
- Study and research support
- Academic skills

Dissertation examples
Listed below are some of the best examples of research projects and dissertations from undergraduate and taught postgraduate students at the University of Leeds We have not been able to gather examples from all schools. The module requirements for research projects may have changed since these examples were written. Refer to your module guidelines to make sure that you address all of the current assessment criteria. Some of the examples below are only available to access on campus.
- Undergraduate examples
- Taught Masters examples
| These dissertations achieved a mark of 80 or higher:
|
| The following two examples have been annotated with academic comments. This is to help you understand why they achieved a good 2:1 mark but also, more importantly, how the marks could have been improved. Please read to help you make the most of the two examples. (Mark 68) (Mark 66) These final year projects achieved a mark of a high first:
For students undertaking a New Venture Creation (NVC) approach, please see the following Masters level examples:
|
|
|
|
|
| Projects which attained grades of over 70 or between 60 and 69 are indicated on the lists (accessible only by students and staff registered with School of Computer Science, when on campus).
|
| These are good quality reports but they are not perfect. You may be able to identify areas for improvement (for example, structure, content, clarity, standard of written English, referencing or presentation quality).
|
|
|
| The following examples have their marks and feedback included at the end of of each document.
The following examples have their feedback provided in a separate document.
|
|
|
| School of Media and Communication . |
|
|
| The following outstanding dissertation example PDFs have their marks denoted in brackets. (Mark 78) (Mark 91) (Mark 85) |
| This dissertation achieved a mark of 84: . |
| LUBS5530 Enterprise
|
| MSc Sustainability
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
| The following outstanding dissertation example PDFs have their marks denoted in brackets. (Mark 70) (Mark 78) |

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write an excellent thesis conclusion [with examples]

Types of Assignment
- Starting an assignment
- Academic poster
- Annotated bibliography
- Project Proposal
- Dissertation or final year project
- Literature review
- Critical Assessment - Assessing Academic Journal Articles
- Systematic Review (Postgraduate resource)
- Presentation
- Reports in Microsoft Word
| n | |
Dissertation of final year project: Things you need to know...
Your first point of reference should always be your Assignment Guidelines provided by your Tutor.
Features of a dissertation/final year project:
- An extended piece of detailed work - it is an investigation.
- Demonstrates skills in: planning, organising, researching, problem solving, time management as well as oral and written communication skills. Dissertations also demonstrate in-depth subject knowledge.
- Effective use of headings, bullet points, and a range of graphical illustrations.
- Written in the academic style: needs to be clear, concise, professional and referenced
Dissertations have sections, which may include:
- Aims - W hat are you trying to achieve by doing this investigation?
- Objectives - What steps are you going to take to achieve this?
- Search Methodology - Which database did you use to find information on this topic?
- Findings - Looking at all the journal articles, what are the overall recommendations or ideas
- Discussion - How does this apply to your overall Dissertation question? What gaps have you identified which you can now research for yourself in more detail?
- Research method - what are you going to do to research this subject? what research method have you selected?
- Ethical issues - are there any ethical issues to be considered - eg: how is data going to be kept safe?
- Findings and discussion - from your investigations what have you found out? And what does it mean? Here you present findings (what you have found out from your investigation) and compare and contrast with evidence in the literature review.
- Recommendations (if requested) - after doing this investigation and research what do you recommend?
- References and/or bibliography
Art Books, have sections, which may include:
- Introduction
- Background
- Methodology
- Critical Anaylsis
- Development process including reflective elements
Essential Staffordshire University guidance: research ethics

- Dissertations How to structure a dissertation and what to include under each heading.
- Dissertation or FYP basic structure Dissertation or FYP basic structure
Need to know more...
- Related pages
- External links
- Literature review This factsheet explains what a literature review is and what to include in a literature review
- Search Strategy Factsheet
HIGH ER EDUCATION ACADEMY AND SHEFFIELD HALLAM UNIVERSITY (2013) Guide to undergraduate dissertations ( Accessed: 20th July 2020)
A note taking strategy that can be very useful for dissertations or longer pieces of work is the Grid Method Grid notes - YouTube [Accessed 10 February 2023]
Final year project back catalogue
"We are very proud of our students and the hard work that goes into their final year projects, GradEX is our showcase exhibition of students’ final year projects to industry experts."
Visit the GradEx Projects portal to view the online exhibition.
- << Previous: Project Proposal
- Next: Literature review >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 10:59 AM
- URL: https://libguides.staffs.ac.uk/assignments
- Library and Learning Services, Staffordshire University, College Road, Stoke-on-Trent, ST4 2DE
- Accessibility
- Library Regulations
- Appointments
- Library Search

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on 6 April 2023.
It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation . One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer’s block is to check out previous work done by other students.
This article collects a list of undergraduate, master’s, and PhD theses and dissertations that have won prizes for their high-quality research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Award-winning undergraduate theses, award-winning master’s theses, award-winning ph.d. dissertations.
University : University of Pennsylvania Faculty : History Author : Suchait Kahlon Award : 2021 Hilary Conroy Prize for Best Honors Thesis in World History Title : “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807”
University : Columbia University Faculty : History Author : Julien Saint Reiman Award : 2018 Charles A. Beard Senior Thesis Prize Title : “A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man”: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947
University: University College London Faculty: Geography Author: Anna Knowles-Smith Award: 2017 Royal Geographical Society Undergraduate Dissertation Prize Title: Refugees and theatre: an exploration of the basis of self-representation
University: University of Washington Faculty: Computer Science & Engineering Author: Nick J. Martindell Award: 2014 Best Senior Thesis Award Title: DCDN: Distributed content delivery for the modern web
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
University: University of Edinburgh Faculty: Informatics Author: Christopher Sipola Award: 2018 Social Responsibility & Sustainability Dissertation Prize Title: Summarizing electricity usage with a neural network
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Education Author: Matthew Brillinger Award: 2017 Commission on Graduate Studies in the Humanities Prize Title: Educational Park Planning in Berkeley, California, 1965-1968
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Social Sciences Author: Heather Martin Award: 2015 Joseph De Koninck Prize Title: An Analysis of Sexual Assault Support Services for Women who have a Developmental Disability
University : University of Ottawa Faculty : Physics Author : Guillaume Thekkadath Award : 2017 Commission on Graduate Studies in the Sciences Prize Title : Joint measurements of complementary properties of quantum systems
University: London School of Economics Faculty: International Development Author: Lajos Kossuth Award: 2016 Winner of the Prize for Best Overall Performance Title: Shiny Happy People: A study of the effects income relative to a reference group exerts on life satisfaction
University : Stanford University Faculty : English Author : Nathan Wainstein Award : 2021 Alden Prize Title : “Unformed Art: Bad Writing in the Modernist Novel”
University : University of Massachusetts at Amherst Faculty : Molecular and Cellular Biology Author : Nils Pilotte Award : 2021 Byron Prize for Best Ph.D. Dissertation Title : “Improved Molecular Diagnostics for Soil-Transmitted Molecular Diagnostics for Soil-Transmitted Helminths”
University: Utrecht University Faculty: Linguistics Author: Hans Rutger Bosker Award: 2014 AVT/Anéla Dissertation Prize Title: The processing and evaluation of fluency in native and non-native speech
University: California Institute of Technology Faculty: Physics Author: Michael P. Mendenhall Award: 2015 Dissertation Award in Nuclear Physics Title: Measurement of the neutron beta decay asymmetry using ultracold neutrons
University: Stanford University Faculty: Management Science and Engineering Author: Shayan O. Gharan Award: Doctoral Dissertation Award 2013 Title: New Rounding Techniques for the Design and Analysis of Approximation Algorithms
University: University of Minnesota Faculty: Chemical Engineering Author: Eric A. Vandre Award: 2014 Andreas Acrivos Dissertation Award in Fluid Dynamics Title: Onset of Dynamics Wetting Failure: The Mechanics of High-speed Fluid Displacement
University: Erasmus University Rotterdam Faculty: Marketing Author: Ezgi Akpinar Award: McKinsey Marketing Dissertation Award 2014 Title: Consumer Information Sharing: Understanding Psychological Drivers of Social Transmission
University: University of Washington Faculty: Computer Science & Engineering Author: Keith N. Snavely Award: 2009 Doctoral Dissertation Award Title: Scene Reconstruction and Visualization from Internet Photo Collections
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Social Work Author: Susannah Taylor Award: 2018 Joseph De Koninck Prize Title: Effacing and Obscuring Autonomy: the Effects of Structural Violence on the Transition to Adulthood of Street Involved Youth
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2023, April 06). Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/prize-winning-dissertations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Overview — Guide With Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A dissertation (a.k.a. a thesis or final year project ) is a long-form academic essay on a niche subject that requires original, primary research alongside an extensive discussion of existing topical secondary works. Your dissertation grade will usually weigh heavily (40%~70%) on your final award. Ideally, your dissertation needs to be your masterpiece.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Overview – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation overview
- 3 Dissertation overview: Research proposal
- 4 Dissertation overview: The structure
- 5 Dissertation overview: Title page
- 6 Dissertation overview: Preface
- 7 Dissertation overview: Abstract
- 8 Dissertation overview: Tables and lists
- 9 Dissertation overview: Introduction
- 10 Dissertation overview: Literature review
- 11 Dissertation overview: Methodology
- 12 Dissertation overview: Results
- 13 Dissertation overview: Discussion
- 14 Dissertation overview: Conclusion
- 15 Dissertation overview: The final pages
- 16 Dissertation overview: Proofreading and editing
- 17 Dissertation overview: Dissertation defense
Dissertation Overview – In a Nutshell
The following article covers:
- Dissertation overview – General help and guidance
- Dissertation overview – Components, layouts, and structure
- Special features, proofreading , referencing, and polish of a dissertation overview
- Example of dissertations
Definition: Dissertation overview
- The overwhelming majority of undergraduate and postgraduate taught courses require the submission of a dissertation to pass.
