Law & Policy Policy

Resources for Journalists
- Food & Farming Media Network
- How to Pitch Us
- Freelance Charter
- Work With Us
Sentient Media
- Environmental Policy
- Code of Ethics
- Testimonials
Are Zoos Good or Bad for Animals? The Argument, Explained
Debates about the ethics of zoos abound — but when it comes to animal welfare, there are certainly more cons than pros.

Explainer • Entertainment • Policy

Words by Björn Ólafsson
For many people, zoos are the only chance they’ll have in their entire lives to see beautiful animals native to far-flung ecosystems — lions, elephants, pandas, lemurs — the list goes on. And they’re popular — over 181 million people visit a U.S. zoo every year . But zoos face criticism from animal welfare organizations and environmental activists for inhumane treatment of the animals they claim to protect. Zoos maintain that they are important aspects of conservation and education.
So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of zoos ? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of these controversial organizations.
What Are Some Pros and Cons of Zoos ?
First, not all zoos are created equal. While it is easy to imagine animal ethics as a binary of evil and moral, zoos can vary widely on how they treat their animals, how much space they are given and how the animals are obtained. Still, most zoos tend to have the same positives and negatives overall.
Arguments Against Zoos
Poor conditions for animals.
Animals Often Only Have Quite Limited Space
Many zoos’ enclosures are too small, especially for animal species that are used to roaming, flying or swimming large distances in the wild. For example, polar bears are used to home ranges of about 1,000 square kilometers in the wild — large swaths of land and ice they enjoy exploring . In zoos, they get a couple hundred square feet.
Zoos Are Crowded
In addition to limited space, many zoos cram in as many animals as possible into the enclosures. Many visitors prefer seeing animals up close, instead of peering at them from afar, hidden in their dens or nests. This encourages zoos to increase the number of animals per exhibit, increasing the likelihood of visitors seeing animals on the move near the boundaries of the enclosure.
Animals Are Trapped in Unnatural Environments
Anyone who has visited a zoo knows the exhibits are a far cry from the natural landscape they are trying to imitate. Nearly all zoo enclosures contain fences, glass or other barriers for visitors to look through, which are inherently artificial. And the natural-seeming landscapes can sometimes be made out of astroturf, concrete or plastic.
Confinement May Alter the Behavior of Animals
The lack of space, unnatural environments and crowded conditions can directly affect the behavior of animals ; most notably in the form of what’s known as “stereotypy.” Stereotypy is a condition in which non-human animals engage in repetitive behaviors with no apparent purpose, such as pacing for hours on end, wagging tails abnormally or picking their own fur.
The structure of zoos increases the likelihood of stereotypic behavior due to a lack of enrichment, mundane environments and boring, repetitive schedules. This prevalence of stereotypy in zoos even has its own name: “zoochosis,” or psychosis caused by zoos .
‘Surplus’ Animals Can Be Killed
After an animal has reproduced successfully and the zoo no longer requires the animal to maintain an exhibit, the animal is deemed “surplus.” At this point, the animal’s welfare is no longer profitable . Zoos can sell the animal to private owners (who may keep the animal in tiny cages for amusement or kill the animal for taxidermy purposes), sell the animal to other zoos or enclosures, or “euthanize” the animal.
Animals Are Often Mistreated
Animal mistreatment is much more than hitting or beating an animal. It also includes harmful training techniques, separation from family members and forcing animals to behave in abnormal ways.
In a report from World Animal Protection, three-fourths of zoos include human-animal interactions , many of which can be very stressful or physically harmful for animals. In some extreme cases, visitors rode on the backs of animals (causing injury) or encroached on the animals’ enclosure (causing stress).
Investigations into popular zoos sometimes reveal that caretakers don’t always clean the exhibits frequently , leaving the animals to live near their feces. The research also reveals many zookeepers hitting animals who “misbehave,” and not helping animals with injuries sustained in the enclosures. While not all animal caretakers behave this way, the reporting suggests many zoos around the world are lax with animal welfare.
Animals Don’t Like Being Visited
The mere presence of human beings can negatively affect wild animals, especially in massive crowds that are common at zoos. Being bombarded by the sounds, smells and appearances of swaths of humans can trigger the stress responses of some animals . Some studies show that the number of visitors correlates with the amount of stress hormones in many animal species.
Animals Struggle to Form Connections
Many animals are highly social creatures. Elephants, lions, pigs, cows and many more species are shown to have complex connections, hierarchies and relationships with members of their own kind — especially with friends and family. However, zoo animals rarely stay with the same herd or family for their entire lives. Instead, zoos opt to transfer, sell, buy or relocate animals throughout their lifespans, making it difficult for animals to form social connections . This lack of bonding can harm the animals emotionally.
Zoos Are for Humans, Not Animals
Most zoos are for-profit enterprises, meaning they have one goal in mind: maximizing revenue. It is easy to see how making more money can come at the expense of animal welfare. For example, a zoo is unlikely to fund an exhibit expansion if it isn’t cost-effective, regardless of its benefits for the animals inside. While many zookeepers form real bonds with their animal companions, the animals still exist under a for-profit, human-centered organization.
Zoos Promote Human Superiority
The aesthetic nature of zoos — animals in panopticon-like enclosures, viewed 24/7 by members of a different species — can reinforce human superiority. As moral philosopher Lori Gruen writes in her book, “visitors leave the zoo more convinced than ever of human superiority over the natural world.” Of course, zoos also reinforce the idea that humans have a right to take away animals’ freedom and bodily autonomy.
Zoos Don’t Always Help with Conservation — Some Wild Animals Have to Be Caught to Bring Them to Zoos
Many animals in zoos are born in captivity, but that’s not the case for all. Many animals are taken directly from the wild , often when they are babies, to make the transition to captivity a bit easier. At times, this is done in the name of conservation, or when a wild animal is very ill. But many zoos will take animals from the wild, or buy animals from unethical animal traders.
It’s Often Not Possible to Return Animals to the Wild
Releasing an animal into the wild isn’t always successful, especially if the animal has spent time in climates different from their native regions, like jungles, savannas or ice caps. Properly preparing animals for success in the wild is a multi-stage process that can require thousands of dollars — and it doesn’t always work . Captive-born predator species — disadvantaged by being born and raised in an artificial environment — only have a survival rate after being released into the wild of 33 percent , according to one study. As a result, re-release is not a priority for many zoos.
Zoos Are Poorly Regulated
While there exist many laws that protect animals, such as the Animal Welfare Act (AWA) and the Endangered Species Act , they only offer minimum protections . For example, the AWA excludes entire species of animals, like mice, farmed animals, birds and all cold-blooded animals. Its “minimum” standards of care usually ensure the animals’ safety, not their welfare or happiness. Many animal law experts say these regulations don’t go far enough .
What Are the Pros of Having Zoos?
They Can Be Important for Researchers
Biologists and zoologists can benefit from studying animals in zoos. Some breakthroughs in animal behavior and treatment, like why elephants swing their trunks or how gorillas develop heart disease, have been made possible because of zoos’ ease of access . However, not all animals behave the same in captivity as they do in the wild, so not all research is possible in zoos.
Zoos Are Educational — People May Behave “Eco-friendlier” After Going To the Zoo
Zoos can kickstart individuals’ interest in biodiversity, which is a critical aspect of environmental protection. Many zoos include calls to action in their exhibits, highlighting how endangered animals are being poached, driven away, or otherwise killed by human activity. This can inspire some people to behave more conscientiously. One limited survey found that 35 percent of eco-friendly people learned sustainable behavior from zoos . ‘
Zoos Can Help Educate Children About Animals
Zoos are a quintessential school experience for many young people. Children love learning about animals up-close in a safe environment — in fact, education is possibly the biggest advantage of modern zoos. Many programs, like school presentations, guided tours, informational exhibits, and talks with zookeepers can trigger a lifelong love of animals in children .
But zoos aren’t perfect in this regard. According to a study of zoo visitors in the UK, only 34 percent of children learned more about animals at zoos (the result was slightly better when the children were given a guided tour). Worse, children did not feel empowered to help with conservation efforts after visiting a zoo. This suggests that if zoos care about education, they need to more actively reach out to schoolchildren for empowerment and education.
Going to the Zoo Is Affordable
More ethical ways of engaging with animals without removing them from their natural habitats — like whale watching, safaris, hikes, or excursions — are usually expensive or inaccessible for many people. Zoos tend to be relatively cheap for the average family that wants to learn about animals.
Conservation
Zoos Can Protect Endangered Species from Extinction
Zoos often claim they can protect entire species from extinction through conservation programs that involve breeding more animals in captivity and then releasing them into the wild. This is especially important for endangered species like pandas.
While these conservation efforts are truly important, they don’t represent the majority of a zoo’s activities, nor are zoos leaders in conservation worldwide. At the National Zoo, for example, only one-fifth of animals are endangered . In North America, zoos only contribute about 14 percent of all animals reintroduced into the wild as part of a conservation program. Zoos also tend to focus on headline-grabbing endangered animals to bring in visitors, like pandas, elephants or tigers, as opposed to lesser-known but crucial species, like tamarins, kakapos or wombats.
Are Zoos Good or Bad for the Environment?
Zoos claim to support global biodiversity through conservation efforts like protecting endangered animals. This is somewhat true, although it varies greatly from zoo to zoo.
On the other hand, zoos are big polluters and use up lots of resources , especially energy and water . Aquariums in particular use tons and tons of water. Zoo animals also generate waste that may or may not be composted or disposed of correctly.
Should Zoos Exist or Be Banned?
Given the many ways that zoos are unethical to animals, the flawed attempts to contribute to conservation, and the positioning of humans as superior to animals, many animal ethicists believe zoos should not exist — or at least, not exist in their current form .
For example, animal philosopher Dale Jamieson says in his book Ethics on the Ark that zoos primarily “alleviate our sense of guilt for what we are doing to the planet, but they do little to help the animals we are driving to extinction.” He continues to argue that zoos exist for humans alone , and that it is very difficult to wave away the inherent immorality of depriving animals their liberty for the sake of human amusement.
Instead, private conservation programs can benefit endangered animals without showcasing them to the public. Animal sanctuaries, which are areas of land in which endangered and other animals are protected by humans, are also advantageous for both individual animals and global biodiversity .
Zoos do have advantages — fostering curiosity and education chief among them. But experts believe there are other ways of accomplishing these goals without resorting to zoos with tiny enclosures. Excursions, nature documentaries, safaris, local gardens, hikes, boat tours and other ways of interacting with nature don’t involve taking animals out of their natural habitats.
The Bottom Line
If you do choose to visit a zoo, opt for zoos that have certifications from independent animal welfare organizations. If you are interested in animal conservation, you’d be more impactful donating to a non-zoo animal protection organization instead. And if you do want to visit animals, consider an animal sanctuary or an ethical safari, where you can see animals in their native environments.
Independent Journalism Needs You
Björn Jóhann Ólafsson is a science writer and journalist who cares deeply about understanding the natural world and her inhabitants through stories and data. He reports on the environmental footprint of the meat industry, the alternative protein sector and cultural attitudes around food. His previous bylines include the EU Observer and Elemental. He lives in Spain with his two lovebirds.
The Loss of Chevron Could Also Be a Major Loss for Animals
Law & Policy • 6 min read
More Law & Policy
How the Amy’s Kitchen Boycott Worked, and What It Might Mean for Other Labor Organizers
Justice • 5 min read
Investigation
Inside the Billion-Dollar Feed Industry’s Ploy to Greenwash Emissions
A new law would allow the livestock industry to fast-track federal review of feed additives.
Law & Policy • 4 min read
Are National Parks Safe Spaces for LGBTQ People This Pride Month — and Beyond?
An email from Interior Secretary Deb Haaland about park officer uniforms did not quell the controversy completely.
Justice • 7 min read
- 13 Animals Going Extinct — in Large Part Thanks To Humans
Climate • 8 min read
Impossible’s New Ad Campaign Doubles Down on Dudes
Food • 6 min read
Humans Can Get Bird Flu, and Here’s What You Need to Know
Health • 8 min read
When Marine Parks Close, Whales and Dolphins Face Uncertain Future
Entertainment • 7 min read
Scientists Are Making Honey Without the Hive
Breakthroughs • 5 min read
Most Read Today
- The 30 Most Intelligent Animals in the World Might Surprise You
- What Are Hot Dogs Really Made Of?
- How Does Dairy Farming Cause Water Pollution?
- The 14 Best Vegan Sources of Omega-3
- What Foods to Avoid If You Are Lactose Intolerant
- Is Salmon Good For You? 6 Alleged Salmon Benefits Debunked
- New Research on Animal Communication Shows Their Cultures Are Often Complex and Cumulative

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
100 Zoo Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Zoos are fascinating places that offer a unique opportunity to observe and learn about a wide variety of animals from all over the world. If you're tasked with writing an essay about zoos, you might be struggling to come up with a topic that is both interesting and informative. To help you out, here are 100 zoo essay topic ideas and examples that you can use as inspiration for your next assignment:
- The ethical implications of keeping animals in zoos
- The role of zoos in conservation efforts
- The impact of zoos on animal behavior
- The history of zoos and how they have evolved over time
- The benefits of zoos for education and research
- The controversy surrounding captive breeding programs in zoos
- The importance of zoos in preserving endangered species
- The challenges of managing a zoo and caring for its animals
- The role of zoos in promoting awareness of wildlife conservation issues
- The impact of zoos on local communities and economies
- The role of zoos in promoting animal welfare and ethics
- The debate over whether zoos should exist in the modern world
- The cultural significance of zoos in different societies
- The impact of climate change on zoos and their animal populations
- The role of zoos in public education and outreach programs
- The challenges of balancing conservation efforts with visitor experiences in zoos
- The impact of captivity on animal behavior and well-being in zoos
- The role of zoos in promoting environmental awareness and sustainability
- The ethics of using animals in zoo entertainment shows and performances
- The impact of zoos on biodiversity and ecosystem health
- The role of zoos in promoting animal rights and welfare legislation
- The impact of zoo closures and budget cuts on animal populations
- The challenges of reintroducing captive-bred animals into the wild
- The role of zoos in supporting local wildlife conservation efforts
- The benefits of zoos for public health and well-being
- The impact of zoos on visitor attitudes towards wildlife conservation
- The role of zoos in promoting sustainable tourism practices
- The challenges of managing invasive species in zoos
- The impact of zoo design and architecture on animal welfare
- The role of zoos in promoting cultural exchange and understanding
- The benefits of zoos for scientific research and discovery
- The impact of zoo accreditation programs on animal welfare standards
- The challenges of breeding endangered species in captivity
- The role of zoos in promoting animal enrichment and mental stimulation
- The ethics of using animals in zoo breeding programs
- The impact of zoos on local ecosystems and biodiversity
- The role of zoos in promoting public awareness of wildlife trafficking
- The benefits of zoos for educating children about conservation
- The challenges of managing a zoo during a pandemic
- The impact of zoo closures on animal welfare and conservation efforts
- The role of zoos in promoting sustainable food and waste management practices
- The ethics of using animals in zoo education programs
- The impact of zoos on wildlife populations in surrounding areas
- The challenges of managing zoo populations and genetics
- The role of zoos in promoting animal welfare legislation
- The benefits of zoos for promoting public engagement with wildlife
- The impact of zoos on local economies and tourism
- The role of zoos in promoting wildlife rehabilitation and release programs
- The challenges of managing zoo populations in the face of climate change
- The ethics of using animals in zoo research and experimentation
- The impact of zoos on animal behavior and social dynamics
- The role of zoos in promoting public awareness of wildlife conservation issues
- The benefits of zoos for promoting sustainable tourism practices
With these 100 zoo essay topic ideas and examples, you should have plenty of inspiration to get started on your next assignment. Whether you're interested in the ethical implications of keeping animals in zoos, the role of zoos in conservation efforts, or the impact of zoos on biodiversity and ecosystem health, there's sure to be a topic that piques your interest. Happy writing!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade

Essay on Zoo

Essay on Zoo – Introduction
Zoos across the globe have witnessed some truly fascinating events over the years. One such event occurred in 1988 at the San Francisco Zoo when Koko, a gorilla, used sign language to communicate with her caregivers. Similarly, the birth of an endangered white rhinoceros in the Toronto Zoo back in 2016 brought joy to everyone. Zoos are not just places to visit; they are an experience that offers a world of excitement and nostalgia for people of all ages. For parents, it’s a chance to share the wonders of the animal kingdom with their children while kids enjoy the playful antics of the animals. Every family has a story to tell about their zoo visit, where they witnessed a lion’s roar for the first time or were mesmerized by the colorful hues of a peacock’s feathers. In this essay on zoo, we will discuss the importance of zoos, their role in education and conservation efforts, as well as the ethical implications of keeping wild animals in captivity.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
Purpose of Zoos
Why do people visit zoos, what types of animals are in zoos.
- Benefits of Zoos
- Problems with Zoos
Are Zoos Cruel to Animals?
Use of technology in zoos, future of zoos.
- Notable Events at Zoos
Infographics on Zoo
Zoos are places where you can see and learn about many different animals. Zoos not only offer fun, but they also teach us the importance of caring for animals and the environment. Some zoos have special provisions for endangered animals. This means that these zoos keep such animals healthy and safe, especially when only a few of them are left in the wild.
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
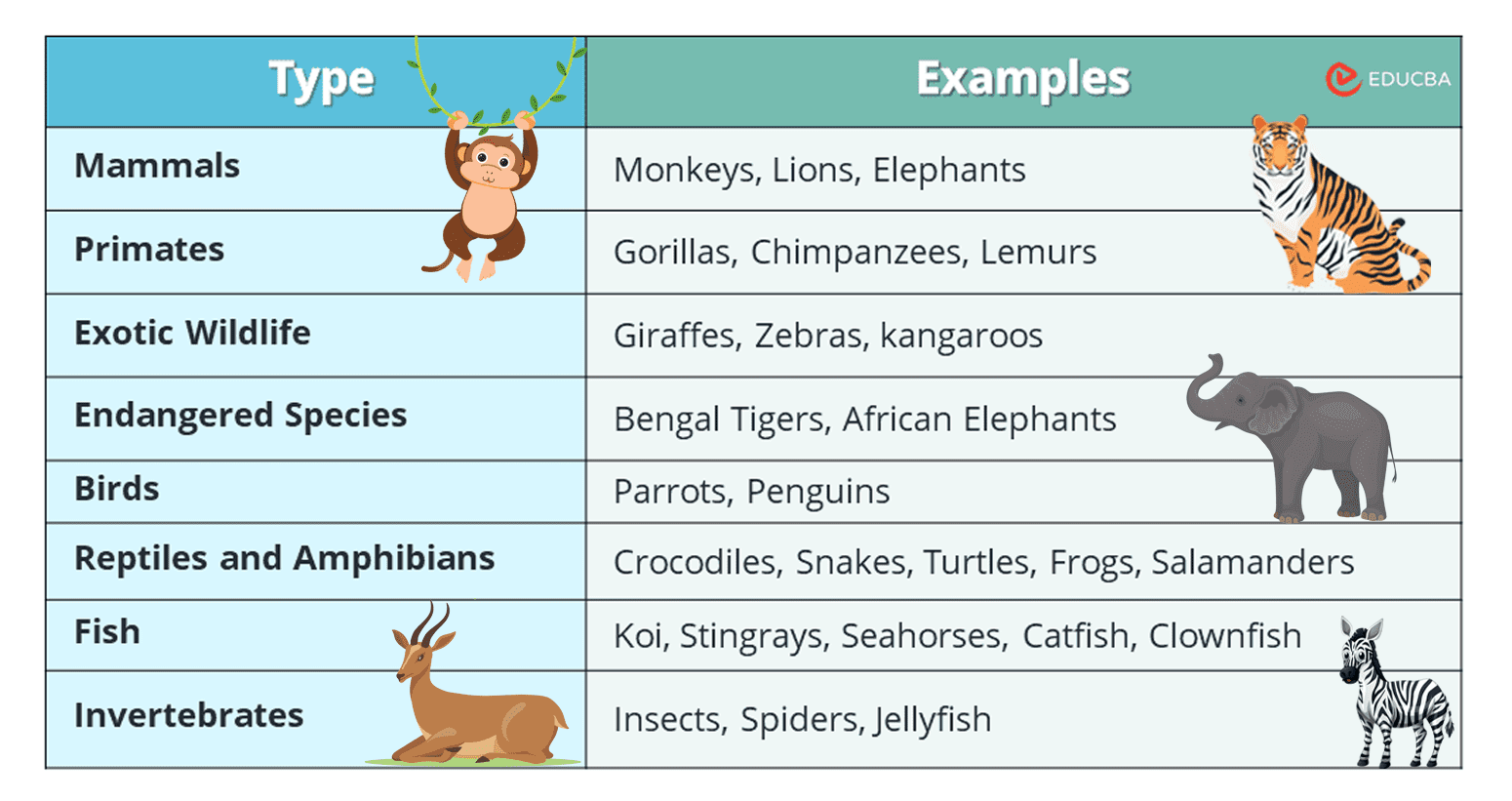
There are many reasons why people visit zoos. Some people visit zoos to see animals that they would not normally have the opportunity to see, such as lions, tigers, and elephants. Others visit zoos to learn about the animals and their habitats. Still, others visit zoos for the entertainment value or because they have fond memories of visiting zoos as children. Whatever the reason, there are many benefits to visiting zoos.
Zoos house a variety of animals, from the common to the exotic. Mammals such as lions, tigers, and bears are popular attractions, as are reptiles like snakes and crocodiles. Birds like parrots and penguins are also often found in zoos. Some zoos also have unusual animals like kangaroos, koalas, and wallabies. These animals come from Australia and are rarely seen in other parts of the world. However, they are available in some zoos in North America and Europe.
Benefits of Zoo
There are many benefits of zoos that often go unnoticed. Here are a few of them:
1. Education and Conservation
Zoos play an important role in educating people of all ages about wild animals and their natural habitats. They also work to conserve endangered species and protect them from extinction.
2. Fun and Memorable Experiences
Zoos offer a chance to see amazing creatures up close and personal, which is an experience that few people ever get in their lifetimes. A trip to the zoo is sure to be a memorable one for people of all ages.
3. Provides a Safe Haven for Displaced Animals
Zoos keep animals safe when they lose their natural homes because of human activity. By keeping these animals safe in captivity, zoos help ensure they will not disappear entirely from the planet.
4. Helps in Animal Rehabilitation
Zoos also help rehabilitate injured or sick animals. They team up with animal rehab centers and other groups to help sick or injured animals that cannot survive in the wild.
5. Supports Scientific Research
Zoos allow scientists to research various species. These research studies aim to learn more about animal behavior and biology.
6. Supports Breeding of Endangered Species
Zoos help endangered species by breeding and protecting them from extinction. Once these animals reach a certain age and are healthy, they are released back into the wild.
7. Involves Local Communities in Conservation Efforts
Zoos often work with local communities to teach them why taking care of wildlife is crucial. They may also offer volunteer and internship opportunities for people who are interested in working with animals.
Problems with Zoos: Why are Zoos Harmful?
There are many problems associated with zoos:
- Animals in some zoos are not treated well. They live in small cages and may not get enough food or water.
- There is a risk of danger to both animals and humans in zoos, as animals may escape from their cages and harm people.
- Some zoos may not provide a comprehensive understanding of animals. Visitors may only see the “cute” side of animals and miss out on learning about their natural habitats and behaviors.
- Zoos usually only care for the popular animals, which means that less popular animals can receive poor treatment.
- Animal rights activists think that humans should not cage animals in zoos.
Many people believe zoos are cruel to animals because they are confined to small spaces and deprived of their natural habitats. Others argue that zoos provide a necessary service by rescuing endangered species and educating the public about wildlife conservation.
Let’s look at four examples where zoos have used new technologies to take care of animals.
Example 1: San Diego Zoo (United States)
In this zoo, the zookeepers have fitted special devices, similar to fitness trackers, on some animals. These devices assist them in tracking the animals’ movement, heart rate, and other health parameters.
Example 2: Singapore Zoo (Singapore)
The Singapore Zoo has designed natural habitats for animals instead of confining them to cages. These habitats have advanced features that control temperature, humidity, and lighting to mimic the animals’ natural surroundings. As a result, the animals feel happier and more comfortable.
Example 3: London Zoo (United Kingdom)
London Zoo has a system called ZSL Instant Wild. This system allows you to watch live videos of animals in their natural habitats worldwide. You can use a mobile app or go to their website to see these videos.
Example 4: Mumbai Zoo (India)
Also known as Veermata Jijabai Bhosale Udyan, this Zoo has modern vet facilities, X-rays, and ultrasound machines. The zoo also has security cameras and electronic fences to keep both the animals and visitors safe.
Zoos may see an increase in the use of Artificial intelligence (AI) technology to create natural habitats for animals and monitor their health, behavior, and well-being in real-time. This will help caretakers to take action immediately if there are any issues. AI can also track animal populations in the wild. Looking to the future, zoos will continue to play an important role in educating the public about wildlife and their habitats. Additionally, zoos will continue to be valuable resources for conservation efforts. As our understanding of animals and their needs grows, so too will our ability to provide them with the best possible care.
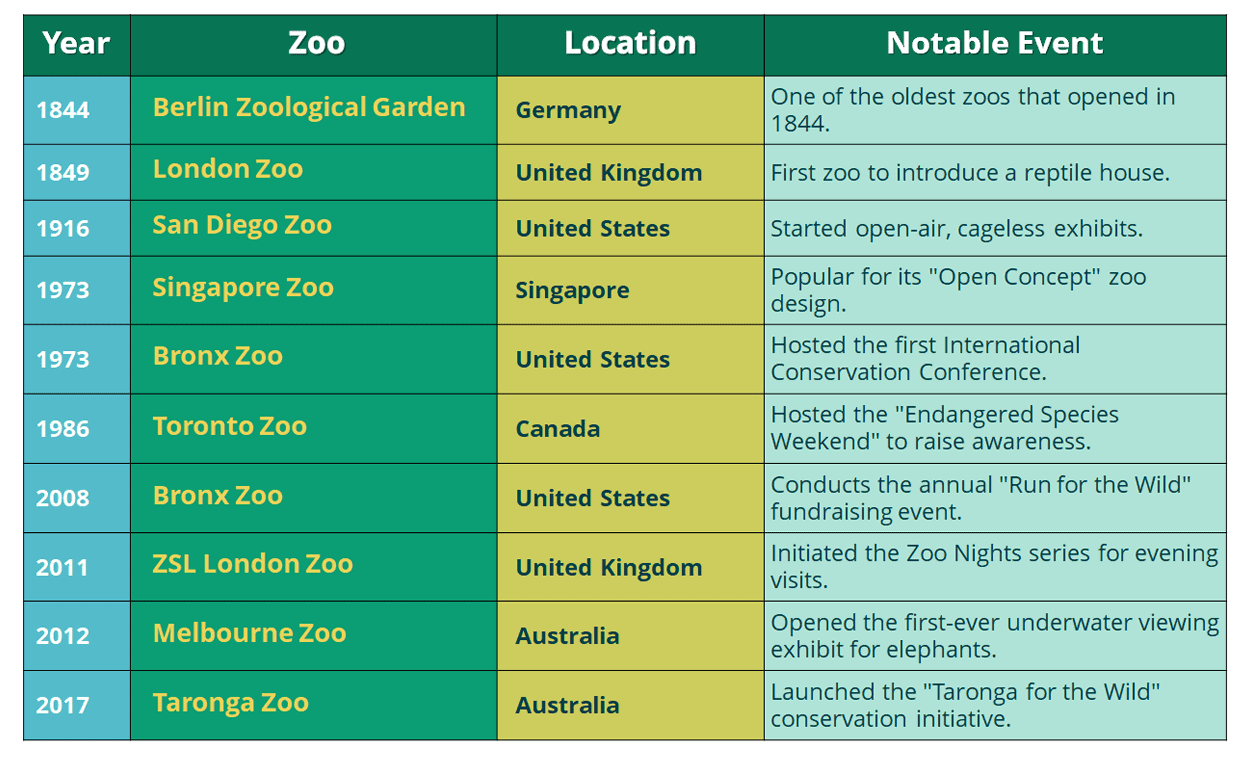
Famous Zoos with Notable Events
Here’s a table featuring famous zoos with notable events:
Final Thoughts – Essay on Zoo
The essay on zoos explains that Zoos are an important part of our society and culture. They provide us with a connection to nature, preserve endangered species, and educate people about animals. Visiting a zoo can be a great way for families to spend time together while learning more about wildlife conservation. By supporting zoos and their efforts, we can help ensure that these valuable resources are around for generations to come. So, next time you are looking for something fun to do on the weekend or during your vacation, consider taking a trip to the local zoo!
Recommended Articles
- Essay on Cleanliness
- Essay on Rain Water Harvesting
- Air Pollution Essay
- Essay on Natural Resources

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
More From Forbes
How zoos benefit society and the animals they protect.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
The benefits of zoos to local communities and to society in general are largely underestimated by the wider population
© Copyright by GrrlScientist | hosted by Forbes
Sun parrots (Aratinga solstitialis) eating food from the open hand of a member of the public in a ... [+] walk-in aviary at a zoo. Experiences such as these add greatly to people's sense of well-being as well as their desire to conserve wildlife.
Zoos, aquariums and aviaries are amongst the most popular tourist attractions in the world, with more than 700 million visitors annually. (Throughout this piece, I will collectively refer to zoos, aquariums and aviaries as ‘zoos’.) This staggering number of visitors alone suggests that these institutions have a unique platform for reaching the public, but — surprisingly — the benefits of zoos to society are generally underestimated.
In addition to making important contributions to nature conservation and to applied animal science, a newly published study finds that zoos also have an important role in how human society perceives and cares about the natural world.
To understand how zoos affect their human neighbors, an international team of researchers from the UK, Ireland and France conducted in-depth reviews of work done by zoos and catalogued zoo strategies for how they meet their four main goals — conservation, education, recreation and research (Figure 1).
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
F I G U R E 1 : Wider integration of the zoo’s aims helps to expand the societal impact they have ... [+] both over visitors directly and human populations further afield. (doi:10.3390/jzbg4010006)
As part of this study, the researchers also went online to assess the presence of zoos there and how well they meet their four established goals, to examine zoo publications, and the activities that they support. After analyzing this work, the researchers proposed that a fifth goal should be added to modern zoos’ established goals: human well-being. Human well-being, they argue, would greatly add to zoos’ wider societal value ( ref ) by providing a more complete picture of the obligations of modern zoos to the animals in their care and to nature as well as to their human visitors and workforce.
“A zoo is more than a place of entertainment and a collection of animals”, said animal behavior scientist Paul Rose, a Lecturer at the Centre for Research in Animal Behaviour and Psychology at the University of Exeter , and senior author of the new study. “Zoos allow us to experience nature and are a great resource for understanding more about conservation, biodiversity and sustainability, as well as bringing many positive benefits to human mental health and well-being.”
People’s well-being could improve as the result of engaging with a zoo’s collection of animals and plants, as well as experiencing the green spaces that a zoo manages. It can also be enhanced by accessibility to education about biodiversity and nature that is essential to inspire long-term, planet-friendly behavioral changes.
“We believe that a well-being aim covers both animal welfare and societal well-being and incentivises zoos to strive for better animal welfare and provide meaningful connection to nature to benefit humans that come into contact with the zoo’s work”, Dr Rose tweeted on Twitter ( here ).
And not to be underestimated is the fact that for many residents of high-density urban areas, zoos may be the only real connection they have with the natural world.
“We need places of conservation, such as zoos, to provide us with the education and understanding about the natural world, and for us to be educated, the aims of the zoos need to incorporate increased and meaningful engagement with society and local communities”, Dr Rose said in a statement.
Dr Rose and his collaborators suggest that further studying the wider impact of zoos on their local communities and on human populations and behavior more generally could help better integrate the relevance of a zoo’s animal collection and its needs, along with the needs, wants and ideals of people.
One of the main strengths of zoos, as I see it, is their combinations of attractive live animal displays with creative educational messaging, such that zoos have the opportunity to influence their visitors, eliciting actions and encouraging them to change their behavior to help conserve wildlife. Further, visiting immersive, naturalistic exhibits in zoos can improve human health and well-being, both physiologically and psychologically.
There is still more work to be done and many questions to investigate, such as evaluating the effect of educational messages on the community, and whether the zoos’ messages are influencing human behavior towards biodiversity, planetary health and sustainability issues.
Phillip J. Greenwell, Lisa M. Riley, Ricardo Lemos de Figueiredo , James E. Brereton , Andrew Mooney and Paul E. Rose (2023). The Societal Value of the Modern Zoo: A Commentary on How Zoos Can Positively Impact on Human Populations Locally and Globally , Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens , 4 (1):53-69 | doi: 10.3390/jzbg4010006
SHA-256 : 9ab94921e06b203a216cb219d873f92ea4083642075e2e0be632939cd42949aa
Socials: Mastodon | Post.News | CounterSocial | MeWe | Newsletter
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
April 15, 2009
How Do Zoos Help Endangered Animals?
There are more to zoos than putting animals on display
Dear EarthTalk: Do zoos have serious programs to save endangered species, besides putting a few captives on display for everyone to see? -- Kelly Traw, Seattle, WA
Most zoos are not only great places to get up close to wildlife, but many are also doing their part to bolster dwindling populations of animals still living free in the wild. To wit, dozens of zoos across North America participate in the Association of Zoos and Aquarium’s (AZA’s) Species Survival Plan (SSP) Program, which aims to manage the breeding of specific endangered species in order to help maintain healthy and self-sustaining populations that are both genetically diverse and demographically stable.
The end goal of many SSPs is the reintroduction of captive-raised endangered species into their native wild habitats. According to the AZA, SSPs and related programs have helped bring black-footed ferrets, California condors, red wolves and several other endangered species back from the brink of extinction over the last three decades. Zoos also use SSPs as research tools to better understand wildlife biology and population dynamics, and to raise awareness and funds to support field projects and habitat protection for specific species. AZA now administers some 113 different SSPs covering 181 individual species.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
To be selected as the focus of an SSP, a species must be endangered or threatened in the wild. Also, many SSP species are “flagship species,” meaning that they are well-known to people and engender strong feelings for their preservation and the protection of their habitat. The AZA approves new SSP programs if various internal advisory committees deem the species in question to be needy of the help and if sufficient numbers of researchers at various zoos or aquariums can dedicate time and resources to the cause.
AZA’s Maryland-based Conservation and Science Department administers the worldwide SSP program, generating master plans for specific species and coordinating research, transfer and reintroductions. Part of this process involves designing a “family tree” of particular managed populations in order to achieve maximum genetic diversity and demographic stability. AZA also makes breeding and other management recommendations with consideration given to the logistics and feasibility of transfers between institutions as well as maintenance of natural social groupings. In some cases, master plans may recommend not to breed specific animals, so as to avoid having captive populations outgrow available holding spaces.
While success stories abound, most wildlife biologists consider SSP programs to be works in progress. AZA zoos have been instrumental, for instance, in establishing a stable population of bongos, a threatened forest antelope native to Africa, through captive breeding programs under the SSP program. Many of these captive-bred bongos have subsequently been released into the wild and have helped bolster dwindling population numbers accordingly.
Of course, for every success story there are dozens of other examples where results have been less satisfying . SSP programs for lowland gorillas, Andean condors, giant pandas and snow leopards, among others, have not had such clear success, but remain part of the larger conservation picture for the species in question and the regions they inhabit.
CONTACTS : AZA’s Conservation & Science Program, www.aza.org/Conscience .
EarthTalk is produced by E/The Environmental Magazine. SEND YOUR ENVIRONMENTAL QUESTIONS TO: EarthTalk , P.O. Box 5098, Westport, CT 06881; [email protected] . Read past columns at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalk/archives.php . EarthTalk is now a book! Details and order information at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalkbook .
There is a moral argument for keeping great apes in zoos

