Lesson Plans
Introduction to phytoplankton.
In this lesson, students investigate and identify various phytoplankton using images that were previously taken with a compound microscope. Credit: National Science Foundation-sponsored Center for Microbial Oceanography: Research and Education (C-MORE)

Materials Required
- TEACHER GUIDE – Lesson 1: Introduction to Plankton
- POWERPOINT SCRIPT
- STUDENT WORKSHEET – POWERPOINT – Lesson 1: Introduction to Plankton (Page 1)

- TEACHER ANSWER KEY to STUDENT WORKSHEET – POWERPOINT – Lesson 1: Introduction to Plankton. NOTE:*Email [email protected] to request a completed teacher answer key. Please include name, school and grade(s) taught in your request.
- STUDENT WORKSHEET – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab (Page 2)
- SLIDES – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab

Advance Preparation:
- Queue the PowerPoint, "Introduction to Plankton." (A narrated version can be found here .) A PPT script is included as a guide.

1. Distribute a STUDENT WORKSHEET – PowerPoint – Lesson 1: Introduction to Plankton to each student. Review the PowerPoint or play the narrated PowerPoint presentation to familiarize your students with marine plankton.
2. Address the main topics of the PowerPoint presentation with your students:
- phytoplankton are plant‐like and have certain adaptations for survival;
- zooplankton are animal‐like and can exist as meroplankton (organisms that are plankton for part of their life cycle) or holoplankton (organisms that remain plankton for their entire life cycle);
- plankton form the basis of the marine food web.
3. Review the answers to the STUDENT WORKSHEET. MAKE OBSERVATIONS:
1. Distribute a STUDENT WORKSHEET – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab to each student.
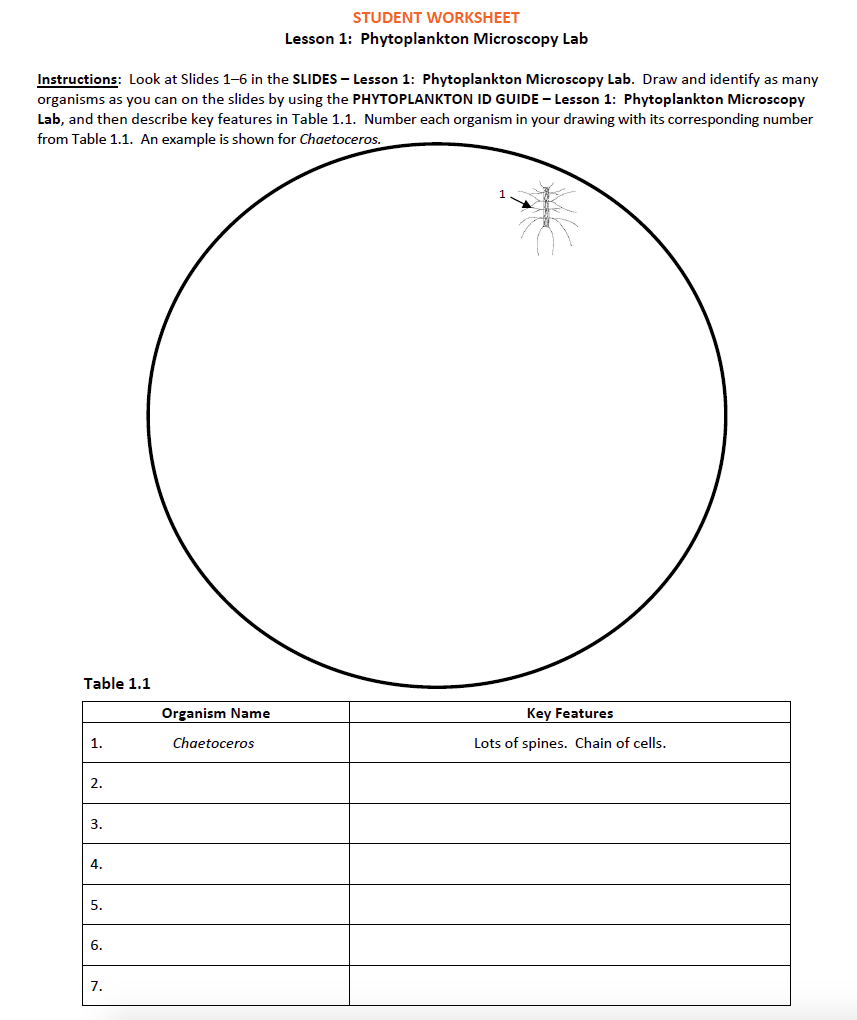
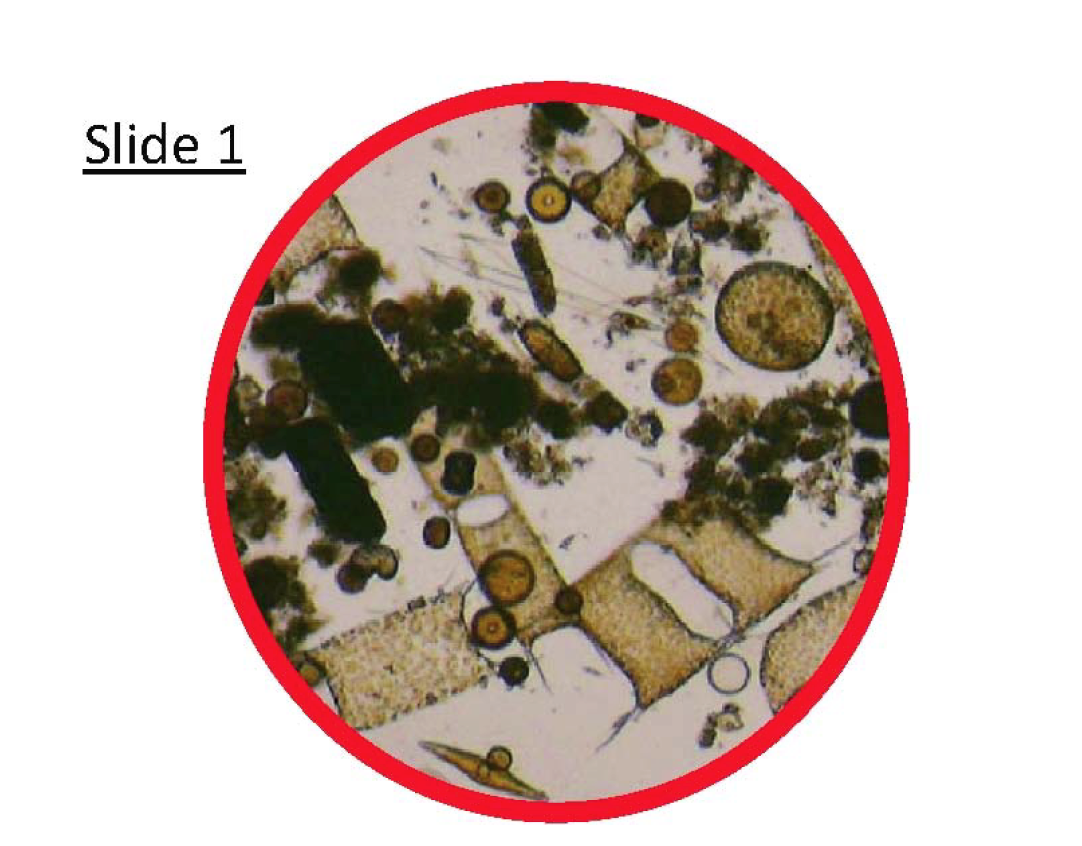
2. Divide the students into five groups. Distribute one copy of SLIDES – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab and two copies of PHYTOPLANKTON ID GUIDE – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab to each group.
