We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more

Business Plan vs. Business Model
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 19, 2023 Updated on August 18, 2024

If you’re starting a business , you have a business model, whether you know it or not. A business model is the foundation of any business idea; it basically outlines how the concept offers value and potential for growth. Essentially, a solid business model ensures that the business will make money.
A business plan , on the other hand, is the business owner’s plan to put that model into action. It’s much more detailed and includes financial projections, objectives, management decisions and further steps.
Still unsure? Have no fear, this handy guide lays out the differences between a business plan and a business model so that you know exactly what you and your business need to succeed.
| Aspect | Business Plan | Business Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal written document that elaborates on the operational, financial, and marketing details of a business. It is often used to secure funding or guide a business's growth. | A conceptual framework that defines how the business creates, delivers, and captures value. Often summarized visually with tools like the Business Model Canvas. |
| Purpose | To detail the company's strategy, milestones, financial projections, market research, and other specifics. Helps in providing direction, attracting investors, or guiding expansion. | To illustrate how a company operates, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the end product/service to customers, and how it intends to achieve profitability. |
| Components | Executive Summary Company Description/Overview Products/Services Offered Market Analysis Marketing and Sales Strategies Operations and Management Financial Plan Appendices | Value Proposition Key Activities Cost Structure Key Partners Key Resources Revenue Streams Customer Segments Customer Relationships Channels |
| Duration | Typically covers a specific time frame (like 1, 3, 5 years). | Timeless as long as the business operations remain consistent, but needs revision when the model changes. |
| Target Audience | Investors, lenders, partners, and internal team members. | Primarily for internal stakeholders but can be used externally for partners and strategic collaborations. |
| Level of Detail | Detailed and comprehensive. Can be dozens of pages long. | High-level and summarized. The Business Model Canvas, for instance, fits on a single page. |
| Flexibility | Tends to be fixed for the time frame it covers but can be updated as needed. | Typically more fluid, with frequent updates as the business learns and pivots. |
| Main Focus | Planning the future based on research, forecasts, and assumptions. | Describing how the business operates in its entirety and how it creates value. |
- Business Model
In simple terms, a business model is how the business will make money. Selling ice to eskimos, for instance, is a bad business model. Selling team jerseys to rabbit sports fans, on the other hand, is a solid business model.
The components of a business model are best illustrated by Swiss entrepreneur Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas, which is a visual representation with nine sections. Four sections represent internal elements of a business that enable it to function and are related to costs.
Four other sections represent external elements that enable the business to bring in revenue and are related to the customer. The ninth section is the business’ value proposition.
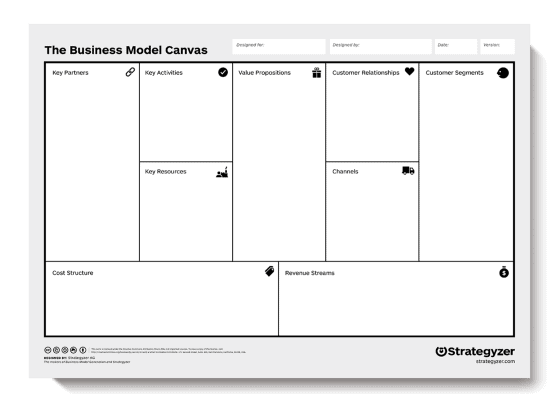
Value Proposition
The value proposition is at the heart of your business model. Your value proposition, which should be no more than two sentences long, needs to answer the following questions:
- What are you offering
- Whose problem does it solve
- What problem does it solve
- What benefits does it provide
- How is it better than competitor products
Key Activities
Key activities are all the activities required to run the business and create the proposed value. These can include product development and distribution and any other necessary activities.
Cost Structure
The cost structure is a sum of all you’ll need to spend to make the business function. It’s the costs you’ll incur to run the business and bring in revenue.
Key Partners
Key partners are external partners involved in delivering value, such as vendors and suppliers, or maybe a bank.
Key Resources
Key resources are any necessary practical elements that come with a cost. These might include your office space, employees, and equipment like computers.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are the ways in which you receive payment from customers. You may have more than one revenue stream, such as via direct sales and subscriptions.
Customer Segments
Customer segments are the groups of people to whom you provide goods or services. In other words, your target market. Maybe your products are aimed at younger women, for instance, or older men. Whatever your target segments, you should build customer personas of each group so that you know how and where to reach them with your marketing.
Customer Relationships
Customer relationships refer to how you interact with your customers to deliver value. Your interactions may be online only, by phone, in-person, or all of the above.
Channels refer to how you reach your customers, such as social media, internet search, direct sales calls, trade shows, and so on.
To Summarize
If you’re just starting a business, the Business Model Canvas is a great way to understand and examine your business model. One thing to remember is that the elements you put in your Canvas will be based on assumptions that will at some point be tested in the market and adapted as needed.
Another thing to remember is that you do not need to do a Business Model Canvas. It’s merely an exercise that can help provide insight into your business model.
- Business Plan
A business plan is a detailed document that describes how the business will function in all facets. The key is in the “plan” part of the name. It will specify how you’ll launch your business, gain customers, operate your company, and make money. A business plan, however, is not a static document .
The initial version will be based largely on assumptions, supported by research. As you run your business you’ll constantly learn what works and what does not and make endless tweaks to your plan.
Thus, creating a business plan is not a one-time action – it’s a dynamic and continuous process of crafting and adapting your vision and strategy.
You’ll present your business plan to potential backers, though in recent years some investors have begun to embrace the Business Model Canvas as a tool to assess a business’ potential.
A strong business plan includes eight essential components .
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the initial section of your business plan , written last, summarizing its key points. Crucial for capturing investors’ and lenders’ interest, it underscores your business’s uniqueness and potential for success. It’s vital to keep it concise, engaging, and no more than two pages.
2. Company Description/Overview
This section provides a history of your company, including its inception, milestones, and achievements. It features both mission (short-term goals and driving force) and vision statements (long-term growth aspirations). Objectives, such as product development timelines or hiring goals, outline specific, short-term targets for the business.
3. Products or Services Offered
Detail the product or service you’re offering, its uniqueness, and its solution to market problems. Explain its source or development process and your sales strategy, including pricing and distribution channels. Essentially, this section outlines what you’re selling and your revenue model.
4. Market Analysis
- Industry Analysis : Research your industry’s growth rate, market size, trends, and future predictions. Identify your company’s niche or sub-industry and discuss adapting to industry changes.
- Competitor Analysis : Examine main competitors , their unique selling points, and weaknesses. Highlight your competitive advantages and strategies for maintaining them.
- Target Market Analysis : Define your target market , their demographics, needs, and wants. Discuss how and where you’ll reach them and the potential for market shifts based on customer feedback.
- SWOT Analysis : Break down your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Detail your unique attributes, potential challenges, market opportunities, and external risks, along with strategies to address them.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Marketing and Advertising Plan : Use insights from your target market analysis to decide advertising channels, emphasizing platforms that best reach your audience, like TikTok over Instagram. Develop a concise value proposition to be central to all marketing, detailing how your product addresses specific needs.
- Sales Strategy and Tactics : Define where and how you’ll sell, such as online, in-store, or through direct sales calls. Sales tactics should highlight the customer’s needs, presenting your solution without overly aggressive promotion.
- Pricing Strategy : Decide on pricing based on market positioning, whether you aim to be a discount or luxury option. Ensure prices cover costs and yield profit, and position your product in a manner that aligns with the chosen price range. Justify your chosen pricing strategy in this section.
6. Operations and Management
- Operational Plan : Outline daily, weekly, and monthly operations, specifying roles, tasks, and quality assurance methods. Include supplier details and order schedules, ensuring clarity on key business functions and responsibilities.
- Technology Plan : For tech-based products, detail the development plan, milestones, and staffing. For non-tech companies, describe the technology tools and software you’ll employ for business efficiency.
- Management and Organizational Structure : Define who’s in charge, their roles, and their backgrounds. Discuss your management strategy and forecast the development of your organizational hierarchy.
- Personnel Plan : List current and future hires, specifying their roles and the qualifications necessary for each position. Highlight the significance of each role in the business’s operations.
7. Financial Plan
- Startup Costs : Clearly detail every anticipated cost before starting operations. This will be vital for understanding the initial investment required to get the business off the ground.
- Sales Projections : Estimate monthly sales for the first year, with an annual forecast for the next two years.
- Profit and Loss Statement : An overview of revenue minus costs, resulting in either a profit or loss.
- Cash Flow Statement : Provides clarity on the business’s liquidity by showing cash inflows and outflows over a specific period.
- Balance Sheet : Displays the company’s net worth by detailing its assets and liabilities.
- Break-even Analysis : Understand at which point revenues will cover costs, helping to predict when the business will start making a profit.
- Funding Requirements and Sources : Enumerate the required capital and the sources of this funding. This should also include the purpose for which these funds will be used at different stages.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) : Identify the metrics vital for measuring the company’s performance. Use these indicators to spot challenges, understand where improvements can be made, and pivot strategies as necessary. Ensure that each KPI aligns with the business’s objectives and offers actionable insights for growth.
Remember, although the financial section might seem daunting, it is pivotal for understanding the economic feasibility of your business. Proper financial planning helps in making informed decisions, attracting investors, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Don’t hesitate to engage financial experts or utilize tools and software to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness in this section.
8. Appendices
The appendices section of a business plan is a repository for detailed information too extensive for the main document. This can include resumes of key personnel, full market research data, legal documents, and product designs or mockups. By placing this data in the appendices, it keeps the main plan concise while allowing stakeholders access to deeper insights when needed. Always ensure each item is clearly labeled and referenced at the relevant point in the main document.
As you can see, business models and business plans have some similarities, but in the main they are quite different. Your business model explains the foundational concept behind your business, while a business plan lays out how you’ll put that model into action and build a business.
When you’re starting a business, it’s best to have both, as the work of getting them done involves learning about your business from every angle. The knowledge you’ll gain is likely to be invaluable, and could even be the difference between success and failure.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review: Features, Cost, Pros & Cons
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

6 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

It might be stating the obvious, but planning and preparation are keys to success in business.
After all, entrepreneurs put in hard work to develop their product, understand the market they plan to serve, assess their competitive landscape and funding needs, and much more.
Successful business owners also take time to document their strategies for guiding the growth of their companies. They use these strategies to take advantage of new opportunities and pivot away from threats.
Two common frameworks for documenting strategies – the business model canvas and the business plan – are also among the easiest to get confused.
Though they can complement each other, a business model canvas and a business plan are different in ways worth understanding for any entrepreneur who’s refining their business concept and strategy.
Let’s start by digging deeper into what a business model canvas is.
- What is a business model canvas?
You may have heard the term “business model” before. Every company has one.
Your business model is just a description of how your business will generate revenue. In other words, it’s a snapshot of the ways your business will be profitable.
Writing a business plan is one way of explaining a company’s business model. The business model canvas takes a different approach.
A business model canvas is a one-page template that explains your business model and provides an overview of your:
- Relationships with key partners
- Financial structure
- And more…
While the business model is a statement of fact, the business model canvas is a strategic process—a method for either documenting or determining your business model.
It’s meant to be quickly and easily updated as a business better understands what it needs to be successful over time. This makes it especially useful for startups and newer businesses that are still trying to determine their business model.
You can think of a business model canvas as a condensed, summarized, and simplified version of a business plan. It’s a great way to quickly document an idea and get started on the planning process.
The business plan is a way to expand on the ideas from the canvas and flesh out more details on strategy and implementation.

Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Components of a Business Model Canvas
The simplest way to think about your business model canvas is to map it out visually. A business model canvas covers nine key areas:
- Value proposition : A company’s unique offering in the market and why it will be successful.
- Key activities: The actions that a company takes to achieve its value proposition.
- Customer segments : The types of people or businesses that are likely to want a company’s products or services.
- Channels : How a company reaches customers through marketing and distribution efforts.
- Customer relationships: How a company interacts with customers and maintains important relationships.
- Revenue streams: The ways in which a company makes money.
- Key resources: The assets such as property, equipment and staffing that a company needs to perform its key activities.
- Key partners: The relationships with suppliers, vendors, customers and other stakeholders a company must maintain in order to be successful.
- Cost structure: The major drivers of company expenses that will need to be tracked and managed.
[Want an even simpler alternative? Try downloading our free one-page plan template and start building your plan in less than 30 minutes.]
To get a better sense of how a business model canvas documents business strategy, consider a company like Netflix. The streaming company’s business model is based on generating subscription revenue through its content library and exclusive content.
If Netflix executives were to create a business model canvas, it would map out how the company leverages key resources, partnerships, and activities to achieve its value proposition and drive profitability. The business model is the destination.
The great thing about a business model canvas is that you can quickly document business ideas and see how a business might work at a high level. As you do more research, you’ll quickly refine your canvas until you have a business idea you think will work.
From there, you expand into a full business plan.
- What is a business plan?
If a business model canvas captures what a company looks like when it’s operating successfully, then a business plan is a more detailed version along with a company’s blueprint for getting there.
Think of your business plan as a process of laying out your goals and your strategies for achieving them.
The business plan is more detailed, and changes over time. It examines each aspect of your business, from operations to marketing and financials.
The plan often includes forward-looking forecasts of a company’s projected financial performance. These are always educated guesses. But these forecasts can also be used as a management tool for any growing business.
Comparing actual results to the forecast can be a valuable reality check, telling a business if they’re on track to meet their goals or if they need to adjust their plan.
Using an investor-approved business plan template is also a must for companies hoping to receive a bank loan , SBA loan , or other form of outside investment . Anyone putting up funds to help you grow will want to see you’ve done your homework.
So a business plan is how you not only prepare yourself, but also show your audience that you’re prepared.
Components of a business plan
While there are several different types of business plans meant for different uses, well-written plans will cover these common areas:
- Executive summary : A brief (1-2 pages) overview of your business.
- Products and services : Detailed descriptions of what you’re selling and how it fills a need in the market.
- Market analysis : Assessing the size of your market, and information about your customers such as demographics (age, income level) and psychographics (interests, values).
- Competitive analysis : Documenting existing businesses and solutions your target customers are finding in the market.
- Marketing and sales plan : Your strategies for positioning your product or service in the market, and developing a customer base.
- Operations plan : Describing how you will run the business from day to day, including how you will manage inventory, equipment, and staff.
- Organization and management team: Detailing the legal structure of the business, as well as key members, their backgrounds and qualifications.
- Financial Plans : Business financials that measure a company’s performance and health, including profit & loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. Effective financial plans also include forward-looking sales forecasts and expense budgets.
How a business plan and business model canvas inform business strategy
Avoid the trap of using the two terms interchangeably. As we’ve shown, the two have different focuses and purposes.
The business model canvas (or our one-page plan template ) is a great starting point for mapping out your initial strategy. Both are easy to iterate on as you test ideas and determine what’s feasible.
Once you have a clearer sense of your idea, you can expand the canvas or one-page plan into a business plan that digs into details like your operations plan, marketing strategy, and financial forecast.
When you understand how – and when – to use each, you can speed up the entire planning process. That’s because the business model canvas lays out the foundation of your venture’s feasibility and potential, while the business plan provides a roadmap for getting there.
The work of business planning is about connecting the dots between the potential and the process.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- How both inform your strategy
Related Articles

11 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline Example to Organize Your Plan

