Direct and Indirect Speech Past Perfect Tense ExamplesDirect and indirect speech past perfect continuous tense examples. If reported verb is in Past Tense & reported speech is in Past Perfect Continuous Tense , it will not change. e.g.  Past Perfect Continuous Sentences with ExamplesPublished by Olivia Drake The Past Perfect Continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing up to a certain point in the past or were ongoing before another action in the past. It is formed using “had been” followed by the present participle (verb + ing). Unlike the Past Perfect Simple, which emphasizes the completion of an action before another past action, the Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes the duration or ongoing nature of the action before another event. The Past Perfect Continuous tense in English is used to describe actions or states that were ongoing up to a specific time in the past. The structure of a Past Perfect Continuous sentence is: Subject + had been + present participle Let’s explore some examples to understand this better: I had been walking to work before it started raining. This sentence indicates that the speaker was in the middle of walking to work, and this action was ongoing until it started raining. She had been watching television for an hour when I called her. This example shows that her action of watching television was ongoing for an hour before the speaker called her. They had been playing soccer for an hour when it started to rain. This sentence describes an action that was ongoing for an hour and was interrupted by another event (it started to rain). We had not (hadn’t) been watching TV for long when the power went out. This sentence expresses a negative ongoing action. The speaker and their companions had not been watching TV for a long time before the power went out. If you had been looking for me, you would have found me in the garden. This example shows that the action of looking for the speaker was ongoing, and had it continued, it would have led to finding them. The Past Perfect Continuous is formed by using “had been” followed by the present participle of the verb. It’s crucial to use the correct form of the verb to maintain the tense. Incorrect: She had been watch television for an hour when I called her. Correct: She had been watching television for an hour when I called her. We can see that the Past Perfect Continuous is often used to talk about actions that were ongoing up to a specific time in the past or were ongoing before another past action. The words “ for ,” “ since ,” and “ when ” are commonly used with the Past Perfect Continuous to add context about the duration or timing of the action. Past Perfect Continuous Sentence Examples- I had been reading for two hours before I went to bed. (The action of reading was ongoing for two hours before going to bed.)
- She had been practicing the piano for three hours when the neighbors complained. (She was practicing the piano for three hours until the neighbors complained.)
- They had been visiting their grandparents every weekend before they moved. (Visiting grandparents was an ongoing action that stopped when they moved.)
- We had been taking the bus to school before we got a car. (Taking the bus to school was an ongoing action until they got a car.)
- He had not (hadn’t) been eating well before his health improved. (He was not eating well for some time before his health improved.)
- The sun had been shining all morning before the clouds appeared. (The action of the sun shining was ongoing all morning until the clouds appeared.)
- Birds had been migrating earlier than usual that year. (The action of birds migrating was ongoing earlier than usual in that specific year.)
- Water had been dripping from the ceiling for hours before they noticed. (The action of water dripping was ongoing for hours before it was noticed.)
- The train had been running late all week before it was fixed. (The train’s action of running late was ongoing all week until it was fixed.)
- She had been working at a bank for five years when she decided to change careers. (Her job at the bank was ongoing for five years until she decided to change careers.)
- He had been speaking French for several years before he moved to France. (He had been speaking French for years before moving to France.)
- The Earth had been experiencing climate changes long before modern times. (A scientific fact describing ongoing climate changes before modern times.)
- Cats had been chasing mice in the old house before it was renovated. (A general truth about cat behavior that was ongoing before the renovation.)
- We had been celebrating New Year’s Eve at home for many years before we started traveling. (Celebrating New Year’s Eve at home was an ongoing action for many years before they started traveling.)
- She had always been forgetting her keys before she got a key holder. (A habitual action of forgetting keys that was ongoing before getting a key holder.)
- They had been playing chess every Sunday until they moved away. (A regular activity that was ongoing every Sunday until they moved.)
- He had not (hadn’t) been drinking coffee regularly before he started his new job. (He was not drinking coffee regularly for some time before starting his new job.)
- The store had been opening at 8 AM every day until it changed its hours. (A fixed schedule that was ongoing until the store changed its hours.)
- I had been working on my novel for several months before I decided to take a break. (This example highlights an ongoing action (working on the novel) that was happening for several months before another past action (deciding to take a break) occurred.)
- She had been teaching English online for several years before she got hired by a school. (Her job of teaching English online was ongoing for several years before she got hired by a school.)
The Past Perfect Continuous tense is essential for describing actions that were ongoing up to a specific time in the past or were ongoing before another action in the past. Using this tense allows for clear communication about past activities and their duration. Mastering the Past Perfect Continuous helps in expressing actions and states that were relevant at particular moments in the past effectively. Feel free to leave comments or ask questions if you need further clarification on any of the points discussed. Happy learning! If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.  Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education! Let’s connectJoin the fun!Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter. Type your email… Recent postsModal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar. Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive. Continue reading - English Grammar
- English Tenses
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense - Meaning, Definition, Formula, Structure, Uses and ExamplesHave you been thinking of learning the past perfect continuous tense? Well, this is your chance. This article will provide you with everything that you need to know about the past perfect continuous tense. It discusses the meaning, definition, formula, structure, rules to be followed when using the tense, functions and uses of the tense. Examples and practice questions are also given to help you understand the usage of the tense and develop a clearer idea of the same.  Table of ContentsDefinition of the past perfect continuous tense, formula and structure of the past perfect continuous tense. - Rules to be Followed When Using the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Uses of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense- Examples of Uses of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Test Your Understanding of the Past Perfect Continuous TenseFrequently asked questions on the past perfect continuous tense, what is the past perfect continuous tense. The past perfect continuous tense is generally used in a sentence to depict an action that started at some time in the past and continued until a specific time in the past. It is also called the past perfect progressive tense since it refers to an action that had been progressing until a certain point in the past. Now, have a look at the different definitions of the past perfect continuous tense provided by various dictionaries. The past perfect continuous tense, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as a tense form used to indicate “an action or a situation that continued for a period of time before another action or situation in the past.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, the past perfect continuous tense is defined as a tense that refers to “actions or events which started before a particular time in the past and were still in progress up to that time in the past.” Understanding the formula of the past perfect continuous tense can help you and make everything easy. Given below is the formula that you can employ when you write a sentence using the past perfect continuous tense. | Subject + + the rest of the sentence | Now, take a look at how sentences are structured in a positive, negative, interrogative and a negative interrogative sentence using the past perfect continuous tense. | | | | | | | | Subject + + the rest of the sentence | Subject + + the rest of the sentence | subject + + the rest of the sentence | subject + + the rest of the sentence (or) subject + the rest of the sentence | | Examples: my mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. your mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. his mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. her mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. their mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. | Examples: my mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. your mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. his mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. her mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. their mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen. | Examples: I my mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? you your mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? he his mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? she her mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? they their mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? | Examples: I my mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? you your mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? he his mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? she her mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? they their mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? you your mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? she her mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? he his mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? they their mom’s favourite dish when she walked into the kitchen? | Rules to be Followed when Using the Past Perfect Continuous TenseSimilar to the present perfect continuous tense , the past perfect continuous tense also consists of two helping verbs and a main verb . Among the three verbs that represent the tense, the first helping verb should always be ‘had’ followed by ‘been’, which is in turn followed by the present participle of the main verb. This rule holds true when the sentence is a positive sentence. In case you are employing the tense form in an interrogative sentence, the helping verb ‘had’ comes first followed by the subject which is in turn followed by the the helping verb ‘been’ and the present participle of the main verb. For a negative sentence, ‘not’ is placed after the first auxiliary verb ‘had’ and for a negative interrogative sentence, you can either use the contraction ‘hadn’t’ or place ‘not’ after the subject. The past perfect continuous tense is used to perform two main functions. They are: - To denote an action that has been the cause of another action or event in the past.
- To represent an action that started at some point in the past and continued or progressed till a particular time in the recent past.
Examples of the Past Perfect Continuous TenseNow, let us look at a few examples to see how the past perfect continuous tense is used to perform the different functions. Denoting an action that is the cause of another action in the past- Asha was completely exhausted as she had been travelling continuously for three days.
- George was angry because he had been waiting for them the whole day.
Representing an action that progressed in the past until another action in the past- Do you know for how long Anitha had been working at the college before she moved to Pollachi?
- I had been waiting to hear from the admissions officer for more than a month before I applied to other colleges.
Fill in the blanks with the right form of the tense in the following sentences: 1. Derrick __________ (work) at the hospital for over two years before he left for Spain. 2. I don’t think the place ____________ (function) well for a very long time before it shut down. 3. Theena __________ (sing) for an hour before her mom arrived. 4. _______ you ___________ (wait – interrogative) at the railway station for over two hours when the train finally arrived? 5. How long _____ you ____________ (stand) there to meet the manager? 6. The dogs ______________ (bark) continuously until the owner finally came home and fed them. 7. My brother _____________ (ask) me to buy him an Axon helmet for years before I could somehow make some money to buy him one. 8. They ______________ (live) in New York for four years when they had to leave due to personal reasons. 9. He __________ (run) around for hours looking for my dog before I found him with my neighbour at the park. 10. My cousins ______________ (suggest) that we called the police when we found the burglars. Check if you used the tense correctly from the answers given below: 1. Derrick had been working at the hospital for over two years before he left for Spain. 2. I don’t think the place had been functioning well for a very long time before it shut down. 3. Theena had been singing for an hour before her mom arrived. 4. Hadn’t you been waiting at the railway station for over two hours when the train finally arrived? 5. How long had you been standing there to meet the manager? 6. The dogs had been barking continuously until the owner finally came home and fed them. 7. My brother had been asking me to buy him an Axon helmet for years before I could somehow make some money to buy him one. 8. They had been living in New York for four years when they had to leave due to personal reasons. 9. He had been running around for hours looking for my dog before I found him with my neighbour at the park. 10. My cousins had been suggesting that we called the police when we found the burglars. What is the past perfect continuous tense?The past perfect continuous tense is generally used in a sentence to depict an action that started at some time in the past and continued until a specific time in the past. It is also called the past perfect progressive tense since it refers to an action that had been progressing until a certain point in the past. What is the definition of the past perfect continuous tense?What is the formula of the past perfect continuous tense. Employing the past perfect continuous tense in a sentence can be done easily if you know the formula of the tense. Given below is the formula of the past perfect continuous tense. Subject + had + been + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence What are the uses of the past perfect continuous tense?Give some examples of the past perfect continuous tense.. Here are a few examples to show you how the past perfect continuous tense can be used in sentences. Leave a Comment Cancel replyYour Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked * Request OTP on Voice Call Post My Comment  Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFsRegister with byju's & watch live videos.  Direct and Indirect Speech  Every day, people relay messages from one person to another. Whether it is to prove a point, describe an event, or disclose an opinion, we use the freedom of speech to share information. There are generally two ways of reporting a spoken idea: direct and indirect speech. This article shall explain and compare these two types of speech. Some examples are also provided to give you a more in-depth understanding. Both direct and indirect speech are methods to narrate the words spoken by a specific person. The difference between them lies in how they are constructed and in the purpose of using them. Direct SpeechIn a direct speech , the actual words of the speaker are quoted explicitly. It is often used to relay something being said in the present tense. It can also be used to recall the exact words of the speaker when retelling a previous conversation. You can recognize a direct speech instantly because it has a text enclosed in a set of quotation marks. That text or idea is known as the reported speech . - He says, “I want to adopt a dog.”
