Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Elements of Argument

9 Toulmin Argument Model
By liza long, amy minervini, and joel gladd.
Stephen Edelston Toulmin (born March 25, 1922) was a British philosopher, author, and educator. Toulmin devoted his works to analyzing moral reasoning. He sought to develop practical ways to evaluate ethical arguments effectively. The Toulmin Model of Argumentation, a diagram containing six interrelated components, was considered Toulmin’s most influential work, particularly in the fields of rhetoric, communication, and computer science. His components continue to provide useful means for analyzing arguments.
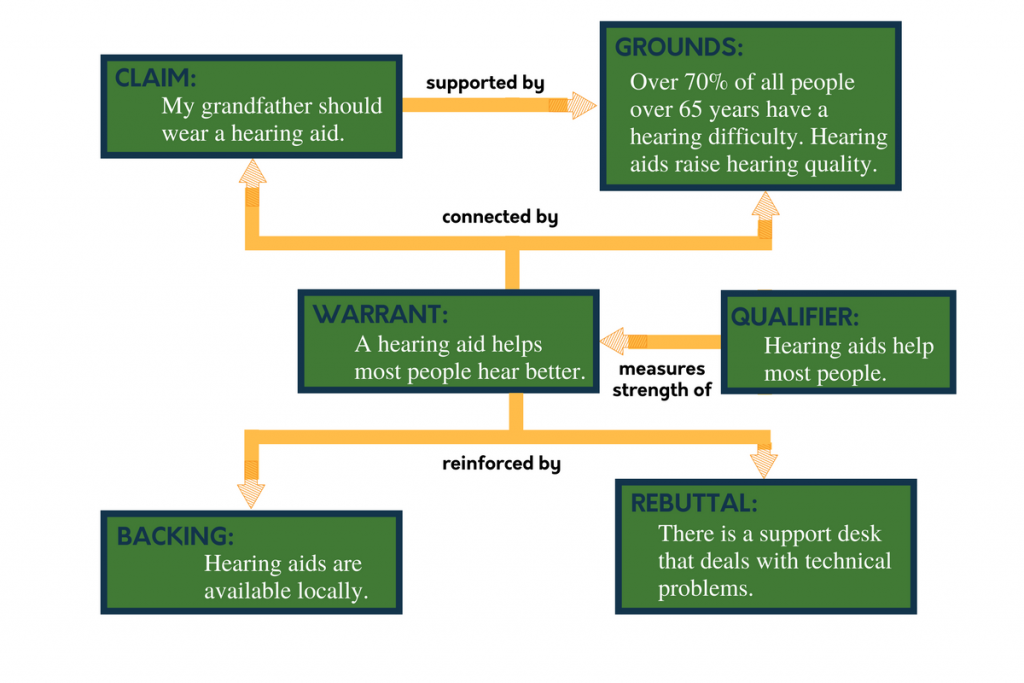
The following are the parts of a Toulmin argument (see Figure 9.1 for an example):
Claim: The claim is a statement that you are asking the other person to accept as true (i.e., a conclusion) and forms the nexus of the Toulmin argument because all the other parts relate back to the claim. The claim can include information and ideas you are asking readers to accept as true or actions you want them to accept and enact. One example of a claim is the following:
My grandfather should wear a hearing aid.
This claim both asks the reader to believe an idea and suggests an action to enact. However, like all claims, it can be challenged. Thus, a Toulmin argument does not end with a claim but also includes grounds and warrant to give support and reasoning to the claim.
Grounds: The grounds form the basis of real persuasion and include the reasoning behind the claim, data, and proof of expertise. Think of grounds as a combination of premises and support. The truth of the claim rests upon the grounds, so those grounds should be tested for strength, credibility, relevance, and reliability. The following are examples of grounds:
Over 70% of all people over 65 years have a hearing difficulty. Hearing aids raise hearing quality.
Information is usually a powerful element of persuasion, although it does affect people differently. Those who are dogmatic, logical, or rational will more likely be persuaded by factual data. Those who argue emotionally and who are highly invested in their own position will challenge it or otherwise try to ignore it. Thus, grounds can also include appeals to emotion, provided they aren’t misused. The best arguments, however, use a variety of support and rhetorical appeals.
Warrant: A warrant links data and other grounds to a claim, legitimizing the claim by showing the grounds to be relevant. The warrant may be carefully explained and explicit or unspoken and implicit. The warrant answers the question, “Why does that data mean your claim is true?” For example,
A hearing aid helps most people hear better.
The warrant may be simple, and it may also be a longer argument with additional sub-elements including those described below. Warrants may be based on logos, ethos or pathos, or values that are assumed to be shared with the listener. In many arguments, warrants are often implicit and, hence, unstated. This gives space for the other person to question and expose the warrant, perhaps to show it is weak or unfounded.
Backing: The backing for an argument gives additional support to the warrant. Backing can be confused with grounds, but the main difference is this: grounds should directly support the premises of the main argument itself, while backing exists to help the warrants make more sense. For example,
Hearing aids are available locally.
This statement works as backing because it gives credence to the warrant stated above, that a hearing aid will help most people hear better. The fact that hearing aids are readily available makes the warrant even more reasonable.
Qualifier: The qualifier indicates how the data justifies the warrant and may limit how universally the claim applies. The necessity of qualifying words comes from the plain fact that most absolute claims are ultimately false (all women want to be mothers, e.g.) because one counterexample sinks them immediately. Thus, most arguments need some sort of qualifier, words that temper an absolute claim and make it more reasonable. Common qualifiers include “most,” “usually,” “always,” or “sometimes.” For example,
Hearing aids help most people.
The qualifier “most” here allows for the reasonable understanding that rarely does one thing (a hearing aid) universally benefit all people. Another variant is the reservation, which may give the possibility of the claim being incorrect:
Unless there is evidence to the contrary, hearing aids do no harm to ears.
Qualifiers and reservations can be used to bolster weak arguments, so it is important to recognize them. They are often used by advertisers who are constrained not to lie. Thus, they slip “usually,” “virtually,” “unless,” and so on into their claims to protect against liability. While this may seem like sneaky practice, and it can be for some advertisers, it is important to note that the use of qualifiers and reservations can be a useful and legitimate part of an argument.
Rebuttal: Despite the careful construction of the argument, there may still be counterarguments that can be used. These may be rebutted either through a continued dialogue, or by pre-empting the counter-argument by giving the rebuttal during the initial presentation of the argument. For example, if you anticipated a counterargument that hearing aids, as a technology, may be fraught with technical difficulties, you would include a rebuttal to deal with that counterargument:
There is a support desk that deals with technical problems.
Any rebuttal is an argument in itself, and thus may include a claim, warrant, backing, and the other parts of the Toulmin structure.
