- Search Search Please fill out this field.

Value Chain Basics
- Starbucks and Porter's Value Chain
Starbucks’ Primary Activities
- Starbucks' Support Activities
The Bottom Line
Analyzing starbucks’ value chain.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/nikki__prableen_bajpai-5bfc262ac9e77c005199a216.jpg)
The business management concept of the value chain was introduced and described by Michael Porter in his popular book, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance . The concept of the value chain involves all aspects of a business’s operational activities and can be studied in combination with the supply chain .
While the supply chain focuses on the procurement process of goods and services from suppliers, a value chain studies the value added at various intervals through a series of activities or processes that aim to create profitable value for a product offering.
Michael Porter discusses value chain analysis from multiple angles in his book; however, there are a few essential components to be aware of when beginning to understand value chain analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Michael Porter introduced value chain models in Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance .
- Value chain analysis can be complementary to other types of business management efficiency analysis.
- Starbucks is one company that is interesting to analyze from a value chain perspective because of the substantial value added from coffee bean procurement to distribution and from store supply to the customer.
In general, value-chain business activities are usually divided into primary activities and secondary activities. The primary activities are directly related to the creation of a good or service. The support activities are those that help in enhancing the efficiency and work of an offering to obtain a stronger competitive advantage among peers.
Comprehensively, businesses and business managers aim to maximize their margins and thus work to ensure that inputs are converted to outputs, which have a greater value when combined together.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is one metric on the income statement where value creation can be easily determined. Gross profit margin looks at the difference between a company’s gross revenue and cost of goods sold divided by the gross revenue overall. The higher the gross margin the more a company is generating from the combination of goods used to build its product.
Operating Margin
Moving on down the income statement, operating margin helps to analyze the value created from indirect business activities like administration, research, marketing, and other unique expenses. The profit margin can be less important to value chain analysis because it focuses on a company’s capital expenditures , taxes, and investment activities, which play less of a part in value chains and supply chains.
Broadly, the more value a company can create in relation to gross margin and operating margin, the more value it can generate for its bottom line; leaving capital expenditures, taxes, and investment activities to become its own isolated variables.
Value Chain Analysis
Porter’s value chain analysis helps to provide deeper insights for breaking down components of gross margin and operating margin, while also breaking out different categories for direct and indirect assessments.
For business managers, value chain analysis is often just as important as supply chain analysis along with other key performance indicators and measurements.
Starbucks and Porter's Value Chain
An analysis of Starbucks ( SBUX ) can help to further illustrate and understand the value chain concept. The Starbucks journey began with a single store in Seattle in the year 1971. From there it grew to become one of the most recognized brands in the world. Starbucks’ mission is, per its website, “to inspire and nurture the human spirit-one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time.”
Michael Porter’s analysis of value chains provides the following visual aid for study. The value chain analysis breaks down business activities into primary activities and supporting activities. Below we discuss how Starbucks' activities fit into the Porter value chain analysis.
Inbound Logistics
The inbound logistics for Starbucks refer to company-appointed coffee buyers selecting the finest quality coffee beans from producers in Latin America, Africa, and Asia. In the case of Starbucks, the green or unroasted beans are procured directly from the farms by the Starbucks buyers. These are transported to storage sites, after which the beans are roasted and packaged.
Value is added to the beans through Starbucks’ proprietary roasting and packaging, which helps to increase their selling value. The beans are then sent to distribution centers, a few of which are company-owned and some of which are operated by other logistic companies. The company does not outsource its procurement, ensuring high-quality standards right from the point of selection of coffee beans.
Starbucks operates in more than 84 markets, either in the form of direct company-owned stores or licensed stores . (Starbucks does not follow the traditional franchising terms.) The company has more than 36,000 stores globally. It is also the owner of several brands , including Teavana and Evolution Fresh.
According to its financial reports, the company generated 51% of its total revenue from its company-operated stores in 2022 while the licensed stores accounted for 49%.
Outbound Logistics
There is very little or no presence of intermediaries in product selling for Starbucks. The majority of the products are sold in stores; however, storage and distribution to retail locations are important.
Marketing and Sales
Starbucks invests more in superior quality products and a high level of customer service than in aggressive marketing; however, need-based marketing activities are carried out by the company during new product launches in the form of sampling in areas around the stores.
Howard Schulz bought Starbucks in 1987 and is responsible for its expansion. He was an employee.
Starbucks aims at building customer loyalty through its in-store customer service. A signature retail objective of Starbucks has always been to provide customers with a unique Starbucks Experience.
Service training is a key component of the value chain that helps to make its offerings unique. A substantial amount of value is created when baristas make drinks for customers.
Starbucks' Support Activities
Infrastructure.
This includes departments like management, finance, legal, etc., which are required to keep the company’s stores operational. Starbucks employs business managers in its corporate offices. It also has store managers on-site that help to oversee well-designed and pleasing stores complemented with good customer service provided by the dedicated team of employees in green aprons.
Human Resource Management
The committed workforce is considered a key attribute in the company’s success and growth over the years. Starbucks employees are motivated through generous benefits and incentives.
The company is known for taking care of its workforce, a key reason for a low turnover of employees, which indicates great human resource management. There are many training programs conducted for employees in a setting of a work culture, which keeps its staff motivated and efficient.
Technology Development
Starbucks is very well-known for the use of technology, not only for coffee-related processes (to ensure consistency in taste and quality along with cost savings) but to connect to its customers. Many customers use Starbucks stores as makeshift offices or meeting places because of free and unlimited Wi-Fi.
Starbucks has launched several platforms where customers can ask questions, give suggestions, openly express opinions, and share experiences. Technology helps to implement this feedback, especially in the area of its rewards program .
Starbucks also uses Apple’s iBeacon system, wherein customers can order a drink through the Starbucks phone app and get a notification of its readiness when they walk into the store.
Procurement
Procurement is integrated across various aspects of the supply chain. Porter discusses procurement as a support activity. Many companies will establish broad terms, requirements, and standards for all of their procurement dealings; however, procurement relationships typically vary widely. Starbucks handles all of the procurement for its own coffee beans, which it sees as one of its competitive advantages.
What Is the Value Chain of a Coffee Shop?
The value chain of a coffee shop generally lies in four stages: cultivation, processing, roasting, and consumption.
What Are Starbucks' Core Competencies?
Starbucks' core competencies include its ability to expand almost everywhere globally, its care and concern for its employees, its focus on quality and providing a quality product, its continuous product development, and its excellent customer service.
What Are the Values of Starbucks?
The values of Starbucks can be seen in the promises it makes in its mission. These promises are to its partners, customers, farmers, community, shareholders, and the environment.
The concept of value chain analysis helps business managers to better identify useful and wasteful activities. By looking beyond standard means of efficiency analysis while also seeking to integrate and capture value chain analysis in business metrics , stakeholders can make important insights related to operational processes.
Overall, value chain analysis can be used to potentially identify value improvement opportunities throughout various steps of a business cycle, also adding to improved margin efficiencies.
Harvard Business School. " The Value Chain ."
Starbucks. " Our Mission ."
Starbucks. " Company Profile ." Click Download
Starbucks. " Fiscal 2022 Annual Report ," Page 6.
Statista. " Starbucks Statistics & Facts ."
Starbucks. " Benefits and Perks ."
Starbucks. " Culture and Values ."
Mordor Intelligence. " Coffee Value Chain Analysis - Growth, Trends, Covid-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2023 - 2028) ."
Starbucks. " Our Mission. Our Promise ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-12446899391-e57beafa9b684e5f8e174f704bb7357f.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