- Julia asks, “What do you want to have for dinner?”
- Penny answers, “I would like to have some soup.”
- “I have a new job,” Kyle says to us.
- “I will be working as a virtual assistant,” he added.
As you can see, direct speech can be presented in different tenses: past, present, or future. It depends on when the actual words were spoken and when the reporter is retelling them. Also, reporting verbs (say, ask, answer, etc.) are not necessarily placed before the quoted text. You can also place them after it. This type of speech is often used in writing novels or telling a story. This is because it gives the text a more actual and realistic effect. Indirect SpeechIndirect speech is usually used to relay what was being said by the speaker without directly quoting the original words. In this case, the tense of the sentence is typically changed. Reporting verbs, such as say, tell, ask, and others, are used as an introduction. The words of the original speaker will not be enclosed inside the quotation marks. Instead, the word “that” is used to connect the reporting verb to the reported text. - He says that he wants to adopt a dog.
- Julia asks Penny what she wants for dinner.
- Penny answers that she would like to have some soup.
- Kyle told us that he got a new job.
- He added that he will be working as a virtual assistant.
The above sentences are actually converted from the previous examples of direct speech. Aside from eliminating the quotation marks, correct pronouns are also used. Additionally, the reporting verbs are now all found before the reported speech. The reporting verb is then followed with “that.” Converting Direct to Indirect SpeechNow, let us specify the rules in converting direct speech to indirect speech. Here are the steps on how to do so: 1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text.The quotation marks are the primary indication of a direct speech. Therefore, it is crucial to take them out if you are forming an indirect one. 2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word “that” after it.You have to retain the tense of the reporting verb to allow consistency of reports. Instead of placing a comma to separate the reporting clause from the reported one, the word “that” is added. However, if the reported speech is a yes-no question, you use “if” instead of “that.” If the question starts with who, what, when, where, etc., no additional words are needed. Instead, you have to rearrange the sentence into a declarative form. - Direct Speech: She says, “I want to go to Paris.”
- Indirect Speech: She says that she wants to go to Paris.
- Direct Speech: She asks, “Do you want to go to Paris?”
- Indirect Speech: She asks me if I want to go to Paris.
- Direct Speech: “Ms. Thompson, where are you going?” I asked.
- Indirect Speech: I asked Ms. Thompson where she was going .
3. Change the tense of the verb in the reported speech, if needed.If the reporting verb is in the past tense, you should change the tense of the verb inside the reported speech into its past tense. This is not necessary if the reporting verb is in the present or future tense. - Direct Speech: He said , “I am watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he was watching a new TV series.
- Direct Speech: He says , “I am watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He says that he is watching a new TV series.
Of course, you have to consider the correlation between the report and the idea on the quoted text. Sometimes, a change in tense is not needed even if the reporting verb is in the past tense. - Direct Speech: He said, “I will be watching a new TV series.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he will be watching a new TV series.
- Direct Speech: He said, “I watch TV series every night.”
- Indirect Speech: He said that he watches TV series every night.
For the first example, the quoted text is still about to happen. So, you don’t need to change the tense of the sentence inside the quotation. For the second example, watching TV series is implied as a habitual action. Therefore, you still have to retain the present tense of the verb. 4. Change the pronouns accordingly.You should also change the pronoun based on who the speaker, doer, and receiver of the action is. - Direct Speech: Wendy says, “Ron, y ou should take care of yourself .”
- Indirect Speech: Wendy told Ron that he should take care of himself .
Appropriate changing of pronouns is done to avoid misunderstanding the whole text. If pronouns are not changed, it might confuse the reader or the listener as to who is saying or doing the action. The change in pronouns gives rise to changes in the plurality of the verb used. That being said, you have to consider and follow correct subject-verb agreement at all times. Tense Changes in Indirect Speech Verb Tenses ChangesPresent Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense For example: - Direct speech: She always wears a coat.
- Reported speech: He said (that) she always wore a coat.
Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense - Direct speech: I ‘m looking for my keys.
- Reported speech: She said that she was looking for her keys.
Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense - Direct speech: She has written three letters for her friend.
- Reported speech: He said she had written three letters for her friend.
Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense - Direct speech: My friend gave me a bar of chocolate.
- Reported speech: He said that his friend had given him a bar of chocolate.
Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense - Direct speech: We were living in London.
- Reported speech: They said that they had been living in London.
Past Perfect Tense ( The tense remains unchanged ) - Direct speech: The bread had gone stale.
- Reported speech: She said the bread had gone stale.
Future Simple Tense (e.g. will ) into “ would “ - Direct speech: I will finish my report in two days.
- Reported speech: He said that he would finish his report in two days.
Future Progressive Tense (e.g. will be ) into “ would be “ - Direct speech: I will be making tea.
- Reported speech: He said (that) he would be making tea.
Future Perfect Tense (e.g. will have ) into “ would have “ - Direct speech: I will have called a doctor.
- Reported speech: He said (that) she would have called a doctor.
Future Perfect Tense (e.g. will have been ) into “ would have been “ - Direct speech: All the money will have been spent.
- Reported speech: He said (that) all the money would have been spent.
Other Verb Form Changes in Reported SpeechCan into Could - Direct speech: I can speak English.
- Reported speech: She said she could speak English.
Could ( The verb remains unchanged) - Direct speech: He could play in the match.
- Reported speech: They said he could play in the match.
Have to into Had to - Direct speech: I have to submit this assignment by 3 pm tomorrow.
- Reported speech: She said she had to submit this assignment by 3 pm tomorrow.
Must into Must/Had to - Direct speech: I must go to the bank and get some money.
- Reported speech: She said she must / had to go to the bank and get some money.
May into Might - Direct speech: I may invite them to dinner.
- Reported speech: She said that she might invite them to the dinner.
Might (The verb remains unchanged) - Direct speech: He might get a flight tomorrow.
- Reported speech: She said he might get a flight the next day.
Should (The verb remains unchanged) - Direct speech: I should start a job.
- Reported speech: She said that she should start a job.
More interesting articles- Changes in Time and Place in Reported Speech
- Changes of Pronouns in Reported Speech: Rules & Examples
- Direct Speech | What is Direct Speech? with Useful Examples
- No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
- Reported Commands and Requests in English
- Reported Questions: Direct and Indirect Questions
- Reported Speech Exercises – Reported Speech Worksheet
- Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
- Reporting Verbs in English Grammar
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
English Grammar & Vocabulary Lessons & Practice Tests Direct and Indirect Speech – Rules and Examples13th June 2020 By Edify English Leave a Comment Any word spoken by a speaker can be written in two different ways. Those two are direct and indirect speech. Direct Speech is when the speaker’s actual words are quoted and these words are put in inverted commas (“…..”) while Indirect Speech is when the speaker’s words are said indirectly with the same meaning without repeating the exact words. For Example, the statement in direct speech She said to me, “I am going to the park” changes into She told me that she was going to the park in indirect speech.  Basic Changes while changing from Direct speech to indirect speech - The comma ( , )after the reporting verb is removed and the conjunction that is added in the indirect speech.
- If the direct speech contains ‘said to’ , it will be converted into ‘told’ in the indirect speech.
- The quotation marks (Inverted commas) are to be removed in the indirect speech.
- I becomes He/ She
- We becomes they
- You becomes He / She/ They
- Me becomes Him/ he r (Depending on the gender in the direct speech)
- My becomes His/ Her .
- Our becomes their
- Us becomes them
- Your becomes His/ her/ their .
Rules in changing a sentence from Direct and Indirect Speech- Rule 1: The Verb in the simple present tense in the direct speech changes into the simple past tense in indirect speech
Example: He said to me, “I am happy” becomes He told me that he was happy (The verb in the direct speech ‘am’ is converted into ‘was’.) - Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: He said to me, “I was happy” changes into He told me that he had been happy - Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech.
Example: The peon said, “The professor is teaching in that classroom” changes into The peon said that the professor was teaching in that classroom. - Rule 4: If the direct speech contains present perfect tense, it changes into the past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: She said, “I have passed the test” becomes She said that she had passed the test. - Rule 5: If the direct speech contains a statement talking about a universal truth or a factual statement, there will be no change of tense in indirect speech.
Example: The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East” becomes The teacher said that the sun rises in the east in indirect speech. Example: Samuel said, “I know the university’s address.” and the indirect speech for that is Samuel said that he knows the university’s address Rules for converting Interrogatory sentences - Rule 6: While converting interrogative sentences, the verb ‘said to’ becomes ‘asked’ and if/ whether will come in the place of ‘that’. The connecting word ‘that’ will not be used in indirect speech. Also, the interrogation mark (?) is not repeated in the indirect speech.
Example: He said to her, “Will you marry me?” changes into He asked her whether she would marry him in the indirect speech. Rules for Converting Imperative Sentences - Rule 7: During the conversion of imperative sentences, the verb “said to” is changed into ordered, advised, requested, suggested, proposed, etc. depending on the situation. Also, the connecting word ‘that’ is not used. Instead of that, ‘ to’ is used before the reporting verb.
Example: My father said to me, “prepare well for your examination” . It can be converted to My father advised me to prepare well for my examination. Rules for Converting Exclamatory Sentences - Rule 8: For exclamatory sentences, the verb is converted into: exclaimed with joy or sorrow or with surprise, wished, prayed, applauded,/ etc. The exclamatory words and the exclamation are not mentioned anymore in the indirect speech. For example,
Example: The coach said, “Hurrah! we won the match!” is changed as The coach exclaimed with joy that we had won the match. These are the changes in helping verbs while changing from Direct and Indirect Speech | | | | Am/ Is | Was | | Are | Were | | Have/ Had/ Did | had | | Do/ Does | Did | | Will | Would | | Shall | Should | | Can | Could | | May | Might | | Must | Had to | | Was/ Were | had been | | Should | Should | | Had | Had | | Would | Would | | Could | Could | Note: There is no change in the helping verbs “would, should, could, might, had” in the direct speech and they remain the s ame in indirect speech as well. Changes in Time and Place | | | | This | That | | These | Those | | Here | There | | Now | Then | | Today | That Day | | Tonight | That Night | | Tomorrow | The next day/ The following day | | The Day after tomorrow | In two days | | The Day before yesterday | Two days before | | Ago | Before | | Next | The following | | Last | The previous | | Thus | So | | This Evening | That Evening | | Hence | Thence | Cha nges in pronoun s The changes in pronouns in indirect speech depends on the subject and the object of the reporting verb. - Rule 1: The first person of reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting verb.