3. Tell your students that they will be completing a phytoplankton microscopy lab. Explain that the SLIDES – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab are phytoplankton images that were taken with a compound microscope. Compound microscopes have very high magnification, which is essential to view these tiny phytoplankton. In Lesson 2, dissecting microscopes (which have lower magnification) suffice to study the larger zooplankton. After a quick introduction to the phytoplankton lab, students should be able to work independently in their groups.
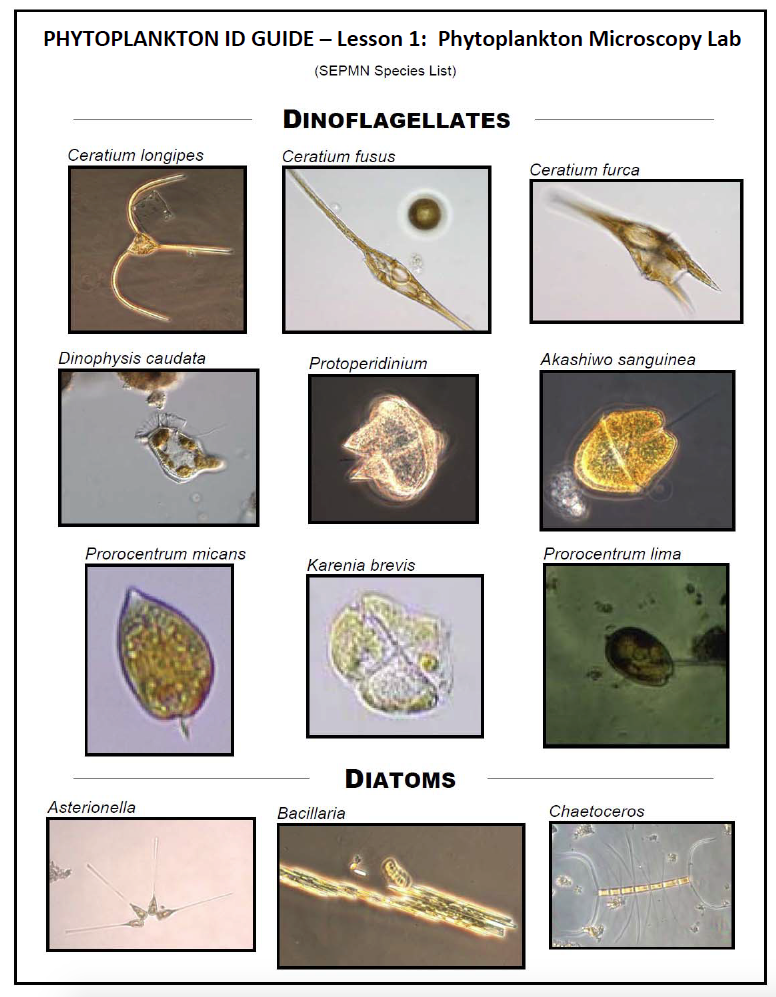
4. Have students use the PHYTOPLANKTON ID GUIDE – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab to identify the marine phytoplankton that are found on the various photomicrographs (microscope images) provided in the SLIDES – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab.
ANALYZE & DESCRIBE YOUR DATA
- Have the students review their slides and identify and document the phytoplankton.
- Students should identify these and draw the phytoplankton on their STUDENT WORKSHEET – Lesson 1: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab in the circle. Students will label them as 1, 2, 3... for identification only. Students also describe the key characteristics of these phytoplankton in the table.
SHARE YOUR IDEAS
- When students are finished, have them check their identifications/descriptions with the class.
- Pleurosigma
- Coscinodiscus
- Skeletonema
- Protoperidinium
- Pseudo-nitzschia
- Rhizosolenia
- Chaetoceros
- Thalassionema
- Present the questions below and facilitate class discussion:
- What phytoplankton appear the most often? Coscinodiscus, Pleurosigma Least often? Thalassionema, Ditylum
What adaptations do these have that makes them unique? What advantages do these adaptations provide to the organism?
