Ertugrul Portakal
Apr 12, 2024

Writing a Research Paper Introduction (with 3 Examples)
Nail your research paper's introduction! Learn to captivate and inform readers from the start—our guide shows how!
%20(3).png)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A catchy and informative introduction is essential in academic writing, especially if you want your readers to have background information about your paper. However, writing an interesting and informative introduction can sometimes be a time-consuming and tiring process. If you don't know where to start when crafting an introduction, no need to worry - we've got you covered!
In this article, we will explain step by step what an introduction is in academic writing and how to write it!
Ready? Let's start!
- An introduction is a paragraph that provides information about your entire paper and aims to attract and inform the reader.
- Before writing an introduction or even starting your paper, you need to research academic sources.
- The first one or two sentences of an introduction paragraph should be a hook to attract the reader's attention.
- Afterwards, you need to prepare the reader for your argument by giving background information about your topic.
- Finally, you should state your argument about your topic with a thesis statement.
- If you are writing a longer paper, you can inform your readers about the map of your paper.
- If you are looking for an AI assistant to support you throughout your writing process, TextCortex is designed for you with its advanced features.
What is an Introduction in a research paper?
In any academic writing, including essays and research papers, an introduction is the first paragraph that the reader will encounter. This paragraph should both attract the reader's attention and give them the necessary information about the paper. In any academic paper, the introduction paragraph constitutes 10% of the paper's total word count. For example, if you are preparing a 3,000-word paper, your introduction paragraph should consist of approximately 300 words. You should also write sentences within these 300 words that will attract the reader's attention and provide them with information about the paper.
Importance of an Introduction Paragraph
The biggest function of an introduction paragraph is to prepare the reader for the author's thesis statement. A traditional introduction paragraph begins with a few sentences or questions that will catch the reader's attention. After attracting the reader's attention, necessary background information on the subject is given. Finally, the author explains to the readers what the whole paper is about by stating the thesis. A thesis statement is the final sentence that summarizes the main points of your paper and conveys your claim.
First Things First: Preliminary Research
When working on any academic writing type, it is essential to start by researching your topic thoroughly before beginning to type. What sets academic writing apart from other writing types is the requirement for it to be written using accurate information from reliable sources.
Researching academic sources can be a time-consuming and unnecessary process. One has to read through hundreds of pages, review dozens of articles and verify the accuracy of each source. However, if you're looking to reduce your workload and maximize efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as literature review, ZenoChat is the perfect solution for you. With its web search feature, ZenoChat can use the entire internet as a data source. Additionally, by activating the "scholar" option of the ZenoChat web search feature, you can ensure that it only uses academic sources when generating output.
How to Create an Introduction for Academic Writing?
Creating an introduction paragraph that is interesting, informative, and conveys your thesis is an easier process than it seems. As long as you have sufficient information about your topic and an outline , you can write engaging introductions by following a few simple steps. Let's take a closer look at how to write an introduction for academic writing.
1-) Start with a Catchy Hook
Your first sentence is one of the factors that most influence a reader's decision to read your paper. This sentence determines the tone of your paper and attracts the reader's attention. For this reason, we recommend that you start your introduction paragraph with a strong and catchy hook sentence.
- Avoid long and complex sentences
- Use clear and concise sentences
- Write a sentence that will spark the reader's curiosity
- You can ask questions that will encourage the reader to read the remaining paragraph
- Avoid fact or overly broad sentences
- Avoid using dictionary definitions as your hook
2-) Give Background Information
After writing a strong hook sentence, you need to provide basic information about your topic so that the reader can understand what they will learn about when they read your paper. In this section, you can benefit from opinions that support or oppose your argument. Additionally, this section should refer to the body paragraphs of your writing.
- You can write a background information sentence for each body paragraph.
- The information here should be concise and compact
- Avoid talking about your evidence and results unless necessary.
3-) State Your Thesis
After attracting the reader's attention and providing background information, it is time to present your approach and argument towards the topic with a thesis statement. A thesis statement usually comprises one or two sentences and communicates the paper's argument to the reader. A well-written thesis statement should express your stance on the topic.
- Avoid merely stating a fact
- Claim your argument
4-) Tell Reader About Your Paper
Although you need to move on to body paragraphs after the thesis statement in short papers, it will be useful to add a few sentences that will guide the reader in your longer papers. This way, your readers can better understand which arguments they will encounter on which pages and the course of your paper. That leads the reader to clearly understand and follow your content.
Let’s Wrap it Up
Writing an interesting and informative introduction is usually a long process that requires a lot of rewriting. You may need to rewrite a sentence dozens of times so that your words and sentences clearly describe your paper and argument. Fortunately, you can generate state-of-the-art introductions using AI tools and use them with a little editing.
When it comes to text generation, paraphrasing, and grammar & spelling checking, TextCortex is the way to go with its advanced LLMs and customization options. With TextCortex, you can generate all writing types, including introduction, from scratch, rewrite your existing texts, change their tone of voice, or fix their grammar. TextCortex is available as a web application and browser extension. The TextCortex browser extension is integrated with 30,000+ websites and apps. So, you can complete your AI-driven writing tasks anywhere and anytime.
Let's examine a few sample introductions generated by TextCortex.
Example Introduction #1
“Should social media platforms be banned from collecting their users' data?”

Example Introduction #2
“Do electric vehicles decrease overall emissions?”

Example Introduction #3
“Is graffiti an act of vandalism or the creation of art?”

Reimagine the way you interact with AI.
Harness knowledge with an AI of your own, define behaviour and integrate your favorite tech stack on over 30,000 platforms.
Did you like this article? Explore a few more related posts.
%20(6).png)
How to Create a Strong Thesis?

Top 3 AI Tools That Write Essays (Free & Paid)
%20(4).png)
5 Main Essay Types & Guide with Examples
Questions answers..
TextCortex is a powerful AI-powered writing tool that can help you reduce your writing time, handle big tasks, and create high-quality content without errors. With its customizable platform, personalized intelligence experience, advanced writing and research capabilities, and error-free content, TextCortex is the perfect tool for creative professionals who want to be a creative force in their industry.
Our AI copilot learned how to write from more than 3 billion sentences and has the ability to create unique content. However, fact-checking is something which still requires a human approval.
TextCortex supports more than 25 languages including English, Dutch, German, Ukranian, Romanian, Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian.
Yes, TextCortex is completely free to use with all of its features. When you sign up, you receive 100 free creations. Then you will receive 20 recurring creations every day on the free plan.
Yes, we have a Text Generation API, please talk to us directly to implement it. You can reach out to us at [email protected]
Account sharing is not allowed. If you have a need for more than 5 seats for an account, you can directly contact us at [email protected]
Yes, TextCortex offers 14-day free trial for users to try out all features extensively with higher number of generations. But keep in mind that you can already try everything with the free plan. There is no feature that is locked behind a premium plan.
Overall, TextCortex AI has over 1000 five-star reviews on reputable review sites such as G2, Trustpilot and Capterra.
TextCortex learns and adapts to your unique writing style and knowledge, making it easier for you to write high-quality & personalized content.
Your premium features will be available until the end of your subscription date, then your account plan will be set to Free plan.
General Questions
Your ai copilot is ready to collaborate with you..
Connect your knowledge, customize the style and start collaborating with your AI copilot.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper

Table of Contents
Writing an introduction for a research paper is a critical element of your paper, but it can seem challenging to encapsulate enormous amount of information into a concise form. The introduction of your research paper sets the tone for your research and provides the context for your study. In this article, we will guide you through the process of writing an effective introduction that grabs the reader's attention and captures the essence of your research paper.
Understanding the Purpose of a Research Paper Introduction
The introduction acts as a road map for your research paper, guiding the reader through the main ideas and arguments. The purpose of the introduction is to present your research topic to the readers and provide a rationale for why your study is relevant. It helps the reader locate your research and its relevance in the broader field of related scientific explorations. Additionally, the introduction should inform the reader about the objectives and scope of your study, giving them an overview of what to expect in the paper. By including a comprehensive introduction, you establish your credibility as an author and convince the reader that your research is worth their time and attention.
Key Elements to Include in Your Introduction
When writing your research paper introduction, there are several key elements you should include to ensure it is comprehensive and informative.
- A hook or attention-grabbing statement to capture the reader's interest. It can be a thought-provoking question, a surprising statistic, or a compelling anecdote that relates to your research topic.
- A brief overview of the research topic and its significance. By highlighting the gap in existing knowledge or the problem your research aims to address, you create a compelling case for the relevance of your study.
- A clear research question or problem statement. This serves as the foundation of your research and guides the reader in understanding the unique focus of your study. It should be concise, specific, and clearly articulated.
- An outline of the paper's structure and main arguments, to help the readers navigate through the paper with ease.
Preparing to Write Your Introduction
Before diving into writing your introduction, it is essential to prepare adequately. This involves 3 important steps:
- Conducting Preliminary Research: Immerse yourself in the existing literature to develop a clear research question and position your study within the academic discourse.
- Identifying Your Thesis Statement: Define a specific, focused, and debatable thesis statement, serving as a roadmap for your paper.
- Considering Broader Context: Reflect on the significance of your research within your field, understanding its potential impact and contribution.
By engaging in these preparatory steps, you can ensure that your introduction is well-informed, focused, and sets the stage for a compelling research paper.
Structuring Your Introduction
Now that you have prepared yourself to tackle the introduction, it's time to structure it effectively. A well-structured introduction will engage the reader from the beginning and provide a logical flow to your research paper.
Starting with a Hook
Begin your introduction with an attention-grabbing hook that captivates the reader's interest. This hook serves as a way to make your introduction more engaging and compelling. For example, if you are writing a research paper on the impact of climate change on biodiversity, you could start your introduction with a statistic about the number of species that have gone extinct due to climate change. This will immediately grab the reader's attention and make them realize the urgency and importance of the topic.
Introducing Your Topic
Provide a brief overview, which should give the reader a general understanding of the subject matter and its significance. Explain the importance of the topic and its relevance to the field. This will help the reader understand why your research is significant and why they should continue reading. Continuing with the example of climate change and biodiversity, you could explain how climate change is one of the greatest threats to global biodiversity, how it affects ecosystems, and the potential consequences for both wildlife and human populations. By providing this context, you are setting the stage for the rest of your research paper and helping the reader understand the importance of your study.
Presenting Your Thesis Statement
The thesis statement should directly address your research question and provide a preview of the main arguments or findings discussed in your paper. Make sure your thesis statement is clear, concise, and well-supported by the evidence you will present in your research paper. By presenting a strong and focused thesis statement, you are providing the reader with the information they could anticipate in your research paper. This will help them understand the purpose and scope of your study and will make them more inclined to continue reading.
Writing Techniques for an Effective Introduction
When crafting an introduction, it is crucial to pay attention to the finer details that can elevate your writing to the next level. By utilizing specific writing techniques, you can captivate your readers and draw them into your research journey.
Using Clear and Concise Language
One of the most important writing techniques to employ in your introduction is the use of clear and concise language. By choosing your words carefully, you can effectively convey your ideas to the reader. It is essential to avoid using jargon or complex terminology that may confuse or alienate your audience. Instead, focus on communicating your research in a straightforward manner to ensure that your introduction is accessible to both experts in your field and those who may be new to the topic. This approach allows you to engage a broader audience and make your research more inclusive.
Establishing the Relevance of Your Research
One way to establish the relevance of your research is by highlighting how it fills a gap in the existing literature. Explain how your study addresses a significant research question that has not been adequately explored. By doing this, you demonstrate that your research is not only unique but also contributes to the broader knowledge in your field. Furthermore, it is important to emphasize the potential impact of your research. Whether it is advancing scientific understanding, informing policy decisions, or improving practical applications, make it clear to the reader how your study can make a difference.
By employing these two writing techniques in your introduction, you can effectively engage your readers. Take your time to craft an introduction that is both informative and captivating, leaving your readers eager to delve deeper into your research.
Revising and Polishing Your Introduction
Once you have written your introduction, it is crucial to revise and polish it to ensure that it effectively sets the stage for your research paper.
Self-Editing Techniques
Review your introduction for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Ensure each paragraph introduces a new idea or argument with smooth transitions.
Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and awkward sentence structures.
Ensure that your introduction aligns with the overall tone and style of your research paper.
Seeking Feedback for Improvement
Consider seeking feedback from peers, colleagues, or your instructor. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improving your introduction. Be open to constructive criticism and use it to refine your introduction and make it more compelling for the reader.
Writing an introduction for a research paper requires careful thought and planning. By understanding the purpose of the introduction, preparing adequately, structuring effectively, and employing writing techniques, you can create an engaging and informative introduction for your research. Remember to revise and polish your introduction to ensure that it accurately represents the main ideas and arguments in your research paper. With a well-crafted introduction, you will capture the reader's attention and keep them inclined to your paper.
Suggested Reads
ResearchGPT: A Custom GPT for Researchers and Scientists Best Academic Search Engines [2023] How To Humanize AI Text In Scientific Articles Elevate Your Writing Game With AI Grammar Checker Tools
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 19, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, what is your plagiarism score.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: Aug 13, 2024 12:57 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

How to write an effective introduction for your research paper
Last updated
20 January 2024
Reviewed by
However, the introduction is a vital element of your research paper . It helps the reader decide whether your paper is worth their time. As such, it's worth taking your time to get it right.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper.
- The importance of an introduction in research papers
The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not. The introduction should provide a meaningful roadmap of your research to help them make this decision. It should let readers know whether the information they're interested in is likely to be found in the pages that follow.
Aside from providing readers with information about the content of your paper, the introduction also sets the tone. It shows readers the style of language they can expect, which can further help them to decide how far to read.
When you take into account both of these roles that an introduction plays, it becomes clear that crafting an engaging introduction is the best way to get your paper read more widely. First impressions count, and the introduction provides that impression to readers.
- The optimum length for a research paper introduction
While there's no magic formula to determine exactly how long a research paper introduction should be, there are a few guidelines. Some variables that impact the ideal introduction length include:
Field of study
Complexity of the topic
Specific requirements of the course or publication
A commonly recommended length of a research paper introduction is around 10% of the total paper’s length. So, a ten-page paper has a one-page introduction. If the topic is complex, it may require more background to craft a compelling intro. Humanities papers tend to have longer introductions than those of the hard sciences.
The best way to craft an introduction of the right length is to focus on clarity and conciseness. Tell the reader only what is necessary to set up your research. An introduction edited down with this goal in mind should end up at an acceptable length.
- Evaluating successful research paper introductions
A good way to gauge how to create a great introduction is by looking at examples from across your field. The most influential and well-regarded papers should provide some insights into what makes a good introduction.
Dissecting examples: what works and why
We can make some general assumptions by looking at common elements of a good introduction, regardless of the field of research.
A common structure is to start with a broad context, and then narrow that down to specific research questions or hypotheses. This creates a funnel that establishes the scope and relevance.
The most effective introductions are careful about the assumptions they make regarding reader knowledge. By clearly defining key terms and concepts instead of assuming the reader is familiar with them, these introductions set a more solid foundation for understanding.
To pull in the reader and make that all-important good first impression, excellent research paper introductions will often incorporate a compelling narrative or some striking fact that grabs the reader's attention.
Finally, good introductions provide clear citations from past research to back up the claims they're making. In the case of argumentative papers or essays (those that take a stance on a topic or issue), a strong thesis statement compels the reader to continue reading.
Common pitfalls to avoid in research paper introductions
You can also learn what not to do by looking at other research papers. Many authors have made mistakes you can learn from.
We've talked about the need to be clear and concise. Many introductions fail at this; they're verbose, vague, or otherwise fail to convey the research problem or hypothesis efficiently. This often comes in the form of an overemphasis on background information, which obscures the main research focus.
Ensure your introduction provides the proper emphasis and excitement around your research and its significance. Otherwise, fewer people will want to read more about it.
- Crafting a compelling introduction for a research paper
Let’s take a look at the steps required to craft an introduction that pulls readers in and compels them to learn more about your research.
Step 1: Capturing interest and setting the scene
To capture the reader's interest immediately, begin your introduction with a compelling question, a surprising fact, a provocative quote, or some other mechanism that will hook readers and pull them further into the paper.
As they continue reading, the introduction should contextualize your research within the current field, showing readers its relevance and importance. Clarify any essential terms that will help them better understand what you're saying. This keeps the fundamentals of your research accessible to all readers from all backgrounds.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information
Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes:
It helps to clarify the topic for the reader
It establishes the depth of your research
The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
For argumentative papers, you'll want to develop engaging background narratives. These should provide context for the argument you'll be presenting.
For empirical papers, highlighting past research is the key. Often, there will be some questions that weren't answered in those past papers. If your paper is focused on those areas, those papers make ideal candidates for you to discuss and critique in your introduction.
Step 3: Pinpointing the research challenge
To capture the attention of the reader, you need to explain what research challenges you'll be discussing.
For argumentative papers, this involves articulating why the argument you'll be making is important. What is its relevance to current discussions or problems? What is the potential impact of people accepting or rejecting your argument?
For empirical papers, explain how your research is addressing a gap in existing knowledge. What new insights or contributions will your research bring to your field?
Step 4: Clarifying your research aims and objectives
We mentioned earlier that the introduction to a research paper can serve as a roadmap for what's within. We've also frequently discussed the need for clarity. This step addresses both of these.
When writing an argumentative paper, craft a thesis statement with impact. Clearly articulate what your position is and the main points you intend to present. This will map out for the reader exactly what they'll get from reading the rest.
For empirical papers, focus on formulating precise research questions and hypotheses. Directly link them to the gaps or issues you've identified in existing research to show the reader the precise direction your research paper will take.
Step 5: Sketching the blueprint of your study
Continue building a roadmap for your readers by designing a structured outline for the paper. Guide the reader through your research journey, explaining what the different sections will contain and their relationship to one another.
This outline should flow seamlessly as you move from section to section. Creating this outline early can also help guide the creation of the paper itself, resulting in a final product that's better organized. In doing so, you'll craft a paper where each section flows intuitively from the next.
Step 6: Integrating your research question
To avoid letting your research question get lost in background information or clarifications, craft your introduction in such a way that the research question resonates throughout. The research question should clearly address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective on an existing problem.
Tell users your research question explicitly but also remember to frequently come back to it. When providing context or clarification, point out how it relates to the research question. This keeps your focus where it needs to be and prevents the topic of the paper from becoming under-emphasized.
Step 7: Establishing the scope and limitations
So far, we've talked mostly about what's in the paper and how to convey that information to readers. The opposite is also important. Information that's outside the scope of your paper should be made clear to the reader in the introduction so their expectations for what is to follow are set appropriately.
Similarly, be honest and upfront about the limitations of the study. Any constraints in methodology, data, or how far your findings can be generalized should be fully communicated in the introduction.
Step 8: Concluding the introduction with a promise
The final few lines of the introduction are your last chance to convince people to continue reading the rest of the paper. Here is where you should make it very clear what benefit they'll get from doing so. What topics will be covered? What questions will be answered? Make it clear what they will get for continuing.
By providing a quick recap of the key points contained in the introduction in its final lines and properly setting the stage for what follows in the rest of the paper, you refocus the reader's attention on the topic of your research and guide them to read more.
- Research paper introduction best practices
Following the steps above will give you a compelling introduction that hits on all the key points an introduction should have. Some more tips and tricks can make an introduction even more polished.
As you follow the steps above, keep the following tips in mind.
Set the right tone and style
Like every piece of writing, a research paper should be written for the audience. That is to say, it should match the tone and style that your academic discipline and target audience expect. This is typically a formal and academic tone, though the degree of formality varies by field.
Kno w the audience
The perfect introduction balances clarity with conciseness. The amount of clarification required for a given topic depends greatly on the target audience. Knowing who will be reading your paper will guide you in determining how much background information is required.
Adopt the CARS (create a research space) model
The CARS model is a helpful tool for structuring introductions. This structure has three parts. The beginning of the introduction establishes the general research area. Next, relevant literature is reviewed and critiqued. The final section outlines the purpose of your study as it relates to the previous parts.
Master the art of funneling
The CARS method is one example of a well-funneled introduction. These start broadly and then slowly narrow down to your specific research problem. It provides a nice narrative flow that provides the right information at the right time. If you stray from the CARS model, try to retain this same type of funneling.
Incorporate narrative element
People read research papers largely to be informed. But to inform the reader, you have to hold their attention. A narrative style, particularly in the introduction, is a great way to do that. This can be a compelling story, an intriguing question, or a description of a real-world problem.
Write the introduction last
By writing the introduction after the rest of the paper, you'll have a better idea of what your research entails and how the paper is structured. This prevents the common problem of writing something in the introduction and then forgetting to include it in the paper. It also means anything particularly exciting in the paper isn’t neglected in the intro.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
What is a "good" introduction?
Citing sources in the introduction, "introduction checklist" from: how to write a good scientific paper. chris a. mack. spie. 2018..
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is where you describe briefly and clearly why you are writing the paper. The introduction supplies sufficient background information for the reader to understand and evaluate the experiment you did. It also supplies a rationale for the study.
- Present the problem and the proposed solution
- Presents nature and scope of the problem investigated
- Reviews the pertinent literature to orient the reader
- States the method of the experiment
- State the principle results of the experiment
It is important to cite sources in the introduction section of your paper as evidence of the claims you are making. There are ways of citing sources in the text so that the reader can find the full reference in the literature cited section at the end of the paper, yet the flow of the reading is not badly interrupted. Below are some example of how this can be done: "Smith (1983) found that N-fixing plants could be infected by several different species of Rhizobium." "Walnut trees are known to be allelopathic (Smith 1949, Bond et al. 1955, Jones and Green 1963)." "Although the presence of Rhizobium normally increases the growth of legumes (Nguyen 1987), the opposite effect has been observed (Washington 1999)." Note that articles by one or two authors are always cited in the text using their last names. However, if there are more than two authors, the last name of the 1st author is given followed by the abbreviation et al. which is Latin for "and others".
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-reports-introductions
- Indicate the field of the work, why this field is important, and what has already been done (with proper citations).
- Indicate a gap, raise a research question, or challenge prior work in this territory.
- Outline the purpose and announce the present research, clearly indicating what is novel and why it is significant.
- Avoid: repeating the abstract; providing unnecessary background information; exaggerating the importance of the work; claiming novelty without a proper literature search.
- << Previous: ABSTRACT
- Next: METHODS >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Blog
How to write a research paper introduction (with examples).