Example: She said, “I watched a movie” can be converted into She said that she had watched a movie . Hence, the first person in the direct speech “I” has become “she” based on the subject. Had there been “he” instead of “she”, the first person in reported speech changes accordingly into “he”. - Rule 2: The second person in reported speech changes based on the object of the reporting verb.
Example: She said to me, “You watched a movie” can be converted into She told me that I had watched a movie. - Rule 3 : The third person in the reported speech remains unchanged.
Example: I said to her, “He will play Chess” can be converted into I told her that he would play Chess. Stay tuned for more examples of direct and indirect speech. For an extensive material on tenses, Click here Follow us on Facebook Share this:Subscribe to blog via email. Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email. Email Address Reader InteractionsLeave a reply cancel reply. Reported Speech – Rules, Examples | Candace Osmond  Candace Osmond Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction. They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech. Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language! Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic. What Does Reported Speech Mean?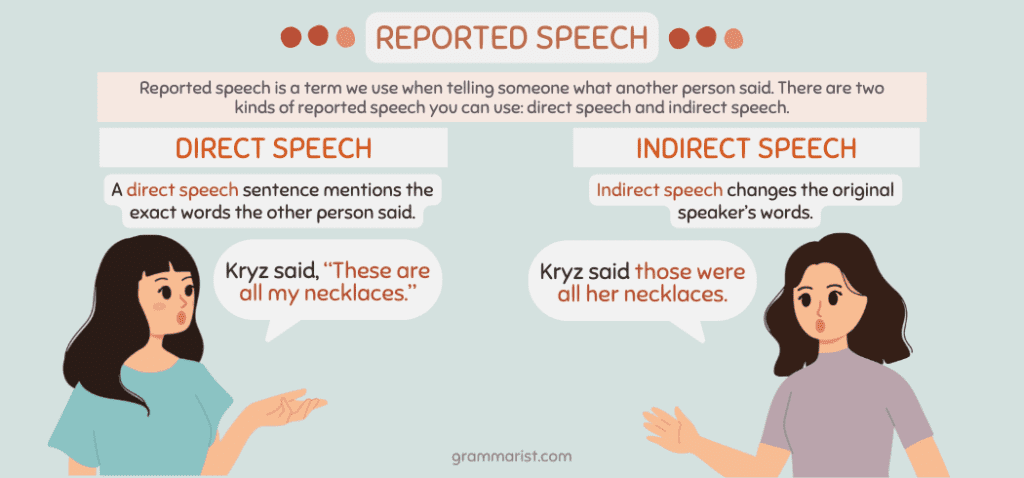 Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing. There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example: - Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example: - Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker. Reported Speech ExamplesWe usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example: - Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting. - Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis. Reported Speech StructureA speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below: - Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help. What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative. Reported Speech RulesThe rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all. Choose Whether to Use That or IfThe most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.” Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example: - Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them. Verb Tense ChangesChange the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example: - Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example: - Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action. Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means: - Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples: - The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect) - Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs. - Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example: - Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment. Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense: - If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time ReferenceChanging the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places. - This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples. - Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then. - Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before. - Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day. Using Modals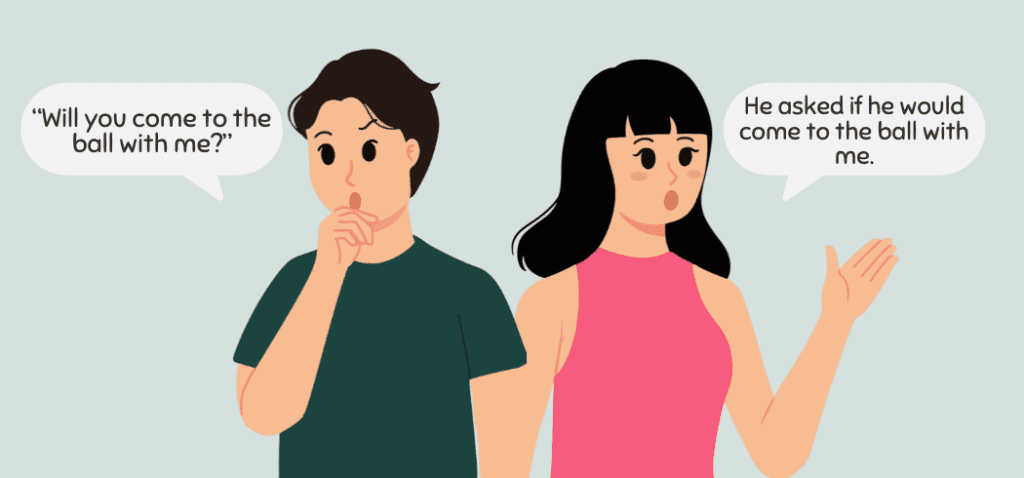 If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly. - Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me. - Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free. However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example: - Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park. Imperative SentencesTo change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example: - “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event. - Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported QuestionsWhen reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms. - Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live. Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech. She asked me where I live. Wrapping Up Reported SpeechMy guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now? Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause. Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references. Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you. 2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.  Search form- Highest rated
- Verb phrase generator
- Test your grammar
Tense changes in indirect speechNo tense changes. There are no tense changes in indirect speech if: Joanna: I have just arrived in Hanoi. Joanna says she has just arrived in Hanoi. (reporting a recent telephone conversation; the reporting verb say is in present simple) George: I 'm meeting Karen tomorrow. George said he is meeting Karen tomorrow. (reported on the same day, tomorrow still refers to tomorrow) George said he was meeting Karen the following day. (reported days later, the meeting has already happened) Copernicus: The planets revolve around the sun. Copernicus stated that the planets revolve around the sun. (it is a general truth) Once, people believed that the earth was flat. (the reported words are no longer true; people do not believe that the earth is flat) Mike: I wish I was a year older; then I could enter the race. Mike wished he was a year older, so he could enter the race. (he is not older) Tense changesTenses change in indirect speech if: Philip in 1980: I have never been to Brunei, but I' m thinking about going there. (the reference point of the present perfect and the present continuous is 1980) When I met Philip in 1980, he said he had never been to Brunei, but he was thinking about going there. (reported years later; the reported words are out of date) Tim: Sorry, I can't go to work this week. I' m ill. Tim isn't coming to work this week. He said that he was ill. Tense backshiftAs can be seen in the examples above, the verbs in the present perfect, present continuous and present simple tenses in the original statements changed into their corresponding past equivalents (past perfect, past continuous and past simple) in indirect speech. This process is called tense backshift. Note that tense backshift is based on how tenses relate to each other in general: When I met Philip in 1980, he said he had never been to Brunei. When I arrived at work, I remembered that I hadn't locked the door to my apartment. (two consecutive actions and an earlier action) When I met Philip in 1980, he said he was thinking about going to Brunei. When I entered the room, I saw that she was studying . (two consecutive actions and a background action in progress) Tim said that he was ill. I went outside. It was a warm day. (a past action and a past state) Tense backshift: | Direct speech | Indirect speech |
|---|
| present simple | past simple | | present continuous | past continuous | | present perfect | past perfect | | present perfect continuous | past perfect continuous | | past simple | past perfect | | past continuous | past perfect continuous |
The past perfect and past perfect continuous tenses do not change. In complex sentences, the past simple and past continuous may remain unchanged if the temporal relationship between the events in the clauses is clear from the context: John: When I got home, I went to bed straight away. John told me that when he got home he went to bed straight away. Bill: I was reading a book when I heard the crash. Bill said that he was reading a book when he heard the crash. Helen: When I was writing my thesis, I spent a lot of time at the library. Helen recalled that when she was writing her thesis she spent a lot of time at the library. Tim: My friends were enjoying themselves playing cards while I was studying in my room. Tim grumbled that his friends were enjoying themselves playing cards while he was studying in his room. Chris: When I got to her house, she had been waiting for hours. Chris said that when he got to her house she had been waiting for hours. Rate this pageRelated topics.  For timeline diagrams, quotes and exercises, check out our e-book The Grammaring Guide to English Grammar  About | Copyright Grammaring – A guide to English grammar | Copyright © 2009-2024  Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and ExamplesAre you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.  Direct and Indirect SpeechWhen someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example: Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza. Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken. To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example: Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park. It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example: Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was. In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing. Differences between Direct and Indirect SpeechWhen it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech: Change of PronounsIn direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example: - Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech. Change of TensesAnother major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example: - Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech. Change of Time and Place ReferencesWhen reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example: - Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech. Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect SpeechWhen you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules. Step 1: Remove the Quotation MarksThe first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a LinkerTo indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech. For example: - Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the VerbWhen you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. - Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the PronounsYou also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb. - Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words. Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct SpeechConverting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech: - Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process: Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home. Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said. By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech. Examples of Direct and Indirect SpeechDirect and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech: Direct Speech ExamplesDirect speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue. - “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech ExamplesIndirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said. Here are some examples of indirect speech: - Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about. Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis. Frequently Asked QuestionsWhat is direct and indirect speech? Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words. How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech? To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech). What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech? The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not. What are some examples of direct and indirect speech? Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza . What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech? The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” What is a summary of direct and indirect speech? Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb. You might also like: - List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
