensory descriptors. Unlike a narrative essay, which tells a story, a descriptive essay has a narrower scope and focuses on one particular aspect of a story. 3. Argumentative essays An argumentative essay is a type of essay that aims to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance based on factual evidence and is one of the most common forms of college essays. 4. Expository essays An expository essay is a common format used in school and college exams to assess your understanding of a specific topic. The purpose of an expository essay is to present and explore a topic thoroughly without taking any particular stance or expressing personal opinions. While this article demonstrates what is an essay and describes its types, you may also have other doubts. As experts who provide essay editing and proofreading services , we’re here to help. Our team has created a list of resources to clarify any doubts about writing essays. Keep reading to write engaging and well-organized essays! - How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps
- How to Write an Essay Header
- How to Write an Essay Outline
Frequently Asked QuestionsWhat is the difference between an argumentative and an expository essay, what is the difference between a narrative and a descriptive essay, what is an essay format, what is the meaning of essay, what is the purpose of writing an essay. Found this article helpful? Leave a Comment: Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’reYour organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing. Subscribe to our Newsletter Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox. How to Copyright Your Book? If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path. © 2024 All rights reserved - Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
 In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.  Chart your future IT career with AI at CambridgeThis expert advice article aims to clarify the fundamental difference between essay and paragraph, helping readers to understand their unique characteristics and proper usage in academic writing. By exploring their structures, purposes and examples, we can highlight why a paragraph and an essay are not the same. Table of ContentsParagraph vs essay: unraveling the difference.  Key Takeaways Shortly- A paragraph is a unit of writing that focuses on a specific idea or point, and has a defined structure and purpose in academic writing.
- An essay is a more complex form of academic writing, with a broader scope and a more detailed structure than a paragraph.
- The difference between a paragraph and an essay lies in their purpose, structure, and scope. They are not interchangeable in academic writing.
- Writing effective paragraphs requires clarity, conciseness, and cohesion to convey the intended message effectively.
- Mastering essay writing involves careful planning, structuring, and refining to ensure it meets academic standards.
Welcome to this enlightening journey where we will explore the key differences between a paragraph and an essay. You know, it’s a common mistake to think that these two are the same. But, let me tell you, they are not. They are as distinct as apples and oranges. This article will serve as your guide, offering expert advice on this topic. We will discuss the specific characteristics of both paragraphs and essays and why they are not interchangeable. This interesting exploration will provide you with a clearer understanding, so stay with us. It’s going to be a fun ride, I promise. Buckle up!  Understanding the Nature of ParagraphsLet’s talk paragraphs. They’re not as simple as they may first appear. In a nutshell, a paragraph is a group of sentences that focus on one main idea. It’s like a mini-story with a beginning, middle, and end. But here’s a cool fact: according to a study from the University of Nevada, a paragraph can consist of just one sentence or even one word! This goes against what many of us learned in school, but it’s part of what makes writing an art, not just a science. So, a paragraph is not just a cluster of sentences. It’s a unit of thought, delivering one point or argument. In essays, these points build upon each other to support a central thesis. But not every paragraph belongs to an essay, and that’s what makes the difference between essay and paragraph so significant. Oh, and before we forget, don’t overlook the power of a well-crafted paragraph. Even if it’s standing alone, it can tell a powerful story! The Key Elements that Distinguish a Paragraph from an EssayNow, let’s get to the meat and potatoes of our discussion: the key elements that create the difference between essay and paragraph. Firstly, a paragraph is, well, just a single block of text. It’s like a single slice of bread. It’s a self-contained unit of a discourse in writing dealing with a particular point or idea. A paragraph will usually contain a single main idea and revolve around that point. On the other hand, an essay is more like a whole sandwich. It’s a short piece of writing on a particular subject, and it’s made up of many paragraphs. An essay will have a clear structure, including an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. In essence, a paragraph is a component of an essay. It’s one part of the whole. But an essay? Well, it’s the whole enchilada. It’s a comprehensive argument or discourse about a topic. And yes, while a paragraph can stand alone as a complete piece, an essay is a connected series of paragraphs that work together to explore a topic in depth. So, you see, while they are related, they are not the same thing. Not by a long shot. And hey, just because an essay is longer doesn’t mean it’s harder or more important. It’s just different, you know? Each has its own role to play in the world of writing. So, keep this in mind next time you’re writing, okay? How Do Essays Encourage Detailed Exploration?An essay, unlike a paragraph, is like a journey through a topic. It’s not a quick stop, but more like a thorough exploration. You know, like going on a road trip rather than just a quick drive around the block. An essay allows, or rather demands, more in-depth analysis. It’s like a detective piecing together clues. There’s a clear beginning, middle, and end. The writer starts by introducing the topic, discussing it in detail, and then wrapping it up nicely. An essay also gives room for the writer’s voice to shine through. This isn’t just about facts and figures, it’s about painting a picture with words. It’s like telling a story, and the writer is the narrator. This space for creativity and personal touch is what makes essays stand out. You see, in an essay, each paragraph is like a piece of a puzzle. Each one adds a new piece of information, a new perspective, or a new argument to the overall picture. So, in a way, an essay is made up of many ‘mini paragraphs’, each serving its own purpose. So, it’s clear as day, ain’t it? Essays are not the same as paragraphs. They’re more complex, more detailed, and more personal. They’re not just about conveying information, they’re about exploring a topic in depth. They’re about starting a conversation, not just stating facts. And that, my friend, is the real beauty of an essay.  Wrapping Up: The Essay vs Paragraph ShowdownLooking back at our exploration of the difference between an essay and a paragraph, it’s clear that these two forms of writing, while closely related, have distinctive characteristics that set them apart. A paragraph is a smaller piece, focusing on a single idea or topic. It’s like a building block, the first step in constructing a larger piece. On the other hand, an essay is a more complex structure. It’s made up of various paragraphs, each contributing to the overall argument or narrative. Just like a house is built from bricks, an essay is built from paragraphs. Isn’t it fascinating how the same words and sentences can take on such different roles depending on how we use them? It’s like a magic trick, you see? The words are our tools, and we, the writers, are the magicians. So, next time you’re tasked with writing an essay or a paragraph, remember this simple difference. Take a moment to plan out your work. If it’s a paragraph, focus on one single idea. If it’s an essay, think about how you can arrange several ideas to create a coherent and convincing argument. Now, isn’t it about time you tried it out for yourself? Why not pick up a pen, or open up your laptop, and start practicing? Who knows, you might just end up surprising yourself with your own writing skills. And hey, don’t forget to have some fun along the way. After all, writing is not just about following rules, it’s about expressing yourself and sharing your thoughts with the world. So, go ahead and add your own splash of creativity. It’s your turn now, my fellow writer. Happy writing! What is a Paragraph?A paragraph is a distinct section of a piece of writing, typically dealing with a single theme and indicated by a new line, indentation, or numbering. It usually contains a topic sentence, supporting sentences and a concluding sentence. The purpose of a paragraph is to express a single idea or concept related to the overall topic of the text. Examples can range from descriptive paragraphs in a novel to explanatory paragraphs in an academic paper. In broader academic writing, a paragraph serves as an essential building block in constructing a more complex argument or narrative. What Makes an Essay?An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument or a perspective on a particular topic. It is typically composed of multiple paragraphs, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each of these paragraphs serves a specific function within the overall essay. Unlike a paragraph, an essay is a more complex and comprehensive piece of writing that explores a topic in depth. Examples can range from persuasive essays to research papers. Why is a Paragraph Not an Essay?While both a paragraph and an essay serve to convey ideas and arguments, they differ significantly in their purpose, structure, and scope. A paragraph is a single unit of thought within a larger piece of writing, while an essay is a complete piece of writing on its own. The purpose of a paragraph is to present a single point or idea, whereas an essay aims to explore a topic in depth, often presenting multiple points or arguments. The structure of a paragraph is simpler, typically containing a topic sentence and supporting sentences, while an essay has a more complex structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. How to Write Effective Paragraphs?Writing effective paragraphs involves clear planning and organization. Begin with a strong topic sentence that clearly states the main idea of the paragraph. Follow this with supporting sentences that expand on the topic sentence with details, examples, or evidence. Finally, conclude the paragraph with a sentence that summarises the main idea and provides a transition to the next paragraph. Ensure that each sentence in the paragraph contributes to the overall idea and that the paragraph maintains a consistent focus. Mastering Essay Writing: Some Useful TipsMastering essay writing requires practice and a clear understanding of the structure and purpose of an essay. Begin by planning your essay, outlining the main points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support them. Write an engaging introduction that clearly states your thesis or main argument. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point or argument, supported by evidence. Finally, conclude your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis. Always remember to revise and edit your essay to ensure it is clear, concise, and free of errors. How useful was this post? Click on a star to rate it! Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0 No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post. - Engage with pure learning, not with assessments.
- Interact directly with Cambridge PhDs.
- Understand AI's real-world impact.
- Add Cambridge prestige to your university application.
