How to Choose and Develop a Research Topic: Ideas and Examples
Discover strategies for choosing and developing a compelling research topic. Generate ideas, refine your topic, and conduct effective research.
Kate Windsor
Jun 26, 2024

Selecting the right research paper topic is a crucial step in the research process. A well-chosen topic can lay the foundation for a successful research project, while a poorly chosen one can lead to frustration and wasted effort. Choosing an interesting research topic can be challenging, especially for those new to the research field.
This article aims to provide guidance and inspiration for researchers seeking to choose and develop a compelling research topic and/or topics to write.

Understanding the Characteristics of a Good Research Topic
A good research topic should possess several key characteristics:
- Originality and novelty: The topic should contribute new knowledge or insights to the field, rather than simply rehashing existing research.
- **Feasibility and relevance: **The topic should be feasible to research within the given timeframe and resources, and relevant to the researcher's field of study.
- **Significance and impact: **The topic should have the potential to make a significant impact on the field and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Strategies for Generating Research Topic Ideas
Generating research topic ideas or thinking of topics to write a research on can be a daunting task, but there are several strategies that can help:
Brainstorming Techniques
- Mind mapping: Create a visual representation of your ideas and how they connect to each other.
- Freewriting: Write down your thoughts and ideas without censoring yourself, and then review what you've written to identify potential topics.
- Questioning: Ask yourself questions about your field of study, such as "What are the current gaps in knowledge?" or "What are the most pressing issues facing the field?".
Exploring Personal Interests and Experiences
Your personal interests and experiences can be a rich source of inspiration for research topics. Consider what you are passionate about and how it intersects with your field of study for your research paper ideas. Choose a topic that interests you.
Keeping Up with Current Trends and Developments
- Reading academic journals and publications: Stay up-to-date with the latest research in your field by regularly reading academic journals and publications.
- Attending conferences and seminars: Attend conferences and seminars to learn about current trends and developments in your field, and to network with other researchers.
Seeking Inspiration from AI for Research
AI for research can be a valuable tool for generating research topic ideas. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent to human researchers.
Easily pronounces technical words in any field
Narrowing Down and Refining Your Research Topic
Once you have generated some potential research topics, the next step is to narrow down and refine your topic:
- Identifying a broad area of interest: Start by identifying a broad area of interest within your field of study.
- Conducting preliminary research: Conduct preliminary research to gain a better understanding of the existing research in your area of interest.
- Formulating a specific research question: Formulate a specific research question that addresses a gap in the existing research or explores a new angle on a familiar topic. This research question will serve as the basis for your thesis or thesis statement.
- Considering the scope and feasibility of the topic: Consider the scope and feasibility of your topic, taking into account the timeframe and resources available to you.
- Ensuring the topic aligns with the requirements of your research paper or scientific paper: Make sure your topic aligns with the requirements of your research paper or scientific paper, such as word count, formatting, and citation style.
Developing Your Research Topic
Once you have narrowed down and refined your research topic, the next step is to develop it further:
Conducting a Literature Review
- Identifying key sources and references: Identify the key sources and references in your field of study that are relevant to your research topic.
- Synthesizing and analyzing existing research: Synthesize and analyze the existing research to identify gaps in knowledge and potential areas for further exploration.
Formulating Hypotheses or Research Objectives
Formulate hypotheses or research objectives based on your analysis of the existing research and your own insights and observations.
Defining Key Concepts and Variables
Define the key concepts and variables that are central to your research topic, and operationalize them in a way that is measurable and testable.
Outlining the Research Methodology
Outline the research methodology you will use to investigate your research topic, including data collection methods, sampling strategies, and data analysis techniques.
Tips on How to Write Faster and Efficiently
Writing a research paper can be a time-consuming process, but there are several tips and strategies that can help you write faster and more efficiently:
- Break your writing into manageable chunks and set achievable goals for each writing session.
- Use outlines and mind maps to organize your thoughts and ideas before you start writing.
- Minimize distractions by finding a quiet workspace and turning off notifications on your devices.
- Take regular breaks to recharge and avoid burnout.
- Utilize writing tools and software, such as Grammarly or Scrivener , to streamline your writing process and improve the quality of your work.
Research Topic Ideas and Examples
Here are some examples of research topics in various fields of study:
Social Sciences
- The impact of social media on interpersonal relationships
- The role of education in reducing income inequality
Natural Sciences
- Exploring the potential of renewable energy sources
- Investigating the effects of climate change on biodiversity
- Analyzing the influence of popular culture on literature
- Examining the evolution of language in the digital age
Business and Economics
- The impact of remote work on employee productivity and job satisfaction
- Investigating the role of corporate social responsibility in consumer decision-making
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Research Topic
When choosing a research topic, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- **Choosing a topic that is too broad or too narrow: **A topic that is too broad may lack focus and depth, while a topic that is too narrow may limit the potential impact and significance of the research.
- Failing to consider the relevance and significance of the topic: A topic that is not relevant or significant to the field may not be worth researching, even if it is personally interesting to the researcher.
- **Neglecting to conduct sufficient preliminary research: **Failing to conduct sufficient preliminary research can lead to a lack of understanding of the existing research in the field, and may result in a topic that has already been thoroughly explored by other researchers. This can lead to wasted time and effort, as well as a lack of originality in the research.
- I**gnoring the importance of a well-crafted research paper title: **A well-crafted research paper title can help to attract readers and convey the significance of the research. Ignoring the importance of the title can lead to a lack of engagement with the research. A strong title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the content and purpose of the research.
Choosing and developing a research topic is a crucial step in the research process, and one that requires careful consideration and planning. By understanding the characteristics of a good research topic, employing strategies for generating ideas, narrowing down and refining your topic, and developing it further through a literature review and research methodology, you can set yourself up for success in your research endeavors.
While the process of topic selection can be challenging, it is also an opportunity to explore your passions and interests, and to contribute new knowledge and insights to your field of study. By investing time and effort in selecting a compelling and feasible research topic, you can lay the foundation for a good research paper and a successful and impactful research project.
Thesis Development
Literature Review
Academic Writing
Research Methodology
Research Idea Generation
Research Topic Selection
Recent articles

Best Business Schools in the US
Glice Martineau
Jul 10, 2024
Graduate School
United States of America
Business School

When Does College Start in the US?
College search tools
College admissions guide
College planning tips
College academic calendar
Summer term
Quarter system calendar
Spring semester start
Fall semester start
College start dates
When does college start

How to Apply to Graduate School? Practical and Helpful Tips
Derek Pankaew
Jul 11, 2024
#GradSchoolApplication
#GraduateSchool
#HigherEducation
#AdmissionTips
#PersonalStatement

9 Things I Wish I Knew Before Starting a PhD
#AcademicJourney
#GradSchoolTips
#PhDStudentLife
#ResearchAndMentorship
Which program are you applying to?

Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted

December 8, 2023
How to Write About Your Research Interests

The most common challenge that my master’s and PhD applicant clients face when writing a statement of research interests or a statement of purpose (SOP) is how to describe in concrete terms what their research interests and goals are. This is understandable. Their ideas are still evolving, and some worry that they’ll later be held to the ideas they stated in their applications, as though they were chiseled in stone. Others simply haven’t yet thought those ideas through very much.
Take a deep breath! By the time you begin writing your thesis, I promise that no one will pop up and wave your SOP or research interests statement around, saying, “But that’s not what you said here!” Everyone knows that your knowledge and ideas will develop throughout your grad program.
Here are the two things that a great statement of research interests or SOP will do:
- It will clearly illustrate to the admissions committee that you possess a depth of interest and comprehension in your field and that you understand what goes into research. You will sound naïve if you talk about ideas that are too vague or nebulous, or ones that cannot be addressed adequately through your discipline.
- It will explain any relevant background you have in this field, why you find it compelling, and why you are well suited for this career track .
Four questions to help you find your statement focus
To narrow your interests into something that is concrete enough for you to be able to write about convincingly, without being overly general, ask yourself these questions:
- What are the broad research questions/issues that interest you? Create a summary of your interests that you can work with, and describe your interests in a sentence – or a paragraph, at most.
- Within those broad areas of interest, can you begin to focus on more specific questions? If you’re not sure what the current questions/problems are in your field, now is the time to start catching up. Read recent journal publications, and go to conferences if you can. Reading the literature in your field will also give you a sense of how to frame your ideas in the language of your field.
- Have you done any research in this field already? If so, do you intend to build on your previous work in grad school or go in a new direction?
- How will your research contribute to the field?
Understanding how to present your goals
Some projects described in SOPs are achievable in the short term, while others are big enough to last a career. If your interests/goals fall into this latter category, acknowledge your ambitions, and try to identify some element of your interests that you can pursue as a first step.
Once you have demonstrated your skills (and past experience) in your field, you will be better equipped to define your next steps.
Focusing your interests will also involve doing more detailed research about the programs to which you plan to apply. For example, consider the following questions:
- Who might be your research supervisor?
- How do your interests relate to the work this scholar or these scholars are doing now?
- How would you contribute to the department and to the discipline?
Your SOP will also address your post-degree, longer-term goals. Consider this: do you envision yourself pursuing a career in research/academia? (For many PhD programs, this remains the department’s formal expectation, even though many PhDs find employment outside the academy.) If you’re applying for a master’s degree, be prepared to discuss what your future plans are and how the degree will help you.
Working on your SOP or statement of research interests?
Your SOP needs to be direct, informative, and… well… purposeful! When you choose Accepted, we match you with a dedicated advisor who will help you create an SOP that best reflects your experiences, goals, and intense desire to attend your target graduate school program. And did you know that Accepted’s clients have received millions of dollars in scholarship offers? Don’t delay – get started now by checking out our Graduate School Application Services .

For 25 years, Accepted has helped applicants gain acceptance to top undergraduate and graduate programs. Our expert team of admissions consultants features former admissions directors, PhDs, and professional writers who have advised clients to acceptance at top programs worldwide, including Harvard, Stanford, Yale, Princeton, Penn, Columbia, Oxford, Cambridge, INSEAD, MIT, Caltech, UC Berkeley, and Northwestern. Want an admissions expert to help you get Accepted? Click here to get in touch!
Related Resources:
- STEM Applicants: Why Your Statement of Purpose is So Important
- Three Must-Have Elements of a Good Statement of Purpose
- Writing Your Career Goals Essay
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted


How to Write About Your Research Interests 101
Wondering how to write about your research interests without loosing all your hair from stress in the process? Don’t worry – you have the power to make it an enjoyable – and enlightening – process! If you’re keen to secure admission into your dream graduate program, then tailoring your application to align with your passion for research is absolutely essential.
In this blog post, we take a deep dive into what exactly goes into writing about one’s research interests and provide invaluable guidance on how to do so to stand out from the competition. By taking the time and putting some thought into crafting this vital component of your application, you will be setting yourself up for success. So get ready because here come our top tips on how to write with flair about your most passionate research pursuits!
Understanding the purpose of your statement of purpose
Many prospective graduate students apply to graduate school without having a clear idea of how to write about their research interests nor having determined which topics or questions they would like to explore during their studies. This is a fairly normal situation. Many of my clients struggle with this challenge. While some people are concerned that they may be held to their still-developing thoughts, others have not yet truly invested time into the thought process.
Yet, no need to panic. The best way to decrease the anxiety related to learning how to write about your research interests is to take a step back and consider the purpose of your statement of purpose.
It’s important to realize that you are applying to graduate school to learn more, and your statement of purpose should never be about what you already know. The purpose of your statement of purpose is to provide a glimpse into your research interests at a particular moment in time . It is meant to demonstrate your research potential and it should not be seen as the presentation of a long-term commitment to research a precise set of ideas or questions.
So take a deep breath and relax! When starting to write your thesis, nobody will suddenly appear out of nowhere with your SOP or research interest statement in hand, accusing you of lying. As you navigate your way through graduate school, your understanding and perspectives will inevitably expand in countless ways. Many prospective students end up working on something entirely different than what they wrote about in their SOP.
And believe us, nobody gets sued or judged for changing their mind. In fact, admissions committees expect applicants’ ideas to take a slightly different or brand-new direction as they take more courses and become more knowledgeable of their target field, so there is no need to worry if you are unsure how committed you are to your current research interests.
Yet, not being clear on what your research interests are can be problematic, as the research process and field of study that you choose will ideally be an area in which you are passionate about and have at least some knowledge, so it is important to take the time to research and explore various topics before applying. The goal is to commit for the time being to a certain set of questions or a topic .
Keep in mind that admissions committees are more concerned with how the applicant communicates their research interests than with any specific content of the research itself. Furthermore, since many programs require students to pursue individualized study plans or take part in interdisciplinary collaborations during their studies, applicants need to demonstrate their ability to communicate and collaborate effectively.
Thus, admissions committees are looking for applicants that can present their research interests in a compelling way and illustrate how they can add value to the program.
To make a good impression on the admissions committee, you need to emphasize your comprehensive understanding of and passion for your field. Learning how to write about your research interests is all about learning to showcase these qualities in detail, thus demonstrating that you have what it takes to excel in research work. If your statement does not include any pertinent experience or qualifications, then you might come across as inexperienced. To avoid this issue and make a convincing argument for why you are well-suited to the chosen career path, be sure to provide specifics on what makes the field exciting for you and back it up with relevant background information.

What are admissions committees considering when looking at your research interests
Graduate admissions committees consider a variety of factors when evaluating an applicant’s research interest statement. Most notably, they assess the depth and breadth of the student’s knowledge in their chosen field or discipline and their ability to communicate why their research interests are relevant to that particular area.
They also look at how well an applicant understands current literature in the field, the research methods and approaches they plan to take, and their overall commitment to pursuing a graduate degree. In addition, committees may evaluate an applicant’s creativity in developing new research ideas or questions as well as their ability to collaborate with other faculty members or students.
Finally, the committee will consider how well an applicant can articulate a clear vision for their future research plans, indicating their interest in long-term scholarship. Taking these factors into account, graduate admissions committees gain an understanding of how well an applicant is suited to pursue a graduate program and contribute to the university’s overall research strength.

Writing about your research interests might involve… preliminary research!
When writing your statement of purpose, it is important to narrow your research interests as much as possible. Start by researching and familiarizing yourself with the particular field or program you are interested in. Ask yourself questions such as, What kind of research is currently being done? What topics are most commonly discussed? What topics are most relevant to your goals and interests?
Once you have a better understanding of the field, start by focusing on specific topics, ideas, or questions that you are passionate about. You can do this by asking yourself what kind of research requires your unique skillset. What kind of research questions do you find yourself most drawn to? What innovative ideas or solutions can you bring to the field?
If you are still not clear about which tangent to follow in your SOP, take the time to begin familiarizing yourself with the ongoing questions and issues in your field: read recent journal publications, and attend conferences when applicable. Additionally, reading related literature reviews will enable you to construct a language-based framework for expressing your ideas that aligns with prevailing trends and discourse.

By asking yourself these questions, you can narrow your research interests and better define the scope of your research interests. This will help you present yourself as a well-rounded and knowledgeable candidate for the program.
When writing about your research interests for an admissions committee, it is important to be concise and clear. First, create a brief overview of the research topic that you are interested in. When possible, provide examples of how your research interests overlap with the topics being explored by the program or institution for which you are applying. Demonstrate a strong understanding of the research methods and theories that apply to the topic. Additionally, if you have already conducted any research in this area, provide a summary of the findings. Finally, outline your long-term research goals and explain why they fit within the context of the program.

Learning how to write about your research interests is also learning to define your goals
Connecting your research interests to achievable goals is an important part of writing a statement of purpose. It helps to demonstrate that you have thought through the research project and how it can be accomplished in the timeframe of PhD studies. By including realistic, achievable goals, it also shows that you understand what is possible and have considered the potential obstacles that may arise. It is important to avoid being overly ambitious in your statement of purpose as this can lead to unrealistic expectations and a loss of focus, potentially leading to failure to achieve the desired outcomes.
Additionally, presenting achievable goals in your statement of purpose demonstrates that you are confident in what you are proposing, yet also realistic about the challenges that need to be overcome. By doing so, you will provide a strong indication that your research project is well-planned and worth investing in.

It is also important to demonstrate that your research interests are well-aligned with the graduate program you are applying to. This can be done by researching the faculty members and research groups of the university or program and looking for professors whose research focuses on topics related to yours. Once you have identified a few faculty members or research projects of interest, you can begin to explain how your research interests dovetail with their work. In doing so, you can demonstrate that your research is compatible with the program’s offerings and that it will contribute positively to the program’s research goals.
Finally, connecting your research interests to your career goals is essential. Your research will allow you to gain expertise, develop ideas, and build knowledge. This experience can be used to create meaningful connections between courses taken during the program and career paths that may come afterward. Additionally, it can serve as a way to form relationships and build networks that may help you establish a successful career. Make sure to share your short-term and long-term goals after graduation are clearly connected to your interests.
In conclusion
In this blog post, we explored the importance of properly conveying your research interests when writing a graduate school essay. The ability to do so can make all the difference between having your application being accepted and overlooked in the shuffle.
While learning about how to write about your research interests may seem like an especially daunting task, it doesn’t have to be with a little preparation and understanding. We hope you found this post helpful in demystifying the process of writing about your research interests when applying to graduate schools. If after reading our post you are still feeling overwhelmed to write up a stunning graduate school essay that showcases your research interests, fear not! I am here to help and take some of the stress of applying away.
The Admit Lab’s mission is to empower you with the tools needed for success by making sure your story stands out. So don’t waste any more time – check out our graduate essay services today! Got questions? Sign up for a consultation or send us a copy of your draft for an assessment, it’s FREE!
With a Master’s from McGill University and a Ph.D. from New York University, Dr. Philippe Barr is the founder of The Admit Lab . As a tenure-track professor, Dr. Barr spent a decade teaching and serving on several graduate admission committees at UNC-Chapel Hill before turning to full-time consulting. With more than seven years of experience as a graduate school admissions consultant, Dr. Barr has stewarded the candidate journey across multiple master’s and Ph.D. programs and helped hundreds of students get admitted to top-tier graduate programs all over the world .
Follow me on Instagram and TikTok for tips and tricks on navigating the grad school application process and weekly live Q&A sessions!
Share this:
Join the conversation.
12 Comments
- Pingback: Your Winning PhD Application Timeline - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Tips on How To Choose a PhD Program - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Getting Admitted into a PhD in Applied Economics - The Admit Lab
- Pingback: Statement of Purpose for Masters in Psychology Essentials -
- Pingback: Perfect History PhD Statement of Purpose (Example) -
- Pingback: Statement of Purpose for Scholarship Tips -
- Pingback: Doctoral Program Consultants: Useless or Helpful? -
- Pingback: Why Statement of Purpose Editing is Crucial for Your Future -
- Pingback: Flawless Statement Of Purpose For PhD: Samples & Tips -
- Pingback: Choosing Topics for PhD Applications: Your Ultimate Guide -
- Pingback: Economics PhD Acceptance Rates 2024: Do You Stand a Chance? -
- Pingback: How to Tackle Graduate School Interview Questions Like A Winner -
Leave a comment
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from admit lab.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Research Paper Topics - Best Picks

Did you know that more than 2.5 million research papers are published worldwide every year? This huge number highlights the vast array of topics students and researchers can explore.
Below, you will find 200 interesting research topics to help spark your creativity and get you started on your next academic venture. Additionally, you can browse essay topics that can also help set your research in the right duration.
Top 10 Research Topics for Students
- Impact of ICT's (Information and Communication Technologies) on Society.
- Role-to-role networks: how Internet and mobile communications have changed the connectivity of social networks in few years.
- The future of electric vehicles and infrastructure: pros, cons and consequences.
- Ethical considerations in the development of autonomous weapons. Shall the World stop?
- Strategies to reduce economic inequality in developing countries.
- The impact of micro-plastics on marine ecosystems. Ways to safe Planet.
- New methods for detecting dark matter particles.
- The use of nano-materials in cancer treatment.
- The impact of vaccination programs on global health. Shall we win or be defeated?
- Studying the impact of solar storms on satellite communications.
Research Paper Topics on Math
- Applications of machine learning algorithms in data analysis and prediction.
- Mathematical modeling of biological systems and population dynamics.
- Cryptography and its applications in secure communication and data protection.
- Theoretical advances in number theory and their practical implications.
- Optimization techniques and their applications in engineering and operations research.
- Chaos theory and its applications in weather forecasting and complex systems.
- Graph theory and its applications in network analysis and social networks.
- Mathematical aspects of game theory and decision-making in economics.
- Topological methods in data analysis and pattern recognition.
- Fractal geometry and its applications in computer graphics and image compression.
- Statistical methods for analyzing large datasets and drawing meaningful conclusions.
- Algebraic geometry and its applications in computer vision and robotics.
- Pricing models for derivatives and risk management strategies.
- Computational methods for solving partial differential equations and fluid dynamics problems.
- Mathematical biology: Modeling biological processes and ecosystems.
- Discrete mathematics and its applications in computer science and information theory.
- Theoretical aspects of machine learning algorithms and their optimization.
- Mathematical logic and its role in computer science and artificial intelligence.
- Combinatorial optimization and its applications in logistics and resource allocation.
- Quantum computing: Mathematical foundations and potential applications in cryptography.
Research Paper Topics on Business
- The impact of remote work on organizational culture and productivity.
- Modern diversity and inclusion initiatives for businesses.
- Digital marketing strategies for small businesses in the post-pandemic era.
- The role of corporate social responsibility in enhancing brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
- Supply chain disruptions: Strategies for building resilience and mitigating risks.
- The rise of e-commerce and its implications for traditional brick-and-mortar businesses.
- Entrepreneurship and innovation for fostering a culture of creativity and growth.
- The future of retail: Trends and challenges in a digital-first world.
- Sustainable business practices: Balancing profitability with environmental responsibility.
- Leadership in times of crisis: Managing uncertainty and driving organizational change.
- Financial management strategies for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Employee engagement and retention: Strategies for cultivating a motivated workforce.
- Strategic partnerships and alliances: Leveraging collaboration for business success.
- Digital transformation: Adopting new technologies to stay competitive in the market.
- The gig economy: Implications for workforce management and talent acquisition.
- Business ethics and corporate governance: Principles for ethical decision-making and accountability.
- International expansion: Challenges and strategies for entering new markets.
- Customer relationship management: Building lasting connections in a digital world.
- Data-driven decision-making: Harnessing analytics for business growth and optimization.
- Crisis management and business continuity planning: Preparing for unexpected challenges.
Research Paper Topics on Psychology
- Psychological implications of social media use across different age groups and cultures.
- The psychology of risk-taking behavior: Understanding motivations and consequences.
- Cognitive biases and their impact on decision-making in various contexts.
- Psychological aspects of online learning: Motivation, engagement, and academic performance.
- The role of self-compassion in mental health and resilience.
- Exploring the psychology of conspiracy theories: Beliefs, motivations, and consequences.
- Cultural differences in emotion regulation and expression: Implications for mental health interventions.
- Psychological perspectives on environmental sustainability and pro-environmental behaviors.
- The psychology of procrastination: Underlying factors and strategies for change.
- Psychological effects of gaming and esports: Benefits, risks, and implications.
- The role of pets in human mental health and well-being.
- Psychological aspects of body image and eating behaviors across diverse populations.
- Exploring the psychology of humor: Effects on mood, social connections, and well-being.
- Psychological resilience in the face of natural disasters and traumatic events.
- The impact of color psychology on mood, behavior, and decision-making.
- Psychological factors influencing the adoption of sustainable lifestyle choices.
- The psychology of music: Emotional responses, preferences, and therapeutic applications.
- Understanding and addressing mental health stigma within healthcare systems.
- Psychological perspectives on aging and successful aging: Factors contributing to well-being in later life.
- The psychology of creativity in problem-solving and innovation across disciplines.
Research Paper Topics on Literature
- Love and loss in Shakespeare's sonnets.
- Gender representation in Jane Austen's novels.
- Mythology in Greek tragedies.
- Colonialism in post-colonial literature.
- "The Great Gatsby" and the American Dream.
- Identity in Toni Morrison's novels.
- Magical realism in García Márquez's "One Hundred Years of Solitude."
- War in Hemingway's novels.
- Alienation and existentialism in Kafka's works.
- Race and racism in African-American literature.
- Folklore and fairy tales in the Brothers Grimm's works.
- Nature in Romantic poetry.
- Political allegory in Orwell's "Animal Farm."
- Heroism in Homer's "The Odyssey."
- Satire in Swift's "Gulliver's Travels."
- Social class and inequality in Dickens' novels.
- Surrealism in García Lorca's poetry.
- Madness in Shakespeare's tragedies.
- Religion and morality in Dostoevsky's works.
- Modernity in the Harlem Renaissance literature.
Looking to Add a Dash of Humor to Your Academic Journey?
Well, why not order our collection of funny research paper topics and let the hilarity begin? Your grades will thank you later!
Research Paper Topics on Environment
- The interplay between urbanization and environmental sustainability.
- Technological innovations for addressing climate change challenges.
- Social, economic, and environmental implications of renewable energy transitions.
- Ecotourism as a tool for conservation and community development.
- Indigenous knowledge and practices in environmental management.
- The role of public policy in promoting sustainable development.
- Sustainable transportation solutions for reducing carbon emissions.
- The impact of consumer behavior on environmental sustainability.
- Green building technologies and their contribution to energy efficiency.
- The potential of circular economy models in waste reduction and resource conservation.
- Water scarcity and management strategies in arid regions.
- The nexus between agriculture, food security, and environmental sustainability.
- The role of citizen science in monitoring and addressing environmental issues.
- Environmental education and its influence on public awareness and behavior.
- Natural resource management and conflicts over land and water resources.
- The effects of pollution on ecosystems and human health.
- Indigenous rights and environmental conservation efforts.
- Environmental governance mechanisms at local, national, and international levels.
- The impact of globalization on natural resource exploitation and conservation.
- Resilience and adaptation strategies for communities vulnerable to environmental hazards.
Research Paper Topics on Biology
- The genetic basis of human diseases and potential therapeutic interventions.
- Evolutionary mechanisms driving biodiversity and speciation.
- Ecological impacts of climate change on species distribution and ecosystems.
- Cellular mechanisms underlying cancer development and progression.
- Genetic engineering and its applications in agriculture, medicine, and industry.
- Neurobiology of learning and memory formation in humans and animals.
- Biodiversity conservation strategies and their effectiveness in preserving ecosystems.
- Microbial communities and their role in human health and disease.
- Molecular mechanisms of aging and potential interventions for lifespan extension.
- Adaptations of extremophiles to extreme environmental conditions.
- Epigenetics and its role in gene expression regulation and disease susceptibility.
- The immune system and its response to pathogens and vaccines.
- Plant-microbe interactions and their impact on plant health and productivity.
- Population genetics and its implications for conservation biology and evolutionary studies.
- Genetic basis of behavior and its evolutionary significance.
- Biotechnology applications in environmental remediation and pollution control.
- Comparative genomics and evolutionary relationships among different species.
- Physiological adaptations of organisms to changing environmental conditions.
- Bioinformatics tools and their role in analyzing genomic and proteomic data.
- Ethical considerations in biotechnological research and applications.
Research Paper Topics on Health and Medicine
- The global impact of telemedicine on healthcare access and patient outcomes.
- Genetic advancements and their role in personalized medicine worldwide.
- Mental health awareness initiatives and their effectiveness across cultures.
- The influence of dietary patterns on chronic disease management in different populations.
- Comparative analysis of universal healthcare systems in various countries.
- The role of vaccines in preventing global infectious diseases.
- Physical activity's effects on mental health and well-being in diverse populations.
- The effectiveness of alternative medicine in various cultural settings.
- Socioeconomic disparities and their impact on global healthcare access.
- International strategies for combating antibiotic resistance.
- Public health campaigns and their success in reducing lifestyle-related diseases globally.
- Environmental determinants of health outcomes in different regions.
- Mental health intervention effectiveness in multicultural contexts.
- Innovations in cancer treatment and their global impact on survival rates.
- Emerging medical technologies and their role in enhancing surgical outcomes.
- The effects of health policies on managing non-communicable diseases worldwide.
- The challenges and opportunities of aging populations on healthcare systems globally.
- Primary care's role in chronic disease management across various healthcare systems.
- Global perspectives on stress management techniques and health outcomes.
- International health initiatives and their success in reducing global health disparities.
Research Paper Topics on Education
- The impact of technology on education systems globally.
- Teacher-student relationships and their effect on academic success.
- The influence of standardized testing on student learning and motivation.
- Innovative strategies for improving literacy rates in various educational settings.
- Benefits and challenges of inclusive education for students with diverse needs.
- The impact of parental involvement on student academic achievement and behavior.
- The role of arts education in fostering creativity and critical thinking.
- Comparing the effectiveness of online learning and traditional classroom education.
- Socioeconomic status and its influence on educational opportunities and outcomes.
- The impact of school leadership on teacher performance and student success.
- Benefits of bilingual education programs in diverse communities.
- The role of extracurricular activities in student development and academic performance.
- Long-term academic benefits of early childhood education programs.
- Strategies for closing the achievement gap in different types of schools.
- Effects of classroom environment on student learning and engagement.
- The role of vocational education in preparing students for various career paths.
- School policies' impact on bullying prevention and student safety.
- Importance of teacher professional development for enhancing instructional quality.
- Cultural diversity's influence on teaching practices and student learning.
- The role of educational technology in supporting personalized and adaptive learning.
Research Paper Topics on Sports
- Mental health benefits of regular sports participation.
- The role of proper nutrition in enhancing athletic performance.
- Gender differences in sports performance and participation rates.
- The ethical and health implications of doping in competitive sports.
- How different coaching styles influence team success and player development.
- The relationship between adequate sleep and peak athletic performance.
- The impact of modern technology on sports training and athlete performance.
- The physical and social benefits of participation in youth sports programs.
- The role of sports in building stronger, more cohesive communities.
- Effects of climate and weather conditions on outdoor sports performance.
- The importance of injury prevention strategies in competitive sports.
- Psychological effects of winning and losing on athletes.
- The evolution and impact of sports equipment design on performance.
- The role of regular sports participation in promoting overall physical fitness.
- The influence of media coverage on public perception of professional athletes.
- Historical development and significance of the Olympic Games.
- Economic impacts of hosting major sports events on local communities.
- Unique challenges faced by female athletes in male-dominated sports.
- The effect of crowd support on the performance of athletes and teams.
- The relationship between participation in sports and academic performance in students.
Seven Signs of Good Topics for Research Paper
.webp)
Here are the main characteristics of engaging research paper ideas:
| Relevance | The topic should be timely and relevant to current issues, trends, or debates in the field of study. |
|---|---|
| Significance | The topic should address an important research question or problem that has implications for theory, practice, or policy. |
| Feasibility | The topic should be feasible to research within the constraints of time, resources, and access to data or information. |
| Originality | The topic should offer a fresh perspective or innovative approach to existing research or fill a gap in the literature. |
| Scope | The topic should be appropriately scoped to allow for in-depth analysis and exploration without being too broad or too narrow. |
| Interest | The topic should be interesting and engaging to the researcher and potential readers or stakeholders in the field. |
| Contribution | The topic should have the potential to contribute new insights, knowledge, or solutions to the field of study and advance scholarship. |
If you don’t feel that your topic meets the abovementioned criteria and the time is too short to brainstorm more research topic ideas, simply say, ‘ write my paper ,’ and one of our experts will be there to help you shortly.
How to Choose a Quality Research Paper Topic
Always select a topic that genuinely interests you and aligns with your passion. Your enthusiasm will fuel your motivation and commitment throughout the research process.
.webp)
Stay Current
Choose a relevant and timely topic. Look for emerging trends, pressing issues, or gaps in the literature that your research can address. Consult this guide if you need more information about how to research a topic .
Consider Your Audience
Think about who your audience is and what topics would be most engaging and relevant to them. Tailor your topic selection to the interests and needs of your audience.
Be Specific
Narrow down your focus to a specific research question or problem. This will help you avoid tackling overly broad topics and ensure your research is focused and manageable.
Assess Feasibility
Consider the resources, time, and access to data or information available for your research. Choose a topic that you can feasibly research within the constraints of your academic program or timeline.
Seek Inspiration
Look for inspiration from miscellaneous sources, including academic journals, news articles, conferences, and conversations with peers or mentors. Explore different perspectives and ideas to spark your creativity.
Gather Feedback
Discuss your potential topics with your peers, instructors, or academic advisors. They can provide valuable feedback, offer different perspectives, and help you refine your research paper ideas. If you want to join forces with a subject-relevant professor, use our research proposal writing service to entice them to work with you.
Access Significance
Measure the significance of your chosen topic in the context of your field of study. Consider its relevance, potential contributions to existing knowledge, and implications for theory, practice, or policy.
Remain Flexible
Be open to adjusting your research topic ideas as you conduct further analysis and gain new insights. Research is an iterative process, and your topic may evolve as you delve deeper into the literature and data.
Stay True to Yourself
Choose a topic that resonates with you and reflects your academic interests, values, and goals. Your research paper is an opportunity to contribute meaningfully to your field and showcase your expertise and passion. If that doesn’t help, buy a research paper from our writing specialists to save time and nerves.
Students often find it difficult to generate research paper topic ideas due to factors such as a lack of clarity on their interests, limited access to relevant resources, and time constraints.
A solution to this challenge is to consider utilizing a professional writing service, which can provide expert guidance and assistance in selecting a research paper topic tailored to the student's interests and requirements.
To bring your academic writing prowess to the next level, please consider the following guide on how to write a reflective essay .
Looking for A+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics?
Let our research essay service be your guide to crafting compelling essays that win debates and top grades!
What Are 5 Good Research Questions for Students?
What are the best research topics, what topic should i use for my research paper.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Added infographics.
- Added new topics.
- Added FAQs.
- Amberstudent. (2024, May 21). Top 10 Research Topics For Students In 2024. Amber. https://amberstudent.com/blog/post/research-topics-for-students
- Research Paper Topics -Ijser. (n.d.). https://www.ijser.org/research-paper-topics.aspx
- ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/
.webp)
61 intriguing psychology research topics to explore
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
Brittany Ferri, PhD, OTR/L
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Psychology is an incredibly diverse, critical, and ever-changing area of study in the medical and health industries. Because of this, it’s a common area of study for students and healthcare professionals.
We’re walking you through picking the perfect topic for your upcoming paper or study. Keep reading for plenty of example topics to pique your interest and curiosity.
- How to choose a psychology research topic
Exploring a psychology-based topic for your research project? You need to pick a specific area of interest to collect compelling data.
Use these tips to help you narrow down which psychology topics to research:
Focus on a particular area of psychology
The most effective psychological research focuses on a smaller, niche concept or disorder within the scope of a study.
Psychology is a broad and fascinating area of science, including everything from diagnosed mental health disorders to sports performance mindset assessments.
This gives you plenty of different avenues to explore. Having a hard time choosing? Check out our list of 61 ideas further down in this article to get started.
Read the latest clinical studies
Once you’ve picked a more niche topic to explore, you need to do your due diligence and explore other research projects on the same topic.
This practice will help you learn more about your chosen topic, ask more specific questions, and avoid covering existing projects.
For the best results, we recommend creating a research folder of associated published papers to reference throughout your project. This makes it much easier to cite direct references and find inspiration down the line.
Find a topic you enjoy and ask questions
Once you’ve spent time researching and collecting references for your study, you finally get to explore.
Whether this research project is for work, school, or just for fun, having a passion for your research will make the project much more enjoyable. (Trust us, there will be times when that is the only thing that keeps you going.)
Now you’ve decided on the topic, ask more nuanced questions you might want to explore.
If you can, pick the direction that interests you the most to make the research process much more enjoyable.
- 61 psychology topics to research in 2024
Need some extra help starting your psychology research project on the right foot? Explore our list of 61 cutting-edge, in-demand psychology research topics to use as a starting point for your research journey.
- Psychology research topics for university students
As a university student, it can be hard to pick a research topic that fits the scope of your classes and is still compelling and unique.
Here are a few exciting topics we recommend exploring for your next assigned research project:
Mental health in post-secondary students
Seeking post-secondary education is a stressful and overwhelming experience for most students, making this topic a great choice to explore for your in-class research paper.
Examples of post-secondary mental health research topics include:
Student mental health status during exam season
Mental health disorder prevalence based on study major
The impact of chronic school stress on overall quality of life
The impacts of cyberbullying
Cyberbullying can occur at all ages, starting as early as elementary school and carrying through into professional workplaces.
Examples of cyberbullying-based research topics you can study include:
The impact of cyberbullying on self-esteem
Common reasons people engage in cyberbullying
Cyberbullying themes and commonly used terms
Cyberbullying habits in children vs. adults
The long-term effects of cyberbullying
- Clinical psychology research topics
If you’re looking to take a more clinical approach to your next project, here are a few topics that involve direct patient assessment for you to consider:
Chronic pain and mental health
Living with chronic pain dramatically impacts every aspect of a person’s life, including their mental and emotional health.
Here are a few examples of in-demand pain-related psychology research topics:
The connection between diabetic neuropathy and depression
Neurological pain and its connection to mental health disorders
Efficacy of meditation and mindfulness for pain management
The long-term effects of insomnia
Insomnia is where you have difficulty falling or staying asleep. It’s a common health concern that impacts millions of people worldwide.
This is an excellent topic because insomnia can have a variety of causes, offering many research possibilities.
Here are a few compelling psychology research topics about insomnia you could investigate:
The prevalence of insomnia based on age, gender, and ethnicity
Insomnia and its impact on workplace productivity
The connection between insomnia and mental health disorders
Efficacy and use of melatonin supplements for insomnia
The risks and benefits of prescription insomnia medications
Lifestyle options for managing insomnia symptoms
The efficacy of mental health treatment options
Management and treatment of mental health conditions is an ever-changing area of study. If you can witness or participate in mental health therapies, this can make a great research project.
Examples of mental health treatment-related psychology research topics include:
The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for patients with severe anxiety
The benefits and drawbacks of group vs. individual therapy sessions
Music therapy for mental health disorders
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for patients with depression
- Controversial psychology research paper topics
If you are looking to explore a more cutting-edge or modern psychology topic, you can delve into a variety of controversial and topical options:
The impact of social media and digital platforms
Ever since access to internet forums and video games became more commonplace, there’s been growing concern about the impact these digital platforms have on mental health.
Examples of social media and video game-related psychology research topics include:
The effect of edited images on self-confidence
How social media platforms impact social behavior
Video games and their impact on teenage anger and violence
Digital communication and the rapid spread of misinformation
The development of digital friendships
Psychotropic medications for mental health
In recent years, the interest in using psychoactive medications to treat and manage health conditions has increased despite their inherently controversial nature.
Examples of psychotropic medication-related research topics include:
The risks and benefits of using psilocybin mushrooms for managing anxiety
The impact of marijuana on early-onset psychosis
Childhood marijuana use and related prevalence of mental health conditions
Ketamine and its use for complex PTSD (C-PTSD) symptom management
The effect of long-term psychedelic use and mental health conditions
- Mental health disorder research topics
As one of the most popular subsections of psychology, studying mental health disorders and how they impact quality of life is an essential and impactful area of research.
While studies in these areas are common, there’s always room for additional exploration, including the following hot-button topics:
Anxiety and depression disorders
Anxiety and depression are well-known and heavily researched mental health disorders.
Despite this, we still don’t know many things about these conditions, making them great candidates for psychology research projects:
Social anxiety and its connection to chronic loneliness
C-PTSD symptoms and causes
The development of phobias
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) behaviors and symptoms
Depression triggers and causes
Self-care tools and resources for depression
The prevalence of anxiety and depression in particular age groups or geographic areas
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder is a complex and multi-faceted area of psychology research.
Use your research skills to learn more about this condition and its impact by choosing any of the following topics:
Early signs of bipolar disorder
The incidence of bipolar disorder in young adults
The efficacy of existing bipolar treatment options
Bipolar medication side effects
Cognitive behavioral therapy for people with bipolar
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizoaffective disorder is often stigmatized, and less common mental health disorders are a hotbed for new and exciting research.
Here are a few examples of interesting research topics related to this mental health disorder:
The prevalence of schizoaffective disorder by certain age groups or geographic locations
Risk factors for developing schizoaffective disorder
The prevalence and content of auditory and visual hallucinations
Alternative therapies for schizoaffective disorder
- Societal and systematic psychology research topics
Modern society’s impact is deeply enmeshed in our mental and emotional health on a personal and community level.
Here are a few examples of societal and systemic psychology research topics to explore in more detail:
Access to mental health services
While mental health awareness has risen over the past few decades, access to quality mental health treatment and resources is still not equitable.
This can significantly impact the severity of a person’s mental health symptoms, which can result in worse health outcomes if left untreated.
Explore this crucial issue and provide information about the need for improved mental health resource access by studying any of the following topics:
Rural vs. urban access to mental health resources
Access to crisis lines by location
Wait times for emergency mental health services
Inequities in mental health access based on income and location
Insurance coverage for mental health services
Systemic racism and mental health
Societal systems and the prevalence of systemic racism heavily impact every aspect of a person’s overall health.
Researching these topics draws attention to existing problems and contributes valuable insights into ways to improve access to care moving forward.
Examples of systemic racism-related psychology research topics include:
Access to mental health resources based on race
The prevalence of BIPOC mental health therapists in a chosen area
The impact of systemic racism on mental health and self-worth
Racism training for mental health workers
The prevalence of mental health disorders in discriminated groups
LGBTQIA+ mental health concerns
Research about LGBTQIA+ people and their mental health needs is a unique area of study to explore for your next research project. It’s a commonly overlooked and underserved community.
Examples of LGBTQIA+ psychology research topics to consider include:
Mental health supports for queer teens and children
The impact of queer safe spaces on mental health
The prevalence of mental health disorders in the LGBTQIA+ community
The benefits of queer mentorship and found family
Substance misuse in LQBTQIA+ youth and adults
- Collect data and identify trends with Dovetail
Psychology research is an exciting and competitive study area, making it the perfect choice for projects or papers.
Take the headache out of analyzing your data and instantly access the insights you need to complete your next psychology research project by teaming up with Dovetail today.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

How To Find A High-Quality Research Topic
6 steps to find & evaluate high-quality dissertation/thesis topics.
By: Caroline Osella (PhD, BA) and Derek Jansen (MBA) | July 2019
So, you’re finally nearing the end of your degree and it’s now time to find a suitable topic for your dissertation or thesis. Or perhaps you’re just starting out on your PhD research proposal and need to find a suitable area of research for your application proposal.
In this post, we’ll provide a straightforward 6-step process that you can follow to ensure you arrive at a high-quality research topic . Follow these steps and you will formulate a well-suited, well-defined core research question .
There’s a helpful clue already: your research ‘topic’ is best understood as a research question or a problem . Your aim is not to create an encyclopedia entry into your field, but rather to shed light on an acknowledged issue that’s being debated (or needs to be). Think research questions , not research topics (we’ll come back to this later).
Overview: How To Find A Research Topic
- Get an understanding of the research process
- Review previous dissertations from your university
- Review the academic literature to start the ideation process
- Identify your potential research questions (topics) and shortlist
- Narrow down, then evaluate your research topic shortlist
- Make the decision (and stick with it!)
Step 1: Understand the research process
It may sound horribly obvious, but it’s an extremely common mistake – students skip past the fundamentals straight to the ideation phase (and then pay dearly for it).
Start by looking at whatever handouts and instructions you’ve been given regarding what your university/department expects of a dissertation. For example, the course handbook, online information and verbal in-class instructions. I know it’s tempting to just dive into the ideation process, but it’s essential to start with the prescribed material first.
There are two important reasons for this:
First , you need to have a basic understanding of the research process , research methodologies , fieldwork options and analysis methods before you start the ideation process, or you will simply not be equipped to think about your own research adequately. If you don’t understand the basics of quantitative , qualitative and mixed methods BEFORE you start ideating, you’re wasting your time.
Second , your university/department will have specific requirements for your research – for example, requirements in terms of topic originality, word count, data requirements, ethical adherence , methodology, etc. If you are not aware of these from the outset, you will again end up wasting a lot of time on irrelevant ideas/topics.
So, the most important first step is to get your head around both the basics of research (especially methodologies), as well as your institution’s specific requirements . Don’t give in to the temptation to jump ahead before you do this. As a starting point, be sure to check out our free dissertation course.

