Information
- Author Services

Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Journal Description
Trends in higher education.
- Open Access — free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
- Trends in Higher Education Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal History
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
- arrow_forward_ios Forthcoming issue arrow_forward_ios Current issue
- Vol. 3 (2024)
- Vol. 2 (2023)
- Vol. 1 (2022)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest books, e-mail alert.

Conferences
Further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 24 April 2023
Artificial intelligence in higher education: the state of the field
- Helen Crompton ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1775-8219 1 , 3 &
- Diane Burke 2
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 20 , Article number: 22 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
114k Accesses
150 Citations
67 Altmetric
Metrics details
This systematic review provides unique findings with an up-to-date examination of artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education (HE) from 2016 to 2022. Using PRISMA principles and protocol, 138 articles were identified for a full examination. Using a priori, and grounded coding, the data from the 138 articles were extracted, analyzed, and coded. The findings of this study show that in 2021 and 2022, publications rose nearly two to three times the number of previous years. With this rapid rise in the number of AIEd HE publications, new trends have emerged. The findings show that research was conducted in six of the seven continents of the world. The trend has shifted from the US to China leading in the number of publications. Another new trend is in the researcher affiliation as prior studies showed a lack of researchers from departments of education. This has now changed to be the most dominant department. Undergraduate students were the most studied students at 72%. Similar to the findings of other studies, language learning was the most common subject domain. This included writing, reading, and vocabulary acquisition. In examination of who the AIEd was intended for 72% of the studies focused on students, 17% instructors, and 11% managers. In answering the overarching question of how AIEd was used in HE, grounded coding was used. Five usage codes emerged from the data: (1) Assessment/Evaluation, (2) Predicting, (3) AI Assistant, (4) Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS), and (5) Managing Student Learning. This systematic review revealed gaps in the literature to be used as a springboard for future researchers, including new tools, such as Chat GPT.
A systematic review examining AIEd in higher education (HE) up to the end of 2022.
Unique findings in the switch from US to China in the most studies published.
A two to threefold increase in studies published in 2021 and 2022 to prior years.
AIEd was used for: Assessment/Evaluation, Predicting, AI Assistant, Intelligent Tutoring System, and Managing Student Learning.
Introduction
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education (HE) has risen quickly in the last 5 years (Chu et al., 2022 ), with a concomitant proliferation of new AI tools available. Scholars (viz., Chen et al., 2020 ; Crompton et al., 2020 , 2021 ) report on the affordances of AI to both instructors and students in HE. These benefits include the use of AI in HE to adapt instruction to the needs of different types of learners (Verdú et al., 2017 ), in providing customized prompt feedback (Dever et al., 2020 ), in developing assessments (Baykasoğlu et al., 2018 ), and predict academic success (Çağataylı & Çelebi, 2022 ). These studies help to inform educators about how artificial intelligence in education (AIEd) can be used in higher education.
Nonetheless, a gap has been highlighted by scholars (viz., Hrastinski et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ) regarding an understanding of the collective affordances provided through the use of AI in HE. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to examine extant research from 2016 to 2022 to provide an up-to-date systematic review of how AI is being used in the HE context.
Artificial intelligence has become pervasive in the lives of twenty-first century citizens and is being proclaimed as a tool that can be used to enhance and advance all sectors of our lives (Górriz et al., 2020 ). The application of AI has attracted great interest in HE which is highly influenced by the development of information and communication technologies (Alajmi et al., 2020 ). AI is a tool used across subject disciplines, including language education (Liang et al., 2021 ), engineering education (Shukla et al., 2019 ), mathematics education (Hwang & Tu, 2021 ) and medical education (Winkler-Schwartz et al., 2019 ),
Artificial intelligence
The term artificial intelligence is not new. It was coined in 1956 by McCarthy (Cristianini, 2016 ) who followed up on the work of Turing (e.g., Turing, 1937 , 1950 ). Turing described the existence of intelligent reasoning and thinking that could go into intelligent machines. The definition of AI has grown and changed since 1956, as there has been significant advancements in AI capabilities. A current definition of AI is “computing systems that are able to engage in human-like processes such as learning, adapting, synthesizing, self-correction and the use of data for complex processing tasks” (Popenici et al., 2017 , p. 2). The interdisciplinary interest from scholars from linguistics, psychology, education, and neuroscience who connect AI to nomenclature, perceptions and knowledge in their own disciplines could create a challenge when defining AI. This has created the need to create categories of AI within specific disciplinary areas. This paper focuses on the category of AI in Education (AIEd) and how AI is specifically used in higher educational contexts.
As the field of AIEd is growing and changing rapidly, there is a need to increase the academic understanding of AIEd. Scholars (viz., Hrastinski et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ) have drawn attention to the need to increase the understanding of the power of AIEd in educational contexts. The following section provides a summary of the previous research regarding AIEd.
Extant systematic reviews
This growing interest in AIEd has led scholars to investigate the research on the use of artificial intelligence in education. Some scholars have conducted systematic reviews to focus on a specific subject domain. For example, Liang et. al. ( 2021 ) conducted a systematic review and bibliographic analysis the roles and research foci of AI in language education. Shukla et. al. ( 2019 ) focused their longitudinal bibliometric analysis on 30 years of using AI in Engineering. Hwang and Tu ( 2021 ) conducted a bibliometric mapping analysis on the roles and trends in the use of AI in mathematics education, and Winkler-Schwartz et. al. ( 2019 ) specifically examined the use of AI in medical education in looking for best practices in the use of machine learning to assess surgical expertise. These studies provide a specific focus on the use of AIEd in HE but do not provide an understanding of AI across HE.
On a broader view of AIEd in HE, Ouyang et. al. ( 2022 ) conducted a systematic review of AIEd in online higher education and investigated the literature regarding the use of AI from 2011 to 2020. The findings show that performance prediction, resource recommendation, automatic assessment, and improvement of learning experiences are the four main functions of AI applications in online higher education. Salas-Pilco and Yang ( 2022 ) focused on AI applications in Latin American higher education. The results revealed that the main AI applications in higher education in Latin America are: (1) predictive modeling, (2) intelligent analytics, (3) assistive technology, (4) automatic content analysis, and (5) image analytics. These studies provide valuable information for the online and Latin American context but not an overarching examination of AIEd in HE.
Studies have been conducted to examine HE. Hinojo-Lucena et. al. ( 2019 ) conducted a bibliometric study on the impact of AIEd in HE. They analyzed the scientific production of AIEd HE publications indexed in Web of Science and Scopus databases from 2007 to 2017. This study revealed that most of the published document types were proceedings papers. The United States had the highest number of publications, and the most cited articles were about implementing virtual tutoring to improve learning. Chu et. al. ( 2022 ) reviewed the top 50 most cited articles on AI in HE from 1996 to 2020, revealing that predictions of students’ learning status were most frequently discussed. AI technology was most frequently applied in engineering courses, and AI technologies most often had a role in profiling and prediction. Finally, Zawacki-Richter et. al. ( 2019 ) analyzed AIEd in HE from 2007 to 2018 to reveal four primary uses of AIEd: (1) profiling and prediction, (2) assessment and evaluation, (3) adaptive systems and personalization, and (4) intelligent tutoring systems. There do not appear to be any studies examining the last 2 years of AIEd in HE, and these authors describe the rapid speed of both AI development and the use of AIEd in HE and call for further research in this area.
Purpose of the study
The purpose of this study is in response to the appeal from scholars (viz., Chu et al., 2022 ; Hinojo-Lucena et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ) to research to investigate the benefits and challenges of AIEd within HE settings. As the academic knowledge of AIEd HE finished with studies examining up to 2020, this study provides the most up-to-date analysis examining research through to the end of 2022.
The overarching question for this study is: what are the trends in HE research regarding the use of AIEd? The first two questions provide contextual information, such as where the studies occurred and the disciplines AI was used in. These contextual details are important for presenting the main findings of the third question of how AI is being used in HE.
In what geographical location was the AIEd research conducted, and how has the trend in the number of publications evolved across the years?
What departments were the first authors affiliated with, and what were the academic levels and subject domains in which AIEd research was being conducted?
Who are the intended users of the AI technologies and what are the applications of AI in higher education?
A PRISMA systematic review methodology was used to answer three questions guiding this study. PRISMA principles (Page et al., 2021 ) were used throughout the study. The PRISMA extension Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis for Protocols (PRISMA-P; Moher et al., 2015 ) were utilized in this study to provide an a priori roadmap to conduct a rigorous systematic review. Furthermore, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA principles; Page et al., 2021 ) were used to search, identify, and select articles to be included in the research were used for searching, identifying, and selecting articles, then in how to read, extract, and manage the secondary data gathered from those studies (Moher et al., 2015 , PRISMA Statement, 2021 ). This systematic review approach supports an unbiased synthesis of the data in an impartial way (Hemingway & Brereton, 2009 ). Within the systematic review methodology, extracted data were aggregated and presented as whole numbers and percentages. A qualitative deductive and inductive coding methodology was also used to analyze extant data and generate new theories on the use of AI in HE (Gough et al., 2017 ).
The research begins with the search for the research articles to be included in the study. Based on the research question, the study parameters are defined including the search years, quality and types of publications to be included. Next, databases and journals are selected. A Boolean search is created and used for the search of those databases and journals. Once a set of publications are located from those searches, they are then examined against an inclusion and exclusion criteria to determine which studies will be included in the final study. The relevant data to match the research questions is then extracted from the final set of studies and coded. This method section is organized to describe each of these methods with full details to ensure transparency.
Search strategy
Only peer-reviewed journal articles were selected for examination in this systematic review. This ensured a level of confidence in the quality of the studies selected (Gough et al., 2017 ). The search parameters narrowed the search focus to include studies published in 2016 to 2022. This timeframe was selected to ensure the research was up to date, which is especially important with the rapid change in technology and AIEd.
The data retrieval protocol employed an electronic and a hand search. The electronic search included educational databases within EBSCOhost. Then an additional electronic search was conducted of Wiley Online Library, JSTOR, Science Direct, and Web of Science. Within each of these databases a full text search was conducted. Aligned to the research topic and questions, the Boolean search included terms related to AI, higher education, and learning. The Boolean search is listed in Table 1 . In the initial test search, the terms “machine learning” OR “intelligent support” OR “intelligent virtual reality” OR “chatbot” OR “automated tutor” OR “intelligent agent” OR “expert system” OR “neural network” OR “natural language processing” were used. These were removed as they were subcategories of terms found in Part 1 of the search. Furthermore, inclusion of these specific AI terms resulted in a large number of computer science courses that were focused on learning about AI and not the use of AI in learning.
Part 2 of the search ensured that articles involved formal university education. The terms higher education and tertiary were both used to recognize the different terms used in different countries. The final Boolean search was “Artificial intelligence” OR AI OR “smart technologies” OR “intelligent technologies” AND “higher education” OR tertiary OR graduate OR undergraduate. Scholars (viz., Ouyang et al., 2022 ) who conducted a systematic review on AIEd in HE up to 2020 noted that they missed relevant articles from their study, and other relevant journals should intentionally be examined. Therefore, a hand search was also conducted to include an examination of other journals relevant to AIEd that may not be included in the databases. This is important as the field of AIEd is still relatively new, and journals focused on this field may not yet be indexed in databases. The hand search included: The International Journal of Learning Analytics and Artificial Intelligence in Education, the International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, and Computers & Education: Artificial Intelligence.
Electronic and hand searches resulted in 371 articles for possible inclusion. The search parameters within the electronic database search narrowed the search to articles published from 2016 to 2022, per-reviewed journal articles, and duplicates. Further screening was conducted manually, as each of the 138 articles were reviewed in full by two researchers to examine a match against the inclusion and exclusion criteria found in Table 2 .
The inter-rater reliability was calculated by percentage agreement (Belur et al., 2018 ). The researchers reached a 95% agreement for the coding. Further discussion of misaligned articles resulted in a 100% agreement. This screening process against inclusion and exclusion criteria resulted in the exclusion of 237 articles. This included the duplicates and those removed as part of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, see Fig. 1 . Leaving 138 articles for inclusion in this systematic review.
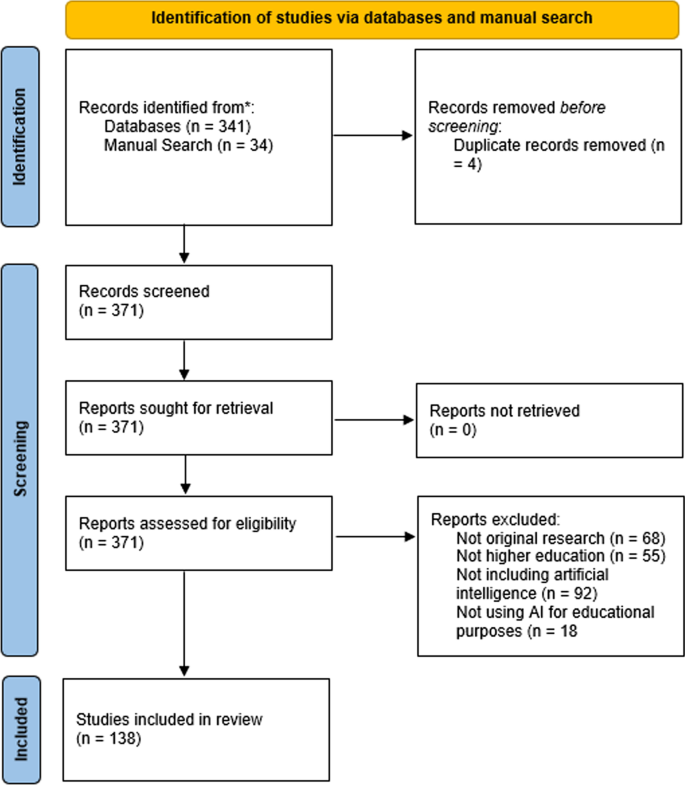
(From: Page et al., 2021 )
PRISMA flow chart of article identification and screening
The 138 articles were then coded to answer each of the research questions using deductive and inductive coding methods. Deductive coding involves examining data using a priori codes. A priori are pre-determined criteria and this process was used to code the countries, years, author affiliations, academic levels, and domains in the respective groups. Author affiliations were coded using the academic department of the first author of the study. First authors were chosen as that person is the primary researcher of the study and this follows past research practice (e.g., Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ). Who the AI was intended for was also coded using the a priori codes of Student, Instructor, Manager or Others. The Manager code was used for those who are involved in organizational tasks, e.g., tracking enrollment. Others was used for those not fitting the other three categories.
Inductive coding was used for the overarching question of this study in examining how the AI was being used in HE. Researchers of extant systematic reviews on AIEd in HE (viz., Chu et al., 2022 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ) often used an a priori framework as researchers matched the use of AI to pre-existing frameworks. A grounded coding methodology (Strauss & Corbin, 1995 ) was selected for this study to allow findings of the trends on AIEd in HE to emerge from the data. This is important as it allows a direct understanding of how AI is being used rather than how researchers may think it is being used and fitting the data to pre-existing ideas.
Grounded coding process involved extracting how the AI was being used in HE from the articles. “In vivo” (Saldana, 2015 ) coding was also used alongside grounded coding. In vivo codes are when codes use language directly from the article to capture the primary authors’ language and ensure consistency with their findings. The grounded coding design used a constant comparative method. Researchers identified important text from articles related to the use of AI, and through an iterative process, initial codes led to axial codes with a constant comparison of uses of AI with uses of AI, then of uses of AI with codes, and codes with codes. Codes were deemed theoretically saturated when the majority of the data fit with one of the codes. For both the a priori and the grounded coding, two researchers coded and reached an inter-rater percentage agreement of 96%. After discussing misaligned articles, a 100% agreement was achieved.
Findings and discussion
The findings and discussion section are organized by the three questions guiding this study. The first two questions provide contextual information on the AIEd research, and the final question provides a rigorous investigation into how AI is being used in HE.
RQ1. In what geographical location was the AIEd research conducted, and how has the trend in the number of publications evolved across the years?
The 138 studies took place across 31 countries in six of seven continents of the world. Nonetheless, that distribution was not equal across continents. Asia had the largest number of AIEd studies in HE at 41%. Of the seven countries represented in Asia, 42 of the 58 studies were conducted in Taiwan and China. Europe, at 30%, was the second largest continent and had 15 countries ranging from one to eight studies a piece. North America, at 21% of the studies was the continent with the third largest number of studies, with the USA producing 21 of the 29 studies in that continent. The 21 studies from the USA places it second behind China. Only 1% of studies were conducted in South America and 2% in Africa. See Fig. 2 for a visual representation of study distribution across countries. Those continents with high numbers of studies are from high income countries and those with low numbers have a paucity of publications in low-income countries.
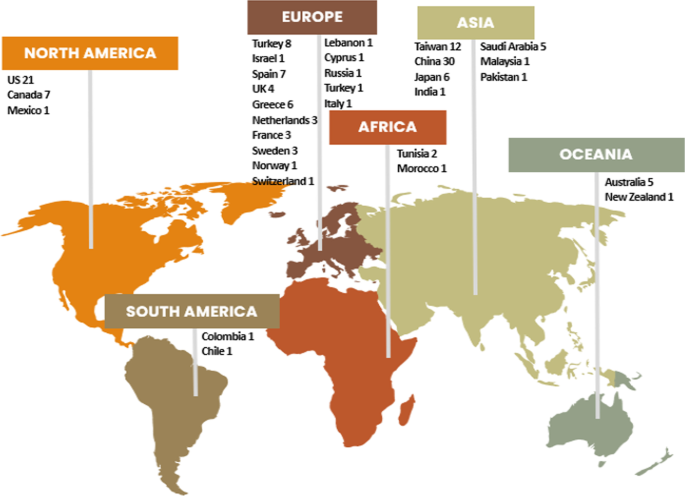
Geographical distribution of the AIEd HE studies
Data from Zawacki-Richter et. al.’s ( 2019 ) 2007–2018 systematic review examining countries found that the USA conducted the most studies across the globe at 43 out of 146, and China had the second largest at eleven of the 146 papers. Researchers have noted a rapid trend in Chinese researchers publishing more papers on AI and securing more patents than their US counterparts in a field that was originally led by the US (viz., Li et al., 2021 ). The data from this study corroborate this trend in China leading in the number of AIEd publications.
With the accelerated use of AI in society, gathering data to examine the use of AIEd in HE is useful in providing the scholarly community with specific information on that growth and if it is as prolific as anticipated by scholars (e.g., Chu et al., 2022 ). The analysis of data of the 138 studies shows that the trend towards the use of AIEd in HE has greatly increased. There is a drop in 2019, but then a great rise in 2021 and 2022; see Fig. 3 .
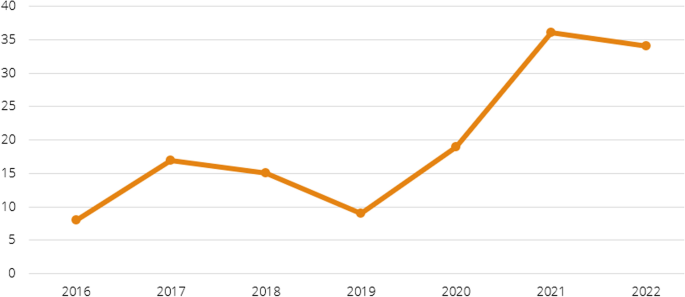
Chronological trend in AIEd in HE
Data on the rise in AIEd in HE is similar to the findings of Chu et. al. ( 2022 ) who noted an increase from 1996 to 2010 and 2011–2020. Nonetheless Chu’s parameters are across decades, and the rise is to be anticipated with a relatively new technology across a longitudinal review. Data from this study show a dramatic rise since 2020 with a 150% increase from the prior 2 years 2020–2019. The rise in 2021 and 2022 in HE could have been caused by the vast increase in HE faculty having to teach with technology during the pandemic lockdown. Faculty worldwide were using technologies, including AI, to explore how they could continue teaching and learning that was often face-to-face prior to lockdown. The disadvantage of this rapid adoption of technology is that there was little time to explore the possibilities of AI to transform learning, and AI may have been used to replicate past teaching practices, without considering new strategies previously inconceivable with the affordances of AI.
However, in a further examination of the research from 2021 to 2022, it appears that there are new strategies being considered. For example, Liu et. al.’s, 2022 study used AIEd to provide information on students’ interactions in an online environment and examine their cognitive effort. In Yao’s study in 2022, he examined the use of AI to determine student emotions while learning.
RQ2. What departments were the first authors affiliated with, and what were the academic levels and subject domains in which AIEd research was being conducted?
Department affiliations
Data from the AIEd HE studies show that of the first authors were most frequently from colleges of education (28%), followed by computer science (20%). Figure 4 presents the 15 academic affiliations of the authors found in the studies. The wide variety of affiliations demonstrate the variety of ways AI can be used in various educational disciplines, and how faculty in diverse areas, including tourism, music, and public affairs were interested in how AI can be used for educational purposes.
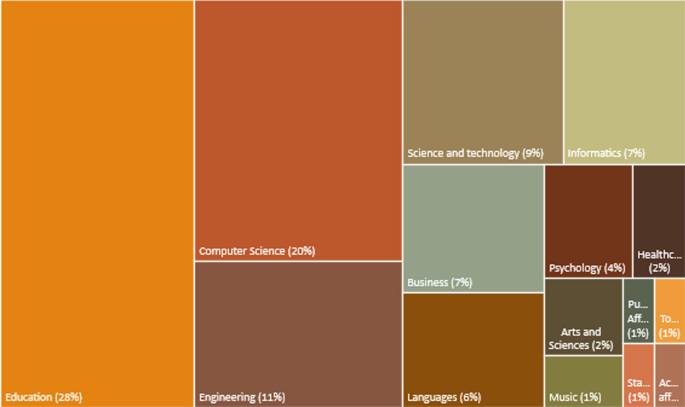
Research affiliations
In an extant AIED HE systematic review, Zawacki-Richter et. al.’s ( 2019 ) named their study Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education—where are the educators? In this study, the authors were keen to highlight that of the AIEd studies in HE, only six percent were written by researchers directly connected to the field of education, (i.e., from a college of education). The researchers found a great lack in pedagogical and ethical implications of implementing AI in HE and that there was a need for more educational perspectives on AI developments from educators conducting this work. It appears from our data that educators are now showing greater interest in leading these research endeavors, with the highest affiliated group belonging to education. This may again be due to the pandemic and those in the field of education needing to support faculty in other disciplines, and/or that they themselves needed to explore technologies for their own teaching during the lockdown. This may also be due to uptake in professors in education becoming familiar with AI tools also driven by a societal increased attention. As the focus of much research by education faculty is on teaching and learning, they are in an important position to be able to share their research with faculty in other disciplines regarding the potential affordances of AIEd.
Academic levels
The a priori coding of academic levels show that the majority of studies involved undergraduate students with 99 of the 138 (72%) focused on these students. This was in comparison to the 12 of 138 (9%) for graduate students. Some of the studies used AI for both academic levels: see Fig. 5
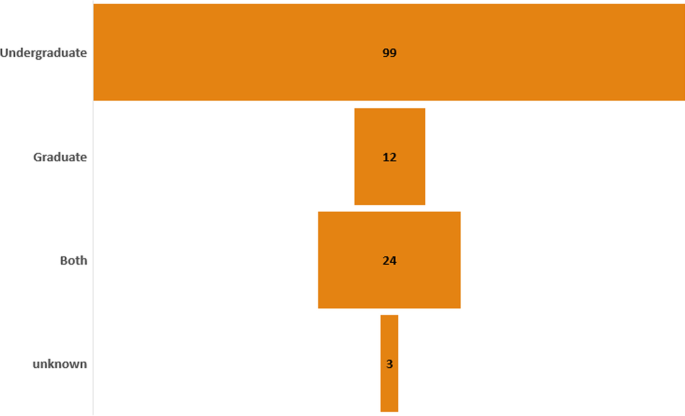
Academic level distribution by number of articles
This high percentage of studies focused on the undergraduate population was congruent with an earlier AIED HE systematic review (viz., Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ) who also reported student academic levels. This focus on undergraduate students may be due to the variety of affordances offered by AIEd, such as predictive analytics on dropouts and academic performance. These uses of AI may be less required for graduate students who already have a record of performance from their undergraduate years. Another reason for this demographic focus can also be convenience sampling, as researchers in HE typically has a much larger and accessible undergraduate population than graduates. This disparity between undergraduates and graduate populations is a concern, as AIEd has the potential to be valuable in both settings.
Subject domains
The studies were coded into 14 areas in HE; with 13 in a subject domain and one category of AIEd used in HE management of students; See Fig. 6 . There is not a wide difference in the percentages of top subject domains, with language learning at 17%, computer science at 16%, and engineering at 12%. The management of students category appeared third on the list at 14%. Prior studies have also found AIEd often used for language learning (viz., Crompton et al., 2021 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ). These results are different, however, from Chu et. al.’s ( 2022 ) findings that show engineering dramatically leading with 20 of the 50 studies, with other subjects, such as language learning, appearing once or twice. This study appears to be an outlier that while the searches were conducted in similar databases, the studies only included 50 studies from 1996 to 2020.
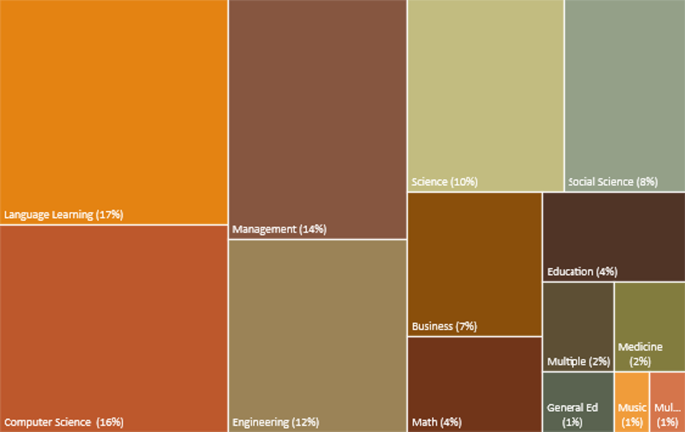
Subject domains of AIEd in HE
Previous scholars primarily focusing on language learning using AI for writing, reading, and vocabulary acquisition used the affordances of natural language processing and intelligent tutoring systems (e.g., Liang et al., 2021 ). This is similar to the findings in studies with AI used for automated feedback of writing in a foreign language (Ayse et al., 2022 ), and AI translation support (Al-Tuwayrish, 2016 ). The large use of AI for managerial activities in this systematic review focused on making predictions (12 studies) and then admissions (three studies). This is positive to see this use of AI to look across multiple databases to see trends emerging from data that may not have been anticipated and cross referenced before (Crompton et al., 2022 ). For example, to examine dropouts, researchers may consider examining class attendance, and may not examine other factors that appear unrelated. AI analysis can examine all factors and may find that dropping out is due to factors beyond class attendance.
RQ3. Who are the intended users of the AI technologies and what are the applications of AI in higher education?
Intended user of AI
Of the 138 articles, the a priori coding shows that 72% of the studies focused on Students, followed by a focus on Instructors at 17%, and Managers at 11%, see Fig. 7 . The studies provided examples of AI being used to provide support to students, such as access to learning materials for inclusive learning (Gupta & Chen, 2022 ), provide immediate answers to student questions, self-testing opportunities (Yao, 2022 ), and instant personalized feedback (Mousavi et al., 2020 ).
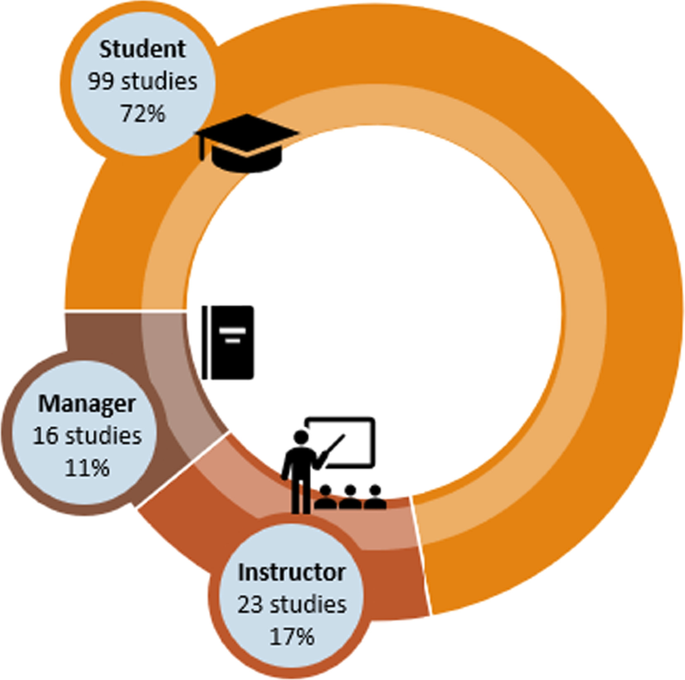
Intended user
The data revealed a large emphasis on students in the use of AIEd in HE. This user focus is different from a recent systematic review on AIEd in K-12 that found that AIEd studies in K-12 settings prioritized teachers (Crompton et al., 2022 ). This may appear that HE uses AI to focus more on students than in K-12. However, this large number of student studies in HE may be due to the student population being more easily accessibility to HE researchers who may study their own students. The ethical review process is also typically much shorter in HE than in K-12. Therefore, the data on the intended focus should be reviewed while keeping in mind these other explanations. It was interesting that Managers were the lowest focus in K-12 and also in this study in HE. AI has great potential to collect, cross reference and examine data across large datasets that can allow data to be used for actionable insight. More focus on the use of AI by managers would tap into this potential.
How is AI used in HE
Using grounded coding, the use of AIEd from each of the 138 articles was examined and six major codes emerged from the data. These codes provide insight into how AI was used in HE. The five codes are: (1) Assessment/Evaluation, (2) Predicting, (3) AI Assistant, (4) Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS), and (5) Managing Student Learning. For each of these codes there are also axial codes, which are secondary codes as subcategories from the main category. Each code is delineated below with a figure of the codes with further descriptive information and examples.
Assessment/evaluation
Assessment and Evaluation was the most common use of AIEd in HE. Within this code there were six axial codes broken down into further codes; see Fig. 8 . Automatic assessment was most common, seen in 26 of the studies. It was interesting to see that this involved assessment of academic achievement, but also other factors, such as affect.
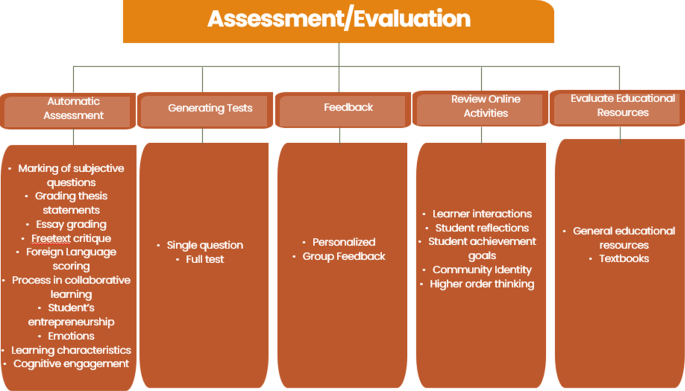
Codes and axial codes for assessment and evaluation
Automatic assessment was used to support a variety of learners in HE. As well as reducing the time it takes for instructors to grade (Rutner & Scott, 2022 ), automatic grading showed positive use for a variety of students with diverse needs. For example, Zhang and Xu ( 2022 ) used automatic assessment to improve academic writing skills of Uyghur ethnic minority students living in China. Writing has a variety of cultural nuances and in this study the students were shown to engage with the automatic assessment system behaviorally, cognitively, and affectively. This allowed the students to engage in self-regulated learning while improving their writing.
Feedback was a description often used in the studies, as students were given text and/or images as feedback as a formative evaluation. Mousavi et. al. ( 2020 ) developed a system to provide first year biology students with an automated personalized feedback system tailored to the students’ specific demographics, attributes, and academic status. With the unique feature of AIEd being able to analyze multiple data sets involving a variety of different students, AI was used to assess and provide feedback on students’ group work (viz., Ouatik et al., 2021 ).
AI also supports instructors in generating questions and creating multiple question tests (Yang et al., 2021 ). For example, (Lu et al., 2021 ) used natural language processing to create a system that automatically created tests. Following a Turing type test, researchers found that AI technologies can generate highly realistic short-answer questions. The ability for AI to develop multiple questions is a highly valuable affordance as tests can take a great deal of time to make. However, it would be important for instructors to always confirm questions provided by the AI to ensure they are correct and that they match the learning objectives for the class, especially in high value summative assessments.