 No comments yet. Leave a comment Cancel replyYour email address will not be published. Required fields are marked * See Other Posts See Recent Posts Search Your Best Result TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution. Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis. - picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
 What is a Paragraph? Definition, Examples of ParagraphsHome » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is a Paragraph? Definition, Examples of Paragraphs Paragraph definition: A paragraph is a unit of writing in a larger body of work. A paragraph expresses a particular topic or theme. What is a Paragraph?A paragraph is a component of fictional prose and non-fiction writings. When writing essays, research papers, books, etc., new paragraphs are indented to show their beginnings. Each new paragraph begins with a new indentation. The purpose of a paragraph is to express a speaker’s thoughts on a particular point in a clear way that is unique and specific to that paragraph. In other words, paragraphs shouldn’t be mixing thoughts or ideas. When a new idea is introduced, generally, a writer will introduce a new paragraph. Basic Paragraph Structure: How to Layout a ParagraphIn non-fiction writing, a body paragraph is any paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion. A good body paragraph will have the following: Topic Sentence Supporting SentencesWhat is a supporting sentence? The supporting sentences of a paragraph are the sentences between the topic sentence and the concluding sentence. The supporting sentences “support” the topic sentence. That is, they explain and elaborate the point of the paragraph. Concluding Sentence Other Features of ParagraphsA good paragraph contains many elements. Here are just a few of them. Unity, Coherence A paragraph should be organized in a way that it builds appropriately. This could be by sequence of ideas or events. Additionally, transitions should be used from one sentence to the next that connect the ideas and concepts. Adequate DevelopmentIn order for a paragraph to be considered “adequate” or “sufficient,” the paragraph should be well-developed. The reader should not be left wanting more information. Similarly, the paragraph should include enough evidence to support its topic sentence. Transitions One paragraph should logically flow to the next. The ideas in a body of work should be organized so each paragraph transitions well to the next. It should not be choppy. Additionally, verbal transitions within and between paragraphs should help the reader move seamlessly through the piece of writing. How Long is a Paragraph? Paragraphs need to be long enough to express any given idea (long enough to thoroughly explain the topic sentence). Research papers may call for paragraphs ten sentences or longer. The overall topic of the writing and content will determine the length of a paragraph. Unfortunately, there is no single number of sentences to a good paragraph. A general rule of thumb is to begin with a topic sentence; develop that topic well with evidence, examples, and explanations; and conclude the paragraph appropriately. Summary: What are Paragraphs?Define paragraph: the definition of paragraph is a group of sentence in which a single topic is developed. In summary, a paragraph is: - a unit of writing
- used in non-fiction and fictional prose
- a part of writing that expresses a certain topic
Have a language expert improve your writingRun a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free. - Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & ExamplesPublished on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023. Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them. Instantly correct all language mistakes in your textUpload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes  Table of contentsWhen should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting. Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts. - Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach. One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made. Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments. Receive feedback on language, structure, and formattingProfessional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on: - Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example  As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place. For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies. This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader. Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example. Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them. | Behaviorism | Cognitive psychology | | Dominant from the 1920s to the 1950s | Rose to prominence in the 1960s | | Mental processes cannot be empirically studied | Mental processes as focus of study | | Focuses on how thinking is affected by conditioning and environment | Focuses on the cognitive processes themselves | Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram. 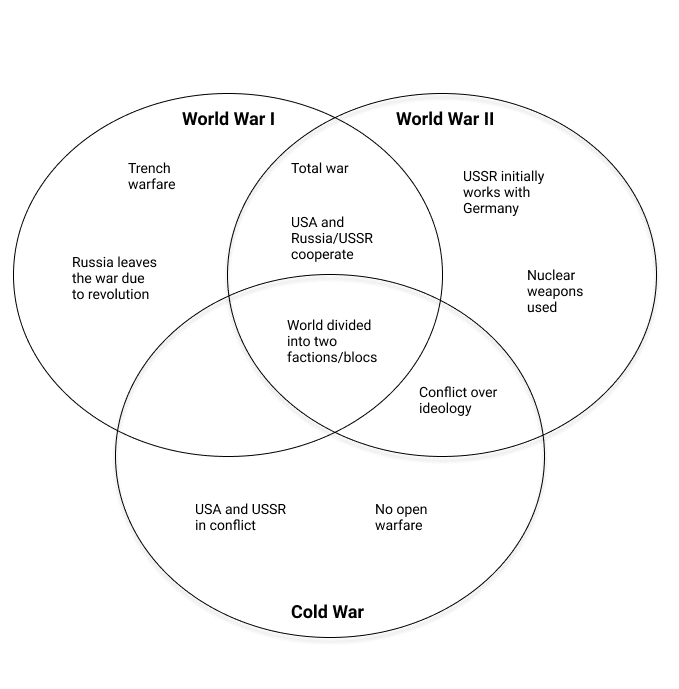 These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments. When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method. The alternating methodIn the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this: Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works. One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves. The block methodIn the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this: - Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others. Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph. Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools! - Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays - Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools - Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response. Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework . Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison. You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing. Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways: - The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric. Cite this Scribbr articleIf you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator. Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/ Is this article helpful? Jack CaulfieldOther students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..". I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes” Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts On Paragraphs Welcome to the Purdue OWLThis page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice. Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use. What is a paragraph?A paragraph is a collection of related sentences dealing with a single topic. Learning to write good paragraphs will help you as a writer stay on track during your drafting and revision stages. Good paragraphing also greatly assists your readers in following a piece of writing. You can have fantastic ideas, but if those ideas aren't presented in an organized fashion, you will lose your readers (and fail to achieve your goals in writing). The Basic Rule: Keep one idea to one paragraphThe basic rule of thumb with paragraphing is to keep one idea to one paragraph. If you begin to transition into a new idea, it belongs in a new paragraph. There are some simple ways to tell if you are on the same topic or a new one. You can have one idea and several bits of supporting evidence within a single paragraph. You can also have several points in a single paragraph as long as they relate to the overall topic of the paragraph. If the single points start to get long, then perhaps elaborating on each of them and placing them in their own paragraphs is the route to go.  Elements of a paragraphTo be as effective as possible, a paragraph should contain each of the following: Unity, Coherence, A Topic Sentence, and Adequate Development. As you will see, all of these traits overlap. Using and adapting them to your individual purposes will help you construct effective paragraphs. The entire paragraph should concern itself with a single focus. If it begins with one focus or major point of discussion, it should not end with another or wander within different ideas. Coherence is the trait that makes the paragraph easily understandable to a reader. You can help create coherence in your paragraphs by creating logical bridges and verbal bridges. Logical bridges - The same idea of a topic is carried over from sentence to sentence
- Successive sentences can be constructed in parallel form
Verbal bridges - Key words can be repeated in several sentences
- Synonymous words can be repeated in several sentences
- Pronouns can refer to nouns in previous sentences
- Transition words can be used to link ideas from different sentences
A topic sentenceA topic sentence is a sentence that indicates in a general way what idea or thesis the paragraph is going to deal with. Although not all paragraphs have clear-cut topic sentences, and despite the fact that topic sentences can occur anywhere in the paragraph (as the first sentence, the last sentence, or somewhere in the middle), an easy way to make sure your reader understands the topic of the paragraph is to put your topic sentence near the beginning of the paragraph. (This is a good general rule for less experienced writers, although it is not the only way to do it). Regardless of whether you include an explicit topic sentence or not, you should be able to easily summarize what the paragraph is about. Adequate developmentThe topic (which is introduced by the topic sentence) should be discussed fully and adequately. Again, this varies from paragraph to paragraph, depending on the author's purpose, but writers should be wary of paragraphs that only have two or three sentences. It's a pretty good bet that the paragraph is not fully developed if it is that short. Some methods to make sure your paragraph is well-developed: - Use examples and illustrations
- Cite data (facts, statistics, evidence, details, and others)
- Examine testimony (what other people say such as quotes and paraphrases)
- Use an anecdote or story
- Define terms in the paragraph
- Compare and contrast
- Evaluate causes and reasons
- Examine effects and consequences
- Analyze the topic
- Describe the topic
- Offer a chronology of an event (time segments)
How do I know when to start a new paragraph?You should start a new paragraph when: - When you begin a new idea or point. New ideas should always start in new paragraphs. If you have an extended idea that spans multiple paragraphs, each new point within that idea should have its own paragraph.
- To contrast information or ideas. Separate paragraphs can serve to contrast sides in a debate, different points in an argument, or any other difference.
- When your readers need a pause. Breaks between paragraphs function as a short "break" for your readers—adding these in will help your writing be more readable. You would create a break if the paragraph becomes too long or the material is complex.
- When you are ending your introduction or starting your conclusion. Your introductory and concluding material should always be in a new paragraph. Many introductions and conclusions have multiple paragraphs depending on their content, length, and the writer's purpose.
Transitions and signpostsTwo very important elements of paragraphing are signposts and transitions. Signposts are internal aids to assist readers; they usually consist of several sentences or a paragraph outlining what the article has covered and where the article will be going. Transitions are usually one or several sentences that "transition" from one idea to the next. Transitions can be used at the end of most paragraphs to help the paragraphs flow one into the next.  Comparing and ContrastingWhat this handout is about. This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.” IntroductionIn your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them. Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignmentsSome assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples: - Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both. But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment: - Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips. Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projectsSometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper. Discovering similarities and differencesMaking a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places: 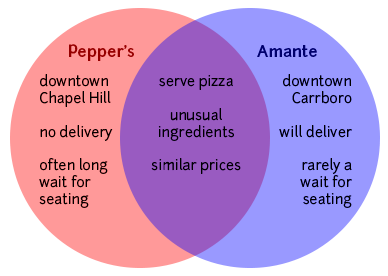 To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered. Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places: | Pepper’s | Amante | Papa John’s | | Location | | | | | Price | | | | | Delivery | | | | | Ingredients | | | | | Service | | | | | Seating/eating in | | | | | Coupons | | | | As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself? Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location. Two historical periods or events- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus onBy now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions: - What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper. Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems. Your thesisThe thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.” Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier: Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture. You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage. Organizing your paperThere are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two: Subject-by-subjectBegin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion. The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together. A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second. Point-by-pointRather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants. If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant. There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you. Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper. Cue words and other tipsTo help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions: - like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these: - Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Make a Gift  Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. 10.7 Comparison and ContrastLearning objectives. - Determine the purpose and structure of comparison and contrast in writing.
- Explain organizational methods used when comparing and contrasting.
- Understand how to write a compare-and-contrast essay.
