myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
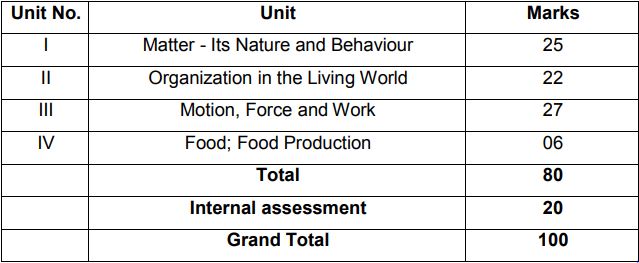
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
| I | Matter- Its Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | Organization in the Living World | 22 |
| III | Motion, Force and Work | 27 |
| IV | Food; Food Production | 06 |
| 80 | ||
| 20 | ||
| 100 |
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions play a crucial role in the field of science education as they provide real-life scenarios for students to analyze, apply their knowledge, and develop problem-solving skills. This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science , covering various topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th SCIENCE Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide students with real-life scenarios that require critical thinking and application of scientific concepts. They help students understand the practical application of scientific principles and develop problem-solving skills in various scientific disciplines.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
The above Case studies for Class 9 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Studies in Science Education
Case studies offer several advantages over traditional teaching methods. Here are some key benefits:
- Real-World Application : Case studies present authentic scenarios, enabling students to understand how scientific concepts are applied in real-life situations.
- Critical Thinking : Analyzing case studies requires students to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific knowledge to solve problems.
- Interdisciplinary Approach : Case studies often involve multiple scientific disciplines, fostering an interdisciplinary understanding of complex issues.
- Engagement and Active Learning : Case studies actively engage students in the learning process, promoting active participation, discussion, and collaboration.
- Skill Development : Case studies develop essential skills such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication of scientific concepts.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions is crucial for Class 9 Science students to enhance their understanding and application of scientific concepts. Here’s why it is important:
- Application of Knowledge : Case studies allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to practical situations, bridging the gap between theory and real-world scenarios.
- Developing Analytical Skills : Analyzing case studies improves students’ ability to identify relevant information, make connections, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Case studies present complex problems that require students to think critically and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
- Enhanced Exam Performance : Practicing case study questions familiarizes students with the format and types of questions they may encounter in exams, leading to improved performance.
Subjects Covered in the Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
The case study questions for Class 9 Science cover the following subjects:
- Motion and Forces
- Light and Reflection
- Electricity
- Matter and Its Properties
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- Chemical Reactions
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Diversity in Living Organisms
- Natural Resources
Tips for Approaching Case Study Questions
To tackle case study questions effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read Carefully : Pay close attention to the details provided in the case study, as they hold crucial information for solving the problem.
- Analyze Methodically : Break down the problem into smaller components and analyze each part systematically.
- Apply Relevant Concepts : Identify the scientific principles relevant to the case study and apply them appropriately.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives : Explore different angles and viewpoints while proposing solutions, taking into account various scientific factors.
- Provide Justifications : Support your answers with scientific explanations and logical reasoning to strengthen your responses.
The Class 9 Science Case Study Questions provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their scientific knowledge and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and their practical applications. Embrace this opportunity to engage with real-world scenarios and strengthen your scientific acumen.
Q1: Are the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions aligned with the official curriculum?
Yes, the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions presented in this article are aligned with the official curriculum. They cover relevant topics and concepts that students need to study for their exams.
Q2: Can practicing case study questions alone guarantee success in Class 9 Science exams?
Practicing case study questions is an important part of exam preparation, but it should be complemented with a thorough understanding of the subject matter. It is advisable to study the concepts in detail, refer to textbooks, and engage in other learning activities to achieve success in exams.
Q3: Where I Can get Class 9 Science Case Study Questions ?
You can practice Class 9 Science Case Study Questions on schools.studyrate.in for free.
You Might Also Like
Class 9 science case study questions chapter 13 why do we fall ill, case study questions class 9 geography of chapter 4 climate, class 9 maths case study questions of chapter 10 circles pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert

Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science PDF Download
Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions .

Case study questions are based on real or hypothetical scenarios that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply scientific concepts to solve problems or make informed decisions. They often present a detailed context, providing students with the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter beyond basic recall.
Table of Contents
Class 9 Science: Case Study Questions
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Syllabus
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid, and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of statementing (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds, and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids, and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Unit III: Motio n, Force, and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Books for Class 9 Science Exams

Benefits of Case Study Questions
- Enhancing Analytical Skills : Case study questions challenge students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. By engaging with these questions, students develop critical analytical skills that are essential for scientific thinking and problem-solving.
- Promoting Critical Thinking : Case study questions encourage students to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They require students to reason, make logical deductions, and justify their answers with supporting evidence. This process helps in honing their critical thinking abilities, enabling them to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Encouraging Practical Application of Concepts : By presenting real-world or hypothetical situations, case study questions promote the application of scientific concepts in practical scenarios. This application-based approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and helps students see the relevance of what they learn in the classroom to everyday life.
Case study questions of Class 9 Science provide students with an opportunity to apply their knowledge, enhance analytical skills, and think critically. By understanding the format, benefits, and effective strategies for answering case study questions, students can excel in this form of assessment. While challenges may arise, practicing time management, improving information extraction skills, and enhancing observation abilities will enable students to overcome these obstacles and perform well. Embracing case study questions as a valuable learning tool can contribute to a holistic understanding of scientific concepts and foster problem-solving abilities.
1. What is the purpose of case study questions in Class 9 Science?
Case study questions serve the purpose of evaluating a student’s understanding of scientific concepts, their ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations, and their analytical and critical thinking skills.
2. How can case study questions help improve analytical skills?
Case study questions require students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. Regular practice with such questions can significantly enhance analytical skills.
3. Are case study questions difficult to answer?
Case study questions can be challenging due to their comprehensive nature and the need for critical thinking. However, with practice and effective strategies, students can develop the skills necessary to answer them effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- CBSE Class 9 Study Material
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Case Study Questions with Answers for Term 2 Exam 2022 (PDF)
Check important case study questions of cbse class 9 science to prepare for the cbse term 2 exam 2022. all these questions have been put together by subject experts..

CBSE Class 9 Term 2 Exam 2022: Important case based questions for CBSE Class 9 Science are provided here students to prepare for the upcoming Term 2 Exam 2022. All the questions provided below are curated by the subject experts. These questions are really helpful to revise important concepts and prepare the case study questions for the exam. Answers to all questions have been provided for reference. So, students should practice the chapter-wise questions to clearly understand the right way to attempt the case based questions. Download the chapter-wise questions in PDF.
Check some of the important case study questions below:
Q. Read the following and answer the questions :
A student was asked by his teacher to verify the law of conservation of mass in the laboratory. He prepared 5% aqueous solutions of NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . He mixed 10 mL of both these solutions in a conical flask. He weighed the flask on a balance. He then stirred the flask with a rod and weighed it after sometime. There was no change in mass.
- Was the student able to verify the law of conservation of mass?
- If not, what was the mistake committed by him?
- In your opinion, what he should have done?
- What is the molar mass of Na 2 SO 4 ?
- No, he could not verify the law of conservation of mass in-spite of the fact that there was no change in mass.
- No chemical reaction takes place between NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . This means that no reaction actually took place in the flask.
- He should have performed the experiment by using aqueous solutions of BaCl 2 and Na 2 SO 4 . A chemical reaction takes place in this case and a white precipitate of BaSO 4 is formed.
- Will the weight of the precipitate be the same as that of the reactants before mixing?
- If not, what she should have done?
- Which law of chemical combination does this support?
- State the law of conservation of mass.
- No, it will not be the same.
- She should have weighed the total contents of the beaker after the reaction and not the precipitate alone.
- It supports the law of conservation of mass.
- Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- Bihar Police Constable Exam Analysis 2024
- UGC NET Admit Card 2024
- AFCAT Admit Card 2024
- IBPS RRB Exam Analysis 2024
- IBPS RRB Clerk Exam Analysis 2024
- UPSC CAPF Question Paper 2024
- SSC CHSL Answer Key 2024
- IBPS RRB PO Exam Review 2024
- India Post GDS Cut Off
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 9
Latest Education News
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Can You Spot the Hidden Gift Among the Sea of Dice in 5 Seconds?
(Updated) Paris Olympics Medal Tally 2024, Day 15: Who is leading the Total Medal Count? Check Here
(Updated) Paris Olympics 2024 India Medal Tally, Check Total Medals Count List
NEET PG 2024 Tomorrow, Check Documents Required Exam Day Guidelines Here
KCET Mock Allotment 2024 Out: Download Allotment PDF by 6 PM Today at cetonline.karnataka.gov.in
IBPS RRB Clerk Exam Analysis 2024: All Shifts Paper Review, Difficulty Level, Good Attempts
AFCAT Exam Analysis 2024, Aug 10: Shift Wise Question Paper Review, Difficulty Level, Good Attempts
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only 1% Highly Observational Can Spot The Hidden Animal In 5 Seconds!
Optical Illusion IQ Test: How Many Cows Can You Find In This Picture In 5 Seconds?
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Only A Sharp Mind Can Find The Pencil Among Carrots In 6 Seconds!
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Can You Spot The Correct Spelling Of 'GARLIC' In 5 Seconds?
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only the Quickest Minds Can Spot the Spring Among The Cluster Of Nails In 5 Seconds!
Personality Test: Your Heart Line Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
Personality Test: Your Pinky Finger Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
(Updated) Paris Olympics Medal Tally 2024, Day 14: Who is leading the Total Medal Count? Check Here
IBPS RRB Clerk Memory Based Questions 2024: Subject Wise Questions Asked
IBPS RRB 2024: Check Exam Day Guideline, Shift Timings and Last Minute Preparation Tips
IBPS RRB PO Exam Analysis 2024, 4th August: All Shifts Exam Review, Difficulty Level, Good Attempts
IBPS RRB PO Expected Cut Off 2024: Check Minimum Qualifying Marks Category Wise
Olympic 2024: आजादी के बाद से अब तक भारत ने जीते है कितने ओलंपिक मेडल? देखें सबके नाम
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9- Gravitation
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 10 Gravitation

NCERT Solutions for Gravitation Class 9 Questions and Answers FREE PDF Download
Class 9 Science Ch 9 explores the concept of gravitational force, understanding its effects on celestial bodies like planets and moons, and Archimedes’ Principle. Vedantu’s Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions solves all the questions in the chapter and helps students navigate through complex concepts with clarity and precision. Access Vedantu's Gravitation Class 9 solutions for step-by-step explanations and problem-solving strategies and enhance your learning experience.

