How to Read Research Papers: A Pragmatic Approach for ML Practitioners

Is it necessary for data scientists or machine-learning experts to read research papers?
The short answer is yes. And don’t worry if you lack a formal academic background or have only obtained an undergraduate degree in the field of machine learning.
Reading academic research papers may be intimidating for individuals without an extensive educational background. However, a lack of academic reading experience should not prevent Data scientists from taking advantage of a valuable source of information and knowledge for machine learning and AI development .
This article provides a hands-on tutorial for data scientists of any skill level to read research papers published in academic journals such as NeurIPS , JMLR , ICML, and so on.
Before diving wholeheartedly into how to read research papers, the first phases of learning how to read research papers cover selecting relevant topics and research papers.

Step 1: Identify a topic
The domain of machine learning and data science is home to a plethora of subject areas that may be studied. But this does not necessarily imply that tackling each topic within machine learning is the best option.
Although generalization for entry-level practitioners is advised, I’m guessing that when it comes to long-term machine learning, career prospects, practitioners, and industry interest often shifts to specialization.
Identifying a niche topic to work on may be difficult, but good. Still, a rule of thumb is to select an ML field in which you are either interested in obtaining a professional position or already have experience.
Deep Learning is one of my interests, and I’m a Computer Vision Engineer that uses deep learning models in apps to solve computer vision problems professionally. As a result, I’m interested in topics like pose estimation, action classification, and gesture identification.
Based on roles, the following are examples of ML/DS occupations and related themes to consider.

For this article, I’ll select the topic Pose Estimation to explore and choose associated research papers to study.
Step 2: Finding research papers
One of the most excellent tools to use while looking at machine learning-related research papers, datasets, code, and other related materials is PapersWithCode .
We use the search engine on the PapersWithCode website to get relevant research papers and content for our chosen topic, “Pose Estimation.” The following image shows you how it’s done.
The search results page contains a short explanation of the searched topic, followed by a table of associated datasets, models, papers, and code. Without going into too much detail, the area of interest for this use case is the “Greatest papers with code”. This section contains the relevant papers related to the task or topic. For the purpose of this article, I’ll select the DensePose: Dense Human Pose Estimation In The Wild .
Step 3: First pass (gaining context and understanding)

At this point, we’ve selected a research paper to study and are prepared to extract any valuable learnings and findings from its content.
It’s only natural that your first impulse is to start writing notes and reading the document from beginning to end, perhaps taking some rest in between. However, having a context for the content of a study paper is a more practical way to read it. The title, abstract, and conclusion are three key parts of any research paper to gain an understanding.
The goal of the first pass of your chosen paper is to achieve the following:
- Assure that the paper is relevant.
- Obtain a sense of the paper’s context by learning about its contents, methods, and findings.
- Recognize the author’s goals, methodology, and accomplishments.
The title is the first point of information sharing between the authors and the reader. Therefore, research papers titles are direct and composed in a manner that leaves no ambiguity.
The research paper title is the most telling aspect since it indicates the study’s relevance to your work. The importance of the title is to give a brief perception of the paper’s content.
In this situation, the title is “DensePose: Dense Human Pose Estimation in the Wild.” This gives a broad overview of the work and implies that it will look at how to provide pose estimations in environments with high levels of activity and realistic situations properly.
The abstract portion gives a summarized version of the paper. It’s a short section that contains 300-500 words and tells you what the paper is about in a nutshell. The abstract is a brief text that provides an overview of the article’s content, researchers’ objectives, methods, and techniques.
When reading an abstract of a machine-learning research paper, you’ll typically come across mentions of datasets, methods, algorithms, and other terms. Keywords relevant to the article’s content provide context. It may be helpful to take notes and keep track of all keywords at this point.
For the paper: “ DensePose: Dense Human Pose Estimation In The Wild “, I identified in the abstract the following keywords: pose estimation, COCO dataset, CNN, region-based models, real-time.
It’s not uncommon to experience fatigue when reading the paper from top to bottom at your first initial pass, especially for Data Scientists and practitioners with no prior advanced academic experience. Although extracting information from the later sections of a paper might seem tedious after a long study session, the conclusion sections are often short. Hence reading the conclusion section in the first pass is recommended.
The conclusion section is a brief compendium of the work’s author or authors and/or contributions and accomplishments and promises for future developments and limitations.
Before reading the main content of a research paper, read the conclusion section to see if the researcher’s contributions, problem domain, and outcomes match your needs.
Following this particular brief first pass step enables a sufficient understanding and overview of the research paper’s scope and objectives, as well as a context for its content. You’ll be able to get more detailed information out of its content by going through it again with laser attention.
Step 4: Second pass (content familiarization)
Content familiarization is a process that’s relevant to the initial steps. The systematic approach to reading the research paper presented in this article. The familiarity process is a step that involves the introduction section and figures within the research paper.
As previously mentioned, the urge to plunge straight into the core of the research paper is not required because knowledge acclimatization provides an easier and more comprehensive examination of the study in later passes.
Introduction
Introductory sections of research papers are written to provide an overview of the objective of the research efforts. This objective mentions and explains problem domains, research scope, prior research efforts, and methodologies.
It’s normal to find parallels to past research work in this area, using similar or distinct methods. Other papers’ citations provide the scope and breadth of the problem domain, which broadens the exploratory zone for the reader. Perhaps incorporating the procedure outlined in Step 3 is sufficient at this point.
Another aspect of the benefit provided by the introduction section is the presentation of requisite knowledge required to approach and understand the content of the research paper.
Graph, diagrams, figures
Illustrative materials within the research paper ensure that readers can comprehend factors that support problem definition or explanations of methods presented. Commonly, tables are used within research papers to provide information on the quantitative performances of novel techniques in comparison to similar approaches.

Generally, the visual representation of data and performance enables the development of an intuitive understanding of the paper’s context. In the Dense Pose paper mentioned earlier, illustrations are used to depict the performance of the author’s approach to pose estimation and create. An overall understanding of the steps involved in generating and annotating data samples.
In the realm of deep learning, it’s common to find topological illustrations depicting the structure of artificial neural networks. Again this adds to the creation of intuitive understanding for any reader. Through illustrations and figures, readers may interpret the information themselves and gain a fuller perspective of it without having any preconceived notions about what outcomes should be.

Step 5: Third pass (deep reading)
The third pass of the paper is similar to the second, though it covers a greater portion of the text. The most important thing about this pass is that you avoid any complex arithmetic or technique formulations that may be difficult for you. During this pass, you can also skip over any words and definitions that you don’t understand or aren’t familiar with. These unfamiliar terms, algorithms, or techniques should be noted to return to later.

During this pass, your primary objective is to gain a broad understanding of what’s covered in the paper. Approach the paper, starting again from the abstract to the conclusion, but be sure to take intermediary breaks in between sections. Moreover, it’s recommended to have a notepad, where all key insights and takeaways are noted, alongside the unfamiliar terms and concepts.
The Pomodoro Technique is an effective method of managing time allocated to deep reading or study. Explained simply, the Pomodoro Technique involves the segmentation of the day into blocks of work, followed by short breaks.
What works for me is the 50/15 split, that is, 50 minutes studying and 15 minutes allocated to breaks. I tend to execute this split twice consecutively before taking a more extended break of 30 minutes. If you are unfamiliar with this time management technique, adopt a relatively easy division such as 25/5 and adjust the time split according to your focus and time capacity.
Step 6: Forth pass (final pass)
The final pass is typically one that involves an exertion of your mental and learning abilities, as it involves going through the unfamiliar terms, terminologies, concepts, and algorithms noted in the previous pass. This pass focuses on using external material to understand the recorded unfamiliar aspects of the paper.
In-depth studies of unfamiliar subjects have no specified time length, and at times efforts span into the days and weeks. The critical factor to a successful final pass is locating the appropriate sources for further exploration.
Unfortunately, there isn’t one source on the Internet that provides the wealth of information you require. Still, there are multiple sources that, when used in unison and appropriately, fill knowledge gaps. Below are a few of these resources.
- The Machine Learning Subreddit
- The Deep Learning Subreddit
- PapersWithCode
- Top conferences such as NIPS , ICML , ICLR
- Research Gate
- Machine Learning Apple
The Reference sections of research papers mention techniques and algorithms. Consequently, the current paper either draws inspiration from or builds upon, which is why the reference section is a useful source to use in your deep reading sessions.
Step 7: Summary (optional)
In almost a decade of academic and professional undertakings of technology-associated subjects and roles, the most effective method of ensuring any new information learned is retained in my long-term memory through the recapitulation of explored topics. By rewriting new information in my own words, either written or typed, I’m able to reinforce the presented ideas in an understandable and memorable manner.

To take it one step further, it’s possible to publicize learning efforts and notes through the utilization of blogging platforms and social media. An attempt to explain the freshly explored concept to a broad audience, assuming a reader isn’t accustomed to the topic or subject, requires understanding topics in intrinsic details.
Undoubtedly, reading research papers for novice Data Scientists and ML practitioners can be daunting and challenging; even seasoned practitioners find it difficult to digest the content of research papers in a single pass successfully.
The nature of the Data Science profession is very practical and involved. Meaning, there’s a requirement for its practitioners to employ an academic mindset, more so as the Data Science domain is closely associated with AI, which is still a developing field.
To summarize, here are all of the steps you should follow to read a research paper:
- Identify A Topic.
- Finding associated Research Papers
- Read title, abstract, and conclusion to gain a vague understanding of the research effort aims and achievements.
- Familiarize yourself with the content by diving deeper into the introduction; including the exploration of figures and graphs presented in the paper.
- Use a deep reading session to digest the main content of the paper as you go through the paper from top to bottom.
- Explore unfamiliar terms, terminologies, concepts, and methods using external resources.
- Summarize in your own words essential takeaways, definitions, and algorithms.
Thanks for reading!
Related resources
- DLI course: Building Transformer-Based Natural Language Processing
- GTC session: Enterprise MLOps 101
- GTC session: Intro to Large Language Models: LLM Tutorial and Disease Diagnosis LLM Lab
- GTC session: Build AI Applications with GPU Vector Databases
- NGC Containers: MATLAB
- Webinar: The Impact of Large Language Models (LLMs) on Life Sciences
About the Authors

Related posts

Improving Machine Learning Security Skills at a DEF CON Competition

Community Spotlight: Democratizing Computer Vision and Conversational AI in Kenya

An Important Skill for Data Scientists and Machine Learning Practitioners

AI Pioneers Write So Should Data Scientists

Meet the Researcher: Peerapon Vateekul, Deep Learning Solutions for Medical Diagnosis and NLP

LLM Research Rewrites the Role of AI in Safeguarding Sustainable Systems
real-time ai shark detection is boosting beach safety, building spatial intelligence from real-world 3d data using deep-learning framework fvdb.

Researchers Use AI to Resurrect Extinct DNA for Fighting Pathogens

Training Sim-to-Real Transferable Robotic Assembly Skills over Diverse Geometries