 This website is AMNAZING  MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO  sure cries l miss my friend  he saiad,” we are all sinners”. convert into indirect speech  He said that they were all sinners. Direct AND Indirect Speech Rules AND Examples Direct speech and indirect speech, also known as reported speech, both express something that has been said. Here we’ll look a t direct and indirect speech rules with examples , and converting direct speech into indirect speech. DIRECT SPEECHDirect speech tells the exact words that someone spoke and these are contained within speech marks “ “, also called quotation marks. “I love dogs,” said Anne. Speech MarksSpeech marks may be double “ “ or single ‘ ’ There is no difference between double and single speech marks, but use the same type for both the opening and closing speech mark, and be consistent throughout any one piece of writing. Both these examples have the exact same meaning and effect “I love dogs,” said Anne. ‘I love dogs,’ said Anne. Reporting ClauseThe reporting clause – said Anne – attributes the words spoken to the person who spoke them. A comma separates the direct speech in the speech marks and the reporting clause. Note the positioning of the commas in these examples: “I love dogs,” said Anne. (inside the closing speech mark) Anne said, “I love dogs.” (before the opening speech mark) “I love dogs,” said Anne, “but my landlord won’t allow pets.” (both sides of the reporting clause) PunctuationIf the sentence continues beyond the end of the spoken words and the closing speech mark, a comma is placed inside the speech mark, and the full stop (question mark or exclamation mark) will come at the end of the sentence as usual (example 1) “I love dogs,” said Anne. If the end of the sentence falls at the end of the spoken words, a full stop (question mark or exclamation mark) is placed inside the closing quotation mark. (example 2) Anne said, “I love dogs.” If the direct speech is broken up by a reporting clause, a comma is placed inside the first closing speech mark, as already seen in example 1, and another comma is also placed after the reporting clause. (example 3) When speech occurs in a passage of writing, each new occurrence of direct speech, usually from a new character, is started on a new line: Anne stopped abruptly as she came to the pet shop window. She stood watching the sleeping puppies. “I love dogs,” she said. “Would you get one?” asked Mary. “I would, but my landlord won’t allow pets.” “Yes, of course, not many do. INDIRECT SPEECHIndirect speech is also known as reported speech. It is the re-telling, or reporting, of what someone said. No quotation marks are used with indirect speech as it does not necessarily report the exact same words that were spoken. Anne said that she liked dogs. She said that she would like to get one but her landlord doesn’t allow pets. The word ‘ that ’ should appear immediately before the reported words, however it is often omitted nowadays and both alternatives are accepted as correct: Anne said that she liked dogs. Anne said she liked dogs. DIRECT TO INDIRECT SPEECHIndirect speech reports what has been said, so by definition it reports on something that has already happened, and must logically be in the past tense. Often when converting direct speech into indirect speech the tense will backshift, meaning move backwards in tense. Two aspects influence this: – the tense of the reporting verb i.e. he says, he said, he will say etc. – the tense of the reported speech itself i.e. the words contained in the speech marks REPORTING VERB IN THE PRESENT & FUTURE TENSESIf the reporting verb is in the Present or Future tenses, then no change is made to the spoken verb tense i.e. the tense of verbs within the speech marks, when converting direct speech into indirect speech. He says, “I am sitting in the garden.” He says that he is sitting in the garden. No change in the spoken verb tense as the reporting verb is in the present tense. He said, “I am sitting in the garden.” He said that he was sitting in the garden. A change in the spoken verb tense as the reporting verb is in the past tense. REPORTING VERB IN THE PAST TENSEIf the reporting verb is in the Past Tense, as is most common, then the tense of the direct speech i.e. the tense of verbs contained within the speech marks and as actually spoken, will backshift when converting from direct speech into indirect speech. 1. DIRECT SPEECH IN THE PRESENT TENSESPresent Simple becomes Past Simple “I want a cup of tea,” she said. She said that she wanted a cup of tea. Present Continuous becomes Past Continuous “I am watching television,” he said. He said that he was watching television. Present Perfect becomes Past Perfect “She has travelled to Mexico often” Tom said. Tom said that she had travelled to Mexico often. Present Perfect Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous “We’ve been learning French for 3 years,” Sam said. Sam said that they had been learning French for 3 years. | |
|---|
| Direct Speech | Indirect speech | | Present Simple | Past Simple | | Present Continuous | Past Continuous | | Present Perfect | Past Perfect | | Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | | Past Simple | Past Perfect | | Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | | Past Perfect | Past Perfect | | Past Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | | Future Tenses will | would |
2. DIRECT SPEECH IN THE PAST TENSESPast Simple becomes Past Perfect “I ate too much last night,” he said He said that he had eaten too much last night. Past Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous “I was lying in the hammock,” said Frances Frances said that she had been lying in the hammock. Past Perfect does not change tense “Amy had fallen asleep before we got home,” said Kim Kim said that Amy had fallen asleep before they got home. Past Perfect Continuous does not change tense “We had been staying in Paris all summer, said Mathew Mathew said that they had been staying in Paris all summer. 3. DIRECT SPEECH IN THE FUTURE TENSESThe Future tenses will becomes would: Future Simple (will) “I will make the cake,” said Laura Laura said that she would make the cake Future Continuous (will be) “Shaun will be coming alone,” said Helen Helen said that Shaun would be coming alone. Future Perfect (will have) “I will have finished the essay,” said Andrew Andrew said that he would have finished his essay. Future Perfect Continuous (will have been) “I will have been running for four hours,” said Lucy Lucy said that she would have been running for four hours. The tense does not change if: the reported speech is in the present tense, and is being reported only a short time afterwards “I’m coming over now,” Fiona said. Fiona said that she is coming over now. (reported immediately) Fiona said that she was coming over right then. (reported some time later, probably after the event) the past simple and past continuous may remain unchanged if the sequence of events and time frame are clear from the context “When I was learning Spanish, I often listened to Spanish radio stations,” said Dom Dom said that when he was learning Spanish he often listened to Spanish radio stations. PRACTICE EXERCISES1. Change these sentences into indirect speech “I hate Mondays.’ said Shirley Mark said, ‘I won the lottery last week.” Children always say, “We don’t want homework!” Simon said, “I will tell her tomorrow.” Teresa said, “They had eaten before they arrived.’ 2. Why are these all incorrect? “I hate apples.” said Lesley. ‘No, you can’t go to the party,’ Said Mum. “Where have all the good men gone?’ asked Natalie. “Do you want some chocolate?,” asked Mary. ‘I want a tea,’ said Larry, ‘but I don’t want a biscuit’. Answers 1. Shirley said that she hated Mondays. Mark said that he had won the lottery last week. Children always say that they don’t want homework. Simon said that he would tell her tomorrow. Teresa said that they had eaten before they arrived. 2. there should be a comma not a full stop before the closing speech mark, no capital letter needed for said , both double and single speech marks used in the same sentence, only the question mark is necessary before the closing speech mark,full stop should be in the speech marks  Onlymyenglish.com Learn English Direct and Indirect SpeechTable of Contents What is Speech (Narration):If we want to describe the speech of some other people with other people in our own words, that speech is called a Reported speech or Narration. Types of SpeechIn the English language, there are certain ways to express the spoken words between two people. The speech has two main types, Direct speech , and Indirect speech , respectively. These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations. Direct and indirect speech is majorly used in any conversations, scripts, or any biographies, etc. where one or more than one person converses with each other. Direct speech:It is also called straight speech or quoted speech, which is spoken or written directly in the text by the speaker, writer, or the first person, who is going to speak with anyone with him. The spoken statements of the speaker normally come under the inverted commas notation, and a speaker who speaks these sentences may come like “he said/he said that.” The speaker’s words or statements are mentioned in a single phrase pattern or direct discussion.  Indirect speech:An Indirect speech is also called a reported speech, or secondary speech means the speech, which has spoken indirectly. It is simply an overlook statement that is used to say about the incident that has happened in the past time. The actual words of the speaker changed into the past tense and the sentence, and hence the reported speech of the direct speech does not come inside the inverted commas. Reporting speech:A person who is going to report the speech or a speech that comes in the first part of the direct speech is called a reporting speech. - He says , “He cooks food”.
Reported speech:Reported speech is a speech that is always in an inverted comma or quotation marks. It is a second part of the direct speech sentence. - He says, “He cooks food.”
Reporting verb:The verb, which is used in a reporting speech to report something in a direct speech, is called a reporting verb. - Zoya said , “I want to go there.”
Reported verb:The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively. - Zoya said, “I want to go there.”
As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like “say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.” These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or indirect speech, change into the past simple form like said, told, asked, informed, instructed, claimed, suggested, enquired, etc. But the verbs used in a speech between the inverted commas will remain as it is. Examples of direct and indirect speech:- Indirect speech: John said that she was looking so beautiful.
- Indirect : He said that he was not a culprit.
- Indirect : He said that she was working on that project.
- Indirect : The teacher asked if he completed his homework.
- Indirect : She says that she is an artist.
- Indirect : Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
- Indirect : He says that she is working on that project.
 Some basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech:Rule 1 : “no inverted commas.”. The reported speech does not come into inverted commas or quotation in an indirect speech. Example: Direct: He said, “I have completed my assignments yesterday.” Indirect: He said that he had completed his assignments the previous day. Rule 2: use of “that” conjunctionUsing the conjunction word “that” in-between the reporting speech and reported speech in an indirect speech. Example: - He said, “I have completed my assignment yesterday.”
- He said that he had completed his assignment the previous day.
Rule 3: Change of tenseWhile writing a direct speech into an indirect speech, we have to change the tense of the reported speech because whatever we are writing in indirect speech has already happened in the past timing. - If the tense of a reporting speech of direct speech is in the present tense or future tense , then the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech will not change. It may be in the present tense, past tense, or future tense, respectively.
- Indirect : He says that he is going to school. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : She says that she will not come with me. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : He says that he wrote a letter. (no change in tense)
If the tense of the reporting verb of direct speech is in the past tense, then the tense will change according to these criteria. For the present tense:Simple present tense will change into simple past tense.. Direct: He said, “They come to meet me.” Indirect: He said that they came to meet him. Present continuous tense will change into past continuous tense.Direct: She said, “They are coming to meet me.” Indirect: She said that they were coming to meet her. Present perfect tense will change into past perfect tense.Direct: He said, “They have come to meet me.” Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him. Present perfect continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.Direct: She said, “They have been coming to meet me.” Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her. For the past tense:Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense. Direct: He said, “They came to meet me.” Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him. Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense. Direct: She said, “They were coming to meet me.” Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her. Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same. Direct: He said, “They had come to meet me.” Direct: She said, “They had been coming to meet me.” For the future tense:There are no changes in the future tense sentences; only shall/will may change into would, can change into could. - Direct: She said, “Can you come tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that could he come on the next day - Direct: He said, “I will never forgive you.”
Indirect: He said that he would never forgive me. Rule 4: Changing the pronounThe pronoun used as an indirect subject speech sometimes needs to be changed accordingly in indirect speech as of the reported verb of the direct speech. - The pronoun used for representing the first person in reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting speech in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report’s object in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech.
- Direct: He said, “ I am going to school.”
- Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
- Direct: She says, “ I will not come with you .”
- Indirect: She says that she will not come with me .
- Direct: They said, “ we are eating our tiffin box.”
- Indirect: They said that they were eating their tiffin box.
Rule 5: Changing the timeThe mentioned time (not the timing) in a direct speech sentence will have to change in indirect speech like now becomes then, tomorrow becomes the next day, yesterday becomes the previous day, today becomes that day, later becomes soon. - Direct: He told, “He is coming from Tokyo today .”
- Indirect: He told me that he was coming from Tokyo that day .
