You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Related Resources
- —Nature and Elements of Communication
Self Learning Module - Quarter 1 -Oral Communication: Grade 11&12, Module 1-7 View Download
Learning Material, Self Learning Module | ZIP
Curriculum Information
| Education Type | K to 12 |
| Grade Level | Grade 11, Grade 12 |
| Learning Area | |
| Content/Topic | Nature and Elements of Communication Functions Of Communication Communicative Competence Strategies In Various Speech Situations Types of Communicative Strategy Types of Speeches |
| Intended Users | Educators, Learners |
| Competencies | Differentiates the various models of communication. Demonstrates sensitivity to the sociocultural dimension of communication situation with focus on a. culture b. gender c. age d. social status e. religion Watches and listens to sample oral communication activities. Identifies strategies used by each speaker to convey his/her ideas effectively. Identifies the various types of speech context Exhibits appropriate verbal and nonverbal behavior in a given speech context Distinguishes types of speech style Identifies social situations in which each speech style is appropriate to use Observes the appropriate language forms in using a particular speech style Responds appropriately and effectively to a speech act Engages in a communicative situation using acceptable, polite and meaningful communicative strategies Explains that a shift in speech context, speech style, speech act and communicative strategy affects the following o language form o duration of interaction o relationship of speaker o role and responsibilities of the speaker o message o Distinguishes types of speeches. Uses principles of effective speech delivery in different situations. Uses principles of effective speech writing focusing on o audience profile o logical organization o duration o word choice o grammatical correctness Uses principles of effective speech delivery focusing on o articulation o modulation o stage presence o facial expressions, gestures and movements o rapport with the audience |
Copyright Information
| Copyright | Yes |
| Copyright Owner | Department of Education |
| Conditions of Use | Use, Copy, Print |
Technical Information
| File Size | 8.79 MB |
| File Type | application/x-zip-compressed |
Oral Communication in Context: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech Style
Uploaded by: Daniel Magno
Description
in Context Quarter 1 – Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech Style Oral Communication in ContextAlternative Delivery ModeQuarter 1 – Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech StyleFirst Edition, 2020
Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work ofthe Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or officewherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Suchagency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties.
Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names,trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders.Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from theirrespective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownershipover them.
Published by the Department of EducationSecretary: Leonor Magtolis BrionesUndersecretary: Diosdado M. San Antonio
Development Team of the Module Writer: Bernadette C. Royo
Editors: Rizza A. Pereyra Marites M. Aguilar
Reviewers: Gilbert C. Alva Bernadette M. Songalia
Illustrator: Mark Razul G. Leal
Layout Artist: Gilbert G. Manaois
Management Team: Wilfredo E. Cabral Job S. Zape Jr. Eugenio S. Adrao Jhonathan S. Cadavido Marites A. Ibañez Edgardo B. Militante Orlando T. Valverde Godofredo C. Mercado Erma S. Valenzuela
Printed in the Philippines by ________________________
Department of Education – Region IV-A CALABARZON
Office Address: Gate 2 Karangalan Village, Barangay San Isidro Cainta, Rizal 1800Telefax: 02-8682-5773/8684-4914/8647-7487E-mail Address: [email protected] Oral Communication in Context Quarter 1 – Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech Style Introductory MessageFor the facilitator:
Welcome to the Oral Communication in Context Grade 11/12 Alternative DeliveryMode (ADM) Module on Types of Speeches and Speech Style!
This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators bothfrom public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helpingthe learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcomingtheir personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling.
This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independentlearning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to helplearners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration theirneeds and circumstances.
In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body ofthe module:
Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners.
As a facilitator you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module.You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to managetheir own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and to assist thelearners as they do the tasks included in the module.
ii For the learner:
The hand is one of the most symbolized parts of the human body. It is often used todepict skill, action, and purpose. Through our hands we may learn, create, andaccomplish. Hence, the hand in this learning resource signifies that you, as a learner,are capable and empowered to successfully achieve the relevant competencies andskills at your own pace and time. Your academic success lies in your own hands!
This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities forguided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be able toprocess the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner.
This module has the following parts and corresponding icons:
What I Need to Know This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module.
What I Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module.
What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one.
What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation.
What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills.
What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module.
What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson.
What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns.
iii Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency.
Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. This also tends retention of learned concepts.
Answer Key This contains the answers to all the activities in this module.
At the end of this module you will also find:
References This is a list of all the sources used in developing this module.
The following are some reminders in using this module:
1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Do not forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the directions carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and in checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone.
We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and will gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it!
iv What I Need to Know
This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you masterthe types of speeches and speech style. The scope of this module permits it to beused in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes the diversevocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to follow the standardsequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed tocorrespond with your needs.
The module is divided into two lessons, namely: • Lesson 1 – Types of Speeches • Lesson 2 – Types of Speech Style
After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. distinguish the types of speeches according to purpose and delivery; 2. determine the types of speeches used in different real-life situations; 3. distinguish the types of speech style; 4. identify the social situations in which each speech style is appropriate to use; and 5. observe the appropriate language forms in using a particular speech style.
1 What I Know
Directions: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separatesheet of paper.
1. The following are types of speech according to purpose EXCEPT __________. A. informative speech C. persuasive speech B. impromptu speech D. entertainment speech
2. All are categorized under types of speech according to delivery EXCEPT __________. A. impromptu speech C. persuasive speech B. extemporaneous speech D. manuscript speech
3. The primary goal of a/an ___________ is to influence the thoughts, feelings, actions, and behaviors or attitudes of your listeners (Gamble & Gamble, 2012). A. informative speech C. persuasive speech B. expository speech D. entertainment speech
4. The _______________ is a type of speech that aims to make the audience relax, enjoy, and even laugh. A. expository speech C. persuasive speech B. entertainment speech D. informative speech
5. Delivering a speech with the help of short notes and a clear outline is known as _________. A. manuscript speech C. extemporaneous speech B. memorized speech D. impromptu speech
6. When you deliver a pre-written speech word for word, it is called __________. A. impromptu speech C. memorized speech B. manuscript speech D. extemporaneous speech
7. A/ an __________ is delivered with little or no advance preparation. A. impromptu speech C. manuscript speech B. memorized speech D. extemporaneous speech
8. The nature of a reporter’s job is to give an expository or __________. A. persuasive speech C. manuscript speech B. informative speech D. impromptu speech
2 9. The President follows a/an __________ during his State of the Nation Address (SONA) so as not to miss any important detail. A. entertainment speech C. memorized speech B. impromptu speech D. manuscript speech
10. The Department of Health (DOH) Spokesperson transitioned from manuscript speech to __________ when she answered various pressing questions during the media press conference. A. extemporaneous speech C. memorized speech B. impromptu speech D. entertainment speech
11. Jeff tried out an online interview which tested his skill in__________. A. impromptu speech C. informative speech B. memorized speech D. entertainment speech
12. The type of speech that appeals to audience’s emotion and provides striking statistics to support the ideas is called __________. A. informative speech C. manuscript speech B. persuasive speech D. extemporaneous speech
13. Knowing your audience well will be most useful in a/an __________. A. informative speech C. memorized speech B. entertainment speech D. manuscript speech
14. The speaker’s credibility is highly important in a/an __________. A. manuscript speech C. entertainment speech B. memorized speech D. persuasive speech
15. Incorporating gestures, facial expressions, and movements in your __________ can help avoid unnatural delivery. A. manuscript speech C. impromptu speech B. memorized speech D. extemporaneous speech
1 Types of Speeches
This lesson introduces you to the world of public speaking. Take a step further toenhance your oral communication skills by learning the types of speeches you canuse in creating meaningful tasks.