7 Min. Read
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free

5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
In this blog...
Business Model Vs. Business Plan: What’s the Difference?
There’s a big misconception about the whole business model vs. business plan debate because both terms have been wrongly used. Today, we’ll look into what they’re really for and why they’re needed for the business.
Strategy has always been a building block of business. In the ever-competitive and highly volatile industry, you have to come up with a sustainable advantage over your competitors. Few lucky entrepreneurs successfully start on the right foot, but luck often runs out while keeping a great momentum. This is where a solid business strategy comes to play.
You can’t just launch your startup without establishing where it’s heading. You need a business strategy to identify which direction you’ll operate towards. This is why a business plan and a business model are essential factors in a company’s success. But because they seemingly have a similar purpose, they’re mistakenly used interchangeably. The truth is, one cannot exist without the other.
To truly understand the difference between a business model vs. a business plan, we’ll need to define what they are and what they’re used for.
What is a Business Model?
A business model is the company’s rationale and plans for making a profit. It explains how a company delivers value to its customers at a specific cost. A business model would include details about the company’s products and services, its target market, and all expenses related to the operations and production.
Why is it necessary?
It’s considered a roadmap for a business to achieve its financial goal in a given period. It maps out how you can sustain the value you deliver to your customers. Entrepreneurs use it as a tool to study, test, and estimate cost and revenue streams.
They can make quick hypothetical changes to the business model to determine how a financial decision can impact their long-term operations . This allows business owners to anticipate and adapt to trends and challenges in their industry.
Consequently, a strong business model also helps attract investors, recruit talent, and motivate employees. The management and staff are often motivated by how well a company adheres to the business model.
Types of Business Model
When it comes to different kinds of business models, there are several options for a company. For example, a software company might go with a subscription model because it’s easier to sell their product through a license subscription. On the other hand, retail companies might go for the accessories model because it’s more straightforward.
In determining which type of business model to use, companies choose the style that best suits their operations and industry. A growing method is using a combination of business models to create a hybrid system for the business.
The following are some of the most widely used types of business models:
- Subscription
- Transactional
- Retail sales
Creating a Business Model
Now that we’ve established what a business model is, it’s time to learn how to create one for your startup. Your business model has to answer all the critical questions about your business.
Here are the key components you must include in your business model:
- Key Objectives
- Target Market
- Product Value
- Product Pricing
- Required Funding
- Growth Opportunity
Keep in mind, the business model has to be updated regularly to fit your goals. All companies undergo a stage of maturity that directly affects the business model it follows.
For early-stage startups, the business model would ideally be simple and straightforward. Most business owners would even opt for a flat organization where staff could communicate their concerns directly to the owner. This, of course, will change as the company expands.
Now that we’ve learned what a business model is, it’s time to move on to the next part of the business model vs. business plan discussion. So, let’s discuss what is a business plan.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that details a company’s goals and its strategies to achieve them . It’s considered the “blueprint of the business” because it summarizes all the essential aspects of the company such as finance, marketing, and operations.
It serves as a reference for the company owner and the management in making major business decisions. It can also be presented to investors when the owner is raising capital. It’s beneficial for startups who have no proven track record since a business plan can pitch its full potential.
A business plan is not only helpful to a business in its early stage, but it also helps it pivot during unforeseen circumstances. In a volatile industry, a company needs to adapt quickly and efficiently. Hence, update the goals and methods should accordingly.
Creating a Business Plan
So, what should a business plan include?
Business plans vary according to industry, but there is a general format for writing a business plan. You can expand or shorten this template based on long-term goals.
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Market Analysis
- Product Development
- Marketing Strategies
- Operations and Management
- Financial Plans
You can choose from a wide selection of business plan templates when it comes to the actual writing. Remember to keep it concise and avoid jargon in the content. You will present your business plans to investors and stakeholders; hence, they need to get a clear idea of it in one reading.
Business Model vs. Business Plan: How to Use Them
At this point, we’ve established that both a business model and a business plan are essential to success. However, both can only take your business so far. How well you execute and follow them is a whole other story. It’s challenging to start a startup , let alone maintain it.
If you want to avoid common startup mistakes , you need to build your business on a strong foundation. Hire the best people, invest in reliable tools, and sign up for mentoring.
Speaking of mentors, Full Scale founders Matt DeCoursey and Matt Watson are incredibly passionate about helping entrepreneurs succeed. They’ve created Full Scale to assist startup owners in launching and managing their companies.
Full Scale is an offshore software development company that offers a wide array of services for startups. We offer the best talent and resources needed to begin your entrepreneurial journey.
We have seasoned project managers, marketing specialists, and technology experts at your service. We’ll take care of all the hassles out of your daily operations so you can focus on your core competencies.
Want to learn more about Full Scale? Get your FREE consultation today!
Learn More about Offshore Development
Copyright 2024 © Full Scale
Business Education
Business Model vs Business Plan: Main Differences
19 Aug, 2024

Distinguishing business models from plans is crucial for success. Models outline value creation and profit generation, while plans detail strategies, research, and projections. Together, they form the blueprint for long-term success and operational execution.
What is a Business Model?
A business model is the backbone of any company, detailing the plan for how it intends to operate, generate revenue , and make a profit. It's less about the nitty-gritty details found in a business plan and more about the overall concept of how the business creates value for customers and captures value for itself. Essentially, a company's business model describes the way the company sells its products or services and how it establishes and maintains customer relationships to achieve financial success.
At its core, a business model involves identifying the value proposition of the company, which is what makes its products or services attractive to customers . It also outlines the customer segments targeted, the key activities and resources needed to operate, and the channels through which it reaches its customer base. Importantly, it details the revenue streams the business will pursue to generate income and the cost structure that outlines the expenses involved.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a detailed roadmap for building a successful business. Unlike the broader strokes of a business model that describes how a company creates and delivers value, business plans are a comprehensive document that outlines the specifics of business strategy. They serve as a guide to what the business intends to do and how it plans to do it and are often used to attract investors and secure financing.
The heart of a business plan includes an executive summary, which is a snapshot of the business and its plans for success. This section briefly explains the business idea, key objectives, and how the business will achieve its goals. It's followed by detailed sections that outline the business's structure, market analysis, value proposition, marketing and sales strategies, financial projections, and more.
Key components of a business plan include the business model canvas, which lays out the key resources and activities needed to operate the business. It also delves into the cost structure, detailing all the expenses the business will face. A thorough market analysis assesses the existing market, target customers, and competitive landscape. This helps in formulating a solid marketing strategy and establishing a unique value proposition that sets the business apart from its competitors.
Financial planning is also crucial, with sections dedicated to expected financial performance, revenue generation, and a detailed financial forecast. This helps potential investors and business owners understand the financial viability and growth potential of the business.
Types of Business Models
There are many types of business models, each defining a unique way a company creates value for its customers and generates profits. Understanding different business models helps owners and entrepreneurs select the right approach for their business concept and target market. Here are some common business models:
- Subscription Services : This model offers customers regular, ongoing access to products or services in exchange for a recurring fee. Popular among digital services and software, it provides steady revenue and customer loyalty.
- Freemium Model : Common in the tech industry, the freemium model offers basic services for free while charging for advanced features. It attracts a large user base quickly, with the potential to convert a portion to paid versions.
- Product Sales : This traditional model involves selling goods directly to customers. It can range from retail operations to online stores, focusing on producing, marketing, and selling physical items.
- Service-Based Model : Professional firms and contractors often use this model, providing specialized services like consulting, design, or maintenance. Success relies on expertise, customer service, and reputation.
- On-Demand Model : Popularized by companies like Uber, this model provides goods or services directly on customer request, often facilitated through a digital platform or app.
- E-commerce : With the rise of the internet, many businesses operate online, selling products or services directly through their website or online marketplaces.
- Affiliate Marketing : This model pays external parties to generate traffic or leads to the company's products and services. It's a way to extend market reach without directly handling sales.
- Advertising Model : Media companies and websites often use this model, providing content or services free of charge, but generating revenue through advertisements.
Understanding these business models helps a company decide the best strategy for market entry and growth. Each model has its own set of operational details, target market strategies, and financial implications. Selecting the right business model is crucial for a company's success, aligning with its core values, customer needs, and long-term goals. As the business evolves, it may adopt multiple models or shift strategies to adapt to changing market conditions or customer feedback.
Business Model vs Business Plan: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between a business model and a business plan is crucial for anyone diving into the world of entrepreneurship or looking to scale their business. Here are the key differences:
- Business Model : A business model is an overarching concept that explains how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It's about the company's core strategy for generating profits and includes elements like value propositions, customer segments, and revenue streams.
- Business Plan : A business plan is a detailed document that outlines the specific strategies, goals, and actions of a business. It's a comprehensive plan that includes market analysis, financial projections, and operational details aimed at guiding the business's trajectory and attracting investors.
- Business Model : Generally broader and more conceptual, a business model provides a high-level view of the business's approach to the market. It's about the fundamental structure of how the business operates and competes.
- Business Plan : More detailed and tactical, a business plan lays out the step-by-step plan for executing the business model. It includes in-depth information on planning, marketing, finances, and more.
- Business Model : Business models often need to be flexible and adaptive, especially in early stages or in rapidly changing markets. They can evolve as the business learns more about its customers and competition.
- Business Plan : While it's a detailed guide, the business plan is also a living document but typically requires formal revisions and updates as the business grows and market conditions change.
- Business Model : Primarily used internally to guide the company's strategy, but it can also be used to succinctly explain the business to external stakeholders and potential partners .
- Business Plan : Often intended for external stakeholders, especially potential investors, lenders, or partners who want a detailed understanding of the business's approach and potential for success.
- Business Model : Includes the business model canvas or similar frameworks detailing the company's value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
- Business Plan : Includes an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, product or service line, marketing and sales strategy, funding request, financial projections, and appendices.
While a business model provides a conceptual framework for understanding how the company creates value and money, the business plan offers a detailed guide on how to implement these concepts and achieve specific business goals. Both are vital, but they serve different purposes and address different needs within the business's lifecycle.
Sign up for more content like this

Career Development
Why is LinkedIn Important? 10 Benefits of a LinkedIn Profile
25 Aug, 2024
Leveraging LinkedIn revolutionizes professional networking. Discover how a strong profile uncovers job opportunities and builds industry con...

How to Create a Company Profile on Linkedin
24 Aug, 2024
Creating a strong LinkedIn company page boosts professional visibility. This guide outlines key steps to build an effective profile, showcas...

When to Fire an Employee: 5 Signs it’s Time to Terminate
23 Aug, 2024
Deciding when to fire an employee requires careful consideration and a clear understanding of how their actions impact the team and company ...
Book a Call
Submit your information, and we will contact you to schedule a call with our program director..
Case Studies
Resource Hub
Featured post
What is a Pitch Deck: Essential Tips, Real Examples, Templates and Purpose

Explore our latest posts
Product-Market Fit: The Ultimate Blueprint for Startups

35 Best Grants for Women-Owned Businesses: Application Tips Inside

Pitch Deck Funding Stages: How to Personalize Your Pitch Deck by the Stage

Business Plan vs. Business Model: What's the Difference?
Dive into the nuances of Business Plans & Models. Uncover their key differences, applications, and tips for strategic growth. Master your business journey today!
November 28, 2023
In the world of business, two terms often emerge as foundational elements to startup founders, seasoned entrepreneurs, and everyone in between: the Business Plan and the Business Model. Both are crucial, yet their roles, purposes, and impacts are distinct, and understanding these differences can mean the difference between the success and failure of an enterprise.
In a landscape where innovation is rampant and industries are constantly evolving, having clarity about one's business direction is indispensable. It's akin to a sailor knowing the direction of the wind and having a map. While the wind's direction can be equated to the broader strategy of the sailor (the Business Model), the map which plots out the course in detail is akin to the Business Plan.
Yet, with these tools being so pivotal, it's alarming how often they are misunderstood or used interchangeably. Some entrepreneurs pour weeks into crafting the perfect business plan, only to realize they haven’t clarified their fundamental business model. Others sketch out a brilliant business model on the back of a napkin but falter when asked for the detailed strategy and projections that a business plan requires.
This guide aims to dissect the nuances between a Business Plan and a Business Model, highlighting their unique roles in the entrepreneurial journey and offering insight into how each can be harnessed most effectively. By the end of this exploration, readers will have a clear roadmap (pun intended!) for their own business endeavors, understanding when, why, and how to leverage each tool.
Definition of Key Terms - Understanding Business Plan and Business Model
In order to delve deep into the distinctions between a Business Plan and a Business Model, it's imperative that we first lay down clear definitions for each term. This ensures that as we progress, we're aligned in understanding and can avoid any ambiguities. So, let's start by putting these cornerstone concepts under the microscope.
Business Plan
A Business Plan can be envisioned as a detailed blueprint for setting up a business and ensuring its success. It's a comprehensive document that articulates what a business intends to achieve and the strategies it will deploy to make those aspirations a reality. Let's break down the typical components:
- Executive Summary: A snapshot of your business, providing a concise overview of what the business is about, its mission, and how it stands out in the market.
- Company Description: An in-depth look at the company, detailing its formation, mission, objectives, and overarching goals.
- Market Analysis: A study of the industry landscape, understanding potential competitors, target audience, market trends, and opportunities.
- Organizational Structure: A delineation of the company's hierarchy, roles, responsibilities, and the dynamics of how operations will be conducted.
- Product or Service Line: A detailed description of the product or service the company offers, its benefits, lifecycle, and relevance in the market.
- Marketing and Sales Strategies: Outlining the approach for promoting the product/service, attracting customers, and the strategies for sales conversion.
- Funding Requirements: If seeking external investment, a clear layout of the capital needed, the reasons, and the strategy for effective utilization.
- Financial Projections: Forecasts for the business, including projected income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and break-even analysis.

Business Model
A Business Model is akin to the conceptual foundation of a business. It succinctly defines how a company plans to generate revenue, make a profit, and ensure sustainability in a competitive market. Core components of a business model include:
- Value Proposition: What makes the company’s offering unique and desirable? How does it solve a problem or fill a need in the market?
- Customer Segments: Who are the primary target customers? What are their needs and how will the business cater to them?
- Channels: Through which avenues will the product/service be delivered to the customers?
- Customer Relationships: How does the business intend to interact with its customers, ensuring retention and loyalty?
- Revenue Streams: The avenues through which the company will make money. This can include sales, subscriptions, licensing, and other revenue models.
- Key Resources: Assets required to run the business, which can be physical, intellectual, human, or financial.
- Key Activities: The main operations and tasks that need to be performed to ensure the business runs smoothly.
- Key Partnerships: Collaborations, alliances, and affiliations that will be essential in supporting the business operations.
- Cost Structure: A clear breakdown of the business’s expenses and financial obligations.

With these definitions at our fingertips, it becomes easier to discern the distinct role each plays in the grand scheme of establishing and running a business. As we progress further, we will delve into how these elements differ in scope, objective, and application.
Main Differences - Navigating the Nuances Between Business Plan and Business Model
Having delineated clear definitions for both a Business Plan and a Business Model, it's now time to pinpoint their distinctive differences. While both tools are essential to a business's success, they serve varied purposes and are used at different stages of the entrepreneurial journey. Let's explore the primary differences between the two:

- Business Model: This represents the broader concept of the business's structure and its fundamental modus operandi. It's an overview of how the business plans to function at its core, capturing, delivering, and creating value.
- Business Plan: This is a comprehensive document that dives deep into the strategy required to make the vision (often illustrated by the business model) a reality. It details everything from operations, marketing, sales, and finances to ensure the business is on the right track.
- Business Model: Its primary aim is to define the method through which the company creates, delivers, and captures value. It's about answering the "What, Why, and For Whom" of the business.
- Business Plan: This seeks to showcase the feasibility of the business model, detailing how the business will operate, generate revenue, manage costs, and expand. The business plan is more about the "How, When, and Where."
- Business Model: While it is primarily crafted for internal stakeholders to align their vision and operations, it also serves as an overview for potential investors, partners, and other external parties who are interested in understanding the company's foundational strategy.
- Business Plan: This is a tool tailored for both internal decision-makers and external stakeholders. When seeking investments, partnerships, or loans, a well-drafted business plan becomes indispensable. It provides the detailed insight that external parties often require before committing resources or capital.
Flexibility
- Business Model: Given its higher-level perspective, the business model is often more adaptable. As market conditions change, customer preferences evolve, or new opportunities emerge, the business model can be adjusted to pivot or capitalize on these shifts.
- Business Plan: Though not rigid, a business plan is more static compared to a business model. While it should be periodically updated as milestones are achieved, market conditions change, or business goals evolve, it typically requires a more formal revision process.
In essence, while the business model is about conceptualizing the heart and soul of the enterprise, the business plan is about putting flesh to that skeleton, bringing it to life with details, strategies, and actionable steps. Grasping these nuanced differences is vital for entrepreneurs as they chart the course of their business journey.
When to Use Which - The Strategic Application of Business Plan and Business Model
The distinctions between a Business Plan and a Business Model are clear, but knowing when to deploy each can be equally as crucial. Their application at the right junctures can enhance clarity, attract resources, and drive effective implementation. Here's a guide on when to use which:

Starting Up a Business
- Business Model: Before any detailed planning commences, it's pivotal for entrepreneurs to draft a Business Model. This helps in conceptualizing the very essence of the business: what value it offers, who it caters to, and how it will generate revenue. Using tools like the Business Model Canvas can provide a visual and concise representation of this.
- Business Plan: Once the fundamental business concept is clear, the Business Plan comes into play. This document will map out the strategy to realize the business model, offering detailed steps, financial projections, marketing strategies, and more. It's a roadmap for how the business will operate and grow.
Seeking Investments
- Business Model: Investors will want a snapshot of your business's core. They want to know why your business exists and how it stands out. Thus, presenting a clear business model is paramount.
- Business Plan: Alongside understanding your business's essence, investors also need reassurance on its feasibility and growth potential. This is where the Business Plan becomes crucial. It offers detailed projections, strategies, and plans that can instill confidence in potential investors, showing them the roadmap to returns on their investment.
Iterating on Business Ideas
- Business Model: In rapidly changing industries or for startups practicing the lean startup methodology, frequent iterations might be needed. Every time there's a significant pivot or change in direction, the Business Model should be revisited and possibly adjusted.
- Business Plan: While the Business Model might be revised more frequently, it's not always necessary to overhaul the entire Business Plan. However, if the pivot is significant enough to alter operations, marketing strategies, or financial forecasts, then a revision of the Business Plan is warranted.
Periodic Review and Expansion
- Business Model: While the core of a business might remain steady, it's beneficial to revisit the Business Model periodically, especially when considering expansion into new markets, launching new products, or diversifying revenue streams.
- Business Plan: As businesses hit milestones, they should update their Business Plan. This could be done annually or during strategic inflection points like mergers, acquisitions, or significant market shifts. A current Business Plan is also invaluable when seeking further investments, opening new branches, or exploring partnerships.
In summation, while the Business Model encapsulates the very soul of the enterprise, the Business Plan serves as the detailed blueprint for bringing that vision to fruition. Knowing when to focus on each, and how to leverage them effectively, can guide businesses through their initial setup, growth, challenges, and expansions. Both tools, when used strategically, are the compass and map guiding a business towards its envisioned success.
Real-world Examples - Illustrating the Nuances of Business Plan and Business Model
A theoretical understanding of the distinction between Business Plans and Business Models is one thing, but observing them in practice can offer an invaluable perspective. Let’s explore some real-world examples that showcase these tools in action:

- Business Model: At its core, Airbnb’s model is about connecting people with spaces to rent to those looking for accommodations. Their value proposition revolves around offering unique, homely, and affordable accommodations compared to traditional hotels. Their primary revenue stream comes from charging hosts a commission on each booking.
- Business Plan: When Airbnb sought investments, they presented a detailed startup business plan that included their marketing strategy, growth projections, financial details, and expansion plans into new markets. This plan articulated how they intended to move from their foundational model to a global powerhouse in the hospitality industry.
- Business Model: Uber’s primary model is a platform connecting drivers with passengers. Their value proposition is offering a convenient, affordable, and reliable alternative to traditional taxis. Revenue primarily comes from taking a cut from each ride a driver completes.
- Business Plan: Uber’s rapid expansion into cities worldwide didn’t happen by chance. It was part of a strategic plan that included targeted marketing campaigns, strategies to onboard drivers, handling regulatory challenges, and financial projections for each new market.
- Business Model: Netflix started as a DVD rental-by-mail service, pivoting to streaming as technology and consumer preferences evolved. Their value proposition revolves around offering an extensive library of content for a fixed monthly price, without ads. Revenue comes from monthly subscriptions.
- Business Plan: When Netflix decided to pivot from DVD rentals to streaming, and later into producing original content, it would have required detailed planning. Their business plan would outline content acquisition strategies, technological infrastructure needs, financial forecasts for the new ventures, and a marketing strategy to promote their evolving services.
- Business Model: Dropbox’s model is based on providing cloud storage solutions for individuals and businesses. Their value proposition is offering a simple, reliable, and accessible means to store digital content. They employ a freemium model where basic services are free, but advanced features come at a cost.
- Business Plan: As Dropbox sought to grow, especially in the competitive cloud storage market, they needed a comprehensive plan. This would include strategies for user acquisition, scaling their technological backend, partnerships with other software providers, and financial plans for managing their freemium model efficiently.
In essence, these examples vividly illustrate how the foundational concept of a business (Business Model) is different from the detailed strategy for its operation and growth (Business Plan). While the model captures the essence, the plan dives into specifics. Both are integral at different stages, and as seen with companies like Netflix, they need to be revisited and revised as the company evolves.
Navigating the Business Landscape with Precision
Throughout this exploration of Business Plans and Business Models, one thing remains abundantly clear: both are indispensable tools in the toolkit of every entrepreneur and business leader. However, understanding the nuanced differences between the two and knowing how to deploy each effectively can significantly impact a company's success.

