
Home > Learn More About Creative writing > Business Writing Vs Creative Writing Core Comparision

Business Writing Vs Creative Writing Core Comparision

Free Counselling :
IN +91 9899577620
US +1 2093823469
Table of Contents
What is Writing
Writing is the way of expressing our ideas and thought on a piece of paper. Of course, nowadays writer does it by typing on a computer screen or laptop screen. So, it is the medium of communication. For the learning of any new language there are four skills that we should qualify for:
1. Listening
2. Speaking
4. Writing.
Content Writing Courses with Gold Membership
45-min online masterclass with skill certification on completion
Mentored By Chetan Bhagat
Access Expires in 24Hrs
Register Now for Free

Upcoming Batches of Creative Writing Courses :-
| Batch | Mode | Price | To Enrol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Live Virtual Classroom | 9500 |
Generally, when we are in the phase of learning our native language, we first listen to it, based on which we started to speak. Then the skill of reading is developed, based on which ultimately the fourth skill writing comes. For knowing of any particular language these skills are underlined ones. These language skills are related to each other with the way of direction of communication and the methods of communication.
Types Of Writing
There are different types of writing from informal to formal types such as:
Content Writing Course with Gold Membership
Upcoming Batches of Content Writing Course:-
| Batch | Mode | Price | To Enrol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Live Virtual Classroom | 17500 |
1. Business and Marketing Writing
2. Technical and Research Writing
3. Creative Writing
4. Academic Writing
Let’s explore more and have some detailed information about Business writing and Creative writing.

About Business Writing
It is the type of writing that provides significant information to the reader. In Business writing, the main aim is to transmit information to a reader. Clear language and concise information are required in Business Writing to help the reader to understand the information written. Business writing is the foundation of any business. In this type of writing, the writer only provides the facts. Formal wording and tone are used in Business writing. And there should be to the point information about any product or services. However cordial tone is necessary to build trust and engagement of readers to the content written. Some main factors to consider in Business writing is:-
1. Information should be accurate, complete, and must be relevant to the readers.
2. From the informatory bundle, there should be an extract of only that information that is relevant and is easy to understand.
3. Must be simple to read, as highlighting the important terms with color or underline the words, using the number or bullet points, usage of a short paragraph, giving the proper heading or title.
4. Use of correct grammar is necessary as these attributes are of much importance in Business Writing.
Business writing as a Career
There is plenty of options for business writing. A business writer works for a business to write proposals, business reports, and plans. They also write the information about any particular product or services. The business writer writes the content to promote or advertise the brand of any product. It includes writing for websites, advertisements, brochures, catalogs, etc. The Business writer also works as a reporter to write stories about economics and businesses. They can work as a full-time employee in a company or can be a freelance contractor. Then there are agencies such as brand promoting companies, web agencies, design agencies, and language consultancy that give employment to both full-time and freelance writers. So, there is your choice of specializing in anything from social media to the corporate office to web editing.
Check- Henry Harvin’s technical writing course in Bangalore
Qualification for Business Writing
The qualification required for Business writing is a Bachelor’s degree in communications, journalism, or business. However, it is not mandatory. In some companies or organizations, it is required. The main pre-requisite is your interest in writing. Since overall your work or portfolio is the main thing that is asked for. And now due to the rise of self-publishing websites, there is the scope of self-publishing our writing. Although if you already qualify for a diploma, degree, etc, in any particular area, it can also be used in the field of Business writing. E.g. if you have qualifications in environmental science you can become an expert in your writing extract about the environment in newspapers, magazines, etc.
Types of Business Writing
For becoming a successful business writer there are some types of Business writing you should be familiar with. Such as E-mail writing, Business Report Writing, Memo Writing, Handbook Writing, Newsletter, Copywriting, Writing product descriptions and reviews, press release, Meeting agendas, resume and cover letter writing, Writing for the landing page of any company website, writing for responses to customer queries and complaints.
Business Writing Course
For effective business writing skill and making your content ready for the market there are the number of the institute and academy providing the required training. Developing your writing skill is an essential career move. As writing always matters, either you are composing emails, memoirs, business proposals, newsletters, making a presentation, or even making your resume stand out, good writing is the skill necessary for a successful business. Business Writing is one of the most important skills for personal and organizational success. These courses will help you to identify and communicate your writing content to the intended audience.
Also check- Henry Harvin’s Technical Writing course in Mumbai
summary some of the commonly asked questions:-
For market place reputation of any particular organization or company and to generate more revenue it is essential to write well-written business proposals, clearly written memos, effective marketing material, systematic email, report writing, etc.
There are many forms of Business Writing as: E-mails Reports Memos Letters Writing for social media Press Release Copywriting Product Description Resume Writing Training & Educational Content etc. So, it refers to any form of writing that is used within the Business environment.
It is the purposeful piece of writing that provides facts or relevant information to the reader, gives knowledge about something, and influences someone to take action.
A Business writer has the role of writing website content, press release, proposals, newsletter, and articles. They may be responsible for conducting necessary research and fact-checking data. Some business writers work for the time of regular office hours or some opt for part-time work or freelance job. Freelance writers are typically paid according to the assignment done. They have the flexibility of setting their schedule and place.
There are many online Business Writing Courses. A particular course should cover exactly what you want from it. Any of the specific skills which you want to learn from it. The business writing course which you choose should start with the basic level and then it should reach the more comprehensive approach. So some of the choices are as follows:- 1. Copy Writing Course by Henry Harvin Education. 2. Business Communication skill: Business Writing And Grammar by Udemy 3. Tips for Better Business Writing by LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com) 4. American Management Association 5. High Impact Business Writing by University of California Irvine Division of Continuing Education 6. Business Writing by University of Colorado Boulder 7. Universal Class Business Course
About Creative Writing
Creative writing is that form of writing which involves the usage of narrative craft, imagination tools, character development, and the use of different figures of speeches or with various methods of poetry. So that it gives beauty to the piece of writing. In Creative writing, both fictional and non-fictional work comes under this category. Novels, short stories, biographies, poems are all types of Creative Writing. In this type of writing, you can step into the imaginary world. It is the art of expressing ideas and thoughts in imaginary ways. When you are in the field of creative writing your imagination must be inflow. Creative Writing is a form of entertainment. This form of writing we can find in T.V. serials, movies, books, poems, and other mediums.
Creative writing can be a part of professional writing as well as there are types of :
Creative Content Writing
Creative SEO Writing
Creative Blog Writing
Creative Copy Writing
Creative Script Writing
Creative Proposal Writing
Creative Writing as a career
The creative writer has plenty of opportunities available. As creative writing is almost used in every field. Creative writing is very useful in business. Be it the designing sentence for advertisement, to write a quote for the product, or even for designing brand name creative writing is used. Writers working in marketing and advertising companies create write-ups that sell products. Writing copy for marketing campaigns and ads is the job of a creative writer. They can work as a fiction writer, scriptwriter, publisher, novelist, creative writing editor, proofreader, entrepreneur, author, and many other job profiles are there which a creative writer can opt for.
Please check- Henry Harvin’s Content writing plus creative writing certification
Qualification for Creative Writing
Creative writing degree for undergraduates students in college are a Bachelor of Fine Arts. Students can also pursue a higher degree of Master of Fine Arts in Creative Writing. Most employers of creative writer and editor have a preference of candidate who possesses the bachelor’s degree. A graduate degree in creative writing may lead to a job that requires creativity, research, writing, and communication of ideas. Having a graduate degree and master’s degree in creative writing allows the students to focus on studies in fiction, creative non-fiction, and poetry. The creative writer usually starts their writing journey with short stories or poetry. The creative writing students should participate in extracurricular writing-based activities such as school or college-based literary magazines or newspapers, writing contests, publishing clubs, etc. Creative writers seeking to progress their education and want to learn and improve new writing techniques can participate in workshops or writing classes that are available online or through the organization, and there are also seminars provided by successful authors. Then there is freelance writing which is also one of the important career opportunities for creative writers. A freelance creative writer can earn a good income by submitting short stories, poems, blogs, etc., or other creative pieces to the organization that publishes both fiction and non-fiction write-ups.
Also check- Creative writing course in Hyderabad
Types Of Creative Writing
There is another form of Creative writing also, that you can find out except fiction and poetry which are the main form of creative writing. As generally writer specializes in one form or genre and becomes efficient in that. However, working with another type of writing is beneficial as it is a good way to acquire a variety of techniques in your writing. So, these are some of the types as; memoir, journals, diaries, letters, essays, poetry, song lyrics, script, storytelling, speech writing, vignettes, free writing. Then there is writing for the screen and stage, known as screenwriting that is often taught separately and comes under the category of creative writing. Experimenting with different forms is good as it prevents your work to be repeated and overladen with a specific form.
Creative Writing Course-
Creative Writing is an ability that requires strong imaginary powers to converts any particular thoughts, imagination, and memories into words. You have to open the door of your imagination for the free-flowing of your thoughts. With the help of writing skills and techniques, this ability and talent can be more enhanced. Today there are great opportunities for creative writers to make a path for themselves in the field of authors, poets, scriptwriters, etc. Writing like any other craft or art form can be taught. There is a wide range of courses available for Creative writing, but it is important to choose the one that suits you and your unique style, not just only in writing but in personality also. Any of the course which you choose should make good improvement in you as a writer, gives confidence in your writing, gives you the understanding of what type of writing you are good at, what should need more improvements and what is working in your writing way. There are many types of courses available to choose from as full-time courses, short courses, home study, night classes, residential courses, and online courses. Some courses all types of creative writing styles, some focuses more on specific genre or aspects such as short stories, books writing, etc.
Difference between Business writing versus Creative writing
There is a clear difference between Business writing and Creative writing. Business writing is a purposeful piece of writing that targets obtaining a successful business response from the reader. Whereas in Creative writing, the writer puts their imaginary ideas or thoughts into engaging words.
Differences between Business Writing and Creative Writing
1. The purpose of Business writing is to provide the facts. And to compel the reader or viewer to say yes to something for making any purchase. The formal tone is used in Business writing. It is written clearly and briefly. The purpose of Creative writing is to reveal information into bits and pieces so that there is a build-up of suspense in readers. Their purpose is not to sell anything but to take their readers into the pretend world. It is a two-way relationship between the thoughts of writer and reader. As the writer has to think in view of the reader’s thoughts and emotions in mind while writing.
2.Business writing is reality-based. And is predictable. It usually involves asking or action response at the end whereas in Creative writing there can be the occurrence of unpredictable events as it gives an infinite number of thinking approaches to the writers.
3.The goals of business writing and creative writing are different. Creative writing is meant for entertainment. And to appreciate the writer’s imagination. Business writing is to handle professional proposals or plans.
4.In Business Writing there are mainly four types of writing: Instructional Writing (E.g. user manual, specifications, memos), Informational writing (E.g. reports, financial statement, write-up of the meeting), persuasive writing( Press release, sales email, proposals), transactional writing( E-mails, official letters). Whereas Creative writing encompasses a wide array of writing types. Almost everything from poetic works to the works of fiction and nonfiction can be in the range of creative writing genres. Some of the varieties in which you can use any choice of word, phrases, and techniques are:- poetry, play, lyrics, speeches, stories, etc.
5.One more point of difference is that there are write-ups of creative writing that may imitate any of the business writing styles in their work, but there is a rare example one can find in business writing where the Creative writing style is adopted. As in Business writing, standard style and structures are adopted.
About creative writing there is the famous quote- “Creativity is the brain’s invisible muscle—that when used and exercised routinely—becomes better and stronger.” – Ashley Ormon
About business writing for successful professional deals business writer has to keep in mind that “Business has only two functions: marketing and innovation”- Milan Kundera
However, from time to time business writing styles and creative writing styles may be related to each other. Business writing seeks to share information, creative writing seeks the best way to share it. Learning the ins and out of one form of writing can open the door to another form. As writing skills are transferrable, and once it is mastered you can use them practically in any genre of writing. But knowing the difference between the two writing is an important factor. Since it is the essential aspect for the writer to know while presenting their content to their readers.
Writing skills are an important part of communication. Language is the medium of communicating our ideas or thoughts in the form of writing. The main task in writing is to present the ideas and thoughts in an organized and logical way. Writing skills has also many other advantages as it is a way of improving your communication skills, it develops your ability to think critically, it enhances your knowledge due to vast research and reading, it helps you expand your abilities, will give you flexible career options. Writing is the primary way business gets done in today’s competitive world. When writing is done well business also gets successful. Writing has become necessary in academic, professional, technical, engineering, and scientific workplaces. Good writing skill helps your business in several ways. It let you express yourself, helps you become more clear and concise in your vision. With writing skill, you can communicate clearly with others and can also create useful resources for the workplace.
Recommended Reads
- Content Writing Courses Online
- Content Writing Courses in Kochi
- Content Writing Courses in Kolkata
- Content Writing Course in Bangalore
- Content Writing Courses in Delhi NCR
- Content Writing Courses in Navi Mumbai
Ans. It is the form of writing that expresses the ideas and thoughts of a writer imaginatively. It is the medium of expressing the writer’s emotions feelings, experiences that are obtained at a conscious or subconscious level. Its main goal is not to present the fact but to express the feeling of the writer. Information given can be real or can be imaginary.
Ans. Good writing skills are highly important in the workplace. In the online job market, creative writing is one of the trendiest terms used. The creative writer’s job is to write editorial articles, promotional marketing materials, screenplays, etc. with the artistic choice of written words. There are options in different fields for creative writers. As in advertising companies, public relations firms, Corporate offices, etc. The Creative writer may be self-employed or they may develop creative work for academic, business, and publishing companies.
Ans. Creative Writing is the way to express your feeling and to entertain others. There are different types of creative writing found in these writing categories: poems, novels, screenplays, short stories, blogging, speeches, etc.
Ans. Creative writing can provide you with endless entertainment as it allows you to let your imagination run freely. If you are thinking to step into the field of creative writing or want to improve your creative writing skill to become a better writer. There are lots of courses available that help you in achieving your goal. Some of the selected ones are: 1. Creative Writing Course from Henry Harvin Education 2. Creative Writing: The Full Course from Udemy 3. Guardian Writing Masterclasses 4. Creative Writing Value Suite from ED2GO 5. The Writer’s Toolkit:6 steps to a successful writing habit course(SkillShare) 6. Creative Writing: The craft of plot from Coursera 7. Start writing fiction course from the open university( Future learn).
Post Graduate Program in Content Writing by Henry Harvin®
Ranks Amongst Top #5 Upskilling Courses of all time in 2021 by India Today

Recommended Programs
*Learn from South Asia's Oldest Content Writing Course | Recognized by American Association of EFL, Content Writing Association of India, UK Cert, UKAF & MSME | Guaranteed Live Projects & Internship Opportunity.
Technical Writing Course with Gold Membership
*A cutting-edge Technical Writing Course which teaches you the fine art of transforming data and information accumulated through a process or experimental work into technical documentations and guides.
Creative Writing Courses with Gold Membership
Henry Harvin® Creative Writing Course Ranks#1 in India by The Statesman! Creative Master the creative writing skills to compose engaging Fiction, Creative Nonfiction, Drama, and Poetry that will snap a reader’s curiosity from the advent to end of your write-up.
Medical Writing Training Course and Certificate
A one-of-a-kind Medical Writing course which helps you get a thorough understanding of pharmaceutical regulatory writing as well as medico-marketing writing. Strengthen your writing prowess as you boost your skills as a medical and scientific writer. The Certified Medical Writer(CMW) certification is your key to success.
Recommended videos for you
Best Content Writing Tutorial for Beginners
Free Content Writing Tutorial for Beginners
Best Technical Writing Course
Technical Writing For Beginners
Creative Writing Course Tutorial
Understanding Creative Writing
Medical Writing Tutorials for Beginners

WHAT IS EFL? HOW DOES EFL DIFFER FROM ESL?