Step 2: Review past dissertations/theses
Unless you’re undertaking a completely new course, there will be many, many students who have gone through the research process before and have produced successful dissertations, which you can use to orient yourself. This is hugely beneficial – imagine being able to see previous students’ assignments and essays when you were doing your coursework!
Take a look at some well-graded (65% and above) past dissertations from your course (ideally more recent ones, as university requirements may change over time). These are usually available in the university’s online library. Past dissertations will act as a helpful model for all kinds of things, from how long a bibliography needs to be, to what a good literature review looks like, through to what kinds of methods you can use – and how to leverage them to support your argument.
As you peruse past dissertations, ask yourself the following questions:
- What kinds of topics did these dissertations cover and how did they turn the topic into questions?
- How broad or narrow were the topics?
- How original were the topics? Were they truly groundbreaking or just a localised twist on well-established theory?
- How well justified were the topics? Did they seem important or just nice to know?
- How much literature did they draw on as a theoretical base? Was the literature more academic or applied in nature?
- What kinds of research methods did they use and what data did they draw on?
- How did they analyse that data and bring it into the discussion of the academic literature?
- Which of the dissertations are most readable to you – why? How were they presented?
- Can you see why these dissertations were successful? Can you relate what they’ve done back to the university’s instructions/brief?

Seeing a variety of dissertations (at least 5, ideally in your area of interest) will also help you understand whether your university has very rigid expectations in terms of structure and format , or whether they expect and allow variety in the number of chapters, chapter headings, order of content, style of presentation and so on.
Some departments accept graphic novels; some are willing to grade free-flow continental-philosophy style arguments; some want a highly rigid, standardised structure. Many offer a dissertation template , with information on how marks are split between sections. Check right away whether you have been given one of those templates – and if you do, then use it and don’t try to deviate or reinvent the wheel.
Step 3: Review the academic literature
Now that you (1) understand the research process, (2) understand your university’s specific requirements for your dissertation or thesis, and (3) have a feel for what a good dissertation looks like, you can start the ideation process. This is done by reviewing the current literature and looking for opportunities to add something original to the academic conversation.
Kick start the ideation process
So, where should you start your literature hunt? The best starting point is to get back to your modules. Look at your coursework and the assignments you did. Using your coursework is the best theoretical base, as you are assured that (1) the literature is of a high enough calibre for your university and (2) the topics are relevant to your specific course.
Start by identifying the modules that interested you the most and that you understood well (i.e. earned good marks for). What were your strongest assignments, essays or reports? Which areas within these were particularly interesting to you? For example, within a marketing module, you may have found consumer decision making or organisation trust to be interesting. Create a shortlist of those areas that you were both interested in and academically strong at. It’s no use picking an area that does not genuinely interest you – you’ll run out of motivation if you’re not excited by a topic.
Understand the current state of knowledge
Once you’ve done that, you need to get an understanding of the current state of the literature for your chosen interest areas. What you’re aiming to understand is this: what is the academic conversation here and what critical questions are yet unanswered? These unanswered questions are prime opportunities for a unique, meaningful research topic . A quick review of the literature on your favourite topics will help you understand this.
Grab your reading list from the relevant section of the modules, or simply enter the topics into Google Scholar . Skim-read 3-5 journal articles from the past 5 years which have at least 5 citations each (Google Scholar or a citations index will show you how many citations any given article has – i.e., how many other people have referred to it in their own bibliography). Also, check to see if your discipline has an ‘annual review’ type of journal, which gathers together surveys of the state of knowledge on a chosen topic. This can be a great tool for fast-tracking your understanding of the current state of the knowledge in any given area.
Start from your course’s reading list and work outwards. At the end of every journal article, you’ll find a reference list. Scan this reference list for more relevant articles and read those. Then repeat the process (known as snowballing) until you’ve built up a base of 20-30 quality articles per area of interest.

Absorb, don’t hunt
At this stage, your objective is to read and understand the current state of the theory for your area(s) of interest – you don’t need to be in topic-hunting mode yet. Don’t jump the gun and try to identify research topics before you are well familiarised with the literature.
As you read, try to understand what kinds of questions people are asking and how they are trying to answer them. What matters do the researchers agree on, and more importantly, what are they in disagreement about? Disagreements are prime research territory. Can you identify different ‘schools of thought’ or different ‘approaches’? Do you know what your own approach or slant is? What kinds of articles appeal to you and which ones bore you or leave you feeling like you’ve not really grasped them? Which ones interest you and point towards directions you’d like to research and know more about?
Once you understand the fundamental fact that academic knowledge is a conversation, things get easier.
Think of it like a party. There are groups of people in the room, enjoying conversations about various things. Which group do you want to join? You don’t want to be that person in the corner, talking to themself. And you don’t want to be the hanger-on, laughing at the big-shot’s jokes and repeating everything they say.
Do you want to join a large group and try to make a small contribution to what’s going on, or are you drawn to a smaller group that’s having a more niche conversation, but where you feel you might more easily find something original to contribute? How many conversations can you identify? Which ones feel closer to you and more attractive? Which ones repel you or leave you cold? Are there some that, frankly, you just don’t understand?
Now, choose a couple of groups who are discussing something you feel interested in and where you feel like you might want to contribute. You want to make your entry into this group by asking a question – a question that will make the other people in the group turn around and look at you, listen to you, and think, “That’s interesting”.
Your dissertation will be the process of setting that question and then trying to find at least a partial answer to that question – but don’t worry about that now. Right now, you need to work out what conversations are going on, whether any of them are related or overlapping, and which ones you might be able to walk into. I’ll explain how you find that question in the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 4: Identify potential research questions
Now that you have a decent understanding of the state of the literature in your area(s) of interest, it’s time to start developing your list of possible research topics. There are (at least) three approaches you can follow here, and they are not mutually exclusive:
Approach 1: Leverage the FRIN
Towards the end of most quality journal articles, you will find a section labelled “ further research ” or something similar. Generally, researchers will clearly outline where they feel further research is needed (FRIN), following on from their own research. So, essentially, every journal article presents you with a list of potential research opportunities.
Of course, only a handful of these will be both practical and of interest to you, so it’s not a quick-fix solution to finding a research topic. However, the benefit of going this route is that you will be able to find a genuinely original and meaningful research topic (which is particularly important for PhD-level research).
The upside to this approach is originality, but the downside is that you might not find something that really interests you , or that you have the means to execute. If you do go this route, make sure that you pay attention to the journal article dates, as the FRIN may already have been “solved” by other researchers if the article is old.

Approach 2: Put a context-based spin on an existing topic
The second option is to consider whether a theory which is already well established is relevant within a local or industry-specific context. For example, a theory about the antecedents (drivers) of trust is very well established, but there may be unique or uniquely important drivers within a specific national context or industry (for example, within the financial services industry in an emerging market).
If that industry or national context has not yet been covered by researchers and there is a good reason to believe there may be meaningful differences within that context, then you have an opportunity to take a unique angle on well-established theory, which can make for a great piece of research. It is however imperative that you have a good reason to believe that the existing theory may not be wholly relevant within your chosen context, or your research will not be justified.
The upside to this approach is that you can potentially find a topic that is “closer to home” and more relevant and interesting to you , while still being able to draw on a well-established body of theory. However, the downside is that this approach will likely not produce the level of originality as approach #1.
Approach 3: Uncensored brainstorming
The third option is to skip the FRIN, as well as the local/industry-specific angle and simply engage in a freeform brainstorming or mind-mapping session, using your newfound knowledge of the theory to formulate potential research ideas. What’s important here is that you do not censor yourself . However crazy, unfeasible, or plain stupid your topic appears – write it down. All that matters right now is that you are interested in this thing.
Next, try to turn the topic(s) into a question or problem. For example:
- What is the relationship between X, Y & Z?
- What are the drivers/antecedents of X?
- What are the outcomes of Y?
- What are the key success factors for Z?
Re-word your list of topics or issues into a list of questions . You might find at this stage that one research topic throws up three questions (which then become sub-topics and even new separate topics in their own right) and in so doing, the list grows. Let it. Don’t hold back or try to start evaluating your ideas yet – just let them flow onto paper.
Once you’ve got a few topics and questions on paper, check the literature again to see whether any of these have been covered by the existing research. Since you came up with these from scratch, there is a possibility that your original literature search did not cover them, so it’s important to revisit that phase to ensure that you’re familiar with the relevant literature for each idea. You may also then find that approach #1 and #2 can be used to build on these ideas.
Try use all three approaches
As mentioned earlier, the three approaches discussed here are not mutually exclusive. In fact, the more, the merrier. Hopefully, you manage to utilise all three, as this will give you the best odds of producing a rich list of ideas, which you can then narrow down and evaluate, which is the next step.

Step 5: Narrow down, then evaluate
By this stage, you should have a healthy list of research topics. Step away from the ideation and thinking for a few days, clear your mind. The key is to get some distance from your ideas, so that you can sit down with your list and review it with a more objective view. The unbridled ideation phase is over and now it’s time to take a reality check .
Look at your list and see if any options can be crossed off right away . Maybe you don’t want to do that topic anymore. Maybe the topic turned out to be too broad and threw up 20 hard to answer questions. Maybe all the literature you found about it was 30 years old and you suspect it might not be a very engaging contemporary issue . Maybe this topic is so over-researched that you’ll struggle to find anything fresh to say. Also, after stepping back, it’s quite common to notice that 2 or 3 of your topics are really the same one, the same question, which you’ve written down in slightly different ways. You can try to amalgamate these into one succinct topic.
Narrow down to the top 5, then evaluate
Now, take your streamlined list and narrow it down to the ‘top 5’ that interest you the most. Personal interest is your key evaluation criterion at this stage. Got your ‘top 5’? Great! Now, with a cool head and your best analytical mind engaged, go systematically through each option and evaluate them against the following criteria:
Research questions – what is the main research question, and what are the supporting sub-questions? It’s critically important that you can define these questions clearly and concisely. If you cannot do this, it means you haven’t thought the topic through sufficiently.
Originality – is the topic sufficiently original, as per your university’s originality requirements? Are you able to add something unique to the existing conversation? As mentioned earlier, originality can come in many forms, and it doesn’t mean that you need to find a completely new, cutting-edge topic. However, your university’s requirements should guide your decision-making here.
Importance – is the topic of real significance, or is it just a “nice to know”? If it’s significant, why? Who will benefit from finding the answer to your desired questions and how will they benefit? Justifying your research will be a key requirement for your research proposal , so it’s really important to develop a convincing argument here.
Literature – is there a contemporary (current) body of academic literature around this issue? Is there enough literature for you to base your investigation on, but not too much that the topic is “overdone”? Will you be able to navigate this literature or is it overwhelming?
Data requirements – What kind of data would you need access to in order to answer your key questions? Would you need to adopt a qualitative, quantitative or mixed-methods approach to answer your questions? At this stage, you don’t need to be able to map out your exact research design, but you should be able to articulate how you would approach it in high-level terms. Will you use qual, quant or mixed methods? Why?
Feasibility – How feasible would it be to gather the data that would be needed in the time-frame that you have – and do you have the will power and the skills to do it? If you’re not confident with the theory, you don’t want something that’s going to draw you into a debate about the relative importance of epistemology and ontology. If you are shy, you won’t want to be doing ethnographic interviews. If you feel this question calls for a 100-person survey, do you have the time to plan, organise and conduct it and then analyse it? What will you do if you don’t get the response rate you expect? Be very realistic here and also ask advice from your supervisor and other experts – poor response rates are extremely common and can derail even the best research projects.
Personal attraction – On a scale of 1-10, how excited are you about this topic? Will addressing it add value to your life and/or career? Will undertaking the project help you build a skill you’ve previously wanted to work on (for example, interview skills, statistical analysis skills, software skills, etc.)?
The last point is particularly important. You will have to engage with your dissertation in a very sustained and deep way, face challenges and difficulties, and get it to completion. If you don’t start out enthusiastic about it, you’re setting yourself up for problems like ‘writer’s block’ or ‘burnout’ down the line. This is the reason personal interest was the sole evaluation criterion when we chose the top 5. So, don’t underestimate the importance of personal attraction to a topic – at the same time, don’t let personal attraction lead you to choose a topic that is not relevant to your course or feasible given your resources.

Narrow down to 3, then get human feedback
We’re almost at the finishing line. The next step is to narrow down to 2 or 3 shortlisted topics. No more! Write a short paragraph about each topic, addressing the following:
Firstly, WHAT will this study be about? Frame the topic as a question or a problem. Write it as a dissertation title. No more than two clauses and no more than 15 words. Less than 15 is better (go back to good journal articles for inspiration on appropriate title styles).
Secondly, WHY this is interesting (original) and important – as proven by existing academic literature? Are people talking about this and is there an acknowledged problem, debate or gap in the literature?
Lastly, HOW do you plan to answer the question? What sub-questions will you use? What methods does this call for and how competent and confident are you in those methods? Do you have the time to gather the data this calls for?
Show the shortlist and accompanying paragraphs to a couple of your peers from your course and also to an expert or two if at all possible (you’re welcome to reach out to us ), explaining what you will investigate, why this is original and important and how you will go about investigating it.
Once you’ve pitched your ideas, ask for the following thoughts :
- Which is most interesting and appealing to them?
- Why do they feel this way?
- What problems do they foresee with the execution of the research?
Take advice and feedback and sit on it for another day. Let it simmer in your mind overnight before you make the final decision.
Step 6: Make the decision (and stick with it!)
Then, make the commitment. Choose the one that you feel most confident about, having now considered both your opinion and the feedback from others.
Once you’ve made a decision, don’t doubt your judgement, don’t shift. Don’t be tempted by the ones you left behind. You’ve planned and thought things through, checked feasibility and now you can start. You have your research topic. Trust your own decision-making process and stick with it now. It’s time to get started on your research proposal!
Let’s recap…
In this post, I’ve proposed a straightforward 6-step plan to finding relevant research topic ideas and then narrowing them down to finally choose one winner. To recap:
- Understand the basics of academic research, as well as your university’s specific requirements for a dissertation, thesis or research project.
- Review previous dissertations for your course to get an idea of both topics and structure.
- Start the ideation process by familiarising yourself with the literature.
- Identify your potential research questions (topics).
- Narrow down your options, then evaluate systematically.
- Make your decision (and don’t look back!)
If you follow these steps, you’ll find that they also set you up for what’s coming next – both the proposal and the first three chapters of your dissertation. But that’s for future posts!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
23 Comments
I would love to get a topic under teachers performance. I am a student of MSC Monitoring and Evaluations and I need a topic in the line of monitoring and evaluations
I just we put for some full notes that are payable
Thank you very much Dr Caroline
I need a project topics on transfer of learning
m a PhD Student I would like to be assisted inn formulating a title around: Internet of Things for online education in higher education – STEM (Science, technology, engineering and Mathematics, digital divide ) Thank you, would appreciate your guidance
Well structured guide on the topic… Good materials for beginners in research writing…
Hello Iam kindly seeking for help in formulating a researchable topic for masters degree program in line with teaching GRAPHIC ART
I read a thesis about a problem in a particular. Can I use the same topic just referring to my own country? Is that being original? The interview questions will mostly be the same as the other thesis.
Hi, thanks I managed to listen to the video so helpful indeed. I am currently an MBA student looking for a specific topic and I have different ideas that not sure they can be turned to be a study.
I am doing a Master of Theology in Pastoral Care and Counselling and I felt like doing research on Spiritual problem cause by substance abuse among Youth. Can I get help to formulate the Thesis Title in line with it…please
Hello, I am kindly seeking help in formulating a researchable topic for a National diploma program
As a beginner in research, I am very grateful for this well-structured material on research writing.
Hello, I watched the video and its very helpful. I’m a student in Nursing (degree). May you please help me with any research problems (in Namibian society or Nursing) that need to be evaluate or solved?
I have been greatly impacted. Thank you.
more than useful… there will be no justification if someone fails to get a topic for his thesis
I watched the video and its really helpful.
How can i started discovery
Analysing the significance of Integrated reporting in Zimbabwe. A case of institutional investors. this is my topic for PHD Accounting sciences need help with research questions
Excellent session that cleared lots of doubts.
Excellent session that cleared lots of doubts
It was a nice one thank you
Wow, This helped a lot not only with how to find a research topic but inspired me to kick it off from now, I am a final year student of environmental science. And have to complete my project in the coming six months.
I was really stressed and thinking about different topics that I don’t know nothing about and having more than a hundred topics in the baggage, couldn’t make the tradeoff among them, however, reading this scrubbed the fuzzy layer off my head and now it seems like really easy.
Thanks GRADCOACH, you saved me from getting into the rabbit hole.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Dissertation vs Thesis: What's the difference? - Grad Coach - […] we receive questions about dissertation and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Choose the Best Topic for Research: Top 150+ Dissertation Topics

Introduction
Understanding the research process, relevance to academic or professional goals, scope and feasibility of the topic, availability of resources and data, novelty and contribution to the field, brainstorming techniques for topic generation, mind mapping, freewriting, idea clustering, swot analysis, consultation with advisors or experts, conduct preliminary research, consider the potential for further exploration and depth, evaluate the availability of research materials, finalizing the research topic, aligns with personal interests and goals, manageable and achievable, discuss with advisors or mentors, below are the top 150+ dissertation topics, business and economics:, technology and engineering:, health sciences:, other topics include:.
Choosing the best topic for research is a crucial step in the dissertation process. It sets the foundation for your study and greatly impacts your research success. In this article, we will explore the factors to consider when selecting a research topic and provide a comprehensive list of the top 150+ dissertation topics across various disciplines. By following these guidelines, you’ll be able to find a topic that aligns with your interests, contributes to the field, and ensures a fulfilling research journey.
Before delving into topic selection, it’s important to understand the research process as a whole. From defining research objectives to data collection and analysis, each step is interconnected. The topic selection phase holds immense significance as it dictates the direction and outcomes of your research .
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Research Topic:
Personal Interest and Passion: Choose a topic that genuinely excites you and aligns with your passions. Your enthusiasm will drive your motivation and commitment throughout the research journey.
Select a topic that aligns with your academic or professional aspirations . Consider how the research can contribute to your desired career path or academic advancement.
Assess the scope of the topic and ensure it is manageable within the given time and resource constraints. Avoid overly broad or narrow topics that might hinder progress.
Consider the availability of research materials, data sources, and access to relevant information. Adequate resources will facilitate a thorough and comprehensive study.
Look for topics that fill gaps in current knowledge or address emerging trends. A novel research topic has the potential to make a significant contribution to your field of study.
To generate topic ideas, employ various brainstorming techniques:
Visualize your ideas and create associations using a mind map.
Set a time limit and write continuously without censoring your thoughts. This helps generate new ideas and insights.
Organize related concepts into clusters and explore connections between them.

Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of potential topics to assess their viability .
Seek guidance from your advisors or experts in your field. They can provide valuable insights and help refine your topic ideas.
Top 150+ Best Topics for Research
We have curated a list of the top 150+ dissertation topics across various disciplines, including Social Sciences, Natural Sciences, Humanities, Business and Economics , Technology and Engineering, and Health Sciences . Each topic is accompanied by a brief description highlighting its importance and relevance to the field.
Tips for Narrowing Down the Topic Options
With a wide range of topics available, it’s essential to narrow down your options:
Gather background information on potential topics to assess their feasibility and relevance.
Evaluate if the topic has the potential for in-depth research and analysis, ensuring a substantial study.
Check the accessibility of resources, literature, and data required for your chosen topic.
Seek feedback and advice from mentors or peers
Share your topic ideas with mentors or peers to gather feedback and gain valuable perspectives.
Choose the research topic that resonates with your personal interests and goals:
Ensure that the topic aligns with your passion and long-term aspirations.
Select a topic that is realistically achievable within the given time frame and resource constraint s.
Seek input and guidance from your advisors or mentors to refine and finalize your research topic.
- The impact of digital marketing on consumer behavior
- Exploring the relationship between corporate social responsibility and financial performance
- The effects of globalization on small businesses
- Analyzing the role of leadership in organizational success
- Understanding the factors influencing consumer trust in e-commerce
- The impact of financial literacy on personal finance management
- Exploring the relationship between employee motivation and job satisfaction
- Investigating the effects of mergers and acquisitions on company performance
- Analyzing the role of corporate governance in preventing financial fraud
- The influence of cultural dimensions on international business negotiations
- The development of smart cities and their impact on sustainability
- Exploring the potential of artificial intelligence in healthcare
- Cybersecurity challenges and strategies in the digital age
- Investigating the applications of blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrency
- The role of robotics in industrial automation
- Analyzing the impact of virtual reality on user experience
- Exploring the potential of 3D printing in manufacturing
- The future of autonomous vehicles: Challenges and opportunities
- Investigating renewable energy technologies for a greener future
- The impact of big data analytics on business decision-making
- The relationship between mental health and physical well-being
- Exploring the effectiveness of alternative therapies in pain management
- Investigating the impact of exercise on cognitive function
- Analyzing the factors influencing medication adherence in chronic diseases
- Understanding the psychosocial factors affecting pediatric obesity
- Exploring the role of nutrition in preventing chronic diseases
- The impact of social determinants of health on healthcare outcomes
- Investigating the effects of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction
- Analyzing the relationship between sleep quality and overall health
- Exploring the challenges and innovations in telemedicine
- The role of social media influencers in shaping consumer behavior
- Analyzing the impact of globalization on cultural diversity
- Exploring the relationship between entrepreneurship and economic growth
- Investigating the effectiveness of corporate training programs on employee performance
- The influence of advertising on children’s consumer behavior
- Understanding the factors influencing job satisfaction among healthcare professionals
- Exploring the relationship between corporate governance and firm performance
- Analyzing the effects of income inequality on social mobility
- Investigating the impact of technology on work-life balance
- The role of emotional intelligence in effective leadership
- Exploring the effects of workplace diversity on organizational innovation
- Analyzing the relationship between corporate social responsibility and brand reputation
- Investigating the impact of globalization on labor markets
- The effects of employee engagement on organizational productivity
- Exploring the role of cultural intelligence in international business
- Analyzing the impact of corporate mergers on consumer choices
- Investigating the relationship between ethical leadership and employee behavior
- The influence of organizational culture on employee motivation
- Exploring the effects of e-commerce on traditional retail businesses
- The impact of data privacy regulations on consumer trust in online services
- Analyzing the relationship between workplace diversity and team performance
- Investigating the effects of digital transformation on organizational competitiveness
- The role of emotional labor in customer service industries
- Exploring the impact of social entrepreneurship on community development
- Analyzing the effects of supply chain disruptions on business operations
- Investigating the influence of corporate branding on consumer loyalty
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job displacement
- Exploring the effects of corporate social media use on brand perception
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational communication and employee satisfaction
- Investigating the effects of workplace mindfulness programs on employee well-being
- The role of corporate entrepreneurship in fostering organizational innovation
- Exploring the impact of social media marketing on consumer engagement
- Investigating the effects of workplace diversity on creativity and innovation
- The influence of organizational justice on employee motivation and job satisfaction
- Analyzing the relationship between corporate governance and corporate social responsibility
- Investigating the effects of digitalization on supply chain management
- Exploring the impact of emotional intelligence on team dynamics
- Analyzing the relationship between employee empowerment and organizational performance
- Investigating the effects of ethical leadership on employee job attitudes
- The role of technology in enhancing customer experiences in the hospitality industry
- Exploring the impact of corporate social responsibility on investor decision-making
- Investigating the effects of workplace flexibility on employee work-life balance
- The influence of organizational culture on organizational resilience
- Analyzing the relationship between sustainable practices and financial performance
- Investigating the effects of employee well-being programs on organizational outcomes
- Exploring the impact of digital marketing strategies on brand equity
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational change management and employee resistance
- Investigating the effects of corporate social responsibility on employee engagement
- The role of corporate entrepreneurship in fostering organizational agility
- Exploring the impact of technological advancements on customer service experiences
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational learning and innovation
- Investigating the effects of workplace empowerment on employee job satisfaction
- The influence of organizational justice on employee performance and commitment
- Exploring the impact of workplace diversity on organizational resilience
- Analyzing the relationship between corporate governance and corporate financial performance
- Investigating the effects of digital marketing on consumer trust and loyalty
- The role of emotional intelligence in conflict resolution in the workplace
- Exploring the impact of corporate social responsibility on employee retention
- Analyzing the relationship between leadership styles and employee motivation
- Investigating the effects of organizational climate on employee well-being
- The influence of ethical leadership on organizational culture
- Exploring the impact of workplace diversity on customer satisfaction
- Investigating the effects of artificial intelligence on job satisfaction
- The role of corporate social responsibility in crisis management
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational trust and employee commitment
- Investigating the effects of employee development programs on organizational performance
- Exploring the impact of technology on customer relationship management
- Analyzing the relationship between workplace happiness and employee productivity
- Investigating the effects of organizational justice on employee well-being
- The role of corporate entrepreneurship in fostering organizational sustainability
- Exploring the impact of digital transformation on customer experiences
- Investigating the effects of workplace diversity on organizational culture
- The influence of ethical leadership on employee well-being
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational trust and customer loyalty
- Investigating the effects of corporate social responsibility on consumer purchasing behavior
- Exploring the impact of technology on supply chain sustainability
- Analyzing the relationship between leadership development and organizational success
- Investigating the effects of workplace empowerment on organizational innovation
- The role of corporate social responsibility in talent acquisition and retention
- Exploring the impact of digital marketing on brand awareness and perception
- Analyzing the relationship between organizational trust and team effectiveness
- Investigating the effects of workplace diversity on organizational performance
- The influence of ethical leadership on organizational trust and reputation
- Exploring the impact of technology on customer loyalty programs
- Analyzing the relationship between workplace motivation and employee engagement
- Investigating the effects of corporate social responsibility on employee job satisfaction
- The role of corporate entrepreneurship in fostering organizational flexibility
- Exploring the impact of technology on supply chain efficiency
- Analyzing the relationship between leadership effectiveness and organizational culture
- Investigating the effects of workplace well-being programs on employee productivity
Please note that these topics can be further refined or tailored to specific research interests and objectives.
Choosing the best topic for your research is a critical decision that can shape the success and satisfaction of your dissertation journey. By considering factors such as personal interest, relevance, feasibility, and novelty, you can select a research topic that fuels your enthusiasm and contributes meaningfully to your field. Take your time, explore various brainstorming techniques, and seek advice from experts to ensure you embark on a fulfilling research endeavor.
If you are embarking on your research journey and in need of professional assistance, look no further than Gradesmiths . Our dedicated team of experts is committed to providing top-notch academic services tailored to your needs. Whether you require assistance in selecting a research topic, conducting literature reviews, or writing your dissertation, our skilled writers are here to support you every step of the way. With a reputation for delivering high-quality work on time, we ensure that your research is in capable hands. Place your order today at Gradesmiths and let us help you achieve your academic goals with excellence and precision.
- RESEARCH PAPER FOR SALE
- RESEARCH PAPER WRITER
- RESEARCH PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICES
- SCHOLARSHIP ESSAY HELP
- SPEECH HELP
- STATISTICS HOMEWORK HELP
- TERM PAPER WRITING HELP
- THESIS EDITING SERVICES
- THESIS PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICE
- TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK HELP
- ADMISSION ESSAY WRITING HELP
- BIOLOGY PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- BOOK REPORT WRITING HELP
- BUY BOOK REVIEW
- BUY COURSEWORKS
- BUY DISCUSSION POST
- BUY TERM PAPER
- CAPSTONE PROJECT WRITING SERVICE
- COURSEWORK WRITING SERVICE
- CRITIQUE MY ESSAY
- CUSTOM RESEARCH PAPER
- CUSTOMER CONDUCT
- DISSERTATION EDITING SERVICE
- DISSERTATION WRITERS
- DO MY DISSERTATION FOR ME
- DO MY POWERPOINT PRESENTATION
- EDIT MY PAPER
- English Research Paper Writing Service
- ENGLISH RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- ESSAY WRITING HELP
- ESSAYS FOR SALE
- GRADUATE PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- LAW ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- MARKETING ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- NON-PLAGIARIZED ESSAYS
- NURSING ASSIGNMENT HELP
- PAY FOR COURSEWORK
- PAY FOR ESSAYS
- PAY FOR LITERATURE REVIEW
- PAY FOR PAPERS
- PAY FOR RESEARCH PAPERS
- PERSONAL STATEMENT EDITING SERVICE
- PERSONAL STATEMENT WRITER
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING HELP
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- PHD THESIS WRITING SERVICE
- PROOFREAD MY PAPER
- PSYCHOLOGY ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- THESIS STATEMENT HELP
- WRITE MY ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR ME
- WRITE MY CASE STUDY
- WRITE MY DISCUSSION BOARD POST
- WRITE MY LAB REPORT

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
113 Great Research Paper Topics
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Request Info
- Iona University
- Research Guides
Research Essentials
- Choosing a Research Topic
Introduction
Choosing a topic, organizing your research, improving your search.
- Finding Sources in WorldCat
- Effective Database Searching
- Artificial Intelligence This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Sources
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- Library Workshops and Events
- Database Access Troubleshooting
Research is a multifaceted process. In searching, you could find that your topic is too broad, pulling up too many irrelevant sources. Conversely, you could find that your topic is too narrow, resulting in too few sources or too many specifically irrelevant sources.
If your research isn't meeting your needs, take a moment to reflect on your research topic. How did you choose your topic? Did you have enough background knowledge before you started searching, or are you trying to make sense of your topic from highly academic journal articles? Use the prompts on this page to guide your reflection and refine your topic for more sustainable and inquiry-driven research.
1. Brainstorm possible topic ideas
- Consider your personal interests
- Talk about topics and your personal interests with classmates and peers
- Reflect on interesting social media content you've recently encountered. Most social media content is not scholarly but can be explored with scholarly research from academic sources
- Review class readings
- Read encyclopedia articles about potential topics
- Browse recent issues of journals, magazines, or newspapers
- Browse the library shelves for books on your subject
2. Review assignment requirements
- What kind of assignment is it - a 5-minute oral presentation, 3-page, or 10-page paper?
- How much information do you need?
- What kind of sources does the assignment require - peer-review, books, journal or newspaper articles, multimedia?
- How current does your information need to be - published in the last 3 years, 5 years, or 10 years?
- What types of publications would further your research - newspaper articles, books, journal articles, primary sources, trade publications?
- What formats do you need - visual, audio, printed, electronic?
- Do you need opinion pieces?
- How much time do you have?
3. List keywords to define your topic
- State your research topic as a question. If you want to write about music festivals, you could ask "How have music festivals affected the prevalence local music venues?"
- Think about the significant terms, concepts, and keywords that describe your topic. These terms will become the keywords for searching in library catalogs, online databases, and other resources.
4. Gather background information on your topic
Do some general reading in reference materials and other library resources to get an overview of your topic and develop your own working knowledge of your topic.
5. Use AI to assist with topic exploration
If your professor allows AI use in your course, experiment with generative AI to do some of the steps above. Find more information about how to use AI on the Artificial Intelligence: For Students guide.
Adapted from Duke University Libraries (Thanks to Duke librarians)
Below are some resources that can assist you in organizing your research process.
Introduction to Organizing - Lumen Learning
Organizing your Research - UMD
Video: Creating a Research Plan
The Writing Process - KU Wingspan: Center for Learning and Writing Support
Tutorial: Synthesizing Information for Academic Writing
Video: Anatomy of a Research Paper
Video: Academic Writing
Video: Writing Help
Artificial Intelligence: For Students Guide
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Broadening Your Topic
Is your search producing too many irrelevant sources? Consider narrowing your topic to make your results list more manageable. Here are some options to consider when narrowing the scope of your paper:
- Aspect or sub-area: Consider only one piece of the subject. For example, if your topic is human cloning, investigate government regulation of cloning animals.
- Time: Limit the time span you examine. If you are writing about genetic testing, contrast public attitudes about genetic testing in the 1950's versus the 1990's.
- Population group: Limit by age, sex, race, occupation, species or ethnic group. Rather than writing about the job market for construction workers, narrow your topic to tunnel diggers.
- Geographical location: A geographic analysis can provide a useful means to examine an issue. If you are writing about climate change, narrow your topic by focusing on the effects of climate change in Bangladesh or Iceland.
- Theoretical approach: Limit your topic to a particular approach to the issue. If you are writing about Greek goddesses, you can further limit your topic by researching feminist approaches to studying the Greek pantheon.
More Suggestions:
- State your topic in the form of a research question or thesis statement.
- Ask "how" or "why" questions rather than who, what, when, and where questions or yes/no questions.
- Use specific words, i.e., use poetry instead of literature.
- Add more than one keyword to your search. Use the Boolean connector AND to narrow your search; AND retrieves documents which include both terms in the search such as "gun control" AND "second amendment.
One narrowing might not be enough to yield relevant results. Keep refocusing your keywords, and keep notes of each time you further narrow your topic. This information is important when writing your introduction, where you define the scope of your inquiry into a topic.
If your professor allows the use of AI in your course, you can also try asking an AI tool to assist with narrowing your topic. Find out more information about how to use AI in your research on the Artificial Intelligence: For Students guide.
Adapted from MIT Libraries Selecting a Research Topic Overview, https://libguides.mit.edu. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License
Video: How to Narrow Your Topic
Video: Refining Search Results
If you're finding too few resources, consider broadening your topic. Think of related ideas, returning to some of your initial research in reference materials. You may not be finding enough information for several reasons, including:
- Your topic is too specific. Generalize what you are looking for. If your topic is genetic diversity for a specific ethnic group in Ghana, broaden your topic by generalizing to ethnic groups in Ghana or West Africa.
- Your topic is too new. If you're researching a breaking news event, you are likely to only find information about it in the news media. Be sure to search databases that contain articles from newspapers. If you are not finding enough in the news - or need scholarly sources for your paper - consider changing your topic to one that has been covered more extensively.
- Y ou have not checked enough databases for information. Find other databases in your subject area which might cover the topic from a different perspective.
- You are using normal, non-academic words to describe an academic topic. When reading background information, note how your topic is discussed, particularly how it is discussed in academic conversations. Keep note of these synonyms and start using them in your search.
Adapted from MIT Libraries Selecting a Research Topic Overview,, https://libguides.mit.edu. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License
- Use broader or more general search terms to describe your topic. For example, use "bioethics" instead of a specific issue like "stem cell research.
- Find alternative words. Search with synonyms. For example, instead of "teenagers" use "adolescents" or "teens" or "young adults."
- Use fewer keywords in your search.
- Use the Boolean connector OR to broaden your search. OR means more; it will search for either term in a search statement such as private OR public education.
- Try truncating your terms to include all variant endings of your keyword, such as legal* gives you legal, legalize, legalizes, legality, and legalization.
Because research is iterative, one broadening might not be enough to yield relevant results. Keep rethinking your keywords and search terms, and keep notes of each time you further broaden your topic. This information is important when writing your introduction, where you define the scope of your inquiry into a topic.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Finding Sources in WorldCat >>
- Last Updated: Jul 16, 2024 3:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.iona.edu/researchessentials
- Graduate School
Research Interest Statement Samples That Worked

A good research interest statement sample can be hard to find. Still, it can also be a beneficial tool for writing one and preparing for a grad school application or post-graduate position. Your research interest statement is one of the key components of your application to get into grad school . In a few cases, admissions committees have used it instead of an interview, so it is important to write a strong essay. We’ve provided research interest statement samples for you in this blog post. We have also included several tips that will help you write a strong statement to help improve your chances of getting accepted into your dream program.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free initial consultation here <<
Article Contents 13 min read
What is a research interest statement.
A research interest statement is essential for most graduate school, post-graduate, and academic job applications. Sometimes, it may be referred to it as a " statement of intent " or "description of research interests." While they are similar, research interest statement may require some additional information. Generally, your statement will pride a brief overview of your research background, including your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future research you'd like to complete, including any required equipment and collaborations. It is usually written in the form of a short essay. Still, of course, different graduate programs can have specific requirements, so make sure to check the program you are applying to and read the particular instructions that they give to ensure your research interest statement meets their requirements.
Your research statement plays a big role in the committee's decision. Ultimately, they are trying to figure out if you, as a person, and your research, would be a good fit for their program. A strong statement can help you convince them of this by showing your passion for research, your research interests and experience, the connection between your interests and the program, and the extent of your writing skills which is really important for paper and grant writing, and thus for earning money for your research!
Undergraduate programs are centered around classes, but graduate and post-graduate programs are all about your research and what your research contributes to your discipline of choice. That is why a research interest statement is so important, because it is essentially a way for you to share this information with the program that you have chosen.
Writing a strong statement can be helpful to you, as well. Having to explain your research and talk about your goals coherently will give you a chance to define your future research and career plans, as well as academic interests.
What Should Your Research Interest Statement Include?
The exact requirements of the research interest statement can vary depending on where you are applying and for what position. Most faculty positions will need you to produce a separate file for your statement, and most of the time, for an academic program, you can simply include your statement within your CV for graduate school .
Need to prepare your grad school CV? This video has helpful advice for you:
Unless otherwise stated by the program or faculty that you are applying to, your statement should be one to two pages long or between 600 and 1000 words. If you are including your description of interest statements on your resume, then it would be ideal to keep it between 400 and 600 words. Most programs will give you guidelines for the research interest statement so make sure you follow those. They rarely include a specific question or prompt but they might ask for a particular detail to be included in your interest statement. For example, a university’s requirements may look something like this: “In your statement of interest, you should detail your study and/or research interests and reasons for seeking admission. You must identify a faculty member from the Anthropology of Department with whom you are interested in being your advisor. The length of a statement of intent should be 2 pages in length (single-spaced, Times New Roman font size 12 point)”
Your statement should include a brief history of your past research. It should tell the committee what you have previously set out to answer with your research projects, what you found, and if it led to any academic publications or collaborations. It should also address your current research. What questions are you actively trying to solve? You will need to tell the committee if you’ve made any progress, what you have found, if you are connecting your research to the larger academic conversation and what the larger implications of your work actually are. Finally, you want to talk about the future of your research. What further questions do you want to solve? How do you intend to find answers to these questions? What are the broader implications of your potential results, and how can the institution you are applying to help you?
Before we show you some examples, let's go over a few essential things that you need to keep in mind while writing your research interest statement to make sure it is strong.