Michael Gwyther Jones/Flickr
by Richard Moore + BIO

I get apprehensive whenever someone asks me about my job. I’m a philosopher who works on the question of how language evolved, I reply. If they probe any further, I tell them that I work with the great apes at Leipzig zoo. But some people, I’ve discovered, have big problems with zoos.
Plenty of philosophers and primatologists agree with them. Even the best zoos force animals to live in confined spaces, they say , which means the animals must be bored and stressed from being watched all the time. Other critics claim that zoos are wrong even if the creatures aren’t suffering, because being held captive for human entertainment impugns their dignity. Such places ‘are for us rather than for animals’, the philosopher Dale Jamieson has written , and ‘they do little to help the animals we are driving to extinction’.
But I want to defend the value of zoos. Yes, some of them should certainly be closed. We’ve seen those terrible videos of solitary apes or tigers stalking barren cages in shopping malls in Thailand or China. However, animals have a good quality of life in many zoos, and there’s a strong moral case for why these institutions ought to exist. I’ve come to this view after working with great apes, and it might not extend to all species equally. However, since great apes are both cognitively sophisticated and human-like in their behaviour, they offer a strong test case for evaluating the morality of zoos in general.
The research my colleagues and I conduct isn’t harmful to the animals and, if it goes well, it will help us get a better grasp on the cognitive differences between humans and apes. For example, we did a study with pairs of orangutans in which we tested their ability to communicate and cooperate to get rewards. We hid a banana pellet so that one orangutan could see the food but couldn’t reach it. The other orangutan could release a sliding door and push the pellet through to her partner, but wasn’t able to take it for herself. They did okay (but not great) when playing with me, and they mostly ignored each other when playing together. We then performed a similar set of studies with human two-year-olds. Compared with the apes, the two-year-olds were very good at getting the reward (stickers) when they played with an adult.
Taken together, these studies tell us something about human evolution. Unlike apes, humans are good at pooling their talents to achieve what they can’t do alone. It’s not that the apes don’t care about getting the food – they got frustrated with one another when things were going wrong, and one orangutan in particular would turn his back and sulk. However, unlike humans, they don’t seem to be able to harness this frustration to push themselves to do better.
The value of research aside, there’s an argument for zoos on the grounds of animal welfare. In the best zoos, such as Leipzig, great apes live in spacious enclosures modelled on their natural habitats, and are looked after by zookeepers who care about them deeply. Large jungle gyms keep them stimulated and stave off boredom; they’re also kept busy with ‘enrichment’ puzzles, which they can unlock with tools to get food. Zoos recognised by the two main accrediting bodies in Europe and the United States are rigorously vetted and required to take part in education and conservation programmes. And there’s no solid evidence that apes living in well-designed enclosures get stressed or disturbed by human observation.
Of course, zoos can’t provide their animals with conditions such as those in an untouched forest. But for the great apes in captivity, there’s rarely a viable alternative. There are estimated to be more than 4,000 great apes living in zoos worldwide. Most of the regions where they are found in the wild – orangutans in Indonesia, chimpanzees and gorillas in Central and West Africa, bonobos in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) – are ravaged by habitat loss, civil war, hunting and disease. As few as 880 remaining mountain gorillas survive, in two small groups in the eastern reaches of the DRC, while orangutan habitats have declined 80 per cent in the past 20 years. While some conservationists dream of rehoming zoo apes in the wild, these vanishing forests mean that it’s rarely feasible. The orangutans in Leipzig are certainly better off than they would be trying to survive in forests razed to make way for palm-oil plantations.
Since zoo apes cannot be returned to their natural environments, specialised sanctuaries are another option. But these require large plots of land that are both safe and uninhabited by existing populations, and such locations are scarce. As things stand, sanctuaries are already struggling to survive because they’re almost exclusively dependent on charitable donations. And most of them are full. In Africa and Indonesia, inhabitants are typically orphans that have been taken from the forest by hunters or palm-oil workers, who kill larger apes and kidnap the babies to sell or keep as pets. Elsewhere, sanctuaries are overflowing with retired lab apes or rescued pets. These institutions lack the capacity to accommodate the thousands of apes currently living in zoos, let alone the money that would be needed to support them.
Given the obstacles and the great expense of rehoming apes, very few places try to do so. Damian Aspinall of Howletts Wild Animal Park in England leads one of the few programmes that release gorillas back into the wild, by taking them to a protected reserve in Gabon. His intentions are heroic and hopefully the plan will succeed. Some gorillas have resettled well. But the results so far have been mixed; in 2014, five members of a family of 11 were found dead within a month of their release. We also don’t really know whether zoo-born apes possess the skills they need to survive, including the ability to retrieve different local foods, and knowledge of edible plants. Young apes learn these skills in the wild by watching the knowledgeable adults around them – but that’s an opportunity that creatures in captivity simply don’t have.
Now, all of this isn’t necessarily an ethical argument for continuing to breed apes in zoos. You might argue that if we can’t save the apes already in captivity, we should at least end breeding programmes and let the existing populations die out. However, captive breeding helps preserve the genetic diversity of endangered species. Moreover, research shows that visiting zoos makes people more likely to support conservation efforts – an effect that’s amplified by more naturalistic enclosures. So first-person encounters in zoos serve to educate visitors about the incredible lives animals lead, and to raise money for wild conservation programmes.
Allowing the ape populations in zoos to wither assumes – without justification – that their current lives are so bad as to be not worth living. It also risks inflicting harm. Boredom is a real risk for zoo animals, and it’s widely believed (although not yet scientifically established) that the presence of infants brings both interest and happiness to the families. Mixed-aged groups create collective dynamics that more closely resemble those in the wild. If we care about the welfare of captive apes, we should allow them to breed – at least in controlled ways.
One day, the prospect of returning captive apes to their natural habitats or housing them in well-funded, spacious sanctuaries might be realistic. Currently, it is not. Instead of condemning zoos, we should dedicate our efforts to supporting them: to pushing bad zoos to reform or close; to funding more research into the welfare of captive animals; and to encouraging all zoos to strive to do more for their inhabitants. That way, perhaps, I will no longer need to shy away from telling strangers what I do.
Computing and artificial intelligence
Algorithms associating appearance and criminality have a dark past
Catherine Stinson

Childhood and adolescence
For a child, being carefree is intrinsic to a well-lived life
Luara Ferracioli

Meaning and the good life
Sooner or later we all face death. Will a sense of meaning help us?
Warren Ward

Philosophy of mind
Think of mental disorders as the mind’s ‘sticky tendencies’
Kristopher Nielsen

Philosophy cannot resolve the question ‘How should we live?’
David Ellis

Rituals and celebrations
We need highly formal rituals in order to make life more democratic
Antone Martinho-Truswell
Are Zoos Ethical? Arguments for and Against Keeping Animals in Zoos
Zoos, if done right, could be a good thing for the animals and the public—yet many so-called zoos get it terribly wrong.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dorislin2-77cc0f7bb4a34be3ba4644a99f6e6a89.jpeg)
- University of Southern California
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Betsy-Petrick-4x5-70cf94b5a1934c9199bddce1f2457f37.jpg)
- Ohio Wesleyan University
- Brandeis University
- Northeastern University
- Animal Rights
- Endangered Species
A Brief History of Zoos
Arguments for zoos, arguments against zoos, the last word on zoos.
A zoo is a place where captive animals are put on display for humans to see. While early zoos (shortened from zoological parks) concentrated on displaying as many unusual creatures as possible—often in small, cramped conditions—the focus of most modern zoos is conservation and education. While zoo advocates and conservationists argue that zoos save endangered species and educate the public, many animal rights activists believe the cost of confining animals outweighs the benefits, and that the violation of the rights of individual animals—even in efforts to fend off extinction—cannot be justified. Let's dive into whether zoos are ethical and if they truly encourage education and conservation.
Humans have kept wild animals for thousands of years. The first efforts to keep wild animals for non-utilitarian uses began about 2,500 BCE, when rulers in Mesopotamia, Egypt kept collections in enclosed pens. Modern zoos began to evolve during the 18th century and the Age of Enlightenment when scientific interest in zoology and the study of animal behavior and anatomy came to the fore.
Early zoos were a dismal affair. Animals were kept in small enclosures with little if any, greenery. With a scant understanding of what the various animals needed, many perished relatively quickly. In accredited zoos in the United States and globally, things are better. Primates have gone from barren cages with little furniture to naturalistic and sometimes semi-free-ranging designs. But is it enough?
- By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species.
- Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe environment for protection from poachers , habitat loss, starvation, and predators.
- Many zoos have breeding programs for endangered species . In the wild, these individuals might have trouble finding mates and breeding, and species could become extinct.
- Some zoos have conservation programs around the world that use the zoo's expertise and funding to help protect wildlife against poaching and other threats.
- Reputable zoos accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums are held to high standards for the treatment of their resident animals. According to AZA, its accreditation guarantees the organization has undergone strict evaluation by recognized experts to ensure the highest standards of "animal management and care, including living environments, social groupings, health, and nutrition."
- A good zoo provides an enriched habitat where the animals are never bored, are well cared for, and have plenty of space.
- Seeing an animal in person is a much more personal and memorable experience than seeing that animal in a nature documentary. People are more likely to foster an empathetic attitude toward animals.
- Some zoos help rehabilitate wildlife and take in exotic pets that people no longer want or can no longer care for.
- Both accredited and unaccredited animal exhibitors are regulated by the federal Animal Welfare Act, which establishes standards for animal care.
- From an animal rights standpoint, humans do not have a right to breed, capture, and confine other animals— even if those species are endangered . Being a member of an endangered species doesn't mean the individual animals should be afforded fewer rights.
- Animals in captivity suffer from boredom, stress, and confinement. No pen—no matter how humane—or drive-through safari can compare to the freedom of the wild .
- Intergenerational bonds are broken when individuals are sold or traded to other zoos.
- Baby animals bring in visitors and money, but this incentive to breed new babies leads to overpopulation. Surplus animals are sold to other zoos, circuses , and hunting facilities . Some zoos simply kill their surplus animals outright.
- Some captive breeding programs do not release animals back into the wild . The offspring may be forever part of the chain of zoos, circuses, and petting zoos .
- Removing individual specimens from the wild further endangers the wild population because the remaining individuals will be less genetically diverse and may have greater difficulty finding mates. Maintaining species diversity within captive breeding facilities is also challenging.
- If people want to see wild animals in real life, they can observe wildlife in the wild or visit a sanctuary . (A true sanctuary does not buy, sell, or breed animals, but instead takes in unwanted exotic pets, surplus animals from zoos, or injured wildlife that can no longer survive in the wild.)
- The federal Animal Welfare Act (AWA) establishes minimal standards for cage size, shelter, healthcare, ventilation, fencing, food, and water. For example, enclosures must provide "sufficient space to allow each animal to make normal postural and social adjustments with adequate freedom of movement. Inadequate space may be indicated by evidence of malnutrition, poor condition, debility, stress, or abnormal behavior patterns." Violations often result in a slap on the wrist and the exhibitor is given a deadline to correct the violation. Even a long history of inadequate care and AWA violations, such as the history of Tony the Truck Stop Tiger, does not necessarily ensure abused animals will be freed.
- Animals sometimes escape their enclosures, endangering themselves as well as people. Likewise, people ignore warnings or accidentally get too close to animals, leading to horrific outcomes. For example, Harambe, a 17-year-old western lowland gorilla , was shot in 2016 when a toddler accidentally fell into his enclosure at the Cincinnati Zoo . While the child survived and was not badly injured, the gorilla was killed outright.
- Petting zoos have been linked with numerous incidents of diseases including E. coli infection, cryptosporidiosis, salmonellosis, and dermatomycosis (ringworm).
In making a case for or against zoos and whether zoos are ethical, both sides argue that they're saving animals. Whether or not zoos benefit the animal community, they do make money. As long as demand remains, zoos will continue to exist.
Since zoos are likely inevitable, the best way to move forward is to ensure zoo conditions are the best possible for the animals that live in captivity and that individuals who violate animal care health and safety sanctions are not only duly punished but denied any future access to animals.
One day we may look back at zoos and marvel at their barbarity. Or, one day we may look back at zoos and be grateful for the species they saved from extinction. Of these two scenarios, only time will tell.
Hosey, Geoff, et al. Zoo Animals: Behaviour, Management, and Welfare . Oxford University Press. 2013.
Hosey, G. (2023). The History of Primates in Zoos . In: Robinson, L.M., Weiss, A. (eds) Nonhuman Primate Welfare. Springer, Cham.
“ Species Survival Plan Programs .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums.
“ Accreditation Basics .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums .
“ Animal Welfare Act and Animal Welfare Regulations .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Meagher, Rebecca K., Georgia J. Mason. “ Environmental Enrichment Reduces Signs of Boredom in Caged Mink .” PLoS ONE , vol. 7, 2012, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049180
Kleiman, Devra G., et al. Wild Mammals In Captivity: Principles And Techniques For Zoo Management, Second Edition . University of Chicago Press. 2010.
Gunasekera, Crystal Allen. “ The Ethics of Killing “Surplus” Zoo Animals .” Journal of Animal Ethics , vol. 8, 2018, doi:10.5406/janimalethics.8.1.0093
Brichieri-Colombi, Typhenn A., et al. “ Limited Contributions of Released Animals from Zoos to North American Conservation Translocations .” Conservation Biology , vol. 33, 2019, pp. 33-39., doi:10.1111/cobi.13160
Krasnec, Michelle O., et al. “ Mating Systems in Sexual Animals .” Nature Education Knowledge, vol. 3, no. 10, 2012, p. 72.
“ 9 CFR § 3.128 - Space Requirements .” Cornell University Legal Information Institute .
“ Animal Welfare Act Enforcement .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Conrad, Cheyenne C. Conrad et al. " Farm Fairs and Petting Zoos: A Review of Animal Contact as a Source of Zoonotic Enteric Disease ." Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, vol. 14, 2017, pp. 59-73., doi:10.1089/fpd.2016.2185
- Arguments for and Against Hunting
- What's the Difference Between a Zoo and a Sanctuary?
- How Animal Rights Activists View Zoos Keeping Endangered Species
- What's Wrong With Aquariums?
- Responses to Top Arguments Against Animal Rights
- Horse Racing and Animal Rights
- Key Facts About Animal Abuse
- Is Pet Ownership Ethical?
- Overview of Animal Cruelty
- Overview of the Animal Welfare Act
- What Will Happen to the Animals If Everyone Goes Vegan
- The Top 10 Animal Rights Issues
- Animal Cruelty in Circuses
- Police Search and Rescue Dogs: The Animal Rights Debate
- Historical Timeline of the Animal Rights Movement
- The Argument for Animal Rights
Essay on Zoo for Students and Children
500 words essay on zoo.
The world is a huge place to see. It consists of so many living organisms that it is impossible to see each and every one of them. Especially for human beings, who are fascinated very much by animals. For the same reasons, zoos were created so that humans can interact better with animals.

