
Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer
Our State of Teams 2024 report is live! Check it out here .


How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
Catch These Benefits! 13 Examples of Critical Thinking in the Workplace

Max 8 min read

Click the button to start reading
Your team is dealing with a sudden decrease in sales, and you’re not sure why.
When this happens, do you quickly make random changes and hope they work? Or do you pause, bring your team together , and analyze the problem using critical thinking?
In the pages ahead, we’ll share examples of critical thinking in the workplace to show how critical thinking can help you build a successful team and business.
Ready to make critical thinking a part of your office culture?
Let’s dive in!
What Is Critical Thinking? A Quick Definition
Critical thinking is the systematic approach of being a sharp-minded analyst. It involves asking questions, verifying facts, and using your intellect to make decisions and solve problems.
The process of thinking critically is built upon a foundation of six major steps:
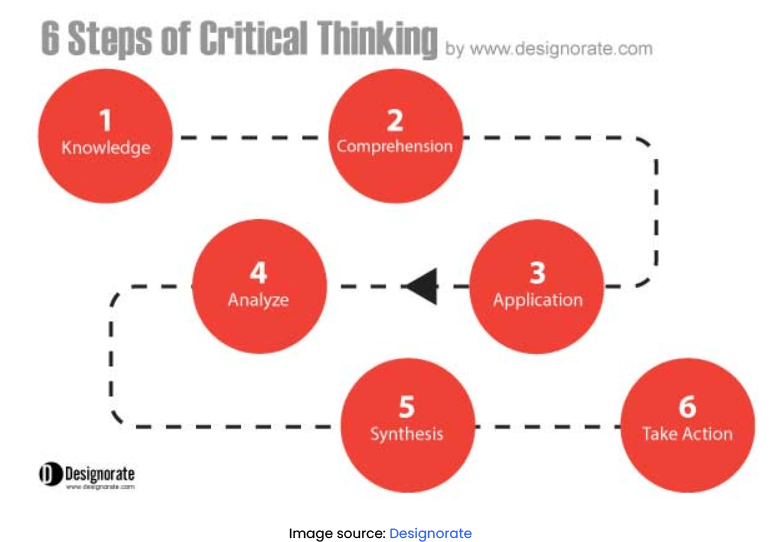
- Comprehension
- Application
- Creation/Action
First, you gather “knowledge” by learning about something and understanding it. After that, you put what you’ve learned into action, known as “application.” When you start looking closely at the details, you do the “analysis.”
After analyzing, you put all those details together to create something new, which we call “synthesis.” Finally, you take action based on all your thinking, and that’s the “creation” or “action” step.
Examples of Critical Thinking in the Workplace
Even if the tasks are repetitive, or even if employees are required to follow strict rules, critical thinking is still important. It helps to deal with unexpected challenges and improve processes.
Let’s delve into 13 real examples to see how critical thinking works in practice.
1. Evaluating the pros and cons of each option
Are you unsure which choice is the best? Critical thinking helps you look at the good and bad sides of each option. This ensures that you make decisions based on facts and not just guesses.
Product development : For example, a product development team is deciding whether to launch a new product . They must evaluate the pros and cons of various features, production methods, and marketing strategies to make an informed decision. Obviously, the more complete their evaluation is, the better decisions they can make.
2. Breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts
In the face of complex problems, critical thinkers are able to make the problem easier to solve. How? They create a step-by-step process to address each component separately.
Product deliveries and customer support . Imagine you work in a customer service department, and there has been a sudden increase in customer complaints about delayed deliveries. You need to figure out the root causes and come up with a solution.
So, you break down the problem into pieces – the shipping process, warehouse operations, delivery routes, customer communication, and product availability. This helps you find out the major causes, which are:
- insufficient staff in the packaging department, and
- high volume of orders during specific weeks in a year.
So, when you focus on smaller parts, you can understand and address each aspect better. As a result, you can find practical solutions to the larger issue of delayed deliveries.
3. Finding, evaluating and using information effectively
In today’s world, information is power. Using it wisely can help you and your team succeed. And critical thinkers know where to find the right information and how to check if it’s reliable.
Market research : Let’s say a marketing team is conducting market research to launch a new product. They must find, assess, and use market data to understand customer needs, competitor tactics, and market trends. Only with this information at hand can they create an effective marketing plan.
4. Paying attention to details while also seeing the bigger picture
Are you great at noticing small things? But can you also see how they fit into the larger picture? Critical thinking helps you do both. It’s like zooming in and out with a camera. Why is it essential? It helps you see the full story and avoid tunnel vision.
Strategic planning . For instance, during strategic planning, executives must pay attention to the details of the company’s financial data, market changes, and internal potential. At the same time, they must consider the bigger picture of long-term goals and growth strategies.
5. Making informed decisions by considering all available information
Ever made a choice without thinking it through? Critical thinkers gather all the facts before they decide. It ensures your decisions are smart and well-informed.
Data analysis . For example, data analysts have to examine large datasets to discover trends and patterns. They use critical thinking to understand the significance of these findings, get useful insights, and provide recommendations for improvement.
6. Recognizing biases and assumptions
Too many workplaces suffer from unfair and biased decisions. Make sure yours isn’t on this list. Critical thinkers are self-aware and can spot their own biases. Obviously, this allows them to make more objective decisions.
Conflict resolution . Suppose a manager needs to mediate a conflict between two team members. Critical thinking is essential to understand the underlying causes, evaluate the validity of each person’s opinion, and find a fair solution.
Hiring decisions . Here’s another example. When hiring new employees, HR professionals need to critically assess candidates’ qualifications, experience, and cultural fit. At the same time, they have to “silence” their own assumptions to make unbiased hiring decisions.
7. Optimizing processes for efficiency
Critical thinking examples in the workplace clearly show how teams can improve their processes.
Customer service . Imagine a company that sells gadgets. When customers have problems, the customer service team reads their feedback. For example, if many people struggle to use a gadget, they think about why that’s happening. Maybe the instructions aren’t clear, or the gadget is too tricky to set up.
So, they work together to make things better. They make a new, easier guide and improve the gadget’s instructions. As a result, fewer customers complain, and everyone is happier with the products and service.
8. Analyzing gaps and filling them in
Discovering problems in your company isn’t always obvious. Sometimes, you need to find what’s not working well to help your team do better. That’s where critical thinking comes in.
Training and development . HR professionals, for instance, critically analyze skill gaps within the organization to design training programs. Without deep analysis, they can’t address specific needs and upskill their employees .
9. Contributing effectively to team discussions
In a workplace, everyone needs to join meetings by saying what they think and listening to everyone else. Effective participation, in fact, depends on critical thinking because it’s the best shortcut to reach collective decisions.
Team meetings . In a brainstorming session, you and your colleagues are like puzzle pieces, each with a unique idea. To succeed, you listen to each other’s thoughts, mix and match those ideas, and together, you create the perfect picture – the best plan for your project.
10. Contributing effectively to problem-solving
Effective problem-solving typically involves critical thinking, with team members offering valuable insights and solutions based on their analysis of the situation.
Innovative SaaS product development . Let’s say a cross-functional team faces a challenging innovation problem. So, they use critical thinking to brainstorm creative solutions and evaluate the feasibility of each idea. Afterwards, they select the most promising one for further development.
11. Making accurate forecasts
Understanding critical thinking examples is essential in another aspect, too. In fact, critical thinking allows companies to prepare for what’s coming, reducing unexpected problems.
Financial forecasting . For example, finance professionals critically assess financial data, economic indicators, and market trends to make accurate forecasts. This data helps to make financial decisions, such as budget planning or investment strategies.
12. Assessing potential risks and recommending adjustments
Without effective risk management , you’ll constantly face issues when it’s too late to tackle them. But when your team has smart thinkers who can spot problems and figure out how they might affect you, you’ll have no need to worry.
Compliance review . Compliance officers review company policies and practices to ensure they align with relevant laws and regulations. They want to make sure everything we do follows the law. If they find anything that could get us into trouble, they’ll suggest changes to keep us on the right side of the law.
13. Managing the crisis
Who else wants to minimize damage and protect their business? During a crisis, leaders need to think critically to assess the situation, make rapid decisions, and allocate resources effectively.
Security breach in a big IT company . Suppose you’ve just discovered a major security breach. This is a crisis because sensitive customer data might be at risk, and it could damage your company’s reputation.
To manage this crisis, you need to think critically. First, you must assess the situation. You investigate how the breach happened, what data might be compromised, and how it could affect your customers and your business. Next, you have to make decisions. You might decide to shut down the affected systems to prevent further damage. By taking quick, well-planned actions, you can minimize the damage and protect your business.

Encouraging Critical Thinking in Your Team: A Brief Manager’s Guide
According to Payscale’s survey, 60% of managers believe that critical thinking is the top soft skill that new graduates lack. Why should you care? Well, among these graduates, there’s a good chance that one could eventually become a part of your team down the road.
So, how do you create a workplace where critical thinking is encouraged and cultivated? Let’s find out.
Step 1: Make Your Expectations Clear
First things first, make sure your employees know why critical thinking is important. If they don’t know how critical it is, it’s time to tell them. Explain why it’s essential for their growth and the company’s success.
Step 2: Encourage Curiosity
Do your employees ask questions freely? Encourage them to! A workplace where questions are welcomed is a breeding ground for critical thinking. And remember, don’t shut down questions with a “That’s not important.” Every question counts.
Step 3: Keep Learning Alive
Encourage your team to keep growing. Learning new stuff helps them become better thinkers. So, don’t let them settle for “I already know enough.” Provide your team with inspiring examples of critical thinking in the workplace. Let them get inspired and reach new heights.
Step 4: Challenge, Don’t Spoon-Feed
Rethink your management methods, if you hand your employees everything on a silver platter. Instead, challenge them with tasks that make them think. It might be tough, but don’t worry. A little struggle can be a good thing.
Step 5: Embrace Different Ideas
Do you only like ideas that match your own? Well, that’s a no-no. Encourage different ideas, even if they sound strange. Sometimes, the craziest ideas lead to the best solutions.
Step 6: Learn from Mistakes
Mistakes happen. So, instead of pointing fingers, ask your employees what they learned from the mistake. Don’t let them just say, “It’s not my fault.”
Step 7: Lead the Way
Are you a critical thinker yourself? Show your employees how it’s done. Lead by example. Don’t just say, “Do as I say!”
Wrapping It Up!
As we’ve seen, examples of critical thinking in the workplace are numerous. Critical thinking shows itself in various scenarios, from evaluating pros and cons to breaking down complex problems and recognizing biases.
The good news is that critical thinking isn’t something you’re born with but a skill you can nurture and strengthen. It’s a journey of growth, and managers are key players in this adventure. They can create a space where critical thinking thrives by encouraging continuous learning.
Remember, teams that cultivate critical thinking will be pioneers of adaptation and innovation. They’ll be well-prepared to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s workplace with confidence and competence.
#ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-title{ font-size: 120%; ; ; } #ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Table of Contents
Manage your remote team with teamly. get your 100% free account today..

PC and Mac compatible

Teamly is everywhere you need it to be. Desktop download or web browser or IOS/Android app. Take your pick.
Get Teamly for FREE by clicking below.
No credit card required. completely free.
Teamly puts everything in one place, so you can start and finish projects quickly and efficiently.
Keep reading.

Best Practices
In a Tangle? How to Be the Solution, Not the Problem
In a Tangle? How to Be the Solution, Not the ProblemDo you have those friends who can’t seem to go anywhere without complaining? They’re aghast by the sauciness of a waitress, the carelessness of a driver, the incompetence of the lady at the salon. And they’re always receiving freebies and coupons on account of the …
Continue reading “In a Tangle? How to Be the Solution, Not the Problem”
Max 7 min read

Time Management
Staying On Target: How Time-Management Fuels Motivation, and Vice Versa
Staying On Target: How Time-Management Fuels Motivation, and Vice VersaThe relationship between motivation and time management is an interesting one. Being super motivated is great, but if you haven’t effectively managed your time, all that motivation will be wasted, as you get bogged down with inefficiency. Excellent time management skills means you’re more likely to …
Continue reading “Staying On Target: How Time-Management Fuels Motivation, and Vice Versa”

Capture the Essentials With Concision: How to Write Meeting Minutes (With Examples!)
Capture the Essentials With Concision: How to Write Meeting Minutes (With Examples!)Why do some meetings really move the needle, while others feel like a colossal waste of time? There’s obviously more than one answer to this question, but more often than not the effectiveness of a meeting is determined by something as simple as its …
Continue reading “Capture the Essentials With Concision: How to Write Meeting Minutes (With Examples!)”
Max 18 min read
Project Management Software Comparisons
Asana vs Wrike

Basecamp vs Slack

Smartsheet vs Airtable

Trello vs ClickUp

Monday.com vs Jira Work Management
Trello vs asana.
Get Teamly for FREE Enter your email and create your account today!
You must enter a valid email address
You must enter a valid email address!
- Open training
- Team training
What is Critical Thinking and Why is it Valuable in the Workplace?
- Articles and Resources
- > Personal Effectiveness and Preparing for Change
- > What is Critical Thinking and Why is it Valuable in the Workplace?
There are times at work when you simply have to “do.” A tight deadline, a demanding project outline, or a highly particular superior might mean that it makes sense to complete a task without too much mental tinkering. But work like this can be unsustainable and worse — it won’t leverage your ability to think critically.
There is value in thinking critically in every aspect of your life. From making decisions in your personal life, to interrogating the media you consume, to assessing your work with a critical eye, applying critical thinking is an essential skill everyone should be trying to hone.
At your workplace, critical thinking can distinguish you as a leader, and a valuable mind to bounce ideas off. It can help improve the quality of your work, and the perception those higher up the chain have of you.
Here’s what you need to know about critical thinking in the workplace:
What Exactly is “Critical Thinking”?
In a nutshell, critical thinking is the ability to think reasonably, detaching yourself from personal bias, emotional responses, and subjective opinions. It involves using the data at hand to make a reasoned choice without falling prey to the temptations of doing things simply because they’ve always been done a certain way.
Critical thinking takes time. It might be quicker simply to take instruction at face value, or rely on the traditions of your team. But without analyzing the reasons behind decisions and tasks, it becomes extremely easy to adopt bad habits. This might be time-wasting meetings, inefficient uses of effort, or poor interactions with team members. Taking the time to ask “why” you’re doing something is the first step to thinking critically.
Sometimes, data is available which allows you to make reasoned decisions based on absolute facts. If you can show that a new best practice can objectively improve current processes with hard data, you’ve used the very basics of critical thinking. That said, actual numbers aren’t always available when making a decision. Real critical thinking involves taking a careful look at situations and making a decision based on what is known, not what is felt.
Why Is Critical Thinking Important in the Workplace?
The short answer to the above question is this: critical thinkers make the best decisions, most often. And in the workplace, where choices about how to complete tasks, communicate information, relate with coworkers, and develop strategy are so common, critical thinkers are extremely valuable.
A savvy hiring manager will make this part of the recruitment process. It’s pretty easy to gauge how someone is inclined to solve a problem — ask them how they would deal with a specific situation, and give them the opportunity to use their critical thinking skills, versus deferring to an emotional, or prescribed reaction. Employing people who can think and act reasonably will pay enormous dividends down the road.
Using your critical thinking skills in the workplace will define you as a problem solver. This is not only useful career-wise (although having upper-level people at your company think highly of you is undoubtedly a benefit) it also establishes you as a leader among your fellow team members. Demonstrating your ability to solve problems and accomplish goals effectively will help instill confidence in you with all your coworkers.
How to Use Critical Thinking in the Workplace
The first step to actually using critical thinking is approaching every situation with an open mind. You need to be receptive to all information available, not just the kind that satisfies your preconceived notions or personal biases. This can be easier said than done, of course — lessons learned and beliefs held are often done so with a reason. But when it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to analyze each situation independently.
Once you’ve analyzed a situation with an open mind, you need to consider how to communicate it properly. It’s all very well and good to approach situations with objective logic, but it doesn’t do you any favours to sound like Mr. Spock when you’re conveying your conclusions. Be tactful, patient and humble when you are explaining how and why you’ve come to decisions. Use data if available to support your findings, but understand that not everyone is able to remove emotion from situations.
The final, and perhaps least obvious, application with critical thinking is creativity. Often, getting creative means pushing boundaries and reshaping convention. This means taking a risk — one that can often be worth the reward. Using a critical thinking approach when getting creative can help you mitigate the risk, and better determine what value your creativity can bring. It will help you and your team try new things and reinvent current processes while hopefully not rocking the boat too much.
Learn More About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a valuable skill for all aspects of your life. It benefits problem solving, creativity, and teamwork. And it translates particularly well to the workplace, where it can distinguish you as a valuable employee and leader.
Taking the extra time to examine things objectively, make decisions based on logic, and communicate it tactfully will help you, those you work with, and your work goals prosper. To learn more about how to do that, have a look at our Critical Thinking and Problem Solving for Effective Decision-Making workshop and register today!
Let us help you create your training solution
Hello we'd love to hear from you.
Complete the form below or reach us at: [email protected] , or 613-234-2020
Contact details
To help you.
- I wish to subscribe to PMC Training content.
Welcome to our new website!
We appreciate your patience as we add the finishing touches. In the meantime, go and explore!
Cookie Usage Disclaimer: This website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience. By continuing to use this site, you consent to our use of cookies. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy .

Critical Thinking Exercises for Employees: Boosting Workplace Problem-Solving Skills

In today’s fast-paced work environment, critical thinking skills are essential for success. By engaging in critical thinking exercises, employees can refine their ability to evaluate information, solve complex problems, and communicate effectively. These skills not only contribute to individual success but also promote a more innovative and productive work environment.
Key Takeaways
Understanding critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a vital skill for employees in the business world, as it enables individuals to analyze complex situations, identify biases, and make informed decisions through creative problem-solving methods. This cognitive process encourages a deeper understanding of problems and promotes the ability to approach them from multiple perspectives.
Developing critical thinking skills involves being aware of one’s own biases and working towards eliminating them. Bias can significantly impact how we approach problems and may result in making distorted decisions. By recognizing and addressing these biases, employees can harness their critical thinking abilities to make impartial and robust decisions in the business landscape.
In the context of problem-solving, critical thinking encourages employees to explore new perspectives and think beyond conventional solutions. By adopting a creative approach, individuals can generate novel ideas and innovations, which can lead to improved business results and overall growth.
In conclusion, it is crucial for employees to develop and hone their critical thinking skills, as they enable individuals to navigate complex business environments effectively. By addressing biases, conducting robust analysis, and adopting creative problem-solving strategies, employees can make well-informed decisions that contribute to the success and longevity of the organization.
The Importance of Critical Thinking in the Workplace
In the workplace , critical thinking allows for a more thorough evaluation of issues, helping to identify potential problems or opportunities. This is particularly important in today’s fast-paced, competitive environment, where companies need to stay ahead of industry trends and anticipate the needs of their customers. Employees who possess strong critical thinking skills can help their team effectively navigate the challenges that arise in any industry.
Ultimately, developing critical thinking skills in employees is not just beneficial for the individual worker and their direct colleagues, but it also impacts the overall success of the organization. By fostering an environment that encourages the growth of critical thinking skills, employers can not only increase productivity but also create a more positive and engaged work culture.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Mindful observation, active listening, asking questions.
Asking questions is a key component of critical thinking, as it encourages employees to inquire deeper into subjects and analyze all aspects of an issue. Employers can foster a work environment that supports curiosity by encouraging team members to ask both open-ended and closed-ended questions and offering guidance when needed.
Assessing Evidence and Drawing Conclusions
Recognizing and managing biases.
By incorporating these exercises and strategies into the workplace, employees can develop critical thinking skills that strengthen their overall performance, communication, and leadership abilities.
Critical Thinking and Communication
Critical thinking and communication go hand in hand in the workplace. Developing both skills can enhance employees’ ability to solve problems, make decisions, and work effectively in teams. By engaging in critical thinking exercises that involve clear communication and open discussion, employees can improve their cognitive abilities and interpersonal skills.
Another useful technique is group discussions, which can stimulate critical thinking and promote clear communication. By engaging in conversations where various perspectives are considered, employees can develop the ability to analyze information objectively and reevaluate their initial assumptions. Fostering open-mindedness and empathy for others’ viewpoints can also build strong communication skills in the workplace .
Applying Critical Thinking to Problem Solving
Effective problem solving requires employees to utilize critical thinking skills. By carefully analyzing information, asking questions, and determining the best course of action, employees will be more likely to arrive at creative and innovative solutions to challenges.
Critical thinking also involves evaluating the effectiveness of potential solutions. Employees should be encouraged to analyze the pros and cons of each option, as well as consider any potential long-term impacts. This process can help identify the most viable and successful solutions for a given problem.
Critical Thinking in Leadership and Management
Developing critical thinking skills in leadership and management positions is crucial for making informed decisions, driving company growth, and ensuring employee satisfaction. By enhancing their cognitive abilities, leaders and managers become better at decision-making, hiring processes, and overall performance.
In the realm of leadership, critical thinking helps leaders to understand the logical relationships between ideas and recognize the importance of an argument. This enables them to identify mistakes in reasoning and make well-informed choices, thus driving superior organizational outcomes as mentioned here .
Incorporating critical thinking exercises into hiring processes allows employers to better assess candidates’ abilities objectively. By focusing on problem-solving and communication skills during the interview process, managers can identify high-potential talent who demonstrate strong critical thinking competencies.
Critical Thinking in Team Building
Incorporating critical thinking exercises within team building activities is essential for fostering creativity, collaboration, and problem-solving amongst employees. By engaging team members in activities that require them to consider multiple perspectives and work together to reach a conclusion, companies can significantly improve their team’s performance.
Brainstorming is another critical thinking team building activity that can generate diverse ideas and encourage innovation. By setting specific goals or challenges, team members collaborate to provide multiple solutions to a given problem. Encourage employees to think beyond the obvious answers, providing a safe space for innovative and unusual ideas.
Evaluating Potential Job Candidates for Critical Thinking Skills
Screening for critical thinking.
A vital step to measure critical thinking is through the initial screening process. To do this effectively, recruiters can utilize pre-employment tests that focus on evaluating candidates’ analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making skills. These assessments can be administered online for a more efficient process while narrowing down the applicant pool.
Assessing Analytical Skills during Interviews
Asking situational and behavioral questions can provide excellent insight into a candidate’s analytical capabilities. Employers may ask questions that require candidates to analyze specific scenarios, or they may inquire about past experiences where candidates employed their critical thinking skills.
By effectively screening and assessing job candidates’ critical thinking skills, companies can confidently hire employees with the necessary abilities to contribute successfully to their organization’s goals and vision.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Critical Thinking
Emotional intelligence also helps employees consider the ethical implications of their decisions. With a heightened understanding of emotions, individuals are more likely to empathize with others and take their perspectives into account. This ability enables them to navigate complex ethical dilemmas and make fair judgments that adhere to the organization’s values.
Fostering an Innovative Work Environment through Critical Thinking
Promoting open discussions.
One way to encourage innovation in the workplace is by promoting open discussions. These encourage employees to share their ideas and contribute to the collaborative push for creative solutions. When a culture of open communication is established, employees feel valued and are more likely to take risks, making it easier for them to come up with innovative solutions. Conducting regular brainstorming sessions and encouraging the exchange of opinions during meetings can further enhance the creative thinking process.
Encouragement of Reflective Practice
Enhancing critical thinking skills in the workplace is an essential step towards cultivating a culture of effective decision-making and problem-solving. By engaging in various training exercises, employees can strengthen their ability to analyze situations, interpret data, and make informed choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective group exercises to improve critical thinking.
There are various group exercises that can help improve critical thinking skills among employees. One example is the Socratic questioning technique in which a facilitator poses a series of questions designed to uncover assumptions and stimulate critical thinking. Another effective activity is the “Case Study Analysis,” where employees are tasked with analyzing real-life business scenarios to identify challenges, gather data, and make informed decisions.
How can team building games enhance critical thinking skills?
What are some fun activities to develop critical thinking in adults, how can a workbook aid in critical thinking development.
A workbook designed for critical thinking development typically contains structured exercises, real-world examples, and reflective activities. These materials guide individuals through a step-by-step process of improving their critical thinking skills by encouraging self-awareness, fostering curiosity, and promoting constructive feedback. Using a workbook can provide an organized and personalized approach to enhancing critical thinking abilities.
What are the top 5 skills essential for critical thinking?
How can virtual activities benefit employees’ critical thinking, you may also like, critical thinking and relationships: how critical thinking can help your relationships in life., the connection between critical thinking and ethics: unraveling the link, all about non-linear thinking.