Even if you do not wish to write an essay using strict Toulmin structure, using the Toulmin checklist can make an argument stronger. When first proposed, Toulmin based his layout on legal arguments, intending it to be used analyzing arguments typically found in the courtroom; in fact, Toulmin did not realize that this layout would be applicable to other fields until later. The first three elements–“claim,” “grounds,” and “warrant”–are considered the essential components of practical arguments, while the last three—“qualifier,” “backing,” and “rebuttal”—may not be necessary for all arguments.
Toulmin Exercise
Find an argument in essay form and diagram it using the Toulmin model. The argument can come from an Op-Ed article in a newspaper or a magazine think piece or a scholarly journal. See if you can find all six elements of the Toulmin argument. Use the structure above to diagram your article’s argument.
Attributions
“Toulmin Argument Model” by Liza Long, Amy Minervini, and Joel Gladd is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Writing Arguments in STEM Copyright © by Jason Peters; Jennifer Bates; Erin Martin-Elston; Sadie Johann; Rebekah Maples; Anne Regan; and Morgan White is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
Encyclopedia
Writing with artificial intelligence, toulmin argument.
Stephen Toulmin's model of argumentation theorizes six rhetorical moves constitute argumentation: Evidence , Warrant , Claim , Qualifier , Rebuttal, and Backing . Learn to develop clear, persuasive arguments and to critique the arguments of others. By learning this model, you'll gain the skills to construct clearer, more persuasive arguments and critically assess the arguments presented by others, enhancing your writing and analytical abilities in academic and professional settings.
Table of Contents
Stephen Toulmin’s (1958) model of argument conceptualizes argument as a series of six rhetorical moves :
- Data, Evidence
- Counterargument, Counterclaim
- Reservation/Rebuttal
Related Concepts
Evidence ; Persuasion; Rhetorical Analysis ; Rhetorical Reasoning
Why Does Toulmin Argument Matter?
Toulmin’s model of argumentation is particularly valuable for college students because it provides a structured framework for analyzing and constructing arguments, skills that are essential across various academic disciplines and real-world situations.
By understanding Toulmin’s components—claim, evidence, warrant, backing, qualifier, and rebuttal—students can develop more coherent, persuasive arguments and critically evaluate the arguments of others. This model encourages students to think deeply about the logic and effectiveness of their argumentation, emphasizing the importance of supporting claims with solid evidence and reasoning. Additionally, familiarity with Toulmin’s model prepares students for scenarios involving critical analysis and debate, whether in writing essays, participating in discussions, or presenting research.
By mastering this model, students enhance their ability to communicate effectively, a crucial skill for academic success and professional advancement.
When should writers or speakers consider Toulmin’s model of argument?
Toulmin’s model of argument works especially well in situations where disputes are being reviewed by a third party — such as judge, an arbitrator, or evaluation committee.
Declarative knowledge of Toulmin Argument helps with
- inventing or developing your own arguments (even if you’re developing a Rogerian or Aristotelian argument )
- critiquing your arguments or the arguments of others.
Summary of Stephen Toulmin’s Model of Argument
| : | A claim is a proposition, a thesis. It’s what you want that audience to think, feel, act, and do. For example, during the course of your day, you may make claims of fact; claims of cause-and-effect relationships; claims about best solutions; or claims about values A claim can be made at the or of a text : Mashed potatoes are superior to baked potatoes. | |
| ) | Data may be called Facts, Evidence, Grounds Data is evidence gathered to support the claim. : Mashed potatoes lower the rates of heart disease. | |
| Warrants serve as bridges between warrants and claims. Warrants clarify how the data supports the claim. Warrants may be rules, inference-licenses, scientific laws, principles of historical interpretation, a law, a psychological generalization about human behavior, an extended scholarly conversation on a topic. : You should eat mashed potatoes lower the rates of heart disease. | ||
| : | When situations are especially tricky–maybe is emotionally charged or complex–additional data may be insufficient to win the argument. In those instances, writers, speakers, knowledge workers may provide backing to support the warrant. : Mashed potatoes lower the rates of heart disease. | |
| Other theories, explanations, evidence that refute a claim : Many claim, however, that baked potatoes are superior to mashed due to the amount of toppings and sides available for baked potatoes. or : But isn’t there also evidence that mashed potatoes are fattening because people use alot of butter and cream cheese in their potatoes. Doesn’t obesity leads to heart disease? | ||
| / | Reservation refers to those elements in an argument that define the conditions in which the audience needs to reconsider whether the warrant applies to the particular subject being examined. A reservation can anticipate objections and narrow the general application of the warrant : Mashed potatoes lower the rates of hear disease so long as the potatoes do not use a lot of butter and cream cheese. |
The Three Essential Components of Argument
Stephen Toulmin’s model of argument posits the three essential elements of an argument are
- Data (aka a Fact or Evidence)
- Warrant (which the writer, speaker, knowledge worker . . . may imply rather than explicitly state).
Toulmin’s model presumes data, matters of fact and opinion, must be supplied as evidence to support a claim. The claim focuses the discourse by explicitly stating the desired conclusion of the argument.
In turn, a warrant, the third essential component of an argument, provides the reasoning that links the data to the claim.
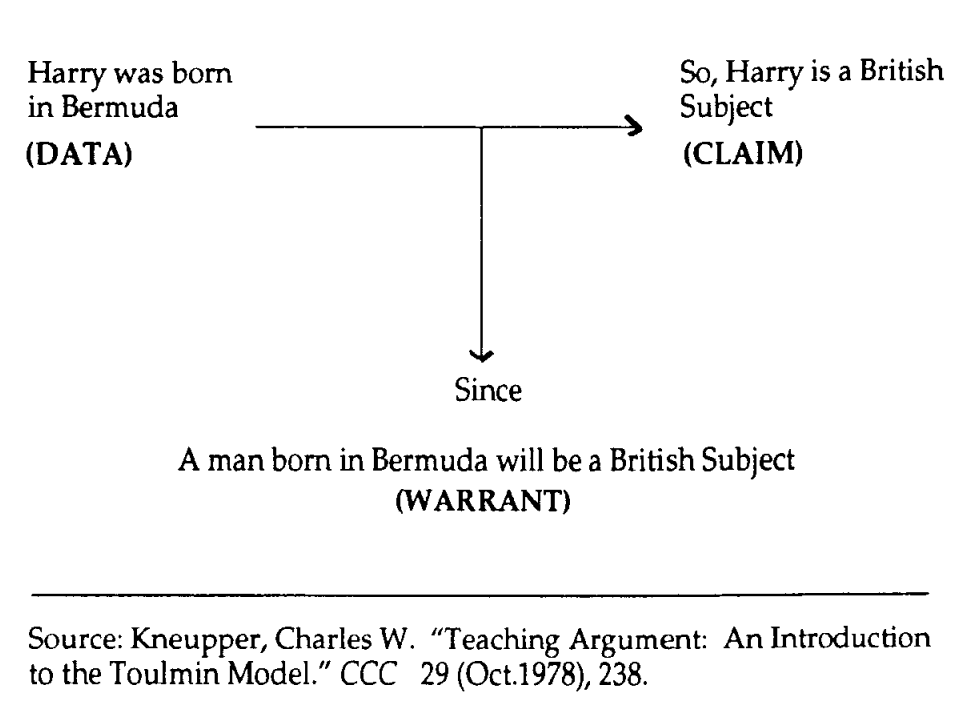
The example in Figure 1 demonstrates the abstract, hypothetical linking between a claim and data that a warrant provides. Prior to this link–that. people born in Bermuda are British–the claim that Harry is a British subject because he was born in Bermuda is unsubstantiated.
