- Sign into My Research
- Create My Research Account
- Company Website
- Our Products
- About Dissertations
- Español (España)
- Support Center

Select language
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Welcome to My Research!
You may have access to the free features available through My Research. You can save searches, save documents, create alerts and more. Please log in through your library or institution to check if you have access.

Translate this article into 20 different languages!
If you log in through your library or institution you might have access to this article in multiple languages.

Get access to 20+ different citations styles
Styles include MLA, APA, Chicago and many more. This feature may be available for free if you log in through your library or institution.

Looking for a PDF of this document?
You may have access to it for free by logging in through your library or institution.

Want to save this document?
You may have access to different export options including Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive and citation management tools like RefWorks and EasyBib. Try logging in through your library or institution to get access to these tools.

- Document 1 of 1
- More like this
- Scholarly Journal

Critical Thinking Skills of Nursing Candidates
No items selected.
Please select one or more items.
Select results items first to use the cite, email, save, and export options
Background: A thought requires various skills regarding intellectual process. This process is examined under three aspects as thinking, emotion and desire.
Objectives: This study was planned to determine the nursing department and the factors affecting the level of critical thinking of students.
Methods: The sample of the study voluntarily participate in the study a total of 272 students who have been accepted. The research was collected using Information Form with the California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory. Frequency analysis of the study, Mann-Whitney U test, t-test and Krusskal Wallis test were performed.
Results: 65.8% of the students were female, 85.7% were single, 33.1% is read in the first grade. 56.7% of students in social activities, participates in scientific activities of 43.3%, and 55.5% identical to their own opinion and are not to pursue programs.
Students with an increased number of classes they read, the truth is found to increase the search and openmindedness. Students' critical thinking trends, the results of analysis of variance according to the class they read, the right of women to male students were found to search and higher dimensions where the open-mindedness and the way highly significant difference.
Conclusion: The right of every step with the increase of students' professional approach, and it was found that they received training in search and broadmindedness increases. To increase awareness of the profession with each passing school year, provide better express themselves and the right to find more comfortable.
Keywords: Critical thinking, nursing student, education
Introduction
A thought requires various skills regarding intellectual process. This process is examined under three aspects as thinking, emotion and desire. The main purpose of thinking is to assign meanings to our life events, to classify these events into categories, and to create an identity for them in a subjective way. Our actions such as judgement, analysis, explanation, comprehension, identification, comparison and making a synthesis occur within the scope of thinking (Sensekerci, & Bilgin, 2008).Critical thinking is an elusive process that is not clearly understood in nursing and has been defined in multiple ways (Polat, Kutlu, Ay, et al. 2018; Riddell, 2007). Walsh and Seldom ridge (2005) specified "critical thinking is not one, monolithic thing" (p. 216); so, capturing the essence of what it means to think critically requires an in-depth exploration. So as to understand the intricacy of how best to advance students' critical thinking in nursing education, investigators should examine nurse educators' critical thinking, along with social and contextual factors that affect how they think critically. Clinical training is heart of nursing education (Sensekerci, & Bilgin, 2008). The aim of clinical teaching in nursing is to enhance students' learning, and to improve the personal growth of clinical instructors in their performance of the educational role in the clinical situation, where the learning situation is often one that cannot be repeated (Colln-Appling, & Giuliano, 2017).Critical thinking is an indispensable reasoning process bearing some characteristics such as gathering information from the resources and analysing them, deciding on the needs in the light of this analysis and selecting and applying among the possible approaches, and evaluating the results (Werner, & Bleich, 2017).Critical thinking is a multifaceted process involving many mental activities. A critical thinker attempts to identify the main point by explaining the cause of the problem, reaching reliable sources and handling it as a whole to determine the main point, and is open to the innovations. A critical thinker respects others' opinions, pays attention toothers, and bases his opinions on a scientific knowledge (Colln-Appling, & Giuliano, 2017). During the last a few decades it has been emphasized that it is vital to acquire critical thinking skills in order to apply them in both personal and professional lives of people who are struggling with the problems in our country and all over the world (Riddell, 2007; Werner, & Bleich, 2017). The development of science and technology gradually increases the need for a qualified human power in the knowledge era that we are in. Thus, today's people should know themselves well, value personal and social development, think, inquire, investigate, and make intelligent decisions, and have critical thinking skills (Colln-Appling, & Giuliano, 2017). The complex care, including the complexity of services offered in various fields, has increased the number of evidence-based practices, technological knowledge and practices, made nurses more flexible and critical. For this reason, critical thinking is very important for nurses who usually have to think more than one option at the same time and make quick decisions (Toofany, 2008; Banning, 2006).
One of the factors affecting the students' critical thinking skills is the evaluation processes of the examinations. According to Glasser (2000) the students tend to forget the information they have obtained for the examinations that require strict memorization only after they are over. Glasser points out that this situation resembles "excavating information pits and later filling them with waste of knowledge". In this sense, for most of the students, passing the tests becomes far more important than acquiring the information. However, the main purpose of the examinations should be raising awareness of the students on obtaining information, skills and assets to apply them to the daily life, establishing relations between concepts and phenomenon, and developing mental abilities such as analysis, synthesis and evaluation rather than directing them to memorise the names and the dates of the concepts and events and phenomenon. Accordingly, rote-learning exams must be replaced by the multidimensional tests that require critical thinking skills of the students and redirect them to improve their creativity. Also, the evaluation process of the learning outcomes of the students must include not only the test results but also the overall evaluation of a whole period of the learning experience by means of assessments considering the performances of the students in portfolio projects and teamwork throughout the term (Carter, Creedy, & Sidebotham, (2017). In order to achieve this goal, the teachers should be educated on this matter. During these processes, the teacher also should be a motivator and the facilitator at the same time. He/she should be focused on forcing the students to do mind exercise and shouldn't intimidate them while asking questions because it is impossible for someone to be able to manage critical thinking skills when he/she is under pressure and cannot explain his/her thoughts freely. A good educator should adopt critical thinking skills in his/her own life and should be humble, courageous, risk-taker and democratic in both communication and administration. The class setting should be free of tension and open to debates and questions (Yue, Zhang, Zhang, et al. 2017). The developing technology and knowledge have made it difficult for nurses to be equipped with the necessary skills to provide a safe care (Lee, Abdullah, Subramanian, et al. 2017). In order fornurses to respond to the needs of the community regarding the health, they are expected to search for information, interrogate, think critically, solve the problems and have a social sensitivity. Critical thinking emerges as an important concept in nursing education and practice by making a nursing diagnosis or determining solutions (Brunt, 2005; Polat, et al., 2018).
Even though the academicians have built a consensus on the necessity of developing critical thinking skills in education system, they do not have a common view about how to teach it to the students. Two approaches have been mentioned in teaching of critical thinking skills. Some academicians claim that critical thinking skills are field based but according to some these are general skills that can be learned and transferred to the other fields. In order to determine how critical thinking skills can be developed, it is a must to identify if these skills are general or field-based (Seferoğlu & Akbıyık 2006). The critical thinking is desirable for nurses working in intensive care units, remote treatment units, institutions where they are educated and all the units they work. Nurses can personalize the care for each patient or case with their broad knowledge. Critical thinking is a desired skill that is required for a safe nursing care (Toofany, 2008). Inclinical applications, nursing educators should develop strategies to help students in their success and improvement in their critical thinking ability (Polat, et al., 2018). They are taught how to maintain their critical thinking skills and how to enhance their competences (Allen, Rubenfeld, & Scheffer, 2004; Brunt, 2005). The inadequacy of critical thinking in nursing negatively affects the quality, efficiency, and competence in service, occupational professionalism, autonomy and competency in the occupation. Therefore, having high critical thinking skills is important to protect, improve and increase the quality of life of a community (Allen, Rubenfeld, & Scheffer, 2004).
Objective: The study was planned to determine the level of critical thinking of the nursing students who continued their education in the Department of Nursing of Gümüşhane University and the factors affecting their level of critical thinking.
Type of the Study: The universe of this descriptive type study consisted of 330 nursing students who were continuing their undergraduate education during 2017/2018 academic year in the Faculty of Health Sciences of Gümüşhane University and the sample of the study included 242 students who agreed to participate voluntarily. For the implementation of the research, the permission was obtained from Gümüşhane Unıversıty Scıentıfıc Research and Publıshıng Commıttee (Approval Number= 95674917-604.01.02-E.834).
Data Collection Tools: The California Critical Thinking Tendency Scale (CCTTS) and an introductory information form were used in the data collection.
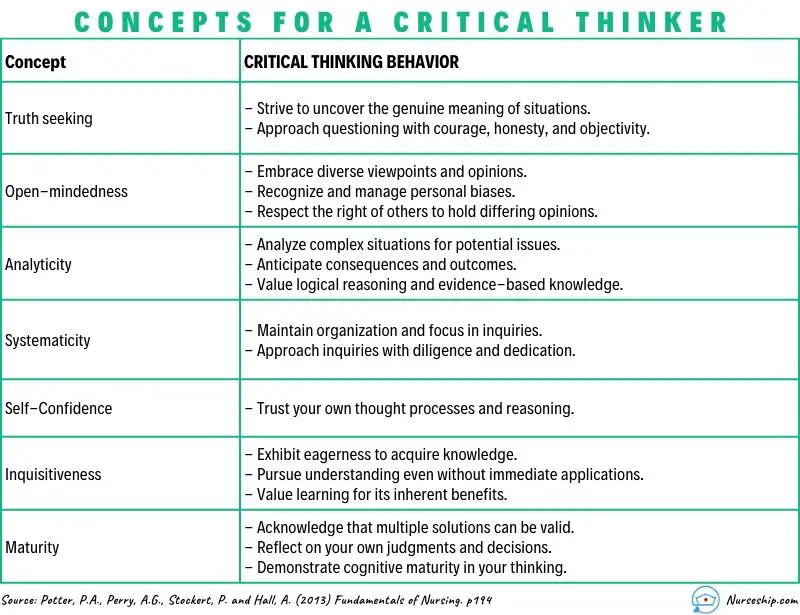
Survey Form: The form consisted of 23 questions that assess the socio-demographic characteristics of the students. The scale was a 6point Likert-type scale including the following sub-dimension: seeking the truth, openmindedness, analytical thinking, systematicity, self-confidence and curiosity. The California Critical Thinking Tendency Scale was developed as a result of the Delphi Project which was organized by the American Philosophy Association in 1990.
Tendencies defined within this scale are:
-Seeking the truth: Assessing the options or different thoughts. The individuals with this tendency show the behaviors such as seeking the truth, asking questions, approaching objectively even against the data that is contrary to their own opinions.
-Open-mindedness: Personal tolerance against different approaches and sensitivity to the own mistakes. It is stated that the individuals with this tendency considersothers' opinions while making any decision.
-Analytical thinking: Being careful about the situations that may cause some problems and reasoning and using objective evidences.
- Systematicity: Conducting an organized, planned a study carefully. It is stated that the individuals with this tendency tend to make a decision based on the knowledge and a specific process.
-Self-confidence: The confidence of the person for own reasoning processes.
-Merrification: A desire to learn new knowledge and new things without any benefit or expectation.
Analysis of the Data: The tendency to think critically increases as the score obtained from the scale increases. According to the CCTTS, a score below 240 points is defined as low critical thinking tendency, a score between 240 and 300 points is defined as medium tendency while a score above 300 points is defined as high tendency. Frequency analysis, Mann Whitney U test, Kruskal Wallis test and t-tests were used in the analysis of the results.
Of the students, 65.8% were female, 85.7% were single, 33.1% were first grade students. 41.6% of the participants expressed their family structure as democratic.It was found that 56.7% of the students preferred to participate in social activities, that 43.3% preferred to participate in scientific activities, that 62.8% did not participate in social activities, that 52.2% followed Facebook and 55.5% followed the programs that are similar or opposite to their ideas (Table 1)The mean score of the students on critical thinking scale was 229.269±25.912. According to the grade of the students, the mean scores of the CCTTS are shown in Table 2.According to the grades of the students and the advanced analysis of CCTTS, it was determined that the evaluation on seeking the truth and open-mindedness was significant. According to the Mann Whitney U advanced analysis test performed among the groups, the significant inter-group differences are shown in Table 2. The differences between seeking the truth and open-mindedness subdimensions were found to increase as the school grade increased. There was no significant difference found between the grades in terms of the total scale score (KW:4.312, p:0.23). In the variance analysis of the students' critical thinking tendencies according to the grades of the students, male students had a higher level of seeking the truth and open-mindedness compared to female students, and a significant difference was found in the meantime.
Systematicity sub-dimension was also found to be higher in male students than that in female students and it was found that there was a statistical difference.A significant difference was found in the analysis results in which the gender and total scale score were evaluated and the mean score of male students was higher (t:-3.36, p:0.01) (Table 3).According to the comparison results, the preference statuses of the students for the programs which were the same with their tendencies, views, and ideas, the evaluation on seeking the truth and open-mindedness were found significant. According to the Mann Whitney U advanced analysis test, the significant differences between the groups are shown in Table 4. The mean score of the individuals who followed the same programs with the students' opinions was 235.58±2.28, the mean score of the individuals who followed the different programs from the students' opinions was 216.58±6.05 and the mean score of the individuals who followed the same and different programs was 226.39±2.18. It was determined that it is especially effective on seeking the truth and open-mindedness (Table 4).Students' willingness to participate in scientific activities and the score of scale were evaluated, there was no statistically significant difference found between them. There was no significant relationship found between the socio-economic status of the students and their total scale scores (KW'5.082, p:0.79).A highly significant difference was found between the scale scores of the students and their participation statuses in social activities. Male students had higher CCTTS scale scores compared to female students (Table 5).
The study showed that the level of critical thinking in nursing is lower in Turkey compared to other countries. It was emphasized that nurses should take responsibility through husing critical thinking and have decision making skills instead of just doing what they were said to them (Dikmen, & Usta, 2013). In the study, the mean score of the nursing students was 229.269±25.912. According to the normal scale scoring, the mean score of the students was low. This result is similar to the results of many studies conducted on critical thinking with nursing students. The low results also suggest that nursing education is an important issue that needs to be emphasized (Eren, et al., 2012; Topoğlu, & Ünal, 2013).
According to the grades of the students and advanced analyses of CCTTS, it was found that the evaluation on seeking the truth and openmindedness was significant. The increased knowledge on the nursing profession, the internships from the second year, the increase in the number of cases, experiences and education from year to year may be effective. In the study conducted by Ozturk and Ulusoy (2008), the undergraduate and master students were evaluated and the mean score was found higher in master students. The education was parallel to the students' critical thinking levels (Ozturk & Ulusoy 2008). However, there are some controversial studies showing that students' scale scores decreased with the increasing grades (Zhang, & Lambert, 2008).
The students' preferences for programs which were same with their opinions and views were assessed by the mean scale score. Same programs were preferred by the highest mean score (235.58±2.28). In the analyses, it was determined that the values on seeking the truth and openmindedness were significant. The individuals who defend the same opinions with their own ideas come to the forefront by their good command of subject and open-mindedness. The level of seeking the truth on a subject and declaration of ideas positively correlate with the level of knowledge of students in this subject. Open-mindedness also enables one to tolerate different approaches and be sensitive to their own mistakes. A highly significant difference was found between the scale scores of the students and their level of participation in social activities.
In the variance analysis of the students' critical thinking tendencies according to their grades, it was found that the sub-dimensions of seeking the truth and open-mindedness were higher in male than those in women, the difference between them was found to be highly statistically significant. The mean CCTTS score was also higher in males than that in females. There was no significant difference in the study conducted with male and female students studying in the department of fine arts in the faculty of the education faculty (Topoglu, & Unal, 2013). Critical thinking is an indispensable part in nursing and ensures us to be able to provide desired and reliable care.
Students' scores regarding the level of critical thinking were found to be low. It is recommended that a training to increase the skills of critical thinking should be provided, that the activities such as group training, case study, seminars, etc. should be organized, and that, if necessary, the curriculum should be corrected in this direction during the education of the students.
The participation of students in social activities should be ensured and supported. Events, conferences, where the ideas are shared, and a discussion environment should be organized.
It was found that students' approach to the profession and the increase in the number of years of education they receive increase their open-mindedness. Increased awareness on occupation with increasing year enables them to better express themselves and find the truth more easily. Turkish community is a paternalistic society and this may cause male students to have a higher level of seeking the truth, openmindedness and critical thinking. In general, 229 CCTS score of nursing candidates demonstrates a low critical thinking tendency. Therefore, it is important to develop programs for this status.
It may be useful to develop institutional policies that will allow nurses to think critically, to support their participation in vocational training events and scientific activities and to gain their critical point of view and autonomy.
Allen, D.G., Rubenfeld, M.G., & Scheffer, B.K. (2004). Reliability of assessment of critical thinking. Journal of Professional Nursing, 20(1), 15-22.
Banning, M. (2006). Measures that can be used to instill critical thinking skills in nurse prescribes. Nurse Education in Practice, 6, 98-105.
Brunt, B. (2005). Critical thinking in nursing: An integrated review. The Journal of Continuing in Nursing, 36(2), 60-67.
Carter, A.G., Creedy, D.K., & Sidebotham, M. (2017). Critical thinking skills in midwifery practice: Development of a self-assessment tool for students. Midwifery. 50, 184-192.
Dikmen, D.Y., & Usta, Y.Y. (2013). Critical thinking in nursing. Süleyman Demirel University Journal of Health Sciences. 4(1), 31-40.
Eren, F.B., Cınar, İ.F., Yıldız, D., Akar, F., Turk, A., Tuncer, S., et al. (2012). Evaluation of the students' level of critical thinking and the factors that affect critical thinking. Journal of Gülhane Medical, 54: 35-39.
Glasser, W. (2000). Reality therapy in action. New York, NY, US: Harper Collins Publishers.
Lee, D.S., Abdullah, K.L., Subramanian, P., Bachmann, R.T., & Ong, S.L. (2017). An integrated review of the correlation between critical thinking ability and clinical decisionmaking in nursing. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 26(23-24), 4065-4079.
Ozturk, N., & Ulusoy, H. (2008). Critical thinking levels of undergraduate and graduate nursing students and factors affecting critical thinking. Maltepe University Journal of Nursing Science and Art, 1(1): 15-26.
Polat, Ş., Kutlu, L., Ay, F., Pur İ.S., & Erkan, H.A. (2018). Decision-making styles, anxiety levels, and critical thinking levels of nurses. Japan Journal of Nursing Science. Nov, 5. doi: 10.1111/jjns.12240.
Riddell, T. (2007). Critical Assumptions: Thinking Critically About Critical Thinking. Journal of Nursing Education, 46(3)
Seferoğlu, S., & Akbıyık, C. (2006). Critical Thinking and Teaching. Journal of Hacettepe University Faculty of Education, 195-200.
Sensekerci, E., & Bilgin, A. (2008). Critical thinking and teaching. Journal of Social Sciences, 9(14).
Toofany, S. (2008). Critical thinking among nurses. Nursing Management, 14(9), 28-31.
Topoglu, O., & Ünal, Ö.E. (2013). To examine the relationship between critical thinking dispositions of the faculty of fine arts education department and various variables. Directory of Open Access Tournals, 8, 1301-1312.
Colln-Appling, V.C., & Giuliano, D. (2017). A concept analysis of critical thinking: A guide for nurse educators. Nurse Education Today, 49, 106109.
Walsh, C.M. & Seldomridge, L.A. (2005). Clinical Grades: Upward Bound. The Journal of Nursing Education, 44, 162-168.
Werner, S.H., & Bleich, M.R. (2017). Critical thinking as a leadership attribute. J Contin Educ Nurs, 48(1), 9-11. .
Yue, M., Zhang, M., Zhang, C., & Jin, C. (2017). The effectiveness of concept mapping on development of critical thinking in nursing education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Education Today, 52, 87-94.
Zhang, H., & Lambert, V. (2008). Critical thinking dispositions and learning styles of baccalaureate nursing students from China. Nursing Health Sciences, 10, 175-181.
You have requested "on-the-fly" machine translation of selected content from our databases. This functionality is provided solely for your convenience and is in no way intended to replace human translation. Show full disclaimer
Neither ProQuest nor its licensors make any representations or warranties with respect to the translations. The translations are automatically generated "AS IS" and "AS AVAILABLE" and are not retained in our systems. PROQUEST AND ITS LICENSORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIM ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTIES FOR AVAILABILITY, ACCURACY, TIMELINESS, COMPLETENESS, NON-INFRINGMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Your use of the translations is subject to all use restrictions contained in your Electronic Products License Agreement and by using the translation functionality you agree to forgo any and all claims against ProQuest or its licensors for your use of the translation functionality and any output derived there from. Hide full disclaimer
© 2019. This work is published under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 (the “License”). Notwithstanding the ProQuest Terms and Conditions, you may use this content in accordance with the terms of the License.
Background: A thought requires various skills regarding intellectual process. This process is examined under three aspects as thinking, emotion and desire. Objectives: This study was planned to determine the nursing department and the factors affecting the level of critical thinking of students. Methods: The sample of the study voluntarily participate in the study a total of 272 students who have been accepted. The research was collected using Information Form with the California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory. Frequency analysis of the study, Mann-Whitney U test, t-test and Krusskal Wallis test were performed. Results: 65.8% of the students were female, 85.7% were single, 33.1% is read in the first grade. 56.7% of students in social activities, participates in scientific activities of 43.3%, and 55.5% identical to their own opinion and are not to pursue programs. Students with an increased number of classes they read, the truth is found to increase the search and openmindedness. Students' critical thinking trends, the results of analysis of variance according to the class they read, the right of women to male students were found to search and higher dimensions where the open-mindedness and the way highly significant difference. Conclusion: The right of every step with the increase of students' professional approach, and it was found that they received training in search and broadmindedness increases. To increase awareness of the profession with each passing school year, provide better express themselves and the right to find more comfortable.
Suggested sources
- About ProQuest
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples, Importance, & How to Improve)