The axial code within assessment and evaluation revealed that AI was used to review activities in the online space. This included evaluating student’s reflections, achievement goals, community identity, and higher order thinking (viz., Huang et al., 2021 ). Three studies used AIEd to evaluate educational materials. This included general resources and textbooks (viz., Koć‑Januchta et al., 2022 ). It is interesting to see the use of AI for the assessment of educational products, rather than educational artifacts developed by students. While this process may be very similar in nature, this shows researchers thinking beyond the traditional use of AI for assessment to provide other affordances.
Predicting was a common use of AIEd in HE with 21 studies focused specifically on the use of AI for forecasting trends in data. Ten axial codes emerged on the way AI was used to predict different topics, with nine focused on predictions regarding students and the other on predicting the future of higher education. See Fig. 9 .
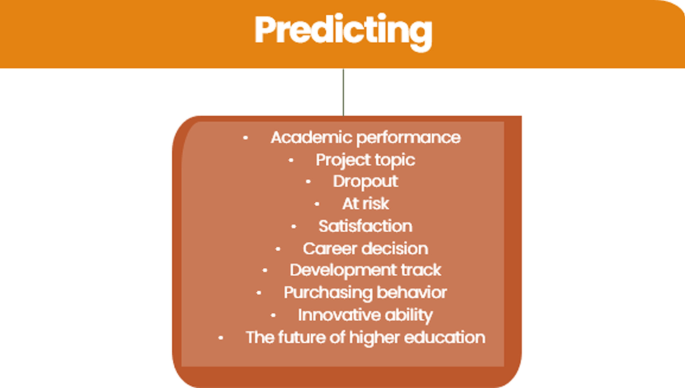
Predicting axial codes
Extant systematic reviews on HE highlighted the use of AIEd for prediction (viz., Chu et al., 2022 ; Hinojo-Lucena et al., 2019 ; Ouyang et al., 2022 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ). Ten of the articles in this study used AI for predicting academic performance. Many of the axial codes were often overlapping, such as predicting at risk students, and predicting dropouts; however, each provided distinct affordances. An example of this is the study by Qian et. al. ( 2021 ). These researchers examined students taking a MOOC course. MOOCs can be challenging environments to determine information on individual students with the vast number of students taking the course (Krause & Lowe, 2014 ). However, Qian et al., used AIEd to predict students’ future grades by inputting 17 different learning features, including past grades, into an artificial neural network. The findings were able to predict students’ grades and highlight students at risk of dropping out of the course.
In a systematic review on AIEd within the K-12 context (viz., Crompton et al., 2022 ), prediction was less pronounced in the findings. In the K-12 setting, there was a brief mention of the use of AI in predicting student academic performance. One of the studies mentioned students at risk of dropping out, but this was immediately followed by questions about privacy concerns and describing this as “sensitive”. The use of prediction from the data in this HE systematic review cover a wide range of AI predictive affordances. students Sensitivity is still important in a HE setting, but it is positive to see the valuable insight it provides that can be used to avoid students failing in their goals.
AI assistant
The studies evaluated in this review indicated that the AI Assistant used to support learners had a variety of different names. This code included nomenclature such as, virtual assistant, virtual agent, intelligent agent, intelligent tutor, and intelligent helper. Crompton et. al. ( 2022 ), described the difference in the terms to delineate the way that the AI appeared to the user. For example, if there was an anthropomorphic presence to the AI, such as an avatar, or if the AI appeared to support via other means, such as text prompt. The findings of this systematic review align to Crompton et. al.’s ( 2022 ) descriptive differences of the AI Assistant. Furthermore, this code included studies that provide assistance to students, but may not have specifically used the word assistance. These include the use of chatbots for student outreach, answering questions, and providing other assistance. See Fig. 10 for the axial codes for AI Assistant.
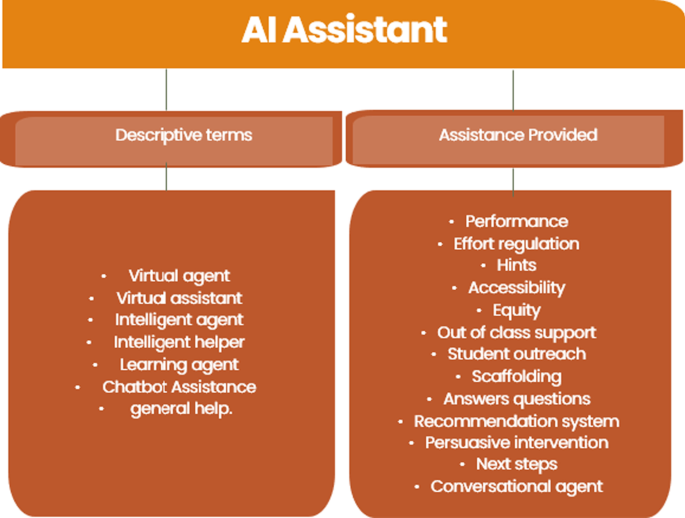
AI assistant axial codes
Many of these assistants offered multiple supports to students, such as Alex , the AI described as a virtual change agent in Kim and Bennekin’s ( 2016 ) study. Alex interacted with students in a college mathematics course by asking diagnostic questions and gave support depending on student needs. Alex’s support was organized into four stages: (1) goal initiation (“Want it”), (2) goal formation (“Plan for it”), (3) action control (“Do it”), and (4) emotion control (“Finish it”). Alex provided responses depending on which of these four areas students needed help. These messages supported students with the aim of encouraging persistence in pursuing their studies and degree programs and improving performance.
The role of AI in providing assistance connects back to the seminal work of Vygotsky ( 1978 ) and the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). ZPD highlights the degree to which students can rapidly develop when assisted. Vygotsky described this assistance often in the form of a person. However, with technological advancements, the use of AI assistants in these studies are providing that support for students. The affordances of AI can also ensure that the support is timely without waiting for a person to be available. Also, assistance can consider aspects on students’ academic ability, preferences, and best strategies for supporting. These features were evident in Kim and Bennekin’s ( 2016 ) study using Alex.
Intelligent tutoring system
The use of Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) was revealed in the grounded coding. ITS systems are adaptive instructional systems that involve the use of AI techniques and educational methods. An ITS system customizes educational activities and strategies based on student’s characteristics and needs (Mousavinasab et al., 2021 ). While ITS may be an anticipated finding in AIED HE systematic reviews, it was interesting that extant reviews similar to this study did not always describe their use in HE. For example, Ouyang et. al. ( 2022 ), included “intelligent tutoring system” in search terms describing it as a common technique, yet ITS was not mentioned again in the paper. Zawacki-Richter et. al. ( 2019 ) on the other hand noted that ITS was in the four overarching findings of the use of AIEd in HE. Chu et. al. ( 2022 ) then used Zawacki-Richter’s four uses of AIEd for their recent systematic review.
In this systematic review, 18 studies specifically mentioned that they were using an ITS. The ITS code did not necessitate axial codes as they were performing the same type of function in HE, namely, in providing adaptive instruction to the students. For example, de Chiusole et. al. ( 2020 ) developed Stat-Knowlab, an ITS that provides the level of competence and best learning path for each student. Thus Stat-Knowlab personalizes students’ learning and provides only educational activities that the student is ready to learn. This ITS is able to monitor the evolution of the learning process as the student interacts with the system. In another study, Khalfallah and Slama ( 2018 ) built an ITS called LabTutor for engineering students. LabTutor served as an experienced instructor in enabling students to access and perform experiments on laboratory equipment while adapting to the profile of each student.
The student population in university classes can go into the hundreds and with the advent of MOOCS, class sizes can even go into the thousands. Even in small classes of 20 students, the instructor cannot physically provide immediate unique personalize questions to each student. Instructors need time to read and check answers and then take further time to provide feedback before determining what the next question should be. Working with the instructor, AIEd can provide that immediate instruction, guidance, feedback, and following questioning without delay or becoming tired. This appears to be an effective use of AIEd, especially within the HE context.
Managing student learning
Another code that emerged in the grounded coding was focused on the use of AI for managing student learning. AI is accessed to manage student learning by the administrator or instructor to provide information, organization, and data analysis. The axial codes reveal the trends in the use of AI in managing student learning; see Fig. 11 .
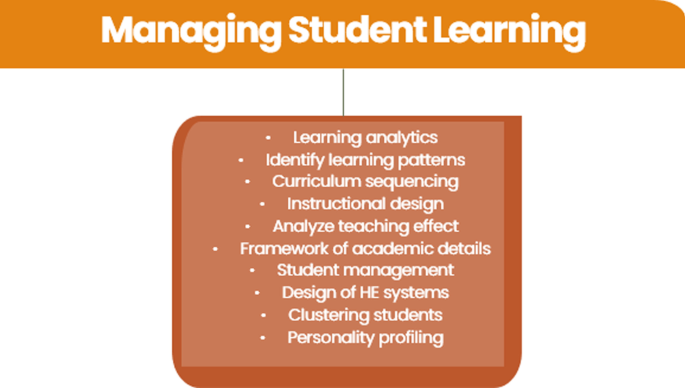
Learning analytics was an a priori term often found in studies which describes “the measurement, collection, analysis and reporting of data about learners and their contexts, for purposes of understanding and optimizing learning and the environments in which it occurs” (Long & Siemens, 2011 , p. 34). The studies investigated in this systematic review were across grades and subject areas and provided administrators and instructors different types of information to guide their work. One of those studies was conducted by Mavrikis et. al. ( 2019 ) who described learning analytics as teacher assistance tools. In their study, learning analytics were used in an exploratory learning environment with targeted visualizations supporting classroom orchestration. These visualizations, displayed as screenshots in the study, provided information such as the interactions between the students, goals achievements etc. These appear similar to infographics that are brightly colored and draw the eye quickly to pertinent information. AI is also used for other tasks, such as organizing the sequence of curriculum in pacing guides for future groups of students and also designing instruction. Zhang ( 2022 ) described how designing an AI teaching system of talent cultivation and using the digital affordances to establish a quality assurance system for practical teaching, provides new mechanisms for the design of university education systems. In developing such a system, Zhang found that the stability of the instructional design, overcame the drawbacks of traditional manual subjectivity in the instructional design.
Another trend that emerged from the studies was the use of AI to manage student big data to support learning. Ullah and Hafiz ( 2022 ) lament that using traditional methods, including non-AI digital techniques, asking the instructor to pay attention to every student’s learning progress is very difficult and that big data analysis techniques are needed. The ability to look across and within large data sets to inform instruction is a valuable affordance of AIEd in HE. While the use of AIEd to manage student learning emerged from the data, this study uncovered only 19 studies in 7 years (2016–2022) that focused on the use of AIEd to manage student data. This lack of the use was also noted in a recent study in the K-12 space (Crompton et al., 2022 ). In Chu et. al.’s ( 2022 ) study examining the top 50 most cited AIEd articles, they did not report the use of AIEd for managing student data in the top uses of AIEd HE. It would appear that more research should be conducted in this area to fully explore the possibilities of AI.
Gaps and future research
From this systematic review, six gaps emerged in the data providing opportunities for future studies to investigate and provide a fuller understanding of how AIEd can used in HE. (1) The majority of the research was conducted in high income countries revealing a paucity of research in developing countries. More research should be conducted in these developing countries to expand the level of understanding about how AI can enhance learning in under-resourced communities. (2) Almost 50% of the studies were conducted in the areas of language learning, computer science and engineering. Research conducted by members from multiple, different academic departments would help to advance the knowledge of the use of AI in more disciplines. (3) This study revealed that faculty affiliated with schools of education are taking an increasing role in researching the use of AIEd in HE. As this body of knowledge grows, faculty in Schools of Education should share their research regarding the pedagogical affordances of AI so that this knowledge can be applied by faculty across disciplines. (4) The vast majority of the research was conducted at the undergraduate level. More research needs to be done at the graduate student level, as AI provides many opportunities in this environment. (5) Little study was done regarding how AIEd can assist both instructors and managers in their roles in HE. The power of AI to assist both groups further research. (6) Finally, much of the research investigated in this systematic review revealed the use of AIEd in traditional ways that enhance or make more efficient current practices. More research needs to focus on the unexplored affordances of AIEd. As AI becomes more advanced and sophisticated, new opportunities will arise for AIEd. Researchers need to be on the forefront of these possible innovations.
In addition, empirical exploration is needed for new tools, such as ChatGPT that was available for public use at the end of 2022. With the time it takes for a peer review journal article to be published, ChatGPT did not appear in the articles for this study. What is interesting is that it could fit with a variety of the use codes found in this study, with students getting support in writing papers and instructors using Chat GPT to assess students work and with help writing emails or descriptions for students. It would be pertinent for researchers to explore Chat GPT.
Limitations
The findings of this study show a rapid increase in the number of AIEd studies published in HE. However, to ensure a level of credibility, this study only included peer review journal articles. These articles take months to publish. Therefore, conference proceedings and gray literature such as blogs and summaries may reveal further findings not explored in this study. In addition, the articles in this study were all published in English which excluded findings from research published in other languages.
In response to the call by Hinojo-Lucena et. al. ( 2019 ), Chu et. al. ( 2022 ), and Zawacki-Richter et. al. ( 2019 ), this study provides unique findings with an up-to-date examination of the use of AIEd in HE from 2016 to 2022. Past systematic reviews examined the research up to 2020. The findings of this study show that in 2021 and 2022, publications rose nearly two to three times the number of previous years. With this rapid rise in the number of AIEd HE publications, new trends have emerged.
The findings show that of the 138 studies examined, research was conducted in six of the seven continents of the world. In extant systematic reviews showed that the US led by a large margin in the number of studies published. This trend has now shifted to China. Another shift in AIEd HE is that while extant studies lamented the lack of focus on professors of education leading these studies, this systematic review found education to be the most common department affiliation with 28% and computer science coming in second at 20%. Undergraduate students were the most studied students at 72%. Similar to the findings of other studies, language learning was the most common subject domain. This included writing, reading, and vocabulary acquisition. In examination of who the AIEd was intended for, 72% of the studies focused on students, 17% instructors, and 11% managers.
Grounded coding was used to answer the overarching question of how AIEd was used in HE. Five usage codes emerged from the data: (1) Assessment/Evaluation, (2) Predicting, (3) AI Assistant, (4) Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS), and (5) Managing Student Learning. Assessment and evaluation had a wide variety of purposes, including assessing academic progress and student emotions towards learning, individual and group evaluations, and class based online community assessments. Predicting emerged as a code with ten axial codes, as AIEd predicted dropouts and at-risk students, innovative ability, and career decisions. AI Assistants were specific to supporting students in HE. These assistants included those with an anthropomorphic presence, such as virtual agents and persuasive intervention through digital programs. ITS systems were not always noted in extant systematic reviews but were specifically mentioned in 18 of the studies in this review. ITS systems in this study provided customized strategies and approaches to student’s characteristics and needs. The final code in this study highlighted the use of AI in managing student learning, including learning analytics, curriculum sequencing, instructional design, and clustering of students.
The findings of this study provide a springboard for future academics, practitioners, computer scientists, policymakers, and funders in understanding the state of the field in AIEd HE, how AI is used. It also provides actionable items to ameliorate gaps in the current understanding. As the use AIEd will only continue to grow this study can serve as a baseline for further research studies in the use of AIEd in HE.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Alajmi, Q., Al-Sharafi, M. A., & Abuali, A. (2020). Smart learning gateways for Omani HEIs towards educational technology: Benefits, challenges and solutions. International Journal of Information Technology and Language Studies, 4 (1), 12–17.
Google Scholar
Al-Tuwayrish, R. K. (2016). An evaluative study of machine translation in the EFL scenario of Saudi Arabia. Advances in Language and Literary Studies, 7 (1), 5–10.
Ayse, T., & Nil, G. (2022). Automated feedback and teacher feedback: Writing achievement in learning English as a foreign language at a distance. The Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 23 (2), 120–139. https://doi.org/10.7575/aiac.alls.v.7n.1p.5
Article Google Scholar
Baykasoğlu, A., Özbel, B. K., Dudaklı, N., Subulan, K., & Şenol, M. E. (2018). Process mining based approach to performance evaluation in computer-aided examinations. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 26 (5), 1841–1861. https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.21971
Belur, J., Tompson, L., Thornton, A., & Simon, M. (2018). Interrater reliability in systematic review methodology: Exploring variation in coder decision-making. Sociological Methods & Research, 13 (3), 004912411887999. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124118799372
Çağataylı, M., & Çelebi, E. (2022). Estimating academic success in higher education using big five personality traits, a machine learning approach. Arab Journal Scientific Engineering, 47 , 1289–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05873-4
Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8 , 75264–75278. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988510
Chu, H., Tu, Y., & Yang, K. (2022). Roles and research trends of artificial intelligence in higher education: A systematic review of the top 50 most-cited articles. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 38 (3), 22–42. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.7526
Cristianini, N. (2016). Intelligence reinvented. New Scientist, 232 (3097), 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0262-4079(16)31992-3
Crompton, H., Bernacki, M. L., & Greene, J. (2020). Psychological foundations of emerging technologies for teaching and learning in higher education. Current Opinion in Psychology, 36 , 101–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.04.011
Crompton, H., & Burke, D. (2022). Artificial intelligence in K-12 education. SN Social Sciences, 2 , 113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-022-00425-5
Crompton, H., Jones, M., & Burke, D. (2022). Affordances and challenges of artificial intelligence in K-12 education: A systematic review. Journal of Research on Technology in Education . https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2022.2121344
Crompton, H., & Song, D. (2021). The potential of artificial intelligence in higher education. Revista Virtual Universidad Católica Del Norte, 62 , 1–4. https://doi.org/10.35575/rvuen.n62a1
de Chiusole, D., Stefanutti, L., Anselmi, P., & Robusto, E. (2020). Stat-Knowlab. Assessment and learning of statistics with competence-based knowledge space theory. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 30 , 668–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-020-00223-1
Dever, D. A., Azevedo, R., Cloude, E. B., & Wiedbusch, M. (2020). The impact of autonomy and types of informational text presentations in game-based environments on learning: Converging multi-channel processes data and learning outcomes. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 30 (4), 581–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-020-00215-1
Górriz, J. M., Ramírez, J., Ortíz, A., Martínez-Murcia, F. J., Segovia, F., Suckling, J., Leming, M., Zhang, Y. D., Álvarez-Sánchez, J. R., Bologna, G., Bonomini, P., Casado, F. E., Charte, D., Charte, F., Contreras, R., Cuesta-Infante, A., Duro, R. J., Fernández-Caballero, A., Fernández-Jover, E., … Ferrández, J. M. (2020). Artificial intelligence within the interplay between natural and artificial computation: Advances in data science, trends and applications. Neurocomputing, 410 , 237–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.078
Gough, D., Oliver, S., & Thomas, J. (2017). An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd ed.). Sage.
Gupta, S., & Chen, Y. (2022). Supporting inclusive learning using chatbots? A chatbot-led interview study. Journal of Information Systems Education, 33 (1), 98–108.
Hemingway, P. & Brereton, N. (2009). In Hayward Medical Group (Ed.). What is a systematic review? Retrieved from http://www.medicine.ox.ac.uk/bandolier/painres/download/whatis/syst-review.pdf
Hinojo-Lucena, F., Arnaz-Diaz, I., Caceres-Reche, M., & Romero-Rodriguez, J. (2019). A bibliometric study on its impact the scientific literature. Education Science . https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010051
Hrastinski, S., Olofsson, A. D., Arkenback, C., Ekström, S., Ericsson, E., Fransson, G., Jaldemark, J., Ryberg, T., Öberg, L.-M., Fuentes, A., Gustafsson, U., Humble, N., Mozelius, P., Sundgren, M., & Utterberg, M. (2019). Critical imaginaries and reflections on artificial intelligence and robots in postdigital K-12 education. Postdigital Science and Education, 1 (2), 427–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42438-019-00046-x
Huang, C., Wu, X., Wang, X., He, T., Jiang, F., & Yu, J. (2021). Exploring the relationships between achievement goals, community identification and online collaborative reflection. Educational Technology & Society, 24 (3), 210–223.
Hwang, G. J., & Tu, Y. F. (2021). Roles and research trends of artificial intelligence in mathematics education: A bibliometric mapping analysis and systematic review. Mathematics, 9 (6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9060584
Khalfallah, J., & Slama, J. B. H. (2018). The effect of emotional analysis on the improvement of experimental e-learning systems. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 27 (2), 303–318. https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.22075
Kim, C., & Bennekin, K. N. (2016). The effectiveness of volition support (VoS) in promoting students’ effort regulation and performance in an online mathematics course. Instructional Science, 44 , 359–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-015-9366-5
Koć-Januchta, M. M., Schönborn, K. J., Roehrig, C., Chaudhri, V. K., Tibell, L. A. E., & Heller, C. (2022). “Connecting concepts helps put main ideas together”: Cognitive load and usability in learning biology with an AI-enriched textbook. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 19 (11), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00317-3
Krause, S. D., & Lowe, C. (2014). Invasion of the MOOCs: The promise and perils of massive open online courses . Parlor Press.
Li, D., Tong, T. W., & Xiao, Y. (2021). Is China emerging as the global leader in AI? Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2021/02/is-china-emerging-as-the-global-leader-in-ai
Liang, J. C., Hwang, G. J., Chen, M. R. A., & Darmawansah, D. (2021). Roles and research foci of artificial intelligence in language education: An integrated bibliographic analysis and systematic review approach. Interactive Learning Environments . https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1958348
Liu, S., Hu, T., Chai, H., Su, Z., & Peng, X. (2022). Learners’ interaction patterns in asynchronous online discussions: An integration of the social and cognitive interactions. British Journal of Educational Technology, 53 (1), 23–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13147
Long, P., & Siemens, G. (2011). Penetrating the fog: Analytics in learning and education. Educause Review, 46 (5), 31–40.
Lu, O. H. T., Huang, A. Y. Q., Tsai, D. C. L., & Yang, S. J. H. (2021). Expert-authored and machine-generated short-answer questions for assessing students learning performance. Educational Technology & Society, 24 (3), 159–173.
Mavrikis, M., Geraniou, E., Santos, S. G., & Poulovassilis, A. (2019). Intelligent analysis and data visualization for teacher assistance tools: The case of exploratory learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50 (6), 2920–2942. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12876
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Reviews, 4 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Mousavi, A., Schmidt, M., Squires, V., & Wilson, K. (2020). Assessing the effectiveness of student advice recommender agent (SARA): The case of automated personalized feedback. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 31 (2), 603–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-020-00210-6
Mousavinasab, E., Zarifsanaiey, N., Kalhori, S. R. N., Rakhshan, M., Keikha, L., & Saeedi, M. G. (2021). Intelligent tutoring systems: A systematic review of characteristics, applications, and evaluation methods. Interactive Learning Environments, 29 (1), 142–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1558257
Ouatik, F., Ouatikb, F., Fadlic, H., Elgoraria, A., Mohadabb, M. E. L., Raoufia, M., et al. (2021). E-Learning & decision making system for automate students assessment using remote laboratory and machine learning. Journal of E-Learning and Knowledge Society, 17 (1), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.20368/1971-8829/1135285
Ouyang, F., Zheng, L., & Jiao, P. (2022). Artificial intelligence in online higher education: A systematic review of empirical research from 2011–2020. Education and Information Technologies, 27 , 7893–7925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10925-9
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T., Mulrow, C., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. British Medical Journal . https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Popenici, S. A. D., & Kerr, S. (2017). Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on teaching and learning in higher education. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 12 (22), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-017-0062-8
PRISMA Statement. (2021). PRISMA endorsers. PRISMA statement website. http://www.prisma-statement.org/Endorsement/PRISMAEndorsers
Qian, Y., Li, C.-X., Zou, X.-G., Feng, X.-B., Xiao, M.-H., & Ding, Y.-Q. (2022). Research on predicting learning achievement in a flipped classroom based on MOOCs by big data analysis. Computer Applied Applications in Engineering Education, 30 , 222–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.22452
Rutner, S. M., & Scott, R. A. (2022). Use of artificial intelligence to grade student discussion boards: An exploratory study. Information Systems Education Journal, 20 (4), 4–18.
Salas-Pilco, S., & Yang, Y. (2022). Artificial Intelligence application in Latin America higher education: A systematic review. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 19 (21), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/S41239-022-00326-w
Saldana, J. (2015). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (3rd ed.). Sage.
Shukla, A. K., Janmaijaya, M., Abraham, A., & Muhuri, P. K. (2019). Engineering applications of artificial intelligence: A bibliometric analysis of 30 years (1988–2018). Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 85 , 517–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.06.010
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1995). Grounded theory methodology: An overview. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (pp. 273–285). Sage.
Turing, A. M. (1937). On computable numbers, with an application to the Entscheidungs problem. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, 2 (1), 230–265.
Turing, A. M. (1950). Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind, 59 , 443–460.
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Ullah, H., & Hafiz, M. A. (2022). Exploring effective classroom management strategies in secondary schools of Punjab. Journal of the Research Society of Pakistan, 59 (1), 76.
Verdú, E., Regueras, L. M., Gal, E., et al. (2017). Integration of an intelligent tutoring system in a course of computer network design. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65 , 653–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-016-9503-0
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind and society: The development of higher psychological processes . Harvard University Press.
Winkler-Schwartz, A., Bissonnette, V., Mirchi, N., Ponnudurai, N., Yilmaz, R., Ledwos, N., Siyar, S., Azarnoush, H., Karlik, B., & Del Maestro, R. F. (2019). Artificial intelligence in medical education: Best practices using machine learning to assess surgical expertise in virtual reality simulation. Journal of Surgical Education, 76 (6), 1681–1690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2019.05.015
Yang, A. C. M., Chen, I. Y. L., Flanagan, B., & Ogata, H. (2021). Automatic generation of cloze items for repeated testing to improve reading comprehension. Educational Technology & Society, 24 (3), 147–158.
Yao, X. (2022). Design and research of artificial intelligence in multimedia intelligent question answering system and self-test system. Advances in Multimedia . https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2156111
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education—Where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Zhang, F. (2022). Design and application of artificial intelligence technology-driven education and teaching system in universities. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine . https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8503239
Zhang, Z., & Xu, L. (2022). Student engagement with automated feedback on academic writing: A study on Uyghur ethnic minority students in China. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development . https://doi.org/10.1080/01434632.2022.2102175
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mildred Jones, Katherina Nako, Yaser Sendi, and Ricardo Randall for data gathering and organization.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Teaching and Learning, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, USA
Helen Crompton
ODUGlobal, Norfolk, USA
Diane Burke
RIDIL, ODUGlobal, Norfolk, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HC: Conceptualization; Data curation; Project administration; Formal analysis; Methodology; Project administration; original draft; and review & editing. DB: Conceptualization; Data curation; Project administration; Formal analysis; Methodology; Project administration; original draft; and review & editing. Both authors read and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Helen Crompton .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Crompton, H., Burke, D. Artificial intelligence in higher education: the state of the field. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 20 , 22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00392-8
Download citation
Received : 30 January 2023
Accepted : 23 March 2023
Published : 24 April 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00392-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial Intelligence
- Systematic review
- Higher education
Center for Studies in Higher Education