A Business Model provides the visionary blueprint of a company – it's the big picture that showcases what the company stands for, its primary methods of generating revenue, and how it intends to deliver value to its target market. It’s the foundation upon which a company is built, a reflection of its core identity.
On the other hand, a Business Plan dives into the specifics, detailing the strategies, operations, financial projections, marketing approaches, and other key components necessary to bring the business model to life. It's the roadmap, detailing the route a business needs to take to achieve its goals.
In the rapidly changing world of business, where consumer preferences evolve, technologies disrupt traditional operations, and markets are continually in flux, having a robust business model is crucial. But it’s the detailed business plan that allows businesses to navigate these complexities with precision, foresight, and strategic acumen.
Drawing inspiration from real-world examples, we've seen how giants like Netflix and Uber have effectively utilized both these tools. They've conceptualized innovative business models and then deployed detailed business plans to capture market share, adapt to changes, and remain at the pinnacle of their respective industries.
In conclusion, as an entrepreneur or business leader, think of the business model as your compass, giving direction and purpose. The business plan is your map, detailing the terrain and showing the path forward. With both in hand, you're not only set for the journey but also equipped to tackle the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities that lie ahead.
Key Takeaways
Foundational Differences: A Business Model provides an overview of how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, whereas a Business Plan delves into the detailed strategies, operations, and financial projections for realizing the model.
Strategic Application: The Business Model sets the core vision and foundation for a business, while the Business Plan acts as a roadmap, detailing steps for achieving business goals and milestones.
Real-world Applications: Successful companies, such as Airbnb, Uber, Netflix, and Dropbox, have effectively conceptualized innovative business models and employed comprehensive business plans for strategic execution and growth.
Necessity for Adaptation: Both the business model and business plan should be revisited and revised periodically to ensure alignment with evolving market realities and business objectives.
Call to Action: Entrepreneurs and businesses should constantly reflect on, refine, and update their models and plans, engage with experts, commit to continuous learning, and actively share insights to ensure sustained success.
.webp)
Table Of Content
Explore Our Services

Explore our top-notch pitch deck service
We help discerning startups and growing businesses create powerful pitch decks that attract investors and secure big deals.

Subscribe to our newsletter and keep in touch with us
An error has occurred somewhere and it is not possible to submit the form. Please try again later.
Only available to newsletter subscribers!
Answers, To The Most Asked Questions
What tools can help in creating a business model, how often should i update my business plan, is a business plan necessary for businesses that aren't seeking external investment, how detailed should a business model be, can a business have multiple business models, you may like.

10 Best Cyber Security Startup Ideas
Discover the most promising cybersecurity startup ideas for 2023. Drive innovation, meet market demands, and elevate digital safety. Start your journey now!
Read Article

10 Best Software Startup Ideas
Discover the hottest software startup ideas for 2023. Dive into trends, market potentials, and launch strategies to kickstart your entrepreneurial journey!

10 Pros and Cons of Venture Capital You Should Know
Explore the dynamics of venture capital. Dive into its benefits, potential pitfalls, and learn how it can shape startup trajectories. Make informed decisions with our guide.

10 Unique Clothing Business Ideas
Discover groundbreaking fashion business concepts for 2023! From sustainability to tech trends, master the art of differentiating your brand. Dive in now!
discover the menu
Get Ready For Funding
Pitch Deck Service
Pitch Training
Financial Modeling
Investor Outreach
Fundraising Consultant
We normally respond within 24 hours
View all our blog articles
The Differences Between a Business Plan & Business Model
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Install a Dynex Web Camera Capture Device
What is a strategic business plan, business plan vs. business model.
- The Importance of a Business Plan
- The Chief Elements of Business Models
Every successful business starts with a concept, a plan and a product or service that customers are willing to pay money to obtain. Business strategies are never conducted in a vacuum, however, and for a business to be successful, there must be a business plan and a business model generated. These two terms are unfortunately used interchangeably, but in reality, they are two very different documents that cannot exist without one another. It is essential that a business owner understand the use of a business model vs a business plan.
Business Plan vs. Business Model
At its simplest, a business plan is a written description of the future of a business. It's a document that not only gets a business concept on paper but also outlines the people and steps that will be involved to lead the business to success. The business plan is where you discuss the industry and the need for a particular product or service, the business structure and how you will achieve success.
The business plan also talks about the market in which the business will operate, lays out the competition and what the plans are to position the business as a leader. Lastly, the business plan lays out the ever-important financial plan, discussing things such as income and cash flow, loans and obligations and when and how investors can expect to see a return.
A business model, on the other hand, is a business's rationale and plan for making a profit. If the business plan is a road map that describes how much profit the business intends to make in a given period of time, the business model is the skeleton that explains how that money will be made. A model covers everything from how a company is valued within an industry to how it will interact with suppliers, clients and partners to generate profits.
There are several different kinds of business models. A software company, for instance, might be based on a subscription model, which generates revenue from customers that renew subscriptions annually for a license to use the software. An example of an accessories model would be a razor company or computer printer company that guarantees future income through the sale of razor blades and printer cartridges.
Interdependence
While it's true that a business plan and business model are two separate documents, the reality is that the business plan cannot live without the business model. While a business plan can describe the structure of a business's financial goals, the business model explains how the money will flow - from customer generation to marketing to sales, and finally, to customer retention. The business model must have room to grow and adapt. Consequently, if the business model changes, so must the business plan.
The Need to Adapt and Change
One of the most prominent examples of a business model changing is currently occurring in the computer software industry. About 10 years ago, the way to purchase software programs was to go to the store and buy a CD-ROM to download the application and license to your computer. Today, the advent of cloud-based subscription services makes it possible for customers to download software and renew licenses remotely over the internet.
This transition to the Software as a Service (SaaS) subscription model has caused many businesses to change their plans. Companies affected by this shift include computer companies that no longer need to build machines with CD-ROM drives in them and software companies that no longer need to make or sell software in physical form.
As a result, software companies have had to change their business plans, including costs and infrastructure costs for cloud storage and bandwidth, as well as maintain a cloud operations team 24 hours a day, seven days a week. These ongoing efforts can increase costs and reduce margins, but they're a necessary adaptation to changing customer needs and market technology with the new business model.
- The Business Plan Shop: Business Model Vs. Business Plan
- Wikipedia: Business Model
- Harvard Business Review: What is a Business Model?
- Entrepreneur: An Introduction to Business Plans
John began his 25-year career in the editorial business as a newspaper journalist in his native Connecticut before moving to Boston in 2012. He started fresh out of college as a weekly newspaper reporter and cut his teeth covering news, politics, police, and even a visit from a waterskiing squirrel. He went on to work in the newsrooms of several busy daily newspapers, and developed a love for detailed storytelling, focusing on the lives and diverse tales that all people have to offer. Moving on to the business arena later in his career, John worked as a managing editor for a healthcare publishing company and a technology software firm. He’s used his background in broadcast journalism as a webinar moderator, voice-over specialist, and podcast narrator. John also holds a master’s degree as an elementary school teacher and spent 10 years working with and tutoring students of various ages and backgrounds, including multilingual students and students with special needs of all ages.
Related Articles
The relationship between the business model and strategy, what is the purpose of a business model, difference between a business plan & a business proposal, the size of a macbook, how to remove unwanted pre-installed programs on a sony vaio, what is the business planning process, components of a business model, business model strategy, what is a business model and how does it differ from a business plan, most popular.
- 1 The Relationship Between the Business Model and Strategy
- 2 What Is the Purpose of a Business Model?
- 3 Difference Between a Business Plan & a Business Proposal
- 4 The Size of a MacBook
Business Model vs Business Plan – What Is The No. 1 Difference
- by IdeaBuddy Team
- April 19, 2024
- 6 minute read

Table of Contents Hide
What should your business model include , the importance of choosing the right business model, what is a business plan , what should your business plan include , business model vs business plan: the difference, business model vs business plan: conclusion.
Whether you are new to the world of entrepreneurship and business or you already have solid experience dealing with business terminology, there is no harm in refreshing your knowledge and making sure you know how to differentiate between a business model vs business plan .
Although both are essential, they serve different purposes and contain distinct information that can determine the success of your business, so in this article we will aim to cover everything you should know about these two terms that stand behind business model vs business plan syntax so you can cross them off from your entrepreneurial to-do list!
So, is there a winner in the business model vs business plan race, or are they simply complementary parts of every business? Let’s find out and explain these two ingredients needed to kick off your business.
What is a business model?
When thinking about what stands between a business model vs business plan, you probably already know that the characteristic of business models is that there are multiple models that can be used in a business, and they always depend on the type of the product a company has.
Some of the most common business models are affiliate , product as a service , subscription model , franchise , and others.
A business model is basically the strategic blueprint that defines how your company creates, delivers, and, most importantly, how it is going to make profit in the future.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/businessmodel-85ce9a0a59e642cd941204a92ee873de.png)
In simpler terms, it outlines how your business plans to make money and achieve its goals , describing what products or services it will offer, the target market it aims to capture, and the expected expenses and revenues.
Remember: a clear and detailed business model is the foundation of every successful venture. It’s not just about having a great idea, but about carefully mapping out how you’ll bring that idea to life and create value.
Your business model should include a compelling value proposition that determines your offerings and makes clear why customers should prefer them. You need to define your customer segments to tailor your approaches effectively, ensuring you understand who you’re serving and what they truly need.
Channels describe how you’ll reach your customers, while customer relationships detail the type of interactions you intend to maintain with them, whether through personalized service, automated systems, or community engagement.
Revenue streams outline how your business will earn money, be it through direct sales, subscriptions, or other creative monetization strategies. In your business plan, you should also provide clarity on key activities (what actions are crucial to deliver on your promise), key resources (what you need to operate), and key partnerships (who you’ll ally with to enhance your capabilities).

Finally, a thorough understanding of your cost structure will ensure that your business model is not only viable but also financially sustainable. Each of these elements works together to provide a comprehensive overview that will guide your business from startup to success.
Your business model sets the stage for introducing a structured, detailed business plan. So, let’s see how choosing the right business model for your business actually helps you:
Selecting the right business model is critical to the success of your business, as it defines the framework through which your business will operate and flourish. Here’s why the strategic choice of the right business model is fundamental:
- It gives you a competitive advantage : by adopting a business model that matches your business’s strengths and market needs, your business can distinguish itself from competitors.
- Enhances flexibility and resilience : The right business model provides a structure that supports growth and facilitates quick adaptation to market changes or internal demands.
- Helps you attract investment : A well-created business model can help demonstrating to investors that your business has a clear plan for revenue generation and long-term viability.

Now that we have a better understanding of the basics of the business model, it’s time to examine the other business ingredient – the business plan. You will learn in more depth the correlation between business model vs business plan, and understand how they overlap.
Just as there are various business models to suit different types of products and services, there are also multiple frameworks for business plans tailored to diverse business objectives. Common types of business plans include traditional , lean startup , and operations plans , each serving different strategic purposes.
A business plan is essentially a comprehensive document that details how your company plans to achieve its goals . It goes beyond the strategic outline provided by your business model to specify the operational steps, financial projections, and marketing strategies your business will employ. It describes in detail what your business will do, who your customers will be, and how you plan to succeed financially .

In simpler terms, a business plan not only maps out the products or services you will offer but also elaborates on the target market, the business structure, the team that will lead your venture, and the financial investments involved. It helps you anticipate any potential challenges and elaborate a plan on how you would address them, ensuring your business navigates towards its strategic goals effectively.
Remember: a clear and well-thought-out business plan is indispensable for translating the vision of your business model into a roadmap that guides every aspect of your business. It’s not just about having an innovative idea, but about methodically planning how to bring that idea into reality and secure its success in the marketplace.
As we mentioned before, a good business plan is a must if you are looking to turning your strategic vision into actionable steps! Here are some key components that your business plan should contain:
- Executive Summary : The summary should capture the main aspects of your business, such as mission statement, business model, key products or services, leadership team, and a brief financial overview.
- Company Description : Provide detailed information about your business, the problems it aims to solve, and the market needs it addresses.
- Market Analysis : Demonstrate a thorough understanding of your industry, market trends, demographics, and competition.
- Organisation and Management : Describe your company’s organisational structure, including details of the ownership, profiles of your management team, and the qualifications of your board of directors.
- Services or Products List : Explain what you’re selling or what service you’re offering.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy : Outline how you plan to attract and retain customers.
- Funding : If you are seeking financing, you should specify the amount of funding needed over the next five years and give a brief explanation on how you plan to use these funds.
- Financial Plan : Introducing the financial data, such as profit and loss, cash flow forecast, balance sheet and other projections can help both you and potential investors get a clear view on the direction and resources needed to succeed.
Each of these components need to work together to provide a comprehensive and detailed overview of your business.
As you develop your business plan, consider using tools like IdeaBuddy to streamline the process and ensure that every aspect of your plan is well-crafted and aligned with your business goals.

Understanding the difference between a business model vs business plan can help you more effectively communicate the core of your business to stakeholders and guide your strategic decisions. The business model focuses on the conceptual aspects of the business, showing the big picture of how value is created and delivered, while the business plan details the operational and financial specifics needed to achieve those goals.
Here’s why understanding the difference matters:
- Focus and Clarity : While the business model offers a high-level view of your strategic direction, the business plan provides the details of exactly how you’ll achieve this.
- Execution vs. Strategy : The business model is your strategy for how you’ll succeed, while the business plan is about execution—how you turn your strategic visions into operational realities.
- Adaptability and Scalability : With a well-defined business model, you can adapt to changes without losing sight of your core objectives. The business plan allows you to scale these efforts, detailing specific actions, timelines, and resources needed as you grow.
We hope that now you understand the distinction and importance that stand behind the business model vs business plan buzzword. Let’s recap one more time: while the business model outlines the strategic blueprint for how your company will create, deliver, and capture value, the business plan details the specific steps and resources necessary to execute and achieve the goals set forth by your business model.
We hope this helps. For more information about the business model vs business plan topic, read the following articles:
Suggested read: What is a business model?
Suggested Read: Why do you need a business plan?

For those ready to dive deeper into the topic of business model vs business plan, or perhaps start a business from scratch, we have crafted an in-depth guide for all the steps of the way as you build your business – check it out here! 💡

IdeaBuddy Team
Business model - explanation, key elements and the top 10 types, using ai for business planning: key advantages, pitfalls, and tips, you may also like.