Boost Your Associative Thinking Skills in Problem Solving: Tips and Strategies
Download this free ebook.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Improve Your Critical Thinking at Work
Helen Lee Bouygues, founder of the Reboot Foundation, believes that a lack of critical thinking is responsible for many business failures. She says organizational leaders often...
- Apple Podcasts
Helen Lee Bouygues, founder of the Reboot Foundation, believes that a lack of critical thinking is responsible for many business failures. She says organizational leaders often rely too heavily on expertise and then jump to conclusions. Instead, leaders should deliberately approach each problem and devote time thinking through possible solutions. The good news, she says, is that critical thinking skills can developed and practiced over time. Bouygues is the author of the HBR.org article “ 3 Simple Habits to Improve Your Critical Thinking .”
Download this podcast
CURT NICKISCH: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Curt Nickisch.
You know the story. Maybe it’s even a nightmare of yours. One day, the company is flying high. No reason to change anything. Customers and contracts will always be there.
And then one day – the money stops flowing in, and the business is suddenly in real trouble.
Our guest today knows this all too well. She has been an interim CEO, CFO, or COO at more than one dozen companies. Sometimes they needed her because they were mismanaged. Some failed to stay in front of changing technologies. In a few cases, members of the senior team were simply negligent. But in her experience, all these organizational problems shared one root cause: A lack of critical thinking.
Our guest is Helen Lee Bouygues. She’s the founder of the Reboot Foundation. Based in Paris, the nonprofit helps parents, teachers and employers think more critically about their problems. She’s also the author of the HBR.org article “ 3 Simple Habits to Improve Your Critical Thinking .” Helen, thanks for being here.
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Thank you for having me Curt.
CURT NICKISCH: Helen, you worked in transitional periods for a bunch of big companies. And, you say that many people’s business problems really come down to simple errors in critical thinking. That just sounds a little surprising to me and I wanted to hear why you say that.
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Yeah, I think at first glance people believe that critical thinking is something that we do every day and it comes very natural. But in reality, critical thinking is not only extremely important for success in life, but it’s also something that needs to be learned and practiced.
Critical thinking skills are very much predictive of making positive financial decisions, even more so than raw intelligence, but people kind of forget what that actually means in terms of tools and practices that they need to exercise in order to make the right decisions, or at least the better decisions.
Based on my 20 years of different turnaround and transformation experience, I have noticed that very often when things go sideways or create problems and companies find themselves in a situation of a need for turnaround, it’s typically been because I would argue that the leadership perhaps lacked some elements of critical thinking.
CURT NICKISCH: Why do you think we lack critical thinking skills, or why do you think we think we’re better at it than we actually are?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: That’s a great question Curt and actually we did a survey at the Reboot Foundation about a year ago, where we asked people questions of everything from ranging from how often do they practice critical thinking to how important they think critical thinking is, and how often they teach their children critical thinking?
I think one of the reasons why it’s more difficult in today’s day and age is that we live in a world of incessant distraction and technology is often to blame as well. We live in a period when we have a question, we want that instant gratification getting the information, just typing the question on Google, having the answer quickly and so, we don’t actually have as much time to stop and think.
And part of the necessity of critical thinking is having that ability to take a step back and actually think about your own thinking. And yet, it’s actually becoming more and more critical because as businesses evolve and there’s more urgency to make decisions, that’s exactly when we need to do more critical thinking than perhaps we used to, because of evolving technology and rapidly changing competitive environments in business.
CURT NICKISCH: You say that getting better at critical thinking is something we can learn and cultivate?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Yes. The opposite of critical thinking could be selective thinking. And naturally selective thinking is something that you can actually do relatively quickly because it’s just a reinforcement of your own opinion. People in business can get better at critical thinking if they just do three things. One, question assumptions. Two, reason through logic. And three, diversify thought.
CURT NICKISCH: How do you actually do that?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: So, the taking a break, and that doesn’t mean doing meditation or yoga, but actually taking the time. It could be going for a run, or a walk around the block. That alone creates that opportunity for an individual to take the time to stop and think. So, that’s one dimension I think that people need to put in their normal practice.
The second element that you wouldn’t necessarily think about in terms of an attribute necessary for critical thinking is management of emotions. So, the number of times that you can imagine, especially in a boardroom for a company that’s going through a difficulty, heated discussions, insults across the room. In that type of environment, it’s very difficult to engage in rational thinking.
As much emotions are important, when it comes to true important decisions, we need to put aside the feelings and emotions that go awry in a meeting setting. In addition to that, I think the other element of what we need to make sure that we conduct is making sure that we have other points of views.
CURT NICKISCH: When you talk about looking at things from opposing viewpoints, sometimes that’s helpful when you have somebody who plays that role, or when you have a diverse team that you can share ideas with and explore. I don’t know that all of us are as good of just thinking from other perspectives when we’re kind of just in our own thoughts.
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Yeah, but it’s again, that’s why I think I started off this conversation Curt, in saying that critical thinking is something that you actually need to practice and you need to learn. Because indeed, it’s natural and it’s very human to stay in your own personal bubble because it’s comfortable.
But you can actually do this from a small scale to a larger scale, and what I mean by that specifically is if you’re starting small, if you work in for example, in accounting. Go have lunch with people in marketing in your organization.
I have a good friend, Mathilde Thomas, she’s actually the founder of Caudalie which is a very successful line of skincare products made from grapes. Mathilde grew up spending her time in her family vineyards, so her family originally was in the wine business. And the idea of the skincare product came about because one day a friend of the family, this physician, came to visit the vineyard and he was looking at the vat of grape skins that were about to be discarded and he said, well that’s a pot of treasure, so why are you just discarding that away? And that’s effectively how the business of Caudalie actually began.
So, that’s a positive story where people who are not necessarily in the same field can get together and actually come up with innovation or here it wasn’t even intended to be an innovation. It just was an idea that sprung from two people from different walks of life getting together and coming up with the business idea. So, that’s a positive example in terms of diversity.
CURT NICKISCH: Where have you seen this failure in some of the companies that you worked with? Where have you seen the inability to diversify thought and opinions and host costly that can be?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: I think in terms of negative, I’ve seen a specific example for a pharmaceutical company where the founder brought in a CFO who actually had very little experience in accounting. He had experience in mergers and acquisitions, in elements of financing, but not pure accounting.
But his true qualification of becoming the CFO was the fact that he was a very, very good friend of the CEO’s and you see that example over and over again, including in boards. The number of times you see the board of a company being surrounded, the CEO being surrounded by his or her friends, which is why often I think from time to time, you have companies, publicly listed companies where sometimes the board may not see certain indications.
Be it the case of a Steinhoff or an Enron, which is an extreme case of fraud, but even in terms of general decisions, strategic decisions, that if you have a board composed of just a group of friends of the CEO’s, you don’t have diversity of thought in that type of environment.
CURT NICKISCH: So, we’ve talked some about questioning assumptions and the power of diversifying thought. But another point you make is that people need to get better about reasoning through logic. And I think this is going to surprise people too because logical is just such a household word. We think that we think logically, so why is logic a deficit and kind of a prerequisite for the critical thinking you think we need to see more of in management?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: So, one of the stories that I like to bring up is a specific company that I encountered a couple of years ago. It’s one of the world’s largest producers of aluminum tubes and they have clients ranging from L’Oréal to Proctor and Gamble, all over the world.
And the CEO of this company was blindsided by his own fervor and probably unreasonable optimism about the outlook for the revenue profile of this company. In reality, the company was in relatively dire financial straits, but again he was blinded with his hope that his clients would never leave because the switching costs of his clients would be too high, or that at least was his hypothesis.
And for some business leaders I think some optimism is obviously a good thing. There wouldn’t be Ubers or EBays if we didn’t have entrepreneurs who have that charisma and exuberance. But what I often find in companies is CEOss with something I call simply WTF. Now Curt, that’s not what you think that we commonly use in text messages, but it’s for me it’s “wishful thinking forever’.
And I think that blinded optimism can often mask the capability and the ability to reason through logic and actually re-question your approach and saying, “well, can my customers decide to change vendors? Is the competitive environment actually shifting? Are there low-cost companies that could actually take over my business even if that hurdle rate is high?”
So, it’s again coming back to being able to ask the right questions and looking at your business and saying, “is there a different way of doing things?” And that’s when you avoid the pitfalls of actually reasoning through logic.
And it comes back to the argument of having different views from your original views and your original sentiments. And obviously in order to do that, we need to really pay close attention to our own chain of logic.
CURT NICKISCH: Which I like by the way, wishful thinking forever. I’m going to read text messages that way now. Probably make them a little more optimistic. Yeah.
A lot of companies pay consultants to do this kind of critical thinking for them and they come in with tools and concept mapping, and all of the sorts of things that maybe they’re a little more deliberate about and also, removed from the emotion of working in the culture of a company. Do you see consultants as essentially paid critical thinkers?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: I think many consultants are good at critical thinking. I don’t believe that the industry of management consulting is a sector that is there to enforce critical thinking for companies. And let me explain why I believe that. A lot of, in a lot of situations CEOs seek validation and look for evidence that supports their preconceived notions. And consultants are often trained to agree with their client’s theories.
So, I would almost counter argue and say, for CEOs to effectively use consultants, they almost need to be very precise and be very upfront in their scope of work with the consultants, demand and ask that the consulting firm give a different point of view, or an opposing point of view than the original thesis of a leader.
Now that is sometimes hard to do. It goes back to the original part of our discussion. It’s less comfortable for leaders and in a lot of situations why CEO’s are hiring consultants are to justify and explain with more detail to their boards of why they’re doing certain strategic activities. So, that’s where we have to be careful about relying on consultants as quote, “a mechanism to do better critical thinking in business”.
CURT NICKISCH: Have you actually seen companies turn around when they change the way they approach problems and instituted critical thinking across the organization in a more deliberate way?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Yes. I worked with a telecom company in Africa, not so long ago. And they had probably the lowest customer satisfaction rate across the board, amongst the different countries in Africa. And the CEO was somebody who was a very open minded, wanted to challenge – now you could argue Curt, they were on the low, they couldn’t get lower in terms of customer satisfaction, so they only had room to go up.
But if you put that aside, what he instituted was to have a sub group of his team to go visit another South African country that had very high customer satisfaction rates. So, it was, I would call creating an environment for its employees to have a bit of a diversity of thought, but also to actually be exposed to give the capacity for its employees to question the assumptions about what they were doing wrong.
So, very good CEOs not only are capable of trying to conduct metacognition for him or herself, meaning questioning his or her own way of thinking, but he’ll challenge his team and help them to challenge their own way of thinking by showing different examples of for example, success stories in the same type of work where in a case of this telecom company in Africa, where they could see and visit customer services centers in other African countries where they had high customer satisfaction rate.
So, it’s giving the exposure to its team to seek out diversity of thought, but also promoting that, and encouraging that its employees think differently than being focused on their own silos of work and being, trying to be efficient in their own capacity, in their existing dimension.
CURT NICKISCH: Yeah. So, if that was a good critical thinker, as a CEO, what do most leaders do in that situation? What does the “uncritical thinker” do?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: The uncritical thinker would be to try to gain more efficiency out of its existing employees and continue to do more of the same thing. But probably putting in more KPI’s. That’s a popular thing that leaders do. And try to put more pressure in the system so that companies are more productive. Rather than thinking out of the box and trying to say, should we be doing something differently than the way we’re doing it today?
CURT NICKISCH: And for individuals? Because whether or not you have a CEO who’s good at this, you can still affect your own team and you can still affect your own work with your own critical thinking. What should they do to get better at critical thinking?
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Be curious. Ask the questions. “ What if” questions are great. It’s important to constantly challenge yourself saying, what if I did something differently than the way I’m doing it now? What if I approached my client differently than the way I’m doing it now? What if I changed the processes? Would there be improvement? That’s the type of individual who can improve by actually questioning the assumptions of what he or she is doing on a daily basis.
And then the second element again, is trying to be very factual and be rigid about gathering facts and proof and accumulating data in order to truly justify why you’re doing what you’re doing. It’s going back to paying close attention to the chain of your own logic.
And then the third is expanding your horizon by interacting with people that are not in your existing silo. So, I go back to the example, very simple example, go have lunch, go have a drink with somebody that’s not in your same department, but go reach out to somebody who’s in a totally different building, or even different division within your group.
CURT NICKISCH: Helen, thanks for coming on the show and talking about thinking through how to be a better critical thinker.
HELEN LEE BOUYGUES: Thank you so much. It was a real pleasure to be on your show.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s Helen Lee Bouygues. She’s the founder of the Paris-based Reboot Foundation and the author of the HBR.org article “ 3 Simple Habits to Improve Your Critical Thinking .”
This episode was produced by Mary Dooe. We get technical help from Rob Eckhardt. Adam Buchholz is our audio product manager.
Thanks for listening to the HBR IdeaCast . I’m Curt Nickisch.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about decision making and problem solving.
- Managing yourself
- Strategy formulation
Partner Center
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Collaboration |
- How to build your critical thinking ski ...
How to build your critical thinking skills in 7 steps (with examples)

Critical thinking is, well, critical. By building these skills, you improve your ability to analyze information and come to the best decision possible. In this article, we cover the basics of critical thinking, as well as the seven steps you can use to implement the full critical thinking process.
Critical thinking comes from asking the right questions to come to the best conclusion possible. Strong critical thinkers analyze information from a variety of viewpoints in order to identify the best course of action.
Don’t worry if you don’t think you have strong critical thinking abilities. In this article, we’ll help you build a foundation for critical thinking so you can absorb, analyze, and make informed decisions.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to collect and analyze information to come to a conclusion. Being able to think critically is important in virtually every industry and applicable across a wide range of positions. That’s because critical thinking isn’t subject-specific—rather, it’s your ability to parse through information, data, statistics, and other details in order to identify a satisfactory solution.
Definitions of critical thinking
Various scholars have provided definitions of critical thinking, each emphasizing different aspects of this complex cognitive process:
Michael Scriven , an American philosopher, defines critical thinking as "the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication as a guide to belief and action."
Robert Ennis , professor emeritus at the University of Illinois, describes critical thinking as "reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do."
Diane Halpern , a cognitive psychologist and former president of the American Psychological Association, defines it as "the use of cognitive skills or strategies that increase the probability of a desirable outcome."
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

Top 8 critical thinking skills
Critical thinking is essential for success in everyday life, higher education, and professional settings. The handbook "Foundation for Critical Thinking" defines it as a process of conceptualization, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation of information.
In no particular order, here are eight key critical thinking abilities that can help you excel in any situation:
1. Analytical thinking
Analytical thinking involves evaluating data from multiple sources in order to come to the best conclusions. Analytical thinking allows people to reject cognitive biases and strive to gather and analyze intricate subject matter while solving complex problems. Analytical thinkers who thrive at critical thinking can:
Identify patterns and trends in the data
Break down complex issues into manageable components
Recognize cause-and-effect relationships
Evaluate the strength of arguments and evidence
Example: A data analyst breaks down complex sales figures to identify trends and patterns that inform the company's marketing strategy.
2. Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness is the willingness to consider new ideas, arguments, and information without prejudice. This critical thinking skill helps you analyze and process information to come to an unbiased conclusion. Part of the critical thinking process is letting your personal biases go, taking information at face value and coming to a conclusion based on multiple points of view .
Open-minded critical thinkers demonstrate:
Willingness to consider alternative viewpoints
Ability to suspend judgment until sufficient evidence is gathered
Receptiveness to constructive criticism and feedback
Flexibility in updating beliefs based on new information
Example: During a product development meeting, a team leader actively considers unconventional ideas from junior members, leading to an innovative solution.
3. Problem-solving
Effective problem solving is a cornerstone of critical thinking. It requires the ability to identify issues, generate possible solutions, evaluate alternatives, and implement the best course of action. This critical thinking skill is particularly valuable in fields like project management and entrepreneurship.
Key aspects of problem-solving include:
Clearly defining the problem
Gathering relevant information
Brainstorming potential solutions
Evaluating the pros and cons of each option
Implementing and monitoring the chosen solution
Reflecting on the outcome and adjusting as necessary
Example: A high school principal uses problem-solving skills to address declining student engagement by surveying learners, consulting with higher education experts, and implementing a new curriculum that balances academic rigor with practical, real-world applications.
4. Reasoned judgment
Reasoned judgment is a key component of higher order thinking that involves making thoughtful decisions based on logical analysis of evidence and thorough consideration of alternatives. This critical thinking skill is important in both academic and professional settings. Key aspects reasoned judgment include:
Objectively gathering and analyzing information
Evaluating the credibility and relevance of evidence
Considering multiple perspectives before drawing conclusions
Making decisions based on logical inference and sound reasoning
Example: A high school science teacher uses reasoned judgment to design an experiment, carefully observing and analyzing results before drawing conclusions about the hypothesis.
5. Reflective thinking
Reflective thinking is the process of analyzing one's own thought processes, actions, and outcomes to gain deeper understanding and improve future performance. Good critical thinking requires analyzing and synthesizing information to form a coherent understanding of a problem. It's an essential critical thinking skill for continuous learning and improvement.
Key aspects of reflective thinking include:
Critically examining one's own assumptions and cognitive biases
Considering diverse viewpoints and perspectives
Synthesizing information from various experiences and sources
Applying insights to improve future decision-making and actions
Continuously evaluating and adjusting one's thinking processes
Example: A community organizer reflects on the outcomes of a recent public event, considering what worked well and what could be improved for future initiatives.
6. Communication
Strong communication skills help critical thinkers articulate ideas clearly and persuasively. Communication in the workplace is crucial for effective teamwork, leadership, and knowledge dissemination. Key aspects of communication in critical thinking include:
Clearly expressing complex ideas
Active listening and comprehension
Adapting communication styles to different audiences
Constructing and delivering persuasive arguments
Example: A manager effectively explains a new company policy to her team, addressing their concerns and ensuring everyone understands its implications.
7. Research
Critical thinkers with strong research skills gather, evaluate, and synthesize information from various sources of information. This is particularly important in academic settings and in professional fields that require continuous learning. Effective research involves:
Identifying reliable and relevant sources of information
Evaluating the credibility and bias of sources
Synthesizing information from multiple sources
Recognizing gaps in existing knowledge
Example: A journalist verifies information from multiple credible sources before publishing an article on a controversial topic.
8. Decision-making
Effective decision making is the culmination of various critical thinking skills that allow an individual to draw logical conclusions and generalizations. It involves weighing options, considering consequences, and choosing the best course of action. Key aspects of decision-making include:
Defining clear criteria for evaluation
Gathering and analyzing relevant information
Considering short-term and long-term consequences
Managing uncertainty and risk
Balancing logic and intuition
Example: A homeowner weighs the costs, benefits, and long-term implications before deciding to invest in solar panels for their house.
7 steps to improve critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that you can build by following these seven steps. The seven steps to critical thinking help you ensure you’re approaching a problem from the right angle, considering every alternative, and coming to an unbiased conclusion.
First things first: When to use the 7 step critical thinking process
There’s a lot that goes into the full critical thinking process, and not every decision needs to be this thought out. Sometimes, it’s enough to put aside bias and approach a process logically. In other, more complex cases, the best way to identify the ideal outcome is to go through the entire critical thinking process.
The seven-step critical thinking process is useful for complex decisions in areas you are less familiar with. Alternatively, the seven critical thinking steps can help you look at a problem you’re familiar with from a different angle, without any bias.
If you need to make a less complex decision, consider another problem solving strategy instead. Decision matrices are a great way to identify the best option between different choices. Check out our article on 7 steps to creating a decision matrix .
1. Identify the problem or question
Before you put those critical thinking skills to work, you first need to identify the problem you’re solving. This step includes taking a look at the problem from a few different perspectives and asking questions like:
What’s happening?
Why is this happening?
What assumptions am I making?
At first glance, how do I think we can solve this problem?
A big part of developing your critical thinking skills is learning how to come to unbiased conclusions. In order to do that, you first need to acknowledge the biases that you currently have. Does someone on your team think they know the answer? Are you making assumptions that aren’t necessarily true? Identifying these details helps you later on in the process.
2. Gather relevant information
At this point, you likely have a general idea of the problem—but in order to come up with the best solution, you need to dig deeper.
During the research process, collect information relating to the problem, including data, statistics, historical project information, team input, and more. Make sure you gather information from a variety of sources, especially if those sources go against your personal ideas about what the problem is or how to solve it.
Gathering varied information is essential for your ability to apply the critical thinking process. If you don’t get enough information, your ability to make a final decision will be skewed. Remember that critical thinking is about helping you identify the objective best conclusion. You aren’t going with your gut—you’re doing research to find the best option
3. Analyze and evaluate data
Just as it’s important to gather a variety of information, it is also important to determine how relevant the different information sources are. After all, just because there is data doesn’t mean it’s relevant.
Once you’ve gathered all of the information, sift through the noise and identify what information is relevant and what information isn’t. Synthesizing all of this information and establishing significance helps you weigh different data sources and come to the best conclusion later on in the critical thinking process.
To determine data relevance, ask yourself:
How reliable is this information?
How significant is this information?
Is this information outdated? Is it specialized in a specific field?
4. Consider alternative points of view
One of the most useful parts of the critical thinking process is coming to a decision without bias. In order to do so, you need to take a step back from the process and challenge the assumptions you’re making.
We all have bias—and that isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Unconscious biases (also known as cognitive biases) often serve as mental shortcuts to simplify problem solving and aid decision making. But even when biases aren’t inherently bad, you must be aware of your biases in order to put them aside when necessary.
Before coming to a solution, ask yourself:
Am I making any assumptions about this information?
Are there additional variables I haven’t considered?
Have I evaluated the information from every perspective?
Are there any viewpoints I missed?
5. Draw logical conclusions
Finally, you’re ready to come to a conclusion. To identify the best solution, draw connections between causes and effects. Use the facts you’ve gathered to evaluate the most objective conclusion.
Keep in mind that there may be more than one solution. Often, the problems you’re facing are complex and intricate. The critical thinking process doesn’t necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision.
6. Develop and communication solutions
Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers. It isn’t enough to think for yourself—you also need to share your conclusion with other project stakeholders. If there are multiple solutions, present them all. There may be a case where you implement one solution, then test to see if it works before implementing another solution.
This process of communicating and sharing ideas is key in promoting critical thinking within a team or organization. By encouraging open dialogue and collaborative problem-solving, you create an environment that fosters the development of critical thinking skills in others.
7. Reflect and learn from the process
The seven-step critical thinking process yields a result—and you then need to put that solution into place. After you’ve implemented your decision, evaluate whether or not it was effective. Did it solve the initial problem? What lessons—whether positive or negative—can you learn from this experience to improve your critical thinking for next time?
By engaging in this metacognitive reflective thinking process, you're essentially teaching critical thinking to yourself, refining your methodology with each iteration. This reflective practice is fundamental in developing a more robust and adaptable approach to problem-solving.
Depending on how your team shares information, consider documenting lessons learned in a central source of truth. That way, team members that are making similar or related decisions in the future can understand why you made the decision you made and what the outcome was.
Example of critical thinking in the workplace
Imagine you work in user experience design (UX). Your team is focused on pricing and packaging and ensuring customers have a clear understanding of the different services your company offers. Here’s how to apply the critical thinking process in the workplace in seven steps:
Step 1: Start by identifying the problem
Your current pricing page isn’t performing as well as you want. You’ve heard from customers that your services aren’t clear, and that the page doesn’t answer the questions they have. This page is really important for your company, since it’s where your customers sign up for your service. You and your team have a few theories about why your current page isn’t performing well, but you decide to apply the critical thinking process to ensure you come to the best decision for the page.
Gather information about how the problem started
Part of identifying the problem includes understanding how the problem started. The pricing and packaging page is important—so when your team initially designed the page, they certainly put a lot of thought into it. Before you begin researching how to improve the page, ask yourself:
Why did you design the pricing page the way you did?
Which stakeholders need to be involved in the decision making process?
Where are users getting stuck on the page?
Are any features currently working?
Step 2: Then gather information and research
In addition to understanding the history of the pricing and packaging page, it’s important to understand what works well. Part of this research means taking a look at what your competitor’s pricing pages look like.
Ask yourself:
How have our competitors set up their pricing pages?
Are there any pricing page best practices?
How does color, positioning, and animation impact navigation?
Are there any standard page layouts customers expect to see?
Step 3: Organize and analyze information
You’ve gathered all of the information you need—now you need to organize and analyze it. What trends, if any, are you noticing? Is there any particularly relevant or important information that you have to consider?
Step 4: Consider alternative viewpoints to reduce bias
In the case of critical thinking, it’s important to address and set bias aside as much as possible. Ask yourself:
Is there anything I’m missing?
Have I connected with the right stakeholders?
Are there any other viewpoints I should consider?
Step 5: Determine the most logical solution for your team
You now have all of the information you need to design the best pricing page. Depending on the complexity of the design, you may want to design a few options to present to a small group of customers or A/B test on the live website.
Step 6: Communicate your solution to stakeholders
Critical thinking can help you in every element of your life, but in the workplace, you must also involve key project stakeholders . Stakeholders help you determine next steps, like whether you’ll A/B test the page first. Depending on the complexity of the issue, consider hosting a meeting or sharing a status report to get everyone on the same page.
Step 7: Reflect on the results
No process is complete without evaluating the results. Once the new page has been live for some time, evaluate whether it did better than the previous page. What worked? What didn’t? This also helps you make better critical decisions later on.
Tools and techniques to improve critical thinking skills
As the importance of critical thinking continues to grow in academic and professional settings, numerous tools and resources have been developed to help individuals enhance their critical thinking skills. Here are some notable contributions from experts and institutions in the field:
Mind mapping for better analysis
Mind mapping is a visual technique that helps organize and structure information. It's particularly useful for synthesizing complex ideas and identifying connections between different concepts. The benefits of mind mapping include:
Enhancing creativity by encouraging non-linear thinking
Improving memory and retention of information
Facilitating brainstorming and idea generation
Providing a clear overview of complex topics
To create a mind map:
Start with a central idea or concept.
Branch out with related sub topics or ideas.
Use colors, symbols, and images to enhance visual appeal and memorability.
Draw connections between related ideas across different branches.
Mind mapping can be particularly effective in project planning , content creation, and studying complex subjects.
The Socratic Method for deeper understanding
The Socratic Method, named after the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, involves asking probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas. This technique is widely used in higher education to teach critical thinking. Key aspects of the Socratic Method include:
Asking open-ended questions that encourage deeper reflection
Challenging assumptions and preconceived notions
Exploring the implications and consequences of ideas
Fostering intellectual curiosity and continuous inquiry
The Socratic Method can be applied in various settings:
In education, to encourage students to think deeply about subject matter
In business, it is important to challenge team members to consider multiple points of view.
In personal development, to examine one's own beliefs and decisions
Example: A high school teacher might use the Socratic Method to guide students through a complex ethical dilemma, asking questions like "What principles are at stake here?" and "How might this decision affect different stakeholders?"
SWOT analysis for comprehensive evaluation
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a strategic planning tool that can be applied to critical thinking. It helps in evaluating situations from multiple angles, promoting a more thorough understanding of complex issues. The components of SWOT analysis are:
Strengths: internal positive attributes or assets
Weaknesses: internal negative attributes or limitations
Opportunities: External factors that could be beneficial
Threats: External factors that could be harmful
To conduct a SWOT analysis:
Clearly define the subject of analysis (e.g., a project, organization, or decision).
Brainstorm and list items for each category.
Analyze the interactions between different factors.
Use the analysis to inform strategy or decision-making.
Example: A startup might use SWOT analysis to evaluate its position before seeking investment, identifying its innovative technology as a strength, limited capital as a weakness, growing market demand as an opportunity, and established competitors as a threat.
Critical thinking resources
The Foundation for Critical Thinking : Based in California, this organization offers a wide range of resources, including books, articles, and workshops on critical thinking.
The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking : This council provides guidelines and standards for critical thinking instruction and assessment.
University of Louisville : Their Critical Thinking Initiative offers various resources and tools for developing critical thinking skills.
The New York Times Learning Network provides lesson plans and activities to help develop critical thinking skills through current events and news analysis.
Critical thinking frameworks and tools
Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework : Developed by Dr. Richard Paul and Dr. Linda Elder, this framework provides a comprehensive approach to developing critical thinking skills.
Bloom's Taxonomy : While not exclusively for critical thinking, this classification system is widely used in education to promote higher-order thinking skills.
The California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory (CCTDI) : This assessment tool measures the disposition to engage in problems and make decisions using critical thinking.
The Ennis-Weir Critical Thinking Essay Test : Developed by Robert Ennis, this test assesses a person's ability to appraise an argument and to formulate a written argument.
By incorporating these tools and techniques into regular practice, individuals can significantly enhance their critical thinking capabilities, leading to more effective problem-solving, decision-making, and overall cognitive performance.
Critically successful
Critical thinking takes time to build, but with effort and patience you can apply an unbiased, analytical mind to any situation. Critical thinking makes up one of many soft skills that makes you an effective team member, manager, and worker. If you’re looking to hone your skills further, read our article on the 25 project management skills you need to succeed .
Related resources