Starbucks Value Chain Analysis
Starbucks value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage for the global coffeehouse chain. Figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis.
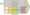
Starbucks Value chain analysis
Starbucks primary activities, starbucks inbound logistics.
Starbucks inbound logistics and supply chain was subjected to a dramatic restructuring in 2010 after Howard Schultz had returned to the role of CEO for the second time. The restructuring initiative of Starbucks inbound logistics involved simplification of supply-chain management and the creation of a single, global logistics system.
Unroasted Arabica coffee beans are brought from Asia, Africa and Latin America to the US and Europe in containers via sea. Also, the coffee chain purchases green coffee beans from multiple coffee-producing regions around the world. These are delivered to one of the following regional roasting plants and distribution centres:
- Kent Flexible Roasting Plant – Kent, Washington.
- Augusta Roasting Plant – Augusta, Georgia.
- Sandy Run Roasting Plant – Gaston, South Carolina.
- York Roasting Plant and Distribution Center – York, Pennsylvania.
- Evolution Fresh Juicery – Rancho Cucamonga, California.
Coffees are roasted and packaged and taken to dozens of central distribution centres around the globe. Along with coffees from regional distribution centres, central distribution centres also receive deliveries from vendors for a wide range of products starting from coffee machines to napkins. Central distribution centres make more than 70,000 deliveries per week to Starbucks 25,085 stores located in 75 countries. [1]
The world’s largest coffeehouse chain also grows its own coffee. Since 2013 Starbucks has its first own 240-hectar coffee farm in PoasVolacno, Costa Rica. [2] Such a shift in the sourcing of products can increase the effectiveness of new product development initiatives for the business as the company will have a chance of experimenting with developing new sorts of coffee.
Strategic relationships with suppliers is one of the main sources of value for Starbucks inbound logistics. The company operates ten farmer support centres staffed with agronomists and sustainability experts who work with coffee farming communities to promote best practices in coffee production designed to improve both coffee quality and yields.
Starbucks Operations
Starbucks operates in 84 markets and there are two store formats:
1. Company-operated stores . Company operated-stores are important for the business because they enable the management to observe shifts in consumer tastes and preferences and collect information about market tendencies in general in a direct manner. As of October 3, 2022 Starbucks had 17,133 company-operated stores, which accounts for about 51% of total numbers of stores. Company-operated stores generated 85% of Starbucks total net revenues during fiscal 2021. [3]
2. Licensed stores . Starbucks receives a margin on branded products and supplies sold to the licensed store operator along with a royalty on retail sales. There were 16,700 licensed stores by October 3, 2022, representing about 49% of total numbers of stores. [4] Revenues from licensed stores accounted for 9% of total net revenues in fiscal 2021.
| North America | US and Canada | 70% |
| International | China, Japan, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, Latin America and Caribbean | 24% |
| Channel Development | Roasted whole bean and ground coffees, Seattle’s Best Coffee®, Starbucks- and Teavana-branded single-serve products, beverages, such as Frappuccino® and Starbucks Doubleshot®, foodservice products and other branded products sold worldwide outside Starbucks stores | 6% |
Starbucks operating segments
Main sources of value in Starbucks operations include positioning of stores in high-traffic, high-visibility locations. Moreover, the company is able to vary the size and format of its stores to locate them in or near a variety of settings, including downtown and suburban retail centres, office buildings, university campuses and in select rural and off-highway locations.
‘Starbucks experience’, i.e. ‘third place’ experience where customers can spend quality time alone or in the company is an additional point, where the company adds value to its operations. The world’s largest coffee retailer also adds value in operations via proving free WiFi internet access in its stores.
Starbucks Outbound Logistics
Customers can purchase Starbucks products from company-operated and licensed stores. Online sales channel is also utilized by Starbucks for certain range of products such as packaged coffee, tea, drinkware and drink-related equipment. In addition, a very limited range of Starbucks products such as 3-in-1 coffees in sachets can be purchased from a set of leading supermarket chains such as Wal-Mart, Tesco and Sainsbury’s.
Apart from supermarket chains that sell limited range of company’s products, the absence of intermediaries such as resellers or wholesalers is the main source of value for Starbucks outbound logistics. The company roasts its products in-house and sells on its own company-operated and licensed stores, thus keeping the margin that otherwise would have gone to wholesalers and resellers.
Furthermore, Seattle-based international coffee house chain partners with Nestlé in distributing their products. Specifically, Nestlé controls distribution of certain finished goods through the Global Coffee Alliance.
Starbucks Marketing and Sales
Traditionally, Starbucks was not keen on investing in marketing. Word-of mouth cost-effective form of marketing based on high quality of products and high level of customer services was the main channel promoting the brand for years. However, rapidly intensifying level of competition motivated the senior management to reassess the marketing strategy and Starbucks marketing budget has been consistently increasing during the last few years to reach USD 305,1 million for the fiscal year 2021 [5] . This budget is invested into various elements of print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing.
High level of integration of social media and technology into sales processes represents one of the solid sources of value for Starbucks Coffee. The company has successfully implemented mobile order and pay system for its products and currently, about 8% of all orders are placed via mobile phones [6] . Moreover, Starbucks has “enabled orders via Amazon’s Alexa last year, announced that the feature would also be integrated into Ford vehicles later this year.” [7]
Starbucks Service
Superior customer services are the core source of Starbucks competitive advantage and this particular primary activity adds an enormous value to the brand image. Starbucks baristas are always genially polite and greet regular customers by their names. Occasionally, regular customer may get their regular coffee free of charge at the discretion of baristas as good gesture and such acts increase the perception of the service quality to a considerable extent. Depending on the country, most locations provide free Wi-Fi internet access.
Furthermore, amid ever-intensifying hectic nature of lifestyle and increasing speed of the provision of customer services, service at Starbucks is never rushed. It has been rightly noted that “Starbucks spends a lot of time measuring and improving how well they match their customers’ speed expectations—delivering a custom (truly from scratch) beverage in a matter of minutes—they don’t let the need for speed suck the life out of the Starbucks experience.” [8]
Starbucks Corporation Report contains a full version of Starbucks value chain analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Starbucks . Moreover, the report contains analyses of Starbucks leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Starbucks marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

[1] Fiscal 2014 Annual Report (2015) Starbucks Corporation
[2] Best, J. (2013) TakePart, Available at: http://www.takepart.com/article/2013/03/19/starbucks-gets-coffee-growing-biz
[3] Fiscal 2021 Annual Report, Starbucks Corporation
[4] Fiscal 2016 Annual Report (2017) Starbucks Corporation
[5] Fiscal 2021 Annual Report, Starbucks Corporation
[6] Taylor, K. (2017) “There’s one huge factor shaping Starbucks and Dunkin’ Donuts’ ‘coffee shop of the future’ Business Insider, Available at: http://www.businessinsider.com/mobile-shapes-future-coffee-shops-2017-3
[7] Whitten, S. (2017) “There are now more ways to order your Starbucks coffee” CNBC, Available at: http://www.cnbc.com/2017/03/22/there-are-now-more-ways-to-order-your-starbucks-coffee.html
[8] Solomon, M. (2014) Forbes, Available at: http://www.forbes.com/sites/micahsolomon/2014/11/01/speed-up-your-customer-service-like-starbucks-and-apple-but-never-ever-rush-it/
Starbucks Value Chain Analysis

1. Introduction
When we talk about international beverage stores, Starbucks has to be one of the first names that come to our minds. Though, if you want to know more about the primary and secondary activities of the company, then you can simply do its value chain analysis. It will help you identify the value provided by the brand on different channels, giving it a competitive edge. Here, I will do a detailed Starbucks value chain analysis , helping you understand its operational and logistical advantages.
2. What is a Value Chain Analysis
In a nutshell, value chain analysis provides a contemporary analysis of the business model of any company to identify its efficiency. In this, we analyze various activities that are undertaken during all kinds of primary and secondary processes by a company.
While the primary activities deal with the overall working of the company, the supportive activities are about enhancing its overall process to get a competitive advantage. To undertake value chain analysis, we simply work on these three steps:
- Identifying primary and secondary activities.
- Determining the cost, effectiveness, and relationship in activities.
- Understanding activities to identify any competitive advantage and extracting other details.
3. Background of Starbucks
Before we do an in-depth value chain analysis of Starbucks , let’s get to know a few vital things about the company. It was founded in 1971 by the famous trio, Jerry Baldwin, Gordon Bowker, and Zev Siegl in Seattle.
The company founders shared their love of coffee and gradually opened three stores in Seattle in 1980. Later, Howard Schultz helped the brand to expand in different parts of the country (and worldwide). Today, the company operates in more than 32 thousand stores globally and has a wide range of products (from beverages to baked goods) on its menu.
|
| Starbucks Corporation |
|
| Gordon Bowker, Zev Siegl, and Jerry Baldwin |
|
| 1971 |
|
| Kevin Johnson |
|
| Seattle, Washington |
|
| 32,600+ |
|
| 80+ countries |
|
| $26.50 billion |
|
| $4.07 billion |
|
| 349,000 (approximately) |
4. Starbucks Value Chain Analysis
Tip: In the Porter model of value chain analysis, we will study five primary activities - Inbound Logistics, Operations, Outbound Logistics, Marketing and Sales, and Service
From the procurement of coffee beans to the distribution of its products, Starbucks has undertaken so many activities in its business model. Therefore, to perform our Starbucks value chain analysis, let’s have a look at its primary activities first.
Inbound Logistics:
To do a value chain analysis of Starbucks, you first have to consider the logistics for its coffee beans and other products. Most of the unroasted coffee beans come from Starbucks-owned farms from Asia, Africa, and South America.
The coffee beans are carefully picked from the farms and are transported to the Starbucks facility for storage and refinement. They undergo a proprietary roasting technique by Starbucks that increases the shelf life of beans. After that, the beans are packed and are sent to distribution. To maintain the quality of coffee beans, the company relies on its native suppliers and does not involve any third-party vendors as of now.
Operations:
Unlike other popular beverage or fast-food outlets, Starbucks does not support a franchise system. This means, all the Starbucks outlets are either owned by the company or are monitored by it.
As of now, the company has more than 32 thousand stores in around 83 countries worldwide. It has been noted that around 80% of revenue in Starbucks is generated by company-owned stores and the remaining part comes from its monitored facilities and sister brands.
Outbound Logistics:
When we consider the overall Starbucks value chain analysis, we won’t find much in its outbound logistics. This is because Starbucks does not have a leading B2B model in which the brands distribute its products or franchises.
Most of the products offered by Starbucks are sold via its stores worldwide. Though, a while back, Starbucks came up with options to sell single-origin coffee beans in the US. Apart from beverages, one can also get all kinds of snacks, baking items, and company products (like mugs or tumblers) in their stores.
Marketing and Sales:
Starbucks is known to have one of the most aggressive marketing strategies in the industry. A substantial amount is invested by the company to maintain the highest standard of customer satisfaction in sales.
Apart from on-ground marketing, Starbucks also has a significant online presence on various social media platforms. It keeps coming up with dedicated marketing plans for product launches, new establishments, and other events.
As per the company reports of Starbucks, the brand has mentioned the following objective:
“To be the leading retailer and brand of coffee in each of our target markets by selling the finest quality coffee and related products, and by providing each customer a unique Starbucks Experience.”
Needless to say, the company has certainly lived up to its brand statement by providing the highest level of customer experience – which has now become a USP for the brand. Apart from its high-quality beverages, the brand also invests in the service training of baristas as they provide a unique experience to customers while making and serving their drinks.