Successful nursing requires learning several skills used to communicate with patients, families, and healthcare teams. One of the most essential skills nurses must develop is the ability to demonstrate critical thinking. If you are a nurse, perhaps you have asked if there is a way to know how to improve critical thinking in nursing? As you read this article, you will learn what critical thinking in nursing is and why it is important. You will also find 18 simple tips to improve critical thinking in nursing and sample scenarios about how to apply critical thinking in your nursing career.
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
4 reasons why critical thinking is so important in nursing, 1. critical thinking skills will help you anticipate and understand changes in your patient’s condition., 2. with strong critical thinking skills, you can make decisions about patient care that is most favorable for the patient and intended outcomes., 3. strong critical thinking skills in nursing can contribute to innovative improvements and professional development., 4. critical thinking skills in nursing contribute to rational decision-making, which improves patient outcomes., what are the 8 important attributes of excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. the ability to interpret information:, 2. independent thought:, 3. impartiality:, 4. intuition:, 5. problem solving:, 6. flexibility:, 7. perseverance:, 8. integrity:, examples of poor critical thinking vs excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. scenario: patient/caregiver interactions, poor critical thinking:, excellent critical thinking:, 2. scenario: improving patient care quality, 3. scenario: interdisciplinary collaboration, 4. scenario: precepting nursing students and other nurses, how to improve critical thinking in nursing, 1. demonstrate open-mindedness., 2. practice self-awareness., 3. avoid judgment., 4. eliminate personal biases., 5. do not be afraid to ask questions., 6. find an experienced mentor., 7. join professional nursing organizations., 8. establish a routine of self-reflection., 9. utilize the chain of command., 10. determine the significance of data and decide if it is sufficient for decision-making., 11. volunteer for leadership positions or opportunities., 12. use previous facts and experiences to help develop stronger critical thinking skills in nursing., 13. establish priorities., 14. trust your knowledge and be confident in your abilities., 15. be curious about everything., 16. practice fair-mindedness., 17. learn the value of intellectual humility., 18. never stop learning., 4 consequences of poor critical thinking in nursing, 1. the most significant risk associated with poor critical thinking in nursing is inadequate patient care., 2. failure to recognize changes in patient status:, 3. lack of effective critical thinking in nursing can impact the cost of healthcare., 4. lack of critical thinking skills in nursing can cause a breakdown in communication within the interdisciplinary team., useful resources to improve critical thinking in nursing, youtube videos, my final thoughts, frequently asked questions answered by our expert, 1. will lack of critical thinking impact my nursing career, 2. usually, how long does it take for a nurse to improve their critical thinking skills, 3. do all types of nurses require excellent critical thinking skills, 4. how can i assess my critical thinking skills in nursing.
• Ask relevant questions • Justify opinions • Address and evaluate multiple points of view • Explain assumptions and reasons related to your choice of patient care options
5. Can I Be a Nurse If I Cannot Think Critically?

- Corpus ID: 207800022
Critical Thinking Skills of Nursing Candidates
- Handan Ozcan , Ayşe Elkoca
- Published 2019
- Medicine, Education
Tables from this paper

8 Citations
The effect of concept mapping on nursing students' critical thinking skills and nursing care plan design, impact of critical thinking and problem solving skills on academic achievement among nursing students', a critical issue: assessing the critical thinking skills and dispositions of undergraduate health science students, cultural adaptation and validation of an instrument about nursing critical thinking skills., moderated mediating effects of gender among the components of critical thinking disposition in undergraduate students., a comparison between chinese and american male and female college students’ critical thinking dispositions, the factors influencing nurses’ clinical decision-making in emergency department, do gpas, entrance exams, or course grades predict outcomes in first semester nursing students, 21 references, critical thinking dispositions and learning styles of baccalaureate nursing students from china., reliability of assessment of critical thinking., critical assumptions: thinking critically about critical thinking., critical thinking skills in midwifery practice: development of a self-assessment tool for students., an integrated review of the correlation between critical thinking ability and clinical decision‐making in nursing, critical thinking in nursing: an integrated review., decision-making styles, anxiety levels, and critical thinking levels of nurses., a concept analysis of critical thinking: a guide for nurse educators., the effectiveness of concept mapping on development of critical thinking in nursing education: a systematic review and meta-analysis., measures that can be used to instill critical thinking skills in nurse prescribers., related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
The Value of Critical Thinking in Nursing

- How Nurses Use Critical Thinking
- How to Improve Critical Thinking
- Common Mistakes

Some experts describe a person’s ability to question belief systems, test previously held assumptions, and recognize ambiguity as evidence of critical thinking. Others identify specific skills that demonstrate critical thinking, such as the ability to identify problems and biases, infer and draw conclusions, and determine the relevance of information to a situation.
Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN, has been a critical care nurse for 10 years in neurological trauma nursing and cardiovascular and surgical intensive care. He defines critical thinking as “necessary for problem-solving and decision-making by healthcare providers. It is a process where people use a logical process to gather information and take purposeful action based on their evaluation.”
“This cognitive process is vital for excellent patient outcomes because it requires that nurses make clinical decisions utilizing a variety of different lenses, such as fairness, ethics, and evidence-based practice,” he says.
How Do Nurses Use Critical Thinking?
Successful nurses think beyond their assigned tasks to deliver excellent care for their patients. For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
Nurses care for many patients during their shifts. Strong critical thinking skills are crucial when juggling various tasks so patient safety and care are not compromised.
Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN, is a nurse educator with a clinical background in surgical-trauma adult critical care, where critical thinking and action were essential to the safety of her patients. She talks about examples of critical thinking in a healthcare environment, saying:
“Nurses must also critically think to determine which patient to see first, which medications to pass first, and the order in which to organize their day caring for patients. Patient conditions and environments are continually in flux, therefore nurses must constantly be evaluating and re-evaluating information they gather (assess) to keep their patients safe.”
The COVID-19 pandemic created hospital care situations where critical thinking was essential. It was expected of the nurses on the general floor and in intensive care units. Crystal Slaughter is an advanced practice nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) and a nurse educator. She observed critical thinking throughout the pandemic as she watched intensive care nurses test the boundaries of previously held beliefs and master providing excellent care while preserving resources.
“Nurses are at the patient’s bedside and are often the first ones to detect issues. Then, the nurse needs to gather the appropriate subjective and objective data from the patient in order to frame a concise problem statement or question for the physician or advanced practice provider,” she explains.
Top 5 Ways Nurses Can Improve Critical Thinking Skills
We asked our experts for the top five strategies nurses can use to purposefully improve their critical thinking skills.
Case-Based Approach
Slaughter is a fan of the case-based approach to learning critical thinking skills.
In much the same way a detective would approach a mystery, she mentors her students to ask questions about the situation that help determine the information they have and the information they need. “What is going on? What information am I missing? Can I get that information? What does that information mean for the patient? How quickly do I need to act?”
Consider forming a group and working with a mentor who can guide you through case studies. This provides you with a learner-centered environment in which you can analyze data to reach conclusions and develop communication, analytical, and collaborative skills with your colleagues.
Practice Self-Reflection
Rhoads is an advocate for self-reflection. “Nurses should reflect upon what went well or did not go well in their workday and identify areas of improvement or situations in which they should have reached out for help.” Self-reflection is a form of personal analysis to observe and evaluate situations and how you responded.
This gives you the opportunity to discover mistakes you may have made and to establish new behavior patterns that may help you make better decisions. You likely already do this. For example, after a disagreement or contentious meeting, you may go over the conversation in your head and think about ways you could have responded.
It’s important to go through the decisions you made during your day and determine if you should have gotten more information before acting or if you could have asked better questions.
During self-reflection, you may try thinking about the problem in reverse. This may not give you an immediate answer, but can help you see the situation with fresh eyes and a new perspective. How would the outcome of the day be different if you planned the dressing change in reverse with the assumption you would find a wound infection? How does this information change your plan for the next dressing change?
Develop a Questioning Mind
McGowan has learned that “critical thinking is a self-driven process. It isn’t something that can simply be taught. Rather, it is something that you practice and cultivate with experience. To develop critical thinking skills, you have to be curious and inquisitive.”
To gain critical thinking skills, you must undergo a purposeful process of learning strategies and using them consistently so they become a habit. One of those strategies is developing a questioning mind. Meaningful questions lead to useful answers and are at the core of critical thinking .
However, learning to ask insightful questions is a skill you must develop. Faced with staff and nursing shortages , declining patient conditions, and a rising number of tasks to be completed, it may be difficult to do more than finish the task in front of you. Yet, questions drive active learning and train your brain to see the world differently and take nothing for granted.
It is easier to practice questioning in a non-stressful, quiet environment until it becomes a habit. Then, in the moment when your patient’s care depends on your ability to ask the right questions, you can be ready to rise to the occasion.
Practice Self-Awareness in the Moment
Critical thinking in nursing requires self-awareness and being present in the moment. During a hectic shift, it is easy to lose focus as you struggle to finish every task needed for your patients. Passing medication, changing dressings, and hanging intravenous lines all while trying to assess your patient’s mental and emotional status can affect your focus and how you manage stress as a nurse .
Staying present helps you to be proactive in your thinking and anticipate what might happen, such as bringing extra lubricant for a catheterization or extra gloves for a dressing change.
By staying present, you are also better able to practice active listening. This raises your assessment skills and gives you more information as a basis for your interventions and decisions.
Use a Process
As you are developing critical thinking skills, it can be helpful to use a process. For example:
- Ask questions.
- Gather information.
- Implement a strategy.
- Evaluate the results.
- Consider another point of view.
These are the fundamental steps of the nursing process (assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate). The last step will help you overcome one of the common problems of critical thinking in nursing — personal bias.
Common Critical Thinking Pitfalls in Nursing
Your brain uses a set of processes to make inferences about what’s happening around you. In some cases, your unreliable biases can lead you down the wrong path. McGowan places personal biases at the top of his list of common pitfalls to critical thinking in nursing.
“We all form biases based on our own experiences. However, nurses have to learn to separate their own biases from each patient encounter to avoid making false assumptions that may interfere with their care,” he says. Successful critical thinkers accept they have personal biases and learn to look out for them. Awareness of your biases is the first step to understanding if your personal bias is contributing to the wrong decision.
New nurses may be overwhelmed by the transition from academics to clinical practice, leading to a task-oriented mindset and a common new nurse mistake ; this conflicts with critical thinking skills.
“Consider a patient whose blood pressure is low but who also needs to take a blood pressure medication at a scheduled time. A task-oriented nurse may provide the medication without regard for the patient’s blood pressure because medication administration is a task that must be completed,” Slaughter says. “A nurse employing critical thinking skills would address the low blood pressure, review the patient’s blood pressure history and trends, and potentially call the physician to discuss whether medication should be withheld.”
Fear and pride may also stand in the way of developing critical thinking skills. Your belief system and worldview provide comfort and guidance, but this can impede your judgment when you are faced with an individual whose belief system or cultural practices are not the same as yours. Fear or pride may prevent you from pursuing a line of questioning that would benefit the patient. Nurses with strong critical thinking skills exhibit:
- Learn from their mistakes and the mistakes of other nurses
- Look forward to integrating changes that improve patient care
- Treat each patient interaction as a part of a whole
- Evaluate new events based on past knowledge and adjust decision-making as needed
- Solve problems with their colleagues
- Are self-confident
- Acknowledge biases and seek to ensure these do not impact patient care
An Essential Skill for All Nurses
Critical thinking in nursing protects patient health and contributes to professional development and career advancement. Administrative and clinical nursing leaders are required to have strong critical thinking skills to be successful in their positions.
By using the strategies in this guide during your daily life and in your nursing role, you can intentionally improve your critical thinking abilities and be rewarded with better patient outcomes and potential career advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Critical Thinking in Nursing
How are critical thinking skills utilized in nursing practice.
Nursing practice utilizes critical thinking skills to provide the best care for patients. Often, the patient’s cause of pain or health issue is not immediately clear. Nursing professionals need to use their knowledge to determine what might be causing distress, collect vital information, and make quick decisions on how best to handle the situation.
How does nursing school develop critical thinking skills?
Nursing school gives students the knowledge professional nurses use to make important healthcare decisions for their patients. Students learn about diseases, anatomy, and physiology, and how to improve the patient’s overall well-being. Learners also participate in supervised clinical experiences, where they practice using their critical thinking skills to make decisions in professional settings.
Do only nurse managers use critical thinking?
Nurse managers certainly use critical thinking skills in their daily duties. But when working in a health setting, anyone giving care to patients uses their critical thinking skills. Everyone — including licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and advanced nurse practitioners —needs to flex their critical thinking skills to make potentially life-saving decisions.
Meet Our Contributors

Crystal Slaughter, DNP, APRN, ACNS-BC, CNE
Crystal Slaughter is a core faculty member in Walden University’s RN-to-BSN program. She has worked as an advanced practice registered nurse with an intensivist/pulmonary service to provide care to hospitalized ICU patients and in inpatient palliative care. Slaughter’s clinical interests lie in nursing education and evidence-based practice initiatives to promote improving patient care.

Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN
Jenna Liphart Rhoads is a nurse educator and freelance author and editor. She earned a BSN from Saint Francis Medical Center College of Nursing and an MS in nursing education from Northern Illinois University. Rhoads earned a Ph.D. in education with a concentration in nursing education from Capella University where she researched the moderation effects of emotional intelligence on the relationship of stress and GPA in military veteran nursing students. Her clinical background includes surgical-trauma adult critical care, interventional radiology procedures, and conscious sedation in adult and pediatric populations.

Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN
Nicholas McGowan is a critical care nurse with 10 years of experience in cardiovascular, surgical intensive care, and neurological trauma nursing. McGowan also has a background in education, leadership, and public speaking. He is an online learner who builds on his foundation of critical care nursing, which he uses directly at the bedside where he still practices. In addition, McGowan hosts an online course at Critical Care Academy where he helps nurses achieve critical care (CCRN) certification.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Critical thinking in nursing clinical practice, education and research: From attitudes to virtue
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, Consolidated Research Group Quantitative Psychology (2017-SGR-269), University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 2 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, Consolidated Research Group on Gender, Identity and Diversity (2017-SGR-1091), University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 3 Department of Fundamental Care and Medical Surgital Nursing, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Nursing, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 4 Multidisciplinary Nursing Research Group, Vall d'Hebron Research Institute (VHIR), Vall d'Hebron Hospital, Barcelona, Spain.
- PMID: 33029860
- DOI: 10.1111/nup.12332
Critical thinking is a complex, dynamic process formed by attitudes and strategic skills, with the aim of achieving a specific goal or objective. The attitudes, including the critical thinking attitudes, constitute an important part of the idea of good care, of the good professional. It could be said that they become a virtue of the nursing profession. In this context, the ethics of virtue is a theoretical framework that becomes essential for analyse the critical thinking concept in nursing care and nursing science. Because the ethics of virtue consider how cultivating virtues are necessary to understand and justify the decisions and guide the actions. Based on selective analysis of the descriptive and empirical literature that addresses conceptual review of critical thinking, we conducted an analysis of this topic in the settings of clinical practice, training and research from the virtue ethical framework. Following JBI critical appraisal checklist for text and opinion papers, we argue the need for critical thinking as an essential element for true excellence in care and that it should be encouraged among professionals. The importance of developing critical thinking skills in education is well substantiated; however, greater efforts are required to implement educational strategies directed at developing critical thinking in students and professionals undergoing training, along with measures that demonstrate their success. Lastly, we show that critical thinking constitutes a fundamental component in the research process, and can improve research competencies in nursing. We conclude that future research and actions must go further in the search for new evidence and open new horizons, to ensure a positive effect on clinical practice, patient health, student education and the growth of nursing science.
Keywords: critical thinking; critical thinking attitudes; nurse education; nursing care; nursing research.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol. MacKinnon K, Marcellus L, Rivers J, Gordon C, Ryan M, Butcher D. MacKinnon K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- Strategies to overcome obstacles in the facilitation of critical thinking in nursing education. Mangena A, Chabeli MM. Mangena A, et al. Nurse Educ Today. 2005 May;25(4):291-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2005.01.012. Epub 2005 Apr 12. Nurse Educ Today. 2005. PMID: 15896414
- Ethics in nursing education: learning to reflect on care practices. Vanlaere L, Gastmans C. Vanlaere L, et al. Nurs Ethics. 2007 Nov;14(6):758-66. doi: 10.1177/0969733007082116. Nurs Ethics. 2007. PMID: 17901186 Review.
- Teaching strategies and outcome assessments targeting critical thinking in bachelor nursing students: a scoping review protocol. Westerdahl F, Carlson E, Wennick A, Borglin G. Westerdahl F, et al. BMJ Open. 2020 Feb 2;10(1):e033214. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033214. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32014875 Free PMC article. Review.
- Higher Vocational Nursing Students' Clinical Core Competence in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Wang S, Huang S, Yan L. Wang S, et al. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024 Mar 1;10:23779608241233147. doi: 10.1177/23779608241233147. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38435341 Free PMC article.
- Effect of the case-based learning method combined with virtual reality simulation technology on midwifery laboratory courses: A quasi-experimental study. Zhao L, Dai X, Chen S. Zhao L, et al. Int J Nurs Sci. 2023 Dec 16;11(1):76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.12.009. eCollection 2024 Jan. Int J Nurs Sci. 2023. PMID: 38352279 Free PMC article.
- Translation, validation and psychometric properties of the Albanian version of the Nurses Professional Competence Scale Short form. Duka B, Stievano A, Caruso R, Prendi E, Ejupi V, Spada F, De Maria M, Rocco G, Notarnicola I. Duka B, et al. Acta Biomed. 2023 Aug 3;94(4):e2023197. doi: 10.23750/abm.v94i4.13575. Acta Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37539614 Free PMC article.
- A study of the effects of blended learning on university students' critical thinking: A systematic review. Haftador AM, Tehranineshat B, Keshtkaran Z, Mohebbi Z. Haftador AM, et al. J Educ Health Promot. 2023 Mar 31;12:95. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_665_22. eCollection 2023. J Educ Health Promot. 2023. PMID: 37288404 Free PMC article. Review.
- Multilevel Modeling of Individual and Group Level Influences on Critical Thinking and Clinical Decision-Making Skills among Registered Nurses: A Study Protocol. Zainal NH, Musa KI, Rasudin NS, Mamat Z. Zainal NH, et al. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;11(8):1169. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11081169. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37108003 Free PMC article.
- Alfaro-Lefevre, R. (2019). Critical thinking, clinical reasoning and clinical judgment. A practical approach, 7th ed. Elsevier.
- Armstrong, A. (2006). Towards a strong virtue ethics for nursing practice. Nursing Philosophy, 7(3), 110-124.
- Armstrong, A. (2007). Nursing ethics. A virtue-based approach. Palgrave Macmillian.
- Banks-Wallace, J., Despins, L., Adams-Leander, S., McBroom, L., & Tandy, L. (2008). Re/Affirming and re/conceptualizing disciplinary knowledge as the foundations for doctoral education. Advances in Nursing Sciencies, 31(1), 67-78. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ANS.0000311530.81188.88
- Banning, M. (2008). Clinical reasoning and its application to nursing: Concepts and research studies. Nurse Education in Practice, 8(3), 177-183.
- Search in MeSH
Grants and funding
- PREI-19-007-B/School of Nursing. Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences. University of Barcelona
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Ovid Technologies, Inc.

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Visit Nurse.com on Facebook
- Visit Nurse.com on YouTube
- Visit Nurse.com on Instagram
- Visit Nurse.com on LinkedIn
Nurse.com by Relias . © Relias LLC 2024. All Rights Reserved.
Account Management
Log in to manage your policy, generate a certificate of insurance (COI), make a payment, and more.
Log in to your account to update your information or manage your policy.
Download a Certificate of Insurance (COI) to provide to your employer.
Make a Payment
Make a one-time payment, set up autopay, or update your payment information.
Submit a notice of an incident or claim in just minutes.
Topics on this page:
Why Critical Thinking in Nursing Is Important
8 examples of critical thinking in nursing, improving the quality of patient care, the importance of critical thinking in nursing.
Jul 24, 2024

While not every decision is an immediate life-and-death situation, there are hundreds of decisions nurses must make every day that impact patient care in ways small and large.
“Being able to assess situations and make decisions can lead to life-or-death situations,” said nurse anesthetist Aisha Allen . “Critical thinking is a crucial and essential skill for nurses.”
The National League for Nursing Accreditation Commission (NLNAC) defines critical thinking in nursing this way: “the deliberate nonlinear process of collecting, interpreting, analyzing, drawing conclusions about, presenting, and evaluating information that is both factually and belief-based. This is demonstrated in nursing by clinical judgment, which includes ethical, diagnostic, and therapeutic dimensions and research.”
An eight-year study by Johns Hopkins reports that 10% of deaths in the U.S. are due to medical error — the third-highest cause of death in the country.
“Diagnostic errors, medical mistakes, and the absence of safety nets could result in someone’s death,” wrote Dr. Martin Makary , professor of surgery at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Everyone makes mistakes — even doctors. Nurses applying critical thinking skills can help reduce errors.
“Question everything,” said pediatric nurse practitioner Ersilia Pompilio RN, MSN, PNP . “Especially doctor’s orders.” Nurses often spend more time with patients than doctors and may notice slight changes in conditions that may not be obvious. Resolving these observations with treatment plans can help lead to better care.
Key Nursing Critical Thinking Skills
Some of the most important critical thinking skills nurses use daily include interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and self-regulation.
- Interpretation: Understanding the meaning of information or events.
- Analysis: Investigating a course of action based on objective and subjective data.
- Evaluation: Assessing the value of information and its credibility.
- Inference: Making logical deductions about the impact of care decisions.
- Explanation: Translating complicated and often complex medical information to patients and families in a way they can understand to make decisions about patient care.
- Self-Regulation: Avoiding the impact of unconscious bias with cognitive awareness.
These skills are used in conjunction with clinical reasoning. Based on training and experience, nurses use these skills and then have to make decisions affecting care.
It’s the ultimate test of a nurse’s ability to gather reliable data and solve complex problems. However, critical thinking goes beyond just solving problems. Critical thinking incorporates questioning and critiquing solutions to find the most effective one. For example, treating immediate symptoms may temporarily solve a problem, but determining the underlying cause of the symptoms is the key to effective long-term health.
Here are some real-life examples of how nurses apply critical thinking on the job every day, as told by nurses themselves.
Example #1: Patient Assessments
“Doing a thorough assessment on your patient can help you detect that something is wrong, even if you’re not quite sure what it is,” said Shantay Carter , registered nurse and co-founder of Women of Integrity . “When you notice the change, you have to use your critical thinking skills to decide what’s the next step. Critical thinking allows you to provide the best and safest care possible.”
Example #2: First Line of Defense
Often, nurses are the first line of defense for patients.
“One example would be a patient that had an accelerated heart rate,” said nurse educator and adult critical care nurse Dr. Jenna Liphart Rhoads . “As a nurse, it was my job to investigate the cause of the heart rate and implement nursing actions to help decrease the heart rate prior to calling the primary care provider.”
Nurses with poor critical thinking skills may fail to detect a patient in stress or deteriorating condition. This can result in what’s called a “ failure to rescue ,” or FTR, which can lead to adverse conditions following a complication that leads to mortality.
Example #3: Patient Interactions
Nurses are the ones taking initial reports or discussing care with patients.
“We maintain relationships with patients between office visits,” said registered nurse, care coordinator, and ambulatory case manager Amelia Roberts . “So, when there is a concern, we are the first name that comes to mind (and get the call).”
“Several times, a parent called after the child had a high temperature, and the call came in after hours,” Roberts said. “Doing a nursing assessment over the phone is a special skill, yet based on the information gathered related to the child’s behavior (and) fluid intake, there were several recommendations I could make.”
Deciding whether it was OK to wait until the morning, page the primary care doctor, or go to the emergency room to be evaluated takes critical thinking.
Example #4: Using Detective Skills
Nurses have to use acute listening skills to discern what patients are really telling them (or not telling them) and whether they are getting the whole story.
“I once had a 5-year-old patient who came in for asthma exacerbation on repeated occasions into my clinic,” said Pompilio. “The mother swore she was giving her child all her medications, but the asthma just kept getting worse.”
Pompilio asked the parent to keep a medication diary.
“It turned out that after a day or so of medication and alleviation in some symptoms, the mother thought the child was getting better and stopped all medications,” she said.
Example #5: Prioritizing
“Critical thinking is present in almost all aspects of nursing, even those that are not in direct action with the patient,” said Rhoads. “During report, nurses decide which patient to see first based on the information gathered, and from there they must prioritize their actions when in a patient’s room. Nurses must be able to scrutinize which medications can be taken together, and which modality would be best to help a patient move from the bed to the chair.”
A critical thinking skill in prioritization is cognitive stacking. Cognitive stacking helps create smooth workflow management to set priorities and help nurses manage their time. It helps establish routines for care while leaving room within schedules for the unplanned events that will inevitably occur. Even experienced nurses can struggle with juggling today’s significant workload, prioritizing responsibilities, and delegating appropriately.
Example #6: Medication & Care Coordination
Another aspect that often falls to nurses is care coordination. A nurse may be the first to notice that a patient is having an issue with medications.
“Based on a report of illness in a patient who has autoimmune challenges, we might recommend that a dose of medicine that interferes with immune response be held until we communicate with their specialty provider,” said Roberts.
Nurses applying critical skills can also help ease treatment concerns for patients.
“We might recommend a patient who gets infusions come in earlier in the day to get routine labs drawn before the infusion to minimize needle sticks and trauma,” Robert said.
Example #7: Critical Decisions
During the middle of an operation, the anesthesia breathing machine Allen was using malfunctioned.
“I had to critically think about whether or not I could fix this machine or abandon that mode of delivering nursing anesthesia care safely,” she said. “I chose to disconnect my patient from the malfunctioning machine and retrieve tools and medications to resume medication administration so that the surgery could go on.”
Nurses are also called on to do rapid assessments of patient conditions and make split-second decisions in the operating room.
“When blood pressure drops, it is my responsibility to decide which medication and how much medication will fix the issue,” Allen said. “I must work alongside the surgeons and the operating room team to determine the best plan of care for that patient’s surgery.”
“On some days, it seems like you are in the movie ‘The Matrix,’” said Pompilio. “There’s lots of chaos happening around you. Your patient might be decompensating. You have to literally stop time and take yourself out of the situation and make a decision.”
Example #8: Fast & Flexible Decisions
Allen said she thinks electronics are great, but she can remember a time when technology failed her.
“The hospital monitor that gives us vitals stopped correlating with real-time values,” she said. “So I had to rely on basic nursing skills to make sure my patient was safe. (Pulse check, visual assessments, etc.)”
In such cases, there may not be enough time to think through every possible outcome. Critical thinking combined with experience gives nurses the ability to think quickly and make the right decisions.
Nurses who think critically are in a position to significantly increase the quality of patient care and avoid adverse outcomes.
“Critical thinking allows you to ensure patient safety,” said Carter. “It’s essential to being a good nurse.”
Nurses must be able to recognize a change in a patient’s condition, conduct independent interventions, anticipate patients and provider needs, and prioritize. Such actions require critical thinking ability and advanced problem-solving skills.
“Nurses are the eyes and ears for patients, and critical thinking allows us to be their advocates,” said Allen.
Image courtesy of iStock.com/ davidf
Last updated on Jul 24, 2024. Originally published on Aug 25, 2021.
- Career Growth
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Berxi™ or Berkshire Hathaway Specialty Insurance Company. This article (subject to change without notice) is for informational purposes only, and does not constitute professional advice. Click here to read our full disclaimer
The product descriptions provided here are only brief summaries and may be changed without notice. The full coverage terms and details, including limitations and exclusions, are contained in the insurance policy. If you have questions about coverage available under our plans, please review the policy or contact us at 833-242-3794 or [email protected] . “20% savings” is based on industry pricing averages.
Berxi™ is a part of Berkshire Hathaway Specialty Insurance ( BHSI ). Insurance products are distributed through Berkshire Hathaway Global Insurance Services, California License # 0K09397. BHSI is part of Berkshire Hathaway’s National Indemnity group of insurance companies, consisting of National Indemnity and its affiliates, which hold financial strength ratings of A++ from AM Best and AA+ from Standard & Poor’s. The rating scales can be found at www.ambest.com and www.standardandpoors.com , respectively.
No warranty, guarantee, or representation, either expressed or implied, is made as to the correctness, accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or sufficiency of any representation or information. Any opinions expressed herein are subject to change without notice.
The information on this web site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment, and does not purport to establish a standard of care under any circumstances. All content, including text, graphics, images and information, contained on or available through this web site is for general information purposes only based upon the information available at the time of presentation, and does not constitute medical, legal, regulatory, compliance, financial, professional, or any other advice.
BHSI makes no representation and assumes no responsibility or liability for the accuracy of information contained on or available through this web site, and such information is subject to change without notice. You are encouraged to consider and confirm any information obtained from or through this web site with other sources, and review all information regarding any medical condition or treatment with your physician or medical care provider. NEVER DISREGARD PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE OR DELAY SEEKING MEDICAL TREATMENT BECAUSE OF SOMETHING THAT YOU HAVE READ ON OR ACCESSED THROUGH THIS WEB SITE.
BHSI is not a medical organization, and does not recommend, endorse or make any representation about the efficacy, appropriateness or suitability of any specific tests, products, procedures, treatments, services, opinions, health care providers or other information contained on or available through this web site. BHSI IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL LIABILITY FOR, ANY ADVICE, COURSE OF TREATMENT, DIAGNOSIS OR ANY OTHER SERVICES OR PRODUCTS THAT YOU OBTAIN AFTER REVIEWING THIS WEB SITE.
Want Berxi articles delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for our monthly newsletter below!
" * " indicates required fields
How we use your email address Berxi will not sell or rent your email address to third parties unless otherwise notified. Other than where necessary to administer your insurance policy or where required by law, Berxi will not disclose your email address to third parties. Your email address is required to identify you for access to the Berxi website. You may also receive newsletters, product updates, and communications about quotes and policies.
Paul Dughi is a contributing writer for Berxi, as well as a journalist and freelance writer. He has held executive management positions in the media industry for the past 25 years.
Related Articles

Breaking Bad News to Patients: A Nurse’s Guide to SPIKES
Michael Walton Jul 24, 2024

Delegation in Nursing: Steps, Skills, & Solutions for Creating Balance at Work
Kristy Snyder Jul 24, 2024

The 7 Most Common Nursing Mistakes (And What You Can Do If You Make One)
Paul Dughi Jul 24, 2024

What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (Explained W/ Examples)