Scaling clinical trial management software with PM solutions
6 ways to develop adaptability in the workplace and embrace change
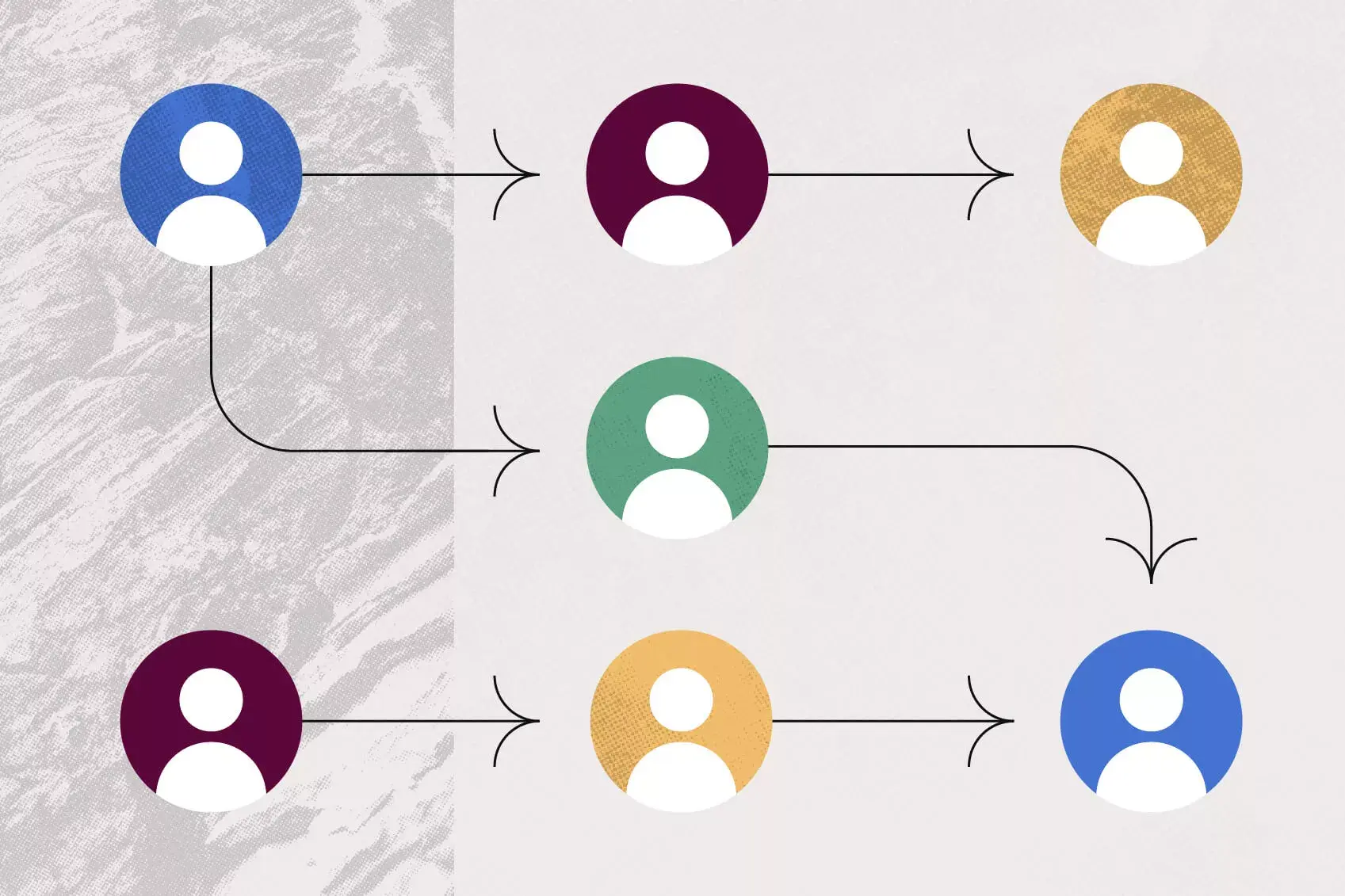
4 ways to establish roles and responsibilities for team success

9 tips for taking better meeting notes

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
Critical thinking is the one skillset you can't afford not to master

Jump to section
What is critical thinking?
5 characteristics of critical thinking, what are critical thinking skills, and why are they important, 6 key critical thinking skills, critical thinking example in real-life, 13 ways to start thinking critically.
Whether you’re aiming to improve your performance at work or simply trying to live a more fulfilling life , you’ll need a variety of hard and soft skills to move the needle. Some skills come naturally to some people, while others need to develop them actively.
One of these skills is critical thinking. But critical thinking itself is made up of several types of skills that contribute to solving problems more effectively.
Let’s explore the different types of critical thinking skills and how you can start improving them to level up your career.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze facts objectively and form a judgment. It is a form of emotional intelligence .
Someone with critical thinking skills can think clearly and rationally when the situation demands it. It allows them to perform problem-solving and decision-making more effectively.
As a result, you can look further than what you see at face value. You’re able to analyze what you see from a situation and gain some insight that goes further than what’s obvious to anyone from the outside.
Critical thinking also requires being able to understand the logical connection between two or more ideas or concepts. For example, a team working on a company’s pricing strategy needs to think critically about several concepts.
Both the marketing and sales teams must work together. They need to analyze how to maximize sales. But they need to do so while also meeting profit goals. It’s important to understand the logical connection between sales strategy and marketing logistics. It’s the only way to get a good outcome.
Critical thinking is different from creative thinking . Creative thinking is the ability to generate brand new, innovative ideas. On the other hand, critical thinking requires you to carefully and logically analyze what information is given to you. Both are important to maximize results in any given situation.

What defines critical thinking? How does it affect the decision-making process? Here are five characteristics that make up the ability to think critically.
1. Dispositions
Critical thinkers have specific traits that allow them to think the way they do. Some people are predisposed to these traits, while others need to develop them actively.
Some of these dispositions include:
- Open-mindedness
- Respecting evidence and reasoning
- Being able to consider different perspectives and points of view: in other words, having cognitive flexibility
- Not being stuck in one position
- Clarity and precision

2. Argument
Good critical thinkers need to make solid arguments.
An argument is making a statement aided by supporting evidence. It’s important to use well thought-out arguments when you’re in a constructive conflict . When analyzing a situation critically, you’ll need to make several arguments in your own mind to come to a judgment.
3. Reasoning
In addition to arguments, critical thinking also requires inferring conclusions. From the facts and arguments presented to you, you need to use reasoning skills to come to a logical conclusion.
This conclusion will determine the best course of action to take.