Download Vedantu's Science Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions, revised to align with the Class 9 Science syllabus . Start your academic journey with Vedantu and pave your way towards academic excellence.
Quick Insights for NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Chapter 9 Science Gravitation
Class 9 Science Ch 9 comprehends the concept of gravitation, the force of attraction that exists between any two objects with mass, and elucidates Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, a cornerstone of classical physics.
Ch 9 Science Class 9 explores the effects of gravitation in maintaining the stability of celestial bodies such as planets, stars, and galaxies.
Class 9 Gravitation Question Answer delves into the concept of acceleration due to gravity, the distinction between weight and mass, and Archimedes’ Principle.
Gravitation Class 9 Questions And Answers develop proficiency in solving numerical problems related to the motion of objects under the influence of the earth's gravitational force, Pressure, and Thrust.
Vedantu offers additional resources such as class notes, important concepts, formulas, and exemplar solutions to reinforce learning and ensure a strong grasp of foundational scientific principles.

Access NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 9 – Gravitation
Intext exercise 1.
1. State the universal law of gravitation.
Ans: Every object in the universe attracts every other object with some force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The force acts along the line joining the centres of two objects.
Let the two objects \[A\] and \[B\]of masses \[M\]and \[m\] lie at a distance \[d\] from each other. Let the force of attraction between two objects be \[F\].
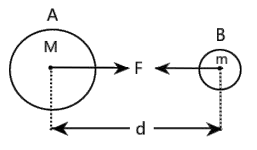
\[F=\frac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}\]
Where,
\[G\]is the universal gravitation constant which is given by:
\[G=6.67\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}\]
2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Ans: Let the mass of the Earth be \[M\] and the mass of an object on its surface be \[m\]. If \[R\]is the radius of the Earth, then according to the universal law of gravitation, the gravitational force (\[F\]) that acts between the Earth and the object can be given by the relation:
\[F=\frac{GMm}{{{R}^{2}}}\].
Intext Exercise 2
1. What do you mean by free fall?
Ans: Each object is drawn towards the centre of the Earth by its gravity. When any object is released from a certain height, under the impact of gravitational force, it falls to the Earth's surface. The movement of the object is said to be in free fall.
2. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
Ans: When any object falls freely from a certain height towards the earth's surface, its velocity changes with respect to time. This change in velocity causes acceleration. This acceleration is known as the acceleration due to gravity (\[g\]). The value of acceleration due to gravity is \[9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\].
Intext Exercise 3
1. What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
Ans: The difference between the mass of an object and its weight is given in the table below:
|
|
|
1. | Mass can be defined as the quantity of matter contained in the body. | Weight can be defined as the force of gravity acting on the body. |
2. | It is the quantity that is a measure of inertia of the body. | It is the quantity that is a measure of gravity. |
3. | Mass is constant everywhere. | The value of weight varies at different places. |
4. | It is a scalar quantity. | Weight is a vector quantity. |
5. | SI unit of mass is \[kg\]. | SI unit of weight is \[N\]. |
2. Why is the weight of an object on the moon \[\frac{1}{6}th\] its weight on the earth?
Ans: Let the mass of the Earth be \[{{M}_{E}}\] and the mass of an object on the surface of earth \[=m\] and the radius of earth \[{{R}_{E}}\].
According to the Universal law of gravitation, weight \[{{W}_{E}}\] of the object on the surface of the earth is given by,
\[{{W}_{E}}=\frac{G{{M}_{E}}m}{{{R}_{E}}^{2}}\]
Let \[{{M}_{M}}\] and \[{{R}_{M}}\] be the mass and radius of the moon. Then, according to the universal law of gravitation, weight \[{{W}_{M}}\] of the object on the surface of the moon is given by:
\[{{W}_{M}}=\frac{G{{M}_{M}}m}{{{R}_{M}}^{2}}\]
So, ratio of weight of object on moon to weight on earth is
\[\frac{{{W}_{M}}}{{{W}_{E}}}=\frac{{{M}_{M}}{{R}_{E}}^{2}}{{{M}_{E}}{{R}_{M}}^{2}}\]
Where, \[{{M}_{E}}=5.98\times {{10}^{24}}kg\]
\[{{M}_{M}}=7.36\times {{10}^{22}}kg\]
\[{{R}_{E}}=6.4\times {{10}^{6}}m\]
\[{{R}_{M}}=1.74\times {{10}^{6}}m\]
Substituting the values in the ratio,
\[\Rightarrow \frac{{{W}_{M}}}{{{W}_{E}}}=\frac{7.36\times {{10}^{22}}\times {{\left( 6.37\times {{10}^{6}} \right)}^{2}}}{5.98\times {{10}^{24}}\times {{\left( 1.74\times {{10}^{6}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{{{W}_{M}}}{{{W}_{E}}}=0.165\approx \frac{1}{6}\]
Hence, the weight of an object on the moon is \[\frac{1}{6}th\] of its weight on the Earth.
Intext Exercise 4
1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag with a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Ans: Pressure can be given by the formula,
\[P=\frac{F}{A}\]
Pressure is inversely proportional to the surface area on which the force is acting. The smaller is the surface area, the larger will be the pressure on the surface on which the force is being acted upon. In the case of a thin strap of the school bag, the contact surface area is very less. Hence, the pressure exerted on the shoulder is very high. Therefore, it becomes difficult to hold a school bag with a thin strap.
2. What do you mean by buoyancy?
Ans: The liquid exerts an upward force on any object when it is immersed in a liquid or fluid. The tendency of the liquid to exert such an upward force on the object is called buoyancy, and the upward force which is exerted on the object by the liquid is called the buoyant force.
3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of the water?
Ans: If the density of an object is greater than the density of the liquid, it will sink into the liquid. This is due to the buoyant force which is acted by the object is less than the force of gravity.
On the contrary, if the density of the object is less than the density of the liquid, it floats on the liquid's surface. This is because the force that is acting on the object is greater than the force of gravity.
Intext Exercise 5
1. You find your mass to be \[42\] kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than \[42\]kg?
Ans: An upward force acts on our body when we weigh our body while standing on a weighing machine. The buoyant force is which is a upward force that is acting. Consequently, the body is pushed up slightly, resulting in the weighing machine showing less reading than the real value.
2. You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of \[100kg\] when measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
Ans: Weight measured \[=\] Actual weight \[-\] buoyant force
Therefore, Actual weight \[=\] Weight measured \[+\]buoyant force
As the surface area of the cotton, the bag is greater than the iron bar, more buoyant force acts on the bag than that on the iron bar. Hence, the mass of the cotton bag is more than that of the iron bar.
NCERT Exercise
1. How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
Ans: According to the universal law of gravitation, the gravitational force (\[F\]) acting between two objects of mass \[{{m}_{1}}\]and \[{{m}_{2}}\], separated by a distance ‘\[r\]’ is given by
\[F=\frac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\]
Where \[{{m}_{1}}\]and \[{{m}_{2}}\]are the masses of two bodies and \[r\]is the distance between them, \[G\] is the universal gravitational constant.
When the distance is reduced to half, i.e., \[{r}'=\frac{r}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow F=\frac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{\left( \frac{r}{2} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow F=\frac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{\frac{{{r}^{2}}}{4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow F=\frac{4G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\]
Hence, if the distance is reduced to half, then the gravitational force becomes four times that of the previous value.
2. Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Ans: All the objects fall towards the ground with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity (if there is no air resistance present). It is constant and independent of the mass of the object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
3. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a \[1kg\]object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is \[6\times {{10}^{24}}kg\] and radius of the earth is \[6.4\times {{10}^{6}}m\]).
Ans: According to the Universal law of gravitation, the gravitational force exerted on an object of mass \[m\]is given by:
Mass of Earth, \[M=6\times {{10}^{24}}kg\]
Mass of object, \[m=1kg\]
Universal gravitational constant, \[G=6.7\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}\]
Since the object is on the surface of the Earth, \[r=\]radius of the Earth (\[R\])
\[r=R=6.4\times {{10}^{6}}m\]
Gravitational force,
\[\Rightarrow F=\frac{6.7\times {{10}^{-11}}\times 6\times {{10}^{24}}\times 1}{{{\left( 6.4\times {{10}^{6}} \right)}^{2}}}=9.8N\].
The magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a \[1kg\]object on its surface is \[9.8N\].
4. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
Ans: According to the Universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other and according to Newton's third law of motion, the force of attraction between two objects is the same but acts in the opposite direction. Thus, the earth attracts the moon with the same force as the moon exerts on earth but the force acts in the opposite direction.
5. If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Ans: The Earth and the moon experience equal gravitational forces acting towards each other.
By Newton's Second Law, \[F=ma\]
\[\Rightarrow a=\frac{F}{m}\]
For a certain force, acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of an object.
\[a\propto \frac{F}{m}\]
Mass of the Earth \[>>\] Mass of the moon.
Hence, the acceleration experienced by earth due to the gravitational pull of the moon is very small when compared to that experienced by the moon due to earth. That is why the Earth does not move towards the moon.
6. What happens to the force between two objects, if
a) The mass of one object is doubled?
Ans: According to the universal law of gravitation, the force of gravitation between two objects is given by: \[F=\frac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}\]
\[F\]is directly proportional to the product of masses of the two objects.
\[F\propto Mm\]
If the mass of one object is doubled, then the gravitational force will also change to double the original.
b) The distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
Ans: \[F\]is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects.
If the distance between the objects is doubled, then the gravitational force becomes one-fourth of its original value. Also, if the distance is tripled, then the gravitational force becomes one-ninth of its original value.
c) The masses of both objects are doubled?
Ans: \[F\]is directly proportional to the product of masses of the objects.
If the masses of both the objects are doubled, then the gravitational force becomes four times the original value.
7. What is the importance of the universal law of gravitation?
Ans: The universal law of gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object.
The force of gravitation binds us to the earth.
It is the cause for the motion of the moon around the earth and planets around the sun.
It results in the formation of tides due to the moon and the Sun. High tide occurs at the side where the moon pulls towards itself.
8. What is the acceleration of free fall?
Ans: A free-falling object is an object that is falling due to gravity without any air resistance. When it falls, there is a variation in velocity with respect to time that is associated with it.
Acceleration of free fall is denoted by \[g\]and its value on the surface of the earth is \[9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\], which is constant for all objects (irrespective of their masses).
9. What do we call the gravitational force between the Earth and an object?
Ans: The gravitational force between the earth and an object is called the weight of that object. It is equal to the product of acceleration due to the gravity and mass of the object.
10. Amit buys a few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why? (Hint: The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator).
Ans: Weight of a body on the Earth is given by:
\[m=\]Mass of the body
\[g=\]Acceleration due to gravity
The shape of Earth is not a perfect sphere. As the radius of the earth increases from the poles to the equator, the value of \[g\]becomes greater at the poles than at the equator. Since the value of \[g\] is greater at the poles than the equator.
Therefore, gold at the equator weighs less than at the poles. Hence, Amit’s friend will not agree with the weight of the gold bought.
11. Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
Ans: When a sheet of paper is crumbled into a ball, then its surface area becomes much lesser than the surface area of a plain non-crumpled sheet of paper.
Hence, the upward force exerted by air on the sheet is greater as compared to the one exerted on the ball. Hence the sheet falls slower as compared to a paper ball.
12.Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only \[\frac{1}{6}\] as strong as the gravitational force on the Earth. What is the weight in newtons of a \[10kg\]object on the moon and on the Earth?
Ans: It is provided that, \[Weight\text{ }of\text{ }an\text{ }object\text{ }on\text{ }the\text{ }moon=\frac{1}{6}\times Weight\text{ }of\text{ }an\text{ }object\text{ }on\text{ }the\text{ }Earth\]
\[Weight=\,Mass\times Acceleration\]
Acceleration due to gravity, \[g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\]
Therefore, the weight of a 10 kg object on the Earth \[=10\times 9.8N=98N\]
Weight of the same object on the moon \[=\frac{1}{6}\times 9.8N=16.3N\]
13. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of \[49m{{s}^{-1}}\]. Calculate
a) The maximum height to which it rises.
Ans: According to the equation of motion under gravity:
\[{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2gh\]
\[u=\]Initial velocity of the ball
\[v=\]Final velocity of the ball
\[h=\]Height achieved by the ball
At maximum height, final velocity of the ball is zero, i.e., \[v=0\]
\[u=49m{{s}^{-1}}\]
During upward motion, \[g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\]
Let \[h\] be the maximum height attained by the ball.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 49 \right)}^{2}}=2\times \left( -9.8 \right)\times h\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\frac{49\times 49}{2\times 9.8}=122.5\]
b) The total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
Ans: Let \[t\] be the time taken by the ball to reach the height \[122.5m\], then according to the equation of motion:
Substituting the values and solving,
\[\Rightarrow 0=49+t\times \left( -9.8 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 9.8t=49\]
\[\Rightarrow t=\frac{49}{9.8}=5s\]
Time of ascent = Time of descent
Therefore, the total time taken by the ball to return is \[5+5=10s\].
14. A stone is released from the top of a tower of height \[19.6m\]. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground.
\[u=\]Initial velocity of the stone \[=0\]
\[v=\]Final velocity of the stone
\[s=\]Height of the stone \[=9.6m\]
g = Acceleration due to gravity \[=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}-{{0}^{2}}=2\times 9.8\times 19.6\]2
\[\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=2\times 9.8\times 19.6={{\left( 19.6 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow v=19.6m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Hence, the velocity of the stone just before touching the ground is \[19.6m{{s}^{-1}}\].
15. A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of \[40m{{s}^{-1}}\]. Taking \[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\], find the maximum height reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone?
\[u=\]Initial velocity of the stone \[=40m{{s}^{-1}}\]
\[v=\]Final velocity of the stone\[=0\]
\[s=\]Height of the stone
g = Acceleration due to gravity \[=-10m{{s}^{-2}}\]
Let \[h\] be the maximum height attained by the stone.
\[\Rightarrow 0-{{\left( 40 \right)}^{2}}=2\times h\times \left( -10 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\frac{40\times 40}{20}=80m\]
Therefore, the total distance covered by the stone during its upward and downward journey is \[80+80=160m\].
The net displacement of the stone during its upward and downward
journey is \[80+\left( -80 \right)=0m\].
16. Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth \[=6\times {{10}^{24}}kg\] and of the Sun \[=2\times {{10}^{30}}kg\]. The average distance between the two is \[1.5\times {{10}^{11}}m\].
Ans: According to the Universal l law of gravitation, the force of attraction between the Earth and the Sun is given by:
\[{{M}_{Sun}}=\]Mass of the Sun \[=2\times {{10}^{30}}kg\]
\[{{M}_{Earth}}=\]Mass of the Earth \[=6\times {{10}^{24}}kg\]
\[R=\] Average distance between the Earth and the Sun \[=1.5\times {{10}^{11}}m\]
\[G=\]Universal gravitational constant \[=6.7\times {{10}^{-11}}N{{m}^{2}}k{{g}^{-2}}\].
\[F=\frac{G{{M}_{Sun}}{{M}_{Earth}}}{{{R}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow F=\frac{6.7\times {{10}^{-11}}\times 2\times {{10}^{30}}\times 6\times {{10}^{24}}}{{{\left( 1.5\times {{10}^{11}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow F=3.57\times {{10}^{22}}N\]
Hence, the force of gravitation between the earth and the sun is \[3.57\times {{10}^{22}}N\].