Last updated on August 23rd, 2023
Critical thinking is a foundational skill applicable across various domains, including education, problem-solving, decision-making, and professional fields such as science, business, healthcare, and more.
It plays a crucial role in promoting logical and rational thinking, fostering informed decision-making, and enabling individuals to navigate complex and rapidly changing environments.
In this article, we will look at what is critical thinking in nursing practice, its importance, and how it enables nurses to excel in their roles while also positively impacting patient outcomes.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
It’s a mental activity that goes beyond simple memorization or acceptance of information at face value.
Critical thinking involves careful, reflective, and logical thinking to understand complex problems, consider various perspectives, and arrive at well-reasoned conclusions or solutions.
Key aspects of critical thinking include:
- Analysis: Critical thinking begins with the thorough examination of information, ideas, or situations. It involves breaking down complex concepts into smaller parts to better understand their components and relationships.
- Evaluation: Critical thinkers assess the quality and reliability of information or arguments. They weigh evidence, identify strengths and weaknesses, and determine the credibility of sources.
- Synthesis: Critical thinking involves combining different pieces of information or ideas to create a new understanding or perspective. This involves connecting the dots between various sources and integrating them into a coherent whole.
- Inference: Critical thinkers draw logical and well-supported conclusions based on the information and evidence available. They use reasoning to make educated guesses about situations where complete information might be lacking.
- Problem-Solving: Critical thinking is essential in solving complex problems. It allows individuals to identify and define problems, generate potential solutions, evaluate the pros and cons of each solution, and choose the most appropriate course of action.
- Creativity: Critical thinking involves thinking outside the box and considering alternative viewpoints or approaches. It encourages the exploration of new ideas and solutions beyond conventional thinking.
- Reflection: Critical thinkers engage in self-assessment and reflection on their thought processes. They consider their own biases, assumptions, and potential errors in reasoning, aiming to improve their thinking skills over time.
- Open-Mindedness: Critical thinkers approach ideas and information with an open mind, willing to consider different viewpoints and perspectives even if they challenge their own beliefs.
- Effective Communication: Critical thinkers can articulate their thoughts and reasoning clearly and persuasively to others. They can express complex ideas in a coherent and understandable manner.
- Continuous Learning: Critical thinking encourages a commitment to ongoing learning and intellectual growth. It involves seeking out new knowledge, refining thinking skills, and staying receptive to new information.
Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an intellectual process of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
Critical thinking in nursing is a vital cognitive skill that involves analyzing, evaluating, and making reasoned decisions about patient care.
It’s an essential aspect of a nurse’s professional practice as it enables them to provide safe and effective care to patients.
Critical thinking involves a careful and deliberate thought process to gather and assess information, consider alternative solutions, and make informed decisions based on evidence and sound judgment.
This skill helps nurses to:
- Assess Information: Critical thinking allows nurses to thoroughly assess patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and test results. By analyzing this data, nurses can identify patterns, discrepancies, and potential issues that may require further investigation.
- Diagnose: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data and collaboratively work with other healthcare professionals to formulate accurate nursing diagnoses. This is crucial for developing appropriate care plans that address the unique needs of each patient.
- Plan and Implement Care: Once a nursing diagnosis is established, critical thinking helps nurses develop effective care plans. They consider various interventions and treatment options, considering the patient’s preferences, medical history, and evidence-based practices.
- Evaluate Outcomes: After implementing interventions, critical thinking enables nurses to evaluate the outcomes of their actions. If the desired outcomes are not achieved, nurses can adapt their approach and make necessary changes to the care plan.
- Prioritize Care: In busy healthcare environments, nurses often face situations where they must prioritize patient care. Critical thinking helps them determine which patients require immediate attention and which interventions are most essential.
- Communicate Effectively: Critical thinking skills allow nurses to communicate clearly and confidently with patients, their families, and other members of the healthcare team. They can explain complex medical information and treatment plans in a way that is easily understood by all parties involved.
- Identify Problems: Nurses use critical thinking to identify potential complications or problems in a patient’s condition. This early recognition can lead to timely interventions and prevent further deterioration.
- Collaborate: Healthcare is a collaborative effort involving various professionals. Critical thinking enables nurses to actively participate in interdisciplinary discussions, share their insights, and contribute to holistic patient care.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Critical thinking helps nurses navigate ethical dilemmas that can arise in patient care. They can analyze different perspectives, consider ethical principles, and make morally sound decisions.
- Continual Learning: Critical thinking encourages nurses to seek out new knowledge, stay up-to-date with the latest research and medical advancements, and incorporate evidence-based practices into their care.
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed.
It’s a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning , problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
What are the Levels of Critical Thinking in Nursing?
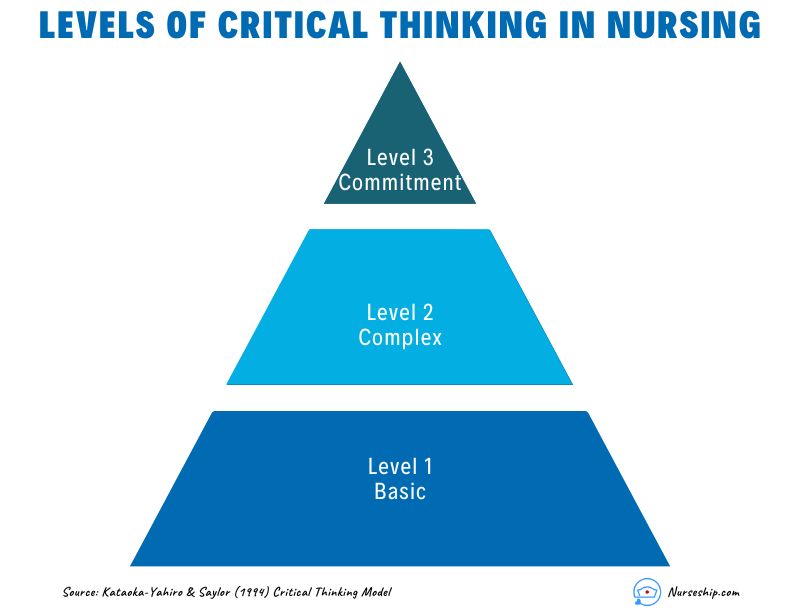
The development of critical thinking in nursing practice involves progressing through three levels: basic, complex, and commitment.
The Kataoka-Yahiro and Saylor model outlines this progression.
1. Basic Critical Thinking:
At this level, learners trust experts for solutions. Thinking is based on rules and principles. For instance, nursing students may strictly follow a procedure manual without personalization, as they lack experience. Answers are seen as right or wrong, and the opinions of experts are accepted.
2. Complex Critical Thinking:
Learners start to analyze choices independently and think creatively. They recognize conflicting solutions and weigh benefits and risks. Thinking becomes innovative, with a willingness to consider various approaches in complex situations.
3. Commitment:
At this level, individuals anticipate decision points without external help and take responsibility for their choices. They choose actions or beliefs based on available alternatives, considering consequences and accountability.
As nurses gain knowledge and experience, their critical thinking evolves from relying on experts to independent analysis and decision-making, ultimately leading to committed and accountable choices in patient care.
Why Critical Thinking is Important in Nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing for several crucial reasons:
Patient Safety:
Nursing decisions directly impact patient well-being. Critical thinking helps nurses identify potential risks, make informed choices, and prevent errors.
Clinical Judgment:
Nursing decisions often involve evaluating information from various sources, such as patient history, lab results, and medical literature.
Critical thinking assists nurses in critically appraising this information, distinguishing credible sources, and making rational judgments that align with evidence-based practices.
Enhances Decision-Making:
In nursing, critical thinking allows nurses to gather relevant patient information, assess it objectively, and weigh different options based on evidence and analysis.
This process empowers them to make informed decisions about patient care, treatment plans, and interventions, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Promotes Problem-Solving:
Nurses encounter complex patient issues that require effective problem-solving.
Critical thinking equips them to break down problems into manageable parts, analyze root causes, and explore creative solutions that consider the unique needs of each patient.
Drives Creativity:
Nursing care is not always straightforward. Critical thinking encourages nurses to think creatively and explore innovative approaches to challenges, especially when standard protocols might not suffice for unique patient situations.
Fosters Effective Communication:
Communication is central to nursing. Critical thinking enables nurses to clearly express their thoughts, provide logical explanations for their decisions, and engage in meaningful dialogues with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
Aids Learning:
Nursing is a field of continuous learning. Critical thinking encourages nurses to engage in ongoing self-directed education, seeking out new knowledge, embracing new techniques, and staying current with the latest research and developments.
Improves Relationships:
Open-mindedness and empathy are essential in nursing relationships.
Critical thinking encourages nurses to consider diverse viewpoints, understand patients’ perspectives, and communicate compassionately, leading to stronger therapeutic relationships.
Empowers Independence:
Nursing often requires autonomous decision-making. Critical thinking empowers nurses to analyze situations independently, make judgments without undue influence, and take responsibility for their actions.
Facilitates Adaptability:
Healthcare environments are ever-changing. Critical thinking equips nurses with the ability to quickly assess new information, adjust care plans, and navigate unexpected situations while maintaining patient safety and well-being.
Strengthens Critical Analysis:
In the era of vast information, nurses must discern reliable data from misinformation.
Critical thinking helps them scrutinize sources, question assumptions, and make well-founded choices based on credible information.
How to Apply Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples)
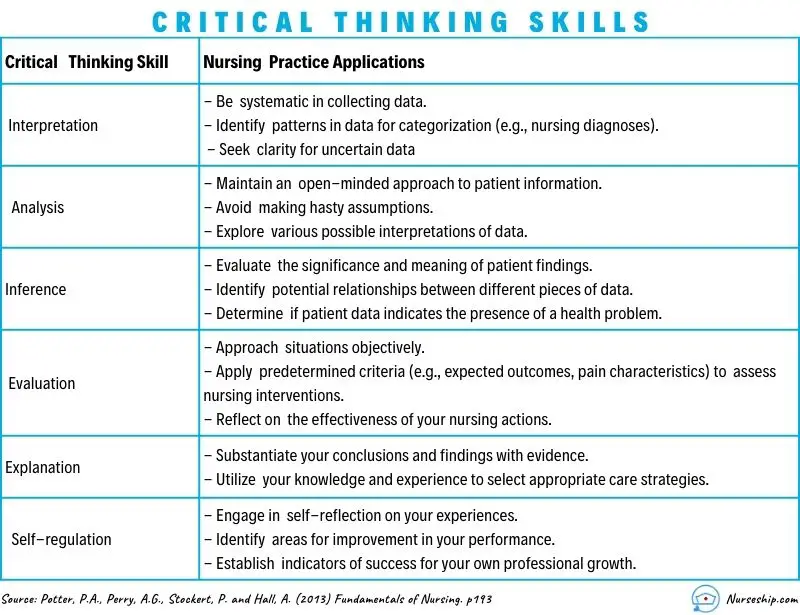
Here are some examples of how nurses can apply critical thinking.
Assess Patient Data:
Critical Thinking Action: Carefully review patient history, symptoms, and test results.
Example: A nurse notices a change in a diabetic patient’s blood sugar levels. Instead of just administering insulin, the nurse considers recent dietary changes, activity levels, and possible medication interactions before adjusting the treatment plan.
Diagnose Patient Needs:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze patient data to identify potential nursing diagnoses.
Example: After reviewing a patient’s lab results, vital signs, and observations, a nurse identifies “ Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity ” due to the patient’s limited mobility.
Plan and Implement Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Develop a care plan based on patient needs and evidence-based practices.
Example: For a patient at risk of falls, the nurse plans interventions such as hourly rounding, non-slip footwear, and bed alarms to ensure patient safety.
Evaluate Interventions:
Critical Thinking Action: Assess the effectiveness of interventions and modify the care plan as needed.
Example: After administering pain medication, the nurse evaluates its impact on the patient’s comfort level and considers adjusting the dosage or trying an alternative pain management approach.
Prioritize Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Determine the order of interventions based on patient acuity and needs.
Example: In a busy emergency department, the nurse triages patients by considering the severity of their conditions, ensuring that critical cases receive immediate attention.
Collaborate with the Healthcare Team:
Critical Thinking Action: Participate in interdisciplinary discussions and share insights.
Example: During rounds, a nurse provides input on a patient’s response to treatment, which prompts the team to adjust the care plan for better outcomes.
Ethical Decision-Making:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze ethical dilemmas and make morally sound choices.
Example: When a terminally ill patient expresses a desire to stop treatment, the nurse engages in ethical discussions, respecting the patient’s autonomy and ensuring proper end-of-life care.
Patient Education:
Critical Thinking Action: Tailor patient education to individual needs and comprehension levels.
Example: A nurse uses visual aids and simplified language to explain medication administration to a patient with limited literacy skills.
Adapt to Changes:
Critical Thinking Action: Quickly adjust care plans when patient conditions change.
Example: During post-operative recovery, a nurse notices signs of infection and promptly informs the healthcare team to initiate appropriate treatment adjustments.