The best AI tools for research papers and academic research (Literature review, grants, PDFs and more)
As our collective understanding and application of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, so too does the realm of academic research. Some people are scared by it while others are openly embracing the change.
Make no mistake, AI is here to stay!
Instead of tirelessly scrolling through hundreds of PDFs, a powerful AI tool comes to your rescue, summarizing key information in your research papers. Instead of manually combing through citations and conducting literature reviews, an AI research assistant proficiently handles these tasks.
These aren’t futuristic dreams, but today’s reality. Welcome to the transformative world of AI-powered research tools!
This blog post will dive deeper into these tools, providing a detailed review of how AI is revolutionizing academic research. We’ll look at the tools that can make your literature review process less tedious, your search for relevant papers more precise, and your overall research process more efficient and fruitful.
I know that I wish these were around during my time in academia. It can be quite confronting when trying to work out what ones you should and shouldn’t use. A new one seems to be coming out every day!
Here is everything you need to know about AI for academic research and the ones I have personally trialed on my YouTube channel.
My Top AI Tools for Researchers and Academics – Tested and Reviewed!
There are many different tools now available on the market but there are only a handful that are specifically designed with researchers and academics as their primary user.
These are my recommendations that’ll cover almost everything that you’ll want to do:
| Find literature using semantic search. I use this almost every day to answer a question that pops into my head. | |
| An increasingly powerful and useful application, especially effective for conducting literature reviews through its advanced semantic search capabilities. | |
| An AI-powered search engine specifically designed for academic research, providing a range of innovative features that make it extremely valuable for academia, PhD candidates, and anyone interested in in-depth research on various topics. | |
| A tool designed to streamline the process of academic writing and journal submission, offering features that integrate directly with Microsoft Word as well as an online web document option. | |
| A tools that allow users to easily understand complex language in peer reviewed papers. The free tier is enough for nearly everyone. | |
| A versatile and powerful tool that acts like a personal data scientist, ideal for any research field. It simplifies data analysis and visualization, making complex tasks approachable and quick through its user-friendly interface. |
Want to find out all of the tools that you could use?
Here they are, below:
AI literature search and mapping – best AI tools for a literature review – elicit and more
Harnessing AI tools for literature reviews and mapping brings a new level of efficiency and precision to academic research. No longer do you have to spend hours looking in obscure research databases to find what you need!
AI-powered tools like Semantic Scholar and elicit.org use sophisticated search engines to quickly identify relevant papers.
They can mine key information from countless PDFs, drastically reducing research time. You can even search with semantic questions, rather than having to deal with key words etc.
With AI as your research assistant, you can navigate the vast sea of scientific research with ease, uncovering citations and focusing on academic writing. It’s a revolutionary way to take on literature reviews.
- Elicit – https://elicit.org
- Litmaps – https://www.litmaps.com
- Research rabbit – https://www.researchrabbit.ai/
- Connected Papers – https://www.connectedpapers.com/
- Supersymmetry.ai: https://www.supersymmetry.ai
- Semantic Scholar: https://www.semanticscholar.org
- Laser AI – https://laser.ai/
- Inciteful – https://inciteful.xyz/
- Scite – https://scite.ai/
- System – https://www.system.com
If you like AI tools you may want to check out this article:
- How to get ChatGPT to write an essay [The prompts you need]
AI-powered research tools and AI for academic research
AI research tools, like Concensus, offer immense benefits in scientific research. Here are the general AI-powered tools for academic research.
These AI-powered tools can efficiently summarize PDFs, extract key information, and perform AI-powered searches, and much more. Some are even working towards adding your own data base of files to ask questions from.
Tools like scite even analyze citations in depth, while AI models like ChatGPT elicit new perspectives.
The result? The research process, previously a grueling endeavor, becomes significantly streamlined, offering you time for deeper exploration and understanding. Say goodbye to traditional struggles, and hello to your new AI research assistant!
- Consensus – https://consensus.app/
- Iris AI – https://iris.ai/
- Research Buddy – https://researchbuddy.app/
- Mirror Think – https://mirrorthink.ai
AI for reading peer-reviewed papers easily
Using AI tools like Explain paper and Humata can significantly enhance your engagement with peer-reviewed papers. I always used to skip over the details of the papers because I had reached saturation point with the information coming in.
These AI-powered research tools provide succinct summaries, saving you from sifting through extensive PDFs – no more boring nights trying to figure out which papers are the most important ones for you to read!
They not only facilitate efficient literature reviews by presenting key information, but also find overlooked insights.
With AI, deciphering complex citations and accelerating research has never been easier.
- Aetherbrain – https://aetherbrain.ai
- Explain Paper – https://www.explainpaper.com
- Chat PDF – https://www.chatpdf.com
- Humata – https://www.humata.ai/
- Lateral AI – https://www.lateral.io/
- Paper Brain – https://www.paperbrain.study/
- Scholarcy – https://www.scholarcy.com/
- SciSpace Copilot – https://typeset.io/
- Unriddle – https://www.unriddle.ai/
- Sharly.ai – https://www.sharly.ai/
- Open Read – https://www.openread.academy
AI for scientific writing and research papers
In the ever-evolving realm of academic research, AI tools are increasingly taking center stage.
Enter Paper Wizard, Jenny.AI, and Wisio – these groundbreaking platforms are set to revolutionize the way we approach scientific writing.
Together, these AI tools are pioneering a new era of efficient, streamlined scientific writing.
- Jenny.AI – https://jenni.ai/ (20% off with code ANDY20)
- Yomu – https://www.yomu.ai
- Wisio – https://www.wisio.app
AI academic editing tools
In the realm of scientific writing and editing, artificial intelligence (AI) tools are making a world of difference, offering precision and efficiency like never before. Consider tools such as Paper Pal, Writefull, and Trinka.
Together, these tools usher in a new era of scientific writing, where AI is your dedicated partner in the quest for impeccable composition.
- PaperPal – https://paperpal.com/
- Writefull – https://www.writefull.com/
- Trinka – https://www.trinka.ai/
AI tools for grant writing
In the challenging realm of science grant writing, two innovative AI tools are making waves: Granted AI and Grantable.
These platforms are game-changers, leveraging the power of artificial intelligence to streamline and enhance the grant application process.
Granted AI, an intelligent tool, uses AI algorithms to simplify the process of finding, applying, and managing grants. Meanwhile, Grantable offers a platform that automates and organizes grant application processes, making it easier than ever to secure funding.
Together, these tools are transforming the way we approach grant writing, using the power of AI to turn a complex, often arduous task into a more manageable, efficient, and successful endeavor.
- Granted AI – https://grantedai.com/
- Grantable – https://grantable.co/
Best free AI research tools
There are many different tools online that are emerging for researchers to be able to streamline their research processes. There’s no need for convience to come at a massive cost and break the bank.
The best free ones at time of writing are:
- Elicit – https://elicit.org
- Connected Papers – https://www.connectedpapers.com/
- Litmaps – https://www.litmaps.com ( 10% off Pro subscription using the code “STAPLETON” )
- Consensus – https://consensus.app/
Wrapping up
The integration of artificial intelligence in the world of academic research is nothing short of revolutionary.
With the array of AI tools we’ve explored today – from research and mapping, literature review, peer-reviewed papers reading, scientific writing, to academic editing and grant writing – the landscape of research is significantly transformed.
The advantages that AI-powered research tools bring to the table – efficiency, precision, time saving, and a more streamlined process – cannot be overstated.
These AI research tools aren’t just about convenience; they are transforming the way we conduct and comprehend research.
They liberate researchers from the clutches of tedium and overwhelm, allowing for more space for deep exploration, innovative thinking, and in-depth comprehension.
Whether you’re an experienced academic researcher or a student just starting out, these tools provide indispensable aid in your research journey.
And with a suite of free AI tools also available, there is no reason to not explore and embrace this AI revolution in academic research.
We are on the precipice of a new era of academic research, one where AI and human ingenuity work in tandem for richer, more profound scientific exploration. The future of research is here, and it is smart, efficient, and AI-powered.
Before we get too excited however, let us remember that AI tools are meant to be our assistants, not our masters. As we engage with these advanced technologies, let’s not lose sight of the human intellect, intuition, and imagination that form the heart of all meaningful research. Happy researching!
Thank you to Ivan Aguilar – Ph.D. Student at SFU (Simon Fraser University), for starting this list for me!

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


- ai generator
6 Best AI tools for Reading Research Papers
HOME » 部落格 » 6 Best AI tools for Reading Research Papers

- 【Tag】 ai read papers , ai text generation , ai writing essay , essay Generator
The advent of AI has also impacted academia. Researchers and scientists no longer need to spend extensive time reading literature and large volumes of data. AI can read papers, perform tasks, and organize extensive literature, eliminating the tedious processes of reading and analysis, thus allowing quicker acquisition of knowledge.
Table of Contents
What AI tools are available for research?
Many researchers often struggle with the overwhelming task of reading and synthesizing data, unsure where to start or how to efficiently organize and analyze literature. AI tools for reading papers enable students and researchers to swiftly and accurately summarize and analyze documents. Here are some recommended AI tools for research :
GenApe AI is an advanced tool for generating text and images. It offers various AI assistants for academic papers, such as AI summarizers, title generators, and descriptive tools. Notably, the AI paper reader we are introducing swiftly analyzes documents and allows you to pose questions based on your specific needs.

I am using the Chatbot Ape from the menu. First, click on “Analyze Document” and upload your file. Next, you can specify your needs, whether you want an outline of the document or a summary.
I chose to have it summarize the document. The overall usage is simple and user-friendly. Unlike other AI tools for reading papers, it allows you to customize the style. The chatbot can provide answers tailored to your needs.
Additionally, for more recent information, you can enable real-time web access, ensuring that the information is accurate and up-to-date.

Immediately avail a complimentary trial without credit card required: https://app.genape.ai/chatApe
Explainpaper
I offer rapid academic paper analysis services utilizing artificial intelligence technology primarily for English language texts. I provide explanations for complex vocabulary found within papers upon highlighting.
Additionally, detailed abstract analysis is available, along with an AI chat feature for querying research-related questions and comprehending intricate content within papers or literature, aiding in a clearer understanding.
The usage is straightforward. After registration, a simple interface will appear. You can upload a file or paste a link to have the file read for you. Then, the tools mentioned earlier will appear in the right-hand column.

I tested a 94-page PDF file here, but it didn’t generate results, possibly due to limitations of the free account or the file’s size. Processing may require additional time. Asking AI questions incurs charges, but overall, it’s user-friendly for beginners and doesn’t require extensive time for writing papers.

ChatPDF is a paper reading tool based on the GPT-3 language model. By uploading a paper PDF, ChatPDF utilizes AI to analyze the paper. On the left side, you’ll see the paper itself, and on the right side, there is an AI chat interface.
It provides prompts on how to ask questions effectively, allowing you to quickly view key points of the paper or extract important keywords. Essentially, the free version of ChatPDF offers sufficient functionality for most users.
I have tested the same paper above and asked him to summarize the abstract for me. He was able to respond quickly. In the chat part, he will answer in Chinese if asked in Chinese and in English if asked in English.
It’s a rather intelligent chatroom that can quickly help you understand this paper. Another advantage is that you can use it without registering.

SciSpace Copilot
SciSpace Copilot is an AI tool designed specifically to enhance the comprehension of academic literature. It offers both a web-based version and an extension, making it accessible and user-friendly. Simply upload your PDF file, and it will identify relevant papers, providing functions for semantic analysis and scholarly discourse.
Once you upload your paper, you’ll see the Copilot chat on the right. It will suggest actions closely related to your paper, such as summarizing and analyzing it. Just follow the prompts, and it will swiftly assist you in analysis.

The analysis results will appear as shown in the diagram below. While he can choose the language, currently only Simplified Chinese is supported. Of course, there are other language options available for selection.

In addition to analyzing the results, it is also possible to quickly summarize a particular segment of literature. Simply select the content on the left and press the “Explain Text” button to obtain the conclusion.

Scholarcy is an AI academic paper abstract tool developed by the UK-based company Cactus Communications. It assists researchers in effortlessly locating, organizing, and comprehending scholarly literature.
Scholarcy utilizes natural language processing to automatically extract information from academic papers and transform it into concise, easily comprehensible abstracts.
Scholarcy requires registration before use. Unlike other AI tools for reading papers, after uploading a file, it allows customization of summaries, such as adjusting the word count or selecting key points, to tailor the summary according to personal preferences.

After analysis, the result will appear as shown in the diagram below, listing numerous items, although some internal content may be null.

Take a look at one example: I find Scholarcy more challenging to use overall compared to other analytical tools, with a more complex operational interface as well.

AI reading thesis extended reading: 5 Best AI Summarizing Tool , Text summarizer
Advantages of AI for reading papers
The main advantages of using AI to read essays are as follows:
Quickly capture the key points of a document
AI’s ability to read papers enables effortless extraction of key points from literature. Compared to manual reading and analysis, AI can swiftly identify content within documents, offering concise summaries and analyses, thereby saving considerable time.
Simplify the complexity
The terminology of academic papers is typically specialized and the content can be lengthy. Using AI to summarize papers reduces the content, making it easier and more efficient for you to comprehend literature and academic papers.
Easy Data Extraction
AI’s ability to read papers can assist in extracting critical information, enabling you to swiftly locate the necessary data.
How to effectively read academic papers?
In addition to using AI for reading papers, there are also techniques that can enhance your efficiency in paper reading. Here are tips to help you improve your effectiveness in reading academic papers:
Start with the Summary and Introduction
Whether you seek understanding of a new topic or wish to conduct research, when reading academic papers, you should begin with the abstract and introduction. The abstract provides an overview of the paper as a whole, aiding in quickly determining its relevance to your research topic.
Meanwhile, the introduction explains the research problem and its significance, allowing you to grasp the background and objectives of the study beforehand.
View Structure
Then, you should check the table of contents of this paper and pay attention to the main parts of the paper, such as introduction, methodology, results and discussion, etc. This will help you to find the part you need quickly and save unnecessary reading time.
Focus on Results and Discussions
When you are sure that the paper will be useful for your research, you can read it in depth for the sections you want to check out, mostly looking at the Results and Discussion sections, which are the 2 sections that will allow you to quickly grasp the core conclusions of the research.
AI reads papers easily and saves time
AI reading tools can enhance the ability to write essays, recommend GenApe AI tools, in addition to the above mentioned analysis of thesis, for academic research has been trained to use a variety of AI assistants, as long as you enter the content you want to quickly have a conclusion, outline, title, and of course, can also be analyzed in the paper, and now do not need to credit card can be free to try it out, hurry up and click on the button below!
Let’s start free trial today!
Join now and start changing the way you write!
RELATED POSTS

5 Best AI Essay Generators in 2024!

How to Write Papers Quickly?

What is Gemini? Can Google's latest artificial intelligence Gemini beat ChatGPT?
- google business
- brand-management
- advertising
Try GenApe Free
Enter referral code GenApeAI when subscribing to receive 5% discount!
The best AI assistants for content generation
AI Tools Blog

What is Suno AI? Suno AI Music Generator Tutorial

Claude 3.5 Sonnet updates, Testing,Really surpass GPT-4o?