In your journey toward elevating your oral communication skill, you have previouslylearned in Module 5 that communication can take place in different speech contexts(intrapersonal, interpersonal, public, and mass). Moreover, you were given ideas onhow you should speak when put in a specific speech context. As you move on to yournext adventure, Module 6 Lesson 1 will prepare you to be an effective public speaker.This exciting lesson will tackle the different purposes and methods of delivering aspeech.
Notes to the Teacher This lesson is composed of five (5) self-paced activities. Each of the activities is scaffolded to assist the learner in discovering the lesson on their own. The activity in the What I Can Do part may be modified to suit your learning set up. Happy teaching!
4 What’s New
SpeechIt is human nature to express thoughts and emotions. Thus, many speeches orforms of communication in spoken language, made by a speaker before an audience,have been created. Speeches are more formal than talking or usual conversations.They are primarily delivered to leave a remarkable message.
Types of SpeechesIn the word puzzle below are seven (7) words that refer to jobs which commonlyrequire to deliver speeches. Try to look for them as fast as you can to lead you to thetypes of speeches.
B T Y P O L I T I C I A N X T J I A K E U W G E S L L E K T D O C T O R P T A U A S F L F O G X I F Q W I C E D O I M B M P A P Y S H W Z B T E S E U Y F E P E C N S M D N A C T O R F R M R P U I I T R O J L E H D I A C A H I P V I J G N E W S A N C H O R Y S
A. Vertical B. Horizontal
1. _________________________ 1. _________________________
2. _________________________ 2. _________________________
3. _________________________ 3. _________________________
4. _________________________
5 Were you able to hunt all the words that we are looking for? Let us look at thefollowing pictures if you got them correctly.
For the jobs written vertically, what do you think are their reasons or purposesfor giving their speeches?
I give a speech to ____________________________ _____________________________________________
I give a speech to ___________________________ _____________________________________________
I give a speech to ____________________________
_____________________________________________
6 For the jobs written horizontally, how do you think do they deliver their speeches?
To deliver my report on television, I____________________________________________ ____________________________________________.
To deliver my lines on stage, I _____________________________________________ ____________________________________________.
To deliver my speech during campaign, I____________________________________________ ____________________________________________.
To deliver the clinical findings to my patient, I _____________________________________________
____________________________________________.
7 What is It
The activity shows that people create speeches for different purposes and throughdifferent methods of delivery. There are two (2) major types of speeches: according topurpose and according to delivery.
1. Types of Speech According to Purpose
a. informative or expository speech • is mainly performed for the purpose of educating the audience on new or relevant piece of information on a particular topic. example: lecture of a teacher
b. persuasive speech • is given solely for the purpose of convincing the audience to agree with the speaker’s opinion on a particular topic. example: speech of a lawyer
c. entertainment speech • aims to share laughter and enjoyment to the audience through witty and humorous lines. example: speech of a comedian
2. Types of Speech According to Delivery
a. manuscript speech • is the word-for-word iteration of a written message using visual aids. example: news anchor with a teleprompter
b. memorized speech • is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. example: actor’s dialogue
c. extemporaneous speech • is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. example: a campaign speech before a voting public
d. impromptu speech • is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation and is for people knowledgeable about the subject. example: a doctor’s response to the question of a patient
8 What’s More
Get to know more how to distinguish the types of speeches according to purposeand delivery. On the left are characteristics of the different speeches. Check (/) theappropriate column described by each statement. Use a separate sheet of paper foryour answer.
Note: More than one column may be selected.Legend: I= informative speech Ma= manuscript speech P= persuasive speech Me= memorized speech
E= entertainment speech Ex= extemporaneous speech Im= impromptu speech
Description Purpose Delivery The speech… I P E Ma Me Ex Im 1. provides the audience with a clear understanding of a concept or idea 2. aims to convince the audience 3. is delivered with limited preparation and is guided by an outline 4. is delivered with no advance preparation and is usually for person knowledgeable about the subject 5. is used by theater actors 6. is commonly used by candidates running for political office 7. is employed when answering a question about oneself in an interview 8. makes use of jokes, funny stories, and vivid descriptions. 9. is written in advance and should be practiced in order to avoid monotony 10. appeals to audience’s emotion and provides striking statistics that can support the ideas
9 What I Have Learned
From the lesson on the types of speeches, I learned that:
1. I will use the following types of speech according to purpose when:
A. informative
B. persuasive
C. entertainment
2. The three (3) types of speech according to purpose are also used in:
Other Speaking Situation
A. informative _______________________________________
B. persuasive _______________________________________
C. entertainment _______________________________________
3. I will use the following types of speech according to delivery when:
A. manuscript
B. memorized
C. extemporaneous
D. impromptu
10 4. The four (4) types of speech according to delivery are also observed in:
A. manuscript ___________________________________
B. memorized ___________________________________
C. extemporaneous ___________________________________
D. impromptu ___________________________________
5. As a speaker, I should know my purpose and method of delivery before giving my speech so…
11 What I Can Do
Now that you know how to distinguish the different types of speeches, try to make ameaningful activity out of it by delivering a simple speech as a life coach. A life coachis someone who helps people identify their goals and develop an actionable plan toachieve them. To help the people who were affected by the recent COVID-19pandemic, give a 2 or 3-minute persuasive memorized speech. Have someone fromthe audience to evaluate your performance by using the criteria below.
4 3 2 1 Category Exceptional Meets Satisfactory Needs Score Expectation Improvement
Introduction The first few The first few The first few The first few lines lines of the lines of the lines of the of the speech did speech really got speech got my speech did not not get my my attention and attention and I really get my attention and I made me want to was curious to attention and I did not want to listen intently. hear the rest. was not sure if I hear more. want to hear more.
Content The speech The speech The speech The speech was explained the focused on the focused on the unclear, did not issue issue and used issue but did explain any of thoroughly, examples but not explain it the issues using examples. did not fully thoroughly and thoroughly and (x 2) explain it. did not use did not use examples. examples.
Delivery The speaker The speaker was The speaker I could not hear spoke in a loud, loud and clear was difficult to or understand clear voice and but was not hear sometimes the speaker. was expressive. expressive. and not expressive.
Conclusion The end of the The end of the The end of the The end of the speech was speech was speech was not speech was not exciting and somewhat very exciting or exciting or lovely lovely. exciting and lovely. at all. lovely.
Overall The speech was The speech was The speech was The speech made exciting and informative and not very me not want to informative that somewhat informative or agree with the made me agree exciting that exciting I would speaker’s with the made me think not probably viewpoint. speaker’s about the agree with the viewpoint. speaker’s speaker’s viewpoint. viewpoint.
Total Score
https://landaua-catcherintherye.weebly.com/rubric-for-persuasive-speech-and-presentation.html
12 Assessment
Directions: Identify whether each statement is TRUE or FALSE. Use a separate sheetof paper for your answer.__________ 1. The types of speech according to delivery are impromptu speech, persuasive speech, extemporaneous speech, and manuscript speech.
__________ 2. The primary goal of an informative speech is to influence the thoughts, feelings, actions, and behaviors or attitudes of your listeners (Gamble & Gamble, 2012).
__________ 3. Extemporaneous speech has no advance preparation and is usually for a person knowledgeable about the subject.
__________ 4. An impromptu speech is delivered with little or no time for preparation.
__________ 5. An expository speech provides the audience with a clear understanding of a concept or idea.
__________ 6. The nature of a reporter’s job is to give a persuasive speech.
__________ 7. The President’ State of the Nation Address (SONA) is guided by a manuscript or teleprompter.
__________ 8. A speaking situation can transform from one type of speech to another.
__________ 9. Entertainment speech is simpler than an informative speech.
__________ 10. A manuscript speech may not be rehearsed anymore.
__________ 11. Short notes are useful in an extemporaneous speech.
__________ 12. A manuscript speech is used to deliver important information.
__________ 13. Vivid descriptions are essential in an entertainment speech.
__________ 14. The types of speech according to purpose are informative speech, persuasive speech, and entertainment speech.