Critical Analysis of Information:
Critical Thinking Action: Evaluate information sources for reliability and relevance.
Example: When presented with conflicting research studies, a nurse critically examines the methodologies and sample sizes to determine which study is more credible.
Making Sense of Critical Thinking Skills
What is the purpose of critical thinking in nursing.
The purpose of critical thinking in nursing is to enable nurses to effectively analyze, interpret, and evaluate patient information, make informed clinical judgments, develop appropriate care plans, prioritize interventions, and adapt their approaches as needed, thereby ensuring safe, evidence-based, and patient-centered care.
Why critical thinking is important in nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing because it promotes safe decision-making, accurate clinical judgment, problem-solving, evidence-based practice, holistic patient care, ethical reasoning, collaboration, and adapting to dynamic healthcare environments.
Critical thinking skill also enhances patient safety, improves outcomes, and supports nurses’ professional growth.
How is critical thinking used in the nursing process?
Critical thinking is integral to the nursing process as it guides nurses through the systematic approach of assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care. It involves:
- Assessment: Critical thinking enables nurses to gather and interpret patient data accurately, recognizing relevant patterns and cues.
- Diagnosis: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data, identify nursing diagnoses, and differentiate actual issues from potential complications.
- Planning: Critical thinking helps nurses develop tailored care plans, selecting appropriate interventions based on patient needs and evidence.
- Implementation: Nurses make informed decisions during interventions, considering patient responses and adjusting plans as needed.
- Evaluation: Critical thinking supports the assessment of patient outcomes, determining the effectiveness of intervention, and adapting care accordingly.
Throughout the nursing process , critical thinking ensures comprehensive, patient-centered care and fosters continuous improvement in clinical judgment and decision-making.
What is an example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice?
An example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice could be:
A nurse is caring for a patient with a complex medical history who is experiencing a new set of symptoms. The nurse carefully reviews the patient’s history, recent test results, and medication list.
While discussing the case with the healthcare team, the nurse realizes that the current treatment plan might not be addressing all aspects of the patient’s condition.
Instead of simply following the established protocol, the nurse independently considers alternative approaches based on their assessment.
The nurse proposes a modification to the treatment plan, citing the rationale and evidence supporting the change.
This demonstrates independent thinking by critically evaluating the situation, challenging assumptions, and advocating for a more personalized and effective patient care approach.
How to use Costa’s level of questioning for critical thinking in nursing?
Costa’s levels of questioning can be applied in nursing to facilitate critical thinking and stimulate a deeper understanding of patient situations. The levels of questioning are as follows:
| Level 1: Gathering | 1. What are the common side effects of the prescribed medication? 2. When was the patient’s last bowel movement? 3. Who is the patient’s emergency contact person? 4. Describe the patient’s current level of pain. 5. What information is in the patient’s medical record? |
| 1. What would happen if the patient’s blood pressure falls further? 2. Compare the patient’s oxygen saturation levels before and after administering oxygen. 3. What other nursing interventions could be considered for wound care? 4. Infer the potential reasons behind the patient’s increased heart rate. 5. Analyze the relationship between the patient’s diet and blood glucose levels. | |
| 1. What do you think will be the patient’s response to the new pain management strategy? 2. Could the patient’s current symptoms be indicative of an underlying complication? 3. How would you prioritize care for patients with varying acuity levels in the emergency department? 4. What evidence supports your choice of administering the medication at this time? 5. Create a care plan for a patient with complex needs requiring multiple interventions. |
- 15 Attitudes of Critical Thinking in Nursing (Explained W/ Examples)
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
- Clinical Reasoning In Nursing (Explained W/ Example)
- 8 Stages Of The Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills In Nursing? 24 Strategies With Examples
- What is the “5 Whys” Technique?
- What Are Socratic Questions?
Critical thinking in nursing is the foundation that underpins safe, effective, and patient-centered care.
Critical thinking skills empower nurses to navigate the complexities of their profession while consistently providing high-quality care to diverse patient populations.
Reading Recommendation
Potter, P.A., Perry, A.G., Stockert, P. and Hall, A. (2013) Fundamentals of Nursing
Comments are closed.
Medical & Legal Disclaimer
All the contents on this site are for entertainment, informational, educational, and example purposes ONLY. These contents are not intended to be used as a substitute for professional medical advice or practice guidelines. However, we aim to publish precise and current information. By using any content on this website, you agree never to hold us legally liable for damages, harm, loss, or misinformation. Read the privacy policy and terms and conditions.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
© 2024 nurseship.com. All rights reserved.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.8(4); 2021 Jul
Factors associated with the critical thinking ability of professional nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Tuan van nguyen.
1 Faculty of Nursing and Medical Technology, Can Tho University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Can Tho Vietnam
2 School of Nursing, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan Taiwan
Hsueh‐Erh Liu
3 Department of Rheumatology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Taiwan
4 Department of Nursing, College of Nursing, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan, Taiwan
Associated Data
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
To measure the level of critical thinking among Vietnamese professional nurses and to identify the related factors.
A cross‐sectional design was used.
The total sample included 420 professional nurses. Data were collected from July to September 2019 in three public hospitals located in Southwestern Vietnam. The level of critical thinking was measured using the Vietnamese version of the Nursing Critical Thinking in Clinical Practice Questionnaire. The data were analysed using the independent Student's t tests, ANOVA, Pearson's correlation and regression analysis.
Most of the participants had a low (48.3%) or moderate (45.5%) level of critical thinking. Age, gender, ethnicity, education level, health condition, duration of working as a nurse, duration of working in the current hospital, having heard the term “critical thinking” and work position had an impact on the critical thinking ability. Work position and gender explained 11% of the total variance in critical thinking ability.
1. INTRODUCTION
Critical thinking is defined as the cognitive process of reasoning that involves trying to minimize errors and to maximize positive outcomes while attempting to make a decision during patient care (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2015 ). The importance of critical thinking in nursing practice has been identified in the literature (Chang et al., 2011 ; Ludin, 2018 ; Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ; Yurdanur, 2016 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2015 ). The current nursing environment has become more complex and demanding, especially regarding the acuity and safety of patients and the rapid turnover rate of hospitalization. If professional nurses want to provide high‐quality care, critical thinking is required (Berkow et al., 2011 ; Brunt, 2005 ; Fero et al., 2009 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2015 ). Nurses are often the first‐line professionals to observe and provide direct care for patients. Therefore, critical thinking is a necessary skill for them to be able to analyse clinical situations in order to make fast and correct decisions (Lee et al., 2017 ). More importantly, critical thinking can also improve patient outcomes by preventing habitual thinking that may lead to incorrect medication or procedures (Fesler‐Birch, 2005 ). The critical thinking ability of nurses can have an impact on the patient's safety, and it is a priority in educational programs for healthcare providers (Berkow et al., 2011 ; Buerhaus et al., 2006 ). We can identify those with poor critical thinking and provide in‐service education. Although critical thinking has been shown that is influenced by the experience and knowledge acquired during clinical practice (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2015 ), other personal information needs to be considered to clarifying. Therefore, it is essential to measure the levels of critical thinking and to identify the work‐related and personal‐related factors that influence the critical thinking of nurses.
2. BACKGROUND
The literature has identified that there is a relationship between leadership and positive patient outcomes, such as fewer medication errors and nosocomial infections, lower patient mortality and higher patient satisfaction (Van Dyk et al., 2016 ; Wong, 2015 ). Alongside leadership, critical thinking is an important factor that supports the management. They can apply critical thinking skills in decision‐making and problem‐solving, and they can develop strategies that help staff nurses to improve their critical thinking ability (Van Dyk et al., 2016 ; Wong, 2015 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). Thus, the ability to think critically is necessary for nurses because it will help them to effectively make decisions and to solve problems in practice.
Although the importance of critical thinking in nursing practice has been identified, a limited number of studies have been conducted in this population. Particularly, few hospitals have evaluated the critical thinking skills of nurses before employment or during the clinical competency evaluation (Lang et al., 2013 ). By reviewing 90 articles to assess the current state of the scientific knowledge regarding critical thinking in nursing, Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., ( 2015 ) found that only 16 studies used working nurses as participants. Furthermore, Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., ( 2018 ) reported that few studies have explored the critical thinking ability of nurse managers (NMs). Moreover, several studies have identified that working nurses have a low (Lang et al., 2013 ; Yurdanur, 2016 ) or moderate level of critical thinking (Chang et al., 2011 ; Lang et al., 2013 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). To the researchers’ knowledge, no studies have investigated this issue in Vietnam.
In order to improve the quality and safety of patient care, various types of professional nurses have been established, such as Registered Nurses (RNs), NMs and administrative assistants (AAs). RNs provide direct care to the patients, NMs are responsible for forwarding management and delivering expert clinical care for patients, and AAs are an integral part of maintaining the quality of patient care. The AAs perform administrative tasks (e.g. filing, taking meeting minutes and distributing them and undertaking regular reports) that help NMs to spend more time assisting staff nurses and taking care of patients (Locke et al., 2011 ). Therefore, RNs, NMs and AAs need to cooperate to help patients to regain their health.
In Vietnam, professional nurses work in three different positions, which are NMs, general nurses (GNs) and AAs (Ministry of Health, 1997 ). Specifically, NMs are recognized as head nurses in Western countries, and their responsibilities are in charge of organizing and implementing comprehensive patient care and conduct a variety of administrative work (e.g. planning and assigning work to nurses, planning the acquisition of tools and consumables, checking care sheets, recording daily labour). GNs are similar to RNs in Western countries, and they provide direct and comprehensive care to patients. AAs perform administrative tasks (e.g. keeping records about the hospitalized and discharged patients, preserving medical records, managing daily medications). They also participate in patients care if necessary (Ministry of Health, 1997 , 2011 ). Although the roles of these three types of professional nurses are different, their final goal is the same to provide holistic care for patients. With the cooperation and effort of these three types of professional nurses, patients can recover. Therefore, more surveys are needed that examine these participants’ level of critical thinking and the associated work‐related factors.
Previous studies have also found that several personal‐related factors are associated with the nurses' critical thinking ability, which are age, gender, ethnicity, education qualification, working experience and shift work (Chang et al., 2011 ; Feng et al., 2010 ; Howenstein et al., 1996 ; Lang et al., 2013 ; Ludin, 2018 ; Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ; Ryan & Tatum, 2012 ; Wangensteen et al., 2010 ; Yildirim et al., 2012 ; Yurdanur, 2016 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). However, the relationships between the critical thinking ability and these variables are inconsistent. For example, age and critical thinking have been found to be positively correlated (Chang et al., 2011 ; Ludin, 2018 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ), negatively correlated (Howenstein et al., 1996 ) and not related (Lang et al., 2013 ; Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ; Yurdanur, 2016 ). Gender and critical thinking have been reported with a statistically significant relationship (Liu et al., 2019 ; Ludin, 2018 ) and no relationship (Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ; Wangensteen et al., 2010 ). Level of education and critical thinking have been found in a positive association (Chang et al., 2011 ; Ludin, 2018 ) and not association (Lang et al., 2013 ; Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ). Year of experiences and critical thinking have been shown to be positively correlated (Chang et al., 2011 ; Ludin, 2018 ), negatively correlated (Howenstein et al., 1996 ) and not related (Lang et al., 2013 ; Mahmoud & Mohamed, 2017 ). Those inconsistent findings indicated the relationships between the personal‐characteristics and the critical thinking ability of professional nurses need further exploration. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the level of critical thinking of professional nurses and to explore the work‐related and personal‐related factors. This is the first study to investigate this issue in Vietnam. The results of the current study will make a significant contribution to the literature because it will provide thorough descriptions of the critical thinking of professional nurses and its associated factors. Furthermore, the findings may be used as a baseline for nurse managers and nurse educators to propose further strategies to improve this ability in professional nurses.
3.1. Research design
A cross‐sectional design was used. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines were applied in this report (Von Elm et al., 2014 ).
3.2. Setting and sampling
Data collection was carried out from July to September 2019 in three representative and major public hospitals located in the Southwestern region of Vietnam. These hospitals have the same organizational structure, role of treating, operation of professional nursing and provide similar quality of health care to people around that area. The total numbers of professional in these three hospitals nurses were around 1,200. Besides, our study has two steps. The first step was to translate the English version of the Nursing Critical Thinking in Clinical Practice Questionnaire (N‐CT‐4 Practice) into the Vietnamese version. In that step, we used data as a pilot study to estimate the sample size in the second step, which was reported here. Sample size calculation was done by the formula: n = 1.96 2 × p × (1‐p)/0.05 2 , where p = .46 came from the poor level of critical thinking among nurses in the first step and 0.05 indicated the acceptable margin of error (5.0%); 382 participants were required by this formula. An additional 10% of participants were done to adjust for potential failures such as withdrawals or missing data (Suresh & Chandrashekara, 2012 ). Therefore, in total, 420 participants were required for this study. Convenience sampling was conducted to recruit the sample. The inclusion criteria were the nurses' employed full‐time employment in the study hospitals. Participants who participated in step 1 or being absent during the data collection such as sick leave or delivering a baby were excluded. Participants were grouped in each hospital and received an envelope with all questionnaires. Then, researchers explained the research's purpose, benefits and risks to the potential participants and the procedure for ensuring confidentiality, and the voluntary nature of the participation. The informed consent form was signed immediately after they agreed to participate in this study. Then, the participants were required to complete the questionnaires in 20 to 30 min and to return them to the data collector.
3.3. Data assessment
3.3.1. sample characteristics.
This instrument collected data about the personal information and occupational variables. The personal information included age, gender, marital status, ethnicity, religion, education level and self‐rated health conditions. The occupational variables were the duration of working as a nurse, the duration of working in the current hospital, the duration of working in the specific position, having heard the term “critical thinking” or not, previous exposure to critical thinking training or education or not, and type of work position.
3.3.2. Vietnamese version of the Nursing Critical Thinking in Clinical Practice Questionnaire ((N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v))
The N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) was used to measure the critical thinking ability of the professional nurses. The original instrument (N‐CT‐4 Practice) was established and classified based on the four dimensions of the 4‐circle critical thinking model of Alfaro‐LeFevre (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2017 ). These four dimensions were personal; intellectual and cognitive; interpersonal and self‐management; and technical dimensions. The personal dimension has 39 items to assess the individual pattern of intellectual behaviours; the intellectual and cognitive dimension has 44 items to assesses the knowledge of activity comprehension connected to the nursing process and decision‐making. For the interpersonal and self‐management dimension, it has 20 items to analyse interpersonal abilities that allow for therapeutic communication with patients and health teams and to gain information that is associated with the patient in the clinical environment. The final one, the technical dimension, has 6 items to is concerned with knowledge and expertise in the procedures that are part of the discipline of nursing. This scale has 109 items that are rated using a four‐point Likert response format (1 = never or almost never, 2 = occasionally, 3 = often, and 4 = always or almost always), for example: “I recognize my own emotions.” (item 1); “I have the scientific knowledge required to carry out my professional practice.” (item 40); “I adapt information to the needs and capacities of the patient.” (item 84); “I possess skills in the use of information and communication technologies needed to produce optimal professional results.” (item 105). The total score is obtained from the sum of the 109 items. The scores range from 109–436, and they are categorized into a low level (score <329), moderate level (score between 329–395) and high level (score >395). The overall Cronbach's alpha was 0.96, and the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was 0.77 (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2017).
The N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) was translated, and its psychometric properties were tested with 545 Vietnamese nurses. The results showed that the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) has acceptable reliability (Cronbach's alpha) and validity (content and construct validity). Particularly, the overall Cronbach's alpha was 0.98, with that of the four dimensions ranging from 0.86–0.97. The ICC was 0.81 over two weeks. The item content validity index was 1.0. Moreover, the goodness‐of‐fit indexes in a confirmatory factor analysis showed acceptable values, which were χ 2 / df = 2.87, root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.059, standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) = 0.063, comparative fit index (CFI) = 0.73 and Tucker Lewis index (TLI) = 0.72 (T. V. Nguyen & Liu, 2021 ). Therefore, the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) can be used to measure the critical thinking ability of Vietnamese professional nurses.
3.4. Ethical considerations
This study conformed with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (Helsinki Declaration, 2013 ), and it was granted research ethics committee approval by the ethical review board of the first author's institution.
3.5. Data analysis
The data were analysed using SPSS for Windows version 23.0 (IBM Corp.), and both descriptive and inferential statistics were calculated. The level of significance for all analyses was set at < 0.05. First, descriptive statistics were employed to summarize the collected data. The continuous variables were described using the mean and standard deviation ( SD ), and the frequency and percentage (%) were used for the categorical variables. Next, independent Student's t tests, analysis of variance (with Scheffe's post hoc comparison) and Pearson's correlation analysis were conducted to explore the association between the critical thinking ability and the personal and occupational factors. Then, a multiple regression analysis using the stepwise method was performed to identify the predictors of critical thinking ability (Pallant, 2010 ).
4.1. Characteristics of the participants
A total of 420 participants completed the questionnaires; the characteristics of overall participants and subjects in each group are listed in Table 1 . Three groups of subjects were included, which were NMs (24.8%), GNs (49.8%) and AAs (25.4%), respectively. Regarding the personal variables, almost all participants were Vietnamese (96.7%), no religion (73.1%) and had good health condition (60%). Meanwhile, the comparison among each group showed that age ( F = 9.89, p < .001), gender (χ 2 = 6.48, p < .05), marital status (χ 2 = 6.77, p < .05) and education level (χ 2 = 147.38, p < .001) had reached the statistical significance. Further analysis showed that the age of NMs was significantly older than subjects in both the GN and AA group, AA group had a higher ratio of that in the GN group, and the AA group had a higher ratio of married one than the GN group. For educational levels, subjects in the NM group had a higher ratio of bachelor and master degree, whereas the other two groups had a high ratio of diploma and associate degree.
Characteristics of the participants ( n = 420)
| Variables | Totals | Comparisons among work position | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM ( = 104) | GN ( = 209) | AA ( = 107) | χ | (1) NM | (2) GN | (3) AA | ‐test | Scheffe's post hoc | |||
| (%) | Mean ± | (%) | Mean ± | ||||||||
| Personal variables | |||||||||||
| Age (years) | 32.54 ± 7.32 | 35.22 ± 7.08 | 31.46 ± 7.0 | 32.05 ± 7.56 | 9.89 | (1) > (2), (3) | |||||
| Gender | |||||||||||
| Male | 105 (25) | 28 (26.9) | 60 (28.7) | 17 (15.9) | 6.48 | ||||||
| Female | 315 (75) | 76 (73.1) | 149 (71.3) | 90 (84.1) | |||||||
| Marital status | |||||||||||
| Single/divorced/widowed | 169 (40.2) | 34 (32.7) | 97 (46.4) | 38 (35.5) | 6.77 | ||||||
| Married | 251 (59.8) | 70 (67.3) | 112 (53.6) | 69 (64.5) | |||||||
| Ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Vietnamese | 406 (96.7) | 101 (97.1) | 205 (98.1) | 100 (93.5) | 4.79 | ||||||
| Other | 14 (3.3) | 3 (2.9) | 4 (1.9) | 7 (6.5) | |||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||
| No | 307 (73.1) | 82 (78.8) | 149 (71.3) | 76 (71) | 2.33 | ||||||
| Yes | 113 (26.9) | 22 (21.2) | 60 (28.7) | 31 (29) | |||||||
| Education level | |||||||||||
| Diploma | 126 (30.0) | 3 (2.9) | 90 (43.1) | 33 (30.8) | 147.38 | ||||||
| Associate | 123 (29.3) | 8 (7.7) | 64 (30.6) | 51 (47.7) | |||||||
| Bachelor's/graduate | 171 (40.7) | 93 (89.4) | 55 (26.3) | 23 (21.5) | |||||||
| Self‐rated health condition | |||||||||||
| Very good | 51 (12.1) | 9 (8.7) | 27 (12.9) | 15 (14) | 6.63 | ||||||
| Good | 252 (60.0) | 71 (68.3) | 126 (60.3) | 55 (51.4) | |||||||
| Fair/bad/very bad | 117 (27.9) | 24 (23.1) | 56 (26.8) | 37 (34.6) | |||||||
| Work‐related factors | |||||||||||
| Duration of working as a nurse (years) | 9.30 ± 7.05 | 12.30 ± 7.12 | 8.08 ± 6.42 | 8.75 ± 7.20 | 13.08 | (1) > (2), (3) | |||||
| Duration of working in the current hospital (years) | 8.81 ± 6.85 | 11.66 ± 7.02 | 7.66 ± 6.33 | 8.29 ± 6.93 | 12.98 | (1) > (2), (3) | |||||
| Duration of working in the specific position (years) | 6.10 ± 5.46 | 5.06 ± 4.94 | 7.41 ± 6.21 | 4.05 ± 3.27 | 14.79 | (2) > (1) > (3) | |||||
| Heard the term "CT" | |||||||||||
| No | 280 (66.7) | 56 (53.8) | 151 (72.2) | 73 (68.2) | 10.74 | ||||||
| Yes | 140 (33.7) | 48 (46.2) | 58 (27.8) | 34 (31.8) | |||||||
| Previous exposure to CT training/education | |||||||||||
| No | 420 (100) | 104 (100) | 209 (100) | 107 (100) | |||||||
Abbreviations: AA, Administrator assistant; CT , Critical thinking; GN, General nurse; NM, Nurses manager ; SD , standard deviation.
Chi‐square and one‐way ANOVA test; significant at * p < .05; ** p < .01; *** p < .001.
Regarding work‐related factors, the characters of all participants and subjects in each group are also listed in Table 1 . The comparison of professional experience, such as duration of working as a nurse, duration of working in the current hospital, duration of working in this specific position and heard the terminology of "critical thinking" showed a significant statistical difference among the three groups ( p < .001). They showed that NMs had a longer duration of working as a nurse (mean = 12.30, SD = 7.12) and duration of working in the current hospital (mean = 11.6, SD = 7.02) than the other two groups; GNs had the longest duration of working in the specific position (mean = 7.41, SD = 6.21). More subjects in the NM group heard the terminology of "critical thinking" than subjects in the other two groups. However, none of the subjects had been exposed to critical thinking training or education. Furthermore, there was a positive correlation among age, the duration of working as a nurse, the duration of working in the current hospital and duration of working in a specific position ( r = .78–.975, p < .01).