How to brainstorm advertising creativity?
About Products
- 60+ AI templates
- Pricing Plan
- YuanSheng Inc.
- Email:[email protected]
- GUI number:83255252
- Term of service
- Phone:+886-7-6075007

A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Thomas Devereaux
- Electronegativity
New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at Ai2.

Affiliate 💸
Get started free
Research Paper Sources
A Full Guide To Using AI For Research: Use Cases, Tips & AI Tools
Interested in using AI for research? These various use cases, tips, and AI tools will help you leverage the power of AI in your research projects.
Apr 7, 2024

Research methods have evolved, thanks to technological advancements. Delving into AI for research can significantly streamline the process. By leveraging AI capabilities, researchers can collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data in record time. Unlike traditional research methods, AI-powered systems can provide accurate results. Besides, AI allows researchers to tap into a wealth of primary vs secondary sources , enabling them to make well-informed decisions based on credible information. In this blog, we will delve deep into how using AI for research can transform the way research is conducted today.
Table of Contents
Understanding the role ai plays in research, 6 ways you can use ai for research, benefits of using ai for research, 10 best ai tools for academic research, effective tips for researchers using ai for their research, supercharge your researching ability with otio — try otio for free today.

AI has revolutionized the research landscape by enabling more efficient and accurate processes. Utilizing AI tools in research can help save time, find relevant papers, plan and execute experiments, analyze data, and even write and edit manuscripts. AI-powered tools offer researchers a way to manage their entire research workflow by integrating various tasks, ultimately aiding in producing higher-quality research output.
Types of AI Technologies Commonly Used in Research Settings
There are several types of AI technologies that are commonly used in research settings. Natural Language Processing (NLP) plays a significant role in aiding researchers in processing vast amounts of textual data, summarizing papers, and extracting key information.
Machine learning algorithms are used to predict trends, analyze data, and optimize experiments. Robotics can be utilized to conduct experiments, gather data, and perform other physical tasks. Neural networks can be employed for tasks such as image recognition and data analysis.
AI research and writing partner
Knowledge workers, researchers, and students today suffer from content overload and are left to deal with it using fragmented, complex, and manual tooling. Too many of them settle for stitching together complicated bookmarking, read-it-later, and note-taking apps to get through their workflows. Now that anyone can create content with the click of a button - this problem is only going to get worse.
Otio solves this problem by providing one AI-native workspace for researchers. It helps them:
a wide range of data sources, from bookmarks, tweets, and extensive books to YouTube videos.
2. Extract key takeaways
with detailed AI-generated notes and source-grounded Q&A chat.
draft outputs using the sources you’ve collected
Otio helps you to go from reading list to first draft faster. Along with this, Otio also helps you write research papers/essays faster. Here are our top features that are loved by researchers: AI-generated notes on all bookmarks (YouTube videos, PDFs, articles, etc.), Otio enables you to chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, just like you chat with ChatGPT, as well as AI-assisted writing.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner — try Otio for free today!
Related Reading
• How To Read Scientific Papers • How Many Sources Should A Research Paper Have • Sources For Research Paper • Google Scholar Search Tips • How To Read A Research Paper • How To Find Sources For A Research Paper • Research Notes • Literature Synthesis

1. Finding and reviewing relevant papers
AI has significantly reduced the time and effort needed for manual literature reviews, saving countless hours. AI tools can comb through vast databases of research papers, identify relevant papers, and summarize key findings. This speeds up paper analysis, identifies trends, gaps in the literature, and helps discover research questions faster.
2. Comprehending academic papers
AI makes academic papers easier to understand by simplifying jargon and complex topics. Interacting with papers through AI assistants allows users to have a conversation with the PDF. This feature can help in language barriers by enabling users to interact with papers in their native languages.
3. Data collection and analysis
AI helps uncover patterns, trends, and correlations in large datasets accurately and quickly. From data entry to analysis, AI tools significantly speed up the process, ensuring high-quality research foundations.
4. Data visualization
AI-assisted optimization tools make data visualization easy. AI tools can help present data in informative ways, such as through images or graphs, making it easier for researchers to identify patterns and gain insights.
5. Enhanced academic writing
AI language models assist in writing by providing grammar and style suggestions, citations, and help in conveying thoughts effectively. Tools like paraphrasers and co-writers aid in improving writing skills instantly, making the writing process more efficient.
6. Seamless team collaborations
AI enhances group projects through automation of tasks, better document management, and improved communication. Project management tools with AI capabilities facilitate better collaboration by creating common online workspaces and translation in real-time.
7. Plagiarism checks
AI tools help detect plagiarism and artificial intelligence in writing. By scanning documents and comparing content to extensive databases, AI tools flag potential instances of plagiarism . AI detectors can recognize patterns of AI writing to highlight such instances in prose.
Otio's AI-Powered Workspace
Knowledge workers, researchers, and students often struggle with content overload and fragmented tools. Otio provides an AI-native workspace to streamline research workflows. Otio helps collect data from various sources, extract key takeaways, and create draft outputs faster. Researchers can benefit from AI-generated notes, source-grounded Q&A chats, and AI-assisted writing.

Accelerating data analysis and processing
AI tools are capable of processing vast amounts of data at a speed that far surpasses human capabilities. This acceleration allows researchers to swiftly identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within data sets, enabling them to draw conclusions and insights more quickly than ever before.
With this enhanced data processing speed, researchers can conduct in-depth analysis and produce results within a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods. This not only saves time but also allows researchers to explore data in ways that were previously unattainable.
Enhancing accuracy and efficiency of research tasks
AI boosts the accuracy and efficiency of research tasks by eliminating human error and biases. AI algorithms can run analyses with high precision, reducing the risk of inaccuracies or inconsistencies in the data.
Researchers can rely on AI to process large volumes of data consistently and meticulously, ensuring the reliability of their findings. This accuracy and efficiency also extend to tasks such as literature reviews, where AI tools can quickly scan and summarize vast amounts of text, saving researchers valuable time and effort.
Enabling predictive modeling and data-driven insights
AI technology is adept at creating predictive models from vast datasets, offering researchers the ability to forecast trends, behaviors, and outcomes with much higher accuracy than traditional methods.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms, researchers can uncover hidden insights and patterns within their data that were previously undetectable. The ability to predict future outcomes based on historical data allows researchers to make more informed decisions and develop strategies based on data-driven insights.
Facilitating automation of repetitive tasks
AI simplifies the research process by automating repetitive tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming and monotonous. For instance, AI tools can automate the collection and cleaning of data, freeing up researchers to focus on analysis and interpretation.
Automation also extends to tasks like citation management and reference formatting, streamlining the writing process and reducing the risk of errors. By automating these repetitive tasks, researchers can dedicate more time to exploring their research questions and generating innovative ideas.
a wide range of data sources, from bookmarks, tweets, and extensive books to YouTube videos.
draft outputs using the sources you’ve collected. Otio helps you to go from reading list to first draft faster. Along with this, Otio also helps you write research papers/essays faster. Here are our top features that are loved by researchers: AI-generated notes on all bookmarks (Youtube videos, PDFs, articles, etc.), Otio enables you to chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, just like you chat with ChatGPT, as well as AI-assisted writing.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner — try Otio for free today
• How To Summarize A Research Article • Reliable Sources For Research • How To Tell If An Article Is Peer Reviewed • Literature Search • Best Databases For Research • Summarize Research Paper Ai • How To Use Chat Gpt For Research • How To Search For Research Articles

1. Otio - Your AI Research and Writing Partner
Otio is an AI-native workspace that simplifies the research process for knowledge workers, researchers, and students by providing a single platform for collecting data from various sources, extracting key takeaways, and creating draft outputs. The AI-generated notes on all bookmarks, the ability to chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, and AI-assisted writing are among the top features praised by researchers.
Otio helps you move from a reading list to a first draft quickly and even assists in writing research papers or essays.
2. Semantic Scholar - Detailed Information at Your Fingertips
Semantic Scholar is an AI-powered tool that helps researchers by offering detailed information in context, highlighting key points, and providing super-short summaries of scientific papers. This tool enhances the research process by providing a more efficient way to extract valuable information from academic articles.
3. SciSpace - Streamlining Your Research Process
SciSpace is a valuable tool that aids researchers in finding relevant research papers and gaining insights into them. This tool can make it easier to locate specific papers within the scientific research field and obtain useful information for academic purposes.
4. Genei.io - Efficient Paper Summarization and Exploration
Genei.io is an AI-powered summarization and research tool that simplifies the process of finding and exploring academic papers. The efficient features of this tool can help researchers save time and effort when conducting literature reviews or other research-related tasks.
5. Connected Papers - Uncover Hidden Research Gems
Connected Papers is a powerful tool designed to help researchers find and explore academic papers. By offering insights into research articles and facilitating the discovery of relevant sources, this tool can help researchers uncover valuable information in their field of study.
6. Scite - Understanding Research Impact and Credibility
Scite is a valuable tool that enables users to see how research has been cited, providing valuable information on the impact and credibility of scientific articles. By offering insights into the citation history of research articles, Scite can help researchers evaluate the reliability and relevance of academic sources.
7. Zotero - Efficient Resource Retrieval for Research
Zotero is a reference management tool that aids researchers in retrieving resources using DOIs effectively. By making it easier to find and manage academic sources for research purposes, Zotero can help streamline the research process and enhance productivity.
8. IBM Watson Discovery - Extracting Insights From Unstructured Data
IBM Watson Discovery is an AI-powered platform that enables researchers to extract insights from large volumes of unstructured data, including scholarly articles, patents, and reports. By using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms , this tool can help researchers analyze and interpret textual data more efficiently.
9. Google Scholar - Accessing a Wealth of Scholarly Literature
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across a variety of disciplines. By helping researchers find academic articles, books, conference papers, and theses, Google Scholar can facilitate the discovery of valuable information and enhance the research process.
10. Cortex - Discovering and Analyzing Scientific Literature
Cortex is an AI-driven platform that helps researchers discover, analyze, and visualize scientific literature. By using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, this tool can extract insights from academic papers and identify trends in research fields. Cortex can help researchers stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field and make informed decisions based on the analysis of scientific literature.

Researchers can significantly benefit from using AI-powered tools to enhance their research process and streamline their time. It is essential for researchers not to rely solely on AI to replace the critical thinking required for the research. Instead, AI should be used as a tool to optimize the research process while maintaining the researcher's intellectual input. Here are some tips for researchers on how they can efficiently use AI in their research projects to boost productivity and optimize research outcomes.
Fact-Check AI-Generated Content: Verifying Information for Accurate Results
While using AI for research tasks, it's crucial to fact-check content generated by AI tools. Users should not take the AI-generated information as 'the truth' but rather cross-verify the results through reliable sources. AI tools can assist in data analysis and generation, but it is the researcher's responsibility to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information.
Avoid Depending on AI for Writing Academic Documents: AI as a Helper, Not Replacement
When using AI tools for research, it's advised not to rely entirely on these tools to write academic articles, theses, or grant applications. Researchers should view AI as assistive technology that can help organize data, conduct analysis, and provide insights, rather than generating full pieces of academic writing. The critical thinking and analysis that researchers bring to their work are irreplaceable by AI.
Utilize AI for Managing and Citing References: Streamlining the Citation Process with AI Tools
For referencing and citation needs, researchers should not rely on AI tools for generating references. Instead, AI tools can be used to manage and cite references effectively. AI-powered citation tools can help researchers organize their citations, format them according to specific guidelines, and ensure that reference lists are accurate and complete. By following these tips, researchers can effectively integrate AI into their research process, improving efficiency, and optimizing outcomes. AI tools should complement researchers' abilities, providing support and assistance without replacing the human intellect and critical thinking essential for high-quality research.
Otio is a dynamic tool designed to help knowledge workers, researchers, and students manage their content overload more efficiently. With a rise in easily accessible content creation, it’s becoming increasingly challenging for people to streamline their research process.
Otio hopes to simplify this process by offering an AI-native workspace for researchers.
1. Collect Diverse Data Sources
Otio enables users to gather data from a wide range of sources, including bookmarks, tweets, extensive books, and YouTube videos. By centralizing this information, Otio streamlines the initial research phase for users.
2. Extract Key Insights
The platform can generate detailed AI-powered notes and Q&A chat based on the collected data. This feature helps users quickly grasp the key takeaways from their research materials.
3. Fast-Track Drafting
Otio empowers users to create draft outputs using their collected sources. By helping researchers transition from their reading lists to initial drafts more efficiently, Otio optimizes the writing process.
Key Features Loved by Researchers
Ai-generated notes.
Otio offers AI-generated notes for all bookmarks, including YouTube videos, articles, and PDFs. This feature enhances the note-taking process and ensures the user has detailed insights from their research materials.
Interactive Chat Interface
Users can engage with individual links or entire knowledge bases via Otio's chat function. This feature allows for seamless communication, similar to engaging with ChatGPT, enhancing the collaborative aspect of research.
AI-Assisted Writing
Otio supports AI-assisted writing, which can be a game-changer for researchers aiming to speed up their writing process. By leveraging AI capabilities, researchers can optimize their writing efficiency.
Otio is an all-encompassing solution for knowledge workers, researchers, and students seeking to streamline their research and writing processes. The AI features embedded within Otio make it a valuable tool for automating tasks, generating insights, and accelerating the writing process. If you're looking to enhance your research workflow, Otio could be your ideal AI research and writing partner .
Try Otio for free today and experience the future of research tools.
• Best Reference Manager • Chatpdf Alternative • Ai Research Tools • Elicit AI • Consensus Ai • Sematic Scholar • Research Paper Writing App • Research Paper Reader • How Does Chatpdf Work • Scholarcy Alternative

Aug 29, 2024
Literature Review
12 Best Tools For Perfect Research Summary Writing

Aug 28, 2024
22 Good Websites For Research Papers and Academic Articles
Join over 50,000 researchers changing the way they read & write

Chrome Extension
© 2024 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Join thousands of other scholars and researchers
Try Otio Free
© 2023 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.