- Direct: She asked, “Will the parcel reach by tomorrow or not?”
- Indirect: She asked whether the parcel will reach by the next day or not.
- Direct: “The teacher has given some assignments yesterday ”, he reminds me.
- Indirect: He reminds me that the teacher had given some assignments on the previous day.
Conversion of statements from direct speech into Indirect speech:Assertive sentences:. Assertive sentences are simple statements that may be affirmative or negative. If we are going to convert assertive sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, we have to replace “said” with “told” sometimes. Here, the subject in direct speech refers to someone in his talk. - Direct: He said to me, “she is working on this project.”
Indirect: He told me that she was working on that project. - Direct: She said to me, “I’m going for a long drive.”
Indirect: She told me that she was going for a long drive. Imperative sentences:Imperative sentences are statements that deliver a command, order, request, appeal, or advice. It depends on the speaker, how he delivers the message to the other person. - Sit properly!
- Stand by my side!
- Come closer!
While converting these types of sentences cum statements from direct speech to indirect speech, we have to check the type of sentence, whether it is a command, order, request, or else. - Direct: The teacher said to me, “Sit properly!”
Indirect: The teacher ordered me to sit properly. - Direct: The Boss said to an office boy, “Bring one coffee for me.”
Indirect: The Boss commanded an office boy to bring a coffee for him. Indirect: The teacher requested me to sit properly. - Direct: The bartender said to me, “try this drink.”
Indirect: The bartender advised me to try that drink. Interrogative sentences:An interrogative sentence is a sentence which interrogates or ask questions. Each interrogative sentence ends with an interrogative sign or a question mark sign “?”. - What is your name?
- Can you do me a favor?
- Why are you laughing in the classroom?
While writing interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, - the reporting verb “said” in the direct speech is changed into “asked” in the indirect speech because it asks the question to another person.
- If any reporting verb comes first in the reporting speech, then “If” is used despite “that.”
- In a reporting speech, if any wh-type question words are present, then no other words will be used, and the sentence ends with a full stop sign instead of a question mark.
- Indirect: He asked me what was my name.
- Indirect: She asked if he could do her a favor.
- Indirect: The teacher asked him why he was laughing in the classroom.
Exclamatory sentences:Exclamatory sentences are those sentences that show emotions, feelings and ends with an exclamation mark! - Congratulations! You have a baby girl.
- I am extremely sorry for your loss!
- Most welcome!
If any interjection comes in an exclamation sentence, then the exclamation sign removes in an indirect speech, and an exclamatory sentence gets converted into an assertive sentence. The replacement of reporting verb “said” with exclaimed with (great wonder, sorrow, joy) exclaimed (joyfully, sorrowfully) Replace with very or very great , if words like how or what comes at the beginning of the reported speech. - Indirect: He exclaimed with joy that I had a baby girl.
- Indirect: She exclaimed with sorrow that she felt sorry for my loss.
- Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that most welcome.
You might also like Past Simple Tense: Definition, Examples, Rules & Formula Future Perfect Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula, Structure & Rules Future Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula & Rules Wh-type Question Words | Wh Question WordsUse of would and could with an example.  Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula, Structure & Rules Direct and Indirect of Past Perfect Tense We talked about direct and indirect of past progressive tense , in the lesson below I am going to elaborate direct and indirect of past perfect tense. You will learn how to convey a message of someone from past perfect tense. Affirmative, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative sentences along with examples. For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules Tense Change: As a rule, whenever we change a sentence from quoted speech into reported speech, we go one tense back. But if we have past perfect tense in direct speech, we use the same tense in indirect speech. Affirmatives - Direct speech: RP, +, + S + had + V3 + ROTS I said to him, “They had played cricket.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had + V3 + ROTS I told him that they had played cricket.
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He said to me, “We hadn’t played cricket.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He told me that they hadn`t played cricket.
Interrogatives - Direct speech: RP +, + had + S + V3 + ROTS He asked, “Had you finished playing cricket before the rain started?
- Indirect speech: RP + whether/if + S + had + V3 + ROTS He asked me whether/if we had finished playing cricket before the rain started.
Negative interrogatives - Direct speech: RP +, + had not + S + V3 + ROTS He asked, “Hadn`t you finished playing cricket before the rain started?”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He asked me if we hadn’t finished playing cricket before the rain started.
WH/Information questions - Direct speech: RP +, + WH + had + S + V3 + ROTS She asked, “Who had you played cricket with before the rain stared?”
- Indirect speech: RP + WH + had + S + V3 + ROTS She wanted to know who I had played cricket with before the rain started.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below. Share this:- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related postsHow to use adverb clause of reason/ cause, adverb clause of supposition or concession exercises, indefinite pronoun exercises with answers, leave a comment cancel reply. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Stack Exchange NetworkStack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. Q&A for work Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. When can Past Continuous become the Past Perfect Continuous in reported speech?Reporting the direct speech we follow the rule of "one tense back". Since that we are able to use Past Perfect instead of Past Simple as well as leave it the same. The Past Perfect tense stays the Past Perfect. I saw the we can leave the Past Continuous the same. I found the example where it becomes Past Perfect Continuous, though. "I was getting bored lying on the beach", Mrs.Jones said. So, which one would be better: Mrs.Jones said (that) she was getting bored lying on the beach. Mrs.Jones said (that) she had been getting bored lying on the beach.  - Most native speakers of AmE would not backshift to "had been getting bored". – TimR Commented Oct 1, 2017 at 14:44
- @Tᴚoɯɐuo, according to you, I'd better use Past Continuos as mentioned in the above. – Anthony Voronkov Commented Oct 1, 2017 at 20:24
Past perfect is not "one tense back" from the past continuous. It has its own use, to indicate one past action happened before another past action. She said she had been sunbathing when the giant wave washed up the beach and drenched everyone. You dont usually backshift to it from the present perfect continuous, because that would change the meaning. She said, "I have been playing piano every day" She said she has been playing piano every day. She said she had been playing piano every day (before something else happened)  - So, what would be better in my example? – Anthony Voronkov Commented Oct 1, 2017 at 20:23
- Mrs. Jones said that she was getting bored lying on the beach. – Andrew Commented Oct 2, 2017 at 6:16
- That's what I wanted to hear. – Anthony Voronkov Commented Oct 2, 2017 at 10:48
You must log in to answer this question.Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged tense reported-speech .. - Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions- Power line crossing data lines via the ground plane
- Three 7-letter words, 21 unique letters, excludes either HM or QS
- Is an invalid date considered the same as a NULL value?
- Guitar amplifier placement for live band
- can a CPU once removed retain information that poses a security concern?
- Isn't an appeal to emotions in fact necessary to validate our ethical decisions?
- Did the Space Shuttle weigh itself before deorbit?
- Will the US Customs be suspicious of my luggage if i bought a lot of the same item?
- Has the application of a law ever being appealed anywhere due to the lawmakers not knowing what they were voting/ruling?
- How is lost ammonia replaced aboard the ISS?
- Why HIMEM was implemented as a DOS driver and not a TSR
- What is the airspeed record for a helicopter flying backwards?
- What is a word/phrase that best describes a "blatant disregard or neglect" for something, but with the connotation of that they should have known?
- How predictable are the voting records of members of the US legislative branch?
- Using relative coordinates with \draw plot
- How to handle stealth before combat starts?
- Base change in Chriss-Ginzburg
- What's wrong with my app authentication scheme?
- Why is this white line between the two vertical boxes?
- Convert a Dataset into a list of lists and back to a Dataset
- Non-linear recurrence for rational sequences with generating function with radicals?
- Largest Eigenvalue Bound of Sum of Two Matrices
- Are there jurisdictions where an uninvolved party can appeal a court decision?
- With 42 supernovae in 37 galaxies, how do we know SH0ES results is robust?