The 6 Elements of Successful Argument
While the argument presented in Figure 1 is a simple one, life is not always simple.
In situations where people are likely to dispute the application of a warrant to data, you may need to develop backing for your warrants. o account for the conflicting desires and assumptions of an audience, Toulmin identifies a second triad of components that may not be used:
- Reservation
- Qualification.
Charles Kneupper provides us with the following diagram of these six elements (238):
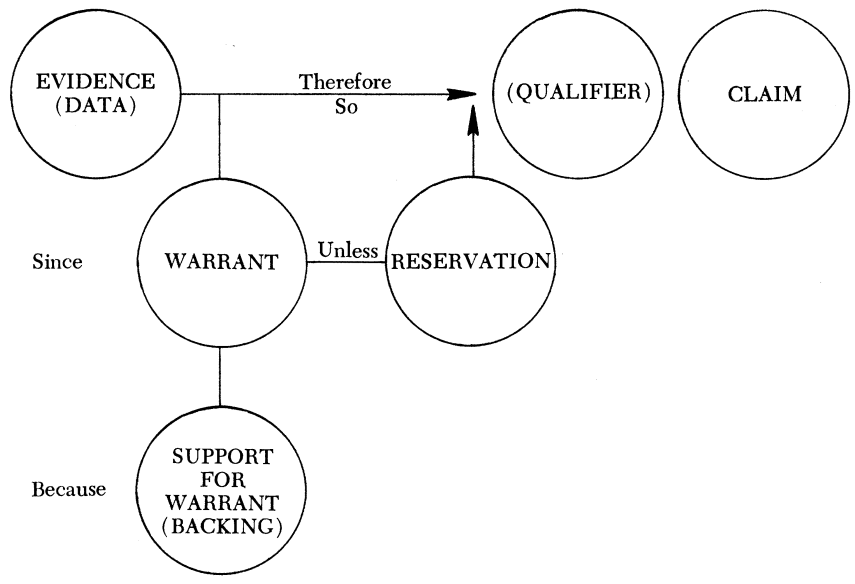
*This article is adapted from Moxley, Joseph M. “ Reinventing the Wheel or Teaching the Basics ?: College Writers ‘ Knowledge of Argumentation .” Composition. Studies 21.2 (1993): 3-15.
Kneupper, C. W. (1978). Teaching Argument: An Introduction to the Toulmin Model. College Composition and Communication , 29 (3), 237–241. https://doi.org/10.2307/356935
Moxley, Joseph M. “ Reinventing the Wheel or Teaching the Basics ?: College Writers ‘ Knowledge of Argumentation .” Composition. Studies 21.2 (1993): 3-15.
Toulmin, S. (1969). The Uses of Argument , Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles


English Composition II - ENGL 1213
- Choosing An Issue
- Find eBooks
- Find Articles
- Search Tips
- Write It, Cite It
- Ask a Librarian
- The Research Proposal
- The Annotated Bibliography
- Essay 1 - The Classical Argument
- Essay 2 - The Rogerian Argument
Requirements
Writing prompt.
Throughout English Composition II, you have utilized research skills, problem solving skills, and analytic skills. The Toulmin Essay provides the student the opportunity to revisit some elements of Classical Argument and analyze another form of argumentative structure.
The essay should include the folllowing:
- 3 to 4 pages (double-spaced), not including the Works Cited page
- In-text citations in the body of the essay
- Works Cited page with your credible sources
- A minimum of 4 sources
To complete this assignment, you should:
- Begin with the issue you used in the Classical Argument
- Gather and evaluate sources
- Establish a thesis and academic level paragraphs
- Write a rough draft and complete revision exercises
- Submit a polished, academic level essay using MLA citation and format
An argument written in this manner unfolds both the strengths and limits of the argument. This is as it should be. No argument should pretend to be stronger than it is or apply further than it is meant to. The point here isn't to "win" or "beat" all the counterarguments; the point is to come as close to the truth or as close to a realistic and feasible solution as we possibly can. Toulmin's model reminds us that arguments are generally expressed with qualifiers and rebuttals rather than asserted as absolutes. This lets the reader know how to take the reasoning, how far it is meant to be applied, and how general it is meant to be. For this essay, you will craft a Toulmin argument utilizing your working annotated bibliography/research proposal and topic and how it applies to a global audience.
This assignment helps you practice the following skills that are essential to your success in school and your professional life beyond school. In this assignment you will:
- Access and collect needed information from appropriate primary and secondary sources
- Synthesize information to develop informed views to produce and refute argumentation
- Compose a well-organized, Toulmin argument to expand your knowledge of a topic
- << Previous: Essay 2 - The Rogerian Argument
- Last Updated: Aug 1, 2024 9:46 AM
- URL: https://libguides.occc.edu/comp2
Toulmin Method: Guide to Writing a Successful Essay
How to write an essay in the toulmin method.
Argumentative essays are a genre of writing that challenges the student to research a topic, gather, generate and evaluate evidence, and summarize a position on the issue. It helps to get as much benefit out of the study as possible. The Toulmin model essay could be part of the shaping and self-understanding of the individual, and one day it will provide evidence to rely on in becoming a professional.
What is the Toulmin Method?
The essay form has become widespread in contemporary higher education, so many students are faced with this question – how to write an essay using the Toulmin model? The idea of an essay comes to us from the Anglo-Saxon educational tradition, where it is one of the basic elements of learning, especially in the early years. Starting an essay, especially an argument one, is a creative and demanding task. Not all students have time for such a job, given their academic schedule. If you want professional assistance, you can hire a writer to write an argumentative essay to make sure of the quality.