Analyze research papers at superhuman speed
Search for research papers, get one sentence abstract summaries, select relevant papers and search for more like them, extract details from papers into an organized table.

Find themes and concepts across many papers
Don't just take our word for it.
.webp)
Tons of features to speed up your research
Upload your own pdfs, orient with a quick summary, view sources for every answer, ask questions to papers, research for the machine intelligence age, pick a plan that's right for you, get in touch, enterprise and institutions, common questions. great answers., how do researchers use elicit.
Over 2 million researchers have used Elicit. Researchers commonly use Elicit to:
- Speed up literature review
- Find papers they couldn’t find elsewhere
- Automate systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- Learn about a new domain
Elicit tends to work best for empirical domains that involve experiments and concrete results. This type of research is common in biomedicine and machine learning.
What is Elicit not a good fit for?
Elicit does not currently answer questions or surface information that is not written about in an academic paper. It tends to work less well for identifying facts (e.g. "How many cars were sold in Malaysia last year?") and in theoretical or non-empirical domains.
What types of data can Elicit search over?
Elicit searches across 125 million academic papers from the Semantic Scholar corpus, which covers all academic disciplines. When you extract data from papers in Elicit, Elicit will use the full text if available or the abstract if not.
How accurate are the answers in Elicit?
A good rule of thumb is to assume that around 90% of the information you see in Elicit is accurate. While we do our best to increase accuracy without skyrocketing costs, it’s very important for you to check the work in Elicit closely. We try to make this easier for you by identifying all of the sources for information generated with language models.
How can you get in contact with the team?
You can email us at [email protected] or post in our Slack community ! We log and incorporate all user comments, and will do our best to reply to every inquiry as soon as possible.
What happens to papers uploaded to Elicit?
When you upload papers to analyze in Elicit, those papers will remain private to you and will not be shared with anyone else.
How accurate is Elicit?
Training our models on specific tasks, searching over academic papers, making it easy to double-check answers, save time, think more. try elicit for free..

The Semantic Reader Open Research Platform
Semantic Reader Project is a collaborative effort of NLP + HCI researchers from non-profit, industry, and academic institutions to create interactive, intelligent reading interfaces for scholarly papers. Our research led to the creation of Semantic Reader, an application used by tens of thousands of scholars each week.
The Semantic Reader Open Research Platform provides resources that enable the broader research community to explore exciting challenges around novel research support tools: PaperMage , a library for processing and analyzing scholarly PDFs, and PaperCraft , a React UI component for building augmented and interactive reading interfaces. Join us in designing the future of scholarly reading interfaces with our open source libraries!
Open Source Libraries
We provide PaperMage + PaperCraft for building intelligent and interactive paper readers. Below we showcase how to extract text from a PDF to prompt a LLM for term definitions and then visually augment the paper with highlights and popups.
Process and Analyze Scholarly PDF Documents
Create Visually Augmented Interactive Readers
Research Prototype Showcase
Here we present several interactive demos to showcase systems you can build with PaperMage and PaperCraft.

Augmenting Research Papers with Author Talk Videos
Demo Paper Presentation

Synergi & Threddy
Clipping Research Threads from Papers for Synthesis and Exploration
Paper Presentation

Paper Plain
Making Medical Research Papers Approachable to Healthcare Consumers
Demo Code Tutorial Paper

LLM Paper Q&A
A GPT-powered PDF QA system with attribution support.
Demo Code Tutorial

Augmenting Citations in Papers with Persistent and Personalized Context
In-Production Paper Presentation

Localizing Incoming Citations from Follow on Papers in the Margins

Automatic highlights for skimming support of scientific papers
In-Production Paper

Augmenting Papers with Just-in-Time Definitions of Terms and Symbols
Founding Project Demo Paper
Publications
Semantic reader project overview.
The Semantic Reader Project: Augmenting Scholarly Documents through AI-Powered Interactive Reading Interfaces Kyle Lo, Joseph Chee Chang, Andrew Head, Jonathan Bragg, Amy X. Zhang, Cassidy Trier, Chloe Anastasiades, Tal August, Russell Authur, Danielle Bragg, Erin Bransom, Isabel Cachola, Stefan Candra, Yoganand Chandrasekhar, Yen-Sung Chen, Evie (Yu-Yen) Cheng, Yvonne Chou, Doug Downey, Rob Evans, Raymond Fok, F.Q. Hu, Regan Huff, Dongyeop Kang, Tae Soo Kim, Rodney Michael Kinney, A. Kittur, Hyeonsu B Kang, Egor Klevak, Bailey Kuehl, Michael Langan, Matt Latzke, Jaron Lochner, Kelsey MacMillan, Eric Stuart Marsh, Tyler Murray, Aakanksha Naik, Ngoc-Uyen Nguyen, Srishti Palani, Soya Park, Caroline Paulic, Napol Rachatasumrit, Smita R Rao, P. Sayre, Zejiang Shen, Pao Siangliulue, Luca Soldaini, Huy Tran, Madeleine van Zuylen, Lucy Lu Wang, Christopher Wilhelm, Caroline M Wu, Jiangjiang Yang, Angele Zamarron, Marti A. Hearst, Daniel S. Weld . ArXiv. 2023 .
Interactive and Intelligent Reading Interfaces
Qlarify: Bridging Scholarly Abstracts and Papers with Recursively Expandable Summaries Raymond Fok, Joseph Chee Chang, Tal August, Amy X. Zhang, Daniel S. Weld . ArXiv. 2023 .
Papeos: Augmenting Research Papers with Talk Videos Tae Soo Kim, Matt Latzke, Jonathan Bragg, Amy X. Zhang, Joseph Chee Chang . The ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. 2023 .
Synergi: A Mixed-Initiative System for Scholarly Synthesis and Sensemaking Hyeonsu B Kang, Sherry Wu, Joseph Chee Chang, A. Kittur . The ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. 2023 .
🏆 Best Paper Award CiteSee: Augmenting Citations in Scientific Papers with Persistent and Personalized Historical Context Joseph Chee Chang, Amy X. Zhang, Jonathan Bragg, Andrew Head, Kyle Lo, Doug Downey, Daniel S. Weld . Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2023 .
Relatedly: Scaffolding Literature Reviews with Existing Related Work Sections Srishti Palani, Aakanksha Naik, Doug Downey, Amy X. Zhang, Jonathan Bragg, Joseph Chee Chang . Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2023 .
CiteRead: Integrating Localized Citation Contexts into Scientific Paper Reading Napol Rachatasumrit, Jonathan Bragg, Amy X. Zhang, Daniel S. Weld . 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. 2022 .
🏆 Best Paper Award Math Augmentation: How Authors Enhance the Readability of Formulas using Novel Visual Design Practices Andrew Head, Amber Xie, Marti A. Hearst . Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2022 .
Scim: Intelligent Skimming Support for Scientific Papers Raymond Fok, Hita Kambhamettu, Luca Soldaini, Jonathan Bragg, Kyle Lo, Andrew Head, Marti A. Hearst, Daniel S. Weld . Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. 2022 .
Exploring Team-Sourced Hyperlinks to Address Navigation Challenges for Low-Vision Readers of Scientific Papers Soya Park, Jonathan Bragg, Michael Chang, K. Larson, Danielle Bragg . Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction. 2022 .
Paper Plain: Making Medical Research Papers Approachable to Healthcare Consumers with Natural Language Processing Tal August, Lucy Lu Wang, Jonathan Bragg, Marti A. Hearst, Andrew Head, Kyle Lo . ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction. 2022 . Presentation at CHI 2024.
Threddy: An Interactive System for Personalized Thread-based Exploration and Organization of Scientific Literature Hyeonsu B Kang, Joseph Chee Chang, Yongsung Kim, A. Kittur . Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. 2022 .
🏆 Best Paper Award SciA11y: Converting Scientific Papers to Accessible HTML Lucy Lu Wang, Isabel Cachola, Jonathan Bragg, Evie (Yu-Yen) Cheng, Chelsea Hess Haupt, Matt Latzke, Bailey Kuehl, Madeleine van Zuylen, Linda M. Wagner, Daniel S. Weld . Proceedings of the 23rd International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility. 2021 .
Augmenting Scientific Papers with Just-in-Time, Position-Sensitive Definitions of Terms and Symbols Andrew Head, Kyle Lo, Dongyeop Kang, Raymond Fok, Sam Skjonsberg, Daniel S. Weld, Marti A. Hearst . Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2020 .
Open Research Resources: Libraries, Models, Datasets
🏆 Best Paper Award PaperMage: A Unified Toolkit for Processing, Representing, and Manipulating Visually-Rich Scientific Documents Kyle Lo, Zejiang Shen, Benjamin Newman, Joseph Chee Chang, Russell Authur, Erin Bransom, Stefan Candra, Yoganand Chandrasekhar, Regan Huff, Bailey Kuehl, Amanpreet Singh, Chris Wilhelm, Angele Zamarron, Marti A. Hearst, Daniel S. Weld, Doug Downey, Luca Soldaini. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Demos. 2023.
A Question Answering Framework for Decontextualizing User-facing Snippets from Scientific Documents Benjamin Newman, Luca Soldaini, Raymond Fok, Arman Cohan, Kyle Lo . undefined. 2023 .
🏆 Best Paper Award LongEval: Guidelines for Human Evaluation of Faithfulness in Long-form Summarization Kalpesh Krishna, Erin Bransom, Bailey Kuehl, Mohit Iyyer, Pradeep Dasigi, Arman Cohan, Kyle Lo . ArXiv. 2023 .
Are Layout-Infused Language Models Robust to Layout Distribution Shifts? A Case Study with Scientific Documents Catherine Chen, Zejiang Shen, D. Klein, G. Stanovsky, Doug Downey, Kyle Lo . ArXiv. 2023 .
The Semantic Scholar Open Data Platform Rodney Michael Kinney, Chloe Anastasiades, Russell Authur, Iz Beltagy, Jonathan Bragg, Alexandra Buraczynski, Isabel Cachola, Stefan Candra, Yoganand Chandrasekhar, Arman Cohan, Miles Crawford, Doug Downey, Jason Dunkelberger, Oren Etzioni, Rob Evans, Sergey Feldman, Joseph Gorney, D. Graham, F.Q. Hu, Regan Huff, Daniel King, Sebastian Kohlmeier, Bailey Kuehl, Michael Langan, Daniel Lin, Haokun Liu, Kyle Lo, Jaron Lochner, Kelsey MacMillan, Tyler Murray, Christopher Newell, Smita R Rao, Shaurya Rohatgi, P. Sayre, Zejiang Shen, Amanpreet Singh, Luca Soldaini, Shivashankar Subramanian, A. Tanaka, Alex D Wade, Linda M. Wagner, Lucy Lu Wang, Christopher Wilhelm, Caroline Wu, Jiangjiang Yang, Angele Zamarron, Madeleine van Zuylen, Daniel S. Weld . ArXiv. 2023 .
VILA: Improving Structured Content Extraction from Scientific PDFs Using Visual Layout Groups Zejiang Shen, Kyle Lo, Lucy Lu Wang, Bailey Kuehl, Daniel S. Weld, Doug Downey . Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics. 2021 .
Document-Level Definition Detection in Scholarly Documents: Existing Models, Error Analyses, and Future Directions Dongyeop Kang, Andrew Head, Risham Sidhu, Kyle Lo, Daniel S. Weld, Marti A. Hearst . Proceedings of the First Workshop on Scholarly Document Processing @ ACL. 2020 .
See the Project Overview Paper to see a full list of contributors. † For questions and inquiries, please contact Joseph Chee Chang (PaperCraft & Intelligent reading interfaces), or Kyle Lo and Luca Soldaini (PaperMage & Scientific document processing).
Research Advisory Board
Intelligent reading interfaces research, scientific document processing research, research libraries and tooling.
Subscribe to the Arize blog
Get the latest
On this page
Suggested reading.