SEO Content Writing vs. SEO Copywriting: Understanding the Difference
Related posts.

Top Career Opportunities in Creative Writing in 2024

Top 10 Ranked Creative Writing Courses in Thiruvananthapuram in 2024 (Updated)

Top 50 Websites to Submit Your Creative Writing

Creative Writing Course in Jaipur in 2024 [Updated]

Best Creative Writing Course In Bangalore in 2024 [Updated]

Best Creative writing course in Varanasi in 2024 [Updated]
.webp)
Our Career Advisor will give you a call shortly

Just purchased a course
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Noida Address:
Henry Harvin House, B-12, Sector 6, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
FREE 15min Course Guidance Session:
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Science of Strong Business Writing
- Bill Birchard

Lessons from neurobiology
Brain scans are showing us in new detail exactly what entices readers. Scientists can see a group of midbrain neurons—the “reward circuit”—light up as people respond to everything from a simple metaphor to an unexpected story twist. The big takeaway? Whether you’re crafting an email to a colleague or an important report for the board, you can write in a way that delights readers on a primal level, releasing pleasure chemicals in their brains.
Bill Birchard is an author and writing coach who’s worked with many successful businesspeople. He’s drawn on that experience and his review of the scientific literature to identify eight features of satisfying writing: simplicity, specificity, surprise, stirring language, seductiveness, smart ideas, social content, and storytelling. In this article, he shares tips for using those eight S’s to captivate readers and help your message stick.
Strong writing skills are essential for anyone in business. You need them to effectively communicate with colleagues, employees, and bosses and to sell any ideas, products, or services you’re offering.
- Bill Birchard is a business author and book-writing coach. His Writing for Impact: 8 Secrets from Science That Will Fire Up Your Reader’s Brain will be published by HarperCollins Leadership in April 2023. His previous books include Merchants of Virtue, Stairway to Earth, Nature’s Keepers, Counting What Counts, and others. For more writing tactics, see his website .
Partner Center
Creative Writing vs. Content Writing: What’s the Difference?

A creative content writer isn’t the same as a creative writer. Did that come as a shocker? A lot of people confuse the two fields of writing because they are often used interchangeably. Although some aspects of the two overlap, the creative writing vs. content writing debate continues.
In this blog, we’ll cover the basics of both types of writing. Moreover, we will draw the key points of differences between creative writing and content writing. It will help you choose the writing style that works best for you.
What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a style of writing that draws inspiration from the subconscious feelings, emotions, attitudes, prejudices, and experiences of the writer. To put it simply, its scope is limitless. It can cover a variety of genres and forms, from long academic essays to Shakespearan poems.
Creative writing, as the name suggests, relies solely on the creative juices flowing in your brain. It is less about information and more about inspiration. It is also not bound by rules and techniques that govern other styles (like content writing). People often confuse creative writing with fiction. But this style of writing spans both fictional and non-fictional works as long as abundant artistic freedom is allowed.
Creative writing is also dependent on the perception of the reader, and perception can vary. For example, a certain piece of creative writing (like a poem) may mean something to you. But other people may interpret it in different ways, owing to their experiences. Creative writing uses many literary devices like metaphors, alliteration, hyperbole, etc.
Examples of Creative Writing
Creative writing can take several forms. Some of the most common examples you must have come across include the following:
● Poetry: The mesmerizing verses of John Keats or the sonnets of Shakespear are all categorized under creative writing. Poetry is one of the most titillating and thought-provoking forms of creative writing.
● Pros: It’s a written form of ordinary language, without any rhythms or rhymes. Stories, novels, or folktales may all come under prose.
● Screenplays and scripts: These are written pieces that give direction to an act on stage or screen. That’s probably how a show you are currently binge-watching was created.
What Is Content Writing?
Content writing is a style of writing that is largely characterized by information and objective. The difference between content and creative writing is that the former aims to fulfill a specific purpose or dispense crucial information to readers. Content writing is usually done on online channels nowadays.
The article that you are reading right now is a form of content writing too. Content writing is part of the marketing, PR, sales, legal, and compliance activities of businesses. Content can also be produced by individuals on personal websites or blogs.
Another difference between creative writing and content writing is structure and rules. Content writing is often governed by writing rules, SEO guidelines , and the needs of the client/business. It can not be entirely left to the perception of the readers. Information has to be accurate and in line with business objectives.

Examples of Content Writing
Content is everywhere if you look closely. Here are some of the most common examples of content writing that you might come across often:
● Blogs: Long-form pieces on websites form a major portion of online content, especially on search engines. These are informative, objective, and solution-oriented.
● Social media content: The various types of posts, Reels, Stories, carousels, and other content you see on social media are created by content writers. This content is also used to inform, engage, or market to the audience.
● Product descriptions: Written pieces specifying different characteristics of a product (whether on online marketplaces like Amazon or on product packaging) also come under content writing.
● Research papers: White papers, published studies, journal articles, and other such types of research content are also an example of content writing.
● Business documents: Proposals, decks, policy documents, mandates, legal paperwork, etc., are also written by content writers, based on certain organizational objectives.
Creative Writing vs. Content Writing: Key Differences
There are vast differences between creative writing and content writing, based on various factors. Up next, we will compare creative writing vs. content writing on several parameters.
Creative writing has varied tones based on the mood of the writer and the type of written piece. The writer has the freedom to choose a tone best suited for their work. It can be jubilant, emotional, fearful, hurtful, consolatory, hopeful, dejected, and more. The artist isn’t confined to a tone that is deemed “appropriate.”
Content writers, whether they are freelancers or working for a website content writing service , have to keep a specific brand tone in mind. Options are also often limited. Content writing pieces often have informative, serious, optimistic, and objective tones. Nowadays, content writers do add a creative touch to their tone, but the extent is governed by the client.
This is another major point of difference between creative writing and content writing. Creative writing is often done with the purpose of expressing, entertaining, and engaging. Sometimes, writers may also do it without any purpose and just as random musings. Content writing is done with a specific goal in mind. It can include marketing, sales, dispensing information, or other business-oriented purposes.
3. Artistic freedom
There is a big difference between creative writing and content writing when it comes to creative freedom. Creative writers enjoy a lot more artistic freedom as compared to content writers. They can choose the length, tone, style, form, and purpose of their written piece.
They also get the creative freedom to exaggerate, use imagery, and employ figurative expressions as they want. Content writers can be creative, but also have to follow SEO and writing guidelines. In the latter, it is important to make the content visible and more readable to the intended audience.
Creative writers adopt an imaginative, fantastical, and colorful style that may be rooted in truth or fantasy. Content writers, on the other hand, have a methodical, articulate, factual, and informative style of writing.
What’s a Better Choice for You?
The answer depends on why you want to write. Do you want to do it for the fun of it? Do you not care as much about its commercial feasibility? Do you simply want to entertain people? If yes, then creative writing is the way to go. But if you want to write to inform people, share your opinions, and help businesses reach their customers, content writing is what you should do.
There is also a huge difference between content writing and creative writing on the basis of commercial viability. Content writers can be paid upfront and sometimes higher because their content helps businesses drive revenue. Creative writers may also earn money, but it’s a long-term process and requires more effort. Finally, there’s no rule under the sun that says you can’t be both. There are many writers who write content to earn money during the day and turn into poets by evening.
That’s a wrap on creative writing vs. content writing. Remember that neither of the writing styles is superior to the other. There are differences between content and creative writing based on the intent and extent of creativity. Good writers often blur the lines between the two forms to create highly engaging content.
No, both are different styles of writing. They differ based on the purpose, intent, target audience, style, and tone of writing.
Creative writing is more imaginative, free-flowing, and unfiltered. On the other hand, content writing is objective, informative, and structured.
Study the work of creative content writers in your industry. Understand the writing process well and practice it often. Improve based on the feedback you get.
Some examples of content writing include blogs, articles, product descriptions, manuals, guides, ebooks, social media posts, research papers, etc.
Some examples of creative writing include poetry, creative essays, stories, novels, flash fiction, fan fiction, screenplays, scripts, and more.
Latest Blogs
In this blog, explore the golden rules of using AI marketing tools so you can leverage the benefits to their maximum potential.
In this blog, you’ll learn how to avoid the pitfalls of SEO over-optimization while enhancing your site’s performance.
In this article, we’ll take a look at what AMP is, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it affects SEO.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar posts.
9 mins read
Content Marketing vs Advertising – Which One is More Effective?