17. A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower \[100m\] high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of \[25m{{s}^{-1}}\]. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet.
Ans: Let the two stones meet after time \[t\]from the start.
a) For the stone dropped from the tower:
Initial velocity, \[u=0\].
Let the displacement of the stone in time t from the top of the tower be s.
From the equation of motion,
\[s=ut+\frac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow s=0\times t+\frac{1}{2}\times 9.8\times {{t}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow s=4.9{{t}^{2}}\]……. (1)
b) For the stone thrown upwards:
Initial velocity, \[u=25m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Let the displacement of the stone from the ground in time \[t\]be \[{s}'\].
Equation of motion,
\[{s}'=ut+\frac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {s}'=25t-\frac{1}{2}\times 9.8\times {{t}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {s}'=25t-4.9{{t}^{2}}\]…… (2)
The combined displacement of both the stones at the meeting point is equal to the height of the tower \[100\]m.
\[s+{s}'=100\]…… (3)
Substituting equation (1) and (2) in (3),
\[4.9{{t}^{2}}+25t-4.9{{t}^{2}}=100\]
\[\Rightarrow 25t=100\]
\[\Rightarrow t=\frac{100}{25}=4s\]
In \[4s\], the falling stone has covered a distance given by equation (1) as
\[s=\frac{1}{2}\times 9.8\times {{4}^{2}}=78.4m\]
Therefore, the stones will meet after \[4s\] at a height \[\left( 100-78.4 \right)=21.6m\] from the ground.
18. A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after \[6s\]. Find
a) The velocity with which it was thrown up,
Ans: Time of ascent is equal to the time of descent. The ball takes a total of \[6s\]for its upward and downward journey.
Hence, time taken for upward journey, \[t=\frac{6}{2}=3s\]
Final velocity of the ball at the maximum height, \[v=0\]
Equation of motion, \[v=u+gt\]will give,
\[\Rightarrow 0=u+\left( -9.8\times 3 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow u=9.8\times 3=29.4m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Hence, the ball was thrown upwards with a velocity of \[29.4m{{s}^{-1}}\].
b) The maximum height it reaches
Ans: Let the maximum height attained by the ball be \[h\].
Initial velocity during the upward journey, \[u=29.4m{{s}^{-1}}\]
Final velocity, \[v=0\]
Acceleration due to gravity, \[g=-9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\]
\[s=ut+\frac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\]
\[h=29.4\times 3+\frac{1}{2}\times \left( -9.8 \right)\times {{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=44.1m\]
c) Its position after \[4s\].
Ans: Ball attains the maximum height after \[3s\]. After attaining this height, it will start falling downwards.
In this case, Initial velocity, \[u=0\]
Position of the ball after \[4s\] of the throw is given by the distance
travelled by it during its downward journey in \[4s-3s=1s\]
\[s=0\times t+\frac{1}{2}\times 9.8\times {{1}^{2}}=4.9m\]
Total height \[=44.1m\]
This means that the ball is \[44.1m-4.9m=39.2m\] above the ground
after \[4\]seconds.
19. In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
Ans: An object immersed in a liquid is acted upon by the buoyant force in the vertically upward direction.
20. Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Ans: The number of forces acting on a certain item in water are two. The first one is the gravitational force pulling down the object, and the other is the buoyant force pushing up the object. If the buoyant force acting in the upward direction is higher than the gravitational force that is acting downward, then the object goes up to the water's surface as quickly as it is released into water. That is why a block of plastic released under the water comes up to the surface of the water.
21. The volume of \[50g\]of a substance is \[20c{{m}^{3}}\] . If the density of water is \[1gc{{m}^{-3}}\], will the substance float or sink?
Ans: If the density of an object is more than the density of a liquid, then it sinks in the liquid. If the density of an object is less than the density of a liquid, then it floats
\[Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }substance=\frac{Mass\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }substance}{Volume\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }substance}\]
\[\Rightarrow Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }substance=\frac{50}{20}\]
\[\Rightarrow Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }substance=2.5gc{{m}^{-3}}\].
The density of the substance \[>\] The density of water \[\left( 1gc{{m}^{-3}} \right)\].
Hence, the substance will sink in water.
22. The volume of a \[500g\] sealed packet is \[350c{{m}^{3}}\]. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is \[1gc{{m}^{-3}}\]? What will be the volume of the water displaced by this packet?
Ans: If the density of an object is greater than the density of a liquid, then the object will sink in the liquid. If the density of an object is less than the density of a liquid, then it will float on the surface of the liquid.
\[Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }500\text{ }g\text{ }sealed\text{ }packet=\frac{Mass\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }packet}{Volume\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }packet}\]
\[\Rightarrow Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }500\text{ }g\text{ }sealed\text{ }packet=\frac{500}{350}\]
\[\Rightarrow Density\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }500\text{ }g\text{ }sealed\text{ }packet=1.428gc{{m}^{-3}}\]
The density of the substance is more than the density of water \[\left( 1gc{{m}^{-3}} \right)\].
Hence, the object will sink in water.
Clearly, the mass of water displaced by the packet can be considered equal to the volume of the packet\[=0.350g\].
Class 9th Science Gravitation Class 9 - Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics
Topic | Subtopics |
Gravitation | |
Free Fall | |
Mass | |
Weight | |
Thrust And Pressure | |
Archimedes’ Principle |
Class 9 Science Ch 9 Gravitation - Important Formula and Concepts
The universal law of gravitation: The force of attraction between any two objects is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Archimedes’ Principle: When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Where \[G\]is the universal gravitation constant, which is given by:
Weight of the object on the moon = (1/6) × its weight on the earth.
Pressure= Thrust/Area
Benefits of Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Science Gravitation Question Answer
Vedantu’s solutions explain all key concepts covered in Ch 9 Science Class 9, including the Universal Law of Gravitation, acceleration due to gravity, the distinction between mass and weight, free fall, and gravitational fields.
Class 9 Science Gravitation Question Answers are presented in a step-by-step format, making it easier for students to follow and understand the problem related to the motion of objects under the influence of the gravitational force of the earth, pressure, and Thrust.
Vedantu’s NCERT Gravitation Class 9 Questions And Answers help students prepare effectively for their exams.
The solutions include various types of questions, from multiple-choice to descriptive, ensuring comprehensive exam readiness.
Class 9 Gravitation Question Answers are prepared by Vedantu Master Teachers with a deep understanding of the curriculum and examination patterns. This ensures that the content is accurate, reliable, and aligned with the latest syllabus.
Using Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions, students can save time by quickly finding answers and explanations for their doubts and questions. This allows them to allocate more time to practice and revision.
Vedantu’s Class 9 Chapter 9 Science solutions are available online, making them accessible anytime and anywhere. This flexibility supports continuous learning and allows students to study independently.
Related Study Materials for Class 9 Science Ch 9 Gravitation
S. No | Related Study Materials for Gravitation Class 9 |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions is an important study material. They provide clear explanations and step-by-step solutions, helping students grasp important concepts like the laws of gravitation, mass, weight, and gravitational force. Focusing on these areas is essential, as they form the chapter's foundation. In previous years, around 7-8 questions on gravitation have been asked in exams, highlighting its importance. By using Gravitation Class 9 Questions And Answers, students can effectively prepare, clear their doubts, and perform well in their exams, ensuring a strong understanding of gravitation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science - Chapter-Wise Links
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter-wise List |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NCERT Study Resources for Class 9 Science
S. No | Important Resources Links for Class 9 Science |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9- Gravitation
1. How can students understand the features of Gravitational Force Properly?
Chapter 9 Science Class 9 is an important part of the Science syllabus. Focus on the classroom sessions and concentrate on what the teachers are explaining. Study the chapter unit-wise and clear your doubts by using the Science Class 9 NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu. You will surely understand these newfound concepts well.
2. How can I solve Gravitation problems quickly?
You must practise regularly using the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 as a reference and become more efficient. Your speed will automatically increase as you can remember the formulas properly.
3. Why do students prefer using NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9?
By using the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Gravitation, a student can save time in finding the right answers. They can focus better in preparing the chapter and score higher in the exams by following the ideal answering format recommended by the experts.
4. Why does the Earth not move towards objects due to Gravitation according to Chapter 9 Gravitation of Class 9 Science?
Newton's third law states, “Every action has its equal and opposite reaction”. It means the force applied by an object on the Earth is equal to the force applied by the earth on the object, but we know that acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. This means when the acceleration is increased, the mass is decreased, or when the mass is increased, the acceleration is decreased. As the mass of the earth is large, the acceleration due to an object is small or negligible. Therefore, it's not noticeable. And the Earth doesn’t seem to be moving.
5. What are the different applications of Archimedes' principle?
The different applications of Archimedes' principle include the following:
It is used in designing ships and submarines.
Lactometers used to determine the purity of a milk sample and hydrometers used to determine the density of a liquid are based on this principle.
6. Why does the Earth doesn’t move towards objects due to Gravitation according to Chapter 9 Gravitation of Class 9 Science?
As per Newton's third law, “Every action has its equal and opposite reaction”. It means the force applied by an object on the Earth is equal to the force applied by the earth on the object, but we know that acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. This means when the acceleration is increased, the mass is decreased or when the mass is increased, the acceleration is decreased. As the mass of the earth is large, the acceleration due to an object is small or negligible. Therefore, it's not noticeable. And the Earth doesn’t seem to be moving.
7. What are topics covered in Vedantu’s Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions?
Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Science Gravitation Question Answer covers all key concepts such as Newton’s Law of Gravitation, the universal law of gravitation, the relationship between gravitational force, mass, and distance, free fall, mass, weight, and the concept of acceleration due to gravity.
8. Why should I refer to Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Gravitation Class 9?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Gravitation Class 9 offers detailed explanations and step-by-step answers to textbook problems, making it easier to understand complex concepts. They also provide diagrams and illustrative examples that aid in better comprehension.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Ncert solutions for class 9.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 10 Class 9 - Gravitation
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Get NCERT Solutions, Notes, Solutions to Intext Questions, Examples of Chapter 10 Class 9 Gravitation free at Teachoo.
In this chapter, we will learn
What is Gravity ?
What is Universal Law of Gravitation
Important Natural Phenomena Occurring Due to Gravitation
What is Free Fall ?
What is Acceleration Due To Gravity
Deriving value of Acceleration due to Gravity
Different Equations of Motion for Free Falling Object
What is the Difference between Mass and Weight
What is thrust ?
What is Pressure
What is buoyancy ?
Density And Relative Density Of An Object
Why do Objects float or sink in Water
Archimedes Principle
Different Factors Affecting Buoyancy
Why is gravity maximum at poles and minimum at equator ?
What is the SI unit of Thrust and Pressur e?
What is the SI Unit of g and G ?
What is the difference between gravity and gravitation ?
Click on a link to open the first post.
To open any other post, like NCERT Question 18, there is a list with arrows at the bottom. You can click on a link to open it.
Or you can also click Next
NCERT Questions
Questions from inside the chapter, examples from ncert book, teachoo questions.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 9 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Gravitation Class 9 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
1: What is the S.I. unit of thrust? Answer: Newton.
2: What is the S.I. unit of pressure? Answer: The S.I. unit of pressure = N/m 2 = Pascal.
3: Define thrust. Answer: The net force exerted by a body in a particular direction is called thrust.
4: Define pressure. Answer: The force exerted per unit area is called pressure.
5: Why is it easier to swim in sea water than in river water?
Answer: The density of sea water is more due to dissolved salts in it as compared to the density of river water. Hence the buoyant force exerted on the swimmer by the sea water is more which helps in floating and makes swimming easier.
6: Why a truck or a motorbike has much wider tyres? Answer: The pressure exerted by it can be distributed to more area, and avoid the wear and tear of tyres.
7: Why are knives sharp? Answer: To increase the pressure, area is reduced, As pressure ∝ 1/Area hence the pressure or force exerted on a body increases.
8: Why is the wall of dam reservoir thicker at the bottom? Answer: The pressure of water in dams at the bottom is more, to withstand this pressure the dams have wider walls.
9: Why do nails have pointed tips? Answer: The force exerted when acts on a smaller area, it exerts larger pressure. So the nails have pointed tips.
10: While swimming why do we feel light? Answer: The swimmer is exerted by an upward force by water, this phenomenon is called buoyancy and it makes the swimmer feel light.
11: Define density and give its unit. Answer: The density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume. Its unit is kg/m 3 .
12: What is relative density? Answer: The relative density of a substance is the ratio-of its density to that of water. Relative density = density of a substance/density of water
Short Answer Type Questions
1: A ship made of iron does not sink but the iron rod sinks in water, why?
Answer: The iron rod sinks due to high density and less buoyant force exerted by the water on it, but in case of ship the surface area is increased, the upthrust experienced by the body is more. So it floats on water.
2: Camels can walk easily on desert sand but we are not comfortable walking on the sand. State reason.
Answer: Camels feet are broad and the larger area of the feet reduces the force/ pressure exerted by the body on the sand. But when we have to walk on the same sand, we sink because the pressure exerted by our body is not distributed but is directional.
3: What is lactometer and hydrometer? Answer: Lactometer is a device used to find the purity of a given sample of milk. Hydrometer is a device used to find the density of liquids.
4: The relative density of silver is 10.8. What does this mean? Answer: It means that the density of silver is 10.8 times more than that of water.
5: The relative density of gold is 19.3. The density of water is 10 3 kg/m 3 ? What is the density of gold in S.I. unit?
Answer: Relative density of gold = 19.3 Relative density of gold = Density of gold/Density of water
∴ Density of gold = Relative density of gold × Density of water = 19.3 × 10 3 Kg/m 3 =19300 Kg/m 3
6: State Archimedes’ principle.
Answer: Archimedes’ principle—When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. It is used in designing of ships and submarines.
7: Two cork pieces of same size and mass are dipped in two beakers containing water and oil. One cork floats on water but another sink in oil. Why?
Answer: The cork floats on water because the density of cork is less than the density of water, and another cork sinks in the oil because the density of cork is more than the oil.
8: What are fluids? Why is Archimedes’ principle applicable only for fluids? Give the application of Archimedes’ principle.
Answer: Fluids are the substances which can flow e.g., gases and liquids are fluids. Archimedes’ principle is based on the upward force exerted by fluids on any object immersed in the fluid. Hence it is applicable only for fluids. Applications of Archimedes’ principle: 1. It is used in designing of ship and submarine. 2. It is used in designing lactometer, used to determine the purity of milk. 3. To make hydrometers, used to determine the density of liquids.