Four Tips on How To Read AI Research Papers Effectively
- AI In the Enterprise
- Large Language Models
Amber Roberts
Machine learning engineer.
According to a recent survey, over two-thirds (66.9%) of developers and machine learning teams are planning production deployments of LLM apps in the next 12 months or “as fast as possible” – and 14.1% are already in production!
Given the rapid rate of progress and constant drumbeat of new foundation models, orchestration frameworks and open source libraries – as well as the workaday challenges of getting an app into production – it can be difficult to find the time to digest and read the dizzying array of cutting-edge AI research papers hitting arXiv.
That task has never been more critical, however, as the time between academic discovery and industry application moves from years to weeks. How can teams read AI research papers without losing nuance, with an eye toward pragmatic application, while balancing real-world challenges?
In a recent webinar with Deep Learning AI, we explored strategies for understanding and applying the latest research, reducing mean time to application. Here are four takeaways.
Follow the Right People

Identify the Type of Paper and Break It Down Accordingly
While there are probably dozens of archetypes of AI research papers across academia and industry, many fall under three general categories that are a useful shorthand for practitioners.
Surveys typically give a detailed overview of a certain topic, providing a summary spread of where the field is right now in a specified area. Generally, the goal with a survey paper is to get an overview of what is happening in a given field to identify trends and common patterns for research opportunities.
An example is illustrative. Say you are wondering whether to read “ A Survey of Large Language Models .” This might be useful if you want to:
- Use one of the LLMs or compare your current LLM
- Compare open vs. closed source capabilities
- Compare pre-training, data curation and prompting methods
- Compare architectures and parameters (Encoder/Decoder, Size, Normalization, Activation, Bias, Attention patterns)
- Compare cost, compute or hardware components
- Review the comparative capacities and evaluations
It’s worth keeping in mind that survey papers aren’t as good at offering a technical deep dive into a specific model or introducing any new or novel ideas.
Benchmarking and Dataset Papers
Benchmarking papers are usually the first step after a breakthrough paper because they often define how we evaluate new breakthroughs. Examples in the world of LLMs many will recognize include MMLU, HellaSwag, and TruthfulQA. These papers typically introduce a dataset for testing or roll out a new evaluation approach on a dataset with a goal of using a new dataset or evaluation metric to evaluate capabilities of an LLM, learning the limitations of a model based on what and how they are evaluated, or considering how to expand benchmark capabilities.
To readers, these papers are worth reading when you want to use the metric to benchmark your current LLM, compare model costs to performance benchmarks, or potentially modify a benchmark to be better for your use case.
A few things to look out for on these papers:
- Bias in the dataset
- Does a single definitive answer exist?
- Does the question provide enough context?
- Does it count if they get the right answer the wrong way?
Generally, these papers are less useful for introducing new capabilities or breakthroughs or detailed breakdowns.
Breakthrough Papers
Breakthrough papers – think Mixtral of Experts , QLoRA: Efficient Fine Tuning of Quantized LLMs, or LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models – are must-reads because they represent major leaps forward in the field. Reading these effectively generally means understanding what novel idea is being introduced and how it impacts the current environment, with potential applications. These papers do not usually provide a good overview of a whole space or show the datasets launched to evaluate a model.
Be An Active, Agile Reader
Approach each paper knowing that it’s a piece of a larger puzzle. Recognize that what you’re reading today might be challenged or built upon tomorrow. This field evolves rapidly, and maintaining an open, inquisitive mind is essential. For technical readers, this means constantly questioning and validating findings, even if they come from reputed sources or established theories. To that end, getting hands-on is critical. Implementing a model from a paper in a notebook, replicating a study, or even proposing an alternative approach can all help not only understand the paper better but also contribute to the field.
Follow Real-Time Progress In the Field
(1/6) Can LLMs Do Time Series Analysis ⏲️? GPT-4 vs Claude 3 Opus 🥊 We have seen a lot of customers trying to apply LLMs to all kinds of data, but have not seen many Evals that show how well LLMs can analyze patterns in data that are not text related – especially timeseries🕰️… pic.twitter.com/7t95VEG9aQ — Aparna Dhinakaran (@aparnadhinak) March 29, 2024
Traditional, peer-reviewed research takes a long time. Even preprint papers involve long review processes and tight reviews of results, with collaboration between many authors. In an industry where foundation model breakthroughs and new frameworks are upending traditional machine learning use cases overnight, however, it is important to stay abreast of research in all of its forms.
To that end, our co-founder and Chief Product Officer Aparna Dhinakaran recently started releasing bi-weekly research on social media and our blog on burning questions from customers, publishing repeatable open source results – reviewing with internal teams prior to publishing to test for “holes.” We are encouraged to see others embracing this approach as well on fast-moving topics, with the understanding that we are going fast so we might make mistakes – and that’s OK so long as we own up to them.
As AI continues to grow, these skills will be increasingly crucial for staying abreast of the latest developments and making meaningful contributions.
Sign up for our monthly newsletter, The Drift.
Copyright © 2024 Arize AI, Inc
Subscribe to get the latest news, expertise, and product updates from Arize. Your inbox is sacred, so we’ll only curate and send the best stuff.
*We’re committed to your privacy. Arize uses the information you provide to contact you about relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
Like what you see? Let’s chat. Fill out this form and we will be in contact with you soon!
The Fastest Way to Read Research Papers self.__wrap_b=(t,n,e)=>{e=e||document.querySelector(`[data-br="${t}"]`);let s=e.parentElement,r=B=>e.style.maxWidth=B+"px";e.style.maxWidth="";let o=s.clientWidth,u=s.clientHeight,a=o/2-.25,c=o+.5,p;if(o){for(r(a),a=Math.max(e.scrollWidth,a);a+1 {self.__wrap_b(0,+e.dataset.brr,e)})).observe(s):process.env.NODE_ENV==="development"&&console.warn("The browser you are using does not support the ResizeObserver API. Please consider add polyfill for this API to avoid potential layout shifts or upgrade your browser. Read more: https://github.com/shuding/react-wrap-balancer#browser-support-information"))};self.__wrap_b(":Riim:",1)
Upload a paper, highlight confusing text, get an explanation. We make research papers easy to read.
Used by the best researchers
See what researchers think of Explainpaper
Become an Expert in Anything.
Explainpaper is free - so let's get started.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How can I read any AI paper?
I have studied linear algebra, probability, and calculus twice. But I don't understand how can I reach the level that I can read any AI paper and understand mathematical notation in it.
What is your strategy when you see the mathematical expression that you can't understand?
For example, in Wasserstein GAN article, there are many advanced mathematical notations. Also, some papers are written by people who have a master's in mathematics, and those people use advanced mathematics in some papers, but I have a CS background.
When you come across this kind of problem, what do you do?
- $\begingroup$ You say that you have a CS background. Does it mean that you have obtained a bachelor's or a master's in CS? Can you clarify this? Also, when you say that you studied linear algebra, probability, and calculus, how exactly did you study those? For example, do you know what the central limit theorem says? Do you know what random variables are? If you don't know the answers to these questions, you probably didn't study enough. $\endgroup$ – nbro Commented Jun 30, 2020 at 14:09
- $\begingroup$ This is not exactly an answer to your question but I'd suggest looking for blog posts. There are lots of good blogs that simplify the math behind those complex looking papers and conveys the core idea in a much more understandable way. For example: gradientscience.org , distill.pub etc. $\endgroup$ – SpiderRico Commented Jul 1, 2020 at 2:00
4 Answers 4
I think the answer depends very much on why you are reading the paper, what are you trying to get out of it? There are plenty of papers that I "read" (or often really just quickly skim through) where I'll definitely not understand all the math. More often than not, this will be because I don't actually care to deeply understand it.
There is plenty of more "practical" research to be done in AI, which definitely doesn't always require a deep understanding of all the math. Intuition can often be enough, at least to get started, for meaningful practical contributions. If this is the sort of research that you're interested in doing, you probably don't need to understand as many of the mathematical parts of AI papers as you do if you're really trying to do research directly in that theoretical area.
Personally, when I write "math-heavy" parts in my own papers (and that will often already be restricted to a rather simple level of math in comparison to the "real theory" ML papers), I always try to make sure to include intuitive, English descriptions of what we're doing around it. Even if you don't immediately understand a full equation, just having the intuitive explanation around it to tell you what it means can be enough for a broad understanding of the paper. Then you only have to dive deep into the details of the equations if -- based on the English text -- you decide that you're actually really interested. So, if there are sufficient, intuitive explanations surrounding the equations, I'd recommend to focus heavily on that first. Not every paper does this though, sometimes there's very little text and very much math, and then this can be difficult.
Even if it turns out that you do have to understand math, you may not have to understand ALL of it right away though. The important parts that I would try to focus on understanding first are:
- A mathematical description of the "problem". This could be an objective function, a metric to be optimised/minimised/maximised, or an existing equation from previous literature that the authors take as a starting point and inspect some detail of in greater detail.
- Mathematical descriptions of the outcomes/results. These could be equations that they actually use in concrete algorithms (see if you can relate them to any pseudocode that may be present), or the final equations stated in theorems / at the end of proofs.
All the complex parts in between are probably less important. Just a vague idea of what the starting point is, and a vague understanding of the final outcome, can be enough to at least know what the paper is about. Then you can decide for yourself whether you really need to know more about the details in between, or if they're maybe not relevant to you / your work / your research.
I think the best way to make reading papers easier is to practice (as in, read lots of papers, try implementing them, etc), and to discuss them with other students/researchers.
Sometimes it's tough to avoid some obscure or really technical math, so you may just need to do extra reading. The Wasserstein metric, for example, is used a lot in ML but I kinda doubt most ML researchers have a good understanding of it. This metric comes from a branch of math called "optimal transportation theory", which is super interesting, but very real-analysis-heavy. If you're really interested in learning about the Wasserstein metric, I recommend Cedric Villani's book "Optimal Transport: Old and New". I also recommend this awesome paper . Nevertheless, learning analysis is likely gonna serve you very well for understanding a wide range of ML papers.
Finally, as a beginning grad student, I have experienced your issue as well. I made a tool to help me with this at this repo , which manages a library of papers you're interested in. It then uses a PageRank algorithm to recommend new papers to you that are commonly referred to by the papers you want to read, with the goal of helping you read up on the foundational "prerequisite" material.
- $\begingroup$ Thanks for your response, Wasserstein is a only example, but when I come across advanced math concept that has many prerequisites in math like algebraic topology, would you suggest that I follow prereqs then learn the topic? Doesn't it take a long time? $\endgroup$ – Huseyin Okan Demir Commented Jun 30, 2020 at 15:35
- $\begingroup$ It can of course take a long time, but (hopefully) these things will be common across much of the papers you read. If not, you might not need such an in-depth understanding of those concepts, you can probably get away with getting an overview of the field just so you can learn something from the ML paper. $\endgroup$ – harwiltz Commented Jun 30, 2020 at 18:26
When I read papers in a new domain and when I started reading theoretical ML paper, I faced similar problems. I usually start with the introduction then related work and try to understand all the concepts and related papers cited that are relevant to understanding the paper.
Specifically when it comes to difficult mathematical formulations, as @harwiltz said the more you read about it the easier it gets. There may be a set of papers with concepts that are similar to the paper you are reading but are well-explained I usually read them first (or if it is an important mathematical concept you can find some blogs describing the intuitions/basics behind it).
From my experience (and I've been reading many research papers for a while), it's rare to find a research paper where you fully understand everything in one go, especially if the research paper was published or released recently or a very long time ago (because, back then, maybe people had a different writing style, used a different notation, or something like that), unless you are an expert on the topic, which is probably not the case, unless you are doing serious research on the topic (i.e. you're doing a Ph.D. and beyond; in that case, you probably don't need to ask questions on this site: hopefully, you have a qualified advisor to whom you can ask these questions!), or the paper is really easy and does not contain any formulas.
Of course, if a paper is published, it must contain something novel, so that something novel could be one of the things that you need to spend some time to understand, but the hardest parts of a paper could also easily be the prerequisites (i.e. the concepts that the paper builds upon), because you may not have a very solid knowledge of those topics (as you probably have already experienced).
There are at least three ways to proceed when you are stuck because you don't understand something
- If you can ignore what you don't understand (i.e. you don't need it for your purposes because e.g. you just need to have a high-level understanding of the topics), ignore it (really!!)
- If it cannot be ignored (e.g. because you really need to know all the details of the paper because e.g. you need to give a presentation at your university), try to understand what you don't understand by picking up a resource on that topic that you don't understand, then read it; spend the time that you think is opportune (i.e. do not spend 6.5 days to understand a detail of a paper if you only have 7 days to read that paper and prepare a presentation or whatever you need to do)
- If you can afford it, stop reading that paper and go back to the basics.
In general, learning is not an easy process and, more specifically, reading research papers is not the easiest reading (because research papers are typically concise, i.e. there's a lot of information compression), so do not expect to understand everything of a paper in one go. In fact, the paper How to Read a Paper by S. Keshav, which gives you some guidelines on how to read a paper, tells you to read a paper in three steps. For more details about these three steps, please, read the paper!
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged research papers academia ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Why was this lighting fixture smoking? What do I do about it?
- Took a pic of old school friend in the 80s who is now quite famous and written a huge selling memoir. Pic has ben used in book without permission
- I overstayed 90 days in Switzerland. I have EU residency and never got any stamps in passport. Can I exit/enter at airport without trouble?
- Why does flow separation cause an increase in pressure drag?
- Writing a random password generator
- Ring Buffer Implementation in C++
- How to logging Preferences library
- The answer is not wrong
- Who was the "Dutch author", "Bumstone Bumstone"?
- Where to donate foreign-language academic books?
- What would be non-slang equivalent of "copium"?
- How does the summoned monster know who is my enemy?
- Suitable Category in which Orbit-Stabilizer Theorem Arises Naturally as Canonical Decomposition
- Book or novel about an intelligent monolith from space that crashes into a mountain
- Is it possible to calculate FPS (frames per second) of video using statistical data?
- Why is Legion helping you whilst geth are fighting you?
- If inflation/cost of living is such a complex difficult problem, then why has the price of drugs been absoultly perfectly stable my whole life?
- How do eradicated diseases make a comeback?
- Which version of Netscape is this, on which OS?
- What prevents a browser from saving and tracking passwords entered to a site?
- Planning to rebuild detached storage room (in the US)
- Is there a phrase for someone who's really bad at cooking?
- Can Shatter damage Manifest Mind?
- If a trigger runs an update will it ALWAYS have the same timestamp for a temporal table?