In other words, a zoo is a facility that has animals, birds, and reptiles of all kinds. They are confined to space where they are given food and medical facilities. The government has given strict guidelines to maintain a zoo. This is done keeping in mind the animal’s safety. In addition, zoos are made breeding grounds for animals to protect their species.
Benefits of Zoo
Zoos were made to bring wildlife closer to humans. It gave humans a better and up-close view of them. This allows various researchers and scientists to note the behavioral pattern of the animals. It helps them in their studies and discover new things.
In addition, zoos are a great source of entertainment for kids. They love visiting zoos and interacting with animals. This helps them learn practical knowledge about the animal. It also gives them exposure to wildlife and widens their knowledge.
Furthermore, zoos give us easy access to rare animals. Had it not been for zoos, we would have never been able to see what some animals looked like. We enjoy their behavior and it also creates awareness about the extinction of the rare species.
Similarly, zoos are a safe breeding ground for animals. They ensure the animal breeds so they never go extinct. This helps in creating a good balance. Moreover, the zoos ensure the animals get all the nutrition in their bodies to lead a healthy life. This is beneficial as the animal may not get guaranteed meals in the forests.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disadvantages of Zoo
While the zoo is a great place for entertainment, it is also very exploitive. It takes advantage of the poor animals to make a profit off them. The zoos keep animals in very bad conditions. It takes unethical methods just to create revenue.
Furthermore, zoos are very unfair to animals. They take the animals out of their natural habitats just for the sake of human entertainment. Why would the animals be put into cages as humans want them to? They are voiceless creatures who are being forced to live in poor conditions. Imagine putting humans into cages so animals could come to see them. It sounds inhumane the other way around but not when we do the same to animals.
Most importantly, zoos do not take proper care of exotic animals. They bring them over in their facility despite knowing that they cannot survive in that climate. Some zoos do not take enough precautionary measures to keep the animals safe. This has resulted in so many deaths of animals that it seems cruel.
In short, though zoos are very helpful to humans and animals to an extent. They must be monitored constantly to ensure the animals are safe. The unethical zoos must be shut down at once to prevent any further loss of animals.
FAQs on Zoo
Q.1 List the advantages of Zoo
A.1 Zoos bring the wildlife close to humans. It helps researchers study them closely and discover new things. It protects rare species and provides a safe breeding ground for them as well.
Q.2 How are zoos harmful to animals?
A.2 Zoos are very harmful to animals. They take them out of their natural habitat for human entertainment. They make them stay in poor conditions due to which they also lose their life and get infections.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos? Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Cover Letter
Works cited.
This essay explores the dilemma of keeping animals in zoos. In this essence, the legitimacy of restricting the animals is investigated.
Moreover, the essay seeks to establish harmony between advocacy for abolition of zoos and the need to preserve some species of animals. In addition, there is the necessity to control the interaction between animals and human beings.
I have observed that there is no solution to such dilemmas. Any observer has to establish a middle ground and maintain balance between the arguments. This is because it is not possible to take a radical action on the issue at hand.
I had an experience of arguing over the issue, which has two equal sides while writing the paper. I was able to examine both sides of the argument and analyze the arguments.
While it seemed appropriate to me that people should keep animals in the zoos prior to this assignment, my perception changed after analyzing both sides of the argument. I had to take a middle ground and analyze the perceptions as a neutral observer.
When writing the arguments in the paper, it became difficult to make an objective analysis of the arguments due to the influence of personal opinion. It is difficult to establish a middle ground that does not favor either side.
The topic of the essay generates significant interest in me because most people assume that animals have their specific places in the ecosystem, which are subject to manipulation by human beings at will.
On the other hand, liberal people advocate that fair competition can exist between animals and people naturally. This article proves that neither case is entirely true.
Throughout the history of humanity, interaction with animals has been inevitable. Superiority of human beings has made them highly competitive. Other living things have to adapt to new environments or leave their natural habitat to create space for human beings and their activities.
The human population is evenly distributed around the world. On the other hand, animal population is partially distributed, with different species occupying different parts of the world. Since animals have always fascinated people, there has always been the urge to observe animals and their behavior.
In addition, all living organisms on earth survive through competition for resources with each other (McKinley & Shepard 65). This has led to endangerment of some species of animals. Generally, animals are considered important to human beings, regardless of the material value of each species.
Gradually, it has become important to protect animal species that are facing the danger of extinction, either due to encroachment of their immediate space in the ecosystem, or due to competition with other organisms whose lives depend on common resources.
For this reason, zoos have been built, and animals are kept inside for the sole purpose of preservation of animal life or for entertainment (Norton 42). It is true that the zoos protect a small number of animals from the competition that exists in their natural habitat.
In this way, they protect the species from extinction, and satisfy human being’s curiosity as people go for sightseeing at zoos as a recreational activity (Norton 21).
Most zoos keep wild animals, and majority of the animal population at the zoos is made up of animals that are rarely seen by human beings in their immediate environment. These animals are used to roaming in the jungle and forests.
Others are used to swimming freely in the seas and rivers. However, due to limited space, zoos keep the animals in a much smaller and controlled environment. Obviously, there is restriction of freedom for the animals in order to contain them in the zoo.
For most of their lives, the animals in the zoo do not lead a normal life like other wild animals. They are protected from the competition in the ecosystem due to their perceived importance to human beings. However, this is a serious impediment to their freedom too.
Animals are not allowed to roam freely during the day or night, as they would have done in a free environment. On the other hand, the rigors of competing with other wild animals are eliminated from their lives.
Moreover, the animals receive special treatment as they are provided with veterinary care, a service that other animals in the jungle and sea do not normally get (Robinson 53).
It is arguable that the setting of a zoo is analogous to a prison were felons are incarcerated to protect the society from their potentially harmful tendencies.
One might easily conclude that the animals in the zoo are in some kind of psychological distress due to disruption of their normal course of life and their detainment.
This view assumes that animals, like human beings, have the ability to discern the importance of freedom. Furthermore, the notion argues that animals have thoughts and feelings just like human beings.
It is difficult to establish these arguments as facts due to the limited emotional interaction between animals in the zoo and their keepers.
Thus, the idea that animals perceive physical freedom in a similar way as human beings is subject to debate (Mullan & Marvin 75).
Zoos are not primarily intended to curtail the freedom of an animal, but are designed to protect the animal from harsh environment. Normally, there are efforts to create an environment similar to the particular animal’s habitat in the zoo.
It is also difficult to assess whether the artificial environment created by zookeepers is identical to the natural habitat suitable for the animals.
This observation means that it is not entirely true that the zoos are aimed at curtailing the freedom of the animals (Brooman & Legge 85). Consequently, the animals may be better off at the zoo.
Moreover, it is not true that zoos completely change the normal course of life for the animals within it since there is an effort to simulate their natural habitat.
Some people are of the opinion that animals are inferior to human beings. This suggests that zoos are meant to restrict the animals within the zoo environment to protect human beings’ interest.
Some animals are dangerous to human life, while others compete against human being for resources. This is an obvious observation that has been under scientific study.
On the other hand, animals could be perceived to be equal to human beings. This means that the animals can compete for resources fairly against human beings.
Some people use this perspective to argue against establishment of zoos, which in their perspective, are the making of an unfair competition between animals and human beings.
The highlighted perceptions and observations present the dilemma of the existence of zoos. In a critical analysis of all radical perceptions, no single argument is proved entirely appropriate for the issue of zoos.
If zoos were to be eliminated as a way of protecting and preserving animal life, there would be dire consequences for humans and the animals themselves (Acampora 45).
It is an obvious observation that some animals would become extinct due to predation and competition from other animals in the natural habitat. People could also be affected by the interactions and conflicts between the animals and human beings.
While some animals would pose direct danger to human beings, others would affect the creations of human beings such as organized agriculture. It is thus obvious that a conflict will result from the freedom of animals.
However, this presents another question for argument since there is fairness in sharing of natural resources by living organisms in such a situation.
Although a relatively small number of animals are kept in the zoo, majority of animals are free and live in the wilderness. This brings up the issue of the scale of restriction of animals within zoos.
Keeping all animals in the zoo and eliminating them from their natural environment is an extreme action. This kind of an action would present a situation of extreme interference with nature. It is only logical that a balance between freedom of animals and existence of zoos has to be established.
Animals could be kept in an open environment that is similar to their natural habitat as much as possible. This would eliminated the problem of having animals in a zoo were cages similar to prison cells are used to contain the animals.
On the issue of competition, it would be unfair to let animals live free and compete against human beings in the natural environment. People would eliminate animals from the ecosystem due to their superiority in terms of logical reasoning.
This makes it necessary to provide some kind of protection for the animals. In this essence, zoos can neither be justified nor completely denounced.
Acampora, Ralph R.. Metamorphoses of the zoo: animal encounter after Noah . Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books, 2010. Print.
Brooman, Simon, and Debbie Legge. Law relating to animals . London: Cavendish, 1997. Print.
Mullan, Bob, and Garry Marvin. Zoo culture . 2nd ed. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1999. Print.
Norton, Bryan G.. Ethics on the ark: zoos, animal welfare, and wildlife conservation . Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1995. Print.
Robinson, Phillip T.. Life at the zoo: behind the scenes with the animal doctors . New York: Columbia University Press, 2004. Print.
Shepard, Paul, and Daniel McKinley. The subversive science; essays toward an ecology of man, . Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1969. Print.
- Hazard Adjustments in Alaska
- Sustainable Development of Toronto
- The Effectiveness of Sustainable Practices, Plans, Programs and Initiatives Implemented by Australian Zoo
- The Analysis of Siamangs’ Behavior in a Zoo Setting
- Zoos: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Structural and Non-Structural Mitigation
- Prospect Reservoir and Surrounding Areas: An Australian National Heritage Site
- South Wales Region: Energy and Economy
- History of the Great Chicago Fire
- The Environmental Sustainability Concept in the Hospitality Industry
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 8). Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos? https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/
"Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" IvyPanda , 8 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos'. 8 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
1. IvyPanda . "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
Zoos – Top 3 Pros and Cons
- Pro/Con Arguments
Discussion Questions
Take Action
Zoos have existed in some form since at least 2500 BCE in Egypt and Mesopotamia, where records indicate giraffes, bears, dolphins, and other animals were kept by aristocrats. The oldest still operating zoo in the world, Tiergarten Schönbrunn in Vienna, opened in 1752. [ 1 ] [ 2 ]
The contemporary zoo evolved from 19th century European zoos. Largely modeled after the London Zoo in Regent’s Park, these zoos were intended for “genteel amusement and edification,” according to Emma Marris, environmental writer and Institute Fellow at the UCLA Institute of the Environment and Sustainability. As such, reptile houses, aviaries, and insectariums were added with animals grouped taxonomically, to move zoos beyond the spectacle of big, scary animals. [ 40 ]
Carl Hegenbeck, a German exotic animal importer, introduced the modern model of more natural habitats for animals instead of obvious cages at his Animal Park in Hamburg in 1907. That change prompted the shift in zoo narrative from entertainment to the protection of animals. In the late 20th century, the narrative changed again to the conservation of animals to stave off extinction. [ 40 ]
Controversy has historically surrounded zoos, from debates over displaying “exotic” humans in exhibits to zookeepers not knowing what to feed animals. A gorilla named Madame Ningo, the first gorilla to arrive in the United States in 1911 who was to live at the Bronx Zoo , was fed hot dinners and cooked meat despite gorillas being herbivores , for example. [ 3 ] [ 4 ]
The contemporary debate about zoos tends to focus on animal welfare on both sides, whether zoos protect animals or imprison them.
Should Zoos Exist?
Pro 1 Zoos educate the public about animals and conservation efforts. As of Apr. 2021, there are 241 accredited zoos in the United States. The zoos attract over 181 million visitors annually, which is more than the approximately 131 million yearly spectators of the NFL, NBA, NHL, and MLB combined. [ 5 ] [ 6 ] [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 10 ] [ 9 ] [ 41 ] According to a study of 26 zoos worldwide published in Conservation Biology, visitors to zoos increased their knowledge of biodiversity and specific individual actions to protect biodiversity. [ 11 ] Robin Ganzert, PhD, President and CEO of American Humane, stated, “zoos provide people, especially impressionable children, with the opportunity to see these remarkable animals up close. People won’t protect what they don’t love, and they can’t love what they don’t know. No matter how closely programs like Planet Earth depict animals, nothing will match the bond of seeing them in real life. Just look at a child’s eyes at the zoo when he or she encounters a tiger or similarly majestic animal.” [ 12 ] Read More
Pro 2 Zoos produce helpful scientific research. 228 accredited zoos published 5,175 peer-reviewed manuscripts between 1993 and 2013. In 2017, 173 accredited US zoos spent $25 million on research, studied 485 species and subspecies of animals, worked on 1,280 research projects, and published 170 research manuscripts. [ 13 ] [ 14 ] Because so many diseases can be transmitted from animals to humans, such as Ebola, Hantavirus, and the bird flu, zoos frequently conduct disease surveillance research in wildlife populations and their own captive populations that can lead to a direct impact on human health. For example, the veterinary staff at the Bronx Zoo in New York alerted health officials of the presence of West Nile Virus. [ 15 ] Zoo research is used in other ways such as informing legislation like the Sustainable Shark Fisheries and Trade Act, helping engineers build a robot to move like a sidewinder snake, and encouraging minority students to enter STEM careers. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] [ 39 ] Read More
Pro 3 Zoos save species from extinction and other dangers. Corroboree frogs, eastern bongos, regent honeyeaters, Panamanian golden frogs, Bellinger River snapping turtles, golden lion tamarins, and Amur leopards, among others, have been saved from extinction by zoos. [ 16 ] Zoos are also working to save polar bears, tigers, and wild African elephants from habitat loss, apes and rhinos from poachers, dolphins and whales from hunters, and bees and butterflies from population declines, among many other efforts to help many other animals. [ 17 ] [ 18 ] [ 19 ] [ 20 ] 23% of birds and 47% of small mammals (weighing less than about 2.2 pounds) are negatively impacted by climate change. By keeping populations of animals and conducting wild repopulation, zoos can help preserve species in danger from climate change. There were only nine California condors in the wild in 1985. A joint conservation effort between the San Diego and Los Angeles Zoos with other organizations resulted in a population of 276 California condors in the wild and another 170 in captivity by 2016. [ 21 ] [ 22 ] [ 23 ] Przewalski’s horses, the last wild horses, were declared extinct in the wild in the 1960s when about 12 lived in zoos. By 2018, breeding programs at zoos increased the number to 2,400 horses, and 800 were reintroduced to the wild. [ 24 ] [ 25 ] Read More
Con 1 Zoos don't educate the public enough to justify keeping animals captive. A review published in Animal Studies Repository concluded, “to date there is no compelling or even particularly suggestive evidence for the claim that zoos and aquariums promote attitude change, education, and interest in conservation in visitors.” Even a study widely cited to justify the argument that zoos educate the public stated, “there was no overall statistically significant change in understanding [of ecological concepts] seen” because visitors know a lot about ecology before going to the zoo. [ 26 ] [ 27 ] TV shows such as Planet Earth bring wild animals into living rooms, allowing people to see the animals in their natural habitats without causing harm to animals such as the endangered snow leopard. Romesh Ranganathan, a British comedian, stated, “It still slightly surprises me that anybody thinks that we should have zoos at all. The animals always look miserable in captivity… [T]he idea that kids only get excited about things they can see in the flesh is ridiculous. My kids are obsessed with dinosaurs that no longer exist, and Skylanders, which have never existed.” [ 28 ] Read More
Con 2 Zoos are detrimental to animals' physical health. A study of 35 species of carnivores, including brown bears, cheetahs, and lions, found that zoo enclosures were too small for the animals to carry out their normal routines, which led to problems such as pacing and more infant deaths. Polar bears, for example, had an infant mortality rate of 65% due to small enclosures. [ 29 ] About 70% of adult male gorillas in North America have heart disease, the leading cause of death among gorillas in captivity, although the condition is almost completely absent in the wild. Other great apes have similar health problems in captivity. [ 4 ] Captive elephants live about half as long as wild elephants: 18.9 years v. 41.7 years for Asian elephants and 16.9 years v. 35.8 years for African elephants. Of 77 elephants in 13 zoos, 71 were overweight and spent 83% of their time indoors, contributing to early death. [ 30 ] Read More
Con 3 Zoo confinement is psychologically damaging to animals. Animal behaviorists often see zoo animals suffering from problems not seen in the wild, such as clinical depression in clouded leopards and gibbons, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in brown bears, and anxiety in giraffes. The animals experience these issues due to smaller enclosures, changes in diet and activities, and the introduction of things not seen in the wild, such as medical exams and people with cameras. The Toledo Zoo ran a psychiatric program in which a gorilla with premenstrual depression was prescribed Prozac. To ease them into new habitats, an agitated tiger was given Valium, and anxious zebras and wildebeests were given Haldol. [ 31 ] [ 32 ] [ 33 ] A study of captive chimpanzees found that “abnormal behaviour is endemic in the population,” and includes behaviors such as eating feces, twitching, rocking back and forth, plucking hair, pacing, vomiting, and self-mutilation, among others. The study concluded that the cause of such behavior could be mental health issues. [ 34 ] About 24% of captive orcas have “major” to “extreme” tooth wear and 60% had tooth fractures as a result of stress-induced teeth grinding. As a result of the 2013 documentary Blackfish, which exposed the psychological damage done to orcas by SeaWorld, California outlawed captive orca breeding. [ 35 ] [ 36 ] [ 36 ] Read More

1. Should zoos exist? If you believe they should, consider whether they should remain the same or change. If you believe they should not, consider how else to accomplish zoo’s conservation efforts.
2. Extend the debate to other human-made animal habitats, such as safari parks and animal sanctuaries.
3. What other conservation efforts are important to saving wildlife? Explain your answer(s).
1. Analyze “ Eight Reasons Zoos Are Good for Conservation ” from conservation scientist James Borrell.
2. Consider the pros and cons with a video from Above the Noise .
3. Explore conservationist Damian Aspinall’s opinion that zoos are “outdated and cruel.”
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | National Geographic, “Zoo,” nationalgeographic.org (accessed May 8, 2019) | |
| 2. | Schönbrunn Palace, “Zoo,” schoenbrunn.at (accessed Apr. 23, 2019) | |
| 3. | CBC, “Trapped in a Human Zoo,” cbc.ca, (accessed Apr. 23, 2019) | |
| 4. | Krista Langlois, “Something Mysterious Is Killing Captive Gorillas,” theatlantic.com, Mar. 5, 2018 | |
| 5. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Currently Accredited Zoos and Aquariums,” aza.org, Apr. 2019 | |
| 6. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Visitor Demographics,” aza.org (accessed May 7, 2019) | |
| 7. | Maury Brown, “Why MLB Attendance Dropped below 70 Million for the First Time in 15 Years,” forbes.com, Oct. 3, 2018 | |
| 8. | NHL, “NHL Attendance (1975-76 through 2018-2019),” records.nhl.com (accessed May. 7, 2019) | |
| 9. | NBA, “NBA Breaks All-Time Attendance Record for Fourth Straight Year,” nba.com, Apr. 12, 2018 | |
| 10. | Brandon McClung, “NFL Attendance Lowest since ’10 Despite Chargers Rebound,” sportsbusinessdaily.com, Jan. 2, 2019 | |
| 11. | Andrew Moss, Eric Jensen, and Markus Gusset, “Evaluating the Contribution of Zoos and Aquariums to Aichi Biodiversity Target 1,” Conservation Biology, Aug. 22, 2014 | |
| 12. | Robin Ganzert, “Zoos Save Species — Visit One This World Wildlife Day,” thehill.com, Mar. 3, 2018 | |
| 13. | Tse-Lynn Loh, et al., “Quantifying the Contribution of Zoos and Aquariums to Peer-Reviewed Scientific Research,” facetsjournal.com, Mar. 15, 2018 | |
| 14. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Research and Science,” aza.org (accessed May 7, 2019) | |
| 15. | C. Robinette, L. Saffran, A. Ruple, and S.L. Deem, “Zoos and Public Health: A Partnership on the One Health Frontier,” One Health, Nov. 23, 2016 | |
| 16. | Taronga Conservation Society Australia, “10 Endangered Species Saved from Extinction by Zoos,” medium.com, May 18, 2017 | |
| 17. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “AZA and Animal Program Conservation Initiatives,” aza.org (accessed Apr. 17, 2019) | |
| 18. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Pollinator Conservation,” aza.org (accessed Apr. 17, 2019) | |
| 19. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Climate Change and Wildlife,” aza.org (accessed Apr. 17, 2019) | |
| 20. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Marine Mammal Conservation,” aza.org (accessed Apr. 17, 2019) | |
| 21. | Michela Pacifici, et al., “Species Traits Influenced Their Response to Recent Climate Change,” nature.com, 2017 | |
| 22. | Association of Zoos & Aquariums, “Conservation Success Stories in AZA-Accredited Zoos and Aquariums,” aza.org, Apr. 20, 2017 | |
| 23. | US Fish & Wildlife Service, “California Condor Population Information,” fws.gov, May 7, 2018 | |
| 24. | Jan Flemr, “Long Way Home as Przewalski’s Horses Fly to Mongolia,” phys.org, July 19, 2018 | |
| 25. | Jane Palmer, “The World’s Last Truly Wild Horse,” bbc.com, Nov. 11, 2015 | |
| 26. | Lori Marino, et al., “Do Zoos and Aquariums Promote Attitude Change in Visitors? A Critical Evaluation of the American Zoo and Aquarium Study,” animalstudiesrepoistory.org, 2010 | |
| 27. | John H. Falk, et al., “Why Zoos and Aquariums Matter: Assessing the Impact of a Visit to a Zoo or Aquarium,” docplayer.net, 2007 | |
| 28. | Romesh Ranganathan, “Zoos Are Prisons for Animals — No One Needs to See a Depressed Penguin in the Flesh,” theguardian.com, Mar. 13, 2017 | |
| 29. | Edna Francisco, “Zoo Carnivores Need More Space,” sciencemag.org, Oct. 1, 2003 | |
| 30. | Ian Sample, “Stress and Lack of Exercise Are Killing Elephants Zoos Warned,” theguardian.com, Dec. 11, 2008 | |
| 31. | Alex Halberstadt, “Zoo Animals and Their Discontents,” nytimes.com, July 3, 2014 | |
| 32. | Daniel Engber, “The Tears of a Panda,” slate.com, Sep. 14, 2006 | |
| 33. | Jenni Laidman, “Zoos Using Drugs to Help Manage Anxious Animals,” toledoblade.com, Sep. 12, 2005 | |
| 34. | Lucy Birkett and Nicholas E. Newton-Fisher, “How Abnormal Is the Behavior of Captive, Zoo-Living Chimpanzees?,” journals.plos.org, June 16, 2011 | |
| 35. | John Jett, et al., “Tooth Damage in Captive Orcas,” sciencedirect.com, May 2018 | |
| 36. | Natasha Daly, “Orcas Don’t Do Well in Captivity. Here’s Why,” nationalgeographic.com, Mar. 25, 2019 | |
| 37. | Shelby Isaacson, “Mote Ranked No. 1 Nonprofit in Published Research by Top Zoos and Aquariums,” mote.org, Apr. 4, 2018 | |
| 38. | Zoo Atlanta, “Representative Research,” zooatlanta.org (accessed May 8, 2019) | |
| 39. | Bronx Zoo, “Bridging the Gap,” bronxzoo.com (accessed May 8, 2019) | |
| 40. | Emma Marris, "Modern Zoos Are Not Worth the Moral Cost,: nytimes.com, June 11, 2021 | |
| 41. | Association of Zoos and Aquariums, "Currently Accredited Zoos and Aquariums," aza.org, Apr. 2021 |
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
In this IELTS Zoo Essay you have to discuss whether you think zoos are cruel and should be shut down or whether they are useful as they protect some wild animals.
Essays on zoos have appeared in the IELTS test before and this was a question that was recently in the test.
Some people think that zoos are all cruel and should be closed down. Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals.
Discuss both opinions and give your own opinion.
Understanding the Question
You must always read the question carefully and note if there is anything restricting the topic.
You have to discuss both sides of the argument and with this zoo essay question it would be very easy to read it and then simply write about the benefits and drawbacks of zoos.
But look at this bit carefully:
- Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals .
One of the arguments is specifically about protecting animals. So when you discuss the second argument you must be careful not to just write generally about the advantage of zoos.
You have to focus on how they may protect wild animals . So when you brainstorm your ideas for the zoo essay, you should be thinking about:
- why animals need protecting and
- how zoos can help with this