Long Answer Type Questions
1: With the help of an activity prove that the force acting on a smaller area exerts a larger pressure?
Answer: Consider a block of wood kept on a table top. The mass of the wooden block is 5 kg. Its dimension is 40 cm x 20 cm x 10 cm. Now, we have to find the pressure exerted by the wooden block on the table top by keeping it vertically and horizontally. The mass of the wooden block = 5 kg Weight of the wooden block applies a thrust on the table top
∴ Thrust = F = m × g = 5 × 9.8 m/s 2 = 49 N
(case a) — when the wooden box is kept vertically with sides 20 cm × 10 cm. Area of a side = length × breadth = 20 cm × 10 cm = 200 cm 2 = 0.02 m 2
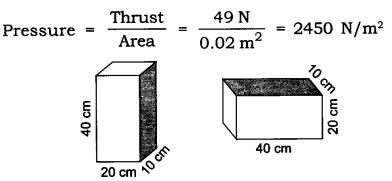
(case b) — When the block is kept horizontally with side 40 cm × 20 cm Area = length × breadth = 40 cm × 20 cm = 800 cm 2 = 0.08 m 2
∴ The pressure exerted by the box in case (a) is more as compared to the pressure exerted in case
(b). The area is reduced and the pressure exerted is more. This shows that pressure ∝ 1/area. Pressure will be larger if the area is reduced.
Application: • Nails have pointed tips. • Knives have sharp edges. • Needles have pointed tips.
Value Based Questions
1: A milkman sold his milk in the city and always carried lactometer with him. The customers trusted him and his business flourished. (a) What is lactometer? (b) What is the principle of working of lactometer? (c) What value of milkman is seen in this case?
Answer: (a) Lactometer is a device that measures the purity of milk. (b) The principle of lactometer is ‘Archimedes’ principle’. It states that when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. (c) Milkman is very honest and trustworthy.
2: Reeta was wearing a high heel shoe for a beach party, her friend told her to wear flat shoes as she will be tired soon with high heels and will not feel comfortable, (a) Why would one feel tired with high heel shoes on beach? (b) Give the unit of pressure. (c) What value of Reeta’s friend is seen in the above act?
Answer: (a) The high heel shoes would exert lot of pressure on the loose sand of beach and will sink more in the soil as compared to flat shoes. Hence large amount of force will be required to walk with heels. (b) Unit of pressure is Pascal. (c) Reeta’s friend showed the value of being helpful, concerned and intelligent.
3: In the school fair, there was a game in which one need to find the heaviest ball without holding them in hand. Three balls were given and few disposable glasses were kept. Tarun saw his friend struggling to win the game but he was unable to find the heaviest ball. Tarun helped him by dipping the three balls one by one in the glass’es full of water upto the brim and finally they won the game.
(a) Why did Tarun told his friend to dip the balls one by one in completely filled glass of water? (b) Name the principle used here. (c) What value of Tarun is reflected in this case?
Answer: (d) Tarun wanted to measure the amount of water displaced by each ball when dipped in water. (b) The principle used is ‘Archimedes’ principle’. (c) Tarun showed the value of being helpful, kind and intelligent.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Case based questions for Class 9 Science involve exploring a real-world situation through scientific analysis and inquiry. These questions allow students to make connections between science concepts and the world around them, as well as develop critical thinking skills. For example, a case study may involve challenging a student to determine the cause of an illness in a local population by researching the disease, its symptoms, and the local environment. Through this exercise, students learn how to identify a problem, break it down into parts, and come up with a solution that is supported by evidence. This type of question helps students to understand how science is at the centre of solving real-world problems.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Science are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the science textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of scientific concepts to real-world situations and events.
The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter 1: Matter In Our Surroundings
Chapter 2: is matter around us pure.
- Case Based Questions: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Chapter 3: Atoms And Molecules
- Case Based Questions: Atoms And Molecules
Chapter 4: Structure Of The Atom
- Case Based Questions: Structure Of The Atom
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit Of Life
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 1
- Case Based Questions: The Fundamental Unit Of Life- 2
Chapter 6: Tissues
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 1
- Case Based Questions: Tissues- 2
Chapter 7: Motion
- Case Based Questions: Motion-1
- Case Based Questions: Motion- 2
Chapter 8: Force And Laws Of Motion
- Case Based Questions: Force And Laws Of Motion
Chapter 9: Gravitation
- Case Based Questions: Gravitation
Chapter 10: Work And Energy
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 1
- Case Based Questions: Work And Energy- 2
Chapter 11: Diversity In Living Organisms
Chapter 12: sound, chapter 13: natural resources, chapter 14: improvement in food resource, chapter 15: why do we fall ill.
- Case Based Questions: Why Do We Fall Ill?
Weightage of Case Based Questions in Class 9 Science
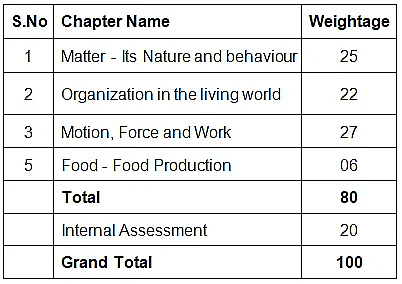
Why are Case Study Questions important in Science Class 9?
- Enhance critical thinking: Case study questions require students to analyze a real-life scenario and think critically to identify the problem and come up with possible solutions. This enhances their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Apply theoretical concepts: Case study questions allow students to apply theoretical concepts that they have learned in the classroom to real-life situations. This helps them to understand the practical application of the concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Develop decision-making skills: Case study questions challenge students to make decisions based on the information provided in the scenario. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and learn how to make informed decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Case study questions often require students to present their findings and recommendations in written or oral form. This helps them to improve their communication skills and learn how to present their ideas effectively.
- Enhance teamwork skills: Case study questions can also be done in groups, which helps students to develop teamwork skills and learn how to work collaboratively to solve problems.
In summary, case study questions are important in Class 9 because they enhance critical thinking, apply theoretical concepts, develop decision-making skills, improve communication skills, and enhance teamwork skills. They provide a practical and engaging way for students to learn and apply their knowledge and skills to real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Curriculum at Glance
The Class 9 Science curriculum in India covers a wide range of topics and concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Science curriculum at a glance:
- Physics: The Physics section includes topics such as motion, force, work and energy, sound, and light.
- Chemistry: The Chemistry section includes topics such as matter, atoms and molecules, structure of the atom, and chemical reactions.
- Biology: The Biology section includes topics such as cell structure and functions, tissues, diversity in living organisms, natural resources, and environmental management.
- Practical Work: The Science curriculum also includes practical work, where students perform experiments to observe and understand scientific phenomena.
The Class 9 Science curriculum is designed to provide a strong foundation in science and prepare students for higher education in the field. The curriculum is structured to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, and to promote the application of scientific concepts in real-life situations. The curriculum is also designed to help students prepare for competitive exams and develop a strong scientific base for future academic and professional pursuits.
Students can also access Case Based Questions of all subjects of CBSE Class 9
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 English
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Hindi
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
Are case-based questions on the class 9 science exam.
Yes, case-based questions are often included in science exams at the class 9 level as they test students' ability to apply their scientific knowledge and skills to real-world situations.
How are case-based questions different from traditional science questions?
Traditional science questions typically focus on testing students' knowledge of specific facts, concepts, and theories. Case-based questions, on the other hand, require students to use their knowledge and understanding to analyze and interpret real-world situations and make informed decisions.
How can students prepare for case-based questions in science?
To prepare for case-based questions in science, students should practice analyzing data and interpreting scientific experiments. They should also work on developing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Top Courses for Class 9
FAQs on CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf
| 1. What are case study questions in Class 9 Science? |
| 2. How are case study questions helpful in Class 9 Science? |
| 3. What is the weightage of case study questions in Class 9 Science? |
| 4. How can students prepare for case study questions in Class 9 Science? |
| 5. Can you provide an example of a case study question in Class 9 Science? |
| Views | |
| Last updated |
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf
Viva questions, semester notes, sample paper, shortcuts and tricks, mock tests for examination, extra questions, practice quizzes, video lectures, study material, past year papers, objective type questions, previous year questions with solutions, important questions.

CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf Free PDF Download
Importance of cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf notes, cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf class 9, study cbse case study questions for class 9 science - pdf on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
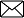
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation – Here are all the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10. This solution contains questions, answers, images, step by step explanations of the complete Chapter 10 titled Gravitation of Science taught in class 9. If you are a student of class 9 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Science, then you must come across Chapter 10 Gravitation. After you have studied lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation in one place. For a better understanding of this chapter, you should also see Chapter 10 Gravitation Class 9 notes , Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation:
- Gravitation
- Thrust and Pressure
- Archimedes’ Principle
- Relative Density
These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science . Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation.
In – Text Questions Solved
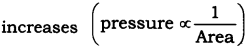
Questin 2. What do you mean by buoyancy? Answer: The upward force exerted by any fluid (liquid, gas) on an object is known as upthrust or buoyancy.
More Resources for CBSE Class 9
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 IT
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
Questin 3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water? Answer: The density of the objects and water decides the floating or sinking of the object in water. The density of water is 1 gm/cm3.
- If the density of an object is less than the density of water then the object will float.
- If the density of an object is more than the density of water then the object will sink.
Formulae Handbook for Class 9 Maths and Science Educational Loans in India
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 142 Questin 1. You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg? Answer: The weighing machine actually measures the weight of the body as the acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ is acting on the body. Hence the mass reading of 42 kg given by a weighing machine is same as the actual mass of the body. As mass is the quantity of inertia, it remains the same.
Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
Question 19. In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act? Answer: The buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid acts upwards, i.e. opposite to the direction of the force exerted by the object.
Question 20. Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water? Answer. The floating or sinking of a body in the water is decided by the density of both the body and water’s buoyant force acting on the body by the liquid. The density of plastic is less than the water and the buoyant force exerted by water on the plastiq block is greater than the force exerted by plastic on the water.
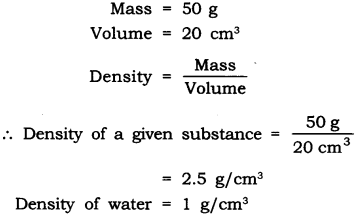
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation and Floatation (Hindi Medium)