4. Criteria
Critical thinking is sometimes a matter of discerning truth from fiction. Not all facts presented to you may have the same level of truth. Certain conditions need to be met for something to be considered believable, and a critical thinker needs to be able to understand that.
5. Metacognition
Metacognition is the ability to think about your own thinking. Critical thinkers should be able to analyze their thoughts so that they can judge whether or not they’ve thought everything through. This helps them come up with better hypotheses.
The critical thinking skills definition is: soft skills that help you in the critical thinking process. Developing these skills can improve your ability to think critically.
Critical thinking skills are considered one of many durable skills in the workplace . Many of these are soft skills that are also useful in other situations.
According to research by America Succeeds, critical thinking is in the top five most requested durable skills in job postings. Those top five durable skills get requested 2.6x more often than the top five hard skills. This goes to show that soft skills like critical thinking skills are in demand in the workplace.
Critical thinking skills are important for several reasons. These include helping you work independently and solve problems . Not all positions require ongoing critical thinking. But, those skills definitely matter to anyone who wants to uplevel their career. And even the most easygoing positions require at least some level of critical thinking skills.
For example, working as an accountant can be straightforward in most cases. But it may require critical thinking skills. For instance, what if certain expenses aren’t easily distributed in simple categories? Without critical thinking skills, an accountant will struggle to work independently and solve problems on their own.
Critical thinking abilities also matter in everyday life. Having a foundation for critical thinking can help you analyze several possible solutions for problems that pop up in the home. It can also help you:
- Analyze different viewpoints
- Come up with the best solution for complex problems
- Become a better learner
The key critical thinking skills are identifying biases, inference, research, identification, curiosity, and judging relevance.
Let’s explore these six critical thinking skills you should learn and why they’re so important to the critical thinking process.
1. Identifying biases
This critical thinking skill is necessary for metacognition, which is the fifth characteristic of critical thinking. It involves knowing when others have a cognitive bias and when you have one yourself.
Biases can influence how someone understands the facts presented to them. But when you’re aware of those biases, you can question yourself on those biases and consider other points of view.
Identifying biases is especially important for people who make hiring decisions. That’s because biases against groups of minorities can lead to inequalities in the workplace when not identified.
For example, imagine a hiring manager comparing two resumes. Their gut feeling could guide them to discount one of the resumes due to a bias against the opposite gender. But let’s say this hiring manager realizes they have this bias. They can then question themselves on whether or not this bias is influencing their judgment.
2. Inference
Inference is the ability to draw conclusions based on the information you have. Without inference, it can be difficult to take action once you’ve analyzed the facts presented to you. Processing information is key to coming up with a reasoned judgment.
For example, let’s go back to the accountant struggling to assign the correct category to a business expense. They can analyze other similar situations and infer the most logical category based on that information.
3. Research
Before you analyze facts and infer a conclusion, you need to find out what those facts are. Researching skills allow you to discover facts and figures to make an argument.
Not all situations will have the required information available to you. Researching skills are necessary to dig into a situation and gather the information you need to think critically.
Some situations don’t require further research. For example, a first responder who arrives on the scene of an automobile accident won’t perform further research. They’ll have to analyze what they see in front of them and decide which injuries are the most urgent to care for.
On the other hand, someone performing a market analysis will need to research competitors and gather information before coming up with an opinion.
4. Identification
Identification is different from inference and research. It involves being able to identify a problem but also what’s influencing that problem.
In short, identification is necessary for someone to realize that they need to think critically about something. Without proper identification skills, it will be difficult for someone to know when it’s time to analyze a situation.
For example, let’s say you’re entering numbers in a spreadsheet. The numbers aren’t coming out as they usually do. Without identification skills, you could easily keep going without realizing there’s an issue. But when you identify what’s going on, you can see that something is broken in the spreadsheet’s formula.
Only once you identify the fact that the formula is broken can you start analyzing what’s going on to solve the issue.
5. Curiosity
Don’t be afraid to question everything and explore what you’re curious about. That’s because intellectual curiosity is a valuable skill, especially when it comes to critical thinking.
One way to practice curiosity is to adopt a beginner’s mindset . When you come into every situation with the mindset of a beginner, you’re able to keep an open mind. You’ll be able to perceive things you may not have noticed when keeping your mind closed.
6. Judging relevance
Not all information is equally pertinent. In order to make a critical judgment, it’s important to be able to judge the relevance of the information you have.
Take, for instance, basic online researching skills. You have access to a plethora of information on virtually every topic imaginable. But performing online research requires you to constantly judge the relevance of what you see.
Without judging relevance, you’d spend too much time on details that don’t matter as much for the final desired outcome. But when you’re able to discern what’s most pertinent, you can give that information more weight as you’re thinking critically.

So what would critical thinking skills look like in a real-life situation?
Let’s imagine you’re working in software quality assurance (QA) as a team lead. But every time your team needs to enter bug regression, everyone gets bottlenecked because you must manually populate the spreadsheet used for the regression. While you do this task, your team cannot be productive without you.
This process happens once a week and easily wastes half an hour for each team member.
First, you must identify what’s going on. The team gets bottlenecked because only you, as the team lead, can access the information required to fill in the regression spreadsheet.
Next, you can research information. You can inquire to higher-ups about the reason why only you have access to this information. You can also speak to other teams about what potential solutions they’ve come up with to solve this problem.
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to analyze the information and judge relevance. Some teams have solutions that don’t apply to you, so that information isn’t relevant anymore.
Figure out if there are any personal biases before you analyze your information.
For example, it’s possible that you don’t get along with one of the other team leads. As a result, you could discount the information they’ve given you. But by identifying this bias, you can look past your personal opinion of this person and see how valuable their solution is.
Based on what you’ve analyzed, it’s time to brainstorm and come up with a solution. You realize that creating a simple, automated script will save your team’s time. And it will do so without consuming too many resources from the engineering department.
Next, present your solution to your manager. Explain how you came to this conclusion.
Now, let’s say your spreadsheet automation solution is approved. It’s important to go back and analyze what happens after implementing the solution. But only do this once the spreadsheet has been in place for long enough to gather plenty of information.
Here’s an example. You could realize that the solution did solve the bottleneck. But, the script also slows down the spreadsheet and makes it difficult to work with. This would require you to go back to the drawing board and start the process all over again.
Want to start improving your own critical thinking skill sets? Here’s how you can improve critical thinking skills using 13 techniques:
- Play games that require critical thinking skills
- Ask more questions, even basic ones
- Question your assumptions
- Develop your technical skills so that you can identify problems more easily
- Find ways to solve more problems (at work and at home)
- Become aware of your mental processes, like the availability heuristic
- Think for yourself: don’t adopt other people’s opinions without questioning them first
- Seek out diversity of thought
- Start developing foresight
- Try active listening
- Weigh the consequences of different actions before you act
- Seek a mentor who can help you develop these skills
- Get professional coaching

How to improve your critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills aren’t always easy to develop. But it’s much easier to start thinking critically when you have someone to work with. Try a custom BetterUp demo to see how a coach can help you develop your critical thinking skills today.
Transform your life
Make meaningful changes and become the best version of yourself. BetterUp's professional Coaches are here to support your personal growth journey.
Maggie Wooll, MBA
Maggie Wooll is a researcher, author, and speaker focused on the evolving future of work. Formerly the lead researcher at the Deloitte Center for the Edge, she holds a Bachelor of Science in Education from Princeton University and an MBA from the University of Virginia Darden School of Business. Maggie is passionate about creating better work and greater opportunities for all.
How to develop critical thinking skills
The most critical skills for leaders are fundamentally human, why self-management is key to success and how to improve yours, the new skill set needed to succeed in the hybrid workplace, what’s convergent thinking how to be a better problem-solver, how intrapersonal skills shape teams, plus 5 ways to build them, how to be optimistic, building strength for tomorrow: new president of betterup care™ on extending proactive mental health across the enterprise, the 5 business communication skills worth perfecting, what is social well-being definition, types, and how to achieve it, foster strong communication skills to enjoy professional success, what are metacognitive skills examples in everyday life, improve your interpersonal communication skills with these 6 tips, self-management skills for a messy world, 7 types of listening that can change your life and work, 4 negotiation strategies: get to “yes” quicker, 9 high-income skills to learn in 2024, 20 marketing skills professionals should have in 2023, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
What Are Critical Thinking Skills? (Example List Included)
Mike Simpson 0 Comments

By Mike Simpson
Ah, critical thinking skills. As a candidate, it’s vital to understand that pretty much all employers are on the hunt for job seekers with critical thinking skills. Why? Because it’s universally helpful on the job.
When employees know how to think critically, they are more effective in their positions. They’ll be more productive and self-sufficient. In the eyes of employers, that matters a ton.
But what are critical thinking skills exactly? And, if you don’t have them, what can you do to improve your ability to think critically?
If you’re asking yourself questions like those, you’re in luck. After all, you’re here, and we’re about to tell you all about the characteristics of critical thinking and how to get better at it. So, if you’re ready to dig in, here’s what you need to know.
What Are Critical Thinking Skills?
If we’re going to talk about critical thinking skills, it’s best to begin by answering a crucial question: what are critical thinking skills?
Well, to figure that out, it’s helpful to know what critical thinking means. According to the Cambridge Dictionary , critical thinking is “the process of thinking carefully about a subject or idea, without allowing feelings or opinions to affect you.” That’s actually a pretty solid place to start.
In many ways, critical thinking is a two-fold process. First, it focuses on information-gathering and fact-analysis. It’s all about understanding a subject thoroughly.
Second, it’s about setting your feelings aside. With critical thinking, it isn’t about what you want the facts to say; it’s about the reality of the situation. It’s a very Vulcans-from-Star-Trek approach to topics. Emotions and personal preference simply aren’t part of the equation in the vast majority of cases. Instead, objectivity reigns.
Alright, so what are critical thinking skills then? Well, critical thinking skills are the soft skills and hard skills that help you assess situations, collect data, analyze information, identify solutions, determine the viability of solutions, and make decisions without letting your emotions run the show. Any capability or trait that makes it easier to do those things can qualify.
In many cases, thinking critically plays a bigger role in your day-to-day than you’d expect. When you approach any task, you usually spend a moment analyzing it. That way, you can find the best path toward success.
When a task is simple, it doesn’t take much time to do a quick critical thinking once over, so you probably don’t even notice you’re doing it. It’s only when an activity is challenging or when something unexpected occurs that your thought process really stands out. As a result, you probably spend far more time thinking critically than you realize.
How Are Critical Thinking Skills Relevant to a Job Search?
Okay, we’ve given you a solid overview of what critical thinking skills are. Now it’s time to talk about the importance of critical thinking during a job search.
When you’re hunting for new opportunities, critical thinking skills are immensely valuable. For example, they can help you figure out if a job opening is genuinely a good fit for your capabilities and career.
When you find a job ad, do you just apply without seeing if it matches your skills and aligns with your goals? Of course not. Instead, you take a look at the requirements, examine the job ad for potential, and decide whether or not that opportunity really fits. That’s critical thinking.
But that’s not the only way these skills make a difference during your job search. They may also help you identify what points to include in your resume and cover letter to stand out to a hiring manager or what to talk about when you’re answering specific job interview questions.
How can it do all of that? Well, when you decide what to list in your resume or cover letter, or add to an interview answer, you have to do some analysis. You consider the hiring manager’s needs. Next, you find a matching accomplishment that highlights what they are after. Then, you figure out present it in an engaging way. That’s all critical thinking, too.
Plus, thinking critically can also make a difference post-interview. You’ll have an easier time assessing your own performance, allowing you to identify areas for improvement. Good stuff, right?
When it comes to why hiring managers prefer candidates with these skills, there are actually several reasons. The biggest is that employees with strong critical thinking skills tend to be more self-sufficient and productive. They are better equipped to assess situations and find their own solutions, and that matters, particularly in faster-paced environments.
Plus, workers that know how to think critically may have an easier time collaborating. They can separate their emotions from the situation, allowing them to focus on what’s best for the team and company.
So, which critical thinking skills are they after? Well, that can depend on the hiring manager. However, most want to see you possess capabilities in four core areas: information-gathering, analysis , problem-solving, and creativity. If you tap into all of those, you usually have what it takes to think critically.
How to Highlight Critical Thinking Skills for Job Search
Okay, at this point, you probably understand the importance of critical thinking skills. Now onto the next part of the equation: how to show off your capabilities during a job search.
Let’s start with the earliest part of the job search: your resume and cover letter. When you’re writing a resume or creating a cover letter , the best thing you can do is focus on achievements.
Highlighting accomplishments where you put your critical thinking skills to work lets you “show” the hiring manager you have what it takes instead of just telling them. After all, anyone can say, “I’m an excellent critical thinker,” even if they aren’t. By having examples, you prove that you have those capabilities. That matters.
How do you pick the right achievements? By using a winning strategy, like the Tailoring Method . The Tailoring Method focuses on relevancy. It helps you choose accomplishments that showcase the skills the hiring manager wants to see, increasing the odds that they’ll view you as an excellent match for their needs.
Now that your resume and cover letter are squared away, it’s time to talk about the interview. Luckily, you can use the Tailoring Method here, too. It’s a great technique for straightforward job interview questions , as well as behavioral interview questions .
When you’re dealing with behavioral interview questions, couple the Tailoring Method with the STAR Method . That way, your answers are engaging and relevant, making them even more impactful.
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills If You Don’t Have Them
Some people may think that they don’t have any critical thinking skills. In reality, that probably isn’t true.
Nearly everyone develops some critical thinking capabilities over the course of their lives; they just may not realize it. Luckily, that’s a good thing. It means you probably have a solid foundation, even if you don’t know it.
Why does that matter? Well, it means you can focus more on developing what you have. You aren’t actually starting from scratch, which can make it easier.
Ready to take your critical thinking skills to the next level? Great! Here’s how you can.
Understand the Critical Thinking Process
When it comes to how to think critically, there is actually a core process involved. By understanding the steps, you can make sure you approach situations properly.
Usually, the critical thinking process involves:
- Observation
- Information-Gathering
- Brainstorming
Typically, you start by observing the issue at hand. Next, you do some research, helping you gather more information. After that, you focus on brainstorming ideas on how to proceed. Then, you consider each option, identifying the best one. Finally, you decide to proceed, taking actions based on what you’ve learned.
It’s a systematic way to address a range of scenarios. By learning the process, you can put it into use more often, allowing you to increase your skills.
Take Up a Hobby
Many hobbies actually require quite a bit of critical thinking. For example, if you want to have a thriving garden, you need to take several factors into account. Soil condition, water availability, the amount of sunlight, aesthetics… those are just some of the points you need to analyze if you want to succeed.
Arts and crafts can also help you boost critical thinking. When you’re making something, you have to evaluate your options for materials, techniques, and more, ensuring you choose a path that leads to the best final product.
Join a Debate Club
If you’re looking for possibly one of the best critical thinking examples around, debate is probably it. That means, if you want to take your skills up a notch, joining a debate club can be a great option.
You have to support a position – at times one that doesn’t align with your personal beliefs – and try to convince others that your side is correct. You’ll dive into unfamiliar topics, gather data to support the perspective you’re assigned, and choose how to present information in a convincing way.
While you might think that, if you aren’t in high school, that this isn’t an option, that isn’t the case. There are many meetups that focus on debate, giving people of all ages a place to boost their skills.
List of Critical Thinking Skills
There are quite a few characteristics and capabilities that support critical thinking. By knowing which skills fall into that category, you can decide what to showcase during your job search.
So, let’s dig in. Here is a quick list of critical thinking skill examples:
- Self-Reliance
- Decision-Making
- Open-Mindedness
- Deductive Reasoning
- Problem-Solving
- Communication
- Collaboration
- Attention to Detail
- Pattern Recognition
- Interpretation
- Active Listening
- Conceptualization
Now, these aren’t the only skills that can help you think critically. Practically anything that enables you to navigate the process can count.
Additionally, you don’t have to fit all of these skills on your resume to show that you know how to think critically. Instead, you want to highlight a range, demonstrating that you have what it takes to navigate situations effectively and accomplish your goals.
Spend some time reflecting on your work history or educational experiences. Then, identify moments where you used critical thinking to accomplish something noteworthy. Once you have, think about the skills that came into play, and make sure to mention them as you describe what led up to the achievement.
If you’re looking for more skills to put on a resume , we’ve actually taken a deep dive into that topic before. Along with various critical thinking skills, we tap on a ton of other areas, making it easier for you to figure out what you should feature during your job search.
Putting It All Together
In the end, critical thinking skills are essential for nearly every member of the workforce. By elevating yours as much as possible and showcasing them during your job search, you won’t just be a stronger candidate but also a more capable employee. That’s all great stuff. It’ll help you have your ideal career and, ultimately, isn’t that what it’s all about?