How To Succeed With Lean Startup Methodology
- October 17, 2023
- 34.8K views
- 30 shares 24 0 6

How To Successfully Write a One Page Business Plan (With 3 Templates)
- March 13, 2023
- 29.4K views
- 49 shares 4 0 45

- 7 minute read
How To Make Accurate Financial Projections For Startups
- September 28, 2023
- 12.4K views

- Investor Business Plan
- SBA Business Plan
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E2 Visa Business Plan
- EB-5 Visa Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Call our business plan experts:

- Schedule Free Consultation
Business Model vs Business Plan: Key Differences Explained
Why do some business owners have to face a failure while the other gets a great business success? You might sometimes wonder and ask yourself. Let us help you understand this. Other than business plan there is a term called “business model” is often used interchangeably. However, they found to have distinct concepts in the world of entrepreneurship and business development. Before embarking on a new venture, understanding the Business model vs business plan is essential for any entrepreneur. Both terms serve different purposes and have distinct scopes that help business owner become successful in their entrepreneurial journey.
So if you want your business to be successful, come up with a business plan and a business model. Although these two terms cannot coexist, likewise implementing these terms could not be possible for you until you get them deeply clear. A thoroughly drafted business plan is a document that outlines the goals, and financial projections of a company over a particular period. Comparatively, when talking about a business model, is a document that dives deeper into how a business drives, delivers and captures value.
Let’s now understand these two terms separately and then closely look into the key difference that makes them equally unique and valuable for every successful business.
What is a Business Model?
It is a written form document that describes how a company establishes, delivers, and captures value. It explains the core aspects of how a business operates, including its revenue streams, target customer segments, distribution channels, value proposition, and cost structure.
Business Model Key Components
- Value proposition
- Customer segments
- Revenue streams
- Cost structure
What is a Business Plan?
Imagine a business plan as a roadmap guiding you to navigate the operational and financial activities. It is a document that talks about your business objectives, strategies, and functions of a business in detail. It typically involves sections such as executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, marketing strategy, product or service description, funding requirements, and financial projections.
Business Plan Key Components
- Executive summary
- Market analysis
- Organization and management plan
- Sales strategies
- Financial projections
Few Major Differences between the Business Model & Business Plan
Comparing a business plan and a business model lets you identify how these two categories in businesses work and may help foresee the differences among them to avoid making mistakes in your future business.
Business models describe how a business manages to deliver products and services to customers. They focus on the fundamental logic of how a company intends to follow sales funnels, and marketing strategies and sustain its operations over time. Whereas, business plans are more comprehensive explanations of every facet of a business that focuses on the specific steps and tactics a company will take to achieve its goals. It provides a direction about how the business will be launched, operated, and grown.
Business Model contains the overarching strategy and framework that guides the entire business. It’s more conceptual and has a high-level view of a company or business tendency. A business plan, on the other hand, turns a thorough synopsis of the enterprise into several tactical measures, such as target markets, financial predictions, operational plans, and short- and long-term goals.
Business plans primary goal is to persuade external parties such as potential investors and other stakeholders. For example, demonstrating a business plan to raise funds, apply for grants, or update investors on business progress.
Alternatively, business models are primarily designed for executives and internal members within a company. These schemes aim to help team members coordinate activities like producing a product, delivering, and capturing value in economic, social, cultural, or other contexts.
Flexibility in Nature
Business model is found to be more flexible and adaptable to changes in the market or business environment. It’s meant to be dynamic and evolve due to being at the center of the business plan.
On the other hand, a Business Plan tends to be more rigid and static, as it’s often used as a formal document for obtaining funding or as a roadmap for initial business operations.
Their Usage
The business owners can use the Business model to understand the fundamental mechanics of how a business will be operated and generate value. It helps the owner in decision-making and identifying opportunities for innovation or optimization.
In comparison business plan is typically utilized for external purposes such as securing funding from investors or loans from financial institutions, or for internal planning and communication purposes.
In general, the business model and business plan are completely different notions. The business model serves as the mechanism, defining the core components that generate the company’s revenue streams and sustainable operations. In contrast business plan is a written document presenting the future of a business. It’s a document that not only gets a business concept on paper but also outlines the company strategy and people’s roles that will be involved to lead the business to success for the years to come.
Although both the business model and the business plan are essential parts of a successful business. Therefore, all businesses must have a well-thought-out business plan along with an exceptional business model supporting them to consistently do hard work to win the competitive market landscape.
Several companies offer Business plan writer service , but you can trust us for numerous services on one platform such as Franchise Business Plan , E2 visa business plan , and Strategic Business Plan .
For more information on other services like Investor Business Plan , and Immigration Business Plan , and to know the Business plan cost , you can stay in touch with us by frequently visiting our website.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get a Free Consultation Now
For free Consultation, please make an appointment with us by filling in the details here and Clicking on the “Submit” button. We will contact you within 24 Hours.
Confidentiality of your information is our foremost priority.
I Agree to get e-mails from BPlanWriter.
| Save $5850+ Today! |
- Business Ideas
- Super Guides
- Innovation Report
- Canvas Examples
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Discounted Bundles
- Search for:
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
What is the difference between Business Model and Business Plan?
It’s very common to make confusion on what’s the difference between Business Model and Business Plan. But, in fact, they are similar only in name. Their functions and purposes are quite different and, actually, complementary. While the business model refers to a one-page representation of how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, the business plan is an in-depth description on a long textual document form about how your company is structured and plan to achieve strategic and financial objectives. This business plan is a document that contains every data of the business – usually including its model. Let’s separate them both, to make it simple.
Business Model Definition
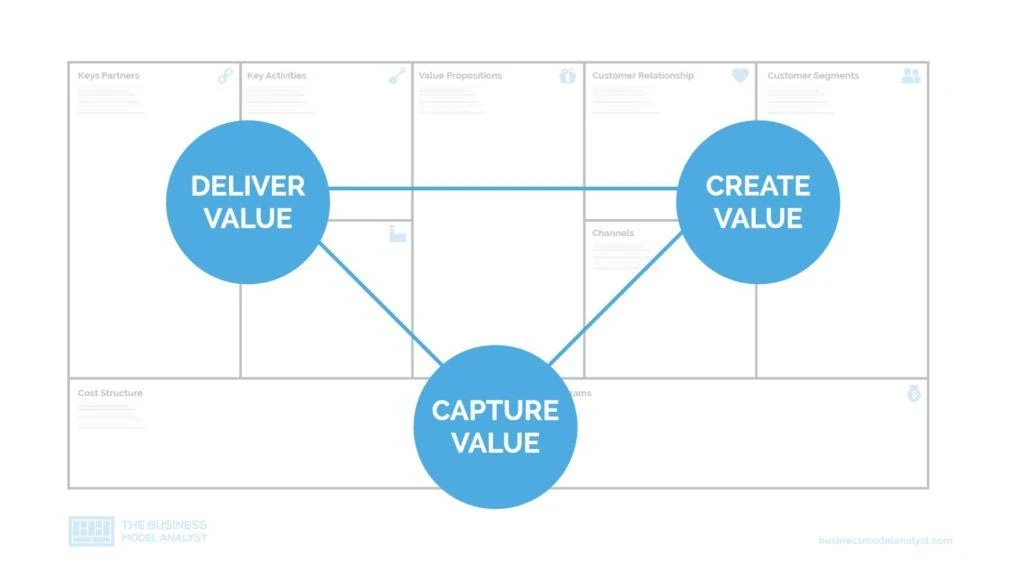
Your company’s business model is all about the way a company creates, delivers, and captures value. For example, a restaurant franchise is a business model. A Software-as-a-Service is another one. A razor-and-blade , a subscription company , a Freemium internet tool, a e-commerce marketplace . Each of that is a business model, with its own peculiarities. What it’s commonly mistaken with the business plan is not the business model itself. It’s, indeed, the business modeling tool . And this tool provides a base to design a business model. It’s, in fact, by modeling your business through this kind of tool that you’ll be able to identify your they main construction blocks of a business, who they relate to each other and combine to form a unique strategy. It’s with the business model tool that you may identify the key resources for your business to succeed, which key activities it must perform, who it has to interact with, and by which means and channels . Usually, this business model tool is a framework, made up of a single page, that allows you to recognize your own business under several perspectives. According to the type of business, you may take a look at different modeling options, such as Business Model Canvas , Value Propositions Canvas, Lean Canvas , and others. Each of them fits a different purpose. For example, if your business is brand new, the Business Model Canvas is likely to be the better option. On the other hand, for early validation of your startup, the Lean Canvas must be the most appropriate. And, to pivot your product, it’s a good idea to check the Value Proposition Canvas. In short, if you aim to understand your business better, from inside, or make predictions for growing your venture, then your need to work on your business model, not make a business plan. So, now, let’s check what the business plan is for.
Business Plan Definition

A business plan is a written document that contains detailed information of the business, product/service, market, and the entrepreneur vision for the company’s future. It is basically the most accurate portrait of the field, products and services, customers, competitors, suppliers, all the operational and financial goals of the company, its marketing and sales strategy. Its purpose is to display the strengths and weaknesses of the business and to project the gains and losses of the organizations, in order to identify the viability and sustainability of the idea. The business plan is often a long document, made up of several pages. In general, it contains:
- Table of Contents;
- Executive Summary;
- Business and product/service description;
- Market analysis;
- Competitive Analysis;
- Marketing Plan;
- Operational and Management Plan;
- Financial Plan;
- Supporting data and documents.
The goal of the business plan is to determine whether your idea is sustainable or not. It also shows the weaknesses to be repaired, as well as the strengths to be potentialized. It is a kind of script, to reduce the chance of failure. The business plan is a core document if you are looking for partners, in order to demonstrate profitability. Its focus is, indeed, to provide executives, investors, and any other stakeholders a full overview of the business. So, it is especially important when you are seeking loans, sources of financing, and investments. It is the best way to demonstrate that your business is trustworthy and solid enough for credit.
Business Model vs Business Plan
the difference between Business Model and Business Plan lies in key points like how they should be developed, where should the focus be, how to organize ideas and what are their main objectives.
Business Models and Business Plans are important documents to help you plan and organize your business strategy. It can be either a document for early-stage companies that need to validate hypothesis or big companies that need to plan ahead, capture investment or even make an IPO .

Whatever the case is, it is very important to understand that these are different terms, with different purposes and have different tools to develop them. To summarize here, the key terms that are commonly confused between each other:
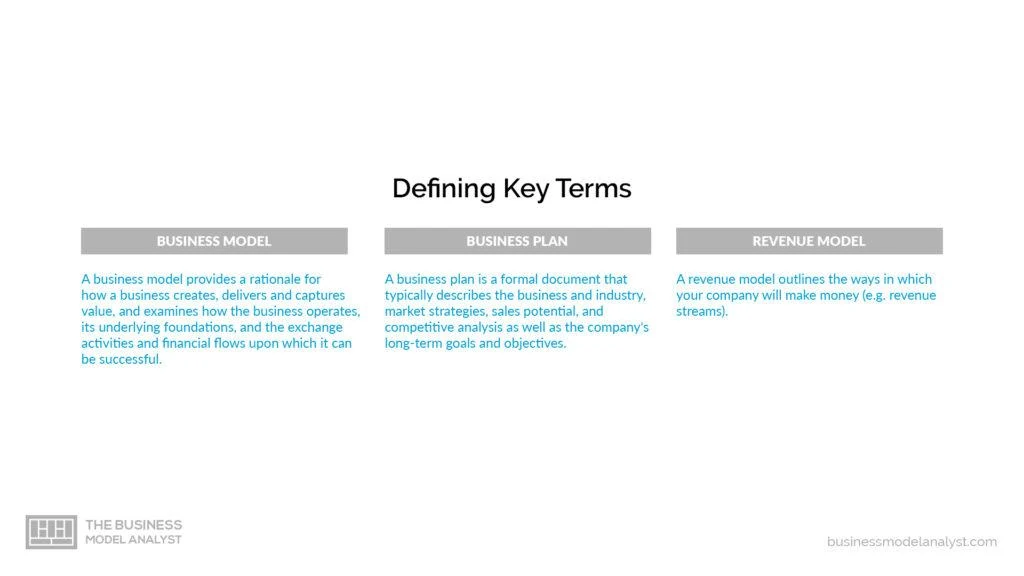
Business model – provides a rationale for how a business creates, delivers and captures value, and examines how the business operates, its underlying foundations, and the exchange activities and financial flows upon which it can be successful. Business Plan – a formal document that typically describes the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. Revenue Model – Outlines the ways in which your company will make money (e.g. revenue streams). Did you better understand the difference between Business Model and Business Plan? Comment below!

Who is Daniel Pereira ?
I love understanding strategy and innovation using the business model canvas tool so much that I decided to share my analysis by creating a website focused on this topic.
More About Me
RECEIVE OUR UPDATES
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Business Model Vs. Business Plan: When And How To Use Them
A business model is a holistic framework to design how a business might create and capture value. A business plan is a document explaining how a business might become viable. Where a business model is made to be tested, a business plan’s primary goal is to gain investments.
| Aspect | ||
|---|---|---|
| A is a strategic framework that outlines how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It focuses on the core components of a business’s operations and revenue generation. | A is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details. It is often used for fundraising and as a roadmap for the business. | |
| The primary purpose of a business model is to describe the of how a business will make money and create value for customers. | A business plan serves as a that provides guidance on how a business intends to operate and grow. It is often used for attracting investors or lenders. | |
| Key components of a business model include the . | A business plan typically includes sections on the . | |
| A business model emphasizes , simplifying complex business operations into key building blocks. | A business plan delves into , including market research, competition analysis, financial forecasts, and strategic milestones. | |
| Business models are often and adaptable to changes in the market and business environment. Entrepreneurs can pivot easily based on customer feedback or market shifts. | Business plans can be and may require extensive updates when the business encounters unexpected challenges or opportunities, potentially leading to delays. | |
| Business models are typically developed and iterated upon , helping entrepreneurs validate their ideas quickly and efficiently. | Business plans are usually created when the business is or when a more detailed operational roadmap is required for established businesses. | |
| Business models are useful for , often at the startup or early stages of a venture. | Business plans are commonly used for for established businesses. | |
| Business models are often represented using visual tools like the , which provides a quick overview of key components. | Business plans are primarily presented as with detailed narratives and financial tables. | |
| Business models encourage as they allow entrepreneurs to explore various ways to create and capture value. | Business plans may prioritize over rapid innovation, potentially leading to slower adaptability. | |
| Investors may appreciate a clear and compelling business model that demonstrates a . | Investors often require a comprehensive business plan to evaluate the of a business. | |
| Business models can evolve and adapt to market changes, allowing businesses to stay relevant over the long term. | Business plans may become outdated and less relevant once a business is operational, often requiring frequent updates. | |
| Developing a business model typically and is suitable for resource-constrained startups. | Creating a comprehensive business plan can be in terms of time and expertise, often involving multiple team members or consultants. | |
| A business model provides and helps in making decisions that align with the core value proposition and revenue generation. | A business plan serves as a for executing strategies, including marketing, operations, and financial management. | |
| Business models can be presented in a that quickly conveys the essence of the business’s value proposition. | Business plans typically involve , which can be lengthy and text-heavy. | |
| ROI on developing a business model can be , as it provides a clear understanding of how the business intends to create value and generate revenue. | ROI on creating a business plan may be if it successfully attracts investors or lenders and helps secure funding. |
Table of Contents
The key difference between a business model and a business plan
It is easy to confuse a business model with a business plan . Yet those tools have specific functions, in some cases similar, in most other cases completely different.
Indeed, while a business model is a framework to understand the way an organization works, a business plan is a document that helps to understand the future strategy of an organization and its expected performance in a three to five years time frame.
While in some cases, a business plan can also serve the purpose of better understanding your own business, and in some other cases, the business model can be comprised within the business plan .
Indeed, as an investor, I want to know exactly how your business works or how you think it will work in the future. Keeping a distinction between those tools is critical.
In particular, I want to focus on the critical difference from two perspectives:
- external (investors, stakeholders, and other parties)
- internal (owners, top management, shareholders)
External: business plan or business model?
If you’re looking for a tool whose aim is to show how attractive your business is, a business plan is the most suited for that.
Indeed, suppose you want to attract investors and grow your business via external resources.
In that case, a detailed business plan is the most effective way to allow those investors to understand the several parts of your business.
Also, the business plan is a way to show where you see the business in the future. Indeed, one key ingredient of a business plan is a set of projections for three-five years.
While investors will also want to know what kind of business model you want to build (depending on whether or not your business model will be scalable will make or break the interests of investors).
The primary tool to show where your business will be in the future and to address the kind of resources needed to get there is the business plan. In short, for external subjects to know about your business and invest in it, the business plan is the best tool.
Internal: business plan or business model?
Among the tools to leverage on to understand your business, a business model is one of the most effective.
Indeed, the business model is a framework (usually a one-page) that allows you to understand how your business works from several perspectives.
Depending on what kind of business you’re trying to build or where you want to steer your organization, you might want to look at a few tools, such as:
- FourWeekMBA Busines Model
- Business Model Canvas
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas
- Value Proposition Canvas
- Lean Startup Canvas
Each of those tools will help you to build a different kind of business.
For instance, in a start-up phase, the business model canvas and the lean startup canvas are the most suited.
In a phase of scale-up, the lean startup is better suited than the business model canvas.
Instead, if you’re trying to blitzscale your business , the Blitzscaling Canvas will be your best companion.
In conclusion, if you’re looking for a way to understand better your business in the present or how to design a business model that can help you grow, the business model frameworks are the most suited to the business plan .
In some cases, though, a business plan might also work for that purpose, especially a one-page business plan.
Key takeaway and resources
A business plan is a tool that is most suited to shot external stakeholders where your business is headed and why they should finance or invest in its future.
The business model instead, is a framework that helps you assess how your business works from several angles and the kind of actions you can take in the now.
Below you can find an example on how to build a one-page business plan as well:

Key Highlights:
- Business Model vs. Business Plan: A business model is a comprehensive framework for creating and capturing value in a business, while a business plan is a document that outlines how a business can become viable. The primary goal of a business plan is often to secure investments.
- Key Difference: The main distinction between a business model and a business plan lies in their functions. A business model explains how an organization operates, while a business plan focuses on the future strategy and expected performance over three to five years.
- External Perspective: For external stakeholders like investors and partners, a detailed business plan is essential. It helps them understand various aspects of the business and provides projections for the future. Investors also want to know about the scalability of the business model.
- Internal Perspective: When looking to understand the current state of your business or design a business model, tools like the Business Model Canvas, Lean Startup Canvas, and others are more effective. These tools offer insights into how the business operates and can guide decision-making.
- Choosing the Right Tool: The choice between a business model and a business plan depends on your goals and the stage of your business. For startups, the Lean Startup Canvas and Business Model Canvas are useful. In a scale-up phase, Lean Startup tools might be more suitable, and for rapid growth , the Blitzscaling Canvas can be valuable.
- Key Takeaway: A business plan is best suited for presenting your business to external stakeholders and securing financing, while a business model is a framework for understanding your business from multiple angles and making informed decisions in the present.
- Resources: Various tools, such as the Business Model Canvas and Lean Startup Canvas, can help you analyze and improve your business model. A one-page business plan can also be effective in clarifying your business’s core problem, target customers, and distribution channels .
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Nike – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Nike utilizes its business model to create, deliver, and capture value. It focuses on the core components of a business’s operations and revenue generation.
- When considering external stakeholders like investors, Nike might develop a detailed business plan to showcase its future strategies and financial projections.
Case Study 2: Coca-Cola – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Coca-Cola employs digital marketing channels like social media and email marketing to better communicate its products and engage with consumers.
- Coca-Cola may use a business model framework to understand how it creates and delivers value through marketing , while a business plan could be used to outline future marketing strategies and financial goals.
Case Study 3: Amazon – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Amazon uses technology not only for its e-commerce platform but also integrates customer feedback into its product design, enhancing its business model .
- In the process of attracting investors or lenders, Amazon might create a comprehensive business plan to demonstrate its long-term growth strategy , financial viability, and risk mitigation.
Case Study 4: Tesla – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Tesla leverages technology to shape its electric vehicles, constantly improving features and performance based on user feedback and data collected from their vehicles.
- Tesla could use a business model to understand how it delivers value through innovation and customer feedback. Simultaneously, a business plan might outline its future growth strategies and financial projections.
Case Study 5: Airbnb – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Airbnb operates a two-sided platform that connects hosts and travelers, creating interactions that generate value for both parties.
- To secure investments for expansion or growth , Airbnb may develop a business plan that outlines its financial outlook, expansion strategies, and risk management, while its business model emphasizes how interactions drive its value.
Case Study 6: Uber – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- Uber’s platform connects riders and drivers, creating a multi-sided marketplace driven by network effects .
- Uber could use a business model to understand the dynamics of its marketplace. When seeking investors or funding, it might present a comprehensive business plan highlighting its growth potential, financial projections, and strategies to address market challenges.
Case Study 7: Apple – Business Ecosystem vs. Business Plan
- Apple’s App Store has evolved into a thriving business ecosystem that benefits both the company and app developers.
- While the business ecosystem concept is central to Apple’s strategy , the company may use a business plan to outline its future ecosystem development, financial projections, and governance design for potential investors.
Case Study 8: Ethereum – Business Ecosystem vs. Business Plan
- Ethereum’s blockchain platform facilitates the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts within a larger business ecosystem .
- Ethereum might use a business model to understand how its ecosystem creates and captures value. For attracting investors or funding, a business plan could illustrate its growth strategies, financial outlook, and governance design.
Key Difference – Business Model vs. Business Plan
- A business model is a strategic framework for understanding how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It focuses on the core components of a business’s operations and revenue generation.
- A business plan is a comprehensive document outlining a company’s goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details, often used for fundraising and as a roadmap for the business.
Choosing the Right Tool
- The choice between a business model and a business plan depends on the goals and stage of the business. While a business model helps understand the present and guide innovation , a business plan is primarily for external stakeholders, showcasing future strategies and financial projections.
Connected Business Frameworks
Business Engineering

Tech Business Model Template

Web3 Business Model Template

Asymmetric Business Models

Business Competition

Technological Modeling

Transitional Business Models

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Scaling

Market Expansion Theory

Speed-Reversibility

Asymmetric Betting

Growth Matrix

Revenue Streams Matrix

Revenue Modeling

Pricing Strategies

Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced Scorecard , OKR , Agile Methodology , Value Proposition , VTDF
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Tech Business Model
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Org. Structures

Business Model vs. Business Plan
You might be wondering what the difference is between a business plan and a business model. The truth is, they are different things with different purposes.
The main difference between a business plan and business model is that a business plan outlines your goals and strategy to grow your company, while a business model shows you how to generate revenues. Read on to learn more about this subject, including what types of business models there are and how to figure out which type best suits your situation.
What is a Business Model?

What is a Business Plan?

What Should Be Included in a Business Plan?
During the business planning process, especially if you are trying to attract investors, there are 10 essential elements of a business plan which you must include as follows:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Customer Analysis
- Market Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Operations Plan
- Management Team
- Financial Plan (Performance & Forecasting)
For each of these sections, you should provide an in-depth description of your research, analysis, and expected financial performance. You can learn more about the components of a business plan and review our repository of 100+ business plan examples to help you get started on writing your own business plan.
What Should Be Included in a Business Model?
A business model should include the details of every way in which your business makes money. It’s important not to leave anything out, even if it seems insignificant. Every dollar counts!
How Does a Business Model Differ from a Business Plan?
Business models outline how your company generates revenues. On the other hand, business plans focus on the specifics of how the business will achieve sales and growth over a given period of time, typically five years. Business plans discuss your business model among other things and are critical if you want to gain investments to grow your business.
The business model strategy is very different from a business plan. While they overlap a bit, the critical difference is that a business plan outlines the goals and business strategy while the basic business model shows you how to make money.
Your needs will change over time so it’s important to be able to switch between these two documents when needed. For example, if your goal is long-term growth then you may want more information about what type of strategy would work best for this situation or which resources might help get there faster. On the other hand, if you’re looking for some immediate income then paying attention to the various types of models available could give you an idea of where to start with generating enough sales quickly without too much cost upfront.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink’s business plan consulting team has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how our professional business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Business Plan Vs Business Model: Understanding The Key Differences

What if I told you that nearly 70% of businesses fail due to a lack of clear direction? Understanding the differences between a business plan and a business model can be pivotal in steering your venture towards success. Let’s delve into these fundamental yet often misunderstood elements of business strategy.
A business plan is a comprehensive document outlining a company’s goals, strategies, and methods of operation, often used to secure investment. In contrast, a business model is the framework for how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, focusing on the mechanisms of revenue generation. Knowing the distinction can streamline your focus and potentially elevate your business above the competition.
Business Plan vs Business Model: An Overview
A business plan and a business model are essential, yet distinct components of a company’s strategy. A business plan is a detailed document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, market research, and financial forecasts. It acts as a roadmap for the business, guiding its growth and operations. On the other hand, a business model describes how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s the blueprint for how a business makes money.
One key difference between the two is their purpose and focus. A business plan covers a broad range of topics, including marketing strategies, target audience, and financial projections. This comprehensive approach helps attract investors and manage business activities. Meanwhile, a business model zeros in on the core process of revenue generation. It answers critical questions like what value the company offers and how it will be delivered to customers.
There’s also a difference in formality. A business plan is typically a written document, often dozens of pages long. It’s used to secure funding and guide the company’s strategy in the long term. In contrast, a business model can often be summarized in a single page or a simple diagram. Key elements of a business model can often be illustrated through frameworks like the Business Model Canvas, which includes sections for key partners, activities, and revenue streams.
Both elements are essential for a successful venture. While the business plan provides a detailed roadmap and strategic direction, the business model ensures that the company’s value proposition carries through to financial success. By understanding and leveraging both, entrepreneurs can structure their businesses more effectively. Each plays a unique role in guiding a company towards its goals.
Definition of a Business Plan
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a company’s goals and the strategies it will use to achieve them. It’s a roadmap for success, detailing each step the business will take along the way. This plan typically includes sections on marketing, financial planning, and operational guidelines. Having a business plan helps companies stay focused on their objectives and adjust tactics as needed. Investors often require a business plan to understand a company’s potential.
Business plans are also used to forecast future growth and determine financial needs. They project income, expenses, and profitability over a period. These documents are essential for budgeting and financial planning. Common elements of a business plan include an executive summary, market analysis, and financial projections. A well-crafted business plan can be a critical tool for a company’s success.
A good business plan answers three main questions: What does the business aim to do, how will it achieve that, and why is it sure to succeed? It should clearly state the target market and how the business intends to reach it. Including detailed financial data and projections helps demonstrate feasibility. Furthermore, a business plan outlines the competitive landscape, highlighting how the business will stand out. This detailed planning aids in risk management .
While creating a business plan may seem daunting, it offers numerous benefits. It forces entrepreneurs to think through every aspect of their business idea. By doing so, they identify potential challenges and develop strategies to overcome them. Additionally, a business plan communicates the business vision to stakeholders. This can be critical for gaining support and investment, ensuring the business gets off to a strong start.
Definition of a Business Model
A business model is a framework that describes how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It outlines the core aspects of the business, including its value proposition, customer segments, and revenue streams. Essentially, it answers the question: “How does the business make money?” Business models help companies understand their path to profitability. They are essential for identifying opportunities and challenges in the marketplace.
Unlike a business plan, which is often a detailed document, a business model can be summarized on a single page. One popular tool for this is the Business Model Canvas. This tool helps entrepreneurs map out key areas like key partners, activities, and customer relationships in a clear and concise manner. Here’s a simplified breakdown of a business model using the Business Model Canvas framework:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Value Proposition | The unique benefits and value provided to customers |
| Customer Segments | Groups of people or organizations the business aims to serve |
| Revenue Streams | Ways the company makes money from each customer segment |
Business models are dynamic and can change as the market evolves. Companies often have to adapt their models to stay competitive. Adjusting elements like pricing strategies or customer engagement methods can help sustain profitability. Successful businesses continuously refine their models to better meet customer demands and market conditions. This flexibility is key to long-term success.
Key Components of a Business Plan
A well-constructed business plan includes several key components that provide a clear roadmap for the company’s future. One of the most crucial elements is the executive summary. This section offers a snapshot of the business, summarizing important details like the mission statement, products or services, and an overview of financial projections. It’s typically the first part investors read, so it needs to be compelling and concise. Capturing attention early can be critical for securing funding.
The market analysis section is also pivotal. This part delves into the industry landscape, examining market trends, target customer demographics, and competitors. Reliable data and research are essential here to validate the business idea. Investors look closely at this section to assess the market potential and competitive edge. By understanding the market, a company can better strategize its entry and growth paths.
Another important component is the marketing and sales strategy. This outlines how the company plans to attract and retain customers. Tactics such as digital marketing , sales promotions, and customer loyalty programs might be included. The plan should also detail the sales process, from acquiring leads to closing sales. Effective marketing and sales strategies can significantly boost a company’s success.
Financial projections are indispensable in a business plan. These projections typically include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. Potential investors and stakeholders use these figures to evaluate the company’s financial health and profitability. Accurate and realistic financial statements can build credibility and trust. They offer a forecast of the business’s financial future and help in making informed decisions.
An operations plan outlines the day-to-day activities that keep the business running. This includes information on inventory management, production processes, and human resources. It ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned and streamlined for efficiency. A robust operations plan can improve productivity and operational capacity. It’s an essential part of the overall business strategy.
Finally, the business plan should cover the management team and organization structure. This section introduces the key players in the company and their roles. Highlighting the team’s expertise and skills can give investors confidence in the management’s ability to execute the plan. An organizational chart may be included to show the hierarchy and departmental responsibilities. Strong leadership is often a critical factor in a company’s success.
Key Components of a Business Model
A business model is composed of several key components that help a business create, deliver, and capture value. One of the most important elements is the value proposition. This defines what makes the product or service unique and why customers would choose it over competitors. It’s the core offering that meets the customers’ needs and solves their problems. A clear value proposition can set the business apart in a crowded market.
Another crucial component is customer segments. This refers to the specific groups of people or organizations that the business aims to serve. Identifying these segments helps tailor marketing efforts and product development. Understanding your consumers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors can aid in delivering better value. Targeted strategies can lead to more effective customer acquisition and retention.
Revenue streams are essential for understanding how a business earns money. This includes various ways through which the company generates income. Possible revenue streams can range from product sales to service fees and subscription models. Diversifying revenue streams can make a business more resilient. Here are some common revenue streams:
- Product sales
- Subscription fees
- Service charges
- Advertising revenue
Key activities are the actions that a business undertakes to operate successfully. These activities can include production, marketing, and sales operations. Identifying key activities helps focus efforts on what truly drives the business. Effective management of these activities is critical to operational efficiency. Streamlined processes can result in better performance.
A business model also includes key partners. These are external entities that help the business succeed. They can be suppliers, distributors, or strategic alliances. Building strong relationships with key partners can provide additional resources and capabilities. Collaboration with partners can lead to innovation and growth opportunities.
Lastly, the cost structure outlines the major expenses required to run the business. Understanding the cost structure helps in budgeting and financial planning. Major cost areas might include manufacturing, labor, and marketing. Keeping costs under control is essential for profitability. Analyzing costs can also identify areas for efficiencies and savings.
The Role of Business Model in a Business Plan
The business model plays a vital role within a business plan. It serves as the foundation for understanding how a company generates revenue and ensures long-term viability. By clearly defining the value proposition, customer segments, and revenue streams , the business model helps align the entire business strategy. It explains the economic logic behind the business. This alignment is crucial for strategic planning and execution.
The business model provides insights that are essential for financial planning. When a business plan includes a well-defined business model, it helps in creating accurate financial projections. Investors and stakeholders can understand how revenue will be generated. This transparency increases investor confidence and enhances the feasibility of the business plan. Financial viability becomes easier to demonstrate.
Additionally, the business model guides the development of marketing and sales strategies. It identifies the target customer segments and how the product or service will meet their needs. This information is critical for devising effective marketing campaigns. A coherent business model ensures that marketing efforts are focused and efficient. This targeted approach can lead to higher market penetration.
The integration of the business model in the business plan also aids in operational planning. It outlines key activities and partnerships necessary for delivering value. Knowing what activities are crucial allows for better resource allocation and process management. This operational roadmap helps in maintaining efficiency and effectiveness. By streamlining operations, the business can achieve its goals more effectively.
A well-defined business model also aligns the team and stakeholders around a common vision. It provides a clear understanding of how the business will succeed, making it easier to communicate goals and strategies. This shared vision fosters collaboration and motivation. Stakeholders can see their role in the bigger picture. Such alignment is often key to achieving long-term success.
Why Understanding the Differences Matters for Entrepreneurs
Understanding the differences between a business plan and a business model is crucial for entrepreneurs. A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap, detailing specific goals, strategies, and financial forecasts. This helps in organizing thoughts and aligning team efforts toward common objectives. Meanwhile, a solid business model focuses on how the company makes money. It provides clarity on revenue streams and customer value propositions.
An entrepreneur who recognizes these distinctions can develop stronger pitches to investors . Investors look for comprehensive business plans that outline long-term potential and growth strategies. They also seek clear business models that demonstrate profitability. By clearly presenting both elements, entrepreneurs can build confidence among potential backers. This increases the likelihood of securing investment.
Furthermore, understanding these differences aids in strategic decision-making. Business plans help identify long-term goals and required resources, while business models offer insights into short-term operations and revenue generation. Knowing when to focus on which aspect allows for better agility in responding to market changes. It ensures that both immediate needs and future aspirations are addressed adequately.
The distinction also assists in effective resource allocation. A detailed business plan reveals areas requiring significant investment or attention, like marketing or product development. On the other hand, a focused business model highlights efficient paths to generate income quickly. By balancing both perspectives, entrepreneurs can manage their resources more effectively.
A clear understanding of these elements fosters better teamwork within an organization. When everyone understands the company’s long-term strategy (business plan) alongside day-to-day operations (business model), it promotes alignment and collaboration. Team members know what they are working towards and how their efforts contribute to overall success. This unified approach can drive higher productivity.
This comprehension helps mitigate risks associated with running a new venture. By having clear plans for various scenarios outlined in both documents, entrepreneurs can navigate challenges more easily. Being prepared reduces uncertainties and allows smoother operational transitions during difficult times.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section covers key questions that entrepreneurs often ask about business plans and business models. Understanding these concepts can provide clarity and support for launching and growing a successful business.
1. What are the main components of a business plan?
A business plan typically includes an executive summary, market analysis , company description, organization structure, marketing strategies, and financial projections. Each part serves to outline the company’s strategy, goals, and how it plans to achieve them.
The executive summary provides a snapshot of the plan’s key elements. Financial projections include income statements and cash flow forecasts to show feasibility. These components help guide operations and attract investors.