More Questions Solved
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option:
- The device used to measure the purity of milk is (a) hydrometer (b) lactometer (d) hygrometer (d) maltometer
- The cork floats while the nail sinks in the water, this is due to (a) density of cork is more than nail (b) density of nail is more than cork. (c) density of cork is less than the density of water. (d) density of iron is less than the density of water.
- The relative density of silver is 10.8 and the density of water is 1o 3 kg/m 2 . The density of silver is (a) 1.8 x 1o 4 N/m 3 (b) 10.8 x 1o 3 N/m 3 (c) 1.8 x 1o 4 kg/m 3 (d) 10.8 x 1o 4 kg/m 3
- Buoyant force exerted by different fluids on a given body is (a) same (b) different (c) zero (d) negligible
- Liquid A is denser than liquid B, a body of wood is dipped in both the liquids? The buoyant force experienced by the body in (a) liquid A is more (b) liquid B is more (c) liquid A is less (d) none of the above Answer. 1 -(b), 2—(c), 3—(b), 4-(b), 5—(a).
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is the S.I. unit of thrust? Answer: Newton.
Question 2. What is the S.I. unit of pressure? Answer: The S.I. unit of pressure = N/m 2 = Pascal.
Question 3. Define thrust. Answer: The net force exerted by a body in a particular direction is called thrust.
Question 4. Define pressure. Answer: The force exerted per unit area is called pressure.
Question 5. Why is it easier to swim in sea water than in river water? Answer: The density of sea water is more due to dissolved salts in it as compared to the density of river water. Hence the buoyant force exerted on the swimmer by the sea water is more which helps in floating and makes swimming easier.
Question 6. Why a truck or a motorbike has much wider tyres? Answer: The pressure exerted by it can be distributed to more area, and avoid the wear and tear of tyres.
Question 7. Why are knives sharp? Answer: To increase the pressure, area is reduced, As pressure ∝ 1/Area hence the pressure or force exerted on a body increases.
Question 8. Why is the wall of dam reservoir thicker at the bottom? Answer: The pressure of water in dams at the bottom is more, to withstand this pressure the dams have wider walls.
Question 9. Why do nails have pointed tips? Answer: The force exerted when acts on a smaller area, it exerts larger pressure. So the nails have pointed tips.
Question 10. While swimming why do we feel light? Answer: The swimmer is exerted by an upward force by water, this phenomenon is called buoyancy and it makes the swimmer feel light.
Question 11. Define density and give its unit. Answer: The density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume. Its unit is kg/m 3 .
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. A ship made of iron does not sink but the iron rod sinks in water, why? Answer: The iron rod sinks due to high density and less buoyant force exerted by the water on it, but in case of ship the surface area is increased, the upthrust experienced by the body is more. So it floats on water
Question 2. Camels can walk easily on desert sand but we are not comfortable walking on the sand. State reason. Answer: Camels feet are broad and the larger area of the feet reduces the force/ pressure exerted by the body on the sand. But when we have to walk on the same sand, we sink because the pressure exerted by our body is not distributed but is directional.
Question 3. What is lactometer and hydrometer? Answer: Lactometer is a device used to find the purity of a given sample of milk. Hydrometer is a device used to find the density of liquids.
Question 4. The relative density of silver is 10.8. What does this mean? Answer: It means that the density of silver is 10.8 times more than that of water. T
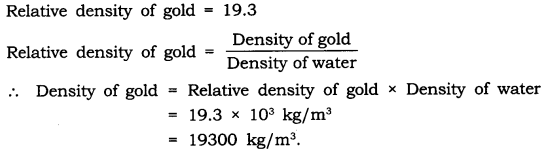
Question 6. State Archimedes’ principle. Answer: Archimedes’ principle—When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. It is used in designing of ships and submarines.
Question 7. Two cork pieces of same size and mass are dipped in two beakers containing water and oil. One cork floats on water but another sink in oil. Why? Answer: The cork floats on water because the density of cork is less than the density of water, and another cork sinks in the oil because the density of cork is more than the oil.
Question 8. What are fluids? Why is Archimedes’ principle applicable only for fluids? Give the application of Archimedes’ principle. Answer: Fluids are the substances which can flow e.g., gases and liquids are fluids. Archimedes’ principle is based on the upward force exerted by fluids on any object immersed in the fluid. Hence it is applicable only for fluids. Applications of Archimedes’ principle:
- It is used in designing of ship and submarine.
- It is used in designing lactometer, used to determine the purity of milk,
- To make hydrometers, used to determine the density of liquids.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Long Answer Type Questions
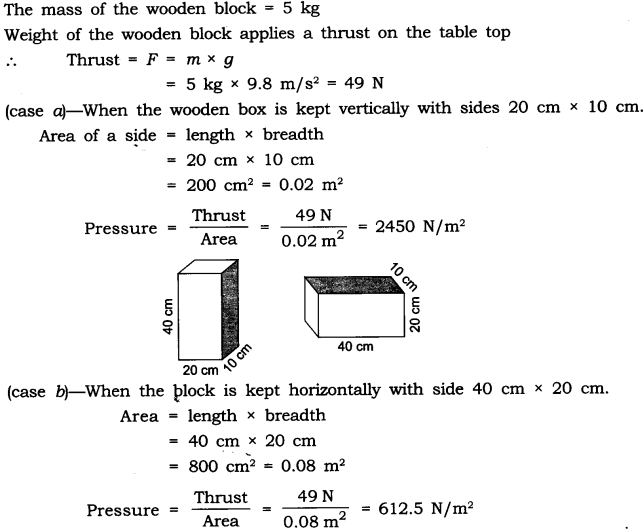
- Nails have pointed tips.
- Knives have sharp edges.
- Needles have pointed tips.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Activity -Based Questions
Question 1.
- Take an empty plastic bottle. Close the mouth of the bottle with an airtight stopper. Put it in a bucket filled with water. You see that the bottle floats.
- Push the bottle into the water. You feel an upward push. Try to push it further down. You will find it difficult to push deeper and deeper. This indicates that water exerts a force on the bottle in the upward direction. The upward force exerted by the water goes on increasing as the bottle is pushed deeper till it is completely immersed.
- Now, release the bottle. It bounces back to the surface.
- Does the force due to the gravitational attraction of the earth act on this bottle? If so, why doesn’t the bottle stay immersed in water after it is released? How can you immerse the bottle in water?
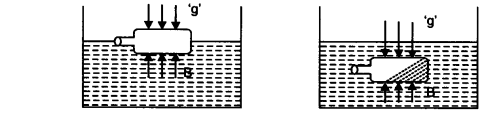
Question 2.
- Take a beaker filled with water.
- Take an iron nail and place it on the surface of the water.
- Observe what happens.
Question 3.
- Take a piece of cork and an iron nail of equal mass.
- Place them on the surface of water.
Answer: The iron nail sinks as.the density of nail is more and the downward force exerted on nail is more than the buoyant force. The cost floats as the density of cost is less and the buoyant force exerted on it is more than the downward force.
Question 4.
- Take a piece of stone and tie it to one end of a rubber string or a spring balance.
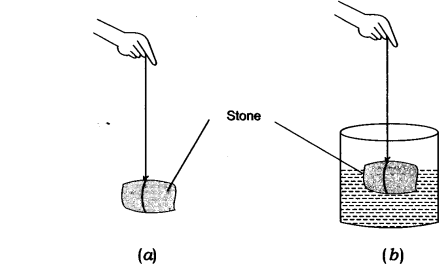
- Note the elongation of the string or the reading on the spring balance due to the weight of the stone.
- Now, slowly dip the stone in the water in a container as shown in Fig. (b).
- Observe what happens to the elongation of the string or the reading on the balance. Observations :
- In Fig. (a) the elongation of the string is 6 cm.
- In Fig. (b) when the stone is dipped in water the length of string reduced to 5 cm.
- The length of the string in case (b) decreases due to the upward force exerted by water on the stone called as buoyant force.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Value-Based Questions
Question 1. A milkman sold his milk in the city and always carried lactometer with him. The customers trusted him and his business flourished. (a) What is lactometer? (b) What is the principle of working of lactometer? (c) What value of milkman is seen in this case? Answer. (a) Lactometer is a device that measures the purity of milk. (b) The principle of lactometer is ‘Archimedes’ principle’. It states that when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it. (c) Milkman is very honest and trustworthy.
Question 2. Reeta was wearing a high heel shoe for a beach party, her friend told her to wear flat shoes as she will be tired soon with high heels and will not feel comfortable, (a) Why would one feel tired with high heel shoes on beach? (b) Give the unit of pressure. (c) What value of Reeta’s friend is seen in the above act? Answer: (a) The high heel shoes would exert lot of pressure on the loose sand of beach and will sink more in the soil as compared to flat shoes. Hence large amount of force will be required to walk with heels. (b) Unit of pressure is Pascal. (c) Reeta’s friend showed the value of being helpful, concerned and intelligent.
Question 3. In the school fair, there was a game in which one need to find the heaviest ball without holding them in hand. Three balls were given and few disposable glasses were kept. Tarun saw his friend struggling to win the game but he was unable to find the heaviest ball. Tarun helped him by dipping the three balls one by one in the glass’es full of water upto the brim and finally they won the game. (a) Why did Tarun told his friend to dip the balls one by one in completely filled glass of water? (b) Name the principle used here. (c) What value of Tarun is reflected in this case? Answer: (d) Tarun wanted to measure the amount of water displaced by each ball when dipped in water. (b) The principle used is ‘Archimedes’ principle’. (c) Tarun showed the value of being helpful, kind and intelligent.
Free Resources
Quick Resources
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Science
- Chapter 10: Gravitation
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 - Gravitation
Ncert solutions class 9 science chapter 10 – cbse free pdf download.
* According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation provides you with the necessary insights into the concepts involved in the chapter. Detailed answers and explanations provided by us in NCERT Solutions will help you in understanding the concepts clearly.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 9 Science Chapter – 10 Gravitation
Download most important questions for class 9 science chapter – 10 gravitation.
Gravity is a fascinating topic that explains many things, from how our planet stays in orbit to why things fall down. Explore Science Chapter 10 – Gravitation of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 to learn everything you need to know about gravity. Content is crafted by highly qualified teachers and industry professionals with decades of relevant knowledge. Moreover, the solutions have been updated to include the latest content prescribed by the CBSE board.
Furthermore, we ensure that relevant content on NCERT Solutions Class 9 is regularly updated as per the norms and prerequisites that examiners often look for in the CBSE exam. This ensures that the content is tailored to be class relevant without sacrificing the informational quotient. BYJU’S also strives to impart maximum informational value without increasing the complexity of topics. This is achieved by ensuring that the language is simple and that all technical jargon is explained at the required school level.
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules
- Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life
- Chapter 6 Tissues
- Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Chapter 8 Motion
- Chapter 9 Force And Laws Of Motion
- Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Chapter 12 Sound
- Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall ill
- Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 – Gravitation
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access Answers to NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 10 – Gravitation ( All In text and Exercise Questions Solved)
Exercise-10.1 page: 134.
1. State the universal law of gravitation.
The universal law of gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force called the gravitational force. The force acting between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Consider F as the force of attraction between an object on the surface of earth and the earth
Also, consider ‘m’ as the mass of the object on the surface of earth and ‘M’ as the mass of earth
The distance between the earth’s centre and object = Radius of the earth = R
Therefore, the formula for the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface is given as
F = G Mm/R 2
Exercise-10.2 Page: 136
1. What do you mean by free fall?
Earth’s gravity attracts each object to its center. When an object is dropped from a certain height, under the influence of gravitational force it begins to fall to the surface of Earth. Such an object movement is called free fall.
2. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
When an object falls freely from a certain height towards the earth’s surface, its velocity keeps changing. This velocity change produces acceleration in the object known as acceleration due to gravity and denoted by ‘g’.
The value of the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is,