11 mins read
Interactive Content vs. Static Content: Which is More Effective?
6 mins read
Unlocking Success: 4 Case Studies of Successful Content Marketing Campaigns Using a Platform
- Colleges and Institutes
- Accessibility tools
- Scholarships
- Pre-degree courses
- Undergraduate study
- Post-Grad Community
- Self-paced online short courses
- On Campus short courses
- Online short courses
- Courses for teenagers
- Courses starting soon
- Summer short courses
- Customised and executive training
- Future Creatives
- CSM Tutor, Elise Valmorbida, is a Victorian Premier’s Literary Award Winner!
- John Fitzpatrick talks BAFTA nominations, his career highlights so far and advice for aspiring screenwriters
- Introduction to Cosmetic Science Short Course
- Student Stories: Elizabeth Bond, Shoe Making
- Ruth Eisenhart, from student to tutor
- Student Stories: Tamsin Balcanquall, Costume Making
- Student Stories: Livia Toso, Special Effects Makeup for Film and Television
- Student Stories: Nick Palmer, Making Latex Clothes
- Meet our Tutors - Magali Avezou
- Student Stories: Matis Swann, Visual Merchandising Intensive
- Spotlight on the 'How To Become An Independent Curator' short course
- Student Stories: Jo Sampson, Interior Design - Module One, Two and Three
- Authentic voices from Magnum Documentary Photography students
- Talking with tutors: Street Photography
- Love and animation with robots
- Celebrating Brutalist Architecture through type
- Merging psychology and street style
- UAL alumna enhances her skillset
- Student explores the creative industries
- Insider's Guide to Starting a Fashion Business
- Meet our Tutors: Nicola Pozzani, Design with Scents
- Student Stories: Beatrice D'Alessandro, Swimwear Designer
- Meet Our Tutors: Carlyn McGuire, Fashion Design Intensive
- How to Promote Your New Clothing Label
- Student Stories: Doina Tapordei, Editorial Styling and Creative Direction
- Fashion Founders - An Interview with Nichole de Carle
- How to Become an Interior Designer
- Meet our tutors: Alice White
- Student Stories: Katie Swindells, The Complete Makeup Artist
- Student Stories: Flavia Myrrha’s Summer of Experimental Jewellery
- Meet our Tutors: Matthew Needham
- Makes, designs and prints: student Zé Monteiro talks Screen Printing and his process
- Student Stories: Geeghislaine (Gee) Gazon, From The Great British Sewing Bee to Short Courses
- Student Stories: The Paintings of Katerina Savvas
- Central Saint Martins Short Courses at The Affordable Art Fair in Hampstead
- A degree in resilience: we talk to UAL alumnus and tutor Ansel Neckles
- How I got here: Tom Oliver Payne
- Student Stories: Ewa Grzeszczuk Karzynska and Art Direction for Film
- Student Stories: Jenia Shchedrova and Create a Fashion Portfolio - Intermediate
- #Passion2Purpose competition: Discovering and rewarding the hard work of African-based fashion entrepreneurs
- Student Stories: Holly Hilton, The Complete Makeup Artist
- Meet the Tutor: Enver Gürsev - Oil Painting tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- Student Stories: Hanna Linnéa Mödder and Fashion Journalism
- How to become an Aesthetic Therapist
- How to start a career in fashion
- Hans Tiley: LCF X CASS Art Further Education Award Winner
- Turning the page: we talk to Book Design and Production tutor Nigel French
- Meet Our Tutors: Georgie Tym, Bag Making courses
- Late at Chelsea and Summer Degree Shows
- Student Stories: Judit Massana and Fashion Photography
- Central Saint Martins Short Courses Window Gallery Exhibition
- Student Stories: Birgitte Kriek and Fashion Drawing Summer School
- Outside of design, I am interested in design – we talk to tutor Ben Richards
- How you can use graphic design to direct and hold your audiences attention
- Meet the Tutor: Debbie Flowerday - Retail design tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- A strong visual identity is like a handshake: Tutor Ansel Neckles shares advice on building yours
- Student Story: Alexander Steenhorst, Graphic Novels and Comic Book Art Short Course
- Magnum Photos scholarship for emerging photographers
- How to get into the creative industries: Try. Try again. Fail again. Fail better. Repeat.
- From short courses to studying full-time at UAL
- Meet the Tutor: Matteo Bianchi - Starting an Interior Design Business tutor
- Course Feature: Build Your Personal Brand
- It's all in the process – studying abroad, making mistakes and learning new skills
- Getting to grips with Digital Pattern Cutting: Juliet Uzor, winner of the Great British Sewing Bee 2019
- Meet our Tutors: Photini Konnarides and Designing a Denim Collection
- Art and Design Workshops for 16 to 18 Year Olds with Ilga Leimanis
- Meet the Tutor: Debbie Blandford - Interior Design tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- Introducing: Short Course Exhibition and Selection Panel
- 5 reasons you should take Millinery Workshop
- UAL: A Springboard for Your Creative Future
- Markas Klisius and Koye Odejinmi - “work in progress” curators
- Student Stories: Odette and Laser Cutting for Textile Design
- Student Stories: Victoria Sills and Applied Surface Design
- Meet the Tutor: Lyndall Fernie - Interior Design tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- Student Stories: Tamara Vázquez, Fashion Design: Intensive
- Kirsten Cooke - Curating the Short Course Exhibition
- 5 reasons you should take Creative Leadership for Fashion Business Weekend
- Short Course Exhibition: Fine Art Exhibitors
- Short Course Exhibition: Illustration Exhibitors
- Short Course Exhibition: Design Exhibitors
- Short Course Exhibition: Teenage Exhibitors
- From Short Courses to Successful Fashion Business Owner: Bolupe Adebiyi
- Student Stories: Michael Eden and Practical Metalwork Workshop
- Can you control the narrative? Zine-making, image selection and the impact of creative decisions with Magnum Photos
- Student Stories: Veronica Giron and Shoe Design for Beginners
- Designing wedding dresses and giving back to the community
- 5 reasons you should take Visual Merchandising - Interiors
- Student Story: Rebbeca Morse, Book Illustration
- Student Stories Summer School WINNER: Eve Donaldson and Urban Sketchbook for 16 to 18 Year Olds
- Meet the Tutors: Design for Sustainability - Fashion and Textiles
- Students look to the world’s current climate for inspiration
- 5 reasons you should take Leather Glove Making Workshop
- How to Start Creative Coding
- Course Feature: Pre-Foundation Portfolio Preparation for 16 - 18 Year Olds
- Fashion Film: Breaking the Glass Ceiling
- How to Make Fashion Drawing and Illustration Templates
- Meet our Tutors: Illustration with Laura McKendry
- Student Story: Sean Kinson, Graphic Design
- Studying with Dominique L’Olive in the studio and online
- Some inspiration for the week from us...
- Learn how to communicate with data...
- Course Feature: Photoshop, Illustrator and InDesign
- Student Story: Elisa Conlan, Pre-Foundation Portfolio Preparation
- All about the Japanese Kimono with tutor Sheila Cliffe
- Pursuing Photography – we talk to Magnum Photos Scholar Anselm Ebulue
- Let’s talk about Portfolios – UAL advise on things to remember
- Student Stories: Tereza Kupcikova and Jewellery with Wood
- Join us on a UAL Short Course
- Studying with Schelay McCarter in the studio and online
- Student Stories: Sophie Grapentin, from a History Degree to Lingerie Design
- Student Stories: Annie Michie, Colour Mixing Workshop and Illustration Workshop
- The learning doesn't stop in the classroom...
- Student Stories: Mandula Pap and Fashion Mix
- Student Stories: Virginia Mackie and Introduction to Silversmithing
- Course Feature: Interior Design - Modules 1, 2 and 3
- Meet our Tutors: Jewellery with Sarah King
- Student Story: Erin Donohoe, Illustration
- Course Feature: Graphic Design
- Student Stories: Melissa Haro and Interior Styling for Editorial and PR
- Meet the Tutor: Augusta Akerman, Illustration tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- Student Stories: Felipe Blasca and Strategic Branding, Identity and Brand Experience
- One week courses that could boost your career in 2020
- Student Story: Samira Modaresifar, Interior Design
- Student Story: Christina Tina, Book Illustration
- 5 Reasons you should take the Intro To Cosmetic Science Short Course
- Utilizing an eye for detail, with photography
- Student Stories Autumn Term Winner: Kate Febbraro and Jewellery Making for Beginners
- Make a new skill one of your new years resolutions
- Meet the Teacher: Roger Healey-Dilkes, Future Creatives
- Student Stories: Ekaterina Vdovichenko and 100 Design Projects
- Special Effects Makeup with tutor, Jennifer Drew
- Keeping up to date with industry practices
- Creating your portfolio with tutor VJ Choolun
- Student Story: Ashni Shah, UAL International Summer School
- Student Stories Christmas School Winner: Erika Cule and 100 Drawing Projects
- Student Stories: Alina Bendikova and Building a Fashion Collection
- What do students really say immediately after a short course?
- Course Feature: Brand Management
- Why should you take a writing course at CSM?
- From Short Course to MA – it's a deeper dive into education
- Meet the Tutor: Debbie Flowerday, Interior Design
- Meet our Tutors: Starting a Successful Project with Mark Aitken
- How to Become a Fashion Designer: Steps to Success
- Student Story: Ona Brickute, Graphic Design - Experience Industry
- Student Story: Nadine Sheikh, Courses for Teenagers
- Enhancing your portfolio post-graduation
- Student Stories: Francesca Navarro and Patternmaking - Level 1
- Meet the Tutor: Alessandra Genualdo, Illustration tutor, Chelsea College of Arts
- Student Story: Juan Jose Sanchez, Landscape Architecture
- Where do I start with Accessories, Footwear and Jewellery short courses?
- Student Stories: Michele Guzman and Fashion Styling for Beginners
- Meet the Tutor: Alasdair Leighton-Crawford, Streetwear and Sportswear
- Upskill in a day – one day short courses in London
- Why is creativity important for your mental health?
- 5 reasons you should take Principles of Personal Fashion Styling Course
- 5 reasons why you should take a 1 week intensive short course at CSM!
- Thinking of taking a short course? See what recent students created with us
- Why does SEO matter?
- CSM x Fashion Law Institute first Professional Development Workshop
- Meet the Tutor: Gianfrancesco De Falco, Interior Design
- Student Stories: Season Butler and Creative Writing
- Student Story: Shibata Maiko, Retail Display and Design
- Why you should take the London Street Style Fashion Subcultural Icons Short Course
- Choose the right digital marketing course for you – with help from our tutor Hana
- Meet the Tutors: Theo Jones and Jacob Valvis, Green Mat Workshop
- Take a one week intensive short course this Easter School
- Update on the Coronavirus outbreak for Short Course students
- Looking for a way to be more productive?
- Our tips on how to look after yourself while self-isolating
- Ways to keep creating at home
- Student Stories: Alex Douglas Newton, Kimono: History Design and Development
- Developing Your Interior Design Skills at Home
- Developing Your Illustration Skills at Home
- How You Can Still Enjoy Fine Art From Home
- Developing your skills at home: Photography and Scriptwriting with Mark Aitken
- Without being active online – it's almost like you don't exist
- Amber Butchart: What to Read, Watch and Listen to
- Why taking an online short course is perfect for you!
- Developing your skills at home: #comfortthroughdoing with Arianwen Shoring
- Developing Your Graphic Design Skills at Home
- Why does tracking social media analytics matter?
- The changing face of the fashion industry - Alison Lowe MBE
- Magazine creative direction - Giulio Mazzarini
- People's Masks - Laura Baker
- Where to begin with interpreting art - Theo Carnegy Tan
- Visual merchandising trends in modern retail - Sarah Manning
- What it takes to be an interior designer – Lyndall Fernie
- Creating professional Instagram posts - Robert Aldous
- Charles II and the evolution of the suit – Amber Butchart
- Learning all about natural beauty – Crystabel Riley
- Starting a fashion label – Toby Meadows
- Watch Listen Learn
- Looking for inspiration? From Instagram to your reading list
- How to become a fashion stylist
- 3D printed model making for designers - Theo Jones
- Student Story: Federico Gambarini, Art Direction
- Looking back – Magnum Photos students respond to the city
- Course Focus: Art Direction (Online Short Course)
- It's time to forget what your english teacher taught you...
- How to build a community on social media in 30 days
- Student Story: Cristina Iazzetta, Interior Design
- Student Story: Christine Newman, Interior Design
- Student Story: Katrien Goossens, Interior Design
- Student Story: Lucy Morgan-Hobbs, Interior Design
- Student Story: Marcella Forster, Interior Design
- Student Story: Maria Pia Polizzi, Interior Design
- Student Story: Mary Curran, Interior Design
- Student Story: Svetlana Kutnyak, Interior Design
- Meet the Tutor: Matt O'Dell, Comic Book Art
- Interior Design Students Present at Dezeen’s Virtual Design Festival
- Staying positive at home with tutor Nada Dahab
- Online Courses for Teenagers
- How do you create a marketing campaign?
- Student Story: Cecilia Casas, The Art of Social Engagement
- Student Stories: Maike Wölfle and Introduction to Fashion Design
- Are you a teenager looking to develop skills, creativity and confidence?
- How to start a sustainable fashion business
- Mood boarding and story boarding for art directors - Giulio Mazzarini
- Finding your fashion path - Lucy London
- Exploring the creative process - Ilga Leimanis & Christopher Kelly
- Concept boards for interior designers - Lyndall Fernie
- It’s never too early to start a career in fashion
- Translating inspiration to illustration - Alessandra Genualdo
- Learn How Pop Up Shops Can Enhance Your Brand
- Fashion questions now - Professor Susan Scafidi & Jeff Trexler
- Take the First Steps Towards a Career in Illustration
- The future of fashion editorial - John William
- Fashion communication methods - Ana Stankovic-Fitzgerald
- Graphic design : creating virtual textures - Alexander Hough
- The art of social engagement - Rosemary Cronin
- Student Story: Crystal McGregor, Footwear Illustration
- Inside the shop window - Debbie Flowerday
- Magnum Intensive Documentary 2019 Scholar - Anselm Ebulue
- It's never too early to develop your fine art skills
- Student Stories: Stephanie Uhart and Fashion Folio
- 12 steps to launching a new product
- Art and Design School at Home for 13 to 16 Year Olds 2020 Showcase
- Student Story: Clara Gröning, Fashion Design and Illustration
- Meet Our Tutors: Lydia Brockless, Future Creatives
- The power of copywriting - Phil Woodford
- It's never too early to start: art classes for kids and teenagers
- Student Stories : Graphic Design for 14 to 17 Year Olds – Isabella Jeanne de Boer
- What can I expect on an illustration course?
- Student Stories : Portfolio Preparation for 16 to 18 Year Olds (Online Short Course) – Alexis Jennings
- Insights on independent curation - Sarah Sparkes
- How to create a graphic design portfolio
- 5 reasons why 2-day intensive short courses fit your busy schedule
- Student Stories: Anna Denise Floor, Illustrating for Books
- Student Stories: Fashion Folio – Jan-Philipp Kosfeld
- Meet The Tutor: Alexander Hinnerskov - Product Design
- Revitalise your passion for Art Direction for Fashion
- How a Short Course can support your career change
- Boost your professional practice with a Short Course
- From Graphics Folio to Masters Degree
- Doing a Short Course alongside your degree
- Online Portfolio Preparation For Teenagers: Short Course Insights
- Drawing skills and creativity with tutor Ilga Leimanis
- The importance of art and creativity in a child’s development
- It's never too late to change career: Interior Design
- Curating Contemporary Art : Short Course Insights
- Student insights on an Illustration short course
- It's never too late to change career : Book Illustration
- Student insights on a Graphic Design short course
- Learning how to build a portfolio to apply to art college
- Insights on Visual Merchandising with tutor Sarah Manning
- Reconnect with your creative side with 100 Design Projects
- Gain new skills and refresh old ones
- Student insights on Experimental Fashion Design short course
- Developing your practice with Graphic Design for teenagers
- We need the arts now more than ever
- One-on-One Training: Experience Design: Digital and Physical
- Foster + Partner: Architectural Photography Training
- Right Angles: Copywriting Training
- Mizuho Bank, UK: Film and Moving Image Training
- British Council East Africa Arts: Creating Content Through Narrative
- Camden Council, UK: Communications Training
- HP Inc: Creativity Bootcamp Training
- King’s College, Hong Kong: Building Robots with the BBC Micro:bit
- Phoenix Publishing and Media Group, PRC: Digital Publishing Training
- Sky: News Interviewing Skills
- What are the top 10 skills graphic designers need?
- Starting an online fashion empire is easier than it sounds
- Unlock your creative potential
- Fashion Textile Design: inspiring creativity with an online short course
- Breaking down the fashion sustainability code
- What are the most important qualities of a creative leader?
- Exploring visual communication in fashion
- Student insights on a Fashion History short course
- How to improve drawing skills for beginners
- How a womenswear design short course inspired a career change
- 5 Reasons to take a Future Creatives course
- The value of after-school art classes for children with tutor René
- Creative things to do with kids during lockdown
- How an online course can build transferrable skills
- Feed your curiosity in fashion with a short course
- Could your freelance career benefit from a short course?
- How a short course helped put sustainability at the forefront of a new fashion business
- Boost your illustration skills with industry experts
- From fashion accessories short course to embroidery studio owner
- Nurture your creativity with tutor Deborah
- How to build your confidence to start a business
- From creative hobby to flourishing business
- How to finesse your skills as a creative
- Let a short course reconnect you with your creative side
- Doing a short course to boost your existing career
- 5 ways to improve your creative professional development
- How to create a fashion portfolio for university
- Can graphic design skills support your job?
- Start your career in fashion design with a short course
- Creative leadership is essential for an uncertain world
- Master the basics of digital animation with an Adobe short course
- Develop your illustration skills with a short course
- How a short course can diversify your illustration practice
- Expand what you know about fashion with a short course
- Learn the foundations of graphic design with a beginner short course
- How to become an animator
- Top 8 British Youth Subcultures
- Enhance your understanding of art with a short course in curation and culture
- How a pattern cutting short course can help you build your foundation in fashion design
- Let a short course improve your eye for interior design
- How to become a graphic designer
- 5 reasons why social design is important
- Boost your skills with a short course in 3D Design and Product Design
- Build transferrable skills for fashion business with a short course
- How a short course can enrich your textiles practice
- Let a short course grow your sustainability practice
- LNER: Bespoke Infographic Design Course
- How to tell a story through photography
- Complement your full-time study with a short course
- Understanding the business side of fashion with short courses
- How to become an illustrator
- Creative education should be fundamental to school culture – Future Creatives opens at Varndean College, Brighton
- Strengthen your digital marketing skills with a short course
- Uncover your artistic potential with short courses in fine art
- Develop a critical understanding of art with short courses
- Empowerment through art with Sara Shamsavari
- UAL x Wool4School: Fashion Design competition
- How short courses can enhance your interior design practice
- How short courses can support professional career development
- Discover the positive power of creative writing
- .International Veil Series: a celebration of Muslim women's hijabs
- Sketching Perspective with Ilga Leimanis
- How can art and creativity improve your health and wellbeing?
- 5 tips to create a successful copywriting portfolio
What is the difference between content writing and creative writing?
- What is the difference between an interior designer and an interior stylist?
- What do employers look for in a graphic design portfolio?
- What to draw as a beginner
- Top 5 types of animation styles
- 5 types of photography to master
- What does a fashion designer do?
- 10 essential painting techniques for artists
- How to build a photography portfolio for an MA
- 5 tips to get started in ceramics
- 5 influential female graphic designers
- Launch your career in fashion with a short course
- Discover the art of book illustration with a short course
- How the Textiles Folio short course can inspire your dream career change
- How to build a foundation in graphic design
- How to start sewing for beginners
- 5 films that were inspired by art
- How to improve your photography skills
- Expand your ceramic practice with a short course
- Acid house and rave: exploring subcultures with Dr Ray Kinsella
- Meet the tutors: Dr Ray Kinsella and Kevin Quinn
- 5 reasons to start sewing
- How to become a professional tailor or dressmaker
- 5 reasons to take the Introduction to Design with Systems Short Course
- How to become a professional photographer
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: René de Lange
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: Seán Myers
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: Hannelore Smith
- Breaking down sustainability terms
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: Pam Williams
- Taking successful photographs
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: Roger Healey-Dilkes
- A sustainable guide to product design
- Develop your textiles practice with a short course
- Meet the Future Creatives Tutor: Antonia Harrowing
- Student work from the Preparation for Foundation Online Short Course
- Discover sustainable product design with a short course
- Explore the world of fashion with a short course
- Learn how to visualise and present data with a short course
- How sustainable initiatives are shaping the fashion world
- The future of digital fashion design
- Kickstart your creative journey with a taster session
- Summer in London: student work from our International Summer School
- Explore the world of design with our teen courses
- Future Creatives Arts Festival Competition 2022
- How a short course can help you grow your business and expand your skills
- Learn how to reduce your environmental impact with a short course
- BIAAF: Fashion Design for Young Professionals
- How to become a journalist
- Discover the importance of undertones and complexion in makeup
- From a short course to a tailoring business
- Understanding fashion and the blockchain
- 7 Influential women in the creative industries
- Create a still life inspired by Patrick Caulfield
- Make a food face
- Create a poster inspired by Lakwena Maciver
- Draw or paint a self-portrait
- Introducing digital badges and credentials
- Discover how design interacts with systems theory
- Master the art of patternmaking with a short course
- Tutor exhibition: Sarah King’s sculptural jewellery
- Learn how to capture an audience with a creative writing short course
- Jewellery Development Programme – Hatton Jewellery Institute
- 3 Golden rules for aspiring fashion stylists
- Boost your creativity with a short course
- Explore new possibilities with a short course
- Embrace lifelong learning with a short course
- Discover the art of professional makeup with a short course
- Unlocking creativity: art direction in the fashion industry
- Hatton Jewellery Institute X UAL Short Courses
- Course feature: Portrait Painting
- Discover the joy of nature writing with a short course
- Learn how to make latex clothes with a short course
- Learn how to build a digital marketing strategy with a short course
- Course feature: Starting Fashion Illustration
- Course feature: Graphic Design Projects
- The importance of drawing skills in the visual effects industry
- Discover the art of life drawing with Joe Richardson
- My account sign in
- Immigration guidance
- Terms and conditions
- Winter short courses in London or online
- Useful information
- Spring short courses in London or online
- Fashion Folio visa information
- Graded Awards in Drawing
- Online courses
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Portfolio advice
- Admissions complaints and appeals
- After you apply
- Your personal statement
- How to apply
- How to pay your tuition fees
- Enrolment visa and immigration information
- New student enrolment
- Returning student enrolment
- Student ID card collection
- Your country
- Immigration and visas
- Contact international
- Pre-sessional English
- Moving to the UK
- Application advice
- International events
- Airport collection discount
- Preparation for BA Online
- Our prospectus
- Halls of residence
- Private accommodation advice
- Summer stays
- Support in halls
- Students with disabilities and health conditions
- Pricing and availability
- Scholarships search
- International students and money
- UAL: where the money goes
- Living expenses and study costs
- Tuition fees
- Undergraduate scholarships and funding
- Foundation scholarships and funding
- PhD and MPhil funding
- Learn English
- Modern Languages
- English language requirements
- Your English language level
- Studying English Language Online
- English Language Development for students
- Intercultural and Communication Training
- Annual Language-Art Project
- Integrated Study Abroad
- UAL Study Abroad Semester
- Summer Study Abroad
- Funding and awards
- Next steps for offer holders
- Study Abroad terms and conditions
- Study Abroad Credits and Assessment
- Virtual tours UAL
- Student surveys
- Tutorial policy
- Student rights and responsibilities
- Student Privacy Policy
- Student liabilities
- Attendance Policy
- Academic Misconduct
- Reporting serious incidents
- Appealing An Exam Board Decision
- Making a Student Complaint
- Student Fees Policy
- Quality Assurance
- Course Transfer
- Extenuating Circumstances and Time Out
- IT network and acceptable use policy for students
- Contextual admissions
- Ask a student
- UAL Student Voices
- Work placements
- Find jobs and internships on Creative Opportunities
- UAL Arts Temps
- Career skills and support
- Exhibit and sell your work
- Freelance and business support
- Awards, funding and support
- Industry and Partners
- Events and workshops
- Develop your skills and strengths
- Support for Graduates
- Careers support for students
- Career resources
- International Futures
- Library service hours
- Special Collections and Archives
- Academic support
- Using the libraries
- Contact Library Services
- IT software and discounts
- Terms of Use
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Your UAL account
- Student Advice Service
- Counselling, Health Advice and Chaplaincy
- Disability Service
- Out of hours and emergency support
- Tell Someone
- Bullying and harassment
- Sexual violence
- Course Support Service
- Locations and opening times
- Certificates and transcripts
- Graduation live stream
- Honorary Awards 2023
- Digital tools
- Students' Union
- Canteens and cafés
- Gender neutral toilets
- Quiet spaces
- Supporting trans and non-binary students
- Student parent and carer support
- Note taking, writing and referencing
- Training and resources
- Information and resources
- Policies and procedures
- Student security
- Health and wellbeing pledge
- Vaccinations for students
- Make a living doing what you love
- Student timetables
- Wellbeing Hub
- Creating accessible digital content
- Outgoing students
- Incoming students
- Partner institutions
- Exchange contacts
- Cost of living support
- Showcase student guidance: How to write about your work
- UAL Showcase student guidance: How to make your work digitally accessible
- UAL Showcase student guidance: sales
- UAL Showcase student guidance: professionalism
- UAL Showcase student guidance: intellectual property
- UAL Showcase student guidance: digital representation
- Alumni of Colour Association
- China (Southwest) Alumni Association
- India Alumni Association
- Sustainability Alumni Network
- Alumni volunteering
- Alumni stories
- Alumni events
- Academic partnerships
- Executive Board
- Our strategy 2022-2032
- Support and donate
- Procurement
- Press Office
- Teaching and Learning strategy
- Professional development
- Awards and funding
- Teaching and Learning events
- Teaching and Learning Resources
- Sell your design products and artwork
- Staff diversity
- Change the way we teach
- Change the way we operate
- Change the way we research and exchange knowledge
- Climate Emergency Network: Changing the way we work together
- Get involved
- Documentation and carbon dashboard
- Climate action staff representation
- Events and projects
- Re-Use units
- Social Purpose
- Working at UAL
- How we work with our partners
- Work with our experts
- Work with our students and graduates
- PhD and MPhil degrees
- About the Doctoral School
- Doctoral support and community
- Fashion and the Embodied Expression of Belief, Worldview and Religion
- Art and Reconciliation: Conflict, Culture and Community
- UAL staff researchers
- Centre for Sustainable Fashion
- Creative Research into Sound Arts Practice (CRiSAP)
- Centre for Fashion Curation (CfFC)
- Groups and networks
- Research standards and ethics
- Accessibility statement for UAL staff research profiles website
- Qualifications
- Training and events
- Become an approved centre
- Schools and Colleges
- Insights: apply
- Insights: shape your portfolio
- What's on: UAL Insights
- Insights: teachers workshops and programmes
- Information for agents
- Global Projects and Partnerships
- UAL Sanctuary
- Staff mobility
- ual-resources
- Written by Carys Thomas
- Published date 28 February 2022
Writing is a skill like any other, and as such, it requires patience and practice to improve.
If you’re hoping to improve your professional writing skills, you’ll need to have an understanding of the difference between content writing and creative writing. Content writing is often confused with creative writing, but you may be surprised to learn just how different these two writing styles are.
We’ve put together this guide to give you an overview of these two popular approaches to help you expand your knowledge and write with confidence. We’ll start by looking at definitions of each style and then we’ll move on to consider how exactly the two approaches differ, with insights from award-winning writer and UAL short course tutor, Elise Valmorbida. By exploring the two types of writing, you may discover which approach suits you best according to your personal interests and creative goals.
Take a look at our creative writing short courses for more inspiration. You may also be interested to discover the positive power of creative writing and the impact it can have on mental health and wellbeing.
So, what is content writing?
The term ‘content writing’ refers to a form of professional writing that is produced to fulfil a particular purpose, often for an online audience. This type of content is generally designed for a specific audience and can be categorised into two key groups, namely, marketing or brand-based writing, which is usually produced for websites or online platforms, and technical writing, which is focused on subjects that require instruction or explanation. When you search how to do something online, for instance, you’re likely to find several examples of technical writing.
Content writers are required to plan, produce and manage content for marketing purposes, including short promotional copy and longer-form stories or articles. They may be involved in producing content for websites, businesses, or government bodies and should have an understanding of SEO (search engine optimisation) principles in order to maximise levels of audience engagement.
Online content may be developed for blogs, social media, newsletters and branding. According to a recent study, 58% of marketers said that original written content is the most important type of content , ranking higher than visuals and videos. Clear, well-crafted copy is essential for businesses hoping to engage with consumers, generate interest in their products or services and increase website traffic.
What is creative writing?
Creative writing refers to a form of writing which draws from imagination or invention in a way that other styles do not. Unlike other forms of writing, creative writing is not limited by the rules or restrictions that dictate other journalistic, technical or academic styles. The term includes a number of different genres and styles in both a fictional and non-fictional context and allows for a level of artistic or creative freedom. Examples include poetry, prose, spoken word, screenplays, personal essays, lyrical writing and playwriting.
There is often a strong emphasis on the value of expression in creative writing, and writers may use character development and plot to express ideas and thoughts in a unique or original way. The process relies on using creativity as a tool to produce a compelling story, which can be achieved by incorporating a series of literary devices like metaphors, alliteration and symbolism to make a work interesting or engaging for audiences.
Elise offers some useful advice for anyone looking to improve their creative writing skills; "the more you practise any craft, the better you get at it. Creative writing classes are great, but you need to continue with practice on your own. This practice involves thinking, writing, editing, reading—and persevering. Do research. Keep a notebook. Read as much as you can, absorbing as much as you can, because reading loves writing. Get feedback. It’s no use just hanging out for applause. Receiving criticism is positive, despite the fact that it might feel painful. This is one of the benefits of classes, groups and organisations dedicated to writing."
So, how are content writing and creative writing different?
Content writing is generally designed for a specific purpose that involves an outcome which can be measured in some way. This kind of writing may be produced to increase website traffic or boost sales figures, for example. Levels of audience engagement or activity can be measured using analytical software to indicate what kind of content or language appeals to users. This commercial purpose is not a priority when writing creatively, however, and the focus here is instead on personal expression and reflection.
For Elise, the difference between content writing and creative writing comes down to the role of the client or brief; "I never talk about ‘content writing’ because I don’t think of words as mere ‘content'", says Elise, "this implies that there’s some void to fill with obligatory stuff, rather than seeing words as integral to the communication of worthwhile ideas. If by ‘content writing’ we mean writing for a client with a brief, then that’s what sets it apart from creative writing: the client and the brief."
"When I write fiction or non-fiction, I do not have a client to please, a brief to follow, a defined audience to inform or persuade. There are no targets. For me, creative writing taps into something mysterious that is deep inside of me. When I teach creative writing, that’s the approach I take: encouraging students to write from the inside out, and to do this as well as possible by honing their skills. Writing is a craft. It is something you can learn."
Writers working creatively have the freedom to experiment with the tone of writing to reflect their personal style, while content writers are often required to follow specific branding guidelines which are stipulated by a company. They may need to utilise precise, technical vocabulary for example, or adopt an impersonal or objective tone to suit a commercial context.
Content writers are frequently required to produce content that reflects a particular style to establish a sense of consistency across a brand. This form of writing is often designed to be clear and precise, and if needed for marketing purposes, may have a persuasive tone or style. Content may be research-based and follow a fixed structure that is designed to reach a clearly defined audience. Creative writing, on the other hand, is not bound to any stylistic limitations, and writers are free to make their own creative choices.
4# Platform
Content platforms for delivery vary between each style of writing. Content writing may be featured on online platforms and is often designed to be quickly visible to a target audience when they search for the topic online, following search engine optimisation (SEO) principles. Creative writing does not need to support such principles, and as such, may be published on other platforms or in other forms, like novels, magazines or newspapers.
5# Timeframe
Content writing often requires a quick turnaround to meet planned deadlines, according to content marketing schedules or campaign milestones. Creative writing is not typically confined to particular time constraints, and the writer is usually able to work at their own pace, allowing time for edits and revisions.
Take a look at our guide on 5 tips to create a successful copywriting portfolio for some useful advice. If you’re interested in developing your writing skills but aren’t sure where to start, you may like to take a look at our creative writing short courses , which aim to help you improve your writing skills in a focused and supportive environment.
Related courses