I hope you enjoy reading this blog post.
If you would like to learn more about research, check out this Research Course .
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on crafting the perfect introduction for your research paper. In this blog, we’ll explore the crucial elements of a strong introduction, highlight common pitfalls to avoid, and provide practical tips to effectively set the stage for your study’s objectives and significance.
Table of Contents
Lack of a clear thesis statement, lack of clear objectives and scope, failure to establish the research significance, insufficient background information, inadequate literature review, ignoring the research gap, overly technical language, poor organization and flow, neglecting the audience, the importance of a good introduction.
A strong introduction sets the tone for the entire paper, guiding the reader through the research journey. It provides context, establishes relevance, and ensures the reader understands the importance of the study.
Starting a research project is exciting, but getting the introduction right is key. It’s like opening the door to your study and inviting readers in. However, there are some common missteps that can trip you up along the way.
Find the U.S. Research Position of your dreams!
Common mistakes to avoid.
A thesis statement is the central argument or claim that guides the entire research paper. It is a concise summary of the main point or claim of the paper and is typically found at the end of the introduction. A clear thesis statement helps to focus the research, provide direction, and inform the reader of the paper’s purpose. Expert reviewers may even skip the rest of the introduction (as they are well versed in the topic) and focus only on your thesis statement, so it’s vital to make sure it is perfect!
When a research introduction lacks a clear thesis statement, several issues can arise:
- Ambiguity : Without a clear thesis, the reader may be confused about the paper’s purpose and the main argument. Do not talk in vague terms. Whenever possible, use terminology established in recent literature. Narrow down the key aspects of the association that you are investigating (the study sample, the outcome and predictor measures) as much as possible.
- Lack of Focus : The paper can become unfocused and meander through unrelated topics, making it difficult for the reader to follow the argument. Do not try to have more than 1-2 main aims in a paper. Even if you have done supplementary analysis, it is better to say so in the discussion. As a rule of thumb, try to answer one major question only!
- Weak Argumentation : A well-defined thesis provides a strong foundation for building arguments. Without it, the arguments may appear weak and unsupported.
Let's be more practical:
1- In this paper, I will discuss climate change.
- Problem: This statement is too broad and vague. It does not provide a clear direction or specific argument.
2- This paper argues that climate change, measured by global average temperature change, is primarily driven by human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, and proposes policy measures to mitigate its impact.(1)
- Strengths: – Specificity : It clearly states that the paper will focus on human activities as the main drivers of climate change. – Argument : It presents a specific claim that the paper will argue. – Direction : It hints at the structure of the paper by mentioning policy measures.
If you would like to learn more about introductions and other aspects of clinical research, check out the Medical Research Course from the Match Guy here .
Powerful Tips:
- Be Specific : Clearly define the main argument or claim. Avoid vague or broad statements.
- Be Concise : Keep the thesis statement concise, ideally one to two sentences.
- Provide Direction : Indicate the structure of the paper by hinting at the main points that will be discussed.
- Revise as Needed : Be prepared to revise the thesis statement as your research progresses and your understanding deepens.
Transform research ideas into published papers!
A clear statement of objectives and scope is crucial in a research paper introduction because it outlines what the study aims to achieve and defines the boundaries within which the research will be conducted.
Example of Lacking Clear Objectives and Scope: This paper examines the impacts of climate change on agriculture.
- Problem : This statement is too broad and vague. It does not specify what aspects of climate change or agriculture will be studied, nor does it define the geographical or temporal scope.
Example with Clear Objectives and Scope: This study aims to investigate the effects of rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns on crop yields in the Midwest United States from 2000 to 2010. The objectives are to (1) assess the impact of temperature changes on corn and soybean yields, (2) analyze how variations in precipitation affect crop growth, and (3) identify adaptive strategies employed by farmers in the region.(2)
Powerful tips:
- Be Specific : Clearly state what the study aims to achieve and avoid vague or broad statements.
- Identify Key Areas : Outline the main areas or aspects that the research will focus on.
- Set Boundaries : Define the geographical, temporal, and conceptual boundaries of the research.
- List Objectives : Clearly articulate specific research objectives or questions that the study will address.
- Stay Realistic : Ensure that the objectives and scope are achievable within the constraints of the research project.
- Make it flow : Make sure you are not repeating the same concepts as the thesis statement, as these two sections are often presented back-to-back in the final paragraph of the introduction! Remember: the thesis statement is your hypothesis or question, and your objectives are ‘how’ you are going to test your thesis.
Master medical statistics and boost your productivity!
This mistake can result in the research appearing trivial or irrelevant, diminishing its potential impact. When the significance of the research is not well-established, readers may struggle to understand the value of the study and why they should care about it.
Example of Failure to Establish Research Significance: This study investigates the effects of social media usage on sleep patterns among teenagers.
- Problem : The significance of studying social media’s impact on sleep patterns is not explained. The reader may wonder why this research is important or what implications it has.
Example with Established Research Significance: This study investigates the effects of social media usage on sleep patterns among teenagers. Understanding this relationship is crucial because insufficient sleep is linked to numerous health issues, including decreased academic performance, heightened stress levels, and increased risk of mental health problems. With the pervasive use of social media among adolescents, identifying how it impacts sleep can inform strategies for promoting healthier habits and improving overall well-being in this vulnerable age group.(3)
- Link to Broader Issues : Connect the research topic to broader issues or trends that highlight its relevance and importance.
- Explain Practical Implications : Discuss the potential practical applications or benefits of the research findings.
- Address Gaps in Knowledge : Identify gaps in the existing literature that the research aims to fill.
- Highlight Potential Impact : Emphasize the potential impact of the research on the field, society, or specific populations.
- Use Concrete Examples : Provide concrete examples or scenarios to illustrate the significance of the research.
Feeling swamped by the complexities of Systematic Reviews?
Insufficient background information in the introduction of a research paper refers to failing to provide enough context for the reader to understand the research problem and its significance. Background information sets the stage for the research by offering necessary details about the topic, relevant theories, previous studies, and key terms.
This may lead to:
- Reader Confusion : Without adequate context, readers may struggle to understand the research question, its importance, and how it fits into the broader field of study.
- Weak Justification : Insufficient background can undermine the rationale for the research, making it difficult to justify why the study is necessary or valuable.
- Misinterpretation : Lack of context can lead to misinterpretation of the research objectives, methods, and findings.
Example of Insufficient Background Information: In recent years, many researchers have studied the effects of social media on teenagers. This paper explores the relationship between social media use and anxiety among teenagers.
- Problem : This introduction lacks specific details about the previous research, the theoretical framework, and key terms. It does not provide enough context for the reader to understand why the study is important.
Example of Adequate Background Information: Social media platforms have become an integral part of teenagers’ daily lives, with studies showing that 95% of teens have access to a smartphone and 45% are online almost constantly. Previous research has linked excessive social media use to various mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying this relationship remain unclear. This paper explores the impact of social media use on anxiety levels among teenagers, focusing on the roles of social comparison and cyberbullying.(4)
If you would like to learn more about manuscript writing, check out the Comprehensive Research Course from the Match Guy here .
- Review Relevant Literature : Summarize key studies and theories related to your topic.
- Provide Context : Explain the broader context of your research problem.
- Define Key Terms : Ensure that any specialized terms or concepts are clearly defined.
- Identify the Research Gap : Highlight what is not yet known or understood about your topic.
- Be Concise : Provide enough information to set the stage without overwhelming the reader with details.
Getting No Replies from Institutions? Don't Stress!
This mistake can occur when the literature review is too brief, lacks depth, omits key studies, or fails to critically analyze previous work. An inadequate literature review can undermine the foundation of the research by failing to provide the necessary context and justification for the study.
Inadequate Literature Review: There has been some research on the relationship between exercise and mental health. This paper will investigate this relationship further.
- Problem : This review is too general and does not provide sufficient detail about the existing research or how it informs the current study.
Example with Adequate Literature Review: Research has consistently shown that regular physical activity has positive effects on mental health. For example, a study by Gujral et al. (2019) demonstrated that aerobic exercise can significantly reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Similarly, Smith and Lee (2020) found that strength training also contributes to improved mood and reduced stress levels. However, much of the existing research has focused on adult populations, with relatively few studies examining these effects in adolescents. Additionally, the specific types of exercise that are most beneficial for different mental health outcomes have not been thoroughly investigated. This study aims to explore the effects of various types of exercise on the mental health of high school students, thereby addressing these gaps in the literature.(5-6)
- Be Comprehensive : Review a broad range of studies related to the research topic to provide a thorough context.
- Be Specific : Cite specific studies, including their methodologies, findings, and relevance to the current research.
- Be Critical : Analyze and evaluate the existing research, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and gaps.
- Be Structured : Organize the literature review logically, grouping studies by themes or findings to create a coherent narrative.
- Be Relevant : Focus on the most relevant studies that directly relate to the research question and objectives.
Unlock your research potential with our dynamic course designed for medical students! Built by an experienced researcher with 150+ publications and 3000+ citations!
Ignoring the research gap in a research paper introduction means failing to identify and articulate what specific aspect of the topic has not been explored or adequately addressed in existing literature. The research gap is a critical component because it justifies the necessity and originality of the study. Without highlighting this gap, the research may appear redundant or lacking in significance.
How huge is this mistake?
- Lack of Justification : The study may not appear necessary or relevant, diminishing its perceived value.
- Redundancy : The research may seem to duplicate existing studies, offering no new insights or contributions to the field. Even if you are using methodology similar to previous studies, it is important to note why you are doing so e.g., few studies have used that specific methodology, and you would like to validate it in your sample population!
- Reader Disinterest : Readers may lose interest if they do not see the unique contribution or purpose of the research.
Example of Ignoring the Research Gap: Many studies have examined the effects of exercise on mental health. This paper looks at the relationship between physical activity and depression.
- Problem : This introduction does not specify what aspect of the relationship between physical activity and depression has not been studied, failing to highlight the unique contribution of the research.
Example of Identifying the Research Gap: Numerous studies have demonstrated the general benefits of physical activity on mental health, particularly its role in alleviating symptoms of depression. However, there is limited research on how different types of exercise (e.g., aerobic vs. anaerobic) specifically impact depression levels among various age groups. This study investigates the differential effects of aerobic and anaerobic exercise on depression in young adults, aiming to fill this gap in the literature.(6)
- Conduct a Thorough Literature Review : Understand the current state of research in your field to identify what has been studied and where gaps exist.
- Be Specific : Clearly articulate what specific aspect has not been covered in existing studies.
- Link to Your Study : Explain how your research will address this gap and contribute to the field.
- Use Evidence : Support your identification of the gap with references to previous studies.
- Emphasize Significance : Highlight why filling this gap is important for advancing knowledge or practical applications.
Do Statistical Analysis on your own with confidence in 2 weeks!
Overly technical language refers to the excessive use of jargon, complex terms, and highly specialized language that may be difficult for readers, especially those not familiar with the field, to understand. While technical language is sometimes necessary in academic writing, overusing it in the introduction can create several problems:
- Reader Alienation : Readers may find the text intimidating or inaccessible, leading to disengagement.
- Lack of Clarity : The main points and significance of the research can become obscured by complex terminology.
- Reduced Impact : The research may fail to communicate its importance effectively if readers struggle to understand the introduction.
Example of Overly Technical Language: The present study examines the metacognitive strategies employed by individuals in the domain of second language acquisition, specifically focusing on the interaction between declarative and procedural memory systems in the process of syntactic parsing.
- Problem : This sentence is loaded with jargon (“metacognitive strategies,” “second language acquisition,” “declarative and procedural memory systems,” “syntactic parsing”), which can be overwhelming and confusing for readers not familiar with these terms.
Example with Simplified Language: This study looks at the thinking strategies people use when learning a second language. It focuses on how different types of memory, such as the knowledge of facts and the skills for doing things, help in understanding sentence structures.(7)
- Know Your Audience : Tailor the language to the intended audience, ensuring it is accessible to both specialists and non-specialists.
- Define Term s: When technical terms are necessary, provide clear definitions or explanations.
- Use Analogies : Simplify complex concepts using analogies or examples that are easy to understand.
- Avoid Jargon : Limit the use of jargon and specialized terms, especially in the introduction.
- Seek Feedback : Ask peers or non-experts to read the introduction and provide feedback on clarity and accessibility.
Curious about delving into research but unsure where to begin?
Poor organization and flow in a research paper introduction refer to a lack of logical structure and coherence that makes the introduction difficult to follow. This can occur when ideas are presented in a haphazard manner, transitions between sections are weak or non-existent, and the overall narrative is disjointed. A well-organized introduction should smoothly guide the reader from the general context to the specific objectives of the study.
Example of Poor Organization and Flow: “Climate change affects agriculture in various ways. Many studies have looked at the impact on crop yields. This paper will discuss the economic implications of these changes. Climate models predict increased variability in weather patterns, which will affect water availability. Researchers have found that higher temperatures reduce the growing season for many crops.”
- Problem : The ideas are presented in a scattered manner without clear connections. The mention of economic implications seems out of place, and there are abrupt shifts between topics.
Example with Good Organization and Flow: Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture by altering weather patterns, impacting crop yields, and affecting water availability. Numerous studies have shown that increased temperatures can shorten the growing season for many crops, leading to reduced yields. Additionally, climate models predict increased variability in weather patterns, which complicates water management for farmers. These changes not only affect food production but also have substantial economic implications for agricultural communities. This paper will examine the economic impacts of climate-induced changes in agriculture, focusing on crop yield variability and water resource management.(1)
- Create an Outline : Before writing, outline the main points you want to cover in the introduction.
- Think in terms of an inverted triangle : Begin broadly to introduce basic concepts related to your topic. As you progress through the introduction, you can introduce more and more specific topics until you have enough information to justify your thesis statement
- Use Transitional Phrases : Employ transitional phrases and sentences to connect ideas and sections smoothly.
- Follow a Logical Sequence : Present information in a logical order, moving from general context to specific objectives.
- Maintain Focus : Stay focused on the main topic and avoid introducing unrelated ideas.
- Revise for Coherence : Review and revise the introduction to ensure that it flows well and that each part contributes to the overall narrative.

Advisor UNLIMITED Access
We get how stressful the residency match process is, so we're here for you - communicate with your personal advisor ANYTIME you need!

Personal Statement Editing
Our editing includes not only language but also context, structure, and content advising.