AI Research Tools
Qonqur is an innovative software that allows you to control your computer and digital content using hand gestures, without the need for expensive virtual reality
Instabooks AI
Instabooks AI instantly generates customized textbooks on any topic you want to explore in depth. Simply type a detailed description of the information you want
Jenni AI is a writing assistant that aims to help academics and researchers supercharge their next paper. With its powerful AI features like autocomplete, citation

Elicit is an AI research assistant that can search, summarize, extract data from, and engage in conversations about over 125 million scientific papers. Elicit’s AI-driven
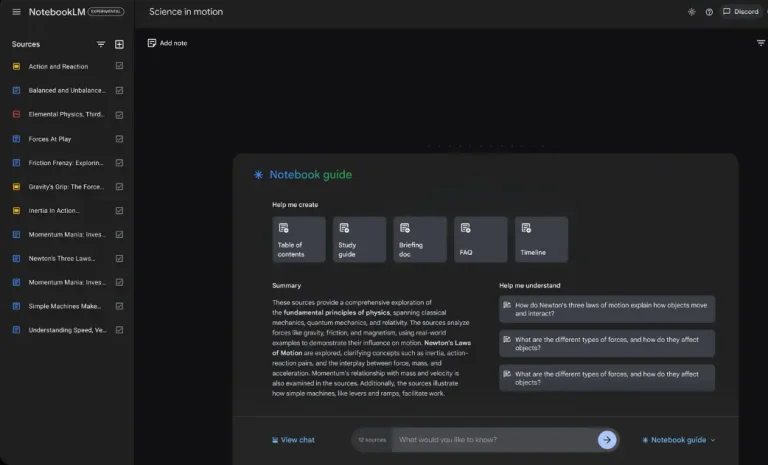
NotebookLM is a free AI-powered research assistant and note-taking tool developed by Google. Leveraging the advanced Gemini 1.5 Pro model, this virtual assistant excels at

Genei is a research tool that automates the process of summarizing background reading and can also generate blogs, articles, and reports. It allows you to
ChatPDF allows you to talk to your PDF documents as if they were human. It’s perfect for quickly extracting information or answering questions from large
Consensus is an AI-powered search engine that helps you find evidence-based answers to your research questions. It intelligently searches through over 200 million scientific papers
SciSummary is an AI-powered tool that uses language models like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 to automatically summarize lengthy scientific articles and research papers. It’s ideal for
Andi is a next-generation search tool powered by generative AI. It provides answers to questions and explains and summarizes information from the best sources, giving
Julius is an AI data analysis tool that helps you visualize, analyze, and get insights from all kinds of data. With Julius, you can simply

Aria is a versatile AI assistant integrated into Opera Browser, offering a range of AI features across desktop and mobile. This free tool provides real-time
Discover the latest AI research tools to accelerate your studies and academic research. Search through millions of research papers, summarize articles, view citations, and more.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Copyright © 2024 EasyWithAI.com
Top AI Tools
- Best Free AI Image Generators
- Best AI Video Editors
- Best AI Meeting Assistants
- Best AI Tools for Students
- Top 5 Free AI Text Generators
- Top 5 AI Image Upscalers
Readers like you help support Easy With AI. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for the latest AI tools !
We don’t spam! Read our privacy policy for more info.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Please check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription. Thank you!
The Fastest Research Platform Ever
All-in-one AI tools for students and researchers.
Try asking or searching for:
Popular Tools
Chat with pdf.
Get all answers backed by citations.
Use AI suggestions to expand notes to paragraphs.
Best for Researchers
Literature review.
Discover new papers for your research.
Find Concepts
Discover concepts from 285M research papers.
Extract Data
Get summary, conclusions & findings from multiple PDFs.
Are you a Student? Try these.
Paraphraser.
Increase fluency of your content.
Citation Generator
Cite sources in 1-click in APA, MLA and 2300+ formats.
AI Detector
Analyze your essays and research papers for AI content.
For Authors
Public profile booster.
Like Google Scholar profile, but better. Share interactive videos about research papers.
Featured in web store
SciSpace for Chrome
Get research-backed explanations for any research paper, technical blog post, or report that you read from your favourite websites.
Used by 200K+ researchers
Papers added today
Papers added this week, recently added by authors, popular papers to read.

Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer

Attention is All you Need

mT5: A Massively Multilingual Pre-trained Text-to-Text Transformer

An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale

Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection

How Good is Your Tokenizer? On the Monolingual Performance of Multilingual Language Models
Machine Learning

Support-Vector Networks

Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning Via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers

Learning Deep Architectures for AI

Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization

An Introduction to Support Vector Machines

Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks

Semi-supervised learning using Gaussian fields and harmonic functions

Manifold Regularization: A Geometric Framework for Learning from Labeled and Unlabeled Examples

Support vector machine learning for interdependent and structured output spaces

A Framework for Learning Predictive Structures from Multiple Tasks and Unlabeled Data
Natural Language

Exploiting Cloze-Questions for Few-Shot Text Classification and Natural Language Inference

Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision

Unified Pre-training for Program Understanding and Generation

Semantic memory: A review of methods, models, and current challenges

A Survey on Recent Approaches for Natural Language Processing in Low-Resource Scenarios.

Foundations of Statistical Natural Language Processing

A framework for representing knowledge

Speech and Language Processing: An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, and Speech Recognitio

Semantic similarity in a taxonomy: an information-based measure and its application to problems of ambiguity in natural language

Cheap and Fast -- But is it Good? Evaluating Non-Expert Annotations for Natural Language Tasks
Top papers of 2023
Top papers of 2022, trending questions, what is the significance of islamic history in the context of desa semuntul rantau bayur, what are the similarities and differences in the philosophical concepts of happiness across various religions, what is the current estimate of the number of true mangrove species in vietnam, who talk about factor affecting teaching and learning skills in acquisition to mathematics in africa, can the concept of giftedness impact the identity development of young adults, and if so, how, what are the psychological and sociological factors contributing to feelings of loneliness among second-generation immigrants compared to native populations, what are the psychological differences between seeking an apology and seeking redemption in interpersonal conflicts, what are research article that related to "teacher professionalism", what is the optimal emg amplitude cut off value for accurate muscle activity detection in clinical settings, can the unique properties of sansevieria trifasciata (snake plant) fibers be harnessed to create sustainable, eco-friendly textiles, what are the most effective methods for extracting and analyzing hormonal content from pollen samples, what percentage of teacher ask question to student in english classroom language, is the protein folding problem solved, what role does cyberpsychology play in online interactions, how was the skylight and ventilation in roman bathrooms write references in apa style, how does retinex method enhance astro-photographs, what metal contamination is usually found in fruit and vegetables, what are the challenges in b2b sales, what are the key factors driving the high demand for fermented foods globally, what factors make the eastern coast of india more vulnerable to climate change, what are the effect of lack of computers to students of learning computer system servicing, how does glutamine synthetase impact yeast protein production, what is the gene cloning in microbiology , how reader can be entertain from reading fiction, how do the principles of minimalism in logo design influence consumer perception and brand recognition in today's market, can fv/fm be used as a reliable indicator of changes in co2 assimilation rate in response to environmental stressors, what types of mountains are found in traditional chinese landscape paintings, can pv system be a uhi mitigating solutio, design and analysis of dynamic wireless charging using square coils, how can labor shortage impact the efficiency and effectiveness of logistics and supply chain management operations, what article mentioned about phase in requirements engineering including elicitation, analysis, specification, and validation, how do bambusa vulgaris fibers differ from traditional textile materials, what is negative effect of self harm in adolescent, what kinds of research topics and subjects are better for 7t mri than 3t mri, what is the mechanism of action of omecamtiv mecarbil in treating heart failure, who das 12-items india hindi, how can cbt and schematherapy be combined for the treatment of obesity, how pocillopora damicornis coral looklike, how sel can contribute to peace education, do cell bio markers have a significant correlation with surgical outcomes in patients with cancer, how has the concept of atomic design evolved since 2013, what are the benefits of vacuum packing lemongrass, what is the most cutting edge protocol for primary pbmc transfection, amino acids application aonla, does calcium supplementation increase cardiovascular risks in ckd patients, how does infrastructure affect settlement, what were the motivations behind the european conquest of south africa, what are the unique properties of bambusa vulgaris fibers, how does fv/fm measurement relate to photosynthetic efficiency, how does the relationship between interest rates and bond yields impact bonds' volatility, what are the key factors that influence the effectiveness of influencer marketing in shaping consumer purchase decisions, what is the impact of tiktok on marketing hospitality industry, how does the growth rate of sansevieria trifasciata compare to bamboo, has fv/fm been used to assess photosynthetic efficiency of lettuce, how is the mycn exression in lung neuroendocrine tumor, efficacy of semaglutide in hfpef, how do cultural differences impact evacuation and displacement processes, how do diffused aerators differ from paddlewheel aerators, what are justification for classical conditioning theory of learning in clinical teaching, how does meenakshi mukerjee explore the concept of anxiety, what are the characteristics of pocillopora damicornis, what is the rodent density in the city, how does wall teichoic acid affect mycobacterium tuberculosis, what was the significance of hal (hindustan aeronautics limited) in the development of indian aircraft industry, is lufthansa technik singapore a good company, what is considered a normal and healthy fv/fm in crisp lettuce, how much percentage of bhi agar is needed to grow bacteria, how can acieve more efficiency in dynmaic wireless charging system, how do eco-friendly hotels impact tourist decision-making, what are the process of kwl of donna m. ogle,1986, which chlorophyll fluorescence parameters can be used to assess plant stress, why transparency is important for interdisciplinary research, how does the lesson study model impact teaching capacity, what are the key factors influencing parental satisfaction in primary private schools, what are the purpose of mtuha in tanzania, what are the key factors that contribute to the development of social capital among second-generation immigrants, what are the geochemical models that are used for showing chemical speciation of potentially toxic elements in copper slag, what are the key factors influencing the purchase decisions of consumers in the digital age, what are the latest findings on aspirin use in cap, can the toe framework be used to identify data management strategies for small-scale enterprises, how do cultural and socioeconomic factors influence the formation of interethnic social ties among second-generation immigrants, how are venous congestion and fluid balance related pathofysiologically, what is the function of carrageenan extracted from eucheumatoid seaweed, what are the most common microbial diseases in humans, i want to write abstract about information technology open sources in library science field , what are the key factors that influence employers to adopt flexible work practices, how does temperature affect pollen production in plants, what are the short-term and long-term risks associated with mungaro injection, what happening for ai after chatgpt, what materials are good for sacrificial anodes in a heat exchanger, do the crowded physiological environments have effects on the structures of protein amyloid fibrils, when did the concept of women empowerment start, how government research foster hong kong construction, can executive function training programs be effective in enhancing the cognitive abilities of adolescents, what are the common factors contributing to flood vulnerability, how does the redshift of light from distant galaxies provide evidence for the universe’s expansion, why microbiota composition in cecum of broiler chicken is higher, how does the revitalization process in pasar gedhe impact the surrounding community and what are the potential long-term effects, what are the key differences in the theoretical frameworks and practical applications of personal mastery, personal development, and self-management, is feedback types in complex adaptive systems different from that of system dynamics modelling, 🔬 researchers worldwide are simplifying papers.
Millions of researchers are already using SciSpace on research papers. Join them and start using your AI research assistant wherever you're reading online.
Mushtaq Bilal, PhD
Researcher @ Syddansk Universitet
SciSpace is an incredible (AI-powered) tool to help you understand research papers better. It can explain and elaborate most academic texts in simple words.
Olesia Nikulina
PhD Candidate
Academic research gets easier day by day. All thanks to AI tools like @scispace Copilot, Copilot can instantly answer your questions and simply explain scientific concepts as you read
Richard Gao
Co-founder evoke-app.com
This is perfect for a layman to scientific information like me. Especially with so much misinformation floating around nowadays, this is great for understanding studies or research others may have misrepresented on purpose or by accident.
Product Hunt
I absolutely adore this product. It's been years since I was in a lab but, I plugged in a study I did way back when and this gets everything right. Equations, hypotheses, and methodologies will be game changers for graduate studies (the current education system severely limits comprehension while encouraging interconnectivity between streams). But, early learners would be able to discover so many papers through this as well. In short, love it
Livia Burbulea
I'm gonna recommend SciSpace to all of my friends and family that are still studying. And I'll definitely love to give it a try for myself, cause you know, education should never stop when you finish your studies. 😀
Sara Botticelli
Product Hunt User.
Wonderful idea! I know this will be used and appreciated by a lot of students, researchers, and lovers of knowledge. Great job, team @saikiranchandha and @shanukumr!
Divyansh Verma
SVNIT'25 Chemical Engineering
SciSpace, is a website where you can easily conduct research. Its most notable feature, in my opinion, is the presence of a #ai-powered copilot which can #simplify and explain any text you highlight in the paper you're reading. #citations and related papers are easily accessible with each paper.
Researcher @ VIU
It´s not only the saved time. Reading scientific literature, specially if you are not an expert in the field is a very attention-intensive process. It´s not a task you can maintain for long periods of time. Having them not just smartly summarised but being able to get meaningful answers is a game-changer for a science journalist
Kalyani Korla, PhD
Product Manager • Healthcare
Upload your pdf and highlight the sections you want to understand. It simplifies those complicated sections of the article in a jiffy. It is not rocket science, but it is always welcome if someone explains the big terms in simpler words.
In the media