Creative Writing Vs Content Writing: 6 Differences You Should Know
Table of contents
Often used interchangeably, content writing and creative writing have similarities but are different. A non-writer may not recognize the differences between the two styles of writing. However, when you approach a professional writer, they will know precisely the nuances that make creative and content writing different.
If anyone is considering stepping into the world of writing, read on. The debate about creative writing vs content writing is ongoing, and you need to know the basics before you choose which kind of writing is better for you.
What is creative writing?
Creative writing is the art of creating stories that communicate ideas. It can involve any form of expression, including poetry, fiction, and non-fiction. Creative writing can help you explore your thoughts and feelings, connect with others, and share your unique perspective. It can also allow you to create something new or improve upon something old. In short, it is the art of engaging in creative thinking.
The following are some critical characteristics of creative writing:
1. It is an individual process, unlike scientific or journalistic research. There is no one defined way to write creatively; every writer has their unique style and approach.
2. Creative writers often explore unusual topics and ideas, creating relatively unstructured texts compared to traditional forms such as essays or reports. This flexibility allows them the creative freedom to communicate their ideas in an innovative way that cannot be done with a more conventional format.
3. Creative writers often use metaphors and other literary devices to convey complex ideas. Thus, they can communicate their ideas in a way that is easily understood and enjoyable to read.
4. The creative writing process uses creative imagination, which often leads to surprising and unexpected results. This element of surprise can add interest and excitement to the reader's experience, leading them to want to read more.
The key elements of creative writing are imagination, memory, and reflection. These three factors work together to help writers develop stories and characters that are interesting, entertaining, and suspenseful. Writers also use these same tools to explore ideas and express their views on life, making creative writing an often personal process.
Is creative writing a part of content writing?
Creative writing focuses on creating new ideas, whereas content writing focuses on distributing and promoting existing ideas. There is a clear-cut difference between creative writing and content writing. But that does not mean that creative writing is not a part of content writing.
Content writers and copywriters need to be able to think creatively to come up with interesting, engaging content that will keep readers interested. They must be able to write in various styles, including creative writing, so readers will find their writing enjoyable and informative. Thus, creativity is an integral element of the field of content writing.
What are the 5 types of creative writing?
Steeped in creativity and imagination, creative writing tends to be associated with many types and genres. Creative writing works can be classified into fiction or non-fiction.
Here is a list of five types of creative writing commonly known to all, followed by examples for each type of writing.
1. Narrative storytelling
Narrative storytelling is an approach to creative writing that emphasizes telling a story through events, characters, and settings. The term "narrative storytelling" has been used differently over the years. Generally, it refers to writing that employs a narrative structure—a sequence of events leading from the beginning to the end and character developments—to tell a story.
Example of narrative storytelling

Lamb to the Slaughter is a story penned by Roald Dahl in the narrative storytelling format. The story follows the protagonist, Mary, a housewife known for her loving nature. But one evening, as she welcomes her husband home, things take a different turn, and readers are enticed by the twist in the storytelling filled with thrill and horror. Do read the story to know more about what happened to Mary.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses metrical and rhyming patterns to create images or feelings. Poetry can be any length but typically remains shorter than standard prose. Poets use different techniques and rhythmical devices to evoke emotion in their readers, including metaphor, alliteration, imagery, and abecedarian rhyme.
Example of poetry

The Red Wheelbarrow is an eight-line poem by William Carlos Williams reflecting the importance of simple things in life that are often taken for granted. It artistically tries to capture the red wheelbarrow, the raindrops, and the white chicks, all essential components of a farmyard/agricultural activity.
Is the poem talking about the reliability of the wheelbarrow for farm activities? Or is it hinting at the chickens' significance? It depends on how you interpret the poem.
3. Screenwriting
Screenwriting is one of the forms of creative writing that typically involves the development of a story, film, or television script. As with all forms of writing, screenwriting requires an acute sense of observation and storytelling ability.
Example of screenwriting

Eric Roth's screenplay for Forrest Gump is the best example of creative writing. How he has adapted the novel creatively to give birth to a movie that has won millions of hearts over the years displays the true power of artistic expression.
Essays are formal pieces of creative writing that typically examine a subject in depth. They can be informative or entertaining, but they usually aim to provide readers with new information or insights.
Example of essay

Here is a snippet from an essay written by a student on her very first local diner visit. It is creatively and descriptively written to ensure that readers are engaged, and their emotions get invoked. The description of the diner in the essay allows the reader to visualize it without visiting it.
5. Memoirs/Bibliographies
Memoirs or bibliographies, as pieces of creative writing, are personal experiences that someone has written down; they often have a unique perspective and can tell stories in ways other types of writing cannot. This makes memoirs an interesting and effective means of conveying information or ideas.
Example of Memoir/Bibliography

Maya Angelou's memoir, I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings , is an excellent example of a creatively written memoir. It illustrates some fantastic life lessons. It follows the life story of Angelou to show how literature and strong character can help overcome trauma and racism.
The above types and examples of creative writing must have clarified why there is a difference between creative writing and content writing. Now let us move on to content writing and its examples to understand the differences better.
What is content writing?
Content writing is creating high-quality, engaging content for a website, social media, or blog. The content writing process involves creating written material that informs and engages the target audience. Content writers are involved in developing original pieces, rewriting existing content, or sourcing and curating information from other sources.
Ideally, the content created would be shareable and influential enough to attract readers (and potential customers) regularly and consistently. The primary purpose of content writing is digital marketing and branding.
Content writers target search engine optimization to create content that boosts business sales and encourages networking between individuals.
Some common skills required for successful content writing are:
- Understanding grammar and syntax
- Researching topics well enough to provide unique insights and thoughtful conclusions
- Using positive reinforcement language when promoting the brand or product
- Observing editorial requirements while maintaining user engagement potential
- Ability to work with various writing platforms, content management systems, social media, or traditional word processors.
The process of content writing works in the following manner:
1. Planning: Outlining topics and ideas for a piece, researching for information, and determining the audience.
2. Writing: Using effective grammar and vocabulary to create coherent, readable, and quality content.
3. Editing & Proofreading: Checking for mistakes before publishing
4. Promotion: Developing marketing strategies to promote your content
Examples of content writing
Content writing skills and strategy are essential to creating content for social media posts, blogs, ebooks, websites, etc. Below are a few real-life examples of popular types of content writing pieces found on the internet.
1. Blogpost example
.webp)
Zoom's blog post is an ideal example of content writing because it showcases its features to specific audience. It offers information to readers about the features and tips for using Zoom for office parties and gatherings during the holiday season.
2. Social media post example