The Purpose of Comparison and Contrast in WritingComparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay , then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both. The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. The purpose of conducting the comparison or contrast is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities. For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic. Drawing distinctions between elements in a similar category will increase the audience’s understanding of that category, which is the purpose of the compare-and-contrast essay. Similarly, to focus on comparison, choose two subjects that seem at first to be unrelated. For a comparison essay, you likely would not choose two apples or two oranges because they share so many of the same properties already. Rather, you might try to compare how apples and oranges are quite similar. The more divergent the two subjects initially seem, the more interesting a comparison essay will be. Writing at WorkComparing and contrasting is also an evaluative tool. In order to make accurate evaluations about a given topic, you must first know the critical points of similarity and difference. Comparing and contrasting is a primary tool for many workplace assessments. You have likely compared and contrasted yourself to other colleagues. Employee advancements, pay raises, hiring, and firing are typically conducted using comparison and contrast. Comparison and contrast could be used to evaluate companies, departments, or individuals. Brainstorm an essay that leans toward contrast. Choose one of the following three categories. Pick two examples from each. Then come up with one similarity and three differences between the examples. - Romantic comedies
- Internet search engines
- Cell phones
Brainstorm an essay that leans toward comparison. Choose one of the following three items. Then come up with one difference and three similarities. - Department stores and discount retail stores
- Fast food chains and fine dining restaurants
- Dogs and cats
The Structure of a Comparison and Contrast EssayThe compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader. Take the following thesis as an example that leans more toward contrasting. Thesis statement: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny. Here the thesis sets up the two subjects to be compared and contrasted (organic versus conventional vegetables), and it makes a claim about the results that might prove useful to the reader. You may organize compare-and-contrast essays in one of the following two ways: - According to the subjects themselves, discussing one then the other
- According to individual points, discussing each subject in relation to each point
See Figure 10.1 “Comparison and Contrast Diagram” , which diagrams the ways to organize our organic versus conventional vegetables thesis. Figure 10.1 Comparison and Contrast Diagram 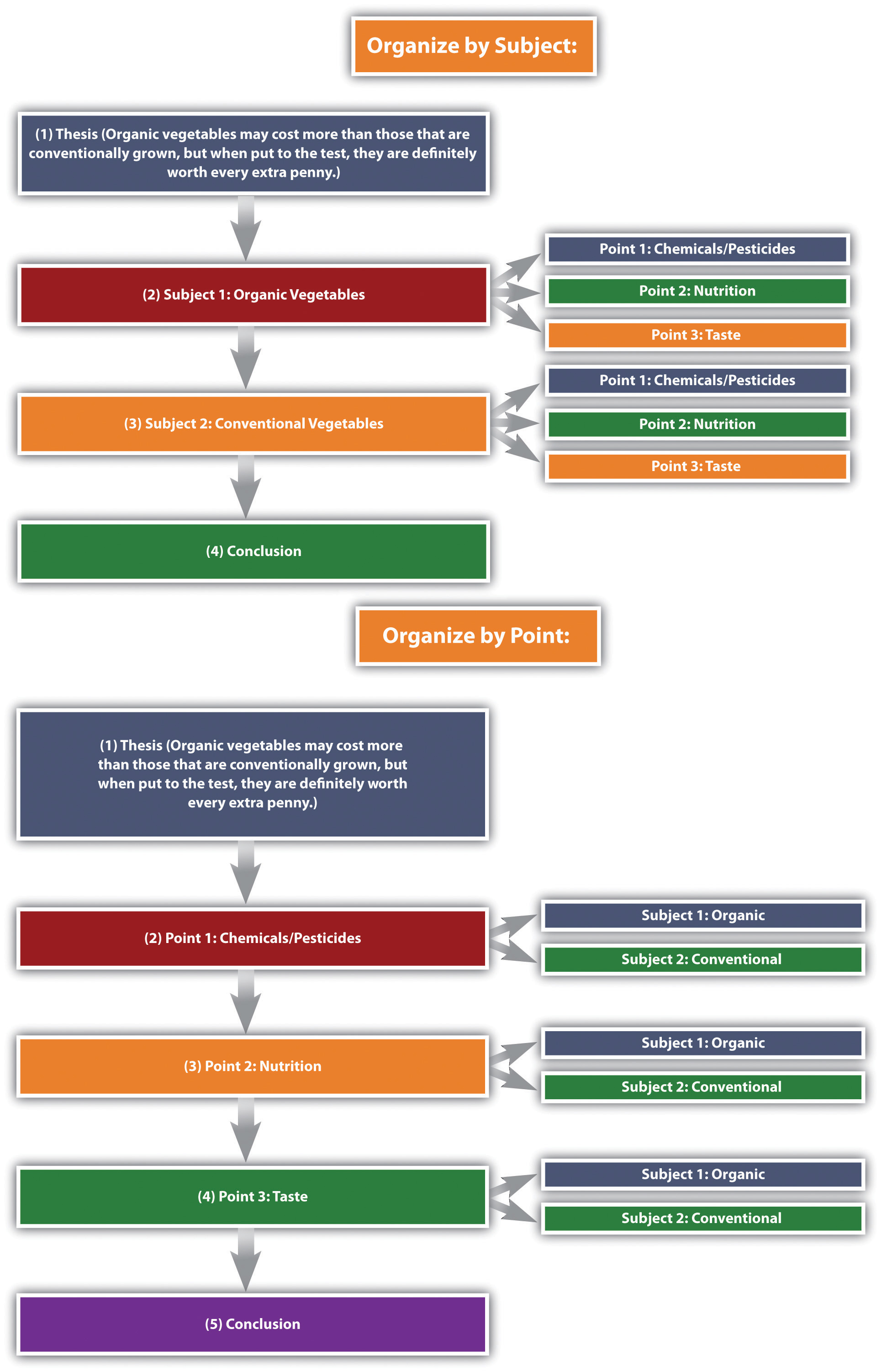 The organizational structure you choose depends on the nature of the topic, your purpose, and your audience. Given that compare-and-contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is helpful to have some phrases on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis. See Table 10.3 “Phrases of Comparison and Contrast” for examples. Table 10.3 Phrases of Comparison and Contrast | Comparison | Contrast | | one similarity | one difference | | another similarity | another difference | | both | conversely | | like | in contrast | | likewise | unlike | | similarly | while | | in a similar fashion | whereas | Create an outline for each of the items you chose in Note 10.72 “Exercise 1” and Note 10.73 “Exercise 2” . Use the point-by-point organizing strategy for one of them, and use the subject organizing strategy for the other. Writing a Comparison and Contrast EssayFirst choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so. The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects. After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis. See Chapter 15 “Readings: Examples of Essays” to read a sample compare-and-contrast essay. Many business presentations are conducted using comparison and contrast. The organizing strategies—by subject or individual points—could also be used for organizing a presentation. Keep this in mind as a way of organizing your content the next time you or a colleague have to present something at work. Choose one of the outlines you created in Note 10.75 “Exercise 3” , and write a full compare-and-contrast essay. Be sure to include an engaging introduction, a clear thesis, well-defined and detailed paragraphs, and a fitting conclusion that ties everything together. Key Takeaways- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
There are two main organizing strategies for compare-and-contrast essays. - Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted. Top Streams- Data Science Courses in USA
- Business Analytics Courses in USA
- Engineering Courses in USA
- Tax Courses in USA
- Healthcare Courses in USA
- Language Courses in USA
- Insurance Courses in USA
- Digital Marketing Courses in USA
Top Specialization- Masters in Data Analytics in USA
- Masters in Mechanical Engineering in USA
- Masters in Supply Chain Management in USA
- Masters in Computer Science in USA
- MBA in Finance in USA
- Masters in Architecture in USA
Top Universities- Cornell University
- Yale University
- Princeton University
- University of California Los Angeles
- University of Harvard
- Stanford University
- Arizona State University
- Northeastern University
- Scholarships to Study in USA
- Project Management Courses in Australia
- Accounting Courses in Australia
- Medical Courses in Australia
- Psychology Courses in Australia
- Interior Designing Courses in Australia
- Pharmacy Courses in Australia
- Social Work Courses in Australia
- MBA in Australia
- Masters in Education in Australia
- Masters in Pharmacy in Australia
- Masters in Information Technology in Australia
- BBA in Australia
- Masters in Teaching in Australia
- Masters in Psychology in Australia
- University of Melbourne
- Deakin University
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Monash University
- University of Sydney
- University of Queensland
- RMIT University
- Macquarie University
- PR Courses in Australia
- SOP for Australia Student Visa
- Data Science Courses in Canada
- Business Management Courses in Canada
- Supply Chain Management Courses in Canada
- Project Management Courses in Canada
- Business Analytics Courses in Canada
- Hotel Management Courses in Canada
- MBA in Canada
- MS in Canada
- Masters in Computer Science in Canada
- Masters in Management in Canada
- Masters in Psychology in Canada
- Masters in Education in Canada
- MBA in Finance in Canada
- Masters in Business Analytics in Canada
- University of Toronto
- University of British Columbia
- McGill University
- University of Alberta
- York University
- University of Calgary
- Algoma University
- University Canada West
- IELTS requirement for Canada Student Visa
- Canada Visa Interview
- Top cities in Canada for International Students
- Project Management Courses in UK
- Data Science Courses in UK
- Public Health Courses in UK
- Digital Marketing Courses in UK
- Hotel Management Courses in UK
- Nursing Courses in UK
- Medicine Courses in UK
- Interior Designing Courses in UK
- Masters in Computer Science in UK
- Masters in Psychology in UK
- MBA in Finance in UK
- MBA in Healthcare Management in UK
- Masters in Education in UK
- Masters in Marketing in UK
- MBA in HR in UK
- University of Oxford
- University of Cambridge
- Coventry University
- University of East London
- University of Hertfordshire
- University of Birmingham
- Imperial College London
- University of Glasgow
Top Resources- Universities in Germany
- Study in Germany
- Masters in Germany
- Courses in Germany
- Bachelors in Germany
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Cost of Living in Germany
- Best Universities in Germany
Top Courses- Masters in Data Science in Germany
- MS in Computer Science in Germany
- Marine Engineering in Germany
- MS Courses in Germany
- Masters in Psychology in Germany
- Hotel Management Courses in Germany
- Masters in Economics in Germany
- Paramedical Courses in Germany
- Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- University of Bonn
- University of Freiburg
- University of Hamburg
- University of Stuttgart
- Saarland University
- Mannheim University
- MBA in Ireland
- Phd in Ireland
- Masters in Computer Science Ireland
- Cyber Security in Ireland
- Masters in Data Analytics Ireland
- Ms in Data Science in Ireland
- Pharmacy courses in ireland
- Business Analytics Course in Ireland
- Universities in Ireland
- Study in Ireland
- Masters in Ireland
- Courses in Ireland
- Bachelors in Ireland
- Cost of Living in Ireland
- Ireland Student Visa
- Part Time Jobs in Ireland
- Trinity College Dublin
- University College Dublin
- Dublin City University
- University of Limerick
- Dublin Business School
- Maynooth University
- University College Cork
- National College of Ireland
Colleges & Courses- Masters in France
- Phd in France
- Study Medicine in France
- Best Universities in Frankfurt
- Best Architecture Colleges in France
- ESIGELEC France
- Study in France for Indian Students
- Intakes in France
- SOP for France Visa
- Study in France from India
- Reasons to Study in France
- How to Settle in France
More About France- Cost of Living in France
- France Study Visa
- Cost of Living in Frankfurt