5. Starbucks’ Support Activities
Tip: The value analysis of a brand can be done by exploring its support activities like Infrastructure, Human Resource Management, Technology Development, and Procurement.
Now when you know about the primary activities of the company, let’s continue our value chain analysis of Starbucks by exploring its secondary or support activities.
Infrastructure
Since Starbucks has been around for almost 5 decades, it has a strong infrastructure in almost every department like finance, management, marketing, and so on. The main corporate office of Starbucks is in Seattle, but the company has several other regional corporate offices worldwide.
Besides its backend management, the company also has a seamless customer service and employee management infrastructure.
Human Resource Management
Starbucks has over 349,000 employees worldwide that includes its baristas, brewing staff, corporate employees, and so on. According to a recent survey done by Hewitt Associates, Starbucks has an employee satisfaction rate of 82 percent, which is one of the highest in the food and service industry.
The company is widely known to have a pleasant working environment and takes care of its employee with friendly policies. Their human resource management team has also worked on elevating its culture and improving the retention rate by keeping its staff motivated.
Technology Development
Starbucks has kept up with the ongoing technological advancements in the foods and beverage industry. The company uses the best-in-class techniques to make the process of selecting coffee beans and brewing drinks in different locations.
Besides that, all the Starbucks stores provide facilities like high-speed WiFi that helps its customers work from their coffee shops. Furthermore, Starbucks also has a unique rewards program and lets us place our orders from its connected stores via numerous food delivery apps.
Procurement
You might already know that procurement involves various activities undertaken for obtaining the goods and services in a company. When we consider the Starbucks value chain analysis, most of its procurement comes from in-house sources.
As listed above, Starbucks doesn’t buy coffee beans from third-party sources. From the production of coffee beans to their packaging, everything is handled in-house. Not just that, the brand does not give franchises and all the stores and directly or indirectly controlled by Starbucks.

6. Key Takeaways
As you can see from our value chain analysis of Starbucks that the company follows a unique operational plan. Since the brand controls everything from production to sales, it yields substantial profit generation. A lot of experts even say that this has given Starbucks a competitive edge, making it a prime contender in the industry.
Just like the Starbucks value chain analysis , you can also analyze the overall working of any other brand. To do this, you can simply take the assistance of EdrawMax Online . You can get a quick strat with the value chain analysis examples . EdrawMax is a complete diagramming tool that has an extensive library to work on more than 200 different diagrams. You can also find readily available value chain analysis templates that you can easily customize to analyze any other brand’s functioning on the go.
7. References
Tim S., 2020. 'WHAT IS A VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS? 3 STEPS', Harvard Business Schoil Online , [online]. Available at: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-value-chain-analysis (Accessed 12 Angust 2021).
edrawmax.com. 2021 'Starbucks PESTEL Analysis', Wondershare EdrawMax , [online]. Available at: https://www.edrawmax.com/article/starbucks-pestel-analysis.html (Accessed 12 August 2021).
Peter B. 'Starbucks', Britannica , [online]. Available at: https://www.britannica.com/topic/Starbucks (Accessed 12 August 2021).
Editorial Staff. 'Starbucks as an Example of the Value Chain Model', Supply Chain Minded , [online]. Available at: https://supplychainminded.com/starbucks-chain-model/ (Accessed 12 August 2021).
Prableen B. 'Analyzing Starbucks’ Value Chain', Investopedia , [online]. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/103114/starbucks-example-value-chain-model.asp (Accessed 12 August 2021).
Maryann H., 2003. 'Starbucks is Pleasing Employees and Pouring Profits', workface.com , [online]. Available at: https://www.workforce.com/news/starbucks-is-pleasing-employees-and-pouring-profits (Accessed 12 August 2021).

Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Under Armour

Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Starbucks

Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Tesla
Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Pharmaceutical Industry

Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Wiki

Detailed PESTEL Analysis of Haiti

Starbucks Value Chain Analysis
Company’s background, current performance of the company, starbucks vision, starbucks primary activities, inbound logistics.
In inbound logistics the buyers appointed by Starbucks select the insubstantial finest beans from coffee producers or coffee suppliers that are in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. At first hand the beans are obtained from the farms by the buyers of Starbucks then they are shifted to the storage units where they are roasted and packaged before being sent to the distribution units. The company owns some of and logistic companies manage them. Starbucks does not contract any supplier to certify and standardize quality from the first step of selecting the beans.
Starbucks Operations
Starbucks operates more than 32 thousand stores globally. It also owns some other brands as well which include Seattle’s Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh, etc. According to the fourth quarter Sep 2020 fiscal year report, there is a recession to about 6% in net revenue from the earlier year caused by the COVID-19 outbreak while according to the annual financial report 2020 there is a decline of 11.3% in net revenue from the previous year. According to America’s segment result, there is a 46% change in operating income from last year. 2% change in store count from last year i.e. 2019. In the international segment results report, there is an 8% change in store count, 5% change in revenues, and 32% change in operating income from last year.
Starbucks Outbound logistics
Starbucks marketing and sales, starbucks service.
The objective of Starbucks is to gain customers’ loyalty through in-store customer service or assist them with their issues with the product. The service training is the lead part of the value chain analysis goal is to provide customers with a distinct experience by making an attractive offering. When baristas make coffee it puts considerable value on the drinks.
Starbucks Supportive activities
Human resource management (hrm).
The good interaction of the customer and the employees who are committed to them are vital for an organization. It’s necessary to build a relationship with customers by dealing better. Starbucks always is caring towards their employees and this results in reduced quality employee turnover which refers to great Human Resource Management. Training of the workforce is also necessary to keep them upgraded and efficient.
Firm Infrastructure of Starbucks
Technology development of company, procurement, bottom line.
There were no modifications in the internal control over financial reporting according to the annual report of Starbucks, 2020.
Related Posts
What is value chain analysis and why it is important, walmart’s value chain analysis, amazon’s value chain analysis.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

Great things in business are never done one. They're done by a team of people.
Email us directly
[email protected]
Call us directly
(123) 567 8901, social network, send a message..
We’re here to answer any question you may have.
Would you like to join our growing team?
Have a project in mind? Send a message.
I am bound by the terms of the Service I accept Privacy Policy
- Blessing Peter Titus
- Bongdap Nansel Nanzip
- Joy Sunday Zaleng
- Obotu Agape Oguche
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Value Chain of Starbucks: Examples and Analysis
Understanding the value chain of Starbucks is important as it will aid us in discovering how the company creates value through its business operation. Starbucks is one of the companies with vertical integration , which has aided it in creating a valuable supply chain. This company which began in 1971 as a coffee bean retailer has established itself as a global coffeehouse that offers a rich variety of coffee and other beverages.
As of 2022 , Starbucks was the largest coffee company in the world with a gross annual revenue of $32.25 billion and a U.S. market share of 37%. In this article, we shall analyze and see some examples of the value chain of Starbucks.
See also: How to scale your business
What is a value chain?
The value chain of any business corporation such as Starbucks is divided into two:
- The primary activities comprise inbound operations, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
- The secondary or supporting activities comprise procurement and purchasing, human resource management, technological development, and company infrastructure.
The value chain aids companies to identify and classify their business operations into primary and secondary activities. When companies identify and classify their business operations using the value chain concept, it is known as a value chain analysis . This analysis aids companies to better understand the interrelatedness of each activity to another. It also helps in identifying aspects of the value chain that need to be improved to obtain optimal output.
To aid us analyze the value chain of Starbucks, we shall break down the company’s business processes based on its primary and secondary activities. This will help us know how each step in Starbucks’ value chain contributes to its overall success and top position in the coffee industry.
Related: Starbucks Supply Chain Issues and Management