- A dissertation will take ca. 6~18 months to complete, usually covering ca. 5000-15,000 words . You can expect to receive your assignment and deadline during the last third of your timetable.
- What you study (within reason) is up to you. Pre-made questions and projects might also be available if sources and inspiration are lacking.
- Your assigned dissertation supervisor will provide valuable input, insight, and advice on structure and substance . Make sure to update them regularly.
- Your deadline will likely coincide with the end of your last academic year . Extensions may be allowed to account for personal setbacks, travel, or complex research projects .
Dissertation research plans are kept deliberately formulaic. Every dissertation develops as so:
- Initial research Potential areas of interest are shortlisted.
- Establishing a question What exactly will the dissertation ask?
- Initial proposal Viability testing and hypothesis fine-tuning.
- Source analysis Collection, exploration, and discussion of sources.
- Writing A dissertation overview begins to form.
- Development Content, polish, detail, and nuance.
- Editing Trimming, referencing, and error checking.
- Submission The dissertation is marked.
There are also slight differences in how British and US academia use the word dissertation. Remember that:
| A dissertation is the final written assignment for a Bachelor's or Master's degree. The text of a PhD is a thesis. | The term "dissertation" is used to refer to a written PhD. |
Dissertation overview: Research proposal
Before you start with the dissertation overview, write a draft dissertation research proposal , refine it, and get it approved by your supervisor(s).
Your draft will broadly cover why you want to research your topic , your plan or methodology , and why your dissertation would benefit academia.
Academic discussion at this stage is critical. Considering constructive advice and ideas from your tutors and field experts helps highlight productive questions.
Better planning usually results in a better end mark.
In practice, your research proposal will be a short paper (ca. 500~2000 words) explaining your ambitions. It contains:
- Introduction: A dissertation overview.
- Background review : A guide to your area of study.
- Literature review : An overview of Existing Sources.
- Methodology : Your main question(s) and research plan.
- Implications : How your research will contribute.
- Conclusion: A summary recap.
Dissertation overview: The structure
Now you can start filling out the skeletal structure of your dissertation overview. Depending on your style, you may find it productive to create extensive notes before ordering them.
Your research will segment by topic, area, purpose, and theme. Your structure will also vary to match your discipline.
- Dissertations in the humanities often read like lengthy essays, building to a central, final argument.
- Dissertations in the sciences tend to divide mechanically. Methodology, experiments, results, and implications place into different, unique chapters.
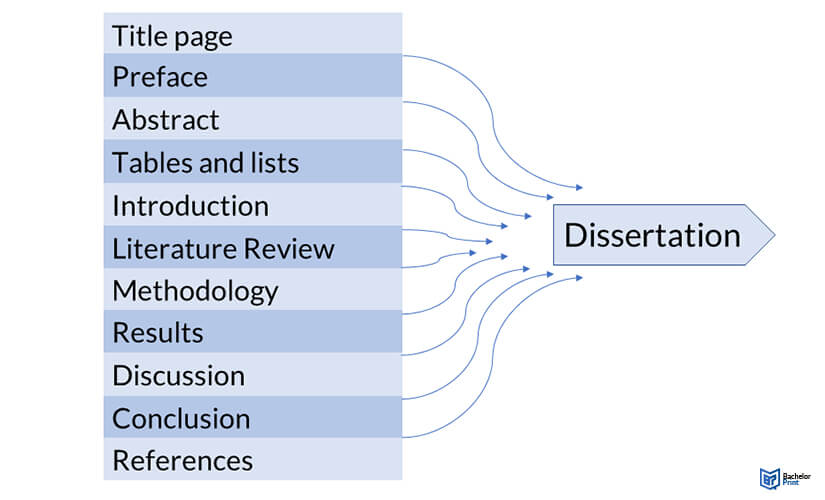
The University of Leeds (UK) maintains an online public archive of award-winning dissertations. You can browse excellent dissertation overview examples here .
Try these pieces to start:
An Investigation into the Relationship between Early Exposure and Brand
Loyalty (Psychology)
Image Processing and Analysis of Porous Materials (Material Sciences)
Faith, Selfhood and the Blues in the Lyrics of Nick Cave (English and Media)
Dissertation overview: Title page
Every dissertation overview starts with a title page. The front cover provides vital information about who you are and what you’re about.
A dissertation title page includes:
- Your full name
- Your student and submission numbers (If relevant)
- Your course and projected award (e.g., BSc Hons. Biology)
- A full dissertation title
- Your university (or awarding institution)
- Your department and supervisor
- A university logo
- Your date of final submission
Your dissertation title should always be placed at the top.
Dissertation overview: Preface
The preface of a dissertation overview is a special place to acknowledge crucial institutions, individuals, or experts who helped you. You can also dedicate the work to a loved one.
You should always politely acknowledge your supervisor, your personal tutor, and any labs, libraries, or archives used extensively.
Dissertation overview: Abstract
The abstract is a ca. 150~500-word paragraph dissertation overview briefly summarizing your topic, questions, methodology, and conclusions. It reads as a dissertation overview and a formal blurb for your work that advertises it to new readers. An effective abstract requires a complete and flowing thesis to draw on. Writing your abstract should be your absolute last task.
Dissertation overview: Tables and lists
Good direction, collation, and indexing help keep your dissertation easy to read, reference, and check for errors. An effective dissertation overview consists of the outline of chapters, inserts, and technical terms.
Dissertation overview: Table of contents
The table of contents tells readers which numbered pages link to which segments. It always appears before the main text. This section helps simplifying your dissertation overview.
Your contents table should cover all chapter headings, major subheadings, and other exceptional points of interest. Page numbers should always follow each entry.
Avoid citing every individual subheading, paragraph, or change of topic. Careful curation of milestones is best.
You can easily use Microsoft Word to autogenerate a table of contents. Remember to activate automatic page numbering.
List of Figures and Tables
Likewise, you should cite all relevant figures, tables, and illustrations here. A table list is optional but highly advisable for a dissertation overview.
Write your items in a numbered list in order of appearance. Again, Microsoft Word can autogenerate this via the Insert Caption feature.
List of Abbreviations
Abbreviations help save space in a packed manuscript. However, unexplained, obscure acronyms can confound even experienced readers.
If your dissertation references unusual, new, or technical abbreviations, include an alphabetical guide that explains their exact meanings. Avoid including commonplace abbreviations (e.g. a.k.a.).
You can also add an explanatory glossary of complex technical names and terms to your dissertation overview. Scientific dissertations may find some (optional) exposition particularly useful.
Again, order your entries by first alphabetical initial and avoid common words. Term descriptions should be 1-3 sentences long.
Dissertation overview: Introduction
Your introduction gives a first glance at your topic, purpose, and impact. Think of it as an expanded abstract. Stay clear, relevant, and assertive – this is your first chance to hook the reader.
Your introduction is also a great chance to make the relevant initial points needed to set up discussion, exploration, and argument. In the dissertation overview, you should:
- Clearly state your research question and objectives
- Set your focus and topical limits
- Detail all necessary background information and context
- Argue why your dissertation is relevant
- Outline your broad structure and methodology
Dissertation overview: Literature review
A topical literature review briefly tells the reader about existing material, comments on relevance, and demonstrates gaps in our collective knowledge.
Your literature review often forms the backbone of your broader theoretical framework in the dissertation overview. Primary, secondary, and meta sources (e.g. commentaries) count as literature.
| • Source credibility • Analysis of each source • Any obvious shortcomings (e.g. Bias, length, outdated methodologies) • Recurring patterns and themes • How you will build on your sources | • Simply repeating your source content (as is) • Taking complex, improbable, or controversial sources at face value • Leaving connections unexamined • Not setting clear study objectives • Missing out major works |
Dissertation overview: Methodology
In the dissertation overview, your methodology section describes the methods you used to collect and process your research data . Stating your methodology keeps your research credible, verifiable , and transparent.
Your methodology section should cover how and why you made your choices (e.g. longitudinal-isolated, qualitative-quantitative ), your collection methods, and how, where, and when you collected your primary data. Make a solid case for why this was the best technical approach available and address ethical concerns.
You should expect to write a far lengthier methodology for dissertations in the sciences over literary subjects (e.g. History).
Dissertation overview: Results
The results in the dissertation overview is where you list what you (objectively) discovered. Discuss all results – even if the data didn’t match your expectations.
Tables, graphics, and prose summaries relevant to your hypothesis can all be displayed. Make sure to differentiate between sections with labels and subheadings.
Careful selection and curation are good ways to keep text flowing. If your datasets are too extensive, abridge and move them to an appendix . Likewise, it’s usually worth trimming down transcripts to highlights .
Make sure to stick to the facts here. Discussion, speculation, and context will come later. However, feel free to add referenced secondary context (e.g. Reprinted data tables from earlier papers).
Dissertation overview: Discussion
The penultimate section in the dissertation overview should cover your thoughts on your discoveries and how your results fit into your theoretical framework. It’s also a place to discuss any potential implications in depth.
Include thorough but concise callbacks alongside your commentary. Using questions to self-interrogate works well. Ask:
- Why are these results relevant?
- Where do they apply?
- Are they replicable?
- How do they fit existing secondary literature?
- Are there any limitations or drawbacks?