The brand-Incogmeato has leveraged Twitter's polling feature in this tweet. It has a graphic added to it to grab attention. The social media content is witty, encouraging dialogue and discussion among the audience.
3. Ebook example

Content Marketing Institute's ‘Content Marketing Survival Guide’ is a great example of content writing. It is informative and provides data related to around 12 social media sites. It also contains tips and tricks to create an effective social media marketing and content strategy.
4. Website content example

The screenshot is from Cupcakes and Cashmere, a website associated with lifestyle and fashion. Emily Schuman is the founder of this website. The content on this particular webpage provides a sneak peek into the founder's life in the most exciting yet simplistic manner.
Creative writing vs content writing: Key differences
Now that you know the basics of creative and content writing, it is time to move on to the key differences between the two.
1. Different purposes
One of the primary differences between creative writing and content writing is related to the specific purpose of writing. Creative writing is used to explore the inner thoughts, emotions, and experiences of the author. Conversely, content writing communicates ideas or information that can help people achieve their goals.
2. Different styles of writing
Another difference revealed by the debate on creative writing vs content writing is that both have different writing styles. Creative writing tends to be more poetic and lyrical, while content writing is more straightforward and persuasive.
3. Tone of voice
There is no definitive tone of voice for creative writing, as the style and approach to writing will vary depending on the author's personal preferences. However, the tone of a creative writing piece can convey action or excitement, rely on vivid imagery, employ intriguing metaphors, and inject humor where appropriate.
In contrast, in content writing, the tone of voice should be respectful and objective. While it's important to evoke the reader's emotions compellingly, the content is written impartially, ensuring readers can share it with a wider audience.
4. Fiction and non-fiction
Creative writing is typically associated with fiction, but sometimes some creative writers produce non-fiction works as well. Content writing, in comparison, is mostly non-fiction, and content writers only get the scope to write fiction if there is a marketing or brand requirement.
5. Word usage
You can use the same word in creative writing multiple times, even in one line. You have the authority and freedom to express yourself however you want. But when it comes to content writing, using a variety of words is especially important to grab readers’ attention. You must ensure that keywords are used but not excessively. Synonymizing is an essential element of content writing.
6. Process of writing
Creative writing resembles an art form. This means that creative writers typically take their time to produce and organize their work. The creative writing process allows the writer to devise a writing style and convey their ideas in whatever form they want.
Content writing must be done within a specific set of parameters decided by the client. The content cannot take any shape desired by the writer and must present facts and information as the client dictates. The writer also has to be mindful of SEO guidelines.
Similarities between creative and content writing
Although the points of difference between creative writing and content writing are quite clear now, understanding the similarities between the two forms is also essential. We will mention the similarities here so that your knowledge regarding the creative writing vs content writing debate is complete.
Both writing styles require the writer to come up with ideas, develop them into sentences, and then string those sentences together into cohesive and comprehensive pieces. They also need to be able to think critically about their work and make sure that it is readable to a large audience.
Whether you publish content pieces or promote creative writing, your writing must be of high quality to be successful. Your writing must also be error-free and formatted correctly if you want people to trust your authority and credibility.
Creative writing vs. content writing: Conclusion
We have successfully demonstrated that there is a difference between creative writing and content writing. While one has to be used creatively, the other has to be deployed strategically. Both styles have benefits that can be leveraged to write powerful and effective content.
Nowadays, content writers are using creative techniques to produce better content. On the other hand, creative writers are optimizing their content pieces and making them SEO-friendly to gain traction.
Also, content writing differs from copywriting. Read this blog, ‘ Copywriting vs Content Writing: What are the Differences & Similarities? ’ to know more.
Can AI writing help you in writing creative content?
Yes, AI writing can help you in developing creative content. It can recommend topics and angles to explore, scan through existing content for inspiration, and even offer corrections or refinements to your writing style.
Do you wish to use AI to write creative content? Use Scalenut. This AI-powered SEO and content marketing platform can help your website rank scale up with free SEO tools that ensure your creativity never gets blocked.
Scalenut is among the 14 best AI writing assistants to help you scale your content marketing . So what are you waiting for? Sign up now.

ABout the AUTHOR
Priya Jamba is a Content Marketer at Scalenut. She loves marketing technologies and believes that with the right combination of tools and creativity, every organization can build sustainable brands. She is on a mission to help marketing teams across the globe produce tangible results from their marketing campaigns. Currently, she is working along with the Product team to enhance the AI content quality through prompt engineering.
Plan, write and optimize long form content with AI Tools
Try our AI Tools to create SEO content faster and better

Related Posts

Keeping Up With Google: August Core Update Edition
Google released its August core update last week. Here’s everything you need to know about it

15 Best AI SEO Content Generators for Quick Results
Master the art of SEO AI with our beginner's guide for 2024. Elevate your digital presence and optimize your website for success.

How accurate is Turnitin AI detection?
Curious about how accurate is Turnitin AI detection? Our blog explores the efficiency of Turnitin's AI detection system.
See how we can help you create SEO content faster and better.
- Features Overview
- Flexibility and Power
- Topic Content Editing
- Single-Sourcing and Content Reuse
- Collaboration and Teamwork
- Easy Navigation and Full-Text Search
- In-Depth Analytics and Reporting
- Security and Reliability
- Translation Management
- Integrations
- Software User Guides and Manuals
- Knowledge Base
- Online Tutorial
- Тraining Documentation
- Case Deflection
- Developer Documentation
- Context Help
- API Documentation
- Policies and Procedures
- Portal Gallery
- Customer Feedback
- Request Demo
Technical vs. Academic, Creative, Business, and Literary Writing: What Is the Difference?

Technical writing is all about the content that focuses on providing detailed and clear information on the product or service. It contains a factual and straightforward message. Technical writers convert complex technical information into useful and easy-to-understand language. You should know that there are different types of technical writing , for example, online tutorials , instruction manuals, API documentation, and so on.
The main idea of all types of technical writing is to help the end-user understand any technical aspect of the product or service.
In addition to technical writing, there are many types of other writings, such as creative, business, and literary writing. All of them have distinctive features. Let’s compare these writings to technical writing and see what they have in common and what makes them different.
Technical Writing vs. Academic Writing
Some people might think these two types of writing are similar. The truth is that these are two completely different categories. It may seem that academic writing should be more complicated since it is focused on some specific and narrow discipline. Indeed, this type of writing may describe very complex concepts and provide specialized knowledge.
Technical writing is intended to describe technical information. It may vary depending on the specifics of a particular industry.
Academic writing is aimed to present a certain point of view on a particular subject. Academic papers show results of research and demonstrate someone’s knowledge. In turn, technical writing explains something to readers and informs them. Technical papers often explain how to use a particular product or service. Technical documents can also describe procedures used by the manufacturer to perform certain tasks. What technical and academic writing have in common is that both types may contain jargon.
Academic and technical writing target different audiences. Academic papers are usually intended for fellow scholars. However, there are also academic pieces of writing intended for a broad audience. Technical writing is intended for people who use a product or service.
Technical Writing vs. Creative Writing
Creative writing is a piece of writing for entertainment and education. It focuses on imaginative and symbolic content, and creative papers are published to entertain, provoke, inspire the user. Technical writing, on the other hand, is not done to amuse its reader. It is used to inform someone. Some technical articles are sometimes made to trigger the reader to take action.
There is no such specific reader who prefers creative papers. Anyone can read the creative paper if they want to, and it gives readers a theme, message, moral, or lesson which is helpful in their real lives or provides temporary entertainment to the reader.
Creative writing has many genres and subgenres. If you want to write creatively, you should have talent. Of course, talent alone is not enough – practice is everything here.
It doesn’t mean that creativity can’t be used in technical writing. Technical articles contain so many facts and data that they can bore and overwhelm readers. This is where creativity in technical writing might come in handy. A tech writer should be creative to encourage their readers to continue reading the document.

Technical Writing vs. Business Writing
Business writing is just about any kind of writing people do at work, if we are not talking about journalism or creative writing. Business writing includes reports, emails, proposals, white papers, minutes, business cases, letters, copywriting, bids, and tenders.
However, many reports, bids, and proposals contain technical data and specifications. So business writers may find themselves editing technical content, and technical writers may be called upon to write persuasive documents for a non-technical audience.
The main objective for both these writings is to inform, be useful, build something or operate the equipment.
The language needs to be clear, concise, and accurate. Wordiness, repetition, and unfamiliar words that the audience may not understand do not belong in either business or technical writing.
Of course, you can use technical jargon in documents where the audience has the same technical background. But too much jargon tends to be a huge problem. So, if in doubt, avoid jargon or explain it.
Some business documents need to be persuasive, whereas technical documents tend to be neutral and objective.
However, there are differences in the content, language, and style of technical and business writing. More on technical writing in business is in our article What Value Technical Writers Bring to Business?
Technical Writing vs. Literary Writing
The main difference between technical writing and literary writing is that literary language is used in literary work while technical writing is used in writing for a particular field. Literary writing is used in fiction. Examples of literary writing include poems, novels, short stories, dramas, etc. The language used in literary writing is creative, imaginative and uses literary techniques like hyperbole, personification, similes, metaphors, etc.
Technical writing is the style of writing that is mostly observed in non-fiction. The language used in technical writing is direct, factual, and straightforward.
Literary writing appeals to emotions. Technical writing appeals to the mind.
Technical writing is aimed at people who have knowledge about a particular subject area. Literary writing is written for general readers.

Every writing style is important in its own way. They are used by writers depending on the subject matter, purpose, language, and target audience. Below is the table that summarizes what you found out about the types of writing mentioned in this article:
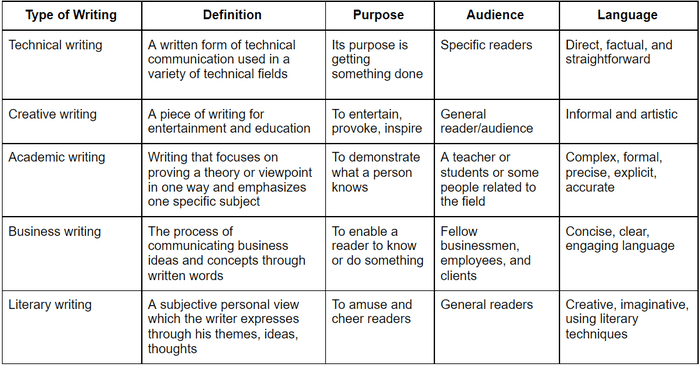
It doesn’t matter what you write: essays, business materials, fiction, letters, or just notes in your journal, your writing will be at its best if you stay focused on your purpose and target audience.
Good luck with your technical writing! ClickHelp Team Author, host and deliver documentation across platforms and devices

Give it a Try!
Want to become a better professional.
Get monthly digest on technical writing, UX and web design, overviews of useful free resources and much more.
" * " indicates required fields
Related Posts
Table of Contents
Academic Writing vs. Creative Writing: Understanding the Key Differences
Both academic writing and creative writing are commonly used in many contexts and serve a variety of goals. While academic writing is widely utilised in educational environments, creative writing is frequently employed in literary and artistic contexts. The ability to write should be universal. No matter what their profession, educational background, or area of interest, everyone may utilise writing to express their ideas, thoughts, and feelings.
What is Academic Writing and its Features?
What is creative writing and its features.
Writing that uses imagination and creativity to convey thoughts, feelings, and ideas is referred to as creative writing. It is a distinctive style of writing meant to enthral, motivate, and arouse the reader’s emotions.
Key Differences Between Academic Writing and Creative Writing
At first glance, writing for academic and creative objectives may appear to be one and the same thing. Nonetheless, there are two different writing styles, and each has its own traits and goals. The main distinctions between academic writing and creative writing will be covered in this section.
Academic writing frequently has researchers, academics, and subject-matter specialists as its audience. A sizable component of the audience for creative writing is made up of readers of fiction, poetry, and other literary genres.
Accuracy and precision are stressed in formal language used in academic writing. The tone is neutral and objective, and the jargon is specialised and technical. Slang and contractions are not appropriate.
The writer has more leeway to experiment with different structures when writing creatively because there is no set structure to follow. Flashbacks, non-linear tales, and other approaches can be used by the author to develop a distinctive framework.
Advantages of Academic Writing and Creative Writing
1.enhance communication skills, 2.increases analytical abilities, 3.builds data analysis skills.
Research and data analysis are crucial parts of academic writing since they call for in-depth subject knowledge. In many fields, notably scientific research, where the interpretation and analysis of data are critical, this talent is essential.
4.Helps in Expressing Emotions
5.enhance imagination.
For various reasons, it’s important to comprehend the difference between academic and creative writing. In the first place, it can aid writers in deciding which genre to use in a particular circumstance. In addition, it can aid authors in honing the abilities and methods required for every kind of writing. As a final benefit, it can assist authors in understanding the demands and expectations of various writing styles, which is helpful in both academic and professional contexts.
About The Author
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Learning and Development Partner
What makes Creative Writing different from other forms of writing?

Interested in writing but don’t know where to begin?
Anyone can be a Creative writer!
Sure, Creative Writing is a skill, and you have to practice it to get better at it. But for that, you first need to understand what Creative Writing is. The goal of a creative writer should be to leave the audience with the pleasure of an emotional experience. As well as search for meaning and depth to invoke emotions.
The majority of the writers are creative. You can pretend anything and can help the potential readers believe the same. If you have a story to share, which you do, share it. It may be as simple as sitting down with a blank paper and letting all your thoughts flow.
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is the ability to create where your imagination, creativity, and innovation are at the forefront. It tells a story through strong written visuals and creates an emotional impact. It makes you step out of reality and into a new realm of your imagination.
Creative writing uses senses and emotions to capture the reader’s mind, unlike other forms of writing, which has facts and information. Some examples of Creative Writing involve writing short stories, novels, poems, plays, blogs, non-fiction narratives, etc.

Creative writing doesn’t begin with the intellect. Rather it begins in the senses, where it creates images, stories, and feelings. And this kind of writing conveys and stirs emotions to arouse feelings in people.
Let us find out what Creative writing is and how it stands out from the others:
Creative writing and what makes it different from other forms of writing
Is Creative Writing different from other forms of writing?
Creative writing is art in its pure form. A major difference between Creative Writing and other kinds of writing is the use of language. It uses color, depth and is suggestive. It leaves the reader with factual information and language like other writing. But, at the same time is not just stating facts or information.
Creative writing involves a lot of creativity, much more than non-creative ones. Because it conveys information more powerfully. The intent of creative writing is not to inform the readers but to stir emotions.
Creative writing has a plot, a unique plot of some sort. In comparison, there could be or not be one for other forms of writing. Yes, remakes are considered creative writing, but they have their unique idea behind them.

Creative writing should have character when writing, unlike journalism, where you state plain facts on paper.
Creative writing always has an underlying message, even if the author did not intend for it. Other forms may not leave you with a theme or message.
Visual descriptions are part of creative writing. It keeps the audience connected with visuals and pictures in newspapers and magazines. Creative writing allows people to imagine themselves in the character’s shoes.
Creative writing has a dialogue to support the story. In contrast, non-creative writing can have dialogue like in interviews. But it is not used in the same way as the other.
All forms of writing need an audience, especially creative writing. Doesn’t matter what kind of audience, even if that audience is you!
Final thoughts:
If you want to write, don’t wait for the right mood to strike you.
At some point in our education, you will likely be faced with writing creative stuff. But, many people overlook that being a writer isn’t about how much you write. It is about challenging yourself as a writer and letting your thoughts flow. A good writer can turn any piece of writing into Creative Writing. Your writing should have an element of discovery and personal involvement in getting to the result.
Yet, if you relate to it, it is easy and enjoyable. It is not always easy, though. You suck when you start but keep getting better at it. Do you want to blog, write a page on social media or Twitter? Whatever that you want to do, start little by little, and you will get better.
Get Creative and start writing!
Afterall, there is an inner genius waiting to unleash!
Book Your Class
Kid's Name
Parent Name
Grade Grade K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Classes Classes English Math Science Social Science Coding Public Speaking Creative Writing College Counselling Math Olympiad Yoga
Phone Number
Email Address
Upcoming classes

Explore our other classes
Related articles.