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com.
His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others.
Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
About The Author
Mike simpson.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com. His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others. Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
Copyright © 2024 · TheInterviewguys.com · All Rights Reserved
- Our Products
- Case Studies
- Interview Questions
- Jobs Articles
- Members Login
- Our solution
- Request a demo
- L&D strategy
- Empowering growth
- Measuring impact
- Trends and insights
- Our Solution
Critical thinking training: 5 key lessons for employees

Employers participating in the AAC&U’s periodic surveys consistently rank critical thinking as one of the most vital skills for success in the workplace. The 2020 survey ranked it second in importance only to the ability to work effectively in teams.
The survey also found that while 60% of employers rated critical thinking skills as very important, only 39% agreed that recent college graduates have been well prepared by the training on critical thinking they received in school.
This is one of the main reasons critical thinking training is growing in demand among organizations across sectors. Learning and development leaders are tasking their teams with determining what it would take to develop critical thinking skills in the workplace, at scale.
Critical thinking training in the workplace
Critical thinking refers to the act of analyzing evidence, observations, and arguments to form a judgment. It often requires the conceptualizing and synthesizing of information. Specific skills that are commonly addressed in critical thinking training include:
- Identifying a problem or question
- Using more than one strategy to approach a problem
- Gathering relevant data, opinions, and observations
- Analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating data
- Understanding patterns and connecting ideas
- Making inferences from data
- Thinking creatively
- Practicing self-reflection, self-regulation, and open-mindedness
- Identifying assumptions and biases
- Identifying and evaluating alternative courses of action
- Anticipating the possible outcomes of different actions
- Testing hypotheses
- Making data-based decisions
While some personality traits are particularly conducive to critical thinking, such as curiosity and creativity, employees without these traits can benefit greatly from critical thinking training. The five lessons below are an excellent starting point for organizations looking to develop this skillset in their workforce.
Common Cognitive Pitfalls in Decision-Making | Liv Boeree
Guarding against the possibility of biases influencing one’s decisions is a key principle that is often discussed in critical thinking training. In her Big Think+ class, Liv Boeree — international poker champion — addresses several cognitive pitfalls that can result in faulty decisions. Watch the clip below to learn more.
As Boeree described, confirmation bias is the tendency to overvalue evidence that confirms one’s existing beliefs, and undervalue evidence that contradicts them. She later goes on to explain status quo bias, which reflects the natural human aversion to change and is defined as a preference for how things have been done previously.
There is also the sunk cost fallacy, which refers to the act of making decisions based on previously invested resources rather than desired outcomes for the future. For example, some organizations cling to legacy systems, creating a nightmarish patchwork of fixes before eventually reaching the conclusion that it’s time to scrap the old and embrace the new.
Open to Think | Dan Pontefract
In his book, Open to Think , award-winning author and professor Dan Pontefract describes “open thinking” as a cyclical process which involves creative thinking (dreaming), critical thinking (deciding), and applied thinking (doing).
The first stage in the process involves generating new ideas unrestricted by constraints. Then in the critical thinking stage, one evaluates and makes data-driven, fact-based decisions about the ideas generated through creative thinking. Finally, applied thinking operationalizes the decisions resulting from critical thinking.
Our thinking is only as good as our ability to continually challenge and question. Dan Pontefract
This dream-decide-do cycle can be repeated as many times as needed to improve outcomes. The true power of the model lies in its iterative nature because it allows for the possibility of failure, treating it as a learning experience and opportunity for improvement.
Let Information Permeate Your Organization | Andrew McAfee
Effective critical thinking doesn’t just rely on the individual thinker. In order for the skill to thrive among individuals, information must flow freely throughout the organization. And employees must have the support of their supervisors in using that information.
Andrew McAfee, MIT scientist and author of Machine, Platform, Crowd , says that in the Information Era, managers should no longer act as gatekeepers of information. Today’s technology makes it easy to distribute data throughout all levels of an organization. Watch the clip below to learn more.
If the marketing team has information that would be useful to the sales or product teams, that information should be easily accessible by all. And as McAfee suggests, team leaders can provide specific suggestions for how to best make use of the information. These are key strategies that leaders can learn in critical thinking training.
The Art of Perception | Amy Herman
Amy Herman — art historian, attorney, and author of The Art of Perception — offers a unique model for thinking critically about observations that she refers to as the “Four As of Visual Intelligence.” Herman defines visual intelligence as the ability to assess, analyze, articulate, and adapt to visual information in one’s environment.
- Assessing your situation involves consciously making observations and determining what information can be extracted from them. Herman suggests asking others to share their observations, as no two people interpret things the same way.
- To analyze the information is to examine it closely and decide what is important and necessary.
- To articulate one’s observations is to describe in words the important observations and the information they provide.
- Finally, adapt to the situation by making a purposeful decision based on the information from the previous steps, and act on that decision.
In her Big Think+ class, Herman suggests consciously practicing the Four As until they become automatic. This develops a mindset of applying critical thinking skills to make sense of information in the world around us.
Making Complex Decisions | Lawrence Summers
Decision-making can be challenging, especially for employees who are new to roles that require planning and strategizing. For this reason, it’s wise to include instruction on decision-making in critical thinking training.
In his Big Think+ class, economist and former director of the U.S. National Economic Council, Lawrence Summers, addresses a key aspect of critical thinking — the ability to be analytical in choosing among different courses of action.

Summers applies a scientific method to making complex decisions that’s grounded in thinking in terms of alternatives. It begins with identifying alternatives to a proposed solution without making any assumptions initially as to which is best. Each alternative is then analyzed from the standpoint of feasibility and the likely consequences of implementation. Then, a judgment is made as to which of the feasible alternatives will produce the most desirable outcomes.
The core challenge, as Summers sees it, is to separate what one would like to be true from what, in fact, is true. Only by understanding what is true is it possible to accurately evaluate the consequences of alternative courses of action.
The benefits of critical thinking training
In today’s business environment where rapid technological innovation is fueling an abundance of information, success depends on strong critical thinking skills. Critical thinking training can improve a person’s ability to come up with innovative solutions and build onto ideas expressed by others. It enhances the creative and collaborative processes that teams work through on a daily basis.
Meetings become more productive when there is greater clarity and depth of thought, and management is more effective when leaders are able to distinguish between emotion and logic. Organization-wide, critical thinking leads to fewer errors in judgment and better overall decision-making. These are just a few of the ways that both individuals and organizations can benefit from critical thinking training.
Sign up to receive new research and insights every other Tuesday.

- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
Business.com aims to help business owners make informed decisions to support and grow their companies. We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
As a business, we need to generate revenue to sustain our content. We have financial relationships with some companies we cover, earning commissions when readers purchase from our partners or share information about their needs. These relationships do not dictate our advice and recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates and recommends products and services based on their research and expertise. Learn more about our process and partners here .
Building Critical Thinking Skills to Solve Problems at Work
Follow this six-step discussion process to foster critical thinking among your team.