Dissertation overview: Conclusion
In the dissertation overview, the conclusion is your dissertation’s final answer. In 500~1000 words, you’ll respond directly to your initial question(s).
Don’t include any further speculation, results, or analysis here. Other segments can house last-minute additions.
Include your overall impressions of your results and how your findings change our understanding. Briefly reflect too on any further study you think is advantageous. Try to end on a suitably optimistic yet punchy note.

Dissertation overview: The final pages
Dissertation overview done? It’s time to cite all of your sources. Include a blank end page for the back cover, too.
Dissertation overview: References
Make sure to fully reference all sources used in the footnotes and your bibliography. Clear referencing helps researchers and avoids plagiarism.
Stick to one referencing style (e.g. APA style , Chicago style , MLA ) for the entire dissertation. You can find style guides and reference generators online. Your supervisor can recommend a “best practice” referencing style for your project.
Is anything vital left over that would take up too much room? Use an appendix.
Essential methodological work (such as questionnaire templates) and full data tables too bulky for the main text can always be stored here.
Dissertation overview: Proofreading and editing
Once you’ve created your final draft, read it back and edit it. You’ll likely need to trim and refine your text to showcase your best work.
It’s also essential to remove grammatical, style, factual, or spelling errors before submission. Presentation counts heavily towards your final mark.
Set aside at least 10% of your dissertation schedule for checking and polishing. You can use online checkers or pay professional proofreading and editing services (as long as they don’t write for you) to help.
Dissertation overview: Dissertation defense
You may also have to attend a dissertation defense . The defense is a meeting in which you give a closed presentation to a supervisory panel and your peers. It’s also a chance to reveal exciting discoveries.
You’ll be prepared well in advance by your supervisor to defend any contentious points, arguments, or methodological approaches made. Defenses can be rerun with modifications if you fail the first attempt.
Once the panel accepts your argument, you’ve officially passed your dissertation. Congratulations!
How do you start the dissertation introduction?
Cover your topic’s what, why, where, how, and when. Establishing a foundation for your research is crucial.
How should I format my dissertation?
Stick to uniform, commonly known, and easy-to-read black fonts, font sizes, and graphics. Ring or book binding your finished work is advisable.
Why is proper referencing so important?
Unreferenced dissertations may be accused of plagiarism and annulled – wrecking years of hard work. Always cite where and whenever you can.
I am so so happy I found BachelorPrint!!! I was first working with Book1One,...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint

Home > College of Social and Behavioral Sciences > Social Work > Social Work Theses
Social Work Theses, Projects, and Dissertations
Theses/projects/dissertations from 2024 2024.
WHAT IS THE READINESS OF SOCIAL WORK STUDENTS TO WORK WITH AUTISTIC INDIVIDUALS? , Ignacio Aguilar Pelaez
EXAMINING EXPERIENCES AMONG SOCIAL WORKERS WORKING WITH PARENTS WHO SUFFER FROM SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER , Alicia Alvarado and Eleno Zepeda
COVID-19, SOCIAL ISOLATION, AND MSW STUDENTS’ MENTAL HEALTH , Cassandra Barajas
Through the Lens of Families and Staff in Emergency Shelters , Elizabeth Barcenas
MACHISMO: THE IMPACT IT HAS ON HISPANIC MALE COLLEGE STUDENTS RECEIVING MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES , Sara Barillas and Alexander Aguirre
THE DISPROPORTIONATE IMPACTS OF CERTAIN FACTORS THAT DIFFERENTIATE THE AMOUNT OF MENTAL HEALTH REFERRALS OF SCHOOL A COMPARED TO SCHOOL B , Jesus Barrientos
Correlation of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Somatic Symptoms in Adolescents , Shannon Beaumont
Caregivers of Dialysis Patients , Alyssa Bousquet and Amelia Murillo
Self-Care Habits and Burnout Among County Social Workers on the Central Coast of California , Jaclyn Boyd and Denise Ojeda
GENDER DYSPHORIA IN ADOLESCENCE AND THE MODELS OF CARE: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW , Arnold Briseno
THE EFFECTS OF PARENTING STYLES ON COMMUNICATION AMONG ASIAN AMERICAN YOUNG ADULTS , Abigail Camarce
BARRIERS TO AND FACILITATORS OF CARE: EXPLORING HOW LOW-INCOME WOMEN ACCESS REPRODUCTIVE HEALTHCARE IN A RURAL COMMUNITY , Sydney Taylor Casey
CLIENT PERPETRATED VIOLENCE AND SAFETY CULTURE IN CHILD WELFARE: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW , Amber Castro
ACCESSIBILITY OF SERVICES FOR TRANSGENDER ADOLESCENTS FROM A CHILD WELFARE PERSPECTIVE , Eduardo Cedeno
WHAT ARE THE BARRIERS TO SEEKING PSYCHOTHERAPY SERVICES ACROSS DIFFERENT RACIAL AND ETHNIC GROUPS? , Deysee Chavez and Elisa Rodarte
Homelessness In The Coachella Valley , Katrina Clarke
Challenges Veterans Encounter Receiving or Seeking Mental Health Services , Denise D. Contreras and Andrea Ramirez
EXAMINING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS FOR OPIOID USE DISORDER: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Elizabeth Ashley Contreras
IS A SOCIAL SUPPORT BASED MODEL BETTER FOR TREATING ALCOHOLISM? A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Jordan Anthony Contreras
SOCIAL WORKERS’ PREPAREDNESS FOR PRACTICE WITH PATIENTS EXPERIENCING PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS , Paula Crespin
INVESTIGATING THE LEVEL OF EVIDENCE OF ADVERSE CHILDHOOD EXPERIENCES AND PARENTING PRACTICES: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Eloisa Deshazer
MENTAL HELP-SEEKING: BARRIERS AMONG AFRICAN AMERICANS: THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN ADDRESSING THOSE BARRIERS , Charneka Edwards
Treatment not Punishment: Youth Experiences of Psychiatric Hospitalizations , Maira Ferrer-Cabrera
THE BARRIERS TO NATURAL OUTDOOR SPACES: PERSPECTIVES FROM PEOPLE WITH MOBILITY DISABILITIES , Sierra Fields and Kailah Prince
IMPLEMENTATION OF MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES AND CURRICULUM FOR ELEMENTARY-AGED CHILDREN , Indra Flores Silva and Jason Kwan
POOR ACADEMICS FROM COLLEGE STUDENTS GRIEVING THROUGH COVID 19 , Sarah Frost
COMPASSION FATIGUE IN SHORT TERM RESIDENTIAL THERAPEUTIC PROGRAM SETTINGS , Sandra Gallegos
A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE GUN VIOLENCE RESTRAINING ORDER , Bonnie Galloway and Yasmeen Gonzalez-Ayala
STRESS AND HELP-SEEKING IN FARMWORKERS IN THE COACHELLA VALLEY , Alexis Garcia and Daniela Mejia
THE EFFECTIVNESS OF FEDERAL PELL GRANT PROGRAM , Maria Delcarmen Garcia Arias and Ashley Hernandez
PARENT INVOLVEMENT AND EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES AMONG LATINO FAMILIES , Diana Garcia and Gabriela Munoz
IMPACT OF SCHOOL-BASED MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES ON STUDENT ATTENDANCE AT A SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SCHOOL DISTRICT , Johanna Garcia-Fernandez and Morgan Stokes
BARRIERS TO GENDER-AFFIRMING CARE , Gloria Garcia
THE CONTRIBUTING FACTORS OF PLACEMENT INSTABILITY FOR PREGNANT FOSTER YOUTH , Amanda Garza and Shayneskgua Colen
PROGRESSION OF BLACK WOMEN IN TENURE RANKED POSITIONS , Unique Givens
Child Maltreatment Primary Prevention Methods in the U.S.: A Systematic Review of Recent Studies , Maria Godoy-Murillo
Assessing and Meeting the Needs of Homeless Populations , Mitchell Greenwald
Parity In Higher Education In Prison Programs: Does It Exist? , Michael Lee Griggs and Vianey Luna
SURROGACY AND IT'S EFFECTS ON THE MENTAL HEALTH OF THE GESTATIONAL CARRIER , DayJahne Haywood
SUBSTANCE USE TREATMENT WITHIN THE US PRISON SYSTEM , Timothy Hicks
LGBTQ+ College Students Hopeful Future Expectations , Savannah Hull
EFFECTS OF VOLUNTARY REMOVAL ON AN IMMIGRANT FAMILY , Miriam Jimenez
THE MOTIVATING FACTORS AFFECTING THE CONTINUANCE AND COMPLETION OF SUBSTANCE USE TREATMENT FOR MOTHERS , Jacquetta Johnson
FACTORS AFFECTING THE ENROLLMENT AND GRADUATION RATES AMONGST AFRICAN AMERICAN MALES IN THE UNITED STATES , Tracie Johnson
SUPPORTING FORMERLY INCARCERATED INDIVIDUALS IN HIGHER EDUCATION: A QUANTITATIVE STUDY , Lisa Marie Jones-Wiertz
PROTESTANT CHURCH WORKERS' KNOWLEDGE OF CHILD ABUSE REPORTING AND REPORTING BEHAVIOR , Rachel Juedes
Social Media Told Me I Have A Mental Illness , Kathleen Knarreborg
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ROLE MODELS, SOCIOECONOMIC MOBILITY BELIEFS, AND ACADEMIC OUTCOMES , Christian Koeu and Marisol Espinoza Garcia
CULTURAL AND STRUCTURAL BARRIERS OF UTILIZING MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A SCHOOL-BASED SETTING FOR LATINX POPULATIONS , Silvia Lozano and Bridgette Guadalupe Calderon
EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES FOR YOUTH THAT PARTICIPATED IN EXTENDED FOSTER CARE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Kassandra Mayorga and Roxana Sanchez
NON-BINARY IDENTITY WITHIN COMPETENCY TRAINING FOR MENTAL/BEHAVIORAL HEALTH PROVIDERS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Alexis McIntyre
Childhood Neglect and Incarceration as a Adult , Marissa Mejia and Diana Gallegos
IMPACT OF RESOURCE SCARCITY ON UNDOCUMENTED STUDENTS IN HIGHER EDUCATION , Sebastian Melendez Lopez
STUDY EXPLORING FEELINGS OF SELF-BLAME AND SHAME AMONG INDIVIDUALS RAISED BY SEVERELY MENTALLY ILL CAREGIVERS , Joanie Minion
THE OBSTACLES FACING HOMELESS VETERANS WITH MENTAL ILLNESS WHEN OBTAINING HOUSING , Melissa Miro
STUDENTS OF HIGHER EDUCATION RECEIVING SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRITION ASSISTANCE PROGRAM AND ITS IMPACT ON MENTAL HEALTH , Cristina Palacios Mosqueda
COMMERCIALLY SEXUALLY EXPLOITED CHILDREN TARGETED WITHIN SOCIAL SERVICES , Britny Ragland
ART THERAPY FOR BEREAVED SIBLINGS AFTER PEDIATRIC CANCER DEATH , Daniela Ramirez-Ibarra
HOW DID THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC IMPACT EXTENDED FOSTER CARE SOCIAL WORKERS WHILE PROVIDING SOCIAL SERVICES , Omar Ramirez and Victoria Lopez
A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF BODY MODIFICATION BIASES IN THE MENTAL HEALTH FIELD , Lonese Ramsey
Bridging Training Gaps: Assessing Knowledge and Confidence of Mental Health Interns in Opioid Misuse Intervention for School-Aged Children and Adolescents , Carolina Rodriguez and Gabriela Guadalupe Gonzalez
PERCEPTIONS OF YOUTH ATHLETE SAFETY PARENTS VS DIRECTORS , Nicole Anais Rodriguez
SPIRITUALITY AND RECOVERY FROM ADDICTION: EXPERIENCES OF NARCOTICS ANONYMOUS MEMBERS , Elizabeth Romberger
ADVERSE CHILDHOOD EXPERIENCES AND ALTRUISM: THE IMPACT ON SOCIAL WORK AS A CAREER CHOICE , Nancy Salas and Brittany Altuna
MAJOR FACTORS OF SUSTAINING RECOVERY AFTER RELAPSE FROM A SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER , Amanda Tei Sandhurst
UNDERSTANDING THE PERSPECTIVES AND ATTITUDES OF 12-STEP PARTICIPANTS TOWARDS MEDICATION-ASSISTED TREATMENT , Christopher Scott
THE UTILIZATION OF MUSIC AND AUTONOMOUS SENSORY MERIDIAN RESPONSE IN REDUCING STRESS , Robert Scott
THE AFTERMATH OF THE PANDEMIC’S EFFECT ON COLLEGE STUDENT DEPRESSION , Lorena Sedano
Exploring the Experiences of Minority Former Foster Youths During and Post Care: A Qualitative Study , Caithlyn Snow
Factors that Contribute to Disparities in Access to Mental Health Services within Hispanic Adults , Jasmine Soriano
THE CHALLENGES TO THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ADMINISTRATION FOR CHILDREN AND FAMILIES MEMORANDUM: FOSTER CARE AS A SUPPORT TO FAMILIES , Rebecca Joan Sullivan-Oppenheim
RESILIENCE IN FATHERHOOD: EXPLORING THE IMPACT OF ABSENT FATHERS ON BLACK AMERICAN MEN'S PARENTING NARRATIVES AND PRACTICES , Ericah Thomas
FACTORS THAT IMPACT FOSTER YOUTHS’ HIGH SCHOOL GRADUATION , Esther Thomas
EXAMINING A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SEXUAL SATISFACTION AND CHILD MALTREATMENT , Amanda Titone
THE PRESENT STRUGGLES OF IMMIGRANT FARMWORKERS IN CALIFORNIA , Leslie Torres and Angelica Huerta
PROGRAM EVALUATION OF SCHOOL-BASED MENTAL HEALTH COUNSELING SERVICES , Yvette Torres and Emily Ann Rodriguez
Stressors, Caffeine Consumption, and Mental Health Concerns among College Students , Stacey Trejo
DISPARITIES SURROUNDING THE AVAILABILITY OF FEMININE HYGIENE PRODUCTS IN THE WORKPLACE , Marlene Ventura
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT HELP SEEKING ATTITUDES AND BEHAVIORS AMONG LATINX COMMUNITY , Nancy Vieyra
JUSTICE-INVOLVED STUDENTS: EFFECTS OF USING SUPPORT SERVICES TO OVERCOME BARRIERS , Gabby Walker and Sofia Alvarenga
MANDATED REPORTERS’ KNOWLEDGE AND REPORTING OF CHILD ABUSE , Alexis Reilly Warye
THE COMMUNITY RESILIENCY MODEL (CRM) APPLIED TO TEACHER’S WELL-BEING , John Waterson
Addressing Rural Mental Health Crises: An Alternative to Police , Faith Ann Weatheral-block
Theses/Projects/Dissertations from 2023 2023
PROLONGED EXPOSURE TO CONGREGATE CARE AND FOSTER YOUTH OUTCOMES , Tiffany Acklin
YOU CALL US TREATMENT RESISTANT: THE EFFECTS OF BIASES ON WOMEN WITH BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER , Cassidy Acosta
EXAMINING SOCIAL DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH OF FORMERLY INCARCERATED CALIFORNIA STUDENTS WHO GRADUATED FROM PROJECT REBOUND , Ashley C. Adams
ALTERNATIVE APPROACHES TO POLICE INTERVENTIONS WHEN RESPONDING TO MENTAL HEALTH CRISES INCIDENTS , Karen Rivera Apolinar
Understanding Ethical Dilemmas in Social Work Practice , Arielle Arambula
IS THERE A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PROFESSORIAL-STUDENT RACIAL MATCH AND ACADEMIC SATISFACTION OF AFRICAN AMERICAN SOCIAL WORK STUDENTS , Ashlei Armstead
NON-SPANISH SPEAKING LATINOS' EXPERIENCES OF INTRAGROUP MARGINALIZATION AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR ETHNIC IDENTITY , Marissa Ayala
SERVICES AVAILABLE IN THE MIXTEC COMMUNITY AND THE BARRIERS TO THOSE SERVICES , Currie Bailey Carmon
IMPACT OF OUTDOOR ADVENTURE ON THE SELF-ESTEEM, SELF-CONFIDENCE, AND COMFORT LEVEL OF BLACK AND BROWN GIRLS , Nathan Benham
THE ROLE UNDOCUMENTED STUDENT RESOURCE CENTERS PLAY IN SUPPORTING UNDOCUMENTED STUDENTS IN HIGHER EDUCATION , Cynthia Boyzo
Program Evaluation of Teen Parent Support Group , Brianne Yvonne Irene Brophy
THE IMPACT THE JOB STRESS OF A CHILD WELFARE SOCIAL WORKER HAS ON THE QUALITY OF THEIR RELATIONSHIP WITH THEIR INTIMATE PARTNER , Nadine Cazares
Adverse Effects for Siblings Who Witness Child Abuse , Leslie Chaires
ASIAN DISCRIMINATION: IN THE FIELD OF SOCIAL WORK , Sunghay Cho
PERCEIVED FINANCIAL STRAIN AND ITS EFFECTS ON COLLEGE STUDENTS’ WELFARE , Monica Contreras and Clarissa Adrianna Martinez
The Media and Eating Disorders , Diane Corey
INCREASING TEACHER AWARENESS OF MENTAL HEALTH IN CHILDREN , Sarah Alexis Cortes
Page 1 of 17
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Department, Program, or Office
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- School of Social Work homepage
A service of the John M. Pfau Library

Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright Acrobat Reader
ScholarWorks
Home > Engineering > Computer Science > Computer Science Graduate Projects
Computer Science Graduate Projects and Theses
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
High-Performance Domain-Specific Library for Hydrologic Data Processing , Kalyan Bhetwal
Evaluating Learning Geometric Concepts to Generate Predicate Abstract Domains in Static Program Analysis , Patrick Chadbourne
Verifying Data Provenance During Workflow Execution for Scientific Reproducibility , Rizbanul Hasan
Remote Sensing to Advance Understanding of Snow-Vegetation Relationships and Quantify Snow Depth and Snow Water Equivalent , Ahmad Hojatimalekshah
Exploring the Capability of a Self-Supervised Conditional Image Generator for Image-to-Image Translation without Labeled Data: A Case Study in Mobile User Interface Design , Hailee Kiesecker
Fake News Detection Using Narrative Content and Discourse , Hongmin Kim
Anomaly Detection Using Graph Neural Network , Bishal Lakha
Robust Digital Nucleic Acid Memory , Golam Md Mortuza
Risk Assessment and Solutions for Two Domains: Election Procedures and Privacy Disclosure Prevention for Users , Kamryn DeAnn Parker
Sparse Format Conversion and Code Synthesis , Tobi Goodness Popoola
Fair Layouts in Information Access Systems: Provider-Side Group Fairness in Ranking Beyond Ranked Lists , Amifa Raj
Virtual Curtain: A Communicative Fine-Grained Privacy Control Framework for Augmented Reality , Aakash Shrestha
Portable Sparse Polyhedral Framework Code Generation Using Multi Level Intermediate Representation , Aaron St. George
Transformer Reinforcement Learning Approach to Attack Automatic Fake News Detectors , Chandler Underwood
Severity Measures for Assessing Error in Automatic Speech Recognition , Ryan Whetten
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Improved Computational Prediction of Function and Structural Representation of Self-Cleaving Ribozymes with Enhanced Parameter Selection and Library Design , James D. Beck
Meshfree Methods for PDEs on Surfaces , Andrew Michael Jones
Deep Learning of Microstructures , Amir Abbas Kazemzadeh Farizhandi
Long-Term Trends in Extreme Environmental Events with Changepoint Detection , Mintaek Lee
Structure Aware Smart Encoding and Decoding of Information in DNA , Shoshanna Llewellyn
Towards Making Transformer-Based Language Models Learn How Children Learn , Yousra Mahdy
Ontology-Based Formal Approach for Safety and Security Verification of Industrial Control Systems , Ramesh Neupane