ERAS Application Editing
The editing goes beyond language and grammar corrections to structure, design, and content based on your personal story and achievement.

- Interview Preparation
The best way to learn something is to do it. That’s why we divide our interview preparation sessions into two parts. Mock Interview + Feedback
Neglecting the audience refers to failing to consider the background, knowledge level, and interests of the intended readers when writing the introduction of a research paper. This mistake can manifest in several ways, such as using overly technical language for a general audience, providing insufficient background information for readers unfamiliar with the topic, or failing to engage the readers’ interest.
Example of Neglecting the Audience: For experts in genomic sequencing, this study explores the epigenetic modifications resulting from CRISPR-Cas9 interventions, focusing on the methylation patterns and histone modifications observed in gene-edited cells.
- Problem : This introduction assumes a high level of expertise in genomic sequencing and epigenetics, which may alienate readers without this background.
Example with Audience Consideration: CRISPR-Cas9 is a groundbreaking tool in genetic research that allows scientists to edit DNA with precision. However, altering genes can lead to unexpected changes in how genes are expressed, known as epigenetic modifications. This study investigates these changes by looking at specific markers on DNA, such as methylation patterns, and how they affect gene activity in cells that have been edited using CRISPR-Cas9. Our goal is to understand the broader implications of gene editing on cellular functions, which is crucial for advancing medical research and treatments.(8)
- Identify the Audience : Determine who the intended readers are (e.g., experts, students, general public) and tailor the language and content accordingly. Read papers from the journals you are considering for submission. Professional editors curate the language used in these papers and are a great starting point to identify the level of expertise of your audience!
- Simplify Language : Use clear and straightforward language, avoiding jargon and technical terms unless they are necessary and well-explained.
- Provide Background Information : Include sufficient background information to help readers understand the context and significance of the research.
- Engage the Reader : Start with an engaging introduction that highlights the relevance and importance of the research topic.
- Anticipate Questions : Consider what questions or concerns the audience might have and address them in the introduction
USMLE Tutoring
By following these guidelines and avoiding common pitfalls, you can create an introduction that not only grabs the attention of your readers but also sets the stage for a compelling and impactful research paper.
Final Tips:
- Revise and refine your introduction multiple times to ensure clarity and coherence.
- Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or advisors to identify areas for improvement.
- Keep your audience in mind and tailor your language and content to their needs and interests.
- Stay focused on your research objectives and ensure that every part of your introduction contributes to achieving them.
- Be confident in the significance of your research and its potential impact on your field or community.
Let your introduction be more than just words on a page. It’s a doorway to understanding. To help you along, we’ve created a practical course on writing and publishing research projects. It’s 100% risk-free, with a money-back guarantee if you’re not satisfied. Try it out now by clicking here .
Wishing you success on your research journey!
Marina Ramzy Mourid, Hamza Ibad, MBBS
Dr. Ibad graduated from the Aga Khan University Medical College and completed a post-doctoral research fellowship at Johns Hopkins in the Department of Radiology (Musculoskeletal Division). Dr. Ibad’s research and clinical interests include deep-learning applications for automated image interpretation, osteoarthritis, and sarcopenia-related health outcomes.

2025 ERAS Application Updates

General Surgery Residency Personal Statement Examples

Emergency Medicine Residency Personal Statement Examples

Internal Medicine Residency Personal Statement Examples
About thematchguy, become a researcher in the united states, interested in learning more about literature search with examples from published literature, the comprehensive research course, the systematic review course, the medical statistics course, how to find research positions in the us.
1. Abbass K, Qasim MZ, Song H, Murshed M, Mahmood H, Younis I. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(28):42539-42559. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19718-6
2. Cai X, Wang D, Laurent R. Impact of climate change on crop yield: a case study of rainfed corn in central illinois. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 2009;48(9):1868-1881. doi:10.1175/2009JAMC1880.1
3. Van Den Eijnden RJJM, Geurts SM, Ter Bogt TFM, Van Der Rijst VG, Koning IM. Social media use and adolescents’ sleep: a longitudinal study on the protective role of parental rules regarding internet use before sleep. IJERPH. 2021;18(3):1346. doi:10.3390/ijerph18031346
4. Schmitt, M. (2021). Effects of social media and technology on adolescents: What the evidence is showing and what we can do about it. Journal of Family and Consumer Sciences Education, 38(1), 51-59.
5. Gujral S, Aizenstein H, Reynolds CF, Butters MA, Erickson KI. Exercise effects on depression: Possible neural mechanisms. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2017;49:2-10. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2017.04.012
6. Smith PJ, Merwin RM. The role of exercise in management of mental health disorders: an integrative review. Annu Rev Med. 2021;72(1):45-62. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-060619-022943
7. Sun Q, Zhang LJ. Understanding learners’ metacognitive experiences in learning to write in English as a foreign language: A structural equation modeling approach. Front Psychol. 2022;13:986301. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.986301
8. Kolanu ND. Crispr–cas9 gene editing: curing genetic diseases by inherited epigenetic modifications. Glob Med Genet. 2024;11(01):113-122. doi:10.1055/s-0044-1785234
How can we help you?
Leave your message here and we will get in touch with you as soon as possible.


Quick Links
- Our Reviews
- Our Podcast
- Residency Advising
- Personal Statement
- Match®Application Package
- P.O. Box 40388 Pittsburgh, PA 15201
- [email protected]
- + 1 412-295-8358
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
WhatsApp Us

Join Over 20,000 Readers
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Introduction
Last Updated: December 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,656,278 times.
The introduction to a research paper can be the most challenging part of the paper to write. The length of the introduction will vary depending on the type of research paper you are writing. An introduction should announce your topic, provide context and a rationale for your work, before stating your research questions and hypothesis. Well-written introductions set the tone for the paper, catch the reader's interest, and communicate the hypothesis or thesis statement.
Introducing the Topic of the Paper

- In scientific papers this is sometimes known as an "inverted triangle", where you start with the broadest material at the start, before zooming in on the specifics. [2] X Research source
- The sentence "Throughout the 20th century, our views of life on other planets have drastically changed" introduces a topic, but does so in broad terms.
- It provides the reader with an indication of the content of the essay and encourages them to read on.

- For example, if you were writing a paper about the behaviour of mice when exposed to a particular substance, you would include the word "mice", and the scientific name of the relevant compound in the first sentences.
- If you were writing a history paper about the impact of the First World War on gender relations in Britain, you should mention those key words in your first few lines.

- This is especially important if you are attempting to develop a new conceptualization that uses language and terminology your readers may be unfamiliar with.

- If you use an anecdote ensure that is short and highly relevant for your research. It has to function in the same way as an alternative opening, namely to announce the topic of your research paper to your reader.
- For example, if you were writing a sociology paper about re-offending rates among young offenders, you could include a brief story of one person whose story reflects and introduces your topic.
- This kind of approach is generally not appropriate for the introduction to a natural or physical sciences research paper where the writing conventions are different.
Establishing the Context for Your Paper

- It is important to be concise in the introduction, so provide an overview on recent developments in the primary research rather than a lengthy discussion.
- You can follow the "inverted triangle" principle to focus in from the broader themes to those to which you are making a direct contribution with your paper.
- A strong literature review presents important background information to your own research and indicates the importance of the field.

- By making clear reference to existing work you can demonstrate explicitly the specific contribution you are making to move the field forward.
- You can identify a gap in the existing scholarship and explain how you are addressing it and moving understanding forward.

- For example, if you are writing a scientific paper you could stress the merits of the experimental approach or models you have used.
- Stress what is novel in your research and the significance of your new approach, but don't give too much detail in the introduction.
- A stated rationale could be something like: "the study evaluates the previously unknown anti-inflammatory effects of a topical compound in order to evaluate its potential clinical uses".
Specifying Your Research Questions and Hypothesis

- The research question or questions generally come towards the end of the introduction, and should be concise and closely focused.
- The research question might recall some of the key words established in the first few sentences and the title of your paper.
- An example of a research question could be "what were the consequences of the North American Free Trade Agreement on the Mexican export economy?"
- This could be honed further to be specific by referring to a particular element of the Free Trade Agreement and the impact on a particular industry in Mexico, such as clothing manufacture.
- A good research question should shape a problem into a testable hypothesis.

- If possible try to avoid using the word "hypothesis" and rather make this implicit in your writing. This can make your writing appear less formulaic.
- In a scientific paper, giving a clear one-sentence overview of your results and their relation to your hypothesis makes the information clear and accessible. [10] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- An example of a hypothesis could be "mice deprived of food for the duration of the study were expected to become more lethargic than those fed normally".

- This is not always necessary and you should pay attention to the writing conventions in your discipline.
- In a natural sciences paper, for example, there is a fairly rigid structure which you will be following.
- A humanities or social science paper will most likely present more opportunities to deviate in how you structure your paper.
Research Introduction Help

Community Q&A
- Use your research papers' outline to help you decide what information to include when writing an introduction. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Consider drafting your introduction after you have already completed the rest of your research paper. Writing introductions last can help ensure that you don't leave out any major points. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid emotional or sensational introductions; these can create distrust in the reader. Thanks Helpful 51 Not Helpful 12
- Generally avoid using personal pronouns in your introduction, such as "I," "me," "we," "us," "my," "mine," or "our." Thanks Helpful 32 Not Helpful 7
- Don't overwhelm the reader with an over-abundance of information. Keep the introduction as concise as possible by saving specific details for the body of your paper. Thanks Helpful 25 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/inverted-pyramid-structure-in-writing.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://dept.writing.wisc.edu/wac/writing-an-introduction-for-a-scientific-paper/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
About This Article

To introduce your research paper, use the first 1-2 sentences to describe your general topic, such as “women in World War I.” Include and define keywords, such as “gender relations,” to show your reader where you’re going. Mention previous research into the topic with a phrase like, “Others have studied…”, then transition into what your contribution will be and why it’s necessary. Finally, state the questions that your paper will address and propose your “answer” to them as your thesis statement. For more information from our English Ph.D. co-author about how to craft a strong hypothesis and thesis, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdulrahman Omar
Oct 5, 2018
Did this article help you?

May 9, 2021
Lavanya Gopakumar
Oct 1, 2016
Dengkai Zhang
May 14, 2018
Leslie Mae Cansana
Sep 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > How to write an introduction for a research paper
How to write an introduction for a research paper
Beginnings are hard. Beginning a research paper is no exception. Many students—and pros—struggle with how to write an introduction for a research paper.
This short guide will describe the purpose of a research paper introduction and how to create a good one.

What is an introduction for a research paper?
Introductions to research papers do a lot of work.
It may seem obvious, but introductions are always placed at the beginning of a paper. They guide your reader from a general subject area to the narrow topic that your paper covers. They also explain your paper’s:
- Scope: The topic you’ll be covering
- Context: The background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in the context of an industry or the world
Your introduction will cover a lot of ground. However, it will only be half of a page to a few pages long. The length depends on the size of your paper as a whole. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper.

Write with Confidence using Editor
Elevate your writing with real-time, intelligent assistance
Why is an introduction vital to a research paper?
The introduction to your research paper isn’t just important. It’s critical.
Your readers don’t know what your research paper is about from the title. That’s where your introduction comes in. A good introduction will:
- Help your reader understand your topic’s background
- Explain why your research paper is worth reading
- Offer a guide for navigating the rest of the piece
- Pique your reader’s interest
Without a clear introduction, your readers will struggle. They may feel confused when they start reading your paper. They might even give up entirely. Your introduction will ground them and prepare them for the in-depth research to come.
What should you include in an introduction for a research paper?
Research paper introductions are always unique. After all, research is original by definition. However, they often contain six essential items. These are:
- An overview of the topic. Start with a general overview of your topic. Narrow the overview until you address your paper’s specific subject. Then, mention questions or concerns you had about the case. Note that you will address them in the publication.
- Prior research. Your introduction is the place to review other conclusions on your topic. Include both older scholars and modern scholars. This background information shows that you are aware of prior research. It also introduces past findings to those who might not have that expertise.
- A rationale for your paper. Explain why your topic needs to be addressed right now. If applicable, connect it to current issues. Additionally, you can show a problem with former theories or reveal a gap in current research. No matter how you do it, a good rationale will interest your readers and demonstrate why they must read the rest of your paper.
- Describe the methodology you used. Recount your processes to make your paper more credible. Lay out your goal and the questions you will address. Reveal how you conducted research and describe how you measured results. Moreover, explain why you made key choices.
- A thesis statement. Your main introduction should end with a thesis statement. This statement summarizes the ideas that will run through your entire research article. It should be straightforward and clear.
- An outline. Introductions often conclude with an outline. Your layout should quickly review what you intend to cover in the following sections. Think of it as a roadmap, guiding your reader to the end of your paper.
These six items are emphasized more or less, depending on your field. For example, a physics research paper might emphasize methodology. An English journal article might highlight the overview.
Three tips for writing your introduction
We don’t just want you to learn how to write an introduction for a research paper. We want you to learn how to make it shine.
There are three things you can do that will make it easier to write a great introduction. You can:
- Write your introduction last. An introduction summarizes all of the things you’ve learned from your research. While it can feel good to get your preface done quickly, you should write the rest of your paper first. Then, you’ll find it easy to create a clear overview.
- Include a strong quotation or story upfront. You want your paper to be full of substance. But that doesn’t mean it should feel boring or flat. Add a relevant quotation or surprising anecdote to the beginning of your introduction. This technique will pique the interest of your reader and leave them wanting more.
- Be concise. Research papers cover complex topics. To help your readers, try to write as clearly as possible. Use concise sentences. Check for confusing grammar or syntax . Read your introduction out loud to catch awkward phrases. Before you finish your paper, be sure to proofread, too. Mistakes can seem unprofessional.

Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

How to write a plot twist in your story
When executed carefully, a plot twist has the power to shock and dazzle your reader. Learn how you can incorporate one into your writing.

What's the difference between a memoir and an autobiography?
Explore the differences between memoirs, autobiographies, and biographies.

When to use 'while' vs. 'whilst'
“While” and “whilst” are usually interchangeable, but not always. See how they differ and learn how to use them effectively.

What is touch typing (and why is it important)?
Learn about the benefits of touch typing and how it can help you type faster and more accurately.
Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.