4.2. Level of the critical thinking of the professional nurses
The mean of the total scores of the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) for all participants was 333.86 ± 40.22 (with the average score/item = 3.06 ± 0.37), the median score was 331 (interquartile range [IQR] = 311–359), and it ranged from 204–436, which indicates that they generally had a moderate level of critical thinking. Meanwhile, most of the participants reported a low (48.3%) or moderate (45.5%) level of critical thinking. Only 6.2% of the participants had a high level of critical thinking. Regarding the four dimensions of the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v), the average sum score was 119.52 ± 14.19 (with the average score/item = 3.06 ± 0.36) in the personal dimension, 136.38 ± 17.62 (with the average score/item = 3.10 ± 0.40) in the intellectual and cognitive dimension, 68.71 ± 12.65 (with the average score/item = 3.44 ± 0.63) in the interpersonal and self‐management dimension and 18.09 ± 3.01 (with the average score/item = 3.01 ± 0.50) in the technical dimension.
4.3. Work‐related and personal‐related factors associated with critical thinking ability
There were statistically significant associations between the critical thinking ability and some work‐related factors, such as work position ( F = 23.30, p < .001), duration of working as a nurse ( r = 0.15, p < .01), duration of working in the current hospital ( r = 0.13, p < .05) and having heard the term "critical thinking" ( t = −2.48, p < .05; Table 2 ). The findings indicated that NMs had higher scores than GNs and AAs. Moreover, nurses who had worked for a longer duration as a nurse or worked longer in the current hospital had a higher critical thinking ability. Meanwhile, those who had not heard the term "critical thinking" had lower scores than participants who had heard this term.
Association between the participants’ characteristics and the critical thinking ability ( n = 420)
| Variables | Mean ± | a/b/ ‐value | ‐value | Scheffe's comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal factors | ||||
| Age | 0.12 | . | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 341.70 ± 37.29 | 2.32 | . | |
| Female | 331.24 ± 40.88 | |||
| Marital status | ||||
| Single/divorced/widowed | 331.24 ± 40.49 | −1.09 | .275 | |
| Married | 335.62 ± 40.03 | |||
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Vietnamese | 334.57 ± 39.57 | 1.97 | . | |
| Other | 313.07 ± 53.73 | |||
| Religion | ||||
| No | 334.63 ± 39.39 | 0.65 | .516 | |
| Yes | 331.75 ± 42.51 | |||
| Education level | ||||
| (1) Diploma | 327.84 ± 38.20 | 7.45 | . | 3 > 1, 2 |
| (2) Associate | 327.50 ± 39.25 | |||
| (3) Bachelor's/graduate | 342.86 ± 40.80 | |||
| Self‐rated health condition | ||||
| (1) Very good | 343.94 ± 37.25 | 3.41 | . | 1 > 3 |
| (2) Good | 334.97 ± 39.47 | |||
| (3) Fair/bad/very bad | 327.06 ± 42.19 | |||
| Occupational factors | ||||
| Duration of working as a nurse | 0.15 | . | ||
| Duration of working in the current hospital | 0.13 | . | ||
| Duration of working in the specific position | 0.07 | .184 | ||
| Heard the term “critical thinking” | ||||
| No | 330.44 ± 39.68 | −2.48 | . | |
| Yes | 340.69 ± 40.56 | |||
| Work position | ||||
| (1) Nurse manager | 355.49 ± 38.53 | 23.30 | 1 > 2, 3 | |
| (2) General nurse | 329.11 ± 32.79 | |||
| (3) Administrative assistant | 322.11 ± 46.89 | |||
The bolded values indicate the level of statistical significance (with p < .05; p < .01; or p < .001) between the independent and dependent variables.
Abbreviations: SD , standard deviation.
There were statistically significant associations between the critical thinking ability and some personal‐related factors, such as age ( r = 0.12, p < .05), gender ( t = 2.32, p < .05), ethnicity ( t = 1.97, p < .05), education level ( F = 7.45, p < .01) and health condition ( F = 3.14, p < .05; Table 2 ). The findings indicated that the older nurses reported a higher critical thinking ability, and male nurses had a higher score than female ones. Vietnamese participants had higher scores than participants with other ethnicities. Participants with a bachelor's/graduate degree level of education had higher scores than participants with a diploma and associate degree level of education. Those with very good health had a higher score than participants who rated their health as fair/bad/very bad.
All of the statistically significant variables identified in the univariate analysis were selected as independent variables to determine the predictors of critical thinking ability. For the regression analysis, the categorical variables were first coded as dummy variables. The factors of having never heard of “critical thinking,” being an NM being male, being Vietnamese, having a diploma degree and being in very good health were selected as the standard factors. The results of the stepwise multiple regression method showed that there were only two predictors, namely the variables of work position and gender. Working as an AA or GN or being female can predict the critical thinking ability, and they accounted for 11% of the total variance ( F = 17.12, p < .001). This indicates that the AAs and GNs had a lower level of critical thinking than the NMs. Besides, when compared with male nurses, the female nurses exhibited a lower level of critical thinking (Table 3 ).
Predictors of the critical thinking ability ( n = 420)
| Model | Beta | ‐value | square | ‐value | ‐value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 362.11 | 0.11 | 17.12 | |||
| Administrative assistant | −32.38 | −0.351 | ||||
| General nurse | −26.55 | −0.330 | ||||
| Female | −9.05 | −0.098 | . |
5. DISCUSSION
This study showed that the critical thinking ability of most professional nurses was at a low or moderate level. This finding is consistent with previous studies (Chang et al., 2011 ; Lang et al., 2013 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). Using the same tool, Zuriguel‐Pérez et al. ( 2018 ) found that the median score of the N‐CT‐4 Practice was 363 (IQR = 340–386) for clinical nurses in Spain. Our study found a slightly lower median score (331; IQR = 311–359) but it was still in a moderate level (range of score: 329–395). Although critical thinking is a relatively new issue in Vietnamese professional nurses, it is not a brand new concept. Certain elements have been included in the nursing curriculum and clinical practice (e.g. the nursing process, problem‐based learning, evidence‐based practice). Therefore, up to 66.7% of participants had never heard the term "critical thinking," but 45.5% still reported a moderate level when measured using the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v).
In Vietnam, clinical professional nurses are categorized into NMs, GNs and AAs with different job descriptions. Critical thinking ability has been identified as an important component for the high quality of care around the world, except in Vietnam. In order to identify this ability, we collected data from 3 hospitals in one region and grouped these data for analysis. Based on the comparison among NMs, GNs and AAs, it was found that NMs had a higher level of critical thinking than GNs and AAs. This can be explained by the fact that NMs have a higher age, work experience and high educational qualification than the other two groups. This result partially supports the finding that NMs report a slightly higher level of critical thinking than RNs (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). Critical thinking is a necessary skill for effective and efficient management. Evidently, at present, NMs with a high level of critical thinking create positive practice environments that can help the staff nurses to deliver high quality and safe patient care (Zori et al., 2010 ). Therefore, all healthcare personnel needs to learn and apply critical thinking in order to conduct their work effectively and efficiently.
For clinical nurses, continuous in‐service education is very important to update their knowledge and skill of care. Literature found various factors associated with curriculum design and learning of critical thinking ability. Therefore, grouping subjects in the present study together in order to identify the related factors could help the development of further in‐service education of critical thinking ability effectively and efficiently. In this study, a statistically significant positive correlation was found between the critical thinking ability and age, the duration of working as a nurse and the duration of working in the current hospital. These findings are consistent with previous studies. For example, older nurses have a higher level of critical thinking than younger ones (Chang et al., 2011 ; Chen et al., 2019 ; Feng et al., 2010 ; Ludin, 2018 ; Wangensteen et al., 2010 ; Yurdanur, 2016 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ), and nurses with more experience report a better critical thinking ability than those with less experience (Chang et al., 2011 ; Chen et al., 2019 ; Feng et al., 2010 ; Ludin, 2018 ). Older and experienced nurses are more mature in their way of thinking (Chen et al., 2019 ; Ludin, 2018 ). Because there were statistically significant positive correlations among age, the duration of working as a nurse and the duration of working in the current hospital. This indicates that older nurses have a longer duration of working as a nurse or working in the current hospital so they have better critical thinking. However, the correlation between these factors and critical thinking in the current study is small; further explorations are suggested.
This study showed that there is a significant association between critical thinking ability and gender and ethnicity, which is also supported by the literature. Ludin ( 2018 ) found that female nurses reported a lower critical thinking ability than male nurses. Traditionally, females have generally had fewer opportunities to receive education and more difficulty asserting their rights during decision‐making than males in Vietnam (L. T. Nguyen et al., 2017 ). Even today, the phenomenon of gender inequality still exists in certain areas in Vietnam. This traditional burden and the limited opportunities to practice in a clinical care setting might lower the levels of the female participants’ critical thinking. Ethnicity has a similar impact, as found in the present study. For example, it has been reported that Caucasian and Hispanic/Latino participants have a significantly higher critical thinking ability than African American participants (Lang et al., 2013 ) and that Malaysian and Indian participants report different levels of critical thinking; nevertheless, only 0.9% of the participants were Indian (Ludin, 2018 ). However, in the present study, as almost all of the participants were Vietnamese (96.7%), the skewed distribution of the ethnicity might limit the generalizability of the results. In future studies, an equal distribution of ethnicity is strongly recommended.
This study also confirmed that those who had a bachelor's/graduate degree had a higher level of critical thinking than those who had a diploma or associate degree, even though the former had never heard the term "critical thinking." A vast amount of studies has found that education has a positive impact on the level of critical thinking (Chang et al., 2011 ; Gloudemans et al., 2013 ; Ludin, 2018 ; Yildirim et al., 2012 ; Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2018 ). Meanwhile, this study found that participants who had heard the term "critical thinking" displayed a higher level of critical thinking than those who had not heard this term. Education might be the major reason for this variation. In the present study, only 40.7% of participants had a bachelor's/graduate degree. In order to promote their levels of critical thinking, it is necessary to arrange for them, to encourage them, to attend advanced education or to provide further content in the in‐service education.
In this study, participants with very good health had a higher level of critical thinking than participants who self‐rated their health as fair/bad/very bad. Health status does have an impact on work productivity, job performance, quality of care and extra learning (Letvak et al., 2011 ). Thus, poor health limits their learning and critical thinking ability. This ability is an important predictor of real‐life outcomes (e.g. interpersonal, work, financial, health and education) (Butler et al., 2017 ). Therefore, the causal effects between health and critical thinking ability need further exploration.
In the current study, only the female gender and the type of work position as an AA or GN were identified as predictors, and they explained only 11% of the total variance of critical thinking ability in the regression model. The uneven distribution of gender and work position might be the reason for the low variance. Even though the male was significantly less than the female, NM was fewer than GN and AA. More factors need to be included in further studies.
The limitations of this study include that it used a convenience sample from only three public hospitals located in the Southwestern part of Vietnam. This sample does not represent all professional nurses in Vietnam. The N‐CT‐4 Practice is the instrument with good psychometric properties specific for clinical practice and translated into English (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2017), Persian (FallahNezhad & Ziaeirad, 2018 ) and Turkish (Urhan & Seren, 2019 ). Different points of the Likert response format were selected by tools to measure critical thinking ability. For example, the N‐CT‐4 Practice selected a four‐point Likert response and it was rated in frequency, such as 1 = never or almost never and 4 = always or almost always. However, a seven‐point Likert scale for the Critical Thinking Disposition Assessment (CTDA) was selected and rated in levels of agreement, such as 1 for very strongly disagree and 7 for very strongly agree (Cui et al., 2021 ). Which response format can be more reprinting the characters of critical thinking ability? Further investigation is strongly suggested. Besides, the N‐CT‐4 Practice (V‐v) questionnaire has too many items that may lead to the boredom of the participants to answer and thus affect the accuracy of the results. Moreover, the collapsing of three distinctly separate groups of nurses into one group for most of the analyses lead to not showing differences in critical thinking and influencing factors among the three groups. These factors all limit the generalization of the present results. Based on these limitations, it is suggested that the use of nationwide systematic sampling and an international comparison are strongly suggested in further studies. Regarding the critical thinking questionnaire, it would be better to use the revised versions with fewer questions. Therefore, developmental and psychometric properties are suggested to shorten this questionnaire.
6. CONCLUSIONS
The results demonstrate that most of the professional nurses had a low or moderate critical thinking ability. Certain personal and occupational variables were significantly associated with the level of critical thinking. Being male or working as an NM were statistically significant predictors of critical thinking ability, and they explained only 11% of the total variance.
The findings of this study indicate that it is necessary to develop strategies to improve the critical thinking ability of professional nurses. The critical thinking ability has been confirmed to be an essential factor for high‐quality health care that focuses on the quality of patient care and patient safety. Besides, providing more opportunities to pursue advanced degrees or enhancing the provision of in‐service education in hospitals that involves classroom teaching or web‐based learning is strongly recommended for this specific group of nurses. Consequently, the quality of patient care could be improved.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the expert panel, translators, research assistants, the hospitals and all of the clinical nurses who participated in this study. We are indebted to the study participants and would like to dedicate the research findings to improving the critical thinking ability of Vietnamese professional nurses in the future. No specific grant was received from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not‐for‐profit sectors.
Van Nguyen T, Liu H‐E. Factors associated with the critical thinking ability of professional nurses: A cross‐sectional study . Nurs Open . 2021; 8 :1970–1980. 10.1002/nop2.875 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
- Berkow, S. , Virkstis, K. , Stewart, J. , Aronson, S. , & Donohue, M. (2011). Assessing individual frontline nurse critical thinking . Journal of Nursing Administration , 41 ( 4 ), 168–171. 10.1097/NNA.0b013e3182118528 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brunt, B. A. (2005). Critical thinking in nursing: An integrated review . The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing , 36 ( 2 ), 60–67. 10.3928/0022-0124-20050301-05 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buerhaus, P. I. , Donelan, K. , Ulrich, B. T. , Norman, L. , & Dittus, R. (2006). State of the registered nurse workforce in the United States . Nursing Economics , 24 ( 1 ), 6. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Butler, H. A. , Pentoney, C. , & Bong, M. P. (2017). Predicting real‐world outcomes: Critical thinking ability is a better predictor of life decisions than intelligence . Thinking Skills and Creativity , 25 , 38–46. 10.1016/j.tsc.2017.06.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang, M. J. , Chang, Y. J. , Kuo, S. H. , Yang, Y. H. , & Chou, F. H. (2011). Relationships between critical thinking ability and nursing competence in clinical nurses . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 20 ( 21–22 ), 3224–3232. 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03593.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen, F.‐F. , Chen, S.‐Y. , & Pai, H.‐C. (2019). Self‐reflection and critical thinking: The influence of professional qualifications on registered nurses . Contemporary Nurse , 55 ( 1 ), 59–70. 10.1080/10376178.2019.1590154 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cui, L. , Zhu, Y. , Qu, J. , Tie, L. , Wang, Z. , & Qu, B. (2021). Psychometric properties of the critical thinking disposition assessment test amongst medical students in China: A cross‐sectional study . BMC Medical Education , 21 ( 1 ), 1–8. 10.1186/s12909-020-02437-2 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Helsinki Declaration (2013). Ethical principels for medical research involving human subject . Helsinki Declaration. [ Google Scholar ]
- FallahNezhad, Z. , & Ziaeirad, M. (2018). The relationship between the quality of working life and critical thinking of nurses in Milad Hospital of Isfahan, Iran . Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal , 8 ( 3 ), 62–68. 10.29252/pcnm.8.3.62 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feng, R. C. , Chen, M. J. , Chen, M. C. , & Pai, Y. C. (2010). Critical thinking competence and disposition of clinical nurses in a medical center . Journal of Nursing Research , 18 ( 2 ), 77–87. 10.1097/JNR.0b013e3181dda6f6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fero, L. J. , Witsberger, C. M. , Wesmiller, S. W. , Zullo, T. G. , & Hoffman, L. A. (2009). Critical thinking ability of new graduate and experienced nurses . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 65 ( 1 ), 139–148. 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2008.04834.x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fesler‐Birch, D. M. (2005). Critical thinking and patient outcomes: A review . Nursing Outlook , 53 ( 2 ), 59–65. 10.1016/j.outlook.2004.11.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gloudemans, H. A. , Schalk, R. M. , & Reynaert, W. (2013). The relationship between critical thinking skills and self‐efficacy beliefs in mental health nurses . Nurse Education Today , 33 ( 3 ), 275–280. 10.1016/j.nedt.2012.05.006 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Howenstein, M. A. , Bilodeau, K. , Brogna, M. J. , & Good, G. (1996). Factors associated with critical thinking among nurses . The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing , 27 ( 3 ), 100–103. 10.3928/0022-0124-19960501-04 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lang, G. M. , Beach, N. L. , Patrician, P. A. , & Martin, C. (2013). A cross‐sectional study examining factors related to critical thinking in nursing . Journal for Nurses in Professional Development , 29 ( 1 ), 8–15. 10.1097/NND.0b013e31827d08c8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee, D. S. , Abdullah, K. L. , Subramanian, P. , Bachmann, R. T. , & Ong, S. L. (2017). An integrated review of the correlation between critical thinking ability and clinical decision‐making in nursing . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 26 ( 23–24 ), 4065–4079. 10.1111/jocn.13901 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Letvak, S. , Ruhm, C. , & Lane, S. (2011). The impact of nurses' health on productivity and quality of care . JONA. The Journal of Nursing Administration , 41 ( 4 ), 162–167. 10.1097/NNA.0b013e3182118516 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu, N.‐Y. , Hsu, W.‐Y. , Hung, C.‐A. , Wu, P.‐L. , & Pai, H.‐C. (2019). The effect of gender role orientation on student nurses’ caring behaviour and critical thinking . International Journal of Nursing Studies , 89 , 18–23. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.09.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Locke, R. , Leach, C. , Kitsell, F. , & Griffith, J. (2011). The impact on the workload of the ward manager with the introduction of administrative assistants . Journal of Nursing Management , 19 ( 2 ), 177–185. 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2011.01229.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ludin, S. M. (2018). Does good critical thinking equal effective decision‐making among critical care nurses? A cross‐sectional survey . Intensive & Critical Care Nursing , 44 , 1–10. 10.1016/j.iccn.2017.06.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahmoud, A. S. , & Mohamed, H. A. (2017). Critical thinking disposition among nurses working in puplic hospitals at port‐said governorate . International Journal of Nursing Sciences , 4 ( 2 ), 128–134. 10.1016/j.ijnss.2017.02.006 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ministry of Health (1997). Decision No. 1895/1997/QĐ‐BYT of the ministry of health on the promulgation of Hospital Regulations . Retrieved from http://vbpl.yte.gov.vn/van‐ban‐phap‐luat/quyet‐dinh‐18951997qd‐byt‐.1.2286.html
- Ministry of Health (2011). Circular No. 07/2011/TT‐BYT dated 26/01/2011 of the Ministry of Health on guiding on patient care in hospitals . Retrieved from https://kcb.vn/wp‐content/uploads/2015/07/TT‐07.2011.TT‐BYT‐ngay‐26.01.2011.pdf .
- Nguyen, L. T. , Annoussamy, L. C. , & LeBaron, V. T. (2017). Challenges Encountered by Vietnamese Nurses When Caring for Patients With Cancer . Paper presented at the Oncology nursing forum. [ PubMed ]
- Nguyen, T. V. , & Liu, H. E. (2021). The Vietnamese version of the nursing critical thinking in clinical practice questionnaire: Translation and psychometric evaluation . Nursing Open , 1–8. 10.1002/nop2.834 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pallant, J. (2010). SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using SPSS . Maidenhead. Open University Press/McGraw‐Hill. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, C. , & Tatum, K. (2012). Objective measurement of critical‐thinking ability in registered nurse applicants . Journal of Nursing Administration , 42 ( 2 ), 89–94. 10.1097/NNA.0b013e318243360b [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suresh, K. , & Chandrashekara, S. (2012). Sample size estimation and power analysis for clinical research studies . Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences , 5 ( 1 ), 7. 10.4103/0974-1208.97779 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ] Retracted
- Urhan, E. , & Seren, A. K. H. (2019). Validity and reliability of Turkish version of the nursing critical thinking in clinical practice questionnaire . University of Health Sciences Journal of Nursing , 1 ( 3 ), 147–156. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Dyk, J. , Siedlecki, S. L. , & Fitzpatrick, J. J. (2016). Frontline nurse managers' confidence and self‐efficacy . Journal of Nursing Management , 24 ( 4 ), 533–539. 10.1111/jonm.12355 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Von Elm, E. , Altman, D. G. , Egger, M. , Pocock, S. J. , Gøtzsche, P. C. , Vandenbroucke, J. P. , & Initiative, S. (2014). The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies . International Journal of Surgery , 12 ( 12 ), 1495–1499. 10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wangensteen, S. , Johansson, I. S. , Bjorkstrom, M. E. , & Nordstrom, G. (2010). Critical thinking dispositions among newly graduated nurses . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 66 ( 10 ), 2170–2181. 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05282.x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong, C. A. (2015). Connecting nursing leadership and patient outcomes: State of the science . Journal of Nursing Management , 23 ( 3 ), 275–278. 10.1111/jonm.12307 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yildirim, B. , Özkahraman, Ş. , & Ersoy, S. (2012). Investigation of critical thinking disposition in nurses working in public hospitals . International Journal of Business, Humanities and Technology , 2 , 61–67. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yurdanur, D. (2016). Critical Thinking Competence and Dispositions among Critical Care Nurses: A Descriptive Study . International Journal , 9 ( 2 ), 489. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zori, S. , Nosek, L. J. , & Musil, C. M. (2010). Critical thinking of nurse managers related to staff RNs’ perceptions of the practice environment . Journal of Nursing Scholarship , 42 ( 3 ), 305–313. 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2010.01354.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuriguel‐Pérez, E. , Falcó‐Pegueroles, A. , Roldán‐Merino, J. , Agustino‐Rodriguez, S. , Gómez‐Martín, M. C. , & Lluch‐Canut, M. T. (2017). Development and psychometric properties of the nursing critical thinking in clinical practice questionnaire . Worldviews on Evidence‐Based Nursing , 14 ( 4 ), 257–264. 10.1111/wvn.12220 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuriguel‐Pérez, E. , Lluch Canut, M. T. , Falcó Pegueroles, A. , Puig Llobet, M. , Moreno Arroyo, C. , & Roldán Merino, J. (2015). Critical thinking in nursing: Scoping review of the literature . International Journal of Nursing Practice , 21 ( 6 ), 820–830. 10.1111/ijn.12347 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zuriguel‐Pérez, E. , Lluch‐Canut, M. T. , Agustino‐Rodríguez, S. , Gómez‐Martín, M. D. C. , Roldán‐Merino, J. , & Falcó‐Pegueroles, A. (2018). Critical thinking: A comparative analysis between nurse managers and registered nurses . Journal of Nursing Management , 26 ( 8 ), 1083–1090. 10.1111/jonm.12640 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