Improving Children's Authentication Practices with Respect to Graphical Authentication Mechanism , Dhanush Kumar Ratakonda
Hate Speech Detection Using Textual and User Features , Rohan Raut
Automated Detection of Sockpuppet Accounts in Wikipedia , Mostofa Najmus Sakib
Characterization and Mitigation of False Information on the Web , Anu Shrestha
Sinusoidal Projection for 360° Image Compression and Triangular Discrete Cosine Transform Impact in the JPEG Pipeline , Iker Vazquez Lopez
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Training Wheels for Web Search: Multi-Perspective Learning to Rank to Support Children's Information Seeking in the Classroom , Garrett Allen
Fair and Efficient Consensus Protocols for Secure Blockchain Applications , Golam Dastoger Bashar
Why Don't You Act Your Age?: Recognizing the Stereotypical 8-12 Year Old Searcher by Their Search Behavior , Michael Green
Ensuring Consistency and Efficiency of the Incremental Unit Network in a Distributed Architecture , Mir Tahsin Imtiaz
Modeling Real and Fake News Sharing in Social Networks , Abishai Joy
Modeling and Analyzing Users' Privacy Disclosure Behavior to Generate Personalized Privacy Policies , A.K.M. Nuhil Mehdy
Into the Unknown: Exploration of Search Engines' Responses to Users with Depression and Anxiety , Ashlee Milton
Generating Test Inputs from String Constraints with an Automata-Based Solver , Marlin Roberts
A Case Study in Representing Scientific Applications ( GeoAc ) Using the Sparse Polyhedral Framework , Ravi Shankar
Actors for the Internet of Things , Arjun Shukla
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Towards Unifying Grounded and Distributional Semantics Using the Words-as-Classifiers Model of Lexical Semantics , Stacy Black
Improving Scientist Productivity, Architecture Portability, and Performance in ParFlow , Michael Burke
Polyhedral+Dataflow Graphs , Eddie C. Davis
Improving Spellchecking for Children: Correction and Design , Brody Downs
A Collection of Fast Algorithms for Scalar and Vector-Valued Data on Irregular Domains: Spherical Harmonic Analysis, Divergence-Free/Curl-Free Radial Basis Functions, and Implicit Surface Reconstruction , Kathryn Primrose Drake
Privacy-Preserving Protocol for Atomic Swap Between Blockchains , Kiran Gurung
Unsupervised Structural Graph Node Representation Learning , Mikel Joaristi
Detecting Undisclosed Paid Editing in Wikipedia , Nikesh Joshi
Do You Feel Me?: Learning Language from Humans with Robot Emotional Displays , David McNeill
Obtaining Real-World Benchmark Programs from Open-Source Repositories Through Abstract-Semantics Preserving Transformations , Maria Anne Rachel Paquin
Content Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) for Brand Logos , Enjal Parajuli
A Resilience Metric for Modern Power Distribution Systems , Tyler Bennett Phillips
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Edge-Assisted Workload-Aware Image Processing System , Anil Acharya
MINOS: Unsupervised Netflow-Based Detection of Infected and Attacked Hosts, and Attack Time in Large Networks , Mousume Bhowmick
Deviant: A Mutation Testing Tool for Solidity Smart Contracts , Patrick Chapman
Querying Over Encrypted Databases in a Cloud Environment , Jake Douglas
A Hybrid Model to Detect Fake News , Indhumathi Gurunathan
Suitability of Finite State Automata to Model String Constraints in Probablistic Symbolic Execution , Andrew Harris
UNICORN Framework: A User-Centric Approach Toward Formal Verification of Privacy Norms , Rezvan Joshaghani
Detection and Countermeasure of Saturation Attacks in Software-Defined Networks , Samer Yousef Khamaiseh
Secure Two-Party Protocol for Privacy-Preserving Classification via Differential Privacy , Manish Kumar
Application-Specific Memory Subsystem Benchmarking , Mahesh Lakshminarasimhan
Multilingual Information Retrieval: A Representation Building Perspective , Ion Madrazo
Improved Study of Side-Channel Attacks Using Recurrent Neural Networks , Muhammad Abu Naser Rony Chowdhury
Investigating the Effects of Social and Temporal Dynamics in Fitness Games on Children's Physical Activity , Ankita Samariya
BullyNet: Unmasking Cyberbullies on Social Networks , Aparna Sankaran
FALCON: Framework for Anomaly Detection In Industrial Control Systems , Subin Sapkota
Investigating Semantic Properties of Images Generated from Natural Language Using Neural Networks , Samuel Ward Schrader
Incremental Processing for Improving Conversational Grounding in a Chatbot , Aprajita Shukla
Estimating Error and Bias of Offline Recommender System Evaluation Results , Mucun Tian
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
Leveraging Tiled Display for Big Data Visualization Using D3.js , Ujjwal Acharya
Fostering the Retrieval of Suitable Web Resources in Response to Children's Educational Search Tasks , Oghenemaro Deborah Anuyah
Privacy-Preserving Genomic Data Publishing via Differential Privacy , Tanya Khatri
Injecting Control Commands Through Sensory Channel: Attack and Defense , Farhad Rasapour
Strong Mutation-Based Test Generation of XACML Policies , Roshan Shrestha
Performance, Scalability, and Robustness in Distributed File Tree Copy , Christopher Robert Sutton
Using DNA For Data Storage: Encoding and Decoding Algorithm Development , Kelsey Suyehira
Detecting Saliency by Combining Speech and Object Detection in Indoor Environments , Kiran Thapa
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Identifying Restaurants Proposing Novel Kinds of Cuisines: Using Yelp Reviews , Haritha Akella
Editing Behavior Analysis and Prediction of Active/Inactive Users in Wikipedia , Harish Arelli
CloudSkulk: Design of a Nested Virtual Machine Based Rootkit-in-the-Middle Attack , Joseph Anthony Connelly
Predicting Friendship Strength in Facebook , Nitish Dhakal
Privacy-Preserving Trajectory Data Publishing via Differential Privacy , Ishita Dwivedi
Cultivating Community Interactions in Citizen Science: Connecting People to Each Other and the Environment , Bret Allen Finley
Uncovering New Links Through Interaction Duration , Laxmi Amulya Gundala
Variance: Secure Two-Party Protocol for Solving Yao's Millionaires' Problem in Bitcoin , Joshua Holmes
A Scalable Graph-Coarsening Based Index for Dynamic Graph Databases , Akshay Kansal
Integrity Coded Databases: Ensuring Correctness and Freshness of Outsourced Databases , Ujwal Karki
Editable View Optimized Tone Mapping For Viewing High Dynamic Range Panoramas On Head Mounted Display , Yuan Li
The Effects of Pair-Programming in a High School Introductory Computer Science Class , Ken Manship
Towards Automatic Repair of XACML Policies , Shuai Peng
Identification of Unknown Landscape Types Using CNN Transfer Learning , Ashish Sharma
Hand Gesture Recognition for Sign Language Transcription , Iker Vazquez Lopez
Learning to Code Music : Development of a Supplemental Unit for High School Computer Science , Kelsey Wright
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Identification of Small Endogenous Viral Elements within Host Genomes , Edward C. Davis Jr.
When the System Becomes Your Personal Docent: Curated Book Recommendations , Nevena Dragovic
Security Testing with Misuse Case Modeling , Samer Yousef Khamaiseh
Estimating Length Statistics of Aggregate Fried Potato Product via Electromagnetic Radiation Attenuation , Jesse Lovitt
Towards Multipurpose Readability Assessment , Ion Madrazo
Evaluation of Topic Models for Content-Based Popularity Prediction on Social Microblogs , Axel Magnuson
CEST: City Event Summarization using Twitter , Deepa Mallela
Developing an ABAC-Based Grant Proposal Workflow Management System , Milson Munakami
Phoenix and Hive as Alternatives to RDBMS , Diana Ornelas
- Collections
- Disciplines
- SelectedWorks Gallery
- Albertsons Library
- Division of Research
- Graduate College
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

Undergraduate Thesis Statement
Ai generator.

Embarking on an undergraduate thesis requires clarity and precision, starting with a well-defined thesis statement . This single, succinct sentence shapes the trajectory of your entire research and determines its depth and breadth. Delving into examples can demystify the process, equipping you with the tools to construct a compelling foundation for your research. This guide offers insightful examples, detailed writing instructions, and invaluable tips to ensure your undergraduate thesis stands out in academic rigor and originality.
What is a thesis statement for an Undergraduate? – Definition
An undergraduate concise thesis statement summary or claim that encapsulates the main idea, argument, or central point of an undergraduate research project or paper. It serves as the backbone of the study, guiding the researcher’s inquiry and providing readers with a clear understanding of the paper’s purpose and direction.