__________ 15. The credibility of a speaker is important in informative, persuasive, and impromptu speech.
13 Additional Activities
Observe three (3) different speaking situations in your environment. Using the tablebelow, list them down and distinguish the type of speech according to purpose anddelivery used in each situation. Also, provide an evaluation by identifying the positivepoint you noticed. For the relevant suggestion, give a piece of advice on how thespeech can further be improved considering the type of speech where it belongs. One(1) point will be given for every correct answer written on each box. Write your answeron a separate sheet of paper.
Speaking Situation Purpose Delivery Positive Point Relevant Suggestion
14 15 What I Know 1. B 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. B 9. D 10. B 11. A 12. B 13. B 14. D 15. BWhat’s New What's More Assessment (Answers may not be in 1. I 1. FALSE the same order) 2. P 2. FALSE 3. Ex 3. FALSE Vertical 4. Im 4. TRUE 1. TEACHER 5. Me 5. TRUE 2. COMEDIAN 6. P/ Ex 6. FALSE 7. I/ Im 7. TRUE 3. LAWYER 8. E 8. TRUE 9. Ma/ Me 9. FALSE Horizontal 10. P 10. FALSE 1. POLITICIAN 11. TRUE 2. DOCTOR 12. TRUE 3. ACTOR 13. TRUE 4. NEWS ANCHOR 14. TRUE 15. TRUE Answer Key What I Know
Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write the chosen letter on aseparate sheet of paper.
1. You are to use a/an __________ style only when you are with your close family members or people. A. casual B. consultative C. intimate D. frozen
2. Conversation between friends uses __________ style even though they do not have close relations. A. consultative B. casual C. formal D. intimate
3. The ___________ style is characterized by a semi-formal communication. A. casual B. consultative C. frozen D. intimate
4. The speech which consists of well-structured, logically sequenced, and strongly coherent sentences and is prepared beforehand is called _________ style. A. formal B. frozen C. consultative D. casual
5. The most formal communicative style that is usually used during solemn events and ceremonies is the __________ style. A. casual B. frozen C. formal D. consultative
6. Lou felt displeased toward Lois after he had shared their private conversation with other people. Lois’ act violates the idea of __________ style. A. formal B. casual C. intimate D. consultative
7. Jargon, slang, and vernacular language are common in __________ style because of the shared background information of the participants. A. casual B. consultative C. frozen D. formal
8. When a person already shares secrets during a conversation, the communication style can be described as __________. A. consultative B. casual C. formal D. intimate
9. Professional or mutually acceptable language is a must in a/an ______ style. A. casual B. consultative C. frozen D. intimate
10. The ___________ style should be observed in regular classroom discussions between a teacher and a student. A. casual B. consultative C. frozen D. intimate
16 11. Sermons by priests, State of the Nation Address of the President, and welcome addresses are examples of __________ style. A. consultative B. frozen C. formal D. casual
12. It is called _________ style because this style remains unchanged. A. casual B. frozen C. formal D. consultative
13. The term YOLO (You Only Live Once) is a commonly used language in a __________ speech style. A. casual B. formal C. consultative D. frozen
14. The use of Mr., Mrs., Dr., Professor, and other honorifics are expected in a/an __________ speech style. A. formal B. intimate C. consultative D. casual
15. Utmost respect should be expressed during the recitation of Panunumpa sa Watawat ng Pilipinas and Panatang Makabayan as used in __________ style. A. consultative B. formal C. frozen D. casual
2 Types of Speech Style
This lesson helps you improve your communication skills by providing you thesocially acceptable ways in delivering your speech. Explore the types of speech stylefor creating better relationships.
How is your experience doing the public speaking? Were you able to apply theprinciples of effective speech delivery? You have come a long way with yourknowledge on the three (3) types of speech according to purpose and the four (4)types of speech according to delivery from Module 6 Lesson 1. Keep making progressas you reach Module 6- Lesson 2 where you will be given tips on how to build yourcommunication skills as well as relation with other people. Enjoy your journey tobecoming a proficient speaker!
Notes to the Teacher This lesson is composed of five (5) activities that will not only enhance the students’ speaking skill but also reveal background information about them. Take time to go through their responses to help you know them better. Happy teaching!
18 What’s New
Speech StyleThe way we communicate varies depending on a lot of factors such as the speechcontext, speech purpose, and speech delivery. The form of language that the speakeruses which [sic] characterized by the degree of formality is known as speech style(Martin Joos, 1976:156).
Types of Speech StyleThere are five (5) types of speech style that can be used in various speakingsituations. To know them, accomplish first the comic strip below by sharing a day inyour life as you go to school. Supply the needed statement(s) in each scenario. Usethe drawings as your guide.
1. __________ ____________
3. __________ ____________
2. __________ ____________
5. __________ ____________
4. __________ ____________
19 What is It
You may have noticed that the forms of language you use in talking to different peoplein different situations change in degree of formality. This is because of speech style.There are five (5) types of speech style.
Types of Speech Style
1. Intimate
• is used for very close relationships. example: couple • note: Language used in this style may not be shared in public. 2. Casual
• is an informal communication between groups and peers who have something to share and have shared background information but do not have close relations. example: classmates • note: Jargon, slang, and vernacular language are used 3. Consultative
• is used in semi-formal and standard communication. example: teacher and student • note: Professional or mutually acceptable language is a must in this style. 4. Formal
• is a one-way straightforward speech. example: State of the Nation Address • note: What the speaker says is something that has been prepared beforehand. 5. Frozen
• is the most formal communicative style that is usually used during solemn ceremonies and events. example: pledges • note: It does not require any feedback from the audience.
20 What’s More
Distinguish how you should communicate in the following speaking situationsthrough the diagram below. Write the letter of the speaking situation to itsappropriate type of speech style. Use a separate sheet of paper for your answer.
a. attending solemn ceremonies f. caring less about grammarb. listening to announcements g. using slang word like “bro”c. conversing with close people h. reciting the Girl/ Boy Scout Lawd. addressing the one in authority i. producing well-formed sentences
e. talking to friends about hobbies j. talking to the utility staff in your school
intimate casual 1. 3. 2. 4.
Speech Styles
frozen consultative 9. 5. 10. 6. formal 7.
21 What I Have Learned
From the lesson on the types of speech styles, I learned that:
1. The following speech styles are also observed in other speaking situations like:
Other Speaking Situations
A. intimate
C. consultative
2. There are principles that you have to keep in mind when talking to people usingthe following speech styles to maintain good communication such as:
A. family member= intimate
B. classmate= casual
C. teacher= consultative
D. principal= formal
E. pledge= frozen
3. I should use the appropriate speech style when talking to certain people so…
22 What I Can Do
Let your knowledge of the different types of speech style make your communicationand relation with other people better.Below are pictures showing some communication problems. To address theseproblems, identify the appropriate speech style to be used then provide a possibledialogue using the appropriate language form of each speech style.
Problem: Anna talks back to her parent who is disciplining her.
1. Speech Style: __________________________
Problem: Camila has no friends in school. Speech Style: __________________________ 2.
Problem: The business partners have not reached an agreement. Speech Style: ________________________ 3.
23 Assessment
Directions: Identify whether each statement is TRUE or FALSE. Write your answeron a separate sheet of paper.________ 1. The MOST informal speech style is the intimate style.
________ 2. The standard style of speech is the casual style.
________ 3. Consultative style is used when talking to someone in authority.
________ 4. Frozen style needs feedback.
________ 5. Honorifics like Mr. and Mrs. should be used when talking to strangers.
________ 6. You can use slang words like “dude” to a stranger.
________ 7. Similar interests form a casual speech style.
________ 8. Correct pronunciation is strictly observed in the intimate style.
________ 9. Talking to strangers should follow the consultative style.
________10. Delivering a formal speech takes the longest time of preparation.
________11. The manager can talk informally to his subordinates in the workplace.
_______ 12. Speech styles develop good values.
________ 13. Using appropriate speech style means varying the degree of formality.
________ 14. Speech context affects speech style.
________ 15. The degree of relationship dictates the type of speech style to be used.
24 Additional Activities
Observe varied speaking situations happening in your environment. Distinguish thetypes of speech style used by completing the table below. Then, point out one goodpractice in each speaking situation that is worthy of imitation. One (1) point will begiven for every correct answer written on each box. Use a separate sheet of paper foryour answer.