Preparation
Give Yourself Ample Time: Much like with other components of your application, like your CV or a graduate school interview question , preparation is the key to success. You should give yourself enough time to thoroughly research the program or faculty you are applying to, gather all the information or documents that can aid you in writing, and then write and rewrite as many times as you need to. Give yourself at least 6 weeks to draft, redraft, and finalize your statement. You may also want to consider investing in a graduate school admissions consultant as they have more experience writing these types of essays and may see things that you can’t.
Research the Program/Faculty: The purpose of your research interest statement is to tell the committee all about your research plans, how it will contribute to the field and convince them that not only is their institution is the best place for it, but that you will be an asset to them as a candidate. To do this, you need to know what kind of candidate they are looking for, what kind of research they have been interested in in the past, and if there is anything particular that they require in the research interest statement. Remember, expectations for research statements can vary among disciplines and universities, so it is essential that you write for the right audience.
The Format / Writing Style
Your research statement should be in an academic essay format. It needs to be concise, well-organized, and easy to read. For graduate school, PhD or post-doc positions, your research interest statement will usually be a part of your resume. We recommend that you stick to the following things when it comes to the format:
Limited Spots Available ","trustpilot":false}" :url=""https:\/\/bemoacademicconsulting.com\/grad-app-webinar-registration"" code="banner2" background-color="#000066" button-color="#ffffff" banner-image>
The Content
Introduction: This is a functional academic document, unlike college essays or personal statements, so you want to go straight to the point and focus on the key information that needs to be conveyed. You want to use this paragraph to tell the committee why you are writing this statement. In other words, you should clearly state what kind of research you are interested in pursuing at the institution in question and explain why you are drawn to the subject.
Body: This is your “why and how” paragraphs. In 2 or 3 paragraphs, you should expand on your interest, background, accomplishments, and plans in the field of research. Depending on your level of experience, you may use this time to talk about your previous or current research. If you do not have much experience, then you may use this paragraph to talk about any skills or academic achievements that could be relevant.
Conclusion: To conclude, you should restate your interest and tie it back to the research you intend to continue at the university. Be specific about the direction you’d like to take the research in, who you’d like to work with, and what the institution has that would help you. We also suggest including a concise statement that reiterates your unique suitability for the program, and what you can contribute to it and your chosen field.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Being Too Personal: Often, students will confuse the statement of purpose and the research interest statement or letter of intent. It is essential to understand the difference between these two documents because some programs will ask for both of these documents. There is quite a bit of overlap between the two essays, so they are very easy to mix up. Both documents ask applicants to focus on their research interests, relevant past academic & professional experiences, and their long-term goals in the field. However, a statement of purpose is more of a personal statement that describes your journey and overall suitability for a program. In contrast, a research interest statement is a more formal academic document specific to the research you intend to pursue in a program. It will include many details such as the faculty members you want to work with, the program facilities and resources you wish to use, etc.
Not Following Guidelines: As mentioned earlier, these statements can vary depending on the discipline and the faculty. It is crucial that you review all the institution's guidelines and follow them. Some schools will have a specific word count, others may simply give you a maximum and minimum word count. Others may even have a specific prompt or question that you will need to answer with your essay. You want to make sure that you are following the instructions provided by the program.
Using Too Much Jargon: Your statement will be read by people who are most likely knowledgeable, but they might not be from your specific field or specialty. We understand that it may not be possible to be clear about your research without using a few niche words, but try to keep them at a minimum and avoid using acronyms that are not well known outside of your specialty.
Having One Generic Statement: The requirements of your research statement are different from one school to another, and you should tailor your letter to the program you are writing to. We know that the research and experience you are talking about are still the same, but the qualities and aspects of that experience you play up should help you appeal to the school you are applying to. For example, if you are applying to a very collaborative program, you should highlight your collaborations and your experience working as part of a team.
Looking for tips on getting into grad school? This infographic is for you:
Research of Interest Statement Samples
Below are sample research interest statements for reference:
Research Statement of Interest 1
Jennifer Doe
As the child of an immigrant, I have always been fascinated by the relationship between identity, geographic territory, and economic development. With the rise of globalization, there is a broader effort in the social sciences to study the link between cultural identity, human mobility, and economic development in the contemporary world. I hope that my research will contribute to this as well. I am applying to the X University Global Anthropology program, as it is the best place for me to explore my research interests and channel them towards my long-term goals. I believe that my undergraduate education and the research experience it gave me have prepared me to undertake advanced research projects, thus making me an excellent candidate for this program.
I spent the first two years of undergraduate studies taking psychology courses. I went to university knowing that I wanted to learn about human behavior and culture. I was thirsty for information, but I did not know what kind of information just yet. It wasn’t until I took an elective anthropology class in my second year and started discussing identity in anthropology that something clicked. Unlike many other social sciences, anthropology explores the different ways that cultures affect human behavior and that connected right away with my experience as an immigrant. I have been passionate about the subject ever since, and I intend on spending my career exploring this topic further.
In the long run, I am interested in understanding how geography affects the construction of one’s cultural identity, especially when it comes to immigrants. Literature already exists on the topic, but most of it examines the upper levels of this process of social reproduction, concentrating on the roles of governments and associations in promoting ties between migrants and their homelands. Prof. Jane Doe Smith is one of the anthropologists researching the transnational migration experience, and I hope to have the opportunity to work with her at X University.
I was fortunate to be part of a summer research experience as an undergraduate, which took place in several west African countries, including Mali, Senegal, and Nigeria. Dr. Sam Smith was leading the research, and my time on his team allowed me to gain hands-on experience in research while living abroad. One of the things that I did almost daily was interview the subjects in a controlled environment, and sometimes I got to be a part of traditional ceremonies. I learnt how to observe without being intrusive and how to interact with clinical subjects. The experience only strengthened my curiosity and conviction that today more than ever, we need to understand what identity is and the different factors that can affect it.
I enrolled in several challenging research-oriented courses such as Applied Statistical Inference for the Behavioral Sciences, Principles of Measurement, and more throughout my degree. I was also able to work as a research lab assistant for one of my mentors, Mr. Jonathan Smith. I worked with him while he studied the relationship between identity, culture and “self.” My main duties were to assist in the creating of surveys and other assessment materials, administer written and verbal tests to participants, create literature reviews for potential resources, create summaries of findings for analysis and other office duties such as reserving testing rooms. This particular experience allowed me to get some hands-on experience with data collection, data analysis, report preparation and the creation of data summaries.
I know that there is a lot more that I can learn from the X University. I have seen the exemplary work in anthropology and other social studies done by the staff and alumni of this school. It has inspired and convinced me beyond the shadow of a doubt that pursuing my graduate studies in your program meets my personal, academic, and professional goals objectives.
My advanced research skills, passion for anthropology and clinical research, as well as my academic proficiency make me the ideal candidate for X University's Clinical Global Anthropology Master’s program. I believe that X University’s rigorous curriculum and facilities make it the perfect place for me, my long-term career goals and my research commitments.
Jamie Medicine
I am applying to the brain and development master's program of X university because it is one of the few universities that not only has a program that combines the two disciplines that I majored in my undergraduate studies: Psychology and Linguistics; but also because it is a program that I know would allow me to grow as a researcher, contribute to my chosen fields and achieve my long-term career goals. My research is motivated by two of my favorite things: language and music. To be more specific, hip-hop music. In 20xx, Rollingstone magazine published an article stating that hip hop was now more popular than rock and roll. The rise in popularity of this initially very niche genre has sparked a conversation in specific academic fields such as psychology, sociology, linguistics, and English about the use of language within it but also the effects that it can have on those who listen to it. I hope to one day contribute to that conversation by studying the relationship between hip-hop music and vocabulary development, and I believe that pursuing this particular research interest at X university is the best way for me to do that.
There are many potential places this research may lead me and many potential topics I may explore. Furthermore, there are many things that it would allow us to learn about the effect that music has on our brains and society at large.
I was fortunate enough to work under Dr. Jane D. Smith at the University of X for two years while conducting her recently published study on vocabulary instruction for children with a developmental language disorder. During my time in her lab, I interviewed participants and put together evaluation materials for them. I was also responsible for data entry, analysis, and summarizing. This experience gave me the skills and the knowledge that allowed me to exceed expectations for my final research project in undergraduate school.
One of my undergraduate degree requirements was to complete a small independent study under the supervision of a professor. I chose to study music's effect on children's vocabulary development. Several studies look for ways to decrease the million-word gap, and I wanted to see if this thing that I am so passionate about, music, had any effect at all. I compiled multiple literature reviews and analyzed their results, and I found that there is indeed a correlation between the number of words that a child spoke and the amount of music that they were exposed to.
This research is currently being explored on a larger scale by Prof. John Doe at X university and learning from him is one of the many reasons I have applied to this program. I took several research methodology courses throughout my degree, and I would love to enroll in the Applied Statistics for Psychology course he is currently teaching to build upon the foundational knowledge I already have. There are several other faculty members in the brain and language department with whom learning from would be a dream come true. In addition to that, working with them is a real possibility because the research they are currently doing and the research I hope to pursue are greatly matched.
I genuinely believe that X university has the curriculum and facilities that I need to meet my long-term goals and research commitments. I also believe that my academic achievements, eagerness to learn, and passion make me the perfect candidate for your program.
Interested in some tips to help you manage grad school once you're there? Check out this video :
It is essentially an essay that provides a brief overview of your research experience and goals. This includes your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future research you'd like to complete. It is also sometimes referred to as a "statement of intent" or "description of research interests."
This statement tells the admissions committee more about you as an applicant. It gives you the opportunity to tell them more about your research (past, present, and future) and show them that you are a good fit for their institution.
No. Some graduate school programs might ask for a statement of purpose and a writing sample instead, or they could ask for none of the above. You should always check the requirements of the specific program that you’re applying to.
Generally, your statement should be 400 to 1000 words or about two pages long. That said, most programs will give you guidelines so make sure you check those and follow them.
You certainly can but we do not recommend it. You should always tailor your statement to the program you are applying to. Remember that the aim is to convince the admissions committee that you are a good fit for their school so make sure you highlight the qualities and values that they care about.
We recommend that you doublecheck the information provided by your chosen program as they often have specific instructions for the format of the letter. If none exist, make sure that the format of your document is pleasing to the eye. Stick to easily legible fonts, a decent font size, spacing, margins, etc. Also, it is best to keep the content of the letter concise and professional.
We recommend giving yourself at least 6 weeks to write your statement. This will give you ample time to brainstorm, write a strong letter, read it again and edit it as many times as necessary. It also gives you enough time to get expert eyes on your letter and work with them to improve it if you wish.
No. Research interest statements are often required for post-graduate school applications and for other positions in academic faculties.
Absolutely! You can always reach out to admissions professionals, such as graduate school admissions consultants or grad school essays tutors .
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions.
Thank you for your excellent site
BeMo Academic Consulting
You are very welcome, Rasool!
Sadia Sultana
hello, thanks for providing guide line for Research Interest statement, the important aspect of scholarship application. Kindly guide me, What should be the title of the Research Statement. Thanks
Hi Sadia! Check the requirements of your school first. They might provide some info on whether a title is even needed.
Sadia Tasnim Epa
I'm very pleased that you have mentioned every detail of research interest which helped me to clear all of my doubts.... Thank you very much.
Hi Sadia! Glad you found this helpful!
Get Started Now
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Topics – Ideas and Examples
Research Topics – Ideas and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Topic
Definition:
Research topic is a specific subject or area of interest that a researcher wants to investigate or explore in-depth through research. It is the overarching theme or question that guides a research project and helps to focus the research activities towards a clear objective.
How to Choose Research Topic
You can Choose a Research Topic by following the below guide:
Identify your Interests
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a research topic is your personal interest. This is because you will be spending a considerable amount of time researching and writing about the topic, so it’s essential that you are genuinely interested and passionate about it. Start by brainstorming a list of potential research topics based on your interests, hobbies, or areas of expertise. You can also consider the courses that you’ve enjoyed the most or the topics that have stood out to you in your readings.
Review the Literature
Before deciding on a research topic, you need to understand what has already been written about it. Conducting a preliminary review of the existing literature in your field can help you identify gaps in knowledge, inconsistencies in findings, or unanswered questions that you can explore further. You can do this by reading academic articles, books, and other relevant sources in your field. Make notes of the themes or topics that emerge and use this information to guide your research question.
Consult with your Advisor
Your academic advisor or a mentor in your field can provide you with valuable insights and guidance on choosing a research topic. They can help you identify areas of interest, suggest potential research questions, and provide feedback on the feasibility of your research proposal. They can also direct you towards relevant literature and resources that can help you develop your research further.
Consider the Scope and Feasibility
The research topic you choose should be manageable within the time and resource constraints of your project. Be mindful of the scope of your research and ensure that you are not trying to tackle a topic that is too broad or too narrow. If your topic is too broad, you may find it challenging to conduct a comprehensive analysis, while if it’s too narrow, you may struggle to find enough material to support your research.
Brainstorm with Peers
Discussing potential research topics with your peers or colleagues can help you generate new ideas and perspectives. They may have insights or expertise that you haven’t considered, and their feedback can help you refine your research question. You can also join academic groups or attend conferences in your field to network with other researchers and get inspiration for your research.
Consider the Relevance
Choose a research topic that is relevant to your field of study and has the potential to contribute to the existing knowledge. You can consider the latest trends and emerging issues in your field to identify topics that are both relevant and interesting. Conducting research on a topic that is timely and relevant can also increase the likelihood of getting published or presenting your research at conferences.
Keep an Open Mind
While it’s essential to choose a research topic that aligns with your interests and expertise, you should also be open to exploring new ideas or topics that may be outside of your comfort zone. Consider researching a topic that challenges your assumptions or introduces new perspectives that you haven’t considered before. You may discover new insights or perspectives that can enrich your research and contribute to your growth as a researcher.
Components of Research Topic
A research topic typically consists of several components that help to define and clarify the subject matter of the research project. These components include:
- Research problem or question: This is the central issue or inquiry that the research seeks to address. It should be well-defined and focused, with clear boundaries that limit the scope of the research.
- Background and context: This component provides the necessary background information and context for the research topic. It explains why the research problem or question is important, relevant, and timely. It may also include a literature review that summarizes the existing research on the topic.
- Objectives or goals : This component outlines the specific objectives or goals that the research seeks to achieve. It should be clear and concise, and should align with the research problem or question.
- Methodology : This component describes the research methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data. It should be detailed enough to provide a clear understanding of how the research will be conducted, including the sampling method, data collection tools, and statistical analyses.
- Significance or contribution : This component explains the significance or contribution of the research topic. It should demonstrate how the research will add to the existing knowledge in the field, and how it will benefit practitioners, policymakers, or society at large.
- Limitations: This component outlines the limitations of the research, including any potential biases, assumptions, or constraints. It should be transparent and honest about the potential shortcomings of the research, and how these limitations will be addressed.
- Expected outcomes or findings : This component provides an overview of the expected outcomes or findings of the research project. It should be realistic and based on the research objectives and methodology.
Purpose of Research Topic
The purpose of a research topic is to identify a specific area of inquiry that the researcher wants to explore and investigate. A research topic is typically a broad area of interest that requires further exploration and refinement through the research process. It provides a clear focus and direction for the research project, and helps to define the research questions and objectives. A well-defined research topic also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and useful, and can contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field. Ultimately, the purpose of a research topic is to generate new insights, knowledge, and understanding about a particular phenomenon, issue, or problem.
Characteristics of Research Topic
some common characteristics of a well-defined research topic include:
- Relevance : A research topic should be relevant and significant to the field of study and address a current issue, problem, or gap in knowledge.
- Specificity : A research topic should be specific enough to allow for a focused investigation and clear understanding of the research question.
- Feasibility : A research topic should be feasible, meaning it should be possible to carry out the research within the given constraints of time, resources, and expertise.
- Novelty : A research topic should add to the existing body of knowledge by introducing new ideas, concepts, or theories.
- Clarity : A research topic should be clearly articulated and easy to understand, both for the researcher and for potential readers of the research.
- Importance : A research topic should be important and have practical implications for the field or society as a whole.
- Significance : A research topic should be significant and have the potential to generate new insights and understanding in the field.
Examples of Research Topics
Here are some examples of research topics that are currently relevant and in-demand in various fields:
- The impact of social media on mental health: With the rise of social media use, this topic has gained significant attention in recent years. Researchers could investigate how social media affects self-esteem, body image, and other mental health concerns.
- The use of artificial intelligence in healthcare: As healthcare becomes increasingly digitalized, researchers could explore the use of AI algorithms to predict and prevent disease, optimize treatment plans, and improve patient outcomes.
- Renewable energy and sustainable development: As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, researchers could investigate the potential of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, and how these technologies can be integrated into existing infrastructure.
- The impact of workplace diversity and inclusion on employee productivity: With an increasing focus on diversity and inclusion in the workplace, researchers could investigate how these factors affect employee morale, productivity, and retention.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy: As data breaches and cyber attacks become more common, researchers could explore new methods of protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious attacks.
- T he impact of mindfulness and meditation on stress reduction: As stress-related health issues become more prevalent, researchers could investigate the effectiveness of mindfulness and meditation practices on reducing stress and improving overall well-being.
Research Topics Ideas
Here are some Research Topics Ideas from different fields:
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being.
- The effectiveness of various teaching methods in improving academic performance in high schools.
- The role of AI and machine learning in healthcare: current applications and future potentials.
- The impact of climate change on wildlife habitats and conservation efforts.
- The effects of video game violence on aggressive behavior in young adults.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques in reducing anxiety and depression.
- The impact of technology on human relationships and social interactions.
- The role of exercise in promoting physical and mental health in older adults.
- The causes and consequences of income inequality in developed and developing countries.
- The effects of cultural diversity in the workplace on job satisfaction and productivity.
- The impact of remote work on employee productivity and work-life balance.
- The relationship between sleep patterns and cognitive functioning.
- The effectiveness of online learning versus traditional classroom learning.
- The role of government policies in promoting renewable energy adoption.
- The effects of childhood trauma on mental health in adulthood.
- The impact of social media on political participation and civic engagement.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between nutrition and cognitive functioning.
- The impact of gentrification on urban communities.
- The effects of music on mood and emotional regulation.
- The impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems and food webs.
- The role of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing cyberattacks.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in managing chronic pain.
- The relationship between personality traits and job satisfaction.
- The effects of social isolation on mental and physical health in older adults.
- The impact of cultural and linguistic diversity on healthcare access and outcomes.
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating depression and anxiety in adolescents.
- The relationship between exercise and cognitive aging.
- The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem.
- The role of corporate social responsibility in promoting sustainable business practices.
- The impact of mindfulness meditation on attention and focus in children.
- The relationship between political polarization and media consumption habits.
- The effects of urbanization on mental health and well-being.
- The role of social support in managing chronic illness.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships and dating behaviors.
- The effectiveness of behavioral interventions in promoting physical activity in sedentary adults.
- The relationship between sleep quality and immune function.
- The effects of workplace diversity and inclusion programs on employee retention.
- The impact of climate change on global food security.
- The role of music therapy in improving communication and social skills in individuals with autism spectrum disorder.
- The impact of cultural values on the development of mental health stigma.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques in reducing burnout in healthcare professionals.
- The relationship between social media use and body dissatisfaction among adolescents.
- The effects of nature exposure on cognitive functioning and well-being.
- The role of peer mentoring in promoting academic success in underrepresented student populations.
- The impact of neighborhood characteristics on physical activity and obesity.
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation interventions in improving cognitive functioning in individuals with traumatic brain injury.
- The relationship between organizational culture and employee job satisfaction.
- The effects of cultural immersion experiences on intercultural competence development.
- The role of assistive technology in promoting independence and quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
- The impact of workplace design on employee productivity and well-being.
- The impact of digital technologies on the music industry and artist revenues.
- The effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy in treating insomnia.
- The relationship between social media use and body weight perception among young adults.
- The effects of green spaces on mental health and well-being in urban areas.
- The role of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing substance use disorders.
- The impact of workplace bullying on employee turnover and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy in treating mental health disorders.
- The relationship between teacher-student relationships and academic achievement.
- The effects of social support on resilience in individuals experiencing adversity.
- The role of cognitive aging in driving safety and mobility.
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- The relationship between social media use and sleep quality.
- The effects of cultural competency training on healthcare providers’ attitudes and behaviors towards diverse patient populations.
- The role of exercise in preventing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- The impact of the gig economy on job security and worker rights.
- The effectiveness of art therapy in promoting emotional regulation and coping skills in children and adolescents.
- The relationship between parenting styles and child academic achievement.
- The effects of social comparison on well-being and self-esteem.
- The role of nutrition in promoting healthy aging and longevity.
- The impact of gender diversity in leadership on organizational performance.
- The effectiveness of family-based interventions in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between social media use and perceived loneliness among older adults.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on pain management in chronic pain patients.
- The role of physical activity in preventing and treating depression.
- The impact of cultural differences on communication and conflict resolution in international business.
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between student engagement and academic success in higher education.
- The effects of discrimination on mental health outcomes in minority populations.
- The role of virtual reality in enhancing learning experiences.
- The impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) in treating chronic pain.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among men.
- The effects of exposure to nature on cognitive functioning and creativity.
- The role of spirituality in coping with illness and disability.
- The impact of automation on employment and job displacement.
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in treating borderline personality disorder.
- The relationship between teacher-student relationships and school attendance.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on workplace stress and burnout.
- The role of exercise in promoting cognitive functioning and brain health in older adults.
- The impact of diversity and inclusion initiatives on organizational innovation and creativity.
- The effectiveness of cognitive remediation therapy in treating schizophrenia.
- The relationship between social media use and body dissatisfaction among women.
- The effects of exposure to natural light on mood and sleep quality.
- The role of spirituality in enhancing well-being and resilience in military personnel.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job training and skill development.
- The effectiveness of interpersonal therapy (IPT) in treating depression.
- The relationship between parental involvement and academic achievement among low-income students.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on emotional regulation and coping skills in trauma survivors.
- The role of nutrition in preventing and treating mental health disorders.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...
Jump to navigation

Search form
Identify your research interests.
As an undergraduate student, you are not expected to know exactly what your area of focus will be. Most likely, you are still discovering and developing your interests and that's okay. However, without having some ideas about what you're interested in, you'll quickly find that searching for opportunities can be overwhelming.
Map Out Your Interests
To figure out what your interests are, take some time and write down 3-5 responses to each of these questions:
- What subjects covered in my field(s) of study interest me the most? (do this for each major/minor you have)
- Which class or classes have been the most interesting, what specifically made them interesting, and what questions did I still have after the class finished?
- What questions or problems am I most interested in exploring and/or solving?
- What other topics, areas, or fields am I interested in outside of my major/minor?
- What research topics relate to that field or sector I want to end up in and/or what interests me in that field?
- What (if any) research topics relate to my hobbies, personal interests, or extracurricular activities?
- What skills am I interested in developing which aren't addressed by my major/minor?
Now, look over all of your responses and see if there are any common themes. Did the same topic come up more than once? Are any of the topics closely related or linked? Make a note these to help focus your search for a research opportunity.
Lastly, think a little bit about the things you know you don't want to do or are not interested in. Make a note of them in order to help you identify opportunities that won't be a good fit.
Think About How You Want To Get Involved
The next thing you'll want to think about is how you might want to get involved in research. Below are some questions to help guide you:
- What kind of experience do you want: do you want to work in a lab or do you want to work in the field?
- Are you ok working on a team as part of a larger research topic/question or do you want to do your own original research?
- Do you want to be part of a big team, do you want to work on a smaller project, or would you prefer to work one-on-one with a faculty member / graduate student?
- Do you want to do research related to your field(s) of study and deepen your understanding / experience or do you want to do research outside your field of study and broaden your understanding / experience?
With this information, you should have a better idea of what you're looking for which will make searching for and finding a research opportunity a bit easier.
Next, visit our Finding Research Opportunities page to learn about searching for a research opportunity.
Choosing and Refining Topics
When we are given a choice of topics to write on, or are asked to come up with our own topic ideas, we must always make choices that appeal to our own interests, curiosity, and current knowledge. If you decide to write an essay on same sex marriage, for instance, it is obvious that you should make that decision because you are interested in the issue, know something about it already, and/or would like to know more about it. However, because we rarely write solely for our own satisfaction, we must consider matters other than our own interests as we choose topics.
A Definition of a Topic
A topic is the main organizing principle of a discussion, either verbal or written. Topics offer us an occasion for speaking or writing and a focus which governs what we say. They are the subject matter of our conversations, and the avenues by which we arrive at other subjects of conversations. Consider, for instance, a recent class discussion. Although your instructor determined what topic you discussed initially, some students probably asked questions that led to other topics. As the subjects of our discussions lead to related subjects, so do the topics we write about lead to related topics in our academic studies. However, unlike the verbal conversations we have, each individual piece of writing we produce usually focuses on a single topic. Most effective writers learn that when they present a well-defined, focused, and developed topic, they do a better job of holding their readers' attention and presenting appropriate information than if they had not attempted to place boundaries on the subject of their writing.
Arriving at Topics for Writing Assignments
In academic writing, topics are sometimes dictated by the task at hand. Consider, for example, that you must conduct a lab experiment before you can sit down to write a report. Or perhaps you have to run a statistical program to get your data. In these situations, your topic is determined for you: You will write about the results of the work you have completed. Likewise, your instructor may simply hand you a topic to explore or to research. In these situations, you are delivered from both the responsibility and the rewards of choosing your own topic, and your task is to try to develop an interest in what you have been given to write about.
More often, however, you will have a bit more leeway in choosing topics of your own. Sometimes you will be asked to find a topic of interest to you that is grounded in ideas developed in shared class readings and discussions. Other times, your assignment will be anchored even less, and you will be responsible for finding a topic all on your own. Many students find that the more freedom they are given to pursue their own interests, the more intimidated they are by this freedom, and the less certain they are of what really is interesting to them. But writing assignments with open topic options can be excellent opportunities either to explore and research issues that are already concerns for you (and which may even have been topics of earlier writing) or to examine new interests. A well chosen writing topic can lead to the types of research questions that fuel your academic interests for years to come. At the very least, though, topics can be seen as occasions for making your writing relevant and meaningful to your own personal and academic concerns.
How Purpose and Audience Affect the Choice of Topics
Before choosing and narrowing a topic to write about, consider why you are writing and who will read what you write. Your writing purpose and audience often dictate the types of topics that are available to you.
In the workplace, purpose and audience are often defined for you. For instance, you might have to write a memo to a co-worker explaining why a decision was made or compose a letter to a client arguing why the company cannot replace a product. In either case, your purpose and audience are obvious, and your topic is equally evident. As a student, you may have to work a little harder to determine which topics are appropriate for particular purposes and audiences.
Oftentimes, the wording of your assignment sheet will offer clues as to the reasons why you are writing and the audience you are expected to address. Sometimes, when assignment sheets are unclear or when you misunderstand what is expected of you, you will need either to ask your instructor about purpose and audience or to make your own educated guess. However you arrive at the purpose and the audience of your writing, it is important to take these elements into consideration, since they help you to choose and narrow your topic appropriately.
Interpreting the Assignment
Steve Reid, English Professor It's important to circle an assignment's key words and then ask the instructor to clarify what these words mean. Every teacher has a different vocabulary. My students always ask me what I'm looking for when I give an assignment. As a writer, you need to know what the words mean in your field and what they mean to your instructor.
Many times, an assignment sheet or verbal assignment given by an instructor will reveal exactly what you are being asked to do. The first step in reviewing an assignment sheet is to circle key words or verbs, such as "explain," "describe," or "evaluate." Then, once you've identified these words, make sure you understand what your instructor means by them. For example, suppose your instructor asks you to describe the events leading up to World War II. This could mean explain how the events prior to World War II helped bring about the beginning of the war, or list every possible cause you think led to the war, or describe and analyze the events. Inquiring before you start writing can help you determine your writing purpose and the expectations of your intended audience (usually your instructor).
How Purpose Affects Topics
Your purpose helps you to narrow a topic, since it demands particular approaches to a general subject. For example, if you're writing about how state policy affects foreign language study in grades K-12 in Oregon, you could have several different purposes. You may need to explain how the Oregon law came about; that is, what influenced it and who was responsible. Or perhaps you would need to explain the law's effects, how curriculum will be altered, etc. Another purpose might be to evaluate the law and to propose changes. Whatever purpose you decide to adopt will determine the questions which give direction to your topic, and (in the case of a research paper) will suggest the type of information you will need to gather in order to address those questions.
How Audience Affects Topics
Steve Reid, English Professor You have to be careful so your topic is not too narrow for your audience. You don't want readers to say, " Well, so what? I couldn't care less." One the most important roles a topic plays is impacting an audience. If your topic gets too narrow and too focused, it can become too academic or too pedantic. For example, every year at graduation, I watch people laugh when they hear the title of a thesis or dissertation. The students who wrote these documents were very narrowed and focused, but their audiences were very restricted.
Having a clear idea of the audience to whom you are writing will help you to determine an appropriate topic and how to present it. For example, if you're writing about how state policy affects foreign language study in grades K-12 in Oregon, you could have many different audiences. You could be writing for teachers, administrators at a specific school, students whose educational program will be affected by the law, or even the PTA. All of these audiences care about the topic since they are all affected by it. However, for each of them you may need to provide different information and address slightly different questions about this topic. Teachers would want to know why the policy was created and how it will affect what goes on in their classrooms. Parents will want to know what languages their children will be taught and why. Administrators will want to know how this will change the curriculum and what work will be required of them as a result. Knowing your audience requires you to adapt and limit your topic so that you are presenting information appropriate to a specific group of interested readers.
Choosing Workable Topics
Most writers in the workplace don't have to think about what's workable and what's not when they write. Writing topics make themselves obvious, being the necessary outcome of particular processes. For example, meetings inspire memos and minutes; research produces reports; interactions with customers result in letters. As a student writer, your task is often more difficult than this, since topics do not always "find you" this easily.
Finding and selecting topics are oftentimes arduous tasks for the writer. Sometimes you will find yourself facing the "blank page" or "empty screen" dilemma, lacking topic ideas entirely. Other times you will have difficulties making your ideas fit a particular assignment you have been given. This section on "Choosing a Workable Topic" addresses both of these problems, offering both general strategies for generating topic ideas and strategies for finding topics appropriate to particular types of writing assignments that students frequently encounter.
How to Find a Topic
Don Zimmerman, Journalism and Technical Communication Professor I look at topics from a problem solving perspective and scientific method. Topics emerge from writers working on the job when they're in the profession, following major trends, developments, issues, etc. From the scientific perspective, topics emerge based on solid literature reviews and developing an understanding of the paradigm. From these then come the specific problems/topics/subjects that professionals or scientists address. Writers generate topics from their professional expertise, their understanding of the issues in their respective disciplines, and their understanding the science that has gone before them.
While your first impulse may be to dash off to the library to dig through books and journals once you've received an assignment, you might also consider other information sources available to you.
Related Information: Making Use of Computer Sources
One valuable source of topic ideas is an Internet search. Many sites can provide you with current perspectives on a subject and can lead you to other relevant sites. You can also find and join newsgroups where your general subject or topic is discussed daily. This will allow you to ask questions of experts, as well as to read what issues are important.
Related Information: Making Use of Library Sources
It is always helpful, particularly in the case of writing assignments which demand research, to visit the library and talk to a reference librarian when generating topic ideas. This way, you not only get to discuss your topic ideas with another expert, but you will also have more resources pointed out to you. There is usually a wealth of journals, reference books, and online resources related to your topic area(s) that you may not even know exist.
Related Information: Talking to Others Around You
The people around you are often some of the best sources of information available to you. It is always valuable to talk informally about your assignment and any topic ideas you have with classmates, friends, family, tutors, professionals in the field, or any other interested and/or knowledgeable people. Remember, too, that a topic is not a surprise gift that must be kept from your instructor until you hand in your paper. Instructors are almost always happy to discuss potential topics with a student once he or she has an idea or two, and getting response to your work early in the writing process whenever possible is a good plan. Discussing your topic ideas in these ways may lead you to other ideas, and eventually to a well-defined topic.
Subjects and Topics
Most topic searches start with a subject. For example, you're interested in writing about languages, and even more specifically, foreign languages. This is a general subject. Within a general subject, you'll find millions of topics. Not only about every foreign language ever spoken, but also about hundreds of issues affecting foreign languages. But keep in mind that a subject search is always a good place to start.
Every time you use Yahoo or other Internet search engines, or even SAGE at the CSU library, you conduct a subject search. These search devices allow you to review many topics within a broad subject area. While it's beneficial to conduct subject searches, because you never know what valuable information you'll uncover, a subject always needs to be narrowed to a specific topic. This way, you can avoid writing a lengthy book and focus instead on the short research paper you've been assigned.
Starting With What You Know
Kate Kiefer, English Professor Most often the occasion dictates the topic for the writing done outside academe. But as a writer in school, you do sometimes have to generate topics. If you need help determining a topic, create an authority list of things you have some expertise in or a general list of areas you know something about and are interested in. Then, you can make this list more specific by considering how much you know and care about these ideas and what the target audience is probably interested in reading about.
In looking for writing topics, the logical first step is to consider issues or subjects which have concerned you in the past, either on the basis of life experience or prior writing/research. If you are a journal writer, look to your journal for ideas. If not, think about writing you have done for other writing assignments or for other classes. Though it is obviously not acceptable to recycle old essays you have written before, it is more than acceptable (even advisable) to return to and to extend topics you have written about in the past. Returning to the issues that concern you perennially is ultimately what good scholarship is all about.
Related Information: Choosing Topics You Want to Know More About
Even though your personal experience and prior knowledge are good places to start when looking for writing topics, it is important not to rule out those topics about which you know very little, and would like to know more. A writing assignment can be an excellent opportunity to explore a topic you have been wanting to know more about, even if you don't have a strong base knowledge to begin with. This type of topic would, of course, require more research and investigation initially, but it would also have the benefit of being compelling to you by virtue of its "newness."
Related Information: How to Pull Topics from Your Personal Experience
It is a good idea to think about how elements of your own life experience and environment could serve as topics for writing, even if you have never thought of them in that way. Think about the topics of recent conversations you have had, events in your life that are significant to you, problems in your workplace, family issues, matters having to do with college or campus life, or current events that evoke response from you. Taking a close look at the issues in your immediate environment is a good place to start in writing, even if those issues seem to you at first to be unworthy of your writing focus. Not all writing assignments have a personal dimension, but our interests and concerns are always, at their roots, personal.
General Strategies for Coming Up With Topics
Before attempting to choose or narrow a topic, you need to have some ideas to choose from. This can be a problem if you are suffering from the "blank page or screen" syndrome, and have not even any initial, general ideas for writing topics.
Brainstorming
As writers, some of our best ideas occur to us when we are thinking in a very informal, uninhibited way. Though we often think of brainstorming as a way for groups to come up with ideas, it is a strategy that individual writers can make use of as well. Simply put, brainstorming is the process of listing rough thoughts (in any form they occur to you: words, phrases, or complete sentences) that are connected (even remotely) to the writing assignment you have before you or the subject area you already have in mind. Brainstorming works best when you give yourself a set amount of time (perhaps five or ten minutes), writing down anything that comes to mind within that period of time, and resisting the temptation to criticize or polish your own ideas as they hit the page. There is time for examination and polishing when the five or ten minutes are over.
Freewriting
Freewriting is a technique much like brainstorming, only the ideas generated are written down in paragraph rather than list form. When you freewrite, you allow yourself a set amount of time (perhaps five or ten minutes), and you write down any and every idea that comes to mind as if you are writing a timed essay. However, your freewrite is unlikely to read like an organized essay. In fact, it shouldn't read that way. What is most important about freewriting is that you write continuously, not stopping to check your spelling, to find the right word, or even to think about how your ideas are fitting together. If you are unable to think of something to write, simply jot out, "I can't think of anything to write now," and go on. At the end of your five or ten minutes, reread what you have written, ignore everything that seems unimportant or ridiculous, and give attention to whatever ideas you think are worth pursuing. If you are able to avoid checking yourself while you are writing for that short time, you will probably be surprised at the number of ideas that you already have.
Clustering is a way of visually "mapping" your ideas on paper. It is a technique which works well for people who are able to best understand relationships between ideas by seeing the way they play themselves out spatially. (If you prefer reading maps to reading written directions, clustering may be the strategy for you.) Unlike formal outlining, which tends to be very linear, clustering allows you to explore the way ideas sprawl in different directions. When one thought leads to another, you can place that idea on the "map" in its appropriate place. And if you want to change its position later, and connect it with another idea, you can do so. (It is always a good idea to use a pencil rather than a pen for clustering, for this very reason.)
This is a good strategy not only for generating ideas, but also for determining how much you have to say about a topic (or topics), and how related or scattered your ideas are.
Related Information: Example of Brainstorming
Ideas on a Current Issue:
- multiculturalism
- training of teachers
- teaching strategies
- cultural difference in the classroom
- teaching multicultural texts
- language issues
- English only
- assimilation, checking cultural identity at the door
- home language/dialect as intentionally different from school language
- How many languages can we teach? (How multi-lingual must teachers be?)
- Is standard English really "standard"?
- success in school
- statistics on students who speak "non-English" languages or established dialects
- the difference between a dialect and a language
- Ebonics v. bi-lingual education
Related Information: Example of Freewriting
Problem: Development of Small Towns in the Rocky Mountain Region
When I grew up in Anyoldtown, New Mexico, it was a small town in the smallest sense: no movie theaters, no supermarkets, nothing. We had to go into town for the things we needed. Land sold for $2000 an acre. Now it sells for about $50,000 an acre. Anyoldtown was also primarily hispanic, and the families who lived there had very little. Now the people who live there are mostly white and almost exclusively professionals: doctors, lawyers, stockbrokers, and an endless number of people who have money that seems to have come from nowhere. There are good things to be had there now: good restaurants, good coffee, and all the other things that come along with Yuppie invasion. But those things were had at quite a cost. People who used to live in Anyoldtown when I was a kid can no longer afford to pay property taxes. I can't think of anything else to write now. Oh, yes...these people made a killing off the sale of their land and properties, but they had to give up the places they had lived all their lives. However, by the time they sold, Anyoldtown was no longer the place where they had lived all their lives anyway.
Strategies for Finding Topics Appropriate to Particular Types of Assignments
Sometimes your ways of generating topics will depend on the type of writing assignment you have been given. Here are some ideas of strategies you can use in finding topics for some of the more common types of writing assignments:
Essays Based on Personal Experience
Essays responding to or interpreting texts.
- Essays in Which You Take a Position on an Issue (Argument)
Essays Requiring Research
Essays in which you evaluate, essays in which you propose solutions to problems.
The great challenge of using personal experience in essays is trying to remember the kinds of significant events, places, people, or objects that would prove to be interesting and appropriate topics for writing. Brainstorming, freewriting, or clustering ideas in particular ways can give you a starting point.
Here are a few ways that you might trigger your memory:
Interview people you've known for a long time.Family members, friends, and other significant people in your life can remember important details and events that you haven't thought about for years.
Try to remember events from a particular time in your life. Old yearbooks, journals, and newspapers and magazines can help to trigger some of these memories.
Think about times of particular fulfillment or adversity. These "extremes" in your experience are often easily recalled and productively discussed. When have you had to make difficult choices, for instance? When have you undergone ethical struggles? When have you felt most successful?
Think about the groups you have encountered at various times in your life. When have you felt most like you belonged to or were excluded from groups of people: your family, cliques in school, clubs, "tracked" groups in elementary school, religious groups, or any other community/organization you have had contact with?
Think about the people or events that "changed your life." What are the forces that have most significantly influenced and shaped you? What are the circumstances surrounding academic, career, or relationship choices that you have made? What changes have you dealt with that have been most painful or most satisfying?
Try to remember any "firsts" in your experience.What was your first day of high school like? What was it like to travel far from home for the first time? What was your first hobby or interest as a child? What was the first book you checked out of the library? These "firsts," when you are able to remember them, can prove to have tremendous significance.
One word of caution on writing about personal experience: Keep in mind that any essay you write for a class will most likely be read by others, and will probably be evaluated on criteria other than your topic's importance to you. Never feel like you need to "confess," dredge up painful memories, or tell stories that are uncomfortable to you in academic writing. Save these topics for your own personal journal unless you are certain that you are able to distance yourself from them enough to handle the response that comes from instructors (and sometimes from peers).
Students are often asked to respond to or interpret essays, articles, books, stories, poems, and a variety of other texts. Sometimes your instructor will ask you to respond to one particular reading, other times you will have a choice of class readings, and still other times you will need to choose a reading on your own.
If you are given a choice of texts to respond to or to interpret, it is a good idea to choose one which is complex enough to hold your interest in the process of careful examination. It is not necessarily a problem if you do not completely understand a text on first reading it. What matters is that it challenges, intrigues, and/or evokes response from you in some way.
Related Information: Writing in the Margins of Texts
Many of us were told at some point in our schooling never to write in books. This makes sense in the case of books which don't belong to us (like library books or the dusty, tattered, thirty year-old copies of Hamlet distributed to us in high school). But in the case of books and photocopies which we have made our own, writing in the margins can be one of the most productive ways to begin the writing process.
As you read, it is a good idea to make a habit of annotating , or writing notes in the margins. Your notes could indicate places in the text which remind you of experiences you have had or of other texts you have read. They could point out questions that you have, points of agreement or disagreement, or moments of complete confusion. Annotations begin a dialogue between you and the text you have before you, documenting your first (and later) responses, and they are valuable when you attempt at a later time to write about that text in a particular way.
Essays in Which You Take a Position on an Issue
One of the most common writing assignments given is some variation on the Arguing Essay, in which students are asked to take a position on a controversial issue. There are two challenges involved in finding topics for argument. One challenge is identifying a topic that you are truly interested in and concerned about, enough so that whatever research is required will be engrossing (or at the very least, tolerable), and not a tedious, painful ordeal. In other words, you want to try to avoid arriving at the "So what?" point with your own topic. The other challenge is in making sure that your audience doesn't respond, "So what?" in reading your approach to your topic. You can avoid this by making sure that the questions you are asking and addressing are current and interesting.
Related Information: Examining Social Phenomena and Trends
In The St. Martin's Guide to Writing , Third Edition, Rise B. Axelrod and Charles R. Cooper discuss the importance of looking toward social phenomena and trends for sources of argument topics. A phenomenon , they explain, is "something notable about the human condition or the social order" (314). A few of the examples of phenomena that they list are difficulties with parking on college campuses, negative campaigning in politics, popular artistic or musical styles, and company loyalty. A trend , on the other hand, is "a significant change extending over many months or years" (314). Some trends they list are the decline of Communism, diminishing concern over world hunger, increased practice of home schooling, and increased legitimacy of pop art. Trying to think in terms of incidental, current social phenomena or long-term, gradual social trends is a good way of arriving at workable topics for essays requiring you to take a position.
Related Information: Making Sure Your Approach to Your Topic is Current and Interesting
In choosing a topic for an arguing essay, it is important to get a handle not only on what is currently being debated, but how it is being debated. In other words, it is necessary to learn what questions are currently being asked about certain topics and why. In order to avoid the "so what" dilemma, you want to approach your topic in a way that is not simplistic, tired, outdated, or redundant. For example, if you are looking at the relationship of children to television, you probably would want to avoid a topic like "the effects of t.v. violence on children" (which has been beaten to death over the years) in favor of a topic like "different toy marketing strategies for young male v.s. female viewers of Saturday morning cartoons" (a topic that seems at least a bit more original).
As a student writer, you are usually not asked to break absolutely new ground on a topic during your college career. However, you are expected to try to find ground that is less rather than more trampled when finding and approaching writing topics.
Trying to think in terms of incidental, current social phenomena or long-term, gradual social trends is a good way of arriving at workable topics for essays requiring you to take a position.
Related Information: Sources of Topics
Looking to Your Own Writing
When trying to rediscover the issues which have concerned you in the past, go back to journal entries (if you are a journal writer) or essays that you have written before. As you look through this formal and informal writing, consider whether or not these issues still concern you, and what (specifically) you now have to say about them. Are these matters which would concern readers other than yourself, or are they too specific to your own life to be interesting and controversial to a reading audience? Is there a way to give a "larger" significance to matters of personal concern? For example, if you wrote in your journal that you were unhappy with a particular professor's outdated teaching methods, could you turn that idea into a discussion of the downfalls of the tenure system? If you were frustrated with the way that your anthropology instructor dismissed your comment about the ways that "primitive" women are discussed, could you think of that problem in terms of larger gender issues? Sometimes your frustrations and mental conflicts are simply your own gripes, but more often than not they can be linked with current and widely debated issues.
Looking to Your Other Classes
When given an assignment which asks you to work with a controversial issue, always try to brainstorm points of controversy that you recall from current or past courses. What are people arguing about in the various disciplines? Sometimes these issues will seem irrelevant because they appear only to belong to those other disciplines, but there are oftentimes connections that can be made. For example, perhaps you have been asked in a communications class to write an essay on a language issue. You might remember that in a computer class on information systems, your class debated whether or not Internet news groups are really diverse or not. You might begin to think about the reasons why news groups are (or aren't) diverse, thinking about the way that language is used.
Reading Newspapers and Magazines
If you are not already an avid newspaper and magazine reader, become one for a week. Pore over the different sections: news, editorials, sports, and even cartoons. Look for items that connect with your own life experiences, and pay attention to those which evoke some strong response from you for one reason or another. Even if an issue that you discover in a newspaper or magazine doesn't prove to be a workable topic, it might lead you to other topic ideas.
Interviewing the People Around You
If you are at a loss to find an issue that lights a fire under you, determine what fires up your friends, family members, and classmates. Think back to heated conversations you have had at the dinner table, or conduct interviews in which you ask the people around you what issues impact their lives most directly. Because you share many experiences and contexts with these people, it is likely that at least some of the issues that concern them will also concern you.
Using the Internet
It is useful to browse the Internet for current, controversial issues. Spend some time surfing aimlessly, or wander through news groups to see what is being discussed. Using the Internet can be one of the best ways to determine what is immediately and significantly controversial.
Although some essays that students are asked to write are to be based solely on their own thoughts and experience, oftentimes (particularly in upper level courses) writing assignments require research. When scoping out possible research topics, it is important to remember to choose a topic which will sustain your interest throughout the research and writing process. The best research topics are those which are complex enough that they offer opportunities for various research questions. You want to avoid choosing a topic that could bore you easily, or that is easily researched but not very interesting to you.
As always, it is good to start searching for a topic within your personal interests and previous writing. You might want to choose a research topic that you have pursued before and do additional research, or you might want to select a topic about which you would like to know more. More than anything, writers must remember that research will often carry them in different directions than they intend to go, and that they must be flexible enough to acknowledge that their research questions and topics must sometimes be adjusted or abandoned. To read more on narrowing and adjusting a research topic, see the section in this guide on Research Considerations.
Related Information: Flexibility in Research
As you conduct your research, it is important to keep in mind that the questions you are asking about your topic (and oftentimes, the topic itself) will probably change slightly. Sometimes you are forced to acknowledge that there is too much or too little information available on the topic you have chosen. Other times, you might decide that the approach you were originally taking is not as interesting to you as others you have found. For instance, you might start with a topic like "foreign language studies in grades K-12 in Oregon," and in the process of your reading you might find that you are really more interested in "bilingual education in rural Texas." Still other times, you might find that the claim you were attempting to make about your topic is not arguable, or is just wrong.
Our research can carry us in directions that we don't always foresee, and part of being a good researcher is maintaining the flexibility necessary to explore those directions when they present themselves.
Related Information: How Research Narrows Topics
By necessity, most topics narrow themselves as you read more and more about them. Oftentimes writers come up with topics that they think will be sufficiently narrow and engaging--a topic like "multiculturalism and education," for instance--and discover through their initial reading that there are many different avenues they could take in examining the various aspects of this broad issue. Although such discoveries are often humbling and sometimes intimidating, they are also a necessary part of any effective research process. You can take some comfort in knowing that you do not always need to have your topic narrowed to its final form before you begin researching. The sources you read will help you to do the necessary narrowing and definition of your focus.
Related Information: Research Topics and Writing Assignments
When you are choosing a research topic, it is important to be realistic about the time and space limitations that your assignment dictates. If you are writing a graduate thesis or dissertation, for instance, you might be able to research a topic as vast and as time-honored as "the portrayal of women in the poetry of William Blake." But if your assignment asks you to produce a five-page essay by next Tuesday, you might want to focus on something a bit more accessible, like "the portrayal of women in Blake's `The Visions of the Daughters of Albion.'"
Related Information: Testing Research Topics
Early in your research and writing process, after you have found a somewhat narrow avenue into your topic, put the topic to the test to see if you really want to pursue it further in research. Rise B. Axelrod and Charles R. Cooper, in The St. Martin's Guide to Writing , Third Edition, suggest some questions writers might ask themselves when deciding whether or not a research topic is workable:
- Does this topic really interest me?
- Do I know enough about it now to plan and write my essay, or can I learn what I need to know in the time I have remaining?
- Is the topic manageable within my time and space limits?
- Do I have a good sense of how others view this issue and what readers I might address in my essay?
- Have I begun to understand the issue and to formulate my own view?
Students are often asked to write essays in which they evaluate something: a product, a piece of writing, a restaurant, an advertising campaign, or some other entity related to their areas of study. Sometimes when you are given this type of writing assignment, you are also given a very specific topic on which to write. Other times, you are asked to find a topic for evaluation on your own.
Related Information: Comparing and Contrasting
After brainstorming a list of possible topics for evaluation, you may find it difficult to determine whether or not you will be able to effectively evaluate those topics. One way of stimulating your mind's evaluative tendencies is to try comparison and contrast. For example, if you are thinking about evaluating a local Thai restaurant, and you are having trouble coming up with points on which to evaluate it, try comparing and contrasting it with another local Thai restaurant. When we begin to compare two items, ideas, places, or people, we invariably wind up evaluating.
Related Information: Generating an Authority List
If the choice of topics to evaluate is open to you, try brainstorming a list of skills, activities, places, or subjects that you consider yourself to be an authority about. A list like this is a good starting point for just about any essay, but it is particularly useful in evaluation. If you are an avid rock climber, for instance, it makes perfect sense for you to evaluate climbing equipment, since your experience will provide you with a basis for evaluation. It may still be necessary to do research, but you will have a head start even before you begin researching.
Related Information: Questions to Ask Yourself as You Evaluate
In testing possible topics for evaluation, you might ask yourself some very general questions about your initial thoughts. Rise B. Axelrod and Charles R. Cooper, in their St. Martin's Guide to Writing , Third Edition, suggest a few such questions:
- How certain am I of my judgment? Do I have any doubts? Why do I feel the way I do?
- Do I like (or dislike) everything about my subject, or only certain parts?
- Are there any similar things I should consider (other products or movies, for example)?
- Is there anything I will need to do right away in order to research this subject authoritatively?
- If I need to do any research, can I get the information I need?
As a writer, you will sometimes be asked to speculate on possible solutions to known problems. Although the process of problem solving is itself quite difficult, one of the greatest challenges about that process is the matter of finding a topic that lends itself to your purpose.
Related Information: Evaluating and Problem Solving
Problem solving is an extension of the evaluating process. If in the past you have written evaluative essays which identify certain problems, these essays might offer you some topic ideas and starting points. You might also look to personal writing you have done (like journal entries) or recent conversations you have had as ways of recalling the types of problems that you have identified in your general environment.
Related Information: Focusing on Solvable Problems
Obviously, not all problems are appropriate topics for short problem solving essays. For example, if your instructor assigns a ten-page problem solving essay dealing with a current problem of your choice, you might want to avoid a topic as vast as "racism." However, if you were to focus on a more context-specific version of this hulking problem, you might find a workable topic (say, for instance, minority enrollment on your campus). For assignments like these, it is important to choose problems that appear solvable (or at least approachable) in the time and space you have available to you.
Related Information: Identifying Problems Within Communities
One excellent source of topics for problem solving essays is your immediate environment. Think about the groups or communities to which you belong: your neighborhood, college, family, ethnic and cultural groups, religious and political groups, workplace, and recreational groups. Try to brainstorm a list of problems that you can readily identify in any of these communities, then consider both how solvable these problems are and how appropriate they are to your writing assignment.
Generating More Than One Topic Idea
In order to choose a topic, you need to have several available to choose from. It is best to avoid being committed to one topic at this first stage of the writing process, since not every topic will pan out. Writers are usually more successful when they have a selection of topics which they can put to the test to determine whether or not they are workable (given the writing assignment).
Narrowing Topics
The scope of a topic depends on how much time and space you have to write and how much detail you are trying to use. For example, describing all the causes of World War II in three pages is impossible. You would have to either narrow your topic some more or write hundreds of pages to adequately discuss every cause. Defining your topic before you start writing will save you time and help you to research and/or to develop your thinking in a clear, methodical way. It is important to examine the topics we choose to determine whether they are too broad (or, in some instances, too narrow) for the writing assignments we are given. Once you have decided that a topic is too broad to be appropriate to your assignment (which is most often the case), you will need to have ways to narrow it. You will also want to consider, when writing essays that require research, how your research resources and limitations affect your choice of topics.
Deciding When a Topic is Too Broad
Kate Kiefer, English Professor If a writer doesn't present details quickly enough, then the topic is usually too broad. If the reader can expect the paper to go in one direction, but it goes in another, the topic is usually too broad or not stated precisely enough. If I can ask six million questions about whether the writer will include this or that point, the topic is too broad. If I do a library search and turn up 200 listings (or an Internet search and discover 1,000 hits), the topic is too broad.
A topic is too broad to be workable when you find that you have too many different (but oftentimes remotely related) ideas about that topic. While you want to start the writing process with as many ideas as possible, you will want to narrow your focus at some point so that you aren't attempting to do too much in one essay.
Where essays requiring research are concerned, your topic is too broad if you are able to find thousands of sources when conducting a simple library or Internet search. For example, conducting a search on "foreign languages in Oregon" will provide you with policies, foreign language departments, and cultural issues (just to name a few). When this happens, you can try various narrowing strategies to determine what most interests you about your topic area and what relates to your own life most readily. For instance, if you plan to study abroad, focusing on the language you'll be speaking might be a way to narrow the scope of your original topic, "foreign languages in Oregon."
Deciding When a Topic Is Too Narrow
Steve Reid, English Professor You have to careful so your topic is not too narrow for your audience. You don't want readers to say, " Well, so what? I couldn't care less." One the most important roles a topic plays is impacting an audience. If you get so narrowed and focused, a topic can become too academic or pedantic. For example, every year at graduation I watch people laugh when they hear the title of a thesis or dissertation. The students who wrote these documents were very narrowed and focused, but their audiences were very restricted.
Though student writers most often face the challenge of limiting a topic that is too broad, they occasionally have to recognize that they have chosen a topic that is too narrow or that they have narrowed a workable topic too much. A topic is too narrow if you can't find any information about it. For example, suppose your foreign language subject to, "foreign language policy in South Dakota." Although you might have a strong interest in this topic, South Dakota may not have a specific policy about foreign languages. If you have chosen the topic, "teaching Chinese in elementary schools," and your research attempts have been fruitless, it may be that you are considering a topic that no one else has previously presented. In other words, no one has determined that Chinese should be a major language taught as commonly as Spanish or French. If this happens to be the case, keep your topic in mind, because it could very well be an excellent topic for a graduate thesis or dissertation. However, it is also likely to be a difficult topic to handle in a ten-page essay for an education class, due in two weeks.
If your topic is too narrow, try making it broader by asking yourself related questions.
- What foreign languages are taught in South Dakota schools?
- Or where is Chinese taught and why?
Once you've found a different direction in which to move with your topic, you can try narrowing it again.
General Strategies for Narrowing Topics
One of the first things writers do when they realize that they need to narrow the scope of their topic is to ask themselves the "w" questions so familiar to journalists: Who? What? Where? When? and Why? (and oftentimes, How?) These questions can help you locate your specific points of interest within your general topic area. For example, to narrow a topic like "foreign languages," you could begin with the "what" and "when" questions and decide you are interested in "foreign language studies in grades K-12." Asking the "where" question, you might arrive at "foreign language studies in grades K-12 in Oregon." And asking the "who" question might cause you to limit the topic again to "state policy regarding foreign language studies in grades K-12 in Oregon." Each time you add something specific to your topic, you place "restrictors" on it, thereby narrowing it. Then, when you conduct a library or Internet search, you can use these "restrictors" as key words.
Related Information: Looping
Looping is an extended version of freewriting in which you begin with an initial five-minute freewrite on a general topic, then select out of that bit of writing the sentence or idea that interests you the most. You then use that sentence or idea as the basis for your next five-minute round of freewriting. You continue this process of elaborating informally on specific ideas until you come to a point where your topic seems sufficiently narrow, researchable, and appropriate to your writing assignment.
Example of Looping If I am freewriting on the general (and overly broad) topic of "development of small towns in the Rocky Mountain region," I might start with the following initial ideas: Problem: Development of Small Towns in the Rocky Mountain Region When I grew up in Anyoldtown, New Mexico, it was a small town in the smallest sense: no movie theaters, no supermarkets, nothing. We had to go into town for the things we needed. Land sold for $2000 an acre. Now it sells for about $50,000 an acre. Anyoldtown was also primarily hispanic, and the families who lived there had very little. Now the people who live there are mostly white and almost exclusively professionals: doctors, lawyers, stockbrokers, and an endless number of people who have money that seems to have come from nowhere. There are good things to be had there now: good restaurants, good coffee, and all the other things that come along with Yuppie invasion. But those things were had at quite a cost. People who used to live in Anyoldtown when I was a kid can no longer afford to pay property taxes. I can't think of anything else to write now. Oh, yes...these people made a killing off the sale of their land and properties, but they had to give up the places they had lived all their lives. However, by the time they sold, Anyoldtown was no longer the place where they had lived all their lives anyway. Rereading what I have written, I might decide that what interests me the most and seems most appropriate to the writing assignment I have been given is my idea about the property tax dilemma. With this in mind, I would write a second "loop" on this area of my thinking, perhaps even starting my freewriting with the exact sentence I used in the first "loop:" People who used to live in Anyoldtown when I was a kid can no longer afford to pay property taxes. This is unfair, because these people spent their entire lives in this town, and land was all they had. Theoretically, the Yuppie Invasion doesn't drive out the "townies" or "natives" of a small town, but in actuality, land values and property taxes (as well as cultural influences, of course) make it impossible (and oftentimes undesirable) for people to hold onto their own land. People have to sell, because if they don't, they can no longer afford to maintain the standard of living that their town has taken on (in more ways than one). This issue obviously has class implications, but I'm sure it also relates to cultural (ethnic) issues as well. This is where I would need to begin researching, if I wanted to see who was most negatively affected by rising property taxes and land values. In rereading this second loop, I might decide that my ideas toward the end of the paragraph interest me the most. I could write another loop expanding these specific ideas on race, class, and property taxes, or I might decide that I have (as my freewrite suggests) arrived at the point where I need to begin researching.
Related Information: Questioning
Alongside the basic "5 W's" ("who," "what," "when," "where," and "why") can be used more formal, directed questions provided by the classical rhetorical "topics." These questions function in four different ways, and can be categorized as follows:
| Definition: | These questions help you to define your topic. |
| Comparison: | These questions ask you to compare and contrast your topic with other related topics. |
| Relationship: | These questions lead you to examine the causes and/or the effects of your topic. |
| Testimony: These questions ask you to determine what has already been said or written about your topic. |
Example of Questioning If my general topic is "Development of Small Towns in the Rocky Mountain Region," I might try to narrow my focus by applying questions with specific functions to this topic area, thereby discovering which approach interests me most. Here are some of the questions I might ask:
| Questions of Definition: | What is the situation in the Rocky Mountain region in terms of development? How can this situation be characterized, described, classified, or analyzed? |
| Questions of Comparison: | How does development in this region compare with development in other regions? In what ways is it similar? In what ways is it different? |
| Questions of Relationships: | What caused this problem of development? What changes occurred which contributed to the problem? What causes people to want to develop this region? What are the effects or the consequences of the development? Who is most directly affected by development of small towns? |
| Testimony: | What do the "natives" or "townies" who have lived all their lives in these towns think about the development? What do contractors think? What have some towns done to control development? What research has already been done on this topic? What is the general opinion(s) in the Rocky Mountain region concerning development, and why? |
After writing the questions, I would write my responses, deciding which particular questions and responses interest me the most. Perhaps, for instance, I would find myself most interested in the effects of development on the "natives" of small towns, particularly the inevitability of increased property taxes. This process of questioning thus provides me with a specific, narrow, well-defined focus within the vast issue of development of small towns in the Rocky Mountain region.
Related Information: Topic Cross
The topic cross helps you to narrow your topic by using a visual strategy. Just as you would focus a camera or a microscope, you arrange key words and phrases about your topic in such a way that they eventually point to your specific area of interest.
Example of a Topic Cross The first step in the process of using the topic cross is brainstorming. Spend a few minutes listing words and phrases that come to mind when you think about your topic. Then decide which words and phrases are most interesting and arrange them in a hierarchy, moving from general (at the top of the list) to specific (at the bottom of the list). This hierarchy will become the vertical axis of your cross. Demonstration: If my topic is "development of small towns in the Rocky Mountain region," I might generate the following useful ideas in brainstorming (arranged from general to specific).
- The appeal of small towns
- Yuppie invasion
- Overcrowding in cities
- Cost of land
- Effects on town "natives."
- Economic effects on impoverished landowners.
- How John Doe in my home town was affected.
- The new espresso bar in town
I would write this list in an imagined middle column of a piece of blank paper or a computer screen, leaving plenty of space between each item. Then I would scan the list to determine where my real interest lies. Which topics in this list will be too broad to write about, given my writing assignment? Which will be too narrow? In this case, I might choose "economic effects on impoverished landowners" as a workable topic area. Once I had thus identified my area of interest, I would begin listing words and phrases about or relevant to that item, placing them on the horizontal axis of my topic cross. The list I would generate about "economic effects on impoverished landowners" might look like this:
- Increased cost of land
- Temptation to sell
- Rising property taxes
- Higher cost of living
- Zoning issues
- Pressure to maintain property value
Examining this list, I might decide that "rising property taxes" is a sufficiently narrow topic that is not too narrow to develop with my own ideas and research I might do. By using this strategy, I have arrived at a narrow, workable topic.
Research Considerations
If your writing assignment requires research, you will probably find that the research process itself will dictate how broad or narrow your topic should be. We have all had the experience of doing a library search on a word like "environment" and coming up with thousands of sources. Almost as common is the experience of searching a term like "cultural animation" and coming up with only one source that seems useful. The topics we choose are often directly related to our research processes and their results.
Moving from Topic to Thesis
It is important to remember that a narrow topic is not the same thing as a thesis statement. Unlike a topic, a thesis makes a claim of fact, provides a claim of value, or makes a recommendation about a topic under consideration. For example, your narrowed topic might be "the underemphasis on foreign language in U.S. secondary schools." A focused thesis statement making a claim about this topic might read, "U.S. secondary schools should require elementary students to take at least one course in a foreign language sometime during the 4th through 6th grades."
Transforming a workable topic into a possible thesis is really just a continuation of the narrowing process, with an emphasis on what you want to say about your topic. In this way, it is much like the "hypothesis" stage of the scientific method. You arrive at a thesis by attempting to make a statement about the topic you have chosen.
Developing a Working Thesis
A working thesis is a tentative statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process, for the purpose of directing your thinking early. This thesis is likely to change somewhat or to be abandoned altogether as you move through the writing process, so it is best not to become too enamored of it.
There are two components of a working thesis. The first is, quite simply, your topic; and the second is your tentative statement about your topic. For example, if my narrowed topic is
"Rising property taxes in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region..."
I might add the following statement about that topic:
"...cause longtime residents and landowners in those towns not to be able to keep their property."
As I begin whatever research is necessary to support this thesis, I might find that I can't make this much of a claim. Or I might find that there are complexities that I hadn't considered. As I uncover new information about my topic, I will want to alter my working thesis accordingly, until it is workable and supportable.
Arriving at a Possible Thesis for an Essay Requiring Research
A In The St. Martin's Handbook , Third Edition [italics], Andrea Lunsford and Robert Connors suggest a process for moving from a topic to a research "hypothesis," by way of examining the "issue" at hand and framing this issue as a "research question." The following is an example of how I might move from topic to hypothesis if my narrowed topic is "rising property taxes in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region."
- Topic: Rising property taxes in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region
- Issue: The effects of these rising taxes on long-time residents and landowners in the small towns
- Research Question: What are the effects of rising property taxes on long-time residents and landowners in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region?
- Hypothesis: Because these taxes are increasingly difficult to pay, small town "natives" find themselves unable to hold onto their property.
This hypothesis, like a working thesis, is simply an early speculation on what I might find when I begin to research. As I read more and more about my topic, I will probably find that I need to make changes to the hypothesis in order to make it a supportable thesis. As I uncover new information about my topic, I will want to alter my working thesis accordingly, until it is workable and supportable.
Arriving at a Possible Thesis for an Essay Requiring You to Take a Position
One of the greatest challenges in written argument is determining what it is that you would like to (and are able to) say about your topic.
Narrowing from Topic to Thesis in Argument
Before you begin drafting an argument paper, you need to decide (tentatively, at least) what it is that you will be arguing about the topic you have chosen. The following prompts should help you focus your argument from a topic to a position on that topic. What is your topic? (e.g.--Rising property taxes in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region) What are three controversies associated with this topic? (e.g.--Rising property taxes make the town affordable only to the wealthy. This changes the flavor the flavor of the town. It forces long-time land owners to sell their land.) What are three questions people might ask about these controversies? (e.g.--Are these rising property taxes, which are the results of development in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region, forcing long-time land owners out of their home towns? Are rising taxes and land values changing the whole cultural and economic foundation of the towns? Given the effects of rising property taxes on impoverished land owners in small towns, is development in this area a good idea?) Decide which of these questions you are most interesting in exploring. (e.g.--Given the effects of rising property taxes on impoverished land owners in small towns, is development in this area a good idea?) Now list several ways people might respond if you asked them your question. (e.g.--No, because impoverished land owners are unable to maintain the new standard of living. Yes, because development is always a good idea. Yes, because development is inevitable, and we can do nothing about it. Perhaps, but city planners and local government must find ways to protect the interests of impoverished land owners when they determine property taxes.) Finally, decide where you stand in this range of responses. Think of a thesis that expresses your view. Write out your thesis and revise it throughout your research process until it is specific and takes a single arguable position. (e.g.--Because impoverished land owners in small towns in the Rocky Mountain region are often badly hurt by the rising property taxes resulting from development, city planners and local government must find ways to protect the interests of these land owners when they determine property taxes.)
Working With Topics in Different Disciplines
Don Zimmerman, Journalism and Technical Communication Professor Writers' understanding of topics and their fields of study allow them to focus on a specific topic. Following a good problem solving process or scientific method can help you select a topic. Whereas on the job, topics emerge from day to day activities. When working, you don't need to look for topics to write about. Your respective field/job responsibilities allow you to find the problems.
The ways that topics are approached and the types of topics that are discussed vary from discipline to discipline. It is important to investigate the types of topics that are discussed (and the ways that they are discussed) in your own discipline. As a writer, it is necessary to determine what topics are talked about and why in your own discipline (or in the discipline for which you are writing). This can be done by way of talking to professionals in the discipline, looking at relevant journals, and conducting Internet and database searches (to name a few possibilities).
Related Information: Browsing Journals Important to Your Discipline
Almost every discipline has journals that are associated with it, and scholars in the discipline depend on these journals in order to remain informed about what topics are being discussed. For example, scholars in the field of psychology rely on psychological journals; doctors rely on medical journals; and English professors rely on literary journals. Because journals are at the center of each discipline's current discussions, it is a good idea to browse them when looking for current topics. If you are unsure of how to go about doing this, talk to a professor in your discipline, a reference librarian in your library, or a librarian in your library's Current Periodicals room. These people can usually provide you with a few titles of important journals relevant to your field. Once you have these titles, you can locate a few issues of each journal in the Current Periodicals room, sit down for an hour or two, and look through the articles to see what is being talked about and what interests you.
Related Information: Online Searches and Databases
One way of getting to the sources which will discuss topics current to your discipline is by searching the various computer databases and search engines related to that discipline. A database is simply an arrangement of information by way of similar subject matter. For example, if you were researching a topic for a Sociology essay on group behavior of Deadheads, you might go to the Social Sciences Index to find sources related to your topic. For information on how to find relevant and useful databases, talk to the reference librarian in your library, or ask an expert in your field which databases he or she uses regularly.
Related Information: Talking to Professionals in Your Discipline
One of the most efficient ways to learn what topics are currently being discussed in your discipline is to talk to the experts: instructors and other professionals working within that discipline. We often forget that these people can be valuable resources to us, and can point us toward books, journals, databases, and other sources of information that scholars in our various fields use often.
Citation Information
Lauel Nesbitt and Dawn Kowalski. (1994-2024). Choosing and Refining Topics . The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