See also: Navigating Economic Downturns: Strategies for Businesses to Survive and Thrive
Value Chain of Starbucks: Examples of Primary Activities
Inbound operations, outbound logistics.
- Marketing and sales
The primary activities of the value chain directly contribute to the physical creation of a product or service. They also contribute to its sale, maintenance, and support. These activities have been listed above and we shall discuss them based on the value chain of Starbucks.
The inbound operation of Starbucks is centered around the company’s handling and management of the resources coming into the company from outside sources such as suppliers. These outside resources are commonly referred to as inputs and usually include raw materials and other equipment used by the company. Apart from coffee beans, other inputs that Starbucks purchases include coffee machines, napkins, and non-dairy milk.
Aside from brokering several partnership deals with coffee growers, Starbucks vertically integrated by growing some of its coffee beans. Through these partnerships, the company aggregates some of the best coffee bean varieties from Asia, Latin America, and Africa. This is because the different coffee growing practices, soil types, and other geographical conditions give a distinct flavor to the coffee beans sourced from these different continents. The company’s involvement in growing coffee beans is an added advantage in its value chain as it affords Starbucks the opportunity to experiment on and develop other possible coffee variants.
Unlike other coffee houses that may outsource the procurement of their coffee beans to third-party procurement companies, Starbucks procure their coffee beans either directly from the farmers or through reliable coffee bean suppliers. This ensures that the company can source the best quality coffee beans for its final products.
One way Starbucks improves its inbound logistics value chain is by providing farmer support centers to farming communities that grow coffee. These centers are equipped with sustainability experts and agronomists who tend to farmer concerns and also educate them on best practices in coffee production that can improve its quality and yield.
Another way the value chain of Starbucks gets impacted is through the refinement and storage of coffee beans. Starbucks implements a proprietary roasting technique that increases the shelf life of coffee beans. The roasting is usually carried out in any of the company’s regional roasting plants and distribution centers which include:
- Augusta Roasting Plant – Augusta, Georgia
- The Carson Valley Roasting Plant and Distribution Centre – Carson Valley, Nevada
- Kent Flexible Roasting Plant – Kent, Washington.
- Sandy Run Roasting Plant – Gaston, South Carolina.
- York Roasting Plant and Distribution Center – York, Pennsylvania.
After roasting, the coffee beans are packaged and transported to Starbucks’ central distribution centers. The central distribution centers further send the coffee beans to the company’s stores scattered around the globe.
See also: McDonald’s Competitive Advantage
The operations stage entails managing the various activities carried out by Starbucks to transform the raw coffee beans (inputs) into roasted coffee beans, ground coffee, VIA ready brew, coffee capsules, and other products of the company (outputs). The outputs are usually sold for a higher price than the cost of both the inputs and the production process; thus it creates value by bringing profit to the company.
As of this year, 2023, Starbucks operates over 35,711 stores scattered around the globe in 84 countries; the United States and China account for 61% of these stores. The stores are classified into two:
- Starbucks stores that are directly operated by the company comprise the more significant percentage of Starbucks stores (51%). These stores generated $26.57 billion out of the $32.2 billion revenue the company made in 2022. These stores are also referred to as direct, owned, or company-operated stores.
- Licensed stores are not directly operated by Starbucks but the company receives a margin on supplies and branded products sold to the licensed store operator. They also receive a royalty on retail sales. The licensed stores comprise 49% of the total number of stores and generated $3.65 billion in 2022
The value chain of Starbucks in this operations aspect rests on the strategic positioning of both company-operated and licensed stores in high-visibility and high-traffic locations. This strategic positioning aids in increased patronage from individuals who frequent the route where the stores are located.
Starbucks additionally adds value by having some of its stores located in varied settings to cater to different kinds of customers. This includes having stores in University campuses, suburban and downtown retail centers, off-highway locations, office buildings, and rural locations. The variety of locations further adds value by giving customers the chance to enjoy the company’s products irrespective of where they are located.
Furthermore, the store spaces generally have sitting tables where customers can enjoy some alone time or share the time out with their family, friends, or colleagues. The provision of free WIFI in most of Starbucks’ stores is an additional value enjoyed by customers who patronize the brand by visiting its stores.
The outbound logistics of Starbucks comprise all the processes that culminate in the delivery of outputs to customers. This includes the storage, collection, and distribution of the company’s products from the end of its production line to the end users (customers). The majority of Starbucks’ products are sold to customers from its direct stores and licensed stores.
However, with the advancements occasioned by the digital revolution , the company also utilizes online sales channels to sell some of its products including packaged coffee, tea, drinkware, and drink-related equipment. Additionally, a very limited range of the company’s products such as its sachet 3-in-1 coffee can be purchased from some of the leading supermarket chains including WalMart, Sainsbury’s, and Tesco.
Starbucks also partners with Nestle for the distribution of some of its finished goods. The distribution is done through the Global Coffee Alliance. Additionally, Starbucks customers in the United States and the United Kingdom can opt for home delivery of the company’s products through Deliveroo , Just Eat, and Uber Eats.
Apart from this distribution of Starbucks products by Nestle and the sale of some of its products by certain supermarkets, the value chain of Starbucks in outbound logistics rests with the company. The company’s handling of the roasting of coffee beans, having an extensive distribution channel, and the sale of its finished products through directly owned and licensed stores, is an additional source of value to the company. This is because the absence of intermediaries such as resellers or wholesalers aids in keeping the margin that otherwise would have gone to wholesalers and resellers to the company. Hence, overseeing its outbound logistics adds value to Starbucks.
The Marketing and Sales aspect of Starbucks’ Value Chain
This aspect of the value chain of Starbucks involves employing marketing strategies , advertising, and brand-building efforts which are geared towards increasing the company’s visibility, increasing consumer confidence, and ultimately increasing the sale of its products. The marketing is targeted at communicating why people should patronize the brand. It also includes market research, sales training, and sales promotions.
Traditionally, Starbucks was not into aggressive marketing. It depended on its high level of customer service and product quality. This resulted in a robust and cost-effective form of marketing which was word-of-mouth from satisfied customers. However, Starbucks’ marketing budget has been steadily increasing in recent years with the company spending $305.1 million in the 2021 fiscal year and a whopping $416.7 million on advertising in the fiscal year 2022.
The advertising expenses are invested in varied product marketing efforts including print and media advertising, public relations, sales promotions, events, and experiences. The company’s adoption of other means of marketing asides from its initial word-of-mouth strategy is due to the competition from other coffee chains. Starbucks has also employed digital marketing using its social media pages to advertise the different product offerings of the company. It also uses digital channels to inform its customers of the establishment of new stores, partnerships, product launches, and other consumer-related events.
Starbucks has further successfully implemented mobile orders and payment for its products. Recently, the company shifted its focus from short-term consumer relations to building long-term and more personal relationships with customers. If implemented well, this could further establish Starbucks as not only the world’s leading coffeehouse but a customer-centric business. This has the potential of building customer loyalty in the long run and affording the brand a lot of comparative advantages .
The Service aspect of Starbucks’ Value Chain
The service aspect of the value chain of Starbucks comprises majorly of customer service aimed at reinforcing a long-term relationship with their customers. The company is constantly analyzing customer expectations to give them the best experience and keep the brand growing. Hence, services are an integral part of the value chain of Starbucks.
Part of the outstanding value of Starbucks at this stage is the genial and polite manner of its baristas. Most of the company’s baristas make it part of their job to recognize regular customers by name; they may even go further by occasionally offering these regulars a free coffee. This extra-mile attitude of Starbucks baristas adds positively to the customers’ perception of the brand and its products. It in turn translates to customer satisfaction and increased patronage. Also, most Starbucks stores offer free WIFI to their customers.
Furthermore, despite the increasing need for speed in the provision of customer services and the intensely hectic nature of lifestyle, service at Starbucks is never rushed. The company spends a lot of time measuring, analyzing, and improving how well they match their customers’ speed expectations while delivering a custom beverage in a matter of minutes.
See also: Amazon’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples

Value Chain of Starbucks: Examples of Supporting Activities
Procurement and purchasing, human resource management, technology development, company infrastructure.
The procurement and purchasing aspect of the value chain of any company involves finding new external vendors, maintaining existing vendor relationships, negotiating prices, and other activities related to bringing in the necessary materials and resources used to build a product or service. Looking at the value chain of Starbucks, the procurement and purchasing consist of purchasing goods and services for the company. It also involves managing the company’s relationships and contracts, including purchase agreements, contracts, and service agreements.
Starbucks aims to offer its customers the highest quality products that are ethically purchased and responsibly produced. Thus, the company’s agents travel to different countries where they purchase various inputs for the company. This direct involvement aids Starbucks in maintaining a high level of quality standards and control. Additionally, it aids the business in sourcing inputs at an affordable rate thereby providing better profit for the company and increased value for its customers.
This part of Starbucks’ value chain comprises the hiring and training of employees. It also comprises building and maintaining the company culture in an environment that fosters a good working relationship between the brand and its employees. The company refers to its employees as partners and states on its website that:
“ We are committed to making our partners proud and investing in their health, well-being, and success and to creating a culture of belonging where everyone is welcome. “ https://www.starbucks.com/about-us/
It is, therefore, no surprise that Starbucks has secured several awards in this aspect including 2022 Aon China Best ESG Employer , Comparably Best Company (2022) , and Best Places to Work in Seattle (2022) . The company has also been on various Forbes lists such as Canada’s Best Employers For Diversity (2023) , Best Employers for Diversity (2023) , America’s Best Large Employers (2023) , and Canada’s Best Employers (2023) .
Additionally, Starbucks’ value chain is obvious in its several training programs conducted for its partners to familiarize them with the brand’s core tenets, keep them motivated and promote their efficiency. One such training is Starbucks’ Barista Basics Training program ; the program is designed to equip new baristas with the skills and knowledge they need to deliver excellent customer experience.
This supporting activity is part of the value chain of Starbucks. It involves research and development of new products, IT management, and cybersecurity. It also includes building and maintaining how the company uses technology. Starbucks has kept up with the ongoing technological advancements in the food and beverage industry where it operates.
Starbucks is well-known for its use of technology for taking orders, queries, and suggestions. It also makes use of big data, machine learning, Artificial intelligence, and cloud computing to develop new products and services for the company and deliver premium customer experience. The company also utilizes technology across different functions including store design, supply chain, production, and customer experience.
Starbucks uses the best technology and techniques available to make the process of selecting coffee beans and brewing drinks in different locations. This is done to ensure that there is consistency in the quality and taste of the coffee and other beverages produced by Starbucks. Besides these, the company’s provision of free WI-FI in most of its stores aids customers, especially remote workers to work from the brand’s coffee shops. Starbucks customers can order coffee through the Starbucks phone app which is available through Apple’s iBeacon System
Furthermore, Starbucks also has a unique rewards program that lets consumers place their orders from its connected stores via numerous food delivery apps. The company launched mystarbucksidea.force.com in 2008. This is a platform where customers can ask questions, give suggestions, openly express opinions, and share personal experiences with the brand. Customers are further assured of the brand’s consideration of its consumers as the company has implemented some of the suggestions given through this forum. These varied use of technology by Starbucks adds value to it.

This aspect of Starbucks’ value chain comprises all the departments that are necessary for the effective operation of the company and its stores. It includes company activities such as quality assurance, legal, finance, general management, public relations, administration, marketing, and accounting. These departments are well structured considering the long time that this company has been in existence.
Starbucks’ main corporate office is in Seattle, but the company has several other corporate offices in the different regions where they operate. The chain of command in Starbucks’ leadership comprises the chief executive officer, vice presidents, senior vice presidents, and executive vice presidents. It also includes store managers and baristas. Besides the company’s backend management, it also has a seamless customer service and employee management infrastructure.
Company infrastructure is the last part of the secondary value chain of Starbucks. The main value in this stage is the company’s well-designed and pleasing stores which are complemented by good customer service provided by the dedicated Starbucks partners in their signature green aprons.
See also: Tesla’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Related: Nike’s Supply Chain Issues and Management
Starbucks is arguably the most popular coffeehouse chain in the world, with over 35,000 stores around the globe. This popularity and success have been tied to how they transformed coffee culture in major countries around the globe. Before Starbucks’ came on the scene and began to expand to other parts of the world, coffee shops were not very common in most countries outside of Europe and Australia. This has now changed due to their company-owned stores as well as licensed stores.
Starbucks has been committed to selling the finest whole bean coffees, ground coffee, coffee beverages, and other food and beverage products of high quality. In the coffee business where it has established a stronghold, Starbucks helps to ensure compliance with its rigorous coffee standards by substantially controlling all coffee purchasing, roasting, packaging, and the global distribution of the coffee used in its operations.
The primary value chain of Starbucks is closely monitored by the company. This is because any challenge or inefficiency that may arise at this stage of the value chain is relatively easy to identify and tackle. The well-managed primary activities of Starbucks’ value chain are the major source of the company’s ability to cut down on expenditure while providing high-quality products to its customers. This means the company can produce at a lower cost than its competitors, thereby, improving their profitability.
The secondary value chain of Starbucks has also been adequately managed to ensure that the company makes the best use of its various parts to satisfy its customers and provide a conducive working environment for its teeming partners. Due to this combination of a robust value chain in both its primary and secondary activities, Starbucks has been able to maintain its position as the largest player in the food and beverage industry by a wide margin both in its presence around the globe as well as the revenue it generates annually.
- IKEA Supply Chain Problems and Issues
- McDonald’s Supply Chain Issues and Process
- Netflix’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
- Telstra’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
You may also like
Examples of B2B Businesses