- Coscinodiscus - These centric diatoms are single cells that do not have adaptations to help them stay afloat in the water column. Instead, they are at the mercy of the ocean's stratified water to keep them at the top of the water column. This phytoplankton often resembles a pillbox.
- Pleurosigma - This diatom usually has a long diamond shape and features regularly pulsating inner organelles to help it move through the water.
- Thalassionema - This phytoplankton have small bristles that stick out from the top and bottom of the cell and around its perimeter. In the middle, is a long thread that it uses to connect itself with another Thalassionema.
- Ditylum - This phytoplankton is easily recognized by its two large spines on its rectangular body. These spines help to increase surface area in order to keep them afloat, instead of sink.
Refer to the Guide and PowerPoint for more information about adaptations and environments.
Supported NGSS Performance Expectations
- 4-LS1-1: Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.
- MS-LS1-4: Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respecti
Learning Objectives
- The student will use images previously taken with a compound microscope to identify various species of common phytoplankton
Essential Questions
- What are phytoplankton?
- What are common structural and behavioral adaptations of phytoplankton?
Teacher Background Information
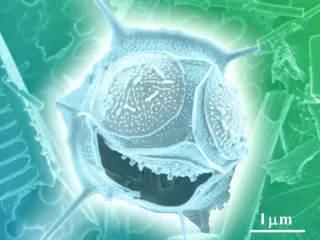
Phytoplankton are the foundation of the aquatic food web, the primary producers, feeding everything from microscopic, animal-like zooplankton to multi-ton whales. Small fish and invertebrates also graze on the plant-like organisms, which are eaten by larger marine animals and so on. Like land plants, phytoplankton consume carbon dioxide and produce oxygen during photosynthesis. In fact, phytoplankton created about half the oxygen we breathe today. Phytoplankton are extremely diverse, varying from photosynthesizing bacteria (cyanobacteria) to plant-like diatoms, to armor-plated coccolithophores (drawings not to scale).