Research and Occasional Papers Series (ROPS)
The Center for Studies in Higher Education publishes online research papers and essays that reflect multidisciplinary fields, contribute to influencing and expanding the body of research on higher education, and enhance dialogue among educators, policy makers, and the public. The CSHE Research and Occasional Paper Series (ROPS) includes working papers, original research studies, reflective essays by authors affiliated with CSHE, and major reports generated by CSHE related research projects. Contribution are reviewed by CSHE affiliated scholars. Authors are responsible for the content, and the views and interpretations expressed are not necessarily those of CSHE's research staff and other affiliated researchers. Questions regarding the content of individual ROPS contributions and CSHE research reports should be directed to the authors.
If you would like to be notified when new CSHE ROPS papers are posted, please email [email protected] (link sends e-mail) to subscribe to our mailing list.
Amal Kumar (California State University, Sacramento)
Email: [email protected] , john a. douglass (uc berkeley), editor emeritus, email: [email protected], recently published rops, special issue: opportunities and challenges for california higher education.
- Read more about Special Issue: Opportunities and Challenges for California Higher Education
Public University Systems and the Benefits of Scale by James R. Johnsen. CSHE 2. 2024 (February 2024)
Multi-campus public higher education governance systems exist in 44 of the 50 U.S. states. They include all the largest and most influential public colleges and universities in the United States, educating fully 75 percent of the nation’s public sector students. Their impact is enormous. And yet, they are largely neglected and as a tool for improvement are underutilized. Meanwhile, many states continue to struggle achieving their goals for higher education attainment, social and economic mobility, workforce development, equitable access and affordability, technological innovation, ...
- Read more about Public University Systems and the Benefits of Scale by James R. Johnsen. CSHE 2. 2024 (February 2024)
How Helpful Are Average Wage-By-Major Statistics In Choosing A Field Of Study? by Zachary Bleemer, CSHE.1.24 (January 2024)
Average-wage-by-major statistics have become widely available to students interested in the economic ramifications of their college major choice. However, earning a major with higher average wages does not necessarily lead individual students to higher-paying careers. This essay combines literature review with novel analysis of longitudinal student outcomes to discuss how students use average-wage-by-major statistics and document seven reasons that they may differ, sharply in some cases, from the causal wage effects of major choice. I focus on the ramifications of two-sided non-random...
- Read more about How Helpful Are Average Wage-By-Major Statistics In Choosing A Field Of Study? by Zachary Bleemer, CSHE.1.24 (January 2024)
ROPS Editorial Advisory Board
Search rops publications, highlights - 20th anniversary of rops.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education: Critical Reflections
Lingnan University, Tuen Mun, Hong Kong, China
This Special Issue has chosen the major focus to examine how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected higher education development and governance. The collection of articles in this Special Issue is organized with three key sub-themes, namely, student mobility, teaching and student learning, and university governance. Papers selected in this Issue were presented at different international conferences examining how the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in late 2019 has affected higher education development from international and comparative perspectives. During the international research events, authors contributing their papers to this Special Issue indeed benefitted from the exchanges and dialogues from international peers. Drawing insights from the papers collected in this Special Issue, this introductory article concludes by drawing the implications for future development of international education.
Teaching and Student Learning
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed higher education systems across different parts of the globe to adopt online platforms for conducting teaching and learning activities. Angela Hou and colleagues , in her article, ask a very important and reflective question: How would COVID-19 drive digitalization, innovations, and crisis management of higher education? More importantly, they also raise the issue of quality assurance when most higher education teaching and learning had been operating through online platforms. Based upon a case study of the INQAAHE Virtual Review, they critically examine issues related to quality assurance when higher education teaching and learning of had been digitalized. Their article does not only offer a case study of Taiwan, showing how one of the East Asian economies responded to the outbreak of the COVID-19 crisis through digitalizing higher education. This case studies also shows relevance to other parts of the world, especially when those countries/regions encounter difficulties in realizing the digitalization of teaching and student learning. International research reports educational inequality and disparity being intensified after the widespread the COVID-19 pandemic (UNESCO, 2020 , 2021 ). International and comparative research report higher education systems from relatively low-income countries/regions have suffered tremendously simply because of the lack of resources/infrastructural support for online teaching/learning, let alone diverse differences in educational cultures/management and practices across different parts of the globe (Vegas, 2020 ; Mok, et al., 2021 ).
The second article contributed by Mok , Xiong, and Ke critically examines how Chinese students evaluate overseas studies during and in the post-COVID-19 crisis, showing the growing interest of Chinese students in making Asia their future destination for studying abroad, especially when becoming more concerned about public health conditions in traditional destinations based in Europe, the UK and the USA (QS, 2020 ). The motivations and desires of Chinese students choosing overseas learning would have been affected by the new geopolitics and different kinds of “cultural shocks”, particularly when Asian students were reportedly being discriminated/stigmatized after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic when studying abroad (Mbous, et al2022; Mok and Zhang, 2021 ).
Institutional Response and University Governance
Moving beyond management of teaching and student learning, Susan Robertson, critically reflecting upon the future of higher education governance set against the COVID-19 context, presented a paper at the Conference for Higher Education Research (CHER) 2020. Based upon recent works on temporality and higher education, Robertson considers such works have made important contributions to work on time, though time-future continues to be under-developed. In her presentation, she attempted to explore anticipatory governance in the contemporary university. Exploring a range of anticipatory practices and their logic in the contemporary academy, from goals to planning, predictions, forecasts, indicators, specialised knowledge, and agreements, Robertson believed we should think beyond our own box of how the future presents potential opportunities for academic development. Adopting the time-future lens in conceiving future university governance, Robertson’s paper shows the anticipatory practices mobilise different kinds of socio-temporal and political sensibilities and expectations, practices, and institutional arrangements, that constitute timescapes in the contemporary academy (Robertson, 2020 ).
Whereas Robertson discusses temporality in general, Tilak critically examines the impact of the pandemic on Indian higher education. In his article, he presents the major challenges confronting higher education development in India against the COVID-19 crisis, discussing major strategies/policy measures adopted by the Indian government in managing challenges for higher education. As India is committed to further increasing its higher education enrolments in order to produce sufficient young talents for the changing economic needs of the country, the current COVID-19 crisis would considerably disrupt its plans for higher education development. To which extent the Indian government and university leaders make use of innovative measures through the technology-enabled platforms to achieve its development goals depends not only on resources but also on careful policy coordination.
Moving away from Asia, the article contributed by O’Shea, Mou, Xu, and Aikins critically examine how higher education institutions (HEIs) in three countries, namely, Canada, China, and the USA, responded to the challenges of COVID-19 over a six-month period at the outbreak of the global pandemic. Employing document analysis, they analyze 732 publicly available communications from 27 HEIs in Canada, China, and the United States. Through the theoretical framework of Situational Critical Communications Theory (SCCT), O’Shea et al ., explore how HEIs respond to the crisis and communicate their response to the crisis to campus stakeholders. While there are important country-level distinctions among HEIs in how they communicate and respond to crisis, this research finds there are common themes across the three countries, including (1) emphasizing social responsibilities of serving the community, (2) referencing public health guidelines, and (3) offering different kinds of financial support to students. The findings shed light on strengths and weaknesses of the SCCT model in analyzing HEI responses to COVID-19 and may be helpful for HEIs to prepare for the next crisis.
Future of International Education
After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, international students are considered to be more adversely affected by COVID-19 restrictions than other student and population groups (e.g., local students) in the world (Dodd, et al., 2021 ). According to research conducted by Amoah and Mok in 2020, international students find themselves living in foreign countries/regions with limited social and economic support and in a context of rising discrimination (Amoah and Mok, 2020 ). With special attention to international student well-being, the article contributed by Amoah and Esther Mok examines the effects that COVID-19 restrictions have had and are having on the lives of international students. Such effects include direct consequences of the disease itself and its disruptive effect on this group of students and the effectiveness of the support offered by universities for the well-being of international students. The study analyzed data from a global survey conducted among international students in April 2020. They found that the well-being of international students is negatively associated with being worried about COVID-19 itself ( B = − 0.218, p = .027); with perceived COVID-19 disruption of academic activities ( B = − 0.162, p = .016); and with feelings of loneliness ( B = − 0.317, p = .000). Notably, COVID-19 information support provided by universities was positively associated with the students’ well-being ( B = 0.224, p = 0.003). These findings are discussed in the context of education policy and practical changes introduced by the COVID-19 pandemic. The discussion also considers the influence of the changing geopolitical and social environment (e.g., racism) on higher education internationalisation, critically reflecting upon management and governance issues faced by universities worldwide when promoting the well-being of international students (Mok, 2022 ).
A critical reflection of how the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the Australian university system, Anthony Welch shows the impact of COVID as a stark reminder that international students are so much more than cash cows for universities. Not merely do they add immeasurably to the vibrant cultural diversity of universities, they “are vital parts of communities. Indeed, many international students are future Australian citizens. It is estimated that between 20,000 and 30,000 international students move from student visas to permanent residency visas every year” a figure that is likely to be an underestimate, since students often gain another form of temporary visa, before attaining permanent residence. During the COVID-19 crisis, we have witnessed how academic cooperation and research collaboration have become highly politicized, especially when the new geopolitics has emerged as an influential force shaping international education and research.
In view of the worsening diplomatic relationship between China and Australia, Welch highlights the potential for COVID to curtail staff and student mobility, restricting research collaboration between colleagues in Australia and China. The growing anti-Chinese and anti-Asian sentiments commonly found not only in Australia but also in other major university systems in Europe and North America would create disincentives for inter-university and cross-border collaboration, which would be detrimental to future development of international education and research. According to Welch, what is urgently needed is a dialogue of civilizations, rather than a clash of civilizations, with the associated rancorous and rivalrous international relations that threaten international academic mobility and collaboration.
This Special Issue brings together thought-provocative pieces, critically reflecting upon the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on higher education development. The challenges confronting contemporary universities are partly caused by the pandemic, disrupting the “normal operation” of universities. Nonetheless, the present global health crisis has also opened new opportunities for university teachers and leaders for exploring innovative modes of teaching and student learning, moving beyond the conventional models in developing new forms of inter-university collaborations. However, part of the problems facing universities globally is the unfavorable influences of new geopolitics creating mistrust across countries/regions. Perhaps world leaders as well as university leaders should be humbled to learn from the global health crisis resulting from the outbreak of COVID-19, seeking appropriate ways for closer and deeper collaboration for the betterment of the humanity.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Amoah, P.A. and Mok, K.H. (2020) ‘The Covid-19 pandemic and internationalisation of higher education: International students knowledge, experiences and well-being’, Higher Education Policy Institute's blog , 13 June. Available on https://www.hepi.ac.uk/2020/06/13/weekend-reading-the-covid-19-pandemic-and-internationalisation-of-higher-education-international-students-knowledge-experiences-and-wellbeing/ , accessed 18 June 2020.
- Dodd RH, Dadaczynski K, Okan O, McCaffery KJ, Pickles K. Psychological Wellbeing and Academic Experience of University Students in Australia during COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18 (3):866. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18030866. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mbous, Y.P.V., Mohamed, R., Rudisill, T.M. (2022) ‘International Students Challenges during the COVID-19 Pandemic in a university in the USA: A focus group study’, Current Psychology . Published online 4 February. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-02776-x. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mok KH. COVID-19 Pandemic and International Higher Education Major Challenges and Implications for East Asia. In: Marginson S, Xu X, editors. Higher Education in East Asia Internationalization Strategy and National Agendas. London: Bloomsbury; 2022. pp. 225–246. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mok KH, Xiong WY, Bin Aedy Rahman HN. COVID-‘19 pandemic’s disruption on university teaching and learning and competence cultivation: Student evaluation of online learning experiences in Hong Kong’ International Journal of Chinese Education. 2021; 10 (1):1–20. doi: 10.1177/22125868211007011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mok, K.H. and Zhang, Y.L. (2021) ‘Remaking International Higher Education for an Unequal World’, Higher Education Quarterly . Published online 13 November. doi.org/10.1111/hequ.12366.
- QS (2020) International Student Survey: Global Opportunities in the New Higher Education Paradigm. QS Report, London: QS. Available on https://unibuddy.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/QS_ISS2020_GLOBAL_FINAL.pdf , accessed 21 February 2022.
- Robertson, S. (2020) Radical Uncertainty and Anticipatory Practices in the Pandemic University. Keynote speech presented at the Conference for Higher Education Research (CHER) 2020, Lingnan University, Hong Kong, 13-14 November 2020.
- UNESCO (2020) Education: From Disruption to Recovery . https://www.unesco.org/en/covid-19/education-response , accessed 6 March 2022.
- UNESCO (2021) About Virtual Student Mobility in Higher Education . https://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/2021/01/20/about-virtual-student-mobility-in-higher-education/#_ftn1 .
- Vegas, E. (2020) ‘School closures, government responses, and learning inequality around the world during COVID-19’ , Brookings, 14 April. Available on https://www.brookings.edu/research/school-closures-government-responses-and-learning-inequality-around-the-world-during-covid-19/ .

Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education
- Submit your paper
- Author guidelines
- Editorial team
- Indexing & metrics
- Calls for papers & news
Before you start
For queries relating to the status of your paper pre decision, please contact the Editor or Journal Editorial Office. For queries post acceptance, please contact the Supplier Project Manager. These details can be found in the Editorial Team section.
Author responsibilities
Our goal is to provide you with a professional and courteous experience at each stage of the review and publication process. There are also some responsibilities that sit with you as the author. Our expectation is that you will:
- Respond swiftly to any queries during the publication process.
- Be accountable for all aspects of your work. This includes investigating and resolving any questions about accuracy or research integrity .
- Treat communications between you and the journal editor as confidential until an editorial decision has been made.
- Include anyone who has made a substantial and meaningful contribution to the submission (anyone else involved in the paper should be listed in the acknowledgements).
- Exclude anyone who hasn’t contributed to the paper, or who has chosen not to be associated with the research.
- In accordance with COPE’s position statement on AI tools , Large Language Models cannot be credited with authorship as they are incapable of conceptualising a research design without human direction and cannot be accountable for the integrity, originality, and validity of the published work. The author(s) must describe the content created or modified as well as appropriately cite the name and version of the AI tool used; any additional works drawn on by the AI tool should also be appropriately cited and referenced. Standard tools that are used to improve spelling and grammar are not included within the parameters of this guidance. The Editor and Publisher reserve the right to determine whether the use of an AI tool is permissible.
- If your article involves human participants, you must ensure you have considered whether or not you require ethical approval for your research, and include this information as part of your submission. Find out more about informed consent .
Generative AI usage key principles
- Copywriting any part of an article using a generative AI tool/LLM would not be permissible, including the generation of the abstract or the literature review, for as per Emerald’s authorship criteria, the author(s) must be responsible for the work and accountable for its accuracy, integrity, and validity.
- The generation or reporting of results using a generative AI tool/LLM is not permissible, for as per Emerald’s authorship criteria, the author(s) must be responsible for the creation and interpretation of their work and accountable for its accuracy, integrity, and validity.
- The in-text reporting of statistics using a generative AI tool/LLM is not permissible due to concerns over the authenticity, integrity, and validity of the data produced, although the use of such a tool to aid in the analysis of the work would be permissible.
- Copy-editing an article using a generative AI tool/LLM in order to improve its language and readability would be permissible as this mirrors standard tools already employed to improve spelling and grammar, and uses existing author-created material, rather than generating wholly new content, while the author(s) remains responsible for the original work.
- The submission and publication of images created by AI tools or large-scale generative models is not permitted.
Research and publishing ethics
Our editors and employees work hard to ensure the content we publish is ethically sound. To help us achieve that goal, we closely follow the advice laid out in the guidelines and flowcharts on the COPE (Committee on Publication Ethics) website .
We have also developed our research and publishing ethics guidelines . If you haven’t already read these, we urge you to do so – they will help you avoid the most common publishing ethics issues.
A few key points:
- Any manuscript you submit to this journal should be original. That means it should not have been published before in its current, or similar, form. Exceptions to this rule are outlined in our pre-print and conference paper policies . If any substantial element of your paper has been previously published, you need to declare this to the journal editor upon submission. Please note, the journal editor may use Crossref Similarity Check to check on the originality of submissions received. This service compares submissions against a database of 49 million works from 800 scholarly publishers.
- Your work should not have been submitted elsewhere and should not be under consideration by any other publication.
- If you have a conflict of interest, you must declare it upon submission; this allows the editor to decide how they would like to proceed. Read about conflict of interest in our research and publishing ethics guidelines .
- By submitting your work to Emerald, you are guaranteeing that the work is not in infringement of any existing copyright.
- If you have written about a company/individual/organisation in detail using information that is not publicly available, have spent time within that company/organisation, or the work features named/interviewed employees, you will need to clear permission by using the consent to publish form ; please also see our permissions guidance for full details. If you have to clear permission with the company/individual/organisation, consent must be given either by the named individual in question or their representative, a board member of the company/organisation, or a HR department representative of the company/organisation.
- You have an ethical obligation and responsibility to conduct your research in adherence to national and international research ethics guidelines, as well as the ethical principles outlined by your discipline and any relevant authorities, and to be transparent about your research methods in such a way that all involved in the publication process may fairly and appropriately evaluate your work. For all research involving human participants, you must ensure that you have obtained informed consent, meaning that you must inform all participants in your work (or their legal representative) as to why the research is being conducted, whether their anonymity is protected, how their data will be stored and used, and whether there are any associated risks from participation in the study; the submitted work must confirm that informed consent was obtained and detail how this was addressed in accordance with our policy on informed consent .
- Where appropriate, you must provide an ethical statement within the submitted work confirming that your research received institutional and national (or international) ethical approval, and that it complies with all relevant guidelines and regulations for studies involving humans, whether that be data, individuals, or samples. Specifically, the statement should contain the name and location of the institutional ethics reviewing committee or review board, the approval number, the date of approval, and the details of the national or international guidelines that were followed, as well as any other relevant information. You should also include details of how the work adheres to relevant consent guidelines along with confirming that informed consent was secured for all participants. The details of these statements should ensure that author and participant anonymity is not compromised. Any work submitted without a suitable ethical statement and details of informed consent for all participants, where required, will be returned to the authors and will not be considered further until appropriate and clear documentation is provided. Emerald reserves the right to reject work without sufficient evidence of informed consent from human participants and ethical approval where required.
Third party copyright permissions
Prior to article submission, you need to ensure you’ve applied for, and received, written permission to use any material in your manuscript that has been created by a third party. Please note, we are unable to publish any article that still has permissions pending. The rights we require are:
- Non-exclusive rights to reproduce the material in the article or book chapter.
- Print and electronic rights.
- Worldwide English-language rights.
- To use the material for the life of the work. That means there should be no time restrictions on its re-use e.g. a one-year licence.
We are a member of the International Association of Scientific, Technical, and Medical Publishers (STM) and participate in the STM permissions guidelines , a reciprocal free exchange of material with other STM publishers. In some cases, this may mean that you don’t need permission to re-use content. If so, please highlight this at the submission stage.
Please take a few moments to read our guide to publishing permissions to ensure you have met all the requirements, so that we can process your submission without delay.
Open access submissions and information
All our journals currently offer two open access (OA) publishing paths; gold open access and green open access.
If you would like to, or are required to, make the branded publisher PDF (also known as the version of record) freely available immediately upon publication, you can select the gold open access route once your paper is accepted.
If you’ve chosen to publish gold open access, this is the point you will be asked to pay the APC (article processing charge) . This varies per journal and can be found on our APC price list or on the editorial system at the point of submission. Your article will be published with a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 user licence , which outlines how readers can reuse your work.
Alternatively, if you would like to, or are required to, publish open access but your funding doesn’t cover the cost of the APC, you can choose the green open access, or self-archiving, route. As soon as your article is published, you can make the author accepted manuscript (the version accepted for publication) openly available, free from payment and embargo periods.
You can find out more about our open access routes, our APCs and waivers and read our FAQs on our open research page.
Find out about open
Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines
We are a signatory of the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines , a framework that supports the reproducibility of research through the adoption of transparent research practices. That means we encourage you to:
- Cite and fully reference all data, program code, and other methods in your article.
- Include persistent identifiers, such as a Digital Object Identifier (DOI), in references for datasets and program codes. Persistent identifiers ensure future access to unique published digital objects, such as a piece of text or datasets. Persistent identifiers are assigned to datasets by digital archives, such as institutional repositories and partners in the Data Preservation Alliance for the Social Sciences (Data-PASS).
- Follow appropriate international and national procedures with respect to data protection, rights to privacy and other ethical considerations, whenever you cite data. For further guidance please refer to our research and publishing ethics guidelines . For an example on how to cite datasets, please refer to the references section below.
Prepare your submission
Manuscript support services.
We are pleased to partner with Editage, a platform that connects you with relevant experts in language support, translation, editing, visuals, consulting, and more. After you’ve agreed a fee, they will work with you to enhance your manuscript and get it submission-ready.
This is an optional service for authors who feel they need a little extra support. It does not guarantee your work will be accepted for review or publication.
Visit Editage
Manuscript requirements
Before you submit your manuscript, it’s important you read and follow the guidelines below. You will also find some useful tips in our structure your journal submission how-to guide.
|
| Article files should be provided in Microsoft Word format. While you are welcome to submit a PDF of the document alongside the Word file, PDFs alone are not acceptable. LaTeX files can also be used but only if an accompanying PDF document is provided. Acceptable figure file types are listed further below. |
|
| Articles should be between 3000 and 6000 words in length. This includes all text, for example, the structured abstract, references, all text in tables, and figures and appendices. Please allow 280 words for each figure or table. |
|
| A concisely worded title should be provided. |
|
| The names of all contributing authors should be added to the ScholarOne submission; please list them in the order in which you’d like them to be published. Each contributing author will need their own ScholarOne author account, from which we will extract the following details: (institutional preferred). . We will reproduce it exactly, so any middle names and/or initials they want featured must be included. . This should be where they were based when the research for the paper was conducted.In multi-authored papers, it’s important that ALL authors that have made a significant contribution to the paper are listed. Those who have provided support but have not contributed to the research should be featured in an acknowledgements section. You should never include people who have not contributed to the paper or who don’t want to be associated with the research. Read about our for authorship. |
|
| If you want to include these items, save them in a separate Microsoft Word document and upload the file with your submission. Where they are included, a brief professional biography of not more than 100 words should be supplied for each named author. |
|
| Your article must reference all sources of external research funding in the acknowledgements section. You should describe the role of the funder or financial sponsor in the entire research process, from study design to submission. |
|
| All submissions must include a structured abstract, following the format outlined below. These four sub-headings and their accompanying explanations must always be included: The following three sub-headings are optional and can be included, if applicable:
The maximum length of your abstract should be 250 words in total, including keywords and article classification (see the sections below). |
|
| Your submission should include up to 12 appropriate and short keywords that capture the principal topics of the paper. Our how to guide contains some practical guidance on choosing search-engine friendly keywords. Please note, while we will always try to use the keywords you’ve suggested, the in-house editorial team may replace some of them with matching terms to ensure consistency across publications and improve your article’s visibility. |
|
| During the submission process, you will be asked to select a type for your paper; the options are listed below. If you don’t see an exact match, please choose the best fit:
You will also be asked to select a category for your paper. The options for this are listed below. If you don’t see an exact match, please choose the best fit: Reports on any type of research undertaken by the author(s), including: Covers any paper where content is dependent on the author's opinion and interpretation. This includes journalistic and magazine-style pieces. Describes and evaluates technical products, processes or services. Focuses on developing hypotheses and is usually discursive. Covers philosophical discussions and comparative studies of other authors’ work and thinking. Describes actual interventions or experiences within organizations. It can be subjective and doesn’t generally report on research. Also covers a description of a legal case or a hypothetical case study used as a teaching exercise. This category should only be used if the main purpose of the paper is to annotate and/or critique the literature in a particular field. It could be a selective bibliography providing advice on information sources, or the paper may aim to cover the main contributors to the development of a topic and explore their different views. Provides an overview or historical examination of some concept, technique or phenomenon. Papers are likely to be more descriptive or instructional (‘how to’ papers) than discursive. |
|
| Headings must be concise, with a clear indication of the required hierarchy. |
|
| Notes or endnotes should only be used if absolutely necessary. They should be identified in the text by consecutive numbers enclosed in square brackets. These numbers should then be listed, and explained, at the end of the article. |
|
| All figures (charts, diagrams, line drawings, webpages/screenshots, and photographic images) should be submitted electronically. Both colour and black and white files are accepted. |
|
| Tables should be typed and submitted in a separate file to the main body of the article. The position of each table should be clearly labelled in the main body of the article with corresponding labels clearly shown in the table file. Tables should be numbered consecutively in Roman numerals (e.g. I, II, etc.). Give each table a brief title. Ensure that any superscripts or asterisks are shown next to the relevant items and have explanations displayed as footnotes to the table, figure or plate. |
|
| Where tables, figures, appendices, and other additional content are supplementary to the article but not critical to the reader’s understanding of it, you can choose to host these supplementary files alongside your article on Insight, Emerald’s content-hosting platform (this is Emerald's recommended option as we are able to ensure the data remain accessible), or on an alternative trusted online repository. All supplementary material must be submitted prior to acceptance. Emerald recommends that authors use the following two lists when searching for a suitable and trusted repository: , you must submit these as separate files alongside your article. Files should be clearly labelled in such a way that makes it clear they are supplementary; Emerald recommends that the file name is descriptive and that it follows the format ‘Supplementary_material_appendix_1’ or ‘Supplementary tables’. All supplementary material must be mentioned at the appropriate moment in the main text of the article; there is no need to include the content of the file only the file name. A link to the supplementary material will be added to the article during production, and the material will be made available alongside the main text of the article at the point of EarlyCite publication. Please note that Emerald will not make any changes to the material; it will not be copy-edited or typeset, and authors will not receive proofs of this content. Emerald therefore strongly recommends that you style all supplementary material ahead of acceptance of the article. Emerald Insight can host the following file types and extensions: , you should ensure that the supplementary material is hosted on the repository ahead of submission, and then include a link only to the repository within the article. It is the responsibility of the submitting author to ensure that the material is free to access and that it remains permanently available. Where an alternative trusted online repository is used, the files hosted should always be presented as read-only; please be aware that such usage risks compromising your anonymity during the review process if the repository contains any information that may enable the reviewer to identify you; as such, we recommend that all links to alternative repositories are reviewed carefully prior to submission. Please note that extensive supplementary material may be subject to peer review; this is at the discretion of the journal Editor and dependent on the content of the material (for example, whether including it would support the reviewer making a decision on the article during the peer review process). |
|
| All references in your manuscript must be formatted using one of the recognised Harvard styles. You are welcome to use the Harvard style Emerald has adopted – we’ve provided a detailed guide below. Want to use a different Harvard style? That’s fine, our typesetters will make any necessary changes to your manuscript if it is accepted. Please ensure you check all your citations for completeness, accuracy and consistency.
References to other publications in your text should be written as follows: , 2006) Please note, ‘ ' should always be written in italics.A few other style points. These apply to both the main body of text and your final list of references. At the end of your paper, please supply a reference list in alphabetical order using the style guidelines below. Where a DOI is available, this should be included at the end of the reference. |
|
| Surname, initials (year), , publisher, place of publication. e.g. Harrow, R. (2005), , Simon & Schuster, New York, NY. |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "chapter title", editor's surname, initials (Ed.), , publisher, place of publication, page numbers. e.g. Calabrese, F.A. (2005), "The early pathways: theory to practice – a continuum", Stankosky, M. (Ed.), , Elsevier, New York, NY, pp.15-20. |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "title of article", , volume issue, page numbers. e.g. Capizzi, M.T. and Ferguson, R. (2005), "Loyalty trends for the twenty-first century", , Vol. 22 No. 2, pp.72-80. |
|
| Surname, initials (year of publication), "title of paper", in editor’s surname, initials (Ed.), , publisher, place of publication, page numbers. e.g. Wilde, S. and Cox, C. (2008), “Principal factors contributing to the competitiveness of tourism destinations at varying stages of development”, in Richardson, S., Fredline, L., Patiar A., & Ternel, M. (Ed.s), , Griffith University, Gold Coast, Qld, pp.115-118. |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "title of paper", paper presented at [name of conference], [date of conference], [place of conference], available at: URL if freely available on the internet (accessed date). e.g. Aumueller, D. (2005), "Semantic authoring and retrieval within a wiki", paper presented at the European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC), 29 May-1 June, Heraklion, Crete, available at: http://dbs.uni-leipzig.de/file/aumueller05wiksar.pdf (accessed 20 February 2007). |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "title of article", working paper [number if available], institution or organization, place of organization, date. e.g. Moizer, P. (2003), "How published academic research can inform policy decisions: the case of mandatory rotation of audit appointments", working paper, Leeds University Business School, University of Leeds, Leeds, 28 March. |
|
| (year), "title of entry", volume, edition, title of encyclopaedia, publisher, place of publication, page numbers. e.g. (1926), "Psychology of culture contact", Vol. 1, 13th ed., Encyclopaedia Britannica, London and New York, NY, pp.765-771. (for authored entries, please refer to book chapter guidelines above) |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "article title", , date, page numbers. e.g. Smith, A. (2008), "Money for old rope", , 21 January, pp.1, 3-4. |
|
| (year), "article title", date, page numbers. e.g. (2008), "Small change", 2 February, p.7. |
|
| Surname, initials (year), "title of document", unpublished manuscript, collection name, inventory record, name of archive, location of archive. e.g. Litman, S. (1902), "Mechanism & Technique of Commerce", unpublished manuscript, Simon Litman Papers, Record series 9/5/29 Box 3, University of Illinois Archives, Urbana-Champaign, IL. |
|
| If available online, the full URL should be supplied at the end of the reference, as well as the date that the resource was accessed. Surname, initials (year), “title of electronic source”, available at: persistent URL (accessed date month year). e.g. Weida, S. and Stolley, K. (2013), “Developing strong thesis statements”, available at: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/588/1/ (accessed 20 June 2018) Standalone URLs, i.e. those without an author or date, should be included either inside parentheses within the main text, or preferably set as a note (Roman numeral within square brackets within text followed by the full URL address at the end of the paper). |
|
| Surname, initials (year), , name of data repository, available at: persistent URL, (accessed date month year). e.g. Campbell, A. and Kahn, R.L. (2015), , ICPSR07218-v4, Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research (distributor), Ann Arbor, MI, available at: https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR07218.v4 (accessed 20 June 2018) |
Submit your manuscript
There are a number of key steps you should follow to ensure a smooth and trouble-free submission.
Double check your manuscript
Before submitting your work, it is your responsibility to check that the manuscript is complete, grammatically correct, and without spelling or typographical errors. A few other important points:
- Give the journal aims and scope a final read. Is your manuscript definitely a good fit? If it isn’t, the editor may decline it without peer review.
- Does your manuscript comply with our research and publishing ethics guidelines ?
- Have you cleared any necessary publishing permissions ?
- Have you followed all the formatting requirements laid out in these author guidelines?
- If you need to refer to your own work, use wording such as ‘previous research has demonstrated’ not ‘our previous research has demonstrated’.
- If you need to refer to your own, currently unpublished work, don’t include this work in the reference list.
- Any acknowledgments or author biographies should be uploaded as separate files.
- Carry out a final check to ensure that no author names appear anywhere in the manuscript. This includes in figures or captions.
You will find a helpful submission checklist on the website Think.Check.Submit .
The submission process
All manuscripts should be submitted through our editorial system by the corresponding author.
The only way to submit to the journal is through the journal’s ScholarOne site as accessed via the Emerald website, and not by email or through any third-party agent/company, journal representative, or website. Submissions should be done directly by the author(s) through the ScholarOne site and not via a third-party proxy on their behalf.
A separate author account is required for each journal you submit to. If this is your first time submitting to this journal, please choose the Create an account or Register now option in the editorial system. If you already have an Emerald login, you are welcome to reuse the existing username and password here.
Please note, the next time you log into the system, you will be asked for your username. This will be the email address you entered when you set up your account.
Don't forget to add your ORCiD ID during the submission process. It will be embedded in your published article, along with a link to the ORCiD registry allowing others to easily match you with your work.
Don’t have one yet? It only takes a few moments to register for a free ORCiD identifier .
Visit the ScholarOne support centre for further help and guidance.
What you can expect next
You will receive an automated email from the journal editor, confirming your successful submission. It will provide you with a manuscript number, which will be used in all future correspondence about your submission. If you have any reason to suspect the confirmation email you receive might be fraudulent, please contact the journal editor in the first instance.
Post submission
Review and decision process.
Each submission is checked by the editor. At this stage, they may choose to decline or unsubmit your manuscript if it doesn’t fit the journal aims and scope, or they feel the language/manuscript quality is too low.
If they think it might be suitable for the publication, they will send it to at least two independent referees for double anonymous peer review. Once these reviewers have provided their feedback, the editor may decide to accept your manuscript, request minor or major revisions, or decline your work.
While all journals work to different timescales, the goal is that the editor will inform you of their first decision within 60 days.
During this period, we will send you automated updates on the progress of your manuscript via our submission system, or you can log in to check on the current status of your paper. Each time we contact you, we will quote the manuscript number you were given at the point of submission. If you receive an email that does not match these criteria, it could be fraudulent and we recommend you contact the journal editor in the first instance.
Manuscript transfer service
Emerald’s manuscript transfer service takes the pain out of the submission process if your manuscript doesn’t fit your initial journal choice. Our team of expert Editors from participating journals work together to identify alternative journals that better align with your research, ensuring your work finds the ideal publication home it deserves. Our dedicated team is committed to supporting authors like you in finding the right home for your research.
If a journal is participating in the manuscript transfer program, the Editor has the option to recommend your paper for transfer. If a transfer decision is made by the Editor, you will receive an email with the details of the recommended journal and the option to accept or reject the transfer. It’s always down to you as the author to decide if you’d like to accept. If you do accept, your paper and any reviewer reports will automatically be transferred to the recommended journals. Authors will then confirm resubmissions in the new journal’s ScholarOne system.
Our Manuscript Transfer Service page has more information on the process.
If your submission is accepted
Open access.
Once your paper is accepted, you will have the opportunity to indicate whether you would like to publish your paper via the gold open access route.
If you’ve chosen to publish gold open access, this is the point you will be asked to pay the APC (article processing charge). This varies per journal and can be found on our APC price list or on the editorial system at the point of submission. Your article will be published with a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 user licence , which outlines how readers can reuse your work.
For UK journal article authors - if you wish to submit your work accepted by Emerald to REF 2021, you must make a ‘closed deposit’ of your accepted manuscript to your respective institutional repository upon acceptance of your article. Articles accepted for publication after 1st April 2018 should be deposited as soon as possible, but no later than three months after the acceptance date. For further information and guidance, please refer to the REF 2021 website.
All accepted authors are sent an email with a link to a licence form. This should be checked for accuracy, for example whether contact and affiliation details are up to date and your name is spelled correctly, and then returned to us electronically. If there is a reason why you can’t assign copyright to us, you should discuss this with your journal content editor. You will find their contact details on the editorial team section above.
Proofing and typesetting
Once we have received your completed licence form, the article will pass directly into the production process. We will carry out editorial checks, copyediting, and typesetting and then return proofs to you (if you are the corresponding author) for your review. This is your opportunity to correct any typographical errors, grammatical errors or incorrect author details. We can’t accept requests to rewrite texts at this stage.
When the page proofs are finalised, the fully typeset and proofed version of record is published online. This is referred to as the EarlyCite version. While an EarlyCite article has yet to be assigned to a volume or issue, it does have a digital object identifier (DOI) and is fully citable. It will be compiled into an issue according to the journal’s issue schedule, with papers being added by chronological date of publication.
How to share your paper
Visit our author rights page to find out how you can reuse and share your work.
To find tips on increasing the visibility of your published paper, read about how to promote your work .
Correcting inaccuracies in your published paper
Sometimes errors are made during the research, writing and publishing processes. When these issues arise, we have the option of withdrawing the paper or introducing a correction notice. Find out more about our article withdrawal and correction policies .
Need to make a change to the author list? See our frequently asked questions (FAQs) below.
Frequently asked questions
|
| The only time we will ever ask you for money to publish in an Emerald journal is if you have chosen to publish via the gold open access route. You will be asked to pay an APC (article-processing charge) once your paper has been accepted (unless it is a sponsored open access journal), and never at submission.
At no other time will you be asked to contribute financially towards your article’s publication, processing, or review. If you haven’t chosen gold open access and you receive an email that appears to be from Emerald, the journal, or a third party, asking you for payment to publish, please contact our support team via . |
|
| Please contact the editor for the journal, with a copy of your CV. You will find their contact details on the editorial team tab on this page. |
|
| Typically, papers are added to an issue according to their date of publication. If you would like to know in advance which issue your paper will appear in, please contact the content editor of the journal. You will find their contact details on the editorial team tab on this page. Once your paper has been published in an issue, you will be notified by email. |
|
| Please email the journal editor – you will find their contact details on the editorial team tab on this page. If you ever suspect an email you’ve received from Emerald might not be genuine, you are welcome to verify it with the content editor for the journal, whose contact details can be found on the editorial team tab on this page. |
|
| If you’ve read the aims and scope on the journal landing page and are still unsure whether your paper is suitable for the journal, please email the editor and include your paper's title and structured abstract. They will be able to advise on your manuscript’s suitability. You will find their contact details on the Editorial team tab on this page. |
|
| Authorship and the order in which the authors are listed on the paper should be agreed prior to submission. We have a right first time policy on this and no changes can be made to the list once submitted. If you have made an error in the submission process, please email the Journal Editorial Office who will look into your request – you will find their contact details on the editorial team tab on this page. |
Editor-in-Chief
- Dr Patrick Blessinger State University of New York at Old Westbury - USA [email protected]
Senior Editor
- Professor Nour El Houda Chaoui Ibn Tofail University - Morocco [email protected]
- Dr Barbara Cozza St. John's University - USA [email protected]
- Dr Martina Jordaan University of Pretoria - South Africa [email protected]
- Dr Madasu Bhaskara Rao Icfai Foundation for Higher Education (IFHE) - India [email protected]
- Professor Abhilasha Singh American University in the Emirates - UAE [email protected]
Commissioning Editor
- Danielle Crow Emerald Publishing - UK [email protected]
Journal Editorial Office (For queries related to pre-acceptance)
- Aman Bhamani Emerald Publishing [email protected]
Supplier Project Manager (For queries related to post-acceptance)
- Subha Sri Aneesh Emerald Publishing [email protected]
Editorial Advisory Board
- Dr Anand Agrawal BlueCrest University College - Ghana
- Mr Majid Ali Sulaiman Al-Rajhi University - Saudi Arabia
- Dr Salvador Baena-Morales University of Alicante - Spain
- Dr Tina Bass University of Derby - UK
- Dr Gavin Baxter University of the West of Scotland - UK
- Dr Arlinda Beka University of Pristina - Kosovo
- Dr Vasiliki Brinia Athens University of Economics & Business - Greece
- Professor Milton Cox Miami University - USA
- Dr Elena García Ansani USA
- Professor Beena Giridharan Curtin University - Malaysia
- Dr Jaimie Hoffman Noodle Partners - USA
- Professor Dirk Ifenthaler University of Mannheim - Germany
- Mr Hari Chandra Kamali Tribhuvan University - Nepal
- Dr Diana A. Karim Al Jahromi University of Bahrain - Kingdom of Bahrain
- Dr Corinne Laverty Queen's University - Canada
- Dr Shahab Alam Malik Minhaj University - Pakistan
- Dr Serpil Meri-Yilan AICU - Turkey
- Dr Charlynn Miller The University of Melbourne - Australia
- Dr Michael Miller University of Arkansas - USA
- Dr Nandita Mishra Amity University - India
- Dr Eugenie A. Panitsides Hellenic Open University - Greece
- Dr Sweta Patnaik Cape Peninsula University of Technology - South Africa
- Dr Krassie Petrova Auckland University of Technology - New Zealand
- Ms Inge Rozendal University of Applied Sciences - The Netherlands
- Dr Damini Saini Indian Institute of Management - India
- Dr Abeer Salem Modern Sciences and Arts University - Egypt
- Dr Mahruf Shohel Institute of Development Studies - Bangladesh
- Dr Tingjia Wang Hiroshima University - Japan
- Dr Rana Zeine Saint James School of Medicine - Caribbean Netherlands
Citation metrics
CiteScore 2023
Further information
CiteScore is a simple way of measuring the citation impact of sources, such as journals.
Calculating the CiteScore is based on the number of citations to documents (articles, reviews, conference papers, book chapters, and data papers) by a journal over four years, divided by the number of the same document types indexed in Scopus and published in those same four years.
For more information and methodology visit the Scopus definition
CiteScore Tracker 2024
(updated monthly)
CiteScore Tracker is calculated in the same way as CiteScore, but for the current year rather than previous, complete years.
The CiteScore Tracker calculation is updated every month, as a current indication of a title's performance.
2023 Impact Factor
The Journal Impact Factor is published each year by Clarivate Analytics. It is a measure of the number of times an average paper in a particular journal is cited during the preceding two years.
For more information and methodology see Clarivate Analytics
5-year Impact Factor (2023)
A base of five years may be more appropriate for journals in certain fields because the body of citations may not be large enough to make reasonable comparisons, or it may take longer than two years to publish and distribute leading to a longer period before others cite the work.
Actual value is intentionally only displayed for the most recent year. Earlier values are available in the Journal Citation Reports from Clarivate Analytics .
Publication timeline
Time to first decision
Time to first decision , expressed in days, the "first decision" occurs when the journal’s editorial team reviews the peer reviewers’ comments and recommendations. Based on this feedback, they decide whether to accept, reject, or request revisions for the manuscript.
Data is taken from submissions between 1st June 2023 and 31st May 2024
Acceptance to publication
Acceptance to publication , expressed in days, is the average time between when the journal’s editorial team decide whether to accept, reject, or request revisions for the manuscript and the date of publication in the journal.
Data is taken from the previous 12 months (Last updated July 2024)
Acceptance rate
The acceptance rate is a measurement of how many manuscripts a journal accepts for publication compared to the total number of manuscripts submitted expressed as a percentage %
Data is taken from submissions between 1st June 2023 and 31st May 2024 .
This figure is the total amount of downloads for all articles published early cite in the last 12 months
(Last updated: July 2024)
This journal is abstracted and indexed by
- Academic Search Alumni Edition
- Academic Search Complete
- Academic Search Elite
- Academic Search Premier
- BFI (Denmark)
- Cabell's Directory of Publishing Opportunities in Higher Education
- Education Research Complete and Education Resources Information Center (ERIC)
This journal is ranked by
- Scopus and Emerging Sources Citation Index (Clarivate Analytics)
Reviewer information
Peer review process.
This journal engages in a double-anonymous peer review process, which strives to match the expertise of a reviewer with the submitted manuscript. Reviews are completed with evidence of thoughtful engagement with the manuscript, provide constructive feedback, and add value to the overall knowledge and information presented in the manuscript.
The mission of the peer review process is to achieve excellence and rigour in scholarly publications and research.
Our vision is to give voice to professionals in the subject area who contribute unique and diverse scholarly perspectives to the field.
The journal values diverse perspectives from the field and reviewers who provide critical, constructive, and respectful feedback to authors. Reviewers come from a variety of organizations, careers, and backgrounds from around the world.
All invitations to review, abstracts, manuscripts, and reviews should be kept confidential. Reviewers must not share their review or information about the review process with anyone without the agreement of the editors and authors involved, even after publication. This also applies to other reviewers’ “comments to author” which are shared with you on decision.