Why equal opportunity is important in STEM?
Feb 23, 2024
Equal opportunity in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields is not just a...

What is STEM and why is it important in modern society?
STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, representing not just a...

Why is health education important for children?
Dec 1, 2022
Kids are the future of the nation. The importance of educating them about health and well-being...

Why Learn Geometry
Nov 21, 2022
Geometry is all about Shapes, Spaces, and Sizes! Many kids struggle with math, especially...

How to prevent students from being distracted by the smartphones
Nov 14, 2022
From infants to old age, everyone is addicted to smartphones today. Though they are more...

How to make Science more Interesting for Students?
Nov 7, 2022
Science education is one of the critical aspects for all in life. It instills the knowledge and...
Share this post with your friends!
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

Business Writing vs Academic Writing: Four Primary Differences
Some might say that the only difference between academic and business writing is the fact that the former is practiced by scholars while the latter by professionals. However, when perused closely, one can discern some stark as well as nuanced demarcation between the two. For individuals, such as college graduates, who need to occasionally shift between academic writing and business writing, knowing these differences can help them format their respective documents appropriately.

To the layman, the business writing vs academic writing dilemma might seem not worth much thought. Rather, citing the similarities they share in terms of tone and diction, these two writing styles would appear similar to an extent. One might even say that the only difference between academic and business writing is the fact that the former is practiced by scholars while the latter by professionals.
However, when perused closely, one can discern some stark as well as nuanced demarcation between the two. For individuals, such as college graduates, who need to occasionally shift between academic writing and business writing, knowing these differences can help them format their respective documents appropriately.
Business writing vs academic writing: Key differences
Below are enlisted some primary differences between the academic and business writing styles. These differences are primarily based on factors such as the purpose of writing, degree of formality, the intricacy of the language, and the audience.
1. Objective
One of the more apparent distinctions between business writing and academic writing concerns the very motive behind their implementation.
Writers employ the academic writing style when they require to showcase their scholarly capabilities. This writing style finds use in research papers, essays, dissertations, and other scholarly texts mandated by educational institutions.
Writers regularly exercising the academic writing style also enrich their research and learning prowess.
The purpose of academic writing is, thus, to create knowledge-rich texts while exploring the subject matter.
Business writing finds use in drafting professional documents such as business letters, emails, financial reports, and the ilk. Thus, it is also called professional writing.
Business documents prioritize explicitness over the usage of fancy words as they, at times, have an array of subsequent readers. Hence, business writing is relatively work-oriented and commands the readers to definitely and sometimes immediately address a document's contents.
To summarize, business writing emphasizes practicality over theoretical appraisal.
2. Language
Language is another writing aspect that sets academic writing apart from its professional counterpart.
Both writing styles demand the usage of language that is formal, sophisticated, and exudes respect and seriousness. However, in the case of academic writing, the degree of formality is marginally, and in some cases significantly, higher. And understandably so, since academics, while writing their manuscripts, need to use a relatively higher amount of jargon .
The academic writing process is comparatively more demanding as writers need to refer to a plethora of credible literature to furnish their texts. Business writing, instead, regurgitates a lot of the formal expressions while accommodating factual information in the text. As such, it is the more approachable of the two.
Also, unlike academic writing, business writing does not dogmatically prohibit the use of first and second pronouns.
Complicated sentence structures are another linguistic factor that differentiates academic and professional writing. Although there are no strict statutes regarding the usage of long sentences in professional writing, readers look down upon them. This is because business writing is comparatively more straightforward and less persuasive.
Hence, to the keen eye, language can be an overt identifier of writing style. But at the same time, the uninformed individuals might not observe the same linguistic differences as apparently.
3. Formatting and document structure
The third factor that segregates academic and professional writing is the document's structure and the formatting requirements.
Academic writing and business writing both abide by different layouts and formatting styles. Academic writers typically arrange their documents as per the IMRaD structure . However, this structure is subject to changes if the teacher or the supervisor states it.
Also, academic writers need to observe the APA, MLA, or Chicago formatting styles for their manuscripts. Failing to do so can welcome some severe repercussions regardless of how well-written the document is.
Business writers, too, employ specific layouts for different professional documents. But these layouts are outrightly different from their academic counterparts.
For instance, while writing business letters, professional writers use the block style for formatting their letters. Semi-block and modified block are the other two formatting styles for business letters.
4. Readership
The intent of any writing, whether it is academic or professional, is to address the readers. Thus, for a significant part, writers need to mold their documents according to the reading requirements of their audience. It is these requirements that further isolate academic writing from professional writing.
Since academic writing is the more complex of the two, writers presume their readers to be well-read and aware of the context of their document. This also implies that academic readers are under less temporal constraints since scholarly texts require ample time to study.
Business documents, conversely, are aimed at readers across all literacy levels. In other words, the writers have a vague idea about their readership.
Also, since a professional environment is competitive and fast-paced, readers are under stricter time constraints.
Business writing vs academic writing: Synopsis
The rationale behind the business writing vs academic writing narrative primarily pillars itself on the above-mentioned differences. Although these distinctions are not exhaustive, they offer readers a premise on which they can base some more differences.
Academic writing and business writing both intend to inform the readers about their contents comprehensively. However, it is the approach they take and the requisites they fulfill that sets them apart.
How to Paraphrase in Academic Writing: A Comprehensive Guide
Taboo Words to Avoid in Academic Writing
Formal Tone in Academic Writing: Tips to Achieve It
Basic Language Rules to Help You Ace Academic Writing
DOs and DON'Ts: Tips to Improve Your Academic Writing
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
If you need us to make your manuscript shine, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering manuscripts with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English manuscript formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
This article discusses the main differences between business writing and academic writing. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Avoid Anthropomorphism in Your Dissertation?
How to Write a Research Methodology Section for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Theoretical Framework for a Dissertation and Thesis?
How to Write Literature Review for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Dissertation and Thesis Introduction
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Whether it is an academic essay or any other thesis paper, all the papers are directly or indirectly associated with one’s future. Therefore, making mistakes here means compromising with the future. However, students are fond of making some habitual errors while composing an academic paper. Let’s learn those mistakes and make sure not to repeat them in your turn.

Academic writing is the type of writing style that requires a lot of attention to details, rules, and regulations. Mainly used for, as you might have guessed, academic purposes, it is one of the most common writing styles for professional works. However, as regulated and strict it is, it is also easier to make mistakes here. One such very common mistake that happens all the time for several researchers is sentence structuring. Sentence structuring has always been a little tricky, academic writing or not. That is why a great emphasis is made on them during the editing and proofreading phases. This article discusses the most common sentence structuring mistakes and how you can avoid them.