What is an example of an Undergraduate thesis statement?
“Analyzing the impact of social media marketing strategies on consumer behavior, this research seeks to determine how businesses can optimize online campaigns to increase customer engagement and loyalty in the e-commerce sector.
100 Thesis Statement Examples for an Undergraduate

Size: 187 KB
Crafting an undergraduate thesis statement requires a fusion of clarity, originality, and precision. Acting as a project’s guiding beacon, it encapsulates your research’s primary objective, offering readers a snapshot into the depth and direction of your inquiry. Below are a myriad of thesis statement examples to illuminate your path in various academic disciplines.
- Digital Marketing: “A comparative study on the efficacy of email marketing versus social media advertising in converting potential leads into sales.”
- Environmental Science: “Assessing the long-term impact of plastic waste on marine ecosystems, focusing on the degradation rate of microplastics.”
- Psychology: “Exploring the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.”
- Cultural Studies: “The influence of pop culture on shaping youth identity in the 21st century.”
- Economics: “A detailed analysis of the factors contributing to the rise and fall of cryptocurrency values over the past decade.”
- Biotechnology: “The potential of CRISPR technology in treating genetically inherited diseases.”
- Architecture: “Modern urban planning: The role of green spaces in enhancing the quality of life in densely populated cities.”
- Political Science: “Assessing the impact of grassroots movements on local electoral outcomes.”
- History: “The influence of Renaissance art on cultural and societal shifts in early modern Europe.”
- Astronomy: “The search for exoplanets: Techniques and technologies paving the way for discovering Earth-like planets.”
- Linguistics: “The evolution of regional dialects in post-colonial African nations.”
- Literature: “Dystopian fiction: A reflection of societal fears and contemporary challenges.”
- Sociology: “The role of social media in shaping public opinions on global events.”
- Pharmacology: “The effectiveness of herbal alternatives in treating chronic pain compared to synthetic drugs.”
- Musicology: “The cultural impact of Afrobeat in global music trends over the last two decades.”
- Gender Studies: “The portrayal of masculinity in modern cinema and its implications on gender norms.”
- Anthropology: “The link between traditional rituals and community cohesion in indigenous tribes of the Amazon.”
- Finance: “Analyzing the effects of Brexit on the investment patterns of European venture capitalists.”
- Artificial Intelligence: “The ethical implications of deep learning technologies in surveillance systems.”
- Nutrition: “The correlation between Mediterranean diet adherence and reduced risks of cardiovascular diseases.”
- Education: “Innovative teaching methods: A study on the efficacy of gamified learning in primary schools.”
- Philosophy: “The existential implications of artificial intelligence: Revisiting consciousness and identity.”
- Theatre Studies: “Modern theatre’s reflection of societal issues, focusing on plays produced in the last decade.”
- Biology: “The role of gut microbiota in influencing mood and mental health.”
- Sports Science: “The impact of high-altitude training on aerobic performance in long-distance runners.”
- Law: “Digital privacy rights: Assessing the effectiveness of GDPR in safeguarding user data.”
- Physics: “Exploring quantum entanglement’s potential applications in secure communication systems.”
- Geography: “Urban heat islands: The interplay between urbanization and localized climate change.”
- Mathematics: “Fractal geometry’s application in modeling natural phenomena.”
- Chemistry: “Green chemistry techniques in developing sustainable industrial processes.”
- Neuroscience: “The role of neuroplasticity in stroke recovery and its implications for rehabilitation.”
- Religious Studies: “The evolution of Buddhist practices and its adaptation in Western cultures.”
- Civil Engineering: “The influence of sustainable materials in modern infrastructure and their longevity.”
- Mechanical Engineering: “The potential of nanotechnology in revolutionizing mechanical systems and components.”
- Zoology: “Behavioral changes in migratory birds due to global climate shifts.”
- Healthcare: “Telemedicine’s role in bridging the urban-rural health divide.”
- Fashion Design: “The resurgence of vintage fashion trends in the 21st century.”
- Entrepreneurship: “The impact of startup incubators in fostering innovation and business growth.”
- Criminology: “The relationship between socioeconomic factors and crime rates in urban environments.”
- Nanotechnology: “Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery systems.”
- Marine Biology: “The effects of ocean acidification on coral reef ecosystems.”
- Journalism: “The transformation of investigative journalism in the digital age.”
- Forensic Science: “Advancements in DNA sequencing and its implications for criminal investigations.”
- Film Studies: “Representation of women in action films and its evolution over time.”
- Dentistry: “Exploring the link between oral health and systemic diseases.”
- Veterinary Medicine: “The effects of urbanization on pet health and behavior.”
- Electrical Engineering: “Wireless charging technologies and their potential in revolutionizing transport.”
- Computer Science: “Cybersecurity challenges in the era of the Internet of Things (IoT).”
- Environmental Engineering: “Rainwater harvesting: Techniques and benefits in urban planning.”
- Graphic Design: “The impact of minimalist design on brand recognition.”
- Agriculture: “Vertical farming and its potential in addressing food security in urban landscapes.”
- Space Science: “Mars exploration: Potential for human colonization and challenges.”
- International Relations: “The role of soft power in shaping global politics in the 21st century.”
- Dermatology: “Skin microbiome’s influence on skin health and aging.”
- Organic Farming: “Analyzing the nutritional differences between organic and conventionally grown crops.”
- Metallurgy: “The future of superalloys in aerospace engineering.”
- Urban Planning: “Car-free cities: Benefits, challenges, and feasibility.”
- Classics: “The impact of Greek philosophical thought on modern western ideologies.”
- Epidemiology: “The role of community behavior in the spread and containment of infectious diseases.”
- Public Policy: “Assessing the impact of universal basic income on poverty alleviation.”
- Statistics: “Applications of Bayesian statistics in real-time prediction models.”
- Tourism and Hospitality: “Sustainable tourism: Balancing economic benefits and ecological conservation.”
- Social Work: “Trauma-informed care in child welfare systems: Benefits and implementation challenges.”
- Petroleum Engineering: “Alternative drilling techniques to reduce environmental impacts.”
- Dance Studies: “The therapeutic implications of dance in mental health treatments.”
- Robotics: “The role of AI-driven robots in eldercare.”
- Aeronautics: “The potential of electric aircraft in revolutionizing the aviation industry.”
- Public Health: “Strategies for effective health campaigns in combating childhood obesity.”
- Naval Architecture: “Design innovations for energy-efficient commercial vessels.”
- Pedagogy: “Incorporating digital literacy in K-12 education: Challenges and benefits.”
- Molecular Biology: “The role of epigenetics in disease manifestation.”
- Meteorology: “Predicting extreme weather events: The role of satellite technologies.”
- Human Resources: “Workplace diversity and its impact on team performance.”
- Telecommunications: “5G technology: Prospects, challenges, and its potential in IoT.”
- Genetics: “The ethical considerations in human gene editing.”
- Horticulture: “Urban gardens and their role in promoting community well-being.”
- Radiology: “Innovations in imaging techniques for early cancer detection.”
- Conservation: “Community-driven conservation efforts and their impact on wildlife preservation.”
- Real Estate: “The effects of urbanization on real estate pricing trends.”
- Pathology: “The role of autophagy in cancer cell survival and resistance to treatment.”
- Finance: “Cryptocurrencies and their influence on global economic structures.”
- Astronomy: “Black holes and their potential in understanding the universe’s origins.”
- Materials Science: “Bio-inspired materials and their applications in medical implants.”
- Maritime Studies: “Marine pollution: Evaluating international laws and their enforcement.”
- Industrial Design: “Ergonomic designs and their impact on user productivity.”
- Nuclear Physics: “The future of fusion reactors as sustainable energy sources.”
- Oceanography: “Deep-sea exploration: Discoveries, technologies, and mysteries.”
- Petrology: “Exploring the formation of gemstones and their geographical distribution.”
- Archeology: “Technological advancements in dating ancient artifacts.”
- Cosmetology: “Natural ingredients and their effectiveness in skin and hair care.”
- Military Science: “The role of AI and drones in modern warfare.”
- Endocrinology: “Hormonal imbalances and their relation to lifestyle diseases.”
- Geology: “Studying tectonic movements and their role in natural disasters.”
- Optometry: “The rise in blue light exposure and its effects on vision.”
- Herpetology: “Conservation efforts for endangered amphibian species.”
- Energy Studies: “Renewable energy solutions and their feasibility in grid-scale applications.”
- Actuarial Science: “Risk analysis in health insurance with the rise in global pandemics.”
- Hematology: “Stem cell research and its potential in treating blood disorders.”
- Psephology: “The influence of social media on voter behavior in 21st-century elections.”
- Virology: “The evolution of coronaviruses and strategies for future outbreak prevention.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Undergraduate Argumentative Essay
Undergraduate argumentative essays thesis statement demand a clear stance on a debatable issue. The thesis statement should reflect this stance unambiguously, offering readers a precise viewpoint that the essay will explore.
- Climate Change: “Human activity, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, is the primary contributor to the escalating problem of global climate change.”
- Education: “Online learning can be just as effective, if not more so, than traditional classroom instruction when implemented with best practices.”
- Media: “Violent video games directly correlate with increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Health: “Vaccinations should be mandatory due to their role in reducing disease outbreaks and protecting public health.”
- Technology: “The growing dependence on smartphones has led to a significant decline in face-to-face social interactions among young adults.”
- Politics: “Campaign financing should be federally regulated to limit the influence of large corporations in political decisions.”
- Social Issue: “Legalizing marijuana will lead to decreased drug-related crime and provide medical and economic benefits.”