Resources to guide you through the review process
Discover practical tips and guidance on all aspects of peer review in our reviewers' section. See how being a reviewer could benefit your career, and discover what's involved in shaping a review.
More reviewer information
Calls for papers
Universities as change agents: social innovation for sustainable futures.
Introduction This special edition will explore the intersections of humanizing pedagogy, social justice, inclusion, and equity in education. It will delve into innovative practices that promote sustainable futures and exam...
Thank you to the 2023 Reviewers of Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education
The publishing and editorial teams would like to thank the following, for their invaluable service as 2022 reviewers for this journal. We are very grateful for the contributions made. With their help, the journal has been able to publish such high...
HETL Conference 2024 – Nelson Mandela University, South Africa
Join us for the 2024 HETL Conference in South Africa, hosted by Nelson Mandela University, from 2 October to 4 October Bringing together Higher Education professionals and students from across the world to provide a platform for d...
Thank you to the 2022 Reviewers of Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education
Hetl conference 2023 – university of aberdeen.
The University of Aberdeen will host the 2023 HETL Conference from 12 - 14 June 2023 Bringing together Higher Education professionals and students from across the world to provide a platform for discussion, debate, networki...
Thank you to the 2021 Reviewers of Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education
The publishing and editorial teams would like to thank the following, for their invaluable service as 2021 reviewers for this journal. We are very grateful for the contributions made. With their help, the journal has ...
Literati awards

Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education - Literati Award Winners 2023
We are to pleased to announce our 2023 Literati Award winners. Outstanding Paper Embracing educational disruption: A...

Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education - Literati Award Winners 2022
We are pleased to announce our 2022 Literati Award winners. Outstanding Paper Basic psychological needs sa...

Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education - Literati Award Winners 2021
We are pleased to announce our 2021 Literati Award winners. Outstanding Paper Health implications of job-r...
Higher education around the world has become a major topic of discussion, debate, and controversy, as a range of political, economic, social, and technological pressures result in a myriad of changes at all levels. But the quality and quantity of critical dialogue and research and their relationship with practice remains limited.

Aims and scope
Internationally peer-reviewed, the Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education (JARHE) , focuses on the scholarship and practice of teaching and learning and higher education, covering:
- Higher education teaching, learning, curriculum, assessment, policy, management, leadership, and related areas
- Digitization, internationalization, and democratization of higher education, and related areas such as lifelong and lifewide learning
- Innovation, change, and reflections on current practices
- Issues around teaching and learning, especially those discussions which seek to inform practice are encouraged, ensuring the journal has validity and relevance in the fast-change higher education landscape

The journal is published in affiliation with the International Higher Education Teaching and Learning Association .
Latest articles
These are the latest articles published in this journal (Last updated: July 2024 )
TPACK based blended learning model to improve engineering graduate attributes - A case study with Kirkpatrick evaluation
Complex thinking and robotics: a proposal for sexual and gender diversity and inclusion training, using a virtual patient system to improve medical students' confidence in clinical diagnosis: a controlled study, top downloaded articles.
These are the most downloaded articles over the last 12 months for this journal (Last updated: July 2024 )
Exploring Key Themes and Trends in International Student Mobility Research "A Systematic Literature Review
Study destination preference and post-graduation intentions "a push-pull factor theory perspective, identifying the opportunities and challenges of artificial intelligence in higher education: a qualitative study.
These are the top cited articles for this journal, from the last 12 months according to Crossref (Last updated: July 2024 )
Exploring determinants of social media addiction in higher education through the integrated lenses of Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and usage habit
Lifelong learning measurement scale (llms): development and validation in the context of higher education institutions, university students' perceived service quality and attitude towards hybrid learning: ease of use and usefulness as mediators, related journals.
This journal is part of our Education collection. Explore our Education subject area to find out more.
See all related journals
Qualitative Research Journal
Qualitative Research Journal is an international journal dedicated to communicating the theory and practice of...

International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education
The issue of sustainability in a higher education context is, to some extent, a recent theme. Since over 600...

Higher Education, Skills and Work-based Learning
Higher Education, Skills and Work-based Learning is the only journal to focus on the interface between higher education...

This journal is aligned with our quality education for all goal
We believe in quality education for everyone, everywhere and by highlighting the issue and working with experts in the field, we can start to find ways we can all be part of the solution.

- Utility Menu
Harvard Undergraduate Student Research into Higher Education
Higher education through student eyes: a collection of student research papers.
| 9.47 MB |

The present collection of research papers reflects students’ perspectives on today’s changing higher education landscape and the challenges or controversies they observe in contemporary higher education. Student research papers featured in this collection are a testimony of students’ genuine interest in studying and contributing to the established and emerging areas of higher education studies, and their commitment to achieving equity and excellence in higher education.
Recent Publications
- “Playing Your/The Part: Examining The Optimal Leadership Structure For Kirkland Drama Society”
- A Case for Higher Education: Addressing Financial Sustainability in Community Colleges
- SOCIOL1104 Fall 2021 Course Review Student Handbook
- The Efficacy, Impacts, and Limits of Harvard College’s Title IX Policies
- Too Rich for Aid, Too Poor for Tuition: The College Affordability Dilemma for the Middle and Upper Middle Class
Higher Education Research Paper Topics