- France Scholarship for Indian Students
- Part Time Jobs in France
- Stay Back in France After Masters
About Finland- Universities in Finland
- Study in Finland
- Courses in Finland
- Bachelor Courses in Finland
- Masters Courses in Finland
- Cost of Living in Finland
- MS in Finland
- Average Fees in Finland Universities
- PhD in Finland
- Jobs in Finland
- Bachelor Degree in Medicine & Surgery
- MBBS Courses in Georgia
- MBBS Courses in Russia
- Alte University
- Caucasus University
- Georgian National University SEU
- David Tvildiani Medical University
- Caspian International School Of Medicine
- Asfendiyarov Kazakh National Medical University
- Kyrgyz State Medical Academy
- Cremeia Federal University
- Bashkir State Medical University
- Kursk State Medical University
- Andijan State Medical Institute
- IELTS Syllabus
- IELTS Prepration
- IELTS Eligibility
- IELTS Test Format
- IELTS Band Descriptors
- IELTS Speaking test
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS score validity
- IELTS Cue Card
IELTS Reading Answers Sample- Animal Camouflage
- Types Of Societies
- Australia Convict Colonies
- A Spark A Flint
- Emigration To The Us
- The History Of Salt
- Zoo Conservation Programmes
- The Robots Are Coming
- The Development Of Plastic
IELTS Speaking Cue Card Sample- Describe A Puzzle You Have Played
- Describe A Long Walk You Ever Had
- Describe Your Favourite Movie
- Describe A Difficult Thing You did
- Describe A Businessman You Admire
- Memorable Day in My Life
- Describe Your Dream House
- Describe A Bag You Want to Own
- Describe a Famous Athlete You Know
- Aquatic Animal
IELTS Essay Sample Sample- Best Education System
- IELTS Opinion Essay
- Agree or Disagree Essay
- Problem Solution Essays
- Essay on Space Exploration
- Essay On Historical Places
- Essay Writing Samples
- Tourism Essay
- Global Warming Essay
- GRE Exam Fees
- GRE Exam Syllabus
- GRE Exam Eligibility
- Sections in GRE Exam
- GRE Exam Benefits
- GRE Exam Results
- GRE Cutoff for US Universities
- GRE Preparation
- Send GRE scores to Universities
GRE Exam Study Material- GRE Verbal Preparation
- GRE Study Material
- GRE AWA Essays
- GRE Sample Issue Essays
- Stanford University GRE Cutoff
- Harvard University GRE Cutoff
- GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- GRE Verbal Reasoning
- GRE Reading Comprehension
- Prepare for GRE in 2 months
Other Resources- Documents Required For Gre Exam
- GRE Exam Duration
- GRE at Home
- GRE vs GMAT
- Improve GRE Verbal Scores
Free GRE Ebooks- GRE Preparation Guide (Free PDF)
- GRE Syllabus (Free PDF)
- GMAT Eligibility
- GMAT Syllabus
- GMAT Exam Dates
- GMAT Registration
- GMAT Exam Fees
- GMAT Sections
- GMAT Purpose
GMAT Exam Study Material- How to prepare for GMAT?
- GMAT Score Validity
- GMAT Preparation Books
- GMAT Preparation
- GMAT Exam Duration
- GMAT Score for Harvard
- GMAT Reading Comprehension
- GMAT Retake Strategy
Free GMAT Ebooks- GMAT Guide PDF
- Download GMAT Syllabus PDF
- TOEFL Exam Registration
- TOEFL Exam Eligibility
- TOEFL Exam Pattern
- TOEFL Exam Preparation
- TOEFL Exam Tips
- TOEFL Exam Dates
- Documents for TOEFL Exam
- TOEFL Exam Fee
TOEFL Exam Study Material- TOEFL Preparation Books
- TOEFL Speaking Section
- TOEFL Score and Results
- TOEFL Writing Section
- TOEFL Reading Section
- TOEFL Listening Section
- TOEFL Vocabulary
- Types of Essays in TOEFL
Free TOEFL Ebooks- TOEFL Exam Guide (Free PDF)
- PTE Exam Dates
- PTE Exam Syllabus
- PTE Exam Eligibility Criteria
- PTE Test Centers in India
- PTE Exam Pattern
- PTE Exam Fees
- PTE Exam Duration
- PTE Exam Registration
PTE Exam Study Material- PTE Exam Preparation
- PTE Speaking Test
- PTE Reading Test
- PTE Listening Test
- PTE Writing Test
- PTE Essay Writing
- PTE exam for Australia
Free PTE Ebooks- PTE Syllabus (Free PDF)
- Duolingo Exam
- Duolingo Test Eligibility
- Duolingo Exam Pattern
- Duolingo Exam Fees
- Duolingo Test Validity
- Duolingo Syllabus
- Duolingo Preparation
Duolingo Exam Study Material- Duolingo Exam Dates
- Duolingo Test Score
- Duolingo Test Results
- Duolingo Test Booking
Free Duolingo Ebooks- Duolingo Guide (Free PDF)
- Duolingo Test Pattern (Free PDF)
NEET & MCAT Exam- NEET Study Material
- NEET Preparation
- MCAT Eligibility
- MCAT Preparation
SAT & ACT Exam- ACT Eligibility
- ACT Exam Dates
- SAT Syllabus
- SAT Exam Pattern
- SAT Exam Eligibility
USMLE & OET Exam- USMLE Syllabus
- USMLE Preparation
- USMLE Step 1
- OET Syllabus
- OET Eligibility
- OET Prepration
PLAB & LSAT Exam- PLAB Exam Syllabus
- PLAB Exam Fees
- LSAT Eligibility
- LSAT Registration
- PLAB Accepted Countries
- TOEIC Result
- Study Guide
Application Process- LOR for Masters
- SOP Samples for MS
- LOR for Phd
- SOP for Internship
- SOP for Phd
- Check Visa Status
- Motivation Letter Format
- Motivation Letter for Internship
- F1 Visa Documents Checklist
Career Prospects- Popular Courses after Bcom in Abroad
- Part Time Jobs in Australia
- Part Time Jobs in USA
- Salary after MS in Germany
- Salary after MBA in Canada
- Average Salary in Singapore
- Higher Studies after MBA in Abroad
- Study in Canada after 12th
- Most Demanding Engineering Fields
Trending Topics- Best Education System in World
- Best Flying Schools in World
- Top Free Education Countries
- Best Countries to Migrate from India
- 1 Year PG Diploma Courses in Canada
- Germany Post Study Work Visa
- Post Study Visa in USA
- Packing List for Indian Students
- Data Science Vs Data Analytics
- Public Vs Private Universities in Germany
- Universities Vs Colleges
- Difference Between GPA and CGPA
- Undergraduate Vs Graduate
- MBA in UK Vs MBA in USA
- Degree Vs Diploma in Canada
- IELTS vs TOEFL
- Duolingo English Test vs. IELTS
- Canada Vs India
- Why Study in Canada
- Cost of Living in Canada
- Education System in Canada
- SOP for Canada
- Summer Intake in Canada
- Spring Intake in Canada
- Winter Intake in Canada
- Accommodation in Canada for Students
- Average Salary in Canada
- Fully Funded Scholarships in Canada
- Why Study in USA
- Cost of Studying in USA
- Spring Intake in USA
- Winter Intake in USA
- Summer Intake in USA
- STEM Courses in USA
- Scholarships for MS in USA
- Acceptable Study Gap in USA
- Interesting Facts about USA
- Free USA course
- Why Study in UK
- Cost of Living in UK
- Cost of Studying in UK
- Education System in UK
- Summer Intake in UK
- Spring Intake in UK
- Student Visa for UK
- Accommodation in UK for Students
- Scholarships in UK
- Why Study in Germany
- Cost of Studying in Germany
- Education System in Germany
- SOP for Germany
- Summer Intake in Germany
- Winter Intake in Germany
- Study Visa for Germany
- Accommodation in Germany for Students
- Free Education in Germany
Country Guides- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- SOP Samples for Canada Student Visa
- US F1 Visa Guide for Aspirants
Exams GuidesRecommended Reads- Fully Funded Masters Guide
- SOP Samples For Australia
- Scholarships for Canada
- Data Science Guide
- SOP for MS in Computer Science
- Study Abroad Exams
- Alumni Connect
- Booster Program
- Scholarship
GPA CALCULATOR Convert percentage marks to GPA effortlessly with our calculator!Expense calculator plan your study abroad expenses with our comprehensive calculator, ielts band calculator estimate your ielts band score with our accurate calculator, education loan calculator discover your eligible loan amount limit with our education calculator, university partner explore growth and opportunities with our university partnership, accommodation discover your perfect study abroad accommodation here, experience-center discover our offline centers for a personalized experience, our offices visit us for expert study abroad counseling.. Difference Between Paragraph and Essay – IELTS Writing Task 2 Samples- IELTS Preparation
- IELTS E-Books
- IELTS Registration
- IELTS Exam Fee
- IELTS Exam Dates 2024
- Documents Required
- IELTS Test Centers
- Test Format
- Band Descriptors
- IELTS Speaking Test
- General Reading Test
- General Writing Task
- IELTS Coaching
- Types of Essays
- IELTS for Australia
- IELTS Results
- Generation Gap Essay
- GPA Calculator
- Study Abroad Consultant In India
- Study Visa Consultants in India
Updated on 10 July, 2024 Urvi Agrawal The difference between an essay and a paragraph is a common topic that you can encounter in the IELTS writing task 2. I have seen many students struggling with the various topics asked in the test. But, with thorough and strategic preparation you can score well in any topic. Here, I have explained how to craft a winning response to the “difference between an essay and a paragraph” task along with some of the key strategies that can help you crack this section of the IELTS exam . Table of ContentsWhat is the difference between paragraph and essay: sample essay 1, is there any difference between paragraph and essay: sample essay 2, frequently asked questions, important ielts exam resources, understanding ielts essay requirement. Before delving into the difference between an essay and a paragraph IELTS writing task, it is important to understand the requirements of the task. This will help you achieve your dream IELTS score and achieve your study abroad dreams. The different types of essays usually asked in the IELTS writing task are: - Opinion Essays
- Discussion Essays
- Problem Solution Essays
- Advantages & Disadvantages Essays
- Double Question Essays
Here’s a detailed guide to help you understand what is expected and how to meet these requirements: Response to Task- Clearly address the main idea.