Title Page Setup
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
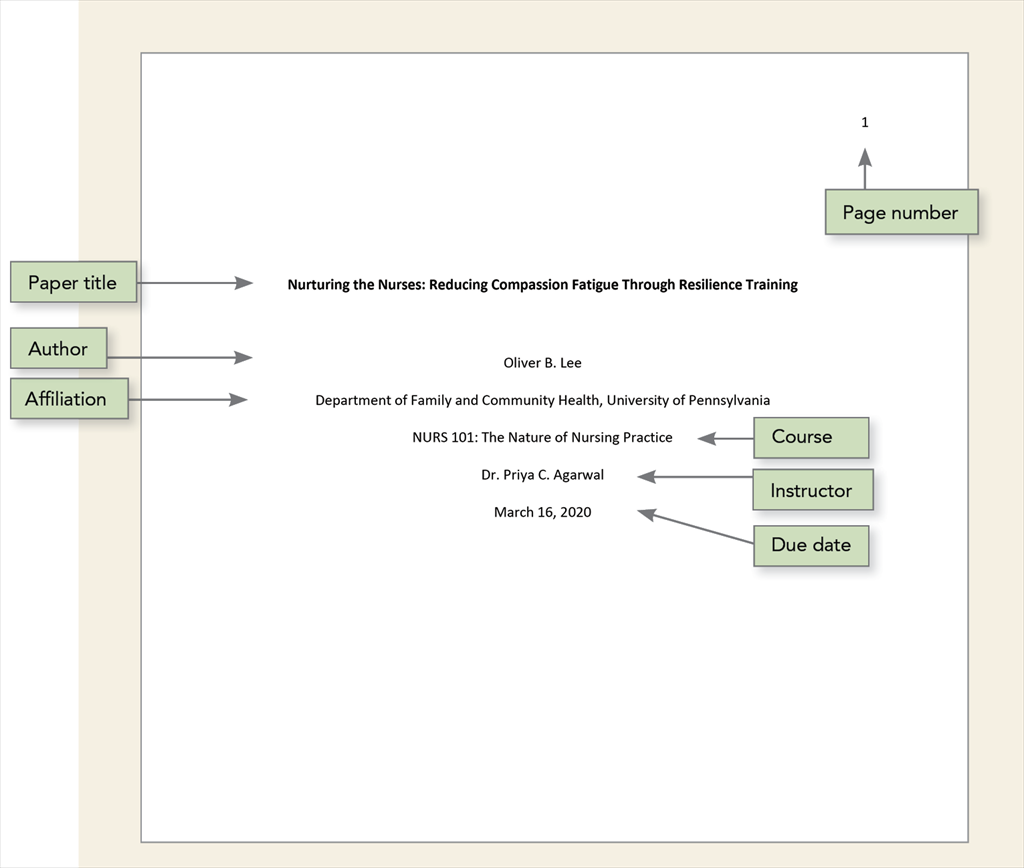
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
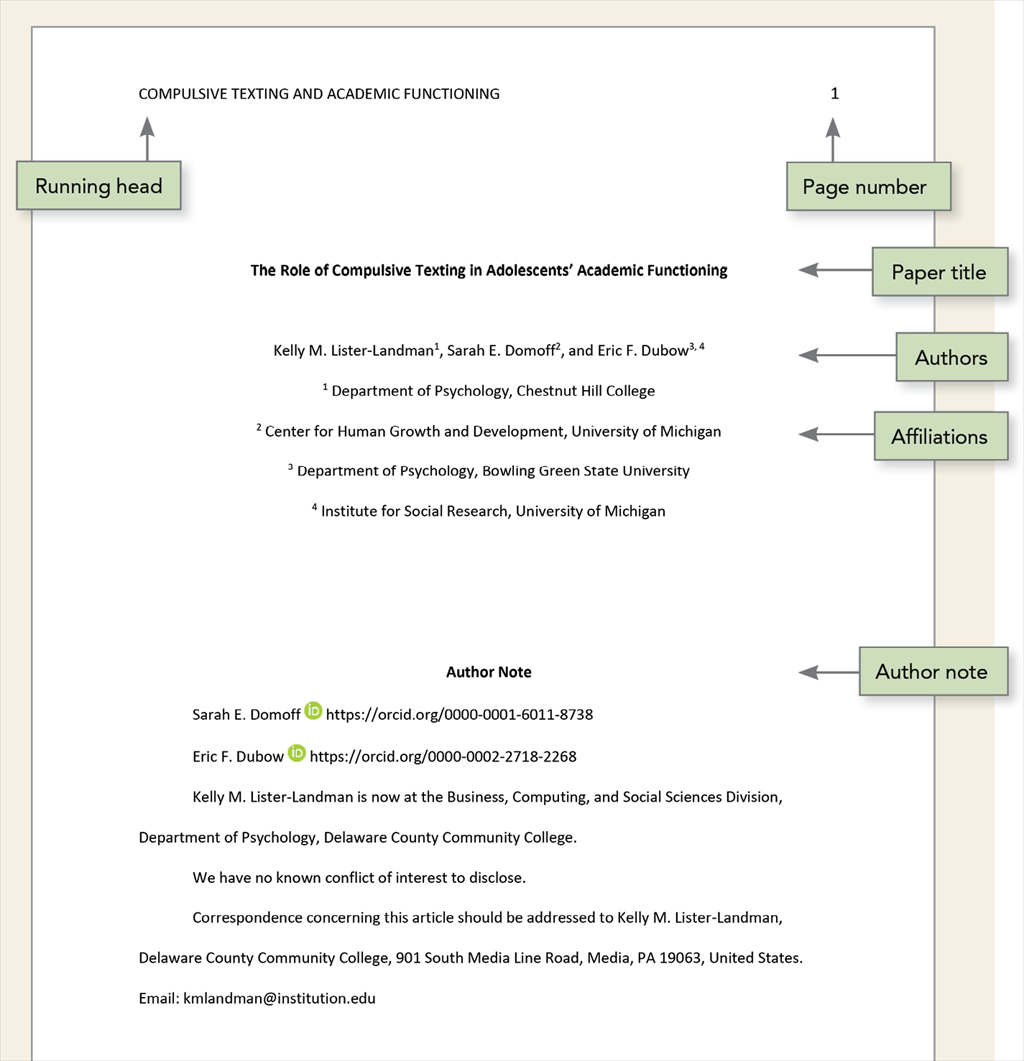
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
- Articles of Word
How to Write a Research Paper [Steps & Examples]
As a student, you are often required to complete numerous academic tasks, which can demand a lot of extra effort. Writing a research paper is one of these tasks. If researching for the topic isn't challenging enough, writing it down in a specific format adds another layer of difficulty. Having gone through this myself, I want to help you have a smoother journey in writing your research paper. I'll guide you through everything you need to know about writing a research paper, including how to write a research paper and all the necessary factors you need to consider while writing one.
Order for Preparation of your research paper
Before beginning your research paper, start planning how you will organize your paper. Follow the specific order I have laid out to ensure you assemble everything correctly, cover all necessary components, and write more effectively. This method will help you avoid missing important elements and improve the overall quality of your paper.
Figures and Tables
Assemble all necessary visual aids to support your data and findings. Ensure they are labeled correctly and referenced appropriately in your text.
Detail the procedures and techniques used in your research. This section should be thorough enough to allow others to replicate your study.
Summarize the findings of your research without interpretation. Use figures and tables to illustrate your data clearly.
Interpret the results, discussing their implications and how they relate to your research question. Address any limitations and suggest areas for future research.
Summarize the key points of your research, restating the significance of your findings and their broader impact.
Introduction
Introduce the topic, provide background information, and state the research problem or hypothesis. Explain the purpose and scope of your study.
Write a concise summary of your research, including the objective, methods, results, and conclusion. Keep it brief and to the point.
Create a clear and informative title that accurately reflects the content and focus of your research paper.
Identify key terms related to your research that will help others find your paper in searches.
Acknowledgements
Thank those who contributed to your research, including funding sources, advisors, and any other significant supporters.
Compile a complete list of all sources cited in your paper, formatted according to the required citation style. Ensure every reference is accurate and complete.
Types of Research Papers
There are multiple types of research papers, each with distinct characteristics, purposes, and structures. Knowing which type of research paper is required for your assignment is crucial, as each demands different preparation and writing strategies. Here, we will delve into three prominent types: argumentative, analytical, and compare and contrast papers. We will discuss their characteristics, suitability, and provide detailed examples to illustrate their application.
A.Argumentative Papers
Characteristics:
An argumentative or persuasive paper is designed to present a balanced view of a controversial issue, but ultimately aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective. The key characteristics of this type of paper include:
Purpose: The primary goal is to convince the reader to support a particular stance on an issue. This is achieved by presenting arguments, evidence, and refuting opposing viewpoints.
Structure: Typically structured into an introduction, a presentation of both sides of the issue, a refutation of the opposing arguments, and a conclusion that reinforces the writer’s position.
Tone: While the tone should be logical and factual, it should not be overly emotional. Arguments must be supported with solid evidence, such as statistics, expert opinions, and factual data.
Suitability:
Argumentative papers are suitable for topics that have clear, opposing viewpoints. They are often used in debates, policy discussions, and essays aimed at influencing public opinion or academic discourse.
Topic: "Should governments implement universal basic income?"
Pro Side: Universal basic income provides financial security, reduces poverty, and can lead to a more equitable society.
Con Side: It could discourage work, lead to higher government expenditure, and might not be a sustainable long-term solution.
Argument: After presenting both sides, the paper would argue that the benefits of reducing poverty and financial insecurity outweigh the potential drawbacks, using evidence from various studies and real-world examples.
Writing Tips:
Clearly articulate your position on the issue from the beginning.
Present balanced arguments by including credible sources that support both sides.
Refute counterarguments effectively with logical reasoning and evidence.
Maintain a factual and logical tone, avoiding excessive emotional appeals.
B.Analytical Papers
An analytical research paper is focused on breaking down a topic into its core components, examining various perspectives, and drawing conclusions based on this analysis. The main characteristics include:
Purpose: To pose a research question, collect data from various sources, analyze different viewpoints, and synthesize the information to arrive at a personal conclusion.
Structure: Includes an introduction with a clear research question, a literature review that summarizes existing research, a detailed analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes findings.
Tone: Objective and neutral, avoiding personal bias or opinion. The focus is on data and logical analysis.
Analytical research papers are ideal for topics that require detailed examination and evaluation of various aspects. They are common in disciplines such as social sciences, humanities, and natural sciences, where deep analysis of existing research is crucial.
Topic: "The impact of social media on mental health."
Research Question: How does social media usage affect mental well-being among teenagers?
Analysis: Examine studies that show both positive (e.g., social support) and negative (e.g., anxiety and depression) impacts of social media. Analyze the methodologies and findings of these studies.
Conclusion: Based on the analysis, conclude whether the overall impact is more beneficial or harmful, remaining neutral and presenting evidence without personal bias.
Maintain an objective and neutral tone throughout the paper.
Synthesize information from multiple sources, ensuring a comprehensive analysis.
Develop a clear thesis based on the findings from your analysis.
Avoid inserting personal opinions or biases.
C.Compare and Contrast Papers
Compare and contrast papers are used to analyze the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. The key characteristics include:
Purpose: To identify and examine the similarities and differences between two or more subjects, providing a comprehensive understanding of their relationship.
Structure: Can be organized in two ways:
Point-by-Point: Each paragraph covers a specific point of comparison or contrast.
Subject-by-Subject: Each subject is discussed separately, followed by a comparison or contrast.
Tone: Informative and balanced, aiming to provide a thorough and unbiased comparison.
Compare and contrast papers are suitable for topics where it is important to understand the distinctions and similarities between elements. They are commonly used in literature, history, and various comparative studies.
Topic: "Compare and contrast the leadership styles of Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X."
Comparison Points: Philosophies (non-violence vs. militant activism), methods (peaceful protests vs. more radical approaches), and impacts on the Civil Rights Movement.
Analysis: Describe each leader's philosophy and method, then analyze how these influenced their effectiveness and legacy.
Conclusion: Summarize the key similarities and differences, and discuss how both leaders contributed uniquely to the movement.
Provide equal and balanced coverage to each subject.
Use clear criteria for comparison, ensuring logical and coherent analysis.
Highlight both similarities and differences, ensuring a nuanced understanding of the subjects.
Maintain an informative tone, focusing on objective analysis rather than personal preference.
How to Write A Research Paper [Higher Efficiency & Better Results]
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before we get started with the research, it's important to gather relevant information related to it. This process, also known as the primary research method, helps researchers gain preliminary knowledge about the topic and identify research gaps. Whenever I begin researching a topic, I usually utilize Google and Google Scholar. Another excellent resource for conducting primary research is campus libraries, as they provide a wealth of great articles that can assist with your research.
Now, let's see how WPS Office and AIPal can be great research partners:
Let's say that I have some PDFs which I have gathered from different sources. With WPS Office, these PDFs can be directly uploaded not just to extract key points but also to interact with the PDF with special help from WPS AI.
Step 1: Let's open the PDF article or research paper that we have downloaded on WPS Office.
Step 2: Now, click on the WPS AI widget at the top right corner of the screen.
Step 3: This will open the WPS PDF AI pane on the right side of the screen. Click on "Upload".
Step 4: Once the upload is complete, WPS PDF AI will return with the key points from the PDF article, which can then be copied to a fresh new document on WPS Writer.
Step 5: To interact further with the document, click on the "Inquiry" tab to talk with WPS AI and get more information on the contents of the PDF.
Research is incomplete without a Google search, but what exactly should you search for? AIPal can help you with these answers. AIPal is a Chrome extension that can help researchers make their Google searches and interactions with Chrome more effective and efficient. If you haven't installed AIPal on Chrome yet, go ahead and download the extension; it's completely free to use:
Step 1: Let's search for a term on Google related to our research.
Step 2: An AIPal widget will appear right next to the Google search bar, click on it.
Step 3: Upon clicking it, an AIPal window will pop up. In this window, you will find a more refined answer for your searched term, along with links most relevant to your search, providing a more refined search experience.
WPS AI can also be used to extract more information with the help of WPS Writer.
Step 1: We might have some information saved in a Word document, either from lectures or during preliminary research. We can use WPS AI within Writer to gain more insights.
Step 2: Select the entire text you want to summarize or understand better.
Step 3: Once the text is selected, a hover menu will appear. Click on the "WPS AI" icon in this menu.
Step 4: From the list of options, click on "Explain" to understand the content more deeply, or click on "Summarize" to shorten the paragraph.
Step 5: The results will be displayed in a small WPS AI window.
Develop the Thesis statement
To develop a strong thesis statement, start by formulating a central question your paper will address. For example, if your topic is about the impact of social media on mental health, your thesis statement might be:
"Social media use has a detrimental effect on mental health by increasing anxiety, depression, and loneliness among teenagers."
This statement is concise, contentious, and sets the stage for your research. With WPS AI, you can use the "Improve" feature to refine your thesis statement, ensuring it is clear, coherent, and impactful.
Write the First draft
Begin your first draft by focusing on maintaining forward momentum and clearly organizing your thoughts. Follow your outline as a guide, but be flexible if new ideas emerge. Here's a brief outline to get you started:
Using WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature, you can quickly elaborate key ideas and points of your studies and articles into a descriptive format to include in your draft, saving time and ensuring clarity.
Compose Introduction, Body and Conclusion paragraphs
When writing a research paper, it’s essential to transform your key points into detailed, descriptive paragraphs. WPS AI can help you streamline this process by enhancing your key points, ensuring each section of your paper is well-developed and coherent. Here’s how you can use WPS AI to compose your introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs:
Let's return to the draft and start composing our introduction. The introduction should provide the background of the research paper and introduce readers to what the research paper will explore.
If your introduction feels too brief or lacks depth, use WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature to expand on key points, adding necessary details and enhancing the overall narrative.
Once the introduction is completed, the next step is to start writing the body paragraphs and the conclusion of our research paper. Remember, the body paragraphs will incorporate everything about your research: methodologies, challenges, results, and takeaways.
If this paragraph is too lengthy or repetitive, WPS AI’s "Make Shorter" feature can help you condense it without losing essential information.
Write the Second Draft
In the second draft, refine your arguments, ensure logical flow, and check for clarity. Focus on eliminating any unnecessary information, ensuring each paragraph supports your thesis statement, and improving transitions between ideas. Incorporate feedback from peers or advisors, and ensure all citations are accurate and properly formatted. The second draft should be more polished and coherent, presenting your research in a clear and compelling manner.
WPS AI’s "Improve Writing" feature can be particularly useful here to enhance the overall quality and readability of your paper.
WPS Spellcheck can assist you in correcting spelling and grammatical errors, ensuring your paper is polished and professional. This tool helps you avoid common mistakes and enhances the readability of your paper, making a significant difference in the overall quality.
Bonus Tips: How to Get Inspiration for your Research Paper- WPS AI
WPS Office is a phenomenal office suite that students find to be a major blessing. Not only is it a free office suite equipped with advanced features that make it competitive in the market, but it also includes a powerful AI that automates and enhances many tasks, including writing a research paper. In addition to improving readability with its AI Proofreader tool, WPS AI offers two features, "Insight" and "Inquiry", that can help you gather information and inspiration for your research paper:
Insight Feature:
The Insight feature provides deep insights and information on various topics and fields. It analyzes literature to extract key viewpoints, trends, and research directions. For instance, if you're writing a research paper on the impact of social media on mental health, you can use the Insight feature to gather a comprehensive overview of the latest studies, key arguments, and emerging trends in this field. This helps you build a solid foundation for your paper and ensure you are covering all relevant aspects.
Inquiry Feature:
The Inquiry feature allows you to ask specific questions related to your research topic. This helps you gather necessary background information and refine your research focus effectively. For example, if you need detailed information on how social media usage affects teenagers' self-esteem, you can use the Inquiry feature to ask targeted questions and receive relevant answers based on the latest research.
FAQs about writing a research paper
1. can any source be used for academic research.
No, it's essential to use credible and relevant sources. Here is why:
Developing a Strong Argument: Your research paper relies on evidence to substantiate its claims. Using unreliable sources can undermine your argument and harm the credibility of your paper.
Avoiding Inaccurate Information: The internet is abundant with data, but not all sources can be considered reliable. Credible sources guarantee accuracy.
2. How can I avoid plagiarism?
To avoid plagiarism, follow these steps:
Keep Records of Your Sources: Maintain a record of all the sources you use while researching. This helps you remember where you found specific ideas or phrases and ensures proper attribution.
Quote and Paraphrase Correctly: When writing a paper, use quotation marks for exact words from a source and cite them properly. When paraphrasing, restate the idea in your own words and include a citation to acknowledge the original source.
Utilize a Plagiarism Checker: Use a plagiarism detection tool before submitting your paper. This will help identify unintentional plagiarism, ensuring your paper is original and properly referenced.
3. How can I cite sources properly?
Adhere to the citation style guide (e.g., APA, MLA) specified by your instructor or journal. Properly citing all sources both within the text and in the bibliography or references section is essential for maintaining academic integrity and providing clear credit to the original authors. This practice also helps readers locate and verify the sources you've used in your research.
4. How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper depends on its topic and specific requirements. Generally, research papers vary between 4,000 to 6,000 words, with shorter papers around 2,000 words and longer ones exceeding 10,000 words. Adhering to the length requirements provided for academic assignments is essential. More intricate subjects or extensive research often require more thorough explanations, which can impact the overall length of the paper.
Write Your Research Paper with the Comfort of Using WPS Office
Writing a research paper involves managing numerous complicated tasks, such as ensuring the correct formatting, not missing any crucial information, and having all your data ready. The process of how to write a research paper is inherently challenging. However, if you are a student using WPS Office, the task becomes significantly simpler. WPS Office, especially with the introduction of WPS AI, provides all the resources you need to write the perfect research paper. Download WPS Office today and discover how it can transform your research paper writing experience for the better.
- 1. How to Write a Hook- Steps With Examples
- 2. How to Write a Conclusion - Steps with Examples
- 3. How to Write a Proposal [ Steps & Examples]
- 4. How to Write an Abstract - Steps with Examples
- 5. How to Use WPS AI/Chatgpt to Write Research Papers: Guide for Beginners
- 6. Free Graph Paper: Easy Steps to Make Printable Graph Paper PDF