2. Why is a business model important for startups?
A well-defined business model helps startups understand their path to profitability by outlining how they will generate revenue and deliver value to customers. It serves as a blueprint for operational activities and decision-making processes.
This model enables entrepreneurs to identify their value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, key activities, partners, and cost structures. Clear understanding aids in attracting investors by demonstrating viability and strategic planning capabilities.
3. Can a company have more than one business model?
Yes, companies can operate multiple business models simultaneously to diversify their revenue streams or target different customer segments. For example, a media company might generate revenue from both subscriptions and advertising.
This approach helps businesses mitigate risk by not relying on a single source of income. Employing various models allows companies to adapt to changing market conditions while exploring new growth opportunities.
4. How do you choose between different business models?
The choice of a business model depends on the industry context, target audience preferences, available resources, and competitive landscape. Entrepreneurs need to assess which model aligns best with their value proposition and customer needs.
Evaluating case studies of successful companies in similar markets can provide insights into potential models. Testing various approaches through pilot projects or limited releases can also help determine the most effective strategy before full-scale implementation.
5. How does a strong business model contribute to long-term success?
A strong business model ensures consistent revenue generation by effectively addressing customer needs through unique value propositions. It provides clarity on essential operational activities required for delivering this value efficiently.
This structured approach facilitates better resource allocation leading towards sustainable growth over time while enabling quick adaptations when necessary according during industry shifts or technological advancements ensuring continuous relevance within target markets.
Understanding the differences between a business plan and a business model is essential for any entrepreneur aiming for success. While a business plan provides a detailed roadmap and strategic direction, the business model focuses on the specific ways to generate revenue. Both elements, though distinct, work together to guide a company towards its goals.
By mastering both concepts, entrepreneurs can better attract investors, allocate resources effectively, and navigate market challenges. This comprehensive approach helps in building a strong, sustainable business. Entrepreneurs who can integrate both elements seamlessly into their strategy are well-prepared to achieve long-term success.

Beverage Manufacturing Start-up Financial Model
The beverage manufacturing industry is a dynamic and rapidly growing sector that caters to a diverse market ranging from soft drinks and juices to alc... read more
- Excel Model – $199.95 Version 5.2
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 5.2

Liquor Distillery Financial Plan Template
Distilleries, with their rich history of crafting spirits, have experienced a resurgence in popularity, driven by consumer interest in artisanal and l... read more
- Excel Version – $199.95 Version 5.5
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 5.5

Corporate Finance Toolkit – 25 Financial Models Excel Templates
The toolkit is an essential resource for any organization, providing a comprehensive collection of tools and templates designed to streamline financia... read more
- All Excel Model Templates – $249.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo & Excel Free Download – $0.00 Version 1

Taxi Company Business Financial Model
Embark on the road to success by starting your own Taxi Company Business. This comprehensive 10-year monthly Excel financial model template offers an ... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.5
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 1.5

Trucking Company Financial Model
Embrace the road ahead, where every mile traveled isn’t just a journey—it’s a commitment to keeping the gears of the global economy turning. Sta... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.2
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1.2

Crypto Trading Platform – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model presenting an advanced 5-year financial plan of a Crypto Trading Platform allowing customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital curr... read more
- Excel Financial Model – $139.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Truck Rental Company Financial Model
This detailed 10-year monthly Excel template is specifically designed to formulate a business plan for a Truck Rental Business. It employs a thorough ... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 2.3
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 2.3

Kayak Boat Rental Business Model
Dive into the future of your kayak boat rental business with our cutting-edge 10-year monthly financial model, tailored to empower entrepreneurs and b... read more
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version .5

Event Organizer Business Model Template
Elevate your event planning business to new heights with our state-of-the-art Event Organizer Business Financial Model Template in Excel. The Excel sp... read more
- Event Organizer Template - Full Excel – $129.95 Version 1.4
- Event Organizer Template PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1.4

Gas / EV Charging Station 10-year Financial Forecasting Model
This model is adaptable and useful for a Gas Station, an EV Charging Station, or a combination of both types of Stations. The model is coherent, easy ... read more
- Full Open Excel – $50.00 Version 7
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 7
Gantt Chart Template: Intuitive and Innovative Planning Tool
Very simple to use, intuitive and innovative planning tool/Gantt Chart
- Gantt Chart Tool – $20.00 Version 1

Student Accommodation / Village Development Model – 20 years
This Student Accommodation 20-year Development Model (hold and lease) will produce 20 years of Three Statement Analysis, Re-valuations and the consequ... read more
- Excel Full Open – $50.00 Version 7
- PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 7

Motorboat Rental Business Financial Model
Dive into the heart of financial planning with our Motorboat Rental Business Financial Model, designed to propel your venture into uncharted waters wi... read more

Webinar Organizer Business Plan Template
Discover the key to financial success in your webinar ventures with our Webinar Organizer Business Plan Template. This webinar business template is an... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.4
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1.4

Paddle Boat Rental Business Model
The Paddle Boat Rental Business Financial Model is a pivotal tool for entrepreneurs venturing into the leisure and tourism industry. Crafted with prec... read more

Party Planning Business Financial Model
Introducing the Party Planning Business Financial Model – Your Ultimate Tool for Flawless Financial Management in Event Planning! In a highly person... read more
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 1.4

Tennis Court and Club Development – 10-year Financial Forecasting Model
Introducing our Tennis Courts and Club Financial Forecasting Model – your winning strategy for tennis court and club development. With unmatched coh... read more
- Full Open Excel – $49.00 Version 8
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 8

Business Plan on Two Pages
Simple but effective business plan template - on two pages.
- Business Plan Template – $32.00 Version 1

Gym and Fitness Club 10 year Financial Forecasting Model
Introducing our indispensable 10-Year Excel Financial Forecasting Model, a vital asset for gym and fitness club owners navigating the complexities of ... read more
- Full Open Excel – $40.00 Version 8
- PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 8

Three Statement Financial Model Template
The three statement financial model template offers a fundamental Excel template designed to project the three key financial statements over the next ... read more
- Free Excel Version – $0.00 Version 1.1

Squash Court and Club Dynamic Financial Model 10 years
Introducing our Squash Courts and Club Financial Forecasting Model – a game-changer for aspiring squash enthusiasts and club developers. With unpara... read more
- Free PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 8

Self-Storage Park Development Model
This Self-Storage Park development model will produce 20 years of three-statement analysis and valuations. There is a sheet focused on the Investor An... read more
- Free PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 7
McKinsey 7S Model Excel Template
Originating in the late 1970s by consultants at McKinsey & Company, the McKinsey 7S framework is a strategic management tool designed to align sev... read more
- Excel Template – $39.00 Version 1

Surfboard Rental Business Financial Model
Surfing is not just a sport—it's a lifestyle booming globally. With eco-tourism on the rise and outdoor adventures in high demand, now's the time to... read more

Manpower Planning and Analysis Model
The Manpower Analysis Model was designed to equip HR managers and analysts with a tool to control the transition of a workforce from one year to anoth... read more
- Excel Model – $50.00 Version 7
- Model Manual – $0.00 Version 7

Brandy Distillery Business Financial Model
Discover the ultimate Brandy Distillery Business Financial Model, meticulously designed to provide 10-year comprehensive insights and strategies for y... read more

3-Statement Financial Model
3-year financial model that is specially designed for early-stage companies.
- 3-Statement-Excel-Model-with-5-year-Forecast.xlsx – $39.00 Version 1

E-Commerce Startup Company (5-year) Financial Forecast Model
By developing a detailed 5-year dynamic financial forecast model for a e-commerce startup, founders, investors, and stakeholders can gain insights int... read more
- Excel Model – $70.00 Version 1
- PDF Model – $0.00 Version 1

Cider Distillery Financial Model
With its longstanding tradition and swiftly growing global demand, the cider industry offers a lucrative opportunity for investors looking to tap into... read more
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 5.5
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Model
Business Model Vs Business Plan – What is the Difference?
Do you want to know the difference between a and a business plan? If YES, here is a detailed comparison and analysis and how each is used. A business plan and a business model look amazingly similar like two peas in a pod, but they are equally different, just like two peas in a pod. They are both part of each other but play different roles thus making the line between them seem dim.
A business plan and a business model both contain , customer retention strategy, revenue generation strategies, and overall, they are used to outline the vision of the company. So what then differentiates a business plan from a business model and how can you make a clear distinction of both?
Business Model Vs Business Plan
What is a business model.
A business model is a company’s outlined plan for making profit. It identifies the products or services the business will sell, the target market it has identified , and the expenses it anticipates. A business model also shows the destination of the business, how it is meant to work, and what it is meant to become.
A business model ascertains how your business makes money. It identifies the services that your customers value and shows how funds are generated for the services your business renders to your customers. A small business can have more than one method of generating income, and it is the duty of the business model to simplify the money process by focusing on the largest income generator.
For instance, a gas station sells gas to customers, but it also provides other services such as a car wash, lube station, etc. The business model only recognizes the majority income generator, which is the sale of gas. Therefore, the business model will reflect the sale of gas to the customer, which generates income at the time of the customer’s purchase.
The business model summarily simplifies and makes revenue-generation easy to understand by focusing on the key generator, highlights exactly how you intend to acquire, retain, and service your customers. The business model can come in different distinct models like:
- Franchise model
- Direct sales model
- Advertising model
- Subscription based model
- Lowcost model
- Freemium model
- Affiliate model
- Production model
The business model is basically at the center of the business plan, as it describes how the company is positioned within its industry’s value chain, and how it organises its relations with its suppliers, clients, and partners in order to generate profits. The business plan translates this positioning in a series of strategic actions and quantifies their financial impact.
What is a BUSINESS PLAN
A business plan is a formal written document that contains business goals, the methods on how these goals can be attained, and the time frame within which these goals need to be achieved. A business plan acts like a GPS. It shows you the roadmap of how you intend to get to your destination as a business person.
It highlights the market opportunities you want to take advantage of, the existing competition, the strength and experience of your team, a detailed description of the products and services you intend to offer, and a roadmap that shows exactly how you intend to execute your plans in the market.
A business plan is a document presenting the company’s strategy and expected financial performance for the years to come.
The business plan provides the details of your business. It takes the focus of the business model and builds upon it. It explains the equipment and staff needed to meet the details of the business model. It also explains the marketing strategy of your small business, or how your business will attract and retain customers, and deal with the competition.
Furthermore, the business plan explains the financial stability of your small business at a particular point in time, as well as in the forecasted future. Overall, the business plan supports the business model and explains the steps needed to achieve the goals of that model
The business plan pays close attention to your goals, projects the cash flow, profits or losses, and ultimately shows how long and what would be required to enable the business break-even.
A sample structure of a business plan is seen below:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Service or Product Line
- Market Analysis & Strategies
- Organization & Management
- Funding Request
- Financial Assumptions
- Financial Projections
Differences Between a Business Plan and a Business Model
Some of the major differences between a business plan and a business model are outlined thus;
- A business model aims at highlighting the profit making potentials of a business, while a business plan highlights every aspect of the business.
- The business plan explains in details the steps needed to achieve the goals of your business model.
- Another difference is that business plans are usually written at the beginning of a business or a business initiative, while a business model is relevant at any time, and can be written at any time.
- Again, business models are less expensive to put together, and may represent a fictional future goal. As a goal, they may be both complete and entirely unprofitable or even infeasible, quite unlike your business plan.
- A business model is centered around Value; while business plan is centered around Resources. The business plan thus lays out how to manage these resources over time to materialize the business model, grow and scale the business.
- A model explains how you will make money: for example, by selling advertising, by earning a commission, by adding a markup to services, working with partners, selling direct, charging by the hour, with additional services, etc. While a business defines specific activities, it includes timeframes, budgets, owners, dependencies and impact.
More on Business Model

Present with Flair: Dynamic Apps Like Google Slides

How to use JavaScript localStorage

Party Planning Apps Like Evite for Your Next Event

How to parse JSON with JavaScript
- Project Management
Business Model Vs Business Plan: What’s The Difference
Sculpting success in the realm of commerce hinges on two critical blueprints: the business model and the business plan . As if peering through a dual-lens, one unveils the anatomy of value creation, while the other charts a course for achieving it. This isn’t about mere documents; it’s the lifeblood of strategic foresight and operational vision.
Here’s the crux: although they waltz together in strategic symbiosis, these entities each spin a unique narrative of your venture’s voyage. One sketches the architecture of your enterprise, laying bare the revenue streams and value proposition.
The other, a meticulous roadmap, presents meticulous market analysis, financial projections, and the operational plan set to navigate the turbulent tides of commerce.
By journey’s end, you’ll not just differentiate between the two but harness their combined power.
Delve into concepts like competitive advantage, customer segmentation, and scalability. Decode the mesmerizing narrative behind a robust strategic planning foundation. Sales forecasting, funding requirements, investor pitch decks.
The differences between business model vs business plan
| A framework for creating economic value and capturing a portion of that value. | A formal document detailing a business’s objectives, strategies, target market, and financial forecasts. | |
| To define how a company creates, delivers, and captures value in economic, social, cultural, or other contexts. | To guide management in running the business and to persuade external parties, like investors, to fund the business. | |
| – Value proposition – Customer segments – Channels – Revenue streams – Cost structure | – Executive summary – Market analysis – Organization and management plan – Sales strategies – Financial projections | |
| Typically more flexible, subject to adjustment as the company grows or market conditions change. | Tends to be a more rigid document, often used for a specific purpose, like seeking investment or a bank loan. | |
| Primarily internal; used by founders and management to understand and operate the business. | Both internal management and external stakeholders, including investors, banks, and potential partners. |
The business model is the foundation of a company, while the business plan is the structure. So, a business model is the main idea of the business together with the description of how it is working.
The business plan goes into detail to show how this idea could work. A business model can also be considered the mechanism that a company has to generate profits. At the same time, the business plan also does its part in being the way a company can present its strategy. It is also used to show the financial performance that is expected for the near future.
Comparing how business models and business plans work to help you in different ways is important. A business model can help you be sure that the company is making money. It helps to identify services that customers value. It also shows the reciprocation of funds for the activity that a business renders to its customers.
Any business can have different ways of generating income, but the goals of the business model should aim to simplify the money process. It does this by focusing on the large income generators.
So, we now understood that a basic business model is a gateway to show how an organization is functioning. A business plan is a document that shows the strategy of an organization together with the expected performance details.
We can find the details of a company when we check its business plan. What it does is offer more info about the business model. It does this by explaining the teams needed to meet the demand of the business model. It explains the equipment needed, as well as resources that need to be obtained to start creating. Explaining the marketing goals, and how the business is going to attract and retain more customers over the competition , will be part of the model.
Another interesting thing when it comes to comparing business models and business plans is that they cannot function without each other. Just remember this, the business model is going to be the center of the business plan.
Business plan
When comparing using a business model versus a business plan, we also need to understand each one better to draw some final conclusions. One of the first goals of a company could be to define its business model.
The business plan is going to be the detailed part that includes all the information and steps like Mayple’s marketing plan template, organization, products or services, sales plan, business proposal for investors , and so on. Some useful questions that you can use when developing your business plan are:
- What do we have now?
- What do we want to have in the future?
- What do we need in order to be there?
Business Model
The Best Project Management Software for Mac

Gap Analysis: What It Is And Why It’s Important

How Virtual Teams Can Work Efficiently in Large Companies

What Is an Agile Team And How To Create One
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Is a Business Model?
- Andrea Ovans

A history, from Drucker to Christensen.
A look through HBR’s archives shows that business thinkers use the concept of a “business model” in many different ways, potentially skewing the definition. Many people believe Peter Drucker defined the term in a 1994 article as “assumptions about what a company gets paid for,” but that article never mentions the term business model. Instead, Drucker’s theory of the business was a set of assumptions about what a business will and won’t do, closer to Michael Porter’s definition of strategy. Businesses make assumptions about who their customers and competitors are, as well as about technology and their own strengths and weaknesses. Joan Magretta carries the idea of assumptions into her focus on business modeling, which encompasses the activities associated with both making and selling something. Alex Osterwalder also builds on Drucker’s concept of assumptions in his “business model canvas,” a way of organizing assumptions so that you can compare business models. Introducing a better business model into an existing market is the definition of a disruptive innovation, as written about by Clay Christensen. Rita McGrath offers that your business model is failing when innovations yield smaller and smaller improvements. You can innovate a new model by altering the mix of products and services, postponing decisions, changing the people who make the decisions, or changing incentives in the value chain. Finally, Mark Johnson provides a list of 19 types of business models and the organizations that use them.
In The New, New Thing , Michael Lewis refers to the phrase business model as “a term of art.” And like art itself, it’s one of those things many people feel they can recognize when they see it (especially a particularly clever or terrible one) but can’t quite define.
- AO Andrea Ovans is a former senior editor at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center
- Start free trial
Business Model vs. Business Plan: Key Differences
A business model is your core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers; a business plan outlines how you’ll execute your goals.