When research is me-search: How researchers’ motivation to pursue a topic affects laypeople’s trust in science
Marlene sophie altenmüller.
Department of Psychology, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany
Leonie Lucia Lange
Mario gollwitzer, associated data.
We provided all materials, the anonymized data and analyses, and supplementary materials online at the Open Science Framework via the following link: https://osf.io/phfq3/ .
Research is often fueled by researchers’ scientific, but also their personal interests: Sometimes, researchers decide to pursue a specific research question because the answer to that question is idiosyncratically relevant for themselves: Such “me-search” may not only affect the quality of research, but also how it is perceived by the general public. In two studies ( N = 621), we investigate the circumstances under which learning about a researcher’s “me-search” increases or decreases laypeople’s ascriptions of trustworthiness and credibility to the respective researcher. Results suggest that participants’ own preexisting attitudes towards the research topic moderate the effects of “me-search” substantially: When participants hold favorable attitudes towards the research topic (i.e., LGBTQ or veganism), “me-searchers” were perceived as more trustworthy and their research was perceived as more credible. This pattern was reversed when participants held unfavorable attitudes towards the research topic. Study 2 furthermore shows that trustworthiness and credibility perceptions generalize to evaluations of the entire field of research. Implications for future research and practice are discussed.
Introduction
“Being a scientist is, at the most fundamental level, about being able to study what’s exciting to you”, says Jeremy Yoder, a gay man studying experiences of queer individuals in science [ 1 ]. Like Yoder, many researchers are passionate about their research and dedicated to their field. After all, they are free to choose research questions they deem important and are interested in. Freedom of science and research secures the independence of the academic from the political and other spheres. In return, researchers are expected to be neutral and objective and make their research process transparent to guarantee that this freedom is not exploited for personal gains.
Just as people differ in what they are interested in in their personal lives, researchers differ in what they find more or less fascinating and worth studying. Such fascination can have multiple causes and is often rooted in a perceived personal connection to a topic. For instance, Sir Isaac Newton allegedly became interested in gravity after an apple fell on his head [ 2 ]. A specific type of personal connection exists when researchers study a phenomenon because they are directly (negatively) affected by that phenomenon. In 1996, Harvard alumni and neuroanatomist Jill Bolte Taylor suffered a rare form of stroke that made her undergo major brain surgery, affected her personal and academic life tremendously, and eventually awakened her interest in studying the plasticity of the brain [ 3 ]. In 2006, she published an award-winning book covering her research and her personal story that led her to pursue this path. The Jill Bolte Taylor case is, thus, a prototypical example for such “me-search”: researchers studying a phenomenon out of a particular personal affection by (or connection to) this phenomenon. “Me-search” thus means pursuing a scientific question when the answer to that question is idiosyncratically relevant for the individual researcher (as opposed to when the answer is relevant per se).
Being directly affected by a phenomenon provides researchers studying it with a high degree of expertise and motivation: Jill Bolte Taylor, for instance, claims to bring a deep personal understanding and compassion to her research and work with patients [ 4 , 5 ]. That said, being personally affected may also come at the cost of losing one’s scientific impartiality and neutrality for the subject: Jill Bolte Taylor was criticized for being overly simplistic in her scientific claims and mixing them with esoteric ideas, and for pushing her own agenda (i.e., selling her story) by dramatizing her own experiences [ 4 – 7 ].
While some criticized Jill Bolte Taylor heavily, the general public does not seem to have a problem with her research as “me-search”. Her book is currently translated into 30 languages, and thousands of people visit her talks and keynote addresses [ 4 – 6 ]. Does that suggest that the general public tends to turn a blind eye on conflicts of interest that may arise from a researchers’ personal affection by their research object? While the Jill Bolte Taylor case seems to suggest so, research on science communication and public understanding of science has shown that people are highly sensitive to potential conflicts of interest arising from researchers’ personal involvement: perceiving researchers as pursuing an “agenda” for personal reasons is a major factor predicting people’s loss of trust in researchers and science [ 8 – 11 ]. On the other hand, people may see personal (“autoethnographic”) experiences of researchers personally affected by their topic as valuable and laudable ‒ it may imply that “they know what they’re talking about” [ 12 – 14 ]. Similarly, revealing a personal interest or even passion for a particular research topic (e.g., due to being personally affected) could also overcome the stereotypical perception of scientists as distant “nerds in the ivory tower” [ 15 , 16 ]: researchers who openly disclose the idiosyncratic relevance of their research topic may appear more approachable, more likeable, and more trustworthy [ 17 – 19 ].
Thus, the public’s reaction to “me-search” seems to be ambivalent and contingent on certain boundary conditions. Thus, the question we are going to address in this article is whether and when ‒ that is, under which circumstances ‒ a researcher’s personal affection by a research topic (“me-search”) positively vs. negatively impacts public perceptions regarding the trustworthiness of the respective researcher (and the entire research area in general) and the extent to which this researcher’s findings are perceived as credible .
Perceivers’ motivated stance as a moderating variable
This potentially ambivalent perception of “research as me-search” can be understood from a motivated reasoning [ 20 ] perspective: Laypeople receive and process information in a manner biased towards their own beliefs, expectations, or hopes. This also applies to the reception of scientific information [ 21 , 22 ]: For example, laypeople are more likely to dismiss scientific evidence if it is inconsistent with their beliefs [ 23 , 24 ] or if it threatens important (moral) values [ 25 , 26 ] or their social identity, respectively [ 27 – 29 ].
However, identity-related and attitudinal motivated science reception might differ in their underlying mechanisms. For identity-related motivated science reception, biased perception of information, which is relevant to a social identity, is driven by a defense motivation to protect this positive social identity [ 30 ]. Thus, identity-threating scientific information is countered by identity-protection efforts, such as discrediting the findings and the source. These efforts will be more pronounced among strongly identified individuals [ 27 – 29 ]. For attitudinal motivated science reception, however, the mechanism might function as a broader perception filter. When confronted with new scientific information about the respective attitude object, the perceptual focus will be directed at clues helping to uphold prior attitudes (i.e., confirmation bias [ 31 ]): Potentially attitude-inconsistent information is attenuated, while potentially attitude-consistent information is accentuated. The ambivalent nature of “me-search” might allow to be easily bend in such a motivated manner and, thus, lead to biased perceptions of a researcher either way: when the findings are in line with one’s prior beliefs, being personally affected may be considered an asset–the respective researcher is perceived as more trustworthy and his/her findings as more credible (compared to no idiosyncratic relevance). However, when the findings are inconsistent with one’s prior beliefs, idiosyncratic relevance may be considered a flaw–the respective research is perceived as biased, untrustworthy, and less competent, and his/her findings are likely perceived as less credible than when idiosyncratic relevance is absent.
Prior research on motivated science reception mainly focused on laypeople’s reactions towards specific scientific findings: after learning about the outcome of a particular study, participants dismiss the research (and devalue the researcher) if these outcomes are consistent vs. inconsistent with their prior beliefs [ 23 – 25 , 27 – 29 ]. However, people might be prone to motivated science reception even before results are known, judging researchers proverbially just by their cover (e.g., by biographical data, personal and scientific interests and motivations). People who hold positive attitudes towards a certain research topic might perceive “me-searchers” as more trustworthy and anticipate their results to be more credible (before knowing the specific outcomes). By contrast, people who hold negative attitudes towards a certain research topic they might trust “me-searchers” less and expect their findings to be less credible.
Additionally, motivated reception processes can be extended over and above the specific information under scrutiny and lead to questioning the scientific method in itself–a phenomenon termed the “scientific impotence excuse” [ 32 ]. In line with that, critical evaluations of specific researchers and their findings are sometimes generalized to the entire field of research [ 27 ]. Thus, the fact that a researcher engages in “me-search” might be interpreted in a way that fits best to one’s preexisting convictions and may generalize to the entire field of research.
The present research
In two studies, laypeople read alleged research proposals concerning potentially polarizing research topics (i.e., LGBTQ issues and veganism) which were submitted by researchers who disclosed being either personally affected or not affected by the respective topic. We investigated whether ( Study 1 ) and when (i.e., moderated by preexisting positive attitudes towards the respective research topic, Studies 1 and 2) such “me-search” information increased or decreased laypeople’s perceptions regarding these researchers’ epistemic trustworthiness and the anticipated credibility of their future scientific findings. Of note, we use the term “credibility” to differentiate evidence-related trust/credibility from person-related trust/credibility (i.e. “trustworthiness”). Further, we test whether one researcher’s “me-search” impacts the evaluation of the entire respective field ( Study 2 ).
For both studies in this paper, we report how we determined our sample size, all data exclusions (if any), all manipulations, and all measures [ 33 ]. All materials, the anonymized data, and analyses are available online at the Open Science Framework (OSF; see https://osf.io/phfq3/ ). Before starting the respective study, informed consent was obtained. Participants read a GDPR-consistent data protection and privacy disclosure declaration specifically designed for the present study. Only participants who gave their consent could start the respective survey. According to German laws and ethical regulations for psychological research [ 34 ], gathering IRB approval is not necessary if (i) the data are fully anonymized, (ii) the study does not involve deception, (iii) participants’ rights (e.g., voluntary participation, the right to withdraw their data, etc.) are fully preserved, and (iv) participating in the study is unlikely to cause harm, stress, or negative affect. The present studies met all of these criteria; therefore, no IRB approval had to be obtained.
In our first study, we conducted an online experiment investigating the main effect of a researcher’s disclosure of being personally affected vs. not affected by their research on their trustworthiness and the credibility of their future research. Further, we tested whether laypeople’s preexisting attitudes towards the research topic moderate this effect.
Four-hundred and eleven German participants were recruited via mailing lists and social networks. Ninety-seven participants had to be excluded due to pre-specified criteria: Sixty-seven participants failed the manipulation check; 25 participants failed the pre-specified time criteria (viewing the manipulation stimulus less than 30sec, taking less than 3min or more than 20min for participation); 5 participants had apparently implausible response patterns (e.g., “straight-lining;” identical responses on every single item on more than one questionnaire page in a row). Eighty-five further participants failed the attention check. Excluding them did not change the overall results, so, for the sake of statistical power, we did not exclude these 85 cases. The final sample consisted of N = 314 participants. We conducted sensitivity analyses using G*Power [ 35 ] for determining which effect sizes can detected with this sample in a moderated (multiple) regression analysis: At α = 0.05 and with a power of 80%, small-to-medium effects (f 2 ≥0.03) can be detected with this sample. Participants were mostly female (74% female, 25% male, 2% other) and their age ranged between 16 and 68 years ( M = 26.79; SD = 10.18). Most participants were currently studying at a university (71%; working: 21%; unemployed or other: 8%). Participants who were currently studying or already had a university degree (93%) came from a variety of disciplines (law, economics, and social sciences: 49%; humanities: 16%; mathematics and natural sciences: 14%; medicine and life sciences: 11%; engineering: 4%).
Materials and procedure
After obtaining informed consent, we asked participants to imagine they were browsing the website of a research institute and came across a short proposal for a new research project by a researcher named Dr. Lohr (no gender was indicated for greater generalizability and avoiding possible gender confounds). Next, participants read the beginning of the alleged proposal of a planned research project for which Dr. Lohr was allegedly applying for external funding. The text briefly introduced the planned project (i.e., investigating social reactions to queer employees at the workplace) and a statement of Dr. Lohr explaining why they were interested in conducting this project. Participants were randomly allocated to two groups. In the “not personally affected” condition, Dr. Lohr wrote:
“ I am interested in investigating this research topic in more detail not only out of scientific reasons but also because I–as someone who does not identify as homosexual and is not affected by my own research–really think we need more evidence-based knowledge about queer topics which we can implement in everyday life .”
In the “personally affected” condition, Dr. Lohr wrote:
“ I am interested in investigating this research topic in more detail not only out of scientific reasons but also because I–as someone who identifies as homosexual and is affected by my own research–really think we need more evidence-based knowledge about queer topics which we can implement in everyday life .”
We added a definition for the word “queer” below the proposal: “ Queer is a term used as self-description by people who do not identify as heterosexual and/or who do not identify with the gender assigned at birth . The term is often used as umbrella term for LGBTQ (lesbian , gay , bisexual , trans and queer) and describes all people who identify as queer .” After completing an attention check question (see pre-registration), we measured participants’ trust in Dr. Lohr with the Muenster Epistemic Trustworthiness Inventory (METI; [ 36 ]), which was constructed for measuring trust in experts encountered online. It consists of 14 opposite adjective pairs measuring an overall trustworthiness score (Cronbach’s α = .95) as well as the sub-dimensions expertise (e.g., competent–incompetent, Cronbach’s α = .92) and integrity/benevolence (e.g., honest–dishonest, Cronbach’s α = .93) on 6-point bipolar Likert scales. Factor analyses (see Appendix A in the supplementary materials, https://osf.io/phfq3/ ) suggest that a two-factor model (with expertise and integrity/benevolence) fit the data better than a three-factor model (as suggested by [ 36 ]), corroborating the idea of a cognitive-rational dimension and an affective dimension of trustworthiness [ 37 ]. Next, participants rated the extent to which they found Dr. Lohr’s research credible on a 6-point Likert scale ranging from 1 = “not at all” to 6 = “very much” (6 items, e.g., “I think Dr. Lohr’s future findings will be credible;” “I will be critical of Dr. Lohr’s research results” (reverse-coded); Cronbach’s α = .84).
Next, we measured participants’ own positive attitudes towards LGBTQ issues—the moderator variable in our design—with eleven statements developed from research on sympathy, group attitudes, and allyship [ 38 , 39 ] rated on a 6-point Likert scale ranging from “not at all” to “very much” (e.g., “I think that LGBTQ-related topics receive more attention than necessary” (reverse-coded); “I am open to learning more about concerns raised by LGBTQ people;” Cronbach’s α = .93). Next, we conducted a manipulation check by asking participants to indicate whether Dr. Lohr disclosed being personally affected by their research (“Dr. Lohr stated being personally affected;” “Dr. Lohr stated not being personally affected;” “Dr. Lohr did not say anything about being affected or not”).
Finally, we measured demographic variables (age, gender, occupation, academic discipline) and control variables: general perceptions of researchers’ neutrality (self-developed 6-point bipolar scale with 4 adjective-pairs, e.g. subjective–objective, and 6 distractor pairs, e.g. introverted–extraverted, Cronbach’s α = .81) and Public Engagement with Science (PES) with two measures adapted from a survey by the BBVA Foundation [ 40 ]: a 5-item scale measuring PES frequency (e.g., “How often do you read news about science?” 5-point Likert scale ranging from 0 =“never” to 5 =“almost daily,” Cronbach’s α = .78) and a multiple choice question measuring 15 potential PES experiences during the last 12 months (e.g., “I know someone who does scientific research;” “I visited a science museum”). Participants had the opportunity to participate in a lottery and sign up for more information and were debriefed.
Our randomized groups did not differ in regard to general perception of neutrality in science ( p = .924) or PES (PES frequency, p = .709; PES experiences, p = .533). Table 1 summarizes all means, standard deviations, correlations and internal consistencies of the measured variables.
| Variable | α | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Expertise | 4.61 | 0.91 | .92 | |||||||
| 2. Integrity/benevolence | 4.94 | 0.79 | .93 | .72 | ||||||
| 3. Epistemic trustworthiness | 4.80 | 0.79 | .95 | .92 | .94 | |||||
| 4. Credibility | 4.10 | 0.92 | .84 | .68 | .68 | .73 | ||||
| 5. Attitudes towards LGBTQ | 4.93 | 1.02 | .93 | .23 | .32 | .30 | .47 | |||
| 6. Neutrality expectation | 4.12 | 0.88 | .81 | .17 | .17 | .18 | .10 | .08 | ||
| 7. PES frequency | 3.25 | 0.71 | .78 | -.08 | -.09 | -.09 | -.08 | -.07 | .10 | |
| 8. PES experiences | 6.92 | 2.98 | - | -.11 | -.05 | -.09 | -.02 | -.03 | .05 | .56 |
Note . N = 314.
* indicates p < .05.
** indicates p < .01.
*** indicates p < .001. α represents internal consistencies (Cronbach’s α). Variables 1–6 ranged from 1 to 6, variable 7 ranged from 1–5 and variable 8 ranged from 0–15.
Main effect of being personally affected
First, we tested the main effect of the researcher’s disclosure of being personally affected on epistemic trustworthiness and credibility of future findings. Laypeople trusted Dr. Lohr significantly more in the “personally affected” condition ( M = 4.92, SD = 0.75) than in the “not personally affected” condition ( M = 4.66, SD = 0.81), t (312) = 2.93, p = .004, d = 0.33, 95% CI d [0.11; 0.56]. For credibility, the difference between the “personally affected” condition ( M = 4.15, SD = 0.96) and the “not personally affected” condition ( M = 4.04, SD = 0.86) was not significant, t (312) = 1.02, p = .306, d = 0.12, 95% CI d [-0.11; 0.34]. Further exploring the two dimensions of epistemic trustworthiness, Dr. Lohr was perceived as higher on integrity/benevolence, t (312) = 3.19, p = .002, d = 0.36, 95% CI d [0.14; 0.59], and on expertise, t (312) = 2.17, p = .030, d = 0.25, 95% CI d [0.02; 0.47] when disclosing being personally affected.
Moderation by pre-existing attitudes
Second, we tested whether the effect of being personally affected by the research topic on trustworthiness was moderated by participants’ pre-existing attitudes towards LGBTQ issues. Using standardized linear regression, we again found a main effect of condition on trustworthiness, beta = 0.15, p = .004, 95% CI beta [0.05, 0.26]. There was a significant main effect of participants’ pre-existing attitudes, beta = 0.30, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.20, 0.40] and the condition × attitudes interaction effect was significant, beta = 0.19, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.08, 0.29], increasing the amount of explained variance in trustworthiness by 3% to R 2 adj = .14. Table 2 summarizes the results. Fig 1A displays the interaction effect and standardized simple slopes analysis further qualifies it: Participants with more positive attitudes towards LGBTQ issues (+1 SD above sample mean) trusted Dr. Lohr more when the researcher was personally affected vs. not affected, beta = 0.34, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.20, 0.49]. For participants with less positive attitudes towards LGBTQ issues (-1 SD below sample mean), this effect appears to be reversed, yet the simple slope was not significant, beta = -0.03, p = .646, 95% CI B [-0.18, 0.11]. The same pattern of interaction effects emerged for both, integrity/benevolence ( p = .009, total R 2 adj = .14) and expertise ( p < .001, total R 2 adj = .10); full analyses are reported in Appendix B (see https://osf.io/phfq3/ ).