And in your other body paragraph you would need to explain why they are also seen as cruel.
And of course you must remember to give your own opinion. In this essay, the author makes it clear at the beginning that they support the closing down of zoos.
The opinion you decide on though is of course your choice.
Zoo Essay Sample
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Zoo Essay Model Answer
Zoos remain popular places for people to visit for entertainment and to learn about wild animals. Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals and so should be kept open, I believe that the cruelty that animals suffer outweighs this benefit, and that they should be shut down.
These days, animals are under threat from humans in many ways, seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed through the cutting down of rain forests, or through poaching. Following on from this, the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals that are under threat. The reason is that they are in a safe environment managed by trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after and can produce offspring. There are examples of successes in this respect, such as with Pandas, which have been endangered for many years but have been protected.
However, there are more convincing arguments for why zoos should be shut down. Firstly, even though some species are under threat, there are lots of animals which do not fall into this category and who are there just for the entertainment of visitors. While it may be fun and educational to see them, animals are not meant to be caged, and their distress can often be seen in the way many of them pace back and forwards all day. Not only this, if the prime reason of zoos is to protect animals, this could be done in other environments such as wild life parks where the animals have more freedom.
In conclusion, animals should be protected but this does not have to be in zoos. Zoos are cruel to animals, not similar enough to their natural habitat, and they should be closed down.
(299 Words)
Band scores are given for task response, coherence and cohesion, lexis (vocabulary) and grammatical range and accuracy.
This zoo essay would get a good score for task response as it fully answers the question by discussing both opinions and giving a personal opinion. Ideas are also well explained, extended and supported.
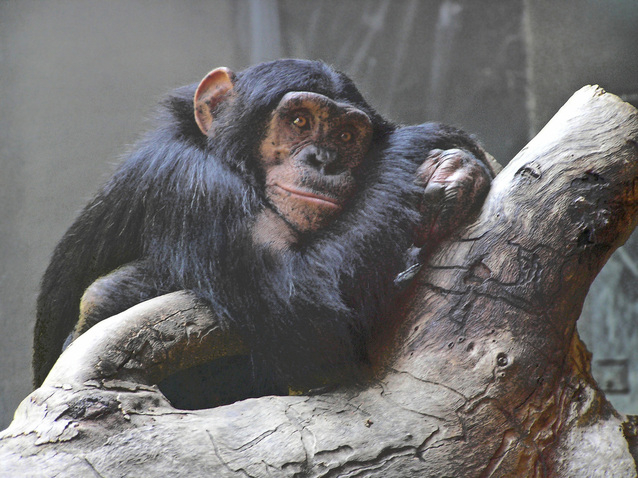

It would get a good score for coherence and cohesion as it is organised coherently and logically and is easy to follow. The introduction introduces the topic then there is a thesis statement.
One body paragraph discusses one side of the argument, and the other discusses the other side. The second body paragraph is also the writers opinion, and this is summarised again in the conclusion
.There is some interesting vocabulary and phrases. For example:
- sanctuary for endangered animals
- under threat from humans
- habitats are being destroyed
- produce offspring
- successes in this respect
- not meant to be caged
- natural habitat
There are also some good complex grammatical constructions and the grammar is precise. For example, the red words show that some of these are adverbial clauses , noun clauses and relative clauses :
- Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals...
- ...seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed...
- ...the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals who are under threat.
- ...trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after...
- Pandas who have been endangered...
- ... even though some species are under threat...
- ... While it may be fun and educational...
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Discuss Two Opinion Essays:

Donating Money to Charity Essay: Where should the money go?
Donating Money to Charity Essay: IELTS model answer to an essay on the topic of giving locally or to national and international charities.

Child Development Essay: What factors influence a child's development?
Child Development Essay for IELTS. The essay is about the factors that affect the way that children develop. It provides you with a model answer and comments on the response to help you know how to improve your band score.

Diet and Health Essay: Who is responsible for diet and health?
Diet and Health Essay for IELTS: This model examines the extent to which individuals or governments should be responsible for health. Read a model answer and useful comments about the essay which will help you to improve your IELTS Score.

IELTS Essays: What is the best way to reduce crime?
IELTS essays online with comments by an IELTS instructor - A writing sample on the topic of reducing crime.

IELTS Essay Becoming Independent
This IELTS essay discussed whether people are becoming more independent than they were in the past. This is a question that has come up a few times in the test. This is discussion type essay as you have to discuss both sides of an argument and come to a conclusion.


Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay
Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay- Model answer for IELTS. Who has had the most influence on our world? In this essay you have to discuss both sides.

Formal and Informal Education Essay: What age should it start?
This formal and informal education essay is about whether it is best for children to begin their formal education at school when they are 7 rather than much younger.

Animal Rights Essay: Should animals be exploited for humans?
Animal Rights Essay for IELTS: Learn how to write an essay where you have to discuss two opinions. People who believe in animal rights think that they should not be treated cruelly, for example in experiments or for sport.

Extraterrestrial Life Essay: Should we look for life on other planets?
This extraterrestrial life essay is an IELTS opinion essay where you have to discuss both sides of an issue then give your own opinion.

Childcare Essay: Should family or carers look after young children?
Childcare Essay: In the essay you have to discuss two sides of an argument. The first is that it is better if pre-school children are looked after at home with relatives such as grandparents. The second opinion is that children should be looked after at childcare centres.
Sources for Stories Essay: Should parents read to their children?
This sources for stories essay asks for your opinion on the best way for children to get stories. Is it from parents reading to them or other ways?

IELTS Writing Example: What are the aims of a university education?
IELTS writing example essays. This is an essay on the aims of university education. In this essay, two opposing opinions need to be discussed. It is important to understand how to answer this type of question in the IELTS exam.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

Bargain eBook Deal! 30% Discount

All 4 Writing eBooks for just $25.86 Find out more >>
IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
IELTS Line Graph: Governments Expenditure on Research
Jul 23, 24 01:27 PM
House History Essay
Jul 16, 24 04:06 PM
Paraphrasing Activity for IELTS Reading
Jul 13, 24 07:48 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Before you go...
30% discount - just $25.86 for all 4 writing ebooks.

Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
Skip to Main Content
- My Assessments
- My Curriculum Maps
- Communities
- Workshop Evaluation
Share Suggestion
"zoos and animal welfare" argumentative/persuasive writing.

"Zoos and Animal Welfare" Argumentative/Persuasive Writing
Grade levels, course, subject.
- Printer Friendly Version
Apply the appropriate models to show interactions among organisms in an environment.
CHANGE AND CONSTANCY
Explain mechanisms organisms use to adapt to their environment.
Describe how selective breeding and biotechnology can alter the genetic composition of organisms.
Compare and contrast observable patterns in the physical characteristics across families, strains and species.
Explain why the extinction of a species may occur when the environment changes.
Explain that mutations can alter a gene and are the original source of new variations in a population.
- Big Ideas Purpose, topic and audience guide types of writing
- Concepts Focus, content, organization, style, and conventions work together to impact writing quality Persuasive writing attempts to influence the audience by presenting an issue and stating and supporting a position. Various types of writing are distinguished by their characteristics
- Competencies Persuasive Writing: Develop substantial, relevant and illustrative content that demonstrates a clear understanding of the purpose (content). Persuasive Writing: Employ a thoroughly elaborated argument that includes a clear position consistently supported with precise and relevant evidence where rhetorical persuasive strategies are evident (content). Persuasive Writing: Employ effective organizational strategies and structures, such as logical order and transitions, which develop a controlling idea (organization). Persuasive Writing: Use proper conventions to compose in the standard form of the English language (conventions). Persuasive Writing: Write with a sharp, distinct controlling point made about a single topic with evident awareness of task and audience (focus). Persuasive Writing: Write with precise control of language, stylistic techniques, and sentence structures that create a consistent and effective tone (style). Write persuasive pieces, specific to a purpose and audience, which have a clearly stated position or opinion, with convincing and properly cited evidence that anticipates and counters reader concerns and arguments. Write to influence the audience by:• stating and supporting a position with detailed evidence, examples, and reasons. • using persuasive techniques (e.g.: emotional appeal, statistics, description, anecdote, example, expert opinion) to strengthen the argument. • employing a distinct structure to organize the argument and the opposing viewpoints. • acknowledging and refuting opposing arguments. • evaluating sources for validity, perspective, bias, and relationship to topic.• documenting sources of information responsibly and ethically. • using sources to achieve a balanced and authoritative argument. • supporting judgments with relevant evidence and detail. Write to influence the audience by:• stating and supporting a position with detailed evidence, examples, and reasons. • using persuasive techniques (e.g.: emotional appeal, statistics, description, anecdote, example, expert opinion, analogies and illustrations) to strengthen the argument. • employing a distinct structure to organize the argument and the opposing viewpoints. • acknowledging and refuting opposing arguments. • evaluating primary and secondary sources for validity, perspective, bias, and relationship to topic. • documenting sources of information responsibly and ethically. • using sources to achieve a balanced and authoritative argument. • supporting judgments with relevant evidence and detail. • presenting the position in either a deductive or an inductive framework. Focus, content, organization, style, and conventions work together to impact writing quality
Description
The Literacy Design Collaborative teaching task provides a blueprint for seamlessly integrating literacy and content standards in a rigorous, authentic classroom experience. After determining the discipline, course, and grade level, educators use teaching tasks built around predefined template prompts. The teaching task requires students to read, analyze and comprehend written materials and then write cogent arguments, explanations or narratives in the subjects they are studying.
Students will examine the zoo as a facility in which animals are confined within enclosures and displayed to the public. In many cases, animals may also be bred to produce offspring. Although enjoyed by many, some feel zoo conditions are detrimental to the health of animals. Students will explain and support their opinion as to whether or not animals should be kept in zoos.
In this extended writing task, students will read, analyze, and gather relevant information from text(s) and write an argumentative essay. Students will…
- Apply knowledge of the distribution and management of natural resources to a current issue
- Apply knowledge of the relationship between an environment and extinction to a current issue
- Read, analyze and gather relevant information from multiple texts
- Write an evidence-based argumentative essay, and address competing views
enclosure - something that "closes" a space
welfare - a condition of being or doing well
conservation - protection from extinction
zoochosis - obsessive, repetitve behavior associated with animals kept in prolonged captivity
extinction - dying out or termination of a species. Occurs when a species can no longer reproduce at replacement levels
endangered species - a species existing in such small numbers that it is in danger of becoming extinct
500 minutes/10 periods
"Animal Ark or Sinking Ship?" BornFree.org . Born Free Foundation, July 2007. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://www.bornfree.org.uk/fileadmin/user_upload/files/zoo_check/ publications/Animal_Ark_or_sinking_ship.pdf >.
Dixon, Thomas. "Zoos: Debatabase - Debate Topics and Debate Motions." IDEA: International Debate Education Association - Debate Resources & Debate Tools. 06 Apr. 2009. Web. 28 Jan. 2011. < http://www.idebate.org/debatabase/topic_details.php?topicID=1 >.
Horton, Jennifer. "Are Zoos Good or Bad." HowStuffWorks.com . 15 Sept. 2008. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://animals.howstuffworks.com/animal-facts/zoos-good-or-bad.htm >.
Lin, Doris. "Should Zoos Keep Endangered Species?" About.com . The New York Times Company. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://animalrights.about.com/od/wildlife/a/EndangeredZoos.htm >.
Van Tuyl, Christine. Zoos and Animal Welfare . Detroit: Greenhaven, 2008. Print.
Related Materials & Resources
Suggested instructional strategies.
| : | The students will analyze and discuss the teaching task to identify what the task is asking them to do and to help students access background knowledge. Sample student papers or texts will be used as models. Students will work with the teacher to interpret the Literacy Design Collaborative rubric. |
| : | The teaching task, which is both relevant and rigorous, engages students in subject specific reading, research, and writing. The teaching task requires the application of content knowledge to a new scenario. |
| : | The teacher will engage students through reading and discussion, note-taking, and the development of a rough draft of the assignment. |
| : | Students will use active reading strategies (e.g., "Talking to the text"), discussion protocols (e.g., think-pair-share, Paideia/Socratic seminar), and writing strategies (e.g., peer editing, teacher modeling and guided practice) with appropriate scaffolds as they develop their final written product. |
| : | The students will create an extended writing assignment which incorporates both their content understanding and text-based information. The Literacy Design Collaborative rubric will be used to provide feedback to students. |
| : | The Literacy Design Collaborative teaching task is a tiered assignment. Individual tasks can be made simple or complex by varying the task demand, with up to three tiers of difficulty. For leveled tasks, teachers can choose to teach Level 1 (L1) alone or add demands to the prompt by including Level 2 (L2) and/or Level 3 (L3). |
| : | The teaching task is designed to help students apply subject area content through reading and writing. The teaching task might be sequenced toward the end of a content unit. The teaching task is an extended, multiple day classroom assignment. |
Instructional Procedures
Teacher Preparation Prior to launching the teaching task in the classroom, a teacher should consider the following questions:
How much support will students need to successfully complete the task?
What parts of the process can be completed independently (during or outside of class)? What parts of the process represent new learning or substantial challenge and warrant direct instruction or guided practice during class?
What content and vocabulary instruction and activities will be provided so that students are able to successfully complete the task?
How will reading be scaffolded for my students? (Read together? Read in groups? Read independently?)
What note-taking method will students use, and does that method align with the writing task?
How will students make the transition from the reading to the writing? (outline, graphic organizer, etc.)
What writing instruction is needed to help students write their thesis statements, organize their notes, embed quotes, and cite evidence?
How will students receive feedback at various stages of the writing process to make sure they are answering the prompt, their papers are focused, their ideas are fully developed with details, examples, etc.?
Daily Plan The daily plan is flexible based on students' prior knowledge, experience and skills in reading, research and writing as well as their ability to apply subject area knowledge to a new scenario. The amount of time, in class instruction, and scaffolds needed can be increased or decreased to provide the appropriate level of challenge and support for students.
Teaching Task 2 (Argumentative/Analysis L1, L2): Should animals be kept in zoos? After reading informational texts, write an essay that addresses the question and support your position wiht evidence from the text(s). L2 Be sure to acknowledge competing views.
Task Engagement and Analysis The teacher introduces the teaching task to students by linking the task to the class content that has been taught previously and to existing knowledge, skills, and interests. The teacher asks students to read the teaching task and make notes or discuss with peers things they already know about this issue or topic.
The teacher helps the students to understand the expectations of the teaching task by asking students what they think a good response to the task might include and creating a classroom list. The teacher may share examples of the type of texts the students will produce (either actual student samples or commercially published texts). Sharing the rubric with students will clarify the expectations. (Clicking on each performance level of the rubric will enable teacher access to annotated student writing for that level.)
The teacher explains the timetable and supports available for completing the task.
Text Selection The teacher has either preselected the texts or will provide access to research sources for students to select texts. The teacher asks students to begin to record information about the sources (e.g., using notebooks, note cards, technology). The teacher may need to provide models or instruction on creating a bibliography or works cited. The students should identify author, title, publisher, date, and any other needed information (e.g., volume, editor) A discussion about the credibility or merit of sources may be needed.
Preview texts The teacher can provide students with all of the texts or offer students a list of acceptable sources from which to choose. The teacher briefly highlights each text with a summary to assist students in making appropriate text selections. The teacher asks the students to skim through each text to identify the genre, purpose, and text structure. A teacher think-aloud explaining rationale for making certain text selections may be beneficial to students.
Note-taking The teacher provides or suggests that a note-taking method be used that is consistent with the expectations for the task and the type of writing (e.g., argumentative-pro/con t-chart). Students should be encouraged to refer to the teaching task so that their notes are relevant to the prompt. Students should be encouraged to include both textual information and their own connections and implications. Students should continue to add to their bibliography or works cited.
Teachers may need to teach or reinforce practices to promote academic integrity and to help students avoid plagiarism. The ability to use and credit sources appropriately shows respect for the work of others and adds credibility to a student's argument and/or research.
Reading and Research The teacher assigns the reading, research and note-taking to students and provides instruction to support analysis and synthesis of texts. The teacher may ask students to reflect orally or in writing on key questions including:
Which parts of the text provide evidence that relates to the prompt?
What historical or current examples did you notice that relate to the prompt?
What is the text explicitly saying? What gaps or unanswered questions do you see?
What competing arguments have you encountered or thought of based on the text (argumentative)?
How do you know your sources are credible?
Depending upon the needs of students in the classroom, additional scaffolds may be necessary (e.g., whole-group reading and teacher modeling of note-taking, paired in-class reading, talking to the text, small group discussion). The teacher may either provide students with print source options or make electronic texts available to them through the use of Web 2.0 tools (e.g., Wikis, Nings) or online library databases (e.g., EBSCO, ProQuest).
Transition to Writing The teacher uses discussion based strategies such as the Paideia/Socratic seminar or small group discussions to help students make connections between their research and notes and the teaching task.
Developing a Thesis or Claim Students write an opening paragraph that includes a controlling idea and sequences the key points that will be made throughout the writing assignment. The teacher may provide models of opening paragraphs and analyze them with the class. Students may provide feedback to each other on their opening paragraphs. Students should compare their opening paragraph to the teaching task and assess whether the paragraph fully address the main points of the prompt (e.g., define and explain, compare, take a position, etc.)
Organizing Notes/Planning Students organize their notes into a graphic organizer or outline that establish a logical structure for the assignment. An outline begins with the thesis or claim, sequences key points and includes supporting evidence from texts.
Development of rough drafts Students begin writing their rough drafts. The teacher frequently checks in with students to answer questions, offer feedback, and provide writing instruction as needed. Through planning, the teacher embeds opportunities for students to receive feedback on their writing prior to the submission of the final draft either through peer conferencing, teacher conferencing, or written teacher feedback. Students revise their drafts based on the feedback they receive. The amount of time needed for the development of rough draft varies and may include time during and outside of class.
Completion of Final Draft Students either self or peer-edit their papers for conventional errors and complete the final draft.
Assessment and Reflection The teacher uses the LDC rubric to assess the students' writing and provide feedback to help students improve their performance. Patterns in student performance guide further instruction.
Analytic Scoring The rubric is structured to facilitate analytic scoring - the awarding of separate scores by readers for each of the seven scoring elements. Scorers should keep in mind that the description of work quality within any particular "cell" of the rubric may still address more than one idea, and therefore may not match a particular essay perfectly. The scorer must identify the descriptor that is the best match to a paper based on the preponderance of evidence. If the decision is truly a "coin toss," the scorer should feel free to use the "in-between" or "half" scores. A variation of analytic scoring might be used in a situation in which the emphasis of instruction at a particular time might be on a subset of the seven scoring elements. For example, if instruction is focused on development and organization, then a teacher might simply award scores for those two scoring elements.
Holistic Scoring Holistic scoring is assigning a single, overall score to a paper. Analytic and holistic scoring rubrics look much the same. The holistic scorer's job is to pick the single score (1, 2, 3, 4) that corresponds to the set of descriptors for scoring elements that best matches a paper. Again, in-between or half scores can be used. Ideally, holistic scorers are thinking about all the scoring elements as they read papers, but over time they find that they can assign holistic scores very rapidly, yet still fairly accurately. This is one of the advantages of holistic scoring. However, analytic information is not generated by this method.
Score Recording and Feedback It would be good practice for teachers to share the rubrics with students and discuss "criteria for success" relative to the scoring elements. However, it is not intended that a clean scoring rubric would be attached to every paper that is scored in all situations. It might be more appropriate to attach score slips that list the scoring element names with blank spaces after them for the recording of scores (and a space for a total score, too, perhaps). A customized rubber stamp could accomplish the same. Analytic scores do provide useful information to the students since they reference descriptors in the rubric. However, nothing beats descriptive comments that are best written in the margins of the papers where they are most appropriate.
Cut Scores for Proficiency Levels Scorers can readily compute a total score (the sum of the seven element scores) or an average score (that sum divided by 7). If translating scores to performance levels is desired, then the structure of the rubrics lends itself to the use of the following cut scores:
| Performance Level | Total Score Cut* | Average Score Cut* |
| Not Yet | 10.5 | 1.5 |
| Approaches Expectations | 17.5 | 2.5 |
| Meets Expectations | 24.5 | 3.5 |
| Advanced | N/A | N/A |
| * The cut scores above are the highest scores possible within their associated performance levels. To score at the Advanced level, a student would have to earn more than 24.5 total points or an average score greater than 3.5 points. The highest scores possible for Advanced (28 and 4.0) are not cut scores because there is no higher performance level than Advanced. | ||
LDC Scores and Grades LDC scores could be translated to grades contributing to students' course grades. How this would be done is an individual teacher's decision. Teachers could establish their own cut scores for letter grades or just re-label the four performance levels as A, B, C, D. They could come up with their own way to convert LDC scores to numerical grades consistent with whatever numerical scale they use for other class work.
Click on each performance level below (Not Yet, Approaches Expectations, Meets Expectations, Advanced) to view annotated student samples.
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Scoring Elements | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | |||
| Focus
| Attempts to address prompt, but lacks focus or is off-task. |
| Addresses prompt appropriately and establishes a position, but focus is uneven. |
| Addresses prompt appropriately and maintains a clear, steady focus. Provides a generally convincing position. |
| Addresses all aspects of prompt appropriately with a consistently strong focus and convincing position. | |||
|
Reading/ Research
| Attempts to reference reading materials to develop response, but lacks connections or relevance to the purpose of the prompt. |
| Presents information from reading materials relevant to the purpose of the prompt with minor lapses in accuracy or completeness. |
| Accurately presents details from reading materials relevant to the purpose of the prompt to develop argument or claim. |
| Accurately and effectively presents important details from reading materials to develop argument or claim. | |||
|
Controlling Idea
| Attempts to establish a claim, but lacks a clear purpose. (L2) Makes no mention of counter claims. |
| Establishes a claim. (L2) Makes note of counter claims. |
| Establishes a credible claim. (L2) Develops claim and counter claims fairly. |
| Establishes and maintains a substantive and credible claim or proposal. (L2) Develops claims and counter claims fairly and thoroughly. | |||
|
Development
| Attempts to provide details in response to the prompt, but lacks sufficient development or relevance to the purpose of the prompt. (L3) Makes no connections or a connection that is irrelevant to argument or claim. |
| Presents appropriate details to support and develop the focus, controlling idea, or claim, with minor lapses in the reasoning, examples, or explanations. (L3) Makes a connection with a weak or unclear relationship to argument or claim. |
| Presents appropriate and sufficient details to support and develop the focus, controlling idea, or claim. (L3) Makes a relevant connection to clarify argument or claim. |
| Presents thorough and detailed information to effectively support and develop the focus, controlling idea, or claim. (L3) Makes a clarifying connection(s) that illuminates argument and adds depth to reasoning. | |||
|
Organization
| Attempts to organize ideas, but lacks control of structure. |
| Uses an appropriate organizational structure for development of reasoning and logic, with minor lapses in structure and/or coherence. |
| Maintains an appropriate organizational structure to address specific requirements of the prompt. Structure reveals the reasoning and logic of the argument. |
| Maintains an organizational structure that intentionally and effectively enhances the presentation of information as required by the specific prompt. Structure enhances development of the reasoning and logic of the argument. | |||
|
Conventions
| Attempts to demonstrate standard English conventions, but lacks cohesion and control of grammar, usage, and mechanics. Sources are used without citation.
|
| Demonstrates an uneven command of standard English conventions and cohesion. Accuracy and/or appropriateness of language and tone is uneven. Inconsistently cites sources. |
| Demonstrates a command of standard English conventions and cohesion, with few errors. Response includes language and tone appropriate to the audience, purpose, and specific requirements of the prompt. Cites sources using appropriate format with only minor errors. |
| Demonstrates and maintains a well-developed command of standard English conventions and cohesion, with few errors. Response includes language and tone consistently appropriate to the audience, purpose, and specific requirements of the prompt. Consistently cites sources using appropriate format. | |||
| Content Understanding
| Attempts to include disciplinary content in argument, but understanding of content is weak; content is irrelevant, inappropriate, or inaccurate. |
| Briefly notes disciplinary content relevant to the prompt; shows basic or uneven understanding of content; minor errors in explanation. |
| Accurately presents disciplinary content relevant to the prompt with sufficient explanations that demonstrate understanding. |
| Integrates relevant and accurate disciplinary content with thorough explanations that demonstrate in-depth understanding. | |||
Sean Houseknecht, Alex Shubert, Monica Cressman - Elizabethtown Area School District
Content Collections
Date published, insert template, information.