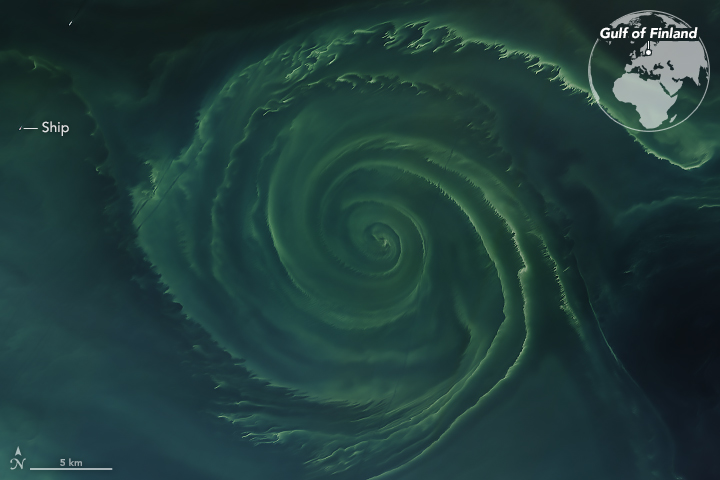
Phytoplankton growth depends on the availability of sunlight and nutrients. When conditions are favorable, phytoplankton populations can grow at a rate faster than they are consumed, a phenomenon known as a bloom. Phytoplankton blooms may cover hundreds of square kilometers and are easily visible from space. In this image, ocean waters glow peacock green off the coast of Scandinavia on July 18, 2018. Phytoplankton blooms often occur along coastlines where deep, nutrient-rich waters well up from the ocean depths. The light color of this ocean water suggests the calcite plating of coccolithophores is turning the water milky.
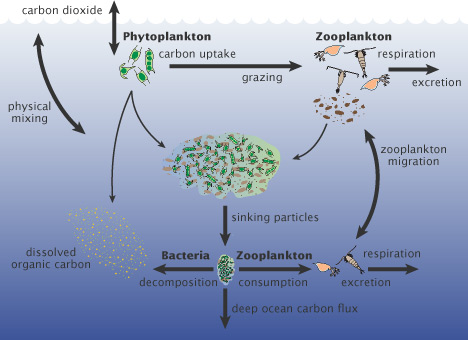
During photosynthesis, phytoplankton consume carbon dioxide on a scale comparable to land plants. Some of this carbon is carried to the deep ocean when phytoplankton die and sink, and some is transferred to different layers of the ocean as phytoplankton are eaten by other creatures, which themselves generate waste and die. Worldwide, this biological carbon pump transfers about 10 gigatons of carbon from the atmosphere to the deep ocean each year. Even small changes in the growth of phytoplankton may affect atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations, which feed back into global surface temperatures.
Credit: NASA Earth Observatory
Video: NASA | Earth Science Week: The Ocean's Green Machines
NASA | Earth Science Week: The Ocean's Green Machines | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H7sACT0Dx0Q | Source: NASA Goddard
Fun "Phyto" Facts:
- If you stack 1000 one micron phytoplankton end to end, the length of the stack would equal the width of a penny! (18,000 would fit across the face)
- If you fill a soda can with seawater sampled from a thick, oceanic phytoplankton bloom, the can may contain a many as 75 to 100 million cells!
- Global Phytoplankton Biomass: < 1% of the plant biomass on earth BUT responsible for nearly half the net photosynthesis of the biosphere!
Prerequisites Student Knowledge
- General understanding of photosynthesis and marine food webs
Student Misconception
- Phytoplankton are too small to be important—trees win.
- Algae (phytoplankton) are plants
Why Does NASA Study This Phenomenon?
Our ocean teems with life and many of its most vital species are invisible to us. Like on land, the ocean has deserts, forests, meadows, and jungles, providing habitats for many forms of life. The types of life in these habitats are determined by microscopic algae that float in our ocean. Known as “phytoplankton,” these tiny organisms come in many different shapes, sizes, and colors. The diversity of phytoplankton types determines the roles they play in ocean habitats. It also determines how well they capture energy from the sun and carbon from the atmosphere.
Phytoplankton provide food for small zooplankton, tiny animals that float in our ocean. Like humans, these grazers actively select their food. In the same way, larger zooplankton prey upon smaller zooplankton. Step by step, energy captured from phytoplankton transfers to bigger creatures. As the energy moves throughout the food web, it can ultimately be used by humans, who consume sea creatures found in the marine food web. The ocean is a fluid that is constantly in motion. Hosting the largest three-dimensional living space on earth, it supports many habitats. For example, the North Atlantic is home to highly productive "forests" each spring. Its blooms of carbon-rich phytoplankton fuel the fisheries of New England. The crystal-clear waters around Florida host productive coral reefs and fisheries. At times, however, this area is plagued by toxic phytoplankton. Today's satellites reveal the quantity of phytoplankton at the ocean surface. Yet we cannot detect the diversity of species. For the first time, NASA's PACE satellite will:
- Reveal the diversity of phytoplankton found in our ocean on global scales;
- Allow us to understand the role that phytoplankton diversity has on life in the ocean; and
- Help us predict the “boom or bust” of fisheries along with marine hazards such as harmful algal blooms.
Video: New NASA Mission Will Set the PACE for Advanced Studies of Earth’s Changing Climate
New NASA Mission Will Set the PACE for Advanced Studies of Earth’s Changing Climate | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSmhslNfkEw | Source: NASA Goddard
STEM Career Connections
- Molecular and Cellular Biologist - Study cellular molecules and organelles to understand cell function and organization.
- Marine Biologist/Biological Oceanographer - research biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical, physical, and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms.
Technology Requirements
- Teacher computer/projector only
Complementary Lesson Plans
Phytopia: exploration of marine ecosystem.
Phytopia's "Light & Color"