Linear regression plots for the interaction effect of attitudes × condition on epistemic trustworthiness (Fig 1A) and credibility (Fig 1B) with 95% confidence intervals: Participants’ attitudes towards the research topic moderated how a researcher’s disclosure of being personally affected (vs. being not personally affected) by one’s own research was perceived.
| Predictor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||
| Epistemic trustworthiness | ||||
| condition | 0.15 | [0.05, 0.26] | .02 | [-.01, .05] |
| attitudes | 0.30 | [0.20, 0.40] | .09 | [.03, .15] |
| condition × attitudes | 0.19 | [0.08, 0.29] | .04 | [-.00, .07] |
| Credibility | ||||
| condition | 0.04 | [-0.06, 0.13] | .00 | [-.01, .01] |
| attitudes | 0.48 | [0.39, 0.58] | .24 | [.16, .32] |
| condition × attitudes | 0.21 | [0.12, 0.31] | .05 | [.01, .09] |
*** indicates p < .001. Condition is standardized by effect coding (-1 = not personally affected, 1 = personally affected). beta represents standardized regression weights. sr 2 represents the semi-partial correlation squared.
Regarding our second dependent variable, credibility, we found no main effect of condition, beta = 0.04, p = .456, 95% CI beta [-0.06, 0.13]. However, there was a significant main effect of participants’ pre-existing attitudes, beta = 0.48, p < .001 95% CI beta [0.39, 0.58]: Participants with more positive attitudes anticipated a higher credibility of future research findings in this condition than participants with less positive attitudes. Similar to epistemic trustworthiness, there was a significant condition × attitudes interaction effect, beta = 0.21, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.12, 0.31], increasing the amount of explained variance in credibility by 4% to R 2 adj = .26. Table 2 summarizes the results. Fig 1B displays this interaction effect: Again, participants with more positive attitudes towards LGBTQ issues (+1 SD above sample mean) anticipated Dr. Lohr’s future research findings to be more credible when the researcher was personally affected vs. not affected, beta = 0.25, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.12, 0.38]. However, for participants with more negative attitudes (-1 SD below sample mean) this effect was significantly reversed: They rated the future research as less credible when the researcher was personally affected vs. not affected, beta = -0.18, p = .009, 95% CI B [-0.31, -0.04].
Results from Study 1 suggest that LGBTQ researchers are perceived as more trustworthy and their future findings as more credible when they disclose being personally affected by their research topic (i.e., being queer themselves), but only if perceivers hold positive attitudes towards LGBTQ issues. By contrast, holding less favorable attitudes towards LGBTQ issues lead to more skeptical reactions towards personally affected vs. unaffected researchers. This finding shows that learning about a researcher’s personal affection by their research can, indeed, go both ways, as suggested by our theoretical reasoning. On a more general level, our research suggests that public reactions towards “me-search” is a matter of pre-existing attitudes, and, thus, a case of motivated science reception [ 21 , 22 ].
There are some limitations to this first study: As most people in our sample held rather positive attitudes towards the LGBTQ community ( M = 4.93, SD = 1.02; on a scale from 1 to 6), predicted values on trustworthiness and credibility at the lower end of the attitude spectrum are probably less reliable. Also, we did not control for participants’ own identification as belonging to the LGBTQ community. Thus, we cannot differentiate clearly between attitudinal and identity-related effects, which is important because attitudes and identity concerns have a psychologically distinguishable impact on motivated science reception [ 27 , 28 ]. Additionally, replicating our results in a different domain is necessary to be able to generalize our findings. Another question of generalizability that is left unanswered is how such individual experiences with one personally affected researcher might impact laypeople’s perception of the entire field. This calls for more research on the double-edged nature of the moderating effect of preexisting attitudes.
In our preregistered second study (see https://osf.io/c9r4e ), we aimed to replicate our findings in a more diverse sample and with a different research topic that has the potential of polarizing participants even more strongly. We used the same design as in Study 1, but changed the proposed research topic to perceptions of vegans and introduced a vegan vs. non-vegan researcher. Again, we hypothesized that laypeople’s attitudes towards veganism moderate the effects on trustworthiness as well as credibility of future research. Additionally, we tested whether the effect of one researcher being personally affected by their own research generalizes to the broader perception of their entire field. Furthermore, we also explored whether the moderation by attitudes towards veganism prevailed when controlling for self-identification as being vegan (not included in preregistration).
We conducted an a-priori power analysis using G*Power [ 35 ] for detecting the hypothesized interaction effect in a moderated multiple regression analysis ( f 2 = 0.04, based on Study 1, with 1- β = 0.90 and α = 0.05, which resulted in a total sample of N = 265. Anticipating exclusions (see specified criteria) of comparable size as in the previous study, we aimed for a sample of at least 350 participants.
We collected data from 364 participants via mailing lists and social media. Fifty-seven participants had to be excluded due to our preregistered criteria (see https://osf.io/c9r4e ): one participant was younger than 16 years, 31 failed the manipulation check, 10 took less than 20sec viewing the proposal, 12 took less than 3min or more than 20min for participation, 3 had apparently implausible patters of response (i.e., “straight-lining;” identical responses on every single item on more than one questionnaire page in a row). The final sample consisted of N = 307 participants (76% female, 23% male, 1 other) who were between 18 and 79 years old ( M = 33.55, SD = 13.92). Approximately half of the sample (50%) was currently studying at a university, further 40% were working and 10% not working, one person was currently in training. Eighty-five percent were currently studying or already held a university degree (social sciences: 49%, humanities: 17%, natural sciences: 14%, life sciences: 8%, engineering: 6% and other 6%). Most participants did not consider themselves as vegans (89%).
We used the same materials and procedure as in Study 1 (see OSF for full materials: https://osf.io/phfq3/ ). However, we changed the research topic to “perceptions of vegans”. Participants were randomly assigned to two conditions. In the “not personally affected” condition, the researcher Dr. Lohr wrote:
“ I was interested in investigating this research questions not only out of scientific reasons but because , as someone who is not living as a vegan and , thus , not personally affected by my own research , I think we have a need for more evidence-based knowledge regarding the social embedding of vegan lifestyles , which we can acknowledge in everyday life .”
“… because , as someone who is living as a vegan and , thus , personally affected by my own research , I think we have a need for more evidence-based knowledge regarding the social embedding of vegan lifestyles , which we can acknowledge in everyday life . ”
As dependent variables, we again used the 14-item METI [ 36 ] to measure epistemic trustworthiness, but we expanded the measure for credibility of future research by adding one more item (“I would express skepticism towards Dr. Lohr’s future findings”) to better capture the behavioral aspects of credibility (now: 7 items; Cronbach’s α = .86). We also added a measure of participants’ evaluation of the entire field (not the specific researcher) as a third dependent variable. This 12-item scale was adapted from a related study [ 28 ] (e.g., “I think researchers who do research on that topic sometimes lack competence,” “I think it is difficult to apply results from this line of research to reality;” 6-point Likert scale ranging from 1 = “not at all” to 6 = “very much;” Cronbach’s α = .85). Next, participants’ attitudes towards veganism (i.e., the moderator variable) were measured with a 14-item scale adapted from the attitude measure in Study 1 by changing and adding items (e.g., “I think veganism is exaggerated” (reverse-coded) and “I can imagine being a vegan myself;” 6-point Likert scale ranging from 1 = “not at all” to 6 = “very much;” Cronbach’s α = .95).
To reduce exclusions after data collection, participants could proceed only if they answered all attention checks correctly (4 items; multiple choice). We added self-identification as vegan as a control variable (“Do you presently consider yourself a vegan?” yes/no); and an open-ended question about participants’ opinion regarding the researcher being personally affected to explore how laypeople rationalize their opinion. These responses were later coded for valence (positive, negative, mixed, or neutral) and content (deductive and inductive coding) by two raters blind to the specific research question (see Appendix C in the supplementary materials, https://osf.io/phfq3/ ; interrater reliability for valence, Cohen’s κ = .86, p < .01; and for content, Cohen’s κ = .74, p < .01). Again, the questionnaire closed with a sign-up for a lottery and more information as well as a debriefing.
Our randomized groups did not differ in regard to PES (PES frequency, p = .147; PES experiences, p = .101). However, they did differ significantly in regard to the general perception of neutrality in science ( p = .049). Possible implications are addressed in the Discussion. Table 3 summarizes all means, standard deviations, correlations and internal consistencies. In the following, we report our findings for all three dependent variables (trustworthiness, credibility, evaluation of the entire field), consecutively.
| Variable | α | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Expertise | 4.68 | 0.91 | .92 | ||||||||
| 2. Integrity/ benevolence | 4.75 | 0.75 | .90 | .71 | |||||||
| 3. Epistemic trustworthiness | 4.72 | 0.76 | .94 | .92 | .93 | ||||||
| 4. Credibility | 3.97 | 0.96 | .86 | .66 | .70 | .73 | |||||
| 5. Evaluation of field | 2.95 | 0.78 | .85 | -.40 | -.43 | -.45 | -.64 | ||||
| 6. Attitudes towards veganism | 4.26 | 1.23 | .95 | .04 | .15 | .11 | .39 | -.46 | |||
| 7. Neutrality expectation | 4.18 | 0.91 | .86 | .05 | .06 | .05 | .08 | -.26 | .02 | ||
| 8. PES frequency | 3.30 | 0.68 | .75 | -.13 | -.06 | -.10 | -.03 | -.03 | .11 | .08 | |
| 9. PES experiences | 6.47 | 3.25 | - | -.14 | -.09 | -.12 | -.09 | .03 | .07 | -.02 | .51 |
Note . N = 307.
*** indicates p < .001. α represents internal consistencies (Cronbach’s α). Variables 1–7 ranged from 1 to 6, variable 8 ranged from 1–5 and variable 9 ranged from 0–15.
Trustworthiness
First, we ran the standardized regression model for epistemic trustworthiness. There was neither a significant main effect of condition on epistemic trustworthiness, beta = 0.04, p = .482, 95% CI beta [-0.07, 0.15] nor a significant main effect of attitudes towards veganism, beta = 0.07, p = .205, 95% CI beta [-0.04, 0.18]. However, the hypothesized condition × attitudes interaction effect was significant, beta = 0.22, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.11, 0.34], increasing the amount of explained variance in trustworthiness by 4% to R 2 adj = .05. Table 4 summarizes the results. Fig 2A and standardized simple slopes analyses show that participants with more positive attitudes towards veganism (+1 SD above sample mean) trusted Dr. Lohr more when personally affected vs. not affected, beta = 0.26, p = .001, 95% CI beta [0.11, 0.42]. This conditional effect was reversed for participants with more negative attitudes (-1 SD below sample mean), who trusted Dr. Lohr less when personally affected vs. not affected, beta = -0.19, p = .020, 95% CI beta [-0.34, -0.03]. The interaction effect remained significant when controlling for participants’ self-identification as being vegan ( p < .001, total R 2 adj = .06). In secondary analyses, we explored the effects on the two facets of epistemic trustworthiness, separately. The same pattern of interaction effects emerged for both integrity/benevolence ( p < .001, total R 2 adj = .08) and expertise ( p = .005, total R 2 adj = .02); full analyses are reported in Appendix D in the supplementary materials (see https://osf.io/phfq3/ ).

Linear regression plots for the interaction effect of attitudes × condition on epistemic trustworthiness (Fig 2A), credibility (Fig 2B) and critical evaluation of the entire field (Fig 2C) with 95% confidence intervals: Participants’ attitudes towards the research topic moderated how a researcher’s disclosure of being personally affected (vs. being not personally affected) by one’s own research was perceived.
| Predictor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||
| Epistemic trustworthiness | ||||
| condition | 0.04 | [-0.07, 0.15] | .00 | [-.01, .01] |
| attitudes | 0.07 | [-0.04, 0.18] | .01 | [-.01, .02] |
| condition × attitudes | 0.22 | [0.11, 0.34] | .05 | [.00, .10] |
| Credibility | ||||
| condition | -0.07 | [-0.17, 0.03] | .01 | [-.01, .02] |
| attitudes | 0.35 | [0.25, 0.45] | .12 | [.05, .18] |
| condition × attitudes | 0.25 | [0.15, 0.35] | .06 | [.01, .11] |
| Critical evaluation of field | ||||
| condition | -0.00 | [-0.10, 0.10] | .00 | [-.00, .00] |
| attitudes | -0.41 | [-0.51, -0.31] | .17 | [.09, .24] |
| condition × attitudes | -0.27 | [-0.37, -0.18] | .07 | [.02, .12] |
Credibility
On credibility, there was no significant main effect of condition, beta = -.07, p = .146, 95% CI beta [-0.17, 0.03] but a significant main effect of attitudes towards veganism, beta = .35, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.25, 0.45]. As predicted, the condition × attitudes interaction effect was also significant for credibility, beta = 0.25, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.15, 0.35], increasing the amount of explained variance in credibility by 6% to R 2 adj = .21. Table 4 summarizes these results. Fig 2B and standardized simple slope analyses qualify the interaction effect: In line with the results for trustworthiness, participants with more positive attitudes (+1 SD above sample mean) anticipated Dr. Lohr’s future findings to be more credible when personally affected vs not affected, beta = 0.18, p = .016, 95% CI beta [0.03, 0.32], while the conditional effect for participants with more negative attitudes (-1 SD below sample mean) changed its sign, beta = -0.32, SE ( B ) = 0.14, p < .001, 95% CI beta [-0.47, -0.18]. As before, the interaction effect remained significant when controlling for self-identification as being vegan ( p < .001, total R 2 adj = .21).
Evaluation of the field
Third, we investigated whether this moderation effect generalizes to the evaluation of the entire field of veganism research. There was no significant main effect of condition, beta = -.00, p = .989, 95% CI beta [-0.10, 0.10] but a significant main effect of attitudes, beta = -.41, p < .001, 95% CI beta [-0.51, -0.31]. Again, we found the hypothesized condition × attitude interaction effect, beta = -.27, p < .001, 95% CI beta [-0.37, -0.18], increasing the amount of explained variance in critical evaluation by 7% to R 2 adj = .27. Again, Table 4 summarizes these results and Fig 2C and standardized simple slopes analyses further qualify the interaction effect: Participants with more positive attitudes towards veganism (+1 SD above sample mean) were less critical of research on veganism when Dr. Lohr was personally affected vs. not affected, beta = -0.28, p < .001, 95% CI beta [-0.41, -0.14]. By contrast, this conditional effect was reversed for participants with more negative attitudes towards veganism (-1 SD below sample mean), beta = 0.27, p < .001, 95% CI beta [0.14, 0.41]. This interaction effect also remained significant when controlling for self-identification as being vegan ( p < .001, total R 2 adj = .28).
Participants’ opinion
Overall, participants who responded to the open-ended question expressed mostly negative opinions about the researcher being personally affected by his own research (negative: 48%, neutral: 21%, positive: 17%, and mixed: 14%). The most frequently mentioned (negative) remark was that a “me-searcher” might be biased towards their research (60%; e.g., “ By introducing himself as being affected , I fear he cannot evaluate the results of his research objectively ”). The second most frequently mentioned remark was that such idiosyncratic relevance is irrelevant (24%; e.g., “ It wouldn’t make a difference ”). Positive remarks were mentioned less frequently: Participants ascribed more motivation (11%; e.g. “ I think interest , also personal interest , is an important prerequisite for determined research ”) or knowledge about the topic (8%; e.g. “ Very good , most likely , he thus is knowledgeable about the subject matter and can conduct the study in a more purposeful manner ”) to the “me-searcher”, or recognized the transparency (7%; e.g., “ The main thing is transparency . People are always biased , perhaps even unconsciously ”; for more details, see Appendix C in the supplementary materials: https://osf.io/phfq3/ ).
In Study 2, we replicated the moderation effect of preexisting attitudes on the effect of a researcher disclosing being personally affected (vs. not affected) by their own research on participants’ epistemic trustworthiness and credibility ascriptions regarding the research and researcher’s future findings. Further, we showed that this effect generalizes to the evaluation of the entire research area. Here, positive attitudes towards veganism determined how learning about an openly vegan researcher impacted participants’ perceptions of trustworthiness and credibility as well as the evaluation of the entire field of veganism research compared to learning about a non-vegan (i.e., non-affected) researcher. Participants who held more positive attitudes towards veganism reported more trust, higher anticipated credibility of future findings, and a less critical evaluation of the field when confronted with a vegan researcher. Conversely, for participants with less positive attitudes this effect was reversed. The moderation by positive attitudes towards veganism persisted when controlling for participants’ self-identification as vegans. Overall, the interaction effects observed in Study 2 explained similar amounts of variance as in Study 1 (epistemic trustworthiness: 3% vs. 4%, and credibility: 4% vs. 6%). Further, qualitative analyses revealed that most participants reported negative–or, at least, mixed–perceptions of a “me-searcher” (e.g., “me-searchers” may be biased, but also highly motivation and knowledgeable), which corroborated our theoretical prediction that “me-search” may be a double-edged sword. Interestingly, these qualitative findings seem somewhat contradictory to the quantitative findings, according to which there was no main effect of researchers’ idiosyncratic affection by their research topic.
In Study 2, one caveat is that the groups differed significantly in regard to participants’ general expectations of neutrality in science. Participants who read about the personally affected researcher had weaker expectations of neutrality; yet, when added to the regression model as a control, the pattern of results remained unchanged (see Appendix E in the supplementary materials, https://osf.io/phfq3/ ). Further, as a second caveat, we show that participants generalized their perceptions to the overall field of veganism research. However, this research area might be considered quite narrow and, thus, future research should investigate how far such generalization processes stretch out to perceptions of broader areas of research (e.g., health psychology).
General discussion
In two studies, we show that laypeople’s perception of researchers who disclose being personally affected by their own research can be positive as well as negative: The effect of such “me-search” was moderated by laypeople’s preexisting attitudes. Queer or vegan researchers were perceived as more trustworthy and their future findings were anticipated to be more credible when participants had positive, sympathizing attitudes towards the related research object (i.e., LGBTQ community or veganism). When participants’ attitudes were less positive, this pattern reversed. In Study 2, we extended our research from individualized perceptions of single researchers and their findings to evaluations of the entire field of research. Participants who were confronted with a personally affected researcher seemed to consider this person a representative example and generalized their judgment to their evaluation of the entire (though here quite narrow) research area.
We explored epistemic trustworthiness in more detail in both studies, namely the cognitive-rational facet of expertise and the affective facet of integrity/benevolence: Both were impacted by researchers’ disclosure of being personally affected, although effect sizes for expertise were descriptively smaller than for integrity/benevolence. This points to “me-search”–when received positively–possibly adding to the perception of competence-related aspects like a deeper knowledge of a phenomenon (e.g., via anecdotal insights) [ 12 – 14 ] and, even more so, warmth-related aspects like seeming more sincere, benevolent, transparent and, thus, approachable [ 15 , 16 , 41 ]. Disclosing such personal interest in a scientific endeavor might be able to bridge the stereotypical perception of cold and distant “science nerds” by revealing passionate, human and, thus, more relatable side of a researcher. When received negatively, however, “me-search” might be regarded as harboring vested interests, which casts doubts on a researcher’s neutrality and objectivity [ 8 – 11 , 42 ].
In general, the main models tested here explained between 5% and 28% of variance which may not appear impressive at first glance. However, our studies posed a very strict test of the effects of “me-search” by only using a subtle manipulation sparse in information followed by measures of very specific perceptions which might have contributed to an understatement of the real-world impact.
“Me-search” neither automatically sparks trust nor mistrust in laypeople, even if their explicit opinions seem rather negative. In line with assumptions from motivated science reception [ 22 , 43 ], our findings suggests that the ambivalence of the fact that a researcher is personally affected can be seized as an opportunity to interpret the situation in a manner that best fits to preexisting attitudes: Researchers, their findings and even their entire field of research are evaluated–even before learning about specific findings–based on prior attitudes towards the research topic. We show in Study 2 that the moderation effect of participants’ positive attitudes towards the respective research topic (i.e., veganism) prevails when controlling for self-identification with the topic (i.e., being a vegan). This suggests that, indeed, in motivated reasoning attitudinal and identity-related processes can be differentiated: Here, social identity protection could be ruled out as alternative explanation for the effects of pre-existing attitudes. Noteworthily, we demonstrate that motivated science reception already operates when the results are not (yet) known. This points towards a perceptual filter made up of pre-existing attitudes that is activated when confronted with scientific information and leads to biased pre-judgments: Ambivalent cues (i.e., “me-search”) are prematurely interpreted in line with prior attitudes without actually knowing whether the new scientific information will be attitude-consistent or inconsistent (when, later, results are reported).
Future research
Future research on the motivated reception of “me-search” should focus on three open questions. First, while we consider it a strength of our studies that the results of the proposed research project were not yet known, it might be interesting to see how being personally affected or not interacts with the perceived direction of the communicated scientific results (e.g. supporting vs. opposing a certain position): To what extent can the first, premature evaluation of a “me-searching” researcher be adapted if the actual results are inconsistent with this pre-judgment?
Second, the investigation of what specific characteristics of “me-search” are instrumentalized by benevolent or skeptical perceivers might not only provide practical tips on how to handle being personally affected (e.g., in science communication) but also important theoretical insights on the building blocks of trust in science and researchers (see discussion above regarding the effects on the facets of epistemic trustworthiness). As one example, knowing that a qualitative level of knowledge is highly valued could further research on the trust-benefit of enriching statistical evidence with anecdotal and narrative elements [ 44 , 45 ]. As second example, we argue that researchers’ self-disclosure of being personally affected by their research might signal transparency and, thus, improve the perception of the trust facets integrity and benevolence. Yet, even the disclosure of not being personally affected could have such an effect on a researcher’s reputation and, at the same time, it might be less ecologically valid (as, presumably, it is rather unusual to explicitly state to not be affected by something). Introducing a control group without any information about a researcher’s relation towards their research object might bring light to this.
Third, we demonstrated the moderation effect of preexisting attitudes for two research areas (i.e., LGBTQ and veganism) and in different populations. Yet, further research should investigate whether this effect will hold up for other areas, more diverse samples and different kinds of “me-search”, as well. For example, in some research fields being personally affected by the research might be perceived as more morally charged than in others and, thus, having stronger polarizing effects [ 46 ]: While, in veganism-research, “me-search” might be grounded in an ideological choice (e.g., thinking its morally wrong to consume animal products and, thus, being vegan), having a stroke and, following, studying stroke-related brain plasticity is likely perceived as less ideological. Also, different scientific methods (typically) used in a field might impact the perceptions of “me-search” depending on how prone for subjectivity these methods are perceived to be (e.g., qualitative “me-search” like autoethnographic analyses might be perceived more critically than when using seemingly objective, quantitative methods like physiological measures). Further, researchers who are not directly personally affected by their research but “merely” interested in something for personal reasons (e.g., being highly empathetic towards queer concerns without identifying as queer) might not profit from disclosure of such personal motivations: Such researchers might be perceived as impostors [ 47 ] lacking the expertise stemming from directly firsthand experiences.
Practical implications
Finally, for the applied perspective on public engagement with science, it should again be noted, that motivated reasoning processes are activated even before specific results are presented (e.g. before hearing a talk or reading about a study). This might be important, as judgments are quickly formed and remembered [ 48 , 49 ] and, therefore, the first impression of a researcher might set the tone for further interactions and, particularly, for the acceptance and implementation of their findings. This emphasizes the importance of researchers knowing their audience (and their attitudes) when engaging in science communication.
Of course, there are also ethical considerations concerning “me-search”: Researchers should always declare any conflict of interests when conducting research [ 50 , 51 ]. Failing to disclose being personally affected by one’s own research might backfire severely on researchers’ reputation–especially concerning their trustworthiness and the credibility of their findings–and in particular, when this information is disclosed by someone else and not themselves. At least for achieving positive reputational effects, it seems researchers need to freely initiate the disclosure of limitations and problems themselves [ 41 , 52 ]. A possible solution for reaping all the benefits and protecting against the potential harms of engaging in “me-search” might be to actively seek out mixed research teams. Including affected as well as non-affected individuals in research projects might be worth considering from the stance of the public’s trust in science: It enables deep, even personal insights to the studied phenomenon, while still securing balanced perspectives and impartiality.
Neuroanatomist Jill Bolte Taylor became famous for turning her “stroke of fate” into productive and well-selling “me-search”. Yet, she was praised as well as heavily criticized for mixing her personal and scientific motivations: When research is also “me-search”, it can be perceived positively as well as negatively depending on laypeople’s preexisting attitudes towards the research object. Researchers who disclose being personally affected by their own research can benefit from this disclosure in terms of trustworthiness and credibility when it is perceived by laypeople with positive attitudes; however, for audiences with more negative attitudes this effect is reversed and disclosure can be harmful. One experience with a personally affected researcher might be enough to impact the evaluation of the whole field. Thus, openly acknowledging “me-search” in one’s research is an ambivalent matter and its communicative framing as well as the targeted audience should be well considered.
Funding Statement
The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Data Availability
- PLoS One. 2021; 16(7): e0253911.
Decision Letter 0
19 Mar 2021
PONE-D-20-38206
When research is me-search: Researcher interests affect laypeople’s trust in science depending on their pre-existing attitudes
Dear Dr. Altenmüller
Thank you for submitting your manuscript to PLOS ONE. After careful consideration, we feel that it has merit but does not fully meet PLOS ONE’s publication criteria as it currently stands. Therefore, we invite you to submit a revised version of the manuscript that addresses the points raised during the review process.
VI have now received three reviews of your MS. All three reviewers see merit in the research presented in the paper. Two reviewers recommend publication after minor revision, whereas the third has recommended major revision, in particular in relation to the statistical analysis applied. In view of the comments of reviewer two, I am recommending major revision and would like to invite you to revise and resubmit the MS. As well as addressing al of the reviewers comments, please address the issues associated with the regression analysis raised by reviewer 2 in your resubmission.
I have received three reviews of your MS. All three reviewers see merit in the research presented in the paper. Two reviewers recommend publication after minor revision, whereas the third has recommended major revision, in particular in relation to the statistical analysis applied. In view of the comments of reviewer two, I am recommending major revision and would like to invite you to revise and resubmit the MS. As well as addressing al of the reviewers comments, please address the issues associated with the regression analysis raised by reviewer 2 in your resubmission.
Please submit your revised manuscript by 1st June 2021 If you will need more time than this to complete your revisions, please reply to this message or contact the journal office at gro.solp@enosolp . When you're ready to submit your revision, log on to https://www.editorialmanager.com/pone/ and select the 'Submissions Needing Revision' folder to locate your manuscript file.
Please include the following items when submitting your revised manuscript:
- A rebuttal letter that responds to each point raised by the academic editor and reviewer(s). You should upload this letter as a separate file labeled 'Response to Reviewers'.
- A marked-up copy of your manuscript that highlights changes made to the original version. You should upload this as a separate file labeled 'Revised Manuscript with Track Changes'.
- An unmarked version of your revised paper without tracked changes. You should upload this as a separate file labeled 'Manuscript'.
If you would like to make changes to your financial disclosure, please include your updated statement in your cover letter. Guidelines for resubmitting your figure files are available below the reviewer comments at the end of this letter.
If applicable, we recommend that you deposit your laboratory protocols in protocols.io to enhance the reproducibility of your results. Protocols.io assigns your protocol its own identifier (DOI) so that it can be cited independently in the future. For instructions see: http://journals.plos.org/plosone/s/submission-guidelines#loc-laboratory-protocols
We look forward to receiving your revised manuscript.
Kind regards,
Lynn Jayne Frewer, MSc PhD
Academic Editor
Journal Requirements:
When submitting your revision, we need you to address these additional requirements.
1. Please ensure that your manuscript meets PLOS ONE's style requirements, including those for file naming. The PLOS ONE style templates can be found at
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/s/file?id=wjVg/PLOSOne_formatting_sample_main_body.pdf and
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/s/file?id=ba62/PLOSOne_formatting_sample_title_authors_affiliations.pdf
[Note: HTML markup is below. Please do not edit.]
Reviewers' comments:
Reviewer's Responses to Questions
Comments to the Author
1. Is the manuscript technically sound, and do the data support the conclusions?
The manuscript must describe a technically sound piece of scientific research with data that supports the conclusions. Experiments must have been conducted rigorously, with appropriate controls, replication, and sample sizes. The conclusions must be drawn appropriately based on the data presented.
Reviewer #1: Partly
Reviewer #2: No
Reviewer #3: Yes
2. Has the statistical analysis been performed appropriately and rigorously?
Reviewer #1: Yes
Reviewer #2: Yes
3. Have the authors made all data underlying the findings in their manuscript fully available?
The PLOS Data policy requires authors to make all data underlying the findings described in their manuscript fully available without restriction, with rare exception (please refer to the Data Availability Statement in the manuscript PDF file). The data should be provided as part of the manuscript or its supporting information, or deposited to a public repository. For example, in addition to summary statistics, the data points behind means, medians and variance measures should be available. If there are restrictions on publicly sharing data—e.g. participant privacy or use of data from a third party—those must be specified.
4. Is the manuscript presented in an intelligible fashion and written in standard English?
PLOS ONE does not copyedit accepted manuscripts, so the language in submitted articles must be clear, correct, and unambiguous. Any typographical or grammatical errors should be corrected at revision, so please note any specific errors here.
5. Review Comments to the Author
Please use the space provided to explain your answers to the questions above. You may also include additional comments for the author, including concerns about dual publication, research ethics, or publication ethics. (Please upload your review as an attachment if it exceeds 20,000 characters)
Reviewer #1: I like this line of research very much and think it's useful and largely well done. I wish you had a more diverse and larger sample but ... maybe next time. It's not necessary, it'd just make the results (especially in study 1 where you don't have a lot of non-LGBTQ friendly respondents.
Some concerns I have ...
1. Ecological validity for the 'non-affected' condition: It's not clear to me why anyone would ever say that they're studying something because they don't identify with it. I think, more likely, someone might just NOT say why they're studying something and just describe what they're studying with no context. Alternatively, a scientist might say they study something because (a) it personal affects them, or (b) it's just an interesting set of puzzles, or (c) both.
2. It's also probably worth making clear that disclosing that research is personally affecting the respondent is conceptually different from saying that a respondent is motivated by benevolence. In this regard, I worry a bit that both respondents are kind of making a (weak) benevolence claim that might be attenuating the results. As future research, you might consider research that adds a clear "and my motivation is to help this community ..." message as a condition. I also don't really understand the last sentence in either condition. They seem fairly vague.
3. Is 'affected' the right word? 'Interested' (as in conflict of interest) seems closer but that word may have too much baggage. But 'affected' has baggage too and we're all 'affected' by research in these areas. Maybe 'involved'?
4. I do not understand your argument about how the second study rules out social identity protection. More generally, I don't know that social identity protection and attitude protection are necessarily incompatible given that my identity might make it more likely that I hold certain evaluative beliefs (aka the basis of attitudes). And the fact you're vegan doesn't mean that veganism is a core part how you identify. If you want to get at identity protection, I'd want more evidence than this. I think you'd be better just to talk about motivated reasoning in a more general sense.
Some technical suggestions ...
1. You sometimes present percentages with two decimals, which is essentially four decimals (inasmuch as 21.34% = .2134), but your sample is less than a 1K people. This would seem to suggest that you're trying to be more precise than is reasonable. Id' just stick to two decimals throughout unless you have a good reason.
2. Does it make sense to call your behavioral trust measure 'credibility'? I worry a bit about this because there's so much variability in the trust literature when it comes to what we call the various constructs. In this regard, I note that credibility is often conceptualized as competence (even going back to Hovland in 1951). I think it might be safer just to talk about 'behavioral trust as willingness' to be vulnerable as that fits with the Roger/Davis/Schoorman model that the Muenster epistemic inventory is derived.
3. It'd be great if your tables and figures were a bit more descriptive such that they can 'stand alone'. In this regard, you might add sample sizes as well as variable range. The figure, in particular, are impossible to understand without referring to the text. In those cases, a detailed note is one important step but it'd also help to better label your axes and use a readable font.
4. Does it really make sense in the second study to include the bit about the overall field? In this regard, is vegan research really 'the field'? Why wouldn't the field be vegetarian studies? Or food studies? Or nutrition? Or biological science? You define field so narrowly that I'm not sure what this additional element adds.
5. You note that the effect sizes for expertise were smaller than the effect sizes for integrity/benevolence but can you really say that? I don't recall you testing the size of the difference, noting that the estimates have error associated with them such that they could easily overlap.
Reviewer #2: Thank you for making your data and analysis scripts openly available. The code seems to run fine and I can reproduce the results.
Method. Sample size
1. I appreciate that you took the effort to provide a power analysis, but post-hoc power is not particularly informative. What the reader needs to know is: given a specific sample size (N = 314), what is the smallest effect one can detect? In this case, it is r = .16 80% of the time, or r = .20 95% of the time. Or, since you’re using means comparisons, this is roughly a d = .32 80% of the time, or a d = .41 95% of the time. [I used the pwr() package for this].
I recommend adjusting this description to provide this information.
What I would like to see presented are the partial r correlations from the regression. It seems that, from your description, the most informative predictor here is ‘participant positive attitude’ and that needs to be compared to the other IV. Yes, there is an interaction, but the slopes are all positive in figure 1a and 1b, suggesting it’s simply a difference in strength rather than a manipulation of the direction of the effect. This can be seen in the figures (which are nice by the way, but please upload higher quality versions).
I recommend reporting the full regression model in a table along with partial correlations and standardised coefficients rather than only the raw coefficients in text.’
It would really be nice to have all the results in one table so that they can be easily compared across studies: I suggest including standardized betas and partial correlations.
‘Evaluation of the field’. It’s claimed that participants positive attitudes towards veganism moderate evaluations such that the effect changes direction, and the text points to Figure 2c. I think this must be a mistake: the slopes and CIs reported in-text are simply opposite of each other (eg b = -.43 and b = .43). Further, the graphs 2c depicts only negative slopes.
Figure 2a, in contrast, shows slopes with opposing directions. Please double check this.
The adjusted R squared for trustworthiness is tiny: R = .05. I’m not sure what to make of these effects, leaving me wondering about the value of this model. The size is similar between both studies, suggesting this is probably accurate.
Again, without partial R values, it’s hard for the reader to compare the relative strength of these effects and judge their merit.
The adjusted R-squared values for credibility and evaluation of the field are upwards of R = .20, which is more convincing (and this is noted in the discussion).
In the Study 2 discussion, the authors suggest that “The moderation…persisted when controlling for self-identification as a vegan… this has to be interpreted carefully.” I suggest you remove this caution or ignore the effect: either interpret something or don’t. There is no carefulness when you report an effect with an accompanying p-value. If you are not convinced that this result is not a fluke then simply describe your data. Either way, please remove this claim of caution.
Finally, you note that the expectations of neutrality was affected by the manipulation and claim this effect is “small” (d = .22). This is actually more of an average effect size in social/personality studies (see Funder & Ozer, 2019 and Gignac & Szodorai, 2016). I wouldn’t be so quick to dismiss it.
Additionally, earlier on in the manuscript (under Main effect of being affected) you interpret a similarly sized d = .25 at face value. If you have determined an alpha level of .05 as your criteria (which you did, and you also can see that smallest effect size based on the power analysis), you should stick to that criteria throughout and simply interpret the effects.
Finally, I admit that I am a bit puzzled by the overall pattern here: participants were less critical when Dr Lohr was affected; they saw results as more credible when Dr Lohr was affected; they trusted the results more when Dr Lohr was demonstrably biased?
What would happen if you asked the participant to rate whether the researcher is biased?
General Discussion
This is again an issue in the general discussion: you claim that ‘when participant attitudes were less positive, this pattern flipped…” but this pattern did not flip. We simply see a reduction in strength.
Conclusions
In sum, I think the key variable here is participant attitudes towards the topic. I’m not convinced of the moderation effect here for several reasons.
First, it does not reverse the direction of the effect: this is key for the claim
Second, the moderation itself is small. There’s not much of a difference between any two given slopes (with the exception of Figur 2a).
Third, the whole idea strikes me as strange: participant attitudes drive the effect always in a positive direction. Even when the researcher admits to being biased, participants don’t evaluate him more negatively. Plus, ‘bias’ itself wasn’t measures as far as I saw.
I think this is an interesting set of studies but it needs a bit more data to rule out some possible effects and I think the interpretation needs to be revised. I’d like to see these points addressed in a revision and I hope my comments are helpful in that regard.
Funder, D. C., & Ozer, D. J. (2019). Evaluating effect size in psychological research: Sense and nonsense. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 2(2), 156-168.
Gignac, G. E., & Szodorai, E. T. (2016). Effect size guidelines for individual differences researchers. Personality and individual differences, 102, 74-78.
Reviewer #3: This paper examines how peoples’ attitudes toward a topic influence their evaluation of research and researchers’ trustworthiness - in the context of research topics which have personal relevance to the researchers.
I believe the aim of this study is very interesting and timely, and a great addition to the research; the study is well done. Also positive is the osf documentation and preregistration of study 2.
While I am quite enthusiastic about the paper, I also have a few issues to remark:
Reading your abstract for the first time, I was a bit confused whose attitudes and interests you were talking about when and what you were measuring – Maybe lead the reader straighter to the point, instead of mirroring your introduction (even though the intro read quite smoothly)?
Methods and Results:
• Please report the results of the factor analyses justifying the scales for testing your hypotheses, can be in the supplement as well.
• p values should be reported in accord with APA reporting guidelines, not p < .05.
• Clearly state what you are testing when comparing the groups with attitudes +- 1SD from mean. “A regression was performed…” or as appropriate.
• Table 1,2 and probably a question of taste: I don’t know of a convention in which Cronbach’s alphas are displayed in the diagonal of a correlation table. Since they’re conceptually something different than correlations, I would suggest moving them to a single column.
• I don’t see a theoretical reason why you should test trustworthiness, and then the two scales separately, would you please justify this? (I think this should be avoided, if there is no indication from theory, and since the results are interdependent anyway. Reminds me of MANOVA)
Discussion (and maybe Introduction):
Finally, and probably most importantly, I am a bit unsure about your interpretation of the main effect on trustworthiness following the experimental variation – you discuss two ideas, and only in the “future research” section: a) there is a preference for anecdotal evidence vs. other types of evidence, i.e. someone affected has some type of special access to a research topic, and b) disclosing being affected / transparency signals benevolence (by the way, in line with intentionalist models of communication). Don’t your results – when dividing the trustworthiness measure into expertise and benevolence/integrity provide some (sure, provisional) evidence that allow you to dive deeper into these explanations in your argumentation? I believe your explanations of this effect could be argued more thoroughly. To that point, while I think it is alright that you only pose an exploratory research question in the introduction, here, you actually almost only provide anecdotal evidence yourselves to argue that question (which you may want to be clear about).
6. PLOS authors have the option to publish the peer review history of their article ( what does this mean? ). If published, this will include your full peer review and any attached files.
If you choose “no”, your identity will remain anonymous but your review may still be made public.
Do you want your identity to be public for this peer review? For information about this choice, including consent withdrawal, please see our Privacy Policy .
Reviewer #1: No
Reviewer #3: No
[NOTE: If reviewer comments were submitted as an attachment file, they will be attached to this email and accessible via the submission site. Please log into your account, locate the manuscript record, and check for the action link "View Attachments". If this link does not appear, there are no attachment files.]
While revising your submission, please upload your figure files to the Preflight Analysis and Conversion Engine (PACE) digital diagnostic tool, https://pacev2.apexcovantage.com/ . PACE helps ensure that figures meet PLOS requirements. To use PACE, you must first register as a user. Registration is free. Then, login and navigate to the UPLOAD tab, where you will find detailed instructions on how to use the tool. If you encounter any issues or have any questions when using PACE, please email PLOS at gro.solp@serugif . Please note that Supporting Information files do not need this step.
Author response to Decision Letter 0
Response to Reviewers
First, we would like to thank all reviewers for raising valid concerns regarding the first version of our manuscript.
Reviewer #1:
I like this line of research very much and think it's useful and largely well done. I wish you had a more diverse and larger sample but ... maybe next time. It's not necessary, it'd just make the results (especially in study 1 where you don't have a lot of non-LGBTQ friendly respondents.
Thank you. We have included this aspect as a potential limitation of our research and an outlook to future research to the General Discussion, p. 28: “Yet, further research should investigate whether this effect will hold up for other areas, more diverse samples and different kinds of “me-search”, as well.”
Thank you for this comment. First, based on your feedback, we have now refined what we mean by “me-search” and what - in our view - is the opposite of “me-search” (see p. 3). We now clarify that “me-search” or “being affected by a certain research topic” means pursuing a scientific question when the answer to that question is idiosyncratically relevant for the individual researcher as opposed to when the answer is relevant per se.
Regarding the design of our studies: Our intention in construing the “not affected” condition in that manner was to keep the factor “self-disclosure” constant. This means that in both conditions the research discloses his personal relation to the topic which is either idiosyncratically relevant (as the researcher is directly affected by it) or not idiosyncratically relevant (as the researcher is not directly affected by it). However, we agree that this way we might have involuntarily reduced the ecological validity as a byproduct. We now voice this concern in the General Discussion (p. 27-28: “Yet, even the disclosure of not being affected could have such an effect on a researcher’s reputation and, at the same time, it might be less ecologically valid (as, presumably, it is rather unusual to explicitly state to not be affected by something).”
This is an interesting point, thanks! With our studies, we are trying to investigate whether respondents actually make these benevolence inferences from researchers’ disclosure of “me-search”, and our results suggest that they do – if they hold a generally positive attitude towards the respective research topic.
Regarding the phrasing of our manipulation, our intention was to keep the research goal (more evidence-based knowledge) constant while varying the driving interest (affected vs. not affected), without producing too much demand by a public statement about desired outcomes (e.g., to support the community’s demands). We agree that both conditions might signal some benevolence (we argue via transparency) and that it would be interesting to test such a benevolence inference process more directly. Thus, in the General Discussion, we suggest to test this in future research thoroughly by introducing a more neutral control group: “Introducing a control group without any information about a researcher’s relation towards their research object might bring light to this.” (p. 28).
With this concern you hit the mark on something we also debated at length before deciding on the word “affected”. We feel, the German word „betroffen sein“ is semantically a combination of “being affected by something” and “being involved in something”. We agree that “involved” might have “less baggage” but it does not reflect the directly personal aspect of me-search (i.e., idiosyncratic relevance). For example, you could already be “involved” in something when a team member is affected. Further, “interested” can also be very unpersonal/neutral (e.g., when I find something scientifically interesting). Thus, we decided on “being affected” to best capture the German “betroffen sein”. We added more clarification in the Introduction (p.3) on what we exactly mean by “me-search”, as mentioned in an Author Response above, by adding the term “idiosyncratic relevance”. Still, we use “being affected” to reflect that it is not just a personal relevance (e.g., when debating whether to become vegan or strongly emphasizing with a certain group) but that you are already affected by the situation (e.g., when you already are vegan). We also extended our discussion on different kinds of me-search in the General Discussion section in line with this reasoning: “Further, researchers who are not directly personally affected by their research but “merely” interested in something for personal reasons (e.g., being highly empathetic towards queer concerns without identifying as queer) might not profit from disclosure of such personal motivations: Such researchers might be perceived as impostors [46] lacking the expertise stemming from directly firsthand experiences.” (p.28).
We fully agree that identity protection and attitude protection might go hand in hand (as you suggest, a social identity makes it most certainly more likely to have some corresponding attitudes). However, while these two might often co-occur, they still could be grounded in different psychological processes. In Study 2, we find some evidence for this.
Here, we asked participants specifically whether they “identified” as vegan (however, we did not ask for the strength or centrality of this identity). This identification as vegan did not have any independent effects and did not diminish the other effects when added as control variable in our regression models. At first, glance this seems at odds with prior findings on motivated reception being also driven by identity protection efforts (e.g., see studies by Nauroth and colleagues: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejsp.1998 , https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0117476 , https://doi.org/10.1177/0963662516631289 ). This might be due to the specific situation we presented: In contrast to most research on motivated reception, we did not confront participants with specific findings or (pro/con) statements but an open-ended situation where results were not yet known. However, while identity did not play a role here, we did find an effect of attitudes in line with motivated reception. Thus, we interpret this as indication that this motivated reception effect based on participants’ attitudes might be functionally different from motivated reception effects based on identity protection. We argue that attitudes might work as broader perception filter that functions even before specific content (i.e., the scientific results) is known, while identity protection might need a specific threat (e.g., scientific evidence calling into question beliefs central to an identity) to lead to motivated responses (e.g. discrediting researchers and their findings when knowing what they say).
As these conclusions are, indeed, tentative, we refrain from overemphasizing their implications by only shortly mentioning them in the General Discussion (see p. 27-28: “This suggests that, indeed, in motivated reasoning attitudinal and identity-related processes can be differentiated: Here, social identity protection could be ruled out as alternative explanation for the effects of pre-existing attitudes.”).
Thank you for the suggestion, we changed the display of our percentages accordingly.
We fully agree, that trust-related concepts are defined differently by different people. Thus, we totally see the point in clearly defining the terms as we used them in our own research: We use the term “credibility” in clear (verbal) contrast to the term “trustworthiness” to make a distinction between person-related and evidence-related trust/credibility. Our factor analyses support this differentiation empirically (see Appendix A https://osf.io/phfq3/?view_only=a3694575674944fababa32b696e6e645 ). In addition, we added a clarifying note in the manuscript: p. 7 “[…] Of note, we use the term “credibility” to differentiate evidence-related trust/credibility from person-related trust/credibility, i.e. “trustworthiness”.”
We added more information to our tables and figures. The figures were uploaded in a higher quality and with better readable labels.
We agree, “veganism research” can only be considered as a very narrow field of research. It might be interesting to investigate how far the generalization stretches out to broader fields as you suggest. The point we make here might be considered a first step, showing that individual experiences of “me-search” are generalized to a broader circle of science reception. In Study 2, we discuss this now as a caveat (p.25: “Further, as a second caveat, we show that participants generalized their perceptions to the overall field of veganism research. However, this research area might be considered quite narrow and, thus, future research should investigate how far such generalization processes stretch out to perceptions of broader areas of research (e.g., health psychology).” And we added a small note in our General Discussion (p. 25: “Participants who were confronted with a personally affected researcher seemed to consider this person a representative example and generalized their judgment to their evaluation of the entire (though here quite narrow) research area.”).
Indeed, we only compared these descriptively. We make this clearer now, by adding “descriptively” in the respective sentence (p. 26 “[…], although effect sizes for expertise were descriptively smaller than for integrity/benevolence.”).
Reviewer #2:
Thank you for making your data and analysis scripts openly available. The code seems to run fine and I can reproduce the results.
Thank you for the recommendation. We changed our post hoc power analyses in Study 1 to sensitivity analyses as you suggested. We used G*Power again and arrive at the same results as you using the pwr() package (p.8: “We conducted sensitivity analyses using G*Power [34] for determining which effect sizes can detected with this sample in a moderated (multiple) regression analysis: At α=0.05 and with a power of 80%, small-to-medium effects (f²≥0.03) can be detected with this sample”).
Thank you for the suggestions. We now report standardized regression analyses and included tabular displays of the standardized regression coefficients and semi-partial correlations for all our multiple regression analyses (see Table 2 and 4). Further, we uploaded the figures in better quality and better readable labels.
Here, we are talking about the simple slopes which are reversed (slope of the predictor when the moderator is held at +/-1 SD). These simple slopes analyses are not directly reflected in the slopes of our figures as we here display the pattern from a different “angle” to help illustrate the conditional effects (mean differences between conditions at different values of the moderator): Here, the moderator is printed on the x-axis (instead of being displayed as slopes held at +/- 1 SD) and the slopes are separated by condition (instead of being displayed on the x-axis). To prevent confusion, we now clarified that in our phrasing in both Results sections (see also below).
As is now easily comparable (thanks to your suggestion regarding the standardized regression model and the semi-partial correlations), the effect we are most interested in, the interaction effect, is actually quite similar in size between all dependent variables in both studies. We agree, that these effects may appear small and that our models do not explain a lot of variance in total. However, we think our results can be considered relevant and we might even have underestimated the real-world impact of “me-search” for two reasons: 1) Our experimental manipulation was relatively subtle. 2) Participants were asked to judge the researchers on quite specific characteristics on the basis of very little information. We added a paragraph in the General Discussion dedicated to this aspect: “In general, the main models tested here explained between 5% and 28% of variance which may not appear impressive at first glance. However, our studies posed a very strict test of the effects of “me-search” by only using a subtle manipulation sparse in information followed by measures of very specific perceptions which might have contributed to an understatement of the real-world impact.” (p. 26).
We removed the claim of caution (see p. 24).
We removed the interpretation of the effect size, as the more important argument we want to make is the fact that adding neutrality expectations as control did not change the pattern of results: “Participants who read about the personally affected researcher had weaker expectations of neutrality; yet, when added to the regression model as a control, the pattern of results remained unchanged (see Appendix E in the supplementary materials, […]).” (p.25)
Thank you for these questions! In response, we analyzed the qualitative data from Study 2 and added these insights to the manuscript. Please, see our response to your last comment below.
Saying „the pattern flipped“, we wanted to express the fact that the conditional effect (mean between the conditions at +/-1 SD of attitudes towards the topic) changes its sign. We clarified that in our phrasing throughout both Results sections.
Regarding your first and second conclusion: please, see Author Responses above. Regarding your third conclusion: We understand that it might appear odd at first glance that „me-search“ might have negative as well as positive effects on trust in science. However, we think that makes our two studies noteworthy. Following your question what – if asked directly – participants might say about an affected researcher, we decided to include the qualitative data we assessed in Study 2 (participants’ self-reported opinion on the researcher being affected) in the paper. Here, it becomes clear that most participants express a negative or at least mixed opinion about a researcher being affected, the argument of potential bias being mentioned most often in the open text responses. However, on average, the affected researchers in both studies were not judged more negatively than the not affected researchers. We added the analyses and interpretation of the qualitative data throughout the text:
Study 2 – Method, p. 18: “[…] and an open-ended question about participants’ opinion regarding the researcher being personally affected to explore how laypeople rationalize their opinion. These responses were later coded for valence (positive, negative, mixed, or neutral) and content (deductive and inductive coding) by two raters blind to the specific research question (see Appendix C in the supplementary materials, https://osf.io/phfq3/?view_only=a3694575674944fababa32b696e6e645; interrater reliability for valence, Cohen’s κ=.86, p<.01; and for content, Cohen’s κ=.74, p<.01).”
Study 2 – Results, p. 23-24: “Participants’ Opinion. Overall, participants who responded to the open-ended question expressed mostly negative opinions about the researcher being affected by his own research (negative: 48%, neutral: 21%, positive: 17%, and mixed: 14%) about the researcher being affected by his own research. The most frequently mentioned (negative) remark was that a “me-searcher” might be biased towards their research (60%; e.g., “By introducing himself as being affected, I fear he cannot evaluate the results of his research objectively”). The second most frequently mentioned remark was that such idiosyncratic relevance is irrelevant (24%; e.g., “It wouldn’t make a difference”). Positive remarks were mentioned less frequently: Participants ascribed more motivation (11%; e.g. “I think interest, also personal interest, is an important prerequisite for determined research”) or knowledge about the topic (8%; e.g. “Very good, most likely, he thus is knowledgeable about the subject matter and can conduct the study in a more purposeful manner”) to the “me-searcher”, or recognized the transparency (7%; e.g., “The main thing is transparency. People are always biased, perhaps even unconsciously”; for more details, see Appendix C in the supplementary materials: https://osf.io/phfq3/?view_only=a3694575674944fababa32b696e6e645 ).”
Study 2 – Discussion, p. 24-25: “Further, qualitative analyses revealed that most participants reported negative – or, at least, mixed – perceptions of a “me-searcher” (e.g., “me-searchers” may be biased, but also highly motivation and knowledgeable), which corroborated our theoretical prediction that “me-search” may be a double-edged sword. Interestingly, these qualitative findings seem somewhat contradictory to the quantitative findings, according to which there was no main effect of researchers’ idiosyncratic affection by their research topic.”
General Discussion, p. 26: “’Me-search’ neither automatically sparks trust nor mistrust in laypeople, even if their explicit opinions seem rather negative. In line with assumptions from motivated science reception […]”
Reviewer #3:
This paper examines how peoples’ attitudes toward a topic influence their evaluation of research and researchers’ trustworthiness - in the context of research topics which have personal relevance to the researchers.
Thank you for this feedback. We clarified the phrasing in the abstract.
We added the factor analyses in appendix A: See also p. 9 Factor analyses (see Appendix A in the supplementary materials, https://osf.io/phfq3/?view_only=a3694575674944fababa32b696e6e645 ) suggest that a two-factor model (with expertise and integrity/benevolence) fit the data better than a three-factor model (as suggested by [36]), corroborating the idea of a cognitive-rational dimension and an affective dimension of trustworthiness [37].”
We changed the display of our p values to exact values with three decimals in the text and to significance-indicators (*) of up to three decimals in the tables.
We performed simple slopes analyses and described the conditional effects (see response to Reviewer 2). This was not made clear enough, so we specified that in our phrasing in the manuscript throughout both Results sections.
We changed the correlation tables (now Table 1 and 3) accordingly.
In this paper, we focused on overall trustworthiness and credibility. However, to gain further insights into the „building blocks of trust in science“ (see discussion on p. 27), we also explored whether and how the two facets of epistemic trustworthiness might be differentially impacted: While highly correlated, both might differentially impacted by “me-search” as there is reason to believe the two facets are, in fact, fueled by different perceptions (i.e., expertise by perceived competence and integrity/benevolence by more communal aspects). Thus, while not the focus of this paper, the separate analyses provide some tentative insights that are worth following up upon in future research (see also Author Response to the following concern).
We fully agree with these assumptions and discuss these in the General Discussion in two paragraphs (i.e., regarding the effects on the two facets of epistemic trustworthiness and in the future research section). We tried to connect and refine these paragraphs, so that the argumentation becomes clearer (p. 26: “This points to “me-search” – when received positively – possibly adding to the perception of competence-related aspects like a deeper knowledge of a phenomenon (e.g., via anecdotal insights) [12–14] and, even more so, warmth-related aspects like seeming more sincere, benevolent, transparent and, thus, approachable [15,16,41].” and p. 27: “[…] but also important theoretical insights on the building blocks of trust in science and researchers (see discussion above regarding the effects on the facets of epistemic trustworthiness). As one example, knowing that a qualitative level of knowledge is highly valued could further research on the trust-benefit of enriching statistical evidence with anecdotal and narrative elements [44,45].”).
Submitted filename: Response to Reviewers.docx
Decision Letter 1
16 Jun 2021
When research is me-search: How researchers' motivation to pursue a topic affects laypeople's trust in science
PONE-D-20-38206R1
Dear Dr. Altenmuller
We’re pleased to inform you that your manuscript has been judged scientifically suitable for publication and will be formally accepted for publication once it meets all outstanding technical requirements.
Within one week, you’ll receive an e-mail detailing the required amendments. When these have been addressed, you’ll receive a formal acceptance letter and your manuscript will be scheduled for publication.
An invoice for payment will follow shortly after the formal acceptance. To ensure an efficient process, please log into Editorial Manager at http://www.editorialmanager.com/pone/ , click the 'Update My Information' link at the top of the page, and double check that your user information is up-to-date. If you have any billing related questions, please contact our Author Billing department directly at gro.solp@gnillibrohtua .
If your institution or institutions have a press office, please notify them about your upcoming paper to help maximize its impact. If they’ll be preparing press materials, please inform our press team as soon as possible -- no later than 48 hours after receiving the formal acceptance. Your manuscript will remain under strict press embargo until 2 pm Eastern Time on the date of publication. For more information, please contact gro.solp@sserpeno .
Acceptance letter
When Research is Me-Search: How Researchers’ Motivation to Pursue a Topic Affects Laypeople’s Trust in Science
Dear Dr. Altenmüller:
I'm pleased to inform you that your manuscript has been deemed suitable for publication in PLOS ONE. Congratulations! Your manuscript is now with our production department.
If your institution or institutions have a press office, please let them know about your upcoming paper now to help maximize its impact. If they'll be preparing press materials, please inform our press team within the next 48 hours. Your manuscript will remain under strict press embargo until 2 pm Eastern Time on the date of publication. For more information please contact gro.solp@sserpeno .
If we can help with anything else, please email us at gro.solp@enosolp .
Thank you for submitting your work to PLOS ONE and supporting open access.
PLOS ONE Editorial Office Staff
on behalf of
Dr. Lynn Jayne Frewer
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
100 Interesting Research Paper Topics for High Schoolers
What’s covered:, how to pick the right research topic, elements of a strong research paper.
- Interesting Research Paper Topics
Composing a research paper can be a daunting task for first-time writers. In addition to making sure you’re using concise language and your thoughts are organized clearly, you need to find a topic that draws the reader in.
CollegeVine is here to help you brainstorm creative topics! Below are 100 interesting research paper topics that will help you engage with your project and keep you motivated until you’ve typed the final period.
A research paper is similar to an academic essay but more lengthy and requires more research. This added length and depth is bittersweet: although a research paper is more work, you can create a more nuanced argument, and learn more about your topic. Research papers are a demonstration of your research ability and your ability to formulate a convincing argument. How well you’re able to engage with the sources and make original contributions will determine the strength of your paper.
You can’t have a good research paper without a good research paper topic. “Good” is subjective, and different students will find different topics interesting. What’s important is that you find a topic that makes you want to find out more and make a convincing argument. Maybe you’ll be so interested that you’ll want to take it further and investigate some detail in even greater depth!
For example, last year over 4000 students applied for 500 spots in the Lumiere Research Scholar Program , a rigorous research program founded by Harvard researchers. The program pairs high-school students with Ph.D. mentors to work 1-on-1 on an independent research project . The program actually does not require you to have a research topic in mind when you apply, but pro tip: the more specific you can be the more likely you are to get in!
Introduction
The introduction to a research paper serves two critical functions: it conveys the topic of the paper and illustrates how you will address it. A strong introduction will also pique the interest of the reader and make them excited to read more. Selecting a research paper topic that is meaningful, interesting, and fascinates you is an excellent first step toward creating an engaging paper that people will want to read.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is technically part of the introduction—generally the last sentence of it—but is so important that it merits a section of its own. The thesis statement is a declarative sentence that tells the reader what the paper is about. A strong thesis statement serves three purposes: present the topic of the paper, deliver a clear opinion on the topic, and summarize the points the paper will cover.
An example of a good thesis statement of diversity in the workforce is:
Diversity in the workplace is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic advantage for businesses, as it fosters innovation, enhances creativity, improves decision-making, and enables companies to better understand and connect with a diverse customer base.
The body is the largest section of a research paper. It’s here where you support your thesis, present your facts and research, and persuade the reader.
Each paragraph in the body of a research paper should have its own idea. The idea is presented, generally in the first sentence of the paragraph, by a topic sentence. The topic sentence acts similarly to the thesis statement, only on a smaller scale, and every sentence in the paragraph with it supports the idea it conveys.
An example of a topic sentence on how diversity in the workplace fosters innovation is:
Diversity in the workplace fosters innovation by bringing together individuals with different backgrounds, perspectives, and experiences, which stimulates creativity, encourages new ideas, and leads to the development of innovative solutions to complex problems.
The body of an engaging research paper flows smoothly from one idea to the next. Create an outline before writing and order your ideas so that each idea logically leads to another.
The conclusion of a research paper should summarize your thesis and reinforce your argument. It’s common to restate the thesis in the conclusion of a research paper.
For example, a conclusion for a paper about diversity in the workforce is:
In conclusion, diversity in the workplace is vital to success in the modern business world. By embracing diversity, companies can tap into the full potential of their workforce, promote creativity and innovation, and better connect with a diverse customer base, ultimately leading to greater success and a more prosperous future for all.
Reference Page
The reference page is normally found at the end of a research paper. It provides proof that you did research using credible sources, properly credits the originators of information, and prevents plagiarism.
There are a number of different formats of reference pages, including APA, MLA, and Chicago. Make sure to format your reference page in your teacher’s preferred style.
- Analyze the benefits of diversity in education.
- Are charter schools useful for the national education system?
- How has modern technology changed teaching?
- Discuss the pros and cons of standardized testing.
- What are the benefits of a gap year between high school and college?
- What funding allocations give the most benefit to students?
- Does homeschooling set students up for success?
- Should universities/high schools require students to be vaccinated?
- What effect does rising college tuition have on high schoolers?
- Do students perform better in same-sex schools?
- Discuss and analyze the impacts of a famous musician on pop music.
- How has pop music evolved over the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of women in music changed in the media over the past decade?
- How does a synthesizer work?
- How has music evolved to feature different instruments/voices?
- How has sound effect technology changed the music industry?
- Analyze the benefits of music education in high schools.
- Are rehabilitation centers more effective than prisons?
- Are congestion taxes useful?
- Does affirmative action help minorities?
- Can a capitalist system effectively reduce inequality?
- Is a three-branch government system effective?
- What causes polarization in today’s politics?
- Is the U.S. government racially unbiased?
- Choose a historical invention and discuss its impact on society today.
- Choose a famous historical leader who lost power—what led to their eventual downfall?
- How has your country evolved over the past century?
- What historical event has had the largest effect on the U.S.?
- Has the government’s response to national disasters improved or declined throughout history?
- Discuss the history of the American occupation of Iraq.
- Explain the history of the Israel-Palestine conflict.
- Is literature relevant in modern society?
- Discuss how fiction can be used for propaganda.
- How does literature teach and inform about society?
- Explain the influence of children’s literature on adulthood.
- How has literature addressed homosexuality?
- Does the media portray minorities realistically?
- Does the media reinforce stereotypes?
- Why have podcasts become so popular?
- Will streaming end traditional television?
- What is a patriot?
- What are the pros and cons of global citizenship?
- What are the causes and effects of bullying?
- Why has the divorce rate in the U.S. been declining in recent years?
- Is it more important to follow social norms or religion?
- What are the responsible limits on abortion, if any?
- How does an MRI machine work?
- Would the U.S. benefit from socialized healthcare?
- Elderly populations
- The education system
- State tax bases
- How do anti-vaxxers affect the health of the country?
- Analyze the costs and benefits of diet culture.
- Should companies allow employees to exercise on company time?
- What is an adequate amount of exercise for an adult per week/per month/per day?
- Discuss the effects of the obesity epidemic on American society.
- Are students smarter since the advent of the internet?
- What departures has the internet made from its original design?
- Has digital downloading helped the music industry?
- Discuss the benefits and costs of stricter internet censorship.
- Analyze the effects of the internet on the paper news industry.
- What would happen if the internet went out?
- How will artificial intelligence (AI) change our lives?
- What are the pros and cons of cryptocurrency?
- How has social media affected the way people relate with each other?
- Should social media have an age restriction?
- Discuss the importance of source software.
- What is more relevant in today’s world: mobile apps or websites?
- How will fully autonomous vehicles change our lives?
- How is text messaging affecting teen literacy?
Mental Health
- What are the benefits of daily exercise?
- How has social media affected people’s mental health?
- What things contribute to poor mental and physical health?
- Analyze how mental health is talked about in pop culture.
- Discuss the pros and cons of more counselors in high schools.
- How does stress affect the body?
- How do emotional support animals help people?
- What are black holes?
- Discuss the biggest successes and failures of the EPA.
- How has the Flint water crisis affected life in Michigan?
- Can science help save endangered species?
- Is the development of an anti-cancer vaccine possible?
Environment
- What are the effects of deforestation on climate change?
- Is climate change reversible?
- How did the COVID-19 pandemic affect global warming and climate change?
- Are carbon credits effective for offsetting emissions or just marketing?
- Is nuclear power a safe alternative to fossil fuels?
- Are hybrid vehicles helping to control pollution in the atmosphere?
- How is plastic waste harming the environment?
- Is entrepreneurism a trait people are born with or something they learn?
- How much more should CEOs make than their average employee?
- Can you start a business without money?
- Should the U.S. raise the minimum wage?
- Discuss how happy employees benefit businesses.
- How important is branding for a business?
- Discuss the ease, or difficulty, of landing a job today.
- What is the economic impact of sporting events?
- Are professional athletes overpaid?
- Should male and female athletes receive equal pay?
- What is a fair and equitable way for transgender athletes to compete in high school sports?
- What are the benefits of playing team sports?
- What is the most corrupt professional sport?
Where to Get More Research Paper Topic Ideas
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original research topic ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Disclaimer: This post includes content sponsored by Lumiere Education.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
717 Good Research Paper Topics