Exercise-10.3 Page: 138
1. What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
The differences between the mass of an object and its weight are tabulated below.
| Mass | Weight |
| Mass is the quantity of matter contained in the body. | Weight is the force of gravity acting on the body. |
| It is the measure of inertia of the body. | It is the measure of gravity. |
| It only has magnitude. | It has magnitude as well as direction. |
| Mass is a constant quantity. | Weight is not a constant quantity. It is different at different places. |
| Its SI unit is kilogram (kg). | Its SI unit is the same as the SI unit of force, i.e., Newton (N). |
2. Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the earth?
The mass of the moon is 1/100 times and its radius 1/4 times that of earth. As a result, the gravitational attraction on the moon is about one-sixth when compared to earth. The moon’s gravitation force is determined by the mass and the size of the moon. Hence, the weight of an object on the moon is 1/6th its weight on the earth. The moon is far less massive than the Earth and has a different radius(R) as well.
Exercise-10.4 Page: 141
1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
It is tough to carry a school bag having a skinny strap because of the pressure that is being applied on the shoulders. The pressure is reciprocally proportional to the expanse on which the force acts. So, the smaller the surface area, the larger is going to be the pressure on the surface. In the case of a skinny strap, the contact expanse is quite small. Hence, the pressure exerted on the shoulder is extremely huge.
2. What do you mean by buoyancy?
The upward force possessed by a liquid on an object that’s immersed in it is referred to as buoyancy.
3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water?
An object floats or sinks when placed on the surface of water because of two reasons.
(i) If its density is greater than that of water, an object sinks in water.
(ii) If its density is less than that of water, an object floats in water.
Exercise-10.5 Page: 142
1. You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg?
A weighing machine measures the body weight and is calibrated to indicate the mass. If we stand on a weighing machine, the weight acts downwards while the upthrust due to air acts upwards. So our apparent weight becomes less than the true weight. This apparent weight is measured by the weighing machine and therefore the mass indicated is less than the actual mass. So our actual mass will be more than 42 kg.
2. You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100 kg when measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
The correct answer is the cotton bag is heavier than an iron bar. The bag of cotton is heavier than the bar of iron. The cotton bag experiences a larger air thrust than the iron bar. Therefore, the weighing machine indicates less weight than its actual weight for the cotton bag. The reason is
True weight = (apparent weight + up thrust)
The cotton bag’s density is less than that of the iron bar, so the volume of the cotton bag is more compared to the iron bar. So the cotton bag experience more upthrust due to the presence of air.
Therefore, in the presence of air, the cotton bag’s true weight is more compared to the true weight of the iron bar.
Exercises-10.6 Page: 143
1. How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
Consider the Universal law of gravitation,
According to that law, the force of attraction between two bodies is

m 1 and m 2 are the masses of the two bodies.
G is the gravitational constant.
r is the distance between the two bodies.
Given that the distance is reduced to half then,

Therefore once the space between the objects is reduced to half, then the force of gravitation will increase by fourfold the first force.

2. Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then does a heavy object not fall faster than a light object?
All objects fall from the top with a constant acceleration called acceleration due to gravity (g). This is constant on earth and therefore the value of ‘g’ doesn’t depend on the mass of an object. Hence, heavier objects don’t fall quicker than light-weight objects provided there’s no air resistance.
3. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 10 24 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 10 6 m.)
From Newton’s law of gravitation, we know that the force of attraction between the bodies is given by

4. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
The earth attracts the moon with a force same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth. However, these forces are in opposite directions. By universal law of gravitation, the force between moon and also the sun can be

d = distance between the earth and moon.
m 1 and m 2 = masses of earth and moon respectively.

5. If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
According to the universal law of gravitation and Newton’s third law, we all know that the force of attraction between two objects is the same, however in the opposite directions. So the earth attracts the moon with a force same as the moon attracts the earth but in opposite directions. Since earth is larger in mass compared to that of the moon, it accelerates at a rate lesser than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the Earth. Therefore, for this reason the earth does not move towards the moon.

6. What happens to the force between two objects, if
(i) The mass of one object is doubled?
(ii) The distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
(iii) The masses of both objects are doubled?
According to universal law of gravitation, the force between 2 objects (m 1 and m 2 ) is proportional to their plenty and reciprocally proportional to the sq. of the distance(R) between them.

If the mass is doubled for one object.
F = 2F, so the force is also doubled.
If the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled
If it’s doubled
F = (Gm 1 m 2 )/(2R) 2
F = 1/4 (Gm 1 m 2 )/R 2
Force thus becomes one-fourth of its initial force.
Now, if it’s tripled
F = (Gm 1 m 2 )/(3R) 2
F = 1/9 (Gm 1 m 2 )/R 2
Force thus becomes one-ninth of its initial force.
If masses of both the objects are doubled, then

F = 4F, Force will therefore be four times greater than its actual value.
7. What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
The universal law of gravitation explains many phenomena that were believed to be unconnected:
(i) The motion of the moon round the earth
(ii) The responsibility of gravity on the weight of the body which keeps us on the ground
(iii) The tides because of the moon and therefore the Sun
(iv) The motion of planets round the Sun

8. What is the acceleration of free fall?
Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. On Earth, all bodies experience a downward force of gravity which Earth’s mass exerts on them. The Earth’s gravity is measured by the acceleration of the freely falling objects. At Earth’s surface, the acceleration of gravity is 9.8 ms -2 and it is denoted by ‘g’. Thus, for every second an object is in free fall, its speed increases by about 9.8 metres per second.
9. What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
The gravitation force between the earth and an object is called weight. Weight is equal to the product of acceleration due to the gravity and mass of the object.
10. Amit buys few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why? [Hint: The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator.]
The weight of a body on the earth’s surface;
W = mg (where m = mass of the body and g = acceleration due to gravity)
The value of g is larger at poles when compared to the equator. So gold can weigh less at the equator as compared to the poles.
Therefore, Amit’s friend won’t believe the load of the gold bought.

11. Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
A sheet of paper has a larger surface area when compared to a crumpled paper ball. A sheet of paper will face a lot of air resistance. Thus, a sheet of paper falls slower than the crumpled ball.

12. Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the earth. What is the weight in newton’s of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the earth?
Given data:
Acceleration due to earth’s gravity = g e or g = 9.8 m/s 2
Object’s mass, m = 10 kg
Acceleration due to moon gravity = g m
Weight on the earth= W e
Weight on the moon = W m
Weight = mass x gravity
g m = (1/6) g e (given)
So W m = m g m = m x (1/6) g e
W m = 10 x (1/6) x 9.8 = 16.34 N
W e = m x g e = 10 x 9.8

13. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s.
(i) The maximum height to which it rises,
(ii) The total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
Initial velocity u = 49 m/s
Final speed v at maximum height = 0
Acceleration due to earth gravity g = -9.8 m/s 2 (thus negative as ball is thrown up).
By third equation of motion,
2gH = v 2 – u 2
2 × (- 9.8) × H = 0 – (49) 2
– 19.6 H = – 2401
H = 122.5 m
Total time T = Time to ascend (T a ) + Time to descend (T d )
0 = 49 + (-9.8) x T a
Ta = (49/9.8) = 5 s
Also, T d = 5 s
Therefore T = T a + T d
14. A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground.
Initial velocity
Tower height = total distance = 19.6m
g = 9.8 m/s 2
Consider third equation of motion
v 2 = u 2 + 2gs
v 2 = 0 + 2 × 9.8 × 19.6
v 2 = 384.16
v = √(384.16)
v = 19.6m/s
15. A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s 2 , find the maximum height reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone?
Initial velocity u = 40m/s
g = 10 m/s 2
Max height final velocity = 0
0 = (40) 2 – 2 x 10 x s
s = (40 x 40) / 20
Maximum height s = 80m
Total Distance = s + s = 80 + 80
Total Distance = 160m
Total displacement = 0 (The first point is the same as the last point)
16. Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 10 24 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 10 30 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 10 11 m.
Mass of the sun m s = 2 × 10 30 kg
Mass of the earth m e = 6 × 10 24 kg
Gravitation constant G = 6.67 x 10 -11 N m 2 / kg 2
Average distance r = 1.5 × 10 11 m
Consider Universal law of Gravitation

17. A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet.
(i) When the stone from the top of the tower is thrown,
Initial velocity u’ = 0
Distance travelled = x
Time taken = t