In this lesson, students investigate and identify various phytoplankton using images that were previously taken with a compound microscope. Credit: This lesson is modified from a lesson of the same name created by The Center for Microbial Oceanography: Research and Education (C-MORE)
Student Resources
- Student Worksheets
Teacher Resources
- Teacher Guide
- PowerPoint Script
- SLIDES & PHYTOPLANKTON ID GUIDE: Phytoplankton Microscopy Lab
- "Introduction to Plankton" PowerPoint
My NASA Data Visualization Tool
- Earth System Data Explorer
Related Resources
- C-MORE Plankton Science Kit (All Lessons and Resources)
- What are Phytoplankton?
- C-MORE Science Kits: Plankton
- Instructional Strategies for the Earth Science Classroom

GLOBE Protocol
- Carbon Cycle
Download this page
Not finding what you are looking for.


- Share on Facebook
- Tweet This Resource
- Pin This Resource

Zooplankton
This zooplankton ppt also includes:.
- Graphic & Image
- Join to access all included materials
Holoplankton are always plankton, whereas meroplankton are only plankton as larvae. Reveal several examples of each to your young marine biologists with this PowerPoint presentation. The first seven slides, an introduction to zooplankton, are hard to read because of a busy background. If you find this problematic, you can change it. Otherwise, this resource proves to be an exhaustive exploration of these tiny marine creatures.
Start Your Free Trial
Save time and discover engaging curriculum for your classroom. Reviewed and rated by trusted, credentialed teachers.
- Collection Types
- Activities & Projects
- Assessments
- Graphics & Images
- Handouts & References
- Interactives
- Lab Resources
- Learning Games
- Lesson Plans
- Presentations
- Primary Sources
- Printables & Templates
- Professional Documents
- Study Guides
- Instructional Videos
- Performance Tasks
- Graphic Organizers
- Writing Prompts
- Constructed Response Items
- AP Test Preps
- Lesson Planet Articles
- Online Courses
- Interactive Whiteboards
- Home Letters
- Unknown Types
- Stock Footages
- All Resource Types
See similar resources:
Marine fisheries management, australian museum: beyond the reef: plankton, find my plankton baby picture, what do you know about marine biology, ck 12: episd: aquatic organisms, a survey of plankton communities, plankton / phytoplankton.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
ZOOPLANKTON.
Published by Blake Compton Modified over 10 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "ZOOPLANKTON."— Presentation transcript:

The term plankton is applied to those organisms that are the drifters of the sea.

What is a Barnacle? You may have seen barnacles along the shoreline attached to pilings or rocks.

Zooplankton Planktos: “drifts” in greek Their distribution depends on currents and gyres Certain zooplankton can swim.

Planktonic Organisms. Introduction Plankton = Organisms that drift in the water Plankton = Organisms that drift in the water Cannot move against the current.

“Lower” Invertebrates I: Sponges & Radiata

GEOL 2503 Introduction to Oceanography

Crustaceans. Phylum Names Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda organisms with segmented bodies, jointed legs or wings, and an external skeleton Subphylum:

Arthropods and Echinoderms Chapter 7. Review What Invertebrates have we learned about so far? Porifera – sponges Cnidaria – jellyfishes, sea anemones,

Phylum Arthropoda “jointed foot” “jointed appendages” the arthropods Things that creep around on the ocean bottom (some don’t really creep!); also crustaceans.

Plankton-drifters Nekton- the swimmers Benthic- bottom dwellers

1 ZOOPLANKTON Zooplankton are the primary consumers, called heterotrophic herbivores, in food webs. They are the smallest and most numerous marine animals.