- Write the topic clearly and comprehensively.
- Include relevant examples to support the given statement.
Ensure Coherent Responses- The structure of the essay should be as follows: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Ensure there is a proper flow between paragraphs.
- Develop each paragraph with a single idea and conclude it within the same paragraph.
- Avoid using unnecessary complex words to convey the idea.
- Avoid grammatical errors and spelling mistakes.
- Include synonyms where required.
Grammatical Range and Accuracy- Use simple sentence structures.
- Ensure the correct use of articles, punctuation, and prepositions.
- Convey complex ideas by creating suitable scenarios.
Tips for Writing Effective EssaySome of the strategies that you can follow to improve your scores in the IELTS writing task 2 are: - Understand the given topic and type of essay.
- Identify the key points to be discussed.
- Plan the essay outline by spending at least 5 to 10 minutes of the given time.
- Every paragraph must convey a single idea and provide a conclusion to the paragraph.
- Use simple and crisp language to ensure the idea behind the essay is communicated clearly.
- Revise the essay by correcting all the spelling, punctuation, or grammatical mistakes.
Paragraphs and essays are different forms of write-ups used to express one's point of view. Both writing pieces should be informational, with an idea explained clearly and concisely. Even though they may appear similar, there exists a difference between paragraphs and essays. A paragraph is a self-sufficient writing unit created with multiple sentences. All these sentences are arranged in an organized manner to convey the author's perspective. Additionally, all the lines must be in coherence with one another. An ideal paragraph should start with an introductory sentence, followed by the text body explaining the topic, and should end with a concluding sentence. A good paragraph will also convey the author's idea to the reader. Each sentence should expand on that point and not stray from the general topic. Usually, paragraphs are composed of 5-7 sentences and don't require much preparation as they do not give out much detail. On the other hand, an essay is a formal write-up consisting of at least 2 to 3 paragraphs. Here, the first paragraph introduces the topic the author plans to discuss in the rest of the essay. The following paragraphs are used to express the views in a detailed manner. Finally, an essay is finished with a concluding paragraph, highlighting the crux of the topic. Explore More Resources About IELTS Essay: In any fictional or non-fictional write-up, we come across multiple texts divided into separate portions for better understanding. Writing sections can be classified as either a paragraph or an essay. Despite the apparent similarities, there is a stark difference between paragraph and essay. A paragraph is an arrangement of multiple sentences. Here, you don't have to form a sync with other parts of the text as it is singular. On the other hand, an essay must follow a specific pattern. It should have an introduction and a conclusion paragraph apart from the general text. You can also add quotes from relevant sources in the essay to make it more credible for the readers. The next difference is the text length in both write-ups. A paragraph is a coherent collection of approximately 5-7 sentences. However, the pattern of an essay has no such limitations. It is composed of multiple paragraphs. Based on the requirements, a short essay can have a minimum of 2-3 paragraphs, and an extensive essay can have 6-8 paragraphs or more. A paragraph is hence a part of an essay. The beginning of a new paragraph is indicated by inserting a line break, while an introductory paragraph marks the beginning of an essay. Read More Essay Samples For IELTS: Download IELTS Preparation Guide For FreeGet to know about the latest updates on the IELTS Exam, Eligibility, Preparation Tips, Test procedure, Exam Pattern, Syllabus, Registration Process, Important Exam Dates, and much more!! This guide is a one-stop solution for every IELTS Aspirant who aims to crack the exam with an impressive band score. Conclusion The IELTS score required is dependent on the country and the university in which you are applying. By practicing thoroughly for topics like the difference between an essay and a paragraph, you can improve your score in the writing task. With the above mentioned strategies, you can surely ace the IELTS Writing Task 2. IELTS Exam OverviewIELTS is required to be taken by international students and workers who wish to study or work in a country where English is the primary language of communication. Know the complete details. IELTS Exam SyllabusWith the right knowledge of the IELTS exam syllabus and pattern, cracking the popular English test won’t be difficult. The IELTS exam pattern encompasses four major sections, i.e. listening, speaking, writing, and reading. Register For IELTSIELTS is the most popular and crucial test for evaluating English language proficiency throughout the world. Learn how to register for the IELTS exam. IELTS Exam Eligibility CriteriaIt becomes necessary for candidates to meet the eligibility for IELTS exam and demonstrate their language proficiency while being assessed on four parameters, namely, Writing, Reading, Speaking and Listening. IELTS Exam FeesThe IELTS exam fee in India varies based on the types of IELTS tests. The link below shows detailed information on the IELTS exam fees. IELTS Exam Dates 2022The IELTS exam dates are allotted on a first-come and first-serve basis. Choose your date and timings beforehand to avoid the delay. You can register for the test both in online and offline mode. IELTS Test Centres in IndiaFully aware of the growing popularity of the language test, we bring to you a list of IELTS exam centers in India. The list will enable aspirants in better planning before registering for the test. Band Score for ReadingIELTS reading band score decides the knowledge and proficiency of the English language of the applicants. IELTS Listening Band ScoreThe listening section evaluates the comprehension level of candidates. The scores also depend on the understanding of different accents and dialects. IELTS Score ValidityThe IELTS score validity for General and Academic is two years across the globe. The IELTS result validity for Canada is two years. There are two types of IELTS tests – i) Academic IELTS and ii) General Training IELTS. Candidates are often confused about making the right choice of IELTS test that can meet their requirements regarding their education or job. Books for IELTS PreparationPicking the best IELTS books for preparation is essential for scoring well. It may seem tough at first but cracking the examination successfully is not impossible. - IELTS Writing Task 2 Topics
Writing task 2 in IELTS is descriptive essay writing. The applicants are supposed to write an essay in response to the statement or situation given in the essay. Tips for IELTS WritingBefore appearing for the test, let’s take a look at the below-mentioned IELTS writing tips and tricks to score well in the writing section. Reading Section IELTSReading is the second part of the IELTS test and takes 60 minutes. It consists of three or sometimes four reading passages to increase difficulty, and there are a total of 40 questions to answer. IELTS Speaking PreparationPlease note that your performance on the speaking test is assessed based on the following criteria- fluency and coherence, grammatical range and accuracy, lexical resource, and pronunciation. Phrases for IELTS SpeakingThere are many phrases for IELTS speaking that a candidate should practice beforehand. If you aim for band 9, you should know these phrases. IELTS is one of the most used English Language Proficiency Tests. The exam is scored in bands. Your IELTS band score determines the performance level of your test. Understanding the IELTS band score is not difficult. The results of the examination are reported on a scale of 9 bands. To book the IELTS exam, the candidates can either visit their nearest test center or book the slot online by visiting the official website of IDP. If they choose to go with the second option, they should follow the steps given below. IELTS Academic Writing Task 1IELTS Academic writing is meant for students who are applying for top-ranked universities and colleges in English-speaking countries. The writing task one is an academic summary writing based on diagrammatic and graphical representation. Writing Task 2 is the second part of the writing section of IELTS, where aspirants are presented with a point of view, argument, or problem and asked to write an essay in response to the question. Writing Task 1 IELTSIn IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 starts with a diagram, a visual representation of information. It can be a table, map, graph, process, diagram, or picture. IELTS Essay SamplesThe essay for IELTS is part of Writing Task 2. It is the same for the General Training and Academic of the IELTS. You will get a topic and have to write an essay on the same. IELTS Cue CardsThe IELTS speaking cue cards come into play for the second part when the candidate will be choosing cue cards and then speaking on a topic for two minutes at least. How many sentences should a typical paragraph contain in an IELTS essay?A paragraph typically contains 3-5 sentences. An essay includes an introduction, body content, and conclusion. It is suggested that candidates include 2 to 3 body paragraphs in the IELTS exam. This strategy can help candidates score well. What is the role of a thesis statement in an essay?A thesis statement plays a prominent role in an IELTS Writing Task 2 essay. This statement conveys the main idea of the given topic. The thesis statement acts as a summary for the examiner about the essay. It represents the writer's opinion on the given topic and is a critical part of the introduction. Can a paragraph be considered an IELTS essay?No, a paragraph can never be considered an essay. A paragraph has no line breaks and includes all text in continuation. On the other hand, an essay has several line breaks marking the beginning of each paragraph. Also, an essay consists of several paragraphs. How many paragraphs are required in an IELTS essay?All essays in IELTS must have an introduction and conclusion. This is two paragraphs. Additionally, the body must be divided into 2-3 paragraphs. Therefore, the total number of paragraphs your IELTS essay must have is 4 to 5. Urvi has 3 years of experience as a content writer and marketer. Over years, she has established herself as a study-abroad expert and is adept at crafting compelling and engaging content for students. Self-driven and passionate professional, she likes writing poetry and has authored a poetry book ‘Thoughts of a Wallflower’. Important ExamsImportant ielts essay resources, get free consultation for ielts, refer your friend & earn upto ₹15000. Help your friend upgrade to a Global Career and earn rewards together. TRENDING SEARCHESEditor's pick, other countries. - BSc in Nursing