IELTS Writing Task 2 Sample Answer Essay: Zoos and Rare Animals
by Dave | Real Past Tests | 2 Comments
This is an IELTS writing task 2 sample answer essay on whether zoos are cruel and exploitive or helpful for rare animals from the real IELTS exam.
Be sure to sign up for on Patreon.com/HowtodoIELTS for my exclusive Ebooks and other materials!
Many people think that zoos are cruel. Others think they are helpful in protecting rare animals. Discuss both sides and give your own opinion. Real Past IELTS Exam
Some concerned groups feel that zoos are cruelly exploitative while others argue they serve the vital function of protecting endangered animals. In my opinion, though zoos are inherently unnatural, their efforts are laudable overall.
Those activists who decry the existence of zoos often point out how animals live in the wild. A lion in the African Serengeti, one of the few remaining preserves for lions in their natural habitat, roams over miles of grassland, hunts for meals and competes with rival prides. This is how lions have lived for thousands of years and is the natural byproduct of a generational process of evolution. The same lion placed in a zoo paces a small cage, is tossed already dead meat to eat, and rarely has other lions to interact or mate with. The evidence for zoos as a cruel institution lies in the contrasting of a natural and unnatural lifestyle and turning proud beasts into scavengers.
Regardless, zoos are essential for the preservation and cultivation of endangered species. There are countless animals ranging from various big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, and other sub-species), to pandas, rhinoceros, gorillas, pangolins and many more that depend on zoos for protection and safe breeding grounds. These animals have been driven to the brink of extinction either by loss of habitat due to rampant development and climate change or hunted for their fur or alleged medicinal properties. Responsible zoos are tasked with breeding them in order to stabilise falling populations and then re-introducing them into the wild. Without these zoos, many species would likely already have gone extinct.
In conclusion, zoos are fundamentally artificial but also a net positive because of their conservation efforts. To ensure this remains the case, these refuges must be well-regulated and governments should enact complementary solutions such as anti-poaching laws.
1. Some concerned groups feel that zoos are cruelly exploitative while others argue they serve the vital function of protecting endangered animals. 2. In my opinion, though zoos are inherently unnatural, their efforts are laudable overall.
- Paraphrase the topic for the essay.
- Give a clear opinion.
1. Those activists who decry the existence of zoos often point out how animals live in the wild. 2. A lion in the African Serengeti, one of the few remaining preserves for lions in their natural habitat, roams over miles of grassland, hunts for meals and competes with rival prides. 3. This is how lions have lived for thousands of years and is the natural byproduct of a generational process of evolution. 4. The same lion placed in a zoo paces a small cage, is tossed already dead meat to eat, and rarely has other lions to interact or mate with. 5. The evidence for zoos as a cruel institution lies in the contrasting of a natural and unnatural lifestyle and turning proud beasts into scavengers.
- Write a topic sentence with a clear main idea/reason at the end of the sentence.
- Begin a specific example.
- Develop the example.
- Continue developing it – here I switch to contrast the life of a lion in a zoo.
- Finish developing it and make an overall statement to relate back to the overall question.
1. Regardless, zoos are essential for the preservation and cultivation of endangered species. 2. There are countless animals ranging from various big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, and other sub-species), to pandas, rhinoceros, gorillas, pangolins and many more that depend on zoos for protection and safe breeding grounds. 3. These animals have been driven to the brink of extinction either by loss of habitat due to rampant development and climate change or hunted for their fur or alleged medicinal properties. 4. Responsible zoos are tasked with breeding them in order to stabilise falling populations and then re-introducing them into the wild. 5. Without these zoos, many species would likely already have gone extinct.
- Another topic sentence with a clear main idea.
- Explain your main idea.
- Here I state the causes for animals to be in zoos because that supports the need for zoos.
- I further develop the main purpose of zoos.
- Conclude your paragraph with a strong sentence.
1. In conclusion, zoos are fundamentally artificial but also a net positive because of their conservation efforts. 2. To ensure this remains the case, these refuges must be well-regulated and governments should enact complementary solutions such as anti-poaching laws.
- Repeat your opinion.
- Add a final thought/detail to get full marks from the IELTS examiner.
What do the words in bold below mean?
Some concerned groups feel that zoos are cruelly exploitative while others argue they serve the vital function of protecting endangered animals . In my opinion, though zoos are inherently unnatural , their efforts are laudable overall .
Those activists who decry the existence of zoos often point out how animals live in the wild. A lion in the African Serengeti , one of the few remaining preserves for lions in their natural habitat , roams over miles of grassland , hunts for meals and competes with rival prides . This is how lions have lived for thousands of years and is the natural byproduct of a generational process of evolution . The same lion placed in a zoo paces a small cage , is tossed already dead meat to eat, and rarely has other lions to interact or mate with . The evidence for zoos as a cruel institution lies in the contrasting of a natural and unnatural lifestyle and turning proud beasts into scavengers .
Regardless , zoos are essential for the preservation and cultivation of endangered species . There are countless animals ranging from various big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, and other sub-species ), to pandas, rhinoceros, gorillas, pangolins and many more that depend on zoos for protection and safe breeding grounds . These animals have been driven to the brink of extinction either by loss of habitat due to rampant development and climate change or hunted for their fur or alleged medicinal properties . Responsible zoos are tasked with breeding them in order to stabilise falling populations and then re-introducing them into the wild . Without these zoos, many species would likely already have gone extinct .
In conclusion, zoos are fundamentally artificial but also a net positive because of their conservation efforts . To ensure this remains the case , these refuges must be well-regulated and governments should enact complementary solutions such as anti-poaching laws .
concerned groups people who care
cruelly exploitative take advantage of badly
serve the vital function are important because of
protecting endangered animals keeping animals safe with low population numbers
inherently unnatural fundamentally artificial
laudable overall good in general
activists people who care about a specific issue
decry denounce
point out argue
African Serengeti grassland preserve in Africa
preserves conservation lands
natural habitat where they normally live
roams over miles of grassland walks around lots of fields
competes fights with
rival prides other groups of lions
natural byproduct the normal result of
generational process of evolution many years of adaptation
placed in put in
paces walks around
cage enclosure
tossed thrown
rarely sometimes
interact be around other lions
mate with breed, have children with
evidence support
cruel institution lies in evil zoos comes from
contrasting different
natural and unnatural lifestyle what are normal and artifical ways of living
proud beasts animals with dignity
scavengers animals that pick up already dead food
regardless nonetheless
preservation keeping safe
cultivation developing
endangered species animal at risk of going extinct
countless many
sub-species species within a species such as types of frogs, cats, etc.
pangolins a scaly mammal that rolls itself into a ball
depend on rely on
protection conservation
safe breeding grounds places where they can mate and have offspring
driven to the brink of extinction nearly all gone
loss of habitat no more home
rampant development changing a lot, industrialisation
climate change global warming
alleged medicinal properties supposed medical effects
responsible zoos good zoos
tasked with breeding have the duty of helping them mate
stabilise falling populations stop the numbers from decreasing
re-introducing them into the wild letting them go free
extinct all gone
fundamentally artificial at base not natural
net positive overall good
conservation efforts trying to keep them safe
To ensure this remains the case so that this is true
refuges places to be safe
well-regulated lots of oversight
enact complementary solutions pass laws to also protect animals
anti-poaching laws prevent people hunting animals
Pronunciation
Listen and repeat:
kənˈsɜːnd gruːps ˈkrʊəli ˈɛksplɔɪt ˈrɛlətɪv sɜːv ðə ˈvaɪtl ˈfʌŋkʃən prəˈtɛktɪŋ ɪnˈdeɪnʤəd ˈænɪməlz ɪnˈhɪərəntli ʌnˈnæʧrəl ˈlɔːdəbl ˈəʊvərɔːl ˈæktɪvɪsts dɪˈkraɪ pɔɪnt aʊt ˈæfrɪkən ˌsɛrɪˈneɪd gɛt hiː prɪˈzɜːvz ˈnæʧrəl ˈhæbɪtæt rəʊmz ˈəʊvə maɪlz ɒv ˈgrɑːslænd kəmˈpiːts ˈraɪvəl praɪdz ˈnæʧrəl ˈbaɪˌprɒdʌkt ˌʤɛnəˈreɪʃən(ə)l ˈprəʊsɛs ɒv ˌiːvəˈluːʃən pleɪst ɪn ˈpeɪsɪz keɪʤ tɒst ˈreəli ˌɪntərˈækt meɪt wɪð ˈɛvɪdəns krʊəl ˌɪnstɪˈtjuːʃən laɪz ɪn kənˈtrɑːstɪŋ ˈnæʧrəl ænd ʌnˈnæʧrəl ˈlaɪfˌstaɪl praʊd biːsts ˈskævɪnʤəz rɪˈgɑːdlɪs ˌprɛzə(ː)ˈveɪʃən ˌkʌltɪˈveɪʃən ɪnˈdeɪnʤəd ˈspiːʃiːz ˈkaʊntlɪs sʌb-ˈspiːʃiːz pæŋˈgəʊlɪnz dɪˈpɛnd ɒn prəˈtɛkʃən seɪf ˈbriːdɪŋ graʊndz ˈdrɪvn tuː ðə brɪŋk ɒv ɪksˈtɪŋkʃən lɒs ɒv ˈhæbɪtæt ˈræmpənt dɪˈvɛləpmənt ˈklaɪmɪt ʧeɪnʤ əˈlɛʤd mɛˈdɪsɪnl ˈprɒpətiz rɪsˈpɒnsəbl zuːz tɑːskt wɪð ˈbriːdɪŋ ˈsteɪbɪlaɪz ˈfɔːlɪŋ ˌpɒpjʊˈleɪʃənz riː-ˌɪntrəˈdjuːsɪŋ ðɛm ˈɪntuː ðə waɪld ɪksˈtɪŋkt ˌfʌndəˈmɛntli ˌɑːtɪˈfɪʃ(ə)l nɛt ˈpɒzətɪv ˌkɒnsə(ː)ˈveɪʃən ˈɛfəts tuː ɪnˈʃʊə ðɪs rɪˈmeɪnz ðə keɪs ˈrɛfjuːʤɪz wɛl-ˈrɛgjʊleɪtɪd ɪˈnækt ˌkɒmplɪˈmɛntəri səˈluːʃənz ˈænti-ˈpəʊʧɪŋ lɔːz
Vocabulary Practice
Remember and fill in the blanks:
Some c______________________s feel that zoos are c_______________________e while others argue they s________________________n of p________________________________s . In my opinion, though zoos are i_________________________l , their efforts are l________________________l .
Those a______________s who d__________y the existence of zoos often p__________________t how animals live in the wild. A lion in the A______________________________i , one of the few remaining p________________s for lions in their n__________________t , r_____________________________d , hunts for meals and c_____________s with r_________________s . This is how lions have lived for thousands of years and is the n____________________t of a g____________________________________________n . The same lion p______________n a zoo p____________s a small c__________e , is t__________d already dead meat to eat, and r_____________y has other lions to i____________t or m_____________h . The e______________e for zoos as a c___________________________n the c________________g of a n___________________________________e and turning p__________________s into s____________________s .
R________________s , zoos are essential for the p__________________n and c_____________________n of e_____________________s . There are c_________________s animals ranging from various big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, and other s_________________s ), to pandas, rhinoceros, gorillas, p_________________s and many more that d_______________n zoos for p________________n and s______________________s . These animals have been d______________________________________n either by l_____________t due to r_______________________t and c__________________e or hunted for their fur or a_______________________________s . R_________________________s are t________________________g them in order to s___________________________s and then r______________________________d . Without these zoos, many species would likely already have gone e_____________t .
In conclusion, zoos are f_________________________l but also a n________________e because of their c__________________________s . T_____________________________________e , these r_________________s must be w_______________________d and governments should e_____________________________________s such as a__________________________s .
Listen and check:
Listening Practice
Listen more about the pros and cons of zoos here:
Reading Practice
Read more about how zoos are exploitative below:
https://slate.com/technology/2014/06/animal-madness-zoochosis-stereotypic-behavior-and-problems-with-zoos.html
Speaking Practice
Answer the questions below from the real speaking exam :
Have you ever had a pet? What kind of pets do people like to have? What kinds of pets are common in your country? Do many people in your country have pets? Real Past IELTS Exam
Writing Practice
Write about the related question below and then check with my sample answer:
Some people say that the main environmental problem of our time is the loss of particular species of plants and animals. Others say that there are more important environmental problems. Discuss both these views and give your own opinion. Real Past IELTS Exam
IELTS Writing Task 2 Sample Answer: Environmental Problems Plants and Animals (IELTS Cambridge 14)
Recommended For You

Latest IELTS Writing Task 1 2024 (Graphs, Charts, Maps, Processes)
by Dave | Sample Answers | 147 Comments
These are the most recent/latest IELTS Writing Task 1 Task topics and questions starting in 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, and continuing into 2024. ...