  Your way to the top of Grammar... Indirect Speech: Formula and Rules We are talking about a very important and interesting topic. We are talking about direct and indirect speech in English and what is the correct formula of the usage. Remember to read How to learn English with audiobooks for FREE This topic can seem complicated at the beginning, but necessary to learn. Having this topic solved, you improve your English to a new level, so let’s start to deal with it. What are Direct and Indirect speech?In English, there are two ways how we can tell what another person said. Two ways you can say what someone else has said before. - Direct Speech
- Indirect (Reported) Speech
Note : Indirect speech in different textbooks can be called differently: Indirect Speech or Reported Speech . But these two names mean the same. Indirect Speech = Reported Speech  Direct speech in English is a type of speech when we retell someone’s speech as it was. We don’t change anything. John says: I’m a good boy. To tell what John said, we will say: We say: John said, “I’m a good boy.” Indirect speech differs from direct speech in that we DO NOT tell exactly what another person said. We are NOT repeating what someone else said. Indirect speech is when we tell the MEANING of what someone else said. We say: John said he was a good boy. Pay attention to what this sentence looks like. Earlier, when John said this, the sentence looked like this: I am a good boy. But after WE retell John’s words, in the indirect speech, this sentence looks like this: John said he was a good boy. The Quotes and the comma that stood after the name John, separating the speaker from his direct speech, disappeared from this sentence. In indirect speech, we do not use the separating comma and quotation marks. Because now it is WE are retelling the meaning of what the other person (John) said.  In direct speech, the speaker most often speaks in the first person. That is, the speaker speaks from his person. John will not talk about himself: John is a good boy . John will say it on his behalf: I am a good boy. But when we retell the words of John (indirect speech), we cannot speak on his behalf. We cannot say “I am a good boy” because those are not our words. This is John a good boy. Therefore, in indirect speech, we change “I” to the third person. He says: I hate you but I need your help. I retell: He said that he hated me but he needed my help. To translate direct speech into indirect speech, we use certain rules that you should know. Let’s take a look at these rules and formulas in order. Quotation marks and commaIn direct speech, we use a comma to separate the speaker from what he is saying. Direct speech (what the speaker says) is in quotation marks. When we translate direct speech into indirect speech, we remove quotes and commas. Jessica says , “I’m from the future.” We retell Jessica’s words: She said that she was from the future. Personal and possessive pronounsWhen translating direct speech into indirect speech, we change personal and possessive pronouns to third-person pronouns. Direct Speech : He says, “ I couldn’t stay” Indirect Speech : He said that he couldn’t stay. Direct Speech : Tom says, “ I am deeply disturbed” Indirect Speech : Tom said that he was deeply disturbed. Note: If in direct speech the speaker tells his own words, then we do not change personal and possessive pronouns. Direct Speech: I said, “ I will do that” Indirect Speech: I said that I would do that. Adverbs in direct speechWhen we translate adverbs from direct speech to indirect, adverbs change their form. You can see how adverbs look in direct speech and how adverbs look in indirect speech in this table: 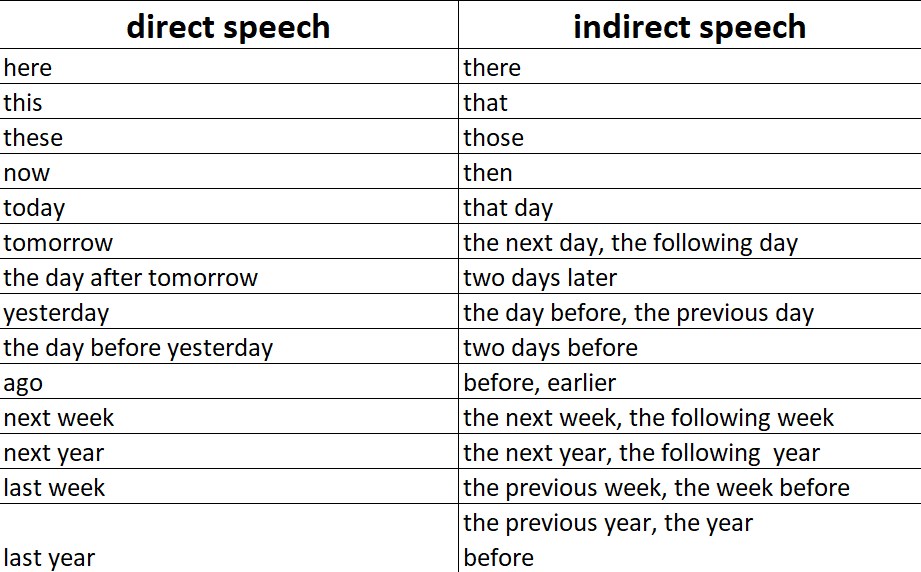 But we don’t always change adverbs this way. We change adverbs only if, when translating from direct speech into indirect speech adverbs cannot express the same meaning as in direct speech. Take a look at an example: Mom says, “ Tomorrow we will go to Uncle John’s.” Mom said that the next day we would go to Uncle John’s. In these examples, we have replaced the adverb tomorrow with the next day . Because we retell Mom’s words on another day. We cannot say tomorrow anymore. Now look at another example: Mom says, “We went to visit Uncle John yesterday .” Now imagine that we are retelling this the next day. We have to say: Mom said that we went to visit Uncle John the day before yesterday . If we said “ yesterday “, it would change the meaning of what we want to tell. If in direct speech in the main sentence the predicate is in Past Simple, then in indirect speech we use the agreement rules. We put the conjunction “ that ” in front of indirect speech. Note: We may not use the conjunction that after verbs such as: He said he found it on the island. He thought he was better than me. He knew he could call you anytime.  Prepositional objectIf in direct speech after the verb to say there is a prepositional object, then in order to translate such a sentence into indirect speech, we change the verb to say to tell . In this case, tell is used without the preposition to . Incorrect : to tell Correct : tell This means: She said to me … changes to She told me that … Note : Remember that in this case we also change the adverbs of place and time and demonstrative pronouns, if they are in direct speech. Modal verbsFor modals, we use several important rules. We change modal verbs as well as main verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech. But we do not change all modal verbs. We leave some verbs in their original form. Let’s talk about modals in more detail. Modal verb mustIf in direct speech the verb must means an obligation or command, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech must does NOT change and looks like must . The teacher says, “You must behave well in class.” The teacher said that we must behave well in class. If in direct speech the verb must expresses the need, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech we change the verb must to had to . Mom says, “You must visit the doctor.” Mom said that I had to visit the doctor. The past form of Modal verbs in indirect speechCan and could.. We change the modal verb can in direct speech to could in indirect speech. Could is the past form of the modal verb can . She says, “I can swim.” She said that she could swim. May and might.We change the modal verb may in direct speech to might in indirect speech. Might is the past form of the modal verb may . John says, “I may propose to Maria.” John said that he might propose to Maria. Must and had to.We change the modal verb must in direct speech to had to in indirect speech (if the verb must expresses the need). Had to is the past analog of the modal verb must .  Modal verbs that do not change in indirect speechThe following verbs move from direct to indirect speech in their original form. They don’t change in any way. - must (if the verb must means an obligation or command)
He says, “I could do this.” He said he could do that. Let’s take a closer look at these verbs: The modal verb would in direct speech remains in the form would in indirect speech too. Mom says, “I would bake a cake.” Mom said she would bake a cake. If we use the modal verb could in direct speech, then we do not change this verb in any way in indirect speech. Because could is a past form already (It’s the past form of the modal verb can ). John says, “I could learn to swim” John said he could learn to swim. The modal verb might does not change its form when we translate this verb from direct to indirect speech. Because the modal might is the past form of the modal may . He says, “I might ask the same question again”. He said that he might ask the same question again. We do not change should when switching to indirect speech. Because should is considered the past form of the modal verb shall . He says, “We should see Mr. Gannon” He said that we should see Mr. Gannon. We do not change the modal verb OUGHT TO when translating this verb into indirect speech. She says, “You ought to be angry with John” She said that I ought to be angry with John Exceptions to the rulesLet’s talk about the important exceptions to the rules of this lesson. - We can exclude the word that out of affirmative sentences in indirect speech. Because in indirect speech in affirmative sentences, the meaning of the sentence does not change, regardless of whether we use that or not.
He said ( that ) he thought you seemed depressed. He said ( that ) there was no need. He said ( that ) he had many friends. - If in direct speech we are talking about a specific event that happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore, then we translate the sentence into indirect speech without the agreement.
He says, “Gagarin went to space in 1961.” He said that Gagarin went to space in 1961. The event that we are talking about in this example happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore.  - If in direct speech we use verbs such as:
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the form of these verbs. These verbs remain in their form. She says, “We might find some treasure” She said that we might find some treasure. He says, “I should do it”. He said that he should do it. - If indirect speech begins with the verb say or tell which is used in the form:
- Present Simple
- Present Perfect
- Future Simple
then we translate such a sentence into indirect speech without changing the tense to the past: She says, “I cook deliciously.” She says that she cooks deliciously. He says, “I have a new smartphone.” He says that he has a new smartphone. She will say, “I didn’t know it.” He will say (that) he didn’t know it. - If in direct speech we are talking about a well-known fact or law of nature, then we do not transfer to the past such a fact or the law of nature when translating from direct speech to indirect.
He says, “After winter comes spring.” He said that after winter comes spring. She says, “Lions don’t hunt camels.” She said that lions don’t hunt camels. - If in direct speech we use tenses:
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the sentence, we do not translate the sentence into the past. He says, “I had fixed my car.” He said he had fixed his car. He says, “I was skiing .” He said he was skiing . He says, “I had been all alone for a very long time”. He said that he had been all alone for a very long time. Interrogative (question) sentences in indirect speechLook at the following rules and nuances to know how to correctly translate interrogative (question) sentences from direct speech to indirect speech: - When we translate a general question into indirect speech, we put one of the conjunctions between the main sentence and the question:
He asks, “Do you play dominoes?” He asked if I played dominoes. He asked whether I played dominoes.  - If we translate an interrogative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, then we change the interrogative word order to direct word order.
We remove the auxiliary verb that was used in the interrogative sentence. We put the subject before the predicate as it should be for the direct word order. He asks, “Where are you going?” He asked where I was going. - If in an indirect sentence we ask a question using the verb say and if there is no indirect object in the main sentence, then we change the verb say to one of these words:
- want to know
She asks, “Where you are?” She wanted to know where you were. - When translating an interrogative sentence from direct speech into indirect speech, we change all pronouns, verbs, adverbs of place, adverbs of time.
She asks, “What do these letters mean?” She asked what those letters mean. Special questions in indirect speechSpecial questions (or Wh-questions) are questions that begin with an additional, question word. In indirect speech, such a question should also begin with a question word. This question word also serves as conjunction. This word attaches the question part to the main sentence. In the question part, we use direct word order. At the same time, we comply with all the rules for the Sequence of tenses. My dad asks, “What do you plan to do with yourself?” My dad asked what I planned to do with myself. Imperative sentences in indirect speechWhen translating imperative sentences from direct to indirect speech, we must take into account several nuances: - Orders in indirect speech look like this:
He said, “ Go now!” He said to go then. She says, “ Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag. We use the verb to say when we translate an ordinary sentence into indirect speech. But in imperative sentences, we change the verb to say to a verb that expresses an order or request: She says , “Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag.  - In direct speech in the imperative mood, we often use:
let’s (let us) let’s encourage the speaker and the person to do something together. In indirect speech, we change let’s to to suggest . For example: She says, “ let’s do that!” She suggested to do that. - In indirect speech, we put a noun after the verb that expresses an order or request. The noun is the one to whom this request or order is addressed. Then we use the infinitive.
She says, “Replace him, John “ She asked John to replace him. - We can strengthen the request or order in indirect speech if we add verbs such as:
- to recommend
- to urge etc.
She says , “Read this book” She ordered ( advised, recommend ) me to read that book. - In order to make a negative imperative sentence in direct speech, we need:
not + infinitive He says, “Don’t cry.” He said to me not to cry. - In direct speech, we often do not name the person to whom the order or request is addressed. But when translating an imperative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, we must indicate the one to whom the order or request is addressed.
For this, we use a noun or a pronoun. She says, “Speak to him!” She asked me to speak to you. Present and future tense in indirect speechMost often, we translate the future and the present into the past. He says, “I have two brothers” He says that he had two brothers She says, “I do this every time” She says that he did that every day. He says, “I write books” He says that he wrote books. She says, “I am reading” She said that she was reading. He says, “I can swim” He said that he could swim. He says, “I will help you” He said that he would help me. Past tense in indirect speechWhen we translate a sentence written in the past into indirect speech, we can leave it unchanged or we can change the past to the Past Perfect. He says, “I saw this movie” He said that he saw that movie. He said that he had seen that movie. What if in direct speech the main verb is already in Past Perfect? In this case, the verb in Past Perfect remains unchanged. The verb in Past Perfect in direct speech remains in Past Perfect in indirect speech too. He says, “I had bought I new house” He said that he had bought a new house. I live in Ukraine. Now, this website is the only source of money I have. If you would like to thank me for the articles I wrote, you can click Buy me a coffee . Thank you! ❤❤❤ Recommended reading: Complex Sentence in English. Related Posts Prepositions of Place in English Grammar Prepositions of Reason and Purpose Direct Word Order in English Sentences Word Order in Interrogative Sentence Difference Between IN ON AT as Prepositions of Place Zero Conditional In EnglishTrending now.   Direct and Indirect Speech, Rules Chart PDFDirect and indirect speech is used in many situations while conversation. In this article, we will learn the rules of direct and indirect speech.  Table of Contents Direct and Indirect Speech : Direct speech is a method of reporting what someone has said in their own words. It is frequently surrounded by quotation marks. Indirect speaking is a method of relaying what someone has said without using their precise words. It is frequently preceded by a verb like “said,” “told,” or “asked.” Direct and Indirect Speech- DefinitionDirect and Indirect Speech: For some children, the difference between direct and indirect speech can be difficult. In order to explain an event or action, we frequently need to quote someone. This article will clear all your doubts regarding Direct and Indirect Speech. Direct and Indirect Speech are the two types of speech that are used to explain what other people say (or reported Speech).  Direct SpeechThe exact same words are quoted using direct speech. When writing in direct speech, we enclose the said words in quotation marks (“”) and leave them alone. We might be writing in inverted commas what is being said (for instance, during a phone call) or subsequently enquiring about a past conversation. For examples: - Rohan said, “There is a dog inside the house.”