In this page on higher education research paper topics , we present a comprehensive guide to help students in the field of education with their research papers. The abstract provides a brief overview of the content covered in the page, including a keyphrase to emphasize the main focus. Throughout the page, you will find a diverse range of higher education research paper topics, expert advice on topic selection, tips for writing an effective research paper, and information about the custom writing services offered by iResearchNet. Whether you are a student in need of topic inspiration or seeking assistance with your research paper, this page will provide valuable insights and resources to support your academic journey in higher education.
100 Higher Education Research Paper Topics
In this section, we present a comprehensive list of higher education research paper topics. These topics are organized into 10 categories, each focusing on a different aspect of higher education. Within each category, you will find 10 research paper topics to spark your imagination and guide your exploration. These topics encompass a wide range of disciplines and subfields within higher education, allowing you to explore various dimensions of this dynamic field. Whether you are interested in policy issues, student experiences, teaching and learning methodologies, or institutional practices, there is something here for everyone. Let this list inspire you and serve as a starting point for your research endeavors.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Higher Education Policy and Governance
- The impact of government funding on higher education institutions
- Evaluating the effectiveness of quality assurance mechanisms in higher education
- The role of accreditation in ensuring educational standards in higher education
- Examining the relationship between government policies and access to higher education
- Exploring the influence of international rankings on university competitiveness
- Analyzing the implications of privatization in higher education
- Investigating the role of higher education in promoting sustainable development goals
- The challenges of promoting diversity and inclusion in higher education institutions
- Examining the role of community colleges in expanding access to higher education
- The impact of globalization on higher education policies and practices
Student Experiences and Success
- Understanding the factors influencing student retention and graduation rates
- Examining the impact of financial aid policies on college access and affordability
- Exploring the experiences of first-generation college students
- Investigating the role of student support services in enhancing student success
- Analyzing the effects of student engagement on academic achievement and personal development
- Examining the influence of cultural and social capital on student experiences in higher education
- The impact of student diversity on campus climate and intercultural learning
- Exploring the experiences of international students in higher education
- Investigating the effects of work-study programs on student outcomes
- The role of technology in enhancing student learning experiences in higher education
Teaching and Learning Methodologies
- Exploring innovative pedagogical approaches in higher education
- Investigating the effectiveness of online learning in higher education
- Analyzing the impact of active learning strategies on student engagement and learning outcomes
- Examining the role of problem-based learning in promoting critical thinking skills
- The use of educational technologies to enhance teaching and learning in higher education
- Investigating the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in higher education settings
- Analyzing the impact of inclusive teaching practices on student learning outcomes
- The role of peer mentoring in supporting student learning and development
- Examining the benefits and challenges of experiential learning in higher education
- Investigating the role of assessment and feedback in promoting student learning and achievement
Higher Education and Society
- Exploring the role of higher education in fostering social mobility
- Analyzing the impact of college education on income inequality
- Investigating the relationship between higher education and economic development
- Examining the role of higher education in addressing societal challenges and promoting social justice
- The impact of community engagement initiatives in higher education institutions
- Analyzing the influence of higher education on democratic participation and civic engagement
- Exploring the role of higher education in promoting sustainable development
- The effects of globalization on higher education and its implications for society
- Investigating the role of higher education in promoting cultural diversity and intercultural understanding
- Examining the relationship between higher education and lifelong learning in a knowledge-based society
Institutional Practices and Management
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of strategic planning in higher education institutions
- Investigating the role of leadership in shaping organizational culture in higher education
- Exploring the effects of performance-based funding on institutional practices and outcomes
- Examining the impact of faculty development programs on teaching and research productivity
- The role of shared governance in decision-making processes within higher education institutions
- Analyzing the effects of resource allocation on institutional effectiveness and efficiency
- Investigating the influence of organizational climate on faculty job satisfaction and retention
- Exploring the role of technology in supporting administrative processes in higher education
- The impact of internationalization strategies on institutional reputation and student recruitment
- Examining the challenges and opportunities of managing diversity in higher education institutions
Higher Education and Technology
- Investigating the impact of online learning platforms on student access and engagement
- Analyzing the effectiveness of blended learning approaches in higher education
- Exploring the use of learning analytics in enhancing student success in higher education
- The impact of educational technologies on teaching practices and student learning outcomes
- Investigating the role of virtual reality in experiential learning in higher education
- Analyzing the implications of artificial intelligence in higher education settings
- Exploring the use of gamification in higher education to promote student motivation and engagement
- Investigating the challenges and opportunities of open educational resources in higher education
- Examining the role of mobile learning in supporting anytime, anywhere access to education
- The effects of social media on student engagement and communication in higher education
Access and Equity in Higher Education
- Analyzing the barriers to access and participation in higher education for marginalized groups
- Investigating the impact of affirmative action policies on diversity in higher education
- Exploring the role of financial aid programs in promoting college access and equity
- Examining the effects of merit-based scholarships on educational opportunities and social mobility
- The impact of college preparatory programs on underrepresented students’ college readiness
- Analyzing the influence of high-stakes testing on college admissions and access to higher education
- Investigating the experiences of students with disabilities in higher education
- Exploring the challenges and opportunities of supporting non-traditional students in higher education
- The effects of community college transfer pathways on access to four-year institutions
- Examining the role of mentoring programs in supporting underrepresented students in higher education
Higher Education and Globalization
- Investigating the effects of international student mobility on higher education institutions
- Analyzing the influence of global rankings on higher education policies and practices
- Exploring the role of transnational education in higher education
- Examining the impact of global partnerships and collaborations on higher education institutions
- The effects of globalization on curriculum development and pedagogical approaches in higher education
- Investigating the influence of internationalization strategies on institutional identity and mission
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of recruiting and retaining international students
- Exploring the role of cross-cultural competence in higher education settings
- Investigating the impact of globalization on faculty recruitment and retention in higher education
- Examining the implications of global competition for funding and resources in higher education
Higher Education Leadership and Administration
- Analyzing the qualities and skills of effective higher education leaders
- Investigating the challenges and opportunities of leadership succession in higher education
- Exploring the role of shared governance in effective institutional leadership
- Examining the impact of leadership development programs on leadership effectiveness in higher education
- The effects of gender and diversity in leadership positions in higher education institutions
- Investigating the role of emotional intelligence in higher education leadership
- Analyzing the influence of political and institutional contexts on leadership decision-making in higher education
- Exploring the challenges and opportunities of leading in times of crisis in higher education
- Investigating the impact of ethical leadership on organizational culture and climate in higher education
- Examining the role of transformational leadership in driving innovation and change in higher education
Higher Education Assessment and Evaluation
- Analyzing the effectiveness of assessment practices in measuring student learning outcomes in higher education
- Investigating the impact of standardized testing on higher education admissions and accountability
- Exploring the role of program evaluation in improving the quality of higher education programs
- Examining the influence of accreditation processes on institutional quality and improvement
- The effects of learning outcomes assessment on instructional practices in higher education
- Investigating the use of rubrics in evaluating student performance and providing feedback in higher education
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of assessing student engagement in higher education
- Exploring the role of learning analytics in informing decision-making and improving student success in higher education
- Investigating the impact of outcomes-based funding on institutional assessment and accountability
- Examining the challenges and opportunities of assessing and recognizing prior learning in higher education
This comprehensive list of higher education research paper topics offers a diverse range of ideas to inspire and guide your research endeavors. Whether you are interested in policy issues, student experiences, teaching and learning methodologies, institutional practices, or global perspectives, there is a wealth of topics to explore within the field of higher education. Remember that the key to selecting a research topic is to align it with your interests, expertise, and the requirements of your research paper. As you embark on your research journey, consider the significance of your chosen topic, its relevance to the field, and the potential contribution it can make to the existing body of knowledge. With careful consideration and thorough research, you can delve into the complexities of higher education and contribute to the ongoing discourse in the field.
Higher Education Research Guide
Welcome to the iResearchNet page on higher education research paper topics. As students embark on their journey in higher education, they encounter numerous opportunities to explore and analyze various aspects of this dynamic field. Research papers play a pivotal role in this process, allowing students to delve deeper into specific areas of interest and contribute to the ever-evolving discourse surrounding higher education. The purpose of this page is to provide students with a comprehensive guide to selecting and developing research paper topics that are not only academically rigorous but also relevant and impactful in the context of higher education.
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, higher education faces a multitude of challenges and opportunities. From exploring innovative teaching methods and educational technologies to examining issues of access, equity, and diversity, there are countless avenues for research within the field. This page aims to present a diverse range of higher education research paper topics, spanning various disciplines and subfields, to inspire and guide students in their exploration.
By engaging with the content on this page, students will gain valuable insights into the current trends, debates, and gaps in knowledge within higher education. They will also find practical advice and strategies for selecting research paper topics that align with their interests and academic goals. Whether you are interested in examining the impact of online learning, exploring student engagement strategies, or investigating the role of higher education in fostering social mobility, this page offers a wealth of ideas and resources to support your research endeavors.
We invite you to delve into the world of higher education research paper topics, to discover new ideas, expand your knowledge, and contribute to the ever-growing body of scholarship in the field. Let this page serve as a valuable tool to ignite your curiosity, fuel your intellectual growth, and empower you to make meaningful contributions to the field of higher education.
Choosing Higher Education Research Paper Topics
Selecting a suitable research topic is a crucial step in the process of writing a higher education research paper. With the vast array of issues and subfields within higher education, it can be overwhelming to decide on a specific topic that aligns with your interests and meets the requirements of your research assignment. In this section, we offer expert advice to help you navigate through the selection process and choose a compelling and relevant topic for your higher education research paper.
- Identify your area of interest : Start by exploring your personal interests within the field of higher education. Reflect on the topics or issues that have caught your attention during your studies or experiences. Consider your career goals and the aspects of higher education that you are passionate about.
- Review current literature : Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in the field of higher education. Read academic journals, books, and research articles to familiarize yourself with the latest trends, debates, and gaps in knowledge. This will help you identify potential research areas that have not been extensively explored or require further investigation.
- Narrow down your focus : Once you have identified your general area of interest, narrow down your focus to a specific research question or problem. A well-defined research question will provide a clear direction for your study and ensure that your research is focused and meaningful.
- Consider the significance and relevance : Evaluate the significance and relevance of your chosen topic. Ask yourself why it is important to study this particular aspect of higher education. Consider its implications for policymakers, educators, students, or other stakeholders. Ensure that your research topic addresses a gap in knowledge or contributes to the existing body of research.
- Assess feasibility : Assess the feasibility of your research topic in terms of data availability, resources, and time constraints. Consider the practicality of conducting research within your chosen topic, including access to relevant data sources, ethical considerations, and the scope of your research project.
- Seek input from professors or experts : Consult with your professors or other experts in the field of higher education. They can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their expertise and experience. Discuss your research interests and potential topics with them to gain further clarity and suggestions for refinement.
- Stay updated with current events : Keep yourself informed about current events and issues in higher education. Follow news, policy changes, and debates related to higher education to identify emerging topics or controversies that could be potential research areas.
- Consider interdisciplinary approaches : Explore interdisciplinary approaches by incorporating perspectives from other fields such as sociology, psychology, economics, or public policy. This can provide a unique angle to your research and contribute to a broader understanding of higher education issues.
- Brainstorm and generate ideas : Engage in brainstorming sessions to generate a list of potential research topics. Write down any ideas or concepts that come to mind, even if they seem unconventional or challenging. The goal is to encourage creativity and explore various possibilities.
- Reflect on personal experiences : Reflect on your personal experiences within higher education. Consider any challenges, observations, or insights you have gained as a student or through other educational roles. These experiences can serve as a foundation for identifying research questions or topics that are personally meaningful to you.
Choosing a higher education research paper topic requires careful consideration and exploration of your interests, current literature, and the significance of the topic. By following the expert advice provided in this section, you can navigate through the selection process and choose a research topic that aligns with your passions, contributes to the field of higher education, and engages with important issues and debates. Remember to seek guidance from professors or experts and stay updated with current events to ensure the relevance and timeliness of your research.
How to Write a Higher Education Research Paper
Writing a higher education research paper requires a systematic and well-structured approach to effectively communicate your ideas, findings, and analysis. In this section, we provide a step-by-step guide on how to write a higher education research paper that meets academic standards and effectively addresses your research question.
- Understand the assignment requirements : Carefully review the assignment guidelines provided by your instructor or institution. Pay attention to the research question or problem statement, formatting requirements, citation style, and any specific instructions or expectations.
- Conduct thorough research : Start by conducting comprehensive research on your chosen topic. Gather relevant literature, data, and scholarly sources to build a strong foundation for your research paper. Use academic databases, library resources, and credible sources to ensure the reliability and validity of your information.
- Develop a clear thesis statement : Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that captures the main argument or purpose of your research paper. The thesis statement should provide a roadmap for your paper and guide the reader in understanding the focus and significance of your study.
- Organize your paper : Create a logical structure for your research paper. Divide it into sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, analysis, and conclusion. Each section should serve a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence and flow of your paper.
- Write a compelling introduction : Begin your research paper with an engaging introduction that provides background information on your topic and presents the research question or problem. Clearly state the purpose of your study and its significance in the context of higher education.
- Conduct a thorough literature review : In the literature review section, critically analyze existing research and scholarly works relevant to your topic. Summarize key findings, identify gaps in knowledge, and highlight debates or controversies in the field of higher education. Use proper citations and references to acknowledge the sources of your information.
- Describe your methodology : Explain the research methodology employed in your study. Clearly outline the research design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques used to gather and interpret your data. Justify your choices and address any limitations or potential biases.
- Present your findings and analysis : Present your research findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, graphs, or visual aids to enhance the clarity and comprehensibility of your data. Analyze your findings and provide interpretations that align with your research question and support your thesis statement.
- Discuss implications and significance : Discuss the implications of your research findings for the field of higher education. Reflect on the broader implications, potential applications, or recommendations for future research or policy development. Highlight the significance of your study in advancing knowledge or addressing practical challenges in higher education.
- Write a strong conclusion : End your research paper with a concise and impactful conclusion. Summarize your key findings, restate your thesis statement, and discuss the broader implications of your research. Avoid introducing new information or ideas in the conclusion.
- Revise and proofread : Review and revise your research paper for clarity, coherence, and grammar. Ensure that your ideas are logically presented and supported by evidence. Proofread your paper for spelling and grammatical errors. Consider seeking feedback from peers, mentors, or writing centers to improve the quality of your paper.
- Follow proper citation and formatting guidelines : Adhere to the specific citation style required by your institution or instructor (such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard). Ensure that in-text citations and the reference list are accurately formatted and follow the guidelines of the chosen citation style.
By following these steps, you can effectively structure and write a higher education research paper that contributes to the field and showcases your analytical skills, critical thinking, and understanding of key concepts in higher education. Remember to allow ample time for research, writing, and revision to produce a well-crafted and high-quality research paper.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
At iResearchNet, we offer comprehensive writing services that enable students to order custom education research papers on any topic. Our team of expert degree-holding writers is committed to delivering high-quality research papers that meet the specific requirements of each student. When you choose our writing services, you can expect the following features:
- Expert degree-holding writers : Our team consists of highly qualified writers who possess advanced degrees in education and related fields. They have the expertise and knowledge to handle complex research topics and provide insightful analysis in your research paper.
- Custom written works : Every research paper we deliver is custom written from scratch according to your unique requirements. We understand the importance of originality and ensure that your paper is free from plagiarism. Our writers conduct in-depth research and use credible sources to support their arguments and findings.
- In-depth research : Our writers are skilled researchers who know how to conduct thorough and comprehensive research on various education topics. They have access to reputable academic databases and libraries, allowing them to gather the most relevant and up-to-date information for your research paper.
- Custom formatting : We offer custom formatting options to meet your specific formatting requirements. Whether you need your research paper formatted in APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, or any other style, our writers will ensure that your paper adheres to the prescribed guidelines.
- Top quality : We strive for excellence in every research paper we deliver. Our writers pay attention to detail, ensuring that your paper is well-structured, coherent, and demonstrates a high level of critical thinking and analysis. We aim to exceed your expectations and deliver a research paper of exceptional quality.
- Customized solutions : We understand that every student has unique needs and expectations for their research paper. Our writers take a customized approach, tailoring their writing to meet your specific requirements and academic goals. We ensure that your research paper aligns with your research question, objectives, and desired outcomes.
- Flexible pricing : We offer competitive and flexible pricing options to accommodate the budgets of students. Our pricing is transparent, and there are no hidden fees. We strive to provide value for your money without compromising on the quality of the research paper.
- Short deadlines : We understand that students may have urgent deadlines for their research papers. Our writing services offer short deadlines, allowing you to receive your completed paper within a timeframe as short as 3 hours. We prioritize timely delivery to ensure that you have sufficient time for review and submission.
- 24/7 support : Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any queries or concerns you may have. We are here to provide guidance and support throughout the entire process, from placing your order to receiving your final research paper.
- Absolute privacy : We prioritize the privacy and confidentiality of our clients. Your personal information and order details are kept strictly confidential, and we take stringent measures to ensure data security.
- Easy order tracking : Our user-friendly platform allows you to easily track the progress of your order. You can stay informed about the status of your research paper and communicate with your assigned writer directly.
- Money back guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our services and the expertise of our writers. If, for any reason, you are not satisfied with the research paper you receive, we offer a money back guarantee. Your satisfaction is our utmost priority.
By choosing iResearchNet for your custom education research paper, you are assured of receiving a well-written, thoroughly researched, and custom-crafted paper that meets your academic requirements. Place your order today and experience the convenience and quality of our writing services.
Get a Custom Education Research Paper Today!
Are you in need of a well-written and meticulously researched education research paper? Look no further! iResearchNet is here to provide you with top-notch custom writing services tailored to your unique needs. Take advantage of our expertise, experience, and commitment to delivering high-quality research papers.
- Place your order : Visit our website and fill out the order form to provide us with all the necessary details about your research paper. Be sure to include the topic, deadline, formatting requirements, and any specific instructions or guidelines.
- Make payment : Once you have submitted your order, proceed to make payment using our secure and convenient payment options. We offer flexible pricing to accommodate your budget.
- Choose your writer : Our team of expert degree-holding writers is composed of specialists in the field of education. You have the option to choose the writer who best aligns with your research topic and requirements. Alternatively, our system will assign a writer to your order based on their expertise and availability.
- Receive your work : Sit back and relax as our writer works diligently to craft your custom education research paper. You will have direct communication with your writer throughout the process, allowing you to provide feedback and monitor progress.
- Free revisions : We value your satisfaction and strive to deliver research papers that meet your expectations. If you require any revisions or modifications, simply let us know, and we will revise your paper accordingly, free of charge.
At iResearchNet, we take pride in our commitment to excellence, timely delivery, and customer satisfaction. Our team is dedicated to ensuring that you receive a research paper that meets the highest academic standards and demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter.
Don’t let the pressure of writing a research paper weigh you down. Trust our professional writing services to help you achieve success in your academic endeavors. Place your order today and let us assist you in creating a remarkable education research paper that showcases your knowledge and research skills.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


ISSN Approved Journal || eISSN: 2582-8185 || CODEN: IJSRO2 || Impact Factor 8.2 || Google Scholar and CrossRef Indexed
Fast Publication within 48 hours || Low Article Processing Charges || Peer Reviewed and Referred Journal || Free Certificate
Research and review articles are invited for publication in July - August 2024 (Volume 12, Issue 2)
Exploring the mediating role of job satisfaction in enhancing lecturer performance: a study of competence and work environment in higher education, indah sari lubis *.
Copyright © 2024 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article. This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Liscense 4.0
For Authors: Fast Publication of Research and Review Papers
Issn approved journal publication within 48 hrs in minimum fees inr 1770 or usd 32, impact factor 8.2, .

Copyright © 2024, International Journal of Science and Research Archive
Designed by World Journal Publication

The rising demand for higher education: the case of Women's University in Africa
Ids item types, copyright holder, identifier issn, usage metrics.

- Carnegie Classification
- American Council on Education
- Higher Education Today
- Race and Ethnicity in Higher Education
2025 Research Designations FAQs
- Research Designations
Frequently Asked Questions
Why change the methodology for calculating R1?
Since 2005, the methodology for classifying R1 institutions has been based on a complicated, 10-metric formula that uses normative and relative scores and places a cap on the number of institutions that can be classified as R1. The result is an opaque process and a moving target that makes it impossible to determine exactly what an institution must do to become classified as R1. This has created unintended competition between institutions that are left to guess what it takes to receive the R1 designation.
The R1 grouping is intended to capture institutions where there is a very high amount of research occurring, measured by the number of research/scholarship doctorates awarded and the amount of spending on research and development. That research activity can be undertaken in any way that an institution chooses to further its mission. The updated methodology makes that clearer.
What are the changes to classifying research? How will you calculate the new R1?
Moving forward, the methodology for determining R1 will return to using a clear threshold. For the 2025 Carnegie Classifications, the threshold will be set at $50 million in total R&D spending and 70 doctoral research degrees. To determine which institutions meet this threshold, the classifications will use the higher of either a three-year rolling average or most recent year data. The research spending will be taken from the National Science Foundation (NSF) Higher Education Research and Development (HERD) Survey, and the doctoral research degree number will be taken from the National Center for Education Statistics IPEDS data. Any institution that meets this new R1 threshold will be included.
We will also change the title of this category to R1: Very High Research Spending and Doctorate Production.
How will you define R2?
Unlike R1, the existing methodology for determining R2 is already based on a threshold, which will continue to remain the same in the next update. The threshold for R2 will continue to be defined as institutions with at least 20 doctoral research degrees that also have at least $5 million in total research expenditures (as reported through the NSF HERD Survey). There will not be a cap on the number of institutions that can be in this category.
We will also change the title of this category to R2: High Research Spending and Doctorate Production.
How will you define the new “Research Colleges and Universities” research designation?
The new Research Colleges and Universities designation will be based on expenditures only and will include any institution that spends more than $2.5 million on research expenditures (as reported through the NSF HERD survey). Institutions that are in the R1 or R2 designations are not included. There will not be a cap on the number of institutions that can be in this category.
Which institutions are eligible for the R1, R2, and RCU categories?
Any institution that meets the criteria for a particular category is able to be designated as an R1 institution, R2 institution, or Research College and University. Previously, the research classifications had only been open to a narrow set of doctoral-granting institutions. Moving forward, any institution – including special focus institutions, baccalaureate-only institutions, Tribal colleges and universities, and others – could be designated as a research institution, depending on that institution’s data.
How will the research designations fit into the structure of the Basic Classification?
The research designations will be separated from the Basic Classification, becoming additional listings for those institutions that meet the definitions. Research activity continues to be an important way to reflect institutional missions for a number of colleges and universities and will continue to be recognized, but it will no longer be the exclusive driver for how American higher education institutions are classified.
Will you change the research designation thresholds in the future?
We expect to adjust the thresholds over time. We will share updated thresholds in advance of each classification release.
How often are the Carnegie Classifications updated?
The Carnegie Classifications will continue to be published on a three-year cycle. The 2021 Carnegie Classifications were released in February 2022, and we expect to release the 2025 Carnegie Classifications in early 2025.
Where can I read more about the changes announced so far?
On November 1, 2023, ACE and the Carnegie Foundation announced the changes outlined above as we work toward the release of the 2025 Carnegie Classifications. In addition, you can read more about the changes and share input on potential characteristics for the new Basic Classification here.
Does the November 1 announcement change an institution’s current Carnegie Classifications?
The changes announced on November 1, including to the R1 threshold, do not impact the current 2021 Carnegie Classifications that were released in February 2022. These changes will be made as a part of the 2025 Carnegie Classifications. The classifications will continue to be revised on a three-year schedule moving forward.
Join Our Mailing List
Join our mailing list to be the first to receive ACE's news on the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
Our email opt-in form uses iframes. If you do not see the form, please check your tracking or privacy settings.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
World Reputation Rankings 2023
The Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings 2023 are based on the world’s largest invitation-only opinion survey of senior, published academics. It asks scholars to name no more than 15 universities that they believe are the best for research and teaching in their field.
View the World Reputation Rankings 2023 methodology
Harvard University tops the ranking for the 13th year in a row, and the US remains the most represented country, with 52 institutions, although this is four fewer than last year.
With six universities, the US also dominates the top 10. The UK, China and Japan also feature in this group.
The order of the top 10 remains mostly unchanged, except for China’s top scorer, Tsinghua University, which rises one place to eighth, and the US’ Yale University, which drops to ninth.
The UK continues to have the second highest number of representatives in the ranking overall, 20, although this is four fewer than last year. Its highest entry is the University of Oxford, in fourth place.
China and Germany follow the UK in terms of representation, with 15 and 14 universities, respectively.
There is a rise in the number of universities from the Middle East, with seven institutions from this region joining the table this year. They represent the United Arab Emirates, Lebanon, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia.
Overall, universities in 31 countries are included in the ranking.
Read our analysis of the World Reputation Rankings 2023 results
To raise your university’s global profile with THE , please contact [email protected]
To unlock the data behind THE ’s rankings and access a range of analytical and benchmarking tools, click here
| rank order | Rank | Name Country/Region | Node ID |
|---|
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail
Read more about the World Reputation Rankings 2023
Student insights.
- The top 50 universities by reputation
Academic Insights
- World Reputation Rankings 2023: results announced
- A challenging year for university reputation management
- Institutional neutrality is not a cold cop-out: it is vital in polarised times
- Talking leadership: Teresa Woodruff on steering a university back to ‘safe harbour’
- Museums, media and mobility: how to put the public in public engagement
Methodology:

Featured jobs
Featured universities.

University of Guadalajara

- Jiying Han 1 ,
- Lei Jin 1 &
- Hongbiao Yin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5424-587X 2
1011 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Given the complexity and high demands of research supervision and the intricate emotional experiences of supervisors, there is a need to explore how they regulate their emotions, particularly across various disciplinary backgrounds. The current study explored the emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors during the process of supervising graduate students. Based on data collected through semi-structured interviews, observations, and documentation from six research supervisors in different institutions in China, seven emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors were identified and further categorized into two groups, that is, antecedent-focused (prevention, intervention, reinterpretation, reconcentration, and detachment) and response-focused (suppression and expression) emotion regulation strategies. The findings shed light on the dilemmas faced by supervisors and the paradox aroused from the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision within an accountability-based managerial context. The implications for supervisors’ emotion regulation in authentic supervisory situations are discussed, and insights for universities’ policy-making are offered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Holding Abusive Managers in Contempt: Why and When Experienced Abusive Supervision Motivates Enacted Interpersonal Justice Toward Subordinates

Towards Safe and Equitable Relationships: Sociocultural Attunement in Supervision