15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 19 June 2024
Why do patients with cancer die?
- Adrienne Boire ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9029-1248 1 na1 ,
- Katy Burke 2 na1 ,
- Thomas R. Cox ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9294-1745 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Theresa Guise 5 na1 ,
- Mariam Jamal-Hanjani 6 , 7 , 8 na1 ,
- Tobias Janowitz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7820-3727 9 , 10 na1 ,
- Rosandra Kaplan 11 na1 ,
- Rebecca Lee ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2540-2009 12 , 13 na1 ,
- Charles Swanton ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4299-3018 7 , 8 , 14 na1 ,
- Matthew G. Vander Heiden ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6702-4192 15 , 16 na1 &
- Erik Sahai ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3932-5086 12 na1
Nature Reviews Cancer volume 24 , pages 578–589 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
17k Accesses
1 Citations
524 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Cancer models
- Cancer therapy
Cancer is a major cause of global mortality, both in affluent countries and increasingly in developing nations. Many patients with cancer experience reduced life expectancy and have metastatic disease at the time of death. However, the more precise causes of mortality and patient deterioration before death remain poorly understood. This scarcity of information, particularly the lack of mechanistic insights, presents a challenge for the development of novel treatment strategies to improve the quality of, and potentially extend, life for patients with late-stage cancer. In addition, earlier deployment of existing strategies to prolong quality of life is highly desirable. In this Roadmap, we review the proximal causes of mortality in patients with cancer and discuss current knowledge about the interconnections between mechanisms that contribute to mortality, before finally proposing new and improved avenues for data collection, research and the development of treatment strategies that may improve quality of life for patients.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others
The changing landscape of cancer in the USA — opportunities for advancing prevention and treatment
Causes of death among people living with metastatic cancer
Deceptive measures of progress in the NHS long-term plan for cancer: case-based vs. population-based measures
Introduction.
The phrase ‘metastasis accounts for 90% of cancer deaths’ is one of the most widely used in cancer research, yet it is overly simplistic, imprecise and it is difficult to find any primary analysis supporting the statement. Although patients with metastatic disease are overwhelmingly more likely to die than patients with non-metastatic cancer 1 , 2 , the determinants of cancer mortality are multifaceted and frequently involve dysfunction of multiple interconnected systems within the body. Understanding the mechanisms underpinning the causes of mortality, and subsequently intervening, has the potential to make cancer a less destructive disease, improving both the quality and length of life for patients with cancer. However, systematic analyses of the acute and root causes of mortality in patients with cancer are scarce, in part because death certificates rarely record enough information to understand the exact reason why the patient died beyond them having a malignancy. Causes of death may be simply listed as ‘metastatic carcinoma’ or ‘complications of cancer’, which give little insights into why a patient actually died. Potentially concomitant comorbidities are also not fully recorded. Even in cases in which the cause of death may be attributed to a single event, for example, a thromboembolism , the underlying cause of that specific event may be complex. Indeed, metastatic cancer leads to perturbed function of multiple organ systems, and importantly, not just the organs to which disease has spread. This is probably due to the exuberant activation of local and systemic inflammatory, tissue repair and immune-suppressive programmes.
A simple view would be that death from metastatic disease correlates with the burden of disease. However, evidence suggests that the situation is more complex, with many factors influencing how metastases impact vital functions and ultimately lead to death. First, metastases to different organs will lead to different impacts on overall health. For example, brain metastases can lead to dysfunction of the central nervous system 3 , whereas peritoneal metastases may cause obstruction of the bowel 4 . In addition, the size or extent of metastases may not necessarily correlate with dysfunction of the organ where it is located 5 . Second, the production of the molecular mediators of organ dysfunction can vary between metastases and cancers of different origins. Third, individual patient characteristics such as age, sex, overall health, pre-existing comorbidities, genetics and socio-economic status vary 6 . Together, these factors directly influence the course of and physiological response to metastatic disease and can have profound indirect effects by limiting available treatment options and/or the ability of patients to tolerate or complete all intended treatment 7 , 8 . To understand why patients with cancer die, a closer examination of the factors contributing to mortality in patients with cancer and a dissection of the intricate web of causes that shape the frequency and dynamics of death are required.
Death may be related to an acute event, but the underlying mechanisms which trigger it may be modifiable or even preventable. In addition, other deaths may be the end stage of a continuum of deterioration, allowing the possibility of targeted intervention to improve quality of life. Moreover, it has been noted that early palliative care improves survival 9 . Ultimately, increased understanding of the processes occurring in patients with advanced disease should lead to improved strategies to minimize ill-health and suffering at the end of life. Coupled to this, patients and those around them should be enabled to have essential discussions about their wishes and preferences, minimizing potentially inappropriate treatments and maximizing quality of life 10 . Therefore, in this Roadmap, we briefly review data considering the immediate causes of mortality, highlight the intricate interconnections between different aspects of patient deterioration and conclude with recommendations for future studies of late-stage cancer that may shed new light on this important aspect of cancer biology and medicine.
Acute events leading to mortality
Although some cancers can be considered a chronic condition, with many patients living with their disease for years, the immediate cause of mortality can often be an acute event. Here, we briefly summarize common acute events leading to death in patients with cancer (Fig. 1 ). Although it is not possible to precisely determine, it is likely that the acute causes discussed subsequently may account for up to half of cancer deaths 11 , 12 . Immediate causes of mortality in other patients are less clear, with a more gradual deterioration typically occurring in vital organ systems (Fig. 1 ).

This schematic shows organs that frequently become dysfunctional in patients with late-stage cancer.
Vascular coagulation and cardiac failure
Patients with cancer are at an elevated risk of thromboembolism, which may trigger respiratory failure, fatal strokes, heart failure or myocardial infarction 13 . In some cases, disseminated intravascular coagulation can lead to thrombotic obstruction of small and midsize vessels leading to organ failure 14 . Haemorrhagic complications from depletion of platelets, via either immune or non-immune mechanisms 15 , 16 , and reduced levels of coagulation proteins can also be life-threatening 14 . Congestive heart failure can also be a proximal cause of mortality, although the underlying causes are complex and include loss of cardiac muscle (associated with cachexia), shifts in intravascular fluid status and thromboembolic events 17 . Interestingly, bone metastases are particularly associated with cardiovascular problems, although the underlying mechanism remains unclear 18 . Comorbidities affecting the cardiovascular system may also make patients more prone to such events. Spatial occlusion of or invasion into vessels by cancer metastases can also lead to failure in blood supply or catastrophic haemorrhage 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 .
Displacement, functional impairment or obstruction of vital organs
The volume of disease may impair the function of a vital organ. This can be the case with brain metastases and glioblastoma or other primary brain cancers, with extensive invasion, brain herniation or oedema resulting in midline shift or increased intracranial pressure irreversibly compromising brain function 22 , 23 , 24 . In addition, patients may develop seizures, which, if uncontrolled, can result in death 25 , 26 . However, this does not apply to all brain metastases, with leptomeningeal metastases having minimal impact on intracranial pressure and brain structure; instead, these commonly obstruct cerebrospinal fluid flow and/or affect nerve function resulting in hydrocephalus , deterioration of neurological function and death 26 .
Large lung metastases may impair the essential function of gas exchange. However, patients with miliary-like disease — characterized by nodules too numerous to count — can live with extensive disease in an organ with surprisingly little impact on function until a hard-to-predict tipping point is reached, which is then followed by rapid deterioration 27 . As with brain metastases, the volume of disease is often not sufficient to account for organ failure, as even a relatively small volume (<100 ml lung metastases volume compared with 4–5 l total lung volume) can be fatal 28 . Lung oedema and pleural effusion are additional common contributors to death. Oedema may be caused by other pathologies such as infection or heart failure, whereas pleural effusion may be related to the presence of disease within the pleura as opposed to total tumour volume 28 , 29 .
Bowel obstruction can be a cause of mortality, especially in patients with peritoneal disease as found in particular in ovarian, colorectal and gastrointestinal cancers 30 . Both liver and kidney failure will also cause death in patients with cancer. Reasons for the failure of these organs include obstruction of the bile duct or ureters by metastases, therapy-induced toxicity leading to compromised normal organ function (discussed subsequently) and reduced tissue perfusion owing to hypotension or dehydration 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 . In addition, sepsis can result from obstruction of the bile ducts or ureters, which occurs unpredictably and often progresses rapidly leading to multiple organ failure and ultimately death.
Bacterial infections are the most common infection in patients with cancer, owing to impaired immune systems resulting from both the cancer itself and certain cancer treatments (discussed in detail subsequently), which induce myelosuppression and leukopenia. Patients with cancer can have an elevated risk of opportunistic viral, fungal and protozoal infections, which would typically be considered mild in healthy individuals, but which can cause serious life-threatening complications in those with cancer. Pneumonia and other lung infections leading to respiratory failure are often listed as causes of mortality in patients with cancer 35 , 36 . One of the most striking recent examples of this is the increased mortality observed in patients with cancer, particularly those with haematological cancers, who succumbed to COVID-19 compared with the general population 36 , 37 .
Paraneoplastic syndromes
Paraneoplastic syndromes are a group of rare disorders that can occasionally cause irreversible damage to critical organs and death. They are most associated with lung, breast, ovarian and lymphatic cancers, causing tissue or organ dysfunction at sites distinct from the location of the tumour 38 . Various mechanisms underpin paraneoplastic syndromes, including the inappropriate production of cytokines, hormones and antibodies. For example, excess parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHRP) production by tumours can lead to hypercalcaemia 39 , 40 . Inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone production is commonly associated with small-cell lung cancer resulting in hyponatraemia 41 . Furthermore, some neuroendocrine pancreatic tumours (insulinomas) secrete large amounts of insulin 42 . Tumours can also trigger the aberrant production of autoantibodies leading to disorders such as Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) or anti- N -methyl- d -aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis and myasthenia gravis 43 . Although treatment can usually manage the symptoms, in a subset of cases the syndromes cannot be controlled and are fatal 38 .
Therapy-induced toxicity
Although therapies are developed and administered with the intent of primarily targeting the tumour, almost all have some detrimental impact on normal tissue function. In some cases, the unintended consequences of therapy can be life-threatening. Autoimmune reactions resulting from targeting immune checkpoints can have fatal consequences, including myocarditis and encephalitis 44 , 45 , 46 . Chemotherapy can lead to death as a result of acute neutropenic sepsis 47 . Depletion of platelets because of therapy can lead to fatal bleeding 16 . Arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy and coronary vasospasm are also a cause of death related to some anticancer treatments such as 5-fluorouracil and capecitabine 48 , 49 , 50 . The long-term detrimental effects of some therapies are discussed in detail subsequently.
Underlying causes
Determination of the proximal cause of mortality prompts further questions around the underlying factors giving rise to lethal pathology and ultimately how metastatic cancer triggers or accelerates those factors. In this section, we consider how chronic disruption of three major physiological organ systems is perturbed in patients with cancer and how these might contribute to mortality.
The immune and haematopoietic systems
In patients with cancer, the immune system becomes progressively less able to mount effective responses to infectious challenge, a phenomenon often generically termed ‘immune exhaustion’ (this usage is distinct from the more specific usage of immune exhaustion as a failure of tumour-reactive T cells to function). As a result, patients with metastatic disease have increased susceptibility to a wide range of infections and typically suffer more severe consequences than would otherwise be observed in healthy individuals 51 . Multiple mechanisms contribute to the reduced capability of the immune system to respond to infection. The presence of cancer cells in diverse organs triggers similar cellular and molecular events to wound responses 52 . The production of cytokines including interleukin 6 (IL-6), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) and granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM–CSF), both by tumour cells and by other cells of the tumour microenvironment (TME), perturbs haematopoiesis leading to altered subsets of leukocytes 53 . Although, in the short term, this may have limited consequences on the ability of the body to respond to other challenges, prolonged disruption to haematopoiesis can strain the ability of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to generate sufficient cells of the right type to cope with infections, with increased myeloid-to-lymphoid cell ratios. Clonal haematopoiesis can be increased in patients with cancer, with myeloid skewing of immune cells and overall myeloid-mediated immune suppression and diminished naive T cell reservoirs 53 . Reduced production of platelets and altered iron metabolism leading to compromised oxygen carrying by red blood cells is also observed in many patients 54 . Other problems such as immunoparesis can arise, with a high frequency observed in patients with multiple myeloma 55 .
T cell responses to infection are impaired in the presence of cancer with decreased proliferation and expression of granzyme B typically observed 56 . The chronic stimulation of T cells with neoantigens arising from ongoing mutational processes may also contribute to their weakened functionality. Moreover, immune surveillance of tumours inevitably selects for the production of immune suppressive factors by cancer cells, which further compound the issue 57 . Once again, comorbidities leading to either immune suppression or autoimmunity can intersect with the detrimental effects of cancer on the immune system.
Other consequences of cancer can indirectly result in an increased likelihood of infection. For example, vessel obstruction from cancer results in decreased flow of fluids such as bile, urine and lymph, creating environments in which bacteria can thrive 58 . Blockage of the bronchial tree can lead to pneumonia 59 . The invasive phenotype of cancer can result in fistula formation (for example, rectovaginal in colorectal cancer), which enables bacteria to invade 60 . Furthermore, patients are often rendered bedbound or have limited mobility as cancer progresses, resulting in an increased chance of infections through decreased respiratory ventilation and atelectasis , as well as pressure sores and oedema 61 .
Disruption to haematopoiesis can also contribute to defects in coagulation and haemostasis . Elevated platelet numbers, termed thrombocytosis, are found in patients with cancer and are correlated with higher mortality 62 . The altered inflammatory cytokine milieu caused by the tumour may promote megakaryopoiesis, potentially through increasing thrombopoietin (TPO) production by the liver, and leading to higher platelet numbers. The risk of clotting can be further increased by the production of tissue factor , which is responsible for initiating the clotting cascade, by tumour cells 63 . These mechanisms increase the likelihood of fatal thromboembolisms 63 .
Iatrogenic effects also have a role in the reduced immune function in patients with cancer. Cytotoxic therapies interfere with the proliferation and division of haematopoietic stem cells and can leave the immune system unable to mount effective responses to pathogens, leading to mortality 64 . In severe cases, pancytopenia results, marked by a substantial decrease in all three major blood cell lineages (red cells, white cells and platelets) 65 . This can lead to severe anaemia, increased infection susceptibility and increased likelihood of bleeding 47 , 66 , 67 . In other cases, more limited subsets of haematopoietic cells are affected. Thrombocytopenia — low platelet levels — leads to hypocoagulation and elevates the likelihood of haemorrhage 66 . Therefore, during cancer development and treatment, haemostasis mechanisms may be either augmented or attenuated; in both cases, the result is less predictable and less well-controlled coagulation. Neutropenia — low neutrophil levels — renders patients less able to fight infection and contributes to cancer mortality from infections that in many cases are thought to arise from resident mucosal flora 68 . Treatments, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy, often result in the breakdown of mucosal barriers (for example, oral mucositis) resulting in higher numbers of infections from pathogens, which normally reside on these surfaces 69 . In addition, corticosteroids, which are often given to alleviate symptoms or manage toxicity, can also contribute to the suppression of immune responses and compound the risk of infections in patients 70 . Clonal haematopoiesis, which as mentioned earlier is already more frequent in patients with cancer, can be further increased by chemotherapy 71 . More generally, cancer therapies can increase ageing-associated processes and reduce organ function 72 . Opioid pain relief administered to those with late-stage disease can also suppress the function of various bodily systems 73 . Finally, infections can arise owing to the insertion of drains and stents, or central venous catheters (CVCs; also known as lines) for the delivery of therapies. Infections from such lines are estimated to be around 0.5–10 per 1,000 CVC-days 74 , 75 .
Immunotherapies present a different set of immune complications from conventional therapies. These primarily relate to over-activation of the immune system leading to autoimmunity and, in some cases, cytokine storms that are treated with anti-cytokine therapies such as tocilizumab, anakinra and ruxilitinib, all of which can further suppress the immune response 76 . However, deaths attributable to autoimmune side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors are rare (<1% in an analysis of more than 8,000 patients) especially if toxicity is managed promptly 77 , 78 . Colitis is a frequent problem, with disruption to colonic barrier function leading to increased susceptibility to perforation, which can be life-threatening. Guillain–Barré syndrome , hepatitis and myocarditis are also causes of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related deaths 79 , 80 , 81 . Once again, high-dose corticosteroids are the main first-line treatment to manage autoimmune side effects in patients receiving immunotherapy and can lead to suppression of the immune system. Hyperprogressive disease is observed in some patients following immunotherapy, the reasons for which are still being delineated, but there is probably a role for innate lymphoid cells releasing pro-growth cytokines 82 . Cell-based immunotherapies can also lead to disrupted bone marrow function and subsequent myelosuppression 83 .
The nervous system
The brain serves as a central nexus, orchestrating all vital functions. It is the hub of thought processes, emotions and sensory perception and regulates, directly or indirectly, everything from heartbeat and breathing to appetite. In addition to physical disruption of brain structure and intracranial pressure (discussed earlier) 84 , brain metastases impact the nervous system in multiple ways. Tumours in the brain or its surrounding tissues can substantially impair neural connections, leading to cognitive deficits, motor and sensory dysfunction, and even personality changes 84 , 85 , 86 . Interactions between brain metastases and neurons lead to changes in cortical function 87 , 88 , 89 . Even in regions of the brain without overt metastases, neuro-excitability can be increased, leading to changes in cognition, alertness and mood 90 . Tumours can slow the posterior dominant rhythm, leading to reduced alertness, loss of working memory and deterioration of quality of life 91 . Circadian rhythms are also impacted, leading to problems in memory and sleep, which is vital for the repair processes of the body that are essential for overall health and functioning 92 . Ultimately, many of these changes are not sustainable long-term. How these changes may lead to death is unclear, but they may follow similar trajectories to those in patients with dementia.
Brain function can also be disrupted in patients without brain metastases, with autonomic nervous system dysfunction often reported 93 . Intriguingly, anhedonia — a lack of ability to experience pleasure — occurs in many patients 94 . The mechanistic causes of this are unclear, but it is not restricted to patients with brain metastasis suggesting that circulating systemic factors may play a role. The wider effects of metastatic cancer on the mental well-being of a patient are discussed in Box 1 . However, beyond an effect on well-being, the disruption of brain function can contribute to anorexia, and reduced nutrition can influence many other physiological and pathophysiological processes 95 , 96 .
The role of the peripheral nervous system in cancer-related death is not well described. Although the burgeoning field of cancer neuroscience provides evidence that the efferent system can support local and metastatic tumour growth 97 , 98 , 99 , at this time, it is unclear whether the reverse is also true. As mentioned earlier, there is clear evidence of autonomic nervous system dysfunction in patients with cancer 93 , raising the possibility that cancer-mediated interruption of afferent impulses might impact overall survival. Further studies are needed to explore this possibility.
Box 1 Psychosocial and societal factors contributing to the deterioration of patients with late-stage cancer
Psychological and social factors can have major and wide-ranging impacts on patients with incurable cancer. This manifests in more than threefold higher suicide rates 145 , 146 , 147 . Of note, these rates were further exacerbated in less advantaged sociodemographic groups 148 , arguing that financial issues and possibly health-care access are linked to suicide in patients with cancer. However, psychological symptoms are far more extensive than those captured in studies of suicide. Anhedonia and depression are frequent in patients with cancer, impacting their overall well-being, treatment adherence and outcomes including mortality 149 . These psychological challenges often intertwine with physical symptoms, compounding the burden of each 150 . Several studies have linked stress-related psychosocial factors to cancer mortality 151 , with recent work beginning to uncover the cellular and molecular mechanisms at play 152 .
Research on the psychosocial aspects of cancer care, including emotional and cognitive well-being, remains under-emphasized. Barriers to the integration of psychosocial care into cancer care include stigma, difficulty identifying substantial distress, limited access to evidence-based psychosocial treatments and concerns about cost 153 . Yet, an integrated system of psychosocial care including population-based screening and targeted treatment and access to good-quality palliative care improves emotional wellbeing 154 and physical symptoms 155 and is likely to be cost-saving 156 . A deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying neuropsychological systems and insights into how metastatic disease impacts the physiological and chemical axes of the brain will be crucial. Such insights could inform tailored interventions, therapies and support structures that address the emotional toll of cancer, enhancing the holistic care approach and improving quality of life. Expanding psychosocial research can help bridge gaps in addressing mental health in patients with cancer, ultimately improving quality of life of patients during and after treatment 146 , 147 .
Metabolism and cachexia — catabolic effects of cancer
The presence of metastases presents altered energetic and anabolic demands on the body, leading to detrimental imbalances in metabolism 100 . Progressive and involuntary loss of body weight — termed cachexia — is a widespread multiorgan phenomenon commonly seen in patients with metastatic cancer 100 , 101 . This complex syndrome is characterized by a net negative energy balance, driven by the combination of increased energy expenditure and catabolism, with reduced appetite and caloric intake. A persistent decrease in nutrient intake is a key component across patients with many different cancer types, leading to breakdown of host tissues, with the degree of loss of adipose tissue and muscle mass varying between patients and among different cancer types 102 . However, the contribution of increased energy expenditure (as a result of tumour burden) is less clear. Sarcopenia may be particularly prominent in some patients, possibly representing an independent pathology from other more global tissue wasting phenotypes, and in extreme cases, loss of cardiac or intercostal muscle mass can be fatal owing to insufficient cardiac or respiratory function, respectively 103 , 104 . These events have also been observed in the context of extreme starvation in patients with non-cancer conditions; for example, anorexia nervosa, in which cardiac dysfunction, in particular bradycardia and sinus pauses, can cause pulseless electrical activity and death 105 , 106 . Electrolyte disturbances and hypoglycaemia that are often observed in cases of severe malnutrition may exacerbate the risk of such arrhythmias 105 . Cachexia also has effects on other organs and tissues, including the brain and immune system 107 . Compromised immune function is a major consequence of starvation-induced tissue wasting 108 and suggests that altered systemic metabolism leading to, or associated with cachexia, may be a contributor to the immune dysfunction present in some patients with cancer 108 . Conversely, several studies have shown that both the brain and immune system can contribute to cachexia 100 , 101 .
Cachexia is multifactorial and has many potential causes. In some limited cases, tumour metabolism leads to systemic changes that increase energy usage. For example, high levels of lactate secretion by tumours can trigger the liver to convert lactate back to glucose, which requires energy input — termed the Cori cycle 109 . Such cycles can increase metabolic demand on the liver leading to further perturbation of liver function. However, cachexia does not correlate with disease volume in many cancer types 110 . Therefore, it is hard to reconcile a model in which the energetic and anabolic demands of the volume of disease are the main trigger for cachexia. Numerous studies have begun to reveal the possible molecular underpinnings of cachexia in some cancer types. Disruption of signalling by transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) and related ligands is a recurring theme 111 , 112 , 113 . For example, circulating growth/differentiation factor 15 (GDF15; also known as MIC1), a highly conserved member of the TGFβ superfamily, is a known mediator of anorexia and weight loss, and increased circulating levels of this molecule in patients with lung cancer have been shown to correlate with cachexia development 114 . Clinical trials are currently underway to determine whether blockade of GDF15 ameliorates cachexia 115 . TGFβ itself can also promote muscle loss via the induction of myostatin 116 , and the induction of signalling by activin — another TGFβ superfamily ligand — can also have similar effects on muscle mass 117 , 118 . Furthermore, modulation of ryanodine receptor 1 (RYR1) downstream of TGFβ can perturb sarcomere organization and thereby lead to muscle weakness 111 . As such, preclinical studies have demonstrated the potential utility of TGFβ blockade in preventing cachexia 112 .
Elevated levels of cytokines, including tumour necrosis factor (TNF), IL-1 and IL-6, can also have roles in cachexia 119 , 120 , 121 . TNF induces multiple aspects of cachexia 122 . Muscle wasting is promoted through increased TNF and downstream nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of muscle protein 123 , 124 . IL-6 triggers muscle loss through both NF-κB-dependent and JAK/STAT-dependent mechanisms 120 . Lipid metabolism is impacted by TNF reducing the expression of lipoprotein lipase and free fatty acid transporters, thereby reducing the accumulation of fat 125 . TNF can also reduce appetite through the production of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). IL-1, which triggers similar proximal changes in cell signalling to TNF, can activate many of the same processes 125 . It is also interesting to note that TGFβ, IL-1 and IL-6 are associated with programmes in cancer cells that drive metastasis, which could potentially explain why metastatic disease is linked to cachexia more strongly than the presence of primary disease alone.
Whole body dysfunction
Although consideration of different organ systems is useful for highlighting some of the key events contributing to cancer mortality, the interconnected nature of body systems and the pleiotropic characteristics of the molecular mediators at play mean that it is essential to consider whole body dysfunction when thinking about causes of cancer mortality. Furthermore, such analyses may explain cancer deaths without an acute proximal cause. As discussed earlier, cytokines with potent effects on the immune system, as well as effects on appetite, can be contributors to cachexia. Therefore, it is unsurprising that tumours impact both immune and metabolic function. The immune and nervous systems are highly sensitive to metabolite availability; for example, the brain has a high demand for glucose 108 , 126 . Several factors, including lactic acid production and kidney dysfunction, can lead to life-threatening systemic acidosis in patients with cancer, particularly haematological malignancies with high cell turnover 127 . These can be further exacerbated upon initiation of cytotoxic therapy resulting in tumour lysis syndrome which can be fatal 128 . Consequently, metabolic perturbations and cachexia impact these systems. Over time, the cumulative stress of metabolic alterations caused by metastases, chronic changes in the level of cytokines, constant generation of tumour (neo)-antigens, aggressive therapies and incidental infections lead to exhaustion of the adaptive immune system and hamper the regenerative capacity of many organ systems with debilitating effects 18 . This multifaceted burden can ultimately trigger a body-wide shutdown leading to death.
Are mortality causes cancer-specific?
Although a subset of mortality causes are cancer-specific, such as metastatic invasion compromising specific organ function, the progressive and interconnected deterioration of multiple organ systems probably underlies many cancer-related deaths. This may be further influenced by interaction with other comorbidities. Of note, similar progressive deterioration is sometimes observed in the context of chronic infection and inflammation, with both cachexia and immune exhaustion associated with diseases such as tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection 129 , 130 , 131 . This raises the question of whether the causes of death in patients with cancer are specific to cancer, or whether cancer (or any other chronic disease) is simply an accelerant of ageing processes occurring in healthy individuals. This hypothesis has practical implications because, if proven, it would suggest that lessons and approaches from other disease contexts could be readily transferable to patients with metastatic cancer. For example, the targeting or modulation of senescent cells is an active area of anti-ageing research, and numerous preclinical studies have indicated that similar strategies can attenuate the systemic effects of cancer 132 , 133 , 134 .
Recommendations
One goal of this Roadmap is to propose ways to improve our understanding of why patients with cancer die and thereby develop better strategies to ameliorate symptoms and prolong life with good quality. To this end, we propose that the following steps would be useful (Fig. 2 ).