Table of Contents
Critical thinking is a vital soft skill that uses one’s experiences and analytical skills to deduce information and make educated decisions. It’s an essential skill to have in the workplace, as the ability to use information from a broader and more impartial perspective allows your employees to make more informed decisions and see a comprehensive view of any situation.
The U.S. Department of Labor identified critical thinking as a key component for essential workplace skills, including problem-solving and decision-making. Here’s how to build – and implement – critical thinking skills in the workplace.
>> Learn more: 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
How to use critical thinking to problem-solve
Here is a six-step problem-solving process to try with your team to build and use this skill.
1. Name the situation.
When you name the situation, you present a single discussion point that everyone in the discussion can identify. This statement can be written on a whiteboard as a visual prompt so that the team can focus on the point and redirect the discussion when the topic shifts. Critical thinking involves keeping an open mind about situations. You help participants remember the goal of the group by naming the situation.
2. List all possible solutions.
Brainstorming takes place during this part of the process. There is nothing outside the realm of possibilities at this point in the discussion. When you open the conversation to unlimited options, you expand thinking beyond one person. The ability to expand your thinking offers the conversation many possible solutions that you may not have considered without the expression of thoughts and opinions. Make sure that all potential solutions discussed during this time stay on task for the situation that has been named in the first step. Critical thinking includes the ability to keep an open mind to other considerations and viewpoints without losing track of the end goal. You expand the discussion to see new options and stay on task by identifying multiple opportunities.
3. Narrow your solutions to three options.
Everyone on the team needs to agree with at least one of the three options. Individuals who can find a compromise and create solutions from many perspectives are better able to bring a team together. Write each solution at the top of a whiteboard and include below each one a list of its advantages and disadvantages. Critical-thinking skills offer the ability to look at situations rationally without judgments of good and bad or wrong and right. You can maintain a rational discussion when you bring consensus to a few intentionally chosen solutions.
4. Choose one option from the three choices.
Make a final choice that offers the best chance of success based on rational discussion about the situation. Review this choice in relation to how well it solves the designated problem. Critical thinking skills help individuals use a more systematic way to come to conclusions. This reduces the chance of making decisions based on incorrect inferences arising from emotional conclusions.
5. Put a plan in place to implement the chosen solution.
Your chosen solution should have timelines and a list that identifies which participants are responsible for what parts of the final plan. Critical-thinking skills include the ability to commit to the chosen solution. You increase attention to detail and interest from the participants in implementing the solution when they are an integral part of the process.
6. Complete the plan.
Some employees find this part of the process the most difficult. Think of the number of times a great plan floundered because there was no follow-up. Make sure each person from the team has a part to play in the process that emphasizes their areas of expertise and interest. Complete regular reviews of people and timelines for project management. Critical thinking involves the ability to see the value of the overall plan. At this point in the process, individuals should be able to see the value of the solution and have buy-in since they were part of the process.
This problem-solving process creates an environment where critical thinking becomes a working part of finding a solution. For individuals who struggle with this method, you may want to consider some training in critical thinking. Overall, though, this process promotes critical thinking in your employees. You can also integrate this activity for making plans and creating a mission. The value added to your organization includes improved engagement , insight and productivity from your team.
Why critical thinking is essential in the workplace
In recent decades, companies have recognized the need for integrating critical thinking into the workplace to help build the success of their organizations. Strong critical-thinking skills can greatly benefit everybody in the workplace. Not only does thinking more openly introduce ideas and solutions that widen the opportunities for success, but it also provides an increase in teamwork and productivity and a decrease in conflict . Here are some additional benefits of critical thinking in the workplace.
Required in certain professions
In many professions – particularly those based on research or that require deductive reasoning, such as finance, education, research and law – acquiring critical-thinking skills is necessary. With critical thinking, employees can solve problems objectively by considering varying perspectives and analyzing facts without bias, allowing for smart decision-making and problem-solving.
Improves decision-making
Those with critical-thinking skills mull over their decisions thoroughly by researching, looking at information objectively, asking questions, and weighing the pros and cons before acting. This skill can help businesses stay on track when making decisions by thoroughly reviewing the risk versus reward of each decision.
Boosts happiness
Critical thinking can boost happiness , as it is empowering to have the skills to make your own, well-informed decisions. Those who possess this skill are more in tune with their goals, needs and personal ethics, and they have a better understanding of what in their situation needs to change to make themselves happy or grow. [Read related article: How Hiring a Chief Happiness Officer Can Save Your Business ]
How to build critical-thinking skills
Here are a few ways you can polish your critical-thinking skills.
Practice active listening.
Practice actively listening by keeping an open mind and being attentive to those around you, from associates to executives. Listen to what others are saying to gain an understanding of each person’s individual perspective, needs and expectations, and show them empathy. This level of understanding will allow you to work together more effectively and make decisions that everyone is satisfied with.
Ask critical questions.
Instead of taking information at face value, be curious and ask questions to ensure you have everything you need to make a well-informed decision. Using open-ended questions offers an opportunity for further exploration, as they dive deeper and provide insightful details that can be helpful when making decisions.
Vet new information.
Don’t assume all new information you hear is true; instead, take time to thoroughly vet it by ensuring it’s up to date and it comes from a trustworthy source. Look at the existing evidence and the new facts being presented, then question thought processes and consider whose voice is missing.
Consider more than one perspective.
While you may feel that you have the “right” perspective, consider all points of view to fully understand others and their reasoning. This will help you improve your working relationships, better understand where your peers are coming from and tailor your communication to meet their needs.
Question your own biases.
Regardless of whether or not you try to avoid it in your decision-making process, everybody has their own biases, which are the foundation of their thinking. By uncovering your own biases and being actively aware of them, you can grow as a critical thinker and work to keep them separate from your decision-making process.
Conduct research.
If there are any unanswered questions or gaps in the information provided, conduct research to further your understanding and reach a decision. Consider a source’s intention when conducting research, avoiding any that are sales-based or contain ill will. Don’t use social media to obtain information; stick to reputable publications free of bias and cite their sources.
Form your own opinion.
Be an independent thinker and form your own opinions by considering the information presented to you, including facts and evidence. Listen to and consider the opinions of others, but use deductive reasoning to form your own opinion – and stay true to it.
Lynette Reed contributed to the writing and reporting in this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
7 critical thinking skills with examples
Critical thinking: you might have seen it listed in job ads or heard people talking about the importance of critical thinking. But what's critical thinking? And how do you go about adjusting the way you think about things to become less emotional, and more critical?
That’s a lot of questions, but this guide has the answers. Below, we’ll break down the complex concept of critical thinking into simpler chunks, as well as providing examples of critical thinking in action. By the end, you’ll have a much clearer picture of what critical thinking is and how it can help you grow in your career and personal life.
- What is critical thinking?
- 7 critical thinking skills in practice
Examples of critical thinking
- 5 benefits of developing critical thinking skills
5 barriers to critical thinking
How to improve critical thinking skills , tools and techniques for critical thinking .
- Benefits of a workplace culture that encourages critical thinking
- The future of critical thinking
What is critical thinking?
Let’s start with a simple definition of critical thinking to understand what it is and the basics of how it works. Critical thinking is simply a way of looking at things in a more rational, logical way.
Usually, when faced with a situation, decision or dilemma, you might let your emotions, biases and other factors get involved in the thinking process. That’s completely natural. We all have our own ways of thinking about things and looking at the world.
But, if you’ve ever wanted to see things differently with a clearer mind, free of emotions and biases, that’s what critical thinking is all about.
Thinking critically is about quieting those emotions that might impact your decision-making. It’s about looking at a situation or problem from rational angles, analysing all the information available and coming to a logical conclusion.
Here are six steps to critical thinking:
- Analysis: The gathering and understanding of data and information.
- Interpretation: Drawing out meaning from the available data.
- Inference: The ability to make conclusions based on the data analysed.
- Explanation: Being able to communicate one’s conclusions and findings with others.
- Evaluation: Questioning the conclusions and looking at other angles and possibilities.
- Self-regulation: Understanding how one’s own biases may impact the process.
7 critical thinking skills in practice
What are some different critical thinking skills? What does it look like when you put these skills into practice at work? Here are some of the ways in which critical thinking can manifest in the workplace:
1. Decision-making processes
Critical thinking is useful for making workplace decisions in a fair way. For example, who to hire for a certain role or whether to take one job over another.
2. Conflict resolution
Critical thinking can also be very useful when you’re dealing with challenging situations with colleagues or your manager. Rather than making emotional or biassed decisions, you can think about how to resolve the issues in the fairest and most reasonable way.
3. Innovation
Critical thinking can also be a driving force for innovation. When you think about problems critically, you may come across unique solutions you might not have otherwise discovered.
4. Evaluating information
Critical thinking at work can help you evaluate complex data and information. It can help you make well-informed decisions, identify potential risks and develop solutions around strategy, project management and problem-solving.
5. Making informed decisions
Critical thinking helps you gather and analyse relevant data and consider various perspectives. It allows you to weigh the pros and cons before arriving at a well-informed decision. So, whether you’re in a leadership role or part of a team, these critical thinking skills can help you make informed decisions:
6. Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills can help you achieve your business objectives. It allows you to break down tough challenges and figure out what's really causing the issue. You’re able to come up with creative fixes and make decisions that work. Ultimately, keeping things efficient and effective.
7. Communication
Critical thinking can also make you a more effective communicator with those around you. You’re able to become a better listener and build your understanding of other people’s views and personalities. It may lead to better and happier friendships and relationships.
One of the best ways to see the benefits of critical thinking is when you’re faced with a problem. When you come up against some sort of challenge, you might find yourself stumped or struggling to find the right solution.
That’s all normal and natural, and critical thinking can help you approach challenges and problems more confidently. You’ll be able to see those kinds of situations from new angles revealing previously unseen solutions along the way.
Example : Suppose you're in an interview and faced with a challenging question about your weaknesses . Instead of avoiding the question, apply critical thinking to identify a genuine weakness. Explain your strategies for improvement, showcase your self-awareness and commitment to growth.
Examples of critical thinking in decision-making
Decision-making. It can be hard. You might struggle when weighing up the pros, cons and potential outcomes of one decision or the other. If you feel that way, then critical thinking could help.
When you apply critical thinking to a big decision, you cut out all the noise and emotion , leaving nothing but the facts and stats. These skills allow you to analyse situations fairly and logically, reaching smart, sensible conclusions with the best potential outcomes.
Example: Imagine you have multiple job offers on the table. By applying critical thinking, you can carefully assess each offer by considering factors like company culture, growth and opportunities. Also, you could consider things like job responsibilities, and alignment with your long-term career goals.
Examples of critical thinking in creativity
Creativity is all about letting your imagination loose and thinking outside the box. It might not seem like critical thinking can help, but in action critical thinking can be the key to helping you unlock more of your imaginative potential. You might discover insights and ideas you wouldn’t have thought of without it.
There are several creative critical thinking techniques, like mind maps and brainstorms, that you can use in many situations. When brainstorming, try to see a situation from lots of angles. Think about a situation in different ways to come up with related ideas, which is one of the cornerstones of critical thinking.
Example: Imagine you’re a teacher trying to think of a new lesson plan to teach kids about a difficult subject. If you rely solely on your experiences and favourite systems, you may struggle to think of anything new. But, by thinking critically, you can explore new ways to approach the subject and teach it to your class.
Examples of critical thinking in communication
Communication is another area where critical thinking can make a massive difference. When you let your emotions influence what you say, you might end up saying something you don’t mean. If you’ve ever felt like your mood has influenced discussions with colleagues or people outside work, critical thinking could help.
It helps you to focus more clearly and have more productive, pleasant conversations with others. It’s also helpful to apply critical thinking if you have a disagreement with someone or simply have differing ideas. It can help you see things from their perspective.
Example: Let’s say that two members of your team are arguing about which one of their solutions to a problem is best. With critical thinking, you can put your opinions to the side and help to resolve the conflict in a rational and level-headed way.
Examples of critical thinking in analysis and evaluation
Analysing and evaluating information is an important part of everyday life. You might be given information that you need to process. But naturally you have biases that may prevent you from independently assessing the data you receive.
Critical thinking can help you see information in a different light, absorbing it in a rational and logical way. It'll allow you to allow you to evaluate it based purely on facts, rather than bias or preconception.
Example: Imagine you just got assigned a new task at work with a technology you haven’t used before. It’s easy to be overwhelmed, but by thinking critically and analysing the relevant instructions, you can set up a clear plan of action. This will help you become better prepared to tackle the challenge of learning something new.
Examples of critical thinking in self-reflection
Another important aspect of critical thinking is being able to reflect on your own thoughts, actions and beliefs. It’s important to question the motives and origins of certain ideas or biases that may be present and could be affecting your decision-making. Through critical introspection, you may uncover biases you were unaware of and can then take actions to improve your future actions or reactions.
Example: Imagine you're reflecting on your recent job performance. Instead of simply accepting your accomplishments at face value, you apply critical thinking. You assess not only what you achieved but also how you achieved it. You question whether there were missed opportunities for improvement, and you identify areas where you can further develop your skills.
5 benefits of developing critical thinking skills
So, why might you want to focus on improving your critical thinking capability through critical thinking exercises? Critical thinking can offer an array of unique benefits, making you a stronger, better and happier worker . Some of the benefits of critical thinking are:
Improved decision making: Critical thinking can help you make more informed decisions. Rather than rushing to hasty calls or letting your emotions and other factors cloud your judgement.
Enhanced problem-solving skills: When you’re able to think critically about things, you can become a much more effective problem solver. You’ll be able to see problems from different angles, gathering information effectively to arrive at a logical solution.
Improved communication skills: Often, emotions and biases can negatively impact our communications with the people around us. But, with a critical thinking approach, it’s much easier to communicate clearly and effectively, even with those who have different views.
Better understanding of different perspectives: A big part of becoming a critical thinker is becoming a better listener. It can be hugely helpful in starting to understand and accept other ways of looking at things.
Increased creativity: Critical thinking can also be helpful for creativity . When looking at problems and situations rationally and analysing information, you might often come across unique and creative ideas you hadn’t previously imagined.
Critical thinking isn’t always easy to practise and you might find you encounter a range of barriers when trying to approach problems critically:
1. Personal biases and prejudices
Personal bias is the number one barrier to critical thinking, and it can be very hard to avoid. When thinking about a problem or trying to make decisions, especially involving other people, our opinions and biases can impact our view.
2. Emotional influences
Emotions can also get in the way when trying to think critically. It’s simply a part of human nature, and it’s very difficult to try to 'switch your feelings off'. It can be challenging to make a rational, logical decision in certain circumstances. But, by improving your critical thinking skills, you can learn to detach emotions from decision making.
3. Lack of knowledge and understanding
In some cases, a simple lack of knowledge can make you unable to approach a situation in a balanced and rational way.
4. External pressures
There may also be external factors beyond our control which influence the decisions you make and the way you think about things. For example, deadlines or the opinions of stakeholders and decision-makers.
5. Lack of time
Sometimes, a simple lack of time is all that’s needed to interfere with the critical thinking process. It takes time to look at things critically and gather information.
Once you’ve got the basics of critical thinking skills, there are still many ways to improve them over time. So, how can you develop critical thinking skills further? The main way to improve is through understanding what critical thinking involves. It’s about using your skills as much as possible in many aspects of everyday life, including work and personal life.
When you face a problem or situation, make the choice to think about it critically, rather than simply acting on instinct or making emotional decisions.
Reflect, analyse different viewpoints and question assumptions or ideas that might be influencing your train of thought. With time and repetition, it’s possible to hone your critical thinking abilities. Here are three important tips to further develop critical thinking:
Active listening
If you’re eager to start working on your own critical thinking skills, a good way to get started is to become a more active listener . Don’t just hear what people are saying - listen actively to understand, considering the why and how behind their words, ideas and opinions. Ask questions to get more data, and challenge assumptions or misconceptions.
Practise mindfulness
Take time to consider your approach. From the words you say to the actions you take, to the behaviour and opinions of those around you. By focusing more on these different aspects, rather than simply letting them pass you by, you can start to master the basics of critical thinking.
Be patient
When dealing with a difficult situation, like a challenge at work or a relationship issue, try to apply the fundamentals of critical thinking. Be patient. Don’t rush to a conclusion or decision. Think carefully and deliberately to reach a decision that seems fair.
It’s also important to remember that critical thinking takes time to develop and practise. Becoming a good critical thinker is a continuous process of learning and development, requiring constant commitment and the ability to self-regulate and self-evaluate.
There are various useful tools and methods that can help you put critical thinking processes and concepts into action, including:
SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis is when you take those factors into account to come to a fair assessment of the situation. It's often a useful way to evaluate how well a project is performing and where it can be improved.
Fishbone diagram
A fishbone diagram is a useful tool that can help you visualise a problem and learn about its causes. It makes it easier to find a solution. The 'fishbone' name comes from the fact that the diagram involves a central line with adjoining lines and arrows coming off either side. These represent various factors that contribute to the problem or situation, making the final diagram look like a fish skeleton.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is another kind of diagram that can be useful for visualising situations and extrapolating information about a given subject or problem. Start with the main subject in the centre, and then branch off with connected thoughts and considerations. You can also think about adding sub-topics and notes, resulting in a 'map' of the situation.
Cost-benefit analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is another handy technique that many businesses use when trying to make decisions. It has a lot in common with critical thinking, as it's all about taking in information and making rational conclusions based on the available data.
As the name implies, a cost-benefit analysis focuses on measuring how much a decision or action will cost and what benefits it can provide. You can then analyse that information to determine if the decision offers good value and makes sense or not.
Decision trees
A decision tree is a simple framework in which you write down a potential decision and then branch off from it. It allows you to imagine what would happen based on various decisions.
Decision trees can help you visualise the prospective consequences of every decision, giving you the information to make the best possible choice.
Benefits of a workplace culture that encourages critical thinking
It can be hugely beneficial to be part of a workplace that encourages critical thinking as part of the culture. It can lead to many advantages, including:
Improved decision-making: When critical thinking is part of the culture, employees are more likely to think carefully about big decisions and make the smartest calls.
Increased innovation and creativity: Critical thinking skills can also help you develop innovation and creativity. They encourage outside-the-box thinking, rather than restricting your own biases and limitations.
Better problem solving: One of the best benefits of critical thinking in the workplace is how it can help you solve problems more effectively. You’re able to take all the necessary info into account to arrive at a sensible and efficient solution.
Higher employee engagement and job satisfaction : When you’re encouraged to think critically, you’re more likely to engage at work and happier overall.
The future of critical thinking
As the world changes and new technologies emerge, the concept of critical thinking could change in the years to come. There's a concern among various experts in the field of AI that the proliferation of AI could give people weaker critical thinking skills. As people grow to rely on technological tools like AI bots to solve problems and make decisions for you.
It could be particularly impactful on children and younger generations. Children grow up in a world with so many technological tools and services to help with almost every aspect of their lives. But even if critical thinking becomes trickier to learn in the future, it'll still be a very valuable and useful skill for all.
There's no doubt that critical and creative thinking skills are important in any workplace. These skills allow you to think about problems in the most fair and reasonable way, making the logical and rational conclusions. These skills can be perfect for problem-solving and dealing with big and tricky decisions.
If you’re wanting to improve the way you deal with everyday situations in a more logical way, then applying critical thinking skills is a great practise.
What are the top 5 critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking involves a range of different skills that can be applied to various situations. Here are 5 critical thinking skills: decision-making, conflict resolution, innovation, evaluating information and making informed decisions
What makes a person a critical thinker?
Critical thinkers have the ability to look at situations in an objective and rational way. They can analyse available data to draw logical conclusions, without letting their own biases interfere. They are able to make rational, logical decisions and solve problems fairly.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills?
There are many ways to work on your critical thinking skills. Practise is key, and skills can improve with repetition. Start by approaching problems and decisions in more rational ways. Clear your mind of biases and focus purely on the facts and information available to you.
What is a good example of critical thinking?
An example of a critical thinking decision in everyday life might be trying to find a new job. You can carry out research and read company reviews. You can also source varying job descriptions and look at specifications like the salary to make the right choice for you. Other examples include deciding on diet and lifestyle factors, buying big purchases or solving problems at home.
What are the most common barriers to critical thinking, and how can I overcome them?
The main barriers to critical thinking are personal or shared biases, emotions and preconceptions. Through your experiences and interactions with other people, you may develop certain ideas or notions that can impact your thinking and decision-making abilities. Emotions like fear or social pressure can also obstruct critical thinking. Overcoming these barriers involves practise and the ability to free your mind of biases.
How can critical thinking skills benefit my career development?
Many employers value critical thinking skills. By using them effectively in the workplace, you may find it easier to deal with difficult colleagues and add value to your company.
How can I encourage my colleagues to develop their critical thinking skills?
A good way is to lead by example. Demonstrate logical and rational thinking to solve problems. You can pull out resources like fishbone diagrams or mind-mapping, where people may feel inspired to follow your approach.
Are there any industries or job roles where critical thinking skills are particularly important?
Industries including Education and Science are particularly reliant on critical thinking, along with Healthcare, Engineering and Finance, but this skill can be valuable in almost any line of work.
What are some common misconceptions about critical thinking?
You might believe that critical thinking has little practical use, or that it's only useful in settings like scientific research and education. But, having an open and analytical mind can be hugely beneficial in many industries and situations.
How can I measure my progress in developing my critical thinking skills?
A good way to measure your critical thinking skills is to think critically about where you’ve used them and the improvements you’ve seen. Consider problems they’ve helped you solve, and the impacts of the decisions you made through critical thinking. You could also ask for feedback from the people around you.
Top search terms
Explore related topics, subscribe to career advice.

Critical Thinking Is All About “Connecting the Dots”
Why memory is the missing piece in teaching critical thinking..
Updated July 17, 2024 | Reviewed by Monica Vilhauer
- Critical thinking requires us to simultaneously analyze and interpret different pieces of information.
- To effectively interpret information, one must first be able to remember it.
- With technology reducing our memory skills, we must work on strengthening them.
I have a couple of questions for my regular (or semi-regular) readers, touching on a topic I’ve discussed many times on this blog. When it comes to power, persuasion , and influence, why is critical thinking so crucial? Alternatively, what are some common traps and pitfalls for those who prioritize critical thinking? It's not necessary that you go in to great detail—just any vague or general information that comes to mind will do.
Great! Regardless of whether you recalled anything specific, the key is you made the effort to remember something. Like many questions I pose here, the real purpose is to illustrate a point. If you aim to be influential and persuasive—i.e., successful—in both work and life, you must be proficient in critical thinking. To achieve this proficiency, you need to cultivate and exercise your memory , a skill that is increasingly at risk in a technology-saturated age.
Remembering Is the Foundation of Knowing
Learning and remembering something are often discussed as if they are two separate processes, but they are inextricably linked . Consider this: Everything you know now is something you once had to learn, from basic facts to complex knowledge and skills. Retaining this information as actual knowledge, rather than fleeting stimuli, depends entirely on memory. Without memory, there is no knowledge. Consequently, there can be no critical thinking, as it relies on prior knowledge, which in turn relies on memory.
Students sometimes tell me that they want to learn how to be good critical thinkers but complain about having to “memorize stuff.” On these occasions I will often say, in a playfully teasing manner, “What I hear you saying is that you're bothered by having to remember stuff.” This usually helps them see how silly and unreasonable it is to complain about memorizing information, as there isn’t a single course in existence that doesn’t require remembering something . The ability to remember is at the core of critical thinking, and I often use the simple visual demonstration that follows to illustrate this point.
Collecting Dots and Connecting the Dots
Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist, developed a model known as the “Taxonomy of Learning.” Originally intended for educational psychology, this model also highlights why memory is the foundation of critical thinking—or any kind of thinking at all.
Humans are creatures of interpretation, constantly processing the information we perceive. This ability has made us the scientists, inventors, and artists that we are today. To interpret information, however, we must first remember it—not all information, obviously, as that’s impossible. Thanks to technology (which we’ll get to momentarily) we have vast amounts of information potentially at our fingertips. But how do you know what information to look up in a given situation? To know where to start and avoid endlessly searching irrelevant data, you need to remember enough of the right kind of information.
Think of a crime movie where an investigator, while reviewing evidence, suddenly has an epiphany and rushes off to confirm their hunch. These scenes illustrate that while the investigator needs more information, they remember enough to know what to search for.
Here’s a visual demonstration I use in class to help my students understand. Imagine you have pieces of information represented as five dots:
Now let’s say that any coherent shape or picture you can draw using these dots is an interpretation of the information. When examined together, what might these five dots mean? Here’s one way to connect the dots.
What does this shape represent? Many people will quickly say it’s a house, a common and reasonable interpretation. But not everyone sees it as a house. Some might say it’s the home plate used in baseball. Even when people connect the dots (i.e., interpret a cluster of information) the same way using the same lines, they don’t necessarily interpret the picture the same way. The situation becomes more complex when people connect the dots differently, creating a completely different shape or picture.
Now, having connected the dots differently, instead of a house, we have a star. Or at least some would consider it a star; others might say it’s an occult or magic symbol—these are all very different interpretations. This shows that with the same pieces of information, people can “connect the dots” differently, and even when they connect them the same way, they see different things.
Now what happens when additional information is added or an alleged “missing dot” is perceived by others?
With just one additional dot, what could have previously been interpreted as a 5-pointed star can now be reasonably interpreted as the Star of David.
Finally, sometimes the additional information can lead to a completely different shape or image, resulting in a “eureka” moment of insight. What previously appeared as different types of stars now looks like a circle.
I use this classroom demonstration to illustrate how people can interpret the same objective information in highly subjective ways, creating different narratives for themselves and others. This is a crucial point to remember when aiming to influence or persuade others—i.e., the need to see things from their perspective. Additionally, this activity powerfully underscores the importance of “collecting dots”—that is, the importance of remembering crucial bits of information. Without enough such dots, you lack the basic information needed to form meaningful ideas. Without meaningful ideas, you can’t think critically, influence, or persuade. It’s as straightforward as that.
Memory in the Age of Omnipresent Technology
Why is it so crucial to recognize that memory is foundational to critical thinking, power, influence, and persuasion? Partly because this fact isn’t widely acknowledged—and it needs to be. Additionally, we live in an era where memory is under unprecedented assault. While technology allows us to achieve remarkable feats unimaginable to previous generations, it comes at a cost. One such cost is “digital-induced amnesia,” where our memory capabilities atrophy due to information overload and technology taking over many of the cognitive tasks we used to perform ourselves.
Memory doesn’t exist in isolation. It’s closely tied to traits like the ability to focus and pay attention . If you’re not paying attention, you can’t absorb the information that you want or need to remember. Unfortunately, technology also impacts our ability to focus , and this doesn’t even touch on the dramatic ways AI ’s explosive development might undermine our thinking skills .
This article won’t delve into specifics on improving focus and memory in an age of tech ubiquity. Fortunately, resources from Psychology Today can help with that. My goal here is to convince you why memory is so vital for anyone who wishes to be a critical thinker and a persuasive, influential person. Now you know. Whether you’ll remember or not...only time will tell.