Toulmin’s approach, based on logic and in-depth analysis, is best suited to solving complex questions. The British philosopher and professor engaged in practical argumentation believed that it is a process of proposing hypotheses involving the discovery of new ideas and verifying existing information. In The Uses of Argument (1958), Stephen Toulmin proposed a set containing six interrelated components for analyzing arguments, and these are what we will talk about today. Toulmin considered that a good argument could be successful in credibility and resistance to additional criticism. We shall therefore take a look at how it is done.
How do you compose an essay based on Toulmin model? Formulate the statement that you intend to defend. Provide evidence to support it. Then use the factors we talk about below. As an alternative, you can use information from a custom essay writing service that guarantees a good grade. Not everyone is really gifted at writing well-organized texts.
The Six Parts of The Toulmin Argument
The structure of Toulmin argumentative essay is slightly more complex than in other types of papers.
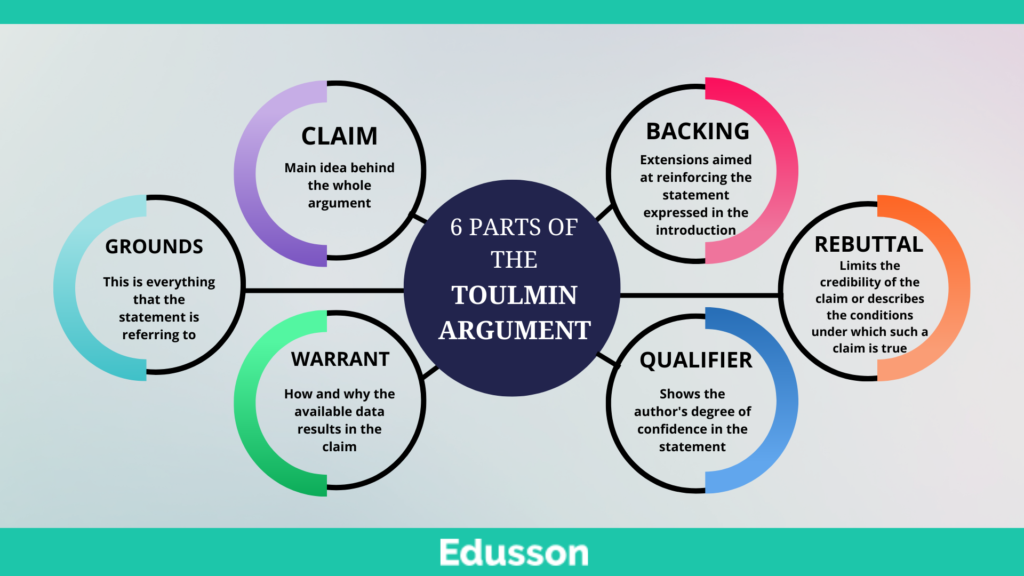
Think of this section as the main idea behind the whole argument. The claim can be divided into five following categories:
- definitions,
- strategies.
This is the part dealing with the answer to the question, “What is the author trying to prove?”.
The arguments are referred to as the basis for the claim. This is everything that the statement is referring to. It can be statistics, facts, evidence, expert opinions, or public attitudes. At this point, the following issue arises: “What is the author trying to demonstrate his point with?”. This is the body where the connection between the data and the argument is established.
Warrants are assumptions that show how and why the available data results in the claim. It gives credibility to the latter. In addition, it is often common knowledge for both the author and the audience, so in most cases, it is not expressed literally but only implied. The guiding question for determining the warrant of an argument has to be asked, “Why does the author draw this conclusion from the data?”.
Warrant Based Generalization
In the simplest Toulmin essays, the generalization essentially summarizes the common knowledge that applies to each specific case. Due to its simplicity, this technique is also used in public speaking as well as in Toulmin model essay.

Warrant Based on Analogy
An argument by analogy is an argument that is made by extrapolating information from one case to another. This is because they share many characteristics. Therefore, an argument by analogy is also very common.
Warrant Based on Sign
It is a matter of one thing deriving from something else. So one thing indicates the existence of another.
Warrant Based on Causality
The relationship between phenomena in which one major thing called the cause, given certain circumstances, brings about another thing called the effect.
Warrant Based on Authority
It is a reference to the views of persons who are recognized or influential in a particular technology or area of activity in society.
Warrant Based on Principle
Values and attitudes are the brightest and most important factors brought in argumentation. They can equally facilitate the achievement of mutual understanding, make it more difficult, and initially block the development of dialogue.
These are extensions aimed at reinforcing the statement expressed in the introduction. Such support should be used when the grounds themselves are not sufficiently persuasive to the readers and listeners.
It limits the credibility of the claim or describes the conditions under which such a claim is true. If the argument does not assume the existence of another opinion, it will be regarded as feeble. If you struggle to conceive of a contrary view, then writing the rebuttal may seem difficult. We advise you to read through the examples.
These can be words or phrases showing the author’s degree of confidence in the statement, namely: likely, possible, impossible, and unconditional.
The first three elements are considered essential to practical argumentation, while the last three are not always indispensable. An argument described in this way in a counter argument essay reveals its strength and limitations. This is the way it should be. There should be no argument that seems stronger than it is or applies more broadly than it is intended to. The point is not to outplay or defeat every counter-argument, but to get as close to the truth or a suitable solution as we are capable of. Once you have familiarized yourself with the process, you may find it complicated; however, don’t get frustrated and use an additional argumentative essay writing service to create a proper sample.
Sample of a Toulmin Argument Model
The following example of body paragraphs is for you to consider:
People should probably have firearms.
- Claim: People should probably have firearms.
- Grounds: People want to be protected.
- Warrant: Self-defense with a firearm is much more effective.
- Backing: Research shows that firearms owners are less likely to be robbed.
- Rebuttal: Not everyone should have access to firearms. Children and people with intellectual disabilities, for example, should not own firearms.
- Qualifier: The percentage of the population with intellectual health illnesses is much lower than that of the average human. The phrase ” probably” in the claim’s wording is a qualifier.
Essay Which Shows Toulmin Method
So why don’t we put all six points into practice and write a good argumentative essay to enhance understanding?
There is an age-old question of the 21st century. However, are current games more harmful or beneficial? To answer it as objectively as possible, one must rely on biology and psychology. Researchers at the University of Central Florida have proven that taking a short break from work to play a video game is far more effective in relieving stress than inactivity with total gadget avoidance and even meditation. Video games can be educational and informative. A popular stereotype is that games are bad for you. They overload the brain or are just a waste of time. Nonsense, there are plenty of benefits to be gained from gameplay if you know the limits.
Play is a way of making the brain stimulated. Games contribute to the socialization of people. Multiplayer games teach social interaction, trust, dialogue, group work, leadership, and management skills. It turns out that those who spend a lot of leisure on a PC or console solve difficult tasks easier. Attention to detail and the speed of brain and eye reactions, accelerated interaction between them, muscle response – all these things are trained to the highest degree. To do this kind of training in real life without threatening your health, you have to try very hard.