This scheme shows how recommendations can interlink to provide both an improved understanding of the underlying biology behind late-stage cancer and strategies to improve quality of life of patients.
Improved records and reporting
It is notable that systematic reviews of the precise causes of cancer mortality are infrequent. This gap in knowledge, and recognition that this is often simply not known, is a major hindrance to learning and progress. Although improved accuracy of reporting on death certificates would be desirable, it would require a shift in longstanding clinical habits and may not be easily achievable in health-care systems under strain. Nonetheless, we advocate for locally enacting more consistency in death certificates, with specific acute causes included in addition to the underlying cause of cancer where known. Palliative care primarily focuses on symptom control for patients while balancing the potential benefits and burdens of additional diagnoses. Nevertheless, to address the gaps in our knowledge, it would be desirable to fund and establish prospective studies that continue active monitoring of patients as they transition from active disease treatment to palliative care. If possible, monitoring should be non-invasive as to not compromise patient comfort at the end of life. The great advances being made in patient monitoring with wearable technologies might facilitate this and could be used for earlier detection of infections enabling quicker intervention. Caregiver involvement in reporting of symptoms may also play a role. Furthermore, consent to obtain more detailed information from the community and palliative care teams on the contributing factors to death would provide further insight. Patient and public engagement in this type of research will be critical, with studies indicating patient desire to participate in the right context 135 , 136 . In addition to information gathered before death, research autopsies have the potential to shed further light on the aetiology of death, such as thromboembolic events that may not have been detected in the absence of symptoms or diagnostic testing — discussed in Box 2 . Moreover, the availability of post-mortem samples can aid research into the biological underpinnings of metastases and processes leading to death. The greatest amount of information would be gained from cohorts additionally enrolled into warm autopsy programmes (Box 2 ).
Box 2 Research Autopsy Programmes and their optimization
Research autopsies are initiatives that involve the prompt collection of tissues from deceased individuals shortly after death, whereas tissue morphology is intact, and cells and tissues have not undergone substantial post-mortem changes. Research autopsy studies can be labour-intensive, and care is required in their logistical planning. The post-mortem interval (PMI) to autopsy can vary depending on the infrastructure available and can have implications for the utility of samples collected after death. For example, shorter PMIs achieved in rapid warm autopsy studies can more effectively facilitate in vitro (for example, cell line) and in vivo (for example, organoid and xenograft) models and can derive better quality RNA 157 , 158 . However, such studies are not easily established in the absence of out-of-hours facilities and expert input. Autopsies performed with longer PMIs, for example, up to several days after death, have been shown to have maintained tissue morphology and adequate DNA and RNA to facilitate cellular imaging techniques and genomic sequencing approaches 159 , 160 . Therefore, there is merit and general scientific value with autopsies regardless of the PMI, provided that consideration is given to the question being addressed, and the experimental approach.
The most powerful data are obtained from patients already involved in clinical studies before death. Information about disease course, longitudinal scans and tissue and blood analysis (cell counts, electrolytes, cytokines, metabolites and possibly circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA)) greatly enhances what can be learnt from post-mortem tissues. However, sensitivity is required to align the desire to acquire data with the wishes of the patients and their families, such that ultimately each autopsy has the potential to be meaningful and shed light on the biological processes leading to death.
More detailed observational clinical studies
Disease burden is not well correlated with survival; however, we propose that the accurate identification of prognostic factors correlating with survival should provide important insights into what ultimately precipitates mortality. As the cost of both targeted and non-targeted analyses of proteins and metabolites decreases, it should also become more feasible to explore molecular predictors of survival. Once identified, such factors could then be monitored in a targeted way prospectively with the potential to intervene where possible. In this setting, both the tumour and patient trajectory would receive precision-tailored treatments, the impact of which would need to be studied in randomized controlled trials. Even in the context of early phase trials, additional data could be obtained about patient symptoms in addition to safety considerations and tumour burden. Clinical imaging could also be exploited. Many patients receive computed tomography (CT) and positron-emission tomography (PET) scans, which contain abundant information about the burden and location of metastases and offer the opportunity to study changes in extent of adipose and muscle tissue and therefore body composition in relation to cachexia. Machine learning and artificial intelligence can be capitalized on to accurately measure these parameters, meaning that what would have previously been prohibitive owing to hours of radiologist time being required is now feasible 137 , 138 . In addition to the analysis of scans, the application of machine-learning approaches to metabolite, cytokine, immune cell and wearable technology-derived multimodal and multidimensional data may also uncover previously unknown parameters that correlate with mortality 139 . As outlined in Box 1 , incorporating psychosocial metrics into the study of late-stage cancer could also enable improvements in mental well-being of patients.
Increasing the relevance of model systems
Preclinical models will also have a place in determining the linkage between events found to precede death and cause of death; however, there should be an emphasis on reverse translation of questions from human studies to preclinical models. By way of example, this could involve modelling how metastases impinge on the ability of the body to respond to infection by challenging metastatic mouse models with a pathogen. Animal ethics and husbandry considerations mean that mice are housed in controlled environments in which exposure to pathogens is rare and the types of pathogen exposure are very narrow, so this type of information is currently lacking. To be optimally informative, practical and ethical complications around studying end-of-life physiology seen in patients need to be considered. Most models are chosen for their rapid progression, often with less than a month between primary or metastatic tumour seeding and death. These are not optimal for studying longer timescale chronic changes in patients. The development of slower progressing models, implementation of multiple lines of treatment and mimicking presence of other comorbidities should enable models to more accurately recapitulate observations made in patients. Furthermore, most preclinical cancer research currently uses young mice that fail to accurately mirror the interplay between ageing and cancer seen in humans 140 , with differences between chronological and immunological age providing a further confounding factor 141 . Researchers need to recognize the importance of and adopt more age-appropriate mouse models to better understand cancer mortality. In addition, most studies focus solely on tumour burden (which may only be possible at the point of death rather than longitudinally) or tumour size as a marker of disease, owing to the technical challenges of accurately quantifying organ impairment. Furthermore, tumour volume response and progression are poor surrogates of mortality in patients 142 ; therefore, better modelling of other metrics of tumour activity and impact on the body system may lead to better drug development. Minimizing and alleviating suffering in experimental animals is critical; hence ethical considerations limit the ability to study mortality in mice. Therefore, an expanded repertoire of analysis would help to understand how metastases impact specific systems and events, including the haematopoietic and nervous systems, as well as whole-body physiology and metabolism. Analysis of small volumes of blood can provide data on metabolites and cytokines, as well as complete blood counts (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets), whereas increasingly sophisticated and automated technology is available to monitor mouse behaviour 143 . It is worth noting that weight loss is frequently used as a humane end point, which indicates that many cancer models trigger cachexia and that with appropriate measurements there is an opportunity to learn more about this phenomenon in existing models. We advocate more detailed reporting of why mice were culled in experimental studies — for example, tumour volume, weight loss, laboured breathing, complete blood cell counts and blood chemistry.
Clinical trials
The types of analyses detailed earlier will provide correlation between different factors and mortality, but not causative linkage. Ultimately, this information depends on testing in the context of clinical trials. Many of the mediators of immune dysfunction and cachexia can now be targeted with function blocking antibodies or forms of receptor traps and are being actively explored in clinical trials 115 , 144 . Several of these interventions were originally developed for chronic inflammatory conditions, which further highlights links between cancer and inflammation. The use of appropriately chosen secondary end points would provide an opportunity for testing whether correlative associations have a causal basis. In addition, many cancer drug trials stop providing an intervention at the point where a cancer progresses. The mechanisms behind cancer cachexia suggest that trials should be adapted to additionally consider clinical benefit in terms of weight, muscle loss and other specific determinants of efficacy, rather than solely monitor cancer progression.
Concluding remarks
Although efforts at cancer prevention and the development of curative treatment rightly receive considerable attention, we argue that understanding the precise events leading to cancer mortality should not be overlooked by funding bodies. Understanding the causes of dysfunction across multiple organ systems may provide novel strategies to manage symptoms of advanced cancer. Furthermore, better knowledge of the processes leading to death could enable patients and those around them to have essential discussions about their wishes and preferences, minimizing potentially inappropriate treatments and maximizing quality and enjoyment of life. In addition, more precise biomarkers of the likely timing of death may enable patients and their families to better utilize the time that is left. In the longer term, strategies to prevent organ dysfunction should offer considerable benefits to both patients with high tumour burden and those who have low disease burden but die from factors produced by cancer.
Dillekås, H., Rogers, M. S. & Straume, O. Are 90% of deaths from cancer caused by metastases? Cancer Med. 8 , 5574–5576 (2019).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Seyfried, T. N. & Huysentruyt, L. C. On the origin of cancer metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 18 , 43–73 (2013).
Schnurman, Z. et al. Causes of death in patients with brain metastases. Neurosurgery 93 , 986–993 (2023).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gallardo-Valverde, J. M. et al. Obstruction in patients with colorectal cancer increases morbidity and mortality in association with altered nutritional status. Nutr. Cancer 53 , 169–176 (2005).
Swanton, C. et al. Embracing cancer complexity: hallmarks of systemic disease. Cell 187 , 1589–1616 (2024).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wheatley-Price, P., Blackhall, F. & Thatcher, N. The influence of sex in non-small cell lung cancer. Onkologie 32 , 547–548 (2009).
Abu-Sbeih, H. et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with preexisting inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 38 , 576 (2020).
Neugut, A. I. et al. Duration of adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer and survival among the elderly. J. Clin. Oncol. 24 , 2368–2375 (2006).
Sullivan, D. R. et al. Association of early palliative care use with survival and place of death among patients with advanced lung cancer receiving care in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Oncol. 5 , 1702–1709 (2019).
Sallnow, L. et al. Report of the Lancet Commission on the value of death: bringing death back into life. Lancet 399 , 837–884 (2022).
Abdel-Karim, I. A., Sammel, R. B. & Prange, M. A. Causes of death at autopsy in an inpatient hospice program. J. Palliat. Med. 10 , 894–898 (2007).
Pautex, S. et al. Anatomopathological causes of death in patients with advanced cancer: association with the use of anticoagulation and antibiotics at the end of life. J. Palliat. Med. 16 , 669–674 (2013).
Khorana, A. A., Francis, C. W., Culakova, E., Kuderer, N. M. & Lyman, G. H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5 , 632–634 (2007).
Levi, M. & Scully, M. How I treat disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood 131 , 845–854 (2018).
Cines, D. B., Liebman, H. & Stasi, R. Pathobiology of secondary immune thrombocytopenia. Semin. Hematol. 46 , S2 (2009).
Ghanavat, M. et al. Thrombocytopenia in solid tumors: prognostic significance. Oncol. Rev. 13 , 43–48 (2019).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Anker, M. S. et al. Advanced cancer is also a heart failure syndrome: a hypothesis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 12 , 533 (2021).
Asdahl, P. H. et al. Cardiovascular events in cancer patients with bone metastases — a Danish population-based cohort study of 23,113 patients. Cancer Med. 10 , 4885–4895 (2021).
Sinn, D. H. et al. Different survival of Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage C hepatocellular carcinoma patients by the extent of portal vein invasion and the type of extrahepatic spread. PLoS ONE 10 , e0124434 (2015).
Zisman, A. et al. Renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus extension: biology, role of nephrectomy and response to immunotherapy. J. Urol. 169 , 909–916 (2003).
Suárez, C. et al. Carotid blowout syndrome: modern trends in management. Cancer Manag. Res. 10 , 5617 (2018).
Lin, A. L. & Avila, E. K. Neurologic emergencies in the cancer patient: diagnosis and management. J. Intensive Care Med. 32 , 99 (2017).
Gamburg, E. S. et al. The prognostic significance of midline shift at presentation on survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 48 , 1359–1362 (2000).
Mokri, B. The Monro-Kellie hypothesis: applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology 56 , 1746–1748 (2001).
Mastall, M. et al. Survival of brain tumour patients with epilepsy. Brain 144 , 3322–3327 (2021).
Steindl, A. et al. Neurological symptom burden impacts survival prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Cancer 126 , 4341–4352 (2020).
Girard, N. et al. Comprehensive histologic assessment helps to differentiate multiple lung primary nonsmall cell carcinomas from metastases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 33 , 1752–1764 (2009).
Lee, P. et al. Metabolic tumor burden predicts for disease progression and death in lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 69 , 328–333 (2007).
Kookoolis, A. S., Puchalski, J. T., Murphy, T. E., Araujo, K. L. & Pisani, M. A. Mortality of hospitalized patients with pleural effusions. J. Pulm. Respir. Med. 4 , 184 (2014).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cousins, S. E., Tempest, E. & Feuer, D. J. Surgery for the resolution of symptoms in malignant bowel obstruction in advanced gynaecological and gastrointestinal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev . https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002764 (2016).
Baker, M. L. et al. Mortality after acute kidney injury and acute interstitial nephritis in patients prescribed immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 10 , e004421 (2022).
Bhave, P., Buckle, A., Sandhu, S. & Sood, S. Mortality due to immunotherapy related hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 69 , 976–978 (2018).
Lameire, N. H., Flombaum, C. D., Moreau, D. & Ronco, C. Acute renal failure in cancer patients. Ann. Med. 37 , 13–25 (2005).
Ries, F. & Klastersky, J. Nephrotoxicity induced by cancer chemotherapy with special emphasis on cisplatin toxicity. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 8 , 368–379 (1986).
Wong, J. L. & Evans, S. E. Bacterial pneumonia in patients with cancer: novel risk factors and management. Clin. Chest Med. 38 , 263–277 (2017).
Lee, L. Y. W. et al. COVID-19 mortality in patients with cancer on chemotherapy or other anticancer treatments: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 395 , 1919–1926 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Williamson, E. J. et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 584 , 430–436 (2020). This study used a platform of 17.4 million pseudo-anonymized health-care records to determine risk factors for COVID-19.
Pelosof, L. C. & Gerber, D. E. Paraneoplastic syndromes: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 85 , 838–854 (2010).
Donovan, P. J. et al. PTHrP-mediated hypercalcemia: causes and survival in 138 patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100 , 2024–2029 (2015).
Burtis, W. J. et al. Immunochemical characterization of circulating parathyroid hormone-related protein in patients with humoral hypercalcemia of cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 322 , 1106–1112 (1990). First study to show that patients with cancer-associated hypercalcaemia had elevated concentrations of plasma parathyroid hormone-related protein .
Ellison, D. H. & Berl, T. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. N. Engl. J. Med. 356 , 2064–2072 (2007).
Okabayashi, T. et al. Diagnosis and management of insulinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 19 , 829–837 (2013).
Giometto, B. et al. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome in the PNS Euronetwork database: a European study from 20 centers. Arch. Neurol. 67 , 330–335 (2010).
Wang, D. Y. et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 4 , 1721 (2018).
Feng, S. et al. Pembrolizumab-induced encephalopathy: a review of neurological toxicities with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 , 1626–1635 (2017).
Coustal, C. et al. Prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced myocarditis: a case series. J. Immunother. Cancer 11 , e004792 (2023).
Kuderer, N. M., Dale, D. C., Crawford, J., Cosler, L. E. & Lyman, G. H. Mortality, morbidity, and cost associated with febrile neutropenia in adult cancer patients. Cancer 106 , 2258–2266 (2006).
Agarwal, M. A. et al. Ventricular arrhythmia in cancer patients: mechanisms, treatment strategies and future avenues. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev . 12 , e16 (2023).
Zafar, A. et al. The incidence, risk factors, and outcomes with 5-fluorouracil-associated coronary vasospasm. JACC CardioOncol. 3 , 101–109 (2021).
Polk, A. et al. Incidence and risk factors for capecitabine-induced symptomatic cardiotoxicity: a retrospective study of 452 consecutive patients with metastatic breast cancer. BMJ Open 6 , e012798 (2016).
Safdar, A., Bodey, G. & Armstrong, D. Infections in patients with cancer: overview. Princip. Pract. Cancer Infect. Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-644-3_1 (2011).
Foster, D. S., Jones, R. E., Ransom, R. C., Longaker, M. T. & Norton, J. A. The evolving relationship of wound healing and tumor stroma. JCI Insight 3 , e99911 (2018).
Park, S. J. & Bejar, R. Clonal hematopoiesis in cancer. Exp. Hematol. 83 , 105 (2020).
Liebman, H. A. Thrombocytopenia in cancer patients. Thromb. Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(14)50011-4 (2014).
Chakraborty, R. et al. Characterisation and prognostic impact of immunoparesis in relapsed multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 189 , 1074–1082 (2020).
Allen, B. M. et al. Systemic dysfunction and plasticity of the immune macroenvironment in cancer models. Nat. Med. 26 , 1125–1134 (2020).
Munn, D. H. & Bronte, V. Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 39 , 1–6 (2016).
Kochar, R. & Banerjee, S. Infections of the biliary tract. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 23 , 199–218 (2013).
Valvani, A., Martin, A., Devarajan, A. & Chandy, D. Postobstructive pneumonia in lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 7 , 357–357 (2019).
Rolston, K. V. I. Infections in cancer patients with solid tumors: a review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 6 , 69–83 (2017).
Wu, X. et al. The association between major complications of immobility during hospitalization and quality of life among bedridden patients: a 3 month prospective multi-center study. PLoS One 13 , e0205729 (2018).
The clinicopathological and prognostic role of thrombocytosis in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis. Oncol. Lett . 13 , 5002–5008 (2017).
Kasthuri, R. S., Taubman, M. B. & Mackman, N. Role of tissue factor in cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 27 , 4834 (2009).
Wade, J. C. Viral infections in patients with hematological malignancies. Hematology 2006 , 368–374 (2006).
Article Google Scholar
Ersvaer, E., Liseth, K., Skavland, J., Gjertsen, B. T. & Bruserud, Ø. Intensive chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia differentially affects circulating TC1, TH1, TH17 and TREG cells. BMC Immunol. 11 , 1–12 (2010).
Kuter, D. J. Treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with non-hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 107 , 1243 (2022).
Rodgers, G. M. et al. Cancer- and chemotherapy-induced anemia. J. Natl Compr. Canc. Netw. 10 , 628–653 (2012).
Nesher, L. & Rolston, K. V. I. The current spectrum of infection in cancer patients with chemotherapy related neutropenia. Infection 42 , 5–13 (2014).
Blijlevens, N. M. A., Logan, R. M. & Netea, M. G. Mucositis: from febrile neutropenia to febrile mucositis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 63 , i36–i40 (2009).
Petrelli, F. et al. Association of steroid use with survival in solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 141 , 105–114 (2020).
Bolton, K. L. et al. Cancer therapy shapes the fitness landscape of clonal hematopoiesis. Nat. Genet. 52 , 1219–1226 (2020). This study identified the molecular characteristics of clonal haematopoiesis that increased risk of therapy-related myeloid neoplasms, with different characteristics associated with different treatment exposures.
Bhatia, R. et al. Do cancer and cancer treatments accelerate aging? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 24 , 1401 (2022).
Eisenstein, T. K. The role of opioid receptors in immune system function. Front. Immunol. 10 , 485158 (2019).
Böll, B. et al. Central venous catheter-related infections in hematology and oncology: 2020 updated guidelines on diagnosis, management, and prevention by the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO). Ann. Hematol. 100 , 239 (2021).
Ruiz-Giardin, J. M. et al. Blood stream infections associated with central and peripheral venous catheters. BMC Infect. Dis. 19 , 1–9 (2019).
Lee, D. W. et al. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome. Blood 124 , 188–195 (2014).
Brahmer, J. R. et al. Safety profile of pembrolizumab monotherapy based on an aggregate safety evaluation of 8937 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 199 , 113530 (2024). Analysis of the toxicity profile of anti-PD1 therapy in more than 8,000 patients.
Larkin, J. et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 , 1535–1546 (2019).
Vozy, A. et al. Increased reporting of fatal hepatitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 123 , 112–115 (2019).
Palaskas, N., Lopez-Mattei, J., Durand, J. B., Iliescu, C. & Deswal, A. Immune checkpoint inhibitor myocarditis: pathophysiological characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 9 , e013757 (2020).
Janssen, J. B. E. et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related Guillain–Barré syndrome: a case series and review of the literature. J. Immunother. 44 , 276–282 (2021).
Camelliti, S. et al. Mechanisms of hyperprogressive disease after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: what we (don’t) know. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39 , 236 (2020).
Kitamura, W. et al. Bone marrow microenvironment disruption and sustained inflammation with prolonged haematologic toxicity after CAR T-cell therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 202 , 294–307 (2023).
Seano, G. et al. Solid stress in brain tumours causes neuronal loss and neurological dysfunction and can be reversed by lithium. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3 , 230 (2019).
Madhusoodanan, S., Ting, M. B., Farah, T. & Ugur, U. Psychiatric aspects of brain tumors: a review. World J. Psychiatry 5 , 273 (2015).
Gerstenecker, A. et al. Cognition in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastasis: profiles and implications. J. Neurooncol. 120 , 179 (2014).