- They said, “We will go to the party.”
- She said, “I don’t know.”
 Indirect SpeechWe use indirect speech when we don’t use the exact copy of the speaker’s words. In simple words, we can say that in indirect speech we convey what someone has said but in our own words. No inverted commas will be used in indirect speech. Instead of commas ‘that’ conjunction will be used. - Rohan said, “There is a dog inside the house.” (Direct Speech)
- Rohan said that there was a dog inside the house. (Indirect Speech)
- They said, “We will go to the party.” (Direct Speech)
- They said that they would go to the party. (Indirect Speech)
- She said, “I don’t know.” (Direct Speech)
- She said that she didn’t know. (Indirect Speech)
 Direct and Indirect Speech RulesRules that must be followed while using direct and indirect speech are given below. Follow and practice these rules to change direct speech into indirect speech. Before learning the rules you need to know these two parts of Direct and Indirect Speech. Reporting Verb: Direct speech has two parts, the first part of the sentence is known as reporting verb as it tells about the person who is speaking (Rohan said, He says, etc.). For Examples: - He says, “I have done my work”.
- The teacher says, “The Earth is round.”
In the above two sentences, the first part is reporting verbs. In the first sentence, ‘He says’ is reporting verb and in the second sentence, ‘The teacher says’ is reporting verb. Reported Speech : The second part of the sentence or the words which is actually said by the speaker is known as reported speech. In the above two sentences, the second part is reported speech which is enclosed in inverted commas. In the first sentence, ‘I have done my work’ is reported speech and in the second sentence, ‘The Earth is round’ is reported speech.  All Direct Indirect Speech RulesDirect and Indirect Speech Rule 1. Remove inverted commas and use ‘that’: While changing direct speech into indirect speech, remove inverted commas and use that instead of commas. Direct to Indirect speech Example: - Rahul says, “There are eight planets.” (Direct Speech)
- Rahul says that there are eight planets. (Indirect Speech)
As in the above sentence inverted commas are removed in indirect speech and the conjunction ‘that’ is also used. Note:- In indirect speech, tense does not change: - If the reported speech (the part of the sentence which is inside inverted commas) is habitual action or universal truth.
- If the reporting verb is in the present tense then the tense will not be changed.
- My teacher says, “The earth is round.”
In the above sentence, reporting verb is in the present tense so it will not change into the past and reported speech is also a universal truth that can not be changed.  Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 2. Change in tense: When the reporting verb is in the past tense then reported speech will be changed into past tense in indirect speech. - She said, “I will go.” (Direct Speech)
- She said that she would go. (Indirect Speech)
As, in the above sentence reporting verb is in the past tense so we have converted reported speech into past tense in indirect speech i.e, will-would. Read the following table to learn the conversion of tenses | | | | Simple Present | Simple Past | | Present Continuous | Past Continuous | | Present Perfect | Past Perfect | | Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | | Simple Past | Past Perfect | | Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | | Will | Would | | May | Might | | Can | Could | | Shall | Should | Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 3. Change in Pronoun: The pronoun or subject of the reported speech is changed according to the subject or the pronoun of the reporting verb (first part) of the sentence. The possessive pronouns (his, hers, mine) are also changed sometimes according to the personal or object pronoun. Direct to Indirect speech Example - He said, “I eat an apple.” (Direct Speech)
- He said that he ate an apple. (Indirect Speech)
In the above example ‘I’ is changed into ‘he’ according to the reporting verb (first part) and the tense is also changed because reporting verb (first part) is in the past tense. Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 4. Change in Time: If the word related to time is given in the sentence then it will be changed in indirect speech. Some rules must be followed while doing this and those are given in the following table. | | | | Today | That day | | Tomorrow | Next day or the following day | | Yesterday | Previous day | | Now | Then | | Tonight | That night | | Yesterday night | Previous night | | Tomorrow night | Following night | | Here | There | Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 5. Interrogative sentences: No conjunction is used, if a sentence in direct speech starts with a question word (what/where/when) as the “question-word” itself acts as conjunction. - “Where are you going?” asked the boy. (Direct Speech)
- The boy asked where I was going. (Indirect Speech)
Note: While changing the interrogative sentence into indirect speech remove the question mark ‘?’. Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 6. Yes/No Interrogative sentences: If a direct speech sentence starts with an auxiliary verb/helping verb, the joining clause will be changed into if or whether. - He asked me “Do you come with me?” (Direct Speech)
- He enquired whether/if I am coming with him. (Indirect Speech)
Note: While changing the interrogative sentence reporting verbs (verbs used in the first part) such as ‘said/ said to’ changes to enquired, asked, or demanded. Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 7. Request, Command, Wished, Enquired: Some verbs, such as requested, ordered, urged, and advised, are used in indirect speech. For the negative statements, the word forbidden is used. As a result, in indirect communication, the imperative mood that is present in direct speech is replaced by the infinitive word. - She said to her, “Please do this work.” (Direct Speech)
- She requested her to complete that work. (Indirect Speech)
Direct and Indirect Speech Rule 8. Exclamatory Sentence: Interjections words are removed from exclamatory sentences that express (grief, sorrow, delight, or applaud) and the sentence is transformed into an assertive sentence. - Students said, “Hurrah! India has won the match.”(Direct Speech)
- Students exclaimed with joy that India had won the match.(Indirect Speech)
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules Chart Direct and Indirect Speech Rules PDFClick here to download Direct Indirect Speech Rules PDF Direct and Indirect Speech- QNAQue. what are direct and indirect speech with examples. Ans. Direct Speech and Indirect Speech are the two types of speech that are used to explain what other people say (or reported Speech). Que. What are the three rules of direct and indirect speech?Ans. The common three rules of direct and indirect speech are: a) Remove inverted commas and use ‘that’. b) Change in tense. c) Change in Pronoun. Que. How can I learn direct and indirect speech?Ans. Read and learn all the rules while changing direct speech into indirect speech and practice it on daily basis. Que. What are the 4 types of reported speech?Ans. The four types of reported speech can be Assertive/Declarative, Imperative, Interrogative, and Exclamatory . Que. What are the two parts of direct speech?Ans. The two parts of direct speech are reporting verb and reported speech. Sharing is caring! Ans. The common three rules of direct and indirect speech are: a) Remove inverted commas and use 'that'. b) Change in tense. c) Change in Pronoun. Ans. The four types of reported speech can be Assertive/Declarative, Imperative, Interrogative, and Exclamatory.  Join the Conversation Some more Examples Please… Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked * Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Leave a comment Trending Articles- NEET PG Admit Card 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CBSE 10th Compartment Result 2024
- NEET Syllabus 2025
- NEET Counselling 2024
- NEET Cut Off 2024
 CBSE Board Exam 2024- CBSE Previous Year Papers
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Previous Year paper
- CUET Participating College & Universities
- JEE Main Syllabus 2025
- NEET State wise Cut off
- NEET Rank Predictor
- NEET OMR Sheet
- NEET College Predictor
Recent Posts- Adjectives List A-Z, Download List of Adjectives PDF
- Demonstrative Adjectives- Definition, Examples, Rules, Exercise
- Formal Letter Format- Check Official Letter Writing in English for Class 10
- Parts of Speech – Know 8 Types Parts of Speech Definition, Examples in Sentence
- Tongue Twisters in English to Improve Your Speaking
- Interjections- Meaning, Definition, Examples, Rules, Types
- Words That Start with X, Places, Food, Flowers, Animal Names with X
- Noun: Definition, Types and Examples
- Interrogative Adjectives: Explanation, Definition, Examples, Exercise
- Possessive Adjectives: Definition, Examples, Common Mistakes to Avoid, Exercise
- Compound Adjectives: Meaning, Definition, Examples, Types, List
- Adverbial Clauses: Meaning, Definition, Examples, How to Use, Placement Rule
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense Formula, Structure, Examples, Rules in Hindi/English
- Speech Writing Examples And Topics For Class 11, Check Format
- Application for TC- Check TC Application for School
- Interrogative Pronoun – Definition, Examples, How to Use, Key Points
- Indefinite Pronouns: Definition, Examples, How to Use, Exercise
- Subject Pronouns: Definition, Examples and Usage
- Object Pronouns: Definition, Examples, Usage and Types
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Meaning, Definition, Examples
- Conjunctive Adverbs- Definition, Examples, Rules, Exercise
- Action Verbs – Definition, Examples, How to Use, Differences, List
- Finite and Non-finite Verbs: Definition, Examples, Difference, Forms, Rules
- Spot The Error and Correct The Sentence in English with Examples