Delayed Perpetuity Examples and Types
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart
SCM Insight
Value chain analysis of starbucks .
Starbucks is a premium retail coffee chain American multinational company. Gordon Bowker, Zev Siegl, and Jerry Baldwin started the retail coffee chain brand in 1971. Today, we’ll discuss the value chain analysis of Starbucks; and the primary and supporting activities involved in the process of value chain analysis Example Company. They’re inbound and outbound logistics, operations, marketing, and services; infrastructure, HRM, technological development, and procurement of the premium coffee chain company as an application of value chain analysis.
Substitutes of Starbucks
- Dunkin Donuts
- Panera Bread
- Costa Coffee
- Café Coffee Day
The value chain analysis of Starbucks would analyze the primary and supporting activities in the process of value chain analysis application. They’re inbound and outbound logistics, operations, marketing, and services; infrastructure, HRM, technology, and procurement. Here’s Starbucks value chain analysis company example as follows;
Value Chain Analysis of Starbucks
Let’s discuss the primary and supporting activities involved in the process of value chain analysis of Starbucks. It is an application of value chain analysis based on Porter’s model; some of the key elements and components of value chain analysis are as follows;
Primary Activities of Starbucks
Some of the five main primary activities in the value chain analysis of Starbucks as corporate value chain analysis example are as follows;
Inbound Logistics of Starbucks
Sourcing is the inbound logistical activity of Starbucks; it allows the company to source the best quality coffee beans from partners and suppliers in Africa, Latin America, and Asia. Along with coffee beans, the retail coffee brand gathers necessary raw supplies for its production process and they’re as follows;
- Non-dairy milk
- Coffee machine
- Coffee beans
Along with sourcing coffee brands, Starbucks is also vertically integrated and growing coffee beans. The plantation of coffee beans in different soils and geographical locations would provide a unique flavor and taste to the coffee.
II-Direct Contact with Farmers
Instead of outsourcing the purchasing process from any 3rd party suppliers, Starbucks establishes direct relationships with the farmers and reliable coffee suppliers. It makes sure that the company has access to the best quality coffee beans. However, the company also offers support to the farmers and coffee-growing communities with equipment to engage in sustainable practices; and expertise in maximizing the output of coffee beans.
III-Storage
Storage and refinement are also the inbound logistical processes of Starbucks, and they significantly impact the quality and value of the product. The coffee brand launches various types of practices and strategies and they improve the shelf life of the coffee beans.
Outbound Logistics of Starbucks
The outbound logistics deals with all those activities of Starbucks that the company employs to deliver the finished goods to the customers. They are like storage, distribution, and gathering the stock from the company and delivering it to the end consumers. However, Starbucks sells a vast majority of its products to customers through its direct retail stores and licensed stores of the company.
II-Distributing Partners
Starbucks has established a partnership with Nestle for the distribution of its products and goods. The coffee brand also offers home delivery service to customers in the US and the UK with the assistance of 3rd party delivery service providers like; Uber Eats, Just East, and Deliveroo. However, Starbucks carefully manages its outbound and delivery services.
Operations of Starbucks
I-roasting operations.
Starbucks implements various forms of roasting operations to transform and convert raw coffee beans into various types of finished products that the company sells at a higher price by adding value. They’re as follows;
- Coffee capsules
- VIA ready brew
- Ground coffee
- Roasted coffee beans
II-Network & Locations
Starbucks has established a very large network comprising 35,711 retail stores in more than 84 countries across the world. According to an estimate, 61% of Starbucks stores are in China and the US, and they contribute significantly to the company’s profitability.
The other thing that adds value is the location of Starbucks stores at different locations to target different types of customer markets. For instance, Starbucks has established its stores in the following places;
- Rural locations
- Office buildings
- Off-highway locations
- Downtown and suburban retail centers
- University campuses
Marketing & Sale of Starbucks
According to an estimate, Starbucks will spend roundabout 416 billion USD on advertisement campaigns by 2022. The company is increasing its annual marketing and advertisement budget consistently. However, some of the marketing and advertisement strategies that the coffee brand employs for the promotion of its products are as follows;
- Customer relevant event
- New product ceremony
- Partnerships
- Opening of new stores
- Word-of-mouth marketing
- Sales promotion events
- Public relations
- Media advertisement
- Print media
- Sales training
- Market research
Services of Starbucks
I-customer service.
Starbucks offers excellent customer service that would increase the brand image and value of the company. Long queues of customers at the store raise concerns and questions about the productivity of employees and the customer service delivery process. However, some of the main services that Starbucks offers to its customers are as follows;
- No rushed service
- Satisfying customer expectations with speed
- Free coffee to Regular customers
- Recognizing regular customers with their names
Supporting Activities of Starbucks
Some of the four main supporting activities in the value chain analysis of Starbucks as corporate value chain analysis example are as follows;
Infrastructure
Starbucks has established an infrastructure of 35,711 retail location points in 84 countries across the world. The coffee brand has developed a functional infrastructure comprising financial accounting, general management, planning, and organizing. The company plans to develop an infrastructure of more than 55000 retail location points by the end of 2030.
Human Resource Management
Starbucks has a very large database of employees comprising more than 402000 employees. The coffee brand carefully focuses on the needs and demands of customers; involves them in the decision-making process, and offers them training and development to improve their skills and expertise. However, some employees are unhappy due to heavy work pressure, abusive behavior of customers, and understaffing.
Some of the awards and recognitions Starbucks has achieved relevant to HR are as follows;
- Best Employer for Women in 2021
- World’s Best Employer 2021
- Ranking in Forbes List of Best Employers for Diversity
Technological Development
Technological development plays a key role in adding value to the coffee chain brand. Starbucks employs the latest technology for conducting supply chain operations, production, and other areas to improve efficiency and customer experience. While developing new products and offering premium customer experience, the company employs the following technology;
- Machine learning
- Cloud computing
- Artificial intelligence
Procurement
The procurement team of Starbucks has the responsibility of purchasing raw supplies and materials for the company to develop the final product. Their job also comprises establishing relationships with customers suppliers and farmers through service agreements, contracts, and procuring agreements. However, the objective of the company is to offer high-quality products to the customers
Conclusion: Starbucks Value Chain Analysis Example Company | Application of Value Chain Analysis
After an in-depth study of the value chain analysis of Starbucks; we have realized that Starbucks is the world’s leading premium retail coffee chain brand. If you are learning about Starbucks value chain analysis company example; then you should keep in mind the abovementioned primary and supporting activities involved in the process of value chain analysis Example Company. They’re inbound and outbound logistics, operations, marketing, and services; infrastructure, procurement, HRM, and technology as an application of value chain analysis.
Ahsan is an accomplished researcher and has a deep insight in worldly life affairs. He goes Live 3 days a week on various social media platforms. Other than research writing, he’s a very interesting person.
Related Posts

Woolworths Supply Chain Management

Amazon Logistics Issues

Logistics and Operation Management

Starbucks business model & supply chain analysis
Starbucks is the premier roaster, marketer, and retailer of specialty coffee in the world, operating in 83 markets. Starbucks purchases and roasts high-quality coffees, handcrafted coffee, tea, and other beverages, and a variety of high-quality food items through company-operated stores.
Starbucks also sells a variety of coffee and tea products and licenses its trademarks through other channels, such as licensed stores, as well as grocery and food service through its Global Coffee Alliance with Nestlé S.A. (“Nestlé”). In addition to its flagship Starbucks Coffee brand, Starbucks sells goods and services under the following brands: Teavana, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Ethos, Starbucks Reserve, and Princi.
Starbucks’ primary objective is to maintain Starbucks standing as one of the world’s most recognized and respected brands. Starbucks invests in its brand and operations to achieve long-term targeted revenue and income growth. This includes expanding its global store base, adding stores in both existing, developed markets such as the U.S. and in higher growth markets such as China, and optimizing the mix of company-operated and licensed stores around the world.
By leveraging experiences gained, Starbucks continues to drive beverage, equipment, process, and technology innovation, including in its digital platform. Starbucks regularly offers consumers new, innovative coffee and other products in a variety of forms across new categories, diverse channels, and alternative store formats.
In this strategy story, we decided to decipher the business model and supply chain of Starbucks.
Business Model of Starbucks
Starbucks generated $32.25 billion in revenues in FY22 . The business model of Starbucks consists of company-operated stores and licensed stores. As of FY22, Starbucks had 35,711 stores, comprising 18,253 company-operated stores (51%) and 17,458 licensed stores (49%).
The mix of company-operated versus licensed stores in a given market generally varies based on several factors, including its ability to access desirable local retail space, the complexity, profitability, and expected ultimate size of the market for Starbucks, and its ability to leverage the support infrastructure within a geographic region.
Total net revenues increased $3.2 billion, or 11%, over fiscal 2021, primarily due to higher revenues from company-operated stores ($2.0 billion).
- The growth in company-operated store revenue was driven by an 8% increase in comparable store sales ($1.8 billion), attributed to a 5% increase in average tickets and a 2% increase in similar transactions.
- Licensed stores’ revenue increased by $972 million, primarily driven by higher product and equipment sales and royalty revenues from its licensees.
- Other revenues increased by $249 million, primarily due to higher product sales and royalty revenue in the Global Coffee Alliance and growth in its ready-to-drink business.
Company-operated Stores
Revenue from company-operated stores accounted for 82% of total net revenues during FY22. Starbucks’ retail objective is to be the leading retailer and brand of coffee and tea in each of Starbucks’ target markets by selling the finest quality coffee, tea, and related products, as well as complementary food offerings, and by providing each customer with a unique Starbucks Experience.
The Starbucks Experience is built upon superior customer service, convenience, and a seamless digital experience, as well as safe, clean and well-maintained stores that reflect the personalities of the communities in which they operate, thereby building a high degree of customer loyalty.
Starbucks company-operated stores are typically located in high-traffic, high-visibility locations. Starbucks’ ability to vary the size and format of its stores allows it to locate them in or near various settings, including downtown and suburban retail centers, office buildings, university campuses, and rural and off-highway locations.
Starbucks has plans to increase the efficiency of its business model while elevating the partner and customer experience (the “Reinvention Plan”). Starbucks believes investing in partner wages and training will increase retention and productivity. At the same time, the acceleration of purpose-built store concepts and technological innovations will provide additional convenience and connection with customers.
Today at Investor Day, Starbucks is unveiling their "Reinvention Plan" for the company. Since workers aren't invited to Investor Day, we wanted to share our own vision for the future of Starbucks. pic.twitter.com/fw2bREozkX — Starbucks Workers United (@SBWorkersUnited) September 13, 2022
Starbucks strongly focuses on increasing digital adoption to provide convenience and elevate the customer experience. These strategies align closely with rapidly evolving customer preferences, including higher levels of mobile ordering, more contactless pick-up experiences, and reduced in-store congestion, all of which naturally allow for greater physical distancing.
Starbucks Marketing Mix (4Ps)
Stored Value Cards and Loyalty Program: The Starbucks Card, Starbucks’ branded stored value card program, is designed to provide customers with a convenient payment method, support gifting, and increase the frequency of store visits by cardholders, in part through the related Starbucks Rewards loyalty program where available.
How does Starbucks’ unique promotion strategy aid in its massive success?
Licensed Stores
Revenues from licensed stores accounted for 11% of Starbucks’ net revenues in fiscal 2022. Licensed stores generally have a lower gross margin and a higher operating margin than company-operated stores. Under the licensed business model, Starbucks receives a margin on branded products and supplies sold to the licensed store operator and a royalty on retail sales.
Licensees are responsible for operating costs and capital investments, which more than offset the lower revenues Starbucks receives under the licensed store model. In its licensed store operations, Starbucks seeks to leverage the expertise of its local partners and share its operating and store development experience. Licensees provide improved and, at times, only access to desirable retail space. Most licensees are prominent retailers with the in-depth market knowledge and access.
As part of these arrangements, Starbucks sells coffee, tea, food, and related products to licensees for resale to customers and receives royalties and license fees from the licensees. Starbucks also sells certain equipment, such as coffee brewers and espresso machines, to its licensees for use in their operations.
| Company-operated stores | 26,576.1 | 24,607.0 | 19,164.6 |
| Licensed stores | 3,655.5 | 2,683.6 | 2,327.1 |
| Other | 2,018.7 | 1,770.0 | 2,026.3 |
| Beverage | 19,553.3 | 18,317.0 | 14,337.5 |
| Food | 5,804.2 | 5,053.4 | 3,799.2 |
| Other | 6,890.8 | 5,690.2 | 5,381.3 |
Other Revenues
Other revenues primarily include sales of packaged coffee, tea, and ready-to-drink beverages to customers outside of its company-operated and licensed stores, as well as royalties received from Nestlé under the Global Coffee Alliance and other collaborative partnerships. Others accounted for 7% of Starbucks’ revenue in FY22.
Supply Chain of Starbucks
Starbucks is committed to selling the finest whole bean coffees and coffee beverages. To help ensure compliance with its rigorous coffee standards, Starbucks substantially controls all coffee purchasing, roasting, and packaging and the global distribution of coffee used in its operations, as part of its supply chain strategy.
Nestlé controls the distribution of certain finished goods through the Global Coffee Alliance. Starbucks purchases green coffee beans from multiple coffee-producing regions around the world and custom roasts them to its exacting standards for many blends and single-origin coffees.
Starbucks SWOT Analysis
The price of coffee is subject to significant volatility. Both the premium and the commodity price depend upon the supply and demand at the time of purchase. Supply and price can be affected by multiple factors in the producing countries, including
- water supply quality and availability throughout the coffee production chain,
- natural disasters,
- crop disease, and pests,
- a general increase in farm inputs and costs of production,
- inventory levels, and political and economic conditions.
Depending on market conditions, Starbucks buys coffee using fixed-price and price-to-be-fixed purchase commitments to secure an adequate supply of quality green coffee.
Starbucks prices products on value not cost. Why?
Starbucks depends upon its relationships with coffee producers, outside trading companies, and exporters for the supply of green coffee. To secure the supply chain of high-quality green coffee, Starbucks operates ten farmer support centers.
Farmer support centers are staffed with agronomists and sustainability experts working with coffee farming communities to promote best practices in coffee production designed to improve coffee quality and yields and agronomy support to address climate change and other impacts.
In addition to coffee, Starbucks also purchases significant amounts of dairy and plant-based dairy-free alternative products, particularly fluid milk, oat milk, and almond milk, to support the needs of its company-operated stores.
Starbucks PESTEL Analysis
Products other than whole bean coffees and coffee beverages sold in Starbucks stores include tea and many ready-to-drink beverages purchased from several specialty suppliers, usually under long-term supply contracts. Food products, such as pastries, breakfast sandwiches, and lunch items, are purchased from national, regional, and local sources.
Starbucks also purchases a broad range of paper and plastic products, such as cups and cutlery, from several companies to support the needs of its retail stores and manufacturing and distribution operations. Starbucks is also expanding its use of reusable packaging to reduce landfill waste.