Recent IELTS Writing Topics and Questions 2024
by Dave | Sample Answers | 342 Comments
Read here all the newest IELTS questions and topics from 2024 and previous years with sample answers/essays. Be sure to check out my ...

Find my Newest IELTS Post Here – Updated Daily!
by Dave | IELTS FAQ | 18 Comments

Cambridge IELTS 17 – The Complete Guide!
by Dave | Cambridge 17 | 0 Comment
The latest Cambridge IELTS 17 book of past tests just came out and I have collected some tips and materials to help you get the most ...

IELTS Essay: Peer Pressure
by Dave | Real Past Tests | 0 Comment
This is my IELTS writing task 2 sample answer essay on the topic of media instead of peer pressure from the real IELTS exam. ...

IELTS Essay: Time Off Work for Fathers
by Dave | General Training | 0 Comment
This is an IELTS writing task 2 sample answer essay on the topic of fathers having time off from work after their children are born from ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Zoos have been operating for thousands of years. While other people believe that it has a lot of helpful effects on animals and society, in my opinion, there are many negative impacts on animals’ physical and psychological health if they are in captivity. The following paragraphs discuss both views and reach a reasonable conclusion.
The motives of zoos preserving animals are indeed for the benefits of the majority. Firstly, zoo owners are protecting endangered animals through confinement because they are at risk when outside. Species such as elephants, tigers, lions, and pandas are the popular creatures people can see inside the zoo. Also, they consider showcasing animals in captivity as a way of educating humankind. It is also regarded as an exciting experience for children to see wild creatures personally. That is why the idea of caging endangered species is useful for human-being.
On the other hand, the well-being of animals in captivity is not ensured. There are some zoos that the resources for proper care are not sufficient. With this, the survival of other species living inside the cage, in terms of food and shelter, is not in a good hand. Besides, animals are not comfortable if they are not in their natural environment. Research shows that the monotonous routine and limited space in the animal’s conditions could lead to depression. For this reason, the behavioral development of these living creatures could become complicated.
In conclusion, there is no denying that capturing and displaying animals to the public could positively affect the people. However, it is also important to promote the diversity of the ecosystem and let animals live in their natural habitat for their survival.
Good Jessica!
While some believe, that they, will discuss, motives for zoos to house wildlife, when living in the wild, zoos where the resources, not as comfortable, could be problematic
Keep working hard!
Exclusive Ebooks, PDFs and more from me!
Sign up for patreon.
Don't miss out!
"The highest quality materials anywhere on the internet! Dave improved my writing and vocabulary so much. Really affordable options you don't want to miss out on!"
Minh, Vietnam
Hi, I’m Dave! Welcome to my IELTS exclusive resources! Before you commit I want to explain very clearly why there’s no one better to help you learn about IELTS and improve your English at the same time... Read more
Patreon Exclusive Ebooks Available Now!
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Who is behind the UK’s far-right riots?
To read this article for free, register now.
Once registered, you can: • Read free articles • Get our Editor's Digest and other newsletters • Follow topics and set up personalised events • Access Alphaville: our popular markets and finance blog
Explore more offers.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
FT Digital Edition
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
Standard Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FT Edit app
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
Duluth zoo’s newest red panda, Pip, has died
Pip came to the lake superior zoo in the spring, joining zoozee, who has been with the zoo for more than a year..
By Jana Hollingsworth
Star Tribune
DULUTH — The Lake Superior Zoo’s one-year-old red panda, Pip, was found dead in her den last week, the zoo announced Monday.
The female panda was the zoo’s second, having joined Zoozee in April.
The cause of death is unknown, a social media post said.
“Each and every staff member at the zoo is devastated by the loss of Pip,” said Haley Hedstrom, the zoo’s chief executive officer. “Though she was with us for only a short time, we all quickly fell in love with her charismatic personality.”
Pip came from the Buttonwood Park Zoo in Massachusetts where she was born in a litter of two. Her small size at birth led to her name, Pipsqueak.
Security camera footage shows that Pip went into her den box at about 10 p.m. Aug. 1 and did not come out again. Prior to that, no unusual behavior or interference from animals or people had been observed, the zoo said.
Pip has been taken to the University of Minnesota for pathology work. The zoo will share findings from the examinations within the next few weeks.
Animal care staff are monitoring Zoozee, who is in good health.
“Our team is confident that this was an individualized incident,” the post said.
Pip was chosen for the zoo by the Species Survival Plan that monitors red pandas within Association of Zoos and Aquariums facilities. Red pandas are native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. The animal is considered critically endangered.
The red panda program at the zoo has become one of its most popular additions, with Zoozee joining last year.
Iron Range man sentenced to 46 years in prison for death of Babbitt couple who took him in
New UMD leader: ‘There is a great story here to be told’
Faribault couple ID'd as victims in northern Minnesota home explosion
Jana hollingsworth.
Jana Hollingsworth is a reporter covering a range of topics in Duluth and northeastern Minnesota for the Star Tribune. Sign up to receive the new North Report newsletter.
More from Duluth
Roger A. Beldo had been living with Clifford and Christine Johnson for a month before he bludgeoned them to death.
What Kamala Harris has said so far on key issues in her campaign
As she ramps up her nascent presidential campaign, Vice President Kamala Harris is revealing how she will address the key issues facing the nation.
In speeches and rallies, she has voiced support for continuing many of President Joe Biden’s measures, such as lowering drug costs , forgiving student loan debt and eliminating so-called junk fees. But Harris has made it clear that she has her own views on some key matters, particularly Israel’s treatment of Gazans in its war with Hamas.
In a departure from her presidential run in 2020, the Harris campaign has confirmed that she’s moved away from many of her more progressive stances, such as her interest in a single-payer health insurance system and a ban on fracking.
Harris is also expected to put her own stamp and style on matters ranging from abortion to the economy to immigration, as she aims to walk a fine line of taking credit for the administration’s accomplishments while not being jointly blamed by voters for its shortcomings.
Her early presidential campaign speeches have offered insights into her priorities, though she’s mainly voiced general talking points and has yet to release more nuanced plans. Like Biden, she intends to contrast her vision for America with that of former President Donald Trump. ( See Trump’s campaign promises here .)
“In this moment, I believe we face a choice between two different visions for our nation: one focused on the future, the other focused on the past,” she told members of the historically Black sorority Zeta Phi Beta at an event in Indianapolis in late July. “And with your support, I am fighting for our nation’s future.”
Here’s what we know about Harris’ views:
Harris took on the lead role of championing abortion rights for the administration after Roe v. Wade was overturned in June 2022. This past January, she started a “ reproductive freedoms tour ” to multiple states, including a stop in Minnesota thought to be the first by a sitting US president or vice president at an abortion clinic .
On abortion access, Harris embraced more progressive policies than Biden in the 2020 campaign, as a candidate criticizing his previous support for the Hyde Amendment , a measure that blocks federal funds from being used for most abortions.
Policy experts suggested that although Harris’ current policies on abortion and reproductive rights may not differ significantly from Biden’s, as a result of her national tour and her own focus on maternal health , she may be a stronger messenger.
High prices are a top concern for many Americans who are struggling to afford the cost of living after a spell of steep inflation. Many voters give Biden poor marks for his handling of the economy, and Harris may also face their wrath.
In her early campaign speeches, Harris has echoed many of the same themes as Biden, saying she wants to give Americans more opportunities to get ahead. She’s particularly concerned about making care – health care, child care, elder care and family leave – more affordable and available.
Harris promised at a late July rally to continue the Biden administration’s drive to eliminate so-called “junk fees” and to fully disclose all charges, such as for events, lodging and car rentals. In early August, the administration proposed a rule that would ban airlines from charging parents extra fees to have their kids sit next to them.
On day one, I will take on price gouging and bring down costs. We will ban more of those hidden fees and surprise late charges that banks and other companies use to pad their profits.”
Since becoming vice president, Harris has taken more moderate positions, but a look at her 2020 campaign promises reveals a more progressive bent than Biden.
As a senator and 2020 presidential candidate, Harris proposed providing middle-class and working families with a refundable tax credit of up to $6,000 a year (per couple) to help keep up with living expenses. Titled the LIFT the Middle Class Act, or Livable Incomes for Families Today, the measure would have cost at the time an estimated $3 trillion over 10 years.
Unlike a typical tax credit, the bill would allow taxpayers to receive the benefit – up to $500 – on a monthly basis so families don’t have to turn to payday loans with very high interest rates.
As a presidential candidate, Harris also advocated for raising the corporate income tax rate to 35%, where it was before the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that Trump and congressional Republicans pushed through Congress reduced the rate to 21%. That’s higher than the 28% Biden has proposed.
Affordable housing was also on Harris’ radar. As a senator, she introduced the Rent Relief Act, which would establish a refundable tax credit for renters who annually spend more than 30% of their gross income on rent and utilities. The amount of the credit would range from 25% to 100% of the excess rent, depending on the renter’s income.
Harris called housing a human right and said in a 2019 news release on the bill that every American deserves to have basic security and dignity in their own home.
Consumer debt
Hefty debt loads, which weigh on people’s finances and hurt their ability to buy homes, get car loans or start small businesses, are also an area of interest to Harris.
As vice president, she has promoted the Biden administration’s initiatives on student debt, which have so far forgiven more than $168 billion for nearly 4.8 million borrowers . In mid-July, Harris said in a post on X that “nearly 950,000 public servants have benefitted” from student debt forgiveness, compared with only 7,000 when Biden was inaugurated.
A potential Harris administration could keep that momentum going – though some of Biden’s efforts have gotten tangled up in litigation, such as a program aimed at cutting monthly student loan payments for roughly 3 million borrowers enrolled in a repayment plan the administration implemented last year.
The vice president has also been a leader in the White House efforts to ban medical debt from credit reports, noting that those with medical debt are no less likely to repay a loan than those who don’t have unpaid medical bills.
In a late July statement praising North Carolina’s move to relieve the medical debt of about 2 million residents, Harris said that she is “committed to continuing to relieve the burden of medical debt and creating a future where every person has the opportunity to build wealth and thrive.”
Health care
Harris, who has had shifting stances on health care in the past, confirmed in late July through her campaign that she no longer supports a single-payer health care system .
During her 2020 campaign, Harris advocated for shifting the US to a government-backed health insurance system but stopped short of wanting to completely eliminate private insurance.
The measure called for transitioning to a Medicare-for-All-type system over 10 years but continuing to allow private insurance companies to offer Medicare plans.
The proposal would not have raised taxes on the middle class to pay for the coverage expansion. Instead, it would raise the needed funds by taxing Wall Street trades and transactions and changing the taxation of offshore corporate income.
When it comes to reducing drug costs, Harris previously proposed allowing the federal government to set “a fair price” for any drug sold at a cheaper price in any economically comparable country, including Canada, the United Kingdom, France, Japan or Australia. If manufacturers were found to be price gouging, the government could import their drugs from abroad or, in egregious cases, use its existing but never-used “march-in” authority to license a drug company’s patent to a rival that would produce the medication at a lower cost.
Harris has been a champion on climate and environmental justice for decades. As California’s attorney general, Harris sued big oil companies like BP and ConocoPhillips, and investigated Exxon Mobil for its role in climate change disinformation. While in the Senate, she sponsored the Green New Deal resolution.
During her 2020 campaign, she enthusiastically supported a ban on fracking — but a Harris campaign official said in late July that she no longer supports such a ban.
Fracking is the process of using liquid to free natural gas from rock formations – and the primary mode for extracting gas for energy in battleground Pennsylvania. During a September 2019 climate crisis town hall hosted by CNN, she said she would start “with what we can do on Day 1 around public lands.” She walked that back later when she became Biden’s running mate.
Biden has been the most pro-climate president in history, and climate advocates find Harris to be an exciting candidate in her own right. Democrats and climate activists are planning to campaign on the stark contrasts between Harris and Trump , who vowed to push America decisively back to fossil fuels, promising to unwind Biden’s climate and clean energy legacy and pull America out of its global climate commitments.
If elected, one of the biggest climate goals Harris would have to craft early in her administration is how much the US would reduce its climate pollution by 2035 – a requirement of the Paris climate agreement .
Immigration
Harris has quickly started trying to counter Trump’s attacks on her immigration record.
Her campaign released a video in late July citing Harris’ support for increasing the number of Border Patrol agents and Trump’s successful push to scuttle a bipartisan immigration deal that included some of the toughest border security measures in recent memory.
The vice president has changed her position on border control since her 2020 campaign, when she suggested that Democrats needed to “critically examine” the role of Immigration and Customs Enforcement, or ICE, after being asked whether she sided with those in the party arguing to abolish the department.
In June of this year, the White House announced a crackdown on asylum claims meant to continue reducing crossings at the US-Mexico border – a policy that Harris’ campaign manager, Julie Chavez Rodriguez, indicated in late July to CBS News would continue under a Harris administration.
Trump’s attacks stem from Biden having tasked Harris with overseeing diplomatic efforts in Central America in March 2021. While Harris focused on long-term fixes, the Department of Homeland Security remained responsible for overseeing border security.
She has only occasionally talked about her efforts as the situation along the US-Mexico border became a political vulnerability for Biden. But she put her own stamp on the administration’s efforts, engaging the private sector.
Harris pulled together the Partnership for Central America, which has acted as a liaison between companies and the US government. Her team and the partnership are closely coordinating on initiatives that have led to job creation in the region. Harris has also engaged directly with foreign leaders in the region.
Experts credit Harris’ ability to secure private-sector investments as her most visible action in the region to date but have cautioned about the long-term durability of those investments.
Israel-Hamas
The Israel-Hamas war is the most fraught foreign policy issue facing the country and has spurred a multitude of protests around the US since it began in October.
After meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in late July, Harris gave a forceful and notable speech about the situation in Gaza.
We cannot look away in the face of these tragedies. We cannot allow ourselves to become numb to the suffering. And I will not be silent.”
Harris echoed Biden’s repeated comments about the “ironclad support” and “unwavering commitment” to Israel. The country has a right to defend itself, she said, while noting, “how it does so, matters.”
However, the empathy she expressed regarding the Palestinian plight and suffering was far more forceful than what Biden has said on the matter in recent months. Harris mentioned twice the “serious concern” she expressed to Netanyahu about the civilian deaths in Gaza, the humanitarian situation and destruction she called “catastrophic” and “devastating.”
She went on to describe “the images of dead children and desperate hungry people fleeing for safety, sometimes displaced for the second, third or fourth time.”
Harris emphasized the need to get the Israeli hostages back from Hamas captivity, naming the eight Israeli-American hostages – three of whom have been killed.
But when describing the ceasefire deal in the works, she didn’t highlight the hostage for prisoner exchange or aid to be let into Gaza. Instead, she singled out the fact that the deal stipulates the withdrawal by the Israeli military from populated areas in the first phase before withdrawing “entirely” from Gaza before “a permanent end to the hostilities.”
Harris didn’t preside over Netanyahu’s speech to Congress in late July, instead choosing to stick with a prescheduled trip to a sorority event in Indiana.
Harris is committed to supporting Ukraine in its fight against Russian aggression, having met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky at least six times and announcing last month $1.5 billion for energy assistance, humanitarian needs and other aid for the war-torn country.
At the Munich Security Conference earlier this year, Harris said: “I will make clear President Joe Biden and I stand with Ukraine. In partnership with supportive, bipartisan majorities in both houses of the United States Congress, we will work to secure critical weapons and resources that Ukraine so badly needs. And let me be clear: The failure to do so would be a gift to Vladimir Putin.”
More broadly, NATO is central to our approach to global security. For President Biden and me, our sacred commitment to NATO remains ironclad. And I do believe, as I have said before, NATO is the greatest military alliance the world has ever known.”
Police funding
The Harris campaign has also walked back the “defund the police” sentiment that Harris voiced in 2020. What she meant is she supports being “tough and smart on crime,” Mitch Landrieu, national co-chair for the Harris campaign and former mayor of New Orleans, told CNN’s Pamela Brown in late July.
In the midst of nationwide 2020 protests sparked by George Floyd’s murder by a Minneapolis police officer, Harris voiced support for the “defund the police” movement, which argues for redirecting funds from law enforcement to social services. Throughout that summer, Harris supported the movement and called for demilitarizing police departments.
Democrats largely backed away from calls to defund the police after Republicans attempted to tie the movement to increases in crime during the 2022 midterm elections.
Related links

Additional credits
On days with heat advisories, daily animal demonstrations may be moved or cancelled. Check out our tips for making the most of your summer visit .
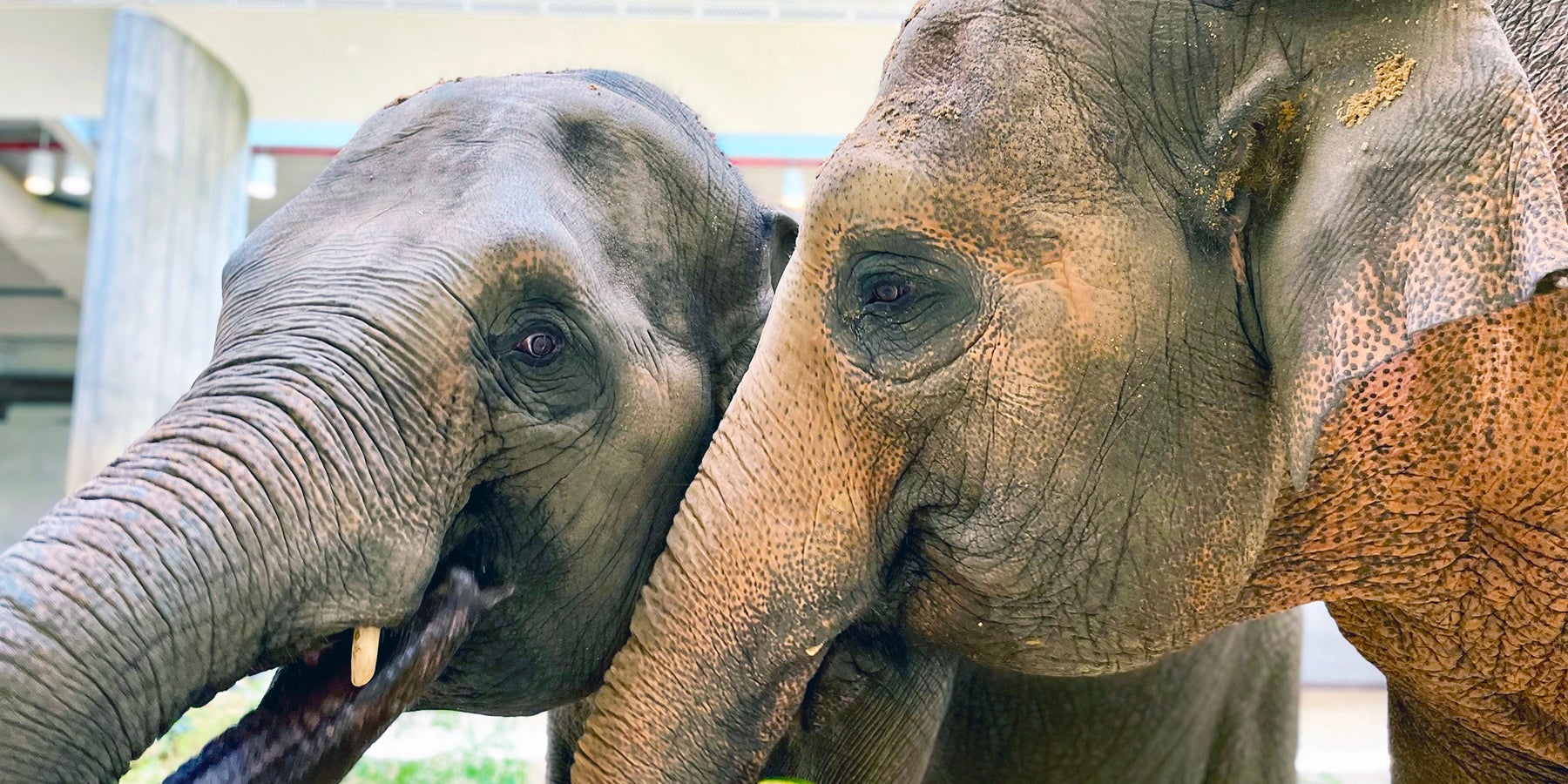

Elephant Cam
See the Smithsonian's National Zoo's Asian elephants — Spike, Bozie, Kamala, Swarna, Maharani, Trong Nhi and Nhi Linh — live on camera.