- Conferences
- Last updated March 17, 2022
- In AI Origins & Evolution
How to read AI/ML research papers

- Published on March 19, 2022
- by Sri Krishna

Research papers are the wellspring of ideas pushing the frontiers of cutting edge technologies. Scholars around the globe rely on platforms like arXiv , JSTOR, Reddit, PapersWithCode to get up to speed on the latest in AI and data science. But let’s face it, research papers are a hard nut to crack. The time and effort you put into unpacking a research paper might go down the drain unless you have a method/reading strategy in place. To that end, we have put together a tutorial to help you get the best out of research papers.
Locking in the right paper/s
Whether you want to learn about Transformers or Hidden Markov Model , finding the right papers is the first step. You can choose relevant papers by number of citations, authors, impact etc. Sorting the reading material as primary, secondary and tertiary will save you a lot of time and effort and optimise your research. Richmond Alake , computer vision engineer at Loveshark, suggested themes based on ML/DS jobs to get you started.

Skim to gain context
Before you dive into the research paper , you should first understand the contents of the paper by taking a quick look at the title, abstract, and conclusion. Skimming the paper will give you an idea about the author’s theories and methodology, and if the paper aligns with your goal.

Get familiar
The next step is to get a feel for the subject matter explored in the paper. Reading the introduction and glancing through the visual aids (graph, diagrams, figures) in the research paper set expectations and help you ease into the complex areas of the research. The introduction provides an overview of the problem statement, research scope, goals, previous research efforts, and methodologies.
The visual representations of data put the research paper in the context. Tables and graphs codify the information in an easy to understand format.
Deep reading
You need to avoid any complicated arithmetic or technical formulations and skip over any words or definitions you don’t understand. Keep a note of these terms, techniques and algorithms, and revisit it later.
The primary goal is to gain a broad understanding of what is covered in the paper . Approach the paper with fresh eyes, beginning with the abstract and ending with the conclusion, but make sure to take breaks between sections. It’s also a good idea to keep a notepad to jot down the key insights and takeaways, as well as unfamiliar terms and concepts.
The final step involves going over the unfamiliar terms, terminologies, concepts, and algorithms noted down earlier. The final stage focuses on using external material to understand the unfamiliar concepts in the paper.
You can use resources like Machine Learning Subreddit and Deep Learning Subreddit to enrich your understanding. Lastly, writing a precis of the paper in your own words will help you get an idea of how much you have learned. Deliberate practice is the key in getting the concepts down cold- rinse and repeat to fill the knowledge gaps.
PS: Watch Andrew Ng ’s lecture on getting the most out of research papers.
📣 Want to advertise in AIM? Book here
Sri Krishna
- arithmetic formulations , Artificial Intelligence , Data Science , Deep Learning , innovation , Machine Learning , methodology , novel techniques , research papers , researchers , technology

The team has built a metric called “virality score”, which is derived from a dataset of 100,000 social media videos.

Top Editorial Picks
Finacus Solutions and pi-labs Develops World’s First eKYC Solution Resistant to Deepfake Frauds Tanisha Bhattacharjee
Andrew Ng and Yann LeCun Joins Korean National AI Committee As Advisors Tanisha Bhattacharjee
Reliance Jio Announces Free Cloud Storage with Jio AI-Cloud Tanisha Bhattacharjee
Apple, NVIDIA in talks to Raise Funding for OpenAI Aditi Suresh
Cursor Rival Codeium Raises $150 Mn, Becomes Unicorn with $1.25 Bn Valuation Mohit Pandey
Subscribe to The Belamy: Our Weekly Newsletter
Biggest ai stories, delivered to your inbox every week., "> "> flagship events.
Discover how Cypher 2024 expands to the USA, bridging AI innovation gaps and tackling the challenges of enterprise AI adoption
© Analytics India Magazine Pvt Ltd & AIM Media House LLC 2024
- Terms of use
- Privacy Policy
Paper, has never been so
Trusted and loved by users from
Discover the Unseen
Gain valuable insights from a vast repository of over 300 million papers spanning nearly every academic discipline, or tap into trillions of web sources for comprehensive research.
Chat with Facts
My name is delightful to say and holds two lovely meanings. It combines 'cat' and 'openread' in a graceful blend. It also represents the spirit of 'OpenRead AI Technology', shining with creativity and cleverness.
Uncover Tomorrow's Innovations
The world is evolving rapidly, don't get left behind.
Reading & Notes Taking
Seamless Research Experience in One Place
Grasp ideas with AI and build your personal knowledge bank
- Artificial Intelligence
Exclusive: New Research Finds Stark Global Divide in Ownership of Powerful AI Chips

W hen we think of the “cloud,” we often imagine data floating invisibly in the ether. But the reality is far more tangible: the cloud is located in huge buildings called data centers, filled with powerful, energy-hungry computer chips. Those chips, particularly graphics processing units (GPUs), have become a critical piece of infrastructure for the world of AI, as they are required to build and run powerful chatbots like ChatGPT.
As the number of things you can do with AI grows, so does the geopolitical importance of high-end chips—and where they are located in the world. The U.S. and China are competing to amass stockpiles, with Washington enacting sanctions aimed at preventing Beijing from buying the most cutting-edge varieties. But despite the stakes, there is a surprising lack of public data on where exactly the world’s AI chips are located.
A new peer-reviewed paper , shared exclusively with TIME ahead of its publication, aims to fill that gap. “We set out to find: Where is AI?” says Vili Lehdonvirta, the lead author of the paper and a professor at Oxford University’s Internet Institute. Their findings were stark: GPUs are highly concentrated in only 30 countries in the world, with the U.S. and China far out ahead. Much of the world lies in what the authors call “Compute Deserts:” areas where there are no GPUs for hire at all.
The finding has significant implications not only for the next generation of geopolitical competition, but for AI governance—or, which governments have the power to regulate how AI is built and deployed. “If the actual infrastructure that runs the AI, or on which the AI is trained, is on your territory, then you can enforce compliance,” says Lehdonvirta, who is also a professor of technology policy at Aalto University. Countries without jurisdiction over AI infrastructure have fewer legislative choices, he argues, leaving them subjected to a world shaped by others. “This has implications for which countries shape AI development as well as norms around what is good, safe, and beneficial AI,” says Boxi Wu, one of the paper’s authors.
The paper maps the physical locations of “public cloud GPU compute”—essentially, GPU clusters that are accessible for hire via the cloud businesses of major tech companies. But the research has some big limitations: it doesn’t count GPUs that are held by governments, for example, or in the private hands of tech companies for their use alone. And it doesn’t factor in non-GPU varieties of chips that are increasingly being used to train and run advanced AI. Lastly, it doesn't count individual chips, but rather the number of compute “regions” (or groups of data centers containing those chips) that cloud businesses make available in each country.
Read More: How ‘Friendshoring’ Made Southeast Asia Pivotal to the AI Revolution
That’s not for want of trying. “GPU quantities and especially how they are distributed across [cloud] providers’ regions,” the paper notes, “are treated as highly confidential information.” Even with the paper’s limitations, its authors argue, the research is the closest up-to-date public estimate of where in the world the most advanced AI chips are located—and a good proxy for the elusive bigger picture.
The paper finds that the U.S. and China have by far the most public GPU clusters in the world. China leads the U.S. on the number of GPU-enabled regions overall, however the most advanced GPUs are highly concentrated in the United States. The U.S. has eight “regions” where H100 GPUs—the kind that are the subject of U.S. government sanctions on China—are available to hire. China has none. This does not mean that China has no H100s; it only means that cloud companies say they do not have any H100 GPUs located in China. There is a burgeoning black market in China for the restricted chips, the New York Times reported in August, citing intelligence officials and vendors who said that many millions of dollars worth of chips had been smuggled into China despite the sanctions.
The paper’s authors argue that the world can be divided into three categories: “Compute North,” where the most advanced chips are located; the “Compute South,” which has some older chips suited for running, but not training, AI systems; and “Compute Deserts,” where no chips are available for hire at all. The terms—which overlap to an extent with the fuzzy “Global North” and “Global South” concepts used by some development economists—are just an analogy intended to draw attention to the “global divisions” in AI compute, Lehdonvirta says.
The risk of chips being so concentrated in rich economies, says Wu, is that countries in the global south may become reliant on AIs developed in the global north without having a say in how they work.
It “mirrors existing patterns of global inequalities across the so-called Global North and South,” Wu says, and threatens to “entrench the economic, political and technological power of Compute North countries, with implications for Compute South countries’ agency in shaping AI research and development.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- How Nayib Bukele’s ‘Iron Fist’ Has Transformed El Salvador
- What if Ultra-Processed Foods Aren’t as Bad as You Think?
- How Ukraine Beat Russia in the Battle of the Black Sea
- Long COVID Looks Different in Kids
- How Project 2025 Would Jeopardize Americans’ Health
- What a $129 Frying Pan Says About America’s Eating Habits
- The 32 Most Anticipated Books of Fall 2024
Write to Billy Perrigo at [email protected]
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: How to Build Consensus Around a New Idea
- Devon Proudfoot
- Wayne Johnson

Strategies for overcoming the disagreements that can stymie innovation.
Previous research has found that new ideas are seen as risky and are often rejected. New research suggests that this rejection can be due to people’s lack of shared criteria or reference points when evaluating a potential innovation’s value. In a new paper, the authors find that the more novel the idea, the more people differ on their perception of its value. They also found that disagreement itself can make people view ideas as risky and make them less likely to support them, regardless of how novel the idea is. To help teams get on the same page when it comes to new ideas, they suggest gathering information about evaluator’s reference points and developing criteria that can lead to more focused discussions.
Picture yourself in a meeting where a new idea has just been pitched, representing a major departure from your company’s standard practices. The presenter is confident about moving forward, but their voice is quickly overtaken by a cacophony of opinions from firm opposition to enthusiastic support. How can you make sense of the noise? What weight do you give each of these opinions? And what does this disagreement say about the idea?
- DP Devon Proudfoot is an Associate Professor of Human Resource Studies at Cornell’s ILR School. She studies topics related to diversity and creativity at work.
- Wayne Johnson is a researcher at the Utah Eccles School of Business. He focuses on evaluations and decisions about new information, including persuasion regarding creative ideas and belief change.
Partner Center
- Search for: Toggle Search
AI Chases the Storm: New NVIDIA Research Boosts Weather Prediction, Climate Simulation
As hurricanes, tornadoes and other extreme weather events occur with increased frequency and severity, it’s more important than ever to improve and accelerate climate research and prediction using the latest technologies.
Amid peaks in the current Atlantic hurricane season, NVIDIA Research today announced a new generative AI model, dubbed StormCast, for emulating high-fidelity atmospheric dynamics. This means the model can enable reliable weather prediction at mesoscale — a scale larger than storms but smaller than cyclones — which is critical for disaster planning and mitigation.
Detailed in a paper written in collaboration with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the University of Washington, StormCast arrives as extreme weather phenomena are taking lives, destroying homes and causing more than $150 billion in damage annually in the U.S. alone.
It’s just one example of how generative AI is supercharging thundering breakthroughs in climate research and actionable extreme weather prediction, helping scientists tackle challenges of the highest stakes: saving lives and the world.
NVIDIA Earth-2 — a digital twin cloud platform that combines the power of AI, physical simulations and computer graphics — enables simulation and visualization of weather and climate predictions at a global scale with unprecedented accuracy and speed.