- Literature: “In ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ Harper Lee uses the character of Atticus Finch to argue against racial prejudice and for moral integrity.”
- Culture: “Cultural appropriation in fashion undermines and disrespects the origins and significance of native traditions.”
- Economics: “A universal basic income is essential for ensuring economic stability in the era of automation.”
Undergraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Research paper
Research papers in undergrad demand thorough investigation. This thesis statement for research paper should highlight the primary focus and direction of the research.
- Biology: “Studying the genetic makeup of the tardigrade might reveal clues about its extraordinary resilience.”
- Physics: “Quantum entanglement could revolutionize data encryption methods.”
- History: “The fall of the Berlin Wall marked not just the end of an era but instigated global political realignments.”
- Chemistry: “Nano-drug delivery systems show high potential in targeting cancer cells more effectively.”
- Sociology: “Urban migration patterns are strongly influenced by digital communication tools.”
- Psychology: “Childhood trauma has lasting effects on decision-making processes in adulthood.”
- Geography: “The melting Arctic ice is influencing global weather patterns.”
- Mathematics: “The application of fractals offers fresh insights into urban planning.”
- Linguistics: “The evolution of creole languages provides evidence of socio-cultural amalgamation.”
- Environmental Science: “Rising ocean temperatures have a direct impact on cyclone intensities.”
Undergraduate 3 Point Thesis Statement Examples
A three-point thesis statement provides a clear structure, highlighting three major points the paper will address. It’s concise and offers readers a roadmap.
- Literature: “In ‘1984’ by George Orwell, the themes of surveillance, totalitarianism, and resistance underscore the dangers of unchecked political power.”
- Philosophy: “Nihilism challenges societal norms, questions life’s inherent meaning, and confronts the fear of oblivion.”
- Business: “Successful startups prioritize innovation, foster a resilient company culture, and adapt to market feedback.”
- Medicine: “Preventive medicine reduces healthcare costs, improves patient quality of life, and alleviates hospital resources.”
- Anthropology: “Ancient civilizations were shaped by their geographical location, religious beliefs, and socio-political hierarchies.”
Undergraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Personal Essay
In personal essays, the thesis often reflects introspection, personal growth, or a profound realization.
- Self-growth: “Confronting my fears during my year abroad taught me resilience, adaptability, and the value of stepping out of my comfort zone.”
- Relationships: “Enduring a long-distance relationship revealed the strengths and challenges of our bond.”
- Identity: “Growing up bilingual fostered a dual cultural identity that shaped my worldview.”
- Career: “Interning at the local newspaper ignited my passion for journalism and defined my career aspirations.”
- Travel: “Traveling solo for the first time, I discovered independence, resourcefulness, and a deep appreciation for different cultures.”
College Thesis Statement Examples
College-essay thesis statements should be clear, specific, and indicate the writer’s stance on the subject.
- Technology: “Artificial intelligence poses as much a challenge to job markets as it does offer efficiency in operations.”
- Healthcare: “Holistic approaches to healthcare, integrating mental and physical wellness, lead to more comprehensive patient outcomes.”
- Politics: “Populist movements are often a reaction to perceived elitism within political establishments.”
- Art: “Renaissance art reflects the socio-political and religious tensions of its time.”
- Economics: “Cryptocurrencies challenge the traditional banking system by offering decentralized financial control.”
How do you write an undergraduate thesis introduction?
The introduction of an undergraduate thesis sets the stage for the entire research. It’s a chance to make a first impression and establish the framework for the forthcoming sections.
- Hook the Reader : Begin with a captivating statement, question, statistic, or anecdote relevant to your topic to grab the reader’s attention.
- Background Information : Provide necessary context for your research. What broader issues or questions surround your specific topic? Why is this area of study important?
- State the Problem : Clearly define the research problem or gap that your study addresses. This highlights the significance of your research.
- Purpose and Objective : Explicitly state the aim of your research. What are you trying to accomplish, prove, or disprove?
- Scope : Briefly outline what aspects of the topic you will be focusing on and any limitations of your study.
- Thesis Statement : Conclude your introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement that encapsulates the central argument or point of your research.
How do you write an undergraduate thesis? – Step by Step Guide
Writing an undergraduate thesis can be a daunting task, but breaking it down into steps can make it more manageable.
- Choose a Topic : Your topic should be something you’re passionate about and is researchable. Consult with professors or mentors for guidance.
- Literature Review : Before delving into your research, familiarize yourself with existing studies on your topic. Understand the existing gaps, debates, and methodologies used.
- Define Your Research Question : Clearly define what you want to discover or shed light on.
- Research Methodology : Decide on how you’ll conduct your research. Will it be qualitative, quantitative, or a mix of both? Design surveys, experiments, or decide on which data to analyze.
- Data Collection : Execute your methodology. This could involve experiments, surveys, interviews, or fieldwork.
- Analysis : Analyze the data you’ve collected. Use statistical tools if necessary and draw connections or contrasts to existing literature.
- Drafting : Start with a rough draft, organizing your research findings under relevant sections: Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion.
- Revision : Once the draft is ready, review it multiple times. Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or professors.
- Citation : Properly cite all the sources and studies you’ve referenced in your thesis.
- Conclusion and Recommendations : Summarize your findings and propose any recommendations or future areas of study.
- Abstract : Write an abstract that gives a brief overview of your research, methodology, and main findings.
- Submission : Follow your university’s guidelines for formatting, binding, and submission.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement for an Undergraduate
- Be Specific : Avoid being too broad. Your thesis statement should be specific enough to give your reader a clear idea of your research’s direction and scope.
- Assert Your Position : An effective thesis statement takes a stand. It should not be a mere statement of fact but should declare your position on the topic.
- Ensure It’s Arguable : If everyone agrees with your statement, it’s probably not making a clear argument.
- Keep It Clear : Avoid jargon or complex language. Your thesis should be understandable even to those outside your field of study.
- Stay Focused : Stick to your main point or argument. Avoid bringing in unrelated ideas or arguments.
- Revise as Necessary : As you delve deeper into your research, you might find the need to tweak or modify your thesis statement to better reflect your findings.
- Seek Feedback : Before finalizing your thesis statement, get feedback from peers, professors, or mentors. They can offer a fresh perspective or point out any ambiguities.
Remember, writing an undergraduate thesis is a process. It’s okay to make revisions, seek help, and take it one step at a time. The journey itself offers invaluable learning experiences. You may also be interested to browse through our other informative speech thesis statement .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Acknowledgement Sample
Sample acknowledgement for a final year Project

In this article, we will provide a sample acknowledgment for a final year project, however similar form can also apply to the acknowledgements for thesis, or research paper.
The most important thing when writing acknowledgement for a final year project is to acknowledge contributions made by your supervisor and institution that supported your work. However, you may also consider acknowledging the support you have received from:
- Staff/colleagues that provided you inputs
- University / College
- Institution that provided you financial support in the project preparation
- Friends and Family
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to several individuals and organizations for supporting me throughout my Graduate study. First, I wish to express my sincere gratitude to my supervisor, Professor Collins, for his enthusiasm, patience, insightful comments, helpful information, practical advice and unceasing ideas that have helped me tremendously at all times in my research and writing of this thesis. His immense knowledge, profound experience and professional expertise in Data Quality Control has enabled me to complete this research successfully. Without his support and guidance, this project would not have been possible. I could not have imagined having a better supervisor in my study.
I also wish to express my sincere thanks to the University of Groningen for accepting me into the graduate program. In addition, I am deeply indebted to the Ministry of Education, Culture and Science of the Netherlands for granting me the doctoral scholarship. This financial support has enabled me to complete my PhD studies successfully. Also, I and grateful the Faculty of Economics and Business , University of Groningen for sponsoring me for participation in the scientific conferences.
I am also grateful to the following university staff: Ahmed Mustafa, Rick Van Dijk, and Breda Van Breda for their consistent support and assistance.
Finally, last but by no means least; also to everyone in the Research institute for Data Science it was great sharing premises with all of you during last five years.
Thanks for all your encouragement!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
Published on May 3, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
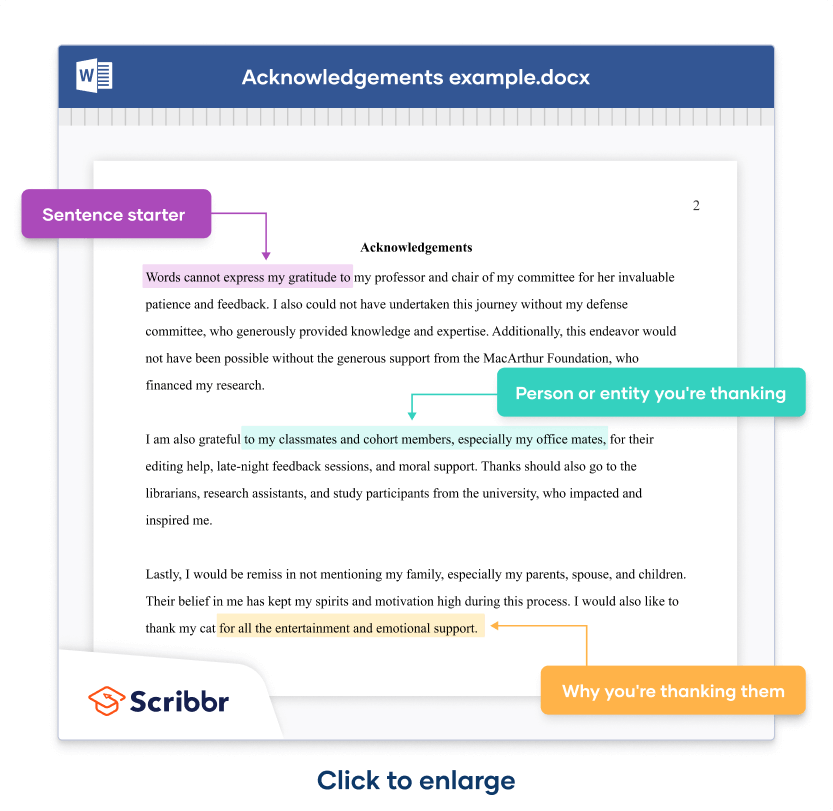
The acknowledgements section is your opportunity to thank those who have helped and supported you personally and professionally during your thesis or dissertation process.