Researchers at the Open University of Catalonia have found that video games can positively affect memory, solve difficult issues, build algorithms, and improve attention span and other cognitive abilities of the brain. They stated that video game enthusiasts have an increase in the right side of the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory, over time. Studies have also shown their effectiveness in second language acquisition, learning math, and science. This is potentially good news for pupils, students, and the millions of people who love to play.
In addition, video games have changed significantly in recent years; they have become more complex, realistic, and socially oriented. Although video games have a pure entertainment status, their popularity has been deployed in the service of medicine with the aim of increasing patient health motivation.
Are all computer games completely harmless, and are they a great form of leisure? When it comes to the harms of computer games, they are mainly associated with excessive use. Taking a break will reduce the negative effects. To label them as “bad”, “violent”, and “aggressive” is to overlook many aspects inherent in modern games. People choose games with their advantages and disadvantages depending on their own inner motivation.
Don’t underestimate the importance of computer games as a stress reliever after a stressful day. It’s important to be able to distract yourself and just relax. And joining a virtual world is one of the easiest and most effective ways to escape from external problems for a while.
Most people who have experienced gaming either perceive the activity in a negative or a positive way. The indifferent ones, by and large, are few.
Related posts:
- How To Write A Good Compare And Contrast Essay: Topics, Examples And Step-by-step Guide
How to Write a Scholarship Essay
- The Best Online AP Courses For High School Students [Full Guide]
- Explaining Appeal to Ignorance Fallacy with Demonstrative Examples
Improve your writing with our guides

Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Argument

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How can I effectively present my argument?
In order for your argument to be persuasive, it must use an organizational structure that the audience perceives as both logical and easy to parse. Three argumentative methods —the Toulmin Method , Classical Method , and Rogerian Method — give guidance for how to organize the points in an argument.
Note that these are only three of the most popular models for organizing an argument. Alternatives exist. Be sure to consult your instructor and/or defer to your assignment’s directions if you’re unsure which to use (if any).
Toulmin Method
The Toulmin Method is a formula that allows writers to build a sturdy logical foundation for their arguments. First proposed by author Stephen Toulmin in The Uses of Argument (1958), the Toulmin Method emphasizes building a thorough support structure for each of an argument's key claims.
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows:
Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument.
Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Warrant (Bridge): In this section, you explain why or how your data supports the claim. As a result, the underlying assumption that you build your argument on is grounded in reason.
Backing (Foundation): Here, you provide any additional logic or reasoning that may be necessary to support the warrant.
Counterclaim: You should anticipate a counterclaim that negates the main points in your argument. Don't avoid arguments that oppose your own. Instead, become familiar with the opposing perspective. If you respond to counterclaims, you appear unbiased (and, therefore, you earn the respect of your readers). You may even want to include several counterclaims to show that you have thoroughly researched the topic.
Rebuttal: In this section, you incorporate your own evidence that disagrees with the counterclaim. It is essential to include a thorough warrant or bridge to strengthen your essay’s argument. If you present data to your audience without explaining how it supports your thesis, your readers may not make a connection between the two, or they may draw different conclusions.
Example of the Toulmin Method:
Claim: Hybrid cars are an effective strategy to fight pollution.
Data1: Driving a private car is a typical citizen's most air-polluting activity.
Warrant 1: Due to the fact that cars are the largest source of private (as opposed to industrial) air pollution, switching to hybrid cars should have an impact on fighting pollution.
Data 2: Each vehicle produced is going to stay on the road for roughly 12 to 15 years.
Warrant 2: Cars generally have a long lifespan, meaning that the decision to switch to a hybrid car will make a long-term impact on pollution levels.
Data 3: Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with a battery-powered electric motor.
Warrant 3: The combination of these technologies produces less pollution.
Counterclaim: Instead of focusing on cars, which still encourages an inefficient culture of driving even as it cuts down on pollution, the nation should focus on building and encouraging the use of mass transit systems.
Rebuttal: While mass transit is an idea that should be encouraged, it is not feasible in many rural and suburban areas, or for people who must commute to work. Thus, hybrid cars are a better solution for much of the nation's population.
Rogerian Method
The Rogerian Method (named for, but not developed by, influential American psychotherapist Carl R. Rogers) is a popular method for controversial issues. This strategy seeks to find a common ground between parties by making the audience understand perspectives that stretch beyond (or even run counter to) the writer’s position. Moreso than other methods, it places an emphasis on reiterating an opponent's argument to his or her satisfaction. The persuasive power of the Rogerian Method lies in its ability to define the terms of the argument in such a way that:
- your position seems like a reasonable compromise.
- you seem compassionate and empathetic.
The basic format of the Rogerian Method is as follows:
Introduction: Introduce the issue to the audience, striving to remain as objective as possible.
Opposing View : Explain the other side’s position in an unbiased way. When you discuss the counterargument without judgement, the opposing side can see how you do not directly dismiss perspectives which conflict with your stance.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): This section discusses how you acknowledge how the other side’s points can be valid under certain circumstances. You identify how and why their perspective makes sense in a specific context, but still present your own argument.
Statement of Your Position: By this point, you have demonstrated that you understand the other side’s viewpoint. In this section, you explain your own stance.
Statement of Contexts : Explore scenarios in which your position has merit. When you explain how your argument is most appropriate for certain contexts, the reader can recognize that you acknowledge the multiple ways to view the complex issue.
Statement of Benefits: You should conclude by explaining to the opposing side why they would benefit from accepting your position. By explaining the advantages of your argument, you close on a positive note without completely dismissing the other side’s perspective.
Example of the Rogerian Method:
Introduction: The issue of whether children should wear school uniforms is subject to some debate.
Opposing View: Some parents think that requiring children to wear uniforms is best.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): Those parents who support uniforms argue that, when all students wear the same uniform, the students can develop a unified sense of school pride and inclusiveness.
Statement of Your Position : Students should not be required to wear school uniforms. Mandatory uniforms would forbid choices that allow students to be creative and express themselves through clothing.
Statement of Contexts: However, even if uniforms might hypothetically promote inclusivity, in most real-life contexts, administrators can use uniform policies to enforce conformity. Students should have the option to explore their identity through clothing without the fear of being ostracized.
Statement of Benefits: Though both sides seek to promote students' best interests, students should not be required to wear school uniforms. By giving students freedom over their choice, students can explore their self-identity by choosing how to present themselves to their peers.
Classical Method
The Classical Method of structuring an argument is another common way to organize your points. Originally devised by the Greek philosopher Aristotle (and then later developed by Roman thinkers like Cicero and Quintilian), classical arguments tend to focus on issues of definition and the careful application of evidence. Thus, the underlying assumption of classical argumentation is that, when all parties understand the issue perfectly, the correct course of action will be clear.