Plankton “To Drift”. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Classification of Marine Organisms Plankton (floaters) Nekton (swimmers) Benthos (bottom dwellers)

Marine Biology Study of living organisms in the ocean LIFE = ? –Ability to capture, store, and transmit energy –Ability to reproduce –Ability to adapt.

Plankton Organisms that drift with the currents. Zooplankton Animal plankton – many different types Heterotrophic – primary consumers.

Strange but true…. Sea Cucumber Echinoderms (like starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars) Radially symmetrical Have a water-vascular system that functions.

STRUCTURE OF THE OCEAN.

Marine Organisms.

Phytoplankton and Zooplankton youtube. com/watch

Amal Al muhanna Lab (1) Study of the following: Topics to be covered: Study of the following: a-Phytoplankton b-Zooplaknton c-Benthos d-Macrophytes.

Ch. 5 The Microbial World pp
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Zooplankton
Sep 07, 2014
170 likes | 533 Views
Zooplankton. Bay Mills Indian Community Water Quality Amanda Bosak. Cladocera. Order: Cladocera Family: Bosminidae Genus: Bosmina. Shell spine. A. Bosak BMIC. First antennae modified to tusks. Bosmina longirostris. Order: Cladocera Family: Daphnidae Genus: Daphnia.
Share Presentation
- outer setae
- caudal rami
- antennae setae
- 5 terminal setae
- order cladocera family leptodoridae

Presentation Transcript
Zooplankton Bay Mills Indian Community Water Quality Amanda Bosak
Order: Cladocera Family: Bosminidae Genus: Bosmina Shell spine A. Bosak BMIC First antennae modified to tusks Bosmina longirostris
Order: Cladocera Family: Daphnidae Genus: Daphnia Ocellus absent Head peak near body midline Front of head not concave Ocellus Antennae setae do not reach end of carapce A. Bosak BMIC A. Bosak BMIC Long tail spine Daphnia galeata mendotae Daphnia retrocurva
Order: Cladocera Family: Holopedidae Humpbacked carapace A. Bosak BMIC Surrounded by a gelatinous mantle Holopedium gibberum
Order: Cladocera Family: Leptodoridae Carapace reduced Single compound eye A. Bosak BMIC Body long and slender Leptodora kintii
Calanoid Copepods
Order: Calanoida Family: Diaptomidae 5 terminal setae A. Bosak BMIC Long antennae Sides of last metosomal segment not wings, but rounded corners Skistodiaptomus oregonensis
Order: Calanoida Family: Temoridae 3 stout terminal setae Caudal rami not elongate A. Bosak BMIC Epishura lacustris
Order: Calanoida Family: Centropagidae A. Bosak BMIC Long caudal rami Extended, comb-like maxillipeds Long antennae Limnocalanus macrurus
Cyclopoid Copepods
Order: Cyclopoida Family: Cyclopidae Lateral setae between middle and end third of rami Outer setae not thicker spine A. Bosak BMIC Short antennae Reach past cephalic segment, but not to genital segment Diacyclops thomasi
Order: Cyclopoida Family: Cyclopidae Short antennae Reach past cephalic segment, but not to genital segment Outer setae modified into spine A. Bosak BMIC Rami not elongate Eucyclops agilis
Order: Cyclopoida Family: Cyclopidae Inner setae twice the length of ramus Inner setae longer than ½ longest setae A. Bosak BMIC Short antennae Reach past cephalic segment, but not to genital segment Mesocyclops edax
- More by User

OXB2005 Zooplankton
684 views • 33 slides

ZOOPLANKTON
ZOOPLANKTON. All of the major phyla of animals are represented in the plankton. Remember: In the sea, microscopic plantlike organisms form the base of the food chain. This means most of the organisms that feed on these plant like organisms are also small.
889 views • 41 slides

Zooplankton. http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk. Planktos: “drifts” in greek. Their distribution depends on currents and gyres Certain zooplankton can swim well, but distribution controlled by current patterns
2.66k views • 70 slides

Lec 8: Zooplankton
Lec 8: Zooplankton. I. Major Types of Zooplankton -Taxonomy, Reproduction, Feeding II. Comparative Zooplankton Feeding -Particle size selection -Size efficiency hypothesis III. Zooplankton Ecology -Factors affecting assemblages (Predation) -Foodwebs and community ecology of lakes.
659 views • 28 slides

ZOOPLANKTON. Diversity of the Heterotrophic Plankton Community. Major Groups of Zooplankton. Ciliates Rhizopods Rotifers Cladocerans Copepods. Ciliate Zooplankton. Animal-like unicellular heterotrophs . All have two different types of nuclei. They move and feed by cilia.
1.26k views • 26 slides