- Bachelors in Aviation
- MA in Communication
- Masters in Accounting
- University of Adelaide
- University of Melbourne Courses
- Courses in Australia
- Masters in Australia
- Masters in Public Health in Australia
- MS in Australia
- Nursing Courses in Australia
- Universities in Australia
- La Trobe University
- Masters in Business Analytics in Australia
- Concordia University
- University of Windsor
- Masters in Data Science in Canada
- Masters in Canada
- Thompson Rivers University
- Universities in Canada
- Courses in Canada
- University of Victoria
- University of Manitoba
- Trent University
- University of Saskatchewan
- University of Bristol
- Liverpool John Moores University Ranking
- University of Leicester Ranking
- Northumbria University Ranking
- University of Sussex Ranking
- Kings College London
- University of Oxford Courses
- Birmingham City University
- Bachelors in UK
- University of Leicester
- Masters in UK
- University of Strathclyde Ranking
- University of Cambridge Courses
- Universities in UK
- De Montfort University
- Courses in UK
- Queen Mary University of London Ranking
- Queen Mary University of London
- University of West London Ranking
- Manchester Metropolitan University Ranking
- University of Texas at Dallas ranking
- DePaul University
- Courses in USA
- George Mason University ranking
- DePaul University Ranking
- Universities in USA
- Saint Louis University Ranking
- Pace University
- Saint Louis University
- New York University Ranking
- New York University
- Bachelors in USA
- Northeastern University acceptance rate
- Columbia University Acceptance Rate
- University of Texas at Arlington ranking
- University of South Florida ranking
- University of Dayton ranking
- Columbia University Ranking
- Masters in USA
- Drexel University Ranking
- masters in computer science in usa
- University at Buffalo
- Purdue University
- Northeastern University ranking
- Purdue University ranking
- George Mason University
- Duolingo Certificate
- IELTS Speaking Scores
- Duolingo Accepted Universities In Australia
- IELTS Introduction Sample
- SAT Exam Syllabus
- Duolingo Exam Fee
- Gre Exam Fee in India
- CEFR Level in IELTS
- Duolingo Accepted Universities In Canada
- MBA In UK Without Gmat
- Top Phrases for IELTS Speaking Test
- 22 July IELTS Exam
- How to download IELTS Scorecard
- Universities in Canada Without IELTS
- Usmle Test Centers In India
- IELTS Common Speaking Topics
- Minimum IELTS Score For Canada
- Gmat Syllabus
- Duolingo vs IELTS
- GRE Waived University In Usa
- Technological University Dublin
- National University of Ireland Galway Courses
- Dublin City University Courses
- University of Limerick Courses
- University of Europe for Applied Sciences Acceptance Rate
- Universities in Netherlands
- Study in Netherlands
- Dundalk Institute of Technology Courses
- Technological University Dublin Courses
- Dundalk Institute of Technology
- Masters Courses in Netherlands
- Maynooth University Courses
- Courses in Netherlands
- Business Courses in Ireland
The above tips are the Author's experiences. upGrad does not guarantee scores or admissions. Call us to clear your doubts at: - Grievance Redressal
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Report a Vulnerability
- University Partner
- Accommodation
- IELTS Band Calculator
- Download Study Abroad App
- Education Loan Calculator
- upGrad Abroad Office
- Expense Calculator
- Knowledge Base
- Business Partner
Top DestinationsMasters programs. - MBA in Germany, IU
- MIM in Germany, IU
- MS in CS in Germany, IU
- MS in Data Analytics in USA, Clark University
- MS in Project Management in USA, Clark University
- MS in IT in USA, Clark University
- MS in Data Analytics & Visualization in USA, Yeshiva University
- MS in Artificial Intelligence in USA, Yeshiva University
- MS in Cybersecurity, Yeshiva University
Study Abroad Important Blogs- Cost of Study:
- Cost of Studying in Canada
- Cost of Studying in Ireland
- Cost of Studying in Australia
- Cost of living:
- Cost of living in UK
- Cost of living in Australia
- Cost of living in Germany
- Cost of living in Ireland
- Cost of living in Canada
- Cost of Living in Singapore
- Cost of Living in Netherlands
- Career Opportunities:
- Career Opportunities in Australia
- Career Opportunities in Germany
- Job Opportunities in After MS in Canada
- Job Opportunities After MBA in Australia
- Job Opportunities After MS in UK
- IELTS Exam Resources:
- Academic IELTS
- IELTS Score for UK
- IELTS Score for USA
- Validity of IELTS Score
- IELTS Speaking Topics
- IELTS Reading Tips
- How to Prepare for IELTS at Home Without Coaching
- IELTS Preparation Books
- IELTS Academic vs General
- IELTS Essay
- IELTS Exam Dates
- Top Streams:
- Fashion Designing Courses in Australia
- Accounting Courses in Canada
- Management Courses in Canada
 Comparison Contrast EssayComparison contrast essay generator.  The art of essay writing is a skill that is not only essential for students but also for professionals. It is a tool that helps in expressing thoughts, ideas, and arguments in a structured and coherent manner. Among the various types of essays, the Comparison and Contrast Essay holds a unique place. This article will guide you through 29+ Comparison and Contrast Essay Examples available in Google Docs, Word, PDF, and will also provide a step-by-step guide on how to write one. 1. Comparison And Contrast Essay Example 2. Sample Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 45 KB 3. Comparison and Contrast Essay Structure Example 4. College Level Comparison and Contrast Essay Example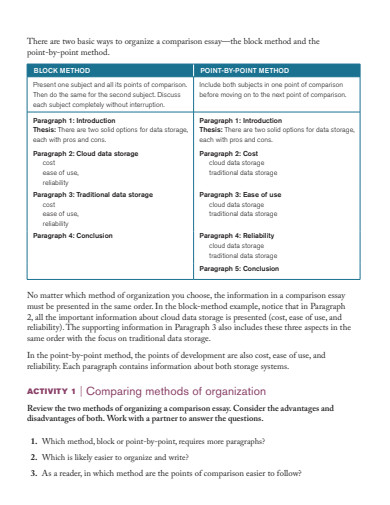 Size: 45 MB 5. Comparison and Contrast Essay Technology Example Size: 14 KB 6. Comparison and Contrast Essay Body Paragraph Example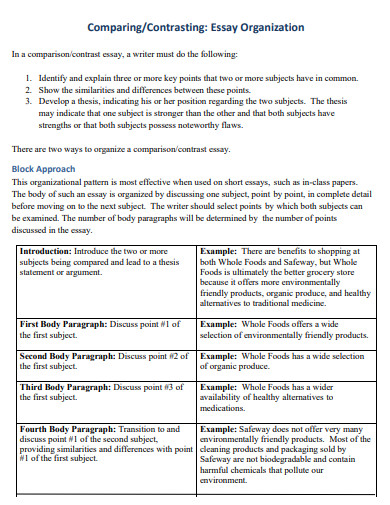 Size: 134 KB 7. Comparison and Contrast Essay Thesis Statement Example Size: 366 KB 8. College Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 141 KB 9. Comparison and Contrast Essay Rough Draft Example Size: 115 KB 10. Comparison and Contrast Essay Similarities Example Size: 539 KB 11. Comparison and Contrast Essay Final Draft Example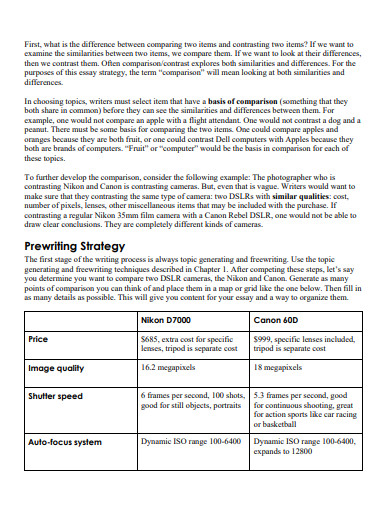 Size: 557 KB 12. Comparison and Contrast Essay Topics Example Size: 92 KB 13. Comparison and Contrast Essay Writing Example Size: 60 KB 14. Comparison and Contrast Essay Guideline Example Size: 261 KB 15. Comparison and Contrast Essay Writing Process Size: 34 KB 16. Simple Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 277 KB 17. Free Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 82 KB 18. Basic Comparison and Contrast Essay Example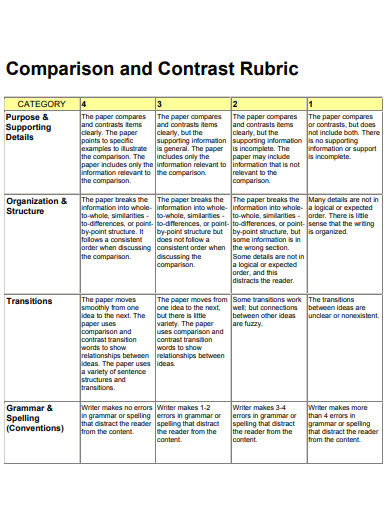 Size: 72 KB 19. Comparison and Contrast Essay Rubic Example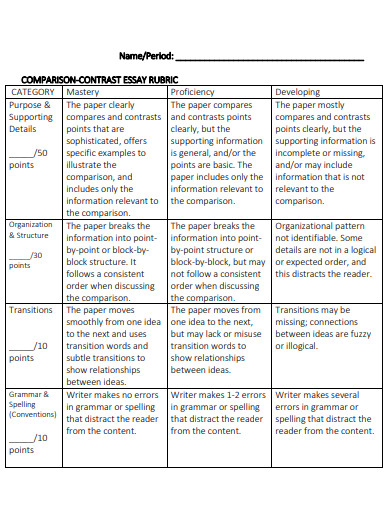 Size: 58 KB 20. Standard Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 130 KB 21. Organization of Comparison and Contrast Essay Size: 194 KB 22. Comparison and Contrast Essay Template Size: 21 KB 23. Comparison and Contrast Essay Introduction Size: 114 KB 24. Comparison and Contrast Essay Paper Example Size: 965 KB 25. Literary of Comparison and Contrast Essay 26. General Comparison and Contrast Essay Example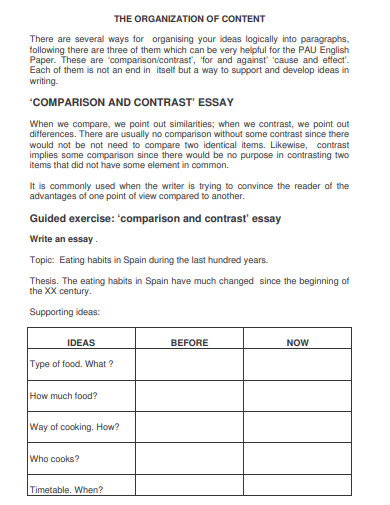 Size: 25 KB 27. Comparison and Contrast Essay Format Size: 311 KB 28. School Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 547 KB 29. Formal Comparison and Contrast Essay Example Size: 61 KB 30. Comparison and Contrast Essay Outline Example What is a Compare and Contrast Essay?A Comparison and Contrast Essay is a type of writing that explores the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It is a form of academic writing where the writer compares and contrasts two or more things based on specific criteria. This type of essay is common in high school and college coursework, and it can cover any subject matter, from simple topics like comparing apples and oranges to complex issues like comparing different theories of economics. How to Write a Compare and Contrast EssayBefore we delve into the steps, it’s important to understand that writing a Comparison and Contrast Essay requires critical thinking and a clear understanding of both the subjects being compared. Step 1: Choose Your SubjectsThe first step in writing a Comparison and Contrast Essay is to choose two subjects that have similarities and differences. These could be two characters in a novel, two different novels, two historical periods, or even two scientific theories. Step 2: Develop a ThesisThe next step is to develop a thesis. A thesis is a statement that expresses the main idea of your essay. It should clearly state what you are comparing and contrasting and why it is important. Step 3: Organize Your EssayOrganizing your essay is crucial for clarity. There are two ways to structure a Comparison and Contrast Essay: the block method and the point-by-point method. The block method presents all arguments related to your first subject, followed by your second subject. The point-by-point method, on the other hand, alternates arguments about the two items you are comparing and contrasting. Step 4: Write the EssayStart with an engaging essay hook to grab your reader’s attention. Then, present your thesis and proceed to write the body of your essay, using metaphors and other literary devices to make your points more compelling. Finally, conclude your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis. What is the purpose of a Comparison and Contrast Essay?The purpose of a Comparison and Contrast Essay is to analyze the differences and/or similarities of two distinct subjects. It helps readers understand the subjects better when they are compared to each other. How is a Comparison and Contrast Essay different from an Argument Essay?While both types of essays require critical thinking and a clear thesis, an Argument Essay presents an argument and supports it with evidence, while a Comparison and Contrast Essay explores the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. Can I use a Comparison and Contrast Essay in a Collage Essay?Yes, you can. A Collage Essay is a creative way to present information, and incorporating a Comparison and Contrast Essay can add depth and complexity to your collage. Writing a Comparison and Contrast Essay can be a challenging task, but with the right approach and understanding, it can be an enjoyable and rewarding experience. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a compelling and insightful essay. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to explore the 29+ Comparison and Contrast Essay Examples in Google Docs, Word, PDF, and other 10+ Comparative Analysis Essay Examples to hone your skills.  