ANA Nursing Resources Hub
Search Resources Hub

What Are the Qualities of a Good Nurse?
4 min read • June, 08 2023
If you're considering a career in nursing and have wondered what the qualities of a good nurse are, you're probably already displaying some of these essential nursing characteristics. Whether you're entering the nursing field or are a seasoned nurse, taking the time to understand nursing strengths demonstrates insight and a desire for ongoing self-improvement.
You might assume those entering the nursing field must have the qualities of a good nurse, but that's not always the case. Some nurses pursue a career in this profession because it's lucrative and offers many growth opportunities. They then end up dissatisfied with their career choice or suffer from burnout when they realize they don't possess the characteristics needed to succeed in nursing.
What Makes a Good Nurse?
There are many ways to define a good nurse. In general, it means bringing your best qualities to work to promote positive patient outcomes and striving to strengthen the nursing profession. While working as an essential member of a health care team, you seek solutions to improve patient care and advocacy. And certain personality traits and characteristics of a nurse go a long way in helping you succeed in the nursing profession.
Essential Qualities of a Nurse
- Communication skills: Excellent verbal and written communication skills are crucial areas of strength for nurses. Practicing active listening and being aware of nonverbal cues help you understand how communication approaches may differ. Clear communication and cultural awareness reduce miscommunication and medical errors and enable patients to make informed decisions about their care.
- Empathy and compassion: Although these characteristics often go hand and hand and are both qualities of a good nurse, they aren't the same. Empathy allows you to have a patient-centered approach to caregiving by relating to what they're experiencing. Compassion fuels your desire to help ease the pain and suffering of others. These two skills contribute to inspiring trust in your patient relationships.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving skills: Nurses often work autonomously under pressure and must make decisions using critical thinking to put their knowledge into practice. A solid analytical skill set lets you collect information, evaluate the facts, and develop a rational conclusion to improve patient outcomes.
- Attention to detail: Mistakes in nursing can have severe consequences, and caring for multiple patients increases the risk of human error. That could cause you to miss changes in a patient's condition if you don't understand the importance of minor details. Excellent time management skills and the ability to balance competing priorities can help you hone this skill.
- Integrity and advocacy: Core nursing strengths include a strong moral compass while providing care with integrity, and a strong focus on patient advocacy . Patients are often vulnerable and trust nurses to be honest and make decisions with their best interests in mind.
- Willingness to learn: Health care is constantly changing, so you must be willing to continue to improve and expand upon your nursing qualifications and skills. Take advantage of education and in-services offered by your employer, review and implement evidence-based nursing practice , participate in nurse mentorship programs , join nursing associations , and pursue continuing education . These are all effective ways to stay current in nursing practice and continue to thrive.
Other sought-after personality traits of a nurse include:
- Being even-tempered, hardworking, and flexible
- Displaying a sense of humor
- Practicing self-care
- Demonstrating leadership skills
How to Develop the Qualities of a Good Nurse

Reviewing the qualities of a good nurse and nurturing those virtues within your nursing practice can help you provide effective care that contributes to your professional growth.
If you want more clarification about the primary goals and values of the nursing profession, the American Nurses Association (ANA) Code of Ethics for Nurses with Interpretive Statements is an excellent resource regarding ethical principles.
Additional ways to nurture strong qualities include:
- Working with a nurse mentor
- Surrounding yourself with nurses who hold the qualities you wish to develop
- Accept and learn from constructive criticism regarding your professional practice
- Pursue continuing education
- Work as a team with your peers to help strengthen the nursing profession
- Practice how to identify and address issues affecting patient and staff safety
Would I Be a Good Nurse?
If you’re a student nurse or considering a career in nursing , understanding the desired characteristics of a nurse can help you determine how to be a good nurse. It also allows the seasoned nurse to assess their own nursing strengths and weaknesses. Health care organizations look for these traits when seeking quality nurses. Regardless of your level of experience, cultivate the positive qualities of a good nurse to get recognized by prospective employers.
Images sourced from Getty Images
Related Resources

Item(s) added to cart
- Oak Brook: (630) 705-9999
- Chicago: (312) 920-8822
- Email: [email protected]
- Make a Payment

- Mission & Vision
- Approvals & Accreditation
- Recognition
- Maps & Directions
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Hours of Operation
- NCLEX PN Passing Rate
- Practical Nursing Program
- Online Hybrid Practical Nursing (PN) Program
- Anatomy and Physiology Course Prep at Verve College
- Apply Online
- Practical Nursing Admission Requirement
- Online Hybrid Admission Requirement
- Transfer Policy
- Entrance Exam Review
- PN Entrance Exam
- Foreign Credits
- Tuition and Fees
- Information Sessions
- Physical Examination Form
- Book a Tour
- ATI Entrance Exam Resources
- New E-Digital Library
- Refer a Friend
- School Newsletter
- Job-Network
- Alpha Beta Kappa Candidates
- Verve College Library
- Graduation and Pinning Ceremony Photo Galleries
- Textbook Information
- Career Services
- School Catalog
- Constitution Day Program
- Verve College Plans
- HEERF Reporting
- Satisfactory Academic Progress
- Apply For Financial Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Return of Title IV Funds (R2T4)
- Financial Aid Office Code of Conduct
- Verification Policy
- Vaccination Policy
- Student Right-to-Know Act
- Misrepresentation
- Information Security Program
- Academic Award Year
- Availability of Employee
- Cost of Attendance
- Health & Safety Exemption Requirement
- Students Rights and Responsibilities
- Leave of Absence
- Pell Formula
- Military Students
- Grants/ Scholarship Policy
- Get Started
- Ask a Question
- Suggestion Box
- Transcript Request
- Oak Brook Student Portal
- Chicago Student Portal
- Testimonials
Is a Nursing Career Right For You?

5 Essential Critical Thinking Skills for Nursing Success & Their Importance
It would help if you learned how to think like a nursing professional nurse. What distinguishes the skills and thinking of a nurse from those of a dentist, doctor, or engineer? The difference is in how nurses approach patient safety, how they view them, and what problems they can solve. Professional & experienced nurses must learn about nursing theories, concepts, and ideas and build their intellectual capacity and communication skills to become self-directed and disciplined critical thinkers. To succeed, healthcare providers must have other innate or acquired clinical skills. Let’s compile what are the 5 critical thinking skills in nursing.
What Are the 5 Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing?
1. critical thinking as a nursing skill.
The ability to think critically is to identify problems, ask questions, collect evidence to support solutions and answers, evaluate alternatives, and effectively communicate with others to implement the best solutions. Critical thinking is essential in nursing. It helps practical nurses to learn how to prioritize and make good decisions. Nurses provide 24/7 nursing care to patients, so critical thinking skills are crucial.
2.Compassion is the Second Critical Nursing Skill
The nursing model demands that nurses give vital care to patients to make them as comfortable as patients can be, attend to their physical, mental, and spiritual needs, and support the patients’ families. The patient’s physical, emotional, and spiritual needs can be overwhelming.
3.The Third Critical Nursing Skill is Technology Proficiency
The technology continues to improve and is used in all aspects of nursing. Nurses use various technologies with every patient during each shift, including point-of-care computing, electronic health records, monitoring equipment, and more. The nurses use technologies such as vents (CCRT), IABPs, and others to help with patient care.
4.Flexible Nursing is the Fourth Critical Nursing Skill
Flexibility is one of the most valuable qualities that a critical care nurse can have. Nurses need to have the ability to adapt quickly and to proceed following changes. Nurses must be able to quickly change their assignments, provide assistance where necessary, and do what is needed to support their patients.
5. Accuracy is the Fifth Critical Nursing Skill
A vital assessment skill is a necessity in clinical settings. If a nurse cannot “diagnose” but can give a physician an accurate assessment, that is still valuable. Nurses must be able to filter out irrelevant and illogical information and provide accurate and factual data to other caregivers, patients, and their families. Critical thinking nurses must be able to express themselves clearly, both verbally and in writing, and explain their clinical reasoning in a variety of healthcare settings.
Related:- Patient Care Skills in LPN Classes: A Holistic Approach
Why is Critical Thinking Important in Nursing?
With Illinois College of Nursing accreditation , you can learn practical skills and evidence-based practice, such as how to dress a wound perfectly, take vitals without hesitation, or start an IV. You can learn all the practical skills you need in licensed practical nursing schools. Still, these skills will only get you far with the ability to think clearly and make rational decisions.
Critical skills are essential to the decision-making & critical-thinking process and impacting patient outcomes. Nursing necessary thinking skills are crucial to the decision-making and quality of care process.
In the emergency department, for example, nurses are often required to make triage decisions. They must decide which patients to treat first when there is a large number of patients. They rely on training to determine vital signs and consciousness levels. Still, they must also use critical thinking when analyzing the effects of delaying treatment.
Nurses use critical thinking in nursing every day, no matter their department. The ability to analyze and solve problems when faced with life-or-death decisions separates good clinical nurses from great ones.
Get Your Nursing Career Training Readiness Score Now!
Beyond Thinking
Now, you know why is critical thinking important in nursing, You can improve your critical thinking even if you use it every day. You will improve the more you practice in the nursing profession. Learn from prerequisite courses of licensed practical nursing schools & get a diploma in nursing.
Most Popular Blogs Posts

Some Work Conditions for LPN Nurses

How to Transfer Your Nursing License…

Pros and Cons of Nurse Sign-On…

Top 5 Strategies to Retain New…

Professional Boundaries: Understanding Your Limits as…

Solutions ∨
Learning and Performance → ∨
Mandatory Training Issue required courses and monitor compliance ∨
Continuing Education Offer clinicians training to meet license requirements ∨
Professional Development Engage staff and empower career growth ∨
Clinical Development Enhance skills with clinician-built content ∨
Certification Review Build knowledge and increase exam pass rates ∨
Competency Management Measure and evaluate knowledge, skills, and abilities ∨
Obstetrics Solution Reduce variation in care with data-driven learning ∨
Onboarding Solution Tailor nurse training and reduce turnover ∨
Recruiting and Staffing → ∨
Talent Acquisition Advertising Target your recruitment to our 3M+ nurse community ∨
Validated Assessments Gauge job fit with clinical, behavioral, situational assessments ∨
Nurse Job Board Post your nurse opportunities on Nurse.com ∨
Compliance Management → ∨
Compliance Software Meet requirements with easy to administer package ∨
View All Solutions → ∨
Who We Serve ∨
Who We Serve → ∨
Hospitals and Health Systems Large multisite systems, critical-access hospitals, staffing agencies ∨
Individual Healthcare Workers Physicians, nurses, clinicians, and allied health professionals ∨
Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Skilled nursing facilities, continuing care retirement communities and life plan communities, assisted living facilities, rehab therapy providers, and hospice agencies ∨
Behavioral and Community Health Behavioral health, intellectual and developmental disabilities, applied behavior analysis, community health centers, and children, youth, and family-serving organizations ∨
Home Health and Home Care Home health and home care agencies and organizations ∨
Government Organizations Federal, state, and local entities ∨
Case Studies ∨
PAM Health Supports Business Growth, Employee Engagement, and Better Patient Outcomes With Relias PAM Health utilized Relias to make post-acquisition employee onboarding easier and to influence positive patient outcomes through high-quality staff training and coaching. ∨
CSIG Depends on the Relias Platform Through Change and Growth Before 2020, Common Sail Investment Group (CSIG) conducted all its senior living staff training and education in person in different locations. ∨
Why Relias ∨
Why Relias → ∨
Technology Engage learners and ease burden for administrators ∨
Measurable Outcomes Improve workforce, organization, and patient results ∨
Services Reduce administrative burden with professional solutions ∨
Expert Content Trust Relias for quality, award-winning courses and tools ∨
Community Tap into clinician resources and peer support ∨
Resources → ∨
How Mental Health and Social Determinants Are Driving Maternal Mortality The CDC has uncovered another dimension affecting the already alarming problem of maternal mortality in the U.S… ∨
2023 DSP Survey Report The 2023 DSP Survey Report highlights feedback from 763 direct support professionals (DSPs) across the country on job satisfaction, supervision… ∨
Resources ∨
Resource Center → ∨
Blog Keep up with industry trends and insights ∨
Articles and Reports Review recently published thought leadership ∨
Success Stories Read about Relias clients improving outcomes ∨
Events Find Relias at an upcoming industry conference ∨
Webinars Register for upcoming key topic discussions ∨
Support Contact us for help with your account ∨
Podcast Explore conversations with healthcare experts ∨
Upcoming Event ∨
Wild on Wounds Conference 2024 Wild on Wounds (WOW) is the third largest wound care conference in the nation, focused on advancing our healthcare workforce with impactful hands-on wound care education built by and for clinicians. ∨
Contact Sales → ∨
About Relias → ∨
Careers View our open positions ∨
Media Review our latest news and make press inquiries ∨
Alliances and Partnerships Scan our industry connections and relationships ∨
Awards Check out our latest recognitions ∨
Diversity Learn more about Relias’ commitment to DEIB ∨
In the News → ∨
Relias Named to Top 10 of Top 100 Healthcare Tech Companies of 2023 Relias announced that it has been named number 10 among the Top 100 Healthcare Technology Companies of 2023 chosen by The Healthcare Technology Report. ∨
Login Portals ∨
Relias Learning ∨
Nurse.com ∨
Relias Academy ∨
Wound Care Education Institute ∨
Relias Media ∨
Need help logging in?

Essential Qualities and Characteristics of a Good Nurse
By Felicia Sadler, MJ, BSN, RN, CPHQ, LSSBB and Elizabeth Snively , on December 15, 2023
Registered nurses are more in demand than ever in terms of projected job growth, impact, and leadership. With the significant need for RNs nationally and globally, understanding the qualities of a good nurse is critical for hospitals and health systems aiming to attract and retain the best nursing talent.
As new nurses enter the workforce, identifying and encouraging specific nursing qualities helps healthcare organizations recognize strong candidates for hire and understand which of their current nurses would make great leaders. With well over five million RNs in the U.S., it’s helpful to consider the essential qualities of a good nurse that help them succeed in today’s fast-paced and everchanging healthcare landscape.
Qualities of a good nurse
1 – caring and compassion.
Many people assume that nurses enter the field because compassion is one of their leading qualities — but this nursing characteristic isn’t necessarily a given. Many who choose nursing prioritize the job security of nursing or see it as a career starting point while failing to consider whether they have the compassion needed to become a good nurse.
But as a nursing quality, compassion makes all the difference to patients. Nurses who show they truly care about their patients — and how well they perform their jobs — have a greater likelihood of advancing, making compassion a key indicator for nurse success.
2 – Excellent communication skills
Strong communication skills are an important nurse characteristic. Good nurses rely on the ability to effectively communicate with other nurses, physicians, and clinicians in other units and with patients and their families.
Without the ability to interpret and accurately convey critical information, medical errors are more likely to occur, patients may feel neglected or misinformed, and an entire unit could feel the impact. By prioritizing great communication skills, nurses provide safer care, which in turn benefits their patients, their units, and the entire hospital or health system — not to mention their own long-term careers.
3 – Empathy
With nurses caring for perhaps thousands of patients during their careers, it can be all too easy to become desensitized or forget what it was like to be a nonclinical person. A good nurse is one who shows empathy for every patient, making a true effort to put themselves in their patients’ shoes.
By practicing empathy, nurses are more likely to treat their patients as individuals, focusing on a person-centered care approach rather than strictly following routines and guidelines. When patients are fortunate enough to encounter this characteristic in a good nurse, it makes for a far better care experience and healing journey.
4 – Organization and attention to detail
Nurses are undoubtedly under immense pressure as they balance following orders from physicians with using their own knowledge, skills, and critical judgement to provide the highest quality patient care. Add to this caring for multiple patients simultaneously, and the possibility of making an error can seem almost inevitable.
A good nurse knows the stakes are high and that unlike most other industries, they’re responsible for peoples’ well-being and — more importantly — their lives. Being organized, accurate, and attentive to details are nursing traits that determine how successful they’ll be in their role.
5 – Problem-solving skills
While clinical training occurs throughout a nurse’s education, on-the-job training is the most effective way to develop a nurse’s problem-solving skills. Years of experience help hone this skill, but good nurses work to improve their problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving skills are essential to nursing, as nurses generally have the most one-on-one time with patients and are often responsible for making decisions about issues that arise with their care. Even seemingly small decisions can proactively improve outcomes — or conversely, cause major adverse impacts if incorrectly made.
6 – Stamina and endurance
The physical demand on nurses is perhaps one of the most underestimated aspects of their role. In one shift, a nurse lifts an average of 1.8 tons (roughly the weight of a hippo) by lifting and adjusting patients. Additionally, studies have found that nurses walk an average of four to five miles per shift .
In an average 12-hour shift, nurses exercise a unique balance of physical and emotional stamina that few other occupations encounter. This extremely important quality impacts nurses, their coworkers, and of course, patients. Having sufficient stamina and staying power are important qualities of a great nurse.
7 – Sense of humor and resilience
To derive satisfaction from such a mentally and physically exhausting role, nurses who can find time for a laugh are typically more successful. Because nurses encounter varying degrees of high-stress situations, taking the opportunity to enjoy the downtime and incorporate a lighthearted attitude can provide a sense of stress relief and ensure their well-being over the long term.
Having a good sense of humor also helps spread positivity to other nurses, patients, and their families. A good sense of humor is not only a characteristic of a nurse leader but reminds patients and their families that nurses are people too and ultimately increases their trust and openness to sharing feedback and concerns.
8 – Commitment to patient advocacy
The concept of advocacy is a core tenet of health care, from the Hippocratic oath to nearly every hospital’s mission statement in one phrasing or another — keep patients safe and deliver the highest quality of care. In other words, be an advocate for patients, with special attention to their overall safety.
As one of the leading qualities of a nurse, patient advocacy is a mindset that a good nurse must practice every day with every patient, throughout every stage of the care continuum. Many patients enter a hospital or healthcare setting feeling disoriented, confused, and unable to advocate for their own safety. A nurse who empowers patients through education and engagement will help them get the best care.
9 – Willingness to learn and grow
With constant technological improvements and breakthroughs in science, the healthcare industry and its workers must successfully adapt. Nurses’ willingness to develop themselves — and put their new knowledge into practice — is one of the leading traits of a good nurse.
Improvements in educational approaches such as interprofessional training and personalized learning can help foster successful learning environments, but a good nurse must possess flexibility and a willingness to learn for them to be truly beneficial. This important skill applies to nurses of all ages, throughout every stage of their career — from recent graduates to the highly experienced.
10 – Strong critical thinking
While having the willingness to learn is an important skill, putting that knowledge into successful practice requires the ability to think critically — especially in high-stress situations. A nurse with high-functioning critical thinking has one of the most important characteristics of a professional nurse.
After years of education and training, the ability to apply clinical guidelines and best practices on the floor depends on a nurse’s capacity for critical thinking, which is quickly noticed by leadership, other nurses, and ultimately, patients. While this skill can improve over time, it may come more readily to some nurses than others.
11 – Good time management
Balancing multiple patients, stressful care settings, and competing priorities is no small feat during a 12-hour shift. Having effective time management is a key personality trait for nursing, as is being able to concentrate on the most critical issues first — and not necessarily the most demanding patient or family.
Setting time aside for self-care is also a crucial component of time management. Neglecting to take a quick break or regroup during an especially intense shift won’t benefit anyone involved in the care process.
12 – Integrity and leadership
While most nurses approach their careers with patient care in mind, some will eventually transition into leadership roles . Unfortunately, it’s all too common for a promotion to happen without adequate training, development opportunities, or sufficient mentoring and support to achieve the level of professionalism and ethics that good leadership requires.
The ability to lead is a quality that continues to become more valuable in nursing and is not limited to individuals who are in leadership roles. Exercising leadership skills in any role or level shows that a nurse can serve as a model of integrity and effectiveness for others. Being a mentor in any capacity helps others become better nurses and benefits both the organization and the nursing profession itself.
13 – Experience
It’s important to note that as veteran nurses leave the healthcare field and begin retirement, they’re taking with them years of experience and knowledge that cannot be quickly replaced. As nursing leaders work to bring in new nurses, available candidates are predominantly new graduate nurses — a stark contrast to their predecessors in terms of experience and the many patient care skills and knowledge that can only come with time and practice.
By engaging with new nurses to instill an expectation of continuous learning — while creating a positive environment for them to learn from experienced nurses without fear of judgment — nursing leaders can set new nurses up for success, benefiting their careers, the organization, and most importantly — their patients.
14 – Cultural sensitivity and awareness
With today’s diverse patient populations, every nurse needs to understand the importance of being culturally inclusive of others. Communication, customs, and expectations for medical treatment may vary depending on patients’ cultural backgrounds. A good nurse takes these factors into consideration when treating patients to better understand their needs and provide culturally sensitive care.
Cultural awareness also factors in when working as part of a clinical team. Nurses must work with a continuously changing staff of providers and clinicians who may have different communication or work styles. Being prepared for diversity in healthcare settings ensures that a nurse can work productively with everyone and contribute to a workplace that fosters teamwork, collaboration, and a sense of belonging for all.
Do you have what it takes to be a great nurse?
Prospective nurses should consider these essential characteristics and where they fall in terms of demonstrating each skill or trait. Those who exemplify most of these traits or have the potential and desire to develop them should do well as a nurse.
Everyone must start somewhere, and the main driver of success is a passion to get there. Motivation is perhaps the strongest force to propel a future successful nurse to take the necessary steps to make their career aspirations a reality.