ZOOPLANKTON. USGS. Zooplankton are the primary consumers, called heterotrophic herbivores, in food webs. They are the smallest and most numerous marine animals. Their population density depends on the availability of phytoplankton upon which they graze. Zooplankton moving.
908 views • 9 slides

Zooplankton. Amal Almuhana 2012. Introduction . It is the microscopic drifting animal component of planktons in the aquatic systems. Most zooplankton belong to 3 major groups : 1) Protozoa 2) Rotifera 3) Cladocera 4) Copepoda are most common.
891 views • 26 slides

Zooplankton Classification
S. Zooplankton Classification. P. P. Ctenophora Comb Jellies. Arthropoda Crustacea Copepods. P. Salps. S. Foraminifera (Forams). Single-celled Calcium carbonate ‘shell’. P. Foraminifera - carbonate. S. Ctenophora. Comb jellies Exclusively marine Bioluminescent.
837 views • 35 slides

Zooplankton. Objectives. Be able to define zooplankton Be familiar with the major groups of zooplankton and their characteristics Explain the benefits of zooplankton Explain how certain zooplankton can gauge reproductive success. Zooplankton.
1k views • 17 slides

Zooplankton Grazing
Zooplankton Grazing. Mechanisms and Impacts on Phytoplankton Amanda Lee Murby Field Limnology PBIO/ZOOL 719/819 FALL 2005. Grazing: Terrestrial. Consumption of a portion of a plant’s tissue is most often referred to as Grazing . Herbivores eat whole plants or parts of plants.
667 views • 28 slides

Mostly Zooplankton
Mostly Zooplankton. Bill Peterson and Rian Hooff NOAA-Fisheries, Newport OR Washington State University, Vancouver WA. My conclusions. If I didn’t know better, I would conclude that the coastal ecosystem of the Pacific Northwest was struck by a major El Niño event in 2005.
499 views • 34 slides

Zooplankton Culture
Zooplankton Culture. Dr. Craig Kasper, HCC Aquaculture Program. Last Time: What’s a LUX??.
353 views • 20 slides

Zooplankton. Fall 2006. Plankton Classification. Holoplankton. Meroplankton. Plankton. Plankton Classification. Picoplankton (0.2 – 2 µm). Nanoplankton (2-20 µm). Plankton. Microplankton (20-200 µm). Mesoplankton (200-2000 µm). Net- plankton. Macroplankton (>2000 µm). Heterotrophs.
976 views • 42 slides
Phytoplankton and Zooplankton
Plankton "Primary Producers" "Primary Consumers". Phytoplankton and Zooplankton. PHYTOPLANKTON. Pelagic environment is the largest marine ecosystem. More food, oxygen and biota (life) are here than anywhere else. Spirogyra.
643 views • 42 slides

493 views • 41 slides

Zooplankton ID Exercise
Zooplankton ID Exercise. 8 broad categories of zooplankton to identify with 10 group pages. Verucca stroem. Balanus crenatus. Calanus helgolandicus. Centropages typicus. Oithona similis. Anchialina agilis. Amphipoda. Fish egg. Zooplankton grid group A. 1mm. Zooplankton grid group B.
273 views • 19 slides
- Preferences