Krishna, S. et al. Glioblastoma remodelling of human neural circuits decreases survival. Nature 617 , 599–607 (2023). This study demonstrated that high-grade gliomas remodel neural circuits in the human brain, which promotes tumour progression and impairs cognition.
Taylor, K. R. et al. Glioma synapses recruit mechanisms of adaptive plasticity. Nature 623 , 366–374 (2023). This study showed that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)–tropomyosin-related kinase B (TRKB) signalling promotes malignant synaptic plasticity and augments tumour progression.
Hanahan, D. & Monje, M. Cancer hallmarks intersect with neuroscience in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 41 , 573–580 (2023).
Ahles, T. A. & Root, J. C. Cognitive effects of cancer and cancer treatments. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol . 14 , 425–451 (2018).
Allexandre, D. et al. EEG correlates of central origin of cancer-related fatigue. Neural Plast. 2020 , 8812984 (2020).
Büttner-Teleagă, A., Kim, Y. T., Osel, T. & Richter, K. Sleep disorders in cancer — a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 , 11696 (2021).
Walsh, D. & Nelson, K. A. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in advanced cancer. Support. Care Cancer 10 , 523–528 (2002).
Ghandour, F. et al. Presenting psychiatric and neurological symptoms and signs of brain tumors before diagnosis: a systematic review. Brain Sci. 11 , 1–20 (2021).
Akechi, T. et al. Somatic symptoms for diagnosing major depression in cancer patients. Psychosomatics 44 , 244–248 (2003).
Nho, J. H., Kim, S. R. & Kwon, Y. S. Depression and appetite: predictors of malnutrition in gynecologic cancer. Support. Care Cancer 22 , 3081–3088 (2014).
Thaker, P. H. et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat. Med. 12 , 939–944 (2006). This study linked chronic behavioural stress to higher levels of tissue catecholamines and tumour angiogenesis, resulting in greater tumor burden and invasion in ovarian cancer.
Chang, A. et al. Beta-blockade enhances anthracycline control of metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med . 15 , eadf1147 (2023).
Magnon, C. et al. Autonomic nerve development contributes to prostate cancer progression. Science 341 , 1236361 (2013). This study showed that the formation of autonomic nerve fibres in the prostate gland regulates prostate cancer development and dissemination in mouse models.
Baracos, V. E., Martin, L., Korc, M., Guttridge, D. C. & Fearon, K. C. H. Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 4 , 17105 (2018).
Fearon, K. et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 12 , 489–495 (2011). International consensus definitions of cancer cachexia.
Bossi, P., Delrio, P., Mascheroni, A. & Zanetti, M. The spectrum of malnutrition/cachexia/sarcopenia in oncology according to different cancer types and settings: a narrative review. Nutrients 13 , 1980 (2021).
Farkas, J. et al. Cachexia as a major public health problem: frequent, costly, and deadly. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 4 , 173–178 (2013).
Dennison, E. M., Sayer, A. A. & Cooper, C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia and insight into possible therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 13 , 340–347 (2017).
Farasat, M. et al. Long-term cardiac arrhythmia and chronotropic evaluation in patients with severe anorexia nervosa (LACE-AN): a pilot study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 31 , 432–439 (2020).
Mehler, P. S., Anderson, K., Bauschka, M., Cost, J. & Farooq, A. Emergency room presentations of people with anorexia nervosa. J. Eat. Disord. 11 , 16 (2023).
Ferrer, M. et al. Cachexia: a systemic consequence of progressive, unresolved disease. Cell 186 , 1824–1845 (2023).
Bourke, C. D., Berkley, J. A. & Prendergast, A. J. Immune dysfunction as a cause and consequence of malnutrition. Trends Immunol. 37 , 386–398 (2016).
Tisdale, M. J. Biology of cachexia. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 89 , 1763–1773 (1997).
Babic, A. et al. Adipose tissue and skeletal muscle wasting precede clinical diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 14 , 4754 (2023).
Waning, D. L. et al. Excess TGF-β mediates muscle weakness associated with bone metastases in mice. Nat. Med. 21 , 1262 (2015). This study showed that bone metastases cause TGFβ to be released from the bone marrow, resulting in leakage of calcium from skeletal muscle cells contributing to muscle weakness.
Greco, S. H. et al. TGF-β blockade reduces mortality and metabolic changes in a validated murine model of pancreatic cancer cachexia. PLoS ONE 10 , e0132786 (2015).
Johnen, H. et al. Tumor-induced anorexia and weight loss are mediated by the TGF-beta superfamily cytokine MIC-1. Nat. Med. 13 , 1333–1340 (2007). This study showed that GDF15 was elevated in patients with cancer-associated weight loss and that this was a central regulator of appetite and therefore a potential therapeutic target.
Al-Sawaf, O. et al. Body composition and lung cancer-associated cachexia in TRACERx. Nat. Med. 29 , 846–858 (2023). This study showed an association among lower skeletal muscle area, subcutaneous adipose tissue and visceral adipose tissue and decreased survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and these were associated with higher levels of circulating GDF15.
Ahmed, D. S., Isnard, S., Lin, J., Routy, B. & Routy, J. P. GDF15/GFRAL pathway as a metabolic signature for cachexia in patients with cancer. J. Cancer 12 , 1125–1132 (2021).
Rebbapragada, A., Benchabane, H., Wrana, J. L., Celeste, A. J. & Attisano, L. Myostatin signals through a transforming growth factor β-like signaling pathway to block adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 , 7230 (2003).
Queiroz, A. L. et al. Blocking ActRIIB and restoring appetite reverses cachexia and improves survival in mice with lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 13 , 1–17 (2022).
Loumaye, A. et al. Role of activin A and myostatin in human cancer cachexia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100 , 2030–2038 (2015).
Barton, B. E. & Murphy, T. F. Cancer cachexia is mediated in part by the induction of IL-6-like cytokines from the spleen. Cytokine 16 , 251–257 (2001).
Webster, J. M., Kempen, L. J. A. P., Hardy, R. S. & Langen, R. C. J. Inflammation and skeletal muscle wasting during cachexia. Front. Physiol. 11 , 597675 (2020).
Strassmann, G., Masui, Y., Chizzonite, R. & Fong, M. Mechanisms of experimental cancer cachexia local involvement of 11-1 in colon-26 tumor. J. Immunol. 150 , 2341–2345 (1993).
Stovroff, M. C., Fraker, D. L., Swedenborg, J. A. & Norton, J. A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: a possible mediator of cancer anorexia in the rat. Cancer Res. 48 , 4567–4572 (1988).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wyke, S. M. & Tisdale, M. J. NF-κB mediates proteolysis-inducing factor induced protein degradation and expression of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in skeletal muscle. Br. J. Cancer 92 , 711 (2005).
Cai, D. et al. IKKβ/NF-κB activation causes severe muscle wasting in mice. Cell 119 , 285–298 (2004). This study showed that activation of NF-κB, through muscle-specific transgenic expression of activated inhibitor of NF-κB kinase subunit β (IKKβ), causes profound muscle wasting in mice.
Patel, H. J. & Patel, B. M. TNF-α and cancer cachexia: molecular insights and clinical implications. Life Sci. 170 , 56–63 (2017).
Mergenthaler, P., Lindauer, U., Dienel, G. A. & Meisel, A. Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci. 36 , 587 (2013).
Sillos, E. M. et al. Lactic acidosis: a metabolic complication of hematologic malignancies case report and review of the literature. Cancer 92 , 2237–46 (2000).
Rampello, E., Fricia, T. & Malaguarnera, M. The management of tumor lysis syndrome. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 3 , 438–447 (2006).
Delano, M. J. & Moldawer, L. L. The origins of cachexia in acute and chronic inflammatory diseases. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 21 , 68–81 (2006).
Lombardi, A., Villa, S., Castelli, V., Bandera, A. & Gori, A. T-cell exhaustion in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria infection: pathophysiology and therapeutic perspectives. Microorganisms 9 , 2460 (2021).
Moldawer, L. L. & Sattler, F. R. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated wasting and mechanisms of cachexia associated with inflammation. Semin. Oncol. 25 , 73–81 (1998).
von Kobbe, C. Targeting senescent cells: approaches, opportunities, challenges. Aging 11 , 12844 (2019).
Shafqat, S., Chicas, E. A., Shafqat, A. & Hashmi, S. K. The Achilles’ heel of cancer survivors: fundamentals of accelerated cellular senescence. J. Clin. Invest. 132 , e158452 (2022).
Wang, L., Lankhorst, L. & Bernards, R. Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22 , 340–355 (2022).
Terry, W., Olson, L. G., Ravenscroft, P., Wilss, L. & Boulton-Lewis, G. Hospice patients’ views on research in palliative care. Intern. Med. J. 36 , 406–413 (2006).
White, C. & Hardy, J. What do palliative care patients and their relatives think about research in palliative care? A systematic review. Support. Care Cancer 18 , 905–911 (2010).
Foster, B., Bagci, U., Mansoor, A., Xu, Z. & Mollura, D. J. A review on segmentation of positron emission tomography images. Comput. Biol. Med. 50 , 76–96 (2014).
Bera, K., Braman, N., Gupta, A., Velcheti, V. & Madabhushi, A. Predicting cancer outcomes with radiomics and artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19 , 132–146 (2022).
Kaczanowska, S. et al. Immune determinants of CAR-T cell expansion in solid tumor patients receiving GD2 CAR-T cell therapy. Cancer Cell 42 , 35–51.e8 (2024).
Dutta, S. & Sengupta, P. Men and mice: relating their ages. Life Sci. 152 , 244–248 (2016).
Alpert, A. et al. A clinically meaningful metric of immune age derived from high-dimensional longitudinal monitoring. Nat. Med. 25 , 487–495 (2019).
Gyawali, B., Hey, S. P. & Kesselheim, A. S. Evaluating the evidence behind the surrogate measures included in the FDA’s table of surrogate endpoints as supporting approval of cancer drugs. eClinicalMedicine 21 , 100332 (2020).
Hong, W. et al. Automated measurement of mouse social behaviors using depth sensing, video tracking, and machine learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112 , E5351–E5360 (2015).
Johnson, D. E., O’Keefe, R. A. & Grandis, J. R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15 , 234–248 (2018).
Bowden, M. B. et al. Demographic and clinical factors associated with suicide in gastric cancer in the United States. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 8 , 897–901 (2017).
Zaorsky, N. G. et al. Suicide among cancer patients. Nat. Commun. 10 , 1–7 (2019).
CAS Google Scholar
Hu, X. et al. Suicide risk among individuals diagnosed with cancer in the US, 2000 – 2016 . JAMA Netw. Open 6 , e2251863 (2023).
Google Scholar
Abdel-Rahman, O. Socioeconomic predictors of suicide risk among cancer patients in the United States: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol. 63 , 101601 (2019).
Pinquart, M. & Duberstein, P. R. Depression and cancer mortality: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 40 , 1797–1810 (2010).
Fitzgerald, P. et al. The relationship between depression and physical symptom burden in advanced cancer. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 5 , 381–388 (2015).
Chida, Y., Hamer, M., Wardle, J. & Steptoe, A. Do stress-related psychosocial factors contribute to cancer incidence and survival? Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 5 , 466–475 (2008).
He, X. Y. et al. Chronic stress increases metastasis via neutrophil-mediated changes to the microenvironment. Cancer Cell 42 , 474–486.e12 (2024). This study found that chronic stress shifts the normal circadian rhythm of neutrophils resulting in increased neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation via glucocorticoid release, resulting in a metastasis-promoting microenvironment.
Fann, J. R., Ell, K. & Sharpe, M. Integrating psychosocial care into cancer services. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 , 1178–1186 (2012).
Jacobsen, P. B. & Wagner, L. I. A new quality standard: the integration of psychosocial care into routine cancer care. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 , 1154–1159 (2012).
Gorin, S. S. et al. Meta-analysis of psychosocial interventions to reduce pain in patients with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 , 539–547 (2012).
Li, M. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of collaborative care interventions for depression in patients with cancer. Psychooncology 26 , 573–587 (2017).
Bova, G. S. et al. Optimal molecular profiling of tissue and tissue components: defining the best processing and microdissection methods for biomedical applications. Mol. Biotechnol. 29 , 119–152 (2005).
Gundem, G. et al. The evolutionary history of lethal metastatic prostate cancer. Nature 520 , 353–357 (2015). This study found that metastasis-to-metastasis spread was common in prostate cancer evolution and that lesions affecting tumour suppressor genes occurred as single events, whereas mutations in genes involved in androgen receptor signalling commonly involved multiple, convergent events in different metastases.
Turajlic, S. et al. Tracking cancer evolution reveals constrained routes to metastases: TRACERx renal. Cell 173 , 581–594.e12 (2018). This study examined evolutionary trajectories of 100 renal cancers and found that metastasis competence was driven by chromosome complexity, not by driver mutation load, and that loss of 9p and 14q was a common driver.
Spain, L. et al. Late-stage metastatic melanoma emerges through a diversity of evolutionary pathways. Cancer Discov. 13 , 1364–1385 (2023). This study examined evolutionary trajectories of melanoma metastasis and observed frequent whole-genome doubling and widespread loss of heterozygosity, often involving antigen-presentation machinery.
Download references
Acknowledgements
A.B. is funded by National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute P30 CA008748 and R01-CA245499. K.B. is employed by the UK National Health Service. T.R.C. acknowledges funding support from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Ideas (2000937), Project (1129766, 1140125), Development (2013881) and Fellowship (1158590) schemes, a Cancer Institute NSW Career Development Fellowship (CDF171105), Cancer Council NSW project support (RG19-09, RG23-11) and Susan G. Komen for the Cure (CCR17483294). T.G. is funded by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas Grant 00011633. M.J.-H. has received funding from CRUK, NIH National Cancer Institute, IASLC International Lung Cancer Foundation, Lung Cancer Research Foundation, Rosetrees Trust, UKI NETs and NIHR. T.J. acknowledges funding from Cancer Grand Challenges (NIH: 1OT2CA278690-01; CRUK: CGCATF-2021/100019), the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research (20-028-EDV), the Osprey Foundation, Fortune Footwear, Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory (CSHL) and developmental funds from CSHL Cancer Center Support Grant 5P30CA045508. R.K. is funded by the Intramural Research Program, the National Cancer Institute, NIH Clinical Center and the National Institutes of Health (NIH NCI ZIABC011332-06 and NIH NCI ZIABC011334-10). R.L. is supported by a Wellcome Early Career Investigator Award (225724/Z/22/Z). E.S. is supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (CC2040), the UK Medical Research Council (CC2040) and the Wellcome Trust (CC2040) and the European Research Council (ERC Advanced Grant CAN_ORGANISE, Grant agreement number 101019366). E.S. reports personal grants from Mark Foundation and the European Research Council. C.S. is a Royal Society Napier Research Professor (RSRP\R\210001). His work is supported by the Francis Crick Institute that receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (CC2041), the UK Medical Research Council (CC2041) and the Wellcome Trust (CC2041) and the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (ERC Advanced Grant PROTEUS Grant agreement number 835297). M.G.V.H. reports support from the Lustgarten Foundation, the MIT Center for Precision Cancer Medicine, the Ludwig Center at MIT and NIH grants R35 CA242379 and P30 CA1405141.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Adrienne Boire, Katy Burke, Thomas R. Cox, Theresa Guise, Mariam Jamal-Hanjani, Tobias Janowitz, Rosandra Kaplan, Rebecca Lee, Charles Swanton, Matthew G. Vander Heiden, Erik Sahai.
Authors and Affiliations
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA
Adrienne Boire
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust Palliative Care Team, London, UK
Cancer Ecosystems Program, The Garvan Institute of Medical Research and The Kinghorn Cancer Centre, Darlinghurst, New South Wales, Australia
Thomas R. Cox
School of Clinical Medicine, St Vincent’s Healthcare Clinical Campus, UNSW Medicine and Health, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Department of Endocrine Neoplasia and Hormonal Disorders, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA
Theresa Guise
Cancer Metastasis Laboratory, University College London Cancer Institute, London, UK
Mariam Jamal-Hanjani
Department of Oncology, University College London Hospitals, London, UK
Mariam Jamal-Hanjani & Charles Swanton
Cancer Research UK Lung Centre of Excellence, University College London Cancer Institute, London, UK
Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour, New York, NY, USA
Tobias Janowitz
Northwell Health Cancer Institute, New York, NY, USA
Paediatric Oncology Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA
Rosandra Kaplan
Tumour Cell Biology Laboratory, The Francis Crick Institute, London, UK
Rebecca Lee & Erik Sahai
Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
Rebecca Lee
Cancer Evolution and Genome Instability Laboratory, The Francis Crick Institute, London, UK
Charles Swanton
Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
Matthew G. Vander Heiden
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors researched data for the article. A.B., K.B., T.R.C., T.G., T.J., C.S., M.G.V.H, R.K., M.J.-H. and E.S. contributed substantially to discussion of the content. T.C., R.L. and E.S. wrote the article. All authors reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Thomas R. Cox or Erik Sahai .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
A.B. is an inventor on pending patents 63/449,817, 63/052,139 as well as awarded patents 11,305,014 and 10,413,522; all issued to the Sloan Kettering Institute. She has received personal fees from Apelis Pharmaceuticals and serves as an unpaid member of the Evren Technologies SAB. K.B., T.R.C., T.G., T.J. and R.K. declare no competing interests. M.J.-H. reports support from Achilles Therapeutics Scientific Advisory Board and Steering Committee, Pfizer, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Oslo Cancer Cluster and Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. R.L. reports personal fees from Pierre Fabre and has research funding from BMS, Astra Zeneca and Pierre Fabre outside the submitted work. E.S. reports grants from Novartis, Merck Sharp Dohme, AstraZeneca and personal fees from Phenomic outside the submitted work. C.S. reports grants and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Roche-Ventana, personal fees from Pfizer, grants from Ono Pharmaceutical, Personalis, grants, personal fees and other support from GRAIL, other support from AstraZeneca and GRAIL, personal fees and other support from Achilles Therapeutics, Bicycle Therapeutics, personal fees from Genentech, Medixci, China Innovation Centre of Roche (CiCoR) formerly Roche Innovation Centre, Metabomed, Relay Therapeutics, Saga Diagnostics, Sarah Canon Research Institute, Amgen, GlaxoSmithKline, Illumina, MSD, Novartis, other support from Apogen Biotechnologies and Epic Bioscience outside the submitted work; in addition, C.S. has a patent for PCT/US2017/028013 licensed to Natera Inc., UCL Business, a patent for PCT/EP2016/059401 licensed to Cancer Research Technology, a patent for PCT/EP2016/071471 issued to Cancer Research Technology, a patent for PCT/GB2018/051912 pending, a patent for PCT/GB2018/052004 issued to Francis Crick Institute, University College London, Cancer Research Technology Ltd, a patent for PCT/GB2020/050221 issued to Francis Crick Institute, University College London, a patent for PCT/EP2022/077987 pending to Cancer Research Technology, a patent for PCT/GB2017/053289 licensed, a patent for PCT/EP2022/077987 pending to Francis Crick Institute, a patent for PCT/EP2023/059039 pending to Francis Crick Institute and a patent for PCT/GB2018/051892 pending to Francis Crick Institute. C.S. is Co-chief Investigator of the NHS Galleri trial funded by GRAIL. He is Chief Investigator for the AstraZeneca MeRmaiD I and II clinical trials and Chair of the Steering Committee. C.S. is cofounder of Achilles Therapeutics and holds stock options. M.G.V.H. is a scientific adviser for Agios Pharmaceuticals, iTeos Therapeutics, Sage Therapeutics, Faeth Therapeutics, Droia Ventures and Auron Therapeutics on topics unrelated to the presented work.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Cancer thanks Vickie Baracos, Clare M. Isacke, who co-reviewed with Amanda Fitzpatrick and Erica Sloan and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
An autoimmune encephalitis characterized by complex neuropsychiatric features and the presence of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptors in the central nervous system.
Partial collapse or incomplete inflation of the lung.
Pressure-induced movement of brain tissue.
An ageing-associated process in which haematopoiesis becomes dominated by one or a small number of genetically distinct stem or progenitor cells. Clonal haematopoiesis is linked to an increased risk of haematological malignancies.
Inability of the heart to pump blood properly.
Constriction of the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
(CRH). One of the major factors that drives the response of the body to stress.
(DIC). A rare but serious condition in which abnormal blood clotting occurs throughout the blood vessels of the body.
Inflammation of the brain.
An abnormal connection that forms between two body parts, such as an organ or blood vessel and another often unrelated structure in close proximity.
A rare disorder in which the immune system of a body attacks the nerves, which can lead to paralysis.
The stopping of flow of blood, typically associated with the bodies response to prevent and stop bleeding.
A build-up of fluid within the cavities of the brain.
Elevated calcium levels in the blood, often caused by overactive parathyroid glands. Hypercalcaemia is linked to kidney stones, weakened bones, altered digestion and potentially altered cardiac and brain function.
(HPD). Rapid tumour progression sometimes observed during immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment.
The condition that occurs when the level of sodium in the blood is low.
Harm, which is often unavoidable, caused by cancer treatments.
The marked suppression of polyclonal immunoglobulins in the body.
(LEMS). A neuromuscular junction disorder affecting communication between nerves and muscles, which manifests as a result of a paraneoplastic syndrome or a primary autoimmune disorder. Many cases are associated with small-cell lung cancer.
When cancer cells spread to the tissue layers covering the brain and spinal cord (the leptomeninges).
Also known as pulmonary oedema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the alveoli compromising function and making it difficult to breathe.
The observation of displacement of brain tissue across the centre line of the brain, suggestive of uneven intracranial pressure.
Decreased blood flow to the myocardium, commonly called a heart attack.
Inflammation specifically of the middle layer of the heart wall.
A group of rare disorders that occur when the immune system reacts to changes in the body triggered by the presence of a neoplasm.
A dense network of nerves that transmit information from the brain (efferent neurons) to the periphery and conversely transmit information from the periphery to the brain (afferent neurons). A component of the peripheral nervous system is the autonomic nervous system.
A build-up of fluid between the tissues that line the lungs and the chest wall.
A condition characterized by loss of skeletal muscle mass and function.
The lodging of a circulating blood clot within a vessel leading to obstruction. Thromboembolisms may occur in veins (venous thromboembolism) and arteries (arterial thromboembolism).
A key component of the pathway regulating blood clotting, specifically the receptor and cofactor for factor VII/VIIa.
A syndrome occurs when tumour cells release their contents into the bloodstream, either spontaneously or more typically, in response to therapeutic intervention.
Devices worn on the body, typically in the form of accessories or clothing, that incorporate advanced electronics and technology to monitor, track or enhance various aspects of human life. Examples include smartwatches and fitness trackers.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Boire, A., Burke, K., Cox, T.R. et al. Why do patients with cancer die?. Nat Rev Cancer 24 , 578–589 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-024-00708-4
Download citation
Accepted : 15 May 2024
Published : 19 June 2024
Issue Date : August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-024-00708-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
The road less travelled.
Nature Reviews Cancer (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Cancer newsletter — what matters in cancer research, free to your inbox weekly.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services