The basic format of the Classical Method is as follows:
Introduction (Exordium): Introduce the issue and explain its significance. You should also establish your credibility and the topic’s legitimacy.
Statement of Background (Narratio): Present vital contextual or historical information to the audience to further their understanding of the issue. By doing so, you provide the reader with a working knowledge about the topic independent of your own stance.
Proposition (Propositio): After you provide the reader with contextual knowledge, you are ready to state your claims which relate to the information you have provided previously. This section outlines your major points for the reader.
Proof (Confirmatio): You should explain your reasons and evidence to the reader. Be sure to thoroughly justify your reasons. In this section, if necessary, you can provide supplementary evidence and subpoints.
Refutation (Refuatio): In this section, you address anticipated counterarguments that disagree with your thesis. Though you acknowledge the other side’s perspective, it is important to prove why your stance is more logical.
Conclusion (Peroratio): You should summarize your main points. The conclusion also caters to the reader’s emotions and values. The use of pathos here makes the reader more inclined to consider your argument.
Example of the Classical Method:
Introduction (Exordium): Millions of workers are paid a set hourly wage nationwide. The federal minimum wage is standardized to protect workers from being paid too little. Research points to many viewpoints on how much to pay these workers. Some families cannot afford to support their households on the current wages provided for performing a minimum wage job .
Statement of Background (Narratio): Currently, millions of American workers struggle to make ends meet on a minimum wage. This puts a strain on workers’ personal and professional lives. Some work multiple jobs to provide for their families.
Proposition (Propositio): The current federal minimum wage should be increased to better accommodate millions of overworked Americans. By raising the minimum wage, workers can spend more time cultivating their livelihoods.
Proof (Confirmatio): According to the United States Department of Labor, 80.4 million Americans work for an hourly wage, but nearly 1.3 million receive wages less than the federal minimum. The pay raise will alleviate the stress of these workers. Their lives would benefit from this raise because it affects multiple areas of their lives.
Refutation (Refuatio): There is some evidence that raising the federal wage might increase the cost of living. However, other evidence contradicts this or suggests that the increase would not be great. Additionally, worries about a cost of living increase must be balanced with the benefits of providing necessary funds to millions of hardworking Americans.
Conclusion (Peroratio): If the federal minimum wage was raised, many workers could alleviate some of their financial burdens. As a result, their emotional wellbeing would improve overall. Though some argue that the cost of living could increase, the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
What Is the Toulmin Model of Argument?
Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
The Toulmin model (or system) is a six-part model of argument (with similarities to the syllogism ) introduced by British philosopher Stephen Toulmin in his 1958 book The Uses of Argument .
The Toulmin model (or "system") can be used as a tool for developing, analyzing, and categorizing arguments.
Purpose of the Toulmin Model
"When I wrote [ The Uses of Argument ], my aim was strictly philosophical: to criticize the assumption, made by most Anglo-American academic philosophers, that any significant argument can be put in formal terms ... In no way had I set out to expound a theory of rhetoric or argumentation: my concern was with twentieth-century epistemology, not informal logic . Still less had I in mind an analytical model like that which, among scholars of Communication, came to be called 'the Toulmin model,'" (Stephen Toulmin, The Uses of Argument , revised ed. Cambridge Univ. Press, 2003).
The Six Components of an Effective Argument
"What is it that makes arguments work? What makes arguments effective? The British logician Stephen Toulmin made important contributions to argument theory that are useful for this line of inquiry. Toulmin found six components of arguments:
- Claim : A statement that something is so.
- Data : The backing for the claim.
- Warrant : The link between the claim and the grounds.
- Backing : Support for the warrant.
- Modality : The degree of certainty employed in offering the argument.
- Rebuttal : Exceptions to the initial claim," (J. Meany and K. Shuster, Art, Argument, and Advocacy . IDEA, 2002).
"[Toulmin's] general model of ' data ' leading to a ' claim ,' mediated by a ' warrant ' with any necessary ' backing ,' has been very influential as a new standard of logical thinking, particularly among scholars of rhetoric and speech communication. He takes seriously the contexts in which arguments emerge and looks to evaluate them in ways relevant to those contexts," (C. W. Tindale, Rhetorical Argumentation . Sage, 2004).
Using the Toulmin System
"Use the seven-part Toulmin system to begin to develop an argument ... Here is the Toulmin system:
- Make your claim.
- Restate or qualify your claim.
- Present good reasons to support your claim.
- Explain the underlying assumptions that connect your claim and your reasons. If an underlying assumption is controversial, provide backing for it.
- Provide additional grounds to support your claim.
- Acknowledge and respond to possible counterarguments.
- Draw a conclusion, stated as strongly as possible," (Lex Runciman, et al., Exercises for the Everyday Writer , 4th ed. Beford/St. Martin's, 2009).
The Toulmin Model and the Syllogism
"Toulmin's model actually boils down to a rhetorical expansion of the syllogism ... Although the reactions of others are anticipated, the model is primarily directed at representing the argumentation for the standpoint of the speaker or writer who advances the argumentation. The other party remains in fact passive: The acceptability of the claim is not made dependent on a systematic weighing up of arguments for and against the claim," (F. H. van Eemeren and R. Grootendorst, A Systematic Theory of Argumentation . Cambridge University Press, 2004).
- Data Definition and Examples in Argument
- Backing (argument)
- Warrants in the Toulmin Model of Argument
- Argument (Rhetoric and Composition)
- Rogerian Argument: Definition and Examples
- What is Sophism in Rhetoric?
- Informal Logic
- The Rhetorical Canons
- The Theory of Poverty of the Stimulus in Language Development
- Inference in Arguments
- Techne (Rhetoric)
- What Does Argumentation Mean?
- Definition and Examples of the Logical Fallacy
- Circular Reasoning Definition and Examples
- What is a Logical Fallacy?
- Narratio in Rhetoric

- Houston Community College
- Eagle Online

- Composition I and II (Prompts / Help / Exercises)
- Essay Prompts and Rubrics
- 1302 Prompts and Sample Essays
Sample Toulmin
To print or download this file, click the link below:

The Visual Communication Guy
Learn Visually. Communicate Powerfully.