Speech Style Sample Speaking Situation Good Practice
1. intimate
3. consultative
25 26What I Know What's More Assessment 1. C 1. C 1. TRUE 2. B 2. F 2. FALSE 3. B 3. E 3. TRUE 4. A 4. G 4. FALSE 5. B 5. D 5. TRUE 6. C 6. J 6. FALSE 7. A 7. B 7. TRUE 8. D 8. I 8. FALSE 9. B 9. A 9. TRUE 10. B 10. H 10. TRUE 11. C 11. FALSE 12. B 12. TRUE 13. A 13. TRUE 14. C 14. TRUE 15. C 15. TRUE Answer Key References
Amadebai, Emidio. “14 TYPES OF SPEECH & EASY TIPS TO MASTER THEM.” Ace the Presentation, April 4, 2020. https://www.acethepresentation.com/10- types-of-speech/.
[Author removed at request of original publisher]. 2016. “Stand up, Speak Out.” Stand up Speak Out. University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing edition, 2016. This edition adapted from a work originally produced in 2011 by a publisher who has requested that it not receive attribution. November 8, 2016. https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/.
Beade, Pedro. “[No Title] - The Five Clocks: A Linguistic Excursion into the Five Styles of English Usage, by Martin Joos. New York: Harcourt, Brace & World, 1967. Pp. Xvi 108.” Canadian Journal of Linguistics/Revue Canadienne De Linguistique 13 (2): 123–24. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0008413100006204.
Four Methods of Delivery. Accessed May 22, 2020. https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/public-speaking-practice-and- ethics/s17-01-four-methods-of-delivery.html.
Gamble, Teri Kwal, and Michael Gamble. Communication Works. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1996.
Learning, Lumen. “Principles of Public Speaking.” Methods of Delivery | Principles of Public Speaking. Accessed May 23, 2020. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny- publicspeakingprinciples/chapter/chapter-12-methods-of-delivery/.
“Rubric for Persuasive Speech and Presentation.” n.d. Banned Books Webquest. Accessed May 22, 2020.https://landaua-catcherintherye.weebly.com/rubric- for-persuasive-speech-and-presentation.html.
“Speech.” Dictionary.com. Dictionary.com. Accessed May 22, 2020. https://www.dictionary.com/browse/speech.
“What Is a Life Coach? Learn What Does a Life Coach Do To Help You.” tonyrobbins.com. Accessed May 22, 2020. https://www.tonyrobbins.com/coaching/results-life-coach/.
www.facebook.com/elcomblusdotcom/. 2020. “Speech Styles.” ELCOMBLUS. February 22, 2020. https://elcomblus.com/speech-styles-definition-types- and-examples/.
27 For inquiries or feedback, please write or call:
Department of Education - Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR)
Ground Floor, Bonifacio Bldg., DepEd ComplexMeralco Avenue, Pasig City, Philippines 1600
Telefax: (632) 8634-1072; 8634-1054; 8631-4985
Email Address: [email protected] * [email protected]
Report "Oral Communication in Context: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech Style"
- No category

ORAL-COM-Quarter-1-Module-6
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key facts about Americans and guns

Guns are deeply ingrained in American society and the nation’s political debates.
The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees the right to bear arms, and about a third of U.S. adults say they personally own a gun. At the same time, in response to concerns such as rising gun death rates and mass shootings , the U.S. surgeon general has taken the unprecedented step of declaring gun violence a public health crisis .
Here are some key findings about Americans’ views of gun ownership, gun policy and other subjects, drawn from Pew Research Center surveys.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to summarize key facts about Americans’ relationships with guns. We used data from recent Center surveys to provide insights into Americans’ views on gun policy and how those views have changed over time, as well as to examine the proportion of adults who own guns and their reasons for doing so.
The Center survey questions used in this analysis, and more information about the surveys’ methodologies, and can be found at the links in the text.
Measuring gun ownership in the United States comes with unique challenges. Unlike many demographic measures, there is not a definitive data source from the government or elsewhere on how many American adults own guns.
The Pew Research Center survey conducted June 5-11, 2023, on the Center’s American Trends Panel, used two separate questions to measure personal and household ownership. About a third of adults (32%) say they own a gun, while another 10% say they do not personally own a gun but someone else in their household does. These shares have changed little from surveys conducted in 2021 and 2017 . In each of those surveys, 30% reported they owned a gun.
These numbers are largely consistent with rates of gun ownership reported by Gallup and those reported by NORC’s General Social Survey .
The FBI maintains data on background checks on individuals attempting to purchase firearms in the United States. The FBI reported a surge in background checks in 2020 and 2021, during the coronavirus pandemic, but FBI statistics show that the number of federal background checks declined in 2022 and 2023. This pattern seems to be continuing so far in 2024. As of June, fewer background checks have been conducted than at the same point in 2023, according to FBI statistics.
About four-in-ten U.S. adults say they live in a household with a gun, including 32% who say they personally own one, according to a Center survey conducted in June 2023 . These numbers are virtually unchanged since the last time we asked this question in 2021.
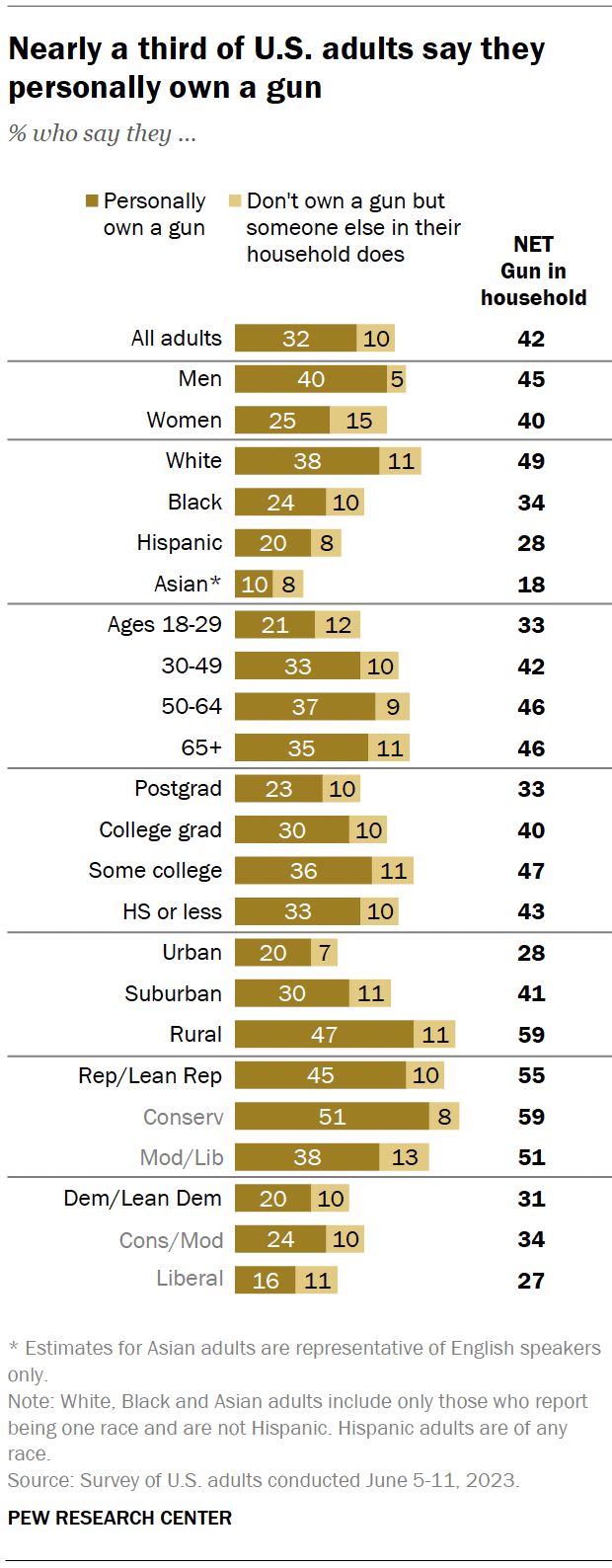
There are differences in gun ownership rates by political affiliation, gender, community type and other factors.