“Take a step back”: teacher strategies for managing heightened emotions
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Since the 1990s, educational research has undergone an “affective turn” as a result of the critique of the long-standing Cartesian dualism between emotionality and rationality (Zembylas, 2021 ). Over the following three decades, the dynamic and complex nature of teacher emotion has been explored from various perspectives and approaches (Agudo, 2018 ). Since emotion can significantly impact various stages of the teaching process, either facilitating or hindering it (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ), opportunities for emotion regulation can be identified in educational contexts at any time (Taxer & Gross, 2018 ). In higher education, although emotion regulation has been proven significant to teacher development and well-being (Xie, 2021 ), the majority of research has been conducted within the context of classroom instruction (Tao et al., 2022 ), leaving that of research supervision in graduate education unexplored.
In graduate education, emotion plays an important role in the supervisory process and relationship building which involves a series of emotional interactions essential for both supervisors and graduate students. The existing research has demonstrated an increasing need for supervisors to develop emotion regulation skills to cope with the challenges and provide emotional support in research supervision (Wollast et al., 2023 ). On the one hand, supervisors need to employ emotion regulation strategies in the challenging supervisory contexts, as accountability-based policies and the blurring of personal and academic relationships between supervisors and graduate students may trigger complex emotional experiences such as anxiety and worry for supervisors (Xu, 2021 ). On the other hand, the provision of support from supervisors is strongly linked to the emotional well-being and research success of graduate students (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ). Specifically, supervisors’ emotion regulation plays a crucial role in providing emotional support to graduate students, which in turn has a positive impact on graduate students’ well-being and their belief about their further academic pursuits (Han & Xu, 2023 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ).
Of the limited research on emotion in graduate education, much has been conducted to investigate the influence of graduate students’ emotion regulation on their mental health and academic engagement (Saleem et al., 2022 ). However, there is a paucity of studies which have researched supervisors’ emotions and emotion regulation during the supervisory process. With the aim of unpacking how research supervisors employ emotion regulation strategies in real supervisory scenarios to effectively fulfill their roles, and to gain insights into the nature of research supervision, this qualitative study explores the emotion regulation strategies used by supervisors in the process of research supervision.
Literature review
Teacher emotion and emotion regulation.
Emotion, once considered inferior to cognition, has gained increasing attention in the social sciences, including in educational research (Han & Xu, 2023 ). The current recognition of the intricate interplay between emotion and cognition in teaching and learning highlights the importance of emphasizing teacher emotion in both teacher development and teacher well-being (Chen & Cheng, 2022 ). Emotion is complex and difficult to define (Chen & Cheng, 2022 ), and the connotation of emotion has shifted from an intrapersonal perspective to a relational one, emphasizing interactions between individuals and their environment during emotion generation (Campos et al., 2011 ).
Under the relational view of emotion, individuals can achieve social goals in most jobs involving interpersonal interactions through emotion regulation (Brotheridge & Grandey, 2002 ). Emotion regulation refers to “the processes by which individuals influence which emotions they have, when they have them, and how they experienced and expressed their emotions” (Gross, 1998 , p. 275). In the educational field, a growing interest of research in emotion regulation has emerged since the 1990s (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ; Zembylas, 2021 ), as teaching has been viewed as “an emotional practice” (Hargreaves, 1998 , p. 835). Due to the importance of emotion in teachers’ professional lives, it is crucial for teachers to regulate their emotions to achieve improved teaching and learning outcomes. Specifically, enhancing positive emotions can foster better teacher-student relationships, promote creativity in teaching, and strengthen students’ learning motivation; inappropriately managed negative emotions can have adverse effects on these aspects (Hargreaves, 1998 ). Although teachers’ emotion regulation has been widely examined (e.g., Taxer & Frenzel, 2015 ; Yin, 2015 , 2016a , 2016b ; Yin et al., 2018 ) most studies, influenced by the concept of emotional labor, have mainly focused on two types of emotion regulation strategies: deep acting (the act of internalizing a desired emotion, matching expressed emotion with felt emotion) and surface acting (the act of altering emotional expression without regulating inner feelings) (Grandey, 2000 ; Hochschild, 1983 ). Comparatively, Gross’s ( 1998 ) process model of emotion regulation provides a more nuanced framework to examine teachers’ employment of a wider range of emotion regulation strategies. According to Gross ( 1998 , 2015 ), emotion regulation could be achieved through two main approaches: the antecedent-focused and response-focused approach. The former entails strategies that seek to avoid or regulate emotions by modifying the factors triggering emotion generation, which include situation selection, situation modification, attention deployment, and cognitive changes. The latter modifies an individual’s expressions and responses after the emotions have fully manifested, directly influencing physiological, experiential, or behavioral responses.
In recent years, the predominant focus of studies, guided by Gross’s ( 1998 ) process model, has been on investigating the motivations, strategies, and outcomes of teachers’ intrapersonal emotion regulation (e.g., Taxer & Gross, 2018 ; To & Yin, 2021 ; Xu, 2021 ). Teachers’ motivations for emotional regulation stem from their diverse teaching goals, including managing the impressions that various parties have of them, adapting to intensive educational reforms for survival, and enhancing students’ concentration levels (Hosotani, 2011 ; Xu, 2021 ). As for emotion regulation strategies, the existing literature has mainly been conducted under Gross’s ( 2015 ) model, and revealed a series of antecedent-focused (e.g., situation selection, attention deployment, and cognitive change) and response-focused strategies (e.g., suppression, relaxation, and avoidance) to cope with the ambivalent demands and enormous workload faced by teachers. Remarkably, certain strategies that reflect the unique nature of teachers’ work, such as genuine expression (Yin, 2015 ; Yin, 2016a , 2016b ) and interpersonal strategies (To & Yin, 2021 ), have been identified. Regarding outcomes of emotion regulation, genuine expression of emotion and cognitive appraisal strategies were found helpful to improve the effectiveness of classroom teaching and to maintain a balance between teachers’ professional and personal dimensions of their identities (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ). In contrast, suppressing, pretending, and restraining emotions may cause emotional dissonance and less received social support (Yin, 2015 ).
Emotion regulation and research supervision
In graduate education, supervisors’ emotional experiences are triggered by the complexity and high demands of research supervision (Han & Xu, 2023 ). The conflicting roles of taking responsibility for both supporter and supervisor simultaneously, the contradiction between supervisors’ high expectations of students’ learning autonomy and graduate students’ unsatisfactory performance, and the blurred boundaries between supervisory relationship and friendship (Han & Xu, 2023 ; Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ) are major challenges encountered by research supervisors. These challenges lead to various emotional experiences on the part of supervisors, including positive emotions, such as joy and love (Halse & Malfroy, 2010 ), and more prevalent negative emotions, such as anger, and disappointment (Sambrook et al., 2008 ). Given the diverse range of emotions that emerge during the supervision process, it is necessary for supervisors to employ various emotion regulation strategies to accomplish effective research supervision.
According to literature, emotion regulation is strongly associated with research supervision in three areas. First, effective research supervision requires a constructive and supportive supervisory relationship, which is facilitated by supervisors’ emotion regulation. As poorly managed supervision relationships contribute to low academic completion rates, supervisors are required to establish a respectful and caring relationship with their students (Halse & Malfroy, 2010 ). However, creating and maintaining such relationships can be challenging. Specifically, during the interactions with graduate students, supervisors are expected to offer emotional supports, including encouragement, motivation, and recognition based on students’ individual needs while ensuring that any critical feedback is delivered constructively (Lee, 2008 ). However, excessive emotional engagement or close relationships with students may hinder their ability to provide constructive criticism (Lee, 2008 ). As such, supervisors must strike a balance between offering emotional support and providing constructive feedback, thereby developing a successful educational partnership with their students.
Second, the emotional support provided by supervisors plays a positive role in facilitating graduate students’ research productivity and emotional well-being (Han & Wang, 2024 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ). In terms of research success, supervisors who encourage critical thinking and support constructive controversies tend to produce higher achievement and retention rates than those who adopt a directive and authoritarian approach (Johnson, 2001 ). Furthermore, emotional support from supervisors has been linked to higher levels of research self-efficacy and emotional well-being among graduate students (Diekman et al., 2011 ). Specifically, structure and autonomy support strongly influence graduate students’ feelings and expectations about their future academic success. Thus, in academic settings, supervisors should adopt effective emotion regulation strategies, offering constructive feedback, close guidance, and attentiveness to maintain graduate students’ motivation and mental well-being.
Third, effective emotion regulation is also critical for the well-being of research supervisors themselves. When faced with repeated frustrating events such as a lack of student progress and demanding requirements in accountability-based supervisory contexts, supervisors may experience feelings of exhaustion, particularly when they perceive their supportive efforts as being ineffective (Xu, 2021 ). Failing to regulate these negative emotions with effective strategies can lead to the accumulation and intensification of undesirable feelings, resulting in detrimental effects on supervisors’ well-being and job satisfaction, which may ultimately lead to their emotional burnout and disengagement (To & Yin, 2021 ).
So far, the very limited research on research supervisors’ emotion regulation in medical and scientific disciplines found that although supervisors use instructional strategy modification (e.g., directly pointing out students’ writing deficiencies), cognitive change (e.g., reappraising the relationship between students’ underachievement and their supervision), and response regulation (e.g., lowering their voice to calm themselves) to deal with negative emotions (Han & Xu, 2023 ), they still have difficulties in stepping out of negative emotions (Sambrook et al., 2008 ). Meanwhile, supervisors from different disciplines may use different emotion regulation strategies due to disciplinary differences in occupational challenges, societal expectations, and specific work environments (Veniger & Kočar, 2018 ). Therefore, it is necessary for researchers to investigate the emotion regulation of supervisors with different disciplinary backgrounds.
Based on the literature, underpinned by Gross’s ( 2015 ) process model, the present qualitative multi-case study aims to investigate the emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors from different disciplinary backgrounds. Specifically, the study seeks to answer this core research question: What strategies do research supervisors use to regulate their emotions during the supervision process?
As the in-depth understanding of supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies relies on the narratives of their journey of research supervision, we used narrative inquiry to explore supervisors’ lived experiences in supervising graduate students. Narrative inquiry emphasizes the co-construction of specific experiences by the researcher and participants (Friedensen et al., 2024 ; Riessman, 2008 ), which allows us to co-construct the meaning of emotion regulation with participants through qualitative data including interviews, observations, and documents.
Research context: Emphasizing the accountability of research supervision
The Chinese research supervision system has its roots in the nineteenth century, evolving alongside the development of graduate education (Xie & Zhu, 2008 ). Within this system, research supervisors play a crucial role in research-based master’s and doctoral education. In 1961, a supervisor accountability system was formalized, placing the responsibility on supervisors for overseeing students in research projects, journal publications, and dissertation completion. Under the guidance of supervisors, students engage in specialized courses, master the latest advancements in a specific field, and conduct research (Peng, 2015 ).
In recent years, with the rapid growth of graduate education in China, both supervisors and graduate students have expressed concerns about the quality of research supervision (Xu & Liu, 2023 ). Thus, national policies have been introduced to stipulate supervisors’ responsibilities and enhance the overall supervision quality, with a particular emphasis on the accountability of research supervisors. In 2020, the Accountability Measures for Educational Supervision, released by China’s Ministry of Education ( 2020 ), outlined a code of conduct for supervisors, emphasizing that supervisors bear the primary responsibility for cultivating postgraduate students. Specifically, supervisors are held accountable for various aspects of graduate students’ academic progress, including the quality of dissertations, academic conduct, and the appropriate utilization of research funds. Failure to fulfill these responsibilities may result in serious consequences, such as disqualification from supervising students or the revocation of teaching credentials.
Participants
To explore a wide range of emotional experiences and emotion regulation strategies that arise when supervising students at various stages of their academic journey, participants were purposively selected based on the following three criteria: (1) doctoral supervisors with the qualifications to oversee research-based master’s students and PhD candidates were considered, which allows us to gain insights into their emotions in supervising students at different academic stages; (2) supervisors with a minimum of 5 years of supervision were selected, as their long-term experience would provide a comprehensive understanding of the depth and evolution of emotion regulation strategies; (3) supervisors of both hard and soft disciplines were involved, as disciplinary features may significantly shape supervisors’ styles, potentially leading to their diverse emotions and emotion regulation strategies. Finally, six doctoral supervisors from four universities in China agreed to participate in the study voluntarily and were informed of the research purpose and ethical principles before the study. Table 1 provides a summary of the demographic information for all participants.
Data collection
The positionality statement is essential as the authors’ roles may influence the data collection process. Specifically, two authors are doctoral supervisors with rich experience in research supervision, and one author is a doctoral student. Participants for this study were recruited from the authors’ colleagues or recommendations from friends. In the spirit of self-reflexivity, we acknowledge our positions in research supervision and recognize that our relationships with participants may impact our collection and interpretations of the data. However, the authors had attempted to minimize the possible influence through continuous reflection, crosscheck, and discussions during the data analysis and interpretation.
To produce convincing qualitative accounts, collecting data from multiple sources including semi-structured interviews, observations, and documentation was employed in the current study from November 2022 to April 2023.
The primary source of data was individual interviews with each participant. To gather participants’ narratives of critical events in their research supervision, an interview protocol was designed according to our research purpose, but the interview questions were sufficiently flexible to enable the interviewer to adapt the content according to the specific interview situation. The interviews lasted between 120 and 150 min, during which the participants were asked to describe critical events in their research supervision, their emotional experiences, and whether and how they regulated their emotions. Follow-up questions were asked to gain a more profound understanding of their emotion regulation strategies when they provided surprising and ambiguous responses. Sample interview questions included “What emotions do you typically experience as a research supervisor?” and “Do you regulate your emotions induced by research supervision? If so, how?” All interview questions were presented in Chinese, the participants’ first language, and were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Observation was used to complement the data obtained from interviews. Before the observation, all supervisors and their students were informed about the research purpose and ethical principles. Then non-participant observation during their group and individual meetings proceeded only with their voluntary participation. Supervisors’ supervisory methods, activities, meeting atmosphere, and emotions of meeting members were recorded to supplement and validate the data collected through the interview. A short follow-up interview was then conducted with supervisors, focusing on their reflections on emotional events that occurred during the observed group and individual meetings.
Documentation was also used as a supplementary method. With the consent of the participants and their students, supervisors’ annotations and feedback on graduate students’ manuscripts, unofficial posts about supervision on social media (e.g., WeChat moments sharing), and chat logs between supervisors and students were collected to obtain additional information about the participants’ emotional experiences and supervisory practices. Table 2 presents the interview durations, the total minutes recorded during observations, the length of follow-up interviews, and the specific number and types of documents reviewed by both supervisors and students.
Data analysis
The analysis involved a three-level coding process (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ). First, interview transcripts were repeatedly read to label data excerpts that addressed the research questions. Initial codes were based on participants’ original perspectives and then iteratively refined and combined. Second, the coding system was organized according to Gross’s ( 2015 ) process model of emotional regulation, which distinguishes between antecedent-focused and response-focused strategies. Meanwhile, the study also remained open to other emotion regulation strategies that were evident in the empirical data. Third, the coding system was distilled to capture the nature of the identified strategies, resulting in three types of emotion regulation strategies. During the analysis process, the data were classified and organized using the NVivo software.
To strengthen the credibility of the data analysis, the interview transcripts were carefully examined multiple times to ensure that the data were accurately reflected in the coding scheme. Moreover, the coding scheme was collaboratively developed by the authors, and any discrepancies in classification were thoroughly deliberated to achieve mutual agreement. The final coding system, along with sub-categories and patterns, is presented in Table 3 .
In sum, seven emotion regulation strategies in research supervision emerged from the empirical data, which can be grouped into two categories, namely, antecedent-focused strategies and response-focused strategies.
Antecedent-focused strategies
Supervisors used antecedent-focused strategies to regulate the external situation and their internal cognition before the emotions were generated.
Prevention involves the prediction and avoidance of situations that may lead to undesirable emotional experiences during supervision prior to the generation of emotions. Prevention strategies were frequently utilized in the graduate student recruitment process and early stages of supervision, as a means of avoiding undesirable situations. On the former occasion, supervisors identified multiple recruitment indicators, such as research experiences and GPA, to avoid supervisory situations that may lead to negative emotions. This is commonly related to their former supervisory experience: “It was frustrating to supervise a student who was not invested in her work, so I have to implement a rigorous recruitment process to prioritize candidates who are truly interested in research, rather than rashly recruiting students” (P1-interview).
Supervisors remain vigilant once a supervisory relationship was established, as they are required by accountability-based policies to be responsible for students’ research performance and safety. Many supervisors stressed the significance of “establishing rules and regulations” (P4-interview) in the early stages of supervision to avoid infuriation and disappointment with students’ academic misconduct. Therefore, establishing an academic code of conduct is an effective prevention strategy for supervisors: “I’m frustrated by academic misconduct among students, as discovering data falsification in student-published articles holds me accountable, risking serious consequences for my academic career. So I frequently emphasize the need for high academic honesty and integrity standards” (P2-interview, observation).
Another concern that worried supervisors, especially those of science and technology, is student safety: “Whenever I hear about a laboratory explosion that causes student injuries, it makes me very nervous” (P3-interview, documentation). It is crucial for the institutions and supervisors to establish comprehensive laboratory safety rules and educate students on safety protocols before conducting experiments: “I told my graduate students: Failure to obey laboratory rules and lack of safety awareness can lead to immediate accidents that not only affect yourself but also pose a risk to other students” (P3-interview).
Intervention
Intervention is the most commonly employed strategy by supervisors to enhance the effectiveness of their supervision once a supervisory relationship is established. They employed various intervention strategies to improve students’ academic attitude and develop their academic ability.
Specifically, supervisors improved their students’ engagement and altered procrastination either by scaffolding their research or enforcing discipline and prohibitions. On the one hand, our participants acknowledged the importance of instructional scaffolding in the supervisory process.
We need to cultivate students’ interest so that they can actively engage in research. For instance, I often demonstrate interesting phenomena between the English and Chinese languages to generate my students’ curiosity. Then I am delighted to see their willingness to immerse themselves in linguistic research. (P5-interview)
On the other hand, some supervisors emphasized the enforcement of discipline in supervision. One supervisor expressed disappointment and dissatisfaction with the lackadaisical research atmosphere within the entire research group. In response, she implemented strict discipline and prohibitions to restrict students from engaging in activities unrelated to research in the office (P2-observation).
Finding a student watching a movie in the office angered me as it may disturb other students trying to focus on their studies. So, activities like watching movies and listening to music are not allowed in our office. By rigorously enforcing these rules, our research group was able to collaborate more effectively and ultimately achieve satisfactory results. (P2-interview)
Furthermore, intervention strategies were also used to enhance graduate students’ academic competency. Modifying supervisory activities was considered as a useful method. One supervisor shared: “We used to read literature in our group meeting together, but it was not effective. I felt frustrated and decided to change our meeting activities this semester.” As a result, the supervisor organized students to provide feedback on each other’s manuscripts in weekly group meetings, because “it was very effective in improving their writing abilities” (P1-interview, observation).
Interestingly, some supervisors opted to micromanage students’ research processes when they were disappointed with their research performance
At first, I encouraged students to independently identify research topics, but I later realized with disappointment that it was challenging for them to identify gaps in the existing literature. To make things more efficient, I started assigning research projects directly to help them complete their dissertation and meet the graduation requirements. (P5-interview)
Reinterpretation
Reinterpretation refers to the process of cognitively reappraising a supervisory situation from different perspectives to change its emotional impact. Supervising a graduate student who lacks interest in research was described as a “prolonged and painful undertaking” (P4-interview). However, one supervisor noted that: “Dwelling on negative emotions can be unproductive as it does not necessarily solve problems. Despite the challenging experience, I have gained valuable insights and will be better equipped to handle such situation” (P4-interview).
In addition to explaining the meaning of the situations from supervisors’ viewpoints, they reconsidered the events from graduate students’ perspectives to rationalize their unsatisfactory performance and procrastination. For example, supervisors understood students’ time arrangements when they procrastinated: “I used to become annoyed when students failed to submit assignments punctually… Now I know that students need a balance between work and rest. They need adequate time for rest” (P5-interview).
On occasion, supervisors reappraised the connection between students’ misbehaviors and the effort they invested from the perspective of the teacher-student relationship.
I felt angry when things happened, but I wouldn’t let that emotion affect my life. I see myself as a supervisor to students, not a parent, so I don’t hold high expectations for them. If students choose not to follow my guidance, it’s not my concern anymore. (P6-interview)
Reconcentration
Reconcentration is the strategy by which supervisors focus on another aspect of supervision or divert attention away from supervision with the intent of changing emotional consequences. Specifically, during the supervisory process, supervisors prepared themselves to be optimistic by reminding themselves of their students’ strengths: “I was anxious about a student who always made slow progress in research. But when I later realized that his incremental results were consistently good, indicating that he was very meticulous, I felt much better” (P2-interview, observation).
Apart from diverting attention during supervision in working environments, the participants highlighted the importance of balancing personal and professional life to manage negative emotions that may arise during supervision.
After giving birth, I realized that caring for a child demands a considerable amount of time and energy. Then I redirected my attention from supervising students to my family. Thankfully, my family provides a supportive environment, and the pleasant moments shared with my family members helped me overcome negative emotions associated with work. (P4-interview)
Detachment refers to the act of separating from or terminating the supervisory relationship to disengage from negative emotions. This strategy was often employed when intervention, reinterpretation, and reconcentration strategies were ineffective. When supervisors found that various proactive measures failed to resolve the challenges in research supervision, they experienced enduring feelings of helplessness, confusion, and distress. One supervisor expressed deep frustration, stating, “I’ve exhausted all efforts—careful communication with her and her parents, and providing my support during her experiments. Yet, she continued to resist making progress with her experiments and dissertation. I felt lost in supervising this student” (P4-interview). As a result, they have to release themselves from the emotionally harmful supervisory relationships.
Some supervisors chose to disengage, meaning they no longer actively push the student: “Continuing to push a student who refused to participate in research despite all my efforts would only increase my frustration. I have decided to let him go and will no longer push him” (P5-interview).
In some extreme cases that evoke negative emotions, supervisors even terminated the supervisory relationship.
Supervising this student was a painful experience as his inaction negatively affected the entire research team. Other students started following his behavior and avoided conducting experiments. It made me feel suffocated. I had to terminate my supervision to avoid any further negative impact on the team and myself… I felt relieved after he left. (P3-interview)
Response-focused strategies
Response-focused emotion regulation involves the use of strategies after an emotion has already been generated.
Suppression
Suppression involves consciously attempting to inhibit behavioral and verbal emotional responses. Although supervisors experienced negative moods during research supervision, some refrained from expressing these emotions to students. Certain supervisors believed that criticism hinders problem-solving. One participant explained, “While interacting with students, I found some are genuinely fearful of supervisor authority. In such cases, venting emotions on students only heightens their fear, makes them hesitant to express themselves or their confusion in research, and ultimately hinders their progress” (P1-interview). In addition, some supervisors believed that expressing anger or disappointment toward students could harm their self-efficacy in research. One supervisor stated, “Obtaining a master’s degree is a challenging journey, especially for novice researchers. Confidence is crucial for their success. As a supervisor, I refrain from expressing negative emotions as it can hurt students’ feelings and even damage their confidence” (P3-interview).
As mentioned by the supervisors above, expressing anger and disappointment to graduate students may not resolve issues but damage their self-efficacy. In challenging situations where negative emotions were hard to suppress, supervisors opted to temporarily suspend supervision activities or introduce new tasks to regain composure: “Sometimes revising students’ manuscripts can be a painful task. To avoid the risk of expressing negative emotions to them, I often temporarily suspend the revision. Sometimes I take a walk until I feel calmer and more collected” (P1-interview).
In supervision, expressing emotion is another effective strategy for regulating supervisors’ emotions. Although supervisors were aware that expressing negative emotions may sometimes negatively affect students’ feelings, the importance of their own emotional well-being was emphasized, as “expressing feelings helped me recover from negative moods faster” (P6-interview). However, supervisors had different expressive styles when interacting with their students.
Some supervisors expressed their anger and dissatisfaction to their students directly, through behavioral or verbal emotional responses. A supervisor recounted an incident, “During a phone call with her, I lost my temper because of her terrible attitude, and ended up throwing my phone” (P4-interview).
Interestingly, given that “graduate students are all adults” (P6-interview), some supervisors expressed their emotions more tactfully, taking care not to lose their temper and cause distress to their students. One supervisor “felt angry with a student’s poor writing.” However, instead of scolding the student directly, he made a joke during a one-to-one meeting, saying “It’s not that you wrote poorly. It’s that I am not clever enough to comprehend your writing.” The student laughed, and then the supervision was conducted in a relaxed atmosphere. The supervisor explained: “I do not hide my emotions but prefer to avoid losing my temper and instead use humor to guide my students better” (P5-interview, observation).
This study contributes to the existing literature on emotion regulation by providing detailed insights into how emotion regulation strategies were utilized by research supervisors. It also sheds light on the dilemmas supervisors encounter and the paradox between the context-dependent nature of research supervision and the accountability-based managerial context.
Supervisors’ dilemmas in research supervision