- About The VCG
- Contact Curtis
- Five Paragraph Essay
- IMRaD (Science)
- Indirect Method (Bad News)
- Inverted Pyramid (News)
- Martini Glass
- Narrative Format
- Rogerian Method
- Toulmin Method
- Apostrophes
- Exclamation Marks (Points)
- Parentheses
- Periods (Full Stops)
- Question Marks
- Quotation Marks
- Plain Language
- APPEALS: ETHOS, PATHOS, LOGOS
- CLUSTER ANALYSIS
- FANTASY-THEME
- GENERIC CRITICISM
- IDEOLOGICAL CRITICISM
- NEO-ARISTOTELIAN
- O.P.T.I.C. (VISUAL ANALSYIS)
- S.O.A.P.S.T.O.N.E. (WRITTEN ANALYSIS)
- S.P.A.C.E.C.A.T. (RHETORICAL ANALYSIS)
- BRANCHES OF ORATORY
- FIGURES OF SPEECH
- FIVE CANONS
- LOGICAL FALLACIES
- Information Design Rules
- Arrangement
- Organization
- Negative Space
- Iconography
- Photography
- Which Chart Should I Use?
- “P” is for PREPARE
- "O" is for OPEN
- "W" is for WEAVE
- “E” is for ENGAGE
- PRESENTATION EVALUTION RUBRIC
- POWERPOINT DESIGN
- ADVENTURE APPEAL
- BRAND APPEAL
- ENDORSEMENT APPEAL
- HUMOR APPEAL
- LESS-THAN-PERFECT APPEAL
- MASCULINE & FEMININE APPEAL
- MUSIC APPEAL
- PERSONAL/EMOTIONAL APPEAL
- PLAIN APPEAL
- PLAY-ON-WORDS APPEAL
- RATIONAL APPEAL
- ROMANCE APPEAL
- SCARCITY APPEAL
- SNOB APPEAL
- SOCIAL APPEAL
- STATISTICS APPEAL
- YOUTH APPEAL
- The Six Types of Résumés You Should Know About
- Why Designing Your Résumé Matters
- The Anatomy of a Really Good Résumé: A Good Résumé Example
- What a Bad Résumé Says When It Speaks
- How to Write an Amazing Cover Letter: Five Easy Steps to Get You an Interview
- Make Your Boring Documents Look Professional in 5 Easy Steps
- Business Letters
- CONSUMER PROFILES
- ETHNOGRAPHY RESEARCH
- FOCUS GROUPS
- OBSERVATIONS
- SURVEYS & QUESTIONNAIRES
- S.W.O.T. ANALYSES
- USABILITY TESTS
- CITING SOURCES: MLA FORMAT
- MLA FORMAT: WORKS CITED PAGE
- MLA FORMAT: IN-TEXT CITATIONS
- MLA FORMAT: BOOKS & PAMPHLETS
- MLA FORMAT: WEBSITES AND ONLINE SOURCES
- MLA FORMAT: PERIODICALS
- MLA FORMAT: OTHER MEDIA SOURCES
- Course Syllabi
- Checklists and Peer Reviews (Downloads)
- Communication
- Poster Prints
- Poster Downloads
- Handout & Worksheet Downloads
- QuickGuide Downloads
- Downloads License Agreements

How To Organize a Paper: The Toulmin Method

What is the Toulmin Method?
The Toulmin Method of Argumentation is a complex argumentation structure that allows you to establish your argument while considering your opponents’ points of view. While this method is intended for giving complex and well-supported arguments that are mindful of what opponents will say in response to your claims, the Toulmin Method is a one-sided argument that does not attempt to build common ground, as the Rogerian Method does.
The goal of the Toulmin Method is to persuade the reader that your argument is reasonable and effective based on thorough research and organization.
When Do I Use the Toulmin Method?
You will find the Toulmin Method most useful to write theoretical essays or academic papers. The Toulmin Method is effective in presenting thorough support for your argument. Thus, it is ideal for arguments in which there will be much dissent or controversy surrounding the argument. It is also useful for making complex arguments.
How Does the Toulmin Method Work?
When you write using the Toulmin Method, you need to be prepared to know and explain every facet of your argument. The goal is to be as detailed and persuasive about your argument as possible, countering opposing views etc.
The main elements that are typically included in the Toulmin Method are as follows:
- Claim: A claim is the main argument that you are trying to express. In terms of the 5-Paragraph Essay , it’s the thesis statement.
- Grounds: The grounds are what the claim is based on. It is the supporting evidence that is needed to understand and accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrant is the piece that connects the grounds to the claim. It explains how you got from the information in the grounds to the claim. It may include legal principles, ethical principles, and laws of nature, etc.
- Backing: This is the support and justification for the warrant.
- Qualifiers: Qualifiers limit your claim by placing conditions on the arguments that do not fully support the claim. These are the “usually,” “will likely,” and “possibly” claims that are not certain.
- Rebuttal: The rebuttal is where you identify opposing arguments to your claim. Any argument will have rebuttals, so this is where you would identify them, to present that you have acknowledged that they exist and can give your evidence to counter these claims.
The Toulmin Method may not convince an opposing party that you are right, but it shows that you have solid evidence and reasoning behind your argument, regardless of what they may think of the argument itself.
The image below shows how the parts of the Toulmin Method are all connected to one another and perhaps don’t necessarily follow a linear format as the steps listed above suggest. The steps only show one possible way of organizing the Toulmin Method. The image shows that there may be a need to go back and re-visit different steps in order to fully support all areas of the argument.
Example of the Toulmin Method
Imagine that you want to present an argument stating that smoking tobacco should be banned on all college campuses. This would be your claim .
The grounds on which you would base this claim would possibly note the health risks associated with secondhand smoke.
The warrant may present the idea that the health risks of secondhand smoke hinder learning, which may be warranted by a study that shows the effects of secondhand smoke on learning.
It may be appropriate to indicate that the health risks will “possibly” hinder learning, or that the hindrance occurs only in at risk groups such as those with asthma to qualify the argument.
A rebuttal to the argument could be that smoking tobacco is a way that some students relax in between classes or that it is only harmful if extremely high levels of secondary smoke are ingested.
Toulmin, Stephen, et al. An Introduction to Reasoning . Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1979.
Shop for your perfect poster print or digital download at our online store!
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
Ideas for a Toulmin Argument
A good argument using British philosopher Stephen Toulmin's model will include a clear opinion or claim backed by grounds or reasons that support it. Toulmin arguments also include a rebuttal section recognizing an opposing point of view. Choose a topic that has a variety of opinions on a political, environmental, health-related or cultural issue for a Toulmin argument paper or speech.
Political Ideas
Political topics like abortion or the death penalty are good fits for a Toulmin argument because they allow you to state your opinion and also have opposing points of view that you can use for the rebuttal portion of the paper. Find a list of political topics on academic websites like procon.org. For example, write about animal testing and the need for more laws to prevent it. Or, write about the debate over whether churches, synagogues and mosques should pay taxes.
Environmental Issues
Water quality, energy conservation, drought, air quality and biodiversity or endangered species are environmental issues suitable for Toulmin arguments, because they include several different perspectives you may use for a clear claim as well as rebuttals. Find a list of environmental topics on websites like Science Daily. For example, craft a paper about the loss of coral reefs around the world and include recommendations to improve the situation. Or, discuss declining air quality and ways scientists suggest to combat it.