(ii) When the stone is thrown upwards,
Initial velocity u = 25 m/s
Distance travelled = (100 – x)

From equations (a) and (b)
5t 2 = 100 -25t + 5t 2
t = (100/25) = 4sec.
After 4sec, two stones will meet
x = 5t 2 = 5 x 4 x 4 = 80m.
Putting the value of x in (100-x)
= (100-80) = 20m.
This means that after 4sec, 2 stones meet a distance of 20 m from the ground.
18. A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6 s. Find
(a) The velocity with which it was thrown up,
(b) The maximum height it reaches, and
(c) Its position after 4s.
g = 10m/s 2
Total time T = 6sec
T a = T d = 3sec
(a) Final velocity at maximum height v = 0
From first equation of motion:-
v = u – gt a
u = v + gt a
= 0 + 10 x 3
The velocity with which stone was thrown up is 30m/s.
(b) From second equation of motion

The maximum height stone reaches is 45m.
(c) In 3sec, it reaches the maximum height.
Distance travelled in another 1sec = s’

The distance travelled in another 1sec = 5m.
Therefore in 4sec, the position of point p (45 – 5)
= 40m from the ground.
19. In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
The buoyant force on an object that is immersed in a liquid will be in a vertically upward direction.
20. Why a block of plastic when released under water come up to the surface of water?
The density of plastic is lesser than that of water. Therefore, the force of buoyancy on plastic block will be greater than the weight of plastic block. Hence, the acceleration of plastic block is going to be in the upward direction. So, the plastic block comes up to the surface of water.
21. The volume of 50 g of a substance is 20 cm 3 . If the density of water is 1 g cm –3 , will the substance float or sink?
To find the Density of the substance the formula is
Density = (Mass/Volume)
Density = (50/20) = 2.5g/cm 3
Density of water = 1g/cm 3
Density of the substance is greater than density of water. So the substance will sink.
22. The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm 3 . Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is 1 g cm –3 ? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Density of sealed packet = 500/350 = 1.42 g/cm 3
Density of sealed packet is greater than density of water
Therefore the packet will sink.
Considering Archimedes Principle,
Displaced water volume = Force exerted on the sealed packet.
Volume of water displaced = 350cm 3
Therefore displaced water mass = ρ x V
Mass of displaced water = 350g.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 – Gravitation
Chapter 10 – Gravitation is a part of Unit 3 – Motion, Force and Work, which carries a total of 27 out of 100. Usually, 2 or 3 questions do appear from this chapter every year, as previous trends have shown.
The topics usually covered under this chapter are:
- Universal Law of Gravitation and its Importance
- Characteristics of Gravitational Forces
- Concept of Free Fall
- Difference between Gravitation Constant and Gravitational Acceleration
Often times, the term gravity and gravitation are used interchangeably and this is wrong. However, these two terms are related to each other but their implications are quite different. Academically, Chapter 10 – Gravitation is an important concept as it carries a considerable weightage in the CBSE exam. Therefore, ensure that all relevant concepts, formulas and diagrams are studied thoroughly.
Explore how gravitation works at the molecular level, discover its applications and learn other related important concepts by exploring our NCERT Solutions.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 – Gravitation
- Solutions provided in an easy-to-understand language
- Qualified teachers and their vast experience helps formulate the solutions
- Questions updated to the latest prescribed syllabus
- A detailed breakdown of the most important exam questions
- Access to additional learning resources like sample papers and previous year question papers
Disclaimer:
Dropped Topics – Following Box Items: a. Brief Description of Isaac Newton, b. How did Newton guess the inverse– square rule? 10.7 Relative Density and Example 10.7.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10
Does the ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 10 help students grasp the features of gravitational force, how to solve the problems based on gravitation quickly in chapter 10 of ncert solutions for class 9 science, why should i use the ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 10 pdf from byju’s, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Byjus is very best app please 🥺🥺 all children and adults download the app for solving doubts.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation

| Study Reference for Class 9 Chapter 10 Gravitation |
|---|
| Mass is the quantity of matter contained in the body. | Weight is the force of gravity acting on the body. |
| It is the measure of inertia of the body. | It is the measure of gravity. |
| Mass is a constant quantity. | Weight is not a constant quantity. It is different at different places. |
| It only has magnitude. | It has magnitude as well as direction. |
| Its SI unit is kilogram (kg). | Its SI unit is the same as the SI unit of force, i.e., Newton (N). |

Chapter 10 Gravitation Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
| |
Contact Form
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Motion
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 8 motion.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Motion. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Motion.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Motion
(i)Which of the following relation is always true when object moves in straight line
(b)distance is always greater than or equal to displacement
| No. | Distance | Displacement |
| 1 | The complete length of the path between any two points is called distance | Displacement is the shortest length between any two point. |
| 2 | Distance is a scalar quantity | Displacement is a vector quantity |
| 3 | The distance can only have positive values. | Displacement can be positive, negative, and even zero. |
(b)distance is greater than and equal to displacement
(iii) What is Displacement when particle moves from point A to C through A-B-C?
(a)speed is scalar
(b)direction
Answer key-3
| No. | speed | Velocity |
| 1 | The speed of an object is the distance covered by object per unit time. | Velocity is defined as the displacement by particle per unit time. |
| 2 | Speed can never be negative or zero | Velocity can be zero, negative, or positive.
|
| 3 | Speed is Scalar quantity
| Velocity is Vector quantity
|
(ii) An object travels 20 m in 5 s and then another 40 m in 5s. What is the average speed in m/s of the object?
(c)velocity is changing
(v) Odometers and speedometers are two of the many instruments used to measure speed of rotation.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 22 solutions স্কুলের অনুষ্ঠান করি, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 21 solutions মাঠে টিফিন ভাগ করে খাই, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 20 solutions নিজের খুশিমতো রং করি, jharkhand board solutions class 5 english chapter 8.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 6 Minutes
Case Study/Passage Based Questions:
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below :
In the figure below the card is flicked with a push. It was observed that the card moves ahead while coin falls in glass.

(i) Give reason for the above observation. (a) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it resists the change and hence falls in the glass. (b) The coin possesses inertia of motion; it resists the change and hence falls in the glass. (c) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it accepts the change and hence falls in the glass. (d) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it accepts the change and hence falls in the glass.
(ii) Name the law involved in this case. (a) Newton’s second law of motion. (b) Newton’s first law of motion. (c) Newton’s third law of motion. (d) Law of conservation of energy
(iii) If the above coin is replaced by a heavy five-rupee coin, what will be your observation. Give reason. (a) Heavy coin will possess more inertia so it will not fall in tumbler. (b) Heavy coin will possess less inertia so it will fall in tumbler. (c) Heavy coin will possess more inertia so it will fall in tumbler. (d) Heavy coin will possess less inertia so it will not fall in tumbler.
(iv) Name the law which provides the definition of force. (a) Law of conservation of mass (b) Newton’s third law. (c) Newton’s first law (d) Newton’s second law.
(v) State Newton’s first law of motion. (a) Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another, total amount of energy always remains constant. (b) A body at rest remains at rest or, if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an external unbalanced force. (c) For every action in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. (d) The acceleration in an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass.
Other Chapters:
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Last modified on:3 years agoReading Time:5MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Last modified on:3 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Last modified on:3 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Last modified on:3 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
Last modified on:3 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

COMMENTS
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: According to the universal law of gravitation, the force between two particles or bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between these particles or bodies. Consider two bodies A and B having masses m 1 and m 2 ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Gravitation. Case 1: (1) Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the product of their masses (m1*m2) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d 2) between them. The force is along the line joining the centers of two objects.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based on it will be … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 ...
Class 9 science case study question 1. Read the passage and answer any four questions: Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas.
Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 10 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science, covering various topics and concepts. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in ...
by experts. Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions. Case study questions are based on real or ...
CBSE Class 9 Science Sample Paper with Solutions for Term 2 Exam 2022. Check some of the important case study questions below: Q. Read the following and answer the questions: A student was asked ...
In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 10 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
NCERT Solutions for Gravitation Class 9 Questions and Answers FREE PDF Download. Class 9 Science Ch 9 explores the concept of gravitational force, understanding its effects on celestial bodies like planets and moons, and Archimedes' Principle. Vedantu's Class 9 Gravitation NCERT Solutions solves all the questions in the chapter and helps ...
Or you can also click Next. Get NCERT Solutions, Notes, Solutions to Intext Questions, Examples of Chapter 10 Class 9 Gravitation free at Teachoo.In this chapter, we will learnWhat isGravity?What isUniversal Law of GravitationImportantNatural PhenomenaOccurring Due to GravitationWhat isFree Fall?What isAcceleration Due To Grav.
Answer: (d) Tarun wanted to measure the amount of water displaced by each ball when dipped in water. (b) The principle used is 'Archimedes' principle'. (c) Tarun showed the value of being helpful, kind and intelligent. Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation with answers is given below.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Gravitation are essential study materials for students who wish to score well in the Class 9 examination. This Exemplar page provides questions with varied difficulty levels.
The CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 9 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes' Principle. Relative Density. These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation. In - Text Questions Solved. NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science - Page 141. Questin 1.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Heredity and Evolution. A scientist cross pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant he will get pea plants of F1 generation. If now self-cross the pea plant of F2 generation is done, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation. [KVS Raipur 2021-22]
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Matter in our Surroundings Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies ...
The PDF of solutions can be downloaded and referred to understand the method of answering complex questions. NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation PDFs are provided here for free. These NCERT Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 10 Gravitation can help students to clear any doubt instantly and ace well in the CBSE exam.
Force of attraction acting between them = F. It will be given by the universal law of gravitation. F = Gm 1 m 2 /d 2. where, G is the universal constant. G = 6.67×10 -11 Nm 2 kg -2. 2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth. Answer.
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Motion. (1) Distance and displacement are two quantities that seem to mean the same but are different with different meanings and definitions. Distance is the measure of "how much distance an object has covered during its motion" while displacement refers to the measure of"how far the abject ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 ...
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below : In the figure below the card is flicked with a push. It was observed that the card moves ahead while coin falls in glass. (i) Give reason for the above observation.(a) The coin possesses … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science ...