“A goal without a plan is just a wish,” wrote famed French author and aviator Antoine de Saint-Exupéry. These words ring especially true in modern business planning. As an entrepreneur, planning is a skill that can help ensure your success.
Business models and business plans are both integral aspects of starting a business. But what are the similarities and differences between the two, and when is the right time to think about each for your company? Here’s a breakdown.
Business model vs. business plan: What’s the difference?
A business model is a company’s core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers. They usually include the customer value proposition and pricing strategy. A business plan outlines your business goals and your strategies for achieving them.
The two documents have a few critical differences, namely their structure and application. But the topics they deal with—such as a company’s finances, goals, and operational framework—are largely the same.
Financial projections
- How they’re similar: Both business models and business plans provide an in-depth description for how a company will generate profits.
- How they’re different: A business plan includes financial performance details relevant to both internal and external stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, or potential business partners. Alternatively, a business model describes your value proposition —what product or service a business will offer and why customers should buy it—as well as the target market .
Operational details
- How they’re similar: Both business models and business plans include overarching information about how a company plans to operate, including components such as distribution channels and management structure.
- How they’re different: Business models explain the fundamental structure of a company, such as how it plans to create and deliver value to customers, while business plans get into the actionable details of how to achieve a company’s operational goals.
- How they’re similar: Business models and business plans are used to outline the goals, strategies, and operations of a business.
- How they’re different: A business plan generally incorporates a business model, explaining how the model should be implemented and executed to achieve the business's goals.
4 examples of business models
- Brick-and-mortar
- Direct to consumer
- Subscription
There are dozens of different templates that you, as a business owner, can draw from when building out your operation. Here are four examples of basic business models:
1. Brick-and-mortar
One of the most common retail business models, brick-and-mortar , includes a traditional physical storefront (or a pop-up shop ) selling either business to business (B2B), in the form of wholesale goods, or business-to-consumer (B2C). Although overhead such as rent is a consideration in this model, physical locations offer the competitive advantage of tapping in-person customers and building brand awareness through exposure.
2. Direct to consumer
Direct to consumer (D2C or DTC) is a retail model that allows your business to sell straight to customers, rather than going through a third-party retailer such as Amazon. There are numerous benefits to D2C, including higher profit margins because you don’t have an intermediary taking a cut. However, the main disadvantage of D2C is that you have to develop your own customer base without the help of an established platform.
3. Subscription
Projections indicate that the subscription ecommerce market has boomed in recent years and is set to hit nearly $900 billion in 2026. The subscription business model includes charging customers a recurring fee for a good or service—anything from home-delivery meal kits to media streaming. Subscription services are dependent on customer relationships and customer loyalty , but they can offer businesses a more predictable revenue stream.
4. Freemium
Under a so-called freemium model, consumers can access part of the business’s goods or services free of charge, but must pay to receive unlimited access to everything the company has to offer. Examples include many media organizations, such as The New York Times, which offers several free articles before requiring a subscription, or audio streaming service Spotify, which has a free version with ads, as well as a paid version without.
What's in a business plan?
A comprehensive business plan details many aspects of your company, including everything from marketing strategies to finances to the legal ownership structure. Here are a few key sections to include when writing your business plan.
- Executive summary . The executive summary includes your mission statement , an explanation of your core values and goals, a brief company history, and descriptions of the products or services you plan to provide to a potential or existing market.
- Organizational structure. Management hierarchy, as well as their roles and responsibilities, would be included in this section.
- Marketing and sales. How do you plan to market your offerings? Who is your target market? What is your pricing strategy and how does it compare to that of your competitors? How do you plan to acquire and retain customers? All these questions should be answered in this section.
- Expected financial performance. This includes projected revenue streams, cash flow management , cost structure, expenses, and anticipated profitability. It typically covers from one to five years in the future.
- Business operations. This section covers everything about the day-to-day running of your business, including your storefront (if you have one), inventory management , supply chain, and production.
Business models vs. business plans FAQ
Which comes first, a business model or business plan.
A business model typically comes before a business plan . Business plans often include the business model, and then explain in detail how you plan to achieve the goals set out in a model.
How can a company test and validate its business model before creating a business plan?
Market research, financial modeling, and even seeking out expert advice or consulting are all ways to review and validate your operation’s business model before developing a business plan.
How often should a company review and update its business plan?
A business should be prepared to update its business plan dynamically, based on changes in the market, shifts within the operation, or new investment or opportunities. Many businesses update their plans annually
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 25, 2024
Aug 23, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
- A Comprehensive Guide to Business Ideas: From Conception to Launch
Updated: August 25, 2024 · Reviewed by: Ahmad Nasrudin

This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we may earn a small commission if you purchase through our links. This helps support our work.
Are you ready to turn your business idea into a reality? This comprehensive guide will provide you with the essential information and tools to help you transform your concept into a thriving enterprise.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting your journey, understanding the fundamentals of business ideas is crucial. We’ll explore everything from generating ideas and evaluating their potential to developing a solid business plan and securing funding.
Understanding Business Ideas
What is a business idea .
A business idea is more than just a concept; it’s the spark that ignites your entrepreneurial journey. It’s the foundation upon which you build your entire business, serving as the guiding light for your decisions and actions. Think of it as the seed you plant in the fertile ground of the marketplace, with the potential to grow into a thriving enterprise.
How do I come up with a business idea?
There are countless ways to generate business ideas. Here are a few proven methods:
- Identify your passions and interests: What are you truly passionate about? What skills do you possess naturally? These can often lead to fulfilling business ventures.
- Solve a problem: Look around your community or industry and identify problems that need solving. Offering a solution to a real-world problem can be a powerful business idea.
- Analyze market trends: Keep an eye on emerging trends and identify opportunities. Understanding what people are looking for can help you create products or services that meet their needs.
- Brainstorm with others: Collaborate with friends, family, or colleagues to spark new ideas. Diverse perspectives can lead to innovative concepts.
- Use online resources: Numerous online tools and resources are available to help you brainstorm business ideas. Explore platforms like Reddit, Quora, and online forums to discover what people are talking about.
What are the key elements of a successful business idea?
A successful business idea is more than just a concept; it’s a carefully crafted plan that has the potential to generate profit and thrive in the marketplace. To be successful, your business idea should possess the following key elements:
- Feasibility: Your idea should be practical and achievable. It should be grounded in reality and have a clear path to implementation.
- Profitability: A successful business idea generates revenue and profit. To assess profitability, consider potential market demand, pricing strategies, and cost structures.
- Scalability: Your idea should have the potential to grow and expand over time. A scalable business can increase its operations and revenue without significant additional effort.
- Uniqueness: Offer something new or different to the market. Your business idea should provide a unique value proposition differentiating it from competitors.
- Sustainability: Your idea should be able to withstand market changes and competition. Consider the long-term viability of your business and its ability to adapt to evolving trends.
What is the difference between a business idea and a business opportunity?
While the terms “business idea” and “business opportunity” are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference between them. A business idea is a concept for a new product or service. The initial spark of inspiration leads to a potential business venture.
A business opportunity is a situation that presents a profit potential. It’s a favorable circumstance or set of conditions that can be exploited to create a successful business.
Essentially, a business idea is the seed, while a business opportunity is the fertile ground for that seed to grow and flourish.
Free Up Your Learning Journey
Note: While those offer many free courses, some might require payment for certificates or additional materials. Please check individual course details.
Can I have multiple business ideas at once?
Absolutely! It’s not uncommon for entrepreneurs to have a variety of ideas brewing in their heads. While it’s tempting to pursue all of them, it’s often more effective to focus on one idea at a time.
Why should I focus on one business idea at a time?
- Limited resources: Starting and running a business requires significant time, energy, and financial resources. Spreading yourself too thin across multiple ventures can lead to burnout and a lack of focus.
- Increased risk: Diversifying your efforts can increase your overall risk. If one business fails, it won’t necessarily jeopardize the others. However, it’s important to allocate your resources wisely to ensure the success of your primary venture.
How can I protect my business idea?
Protecting your business idea is crucial to prevent others from stealing your concept and benefiting from your hard work. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain confidentiality: Keep your idea secret until you’re ready to share it with trusted individuals or investors. Avoid discussing your idea openly in public places or with strangers.
- Document your idea: Create a detailed written record of your business idea, including its origin, key features, and potential market. This documentation can be valuable evidence if you need to prove ownership.
- Seek legal advice: Consult with an intellectual property attorney to discuss options for protecting your idea. Depending on the nature of your concept, you may consider obtaining a patent, copyright, or trademark.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage multiple business ideas and protect your intellectual property. Remember, a well-executed business idea is far more valuable than a scattered collection of concepts.
Evaluating Business Ideas
How can i evaluate the potential of a business idea .
Conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if your business idea is a viable venture. This involves assessing various factors, including market demand, competition, and financial feasibility.
Market Research
- Understand your target market: Identify the specific group of people who are most likely to purchase your product or service.
- Assess market demand: Determine if there is a sufficient demand for your offering. Use surveys, focus groups, and market research data to gauge interest.
- Analyze market trends: Identify any relevant trends or changes in your industry that could impact your business.
Competitive Analysis
- Identify competitors: Determine who your direct and indirect competitors are.
- Analyze their strengths and weaknesses: Evaluate your competitors’ products, pricing, marketing strategies, and customer satisfaction.
- Identify your unique selling proposition: Determine what sets your business apart from the competition.
Financial Analysis
- Develop a financial projection: Create a detailed financial plan that includes projected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Assess profitability: Determine if your business idea can generate sufficient profit to cover costs and achieve your financial goals.
- Consider funding options: Evaluate various funding sources, such as loans, investments, or personal savings.
Feasibility Study
- Assess technical feasibility: Determine if you have the necessary skills, resources, and technology to implement your idea.
- Evaluate economic feasibility: Consider your business’s potential costs and benefits, including startup costs, operating expenses, and potential revenue.
- Consider legal feasibility: Ensure your business idea complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can better understand your business idea’s potential and make informed decisions about whether to pursue it. Remember, a well-thought-out evaluation is crucial for increasing your chances of success.
How can I identify my target market?
Your target market is the specific people most likely to purchase your product or service. Identifying your target market is crucial for effectively marketing your business and tailoring your offerings to meet their needs.
Here are some strategies to help you identify your target market:
- Create customer personas: Develop detailed profiles of your ideal customers, including their demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Analyze your existing customers: If you have an existing business, analyze the characteristics of your current customers to identify patterns and trends.
- Conduct market research: Use surveys, focus groups, and interviews to gather data about potential customers and their preferences.
What is a value proposition?
Your value proposition is a clear statement of your product or service’s benefits to your target market. It should be compelling and differentiate your business from competitors.
A strong value proposition should:
- Highlight unique benefits: Clearly articulate the specific advantages that your product or service provides.
- Address customer needs: Demonstrate how your offering solves a problem or fulfills a desire for your target market.
- Be concise and memorable: Keep your value proposition short, sweet, and easy to remember.
How can I conduct market research?
Market research is essential for gathering data about your target market, competitors, and industry trends. Here are some common market research methods:
- Surveys: Create surveys to collect quantitative and qualitative data from potential customers.
- Focus groups: Conduct group discussions with potential customers to gather insights and feedback.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews with individuals in your target market to gain deeper insights.
- Online research: Use online tools and databases to gather information about market trends, industry statistics, and competitor analysis .
Understanding your target market and developing a compelling value proposition can increase your chances of success in your business venture.
Turning Your Business Idea into a Reality
How do i turn my business idea into a reality .
Once you have a promising business idea, you need to take the following steps:
- Develop a business plan: Create a detailed business plan that outlines your business strategy, financial projections, and marketing plan.
- Secure funding: Determine your funding needs and explore different financing options, such as loans, grants, or investments.
- Choose a legal structure : Decide on the legal structure of your business, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or limited liability company (LLC).
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses: Obtain any permits or licenses required to operate your business.
- Build your team: Assemble a team of talented individuals who can help you execute your business plan.
- Launch your business: Launch your business and start generating revenue.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines your business strategy, goals, and financial projections. It serves as a roadmap for your venture, guiding your decisions and attracting potential investors.
A well-crafted business plan typically includes the following sections:
- Executive summary: A concise business overview, including your mission, vision, and key value proposition.
- Market analysis: A detailed analysis of your target market, competition, and industry trends.
- Company description: A description of your business, including its legal structure, ownership, and management team.
- Organizational structure: A breakdown of your company’s organizational chart and responsibilities.
- Marketing and sales plan: Your strategy for promoting your products or services and generating sales.
- Financial projections: Your projected income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
What is a business model?
A business model describes how your business will generate revenue. It outlines the core activities, resources, and partnerships necessary to create, deliver, and capture value.
There are many different business models, including:
- Product-based: Selling physical products to customers.
- Service-based: Providing services to customers, such as consulting, education, or healthcare.
- Subscription-based: Offering a subscription to a product or service, such as a software application or streaming service.
- Freemium: Offering a basic version of a product or service for free and charging for premium features.
- Advertising-based: Generating revenue through advertising on a platform or website.
Understanding your business model is essential for developing a sound business plan and attracting investors. It helps you clarify your value proposition, identify your target market, and develop a sustainable revenue stream.
What is a business idea pitch?
A business idea pitch is a concise and persuasive presentation that you use to convince investors or potential partners to support your business. It’s your opportunity to showcase your idea, its potential, and why it’s worth investing in.
A successful pitch should be:
- Clear and concise: Clearly articulate your business idea, its unique value proposition, and the problem it solves.
- Persuasive: Use compelling storytelling and evidence to demonstrate the potential of your business.
- Memorable: Create a lasting impression by delivering a strong and engaging presentation.
How can I find funding for my business idea?
Various funding sources are available to support your business, depending on your specific needs and circumstances. Here are some common options:
- Bootstrapping: Using your own savings or personal funds to finance your business. This approach is common for many entrepreneurs but can limit your growth potential.
- Angel investors: Individuals who invest their own money in early-stage businesses. Angel investors often provide capital in exchange for equity.
- Venture capital firms: Companies that invest in high-growth businesses. Venture capital firms typically invest larger sums of money and expect higher returns.
- Small business loans: Loans from banks or other financial institutions specifically designed for small businesses. These loans can be a valuable funding source, but they often require collateral.
- Crowdfunding: Raising funds from a large number of people through online platforms. Crowdfunding can be a great way to generate initial capital and build a community around your business.
When seeking funding, a well-crafted business plan and a compelling pitch are important. Building relationships with potential investors can also increase your chances of securing funding.
What is the role of a business plan in securing funding?
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting investors and securing funding. It serves as a comprehensive roadmap for your business, demonstrating your understanding of the market, business strategy, and financial projections.
Investors seek businesses with a clear vision, a solid market opportunity, and a sound financial plan. A well-written business plan can help you:
- Convince investors of your idea’s potential: Demonstrate the market demand for your product or service and your ability to capitalize on it.
- Showcase your expertise: Highlight your industry knowledge and your team’s capabilities.
- Provide a financial roadmap: Present your financial projections and demonstrate your understanding of your business’s financial needs.
What are some common mistakes made by new entrepreneurs?
While starting a business can be exciting, it’s important to avoid common pitfalls that can hinder your success. Here are some common mistakes made by new entrepreneurs:
- Underestimating the time and effort required: Running a business is demanding and time-consuming. Be prepared to dedicate significant effort to your venture.
- Lack of a solid financial plan: A sound financial plan is essential for managing your business’s finances and ensuring its long-term viability.
- Inadequate market research: Conduct thorough market research to understand your target market, competition, and industry trends.
- Neglecting networking: Building relationships with other entrepreneurs, industry professionals, and potential customers can be invaluable for your business’s growth.
What is the importance of networking for a new business?
Networking is essential for building relationships, gaining valuable insights, and expanding your business network. Here are some benefits of networking:
- Connecting with potential customers: Networking can help you identify and reach out to potential customers.
- Finding partners and collaborators: Building relationships with other businesses can lead to partnerships, collaborations, and shared resources.
- Gaining industry insights: Networking with industry professionals can provide valuable insights into market trends, best practices, and emerging opportunities.
- Finding mentors and support: Connecting with experienced entrepreneurs can offer guidance, mentorship, and support.
By avoiding common pitfalls and actively engaging in networking, new entrepreneurs can increase their chances of success.
Additional Resources
- Small Business Administration (SBA) : The SBA provides resources and support for small businesses, including business planning, financing, and training.
- Local Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs) : SBDCs offer free business counseling and training services.
- Online resources: Many online resources, including blogs, articles, and online courses, are available to help you learn more about starting a business.
Following these steps and utilizing the available resources can turn your business idea into a successful reality.
Start building your dream business today. Click here to learn more.
- Business Idea: How to Find and Evaluate It Before Launching Your Business
- Good Business Idea: Launch Your Entrepreneurial Journey
- The Ultimate Guide to Entrepreneurship and Starting a Business
- Business Plan: Guide for Startups & Investors (Funding, Strategy)
- Where Do Entrepreneurs’ Business Ideas Come From?
About Ahmad Nasrudin
Introverted writer with a passion for storytelling. Leveraged analytical skills from financial background (equity research, credit risk) at a leading rating agency to enhance writing with a unique statistical and macroeconomic perspective. Learn more about me
- Business Size: How Business Scale Shapes Success (Importances, Measurement, Classification)
- From Idea to Implementation: Essential Business Planning Strategies
- Top-Level Management: Examples, Roles and Responsibilities, Skills
- Positive and Negative Effects of Industrialization

- Business Coach
- Career Coach
- Leadership Coach
- Stakeholder Centered Coach®
- Goal & Development Planning
- Stakeholder Integration
- Action Plans
- Coaching Programs
- Coach Matching
- Scheduling Software for Coaches
- Client Workspace
- Resource Library
- Team Engagements
- Subscription & Session Packages
- Showcase Page
- Invoicing & Payments
- Email Integration
- LinkedIn Intergration
- Contact Management
- Prospect Management
- Embedded Video Conferencing
- Professional Development Log
- Pricing Solopreneurs Pricing plans that help you grow and flourish as a solopreneur Businesses Agile pricing plans that keep up with your business’ needs
What’s the Difference Between Coaching and Training (Explained)