- Party: 45% of Republicans and GOP-leaning independents say they personally own a gun, compared with 20% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
- Gender: 40% of men say they own a gun, versus 25% of women.
- Community type: 47% of adults living in rural areas report owning a firearm, as do smaller shares of those who live in suburbs (30%) or urban areas (20%).
- Race and ethnicity: 38% of White Americans own a gun, compared with smaller shares of Black (24%), Hispanic (20%) and Asian (10%) Americans.
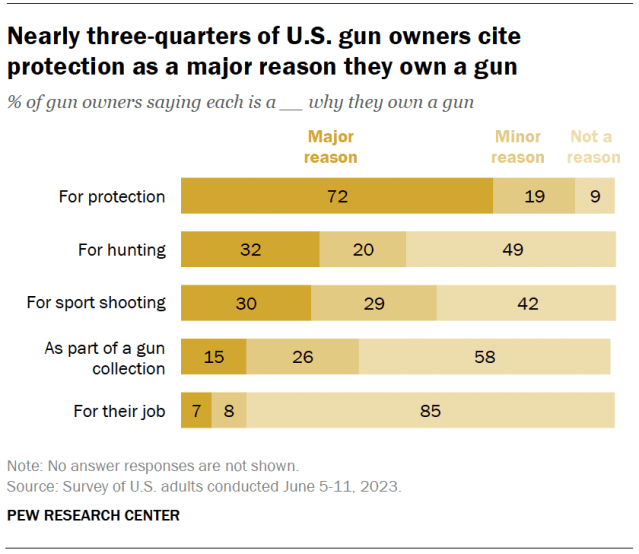
Personal protection tops the list of reasons gun owners give for having a firearm. About seven-in-ten gun owners (72%) say protection is a major reason they own a gun. Considerably smaller shares say that a major reason they own a gun is for hunting (32%), for sport shooting (30%), as part of a gun collection (15%) or for their job (7%).
Americans’ reasons behind gun ownership have changed only modestly since we fielded a separate survey about these topics in spring 2017. At that time, 67% of gun owners cited protection as a major reason they had a firearm.
Gun owners tend to have much more positive feelings about having a gun in the house than nonowners who live with them do. For instance, 71% of gun owners say they enjoy owning a gun – but just 31% of nonowners living in a household with a gun say they enjoy having one in the home. And while 81% of gun owners say owning a gun makes them feel safer, a narrower majority of nonowners in gun households (57%) say the same. Nonowners are also more likely than owners to worry about having a gun at home (27% vs. 12%).
Feelings about gun ownership also differ by political affiliation, even among those who personally own a firearm. Republican gun owners are more likely than Democratic owners to say owning one gives them feelings of safety and enjoyment, while Democratic owners are more likely to say they worry about having a gun in the home.
Non-gun owners are split on whether they see themselves owning a firearm in the future. About half of Americans who don’t own a gun (52%) say they could never see themselves owning one, while nearly as many (47%) could imagine themselves as gun owners in the future.
Among those who currently do not own a gun, attitudes about owning one in the future differ by party and other factors.
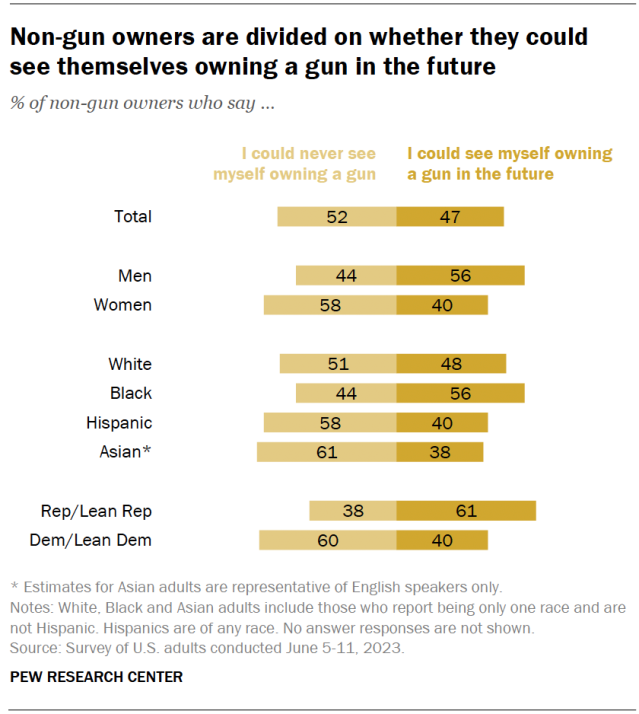
- Party: 61% of Republicans who don’t own a gun say they could see themselves owning one in the future, compared with 40% of Democrats.
- Gender: 56% of men who don’t own a gun say they could see themselves owning one someday; 40% of women nonowners say the same.
- Race and ethnicity: 56% of Black nonowners say they could see themselves owning a gun one day, compared with smaller shares of White (48%), Hispanic (40%) and Asian (38%) nonowners.
A majority of Americans (61%) say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun in this country, according to the June 2023 survey. Far fewer (9%) say it is too hard, while another 30% say it’s about right.
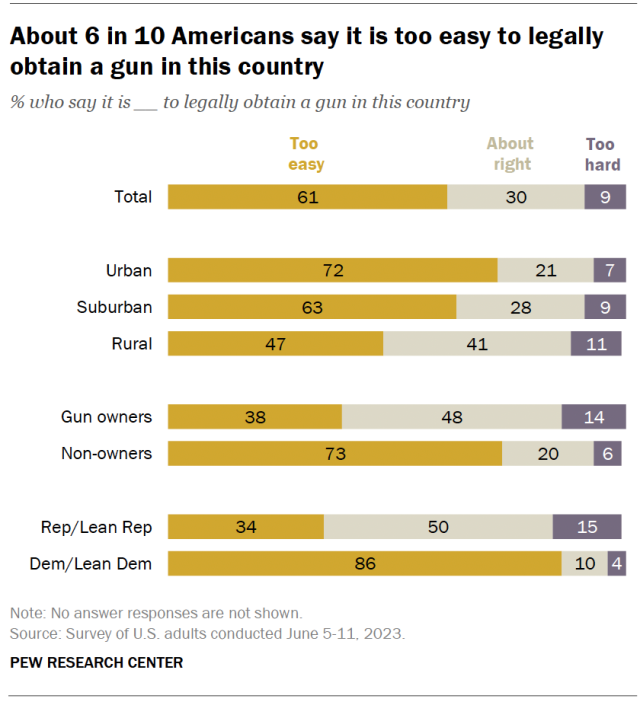
Non-gun owners are nearly twice as likely as gun owners to say it is too easy to legally obtain a gun (73% vs. 38%). Gun owners, in turn, are more than twice as likely as nonowners to say the ease of obtaining a gun is about right (48% vs. 20%).
There are differences by party and community type on this question, too. While 86% of Democrats say it is too easy to obtain a gun legally, far fewer Republicans (34%) say the same. Most urban (72%) and suburban (63%) residents say it’s too easy to legally obtain a gun, but rural residents are more divided: 47% say it is too easy, 41% say it is about right and 11% say it is too hard.