A passionate writer and a business enthusiast having 6 years of industry experience in a variety of industries and functions. I just love telling stories and share my learning. Connect with me on LinkedIn. Let's chat...
Related Posts

How does Instacart work and make money: Business Model

What does Zscaler do | How does Zscaler work | Business Model

What does Chegg do | How does Chegg work | Business Model

What does Bill.com do | How does Bill.com work | Business Model

What does Cricut do | How does Cricut work | Business Model

What does DexCom do? How does DexCom business work?

What does CarMax do? How does CarMax business work?

What does Paycom do? How does Paycom work?
What does FedEx do | How does FedEx work | Business Model

How does Rumble work and make money: Business Model

Dollar General Business Model & Supply Chain Explained

What does C3 AI do | Business Model Explained

What does Aflac do| How does Aflac work| Business Model

How does Booking.com work and make money: Business Model

What does Okta do | How does Okta work | Business Model

What does Alteryx do | How does Alteryx work | Business Model
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Advanced Strategies
- Brand Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Luxury Business
- Startup Strategies
- 1 Minute Strategy Stories
- Business Or Revenue Model
- Forward Thinking Strategies
- Infographics
- Publish & Promote Your Article
- Write Article
- Testimonials
- TSS Programs
- Fight Against Covid
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and condition
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Master Sessions
- Live Courses
- Playbook & Guides
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Silver Bee Group
- [email protected]

- NEW SOLUTION
- Top Visitors
- Popular Topics
- Newest Members
- Newest Papers
- Top Donators
Value Chain Analysis (Starbucks)
| Word (s) : | 1037 |
|---|---|
| Pages (s) : | 5 |
| View (s) : | 6152 |
| Rank : | 0 |

- University Login
| Google+ | |
| or Login with Email | |
Recent Topics
New entries.
- Quality Parts Company
- Lincoln Electric
- Vêtements Ltée
- Google Case Analysis
Most Recent Request
- oilwell cable comp
- research methods
- human resource sho
- toyota adopts a st
Ease your MBA workload and get more time for yourself

Value Chain Analysis: A Case Study on Starbucks
Added on 2023-04-24
About this Document