Researchers develop theories to explain phenomena, build connections, and make educated guesses. Therefore, you illustrate the existing ideas supporting your dissertation or thesis in a theoretical framework, depicting that your work has a solid foundation.
Creative Writing Vs. Technical Writing Vs. Academic Writing
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on Published: June 7, 2023 - Last updated: July 31, 2023
Categories Writing
You’re a writer, and you’ve got the passion and talent to explore various realms of writing. You might wonder how to navigate the diverse creative, technical, and academic writing landscapes.
Each style has its unique purpose, goals, and characteristics that can open new avenues for creative expression and professional growth.
In this article, we’ll delve into the defining aspects of these three writing styles, helping you understand their differences while offering tips on balancing creativity and accuracy.
As you develop skills in multiple writing domains, you’ll discover how to adapt your voice for different audiences and contexts. Embrace the freedom that comes from mastering these distinct forms of communication!
Key Takeaways
- Each writing style has its unique characteristics and requires different approaches for success.
- Adapting writing style to fit different audiences and contexts is important for effective communication.
- Versatile writers who master multiple writing styles have greater career and creative opportunities.
- Writing quality is crucial regardless of the style and requires clarity, precision, and continuous skill refinement.
Defining the Three Writing Styles
You’re strolling through a literary garden, where three distinct paths emerge – creative writing with vivid blooms, technical writing with structured hedges, and academic writing adorned by meticulously pruned scholarly trees.
Each path offers a unique experience as you explore the world of written communication.
A writing styles comparison reveals that each style has its own rules and unique challenges to overcome.
Creative writing allows your imagination to run wild, painting pictures with words and evoking emotions in your readers.
Technical writing, on the other hand, demands precision and clarity as you explain complex concepts or provide instructions for specific tasks.
Academic writing requires rigorous research and adherence to established guidelines while presenting arguments or findings clearly and concisely.
As you navigate these paths in the literary garden, remember that mastering each style will grant you the freedom to express yourself effectively in any situation life throws you.
Purpose and Goals of Each Style
Diving into each style’s purpose and goals, it’s crucial to understand how they uniquely cater to various communication needs and audiences.
Creative writing aims for audience engagement by evoking emotions, sparking imagination, and telling a story. Its main goal is to entertain, inspire, or provoke thought through stylistic choices such as figurative language, vivid descriptions, and memorable characters.
On the other hand, technical writing focuses on providing clear and concise information to help readers understand complex concepts or complete tasks. This style prioritizes accuracy and user-friendliness while employing straightforward language with minimal jargon.
In contrast, academic writing seeks to explore intellectual ideas or present research findings in a structured format like essays or research papers. The primary goal is contributing knowledge within a specific field by adhering to established standards of evidence-based argumentation.
Unlike creative writing that encourages personal expression and flexibility in form, academic writing demands strict adherence to guidelines concerning citation styles, tone consistency, and logical organization.
Ultimately, your ability to adapt between these different styles will free you from the constraints of one-dimensional communication skills – allowing you greater complexity in your thoughts and ideas while efficiently conveying them across various platforms.
Characteristics of Creative Writing
Imagine a world where words paint vivid pictures and stories come to life, captivating your senses – that’s the realm of artistic expression in literature.
Creative writing is about emotionally impacting your audience, using sensory language to craft immersive experiences that transport readers into the world you’ve built for them.
Some key characteristics of creative writing include:
- Emotional impact: Inspiring emotions such as joy, sadness, or fear in your reader
- Sensory language: Utilizing descriptive words and phrases that engage the five senses
- Artistic freedom: Experimenting with different styles, formats, and structures
Remember to focus on creating an emotional impact through sensory language so your readers can truly experience the world you’ve created.
By doing this, they will enjoy what’s written and indulge their subconscious desire for freedom – allowing them to escape from reality into a universe crafted by their imagination.
Elements of Technical Writing
In technical writing, focusing on clarity, precision, and a straightforward approach is essential.
You’ll need to master technical terminology and document design to effectively convey complex information in a way that’s easy for your audience to understand.
When dealing with specialized subject matter, you must ensure that your writing is accurate and concise while meeting the needs of both experts and novices alike.
To create engaging content that satisfies your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom, consider incorporating visual aids like charts or diagrams into your document design. This helps break up large blocks of text and makes it easier for readers to grasp difficult concepts at a glance.
Additionally, don’t be afraid to use contractions and an active voice in your writing – this can help make your work more relatable and enjoyable to read, even when dealing with highly technical subjects.
Clear communication is key in technical writing, so always prioritize simplicity over complexity whenever possible.
Features of Academic Writing
Academic writing, often characterized by its formal tone and precise structure, serves as a vehicle for critical thinking and the dissemination of knowledge. Through metaphorical language, it’s possible to paint a vivid picture that illuminates complex ideas for readers across various disciplines, ensuring they’re more likely to engage with the content on a deeper level.
Maintaining an academic tone requires avoiding colloquial expressions or emotional language while adhering to grammatical conventions.
Additionally, it’s important to recognize the different referencing styles used in academia. These styles enable writers to provide proper credit for sources while maintaining consistency throughout their work.
To help you better understand some key features of academic writing, take a look at this table illustrating common attributes:
| Formality | Academic writing maintains a formal tone – avoiding slang, contractions, and jargon |
| Structure | A clear structure is essential in presenting logical arguments |
| Referencing Styles | Proper citation using consistent formats such as APA or MLA |
| Evidence-Based | Relies on empirical data and research findings rather than personal opinions |
| Precision & Clarity | Clear explanations with accurate vocabulary choices are crucial |
Embrace these characteristics in your academic writing endeavors! By practicing clarity, accuracy, and conciseness – along with proper referencing styles – you’ll foster an environment where readers can freely explore new ideas and expand their understanding of complex concepts.
In turn, this will contribute positively towards your intellectual growth while making your work enjoyable and relatable for others who share your desire for freedom through knowledge acquisition.
The Role of Imagination and Artistry
While it’s often overlooked, the infusion of imagination and artistry can greatly enhance the impact of academic writing by drawing readers into a vivid landscape of ideas and fostering deeper engagement with complex concepts.
Imagination limitations are sometimes seen as necessary in scholarly work to maintain objectivity, but incorporating elements of creativity can help you break free from conventional thinking patterns and present your research more engagingly.
Artistry may not be explicitly required in academic writing, but it can elevate your work when applied judiciously. To harness the power of imagination and artistry in your academic writing, consider these strategies:
- Use metaphors or analogies to clarify abstract or complex ideas
- Experiment with narrative techniques to build suspense or intrigue around your research questions
- Employ active voice and vivid language for more dynamic descriptions
- Integrate visuals such as graphs, charts, or illustrations to support your arguments visually
- Choose an innovative structure that complements the content
Remember that combining creative approaches with rigorous scholarship doesn’t compromise your credibility; it demonstrates your ability to think beyond traditional boundaries and present information in a fresh light.
The Importance of Clarity and Precision
Clarity and precision can’t be overstated in academic writing, as they ensure your arguments are well-structured, your ideas easily understood, and your evidence compellingly presented.
The significance of clarity lies in its ability to eliminate confusion and ambiguity, allowing readers to grasp complex concepts without getting lost in a maze of jargon or convoluted sentences.
Similarly, the benefits of precision include fostering trust with your audience by demonstrating that you’ve conducted thorough research and can present information accurately.
In embracing these principles, you’ll empower others to comprehend and engage with your work and grant them the freedom to explore new thoughts and perspectives.
By presenting clear and precise content, you’re inviting readers into a world where they can freely navigate ideas without feeling overwhelmed or confined.
Formality and Structure in Writing
Transitioning from the importance of clarity and precision in writing, another crucial aspect is the formality and structure employed in your work.
As a writer, you need to be aware of these elements as they vary across different types of writing.
When it comes to creative writing, informal language, and unconventional structures are often embraced. This allows for more freedom and flexibility in expressing ideas, emotions, or storytelling.
On the other hand, technical and academic writing generally requires more formal language usage and structured formats. These guidelines help ensure that your audience clearly communicates and easily understands information.
It’s important to strike the right balance between formality and structure based on your purpose – engaging readers with an enjoyable narrative or providing concise, accurate information they can rely on.
Common Applications for Each Style
As you’re exploring various writing styles, it’s essential to understand their common applications and how each can serve a unique purpose in effectively conveying your message.
To evoke an emotional response from your audience, consider the following applications for each style:
- Creative writing: Unleash your imagination through storytelling, poetry, or personal essays. With this style, you have the freedom to express yourself without limitations.
- Technical writing: Simplify complex concepts and procedures by crafting clear and concise manuals, reports, or user guides. This allows your readers to grasp new information easily.
- Academic writing: Showcase your critical thinking skills with research papers, dissertations, or journal articles. Rigorous analysis and synthesis of ideas are key in this style.
- Style integration: Combine elements from different styles to create engaging content that caters to diverse audiences – a blog post blending creativity with research insights or a business proposal incorporating data analysis with persuasive language.
- Application challenges: Hone your adaptability by tackling projects requiring multiple writing styles, such as grant proposals or marketing campaigns.
By recognizing the value of each writing style and understanding when to apply them effectively, you’ll be well-equipped to face any communication challenge.
Career Opportunities and Professional Paths
You might wonder how mastering different writing styles can benefit your career, so let’s dive into the various opportunities and professional paths that await you.
Whether you’re interested in creative, technical, or academic writing, each field offers unique prospects for career growth. As a creative writer, you could pursue careers such as novelist, screenwriter, copywriter, or content creator for various mediums.
Technical writers are highly sought after in industries like technology, healthcare, engineering, and manufacturing, to name a few.
Academic writers often find their niche in research institutions or universities where they contribute to scholarly publications.
No matter which path you choose, strong networking strategies will play an important role in propelling your career forward.
Attending conferences and workshops related to your chosen field helps sharpen your skills. It allows you to connect with industry professionals who can provide guidance and possible job leads.
The Writing Process: Differences and Similarities
Now that we’ve explored various career paths, let’s delve into the writing process and examine how different styles share similarities and distinctions.
Whether you’re working on creative, technical, or academic writing projects, certain aspects of the writing process remain consistent across all fields.
To keep your audience engaged and satisfy their subconscious desire for freedom, your writing must maintain clarity, accuracy, and conciseness. Finding the right writing motivation can help you stay focused and produce high-quality content.
- Planning: Before starting any project, plan your approach by identifying your goals and target audience. This will ensure your content is well-suited for its purpose.
- Writing: Regardless of the style you’re working with, always strive to write clearly and concisely while maintaining an engaging tone.
- Editing: Once your draft is complete, use effective editing techniques to refine your work by removing redundancies or errors that could hinder comprehension.
By following these steps in each type of writing project (creative, technical, or academic), you’ll be better equipped to create captivating content tailored specifically for its intended purpose while keeping in mind the inherent differences between each style.
Balancing Creativity and Accuracy
Striking the perfect balance between imagination and precision is essential for crafting content that captivates readers while conveying accurate information.
Creative constraints and accuracy challenges can push you to think outside the box, allowing your work to stand out. Embrace these limitations as opportunities for growth, whether creating an imaginative story or composing a well-researched academic paper.
Remember that your audience has a subconscious desire for freedom – don’t be afraid to use creative techniques to engage them while maintaining accuracy. When it comes to balancing creativity and accuracy, practice makes perfect.
Experiment with different writing styles, methods, and sources of inspiration until you discover what works best for your unique voice.
Clarity, accuracy, and conciseness are crucial to effective communication.
However, don’t let those requirements stifle your creativity entirely. By consciously honing your skills in both areas simultaneously, you’ll find that striking the ideal balance becomes second nature over time – allowing you to create captivating content that resonates with readers while remaining true to the facts.
Adapting to Different Audiences and Contexts
Mastering the art of adapting your content to various audiences and contexts can be an exhilarating challenge, as it’s essential to tailor your message while maintaining authenticity – but how will you achieve this delicate balance?
One key component is audience engagement, which requires understanding who you’re addressing and their needs, desires, or interests.
By empathizing with your readers and crafting messages that appeal to them personally, you’ll capture their attention and motivate them to engage with your content.
Contextual adaptation comes into play when you consider the specific circumstances surrounding each piece of writing.
Whether it’s a creative story meant for entertainment purposes or an academic article discussing complex theories, adjusting language, tone, and style accordingly will ensure that your message is clear and concise for the intended audience.
Remember that people have a subconscious desire for freedom – so make sure your writing connects with them emotionally while still providing accurate information they need.
Developing Skills in Multiple Writing Styles
Diversifying your skill set in various writing styles can truly set you apart as a versatile and dynamic wordsmith. This will enable you to excel in any literary arena, making you a more appealing candidate for job opportunities and allowing you to connect with different audiences and contexts through your writing.
As a result, versatile writers often find themselves enjoying greater freedom in their careers and creative pursuits.
To achieve this level of versatility, consider focusing on the following four areas:
- Practice multiple writing styles : Challenge yourself to write creatively, technically, and academically – even outside your comfort zone.
- Study diverse genres : Read widely across different genres and formats to understand the unique requirements for each type of writing.
- Seek constructive feedback : Share your work with others with experience or expertise in various fields, requesting feedback on improving clarity, accuracy, and conciseness.
- Continuously refine your skills : Review and revise your work to ensure it meets the highest quality standards while remaining engaging for readers.
By embracing these strategies, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a versatile writer who can navigate any literary landscape with confidence and ease. Enjoy the freedom that comes from mastering multiple writing styles!
Tips for Success in Each Writing Domain
To excel in each writing domain, it’s essential to understand the unique requirements and techniques for success.
Did you know that 73% of employers value strong writing skills?
You’ll be better equipped to meet diverse demands and seize opportunities by honing your abilities in various domains. Skill-building exercises can help strengthen your proficiency in creative, technical, and academic writing styles while boosting your writer’s motivation.
For creative writing, practice painting vivid images with words by describing settings, characters, or emotions from personal experiences or imagination.
Experiment with different narrative structures and use stylistic devices like metaphor and simile.
In contrast, technical writing requires clarity and precision above all else; try breaking down complex processes into simple steps or creating concise user guides for software or tools.
Finally, academic writing calls for a formal tone and well-structured arguments supported by credible evidence; practice synthesizing research findings into clear thesis statements followed by logical analysis.
As you explore these distinct realms of expression, embrace your freedom to create compelling stories, convey helpful information effectively, and contribute valuable insights to scholarly discourse – the world needs all three!
Frequently Asked Questions
How can a writer effectively transition between creative, technical, and academic writing styles within the same project or document.
To effectively transition between styles, master transition techniques and enhance your writing versatility. Embrace clarity, accuracy, and conciseness while engaging your audience’s subconscious desire for freedom through your adaptable writing approach.
Are there any specific tools or software programs that can help writers improve their skills in each of these writing styles?
Explore various software programs to boost your skill development in different writing styles. Embrace the freedom of mastering creative, technical, and academic writing with tools designed for clarity, accuracy, and conciseness.
How do cultural differences and language barriers impact the effectiveness of creative, technical, and academic writing when communicating with international audiences?
Imagine trying to solve a puzzle with mismatched pieces. Cultural adaptability and language sensitivity are crucial for effective communication, as they bridge gaps in understanding when addressing international audiences.
Can you provide examples of successful writers who have mastered all three writing styles and have been able to use them interchangeably in their work?
Mastering versatility in writing is key to success! Successful writer examples include Isaac Asimov, who skillfully switched between creative, technical, and academic styles. Embrace your freedom to adapt and excel in all three.
Are there any interdisciplinary fields or industries where a writer may need to utilize all three writing styles regularly, and how can they prepare for such a diverse writing landscape?
In the dance of interdisciplinary writing, you’ll glide between styles. Diverse preparation is your key to mastering this choreography. Embrace clarity, accuracy, and conciseness while engaging your audience’s desire for freedom.
So, think of yourself as a chef in the writing kitchen. Each style – creative, technical, and academic – is like a different ingredient you can mix and match to cook the perfect dish for your audience.
Remember to keep it clear, accurate, and concise so your readers can savor every bite of your literary feast.
Bon appétit!
- Software Testing Course
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Waterfall Model
- Software Requirements
- Software Measurement and Metrics
- Software Design Process
- System configuration management
- Software Maintenance
- Software Development Tutorial
- Software Testing Tutorial
- Product Management Tutorial
- Project Management Tutorial
- Agile Methodology
- Selenium Basics
Difference between Technical Writing and Creative Writing
1. Technical Writing : Technical writing is a piece of writing which focuses on factual and straight forward content and technical papers are published to inform and instruct and educate the user about some specific topic. There exists specific readers who prefers technical papers. It gives readers information about some technical topics or it gives directions on how to do something.
2. Creative Writing : Creative writing is a piece of writing which focuses on imaginative and symbolic content and creative papers are published to entertain, provoke, inspire the user. There is no such specific readers who prefers creative papers. Anyone if wants can read creative paper and it gives readers a theme, message, moral or lesson which is helpful in their real lives or gives a temporary entertainment to the reader.
Difference between Technical Writing and Creative Writing :
| S.No. | TECHNICAL WRITING | CREATIVE WRITING |
|---|---|---|
| 01. | Technical writing is based on facts and concepts. | General writing is based on imaginations and creativity. |
| 02. | Technical writing focuses on factual and straight forward content. | Creative writing focuses on imaginative and symbolic content. |
| 03. | Technical writing has its specific reader/audience. | Creative writing has general reader/audience. |
| 04. | The purpose of technical writing is to inform and instruct and educate the user. | The purpose of creative writing is to entertain, provoke, inspire. |
| 05. | It follows formal and standard style of writing. | It follows informal and artistic style of writing. |
| 06. | It gives readers information about some technical topics or it gives directions on how to do something. | It gives readers a theme, message, moral or lesson which is helpful in their real lives or gives a temporary entertainment to the reader. |
| 07. | It uses text features like the table of contents, index, labels, charts, photos and graphs. | It uses narrative elements such conflict, character, theme, setting and resolution. |
| 08. | The tone of technical writing is objective. | The tone of creative writing is subjective. |
| 09. | It is based on specialized vocabulary. | It is based on general, evocative vocabulary. |
| 10. | It is organized in a sequential and systematic manner. | It is organized in an arbitrary and artistic manner and may not be systematic. |
| 11. | In technical writing graphics are included to give more information to the topic. | In creative writing graphics are included to give more attraction to the topic. |
| 12. | Technical writing depends on any result, research, information etc. | Creative writing depends on schedule and mindset of the writer. |
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Difference Between
- Software Engineering
- How to Delete Discord Servers: Step by Step Guide
- Google increases YouTube Premium price in India: Check our the latest plans
- California Lawmakers Pass Bill to Limit AI Replicas
- Best 10 IPTV Service Providers in Germany
- 15 Most Important Aptitude Topics For Placements [2024]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
EnglishClub ESL Forums
English-language discussion for learners of English
Skip to content
- Board index Discussion Creative Writing
Creative Writing or Business Writing?
Moderator: EC

Post by markcoblin » Mon Dec 09, 2019 8:26 am
Re: Creative Writing or Business Writing?
Post by Mohsen » Tue Jan 21, 2020 11:50 am
markcoblin wrote: ↑ Mon Dec 09, 2019 8:26 am Hi, Can anyone tell me the difference Between Creative and Business writing? About Creative writing, I have a little bit of knowledge like write content about your personal experience and imagination but no idea about business writing anyone explains to me?
Post by marekdeny » Wed Mar 04, 2020 5:01 am
Post by MicheleDouglas » Mon Jan 25, 2021 1:30 pm
Post by inglesteacha » Tue Dec 07, 2021 7:16 pm

Post by kellyf » Tue Jan 25, 2022 10:11 am
Post by harrywilbert » Thu Apr 07, 2022 4:13 pm
Post by maidensedate » Fri Apr 15, 2022 8:36 am
Post by marievangundy » Wed May 18, 2022 11:50 am
Post by SummerFrog » Fri Jun 24, 2022 10:15 am
Post by emilyparker » Mon Sep 26, 2022 4:41 pm
Post by emilyparker » Tue Sep 27, 2022 8:18 am
SummerFrog wrote: ↑ Fri Jun 24, 2022 10:15 am In my time at college, when I worked for a newspaper, I'd remain up until late into the night, and sometimes till the morning, writing my story within the workplace. It's not like it took an incredibly long time writing, but I'd take my time, write it, hand it over to my editor and return it full of red marks and remarks and notes about what my editor is looking for. Rinse, repeat. It was a challenging course, no doubt however it helped make professional writing simpler for me later. At present, I'm working on an assignment as a copywriter which is a breeze for me. Writing is a procedure. Business writing, creative writing, or whatever... writing is an ongoing process. It's not a magical process to write an amazing story. The actual writing process is just one part of what we refer to as "writing." In actuality, story planning and structuring the story prior to draft as well as post-draft analysis and editing, proofreading, and revision are all as essential to "writing" as... well, writing.
Post by mmoexpgong » Thu Dec 29, 2022 6:43 am
Post by opgroup » Mon Jul 03, 2023 1:20 pm
Post by Robinson » Fri Jul 28, 2023 11:51 am
Return to “Creative Writing”
- English Help
- ↳ Grammar Help
- ↳ Help Each Other with English
- ↳ Learning Tips
- ↳ English Language FAQ
- ↳ Student Discussion
- ↳ Teacher Discussion
- ↳ Adventure & Travel
- ↳ Books & Authors
- ↳ Creative Writing
- ↳ Current News
- ↳ Food & Fitness
- ↳ Entertainment
- ↳ Ideas and Opinions
- ↳ Music & Movies
- ↳ Sports & Hobbies
- Talking Point
- ↳ Talking Point discussion
- ↳ Talking Point homework
- Board index
- All times are UTC
- Delete cookies
Powered by phpBB ® Forum Software © phpBB Limited
Privacy | Terms
Filter by Keywords
How to Write Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
September 3, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
Imagine assembling furniture without instructions. You might get some parts right, but soon you’ll hit a snag. Missing screws, misaligned pieces, or parts that don’t fit—what started as a simple task quickly turns into a frustrating mess, leaving you with a half-built disaster and wasted time.
This is exactly what happens in the workplace with vague guidelines that no one understands.
When team members handle tasks differently, it creates inconsistencies and errors, turning a smooth process into a chaotic scramble. This leads to frustration, delays, and a final product that falls short.
If your instructions are causing chaos instead of streamlining operations, it’s time to revamp them with a well-crafted standard operating procedure (SOP).
An SOP isn’t just another document to check off your to-do list. When done right, it’s a powerful tool that demystifies processes, sets clear expectations, and keeps everyone on the same page.
Let’s discuss how to write a standard operating procedure that solves operational headaches, and explore some real-world SOP examples to see these practices in action.
Benefits of SOPs in business operations
Difference between a process and a standard operating procedure, 1. hierarchical steps format, 2. flowchart format, 3. checklist format, 1. gather the required information , 2. define the objective, stakeholders, and end-users , 3. outline the sop document, 4. write the sop, 5. proofread and test the sop, 6. onboard and train employees , 7. regularly review and update your sop , implementing the sop with clickup , example 1: sop for incident management, example 2: sop for audit processes, example 3: sop for accounting , 1. inaccessibility , 2. lack of proper maintenance , 3. lack of training , 4. collaborative sop development.
Understanding Standard Operating Procedures
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are detailed, written instructions designed to guide individuals through specific tasks or processes within an organization.
Incorporating standard operating procedure documents in your routine operations brings multiple advantages, including:
- Improved quality control : SOPs ensure tasks are executed consistently and accurately according to predefined standards. This reduces errors and variability, leading to reliable and high-quality outcomes
- Training and onboarding : Well-documented procedures and policies help new employees learn and adapt quickly, reducing both training time and costs
- Compliance and risk management : SOPs ensure regulatory compliance by helping businesses adhere to industry standards, minimizing the risk of legal issues and penalties
- Knowledge preservation : SOPs document essential processes and practices. This ensures valuable knowledge is retained within the organization even if experienced employees leave the company
- Standardized customer services: By providing reliable and standardized services, SOPs guarantee consistent handling of all customer interactions. This enhances customer satisfaction and builds trust
Mixing up processes and SOPs can lead to confusion, making it hard to document and execute tasks consistently. To avoid this, know the key differences:
| Meaning | It’s a high-level overview that outlines the flow of activities within a system | It’s a step-by-step instruction manual that tells you exactly how to handle each part of the process |
| Example | A process like “Handling Customer Complaints” includes steps like receiving the complaint, assessing it, and resolving it | An SOP for the “Handling Customer Complaints” process provides precise instructions on what to say when receiving a complaint, how to fill out forms, and how to follow up with customers |
Formats for Standard Operating Procedures
Different SOP formats suit various needs. Pick one that aligns with your team’s workflow to enhance clarity, reduce errors, and improve adherence to rules and regulations.
Here’s a breakdown of the most impactful formats:
A hierarchical SOP format organizes complex procedures in a clear, layered structure. It starts with broad steps and breaks them down into detailed sub-steps. This ensures nothing gets missed and helps maintain consistency and accuracy in task execution.