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Some examples of common research paper styles include:
- Argumentative Research Papers
- Persuasive Research Papers
- Education Research Papers
- Analytical Research Papers
- Informative Research Papers
Your research essay topic may also need to be related to the specific class you are taking. For example, an economics class may require a business research paper, while a class on human behavior may call for a psychology research paper.
The requirements for your paper will vary depending on whether you are in high school, college, or a postgraduate student. In high school, you may be able to choose an easy topic and cite five or six sources you found on Google or Yahoo!, but college term papers require more in-depth research from reliable sources, such as scholarly books and peer-reviewed journals.
Do you need some help with brainstorming for topics? Some common research paper topics include abortion, birth control, child abuse, gun control, history, climate change, social media, AI, global warming, health, science, and technology.
But we have many more!
On this page, we have hundreds of good research paper topics across a wide range of subject fields. Each of these topics could be used “as is” to write your paper, or as a starting point to develop your own topic ideas.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
How to Choose Your Research Paper Topic
The first step to developing an interesting research paper is choosing a good topic. Finding a topic can be difficult, especially if you don’t know where to start. Finding the Right Research Paper Topic
If you are in a class that allows you to choose your own term paper topic, there are some important areas to consider before you begin your project:
Your Level of Interest: Research papers are time-consuming; you will be spending countless hours researching the topic and related topics, developing several primary and secondary sources, and putting everything together into a paper that is coherent and accomplishes your objectives. If you do not choose a topic you are passionate about, the process will be far more tedious, and the finished product may suffer as a result.
Your Level of Experience: Being interested in a topic is great, but it is even more helpful if you already know something about it. If you can find a topic that you already have some personal and/or professional experience with, it will vastly reduce the amount of research needed and make the whole process much easier.
Available Information on the Topic: Be sure to choose a topic that is not only interesting but also one that has numerous sources available from which to compile your research. A researchable topic with several potential sources gives you access to the level of information you need to become an authority on the subject.
Your Audience: An interesting topic to you may not necessarily be interesting to your professor or whoever is grading your research paper. Before you begin, consider the level of interest of the person(s) who will be reading it. If you are writing a persuasive or argumentative essay, also consider their point of view on the subject matter.
As you begin researching your topic, you may want to revise your thesis statement based on new information you have learned. This is perfectly fine, just have fun and pursue the truth, wherever it leads. If you find that you are not having fun during the research phase, you may want to reconsider the topic you have chosen.
The process of writing the research paper is going to be very time consuming so it’s important to select a topic that is going to sustain your interest for the duration of the project. It is good to select a topic that is relevant to your life since you are going to spend a long time researching and writing about it. Perhaps you are considering starting your own business or pursuing a career in politics. Look through the suggested research paper topics and find one in a category that you can relate to easily. Finding a topic that you have some personal interest in will help make the arduous task a lot easier, and the project will have better results because of your vested interest.
Our List of Research Topics and Issues
Affirmative action, health, pharmacy, medical treatments, interpersonal communication, marketing and advertising, barack obama, discrimination, bill clinton, hilary clinton, computer crimes and security, cosmetic surgery, controversial, criminal justice, donald trump, easy/simple, environment, family violence, foreign policy, gambling and lotteries, the lgbtq community, generational conflict, gun control, hate crimes, immigration, middle east, maternity/paternity leave, natural disasters, police work, population explosion, pornography, prisons and prisoners, prostitution, ronald reagan, student loan debt, teen issues, women, mothers, what, why, and how, relationships.
We compiled an exhaustive list of topics that would make excellent research papers. The topics are specifically organized to help you find one that will work for your project. Broad topics are headed, and then below them are narrowed topics, all to help you find an area to focus on. The way we have organized the topics for research papers can save you lots of time getting prepared to write your research paper.
We have topics that fit into categories that cover such areas as education, environmental sciences, communication and languages, current events, politics, business, criminal justice, art, psychology, economics to name just a few. Simply get started by choosing the category that interests you and peruse through the topics listed in that category and you’ll be well on your way to constructing an excellent research paper.
Be sure to check other topics ideas: persuasive speech topics , argumentative speech topics , policy speech topics . We also have some sample outlines and essay templates .
- What limits are responsible?
- What limits are realistic?
- How to protect abortion doctors, pregnant women, and the protection of abortion clinics vs. the right to protest
- Partial birth abortion
- Scientific evidence vs. definition of viability
- Stem cell research
- Unborn victims of violence
- Relative equality has been achieved vs. serious inequities continue
- Can racial balance in business, education, and the military be achieved without policies that promote Affirmative Action
- Reverse discrimination
- NOW, National Organization for Women
- No government support vs. fairness to parents who pay twice for education
- Separation of church and state vs. religion’s contribution to the public good
- Placement by age vs. placement by academic ability
- Mainstreaming students with disabilities vs. special classrooms for their special needs
- Required standardized tests for advancement vs. course requirements only
- National standardized tests vs. local control of education
- Discrimination in education
- Multicultural/bilingual education vs. traditional basics
- Teacher competency tests vs. degree requirements only
- Teacher’s needs/demands vs. teaching as a service profession
- Policing schools
- School’s responsibility vs. parental responsibility for school violence
- Drug and alcohol abuse, pregnancy, suicide
- Zero tolerance toward violence vs. toughness with flexibility
- Permit corporal punishment
- Exams often do little more than measure a person’s ability to take exams. Should exams be outlawed in favor of another form of assessment?
- Should teens in the U.S. adopt the British custom of taking a “gap year” between high school and college?
- In some European schools, fewer than 10% of students get “As”. Is there grade inflation in the U.S.? Why so many “As” for Americans?
- Education and funding
- Grade inflation
- No Child Left Behind Act: Is it working?
- Home schooling
- Standardized tests
- Are children smarter (or more socialized) because of the Internet?
- Should the federal government be allowed to regulate information on the internet?
- How has the music industry been affected by the internet and digital downloading?
- How does a search engine work?
- What are the effects of prolonged steroid use on the human body?
- What are the benefits and hazards of medical marijuana?
- How does tobacco use affect the human body?
- Do the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks?
- What are some common sleep disorders and how are they treated?
- What are the risks of artificial tanning or prolonged exposure to the sun?
- Should thin people have to pay Medicare and other health costs for the health problems of obese people? Should obese people have higher premiums?
- Low carbohydrate vs. low fat diets
- Benefits of weight training vs. aerobics
- How much weekly exercise is needed to achieve lasting health benefits
- Health websites give too much information
- Psychological disorders, such as cutting and self-harm, eating disorders, Autism, Tourette Syndrome, ADHD, ADD, Asperger Syndrome
- Are we taking it too far by blaming fast food restaurants for obesity? When is it individual responsibility and when is it appropriate to place blame?
- Should companies allow employees to exercise on work time?
- Steroids, Antibiotics, Sprays; Are food manufacturers killing us?
- Alternative medicine
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Causes of eating disorders, society’s portrayal of women
- Eating disorders statistics
- Down’s syndrome
- Birth control
- Dietary supplements
- Exercise and fitness
- Heart disease
- In vitro fertilization
- Attention deficit disorder
- Investigate the history and authenticity of ADHD and ADD.
- Organic foods
- Prescription drugs
- Vegetarianism
- Learning disabilities
- Schizophrenia
- Coma recovery: techniques, successes, new strategies.
- What are the primary types of cancer, and in what ways are they related?
- Investigate the success ratio of holistic and non-medical cancer treatments.
- Is Alzheimer’s inevitable? Examine theories regarding its prevention.
- What forms of physical degeneracy are seen as linked to aging?
- Investigate the connections between emotional stability and physical well-being, and provide evidence as to how the two may be related.
- Investigate differences in rates of injury recovery and overcoming illness based on cultural parameters.
- Examine the modern history of viral epidemics, researching what is known about the emergence of deadly viruses.
- Examine how congenital heart disease may be treated, and how it differs from other forms of heart disease.
- Is occasional depression a natural state to an extent, and is society too eager to treat this as a disorder?
- Investigate Sociopathy, determine biological and psychological roots, typical patterns, and potentials of treatment.
- How are compulsive behaviors determined as such? Explore examples of anal retention and expulsion, OCD, etc., as offering accepted criteria.
- Research and analyze the nature of codependency as both a normal state of relations and as an unhealthy extreme.
- Investigate the history and practice of electroshock, analyzing how and why this extreme treatment came to be widely used.
- Hoarding: symptoms and treatments, causes, types of hoarding
- Limits on extraordinary, costly treatments vs. doing everything possible
- Nutritional/alternative therapy vs. mainstream medical treatment insurance coverage for alternative treatment?
- Government grants for alternative treatment research?
- Health superiority of alternative treatments?
- Assisted suicide vs. preservation of life
- Governmental insurance requirements
- Should there be a national database to track controlled substances (i.e., OXYCODONE) or should it be a state issue?
- Should parents avoid vaccinating their children?
- Decline of communication due to technology
- Online social networks and their influence
- Impact of texting and cell phones
- How do men and women communicate differently using body language, and why does it matter (in dating, the workplace, and social circles)?
- Limitations of the media
- Marketing to children
- Sexual innuendos in marketing
- Global marketing trends
- Should certain kinds of ads be banned in the interest of health/morality/annoyance – alcohol, cigarettes, prescription meds, etc…?
- Children’s programming and advertising
- Most controversial political ads
- Media response and public outcry to political ads
- Campaign funds and their relation to political advertising
- Domestic policy
- Separation of church and state
- Judge nominations and make up of supreme court
- Congressional opposition to presidential nominees/filibusters
- Affirmative action
- Erosion of civil liberties vs. protection against terrorism
- Patriot Act One and Two
- Most developed nations have universal health coverage. Why doesn’t the U.S., the wealthiest nation, have it?
- Tax cut as economic stimulation
- Needs of the states vs. needs of the individuals
- Budget deficits and deficit spending
- Rich vs. poor
- Protection of victims vs. freedom of speech/rights of the accused
- How to improve race relations
- Women still earn only 75 cents for every $1 a man earns. Explain why.
- Discrimination in the workplace: analyzing issues for today’s corporations.
- Gender discrimination
- Interracial marriage
- Should government impose restrictions on what kinds of foods can be served in school cafeterias?
- Pros and cons of school uniforms.
- Do children learn better in boys-only and girls-only schools?
- Charter schools
- Prayer in schools
- Rights of the individual vs. community safety (or campus safety)
- Funding for research
- U.S. obligation to third world countries
- Manufacturing of generic drugs vs. U.S. pharmaceutical companies
- How contagious diseases “jump” from animal hosts to human
- What treatments are available to people infected with HIV and are they effective?
- Right to privacy of a child with AIDS vs. safety of other children
- Limits for campus safety vs. personal freedom
- Implications on violence and crime
- Issues with binge drinking
- Should the U.S. lower the drinking age to 18?
- Leniency because of condition vs. community safety
- Revoking drivers license vs. being able to attend classes and work
- Age discrimination of violators
- Animal rights vs. medical research
- Should it be illegal to use animals for sports and entertainment?
- Humane treatment of animals vs. factory farms
- Animal welfare in slaughter houses
- Animal protection vs. business, employment interests
- School prestige vs. academic standards
- Should shoe companies be able to give away free shoes and equipment to high school athletes?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- Doping in sports
- What are the effects on children whose parents push them in sports?
- Steroids: Should they be legalized?
- Title IX: Has it helped women’s sports? Has it harmed men’s sports?
- Social effects of team sports
- Needed in public school library/curriculum?
- Needed in entertainment industry?
- Needed on the Internet?
- Should parents censor textbooks and other literature for children in schools?
- Parental filters on the Internet. Does censorship actually increase curiosity and use of pornography?
- How is internet censorship used in China and around the world?
- How has United States censorship changed over the decades?
- Democratic kingmaker, influence on political succession
- Impact of global initiative
- Influence on fundraising
- Influence as Secretary of State
- Foreign policies
- Influence on women
- ACT or SAT score requirements
- Promotional techniques, such as 1st time scholarships
- 4 year vs. 2 year colleges
- College admission policies
- College tuition planning
- Distance education
- Diploma mills
- Online porn vs. freedom of speech
- Stalking, invasion of privacy vs. reasonable access
- Hacking crimes–workable solutions?
- What are the latest ways to steal identity and money?
- From where does spam email come and can we stop it?
- How do computer viruses spread and in what ways do they affect computers?
- Cyber security
- Securing Internet commerce: is it possible in today’s arms’ race of hackers and evolving technology?
- Is downloading of media (music, videos, software) infringing on the rights of media producers and causing economic hardships on media creators?
- Should media producers prosecute students and individuals that they suspect of downloading copyrighted materials?
- Programs such as SPOTIFY and PANDORA
- Copyright Law
- Age limitations on surgery
- Addiction to surgery
- Demand for beauty by society
- The dangers of breast implants for teenagers
- The cost of cosmetic surgery
- Plastic surgery
- Weight loss surgery
- Are surgeons “scissor happy,” and are surgeries widely unnecessarily
- Negative texting, instant messaging, email
- Is cyber-bullying as bad as face-to-face?
- Kinds of punishment for cyber-bullying
- Media response
- Should the state or federal government put laws into place to prevent bullying?
- Is homosexuality a choice, or are people born gay?
- Evolution vs. Creationism.
- Should “under God” remain in the Pledge of Allegiance?
- Is healthcare a right or a privilege?
- Fossil fuels vs. alternative energy.
- Transgender bathroom policies.
- Capitalism vs. socialism.
- Should parents be allowed to spank their children?
- Should sanctuary cities lose their federal funding?
- The pros and cons of gun control.
- Should the U.S. continue drone strikes in foreign countries?
- Was the U.S. justified in going to war with Iraq?
- How to solve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- The pros and cons of animal testing.
- Do pro athletes have the right to sit during the national anthem?
- Incarceration rates in the U.S.
- Technology and the criminal justice system.
- Police brutality and minorities.
- Should the police wear body cameras?
- In what circumstances should the death penalty be allowed?
- Should we have stiffer penalties for drunk driving?
- Should those who text while driving be put in jail?
- White-collar crime and punishment.
- Criminalizing protests and activism.
- The rise of wrongful convictions.
- Mutual consent vs. exploitation
- Campuses with “no touch” policy
- Drugs associated to Date Rape
- Violence and Rape
- Government support vs. parental financing
- Benefits vs. harmful effects
- Trump’s unconventional presidential campaign.
- The psychology of Donald Trump.
- Who is behind Trump’s political rise?
- Donald Trump and evangelical voters.
- Donald Trump the businessman.
- Trump’s war on the press (aka “fake news”).
- The Trump Organization and conflicts of interest.
- The border wall and illegal immigration policy.
- Global warming and climate change policy.
- Trump-Russia collusion.
- The rapid rise of “The Resistance.”
- Trump’s legislative agenda; e.g., health care, tax policy, deregulation, etc.
- Trump’s “America First” trade and foreign policy.
- The case for (or against) the Trump presidency.
- Punishment vs. treatment
- Family reactions
- Social acceptance
- Community safety vs. legalization
- United States military involvement in Colombian drug trade?
- Drug legalization
- Abstinence Program: Do they work?
- Should the federal government legalize the use of marijuana?
- What is the true key to happiness?
- What is the cause of America’s obesity crisis?
- Why sleep is necessary.
- Are plastic bottles really bad for you?
- How to encourage people to recycle more.
- How 3D printers benefit everyone.
- How do GPS systems on smartphones work?
- How have oil spills impacted the environment?
- Verbal vs. nonverbal communication.
- The accuracy of lie detector tests.
- How Bill Gates and Steve Jobs changed the world.
- The pros and cons of hitchhiking.
- The PC vs. the Mac.
- What causes tornadoes?
- Pollution, air, and water
- Endangered species
- What are the risks of climate change and global warming?
- Rain forests
- Alternative energy
- Alternative fuel/hybrid vehicles
- Conservation
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse effect
- Marine pollution
- How have oil spills affected the planet and what steps are being taken to prevent them?
- Sustainability of buildings
- Recycling programs
- Cost of “green” programs
- Wind turbines
- Landfill issues
- Renewable fuels
- Radioactive waste disposal
- Soil pollution
- Wildlife conservation: what efforts are being taken to protect endangered wildlife?
- Excessive burden on industries?
- Drilling for oil in Alaska’s ANWR (Arctic National Wildlife Refuge)
- Gasoline consumption vs. SUV’s popularity
- Wildlife protection vs. rights of developers
- Clean air and water standards–weakened vs. strengthened
- What are the dangers of scuba diving and underwater exploration?
- Should the use of coal be subjected to stricter environmental regulations than other fuels?
- Is global warming a hoax? Is it being exaggerated?
- How much is too much noise? What, if anything, should we do to curb it?
- Protecting victims vs. rights of the accused
- Women who kill abusive husbands vs. punishment for murder
- Marital rape?
- How to protect children vs. respect for parental rights
- Children who kill abusive parents
- Child abuse–workable solutions?
- Child abuse
- Domestic abuse
- Organic farming vs. mainline use of chemical sprays
- How to best protect the environment; conservation
- Family vs. corporate farms
- Food production costs
- Interventionism?
- Third world debt and World Bank/International Monetary Fund
- Military support vs. economic development of third world countries
- Human rights violations
- European Union in competition with the U.S.
- Unilateralism
- Relevance of the United Nations
- Neocon role in foreign policy
- Christian right influence on foreign policy
- Pentagon vs. State Department
- Nation building as a policy
- Arms control
- Obama’s National Strategy for Counterterrorism
- Control of al Qaeda
- Drawdown of U.S. Armed Forces in the Middle East
- Cats vs. dogs: which makes the better pet?
- My pet can live forever: why I love animal clones.
- According to my social media profile, my life is perfect.
- Football vs. baseball: which sport is America’s favorite pastime?
- Starbucks vs. Caribou: whose coffee is better?
- What does your dog really think of you?
- Why millennials deserve lower pay.
- What makes people end up with so many mismatched socks?
- How to become a research paper master.
- How reading Tuesdays with Morrie can make you wiser.
- Easy way to earn revenues vs. social damage
- Individual freedom vs. social damage
- Do lotteries actually benefit education or is it a scam?
- Can gamblers ever acquire a statistical advantage over the house in casino games?
- Should there be a constitutional amendment that allows gays and lesbians to legally marry?
- Adoption rights?
- Need special rights for protection?
- College campus response
- Gay, lesbian, bisexual, or transgender
- Gay parenting
- Elderly to share in the tax burden vs. government support of elderly
- Future of social security
- Job discrimination
- Child rearing
- Employment issues
- Generational differences
- Community and police safety vs. unrestricted right to bear arms
- NRA (National Rifle Association)
- 2nd Amendment
- Do states that allow citizens to carry guns have higher or lower crime rates?
- Community safety vs. freedom of Speech
- Punishment inequities
- Persecution of alternative lifestyles
- Church Arson: Hate crime?
- Prevention of hazing
- Greek organizations and rituals of hazing
- Statistics of death or injury due to Hazing
- High Schools and Hazing
- What happened during the Salem witch trials?
- How did trains and railroads change life in America?
- What may have occurred during the Roswell UFO incident of 1947?
- What Olympic events were practiced in ancient Greece?
- How did Cleopatra come to power in Egypt? What did she accomplish during her reign?
- What are the origins of the conflict in Darfur?
- What was the women’s suffrage movement and how did it change America?
- How was the assassination of Abraham Lincoln plotted and executed?
- How did Cold War tension affect the US and the world?
- What happened to the lost settlers at Roanoke?
- How did Julius Caesar affect Rome?
- How did the Freedom Riders change society?
- What was the code of the Bushido and how did it affect samurai warriors?
- How did Joan of Arc change history?
- What dangers and hardships did Lewis and Clark face when exploring the Midwest?
- How are the Great Depression and the Great Recession similar and different?
- What was the Manhattan Project and what impact did it have on the world?
- Why did Marin Luther protest against the Catholic Church?
- How did the Roman Empire fall?
- How did the black plague affect Europe?
- How did Genghis Khan conquer Persia?
- How did journalists influence US war efforts in Vietnam?
- Who is Vlad the Impaler and what is his connection to Count Dracula?
- Who was a greater inventor, Leonardo di Vinci or Thomas Edison?
- What was the role of African Americans during the Revolutionary War?
- What was Britain’s view of India during British rule?
- What were the factors in the China-Tibet conflict?
- Research and analyze the emergence of the Catholic Church as a political force following the collapse of the Roman Empire.
- Investigate Dr. Eileen Powers’ claim that the Roman Empire was lost primarily due to an inability to perceive itself as subject to the change inevitable to all governments, or her “force of nature” theory.
- Explore and discuss the actual cooperation occurring through the centuries of Barbarian conquest of Rome.
- Examine the differences and similarities between Western and Eastern concepts and practices of kingship.
- Investigate and explain the trajectory of ALEXANDER THE GREAT’s empire, with minimal emphasis on personal leadership.
- To what extent did commerce first link Eastern and Western cultures, and how did this influence early international relations?
- Research and analyze how Japan moved from a feudalistic to a modern state, and how geographic isolation played a role in the process.
- Analyze the process and effects of Romanization on the Celtic people of ancient England: benefits, conflicts, influences.
- Overview of British dominance of Ireland, Wales, and Scotland! How was this justified in each case, and what motivated the attempts over centuries of rebellion and failure?
- Investigate the known consequences of Guttenberg’s printing press within the first 30 years of its invention, and only in regard to the interaction between European nations.
- Identify and analyze the point at which the Reformation became fused with European politics and nationalist agendas.
- To what extent did Henry VIII promote the Reformation, despite his vigorous persecution of heretics in England?
- Trace and discuss the uses of papal power as a military and political device in the 14th and 15th centuries.
- Research the city/state of Florence from the 13th to the 16th centuries, discussing how and why it evolved as so fiercely republican.
- Compare and contrast the Russian Czarism of Peter, Elizabeth, and Catherine with the monarchies of England and France in the 18th and 19th centuries.
- Investigate the enormous significance of Catholic Orthodoxy as the dominant faith in Russia, and its meaning and influence in an empire populated by a minimal aristocracy and predominant serfdom.
- To what extent did Philip II’s religious convictions shape European policy and conflict in the 16th century?
- Trace the path leading to the convocation of the Estates in France in the late 18th century, leading to the Revolution. Assess political and social errors responsible.
- What eventually ended serfdom in Russia, and why were numerous attempts to end it by the Czars in power consistently unsuccessful?
- Research and report on how England was transformed in the 19th century by the industrial revolution and the advent of the railroad.
- Compare and contrast the consequences of the industrial revolutions in England and America in terms of urbanization.
- What were the circumstances leading to World War I, and how might the war have been averted?
- Assess the Cold War of the 20th century in an historical context: can any parallels be made between this conflict and other ongoing tensions between major powers in earlier centuries?
- Analyze Roosevelt’s decisions in implementing the New Deal, beginning with the closing of the banks. Suggest alternative strategies, or reinforce the rationale of the actions.
- What architectural marvels were found in Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire?
- What was the cultural significance of the first moon landing?
- Food programs
- Welfare reform
- Governmental supplementation
- Homeless: urban restrictions vs. needs of the destitute
- Workable solutions?
- Realistic limits vs. openness toward people in need
- English as official language vs. respect for diversity
- Should illegal immigrants be made legal citizens?
- Access to public school and public programs for Illegal Aliens
- Policing borders–workable solutions?
- Employment and/or taxation for Illegal Aliens
- International trade
- Democratization
- “Shock and awe”
- U.S. occupation vs. liberation
- Iraqi run vs. U.S. puppet state
- Oil and Gas prices-Control of resources
- Effective self-government
- War on Terrorism
- Is America winning or losing the War? What is the measurement of success? Have the benefits outweighed the costs?
- Parental leave for both parents
- FMLA (Family Medical Leave Act)
- Bonding time
- Preemptive strike policy
- Precision weapons
- Intelligence reliability
- Afghanistan – a success or stalemate
- Should the U.S. have mandatory military conscriptions? For whom?
- Governmental support
- Preparedness
- School emergency plans
- Community warning systems
- Damage costs
- U.S. presidential elections should be decided by the popular vote, rather than the Electoral College.
- The minimum wage should be increased to provide a “livable” wage for working families.
- There should be stiffer penalties for those who commit animal cruelty.
- School vouchers increase competition and create better quality schools.
- The corporate tax rate should be lowered to create more jobs.
- Social Security should be privatized.
- Human torture should be banned in all circumstances.
- Affirmative action is still needed to ensure racial and gender equality.
- The U.S. dollar should go back on the gold standard.
- Euthanasia and assisted suicide should be outlawed.
- Police brutality vs. dangers that police face
- Racially motivated brutality?
- Politician’s right to privacy vs. the public’s right to know
- Amount of money going into presidential campaigns
- Views on abortion, gay marriage, and other controversial topics
- Political debates throughout history
- Third-party candidates at presidential debates
- Rights of religious citizens vs. freedom from imposition (e.g. prayer in schools)
- Religious motivation for political involvement vs. cultural pluralism
- Christian Right’s influence on foreign policy
- How serious? Causes? Workable solutions?
- Funding abortion as a form of birth control in third world countries?
- What would happen globally if the demand for natural resources is greater than the supply?
- Limitation of social deterioration vs. freedom of speech
- Definition of Pornography
- Child Pornography
- Building prisons vs. alternative sentencing
- Adjusted sentencing for lesser crimes
- Community service
- Diversion Programs for inmates
- How does the prison population in America compare to other nations?
- Prostitution laws in the US and abroad
- Benefits and drawbacks to legalizing prostitution
- Psychological effect on prostitutes and former prostitutes
- Sex slavery, buying and selling
- Should the government be allowed to wire tap without permission?
- What limitations, if any, should be applied to the paparazzi?
- What medical information should be confidential? Who, if anybody, should have access to medical records?
- Does the public have a right to know about a public figure’s private life?
- Privacy rights
- Do harsher punishments mean fewer convictions?
- Date rape: consent vs. exploitation
- Drugs-Rohypnol, GHB, KETAMINE
- Legalization of Date Rape Drugs
- Recently, a 17-year-old boy was sentenced to 10 years in prison for having consensual oral sex with a 15-year-old girl. Are statutory rape laws patronizing to girls and discriminatory to boys?
- Acquaintance rape
- Is there one true religion?
- Freedom of religion
- Offer distinct reasons why the Bible should be studied as literature, removed from religious significance.
- From Hollywood to the White House: the political rise of Ronald Reagan.
- The Great Communicator: how Reagan captured the hearts of Americans.
- 1981 assassination attempt: bullet wound leaves Reagan inches away from death.
- Reagan appoints the first female Supreme Court justice.
- The PATCO breakup and decline of the labor unions.
- Tax cuts and “Reaganomics.”
- The “Iran-Contra” scandal.
- Reagan, Gorbachev, and the end of the Cold War.
- The final act: Reagan’s Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and long goodbye.
- How has airport security intensified since September 11th, 2001?
- Identity theft
- Homeland Security: Are we safer since the creation of this department?
- Should the government use invasive pat-downs and body scans to ensure passenger safety or are there better methods?
- Is arming Pilots a good idea?
- What responsibilities do secret service agents have?
- Student loan scams
- How to avoid student loan debt
- Managing student loan debt
- Driverless cars and the future of transportation.
- Breaking the glass ceiling: the impact of the women’s rights movement.
- How seniors contribute to societal well-being.
- How disabled individuals are viewed by society.
- The modern-day civil rights movement.
- Has technology made us more detached from society?
- The role of religion in society.
- In today’s society, are we better off or worse off than previous generations?
- Popular music and its impact on the culture.
- Class and geographical segregation.
- The differences between life in the city, suburbs, and/or rural areas.
- Should parents be able to create designer babies?
- Should microchips be implanted inside humans for better tracking and security?
- Will smart watches eventually replace cell phones?
- The pros and cons of being a global citizen.
- Progressive vs. flat tax
- Excessive taxes vs. worthwhile programs
- Is text messaging contributing to teen illiteracy?
- How eating disorders impact teens.
- Tablets vs. textbooks.
- Do standardized tests improve teen education?
- Are violent video games contributing to juvenile delinquency?
- Is English literature relevant for today’s teens?
- Should the HPV vaccine be required for teen girls?
- Do teachers inflate grades so students can pass?
- Should advertisers be allowed to target teens?
- How to encourage teens to stop smoking.
- The causes and effects of teen alcohol and drug abuse.
- How to prevent teen pregnancy.
- Osama Bin Laden
- World Trade Center and Pentagon bombings
- September 11, 2001
- War on terrorism
- Afghanistan
- Bioterrorism
- Al Qaida: Has U.S. policy actually spread terrorism rather than contained it? Will it get better or worse? Why and how?
- Can terrorism ever be justified?
- What kind of person becomes a suicide bomber?
- What were the circumstances surrounding the death of Osama Bin Laden?
- Has the Patriot Act prevented or stopped terrorist acts in America?
- How is text messaging affecting teen literacy?
- Cell Phones: How have they changed us socially?
- Does the Information Age mean we are losing important historical information?
- Where did hip-hop music originate?
- A day in the life of a Buddhist monk.
- How does the brain store and retrieve memories?
- What life is like inside an ant colony.
- The case for and against the existence of UFOs.
- Can virtual reality adequately substitute for actual reality?
- Are dreams hidden messages or just hot air?
- Why do people collect the most ridiculous things?
- When is it time to get out of an abusive relationship?
- The art of pretending to care.
- Public attitudes toward veterans
- Health issues caused by service time
- Organizations for veterans
- Governmental support for veterans
- What programs are available to help war veterans get back into society?
- Iraq War Vets: Are they being cheated on medical benefits?
- Is there a glass ceiling?
- Obstacles to women running for political office?
- Should women be priests, pastors, ministers, and rabbis?
- What differences, if any, are there in children who are raised by stay-at-home moms and working moms? Does society today still discriminate against working mothers who wish to have flexible work schedules?
- Should stay-at-home moms get a salary from the government?
- Why do we sleep?
- How do GPS systems work?
- Who was the first person to reach the North Pole?
- Did anybody ever escape Alcatraz?
- What was life like for a gladiator?
- Are there any effective means of repelling insects?
- How is bulletproof clothing made?
- How was the skateboard invented and how has it changed over the years?
- What is life like inside of a beehive?
- Where did hip hop originate and who were its founders?
- What makes the platypus a unique and interesting mammal?
- What is daily life like for a Buddhist monk?
- How did gunpowder change warfare?
- How were cats and dogs domesticated and for what purposes?
- What do historians know about ninjas?
- Are humans still evolving?
- What is the curse of the pharaohs?
- Why was Socrates executed?
- How did ancient sailors navigate the globe?
- How are black holes formed?
- How do submarines work?
- Do lie detector tests accurately determine truthful statements?
- How does a hybrid car save energy?
- What ingredients can be found in a hotdog?
- How does a shark hunt?
- How does the human brain store and retrieve memories?
- How does stealth technology shield aircraft from radar?
- What causes tornados?
- How does night vision work?
- What causes desert mirages, and how do they affect wanderers?
- What are sinkholes, and how are they formed?
- What are the major theories explaining the disappearance of the dinosaurs?
- Should we reform laws to make it harder to get a divorce?
- Divorce rates
- Family relationships
- Family values
- Race relations
- Marriage and Divorce
- A view of home life and its effect on child development
- How 4 generations in the workplace can work together.
- Building positive employee relationships
- Modern work environments
- Business leadership
- Workforce regulations
- Small business and taxation
- Corporate law
- Issues in modern Human Resources: Are today’s corporations patronizing employees or being more responsible for them?
- Cultural conflict in globalization: Strategies for successfully establishing a presence in a foreign culture
- Corporate abuse: How can executives so successfully manipulate corporations criminally?
- Identifying stakeholders in non-public companies: is the corporate responsibility the same as for public offerings?
- Devise a new model of leadership for business today, incorporating elements of existing leadership models and theories.
- Examine the actual impact of social media as a business promotion instrument.
- Devise a scenario in which traditionally unethical business practices may be justified.
- Should newspaper reporters be required to reveal their sources?
- Do the media (both print and broadcast) report fairly? Do they ever cross the line between reporting the news and creating the news?
- Does news coverage favor whites?
- What steps are involved in creating a movie or television show?
- How have the film and music industries dealt with piracy?
- Media conglomerates/ownership
- Minorities in mass media
- Portrayal of women
- Reality television
- Television violence
- Media portrayals
- Sensationalized media
- Examine the issues of responsibility in pharmaceutical companies’ promotion of drugs in the media.
- Forensic science technology
- What are the current capabilities and future goals of genetic engineers?
- What obstacles faced scientists in breaking the sound barrier?
- What is alchemy and how has it been attempted?
- What technologies are available to home owners to help them conserve energy?
- Nuclear energy
- Clean energy resources
- Wind energy: Is wind energy really that inexpensive? Is it effective? Is it practical?
- What are the dangers and hazards of using nuclear power?
- Investigate Freud’s contributions to psychology as they exist today: what value remains?
- Are there gender foundations to psychology and behavior that are removed from cultural considerations? To what extent does gender actually dictate thought process?
- To what extent is sexual orientation dictated by culture, and is there an orientation not subject to social and cultural influences?
- Investigate the psychological process in group dynamics with regard to the emergence of leaders and the compliance of others.
- Compare and contrast Jung, Freud, and Adler: explore distinctions and commonalities.
- What is “normal,” and to what extent is psychology reliant on culture to define this?
- Research and assess the effectiveness of radical psychotherapies and unconventional treatments.
- Research the concept of human will as both a component of individual psychology and a process or element removed from it.
- To what extent is self-image influenced by culture in regard to eating disorders? Are external factors entirely to blame?
- How do centuries-old beliefs of madness and dementia relate to modern conceptions of mental illness?
- Is psychology itself inevitably a non-science in that virtually any theory may be substantiated, or is there a foundation of science to the subject to which all theorists must conform?
- Examine Euripides and gender psychology: what do the Trojan Women and Medea reveal?
- Using three characters, explore Chaucer’s insight into human behavior in The Canterbury Tales.
- Identify the true relationship between Dante and Virgil in The Divine Comedy, emphasizing Dante’s reliance on the poet.
- Research and discuss the English fascination for euphemism and ornate narratives in the 16th century, beginning with John Lyly.
- Examine any existing controversies regarding Shakespearean authorship, citing arguments on both sides.
- Analyze similarities and differences between Marlowe and Shakespeare in regard to Tamburlaine and Titus Andronicus.
- Defend or support Bloom’s assertion of Shakespeare as the “inventor of the human being.”
- To what degree are Shakespeare’s plays influenced by, or reflective, of the Elizabethan era? Identify specific cultural and national events linked to at least 3 plays.
- Analyze the unusual construction of A Winter’s Tale in regard to transition from comedy to drama. Is this valid? Does the transition benefit or harm the play?
- Support the belief that Shakespeare is representing himself as Prospero through evidence, or similarly refute the belief.
- Why was extreme violence so popular in English Reformation drama? Cite Marlowe, Kyd, Webster, and Shakespeare.
- Analyze the metaphysical in Donne’s poetry: is it spiritual, existential, or both?
- What is Shelley seeking to say in Frankenstein? Support your answer with passages from the novel.
- Compare and contrast Tolstoy’s Anna Karenina with Flaubert’s Madame Bovary, noting the characters of the heroines.
- It is argued that Dickens failed when he turned to serious, romantic narrative in his novels. Using Copperfield, Great Expectations, and Dombey and Son, defend or refute this claim.
- Assess Dickens’ stance as a moralist in Bleak House and Hard Times: to what extent does he seek reform, and to what does he comment on the human condition?
- Was the Harry Potter phenomenon warranted by quality of storytelling or more a matter of public receptivity at the time combined with media exposure?
Top 10 Microphone Isolation Shield Reflectors + Buyer’s Guide 2021
Best Microphones for Streaming, Gaming and Live Chats in 2022
20 thoughts on “717 Good Research Paper Topics”
How has music evolved? How has music effected history? Music of the past vs music of the present. How has the music industry effected the music’s quality?
Do you think abortion is legal? Why they do abortion?
Why are people instinctively afraid of animals that are not mammals?
Should abortion be legalized? Should domestic abuse and child abuse victims be granted clemency for killing their abuser?
Jewish holocaust and its contribution to European History, specifically Germany
What is the most popular college in the United States?
The Black Knight: Space Waste or Alien Satellite? The Moon Landing: Real or Hollywood Hoax? Have We Become Too Politically Correct? Paranormal Research: Real? Fake? Should it be offered in college? Who really was Jack the Ripper? Can a zombie apocalypse truly occur? Who is the best or worst president of the USA? The Men in Black: real or hoax?
Why Marching Band is a sport.
Marching band is not a sport
how did aids start?
Topic : Alternative medicine Research question : Does the alternative medicine is safe and standardized Hypothesis : analyse the quality controle of alternative medicine formulations
Does our nostalgic music/childhood songs affect our present lifestyle, and in what ways?
reverse discriminations is still discrimination so there’s no such thing as that. like reverse racism isn’t a thing because that is still racism
Men on birth control and not women.
You forget the topic Islamophobia 😉
You should add a music section. Is Muzio Clementi overshadowed by Mozart? The Toccata and Fugue in D- really wasn’t written by Bach The use of the “Dies Irae” in cinema Why is modern music so repetitive and simple compared to classical music?
I want to do a research project on Education
I want to research but not get a perfect topic help me give me a best topic about current affairs
Topic: History. Are the Crusades oversimplified? where they justified? If so, how? Topic: Current affairs. Is the term “conspiracy theory” used to discredit any non-mainstream, controversial opinions. Topic: Gun control. Does limiting magazine capacity for firearms have any effect on gun crime? Are high-capacity magazines ever necessary for self-defense? Topic: Economics. Are minimum wage laws necessary to guarantee “decent”, or do the laws of supply and demand automatically ensure that?
Are women funny?
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
A List of 580 Interesting Research Topics [2024 Edition]
In school and college, you will be required to write research papers. Yes — papers in the plural. And that’s the first reason you may want to turn to Custom Writing and seek help with research projects.
When assigned a paper, the very first undertaking is to choose from a list of research topics. This is a daunting, even intimidating task, one that many people would prefer to circumvent altogether.
The good thing is:
There are hundreds of exciting and fun research topics for high school or college students from which to choose. With a variety of options, you are likely to find some interesting things to research. When you have good ideas and help available, this task becomes less threatening and more engaging.
But first: Let’s verify you have a complete comprehension of what writing a research paper entails. After all, you can’t be creative with an idea if you don’t know how to write about it. Then, you’ll find numerous interesting research topics for your work.
- 🔝 Top 10 Research Topics
❓ What Is a Research Paper?
- ✍️ How to Find Topics to Write About
⭐ A List of Research Topics
- 💻 IT Topics
- 🏺 History Topics
- 🧠 Psychology Topics
- 🎓 Education Topics
- 📺 Cultural Topics
- 🗣️ Topics for an Argumentative Essays
🔬 Science Research Topics
💉 health topics for research papers.
- 👔 Business Research Topics
- 📚 Literature Topics
- 🗳️ Political Topics
😂 Fun Research Topics
- 👥 Sociology Research Papers
🎯 Specific Research Proposal Topics
- 👩⚕️ Nursing Research Papers
- 🎨 Art Topics
- 🎼 Music Topics
- ✍️ Creative Writing Topics
- 🎈 Other Topics
🔝 Top 10 Research Topics for 2024
- Maintaining social bonds via music
- Use of AI in robotics
- Narcissistic personality disorder: genetic factors
- Mental effects of remote work
- Use of infrared detectors in alarm systems
- Cosmological simulations and machine learning
- Achieving climate-positive agriculture
- Emerging infectious diseases: detection and prevention
- Technology-enhanced education in the post-COVID era
- Disability inclusion in the workplace
If you aren’t clear on what a research paper is, then you won’t get very far when writing one. A research paper is just as its name suggests — a form of academic writing that necessitates the independent investigation of a specified topic and reports the unique results of that investigation.
Suny Empire State College provides a great and exhaustive explanation of what a research paper is.
In order to write a paper, you are required to formulate a research question. This is a question associated with your topic that acts as a guide during your research, enabling you to focus and provide unique arguments.
Before you can produce a research question, you have to choose from countless research topics available. Another useful thing to do would be checking out free sample research papers . With that in mind, let’s examine how you can discover some unique research paper topics.
✍️ How to Find Research Topics to Write About
The choice of a research paper topic can be influenced by a number of factors, including:
- The course for which the paper is assigned
- Whether there is a topic assigned to you by the professor
- Whether you are given a broad-spectrum subject area
- How much freedom you are given to branch out and select a topic
Hopefully, you have been given some freedom of choice regarding academic paper topics. However, if you do have some choice in the matter, you might be speculating about how to narrow it down.
You are in luck!