Now more than ever, we need your support. Make a donation to the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute today!

Become a Member
Members are our strongest champions of animal conservation and wildlife research. When you become a member, you also receive exclusive benefits, like special opportunities to meet animals, discounts at Zoo stores and more.

Education Calendar
Find and register for free programs and webinars.

About the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute
Assistant Curator - Amazonia
The Biologist (Assistant Curator - Amazonia) will provide daily care of animals for the National Zoo. This involves, breeding, education, conservation, exhibition, collection planning and support of research for a collection. Salary: $68,405 - $88,926 per year.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
‘White Dudes for Harris’ is the latest in a series of Zoom gatherings backing the vice president
Vice President Kamala Harris delivers remarks at a campaign event in Pittsfield, Mass., Saturday, July 27, 2024. (AP Photo/Stephanie Scarbrough, Pool)

- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — On a “White Dudes for Harris” virtual call, it was probably fitting that “The Dude” dropped in.
Actor Jeff Bridges addressed a fundraising event geared toward white men supporting Vice President Kamala Harris and sang her praises on Monday night, before channeling his iconic role as “The Dude” in 1998’s “The Big Lebowski,” declaring, “As the Dude might say, ‘That’s just my opinion, man.’” (The original line was “That’s just, like, your opinion, man.”)
The call lasted more than three hours and organizers said it attracted 180,000-plus people who donated more than $3.7 million. It was the latest in a series of Zoom gatherings to raise money and rally support among tens of thousands of supporters for Harris, after President Joe Biden announced he was leaving the presidential race and endorsing her.
Zooms have previously been organized by supporters’ backgrounds — including Black women, Hispanic women, Black men, Asian Americans, Native Americans and the LGBTQ+ community.
It reflected how Democrats, including Biden, have frequently relied on voters from broad and disparate backgrounds to piece together a diverse coalition of support. The president’s 2020 victory, for example, relied on segments of the population ranging from organized labor to conservative, suburban women disillusioned with Republican Donald Trump .
The “white dudes” Zoom event also featured appearances from actors Mark Ruffalo, Mark Hamill and Bradley Whitford, who deadpanned about so many white male speakers being “a rainbow of beige.”
Also participating were Democratic officials including Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg , Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz and Illinois Gov. JB Pritzker, all of whom have been mentioned as potential Harris running mates .
Pritzker joked that he wouldn’t normally attend “an event with a name like, White Dudes for” something, while Buttigieg talked about what an honor it was to share a call with Bridges as “The Dude” before striking a more serious tone: “Men are also more free in a country where we have a president who stands up for things like access to abortion rights.”
Walz said Trump supporters aren’t inherently bad people but urged participants: “Don’t ever shy away from our progressive values. One person’s socialism is another person neighborliness.”
Ross Morales Rocketto, a progressive operative who founded the “dudes” group, said, “We know that the silent majority of white men aren’t MAGA supporters,” referring to Trump’s ”Make America Great Again” movement.
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Democracy: American democracy has overcome big stress tests since 2020. More challenges lie ahead in 2024.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
- Stay informed. Keep your pulse on the news with breaking news email alerts. Sign up here .
The Zoom calls haven’t been organized by Harris’ team, but her campaign welcomes the assist — and the millions of dollars in fundraising. “Winning campaigns are powered by real, organic support,” said Harris campaign communications director Michael Tyler.
Amit Ahuja, a political science professor at the University of California at Santa Barbara whose research focus includes the processes of inclusion and exclusion in multiethnic societies, said that “no campaign’s going to say no” to groups from different backgrounds organizing themselves and bolstering enthusiasm and fundraising.
But he said that it is up to the candidate to accept support from individual groups while offering a larger personal story that can resonate with the larger country as a whole. An example, he said, is then-candidate Barack Obama, who rose above early campaign questions about racial identities to build a narrative around his personal story and hope.
“This is a challenge for both sides. This is a tight race. They both have to compile the largest possible coalition. And, by leaning into one identity or the other, they could actually really hurt themselves,” Ahuja said. He said the best response is to urge voters to “look at the candidate, don’t look at the groups.”
The calls for Harris often feature celebrities who have supported Biden’s campaign in the past . And their sheer number demonstrates how the vice president will need to appeal to different facets of the increasingly pluralistic population.
The political networking group “Win With Black Women” held a Zoom meeting the same night that Biden dopped out, and saw its number of participants swell to more than 44,000. It featured celebratory speeches from activists, business leaders, members of Congress and staff from the vice president’s office.
After that, a “Win With Black Men” virtual fundraising event attracted more than 53,000 attendees. They heard several presentations, including by 27-year-old Democratic Rep. Maxwell Frost of Florida, who had been a leading advocate for Biden’s campaign among younger voters, and Georgia Sen. Raphael Warnock.
A Zoom of “White Women for Harris” attracted more than 164,000 participants — so many that the platform struggled to meet the demand. It was headlined by the likes of singer Pink, soccer star Megan Rapinoe and actor Connie Britton .
Trump’s campaign has also organized different groups of supporters by their distinct backgrounds, including events in battleground states like Pennsylvania and Georgia for Black voters and “Latino Americans for Trump.”
Some Republicans have criticized Harris for her “diversity, equality and inclusion politics,” arguing that the vice president’s political career was helped by Democratic efforts to promote diversity. That’s despite House Speaker Mike Johnson and other GOP leaders on Capitol Hill discouraging lines of criticism that they considered racist and sexist — instead urging members of the party to focus their criticisms on Harris’ political record.
North Carolina Democratic Gov. Roy Cooper, who announced he didn’t want to be considered as Harris’ running mate just before Monday’s night call began, asked those assembled about GOP attacks, “A DEI candidate?”
“Here’s what they’re saying, that women and people of color don’t deserve to lead,” Cooper said. “We know better than that, guys.”
Associated Press writers Matt Brown in Washington and Bill Barrow in Atlanta contributed to this report.

Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Zoo — Zoos Should Be Banned: The Reasons
Zoos Should Be Banned: The Reasons
- Categories: Animal Welfare Zoo
About this sample

Words: 531 |
Updated: 20 December, 2023
Words: 531 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Video Version

Works Cited
- Bostock, S. (2016). Zoos and animal welfare. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Environmental Science. Oxford University Press.
- Carr, N., & Cohen, S. (2011). Banning zoos: Can animals be liberated from captivity? Anthrozoös, 24(4), 449-461.
- Fuentes, A. (2018). Zoos and conservation: On the need for evidence-based decision-making. Cambridge University Press.
- Gusset, M., & Dick, G. (2011). The global reach of zoos and aquariums in visitor numbers and conservation expenditures. Zoo Biology, 30(5), 566-569.
- Mason, G., & Latham, N. (2004). Can’t stop, won’t stop: Is stereotypy a reliable animal welfare indicator? Animal Welfare, 13(1), 57-69.
- Marino, L. (2017). Thinking chickens: A review of cognition, emotion, and behavior in the domestic chicken. Animal Cognition, 20(2), 127-147.
- Marino, L., & Lilienfeld, S. O. (2007). Dolphin captivity: A review of the evidence. In E. J. Capaldi (Ed.), The psychology of animal behavior (Vol. 1, pp. 217-243). ABC-CLIO.
- Melfi, V., & Ward, S. J. (2014). The role of zoos in contemporary society: A conservation perspective. International Zoo Yearbook, 48(1), 7-28.
- Sandøe, P., Palmer, C., & Corr, S. (Eds.). (2018). Companion animal ethics. John Wiley & Sons.
- Singer, P. (2009). Animal liberation. Harper Perennial.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1352 words
3 pages / 1281 words
1 pages / 552 words
2 pages / 745 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Zoo
The existence of zoos serves a broader purpose beyond mere entertainment. The benefits that zoos provide in terms of conservation, education, research, and public engagement are undeniable. Through dedicated efforts, zoos [...]
The question of whether zoos help or harm animals is a contentious and complex issue that has sparked widespread debate among animal rights advocates, conservationists, and the general public. On one hand, zoos are touted as [...]
The Secret Life of Bees, a novel by Sue Monk Kidd, explores profound themes of race, family, identity, and the search for belonging. Set in South Carolina during the 1960s, a time of intense racial tension and civil rights [...]
Endangered species are those plants and animals that are at significant risk of extinction. This alarming status results from various factors, most notably human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, overhunting, [...]
I went to the zoo a few weeks ago, and I was watching the Rainforest Fights Back Show. You can tell if the animal is happy or not by looking at their facial expression and how they behave. The animals that were performing didn’t [...]
It is important to study how animals utilize their enclosures to know how to better design healthier and more effective exhibits. This study attempted to determine if the otters in the Lost Forest mixed-species exhibit at the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article

Opinion Guest Essay
My Fellow Republicans, Stop the Trash Talk
Credit... Thalassa Raasch for The New York Times
Supported by
By Christopher T. Sununu
Mr. Sununu is the governor of New Hampshire.
- Aug. 1, 2024
As a Republican governor who has won four elections in a purple state, I’ve learned a thing or two about how to win. As Donald Trump and my fellow Republicans navigate the next steps of their campaigns, my message to them is this: The path to victory in November is not through character attacks or personal insults.
In fact, those attacks are unlikely to bring a single new voter on board. Catchy one-liners — calling Vice President Kamala Harris a “bum,” “not a serious person” and “bottom of the barrel” — might rile up the base, but they do little to connect with independent voters needed to close the deal in November.
Independent voters are independent for a reason. They are not driven to the polls by personal attacks. Candidates need to give them a reason to turn out and vote. What solutions are you going to provide that will make life better for them, their families and their communities? This election will likely be a coin toss, and whoever turns out these voters will be well positioned to win.
Now, instead of giving independents a reason to show up and vote for the solutions the Republican Party can offer, our candidates are responding to comments by Democrats like Gov. Tim Walz of Minnesota that the G.O.P. is led by “weird people.” Don’t get me wrong: Such comments from Democrats do nothing to move the conversation forward, either. The message from both sides must be inspirational and focused and about the results that can be delivered for the American people.
Politicians usually don’t lose votes for laughing or smiling too much. Attacks like those waged against Ms. Harris are unserious and don’t meet the moment that American families find themselves in. You have to connect with voters on their issues and their concerns. You earn their trust by appreciating that the job is bigger than yourself. You win tough elections by showing real empathy and addressing the anxieties that keep them up at night.
Donald Trump has led in the polls, and his return to the White House has seemed almost inevitable — and not only because Joe Biden was until recently his opponent. Americans are hungry for change. Under the Biden-Harris administration they have seen interest rates skyrocket. Housing prices have risen drastically. Families are struggling to pay their credit card debt and buy groceries. Those kitchen table issues have a real impact on millions of Americans.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By highlighting the benefits of zoos, this essay underscores the invaluable role these institutions play in the broader conservation efforts, making a compelling case for their continued support and recognition in safeguarding our planet's biodiversity. This essay was reviewed by. Alex Wood. More about our Team.
Zoos claim to support global biodiversity through conservation efforts like protecting endangered animals. This is somewhat true, although it varies greatly from zoo to zoo. On the other hand, zoos are big polluters and use up lots of resources, especially energy and water. Aquariums in particular use tons and tons of water.
The role of zoos in supporting local wildlife conservation efforts; The benefits of zoos for public health and well-being; ... With these 100 zoo essay topic ideas and examples, you should have plenty of inspiration to get started on your next assignment. Whether you're interested in the ethical implications of keeping animals in zoos, the role ...
They are unable to make seasonal migrations, some are unable to mate to have offspring, and predators are unable to hunt. In addition, not all zoos follow elementary sanitary standards or the appropriate temperature regime. Thus, animals cannot live freely and happily while in captivity. Summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of zoos, one ...
The essay on zoos explains that Zoos are an important part of our society and culture. They provide us with a connection to nature, preserve endangered species, and educate people about animals. ... By supporting zoos and their efforts, we can help ensure that these valuable resources are around for generations to come. So, next time you are ...
Human well-being, they argue, would greatly add to zoos' wider societal value ( ref) by providing a more complete picture of the obligations of modern zoos to the animals in their care and to ...
Zoos should be banned: a for and against essay Throughout the past few years, many people have been debating on whether zoos are actually relevant in this day and age. Undeniably, since they still exist, it means that the cons of banning them overweigh. ... In conclusion, I fully support keeping animals in the zoo Log in or register to post ...
Animals despise being captives in zoos. No matter how you "enhance" enclosures, they do not allow for freedom, a natural diet or adequate exercise. Animals end up stressed and unhealthy or ...
Zoos also use SSPs as research tools to better understand wildlife biology and population dynamics, and to raise awareness and funds to support field projects and habitat protection for specific ...
However, animals have a good quality of life in many zoos, and there's a strong moral case for why these institutions ought to exist. I've come to this view after working with great apes, and it might not extend to all species equally. However, since great apes are both cognitively sophisticated and human-like in their behaviour, they offer ...
Arguments for Zoos. By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species. Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe ...
Q.1 List the advantages of Zoo. A.1 Zoos bring the wildlife close to humans. It helps researchers study them closely and discover new things. It protects rare species and provides a safe breeding ground for them as well. Q.2 How are zoos harmful to animals? A.2 Zoos are very harmful to animals.
For this reason, zoos became almost the only hope for the preservation and conservation of endangered species. If to compare with the past century, their role has altered greatly. In the 50s, zoos used to be fun centers where animals were kept just for entertainment. However, at the moment, they could be considered important scientific and ...
Pros of Zoos. One of the primary arguments in favor of zoos is their role in conservation. Zoos often participate in breeding programs for endangered species, helping to increase the population of these animals and prevent them from becoming extinct. This is particularly important in the face of habitat destruction and poaching, which are major ...
Get custom essay. Most zoos keep wild animals, and majority of the animal population at the zoos is made up of animals that are rarely seen by human beings in their immediate environment. These animals are used to roaming in the jungle and forests. Others are used to swimming freely in the seas and rivers.
The debate over whether zoos help or harm animals underscores the need for a balanced approach that prioritizes both conservation and animal welfare. Well-managed zoos can contribute to vital conservation efforts, inspire public support for wildlife, and conduct valuable research. However, it is imperative that zoos uphold the highest ethical ...
Zoos produce helpful scientific research. 228 accredited zoos published 5,175 peer-reviewed manuscripts between 1993 and 2013. In 2017, 173 accredited US zoos spent $25 million on research, studied 485 species and subspecies of animals, worked on 1,280 research projects, and published 170 research manuscripts.
This is a recent zoo essay question from the IELTS test (June 2018). Essay about zoos have come up a few times in the IELTS test so it's worth studying same sample questions and sample essays about the topic. ... In this essay, the author makes it clear at the beginning that they support the closing down of zoos. ...
Students will examine the zoo as a facility in which animals are confined within enclosures and displayed to the public. In many cases, animals may also be bred to produce offspring. ... After reading informational texts, write an essay that addresses the question and support your position wiht evidence from the text(s). L2 Be sure to ...
In many modern zoos, animals are well cared for, healthy and probably, for many species, content. Zookeepers are not mustache-twirling villains. They are kind people, bonded to their charges and ...
1. Some concerned groups feel that zoos are cruelly exploitative while others argue they serve the vital function of protecting endangered animals. 2. In my opinion, though zoos are inherently unnatural, their efforts are laudable overall. Paraphrase the topic for the essay. Give a clear opinion.
Roula Khalaf, Editor of the FT, selects her favourite stories in this weekly newsletter. Sir Keir Starmer wants to "put a stop" to the far-right violence that is spreading across the UK. The ...
DULUTH — The Lake Superior Zoo's one-year-old red panda, Pip, was found dead in her den last week, the zoo announced Monday. The female panda was the zoo's second, having joined Zoozee in ...
Some church leaders and politicians have condemned the performance from the opening ceremony for mocking Christianity. Art historians are divided.
A Good Hook Examples for Essay about Zoos. A Thought-Provoking Quote: Eleanor Roosevelt once said, "The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams." As I explore the controversial topic of zoos, I can't help but wonder if these institutions align with our dreams for a compassionate and ethical future.
Harris is committed to supporting Ukraine in its fight against Russian aggression, having met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky at least six times and announcing last month $1.5 billion ...
The Biologist (Assistant Curator - Amazonia) will provide daily care of animals for the National Zoo. This involves, breeding, education, conservation, exhibition, collection planning and support of research for a collection. Salary: $68,405 - $88,926 per year.
WASHINGTON (AP) — On a "White Dudes for Harris" virtual call, it was probably fitting that "The Dude" dropped in. Actor Jeff Bridges addressed a fundraising event geared toward white men supporting Vice President Kamala Harris and sang her praises on Monday night, before channeling his iconic role as "The Dude" in 1998's "The Big Lebowski," declaring, "As the Dude might ...
The issue that has been lingering for a long time, why zoos should be banned, is discussed in this essay. "We do not own planet Earth; we belong to it. We must share it with our wildlife" - Steve Irwin. Keeping animals in zoos means that they do not have any freedom, they live in an unnatural habitat and they get bored stressed and lonely.
The Democrats have a record to answer for. I've traveled to the southern border. The flow of illegal migrants, deadly drugs and human trafficking is a humanitarian crisis that affects all 50 states.