Text prompt Write a comparison contrast essay on living in the city versus the countryside. Compare and contrast in an essay the differences between summer and winter vacations. b. False 5. Cash Flow is the difference between income and expenses. a. True b. FalseTrue. (Cash Flow is the difference between profit and loss) Related Questionsdoes entitled mean deserve??? Yes it simply refers to deserve 25) Which is an example of self-contradiction? A) It is important to water the grass well because it will dry out. B) It is important to have a part-time job if you want to make extra money for the trip. C) It is important to eat a well-balanced meal a day, so I eat french frys and churros everyday. D) It is important to follow the rules of traffic, so that you do not harm yourself or anyone else. Explanation:A self-contradiction is saying something but not following through with what you said. In the statement of letter C it says eat a well-balanced meal a day then it says I eat french frys and churros everyday which isn't a well balanced meal so the statement self-contradicte itself. Question 1 The new policy was _________ difficult to implement • A. extreme • B. extremes • C. extremely • D. to extreme Question 2 Every country _________ interested in the global trade issue • A. have • B. are • C. is • D. has Question 3 The president and the vice president _________ in the conference room at the moment • A. are • B. being • C. is • D. was Question 4 Your company should take _________ action to solve the problem • A. proper • B. permanent • C. competitive • D. complimentary Question 5 Physics ... one of my favourite subjects. • A. be • B. to be • C. is • D. are Question 6 The team made a presentation in a very _________ way • A. impress • B. impressive • C. impressiveness • D. impressively Question 7 John as well as Mary __________ very kind. • A. were • B. are • C. is • D. have been Question 8 Half of the annual profit … to paying taxes and insurance fees. • A. go • B. goes • C. going • D. is going Question 9 Everybody_________ to be rich and happy in entire life • A. want • B. wanting • C. wanted • D. wants câu 10. Nothing in inheritance _________ to you • A. belongs • B. belong • C. belonged • D. belonging The right choices for the blanks have been inserted below: 1. The new policy was C. extremely difficult to implement 2. Every country C. is interested in the global trade issue 3. The president and the vice president A. are in the conference room at the moment 4. Your company should take A. proper action to solve the problem 5. Physics C. is one of my favorite subjects. 6. The team made a presentation in a very B. impressive way 7. John, as well as Mary, B. are very kind. 8. Half of the annual profit B. goes to paying taxes and insurance fees. 9. Everybody D. wants to be rich and happy in entire life 10. Nothing in inheritance A. belongs to you A part of speech refers to a group of words that share the same grammatical form. In the blanks provided, the parts of speech provided range from nouns , to verbs , adverbs , and adjectives . The relevant forms have been inserted in the blanks. Learn more about parts of speech here: https://brainly.com/question/721326 Please Hurry). What is the main idea of this poem? Answer choices) A) Trophies are susceptible to dust and varnish. B) Choose heroes wisely. C) Be careful when choosing friends. ( I posted a picture of the poem) Only answer if your 100% sure. Will Mark Brainliest The answer to your question would be B) Choose Heroes Wisely Explanation: The poem says nothing about your friends being like a trophy. And answer A is to obvious and doesn't make to much sense because it already states that your "special treasure" is known to varnish. So B is your most trust-able answer. Mark Brainliest as promised!! writing about daily life you can remove some sentenses if u want everyday i wake up in the mornning around 10am i brush my teeth and wash my hands and face. after that i go out with my friends to the mall and have fun i get back from the mall wash my hands eat dinner and watch my fav shows on netflix and then i have a desert and go to sleep Select the best answer for the question. 11. Which of the following sentences contains a verb phrase? I shall be all that I am and more rewrite the following sentence replacing the underlined words right my brother speak fluently English All My Points Lpoinsts im sorry about that it would be cool if users could donate/trade points between one another lol I need an essay for this question ...In what ways does transformation play a role in stories that are meant to evoke intense emotions? To write an effective essay , the writer needs to be careful to use the correct structure , which is to start with an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs with development and support, and a final concluding paragraph. Here are some tips that can help you write an essay: This is a question of creativity that should be written exclusively by you , but I hope that with these tips you will succeed and write a great essay! Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/1334265 Which is not a type of support in the paragraph? A)Statistics B)Examples C)A page number D)quotations C A PAGE NUMBER HAVE A BEAUTIFUL DAY Which two statements are true with regard to the information related in the text? A) Imprinting meant that many peregrines remained within cities. B) Imprinting is a controversial practice which has many detractors. C) Imprinting largely failed as a strategy to help peregrines survive. D) Imprinting was initially an effort to return peregrines to natural settings. E) Imprinting has recently been adapted to try to induce peregrines to return to natural settings. I think it is E and A I'm sorry if I'm wrong but based off of what I understood from the text I think these re the best two answers because in the passage the writer goes on to explain that because of imprinting the birds would nest in the city, so now they are trying to release the birds in the wilderness so they can come back to the wilderness. Hope that isn't confusing, take care! write five sentences about fishing? Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fishing can be done in the sea, or in a lake or river, and by boat or from the shore. Fishing can be done for income, fun or dinner. Fisheries and aquaculture provide direct and indirect employment to over 500 million people in developing countries. Hope this helps.. what happen when we become proud When we are proud, we are feeling pride, or satisfaction with ourself. It's also possible to feel proud of someone else. If your best friend gets the lead in the school play, you may find yourself feeling as happy for him as if you'd got the lead yourself. When you proud you feel pride and satisfaction with yourself You need to get a ------to twist the wire round the pole. I think ladder is the answer brother Mia has breakfast at a restaurant. She leaves a tip of $1.80, which is the 20% of what she spent. What is the price of Mia's breakfast, before tip 1.80 divided by 20 multiply by 100 9 divided by 100 multiply by 20 1.8 there is no value for zero after any number on point hope you understand Write a letter to your friend giving her the direction to your school I don't think he is guided by my opinion Fill in each blank with the term that correctly completes each sentence. 2. Universal theme 3. Culturally specific Can anyone tell me a story with there verb moods in it I literally need to submit it tomorrow and I been trying to think of something to write but nothing really comes to my mind What I found on the interenet: Verbs have three moods—indicative, imperative, and subjunctive. Examples of sentences with verbs having indicative mood: I want a chocolate ice cream cone. Atlanta is the capital of Georgia. Coconut tastes funny. Are you going to the party? I suggest you do an essay on an important trip/event that happened in your life. But really emphasize what happened. So as an indicative essay, show the reader what you are experiencing. It can be observed that the Hadley's have allowed the nursery to become a kind of substitute father and mother to their children. Does technology play the same role in today society. Why do parents permit such situations occur They decide to move, close the house and live in a more simple and traditional way. Mr. and Mrs. Hadley, together with their children, moved to a fully automated and technological house, which does everything for them, without them having to make any effort. in addition, the house has a bedroom, called a nursery, which offers interactive and realistic scenarios that allow the user to experience any type of adventure they want. Mr. and Mrs. Hadley are a little uncomfortable with the autonomy of the house, especially Mrs. Hadley, who feels that she is not playing the role of mother and wife. In addition, they are concerned that their children are having undue experiences for their age in the nursery room, which they really are. When Mr. and Mrs. Hadley discover that they are addicted to the room and having experiences that they shouldn't have, they decide to move, close the house and live in a simple and traditional way. please answer the questions fast please nervoous feeling Correct the four pronoun-related errors in this paragraph: Fast-forwarding to modern times, the heyday of the human-powered flight is far from over. Lucrative prizes still abound for rotor-driven craft, whilst experimental versions of helicopters and ornithopters (flying machines with flapping, bird-like wings) are both on the drawing board and leaping off it with great abandon. The dream of human-powered flight has been an official reality now for more than 50 years, but the limits of their ingenuity are boundless - especially when inventors and engineers are spurred on by prizes as large as the $250,000 on offer from the American Helicopter Society's Igor Sikorsky Prize Fund. And who knows, perhaps one day his commute to work will take place not on a bicycle but on a bicycle-powered craft. Does your office have a landing pad on the roof or a runway nearby? The day when she does might just be closer than they think! cbkab 2021 Exit < Back Next > 11 Type here to search O 11 + 120 é ^ 0 GENG 11:06 PM 15/09/2021 E The four pronoun - related errors " their ingenuity," " his commute," "when she does," and "closer than they think" can be corrected with its , our , it and we . We have a pronoun - related error when we use the wrong pronoun to refer to a word in the text. For example, in "My dreams are too big. It cannot come true," the error is in the use of " it ", a singular pronoun , to refer to " dreams ", a plural pronoun . The correct pronoun would be " they ". With that in mind, we can identify and correct the four pronoun - related errors in the paragraph: Learn more about pronouns here: https://brainly.com/question/26257764 All info is in the pic please help I’m dying!! 