There are a number of ways to effectively comb through the abundance of research paper topics and discover one that will work well for you. Here are some suggestions:
- Ask your professor. Chances are your professor has some fabulous research paper ideas. You can also inquire with other university staff and graduate students for ideas. These people know your discipline well, which can work to your advantage.
- Browse through scientific journals and research papers , but be sure to adhere to the most recent research possible. You will definitely find interesting ideas in published papers that would make great research paper topics.
- Investigate other professional and government publications for research project ideas. Again, keep to the most recent publications within the last three to five years, if possible.
- Browse through your library catalog to uncover the most interesting areas of study in your field.
- Take notes everywhere you go! It doesn’t matter if you are in class listening to your professor, traveling, reading a magazine, or watching TV. Research paper ideas are absolutely everywhere! Write things down whenever you come across something unique and interesting, and you just might find a topic to pursue.
When it comes down to it, deciding on one of the many academic essay topics is the most substantial step of the process.
Once you have that narrowed down, you can focus your research and write a remarkable paper. Now, we want to give you some help. What follows is an extensive list of the most interesting research topics to get you started.
Now that you have a good idea of how to search for college research paper topics, you are ready for some suggestions. You might like one of them right off the bat, or you might be inspired by a particular topic and write something related to it.
Want to know the best part?
By the time you are finished reading this academic topics list, you will feel much more equipped for writing your research paper. For even better result, have a brainstorming session with a research topic generator to introduce a bigger variety of options.
💻 IT Research Paper Topics
Perhaps some of the best college research topics these days are in the IT field. Explore one of these interesting ideas in your paper:
- Has big data changed our lives for the better? Big data is a trendy study subject. Large IT companies use it for purposes such as advertising and logistics. However, it has also raised substantial privacy concerns over non-consensual data gathering. Are the benefits companies get by collecting your data worth them learning everything about you?
- Neural networks are algorithms that can learn to solve problems. Both their name and method of learning are derived from how the human brain works. Can neural networks lead to the creation of a true AI? If so, how soon?
- The current state of cryptography and how it may develop. The entire Internet’s security relies on a relatively small number of ciphers. If they were to be broken, the potential damage would be immeasurable. How likely is that to happen? What challenges are we likely to face in the future?
- The pros and cons of transitioning to cloud technologies. Cloud services are very convenient for various purposes. They might not work as fast as physical devices, but they are portable, cheap, and very convenient. Should humanity switch entirely to cloud services?
- What issues does automation raise, and how can they be solved? Robots don’t get tired and work very precisely. That’s why automation is great for business. Many manufacturing companies rely on robots heavily in their production. However, robots in the workplace mean fewer jobs for humans. When most blue-collar positions disappear, what will humanity do?
- Should we keep using multi-factor authentication?
- Are big tech companies monopolistic in their behaviors?
- Is remote work the future of office jobs employment?
- The pros and cons of software ownership vs. subscription models.
- Explore the evolution of wireless communication standards and their implications.
- Describe the Internet of things and its effects on security.
- The issues of IPv4 and the adoption of IPv6.
- How do computers manage to generate random numbers?
- The infrastructure and contingencies of the World Wide Web .
- Are computers entirely unbiased in their treatment of people?
- Procedures to enhance IT security
- New methodologies and challenges to IT management in health
- Interrelation, patterns, and existing theories on behavior and IT
- Common services center vs. community multimedia center: selecting the correct variety of IT service
- Racial and gender issues in the IT domain
- Innovative theories regarding computer imitation of a human being
- The impact of digitization of medical records on the IT domain
🏺 Topics for your Research Project on History
Human history is full of exciting events, and despite what you might believe, not all of them have been explored. There are many incredible history research topics, such as:
- The history of the Chinese Empire over the millennia. The Chinese Empire is rarely discussed in history classes as much as its Western counterparts. However, it existed for over two millennia, only falling in 1912. Many curious events happened in that time that merit discussion.
- The Ottoman Empire and the Barbary slave trade. The word “barbarian” comes from the Barbary Coast in Africa. It was infamous for its pirates, who raided European vessels for loot and slaves. Only ending in the 19th century, this phenomenon can make for an interesting case study.
- The rise and fall of Ancient Greek city-states. Ancient Greece is often viewed as mostly monolithic and united against threats. In fact, it was comprised of numerous city-states that fought as much as they cooperated. Research the region’s fascinating and nuanced history.
- The effects of the printing press on the world . The printing press was invented in 1440 AD by Johannes Gutenberg. Before it, each copy of a book had to be written by hand. It limited the literature’s availability dramatically. What effects did mass production of books have on Europe and the world?
- The fracturing of Christianity: causes and effects. Since its inception, Christianity has gone through multiple schisms. Some of them were remarkably violent. As a result, there are now three main Christian churches and a multitude of lesser ones. Explore what caused believers to split apart into Orthodox Christians, Catholics, and Protestants.
- The underlying causes of the World War I.
- Provide a detailed history of the Hundred Years’ War and its results.
- Holy Roman Empire: from successor to the Romans to a Nazi symbol.
- Liberalism in national politics: emergence and evolution.
- The history of the world as a series of conquests.
- Were the Crusades motivated purely by religious devotion?
- Why did Texas secede from Mexico to the United States?
- Apartheid in South Africa and its heritage.
- Centers of scientific activity throughout history.
- How did China’s geography influence its history?
- Palestine and the Golan Heights
- Premises, progression, and consequences of the cold war
- The most remarkable revolutions in history
- Has Slavery transformed the development of the western world?
- Could damage from the bubonic plague have been diminished?
- Strange medieval family laws and their influence on society
- Life in London in the 15th century
- Religious cults in ancient societies
🧠 Psychology Research Paper Topics
Psychology has to offer plenty of interesting ideas for you to research. Just look through the discoveries made over the past decades, and you can understand that the human mind holds as many mysteries as the deep ocean.
It is why we would like to suggest a list of great experimental research topics in psychology. The science of human behavior is even more exciting when you can try your theories on practice.
If you still can’t decide on the topic for your research paper or thesis, just look through this collection of compelling proposals to give yourself an inspirational boost.
- What is the correlation between personality and taste in literature? It’s obvious that people with similar interests get in groups. Does it mean that they have similar personalities, though?
- Conformity in college and high school: a scientific approach. Check how your course mates tend to agree with others and don’t forget to write it down!
- Do men and women have different short-term memory mechanisms? It’s quite easy to conduct an experiment, but be careful approaching it in terms of gender issues.
- Optical illusions from the perspective of people with creativity skills. What if people who tend to be artistic and creative can see something in the common optical illusions that others can’t?
- The gut feeling: how do you feel when others stare at you? Some studies showed that you are more likely to wake up in the night because someone is staring at you. It’s creepy, though…
- Tricking the taste buds: how does smell affect the taste? How much can the smell of an onion confuse your sense of taste while you are eating an apple?
- What is the Stroop Effect, and how does age influence it? Check whether the age of the participants influences their ability to name the colors.
- Does having a symmetrical face make us seem more attractive? It is very rare that someone has perfectly identical left and right sides of the face. But how noticeable is it?
- Analyze the capacity of the short-term memory of your peers. The easiest way is to measure it by memorizing words and comparing the numbers later.
- Do people eat more popcorn when watching movies of a specific genre? Chewing something is almost a must-do in the cinema. But what type of movies triggers this behavior more than others?
- What signs of social media addiction are noticeable in public? Spend some time in the local coffee shop, watching people on their phones, and note any signs of addiction they show.
- The psychological effects of having breakfast: learning performance. Check if your course mates who have breakfast are more successful in learning than those who don’t.
- Music vs. body: how does your body respond? Measure different biomarkers while listening to different types of music. Maybe you’ll find perfect motivational beats!
- What color should your room be to improve your learning outcome? Blue is more calming than red, which is often used in sports halls. But what about boosting your learning abilities?
- Favorite color as a result of childhood attraction. Try to trace the childhood memories of your friends. Maybe their favorite color is pink because they had pink walls in their room.
- Biomarkers and colors: what is the correlation? Check how seeing different colors can stimulate specific responses from the body, for example, in heart rate.
- Colors and mood: can the color of your bedsheets make your day? The first thing you see in the morning is quite important. How would a specific color affect your mood?
- What is the correlation between stress levels and procrastination? There is a relation for sure, but does procrastination cause stress or the other way around?
- How much can we trust the long-term memory? Ask people to tell you about some random event from their past. Then, ask them to do the same later. Do the stories match?
- Negative influences of sleep deprivation on social behavior. Track some students’ behavior when they don’t get enough sleep and see how it affects their relationship with others.
- The origin of phobias and fears: engaging the monster within
- Dreams : are they messages from within?
- Mechanisms of thinking: it’s all in your head
- Factors that influence behavior and character
- Mechanisms of aggravating habits
- The function of short- and long-term memory
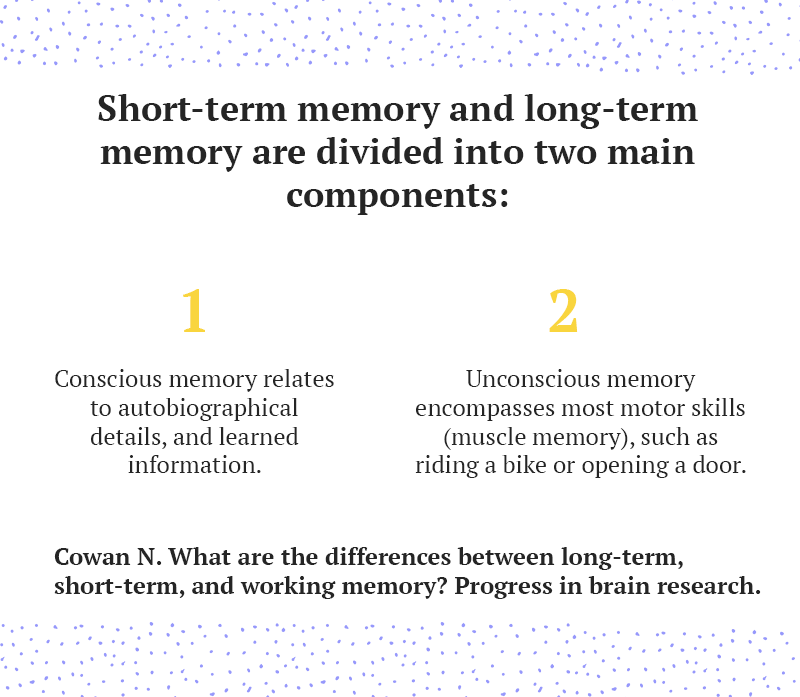
- Why people yearn for their past
- What entices people to amass the most preposterous things?
- Is autism a disease or a natural variation of the norm?
- The impact and outcomes of social networks and mental health
- How memory works: recalling the essential
- How depression impacts the immune system

- A phenomenon-oriented approach to the study of depression
- How to manage post-traumatic stress disorder in children
- Depression as a cause of celiac disease
- Fighting depression with techniques to relieve anxiety
- The consequences of depression and relationship problems
- Eating behaviors in different cultures
- How behavioral patterns develop
- How to forecast and shape behavioral patterns
- Differences and similarities in the behavioral patterns of diverse cultures
- Is there a genetic link to optimism that can shape behaviors and attitudes?
- The causes and consequences of insomnia
- How to combat child violence

- How defense mechanisms and behavioral patterns work
- How bilingualism works: the secret of processing mechanisms
- How fear-related beliefs fit into the cognition process
- Following the cognitive process involved in anxiety disorders
- How to fight emotional distress
- Unusual mental health cases and cognition deviations
- Applying psychological approaches to ethical reality
- How motivation plays a role in human development
- The shared elements of self-affiliation and self-determination
- An examination of the causes and results of drug and alcohol abuse
- New ideas regarding the peculiarities of rational and social development
- How practicing a healthy lifestyle cures disease and promotes wellness
- Conflict solution in parent-child relationships
- Evaluating the challenges of preterm development in children
- How to battle cognitive deficit in Parkinson’s disease
- Is attention deficit disorder a neuropsychological problem?
- Examining the process of making decisions and taking risks
- The impact of music genres on how the brain works
- How to fight childhood disorders
- Shattering long-standing myths about ADHD
- Intellectually gifted people: how is it possible?
🎓 Research Paper Topics on Education
Research project ideas around education are always changing. This has resulted in a wide range of research topics, such as:
- Computers in classrooms: useful tool or obstacle to equality ? Computers have proved to be capable of improving many aspects of our lives. For instance, they allow children to interact with content instead of just consuming it. However, computers further the disparities between those who can and cannot afford one. Explore these factors in your research paper.
- A review of potential methods for solving America’s education crisis. The US invests a substantial portion of its budget into education. However, the system’s equality is average at best. You can study proposals on how we may change its design for the better. Choose the most promising ones, or suggest one of your own.
- Individualized vs. group learning: which is better suited for current reality? Every child’s learning should be tailored to their specific situation. Unfortunately, there are far more children than teachers. Answer these questions: is group learning the only available option despite its drawbacks? Can we reduce its shortcomings by blending the models?
- Are standardized tests helpful or damaging to children’s education ? Standardized tests are convenient from a bureaucratic standpoint. They convert children’s learning into numbers that are easy to work with. But the practice is often criticized for prioritizing memorization over understanding. Should standardized tests be abandoned?
- How should the education system approach children with special needs ? Special needs children have experienced a broad range of treatment throughout history. What are the current ideas on how to teach them? What are their special needs in an educational context, and how can schools satisfy them?
- Are the world’s best education systems based on similar foundations?
- How can schools help children maintain their mental health ?
- What does equality of opportunity mean in the context of the school?
- Review how the essential qualities of a teacher evolved since 2000.
- Should every school student aim for higher education
- What traits define an excellent teacher, and can they be cultivated?
- Is homeschooling a viable alternative to public schools ?
- The school choice debate in the US: arguments for and against.
- Authoritative sources: what qualities make information available on the Internet valid?
- Is cheating on tests an expression of an educational failure?
- Where theory encounters reality in gender issues
- Test anxiety with regard to contemporary methods of teaching
- The effects of contemporary teaching methods
- The mental process behind human learning
- The interpretation of IQ test results
- Should children be rebuked when they misbehave?
- How to prevent bullying and harassment in schools

- The creation of particular learning methods for blind children
- Positives and negatives of contemporary methods of teaching and state-of-the-art innovations
- The function of technology in lesson planning
- Is there a one-size-fits-all strategy for education?
📺 Cultural Research Topics for Papers
Perhaps there is nothing more complex than human culture and how people have interacted with each other throughout history. For this reason, these cultural topics might be of interest to you:
- Harlem Renaissance: how a single neighborhood created modern African American culture. In the 1920s, numerous African Americans moved to the Harlem neighborhood of New York. Influenced by the ideas of thinkers such as W. E. B. Du Bois , they built the foundations of Black culture and art. How did this happen?
- Is third-wave feminism still a movement for equality? First-wave feminism gave women equal rights with men. Then the second wave started the fight with discrimination. However, third-wave feminism claims that the second wave failed, especially with regards to matters such as race and ethnicity. Are its claims valid, and what does it work to achieve?
- Is the Western way of thinking the only correct one? Non-Western civilizations lay claim to different schools of thought that emphasize different viewpoints. Should Westerners adopt aspects of non-Western philosophical thought?
- Are the factors that informed the Constitution still relevant? The Constitution was created in a different time than now. Some of its provisions, notably the Second Amendment, have been challenged repeatedly in recent years. Explore if the ideas of the Founding Fathers still apply today.
- Should the postmodern school of art be considered art? Postmodern art is challenging to define in plain terms. Many people are confused when a seemingly random series of brush strokes sells for millions of dollars. Think of how such artworks fit into the history of art movements.
- The impact of advertisements and commercials on how people comprehend the world
- The implicit messages of mass media : what you see is what you get
- How the most remarkable cultural achievements of the 20 th century influenced contemporary art
- The repetition of cultural tendencies: the Greeks did it first
- Social roles adults endorse to children via toys
- Social models mass media bestows on teenagers and adults
- Eating habits in dissimilar cultures
- The origin of racial discrimination
- The segmentation and integration of humans
- The impact of AIDS on mankind
- A new comprehension of past events
- Unearthing a common language: divorce prevention and family therapy
- Painting a portrait of the average American family
- The roots of antisemitism and how it manifests today
- A case against cruelty to living beings
- An examination of the current job market and unemployment
🗣️ Argumentative Essay Topics
It is easy to find unique argumentative research paper topics. After all, we live in a crazy world in which all kinds of interesting things happen. Here are some suggestions:
- Is the Electoral College a better system than the popular vote? The United States uses the unique Electoral College system for its presidential elections. Over the centuries, calls have been made to change it to the popular vote approach. So far, these attempts have been fruitless. In this debate, whose position has more merit?
- Should the continued expansion of the government be reversed? Starting small, governments around the world took on more and more functions. As a result, they now guarantee the operation of many services. They also collect massive taxes and demonstrate bureaucratic inefficiencies. Is there a valid argument for privatizing most public services?
- Should the US continue acting as the world’s peacekeeper? The US’s military is present in many areas around the world. Usually, they take the form of military bases and peacekeeping forces. However, its efforts often fail, with Iraq as a recent example. Should the nation continue spending its resources abroad?
- Does the public or private healthcare produce better results for the cost? The US’s healthcare system is often criticized for its massive costs and underwhelming quality. There have been calls to both make it more private and more public. Which of the two approaches ensures a more affordable, efficient system?
- Is teenage gender transition ethical? Recently, medical professionals in the US have started transitioning teenagers with gender dysphoria. Yet, some of them de-transition later. Should the practice continue regardless?
- Political commitment and television
- Should marijuana be legalized?
- Can people of different races ever understand each other
- Abusive relationships: where to draw the line on what relationships should Be allowed to exist
- Are there realistic limitations on abortion?
- The many guises of violence in society
- The impact of women on world history

- Are social interactions possible without lies?
- Dealing with overpopulation: can it be accomplished ethically ?
- Torture: is it ever acceptable?
- The ethics of using animals in research
- Human dependence on computers: beneficial or harmful
- Post-9/11 security measures: an invasion of privacy or good sense
Science is always bursting with new and exciting topics as we delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe and technology. Here are a few topic suggestions:
- The potential of space resources and the technologies for extracting them. Space contains a vast quantity of resources, many of which are rare or expensive on Earth. Plans to use them have been arising for a long time. Can we implement any of them in the near future, and do they justify the costs?
- Recent promising developments in cancer treatment and their validity. Cancer is a significant concern for humanity largely because it cannot be treated without harming the body. However, ideas such as targeted medications and imitations of whale biology have promised an end to this problem. Research them and assess their validity.
- Large-scale recycling methods and their effectiveness in reducing waste . Most of the resources humanity uses are still on the planet in the form of waste. Some, such as fossil fuels, cannot be recovered, while metals and many others can. Is it possible to address resource scarcity through large-scale recycling? Is it economically viable?
- Advantages and disadvantages of proposed thorium nuclear reactor designs. Thorium has been touted as the solution to the problems of uranium-based atomic reactors. It’s not as dangerous and produces less waste. Is it indeed superior, or should its issues prevent its use?
- Potential benefits and issues of genetic modification. Genetic modification is broadly used but also criticized by many. It has its benefits, but critics argue that overreliance may lead to unexplored side effects. Are there reasons to believe these claims?
- What cloning has in store for humanity: altering the personality
- How nanotechnology will impact modern science
- Will uranium isotopes precipitate the next scientific revolution?
- How psychoactive drugs influence the central nervous system
- Deafness and using echolocation
- The role of erythropoietin and calcitriol in the human body
- The process of feeling pain: treatment and pain relievers of the future
- Is nuclear energy too hazardous to use?
- Nuclear weapons: a responsibility for which no country is prepared
- People’s impact on climate change: the cost of a technological breakthrough
- Key issues and potential solutions for toxic waste disposal
- Are the effects of global warming reversible ?
- The future of NASA
- Endangered species : causes and concerns
- Black mold: the bathroom invasion
Just like science, health care is always changing, particularly as technology advances. With new discoveries in disease research and new technology being developed every day, the following topics are great examples of what you can write about in your paper:
- Race and ethnicity-based differences in normal health indicators. People of different races and ethnicities tend to have varying normal health indicators. For example, African Americans tend to have a higher blood pressure than average. What causes such differences? Why do medical workers need to understand them?
- The effects of the Affordable Care Act on American healthcare. The Affordable Care Act, colloquially known as Obamacare, was introduced to improve health insurance’s affordability for disadvantaged people. However, the costs of insurance have grown since through premiums. Did Obamacare cause this increase, or did it happen independently?
- Strategies for prevention of obesity and associated heart disease risks. Heart disease is a leading cause of death in the United States. Obesity, which is also prevalent in the nation, is associated with the condition. How can the healthcare system reduce the rates of obesity and associated heart disease?
- For- or non-profit hospitals: which offer superior treatment? Both for- and non-profit hospitals are private entities. The former operate as businesses, while the latter only seek to cover their costs. Is the former’s drive to compete and lower prices preferable to the latter’s not charging a profit margin?
- Mental health in the United States: issues and proposed solutions. Mental healthcare is a complicated topic. Many conditions are difficult to diagnose, and some are associated with stigma. Conflicts of interest often arise among psychiatrists, incentivizing them to diagnose fake conditions. How can mental health be improved in the US?
- Should medicine be more focused on the prevention of illnesses or their treatment?
- Is it possible to eliminate a disease forever?
- The development of prosthetics: current technologies and promising ideas
- Barriers to the adoption of electronic health systems and how to overcome them.
- Sedentary behavior and sports: what are the health outcomes?
- Psychological treatment for adolescents: how to address their needs.
- Caring for seniors: current problems and potential solutions.
- US nursing shortage: causes and potential effects on the nation’s health.
- The effects of circumcision on the health of newborn infants.
- Analyze the experiences of children with autism in school and at home.
- Should image scan radiation be reduced to a minimum level?
- Health care and insurance: concerns and problems
- The most likely outcomes of recent health care reform
- Old theories and new methods of sports injury rehabilitation
- A look at celebrities who have battled cancer
- A comparison of conventional and alternative cancer treatments
- How clean needle programs benefit society
- The need for education on nutrition in school
- The impact of diet on health
👔 Business Research Paper Topics to Write About
Business is a broad field, so there are plenty of topics you can write about, such as:
- Best contemporary practice in green supply chain management for businesses. Green supply chain management aims to overturn the stereotype of polluting factories. Companies that adopt it seek to generate as little waste as possible and require their suppliers to do the same. What policies do researchers currently recommend for this purpose?
- Corporate social responsibility : theoretical framework and practical implementations. Corporate social responsibility is an approach where a company seeks to give back to the community where it works. It’s a popular concept, often discussed in business schools. But how does it translate into practice?
- The effects of different office arrangements on the productivity of employees . Offices have evolved substantially over the 20th century. Cubicles replaced isolated rooms, and today open offices are popular. Is there a meaningful difference between these different arrangements? Are the changes improvements or lateral movements?
- Remote work and its effects on the operations of businesses. Remote work is more popular than ever. It seems convenient for workers, but some companies worry that they will stop being productive without oversight. Are their concerns reasonable?
- A cross-cultural comparison of leadership styles . In the West, a number of leadership style theories have crystallized that are considered best. However, other regions use distinct approaches that work for them. They’re also not rushing to change to the Western model. Do Western styles work best everywhere, or are they limited to the appropriate mindset?
- Social media marketing strategies and the determinants of success.
- Compare the functions of administration and management.
- Prevention of organizational misconduct: barriers and strategies.
- Review the latest developments in performance management theory and practice.
- What is the future of e-commerce business environments ?
- Innovation in the workplace: current thought and generation methods.
- How does outsourcing influence business performance?
- Describe the effects of kaizen and total quality management on performance.
- Discuss economic viability in corporations that operate at a loss.
- Overtime work, employee well-being , and company performance.
- Deliberating in the secrets of effective leadership
- How time management influences the prosperity of a company
- How to resolve a conflict between staff and management
- The function of diversity in the workplace of the 21 st century
- Management by walking around: effective or fruitless?
- Should businesses be regulated: pros and cons
- Social media and word-of-mouth in the digital age
- How the digital age has transformed small businesses
- How mobile technology is altering the workplace
- The future of the franchise
- How the millennial employee is transforming the workplace
📚 Literature Research Paper Topics
Sometimes, there is no surrogate for a great paper on literature, and with the changing world, there are always innovative ways to observe literature, even the classics. Here are a few topic suggestions:
- The depiction of the American Dream in The Great Gatsby . Jay Gatsby first appears as an example of the American Dream. Starting poor, he becomes wealthy and popular in the city. However, he does not achieve his desires and stays unhappy. You can research how the novel criticizes the concept while also reinforcing its idea.
- The evolution of Japanese literature in the Meiji Era. The Meiji Era began after the end of Japanese isolationism. Due to encountering new cultures, its art evolved rapidly. Writers such as Akutagawa Ryunosuke and Dazai Osamu created unique works. From what context did they emerge?
- The traits of 20th century dystopian works. The worlds of Aldous Huxley, Ray Bradbury, George Orwell, and others are bleak. However, they are all substantially different. Can you distinguish unifying themes in the stories that these writers tell?
- How does literature reflect contemporary social issues? Writers often try to draw attention to problems of their time. Dickens wrote about the exploitation of the poor, and Langston Hughes discussed racial discrimination. Can this trend be traced across most literature?
- Classic vs. modern poetry. Classical poetry follows a variety of rules, such as rhymes and stanza organization. Contemporary poets often reject these constraints and create works that are closer to prose in form. What caused this change?
- Study the Four Great Works of Chinese Literature as cultural reflections.
- Examine the influence of romantic tendencies on Walther Scott’s works.
- What issues are raised in contemporary African literature?
- Analyze Milton’s interpretation of Biblical myth in Paradise Lost .
- What characterizes the depiction of war in Heller’s Catch-22 ?
- Discuss real and fake loyalty in King Lear .
- How was grotesque used in 19th century American Gothic fiction?
- The Old Man and the Sea : Hemingway’s depiction of the unconquerable spirit.
- How were gender issues depicted in 19th and 20th-century feminist literature?
- Compare the themes of The Iliad and The Odyssey.
- The innovative era: poets of the 21 st century
- A dissection of the most illustrious novels in history
- The hunger games: over and above pulp fiction
- The future of copyright
- An examination of racism in novels from the 1960s and 1970s
- The perception of exile in literature
- Culture and literature: which affects which?
- An examination of homosexuality in literature
🗳️ Political Research Topics
The world of politics is ever-changing. Understanding the complex mechanisms that regulate our lives is challenging. That’s why a research paper is a great way to clarify the matter. Whether you’re interested in global or local affairs, this section has got you covered.
- What is the origin and purpose of powers separation in government? Most modern governments are separated into three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. Thus they limit each other to avoid government overreach. How was this system founded, and how does it work?
- The structure of the legislation approval process in the US. Every bill has to be approved by the Congress, the Senate, and the President. What factors can hinder the process?
- A comparison between the two-party system and multi-party nations. The US is often critiqued for its two-party system by nations that have numerous parties. With that said, a common counterargument is that American parties made of people with diverse views. How do the political climates of the US and multi-party democracies differ in practice?
- The purpose and effectiveness of term limits for government positions. Some government positions, such as that of the President, are limited to a specific number of years. At the same time, jobs in the Congress and Senate are not. Discuss the purpose of term limits and say if they’re effective.
- Pros and cons of globalism as a political philosophy. The concept of globalism requires worldwide bodies that supersede governments. It looks past nations and ignores their interest in favor of global benefits. Is this approach valid, or are there problems with it?
- How does the European Union membership affect its countries?
- Review the evolution of China’s political system in the 20th-21st centuries.
- The threat of terrorism in a world without ISIS.
- Discuss the issue of mass incarceration in the United States.
- What were the causes of the Soviet Union’s collapse ?
- Write about violations of human rights worldwide and their causes.
- Examine the critiques of capitalism .
- What are the political aims of the Black Lives Matter movement?
- Review the methods for effectively combating governmental corruption.
- The issues of democracy and how to overcome them.
- The American policy of intervention
- The future of the European union
- Causes of world hunger
- Iraq’s weapons of mass destruction
- The Justice system and juvenile criminals
- Afghanistan—success or stalemate?
- Was media coverage of SARS adequate
- The new world war: fighting terrorism
- Same-sex marriage: are laws keeping up with changing attitudes?
- BREXIT: good or bad?
Who says you can’t combine academia and entertainment? Great conclusions can come from fun research. The most important thing is to ask the right questions. Check out the following prompts and get inspired:
- Parallel universes, their origins, and potential organizations. Numerous authors have imagined parallel universes. Even some quantum physics theories assert their existence. Are parallel universes slightly different versions of our world, or are they entirely distinct?
- The theories and paradoxes of various time travel mechanisms. Time travel is a popular science fiction trope. It’s also associated with multiple contradictions, such as the grandfather paradox. How do science fiction authors try to overcome these problems?
- The attempts to create the theory of everything. Physicists are trying to develop an approach that would explain everything in the universe. It doesn’t exist yet, as general relativity and quantum physics often contradict each other.
- What are the possibilities and problems of interstellar travel? Without a method to travel much faster than light, expansion beyond the Solar System is impossible. If it becomes feasible, what possibilities can it offer?
- The history of the moon landing conspiracy theory. The moon landing conspiracy theory asserts that the Apollo 11 mission didn’t occur, and the evidence was filmed on Earth. It tries to find various flaws in this evidence and use them to prove its illegitimacy. How did it emerge, and does it still exist?
- Are people who claim to have extrasensory perception frauds?
- Research stories of the supernatural based on facts.
- What is the origin of the modern Santa Claus?
- If an afterlife exists, what form does it take?
- Does meditation have benefits for physical and mental health?
- Did Nostradamus’s prophecies come to pass?
- Why do some people believe the Earth is flat?
- Does Murphy’s Law always work?
- Examine 19th-century occultism and its prominent leaders.
- Alchemy and the quest for the Philosopher’s Stone.
- How people are affected by the death of a game character
- Challenges faced by people creating their own cartoon
- Beloved comic strip characters and their influence on society
- An examination of UFOs: fact or fiction
- What if aliens do exist: the impact on humanity
- Is there a differentiation between déjà vu and precognition?
- The existence of spirits and how to communicate with them
- Theories regarding the Bermuda triangle
- Investigating alternative cosmology theories
- Does fortune telling have a scientific basis?
- Law of attraction: fact or fiction?
- Men and women’s brain: what’s the difference?
👥 Sociology Research Paper Topics
As an additional interest for studies, a sociology research paper can be written with the purpose of learning this or that aspect of society’s life. You may use personal experience or continue the research started by other authors. Interesting research projects in this area can be based on the following topics:
- Problems of the marriage and family: a divorce research paper. This article can study the relationship in different families and problems that can arise.
- Observance of public behavior standards as the feature of the civilized society. You can describe modern social ideals.
- Comparison of sociological laws in different historical epochs. In your paper, study the attitudes towards various social phenomena.
- The influence of personality on public development and progress. You can describe the power of the personality and what one person can do to contribute to social development.
- Opportunities for searching optimal criteria for the personality socialization. Such a paper aims at revealing the ways of how people can uncover their potential.
- The society’s attitude to global problems : a global warming research paper and the impact of this phenomenon on people’s way of life. Describe this well-known ecological problem in your paper.
- Cultural formation of the personality in the context of modern public reality. This type of work can be connected with describing the ways of people’s cultural development.
- Attempts to socialize adolescents and people with deviant behavior. A research paper on this relevant topic should describe how people who are prone to criminal behavior can correct their way of life.
- Ways of improving the microclimate in the work collective and creating conditions for comfortable work. The theme aims at finding optimal techniques to improve relationships among employees.
- Equality problems in society. A paper on this topic should uncover modern problems connected with inequality and various forms of racism.
- Explore the causes of poverty in disadvantaged communities around the US.
- Review the health and education outcomes of children raised in single-parent families.
- What are the effects of social media on users’ mental health?
- Look into the presence of gender stereotypes in popular culture.
- What are the effects of mass immigration on communities and nations?
- Study the effects of lockdown-related social isolation on mental health.
- Is the Internet an adequate replacement for face-to-face communication?
- Research the causes of bullying and potential strategies for its prevention.
- What’s the status of LGBT communities in nations around the world?
- The effects of juvenile convictions on one’s life prospects.
- Write about the American population’s views on the dangers of pollution .
- Explore the stigma and social acceptance issues associated with transgender status.
- How does cyberbullying affect one’s health ?
- Review the Internet’s influence on education.
- Assess the rationale of policies that restrict citizen reproduction.
- Research your community’s views on the concept of privacy.
- Health and education outcomes of children raised in same-sex families.
- Explore intergenerational differences in views on social topics.
- How do views on freedom of speech vary among people of different social categories?
- Make a case study on the prevalence of workplace gender discrimination in your community.
It is essential to remember that a good research paper on the subject of sociology will be appreciated by readers if you study a specific social phenomenon in detail, carry out statistical analysis, and perform a number of important procedures. The purpose of a research paper in this field is to cover current public issues, reveal important aspects of various problems, and, if possible, offer optimal solutions. This science requires concrete and well-grounded answers. Any deviations and ambiguous arguments can be regarded as an author’s incompetent attempt to investigate a complex topic.
With all of these topics at your disposal, you might still be feeling a little overwhelmed. However, they are divided into categories to make choosing one easier. It might also be helpful to look at some great research paper samples .
Composing a research proposal can sometimes be a part of a big study. If you not only want to describe a specific problem or to convey an idea to your readers, but also expect to promote your personal theory and receive the approval of a respected scientific community, it’s necessary to choose a topic which allows you to present your own ideas. Different types of writing can be included in this category: an analytical research paper, work on identifying the best ways and techniques for a particular topic, etc. The preparation of research proposal articles has some nuances, and the following topics can be studied:
- The way to conduct optimal trade relationships. Review appropriate techniques and offer specific methods to improve the situation in a particular company.
- The advantages of electronic management systems. This theme will be connected with describing the merits of modern ways of managing specific spheres of production.
- Useful innovations in modern life. Research paper subjects can be different: medicine, sociology, business, etc.
- The best management techniques: methods of control . A paper on this topic should describe the behavioral features of successful managers.
- The implementation of nursing theories in practice. The research paper proposal should have an appropriate scientific basis and describe corresponding medical issues.
- Best practice in the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis.
- What challenges are associated with the nationwide adoption of the DNP standard?
- Research current developments in palliative care for senior patients.
- Are there differences in leadership and management styles between genders?
- Assess the effects of tutoring on the educational attainment of school children.
- Compare the preferred management styles in different cultures.
- How do different states’ populations view the legalization of marijuana?
- Write about the underlying causes of Ancient Rome’s fall.
- Challenges in the adoption of electronic health records in medical facilities.
- What are the potential vulnerabilities of the AES-256 encryption standard?
- Research the link between loyalty to a company and career growth.
- How did Dante’s Inferno influence Christian depictions of Hell?
- A case study of Singaporean government and its economic policies.
- Review the financial environment and economic growth of Hong Kong.
- Causes and implications of the human waste issues in San Francisco.
- Assess the prevalence of smoking in the United States.
- Study the beneficial effects of early childhood musical education on later development.
- The philosophical and political underpinnings of the French Revolution .
- What are the effects of successful social media marketing campaigns on videogame sales?
- How did Confucian writings influence Chinese political thought?
The video below provides detailed instructions on how to write a research proposal. It is crucial to follow these rules so that the article to be up-to-date and properly formatted. Any attempts to bring something new are generally welcome; however, it is important not to forget about established rules.
👩⚕️ Nursing Research Paper Topics
A nursing research paper is an academic article that has specific format requirements. Citation rules in particular are very important, for example, an APA research paper format . In order to write a perfect paper and conduct high-quality research, follow the formatting rules and use any of these topics:
- Nursing techniques to care for patients in intensive care units. The summary of your research paper can include a description of the best practical methods.
- How do you implement nursing theories ? Your paper can consist of the enumeration of specific nursing theories and the ways of their implementation in practice.
- Patients’ education and useful materials. The theme aims at discovering the best educational materials that would be suitable for patients.
- Ideas on how to achieve a better quality of nursing care . You can offer various interpretations of this topic in your research paper.
- Experienced researchers’ opinions on improving the state of nursing in hospitals. Use the ideas of different authors and don’t forget to follow the citation rules.