- Stative Verbs – Definition, Examples, How to Use, List
- Linking Verbs- Definition, Examples, Types, How to Use, Exercise
- Regular Verbs- Meaning, Examples, How to Conjugate, List
- Coordinating Conjunctions: Definition, List, Rules, Types, Exercises
- Correlative Conjunctions- Definition, Examples, Rules, Exercises with Answers
- Subordinating Conjunctions- Meaning, Definition, List, Examples
IMPORTANT EXAMSNcert solutions. - NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT Class 10
- NCERT Class 9
NCERT BooksSchool syllabus. - CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 9
- JEE Mains 2024
Our Other Websites- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Current Affairs
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School
 Get all your queries solved in one single place. We at Adda247 school strive each day to provide you the best material across the online education industry. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day. Download Adda247 App Follow us on - Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo? We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you Direct Indirect Speech - Verbs and tenses
- Prepositions
- Articles,Vowels and Consonants
- Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Gender-Masculine and Feminine
- Singular and Plural Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Direct Indirect Speech Rules of Past PerfectLast updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo  - In this case,there is no change
- In this case,Past Perfect of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect of Indirect Speech
The teenager said"I had pizza for lunch" The teenager said that he had pizza for lunch The rich man said"I had 2 private jets The rich man said that he had 2 private jets Father said"I had passed school with 80%" Father said that he had passed school with 80% Mother said"I had not received any phone call " Mother said that she had not received any phone call  CA Maninder SinghCA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years. He also provides Accounts Tax GST Training in Delhi, Kerala and online. Get E-filing Return Practice Watch videos and do assignments Add more skills to your resume Get Professional Certification in Accounts and Taxation Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black. English Study Here24 Direct and Indirect Speech Examples with Tenses 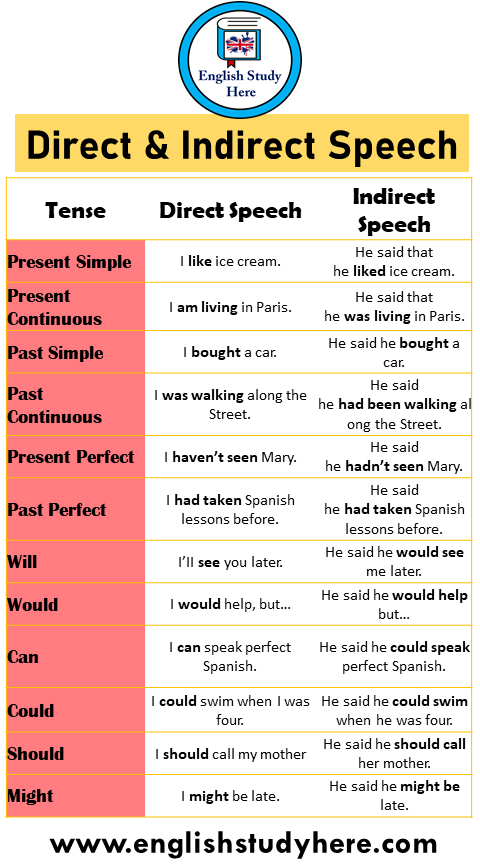 | Tense | Direct Speech | Indirect Speech | | Present Simple | I ice cream. | He said that he ice cream. | Present
Continuous | I in Paris. | He said that he in Paris. | | Past Simple | I a car. | He said he a car. | Past
Continuous | I along the Street. | He said he along the Street. | | Present Perfect | I Mary. | He said he Mary. | | Past Perfect | I Spanish lessons before. | He said he Spanish lessons before. | | Will | I’II you later. | He said he me later. | | Would | I help, but… | He said he but… | | Can | I speak perfect Spanish. | He said he perfect Spanish. | | Could | I swim when I was four. | He said he when he was four. | | Should | I call my mother | He said he her mother. | | Might | I be late. | He said he late. |
Related Posts Prepositional Phrases in English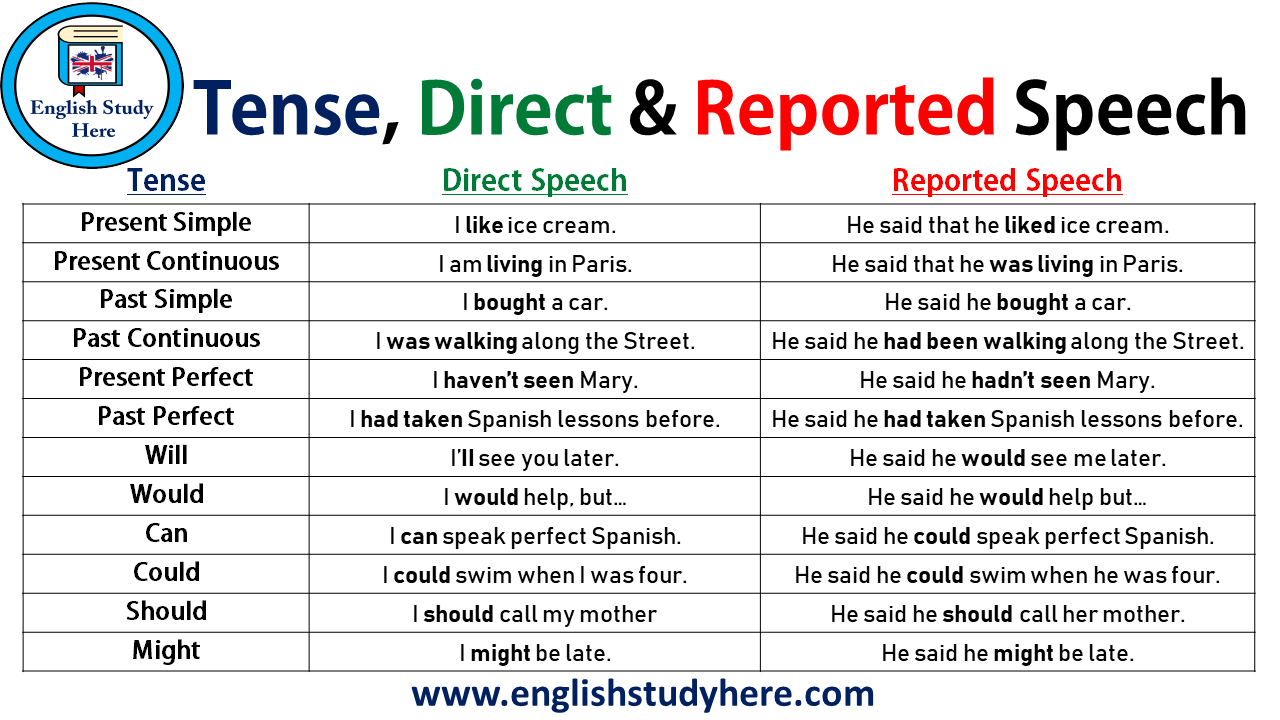 Tense, Direct and Reported Speech Using A few and Few in EnglishAbout the author.   | 





















































IMAGES
COMMENTS
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in Past Continuous Tense. If reported verb is in Past Tense, reported speech will change from Past Continuous Tense to Past Perfect Continuous Tense. Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. The government said, "We were planning a new bill.". The government said that they had been planning a new bill.
In this case,there is no changePast Perfect Continuous of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect Continuous of Indirect SpeechThe teacher said"I had been watching you"-a-The teacher said I had been watching you-ea-The girl said"I had been going to Aerobics classes"-a-The girl said I had been going to Ae.
The Past Perfect Continuous tense in English is used to describe actions or states that were ongoing up to a specific time in the past. The structure of a Past Perfect Continuous sentence is: Subject + had been + present participle. Let's explore some examples to understand this better: Example 1: I had been walking to work before it started ...
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense talks about an action that started in the past and continued up until another point in the past. Positive Sentence: S + had + been + V-ing ( present participle) +…. Example: They had been playing tennis. Negative Sentence: S + had not/ hadn't + been +V-ing (present participle) +…. Example:
The past perfect continuous tense is generally used in a sentence to depict an action that started at some time in the past and continued until a specific time in the past. It is also called the past perfect progressive tense since it refers to an action that had been progressing until a certain point in the past. Q2.
The formula for the past perfect continuous tense is had been + [present participle (root form of verb + -ing)]. Unlike the present perfect continuous, which indicates an action that began in the past and has continued up to the present, the past perfect continuous indicates something that began in the past, continued in the past, and also ...
Here are the steps on how to do so: 1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. The quotation marks are the primary indication of a direct speech. Therefore, it is crucial to take them out if you are forming an indirect one. 2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word "that" after it.
Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech. Example: He said to me, "I was happy" changes into He told me that he had been happy. Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech. Example: The peon said, "The professor is teaching in that ...
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
Tense backshift. As can be seen in the examples above, the verbs in the present perfect, present continuous and present simple tenses in the original statements changed into their corresponding past equivalents (past perfect, past continuous and past simple) in indirect speech. This process is called tense backshift.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
If the end of the sentence falls at the end of the spoken words, a full stop (question mark or exclamation mark) is placed inside the closing quotation mark. (example 2) Anne said, "I love dogs.". If the direct speech is broken up by a reporting clause, a comma is placed inside the first closing speech mark, as already seen in example 1 ...
Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense. Direct: She said, "They were coming to meet me." Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her. Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same. Direct: He said, "They had come to meet me." Indirect: He said that they had come to ...
For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules Direct and Indirect of Past Perfect Progressive Tense Change: As a rule, when we convey a message we go one tense back, but remember we have to use the same tense both in quoted and reported speech when we convey a message from past perfect ...
As a rule, whenever we change a sentence from quoted speech into reported speech, we go one tense back. But if we have past perfect tense in direct speech, we use the same tense in indirect speech. Affirmatives. Direct speech: RP, +, + S + had + V3 + ROTS. I said to him, "They had played cricket.". Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had + V3 ...
Reporting the direct speech we follow the rule of "one tense back". Since that we are able to use Past Perfect instead of Past Simple as well as leave it the same. The Past Perfect tense stays the Past Perfect. I saw the we can leave the Past Continuous the same. I found the example where it becomes Past Perfect Continuous, though. Example:
If in direct speech we use tenses: Past Continuous; Past Perfect; Past Perfect Continuous; then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the sentence, we do not translate the sentence into the past. He says, "I had fixed my car." He said he had fixed his car. He says, "I was skiing." He said he was skiing.
Direct to Indirect speech Example. He said, "I eat an apple." (Direct Speech) He said that he ate an apple. (Indirect Speech) In the above example 'I' is changed into 'he' according to the reporting verb (first part) and the tense is also changed because reporting verb (first part) is in the past tense. Direct and Indirect Speech ...
View Answer View Answer. Next: Direct Indirect Speech Rules of Present Perfect → Go Ad-free. If Direct Speech is Past Continous−−>In indirect Form it becomes Past Perfect ContinousExampleDirect SpeechMom said"I was cooking your favorite dish"Indirect SpeechMom said that she had been cooking my favorite dish"Note:-In Direct Speech,we use ...
Indirect speech: He said that Sara was going to school. (Tense changed) Rules for change of tense and examples are as follows: Present simple tense into Past simple tense. Present continuous tense into Past continuous tense. Present perfect tense into Past perfect tense. Present perfect continuous tense into Past perfect continuous tense.
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo. In this case,there is no change. In this case,Past Perfect of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect of Indirect Speech. The teenager said"I had pizza for lunch". View Answer View Answer. The rich man said"I had 2 private jets.
Tense: Direct Speech: Indirect Speech: Present Simple: I like ice cream. He said that he liked ice cream. Present Continuous: I am living in Paris. He said that he was living in Paris. Past Simple: I bought a car. He said he bought a car. Past Continuous: I was walking along the Street. He said he had been walking along the Street. Present Perfect