Making AI work for you
Cisco AI is where the AI hype ends and meaningful help begins.
Certifications
Cisco Validated
Our latest innovations
Cisco XDR with AI Assistant
Remediate the highest-priority incidents with an AI-first XDR solution.

Cisco Networking Cloud
One platform experience. Assured, secured, and simplified.

Secure Firewall 1200 Series
Compact, all-in-one firewall for your distributed enterprise branch.

Break new ground in AI with Cisco U.
Be AI-ready with free Cisco U. tutorials and meet the future head-on.
Identity is the new perimeter
Stop identity-based attacks while providing a seamless authentication experience with Cisco Duo's new Continuous Identity Security.

Engineering excellence with McLaren F1
In the race against time, McLaren Formula 1 trusts Cisco connectivity, performance, and security solutions to power its operations.
Inside Cisco
- More events
Press Release
Cisco reports fourth quarter and fiscal year 2024 earnings
Bringing our portfolio together by chuck robbins.
Industry report
Cisco unveils 2024 State of Industrial Networking Report
Analyst report
Forrester names Cisco a Leader in OT cybersecurity
2024 global networking trends report, cisco becomes official network equipment partner of la28 games.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Generally speaking, a good research paper introduction includes these parts: 1 Thesis statement. 2 Background context. 3 Niche (research gap) 4 Relevance (how the paper fills that gap) 5 Rationale and motivation. First, a thesis statement is a single sentence that summarizes the main topic of your paper.
1-) Start with a Catchy Hook. Your first sentence is one of the factors that most influence a reader's decision to read your paper. This sentence determines the tone of your paper and attracts the reader's attention. For this reason, we recommend that you start your introduction paragraph with a strong and catchy hook sentence.
Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question (s) or hypothesis (es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
1. Get your readers' attention. To speak to your readers effectively, you need to know who they are. Consider who is likely to read the paper and the extent of their knowledge on the topic. Then begin your introduction with a sentence or two that will capture their interest.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
After you've done some extra polishing, I suggest a simple test for the introductory section. As an experiment, chop off the first few paragraphs. Let the paper begin on, say, paragraph 2 or even page 2. If you don't lose much, or actually gain in clarity and pace, then you've got a problem. There are two solutions.
Introducing Your Topic. Provide a brief overview, which should give the reader a general understanding of the subject matter and its significance. Explain the importance of the topic and its relevance to the field. This will help the reader understand why your research is significant and why they should continue reading.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
1. Choose your topic. Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information. Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes: It helps to clarify the topic for the reader. It establishes the depth of your research. The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
The introduction supplies sufficient background information for the reader to understand and evaluate the experiment you did. It also supplies a rationale for the study. Goals: Present the problem and the proposed solution. Presents nature and scope of the problem investigated. Reviews the pertinent literature to orient the reader.
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. ... Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with ...
1- In this paper, I will discuss climate change. Problem: This statement is too broad and vague. It does not provide a clear direction or specific argument. 2- This paper argues that climate change, measured by global average temperature change, is primarily driven by human activities, such as.
After the title page and abstract, the reader's first true interaction with your research paper is the introduction. Your introduction will establish the fou...
Download Article. 1. Announce your research topic. You can start your introduction with a few sentences which announce the topic of your paper and give an indication of the kind of research questions you will be asking. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your topic and pique their interest.
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
Start with a general overview of your topic. Narrow the overview until you address your paper's specific subject. Then, mention questions or concerns you had about the case. Note that you will address them in the publication. Prior research. Your introduction is the place to review other conclusions on your topic.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research. To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery.
The key thing is. to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas. Step 2: Describe the background. This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is ...
As part of the research paper's introduction (and included in the outline), it broadly tells the reader where you're going in the paper. In the thesis statement, you answer the question that inspired your research and summarize your main points in a sentence or two. 5. Write your first draft
The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution. ... Introduction to Psychology. ... the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. ...
The introduction should provide the background of the research paper and introduce readers to what the research paper will explore. If your introduction feels too brief or lacks depth, use WPS AI's "Make Longer" feature to expand on key points, adding necessary details and enhancing the overall narrative.
Your official source for the latest T-Mobile news and updates, along with the newest devices, offers, and stories from the world of T-Mobile.
In this Roadmap, we review the proximal causes of mortality in patients with cancer and discuss current knowledge about the interconnections between mechanisms that contribute to mortality, before ...
In the race against time, McLaren Formula 1 trusts Cisco connectivity, performance, and security solutions to power its operations.