- Patient-oriented type of care and its advantages. This scientific research essay can reveal the merits of a specific nursing approach.
- Potential risks for nurses in the workplace. Both a junior research paper and a senior research paper of this theme should competently describe all possible dangers that medical employees can face.
- Care for people of different social backgrounds. If this research paper is written in English, it should uncover the ways how to care for people speaking other languages and having different cultural and social levels of development.
- Do nurses need additional stimuli to improve their qualifications? You can write many interesting research papers on this topic, and all of them can include lists of possible bonuses and incentives for nurses.
- The necessity for nurses’ additional education. A paper on this topic can describe subjects suitable for nursing education.
- How do you promote healthy eating practices in disadvantaged communities through educational programs?
- Research ways of providing preventative care for veterans affected by PTSD.
- Review the strategies of organizing nurse shifts to maximize the quality of care in understaffed conditions.
- Study cases of patient violence toward nurses in the intensive care unit.
- Preventing pressure ulcers in immobile patients.
- Ways of implementing quality improvement in nursing units.
- What cultural competencies and challenges are typically encountered in nursing care?
- Review the methods for controlling delirium in the intensive care unit .
- Propose adjustments in sexual education to spread awareness of STD risks in same-sex relationships.
- Suggest interventions to prevent falls in patients staying at home.
- What are the issues of advanced practice nursing in different countries?
- Strategies for remaining productive under pressure as a nurse.
- Research alternatives to prescribing patients with infections antibiotics that bypass resistance.
- How to design effective interventions for child obesity rates reduction.
- Explore using exercise to maintain the physical well-being of hospital patients.
- What interventions can reduce alcoholism rates in your community?
- Analyze the implementation of evidence-based practice in nursing facilities.
- Ethical standards and issues that arise in the nursing profession.
- Review the methods of providing holistic care to patients.
- The dangers associated with telemedicine in medical-surgical nursing.
The compliance with the specific research project ideas will allow you to write a high-quality paper and will give you the opportunity to conduct research at a high level. Having completed the document, you can summarize and identify its crucial points. Following the rules of formatting is an integral part of working on any academic text.
🎨 Research Project Topics on Art
In the process of writing research articles, it is necessary to adhere to a certain topic. You can choose any theme you want. A research paper will be successful if you stick to your topic and provide a real search for optimal ways of solving a particular issue. There are a few suggestions that can be helpful in the process of writing. If we talk about such an interesting sphere as the world of art, themes can be as follows.
- How is ideology reflected in architecture? Naturally, ideologies are largely represented in media, but they also influence architecture in many ways. You can study this topic at several points in time.
- How does photography represent reality? In this paper, you can discuss if photography reflects reality, interprets it, or constructs it.
- The significance of linear perspective. If you draw a linear perspective on a flat surface, you will create the illusion of depth. Discuss how this magic trick works in your paper!
- Art and the unconscious mind. It’s an excellent topic that lets you explore psychology. Try to answer the questions of how the unconscious mind influences the creation and perception of art.
- The evolution of horror movies . This film research paper topic covers everything from silent films to modern horror movies. You can discuss the influence of film noir on the genre, literary works that influenced it, the concept of “suspense,” and so on.
- Physiological aesthetics in Surrealism. It is a known fact that Surrealists were inspired by psychoanalysis and dream imagery. You can explore this topic in a paper or use it for a presentation!
- Deconstruction in architecture. The philosophical movement of deconstructivism influenced many spheres of life and art, including architecture. It allowed the creation of seemingly nonsensical forms and environments.
- Sociology of fine art. This is a relatively new branch of sociology, which deals with arts and social structures of their production. It also includes political trends that influence art, consumerism, and other social phenomena.
- Jewelry as sculpture. This topic lets you explore fantastic avant-garde jewelry and how contemporary artists such as Jeff Koons use it to create sculptures.
- The discourse of Modernist painting in the 1950s. This topic covers experimental and abstract paintings of artists who rejected the realistic approach. Mention political agendas that influenced modernism in the ’50th.
- Abstract Expressionism. Here you can discuss postwar artists such as Rothko and Pollock , as well as their predecessors Ernst and Kandinsky.
- Andy Warhol’s influence on art. This art research paper topic covers not only pop art, but also films, music, aphorisms, the concept of “superstars,” and other aspects of Andy Warhol’s influence.
- The art of street photography. Street photography is usually spontaneous, which helps to create realistic and powerful imagery. Write about the art of photographing urban landscapes and the most influential candid photographers.
- The history of animation. Techniques preceding animation have existed long before the invention of cinematography. Puppetry, shadow play, magic lantern – all these things relate to animation in one way or another.
- Are video games art? This idea seemed impossible in the past, but now many video games are considered art for their use of imagery, music, and compelling narrative.
- Art as a form of protest. This includes protests against tradition or political causes. You may also talk about the role of art in bringing about a change in society.
- Renaissance sculpture. This topic is just as interesting as the Renaissance painting. During that period, the art of sculpture had reached its peak. Sculptors of the Renaissance were influenced by Ancient Greek sculptures, as well as by Humanism.
- Relationship between architecture and environment. Here you can discuss eco-friendly or “ green” architecture .
- Modern ceramics as an art form. In the last decade, ceramics became a very popular art form. From prehistoric pottery to intricate porcelain forms – ceramics is a great medium that can often be compared to sculpture.
- Science fiction in cinema. The earliest science fiction films were created back in the late 19th century by Georges Melies. In 1927, Fritz Lang’s silent film Metropolis revolutionized science fiction cinema. Explore it in your research paper!
- The peculiarities of Da Vinci’s masterpieces. The paper will reflect the talent of the great European master and describe his Best Works.

- The trends of art in Medieval Europe. The topic should uncover modern trends in the art of the Middle Ages and include the description of some styles; it can the article of any format, even a 10-page research paper. The main thing is to fully reveal all the distinctive features of that epoch.
- The history of European Art in the 20th century . The research can be devoted to some trends in the previous century.
- The most outstanding artists in the world’s history. The paper should tell about the most famous artists of all the epochs.
- Why do people appreciate art? This article can include your own ideas concerning the subject.
- How do artists reflect their talent today? Your task is to try to study the methods that modern artists use to attract the audience.
- Skills that a professional artist should possess. The aim of this article is to study some skills that should be necessary for the work of the artist. Regardless of whether you write research papers for sale or not, you should try to express not only well-known ideas but also your personal point of view.
- Is it possible to develop artistic talent? Try to express your ideas concerning the opportunity for mastering proper skills.
- The benefits of cooperation with other artists. This topic touches upon probable advantages that artists can gain when cooperating with their colleagues.
- Themes that are the best for the canvas. You can develop a number of research abstract topics on this theme and convey the best motives to paint that seem the most successful for you.
- The absence of inspiration. The theme should reveal what authors should do to develop their inspiration.
- Chronological order of art development in the world. It is a rather accurate paper that should mention the most significant stages of art development.
- Do people appreciate the work of artists? You could try to study the audience’s attitude toward artists’ work.
- The methods to attract young people to art. The topic is connected with a social issue and aims at popularizing art in masses.
- Do artists need additional knowledge? This theme implies for describing the necessity of education among all the professions, including artists and other creative posts.
🎼 Music Research Topics
Every culture has its distinct music. For many people, music is an integral part of everyday life. Film and theater productions use it to steer our emotions. When writing about music, you can choose from an endless number of ideas to research. Here are some examples:
- Music as a ritual. Back in prehistoric times, music was considered to be a powerful ritualistic practice. Some mythologies even include stories about gods introducing the art of music to humans.
- Early polyphony in Christian Europe. The earliest choral music was mostly performed in a single melodic line. See how it changed when more melodic lines were added.
- Indian ethnomusicology. This interesting music research topic is concerned with the peculiarities of Indian music culture. You can include the discussion of how Indian music influenced psychedelic rock in the ’60s.
- Jazz performance and improvisation. The element of spontaneity is very important in jazz performance, and improvisation is its key component.
- Medieval troubadours and their legacy. Troubadours were poets who sang their own music and played instruments. Their performances differed greatly from the traditional church music of that time.
- Ecomusicology of North America. This research topic allows you to discover the ways in which American landscape and nature influenced music, including Native American music, folk music, and modern songwriters.
- Baroque music. During the Baroque era, many important features of modern music were introduced. You can choose this topic if you like grandiose, dramatic, or playful classical music.
- The classical period in music. This period followed the after the Baroque and was very different from it. You can recognize it by simple structures and minimalistic arrangements. Many of the world’s greatest composers, such as Mozart and Beethoven, lived during the Classical era.
- Classical music of the 20th century. Over the course of the previous century, the music styles were changing like never before. Still, classical music survived, while also transforming itself in accordance with times.
- Music therapy for children. In this exciting music research topic, you can discover how music is used to help children with developmental dyspraxia, autism, ADHD, and other disorders.
- Music and sound in film. Discover for yourself the art of scoring – from improvised piano arrangements of early movies to modern stereo surround sound.
- The history of Italian opera. The Italian language played a key role in the formation of classical singing techniques. This includes opera – an art form that unites music and singing with storytelling.
- The 20th-century music industry. This topic is centered on various ways of recording and selling music. Vinyl records, wax cylinders, cassette tapes, and CDs – 20th-century technology allowed turning music into a business.
- The birth of pop music. The history of popular music begins in the 1950s. The term refers to the songs appealing to a large audience, as opposed to classical or jazz music. You can discuss the elements of early pop music that made it so accessible.
- The ideology and aesthetics of punk rock. Punk rock was enormously influential in the 1970th. Its philosophy of anti-conformity appealed to young people of post-war Britain and the USA.
- The musicology of electronic music. This exciting topic covers the earliest repetitive devices such as Hammond organ, early experimentations with electronics, the first use of computers and synthesizers in songwriting, and more!
- Sampling in electronic music: context and aesthetics. Sampling is a very interesting technique that allows using audio fragments in different contexts. It can be used for aesthetic or political reasons, or as a cultural commentary.
- What is a sound sculpture? A combination of an art object and music, sound sculptures are exciting to research. You can use this topic for presentation and demonstrate sound sculptures in action!
- Dadaism and music. Dadaist ideas of randomness and paradox influenced art as well as music. Discuss the noise compositions and avant-garde sonic experiments that influenced the latter half of the 20th century.
- Robotic musical instruments. You may think that robots playing music is a relatively new idea, but in fact, they date back to ancient times.
✍️ Creative Writing Research Topics
There are more rules to creative writing than one might think. For example, narratives should be coherent, and world-building has to follow certain logic. Analyzing these peculiarities brings you one step closer to becoming a better writer.
- The role of reality within the psychological thriller genre. Psychological thrillers often aim at distorting or questioning reality. Study the ways in which this idea manifests in different narratives.
- Graphic novels and their peculiarities. In modern times comic books are no longer considered to be just for entertainment, and graphic novel format is used to produce award-winning narratives.
- Writing about the past: historical research and archaeology. When your narrative takes place in the distant past, you need to do extensive research to represent the time period properly. One way to do it is to turn to archaeology.
- What is the role of landscape in supernatural narratives? Supernatural narratives rely on the atmosphere to evoke the feeling of uncanny. The setting and landscape are especially important to the writes of the supernatural genre.
- How to write engaging crime fiction? This topic includes the ways of building suspense, the use of “red herrings,” complex character development, and other tips.
- Digital storytelling. Here you can explore how to present your narrative in interactive digital form. It can be a video game, a visual novel, or a walking simulator.
- Writing about the future. When you write about the past, you already know the characteristics of an epoch. But how do you invent the attributes of the future? Discuss it in your paper!
- The influence of the author’s personal life on their writing. People often want to learn more about their favorite writers in the hope to understand their work better. But is there really such a connection between one’s personal and creative lives?
- The role of diaries in creative writing . Almost all writers keep diaries. Sometimes the diaries are published and used in research or literary analysis. But how do authors themselves use their diary entries?
- Creative writing for children. This excellent creative writing research topic deals with the ways of teaching children how to create their own narratives. You can discuss why writing is beneficial for children and how you can encourage them to be creative.
- The art of teaching poetry. Poetry is one of the most exciting art forms that never gets old. However, not everybody appreciates poetry right away. See how you can change it!
- What is the role of nature in romantic literature? Romantic artists and writers took lots of inspiration from nature, using it as a metaphor for one’s life and feelings.
- The role of authorial intent. Some readers think that it’s essential to know what the author wanted to say in their literary work. Others believe that it’s one’s personal interpretation that matters the most.
- A persona in poetry. The lyrical subject is someone who narrates a poem. Some people see it as the manifestation of the author, and others as a fictitious character. And what do you think?
- Degrees of realism in fiction. When writing a work of fiction, some writers use excessive descriptions, while others keep things relatively minimalistic. Discuss the positive and negative sides of these approaches.
- Forms of structure in films and novels: a comparison. Here you can compare different forms of narrative structures used in cinema and literature, such as linear and non-linear narratives, the use of flashbacks, and so on.
- How to write a comedy. Comics say that making people laugh is much harder than to make them cry. Discuss what makes a literary work funny, and how one can write effective comedy.
- The recontextualization of Hamlet . Recontextualization is a process by which something (e.g., a character) is taken from one context and introduced into another context. You can explore this notion through different recontextualizations of Shakespeare’s character Hamlet.
- Writing a dystopia . See what techniques you can use when writing a narrative set in a bleak society.
- Monomyth in literature. This exciting topic deals with the concept of “hero’s journey,” which serves as a basis for nearly all myths as well as countless works of fiction.
🎈 Other Research Paper Topics
You still haven’t found what you were looking for? This section might have what you need! Here you’ll find all kinds of topics. From psychology over physics to sociology, we compiled the most engaging ideas for you.
- American teenagers–can they be called new species?
- William Shakespeare : was this man the author of famous plays and sonnets?
- Do you have any ideas about the field circles?
- Black magic. Does it exist?
- Censorship and its role in forming a society
- The phenomenon of the penny press in the USA
- Symbolism in literature
- Alcatraz and its famous fugitives
- Major sources of stress
- Government grants–how do they work?
- Election falsification: is it commonly used, and what are its main techniques?
- Genetic engineering and your point of view on it
- Stem cell research
- What is a black hole
- Loch Ness monster and your attitude towards this mystery
- Joan of Arc –did she manage to escape the fires of Inquisition?
- Do some research on techniques of brainwashing
- Who invented the radio ?
- There is a belief that American astronauts didn’t step on the Moon. Did they?
- American international policy
- Unique people who changed the world
- Genius ideas that made their inventors famous and wealthy
- Is education a necessary factor to become successful in today’s world?
- Differences between the high school systems in the USA and Japan
- Schindler’s list : the importance of moral roles over wealth
- Educational programs’ impact on professional careers
- Why do college students from all over the world come to the USA to pursue further education?
- Examples of crop circles: Fake or real?
- Humanity’s technological achievements in 2020

- The importance of outlines in books and articles
- Web-designers seem to be using the same template in their works
- Exciting inventions of humankind in the nearest future
- Modern students do not know how to do their homework without access to the Internet
- The original cover page of the Holy Bible
- The development of the MLA style
- The cradle of psychology
- Controversial policies of the USA and the USSR
- How abortion affects a woman’s organism
- What did Homer write about his lifestyle?
- Famous people in the world’s history that did not exist
- Would people have become what they are today without science?
- Parts of the world that will always remain uninhabited
- Philosophical questions that humanity cannot answer for centuries
- Medical stereotypes around the world
- Will global warming ruin America’s economic system?
- The USA government should be thankful for the mass immigration
- The majority of scientific works are useless
- Things to research in the sphere of modern gadgets
- Should sociology make people happier?
- The lack of pure water sources on Earth
- The environment’s effect on human health
- Humanity’s steps towards eco-friendly products, cities, and vehicles
- Sherlock Holmes’ analytical mind and deduction skills
- Should parents teach their children how to make the world better for other people?
- Is business the only way to become wealthy in Third World countries?
- Analysis of William Shakespeare’s literary language
- Does a title tell everything about a book’s context?
- The Great Wall: A legendary monument or China’s income source?
- Should families report to the police that their relatives are guilty of something?
- The first websites, available on the World Wide Web
- New challenges to the society introduced by social media
- If you created your government, what would you do for your citizens?
- What career options are prevalent in modern societies?
- Chemistry in people’s everyday life
- Is there any person on Earth, whose life is considered to be easy?
- Is bribery acceptable for criminal justice?
- The most popular sports in Britain
- The population biology of India
- Basic nursing knowledge of everyday life
- Renaissance literature in France
- Think of a technology that would make our atmosphere cleaner
- Development of different animals after forty days on Noah’s Ark.
- What will the food be like in a hundred years?
- Socialization of children with autism
- The medieval art of Scandinavian people
- Different ways to save Earth’s environment from pollution
- Depression in adolescents: reasons and outcomes
- The importance of computer science in today’s world
- Coca-Cola marketing strategies

- Express your opinion on people’s purpose in life on Earth
- How do early childhood memories and experiences influence our lives?
- The history of video games era
- Regulation of bullying in schools by law
- Drugs industry in California, New Mexico, and Texas
- The most prevalent economic issues in Greece after joining the EU
- China’s rapid growth: is it going to become the first country in the world?
- Global dangers that influence our planet’s ecology
- Significant changes in the American media since the 1970s
- What makes medicine an interesting subject to study?
- The main factors to consider while conducting qualitative research
There are so many resources out there that will help you choose a topic and write an outstanding paper. This video gives you a bunch of topics for research papers, which means you now have even more from which to choose!
There is no doubt that writing a research paper is a daunting task.
If you feel you need help, even if you have managed to choose a topic, you can always hire a custom writing service to help you produce a fabulous research paper of which you will be proud and will guarantee you a good mark.
Whether you choose to write it on your own or get some help, we wish you luck writing your paper!
🤔 Research Topics FAQ
There are literally thousands of topics to choose from. “Biomarkers and colors: what is the correlation?” is a great topic on psychology. Should businesses be regulated: pros and cons is an exciting business research topic. Finally, Art as a form of protest is an art research topic worth exploring.
The first option is to ask your professor. Then you can browse through scientific journals and take a look at your library catalog. The final option for those who search for a creative idea is to take notes everywhere. Write things down while traveling, watching TV, and reading.
The Big Bang theory, Dwarf galaxies, and Supernova Astronomy are just a few of numerous astronomy research topics. Genetically modified organisms, Neurobiology of sleep, and Rainforest conservation are exciting research biology research topics. Artificial intelligence, Computer modeling, and Voice recognition are trendy computer science topics.
There are numerous exciting topics in various education research areas. Some of them are: Ability grouping, Computer literacy, Early childhood education, Multiculturalism, Parental involvement, Sex education, Violence in schools, and Virtual classrooms.
You might also be interested in:
- 280 Good Nursing Research Topics & Questions
- 226 Research Topics on Criminal Justice & Criminology
- 204 Research Topics on Technology & Computer Science
- 178 Best Research Titles about Cookery & Food
- 497 Interesting History Topics to Research
- 180 Best Education Research Topics & Ideas
- 110+ Micro- & Macroeconomics Research Topics
- 417 Business Research Topics for ABM Students
- 190+ Research Topics on Psychology & Communication
- 512 Research Topics on HumSS
- 281 Best Health & Medical Research Topics
- 501 Research Questions & Titles about Science
- Good Research Topics, Titles and Ideas for Your Paper
🔗 References
- APA Sample Paper
- Painting Movements in the 20th Century Topic
- The Discovery Themes Initiative at The Ohio State University
- Quantitative Research in Education
- Quantitative Research Works, Indiana University
- Organizing Academic Research Papers: Choosing a Title
- Research Topics, The University of Arizona
- Research Topic Ideas, University of Michigan-Flint
- National Archives—Research by Topic
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory—Research Topics List
- Global Health Research Topics
- National Institute of Justice—Topics
- National Institute of Standards and Technology—Topics
- Research Topics at U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research & Development
- National Institutes of Health—A to Z Topics Index
- Evaluating Print Sources
- Working With Sources
- Developing a Thesis
- Psychiatry: Medscape
- Information Technology: NIST
- Topics: History.com
- Research Programs: National Center for Education Research
- Recent Computer and Education Articles: Elsevier
- Basic Guide to Cross-Cultural Research: Yale University
- Cultural Anthropology: Britannica
- Top Physical and Tech News: Science Daily
- Health Topics: National Institute of Mental Health
- PhDs in Business & Management: Five Hot Research Topics: Top Universities
- Research and Focus Areas in Business and Government: Victoria University of Wellington
- Modern Literature: University of Portsmouth
- Research Areas: Political Science: Florida University
- Sociology Research Areas: Cornell University
- Focus Areas: Nursing Research: Mayo Clinic
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![possible research topics about personal interest 335 Unique Essay Topics for College Students [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/smiling-students-walking-after-lessons1-284x153.jpg)
The success of any college essay depends on the topic choice. If you want to impress your instructors, your essay needs to be interesting and unique. Don’t know what to write about? We are here to help you! In this article by our Custom-Writing.org team, you will find 335 interesting...

Social studies is an integrated research field. It includes a range of topics on social science and humanities, such as history, culture, geography, sociology, education, etc. A social studies essay might be assigned to any middle school, high school, or college student. It might seem like a daunting task, but...

If you are about to go into the world of graduate school, then one of the first things you need to do is choose from all the possible dissertation topics available to you. This is no small task. You are likely to spend many years researching your Master’s or Ph.D....

Looking for a good argumentative essay topic? In need of a persuasive idea for a research paper? You’ve found the right page! Academic writing is never easy, whether it is for middle school or college. That’s why there are numerous educational materials on composing an argumentative and persuasive essay, for...

Persuasive speech is the art of convincing the audience to understand and trust your opinion. Are you ready to persuade someone in your view? Our list of sports persuasive speech topics will help you find a position to take and defend. If you need more options quick, apart from contents...

Can there possibly be anything fun about academic writing? It seems there is – what are all those fun persuasive speech topics then for, after all? However, creating a bunch of good topics might seem hard the first time around. No need to worry though – there’s always plenty of...

A persuasive speech on any topic is a performance designed to convince people about something and prove your point. Choosing a suitable topic is crucial for your speech’s success. Do you need some help with finding easy topics for a persuasive speech? Then check these fantastic and easy ideas from...

Do you know the secret place where people go to get their good informative speech topics? Looking for an interesting topic for speech? Congratulations, because you’ve just found it! So, if you’re ready to get some really good topics for an informative speech, all you need to do is to...

A proposal argument is an essay in which you describe a specific issue that needs fixing. It focuses on problem solutions. Are you interested in writing high-quality proposal essays? Or maybe you’re wondering what can make your writing truly outstanding? Here you will find answers to these questions as well...

Sometimes you just wish there was a marketplace with vendors shouting, “Topics for argument essays! Who wants inspirational topics to write about?” Well, you are lucky enough: you’ll find plenty of inspiring things here! Coming up with some argument essay topics is quite easy! In this article, you’ll find some...

Are you searching for original, thought-provoking, and really controversial debate topics? Here they are! Selecting any of these 25 controversial topics for debate from Custom-writing.org, you can guarantee a heated dispute in class or exciting polemics with your friends. But first, let’s figure it out, what is debate and how you should pick up great...

Perhaps, each person has unforgettable memories of school life. It might be their first day when everything seemed to be exciting and unknown. Or it might be some picnic or trip when they spent a great day outside with their classmates. Writing a high school experience essay requires you to...
I want an essay research on The implementation of nursing theories in practice
I want an easy research in linguistics can u suggest an easy topic?
I didnt saw research topics in suggestion for linguistics
am looking for research topic on politics or ethics
I’m looking for a research paper on the vape culture among the youth.
I ‘m looking for research topic on digital marketing
I’m doing a mini research on qualitative research. I need some topics for qualitative research.Can you help me?
I am looking for research topics on dispensary optician care
Rooftop where gunman shot at Trump was identified as a security vulnerability before rally: sources
The rooftop where a gunman shot at former President Donald Trump during a campaign rally was identified by the Secret Service as a potential vulnerability in the days before the event, two sources familiar with the agency’s operations told NBC News.
The building, owned by a glass research company, is adjacent to the Butler Farm Show, an outdoor venue in Butler, Pennsylvania. The Secret Service was aware of the risks associated with it, the sources said.
“Someone should have been on the roof or securing the building so no one could get on the roof,” said one of the sources, a former senior Secret Service agent who was familiar with the planning.
Understanding how the gunman got onto the roof — despite those concerns — is a central question for investigators scrutinizing how a lone attacker managed to shoot at Trump during Saturday’s campaign event.
The Secret Service worked with local law enforcement to maintain event security, including sniper teams poised on rooftops to identify and eliminate threats, Secret Service spokesman Anthony Guglielmi said. But no officers were posted on the building used by the would-be assassin, outside the event’s security perimeter but only about 148 yards from the stage — within range of a semiautomatic rifle like the one the gunman was carrying.
The Secret Service had designated that rooftop as being under the jurisdiction of local law enforcement, a common practice in securing outdoor rallies, Guglielmi said.Butler County District Attorney Richard Goldinger said his office maintains an Emergency Services Unit team, which deployed four sniper teams and four “quick response teams” at the rally. But he said the Secret Service agents were in charge of security outside the venue.
“They had meetings in the week prior. The Secret Service ran the show. They were the ones who designated who did what,” Goldinger said. “In the command hierarchy, they were top, they were No. 1.”
Goldinger said the commander of the Emergency Services Unit told him it was not responsible for securing areas outside the venue. “To me, the whole thing is under the jurisdiction of the Secret Service. And they will delineate from there,” he said.
The former senior Secret Service agent also said that even if local law enforcement “did drop the ball,” it’s still the agency’s responsibility “to ensure that they are following through either beforehand or in the moment.”
“Just because it is outside of the perimeter, it doesn’t take it out of play for a vulnerability, and you’ve got to mitigate it in some fashion,” the source added.

A volley of shots rang out minutes into Trump’s speech. He reached for his right ear — he said later it was pierced by a bullet — then dropped to the ground as Secret Service agents rushed to shield him. Trump emerged with blood on his ear and his face. One attendee was killed , and two others were injured.Witnesses listening to Trump’s speech from outside the event’s security perimeter recalled pointing out the gunman to law enforcement a couple of minutes before the shooting began. After the gunfire started, Secret Service personnel shot and killed the 20-year-old gunman, Thomas Matthew Crooks .
The clamor over the Secret Service’s biggest failure since the shooting of President Ronald Reagan in 1981 is coming from both political parties, from former agents and from security experts.
“My question is: How did he get onto that roof undetected?” said Anthony Cangelosi, a former Secret Service agent who worked on protective details for presidential candidates, including John Kerry in 2004.
The Secret Service’s work on campaign events like Saturday’s begins with advance planning, setting up a security perimeter and positioning teams on the ground and on rooftops — often in partnership with local law enforcement. The ground deployments include a counterassault team, and the rooftop personnel include counter-sniper teams.

Guglielmi, the Secret Service spokesman, said the agency had two of its counterassault agents at the event and filled out the rest of the platoon with at least six officers from Butler County tactical units. The Secret Service also deployed two counter-sniper teams. Two other security units needed for the event were staffed by local law enforcement agencies, Guglielmi said. Those details were first reported by The Washington Post.Investigators will want to examine the Secret Service’s site security plan for the rally, said Cangelosi, the former Secret Service agent. He expects they’ll discover one of two things: Either officials failed to make an effective plan for keeping potential shooters off the building Crooks fired from, or officers on the ground failed to execute the plan.
“I don’t like making any assumptions, but it does look like some mistakes were made, that this was preventable,” said Cangelosi, now a lecturer at John Jay College of Criminal Justice in New York.
Although it’s common to task local law enforcement agencies with patrolling outside an event’s security perimeter, Cangelosi said, the ultimate responsibility for ensuring that all vulnerabilities are covered rests with the Secret Service.
If officials had placed an officer on the building where the gunman fired from, Cangelosi said, chances are he “wouldn’t even attempt what he attempted.”
“You don’t surrender the discretion of what’s supposed to be done to the local police,” he said. “In other words, you guys have the outer perimeter, but you would want to say, ‘We need an officer on that roof.’ Not ‘that’s your responsibility; do what you see fit.’”
Jim Cavanaugh, a retired special agent in charge with the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives who has worked on Secret Service details, told NBC News that while the Secret Service did a good job taking out the gunman after shots began, the failure to post officers on the building he scaled was “a tremendous lapse.”
“The only way to stop that is you have a lot of people, you get there first, and you command the high ground,” Cavanaugh said. “This is basic, and the Secret Service has done it for years successfully, so I’m really surprised that they did not have that high ground covered.”

The questions extended to Congress, where members demanded answers from the Secret Service and its parent agency, the Department of Homeland Security.“This raises serious concerns regarding how a shooter was able to access a rooftop within range and direct line of sight of where President Trump was speaking,” House Homeland Security Committee Chairman Mark Green, R-Tenn., wrote in a letter to Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas.
Green asked Mayorkas to provide documentation relating to the event’s security plan, the screening of attendees and the level of resources provided to Trump’s Secret Service detail. A committee spokesperson told NBC News that Republican members would hold a briefing with Secret Service Director Kimberly Cheatle on Monday “to voice their concerns and ask pressing questions.”
Another lawmaker, Rep. Ruben Gallego, D-Ariz., wrote Cheatle asking who approved the security plan, whether a proper threat assessment was conducted, whether attendees raised alarms and whether there were failures in following protocols that allowed the attack to happen.
“I call on all those responsible for the planning, approving, and executing of this failed security plan to be held accountable and to testify before Congress immediately,” Gallego wrote in a letter to Cheatle .
Robert McDonald, a former Secret Service agent who ran protection for Joe Biden when he was vice president, told NBC News that he believes the assassination attempt will prompt soul-searching and procedural changes at the agency.
“The Secret Service is going to need to ask some hard questions of itself here and be prepared to stand up and represent why, what happened,” McDonald said.

Cangelosi, the former Secret Service agent, said investigators are also likely to ask when agents identified Crooks as a potential threat, how they reacted and whether it’s possible they could have taken him down before he fired at Trump.Secret Service snipers are trained to make rapid decisions, he said. But it’s possible that if they noticed Crooks on the roof but couldn’t tell whether he had a rifle, agents might have waited to fire on him.
“If the sniper can’t tell whether he has a gun, he or she is not going to take the shot,” Cangelosi said. “Because God forbid it’s a child who’s just excited to see a political candidate, right? So you want to make sure that there’s actually a threat.”
If there was uncertainty, Cangelosi said, it’s possible the sniper team would have dispatched officers to investigate and confirm. But investigating a potential threat can take minutes, he said, while a gunman with a semiautomatic rifle can fire several shots in a matter of seconds.
That’s why, Cangelosi said, the best defense would have been to plan ahead to keep the shooter off the roof in the first place.
“Who wants to be in that position?” he said of the snipers protecting Trump on Saturday. “You’ve got to make a split-second call. And imagine if you’re wrong.”
Sarah Fitzpatrick is a senior investigative producer and story editor for NBC News. She previously worked for CBS News and "60 Minutes."
Julia Ainsley is the homeland security correspondent for NBC News and covers the Department of Homeland Security for the NBC News Investigative Unit.
Mike Hixenbaugh is a senior investigative reporter for NBC News, based in Maryland, and author of "They Came for the Schools."
Andrea Mitchell is chief Washington correspondent and chief foreign affairs correspondent for NBC News.
Jon Schuppe is an enterprise reporter for NBC News, based in New York.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Discover 250+ interesting topics to research that captivate readers' interest. Explore categories, techniques, and tips for engaging research. ... Personal Interests: Researching a topic you're genuinely passionate about can turn the entire process into an exciting adventure. Your enthusiasm will show in your work and make it more engaging ...
In conclusion, choosing a research topic (from research topic examples for students) is a pivotal step in a student's academic journey. By considering personal interests, aligning with academic goals, and exploring examples across different domains, students can unlock the potential for meaningful and impactful research.
Exploring Personal Interests and Experiences. Your personal interests and experiences can be a rich source of inspiration for research topics. Consider what you are passionate about and how it intersects with your field of study for your research paper ideas. Choose a topic that interests you. Keeping Up with Current Trends and Developments
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas. Select your area of interest to view a collection of potential research topics and ideas. AI & Machine Learning. Blockchain & Cryptocurrency. Biotech & Genetic Engineering. Business & Management. Communication. Computer Science & IT. Cybersecurity.
Here are the two things that a great statement of research interests or SOP will do: It will clearly illustrate to the admissions committee that you possess a depth of interest and comprehension in your field and that you understand what goes into research. You will sound naïve if you talk about ideas that are too vague or nebulous, or ones ...
This will help you present yourself as a well-rounded and knowledgeable candidate for the program. When writing about your research interests for an admissions committee, it is important to be concise and clear. First, create a brief overview of the research topic that you are interested in. When possible, provide examples of how your research ...
The best research topics include personal interests, academic relevance, and potential impact. For example, if you're passionate about environmental conservation, you might explore the effectiveness of reforestation efforts in mitigating climate change, examining case studies from different regions for comprehensive analysis.
Examples of systemic racism-related psychology research topics include: Access to mental health resources based on race. The prevalence of BIPOC mental health therapists in a chosen area. The impact of systemic racism on mental health and self-worth. Racism training for mental health workers.
Step 5: Narrow down, then evaluate. By this stage, you should have a healthy list of research topics. Step away from the ideation and thinking for a few days, clear your mind. The key is to get some distance from your ideas, so that you can sit down with your list and review it with a more objective view.
Finalizing the Research Topic. Choose the research topic that resonates with your personal interests and goals: Aligns with personal interests and goals. Ensure that the topic aligns with your passion and long-term aspirations. Manageable and achievable. Select a topic that is realistically achievable within the given time frame and resource ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. Posted by Christine Sarikas. General Education. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and ...
Choosing a Topic. 1. Brainstorm possible topic ideas. Consider your personal interests. Talk about topics and your personal interests with classmates and peers. Reflect on interesting social media content you've recently encountered. Most social media content is not scholarly but can be explored with scholarly research from academic sources.
A good research interest statement sample can be hard to find. Still, it can also be a beneficial tool for writing one and preparing for a grad school application or post-graduate position. Your research interest statement is one of the key components of your application to get into grad school.In a few cases, admissions committees have used it instead of an interview, so it is important to ...
The purpose of a research topic is to identify a specific area of inquiry that the researcher wants to explore and investigate. A research topic is typically a broad area of interest that requires further exploration and refinement through the research process. It provides a clear focus and direction for the research project, and helps to ...
Identify Your Research Interests. As an undergraduate student, you are not expected to know exactly what your area of focus will be. Most likely, you are still discovering and developing your interests and that's okay. However, without having some ideas about what you're interested in, you'll quickly find that searching for opportunities can be ...
Not all writing assignments have a personal dimension, but our interests and concerns are always, at their roots, personal. ... When scoping out possible research topics, it is important to remember to choose a topic which will sustain your interest throughout the research and writing process. The best research topics are those which are ...
Similarly, revealing a personal interest or even passion for a particular research topic (e.g., due to being personally affected) could also overcome the stereotypical perception of scientists as distant "nerds in the ivory tower" [15, 16]: researchers who openly disclose the idiosyncratic relevance of their research topic may appear more ...
66 research ideas Here are 66 research ideas divided into categories to help you generate your next research topic: Health research ideas Here are some research ideas related to health:. Diagnostic testing: You can use this topic to write about a specific type of test, such as x-ray technology, or you could compare several tests. Allergy and asthma: You can study the effects or causes of ...
Interests related to technology including information technology, physical technology and digital media.Personal interests can include hobbies, leisure activities, arts, sports, community activities, volunteer positions, cultural activities, traditional practices, recreation, extracurricular activities, research topics, self-learning and ...
Composing a research paper can be a daunting task for first-time writers. In addition to making sure you're using concise language and your thoughts are organized clearly, you need to find a topic that draws the reader in. CollegeVine is here to help you brainstorm creative topics! Below are 100 interesting research paper topics that will ...
Some examples of common research paper styles include: Argumentative Research Papers. Persuasive Research Papers. Education Research Papers. Analytical Research Papers. Informative Research Papers. Your research essay topic may also need to be related to the specific class you are taking. For example, an economics class may require a business ...
The Big Bang theory, Dwarf galaxies, and Supernova Astronomy are just a few of numerous astronomy research topics. Genetically modified organisms, Neurobiology of sleep, and Rainforest conservation are exciting research biology research topics.
The rooftop where a gunman shot at former President Donald Trump during a campaign rally was identified by the Secret Service as a potential vulnerability in the days before the event, two sources ...