In Taiwan , for example, the National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction plans to predict fine-scale details of typhoons using CorrDiff , an NVIDIA generative AI model offered as part of Earth-2.
CorrDiff can super-resolve 25-kilometer-scale atmospheric data by 12.5x down to 2 kilometers — 1,000x faster and using 3,000x less energy for a single inference than traditional methods.
That means the center’s potentially lifesaving work, which previously cost nearly $3 million on CPUs, can be accomplished using about $60,000 on a single system with an NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU . It’s a massive reduction that shows how generative AI and accelerated computing increase energy efficiency and lower costs.
The center also plans to use CorrDiff to predict downwash — when strong winds funnel down to street level, damaging buildings and affecting pedestrians — in urban areas.
Now, StormCast adds hourly autoregressive prediction capabilities to CorrDiff, meaning it can predict future outcomes based on past ones.
A Global Impact From a Regional Focus
Global climate research begins at a regional level.
Physical hazards of weather and climate change can vary dramatically on regional scales. But reliable numerical weather prediction at this level comes with substantial computational costs. This is due to the high spatial resolution needed to represent the underlying fluid-dynamic motions at mesoscale.
Regional weather prediction models — often referred to as convection-allowing models, or CAMs — have traditionally forced researchers to face varying tradeoffs in resolution, ensemble size and affordability.
CAMs are useful to meteorologists for tracking the evolution and structure of storms, as well as for monitoring its convective mode, or how a storm is organized when it forms. For example, the likelihood of a tornado is based on a storm’s structure and convective mode.
CAMs also help researchers understand the implications for weather-related physical hazards at the infrastructure level.
For example, global climate model simulations can be used to inform CAMs, helping them translate slow changes in the moisture content of large atmospheric rivers into flash-flooding projections in vulnerable coastal areas.
At lower resolutions, machine learning models trained on global data have emerged as useful emulators of numerical weather prediction models that can be used to improve early-warning systems for severe events. These machine learning models typically have a spatial resolution of about 30 kilometers and a temporal resolution of six hours.
Now, with the help of generative diffusion, StormCast enables this at a 3-kilometer, hourly scale.
Despite being in its infancy, the model — when applied with precipitation radars — already offers forecasts with lead times of up to six hours that are up to 10% more accurate than the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s state-of-the-art 3-kilometer operational CAM.
Plus, outputs from StormCast exhibit physically realistic heat and moisture dynamics, and can predict over 100 variables, such as temperature, moisture concentration, wind and rainfall radar reflectivity values at multiple, finely spaced altitudes. This enables scientists to confirm the realistic 3D evolution of a storm’s buoyancy — a first-of-its-kind accomplishment in AI weather simulation.
NVIDIA researchers trained StormCast on approximately three-and-a-half years of NOAA climate data from the central U.S., using NVIDIA accelerated computing to speed calculations.
More Innovations Brewing
Scientists are already looking to harness the model’s benefits.
“Given both the outsized impacts of organized thunderstorms and winter precipitation, and the major challenges in forecasting them with confidence, the production of computationally tractable storm-scale ensemble weather forecasts represents one of the grand challenges of numerical weather prediction,” said Tom Hamill, head of innovation at The Weather Company. “StormCast is a notable model that addresses these challenges, and The Weather Company is excited to collaborate with NVIDIA on developing, evaluating and potentially using these deep learning forecast models.”
“Developing high-resolution weather models requires AI algorithms to resolve convection, which is a huge challenge,” said Imme Ebert-Uphoff, machine learning lead at Colorado State University’s Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere. “The new NVIDIA research explores the potential of accomplishing this with diffusion models like StormCast, which presents a significant step toward the development of future AI models for high-resolution weather prediction.”
Alongside the acceleration and visualization of physically accurate climate simulations, as well as a digital twin of our planet , such research breakthroughs signify how NVIDIA Earth-2 is enabling a new, vital era of climate research.
Learn more about sustainable computing and NVIDIA Research, a global team of hundreds of scientists and engineers focused on topics including climate AI, computer graphics, computer vision, self-driving cars and robotics.
Featured image courtesy of NASA.
See notice regarding software product information.
Share on Mastodon
arXiv's Accessibility Forum starts next month!
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: automated design of agentic systems.
Abstract: Researchers are investing substantial effort in developing powerful general-purpose agents, wherein Foundation Models are used as modules within agentic systems (e.g. Chain-of-Thought, Self-Reflection, Toolformer). However, the history of machine learning teaches us that hand-designed solutions are eventually replaced by learned solutions. We formulate a new research area, Automated Design of Agentic Systems (ADAS), which aims to automatically create powerful agentic system designs, including inventing novel building blocks and/or combining them in new ways. We further demonstrate that there is an unexplored yet promising approach within ADAS where agents can be defined in code and new agents can be automatically discovered by a meta agent programming ever better ones in code. Given that programming languages are Turing Complete, this approach theoretically enables the learning of any possible agentic system: including novel prompts, tool use, control flows, and combinations thereof. We present a simple yet effective algorithm named Meta Agent Search to demonstrate this idea, where a meta agent iteratively programs interesting new agents based on an ever-growing archive of previous discoveries. Through extensive experiments across multiple domains including coding, science, and math, we show that our algorithm can progressively invent agents with novel designs that greatly outperform state-of-the-art hand-designed agents. Importantly, we consistently observe the surprising result that agents invented by Meta Agent Search maintain superior performance even when transferred across domains and models, demonstrating their robustness and generality. Provided we develop it safely, our work illustrates the potential of an exciting new research direction toward automatically designing ever-more powerful agentic systems to benefit humanity.
| Comments: | Website: |
| Subjects: | Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) |
| Cite as: | [cs.AI] |
| (or [cs.AI] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Finding research papers. One of the most excellent tools to use while looking at machine learning-related research papers, datasets, code, and other related materials is PapersWithCode. We use the search engine on the PapersWithCode website to get relevant research papers and content for our chosen topic, "Pose Estimation.".
Mirror Think - https://mirrorthink.ai; AI for reading peer-reviewed papers easily. Using AI tools like Explain paper and Humata can significantly enhance your engagement with peer-reviewed papers. I always used to skip over the details of the papers because I had reached saturation point with the information coming in.
AI reading thesis extended reading:5 Best AI Summarizing Tool , Text summarizer. Advantages of AI for reading papers. The main advantages of using AI to read essays are as follows: Quickly capture the key points of a document. AI's ability to read papers enables effortless extraction of key points from literature.
Our API now includes paper search, better documentation, and increased stability. ... Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual. Try it for select papers. ... AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at Ai2. Learn More. About
AI makes academic papers easier to understand by simplifying jargon and complex topics. Interacting with papers through AI assistants allows users to have a conversation with the PDF. This feature can help in language barriers by enabling users to interact with papers in their native languages. 3.
Now it is time to apply the algorithms in the paper to the data in your project. Here is how you can approach this: 1. Check the availability of the paper data and code: Have a look at the paper with the code website and see whether the code and the data of this paper are available or not.
That's exactly what you get with SciSpace ChatPDF! Use this AI assistant to get explanations and answers on any research paper as you read. Works for tables, equations, diagrams, jargon, and even lengthy blocks of text. You don't have to pause and search for it elsewhere. And your learning flow won't be disrupted.
Andrew Ng, Adjunct Professor & Kian Katanforoosh, Lecturer - Stanford Universityhttp://onlinehub.stanford.edu/Andrew NgAdjunct Professor, Computer ScienceKia...
So let's use Pose Estimation as a guide to how we would approach reading research papers related to the subject matter: pose estimation. 1. Assemble collections of resources that focus on the subject matter. Resources can come in the form of research papers, Medium articles, blog posts, videos, GitHub repository etc.
In a survey of users, 10% of respondents said that Elicit saves them 5 or more hours each week. 2. In pilot projects, we were able to save research groups 50% in costs and more than 50% in time by automating data extraction work they previously did manually. 5. Elicit's users save up to 5 hours per week 1.
Semantic Reader Project is a broad collaborative effort across multiple non-profit, industry, and academic institutions to create interactive, intelligent reading interfaces for research papers. The Semantic Reader research papers summarizes our efforts in combining AI and HCI research to design novel, AI-powered interactive reading interfaces that address a variety of user challenges faced by ...
Published Apr 25, 2024. AI In the Enterprise. Large Language Models. According to a recent survey, over two-thirds (66.9%) of developers and machine learning teams are planning production deployments of LLM apps in the next 12 months or "as fast as possible" - and 14.1% are already in production! Given the rapid rate of progress and ...
The best way to read research papers. Explainpaper. Pricing Sign Up Get Started. The Fastest Way to Read Research Papers. ... academic papers are filled with so much jargon that it's hard to grok them at first pass. being able to ask an AI questions about a research paper is such a cool tool killer product @amanjha__ + @functionofjade.
If you can afford it, stop reading that paper and go back to the basics. In general, learning is not an easy process and, more specifically, reading research papers is not the easiest reading (because research papers are typically concise, i.e. there's a lot of information compression), so do not expect to understand everything of a paper in ...
6. Computer Vision Foundation. 7. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 8. Association for Computational Linguistics. The Internet has been a godsend for many AI and ML enthusiasts who are looking to learn more about the technology, as it has opened up many journals, documents and research papers for those who need it.
Elicit is an AI research assistant that can search, summarize, extract data from, and engage in conversations about over 125 million scientific papers. Elicit's AI-driven. Discover the latest AI research tools to accelerate your studies and academic research. Analyze research papers, summarize articles, citations, and more.
According to a recent survey, over two-thirds (66.9%) of developers and machine learning teams are planning production deployments of LLM apps in the next 12...
Join them and start using your AI research assistant wherever you're reading online. Chat with PDF and conduct your literature review faster using SciSpace. Discover 200M+ papers or upload your own PDF, highlight text or ask questions, and extract explanations and summaries.
How to read AI/ML research papers . You can use resources like Machine Learning Subreddit and Deep Learning Subreddit to enrich your understanding. Research papers are the wellspring of ideas pushing the frontiers of cutting edge technologies. Scholars around the globe rely on platforms like arXiv, JSTOR, Reddit, PapersWithCode to get up to ...
Capture insights right alongside the relevant paper, ensuring seamless integration with your notes. With OpenRead, organizing your notes and knowledge becomes intuitive and efficient. Elevate your research by keeping everything in one place at OpenRead. OpenRead employs cutting-edge AI technology to enhance and revolutionize your research ...
It's part of Ai2, the AI research institute founded by late Microsoft cofounder Paul Allen, and today it includes features to help users understand papers, like surfacing definitions of ...
How to Read Research Papers. Take multiple passes through the paper. Worst strategy: reading from the first word until the last word! Read the Title/Abstract/Figures. Especially in deep learning, there are a lot of papers where the entire paper is summarized in one or two figures. You can often get a good understanding about what the whole ...
9. IBM Watson Discovery. An AI-powered tool called IBM Watson Discovery makes it possible to analyze and summarize academic publications. It makes use of cutting-edge machine learning and NLP techniques to glean insights from massive amounts of unstructured data, including papers, articles and scientific publications.
How To Read A Research Paper. A research paper is primarily divided into seven sections: 1. Title and Abstract. The title is a quick summary of the paper and the abstract a short summary of the paper. 2. Introduction. The introduction outlines the problem being discussed. 3.
Even with the paper's limitations, its authors argue, the research is the closest up-to-date public estimate of where in the world the most advanced AI chips are located—and a good proxy for ...
New research suggests that this rejection can be due to people's lack of shared criteria or reference points when evaluating a potential innovation's value. In a new paper, the authors find ...
Part of the study included an experiment where people read the same paragraph from a college essay. While the paragraphs stayed the same, the information about how the student wrote the essay changed.
Learn more about sustainable computing and NVIDIA Research, a global team of hundreds of scientists and engineers focused on topics including climate AI, computer graphics, computer vision, self-driving cars and robotics. Featured image courtesy of NASA. See notice regarding software product information.
Researchers are investing substantial effort in developing powerful general-purpose agents, wherein Foundation Models are used as modules within agentic systems (e.g. Chain-of-Thought, Self-Reflection, Toolformer). However, the history of machine learning teaches us that hand-designed solutions are eventually replaced by learned solutions. We formulate a new research area, Automated Design of ...
Minx says the study's AI-enhanced approach allowed the researchers, for the first time, to evaluate the effectiveness of a large number of climate policies from a global set of emission ...