- Share this article
Table of Contents
Are you often confused about the distinction between coaching vs training?
You’ve probably heard the terms tossed around interchangeably. Understanding the clear distinction between coaching and training is vital. By recognizing these differences, you can craft development strategies that maximize potential and achieve outstanding results. Think of yourself as a seasoned mountain guide. Your clients are the climbers with the potential to conquer their peaks. Your job isn’t to do the climbing for them but to provide the expertise, equipment, and unwavering support needed to reach the summit.
Training is like equipping your climbers with essential gear. It’s about teaching them the fundamentals: how to use the ropes, ice axes, and harnesses safely and effectively. It’s laying the groundwork for their journey, ensuring they have the basic skills to navigate the mountain. But remember, while gear is essential, it’s the climber’s determination and skill that ultimately conquers the peak.
Still confused? Let’s clear up the confusion and take a brief look into it.
Coaching Vs Training
We see both coaching and training aim to foster growth, but they do it differently. Coaching is a personalized, ongoing process that focuses on individual development and goal achievement. It’s about exploring the strengths, identifying areas for growth, and creating a plan that aligns with the objectives.
Training , in contrast, is typically a structured approach designed to teach specific skills or knowledge to groups. It’s often more focused on providing uniform information and techniques to all participants.
Coaching:
- Enhances existing skills & developed self-awareness: Your role is to refine your clients’ existing skills and guide their growth through fostering self-awareness and personal insights.
- Personalized: Your coaching typically involves individual sessions designed specifically to meet your client’s needs and goals.
- Follow agenda: The process is flexible, with sessions tailored to your client’s goals and pace. This allows for a personalized approach to their development.
- Long-term: You provide ongoing support, helping them work towards their objectives and adjusting strategies as needed.
Training:
- Develop specific skills : Your training should impart specific techniques or processes relevant to your job or personal development.
- Knowledge transfer: Your sessions often involve multiple participants and aim to equip the entire group with the same essential knowledge.
- Predetermined agenda: You lead the session based on a set curriculum, guiding participants through the material in a structured manner.
- Short-term: Your training sessions should have a clear structure with predetermined content and objectives, typically delivered over a specific timeframe.
Key Characteristics of Training and Coaching
The following table outlines the key characteristics of each approach, highlighting their unique focus and outcomes:
| Aims at a uniform experience for group participants | Focuses on individual goals and tailored feedback |
| Facilitates organizational goals and knowledge transfer | Encourages self-awareness and behavior change |
| Emphasizes teaching new information and basic skill | Enhances pre-existing skills with personal and ongoing support |
| Improvement assessed through feedback, often intangible |
When to Use Coaching Vs Training
As a coach, your role is crucial in determining whether coaching or training is the best approach for your client. To make an informed decision, you need to delve deep into their specific challenges and goals:
When to consider coaching?
- Performance issues: If your client is struggling to achieve desired results despite possessing the necessary skills, coaching can be a powerful tool. By exploring underlying motivations, beliefs, and behaviors, you can help them unlock their potential.
- Career development: Career coaching can guide individuals in defining their career aspirations, building confidence, and creating a roadmap for success.
- Leadership challenges: If your client is facing leadership hurdles, leadership coaching can help them develop their emotional intelligence, build strong teams, and enhance their overall leadership effectiveness.
- Change management: When your client is navigating organizational changes, coaching can provide support, guidance, and accountability to help them adapt successfully.
When should you use training?
- Skill gaps: If your client lacks specific technical skills, software proficiency, or process knowledge, training is essential to equip them with the necessary foundation.
- Knowledge transfer: When sharing critical information about company policies, procedures, or industry best practices, training is the most efficient method.
- Compliance requirements: To ensure adherence to regulations or standards, training is often mandatory.
Key questions for your client
To clarify the situation, consider asking your client these questions:
- What specific challenges are you facing?
- What are your desired outcomes?
- Do you feel you have the necessary skills and knowledge to achieve your goals?
- Are you struggling to apply your existing skills effectively?
By understanding their responses, you can determine whether coaching, training, or a combination of both is the most appropriate solution.
Complementary Nature of Training and Coaching
Training and coaching have a complementary nature. Training provides the building blocks – knowledge and skills. Coaching is the architect, shaping these blocks into a personalized strategy. Together, they transform potential into performance.
Your clients are facing unprecedented challenges in today’s hyper-competitive landscape. Technical skills alone are no longer sufficient to drive success. To truly thrive, they need a holistic development that combines solid foundational knowledge with the essential soft skills that drive career advancement.
Coaching is the key to unlocking your clients’ full potential. It’s the catalyst that ignites passion, creativity, and leadership. While training undoubtedly builds the essential knowledge base, coaching is the spark that transforms individuals into high-performing, engaged professionals.
By investing in both coaching and training, you’re empowering your clients to achieve extraordinary results. You’re not just building a team; you’re cultivating a culture of high performance where individuals reach their full potential and drive your business forward.
Also read: A Detailed Guide to a 12-Week Coaching Program Template
Coaching and training are indispensable tools in your arsenal for fostering personal and professional growth. While training serves as the foundation for building skills and knowledge, coaching is the catalyst for igniting self-awareness and goal-setting. By strategically combining these two approaches, you create a potent formula for achieving enduring success.
Digitize your operations with Simply.Coach , an all-in-one coaching management platform that manages schedules, tracks progress, and delivers effective training at your ease.
Book a free trial session with us today!
How to Create and Maintain a Coaching Log Template
How to Become a Certified Executive Functioning Coach?
6 Best Mindset Coach Certifications and Training Programs (2024)
Strategies for Conducting Great One-on-One Coaching Sessions
The Ultimate Guide to Executive Coaching Pricing in 2024
Crafting Effective Payment Policies for Your Coaching Business: A Guide with Examples
About Simply.Coach
Simply.Coach is an enterprise-grade coaching software designed to be used by individual coaches and coaching businesses. Trusted by ICF-accredited and EMCC-credentialed coaches worldwide, Simply.Coach is on a mission to elevate the experience and process of coaching with technology-led tools and solutions.
Other Categories
- Business Coaching
- Career Coaching
- Coaching Business
- Coaching Enterprise
- Coaching Management Software
- Coaching Tools
- Executive Coaching
- Featured Blogs
- Independent Coaching
- International Blogs
- Leadership Coaching
- Life Coaching
- Relationship Coaching
- The Business of Coaching
- Therapy & Counselling
- Training & Development
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Why Simply.Coach
- Coach Reviews
- All-In-One Coaching Software
- Affiliate Program
- Refer and Earn
- Press Release
- Web Stories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Platform Status
- Business Coach Software
- Life Coach Software
- Career Coach Software
- Leadership Coach Software
- Pricing for Solopreneurs
- Pricing for Businesses
- Coaching Software Comparison
- Client Management
- Business Management
- [email protected]
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Retirement Planning
SIMPLE IRA vs. SIMPLE 401(k): Knowing the Difference
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/denisepic__denise_a-5bfc262f4cedfd0026c01131.jpg)
SIMPLE IRA vs. SIMPLE 401(k): An Overview
Small business employers have a variety of choices if they want to offer a tax-advantaged retirement plan . It is essential to think about them carefully and review the options with financial and tax advisors .
For example, instead of a traditional 401(k) plan, a small business owner can opt for a SIMPLE 401(k) . They sound similar, but there are important differences between them that employers need to review. Or an employer could choose between a SIMPLE 401(k) and a SIMPLE IRA . These plans share many similarities, but they also have differences that could provide enough reason to choose one type of SIMPLE plan over the other.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing a retirement plan is one of the most important financial decisions a business owner will make for their business.
- The retirement plan not only allows the employer to claim a tax deduction for contributions but also serves as a means of attracting highly competent employees.
- Some plans are an administrative burden and can be quite costly to maintain.
- A small business owner who wants to avoid complex administration and limit costs may find SIMPLE plans attractive.
- Before choosing, the owner may want to review certain specifics, including the average age of the business's employees and whether they would prefer loans to be allowed under the plan.
A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) is a tax-deferred retirement savings account. SIMPLE accounts can be established by employers, including self-employed individuals .
To qualify, employers must have no more than 100 employees who have received at least $5,000 in compensation from the employer for the previous year. An employer who chooses a SIMPLE IRA is not allowed to maintain any other plan while maintaining a SIMPLE IRA.
Exceptions are allowed for employees covered under a collective bargaining agreement, and plans that cover these employees are disregarded for this purpose.
There is no age requirement for the SIMPLE IRA. Instead, any employee who earned at least $5,000 during any two preceding years and is reasonably expected to earn $5,000 in the current year must be allowed to participate in the plan.
For the SIMPLE IRA, an employer who elects to make matching contributions may choose to reduce the amount to one that is less than 3% but no less than 1% for two out of every five years. This option is not available for SIMPLE 401(k)s.
SIMPLE 401(k)
The SIMPLE 401(k) plan is a cross between a SIMPLE IRA and a traditional 401(k) plan and offers some features of both plans.
For both the SIMPLE IRA and the SIMPLE 401(k), eligible employers must have no more than 100 employees who have received at least $5,000 in compensation from the employer for the previous year. Employers cannot maintain any other retirement plan for employees who are eligible to participate in the SIMPLE 401(k).
However, the employer can choose to maintain a second retirement plan to cover those employees who are not eligible to participate in the SIMPLE 401(k) plan. No non-discrimination testing is required for either plan, and both plans are subject to the 60-day annual notification requirement.
The deadline to establish either plan is from January 1 to October 1 of the year, and this deadline allows employees to make salary-deferral contributions before year-end. To be eligible to participate in the SIMPLE 401(k) plan, employees may be required to perform service for at least one year and reach the age of 21.
Because the SIMPLE IRA is an IRA-based plan, loans are not allowed. On the other hand, an employer may include loans as a feature in a SIMPLE 401(k) plan. For employees who need to tap into their retirement assets when they are ineligible to receive distributions from the plan, loans can be an attractive plan feature.
For both the SIMPLE IRA and the SIMPLE 401(k) plans, all contributions are immediately 100% vested.
Special Considerations
Both plans permit the same type of contributions. Employees may make salary-deferral contributions, while employers may choose to make matching contributions to employees who make salary-deferral or non-elective contributions.
For the matching contributions, employers must contribute dollar for dollar up to 3% of the employee's compensation. For the non-elective contributions, employers must contribute 2% of the employee's compensation.
| Year | SIMPLE DEFERRAL Limit |
| 2005 | $10,000 |
| 2006 | $10,000 |
| 2007 | $10,500 |
| 2008 | $10,500 |
| 2009 | $11,500 |
| 2010 | $11,500 |
| 2011 | $11,500 |
| 2012 | $11,500 |
| 2013 | $12,000 |
| 2014 | $12,000 |
| 2015 | $12,500 |
| 2016 | $12,500 |
| 2017 | $12,500 |
| 2018 | $12,500 |
| 2019 | $13,000 |
| 2020 | $13,500 |
| 2021 | $13,500 |
| 2022 | $13,500 |
| 2023 | $15,500 |
| 2024 | $16,000 |
Workers age 50 or older by the end of the year can make additional catch-up contributions of $3,500, for a total of $19,500.
However, employer contributions for the SIMPLE IRA and the SIMPLE 401(k) are subject to different rules. As a result, the two plans will require/allow different employer contribution amounts. For instance, all employer contributions to a SIMPLE 401(k) are subject to the compensation cap (which is $330,000 for 2023, and $345,000 in 2024), while only non-elective employer contributions to SIMPLE IRAs are subject to the compensation cap. The following is an example of how this could affect the contributions that employees receive.
Example of a SIMPLE IRA
ABC Company established a SIMPLE for its employees and has elected to make a matching contribution to the plan for the 2023 calendar year. Jane, an employee, is eligible to participate in the plan. She receives compensation of $350,000 for the year from the company. Jane has decided to defer the maximum allowable amount of $15,500 ($16,500 for 2024) to the plan.
The amount Jane receives as an employer contribution is determined by the type of SIMPLE that ABC adopted:
- If ABC Company adopts a SIMPLE IRA, Jane may receive a matching contribution of $10,500 (3% of $350,000).
- If ABC Company adopts a SIMPLE 401(k), Jane would receive no more than $9,900 as a matching employer contribution. This is because ABC Company may consider no more than $290,000 of Jane's compensation for plan purposes due to IRS limits (3% of $330,000).
As stated earlier, the non-elective contribution is subject to the same compensation cap for both plans. Therefore, if ABC Company had elected to make non-elective contributions, Jane's contribution amount would be the same under both plans.
Internal Revenue Service. " SIMPLE IRA Plan FAQs ."
Internal Revenue Service. " SIMPLE IRA Plan ."
Internal Revenue Service. " 401(k) Plan Qualification Requirements ."
Internal Revenue Service. “ SIMPLE IRA Plan .”
Internal Revenue Service. " Choosing a Retirement Plan: SIMPLE 401(k) Plan ."
Internal Revenue Service. " 401(k) Limit Increases to $23,000 for 2024, IRA Limit Rises to $7,000 .”
Internal Revenue Service. " COLA Increases for Dollar Limitations on Benefits and Contributions .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/borrowfromrothira-cccabe3322274bf6acdd90239f7d0fb8.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
COMMENTS
By learning what exactly a business plan and business model are and how they work, you can gain a deeper understanding of the fundamentals of business operations. In this article, we explain the differences between a business model versus a business plan and provide common examples of business models.
A business model is the foundation of any business idea; it basically outlines how the concept offers value and potential for growth. Essentially, a solid business model ensures that the business will make money. A business plan, on the other hand, is the business owner's plan to put that model into action. It's much more detailed and ...
Ensuring coherence between the business model and business plan. Maintaining coherence between your business model and your business plan is necessary. For example, if a retail store decides to shift from a traditional brick-and-mortar model to an e-commerce model, this change of business model would need to be reflected in the business plan.
How a business plan and business model canvas inform business strategy. Avoid the trap of using the two terms interchangeably. As we've shown, the two have different focuses and purposes. The business model canvas (or our one-page plan template) is a great starting point for mapping out your initial strategy. Both are easy to iterate on as ...
A business model is the company's rationale and plans for making a profit. It explains how a company delivers value to its customers at a specific cost. A business model would include details about the company's products and services, its target market, and all expenses related to the operations and production.
Understanding the difference between a business model and a business plan is crucial for anyone diving into the world of entrepreneurship or looking to scale their business. Here are the key differences: Definition and Purpose: Business Model: A business model is an overarching concept that explains how a company creates, delivers, and captures ...
In the world of business, two terms often emerge as foundational elements to startup founders, seasoned entrepreneurs, and everyone in between: the Business Plan and the Business Model. Both are crucial, yet their roles, purposes, and impacts are distinct, and understanding these differences can mean the difference between the success and ...
A business model, on the other hand, is a business's rationale and plan for making a profit. If the business plan is a road map that describes how much profit the business intends to make in a ...
Business Model vs Business Plan: The difference. Understanding the difference between a business model vs business plan can help you more effectively communicate the core of your business to stakeholders and guide your strategic decisions. The business model focuses on the conceptual aspects of the business, showing the big picture of how value ...
A business model is a company's core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers. They usually include the customer value proposition and pricing strategy. A business plan outlines your business goals and your strategies for achieving them. The two documents have a few critical differences, namely their structure and ...
Few Major Differences between the Business Model & Business Plan. ... In general, the business model and business plan are completely different notions. The business model serves as the mechanism, defining the core components that generate the company's revenue streams and sustainable operations. In contrast business plan is a written ...
While the business model refers to a one-page representation of how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, the business plan is an in-depth description on a long textual document form about how your company is structured and plan to achieve strategic and financial objectives. This business plan is a document that contains every data ...
Business Model: A business model is a company's plan for how it will generate revenues and make a profit . It explains what products or services the business plans to manufacture and market, and ...
Aspect Business Model Business Plan; Definition: A Business Model is a strategic framework that outlines how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It focuses on the core components of a business's operations and revenue generation. A Business Plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details.
The truth is, they are different things with different purposes. The main difference between a business plan and business model is that a business plan outlines your goals and strategy to grow your company, while a business model shows you how to generate revenues. Read on to learn more about this subject, including what types of business ...
Understanding the differences between a business plan and a business model is essential for any entrepreneur aiming for success. While a business plan provides a detailed roadmap and strategic direction, the business model focuses on the specific ways to generate revenue. Both elements, though distinct, work together to guide a company towards ...
Business Plan Development: Once the business model has been validated, entrepreneurs can use it as a starting point to develop a detailed business plan. The plan will expand on the core elements ...
A business model is centered around Value; while business plan is centered around Resources. The business plan thus lays out how to manage these resources over time to materialize the business model, grow and scale the business. A model explains how you will make money: for example, by selling advertising, by earning a commission, by adding a ...
The major difference is that a business plan is a detailed document outlining the company's objectives, strategies, and financial projections. In contrast, a business model is a conceptual ...
Both internal management and external stakeholders, including investors, banks, and potential partners. The business model is the foundation of a company, while the business plan is the structure. So, a business model is the main idea of the business together with the description of how it is working. The business plan goes into detail to show ...
In The New, New Thing, Michael Lewis refers to the phrase business model as "a term of art.". And like art itself, it's one of those things many people feel they can recognize when they see ...
If the business plan is a road map that describes how much profit the business intends to make in a given period of time, the business model is the vehicle that gets you there. A model covers ...
A business model is a company's core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers. They usually include the customer value proposition and pricing strategy. A business plan outlines your business goals and your strategies for achieving them. The two documents have a few critical differences, namely their structure and ...
What is a business plan? A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines your business strategy, goals, and financial projections. It serves as a roadmap for your venture, guiding your decisions and attracting potential investors. A well-crafted business plan typically includes the following sections: Executive summary: A concise ...
Coaching Vs Training. We see both coaching and training aim to foster growth, but they do it differently. Coaching is a personalized, ongoing process that focuses on individual development and goal achievement. It's about exploring the strengths, identifying areas for growth, and creating a plan that aligns with the objectives.
SIMPLE IRA vs. SIMPLE 401(k): An Overview . Small business employers have a variety of choices if they want to offer a tax-advantaged retirement plan.It is essential to think about them carefully ...