This SOP format uses a visual diagram to map processes, making complex procedures easy to grasp.
Each step is featured as a box or shape, with arrows guiding you from one step to the next. You can break it down even further by highlighting who’s responsible for each part—whether it’s a department or a specific person.

The checklist format is a straightforward list of tasks or steps that need to be completed, often with checkboxes next to each item. This format is especially useful for keeping things sorted in routine procedures.

Developing an Effective Standard Operating Procedure
Writing standard operating procedures is more than just filling in the blanks. It’s about making a clear, actionable guide your team can use. Here’s how to do it right:
Dive into the nitty-gritty of the procedure you’re documenting. This means:
- Observing how things are currently done
- Interviewing people who are directly involved
- Reviewing existing company policies and procedures to get insights into the process
You can talk to subject matter experts (SMEs) and key stakeholders—they have insights that can strengthen your SOP further. Also, ensure your SOP documents align with industry standards and regulations—it’s not just about what works but what’s legally and ethically sound.
💡Pro Tip: Use a company policy and procedure template to ensure comprehensive coverage of company operations and key areas such as workplace conduct, harassment policies, and safety regulations.
A clear goal keeps your SOP focused and effective. So, jot down what you want your standard operating procedure document to achieve. Are you aiming to boost efficiency, ensure compliance, or bring consistency to how things are done?
For instance, if you’re working on customer onboarding, your goal might be to cut the onboarding time by 20% while ensuring 95% customer satisfaction.
Next, identify who will be involved and affected by this SOP. This includes:
- Team leaders who can provide insights into daily operations and ensure the SOP aligns with team workflows
- Department heads who oversee how the SOP integrates into the department and supports broader organizational goals
- Compliance officers who can check that the SOP meets legal and regulatory requirements and update it as needed
You must also consider the expertise level and needs of end-users so you can create a user-friendly SOP document.
With your research and audience insights in place, transform your raw materials into a structured outline. It serves as a blueprint of your SOP, where all critical sections, detailed steps, and sub-steps are organized logically.
💡Pro Tip: For effective SOP outlines, envision the final goal of process documentation and work backward to detail every step needed to achieve that outcome.
Now, it’s time to start writing. Your goal is to create a SOP document that’s easy to follow, even for someone unfamiliar with the process.
Here’s how to do it:
- Avoid jargon and overtly technical terms unless absolutely necessary
- Use numbered lists for step-by-step instructions and bullet points for highlighting key information or considerations
- Incorporate diagrams, flowcharts, or screenshots to clarify complex steps
- Specify each step clearly. Name tools, materials, or software involved
- Highlight health and safety warnings where applicable to ensure users are aware of risks and precautions
Include these components to make SOPs comprehensive and clear:
- Title page: It sets the stage for everything that follows and consists of the SOP title, identification number, revision date, and author
- Purpose: A brief description of why the SOP exists and what it aims to achieve
- Scope: Define what the SOP covers and what it doesn’t, to set clear expectations
- Responsibilities: Specify who’s responsible for implementing and overseeing the SOP to ensure accountability and clarity
- Procedure: This is the meat of the SOP. Offer detailed, step-by-step instructions on performing the task or process, keeping it precise and straightforward
- Definitions: Explain technical terms or industry-specific abbreviations to avoid confusion
- References: List related documents or resources to add depth and context to the SOP
Once your SOP writing process is complete, proofread it to catch any grammatical errors, clarity issues, or inconsistencies.
Have actual users test it to see how it performs in real-life scenarios. Gather their feedback on the difficulties they experienced and use it to make necessary adjustments.
Finally, the SOP must be reviewed and approved by relevant stakeholders or management to ensure its compliance.
Read More: 8 Process Improvement Templates in ClickUp & Word to Optimize Efficiency
Once the SOP is approved, roll it out to your team. Train everyone on using it effectively through hands-on demonstrations, step-by-step walkthroughs, interactive workshops, and detailed Q&A sessions.
Monitor progress, gather feedback, and tweak the SOP to enhance its usability and boost operational efficiency.
Schedule quarterly or annual reviews to assess the SOP’s relevance.
A good practice is to gather feedback from team members who use the SOP daily and monitor for any procedural changes or new regulations that could impact its content. The SOP should also be compared against current industry standards to identify areas for improvement.
When updates are necessary, revise the document, send it to stakeholders for review, and train your team again to ensure everyone is on the same page with the latest version.
Read More: Establish Consistency in Operations: The Ultimate Guide to Process Standardization
ClickUp is a robust document collaboration software that streamlines SOP creation, management, and distribution.
It is your go-to SOP software for effectively implementing, managing, and distributing standard operating procedures.
Teams can collaboratively draft SOPs in real time, ensuring that input from all relevant stakeholders is captured efficiently. The platform allows easy version control to track and manage updates without confusion.
ClickUp Docs make writing and drafting procedures a breeze. You can start from scratch or use a template, and everyone on your team can add their input in real time. No more messy email threads or lost versions—everything’s right there in one place.
With extensive formatting options, you can organize your steps clearly into sections with headings, make numbered and bulleted lists, add images or links, and even tag team members for their feedback.
You can leverage ClickUp Brain to further accelerate the process by generating an automatic outline or summary based on your research of existing SOPs and industry standards. This AI-powered assistance saves you time and ensures you don’t miss any critical steps.
You can give ClickUp Brain prompts and get relevant results for your queries. For example, when you ask for a checklist for creating an Onboarding SOP, it would give you about 8-9 pointers to get your initial SOP draft in place.

ClickUp Brain also provides follow-up prompts for your query to make your SOP more detailed and insightful.

This AI tool for documentation helps keep your tone consistent and your content clear. It also automatically checks for spelling errors and suggests improvements.
ClickUp also has a vast library of pre-built standard operating procedure templates, including statement of work templates and process maps.
For example, the ClickUp Standard Operation Procedure Template is designed to help you create clear and organized SOPs from the get-go.
It allows you to:
- Create tasks with statuses like ‘Not Started’, ‘In Progress’, and ‘Completed’ to keep tabs on where each step stands
- Add attributes like ‘Priority Level’ or ‘Due Date’ to your tasks. This helps you categorize and manage tasks more effectively
- Switch between various views—the List View for a simple task overview, the Gantt View for a timeline view, and the Workload View to see team capacity
- Automate routine tasks like setting reminders for review dates or use AI to summarize progress
Real-World Use Cases of SOPs
Now that you know how to write standard operating procedures (SOPs) let’s examine how they streamline operations and drive success across diverse industries. The best part? You can create them much faster using ClickUp’s SOP templates .
Establish guidelines and procedures for managing incidents to ensure timely resolution, minimize impact, and prevent recurrence.
Scope
This SOP applies to all employees, the incident response team, and relevant stakeholders involved in incident management. It covers activities from incident identification to resolution and post-incident review.
- Identify and report incidents using monitoring systems and reporting channels
- Assess and categorize incidents by severity and impact
- Contain and mitigate incidents to prevent further damage
- Resolve root causes and restore systems to normal operations
- Document actions taken and conduct a post-incident review
- Communicate status and resolution updates internally and externally
Establish guidelines and procedures for conducting audit processes to ensure accuracy, compliance, and transparency in evaluating organizational activities and records.
This applies to internal audit teams, finance departments, compliance officers, and other relevant departments involved in audit activities. It covers the entire process from planning to reporting and follow-up.
- Define audit scope and objectives with relevant departments
- Develop a detailed audit plan with the methodology, timelines, and resources
- Collect and examine data, records, and documents for compliance and performance
- Identify and document discrepancies, risks, or areas for improvement
- Review and validate findings with stakeholders for accuracy
- Prepare and submit an audit report with findings and recommendations
- Communicate results to management and ensure follow-up on corrective actions
Read More: The Ultimate Guide to Workflow Documentation for Businesses
Establish guidelines and procedures for accounting processes to ensure accuracy, consistency, and compliance with financial regulations.
This applies to the finance department, accounting personnel, and other relevant stakeholders involved in financial management activities. It covers the entire accounting process, including transaction recording, reconciliation, financial reporting, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Record financial transactions accurately with supporting documentation
- Reconcile bank statements, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and other records regularly
- Prepare financial statements monthly, quarterly, and annually while observing strict adherence to standards
- Process payroll, including calculations for wages, deductions, and taxes
- Prepare and file tax returns in compliance with regulations
- Conduct internal audits and address findings with corrective actions
- Securely organize and store financial records, retaining them as required
ClickUp’s Accounting SOP Template is designed to assist you in documenting and managing your accounting department’s standard operating procedures.

You can use this template for:
- Minimizing the time required to conduct regular tasks
- Maintaining uniformity in accounting procedures
- Ensuring that important actions are not skipped or neglected
- Providing a verification trail to ensure accountability and conformity
Overcoming the Challenges of Developing SOPs
Standard operating procedures are game-changers, but getting them right can be tricky. Here’s why many businesses stumble:
Imagine writing detailed SOPs only to have them buried under layers of old folders and forgotten emails or locked behind complicated access controls. If employees can’t easily find and access the SOP, it’s as good as a blank sheet of paper. This usually comes down to lousy document management or outdated digital tools.
To tackle this:
✅ Store your SOPs in a centralized, easily accessible location—think cloud-based storage with user-friendly interfaces
✅ Ensure the SOP is easily accessible with the right permissions so everyone who needs it can view and use it without hassle
Creating an SOP is just the beginning; keeping it relevant at all times is a task in itself. If not properly maintained, SOPs can quickly become outdated, leading to errors, inefficiencies, and compliance issues.
To avoid this pitfall:
✅ Set up a maintenance schedule
✅ Designate someone to oversee and manage updates and ensure they’re well-informed about changes in procedures or regulations
✅ Use a system for tracking revisions and managing document versions
✅ Ask users for input to spot and fix issues quickly
It’s not enough to just distribute the SOP document—people need to understand and apply it. Without proper training, employees may misinterpret or overlook steps, leading to mistakes and inconsistencies.
To solve this:
✅ Create a training program that covers key SOP aspects and provides practical, hands-on experience—via workshops, training sessions, or e-learning modules
✅ Develop user-friendly materials and resources for easy reference
✅ Ensure the training is interactive and addresses potential questions or issues
✅ Offer continuous training and refresher courses as processes evolve
Developing standard operating procedures in a vacuum is a recipe for disaster. If the process is handled in isolation without relevant parties’ insights and feedback, you’ll likely end up with a document that overlooks real-world needs.
To handle this:
✅ Involve frontline workers, managers, and other stakeholders in the development process. Plus, share drafts for review and incorporate their feedback before finalizing the SOP
✅ Use document collaboration platforms for editing and version control
Streamline SOPs Like a Pro with ClickUp
SOPs are your team’s ultimate guidebook, ensuring tasks are done right. They prevent chaos, streamline training, preserve key processes, keep you compliant, and guarantee consistent customer service.
Historically, SOPs started in the military and industrial sectors, where precision was key. Now, they’re vital in modern business to keep operations smooth and reliable across industries. However, SOP creation can get complex as your business grows and processes become more complex.
ClickUp offers a suite of features to make SOP management easier and smarter. You can create SOPs, collaborate in real time, and keep everyone in the loop. Plus, it lets you easily track changes, update content, and roll back if needed to keep your SOPs up-to-date.
ClickUp Brain offers tips and corrections to make SOP documentation clearer and more precise. Additionally, ClickUp’s ready-made SOP templates kickstart your documentation process effortlessly.
Level up your SOPs with ClickUp’s smart tools and templates. Sign up on ClickUp today for free .
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5.One more point of difference is that there are write-ups of creative writing that may imitate any of the business writing styles in their work, but there is a rare example one can find in business writing where the Creative writing style is adopted. As in Business writing, standard style and structures are adopted.
Most professional writing falls into two categories: creative writing—which includes novels, short stories, poems, and screenplays—and content writing, which includes manuals, guidebooks, and marketing products. Here are some key differences between the two types of writing.
Strong writing skills are essential for anyone in business. You need them to effectively communicate with colleagues, employees, and bosses and to sell any ideas, products, or services you're ...
How is business writing different from academic writing? Tone, style, and structure, to name a few ways. Learn the rest and improve your writing skills.
Business Writing Vs. Creative Writing - What You Need To Know Those who think that business writing and creative writing are the same thing, are sorely mistaken. There is a clear difference between business writing (attempting to make an audience aware of and potentially purchase your product), and writing creatively (for the benefit of someone's imagination or enjoyment).
The difference between content and creative writing is that the former aims to fulfill a specific purpose or dispense crucial information to readers. Content writing is usually done on online channels nowadays. Source. The article that you are reading right now is a form of content writing too.
We discuss the difference between content writing and creative writing with award-winning writer and UAL short course tutor, Elise Valmorbida.
Are you confused about the difference between content writing and creative writing? In this blog, learn the features and key differences between the two.
Find out the difference between technical writing and other forms of writing, i.e., academic, creative, business, and literary writing, in the ClickHelp Blog.
Instructional Instructional business writing is similar to informational writing in that both help the reader learn something new. The difference, however, is the end goal. Instructional writing should teach the reader how to do something—how to use one of your products or how to troubleshoot common issues, for example.
The main distinction between academic writing and creative writing is the reason for the writing. In a formal and objective way, information, facts, and knowledge are communicated through academic writing. It is employed to investigate and examine a certain subject or problem and to give arguments supported by facts.
It makes you step out of reality and into a new realm of your imagination. Creative writing uses senses and emotions to capture the reader's mind, unlike other forms of writing, which has facts and information. Some examples of Creative Writing involve writing short stories, novels, poems, plays, blogs, non-fiction narratives, etc.
You've always had a passion for writing, but now you're faced with choosing between two distinct paths: technical writing or creative writing. As an aspiring writer, it's essential to understand the differences between these two forms of written communication, as each has its nuances and unique requirements that can make all the difference in which path leads to your career success.
Business writing vs academic writing: Key differences. Below are enlisted some primary differences between the academic and business writing styles. These differences are primarily based on factors such as the purpose of writing, degree of formality, the intricacy of the language, and the audience. 1. Objective.
By following these steps in each type of writing project (creative, technical, or academic), you'll be better equipped to create captivating content tailored specifically for its intended purpose while keeping in mind the inherent differences between each style.
The difference between business writing and academic writing mostly comes down to style. Learn key differences between the two and adjust accordingly!
The main difference between creative writing vs academic writing is that writers are free to express themselves however they want when writing creatively, while academic writing provides a set of constraints the writer must stay within.
Academic writing must be taught, but rarely is; creative writing is optional, but is almost always the focus of writing curricula.Creative writing focuses on story-telling and recounting personal experiences. Its students author fiction and poetry—using style, voice, and technique to make their writing entertaining, smart, and packed with ...
01. Technical writing is based on facts and concepts. General writing is based on imaginations and creativity. 02. Technical writing focuses on factual and straight forward content. Creative writing focuses on imaginative and symbolic content. 03. Technical writing has its specific reader/audience.
Hi, Can anyone tell me the difference Between Creative and Business writing? About Creative writing, I have a little bit of knowledge like write content about your personal experience and imagination but no idea about business writing anyone explains..
Writing standard operating procedures is more than just filling in the blanks. It's about making a clear, actionable guide your team can use. Here's how to do it right: 1. Gather the required information . Dive into the nitty-gritty of the procedure you're documenting. This means: Observing how things are currently done