Health-Related Concepts
Find a list of health topics affecting the globe at the World Health Organization website. Differing approaches to health problems can serve as good claims for a Toulmin argument as well as rebuttals. Write about the increase in diseases such as diabetes and cancer around the world and ways to prevent them. Or, craft an argument in support of telemedicine and mobile technology and how they bring health care for people living in remote areas. Another option could be writing about an individual health choice like vegetarianism.
Cultural Debates
Same-sex marriage, video games and violence and social media affect popular culture and society and spark diverse opinions, some of which you may select to support your Toulmin model claim. Opposing perspectives on these issues are readily available. Find a list of social and cultural topics on websites like procon.org. For example, explore reasons to pay student-athletes in college. Write about a current issue like the impact of tablet computers instead of textbooks, or ways to stop school bullying.
- Changing Minds: Toulmin's Argument Model
- Writing@CSU: The Toulmin Method
- San Diego State University: The Toulmin Model of Argumentation
Amy Sterling Casil is an award-winning writer with a Master of Fine Arts in creative writing from Chapman University in Orange, Calif. She is a professional author and college writing teacher, and has published 20 nonfiction books for schools and libraries.

COMMENTS
What is the Toulmin Method? Developed by philosopher Stephen E. Toulmin, the Toulmin method is a style of argumentation that breaks arguments down into six component parts: claim, grounds, warrant, qualifier, rebuttal, and backing.In Toulmin's method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: the claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
Sample Toulmin Argument. Now that you have had the chance to learn about Toulmin, it's time to see what a Toulmin argument might look like. Below, you'll see a sample argumentative essay, written according to MLA formatting guidelines, with a particular emphasis on Toulmin elements. Click the image below to open a PDF of the sample paper.
The Toulmin Method is a way of doing very detailed analysis, in which we break an argument into its various parts and decide how effectively those parts participate in the overall whole. ... In other words, if you are attempting to respond to that argument--whether in a formal response essay or in an arguing essay where you are using the ...
Toulmin Exercise. Find an argument in essay form and diagram it using the Toulmin model. The argument can come from an Op-Ed article in a newspaper or a magazine think piece or a scholarly journal. See if you can find all six elements of the Toulmin argument. Use the structure above to diagram your article's argument. Attributions
The grounds give place to the warrant, which is the assumption that connects the grounds to the main idea, or the claim. An example of the Toulmin method structure: Claim: The street is safely guarded in the night. Grounds: There are police officers that go through the street every hour from 8 PM to 6 AM. Warrant: The main function of a police ...
However, the Toulmin Method offers not just reasons, data, and evidence to support an argument but also: Warrants: to show how the data is logically connected to the data. Backing: to show that the logic of the warrants is realistic and believable. Counter-arguments: to admit the other sides of the question.; Rebuttal: to explain why the counter-arguments are wrong, or to limit or qualify the ...
Table 1 The Three Essential Components of Argument. Stephen Toulmin's model of argument posits the three essential elements of an argument are. Data (aka a Fact or Evidence); Claim; Warrant (which the writer, speaker, knowledge worker . . . may imply rather than explicitly state).; Toulmin's model presumes data, matters of fact and opinion, must be supplied as evidence to support a claim.
Toulmin's model reminds us that arguments are generally expressed with qualifiers and rebuttals rather than asserted as absolutes. ... For this essay, you will craft a Toulmin argument utilizing your working annotated bibliography/research proposal and topic and how it applies to a global audience. ... Toulmin argument to expand your knowledge ...
Argumentative essays are a genre of writing that challenges the student to research a topic, gather, generate and evaluate evidence, and summarize a position on the issue. It helps to get as much benefit out of the study as possible. The Toulmin model essay could be part of the shaping and self-understanding of the individual, and one day it ...
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows: Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument. Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
In this assignment, you will be writing a grammatically correct, clearly organized essay that uses the Toulmin model to argue in favor of one of the possible points-of-view on a controversial social, ethical, historical, or intellectual issue. By following the Toulmin model, your paper should: In the Introduction: Briefly define your topic.
Updated on June 04, 2020. The Toulmin model (or system) is a six-part model of argument (with similarities to the syllogism) introduced by British philosopher Stephen Toulmin in his 1958 book The Uses of Argument . The Toulmin model (or "system") can be used as a tool for developing, analyzing, and categorizing arguments.
Argumentative Writing Outline/Structure - The Toulmin Method (With Attached Outline Template) Introductory Paragraph Hook - Quote, Fact, Example, Anecdote, Statistic General Information - Background of the Topic Thesis - CLAIM (One to Two or Three Point CLAIM STATEMENTS/Thesis Statements are st...
Essay Prompts and Rubrics. 1302 Prompts and Sample Essays. Sample Toulmin.
The main elements that are typically included in the Toulmin Method are as follows: Claim: A claim is the main argument that you are trying to express. In terms of the 5-Paragraph Essay, it's the thesis statement. Grounds: The grounds are what the claim is based on. It is the supporting evidence that is needed to understand and accept the claim.
The Toulmin method is the most common and logical way of organizing an argument. Its divided into the claim, data, warrant or the bridge, backing or the foundation, the counterclaim, and the rebuttal. The claim is the writer's thesis for the argument. Data is the evidence to use to support. 682 Words. 3 Pages.
Toulmin Argument. The Toulmin method, developed by philosopher Stephen Toulmin , is essentially a structure for analyzing arguments. But the elements for analysis are so clear and structured that many professors now have students write argumentative essays with the elements of the Toulmin method in mind. This type of argument works well when ...
Ideas for a Toulmin Argument. A good argument using British philosopher Stephen Toulmin's model will include a clear opinion or claim backed by grounds or reasons that support it. Toulmin arguments also include a rebuttal section recognizing an opposing point of view. Choose a topic that has a variety of opinions on a political, environmental ...
The Toulmin model is a process for evaluating or creating an argument named after English philosopher Stephen E. Toulmin. Toulmin came up with this model for examining arguments during the 20th century. Also called the Toulmin method, the Toulmin model is a structured way to analyze or construct logical and thorough arguments.
The Toulmin method, based on the work of philosopher Stephen Toulmin, is one way of analyzing a text that we read, with an eye toward responding to that particular argument (as in a writing assignment that asks us to respond) and, ultimately, toward analyzing and improving the arguments we ourselves make. Definition of the Toulmin Method
The Toulmin Model of argumentation asserts that a good argument consists of six parts which intend to develop a practical argument. The first element is the "claim," or the conclusion that the argument must establish. The next part is the "data," or the facts and evidence collected and used to confirm the argument.