Relias Vitals+Vision Podcast
Organizations need solutions to ongoing challenges like retention, compliance, competency management, revenue cycle management, diversity, and employee well-being. In this podcast, Relias talks to experts across the healthcare continuum who address and solve those problems every day.
Browse episodes →
How to prepare for a nursing career
With the global nursing workforce still experiencing a significant shortage of new nurses entering the field for the foreseeable future, hospitals and health systems can welcome and encourage aspirational nurses through a range of career entry points. Explore the following steps to help prospective clinicians begin their nursing journey:
- For prospective nurses, it is never too early to learn about nursing. They should connect with nurses they know among their family or community, shadow a nurse, or volunteer at a healthcare facility. One advantage of finding a mentor early is that they can help prospective nurses take the appropriate steps when considering educational options at the high school and college levels.
- Those who are ready to consider nursing school should look for available programs and funding options. There may be opportunities to support future nurses. If nursing schools are not available or at capacity, there may be alternatives online or nearby.
- Those who are currently working in a healthcare setting but want to make the switch to nursing have the advantage of observing nurses in action. They can work on the requirements of their new career and ultimately achieve their goal of caring for patients and even saving lives.
Nursing is one of the most rewarding healthcare professions, and many nurses could not see themselves doing anything else. Even with the considerable challenges of the role, many nurses are fulfilled just by knowing they make a difference every day. Nurses have both the privilege and satisfaction of a career spent in service to both the greater good and every patient entrusted to their care.
How Relias can help
As the national leader in holistic healthcare assessments, Relias empowers nursing leaders to leverage data to make informed hiring and placement decisions, helping them achieve better long-term nurse success, satisfaction, and retention. Assessment data helps nursing leaders identify developmental areas and skill gaps, continuously measure competencies, and cultivate future leaders.
Additionally, Relias offers a wealth of professional development for nursing leaders on management and leadership education, including:
- 100+ courses specific to management and leadership training for nurses, such as Developing Your Leadership Potential and Coaching: An Essential Skill for Nurses .
- Certification review courses on nursing’s most in-demand topics to help nurse managers prepare for certification exams and recertification and earn CE hours while improving their knowledge.
- Our Focused CE Series on Nursing Preceptor Specialty Practice maximizes nurses’ knowledge on preceptoring. Topics include boundaries between preceptor and preceptee, critical thinking, time management, evaluation of competency, goal-writing, constructive feedback, patient/family engagement, HCAHPS, NDNQI, and more.
Felicia Sadler, MJ, BSN, RN, CPHQ, LSSBB
Vice President, Quality, Relias

Elizabeth Snively
Content Marketing Manager, Relias
Share This Article

15 Behavioral Interview Questions for Nurse Candidates
Download our guide containing 15 examples of behavioral interview questions to identify great nurses who possess essential characteristics and skills, including communication, empathy, problem-solving, resilience, and a patient-safety orientation.
Related Resources
Nursing leadership: what is it and why is it important.
5 min read | Posted June 6, 2024
Good leadership in nursing motivates and inspires nurses to practice at the top of their licensure and drives the entire team’s success. We look at the impact good leadership has on healthcare organizations.
How to Become a Transformational Leader in Four Steps
2 min read | Posted September 19, 2023
Anyone can become a transformational leader by reflecting on their attitudes and mindset. Get started by putting these four elements into action.
Characteristics and Examples of Transformational Leadership in Nursing
5 min read | Posted September 4, 2023
Transformational leadership, the preferred management style of Magnet®-designated hospitals, transform teams to higher levels of practice.
Connect with Us
to find out more about our training and resources
Get Started
More From Forbes
5 Interview Questions That Gauge Critical Thinking Skills
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
As a job candidate, you're likely to encounter interview questions designed to assess your critical thinking skills. Employers highly value these skills because they demonstrate your ability to analyze information, solve problems creatively, and make sound decisions. In a world filled with AI, an overabundance of data, increasingly rapid decision-making, and greater autonomy with remote work, critical thinking skills are atop employers' lists of desired candidate traits.
Questions That Assess Critical Thinking Skills
Every company will put their own spin of critical thinking interview questions, but here are five of the most common questions that you should be ready to answer:
- Tell me about a time you had to solve a complex problem at work. What was your approach?
- What do you think are the three biggest challenges facing our industry right now? How would you address them?
- Describe a time when you had to make an important decision with limited information or time. How did you handle it?
- Tell me about a time your initial approach to solving a problem didn't work. How did you pivot?
- If you were in charge of our company, what's one major change you would make and why?
The good news with these five questions is that if you construct good answers for each of them, you'll be well-positioned to handle any other variations you come across.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, key points, words and themes to included in your response.
When you're answering critical thinking interview questions, it's vital for you to demonstrate how you analyze situations, assess and solve challenges, and reflect and learn from your experiences. And that's where the SHER Method can be especially helpful.
The SHER Method is a structured approach to answering interview questions that stands for Situation, Hurdle, Endgame, and Reflection. When using this method, you start by briefly describing the Situation or context of the experience you're sharing. Next, you explain the Hurdle or challenge you faced. Then, you detail the Endgame, which includes the actions you took to address the challenge and the results you achieved. Finally, you conclude with a Reflection, sharing what you learned from the experience and how it has influenced your subsequent professional conduct.
The SHER Method is particularly powerful for demonstrating critical thinking skills because it guides candidates to systematically analyze a situation, identify challenges, explain their problem-solving process, and reflect on outcomes and lessons learned. It showcases your ability to think critically and learn from experiences in a structured and compelling way. And that's really the foundation of critical thinking skills.
When answering critical thinking interview questions, keep these points in mind:
- Use specific examples from your experience
- Clearly explain your thought process and reasoning
- Demonstrate a systematic approach to problem-solving
- Show that you consider multiple perspectives
- Emphasize data-driven decision making
- Highlight your ability to adapt and learn from experiences
- Be prepared to discuss both successes and failures
- Show how you've applied lessons learned to future situations
Specific Answers To Critical Thinking Interview Questions
Let's look at some specific answers to some of the aforementioned questions that assess critical thinking skills.
Question 1: Tell me about a time you had to solve a complex problem at work. What was your approach?
Why is this an important question that is often included in interviews? It's because there is no shortage of complex problems that need solving, and when a company is making a big hire, it hopes the candidate has some good solutions.
In your answer, describe the complex problem you faced, explain the main challenges you encountered, detail the steps you took to solve the problem, and share what you learned from the experience.
Here's an example answer: "In my previous role as a project manager, we were tasked with implementing a new software system that would integrate multiple departments. The primary challenge was significant resistance to change from each department. I started by mapping out all the current processes and identifying areas of overlap. Then, I conducted interviews with key stakeholders from each department to understand their specific needs and concerns. Using this information, I created a phased implementation plan that addressed each department's unique requirements while still achieving our overall integration goals. This experience taught me the importance of stakeholder engagement in managing complex changes. I've since incorporated regular cross-departmental meetings into all my projects to ensure alignment and address concerns proactively."
Question 2: What do you think are the three biggest challenges facing our industry right now? How would you address them?
Why is this an important question that is often included in interviews? Simply put, it evaluates your strategic thinking and industry knowledge. If you're interviewing somewhere that prioritizes industry veterans, this question is quite common.
In your response, acknowledge the current state of the industry, identify three specific challenges, propose solutions for each challenge, and conclude with a forward-looking statement.
Here's an example answer: "The [specific] industry is currently facing significant disruption due to technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and regulatory pressures. The three biggest challenges I see are: 1) Adapting to rapidly evolving technology, 2) Meeting increasing customer demands for personalization, and 3) Navigating complex regulatory environments. To address these challenges, I would: 1) Implement a continuous learning program to keep our team updated on the latest technologies, 2) Invest in data analytics to better understand and predict customer preferences, and 3) Establish a dedicated regulatory compliance team to ensure we stay ahead of legal requirements. These challenges also present opportunities for companies that can adapt quickly. By addressing them proactively, we can position ourselves as industry leaders."
Question 3: Describe a time when you had to make an important decision with limited information or time. How did you handle it?
This question assesses your decision-making skills under pressure, which are relevant to lots of companies these days. In your answer, set the scene, explain the constraints you faced, detail your decision-making process, and share the outcome and lessons learned.
For example: "During a critical product launch, we discovered a potential safety issue just 24 hours before the scheduled release. We had limited time to gather information and make a decision, and any delay would result in significant financial losses. I quickly assembled a cross-functional team including engineering, legal, and marketing. We conducted a rapid risk assessment, weighing the potential safety concerns against the impact of delaying the launch. Based on our analysis, we decided to postpone the launch by one week to thoroughly address the safety issue. This decision ultimately saved us from potential legal issues and reputational damage. It reinforced for me the importance of prioritizing safety and quality over short-term gains, and the value of having a diverse team for rapid problem-solving."
Demonstrate Critical Thinking Skills Through Your Answers
Remember that when companies ask about critical thinking skills, they're not just looking for the correct answer but for insight into how you think and approach challenges. By demonstrating your ability to analyze situations, overcome obstacles, implement solutions, and learn from outcomes, you'll position yourself as someone who exercises critical thinking skills all day, every day.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This process is examined under three aspects as thinking, emotion and desire. Objectives: This study was planned to determine the nursing department and the factors affecting the level of critical thinking of students. Methods: The sample of the study voluntarily participate in the study a total of 272 students who have been accepted.
Critical thinking is applied by nurses in the process of solving problems of patients and decision-making process with creativity to enhance the effect. It is an essential process for a safe, efficient and skillful nursing intervention. Critical thinking according to Scriven and Paul is the mental active process and subtle perception, analysis ...
Critical thinking in nursing is invaluable for safe, effective, patient-centered care. You can successfully navigate challenges in the ever-changing health care environment by continually developing and applying these skills. Images sourced from Getty Images. Critical thinking in nursing is essential to providing high-quality patient care.
They are taught how to maintain their critical thinking skills and how to enhance their competences (Allen, Rubenfeld, & Scheffer, 2004; Brunt, 2005). The inadequacy of critical thinking in nursing negatively affects the quality, efficiency, and competence in service, occupational professionalism, autonomy and competency in the occupation.
The following are examples of attributes of excellent critical thinking skills in nursing. 1. The ability to interpret information: In nursing, the interpretation of patient data is an essential part of critical thinking. Nurses must determine the significance of vital signs, lab values, and data associated with physical assessment.
Students' critical thinking trends, the results of analysis of variance according to the c lass they read, the right of women to male students were found and it was found that they received training in search and broadmindedness. Background: A thought requires various skills regarding intell ectual process. This process is examined under three aspects as thinking, emotion and desire.
The importance of nurses' critical thinking skills in improving clinical decision-making is well known (Lee et al., 2017; Ludin, 2018). It has been emphasized that critical thinking and decision-making skills are at the center of all nursing curricula in nursing education (Lee et al., 2017; Reji & Saini, 2022).
Successful nurses think beyond their assigned tasks to deliver excellent care for their patients. For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood ...
Critical thinking is a complex, dynamic process formed by attitudes and strategic skills, with the aim of achieving a specific goal or objective. The attitudes, including the critical thinking attitudes, constitute an important part of the idea of good care, of the good professional. It could be said that they become a virtue of the nursing ...
2. Meeting with Colleagues: Collaborative Learning for Critical Thinking. Regular interactions with colleagues foster a collaborative learning environment. Sharing experiences, discussing diverse viewpoints, and providing constructive feedback enhance critical thinking skills. Colleagues' insights can challenge assumptions and broaden ...
A popular strategy to teach critical thinking skills in nursing education is simulation. Both live and virtual simulation can be implemented to improve critical thinking skills and clinical outcomes. Shin et al. (2015) studied the effects of multiple simulation exposures on critical thinking skills.
Critical thinking in nursing involves the ability to question assumptions, analyze data, and evaluate outcomes. It's a disciplined process that includes observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, and communication. For nurses, critical thinking means being able to make sound clinical judgments that can significantly affect patient outcomes.
Some of the most important critical thinking skills nurses use daily include interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and self-regulation. Interpretation: Understanding the meaning of information or events. Analysis: Investigating a course of action based on objective and subjective data. Evaluation: Assessing the value of ...
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed. It's a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning, problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
To investigate the impact of web-based concept mapping education on nursing students' critical-thinking and concept-mapping skills. 34: Zarshenas et al., 2019 : n = 90: 2 h for 6 days: Problem-solving: To investigate how training problem-solving skills affected the rate of self-handicapping among nursing students. 33: Svellingen et al., 2021 ...
Critical thinking skills. Critical thinking (CT) in nursing education is an essential tool that directs nursing judgment in optimal patient outcomes. Strong critical thinkers are inquisitive, open-minded, demonstrate flexibility in considering alternatives, and are prudent when suspending or altering judgments.
1. INTRODUCTION. Critical thinking is defined as the cognitive process of reasoning that involves trying to minimize errors and to maximize positive outcomes while attempting to make a decision during patient care (Zuriguel‐Pérez et al., 2015).The importance of critical thinking in nursing practice has been identified in the literature (Chang et al., 2011; Ludin, 2018; Mahmoud & Mohamed ...
Compassion fuels your desire to help ease the pain and suffering of others. These two skills contribute to inspiring trust in your patient relationships. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills: Nurses often work autonomously under pressure and must make decisions using critical thinking to put their knowledge into practice. A solid ...
According to Scheffer and Rubenfeld´s (2000) Delphi study, critical thinking in nursing is twofold: habits of the mind (affective components) and skills (cognitive components). Critical thinking can also be seen as a successive four-step process beginning with gathering information, followed by questioning and analysis and, lastly, involving ...
Some nurses are expert critical thinkers, while others struggle to comprehend and master this skill. Behavioral interview questions can help identify candidates who can make sound decisions based on informed thinking when faced with complex problems. Give an example of a time when you used critical thinking skills to solve a problem.
2.Compassion is the Second Critical Nursing Skill. The nursing model demands that nurses give vital care to patients to make them as comfortable as patients can be, attend to their physical, mental, and spiritual needs, and support the patients' families. The patient's physical, emotional, and spiritual needs can be overwhelming.
10 - Strong critical thinking. While having the willingness to learn is an important skill, putting that knowledge into successful practice requires the ability to think critically — especially in high-stress situations. A nurse with high-functioning critical thinking has one of the most important characteristics of a professional nurse.
Clinicians today need strong critical thinking skills in order to properly diagnose and treat patients. That's one reason why it is critical for educators to help medical students cultivate these skills early in their training. "Teaching critical thinking and clinical reasoning is the most transformational part of medical education.
The SHER Method is particularly powerful for demonstrating critical thinking skills because it guides candidates to systematically analyze a situation, identify challenges, explain their problem ...