About six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) favor stricter gun laws. Another 26% say that U.S. gun laws are about right, while 15% favor less strict gun laws.
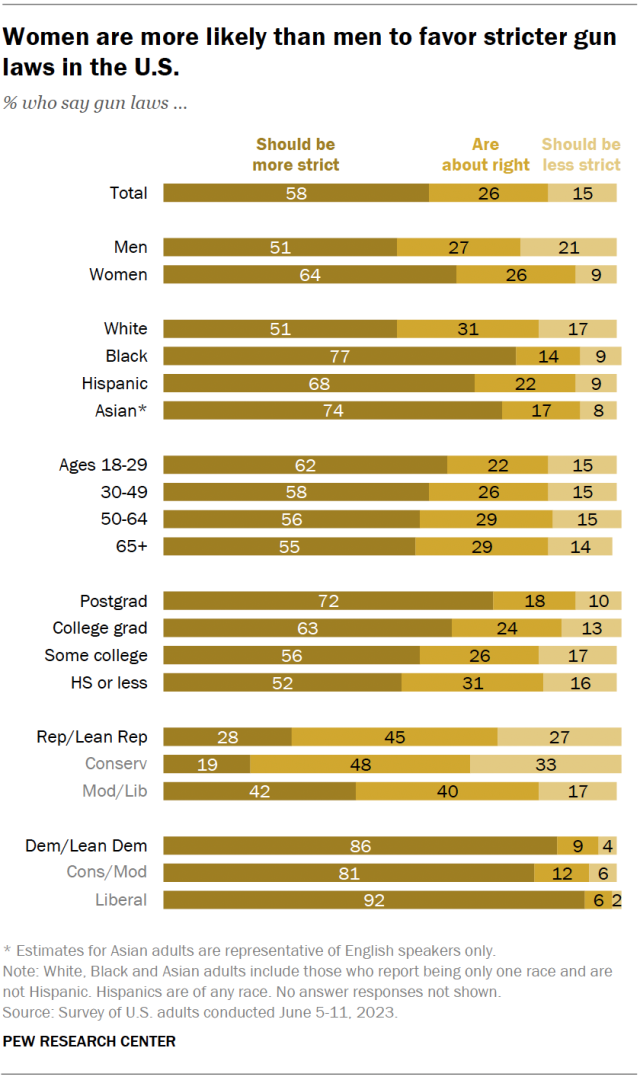
There is broad partisan agreement on some gun policy proposals, but most are politically divisive. Majorities of U.S. adults in both partisan coalitions somewhat or strongly favor two policies that would restrict gun access: preventing those with mental illnesses from purchasing guns (88% of Republicans and 89% of Democrats support this) and increasing the minimum age for buying guns to 21 years old (69% of Republicans, 90% of Democrats). Majorities in both parties also oppose allowing people to carry concealed firearms without a permit (60% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats oppose this).
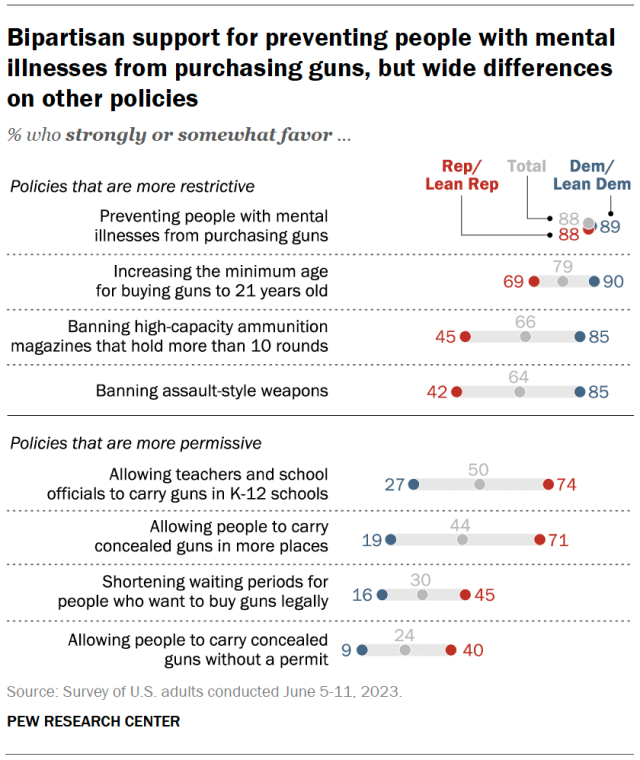
Republicans and Democrats differ on several other proposals. While 85% of Democrats favor banning both assault-style weapons and high-capacity ammunition magazines that hold more than 10 rounds, majorities of Republicans oppose these proposals (57% and 54%, respectively).
Most Republicans, on the other hand, support allowing teachers and school officials to carry guns in K-12 schools (74%) and allowing people to carry concealed guns in more places (71%). These proposals are supported by just 27% and 19% of Democrats, respectively.
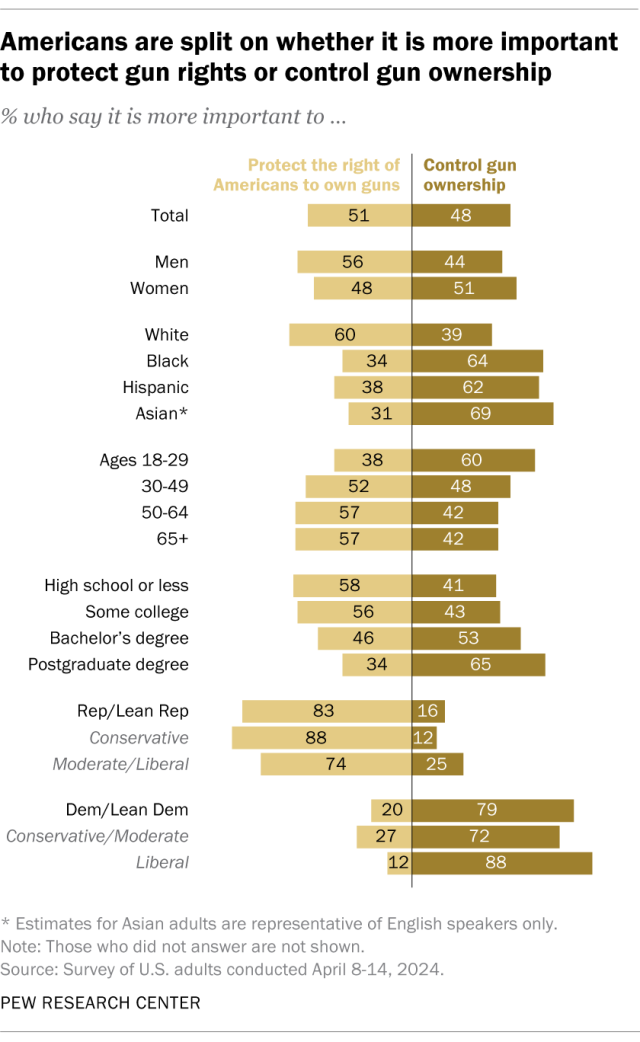
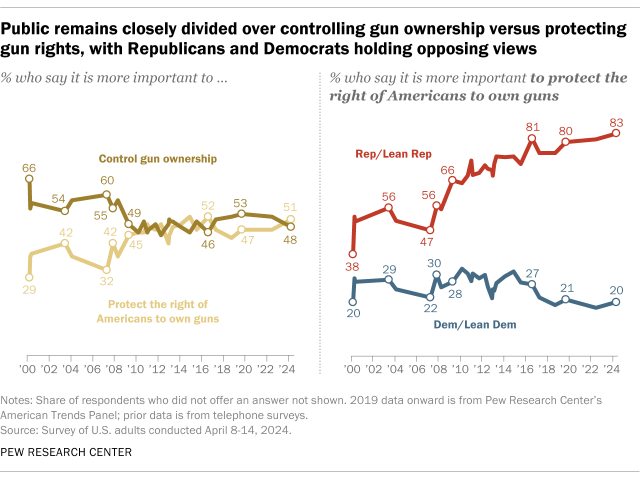
The public remains closely divided over whether it’s more important to protect gun rights or control gun ownership, according to an April 2024 survey . Overall, 51% of U.S. adults say it’s more important to protect the right of Americans to own guns, while a similar share (48%) say controlling gun ownership is more important.