Craig Barkacs, MBA, JD, is a professor of business law at the University of San Diego School of Business and a trial lawyer with three decades of experience as an attorney in high-profile cases.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
More From Forbes
5 Interview Questions That Gauge Critical Thinking Skills
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
As a job candidate, you're likely to encounter interview questions designed to assess your critical thinking skills. Employers highly value these skills because they demonstrate your ability to analyze information, solve problems creatively, and make sound decisions. In a world filled with AI, an overabundance of data, increasingly rapid decision-making, and greater autonomy with remote work, critical thinking skills are atop employers' lists of desired candidate traits.
Questions That Assess Critical Thinking Skills
Every company will put their own spin of critical thinking interview questions, but here are five of the most common questions that you should be ready to answer:
- Tell me about a time you had to solve a complex problem at work. What was your approach?
- What do you think are the three biggest challenges facing our industry right now? How would you address them?
- Describe a time when you had to make an important decision with limited information or time. How did you handle it?
- Tell me about a time your initial approach to solving a problem didn't work. How did you pivot?
- If you were in charge of our company, what's one major change you would make and why?
The good news with these five questions is that if you construct good answers for each of them, you'll be well-positioned to handle any other variations you come across.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, key points, words and themes to included in your response.
When you're answering critical thinking interview questions, it's vital for you to demonstrate how you analyze situations, assess and solve challenges, and reflect and learn from your experiences. And that's where the SHER Method can be especially helpful.
The SHER Method is a structured approach to answering interview questions that stands for Situation, Hurdle, Endgame, and Reflection. When using this method, you start by briefly describing the Situation or context of the experience you're sharing. Next, you explain the Hurdle or challenge you faced. Then, you detail the Endgame, which includes the actions you took to address the challenge and the results you achieved. Finally, you conclude with a Reflection, sharing what you learned from the experience and how it has influenced your subsequent professional conduct.
The SHER Method is particularly powerful for demonstrating critical thinking skills because it guides candidates to systematically analyze a situation, identify challenges, explain their problem-solving process, and reflect on outcomes and lessons learned. It showcases your ability to think critically and learn from experiences in a structured and compelling way. And that's really the foundation of critical thinking skills.
When answering critical thinking interview questions, keep these points in mind:
- Use specific examples from your experience
- Clearly explain your thought process and reasoning
- Demonstrate a systematic approach to problem-solving
- Show that you consider multiple perspectives
- Emphasize data-driven decision making
- Highlight your ability to adapt and learn from experiences
- Be prepared to discuss both successes and failures
- Show how you've applied lessons learned to future situations
Specific Answers To Critical Thinking Interview Questions
Let's look at some specific answers to some of the aforementioned questions that assess critical thinking skills.
Question 1: Tell me about a time you had to solve a complex problem at work. What was your approach?
Why is this an important question that is often included in interviews? It's because there is no shortage of complex problems that need solving, and when a company is making a big hire, it hopes the candidate has some good solutions.
In your answer, describe the complex problem you faced, explain the main challenges you encountered, detail the steps you took to solve the problem, and share what you learned from the experience.
Here's an example answer: "In my previous role as a project manager, we were tasked with implementing a new software system that would integrate multiple departments. The primary challenge was significant resistance to change from each department. I started by mapping out all the current processes and identifying areas of overlap. Then, I conducted interviews with key stakeholders from each department to understand their specific needs and concerns. Using this information, I created a phased implementation plan that addressed each department's unique requirements while still achieving our overall integration goals. This experience taught me the importance of stakeholder engagement in managing complex changes. I've since incorporated regular cross-departmental meetings into all my projects to ensure alignment and address concerns proactively."
Question 2: What do you think are the three biggest challenges facing our industry right now? How would you address them?
Why is this an important question that is often included in interviews? Simply put, it evaluates your strategic thinking and industry knowledge. If you're interviewing somewhere that prioritizes industry veterans, this question is quite common.
In your response, acknowledge the current state of the industry, identify three specific challenges, propose solutions for each challenge, and conclude with a forward-looking statement.
Here's an example answer: "The [specific] industry is currently facing significant disruption due to technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and regulatory pressures. The three biggest challenges I see are: 1) Adapting to rapidly evolving technology, 2) Meeting increasing customer demands for personalization, and 3) Navigating complex regulatory environments. To address these challenges, I would: 1) Implement a continuous learning program to keep our team updated on the latest technologies, 2) Invest in data analytics to better understand and predict customer preferences, and 3) Establish a dedicated regulatory compliance team to ensure we stay ahead of legal requirements. These challenges also present opportunities for companies that can adapt quickly. By addressing them proactively, we can position ourselves as industry leaders."
Question 3: Describe a time when you had to make an important decision with limited information or time. How did you handle it?
This question assesses your decision-making skills under pressure, which are relevant to lots of companies these days. In your answer, set the scene, explain the constraints you faced, detail your decision-making process, and share the outcome and lessons learned.
For example: "During a critical product launch, we discovered a potential safety issue just 24 hours before the scheduled release. We had limited time to gather information and make a decision, and any delay would result in significant financial losses. I quickly assembled a cross-functional team including engineering, legal, and marketing. We conducted a rapid risk assessment, weighing the potential safety concerns against the impact of delaying the launch. Based on our analysis, we decided to postpone the launch by one week to thoroughly address the safety issue. This decision ultimately saved us from potential legal issues and reputational damage. It reinforced for me the importance of prioritizing safety and quality over short-term gains, and the value of having a diverse team for rapid problem-solving."
Demonstrate Critical Thinking Skills Through Your Answers
Remember that when companies ask about critical thinking skills, they're not just looking for the correct answer but for insight into how you think and approach challenges. By demonstrating your ability to analyze situations, overcome obstacles, implement solutions, and learn from outcomes, you'll position yourself as someone who exercises critical thinking skills all day, every day.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

Important Skills Needed to Be Successful in the Workplace
Employers are looking for talent right now. Open jobs outnumber applicants, but you still need to bring the necessary skills to the table. Today’s workplace is collaborative and technological, but what other skills should you bring to the table. Here are the essential skills you need for the modern workplace to find your next opportunity.
Active Listening
Active listening isn’t just about communication, though it is an essential part. As humans, we tend to listen to someone else only as long as it takes for us to form an answer. That means we often tune out anything else that’s said. Active listening is about being fully present for the other person. Engage with them by repeating what they’ve said back to ensure you’ve understood and asked questions for clarification.
Problem Solving
Companies are often only as good as the last problem they solve. That means you need to bring problem-solving skills to the table. How would you approach a problem? How do you take responsibility for your actions and determine the best solution? How are you able to work with a team to accomplish a better outcome?
Critical Thinking
Similarly, critical thinking is an essential part of the workplace. Employers want to know that you take steps to think about every situation with a critical eye, see it from all angles, and develop ideas and solutions around the core situation. Critical thinking is an objective analysis rather than one informed explicitly by your expectations.
Time Management
Companies also don’t want to work with employees who rush, avoid deadlines, or procrastinate. Good time management skills will help an employer see that you can work efficiently and manage your own time. Practical skills help you do this, including keeping a planner or calendar and checking off a daily “To Do” list.
Collaboration
Today’s workplace is highly collaborative. This is an evolution and partially due to the shift in generations currently working. But companies want to see their employees working together to accomplish a common goal. Healthy competition is good, but ultimately the entire team needs to be on the same page and work well together.
Are you ready to find your next opportunity? Visit our job board to view our current openings.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Franchise Support Center
11101 Switzer, Suite 110
Overland Park, KS 66210
(913) 562-5610
(800) 581-NEXT (6398)
Looking for Quality People?

Meet Cary...
When it comes to operating a staffing firm, Cary has worn every hat. From recruiting, to sales, to management, to ownership, he has been involved in every aspect of running a successful staffing business. He has successfully led three separate companies to the Inc. 500 and Inc. 5000 lists, which puts him in an elite class of staffing entrepreneurship. Combining that experience with a strong passion for entrepreneurs makes Cary an ideal leader for driving the Nextaff vision.
Describe yourself in three words.
Loyal, Driven, Creative
Is there a mantra or affirmation you live by?
Do what you said you were going to do.
Do you have a celebrity doppelganger?
Back in the day, it was John Cusak. “I want my two dollars!”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Instead, most managers employ a sink-or-swim approach, ultimately creating work-arounds to keep those who can't figure out how to "swim" from making important decisions. But it doesn't ...
It's a challenge, but it's well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems. 7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper. Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you'll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions).
Critical thinking is considered a soft skill, which means it's a skill inherent in a person's personality. That said, it is possible to develop this skill. Related: 5 Examples of Critical Thinking Skills Critical thinking in the workplace Here are some of the ways critical thinking is important to the workplace: Some professions require it
7. Optimizing processes for efficiency. Critical thinking examples in the workplace clearly show how teams can improve their processes. Customer service. Imagine a company that sells gadgets. When customers have problems, the customer service team reads their feedback.
Using your critical thinking skills in the workplace will define you as a problem solver. This is not only useful career-wise (although having upper-level people at your company think highly of you is undoubtedly a benefit) it also establishes you as a leader among your fellow team members. Demonstrating your ability to solve problems and ...
Critical thinking skills examples. There are six main skills you can develop to successfully analyze facts and situations and come up with logical conclusions: 1. Analytical thinking. Being able to properly analyze information is the most important aspect of critical thinking. This implies gathering information and interpreting it, but also ...
Top 5 critical thinking skills. Here are five common and impactful critical thinking skills you might consider highlighting on your resume or in an interview: 1. Observation. Observational skills are the starting point for critical thinking. People who are observant can quickly sense and identify a new problem.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life. You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when ...
Enhancing critical thinking skills in the workplace is an essential step towards cultivating a culture of effective decision-making and problem-solving. By engaging in various training exercises, employees can strengthen their ability to analyze situations, interpret data, and make informed choices.
Critical thinking skills in the workplace can be beneficial for these reasons: Purposeful action: Employees take more pride in their work because they understand the necessary steps required to complete a project. Data-based decision making: Decisions are well-informed and contribute to overall improvement.
Instead, leaders should deliberately approach each problem and devote time thinking through possible solutions. The good news, she says, is that critical thinking skills can developed and ...
Example: A journalist verifies information from multiple credible sources before publishing an article on a controversial topic. 8. Decision-making. Effective decision making is the culmination of various critical thinking skills that allow an individual to draw logical conclusions and generalizations.
2. Understand your mental process. Identify and evaluate how you receive and process information. Understanding how you listen, then interpret, and finally react to information is vital to becoming more mentally efficient in the workplace. Being a critical thinker means you recognize your prejudices and how they influence solutions and decisions.
The key critical thinking skills are identifying biases, inference, research, identification, curiosity, and judging relevance. Let's explore these six critical thinking skills you should learn and why they're so important to the critical thinking process. 1. Identifying biases.
4. Evaluate all existing evidence and be open to revising your hypothesis. Pull in related information for a more systemic, broader understanding of the issue. 5. Develop conclusions based on data and present recommendations. Drawing conclusions is the final and most crucial part of critical thinking.
How to Use These Critical Thinking Questions. We've included five questions for each milestone below. There are five, rather than just one, for two reasons: Often one question alone won't be sufficient to help someone fully unpack their thoughts. You will likely find yourself in a position to ask these questions many times a week, if not daily.
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, critical thinking is "the process of thinking carefully about a subject or idea, without allowing feelings or opinions to affect you.". That's actually a pretty solid place to start. In many ways, critical thinking is a two-fold process. First, it focuses on information-gathering and fact-analysis.
Critical thinking allows you to always soberly assess the situations taking place in your work, give an objective assessment, including your own actions and the actions of others, effectively ...
Employers participating in the AAC&U's periodic surveys consistently rank critical thinking as one of the most vital skills for success in the workplace. The 2020 survey ranked it second in ...
Critical thinking is a vital soft skill that uses one's experiences and analytical skills to deduce information and make educated decisions. It's an essential skill to have in the workplace, as the ability to use information from a broader and more impartial perspective allows your employees to make more informed decisions and see a comprehensive view of any situation.
Here are six steps to critical thinking: Analysis: The gathering and understanding of data and information. Interpretation: Drawing out meaning from the available data. Inference: The ability to make conclusions based on the data analysed. Explanation: Being able to communicate one's conclusions and findings with others.
With technology reducing our memory skills, we must work on strengthening them. I have a couple of questions for my regular (or semi-regular) readers, touching on a topic I've discussed many ...
In a world filled with AI, an overabundance of data, increasingly rapid decision-making, and greater autonomy with remote work, critical thinking skills are atop employers' lists of desired ...
Critical Thinking. Similarly, critical thinking is an essential part of the workplace. Employers want to know that you take steps to think about every situation with a critical eye, see it from all angles, and develop ideas and solutions around the core situation. Critical thinking is an objective analysis rather than one informed explicitly by ...
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 58.26% This skill goes back to business basics. Proper negotiation skills come in handy in any aspect of life, whether you're negotiating a $1 ...
CROWNED 'THE MAKING OF A CARNIVAL QUEEN' (WEDNESDAY 5TH JUNE 2024)