End of preview
Want to access all the pages? Upload your documents or become a member.
Value chain analysis of Starbucks lg ...
International rivalry analysis: starbucks vs dunkin donuts lg ..., strategy management accounting report 2022 lg ..., marketing strategy and practices lg ..., competitive advantage and entrepreneurship lg ..., to investigate the impact of different talent management strategies in organisational success. a study on starbucks. lg ....
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, what drives experiential loyalty a case study of starbucks coffee chain in taiwan.
British Food Journal
ISSN : 0007-070X
Article publication date: 6 March 2017
The purpose of this paper is to identify the dimensions of experiential quality and examining the interrelationships among experiential quality, experiential satisfaction, perceived value, experiential trust and experiential loyalty using a multi-dimensional and hierarchical model as a framework perceived by coffee chain customers.
Design/methodology/approach
The data used in this study were based on a sample of 428 customers at Starbucks in Taipei City of Taiwan. Data were analyzed using exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis.
The findings reveal that there are four primary dimensions and 13 sub-dimensions of experiential quality in a coffee chain. In addition, the results indicate that affective quality is identified as the most primary dimension of experiential quality perceived by coffee chain customers. Experiential quality significantly influences perceived value and experiential trust, respectively. Also, experiential satisfaction is influenced by perceived value, experiential quality and experiential trust. Furthermore, experiential satisfaction and experiential trust are determinants of experiential loyalty.
Originality/value
This is the first study identifying experiential quality, experiential satisfaction, perceived value, experiential trust and experiential loyalty in the context of coffee chains.
- Perceived value
- Dimensions of experiential quality
- Experiential loyalty
- Experiential satisfaction
- Multi-dimensional and hierarchical model
Wu, H.-C. (2017), "What drives experiential loyalty? A case study of Starbucks coffee chain in Taiwan", British Food Journal , Vol. 119 No. 3, pp. 468-496. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-08-2016-0349
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2017, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
More From Forbes
Intuitive intelligence and 8 common blocks that impact it.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Hulan Hagen is the founder and CEO of the Business Intuition Institute , an international executive coach, and strategy consultant.
What is intuitive intelligence, and how can it help you solve today’s business challenges? According to experts , there are several problems of emerging importance in the business world. A few key issues are hiring for mindset, staying focused, adapting to consumer preferences, navigating change and integrating artificial intelligence. All of these demand foresight and creativity, which are elements of intuitive intelligence.
How can business leaders develop the intuitive intelligence necessary to flourish in the face of relentless technological, economic and social change? They must better comprehend this skill set and recognize common barriers that can negatively impact it.
Understanding Intuitive Intelligence
Intuitive intelligence is the ability to make decisions based on insights that aren't obvious through logical reasoning. It synthesizes experience, instinct and subconscious information. In their 1958 book Organizations , James March and Herbert Simon showed how decision-making models that depend on complete knowledge of parameters, like return on investment and probabilities of outcomes, are unrealistic. Rationality is bounded or limited, and economists who claim that firms optimize profit assume too much. Bounded rationality necessitates satisficing, or just-good-enough, solutions .
But from the standpoint of intuitive intelligence, optimizing profit may amount to very little. Breakthrough innovation—the leap from zero to one, as entrepreneur Peter Thiel puts it —creates returns that blow past improvements possible through optimization. In Thiel’s terminology, optimizing can take a firm from one to n , with n being the optimal iteration of a product or service. But the blowoff profits are made from monopolizing innovations, or taking them from "zero to one" by creating something new.
WWE SmackDown Results: Winners And Grades On July 26, 2024
Today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for saturday, july 27, noche ufc 306 card announced with 2 world-title fights.
The recognition that rationality is bounded can expand, rather than limit, outcomes because innovations that result from intuitive intelligence in the face of ambiguity can create new industries and monopoly profits. The best business decision-makers develop their intuitive intelligence to broaden their perceptual scope, jettisoning biases like stereotyping, thinking in one language and selective perception.
Masters Of Intuitive Intelligence
Beyond Peter Thiel, there are many leaders and entrepreneurs who saw opportunities for innovation and ran with them. For example, Richard Branson's decision to start Virgin Atlantic—despite having no experience in the airline industry—was driven by the belief that he could offer better service than existing airlines.
Spanx's founder Sara Blakely was getting ready for a party when she decided to cut the feet off some pantyhose and wear them under a pair of white pants to ensure her outfit had clean lines. Her intuitive thinking and firm understanding of her target market’s needs were key to her company's success.
Howard Schultz, the former CEO of Starbucks, relied on his intuition to transform a dry-coffee store into a global coffeehouse chain by recreating the Italian coffeehouse experience in the United States. Starbucks, which was named after a character from Melville’s Moby Dick , was able to grow because Schultz intuited that customers would value a place to relax and socialize over a cup of coffee.
8 Common Blocks To Intuitive Intelligence
At the Business Intuition Institute, we've identified eight blocks to intuitive intelligence.
1. Lack Of Self-Awareness: Understanding your own thought processes and emotional responses is crucial. Intuitive intelligence requires reflection and pattern recognition.
2. Lack Of Experience And Knowledge: The more varied your experiences, the richer your pool of subconscious knowledge. By engaging in activities outside your usual scope, you can broaden your perspective and enhance your intuitive abilities.
3. Bias Against Intuition: Many professionals believe that only left-brained thinking, which is associated with logic, can result in profitable solutions. However, some of the greatest, revenue-generating innovations can come from right-brained, or creative and qualitative, thinking.
4. Thinking In One Language: A major barrier to intuitive intelligence is being locked into the process of deductive reasoning. Many of us think only in words or numbers. But intuitive insights arrive when we tap into the flow of our subconscious.
5. Selective Perception: Because of habits or unconscious blockages, we often instinctively restrict the kind of information we receive. To build up our intuition, we must overcome things like perceptual distortion and biases, artificial constraints or thinking inside the box.
6. Failing To See The Forest For The Trees: It's common for decision-makers to get lost in detail and suffer from analysis paralysis . Being so caught up in the granular can keep people from big-picture, intuitive insights.
7. Conformity To Organizational Norms: When organizations have cultures that are overly uniform, they tend to block creativity and intuition.
8. Gresham’s Law: When ways of operating and thinking become the default process, the possibility of breakthrough intuitive thinking is hindered. Sir Thomas Greshman said that " bad money drives out good ," meaning that overuse of poor currency (or thinking, in this case) keeps people from making better currency. This phenomenon causes us to rely on second-rate forms of problem-solving because they're familiar, which drives away creative, breakthrough solutions.
Business leaders who can overcome these barriers to intuitive intelligence will help open the doors for breakthrough innovation.
To harness the power of intuitive intelligence, we need to tap into our inner wisdom. Used alongside analytical thinking, this skill can help us generate innovative, original solutions that transform our businesses and create a bold future.
Forbes Coaches Council is an invitation-only community for leading business and career coaches. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An analysis of Starbucks ( SBUX) can help to further illustrate and understand the value chain concept. The Starbucks journey began with a single store in Seattle in the year 1971. From there it ...
2.1) Industry Overview and Analysis: Starbucks primarily operates and competes in the retail coffee and snacks store industry. This industry ... The main inputs into the value chain of Starbucks is coffee beans and premium Arabica coffee grown in select regions which are standard inputs, which makes the cost of switching between substitute ...
By John Dudovskiy. October 8, 2022. Starbucks value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage for the global coffeehouse chain. Figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis.
Starbucks Value-Chain Analysis 2014 John Dudovskiy. Value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that is used to analyse relationships between various parts of operations and the manner in which each part adds value to contribute to the level of revenues. Company value-chain can be divided into two groups: primary and support activities.
Starbucks Value Chain Analysis. Tip: In the Porter model of value chain analysis, we will study five primary activities - Inbound Logistics, Operations, Outbound Logistics, Marketing and Sales, and Service. From the procurement of coffee beans to the distribution of its products, Starbucks has undertaken so many activities in its business model.
Starbucks Value Chain Analysis. The objective of the value chain analysis is to analyze the primary and supportive activities for adding value to the company's product to gain the customer and provide the best quality at minimum cost. A company deals with many problems and obstructions during its growing and mature phase. To solve the problems, it is important to study and analyze the value ...
The value chain of any business corporation such as Starbucks is divided into two: The primary activities comprise inbound operations, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. The secondary or supporting activities comprise procurement and purchasing, human resource management, technological development, and company ...
The paper discusses the value chain of coffee, issues surrounding the coffee supply chain and the need for sustainable coffee production. In addition it also discusses Starbucks' position and influence on the coffee trade, and the measures that Starbucks is taking to ensure sustainability efforts throughout the coffee supply chain.
After an in-depth study of the value chain analysis of Starbucks; we have realized that Starbucks is the world's leading premium retail coffee chain brand. If you are learning about Starbucks value chain analysis company example; then you should keep in mind the abovementioned primary and supporting activities involved in the process of value ...
for in-depth analysis that considers the company's entire value chain, ... on CSR Effort Toward Sustainable Development: Case Study Starbucks Greener Nusantara. ... an analysis of 21 studies, ...
This study addresses and identifies how Starbucks, a famous Western coffee brand, is perceived by Asian consumers, particularly Taiwanese and Korean consumers, by providing qualitative evidence to ...
The value chain analysis is a very important process that has the ability to create newer ways for a business to develop its various sectors and improve the quality of its products which ...
Starbucks' supply chain transformationA well-run supply chain helps baristas pour good Starbucks coffee. Because bean-to-cup is a complicated process. Starbu...
To illustrate, let's consider the VRIO framework example of Starbucks. Kristin Kennedy, Jennifer Azarian, and Colleen Steele conducted a VRIO analysis of Starbucks as part of their research. Consequently, they came up with three of their key business resources: Here are some of the findings from their analysis: 1.
Starbucks generated $32.25 billion in revenues in FY22. The business model of Starbucks consists of company-operated stores and licensed stores. As of FY22, Starbucks had 35,711 stores, comprising 18,253 company-operated stores (51%) and 17,458 licensed stores (49%). The mix of company-operated versus licensed stores in a given market generally ...
In 2003, Starbucks marketed Fair Trade Certified coffee at most of its retail stores through some 350 universities and hotel locations that were licensed to sell Starbucks coffees. • Operation: Starbucks was able to expand its market through a number of channels such licensing with a reputable and capable local company with retailing know how ...
Analyze Starbucks' value chain for competitive advantage with literature review, research, results, and recommendations. ... Past Papers; Plagiarism Checker; Expert Help; Subscription; Subscribe Now. Login. Value chain analysis of Starbucks ... Globalization and its Impact on Starbucks: A Case Study... | 12 | 756 | 93. View document. Business ...
Starbucks Supply Chain Analysis. ... What is the expected impact of covid-1 9 on downstream coffee value chain operations in . ... using Uniqlo as a case study. It analyzes the operational ...
The value chain represents a useful concept in exercising how an individual can lead to. the creation of value for the customers. Value chain analysis thus represents a strategic tool used. for analyzing the internal activities of the firm (Letizia and Hendrikse 2016.). Its goal lies in.
A case study of Starbucks coffee chain in Taiwan - Author: Hung-Che Wu ... Data were analyzed using exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis.,The findings reveal that there are four primary dimensions and 13 sub-dimensions of experiential quality in a coffee chain. ... Originality/value. This is the first study identifying ...
Howard Schultz, the former CEO of Starbucks, relied on his intuition to transform a dry-coffee store into a global coffeehouse chain by recreating the Italian coffeehouse experience in the United ...