1. Owning a car in Vietnam is very expensive due to high government taxes; therefore, there are many more motorcycles than cars. 2. Rabbits are natural runners that can run at 30 mph, but they can reach speeds of up to 40 mph. 3. The highest score in a World Cup game occurred in 1954 when Austria defeated Switzerland in the quarterfinal with a score of 7-5. hope this helps :) Question 2 of 10 What enables a whale to move its fins in the ocean? A. Energy directly from its food B. Energy directly from the sun C. Energy from the rotation of Earth D. Energy from the ocean currents Communication is the transmission of information and meaning from one individual or group to another. The central objective of communication is to transmit meaning. The communication process is generally defined in five steps: sender has an idea, sender encodes the idea in a message, message travels over a channel, receiver decodes the message, and feedback travels to sender. Complete the sentence with the most appropriate choice. Feedback helps the know that the message was received and understood. Complete the sentence with the most appropriate choice. The is the medium over which a message is transmitted. Identify the appropriate step in the communication process. John begins to draft a message to his boss. Sender encodes message Message travels over channel Receiver decodes message Feedback travels to sender Sender has an idea Identify the appropriate step in the communication process. Dr. Pendelton listens to an oral status report from his research partner. Receiver decodes message Message travels over channel Sender encodes message Feedback travels to sender Sender has an idea Identify the appropriate step in the communication process. Crystal Jenkins writes a recommendation report. Sender encodes message Receiver decodes message Feedback travels to sender Sender has an idea Message travels over channel 1. Feedback helps the sender of the message to know that the message is received and understood. 2. Channel is the medium over which a message is transmitted. 3. The appropriate step in this communication process when "John begins to draft a message to his boss" is the Sender encodes the message . 4. The appropriate step in this communication process when "Dr. Pendelton listens to an oral status report from his research partner" is Receiver decodes the message. 5. The appropriate step in the communication process when "Crystal Jenkins writes a recommendation report " is Sender encodes the message . Thus, the communication process always involves five steps. Read more about communication process at https://brainly.com/question/18291853 50 points Read this excerpt from paragraph 13 in the passage: He stayed that way for a long time and when he aroused himself and again looked out of the car window the town of Winesburg had disappeared and his life there had become but a background on which to paint the dreams of his manhood. How do the underlined words shape the theme of the story? A. They suggest that the character is not mature enough to change. B. They demonstrate that the character has a difficult relationship with his father. C. They imply that the character is experiencing grief and loss. D. They show that the character is heading to a new phase in life. D. they show that the character is heading to a new phase in life 1. Many plants provide food, but we have not discovered most of them yet. * O A simple sentence O B compound sentence O C complex sentence O D compound-complex sentence compound sentence jsisbevisjapbzbshsbvsushs What is a central idea of the passage about combatting imposter syndrome? O A. Comparing yourself to others can help you can gain perspective. B. Watching movies and reading books where underdogs come out on top can provide inspiration O C. Seeking medication and psychotherapy is necessary for recovery. D. Practicing regular self-compassion improves self-image long term. BEST: FLAK 2.6.21 LELAKI281 Your question is incomplete, but i will try my best to give you a correct answer or a general overview that will assist you in getting the right answer. A central idea of the passage about combatting imposter syndrome is most probably option C Seeking medication and psychotherapy is necessary for recovery. A central idea is the main point that an article, essay or story is all about. This helps the writer to write the plot and outline his work properly Impostor syndrome has to do with the feelings of inadequacies that a person gets as a result of doubting his abilities or attributes his success to luck or chance. Therefore, the correct answer is most likely option C. This is because, this is the best solution to impostor syndrome. Read more here: https://brainly.com/question/19356088 Identify the adjective in each sentence. Write the adjective in the space provided 1. It is a blue car. 2. I can see a fluffy kitten. 3. The floor is cold. 4. I lost my new ring. 5. My dinner was hot. blue which modifies car. It distinguishes something about the car. fluffy: which modifies kitten cold: what type of floor is it? It's a cold one. new: modifies ring. It's a new one. hot: modifies dinner. 1. blue 2. fluffy 3. cold 4. new 5. hot Adjectives describe nouns (a person, place, or thing). Example: It (subject) is a blue (adjective describing color) car (noun). can someone help me plz if you don't know don't answer it plz or I'll report you thanks I'll give crown Alvaro wants to become a programmer. What should he do? to study if you want to be a programmer? To become computer programmers, individuals must obtain a degree in computer science, information technology, mathematics, or a related discipline. Many employers hire entry-level computer programmers with associate degrees, but they often prefer candidates with bachelor's degrees.  | 


























































































COMMENTS
An essay is a formal writing sample of a given topic composed of multiple paragraphs. The largest difference between the two types of writing is that the essay usually involves more preparation work.
The Difference between an Essay and a Paragraph. Paragraphs are the building blocks of an essay, so the difference between the two is comparative to the difference between a brick and a house. Your house may be made of bricks, but it's not likely you'll ever live in just a single brick. Yes, There Are Similarities, But...
The relationship between a paragraph and an essay is symbiotic; you can't write an essay without using paragraphs, and four or more consecutive paragraphs about the same subject matter become an essay. Both paragraphs and essays have a distinct beginning, middle and end. They're also both composed of five ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Differences between Paragraph and Essay. Paragraphs build up to create an essay, and an essay is composed of multiple paragraphs. They work together in a cooperative way to present a thorough discussion on a topic. The paragraph provides a focused look at one aspect, while the essay combines several paragraphs to give a broader view of a subject.
We have highlighted the following key difference between a paragraph and an essay -. Definition. A paragraph is usually short. It may include 4 to 6 sentences. The paragraph will address a specific topic or theme, but that is about it. On the other hand, an essay will include 4 to 6 paragraphs.
An essay is a special type of writing focused on proving a point called the thesis. Essays are composed of special types of paragraphs with very particular content. The rules for punctuation and sentence structure are covered in the Grammar section. This section will cover how to compose paragraphs and an academic essay which is also, generally ...
Parts of an essay. An impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. 1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader's attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers. Many students define paragraphs in terms of length: a paragraph is a group of at least five sentences, a paragraph is half a page long, etc. In reality, though, the unity and coherence of ideas among sentences is what constitutes a paragraph. A paragraph is defined as "a group of sentences or a ...
There is often some confusion about what the difference is between a paragraph and an essay. The best way to understand the difference is to think of the essay as a bigger version of a paragraph ...
An essay is a more complex form of academic writing, with a broader scope and a more detailed structure than a paragraph. The difference between a paragraph and an essay lies in their purpose, structure, and scope. They are not interchangeable in academic writing.
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
A paragraph is a component of fictional prose and non-fiction writings. When writing essays, research papers, books, etc., new paragraphs are indented to show their beginnings. Each new paragraph begins with a new indentation. The purpose of a paragraph is to express a speaker's thoughts on a particular point in a clear way that is unique and ...
Making effective comparisons. As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place. For example, you might contrast French ...
Here are the differences : Whereas a paragraph has a single topic sentence with a single opinion, an essay has a thesis statement that contains three opinions. Whereas a paragraph has a support as ...
Coherence is the trait that makes the paragraph easily understandable to a reader. You can help create coherence in your paragraphs by creating logical bridges and verbal bridges. Logical bridges. The same idea of a topic is carried over from sentence to sentence. Successive sentences can be constructed in parallel form.
By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship ...
1. PDF. Talk with Paper. Essays consist of multiple paragraphs and have a specific structure, while paragraphs are individual units of text within an essay. Load More Papers. Essays and paragraphs have some key differences. Essays are longer pieces of writing that typically consist of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both.
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader.
Paragraphs and essays are different forms of write-ups used to express one's point of view. Both writing pieces should be informational, with an idea explained clearly and concisely. Even though they may appear similar, there exists a difference between paragraphs and essays. A paragraph is a self-sufficient writing unit created with multiple ...
What is a Compare and Contrast Essay? A Comparison and Contrast Essay is a type of writing that explores the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It is a form of academic writing where the writer compares and contrasts two or more things based on specific criteria. This type of essay is common in high school and college ...
Here are some tips that can help you write an essay: Conduct analytical research and collect relevant information about the topic of the essay. Be clear and precise when starting to write your essay. Use quotes to support your argument. Summarize important topics to help you build the essay. Use reliable and reliable evidence to support your ...