Views have shifted slightly since 2022, when we last asked this question. That year, 47% of adults prioritized protecting Americans’ rights to own guns, while 52% said controlling gun ownership was more important.
Views on this topic differ sharply by party. In the most recent survey, 83% of Republicans say protecting gun rights is more important, while 79% of Democrats prioritize controlling gun ownership.
Americans are slightly more likely to say gun ownership does more to increase safety than to decrease it. Around half of Americans (52%) say gun ownership does more to increase safety by allowing law-abiding citizens to protect themselves, while a slightly smaller share (47%) say gun ownership does more to reduce safety by giving too many people access to firearms and increasing misuse. Views were evenly divided (49% vs. 49%) when we last asked in 2023.
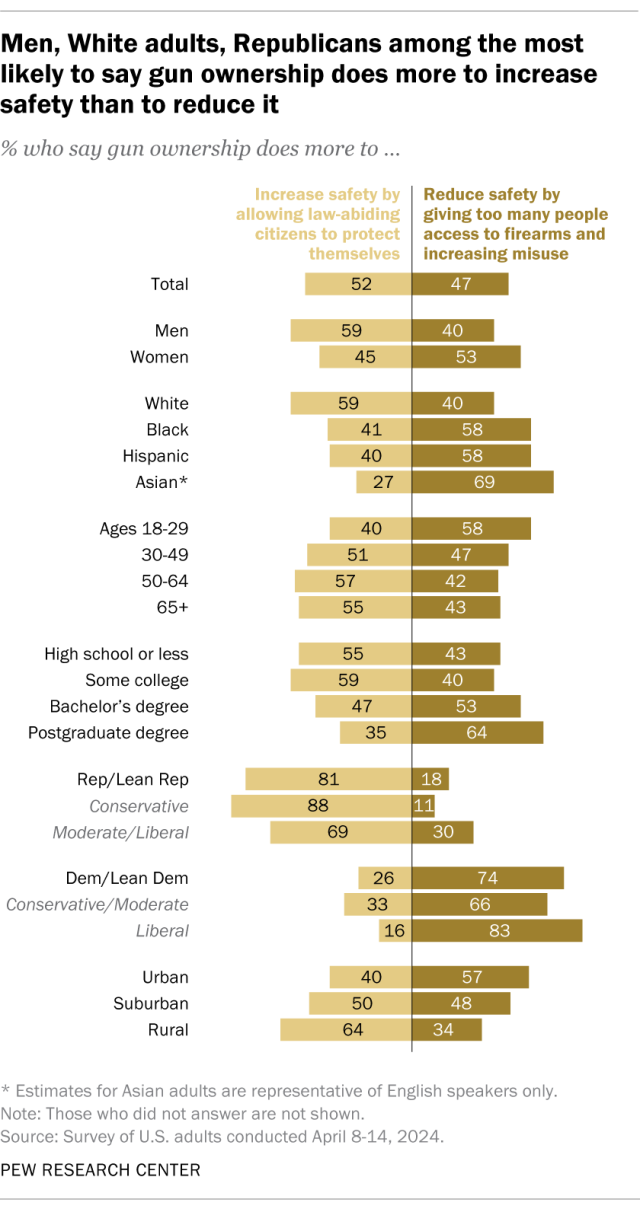
Republicans and Democrats differ widely on this question: 81% of Republicans say gun ownership does more to increase safety, while 74% of Democrats say it does more to reduce safety.
Rural and urban Americans also have starkly different views. Among adults who live in rural areas, 64% say gun ownership increases safety, while among those in urban areas, 57% say it reduces safety. Those living in the suburbs are about evenly split in their views.
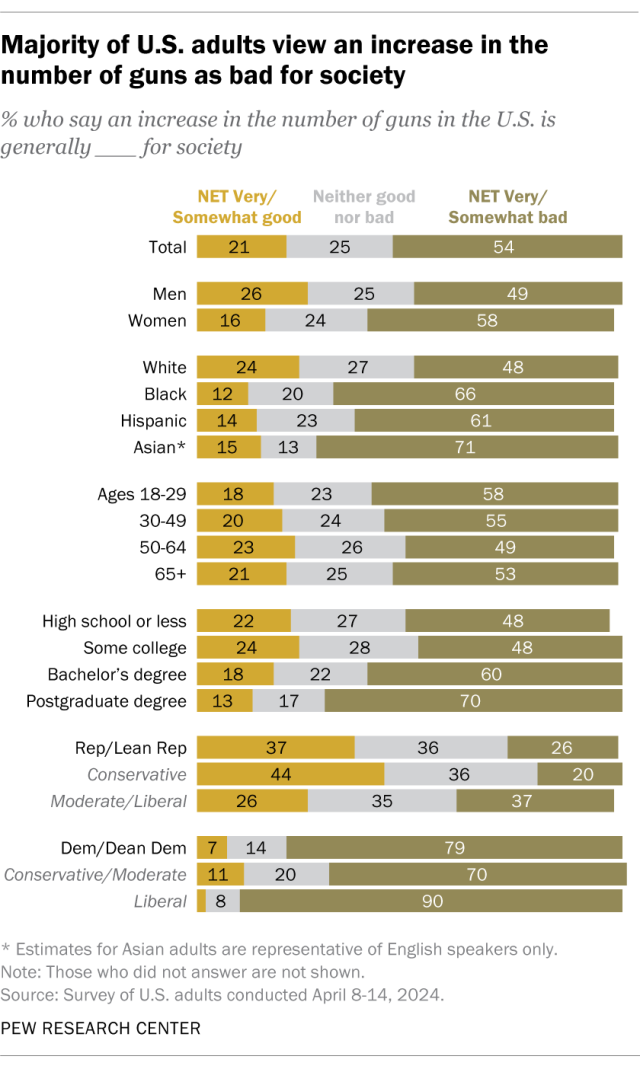
More than half of U.S. adults say an increase in the number of guns in the country is bad for society, according to the April 2024 survey. Some 54% say, generally, this is very or somewhat bad for society. Another 21% say it is very or somewhat good for society, and a quarter say it is neither good nor bad for society.
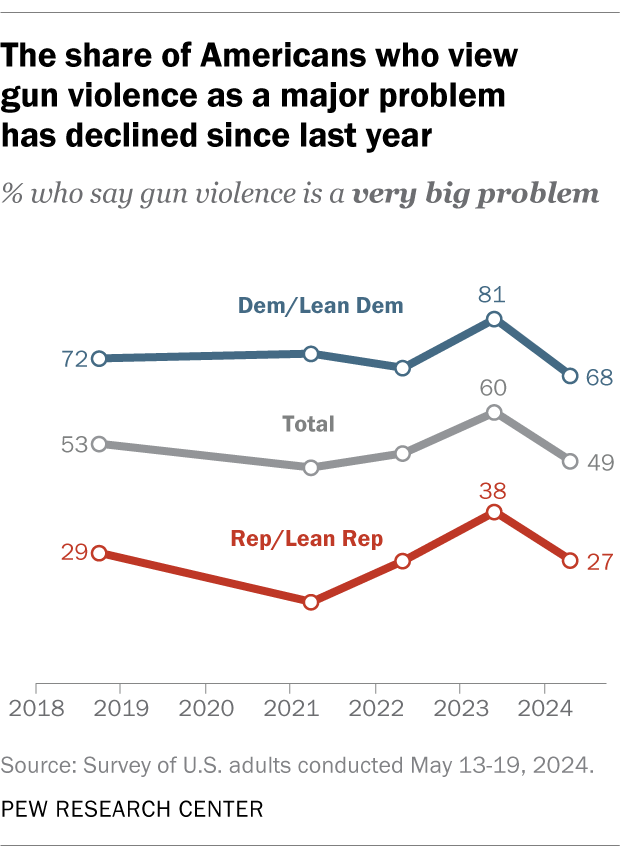
About half of Americans (49%) see gun violence as a major problem, according to a May 2024 survey. This is down from 60% in June 2023, but roughly on par with views in previous years. In the more recent survey, 27% say gun violence is a moderately big problem, and about a quarter say it is either a small problem (19%) or not a problem at all (4%).