Thesis or dissertation acknowledgements appear between your title page and abstract and should be no longer than one page.
In your acknowledgements, it’s okay to use a more informal style than is usually permitted in academic writing , as well as first-person pronouns . Acknowledgements are not considered part of the academic work itself, but rather your chance to write something more personal.
To get started, download our step-by-step template in the format of your choice below. We’ve also included sample sentence starters to help you construct your acknowledgments section from scratch.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Who to thank in your acknowledgements, how to write acknowledgements, acknowledgements section example, acknowledgements dos and don’ts, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the acknowledgements section.
Generally, there are two main categories of acknowledgements: professional and personal .
A good first step is to check your university’s guidelines, as they may have rules or preferences about the order, phrasing, or layout of acknowledgements. Some institutions prefer that you keep your acknowledgements strictly professional.
Regardless, it’s usually a good idea to place professional acknowledgements first, followed by any personal ones. You can then proceed by ranking who you’d like to thank from most formal to least.
- Chairs, supervisors, or defense committees
- Funding bodies
- Other academics (e.g., colleagues or cohort members)
- Editors or proofreaders
- Librarians, research/laboratory assistants, or study participants
- Family, friends, or pets
Typically, it’s only necessary to mention people who directly supported you during your thesis or dissertation. However, if you feel that someone like a high school physics teacher was a great inspiration on the path to your current research, feel free to include them as well.
Professional acknowledgements
It is crucial to avoid overlooking anyone who helped you professionally as you completed your thesis or dissertation. As a rule of thumb, anyone who directly contributed to your research process, from figuring out your dissertation topic to your final proofread, should be mentioned.
A few things to keep in mind include:
- Even if you feel your chair didn’t help you very much, you should still thank them first to avoid looking like you’re snubbing them.
- Be sure to follow academic conventions, using full names with titles where appropriate.
- If several members of a group or organization assisted you, mention the collective name only.
- Remember the ethical considerations around anonymized data. If you wish to protect someone’s privacy, use only their first name or a generic identifier (such as “the interviewees”)/
Personal acknowledgements
There is no need to mention every member of your family or friend group. However, if someone was particularly inspiring or supportive, you may wish to mention them specifically. Many people choose to thank parents, partners, children, friends, and even pets, but you can mention anyone who offered moral support or encouragement, or helped you in a tangible or intangible way.
Some students may wish to dedicate their dissertation to a deceased influential person in their personal life. In this case, it’s okay to mention them first, before any professional acknowledgements.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
After you’ve compiled a list of who you’d like to thank, you can then sort your list into rank order. Separate everyone you listed into “major thanks,” “big thanks,” and “minor thanks” categories.
- “Major thanks” are given to people who your project would be impossible without. These are often predominantly professional acknowledgements, such as your advisor, chair, and committee, as well as any funders.
- “Big thanks” are an in-between, for those who helped you along the way or helped you grow intellectually, such as classmates, peers, or librarians.
- “Minor thanks” can be a catch-all for everyone else, especially those who offered moral support or encouragement. This can include personal acknowledgements, such as parents, partners, children, friends, or even pets.
How to phrase your acknowledgements
To avoid acknowledgements that sound repetitive or dull, consider changing up your phrasing. Here are some examples of common sentence starters you can use for each category.
| Major thanks | Big thanks | Minor thanks |
|---|---|---|
Note that you do not need to write any sort of conclusion or summary at the end. You can simply end the acknowledgements with your last thank you.
Here’s an example of how you can combine the different sentences to write your acknowledgements.
A simple construction consists of a sentence starter (in purple highlight ), followed by the person or entity mentioned (in green highlight ), followed by what you’re thanking them for (in yellow highlight .)
Acknowledgements
Words cannot express my gratitude to my professor and chair of my committee for her invaluable patience and feedback. I also could not have undertaken this journey without my defense committee, who generously provided knowledge and expertise. Additionally, this endeavor would not have been possible without the generous support from the MacArthur Foundation, who financed my research .
I am also grateful to my classmates and cohort members, especially my office mates, for their editing help, late-night feedback sessions, and moral support. Thanks should also go to the librarians, research assistants, and study participants from the university, who impacted and inspired me.
Lastly, I would be remiss in not mentioning my family, especially my parents, spouse, and children. Their belief in me has kept my spirits and motivation high during this process. I would also like to thank my cat for all the entertainment and emotional support.
- Write in first-person, professional language
- Thank your professional contacts first
- Include full names, titles, and roles of professional acknowledgements
- Include personal or intangible supporters, like friends, family, or even pets
- Mention funding bodies and what they funded
- Appropriately anonymize or group research participants or non-individual acknowledgments
Don’t:
- Use informal language or slang
- Go over one page in length
- Mention people who had only a peripheral or minor impact on your work
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
In the acknowledgements of your thesis or dissertation, you should first thank those who helped you academically or professionally, such as your supervisor, funders, and other academics.
Then you can include personal thanks to friends, family members, or anyone else who supported you during the process.
Yes, it’s important to thank your supervisor(s) in the acknowledgements section of your thesis or dissertation .
Even if you feel your supervisor did not contribute greatly to the final product, you must acknowledge them, if only for a very brief thank you. If you do not include your supervisor, it may be seen as a snub.
The acknowledgements are generally included at the very beginning of your thesis , directly after the title page and before the abstract .
In a thesis or dissertation, the acknowledgements should usually be no longer than one page. There is no minimum length.
You may acknowledge God in your dissertation acknowledgements , but be sure to follow academic convention by also thanking the members of academia, as well as family, colleagues, and friends who helped you.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/acknowledgements/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation layout and formatting, thesis & dissertation title page | free templates & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A final year thesis has to demonstrate academic structure, content, and integrity, something that is not always presented clearly by supervisors. As a supervisor, I designed a handout to help and ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
What's Included: The Dissertation Template. If you're preparing to write your dissertation, thesis or research project, our free dissertation template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples. The template's structure is based on the tried ...
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Download Example. Title: Essays in Firm-Level Patenting Activities and Financial Outcomes. Author: Michael J Woeppel. Year: 2020. This doctoral dissertation explores financial dynamics in two key areas: investment valuation and the performance of small innovative firms.
Dissertation examples. Listed below are some of the best examples of research projects and dissertations from undergraduate and taught postgraduate students at the University of Leeds We have not been able to gather examples from all schools. The module requirements for research projects may have changed since these examples were written.
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile.
As a final year supervisor for twelve years on the degree, masters, and PhD, I have noticed time and time again students approached their thesis confused and unsure what is expected from them; and rightly so. What is involved in the write up of the final year thesis is not something students are introduced to during their studies. The structure, content, and format of a thesis are only ...
Your first point of reference should always be your Assignment Guidelines provided by your Tutor. Features of a dissertation/final year project: An extended piece of detailed work - it is an investigation. Demonstrates skills in: planning, organising, researching, problem solving, time management as well as oral and written communication skills.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on 6 April 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students.
Definition: Dissertation overview. The overwhelming majority of undergraduate and postgraduate taught courses require the submission of a dissertation to pass. A dissertation will take ca. 6~18 months to complete, usually covering ca. 5000-15,000 words. You can expect to receive your assignment and deadline during the last third of your timetable.
Theses/Projects/Dissertations from 2024 PDF. WHAT IS THE READINESS OF SOCIAL WORK STUDENTS TO WORK WITH AUTISTIC INDIVIDUALS?, Ignacio Aguilar Pelaez PDF. EXAMINING ...
The Department of Computer Science is a discipline concerned with the study of computing, which includes programming, automating tasks, creating tools to enhance productivity, and the understanding of the foundations of computation. The Computer Science program provides the breadth and depth needed to succeed in this rapidly changing field. One of the more recent fields of academic study ...
Here are some of the basic information that you can include in a simple final year project proposal: 1. Present a title for the final year project proposal. This will help you present an overview of what the proposal is all about or the subject that you would like to discuss and further look into. 2.
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
For this, we have created a sample dataset and pre-processed it using a label binarizer. Afterward, feature extraction was done using two models, first for the palm region and the other for the fingers. Later on, this dataset was fed into a custom-made CNN model whose learning parameters were provided as 0.001 learning rate, 128 batch-size, and
Undergraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Personal Essay. In personal essays, the thesis often reflects introspection, personal growth, or a profound realization. Self-growth: "Confronting my fears during my year abroad taught me resilience, adaptability, and the value of stepping out of my comfort zone."
In this article, we will provide a sample acknowledgment for a final year project, however similar form can also apply to the acknowledgements for thesis, or research paper. The most important thing when writing acknowledgement for a final year project is to acknowledge contributions made by your supervisor and institution that supported your work.
Separate everyone you listed into "major thanks," "big thanks," and "minor thanks" categories. "Major thanks" are given to people who your project would be impossible without. These are often predominantly professional acknowledgements, such as your advisor, chair, and committee, as well as any funders. "Big thanks" are an ...