Zooplankton in lakes and grazing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Zooplankton in lakes and grazing
(2) copepods. http://tidepool.st.usm.edu/pix/biginfectedacartia.jpg ... copepod life cycle. cyclopoid. calanoid. instar development of cyclopoid copepod. nauplii ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- 23 April 2007
- Nutrient recycling
- As fish food
- Part of microbial loop
- Ciliates and heterotrophic nanoflagellates
- Ceriodaphnia reticulata
- Chaeoborous Phantom Midge!
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lec 8: Zooplankton. I. Major Types of Zooplankton -Taxonomy, Reproduction, Feeding II. Comparative Zooplankton Feeding -Particle size selection -Size efficiency hypothesis III. Zooplankton Ecology -Factors affecting assemblages (Predation) -Foodwebs and community ecology of lakes. 659 views • 28 slides
ZOOPLANKTON. All of the major phyla of animals are represented in the plankton. Remember: In the sea, microscopic plantlike organisms form the base of the food chain. This means most of the organisms that feed on these plant like organisms are also small. Slideshow 1317230 by olesia
660 likes | 2.31k Views. Zooplankton. Zooplankton. Planktonic animals can be found in almost all animal phyla Most zooplankton belong to 3 major groups: rotifers, Cladocera, and Copepoda. Zooplankton. One other group may, at times, be important: Protozoa. Download Presentation. diploid males. unfavorable conditions.
Zooplankton Zooplankton Planktonic animals can be found in almost all animal phyla Most zooplankton belong to 3 major groups: rotifers, Cladocera, and Copepoda Zooplankton One other group may, at times, be important: Protozoa Spend only portion of lives in plankton (mostly sediment-dwelling) Feed on bacteria, detritus (little used by other ...
Presentation on theme: "Plankton Ecology: Primary production, Phytoplankton and Zooplankton"— Presentation transcript: 1 Plankton Ecology: Primary production, Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Scripps Classroom Connection GK-12 Moira Décima, Scripps Institution of Oceanography Steve Halpern, San Diego High School (MVAS) Summary: This is a four lesson unit that explores general plankton ecology ...
About This Presentation. Title: Zooplankton. Description: Zooplankton Fall 2006 Zooplankton Drifting animals, organisms that eat other plankton ZOOPLANKTON Animals that can swim and pursue prey. Radiolarians, Foraminiferans ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 1032. Avg rating:3.0/5.0.
A Review of Zooplankton Communities in the Massachusetts Bay/Cape Cod Bay System - A Review of Zooplankton Communities in the Massachusetts Bay/Cape Cod Bay System Jefferson T. Turner UMass Dartmouth OMSAP Meeting October 21, 2003 | PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
2. Address the main topics of the PowerPoint presentation with your students: phytoplankton are plant‐like and have certain adaptations for survival; zooplankton are animal‐like and can exist as meroplankton (organisms that are plankton for part of their life cycle) or holoplankton (organisms that remain plankton for their entire life cycle);
Zooplankton Planktonic animals can be found in almost all animal phyla Most zooplankton belong to 3 major groups: rotifers, Cladocera, and Copepoda. ... Download ppt "Zooplankton." Similar presentations . Population Dynamics The change in the size, density, dispersion, and age distribution of a population in response to changes in environmental ...
Presentation Transcript. Zooplankton. Objectives • Be able to define zooplankton • Be familiar with the major groups of zooplankton and their characteristics • Explain the benefits of zooplankton • Explain how certain zooplankton can gauge reproductive success. Zooplankton • Zooplankton are the "animal-like" members of the ...
About This Presentation. Title: Zooplankton. Description: Zooplankton abundance is controlled by interactions between food abundance, fish ... Zooplankton grazing exerts major control on lake metabolism, nutrient cycling ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views:124. Avg rating:3.0/5.0.
This Zooplankton PPT is suitable for 9th - 12th Grade. Holoplankton are always plankton, whereas meroplankton are only plankton as larvae. Reveal several examples of each to your young marine biologists with this PowerPoint presentation.
Download ppt "ZOOPLANKTON." Similar presentations . The term plankton is applied to those organisms that are the drifters of the sea. What is a Barnacle? You may have seen barnacles along the shoreline attached to pilings or rocks. ... 1 ZOOPLANKTON Zooplankton are the primary consumers, called heterotrophic herbivores, in food webs. They are ...
Presentation Transcript. ZOOPLANKTON USGS Zooplankton are the primary consumers, called heterotrophic herbivores, in food webs. They are the smallest and most numerous marine animals. Their population density depends on the availability of phytoplankton upon which they graze. Zooplankton moving. There are two groups of zooplankton: 1.
Haloplankton permanent members of the plankton. Live in the ... Copepod. Copepod. Ctenophore. Ctenophore. Cubozoan. Gastropod larva. Magacytophanes. Nautilus ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 665b9-ZDc1Z
Presentation Transcript. Zooplankton AmalAlmuhana 2012. Introduction • It is the microscopic drifting animal component of planktons in the aquatic systems. Most zooplankton belong to 3 major groups:1) Protozoa2) Rotifera 3)Cladocera4) Copepoda are most common. • They can also be larger organisms like fish larva, insect larva or jellyfish.
Zooplankton. An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Download presentation by click this link.
World's Best PowerPoint Templates - CrystalGraphics offers more PowerPoint templates than anyone else in the world, with over 4 million to choose from. Winner of the Standing Ovation Award for "Best PowerPoint Templates" from Presentations Magazine. They'll give your presentations a professional, memorable appearance - the kind of sophisticated look that today's audiences expect.
World's Best PowerPoint Templates - CrystalGraphics offers more PowerPoint templates than anyone else in the world, with over 4 million to choose from. Winner of the Standing Ovation Award for "Best PowerPoint Templates" from Presentations Magazine. They'll give your presentations a professional, memorable appearance - the kind of sophisticated look that today's audiences expect.