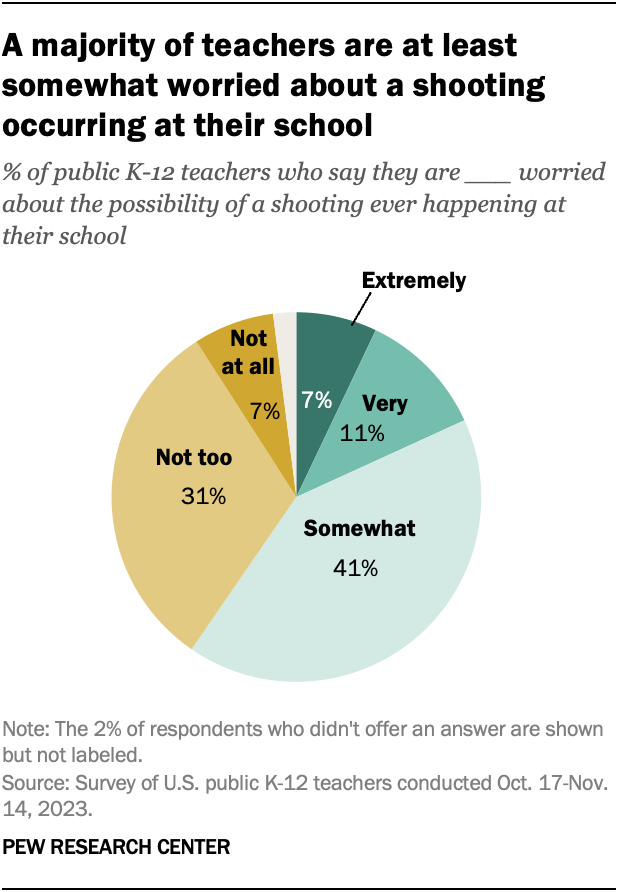
A majority of public K-12 teachers (59%) say they are at least somewhat worried about the possibility of a shooting ever happening at their school, including 18% who are very or extremely worried, according to a fall 2023 Center survey of teachers . A smaller share of teachers (39%) say they are not too or not at all worried about a shooting occurring at their school.
School shootings are a concern for K-12 parents as well: 32% say they are very or extremely worried about a shooting ever happening at their children’s school, while 37% are somewhat worried, according to a fall 2022 Center survey of parents with at least one child younger than 18 who is not homeschooled. Another 31% of K-12 parents say they are not too or not at all worried about this.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Jan. 5, 2016 .
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center .
Americans’ Extreme Weather Policy Views and Personal Experiences
U.s. adults under 30 have different foreign policy priorities than older adults, many adults in east and southeast asia support free speech, are open to societal change, nato seen favorably in member states; confidence in zelenskyy down in europe, u.s., same-sex marriage around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The module is about Types of Speech. After going through this module, you are expected to: distinguish types of speeches according to purpose; use principles of effective speech delivery in different contexts; differentiate the types of speech delivery; identify the speech used in different situations; write a sample speech according to purpose ...
The module is about Types of Speech. After going through this module, you are expected to: • distinguish types of speeches according to purpose; • use principles of effective speech delivery in different contexts; • differentiate the types of speech delivery; • identify the speech used in different situations; • write a sample speech ...
Welcome to the Oral Communication in Context Grade 11 Self-Learning Module (SLM) on Types of Speeches and Speech Style! ... They are called the types of speeches, according to purpose. In the second set of pictures, it shows different social relationships. As you have noticed, the manner of speaking and in the use of language forms as seen in ...
according to purpose and delivery. two classifications of speech. 3 puposes. amount of purposes for speech. Expository/Informative Speech. purpose; 1. given to provide the audience with information regarding a topic or to expand their knowledge about a topic that they were already familiar with. Persuasive Speech.
• Lesson 1 - Types of Speeches • Lesson 2 - Types of Speech Style After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. distinguish the types of speeches according to purpose and delivery; 2. determine the types of speeches used in different real-life situations; 3. distinguish the types of speech style;
clinical reasoning. 16 terms. kenzi4488. Preview. Public Relations Mid-Term: Chapters 1-4. 31 terms. schilterc21. Preview. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Public speaking, Speeches can be classified in two ways:, three basic types of speeches and more.
Oral Communication: Module 6. Flashcards. Learn. Test. Match. Flashcards. Learn. Test. Match. Created by. agulto_shaine. types of speech according to purpose and presentation aids. Terms in this set (15) Informative (type of speech according to purpose)
Oral Communication 11&12-Module 5: Types of Speech Context. 6. Oral Communication 11&12-Module 6A: Types of Speeches. 7. Oral Communication 11&12-Module 6B: Types of Speech Style. ... 14. write a sample speech according to purpose; and 15. apply learning and thinking skills, life skills, and ICT literacy in understanding the principles of ...
Lesson 1 - Types of Speeches; Lesson 2 - Types of Speech Style; After going through this module, you are expected to: distinguish the types of speeches according to purpose and delivery; determine the types of speeches used in different real-life situations; distinguish the types of speech style;
Oral Communication in Context Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 - Module 6: Types of Speeches and Speech Style First Edition, 2021. ... The types of speech according to purpose are informative speech, persuasive speech, and entertainment speech. _____ 15. The credibility of a speaker is important in informative, persuasive, and impromptu ...
Q-Chat. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like is a form of oral communication where a speaker delivers a message orally to an audience., 2 Types of Speeches, •Defines, explains, describes, or demonstrates • It's purpose is to "provide information" clearly and completely for the audience to understand. and more.
After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. distinguish the types of speeches according to purpose and delivery; 2. determine the types of speeches used in different real-life situations; 3. distinguish the types of speech style; 4. identify the social situations in which each speech style is appropriate to use; and 5. observe the ...
Extemporaneous Speech. Speeches can be categorized into four broad areas depending on the amount of preparation that is undertaken and depending upon the nature of the occasion. The four types of speeches are manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu. Our aim is to acquaint you with these four different modes of delivery, to provide ...
If your plan in your speech is to use funny or witty anecdotes to make the audience feel relaxed, your purpose is to use_____. a. expository type of speech b. informative type of speech c. persuasive type of speech d. entertainment type of speech 4. The type of speech style which occurs between a husband and a wife is called _____. a.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like To inform, instruct, persuade, and entertain, Effective speech delivery, Informative, demonstrative, persuasive, and entertaining and more.
After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. identify the various types of speech context; 2. use the types of speech context in order to communicate; 3. list down a communication situation in different speech context and 4. appreciate the importance of understanding the different types of speech context. What I Know Directions.
Topic: Online Class Purpose: to discuss the pros and cons of maximizing the use of technology as a medium of learning Persuasive Speech aims to influence the thinking or behavior of its audience
About four-in-ten U.S. adults say they live in a household with a gun, including 32% who say they personally own one, according to a Center survey conducted in June 2023.These numbers are virtually unchanged since the last time we asked this question in 2021. There are differences in gun ownership rates by political affiliation, gender, community type and other factors.