Our study demonstrated supervisors’ capacity to proactively employ diverse emotion regulation strategies when coping with difficulties in research supervision. It also revealed some paradoxical phenomena within the supervisors’ utilization of these emotion regulation strategies, highlighting the dilemmas they encountered in the context of research supervision.
In general, supervisors in our study demonstrated a higher tendency to employ antecedent-focused strategies for emotion regulation rather than response-focused strategies, which can alleviate their emotional burnout and enhance their well-being. Specifically, participants utilized intervention strategies as antecedent-focused strategies to improve the effectiveness of research supervision, rather than seeking consolation to alleviate generated emotions. Previous research has indicated that antecedent-focused strategies were associated with increased life satisfaction (Feinberg et al., 2012 ). By intervening in the emotion generation process at an early stage, these strategies can potentially alter the emotional trajectory, contributing to improved well-being among supervisors (Gross & John, 2003 ).
While supervisors displayed a strong inclination to utilize diverse strategies to enhance the effectiveness of their supervision, our findings unveiled two paradoxical phenomena in their emotion regulation strategies, indicating the dilemmas that supervisors faced in authentic supervisory situations. First, in antecedent-focused strategies aimed at modifying situations that may trigger negative emotions, numerous interventions and detachments highlighted the conflicts supervisors encountered as they strived to balance adequate assistance and excessive interference. Specifically, while participants in our study “inspired students through scaffolding” or “encouraged students’ autonomous learning,” they also “micromanaged students’ research process” or “enforced discipline” to enhance supervision efficiency. This pedagogical paradox concerning the choice between intervening and non-intervening approaches has generated ongoing debate in existing research (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). Both approaches have the potential to evoke negative emotional experiences for supervisors and graduate students. Research found that a highly intervening approach has negative implications for both supervisors and graduate students (Lee, 2020 ). Students who have encountered autonomy-exploitative behavior from their supervisors, such as being restricted to specific research topics and methodologies, have reported experiencing negative emotions (Cheng & Leung, 2022 ). For supervisors, the burden of an intervening approach, the dissonance between supervisors’ expectations and students’ actual research progress, as well as students deviating from conventional practices (Han & Xu, 2023 ), all contribute to feelings of frustration, sadness, and exhaustion. Nevertheless, non-intervening approaches do not always fulfill the expectations of both parties either. Supervisors who encouraged graduate students’ autonomous action acknowledged the value of promoting their independent thinking, which has been identified as a significant predictor of students’ research self-efficacy (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ). However, students who initially expected their supervisors to play a leadership role felt dissatisfied and disappointed when supervisors were reluctant to offer explicit guidance (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). This misunderstanding of supervisors’ intentions can ultimately generate negative effects on supervisors’ emotional experiences (Xu, 2021 ).
Another evident paradoxical phenomenon arises in the response-focused strategies employed after emotions have already been triggered. Although supervisors opted to suppress their negative emotional expression to safeguard the confidence and self-esteem of mature learners, there were instances when they outpoured their disappointment and anger to students, aiming to swiftly step out of their negative moods. The act of expressing and suppressing emotions highlights the dilemma of cultivating a mutually beneficial relationship that promotes emotional well-being for both supervisors and students. On the one hand, the existing literature emphasizes the importance of supervisors being sensitive to students’ emotional experiences (Bastalich, 2017 ). The inherent power imbalance in supervisor-student relationships may create a sense of student dependency on their supervisors (Friedensen et al., 2024 ; Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). Excessive criticism from supervisors can potentially lead to feelings of loss, and alienation throughout students’ academic journey, which highlights supervisors’ responsibility to manage their emotional criticism in supervisory interactions (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). On the other hand, although pursuing a research degree is a challenging journey for graduate students, it is important to acknowledge the vulnerability of research supervisors and their need for support (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). Power dynamics within supervisory relationships, particularly when students challenge or disregard supervisors’ advice, can lead to repression and disengagement for supervisors if negative emotions are not effectively regulated (Xu, 2021 ). Thus, recognizing supervisors’ needs and allowing for emotional expressions are also essential in developing a relationship that is mutually beneficial and conducive to the well-being of both parties (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ).
The conflicts between research supervision and institutional policies
The dilemmas present in supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies inherently illustrate the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision. However, as modern higher education institutions move toward implementing accountability-based policies that aim to standardize and quantify research supervision (Jedemark & Londos, 2021 ), conflicts between the nature of supervision and these institutional policies not only place an emotional burden on supervisors, but also endanger the quality of graduate education.
The dilemmas observed in supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies highlight the divergent understandings between supervisors and graduate students regarding their respective responsibilities and the boundaries of the supervisor-student relationship. This divergence is influenced by context-dependent factors in research supervision, including the beliefs, motivations, and initiatives of the individuals involved (Denis et al., 2018 ). Due to the difficulty in achieving a perfect agreement on these context-dependent factors, it becomes challenging to establish a standard for what constitutes an ideal beneficial research supervision (Bøgelund, 2015 ). In authentic supervisory situations, the relationships between supervisors and graduate students can range from formal and distant to informal and intimate in both academic and social interactions (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). Therefore, research supervision is a highly context-dependent and non-standardized practice that relies on the capabilities of supervisors and students, which are shaped by their individual experiences and personalities.
This nature of research supervision underscores the significance of avoiding standardization and a “one size fits all” approach. However, as higher education institutions move toward a corporate managerial mode, research supervision is increasingly perceived as a service provided within a provider-consumer framework, and the fundamental aspects of research supervision are being reshaped to align with a culture of performance measurement, control, and accountability (Taylor et al., 2018 ). In modern academia, universities and institutions have established specific guidelines and protocols for research supervision, which require supervisors to follow diligently and take accountability in the supervision process (Figueira et al., 2018 ).
The presence of extensive external scrutiny or accountability ignored the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision, leading to adverse effects on both supervisors and graduate students. On the one hand, supervisors face significant pressure within an accountability-based context. They are expected to serve as facilitators of structured knowledge transmission, which is enforced through the demanding requirements and time-consuming tasks associated with supervisory practices (Halse, 2011 ). However, the distinctive characteristics of various disciplines and the interdependent relationship between the supervisory context and graduate students’ learning process are neglected (Liang et al., 2021 ). Such a narrow focus on knowledge transmission may pose potential threats to supervisors’ autonomy and academic freedom, generating their feelings of self-questioning, helplessness, and demotivation (Halse, 2011 ). Supervisors in our study reported many examples of emotion regulation strategies utilized to cope with performative and accountability pressures in their workplace. Specifically, the responsibility to ensure timely doctoral completions, prioritize students’ safety, and maintain accountability for those experiencing delays or violating research codes evoked feelings of nervousness, pressure, and insecurity among supervisors.
On the other hand, interventionist supervision within accountability-driven supervisory contexts is perceived as detrimental to students’ academic innovation (Bastalich, 2017 ). The prevailing environment of heightened performativity and accountability alters supervisors’ attitudes toward academic risk-taking, thereby influencing their supervisory practices (Figueira et al., 2018 ). For example, participants in our study utilized prevention and intervention strategies to mitigate potential negative occurrences. This included adopting a directive approach to supervise students’ work and dissuading them from undertaking risky or time-consuming methods to ensure timely completion. However, such micromanagement may stifle innovation, thereby inhibiting doctoral students’ development as independent researchers (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ). Providing pre-packaged research projects or excessive support may hinder students’ acquisition of essential knowledge, skills, and expertise required for their future pursuits, potentially obstructing their progress toward independent thinking (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ).
The conflicts between the prevailing shift from autonomy to accountability in higher education and the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision highlight the necessity for practice-informed evaluations for research supervision. This finding resonates with previous studies on policy-making in graduate education (Taylor et al., 2018 ), which emphasized the challenges of establishing evidence-based institutional policies to capture the intricate realities of supervision in practice.
Limitations
This study contributes to the understanding of research supervisors’ work by examining their emotion regulation strategies in authentic supervisory situations. However, certain limitations should be addressed for future research. First, the small sample size is a significant limitation, as only six supervisors participated. Future studies may increase the sample size and enhance diversity within the sample. Second, as our study only involved perspectives from research supervisors, future studies may consider incorporating the perceptions of both supervisors and graduate students and analyzing the level of convergence and divergence between the obtained results to enhance the validity of data collection.
Implications for practice
Despite being situated in China’s supervisory accountability system, our study holds broader implications in the global context. As the shift toward corporatized management models in higher education worldwide reshapes research supervision to align with performance measurement and accountability culture (Jedemark & Londos, 2021 ), our results offer implications for research supervision and policy-making beyond the Chinese context.
First, for research supervisors and graduate students, the intricate and dynamic nature of research supervision revealed in our study makes it challenging to offer direct recommendations for optimal emotion regulation strategies. Instead, supervisors are encouraged to adaptively employ a range of emotion regulation strategies in different supervisory situations to enhance their emotional well-being. Additionally, recognizing the context-dependent nature of research supervision, both research supervisors and graduate students are urged to take into account factors such as each other’s beliefs, motivations, and initiatives in their research and daily interactions.
Second, in light of the discrepancy between the current standardized accountability measures in higher education and the context-dependent nature of research supervision, it is imperative for universities and institutions to develop practice-based policies that are tailored to supervisors’ and students’ academic development, avoiding generic and assumed approaches. To effectively address the distinctive requirements of research supervision, policy-makers are strongly encouraged to implement multi-dimensional, discipline-oriented evaluation systems for supervisors in the future.
Data Availability
Data from this study cannot be shared publicly because participants may still be identifiable despite efforts to anonymise the data. Therefore, data will only be made available for researchers who meet criteria for access to confidential data.
Agudo, J. D. M. (Ed.). (2018). Emotions in second language teaching: Theory, research and teacher education . Springer.
Google Scholar
Bastalich, W. (2017). Content and context in knowledge production: A critical review of doctoral supervision literature. Studies in Higher Education, 42 (7), 1145–1157.
Article Google Scholar
Bøgelund, P. (2015). How supervisors perceive PhD supervision-and how they practice it. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 10 , 39–55.
Brotheridge, C. M., & Grandey, A. A. (2002). Emotional labor and burnout: Comparing two perspectives of “people work.” Journal of Vocational Behavior, 60 (1), 17–39.
Campos, J. J., Walle, E. A., Dahl, A., & Main, A. (2011). Reconceptualizing emotion regulation. Emotion Review, 3 (1), 26–35.
Chen, J., & Cheng, T. (2022). Review of research on teacher emotion during 1985–2019: A descriptive quantitative analysis of knowledge production trends. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 37 (2), 417–438.
Cheng, M. W. T., & Leung, M. L. (2022). “I’m not the only victim...” Student perceptions of exploitative supervision relation in doctoral degree. Higher Education, 84 (3), 523–540.
Denis, C., Colet, N. R., & Lison, C. (2018). Doctoral supervision in North America: Perception and challenges of supervisor and supervisee. Higher Education Studies, 9 (1), 30–39.
Diekman, A. B., Clark, E. K., Johnston, A. M., Brown, E. R., & Steinberg, M. (2011). Malleability in communal goals and beliefs influences attraction to stem careers: Evidence for a goal congruity perspective. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101 (5), 902–918.
Feinberg, M., Willer, R., Antonenko, O., & John, O. P. (2012). Liberating reason from the passions: Overriding intuitionist moral judgments through emotion reappraisal. Psychological Science, 23 (7), 788–795.
Figueira, C., Theodorakopoulos, N., & Caselli, G. (2018). Unveiling faculty conceptions of academic risk taking: A phenomenographic study. Studies in Higher Education, 43 (8), 1307–1320.
Friedensen, R. E., Bettencourt, G. M., & Bartlett, M. L. (2024). Power-conscious ecosystems: Understanding how power dynamics in US doctoral advising shape students’ experiences. Higher Education, 87 (1), 149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-023-00998-x
Grandey, A. A. (2000). Emotional regulation in the workplace: A new way to conceptualize emotional labor. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 (1), 95–110.
Gross, J. J. (1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: An integrative review. Review of General Psychology, 2 , 271–299.
Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26 (1), 1–26.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85 (2), 348.
Gruzdev, I., Terentev, E., & Dzhafarova, Z. (2020). Superhero or hands-off supervisor? An empirical categorization of PhD supervision styles and student satisfaction in Russian universities. Higher Education, 79 (5), 773–789.
Gu, J., Levin, J. S., & Luo, Y. (2018). Reproducing “academic successors” or cultivating “versatile experts”: Influences of doctoral training on career expectations of Chinese PhD students. Higher Education, 76 (3), 427–447.
Halse, C. (2011). ‘Becoming a supervisor’: The impact of doctoral supervision on supervisors’ learning. Studies in Higher Education, 36 (5), 557–570.
Halse, C., & Malfroy, J. (2010). Retheorizing doctoral supervision as professional work. Studies in Higher Education, 35 (1), 79–92.
Han, Y., & Xu, Y. (2023). Emotional support from the perspective of extrinsic emotion regulation: Insights of computer science. Teaching in Higher Education, 28 (7), 1725–1743.
Han, J., & Wang, T. (2024). Exploring graduate students’ research characteristics, emotional exhaustion, mastery approach, and research career commitment: insights from the JD-R theory. Studies in Higher Education, 1–15.
Hargreaves, A. (1998). The emotional practice of teaching. Teaching and Teacher Education, 14 (8), 835–854.
Hochschild, A. R. (1983). The managed heart: Commercialization of human feeling . University of California Press.
Hosotani, R. (2011). Emotional experience, expression, and regulation of high-quality Japanese elementary school teachers. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27 (6), 1039–1048.
Janssen, S., & Vuuren, M. (2021). Sensemaking in supervisor-doctoral student relationships: Revealing schemas on the fulfillment of basic psychological needs. Studies in Higher Education, 46 (12), 2738–2750.
Jedemark, M., & Londos, M. (2021). Four different assessment practices: How university teachers handle the field of tension between professional responsibility and professional accountability. Higher Education, 81 (6), 1293–1309.
Johnson, J. W. (2001). The relative importance of task and contextual performance dimensions to supervisor judgments of overall performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86 (5), 984–996.
Lee, A. (2008). How are doctoral students supervised? Concepts of doctoral research supervision. Studies in Higher Education, 33 (3), 267–281.
Lee, A. (2020). Successful research supervision: Advising students doing research (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Liang, W., Liu, S., & Zhao, C. (2021). Impact of student-supervisor relationship on postgraduate students’ subjective well-being: A study based on longitudinal data in China. Higher Education, 82 (2), 273–305.
Ministry of Education, PRC. (2020). The accountability measures for educational supervision [yanjiusheng zhidao xingwei zhunze]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A22/s7065/202011/t20201111_499442.html . Accessed 17 May 2024.
Parker-Jenkins, M. (2018). Mind the gap: Developing the roles, expectations and boundaries in the doctoral supervisor–supervisee relationship. Studies in Higher Education, 43 (1), 57–71.
Peng, H. (2015). Assessing the quality of research supervision in mainland Chinese higher education. Quality in Higher Education, 21 (1), 89–100.
Riessman, C. K. (2008). Narrative methods for the human sciences . Sage.
Saleem, M. S., Isha, A. S., Awan, M. I., Yusop, Y. B., & Naji, G. M. (2022). Fostering academic engagement in post-graduate students: Assessing the role of positive emotions, positive psychology, and stress. Frontiers in Psychology, 13 , 920395.
Sambrook, S., Stewart, J., & Roberts, C. (2008). Doctoral supervision... A view from above, below and the middle! Journal of Further and Higher Education, 32 (1), 71–84.
Tao, Y., Liu, X., Hou, W., Niu, H., Wang, S., Ma, Z., & Zhang, L. (2022). The mediating role of emotion regulation strategies in the relationship between big five personality traits and anxiety and depression among Chinese firefighters. Frontiers in Public Health, 10 , 901686.
Taxer, J. L., & Frenzel, A. C. (2015). Facets of teachers’ emotional lives: A quantitative investigation of teachers’ genuine, faked, and hidden emotions. Teaching and Teacher Education, 49 , 78–88.
Taxer, J. L., & Gross, J. J. (2018). Emotion regulation in teachers: The “why” and “how”. Teaching and Teacher Education, 74 , 180–189.
Taylor, S., Kiley, M., & Humphrey, R. (2018). A handbook for doctoral supervisors (2nd ed.). Routledge.
To, K. H., & Yin, H. (2021). Being the weather gauge of mood: Demystifying the emotion regulation of kindergarten principals. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 30 (4), 315–325.
Veniger, K. A., & Kočar, S. (2018). The impact of academic discipline on university teaching and pedagogical training courses. Croatian Journal of Education, 20 (4), 1261–1298.
Wollast, R., Aelenei, C., Chevalère, J., Van der Linden, N., Galand, B., Azzi, A., Frenay, M., & Klein, O. (2023). Facing the dropout crisis among PhD candidates: The role of supervisor support in emotional well-being and intended doctoral persistence among men and women. Studies in Higher Education, 48 (6), 813–828.
Xie, A. B., & Zhu, Y. (2008). Retrospect and prospect of Chinese degree and graduate education development in the past three decades. Degree and Graduate Education, 11 , 19–29.
Xie, F. (2021). A study on Chinese EFL teachers’ work engagement: The predictability power of emotion regulation and teacher resilience. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 735969.
Xu, Y. (2021). Unpacking the emotional dimension of doctoral supervision: Supervisors’ emotions and emotion regulation strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 651859.
Xu, Y., & Liu, J. A. (2023). Exploring and understanding perceived relationships between doctoral students and their supervisors in China. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 10 (1), 1–10.
Yin, H. (2015). The effect of teachers’ emotional labour on teaching satisfaction: Moderation of emotional intelligence. Teachers and Teaching, 21 (7), 789–810.
Yin, H. (2016a). Knife-like mouth and tofu-like heart: Emotion regulation by Chinese teachers in classroom teaching. Social Psychology of Education, 19 (1), 1–22.
Yin, H., Huang, S., & Lv, L. (2018). A multilevel analysis of job characteristics, emotion regulation and teacher well-being: A job demands-resources model. Frontiers in Psychology, 9 , 2395.
Yin, R. K. (2016b). Qualitative research from start to finish (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
Zembylas, M. (2021). The affective turn in educational theory. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.1272 . Accessed 17 May 2024.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants who made this publication possible.
This work was supported by the Project of Outstanding Young and Middle-aged Scholars of Shandong University, Shandong University Program of Graduate Education and Reform (grant number XYJG2023037) and the General Research Fund of Hong Kong SAR (grant number CUHK 14608922).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Foreign Languages and Literature, Shandong University, Jinan, 250100, Shandong, China
Jiying Han & Lei Jin
Department of Curriculum and Instruction, Faculty of Education, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, N.T., Hong Kong, SAR, China
Hongbiao Yin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jiying Han: writing—original draft preparation, writing—reviewing and editing; Lei Jin: writing—original draft preparation, formal analysis; Hongbiao Yin: conceptualization, validation, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hongbiao Yin .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Han, J., Jin, L. & Yin, H. Supervisors’ emotion regulation in research supervision: navigating dilemmas in an accountability-based context. High Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-024-01241-x
Download citation
Accepted : 13 May 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-024-01241-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Emotion regulation
- Research supervision
- Accountability
- Graduate education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Timeframe: August-December 2024. Research in Higher Education is a journal that publishes empirical research on postsecondary education. Open to studies using a wide range of methods, with a special interest in advanced quantitative research methods. Covers topics such as student access, retention, success, faculty issues, institutional ...
the tension between how academics and government policies view higher education, an analysis that compares and contrasts the personal or private purpose(s) of higher education may help educators better understand the current disconnect between higher education institutions and college graduates (McClung, 2013; World Bank, 2012).
Journal metrics Editorial board. Founded in 1930, The Journal of Higher Education ( JHE) publishes original research and theoretical manuscripts on U.S. higher education. We publish two kinds of articles: empirical articles and scholarly, theoretical, or conceptual articles. Authors publishing empirical articles report the methodology, methods ...
Research in Higher Education publishes empirical studies that enhance our understanding of an educational institution or allow comparison among institutions. It focuses on post-secondary education, including two-year and four-year colleges, universities, and graduate and professional schools. Papers in the journal assist faculty and ...
Trends and Motivations in Critical Quantitative Educational Research: A Multimethod Examination Across Higher Education Scholarship and Author Perspectives. Christa E. Winkler. Annie M. Wofford. OriginalPaper Open access 04 June 2024.
HIGHER EDUCATION is an international journal in the multidisciplinary field of higher education research. Its policy is to give priority to papers that are relevant to the international higher education research and policy community.
Aims and scope. Studies in Higher Education is a leading international journal publishing research-based articles dealing with higher education issues from either a disciplinary or multi-disciplinary perspective. Empirical, theoretical and conceptual articles of significant originality will be considered.
Trends in Higher Education is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on higher education published quarterly online by MDPI.. Open Access — free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.; Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.5 days after submission ...
The impact of large language models on university students' literacy development: a dialogue with Lea and Street's academic literacies framework. Daniel W. J. Anson. Published online: 26 Mar 2024. 2205 Views.
Higher Education Quarterly. Higher Education Quarterly (HEQU) is an international educational research journal publishing articles on policy, organization, leadership, governance, management and the professions in higher education. It aims to develop our understanding of higher education and its current challenges from a diversity of approaches ...
To understand how higher education can effectively address these challenges, this paper investigates the public and private purpose of higher education and what it means for higher education's future.
This systematic review provides unique findings with an up-to-date examination of artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education (HE) from 2016 to 2022. Using PRISMA principles and protocol, 138 articles were identified for a full examination. Using a priori, and grounded coding, the data from the 138 articles were extracted, analyzed, and coded. The findings of this study show that in 2021 ...
A Quarterly Review of Innovations in Post-secondary Education. The Internet and Higher Education is a quarterly journal devoted to addressing contemporary issues and future developments related to Internet-enabled learning and teaching in higher education settings. It is a peer-reviewed journal intended to be a vehicle for scholarly presentation and dissemination of contributions significantly ...
The Center for Studies in Higher Education publishes online research papers and essays that reflect multidisciplinary fields, contribute to influencing and expanding the body of research on higher education, and enhance dialogue among educators, policy makers, and the public. ... Multi-campus public higher education governance systems exist in ...
Papers selected in this Issue were presented at different international conferences examining how the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in late 2019 has affected higher education development from international and comparative perspectives. ... Keynote speech presented at the Conference for Higher Education Research (CHER) 2020, Lingnan ...
There are several reasons to review access and equity in HE research. First, most of the research on this topic to date has mainly focused on two areas: policy and quantitative data (Jia and Ericson, 2017; Leach, 2013).Second, previous research about this topic has been scattered among countries, based on disadvantaged student criteria and policy or programs that the government had to support ...
Aims and scope. Internationally peer-reviewed, the Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education (JARHE), focuses on the scholarship and practice of teaching and learning and higher education, covering: Higher education teaching, learning, curriculum, assessment, policy, management, leadership, and related areas.
This report draws on a substantial body of research undertaken by the Open University's Centre for. Higher Education Research and Information (CHE RI) on the changing relati onships between ...
The present collection of research papers reflects students' perspectives on today's changing higher education landscape and the challenges or controversies they observe in contemporary higher education. Student research papers featured in this collection are a testimony of students' genuine interest in studying and contributing to the ...
education, choice of major, etc.). Our results underscore the fact that the COVID-19 shock is likely to exacerbate socioeconomic disparities in higher education. This is consistent with ndings regarding the impacts of COVID-19 on K-12 students. Kuhfeld et al.,2020project that school closures are likely to lead to signi cant learning losses in math
Higher Education Research Paper Topics. In this page on higher education research paper topics, we present a comprehensive guide to help students in the field of education with their research papers. The abstract provides a brief overview of the content covered in the page, including a keyphrase to emphasize the main focus.
This research explores the mediating role of job satisfaction in the relationship between competence, work environment, and lecturer performance in higher education. By applying Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), data from 250 lecturers at various universities were analyzed. The findings suggest that job satisfaction significantly mediates the relationship between competence
The Times Higher Education World University Rankings are the only global performance tables that judge research-intensive universities across all their core missions: teaching, research, knowledge transfer and international outlook.. This year's methodology, for the 20th edition of the World University Rankings, has been significantly updated, so that it continues to reflect the outputs of ...
holistic approach to education. This research paper explores the importance, progress, challenges, and potential impact of NEP at HEIs. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 in India represents a landmark reform in the country's education ... NEP 2020 lays the groundwork for promoting research and innovation in higher education and creating ...
About the Carnegie Classification® The Carnegie Classification® is the leading framework for recognizing and describing institutional diversity in U.S. higher education. The Carnegie Commission on Higher Education developed the classification in 1973 to support its program of research and policy analysis. Derived from empirical data on colleges and universities, the Carnegie Classification ...
Higher education worldwide is undergoing a continuous process of transformation and differentiation as new challenges emerge in the macro socio-economic and political environment. Not only have existing institutions expanded their curricula to offer a wider range of courses, hut new types of institutions have been established to cater for groups which have not been able to access higher ...
The research spending will be taken from the National Science Foundation (NSF) Higher Education Research and Development (HERD) Survey, and the doctoral research degree number will be taken from the National Center for Education Statistics IPEDS data. Any institution that meets this new R1 threshold will be included.
Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. is an established international peer-reviewed journal which publishes papers and reports on all aspects of assessment and evaluation within higher education. Its purpose is to advance understanding of assessment and evaluation practices and processes, particularly the contribution that these make to ...
The Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings 2023 are based on the world's largest invitation-only opinion survey of senior, published academics. It asks scholars to name no more than 15 universities that they believe are the best for research and teaching in their field. View the World Reputation Rankings 2023 methodology Harvard University tops the ranking for the
In higher education, although emotion regulation has been proven significant to teacher development and well-being (Xie, 2021), the majority of research has been conducted within the context of classroom instruction (Tao et al., 2022), leaving that of research supervision in graduate education unexplored.