

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
Body paragraphs
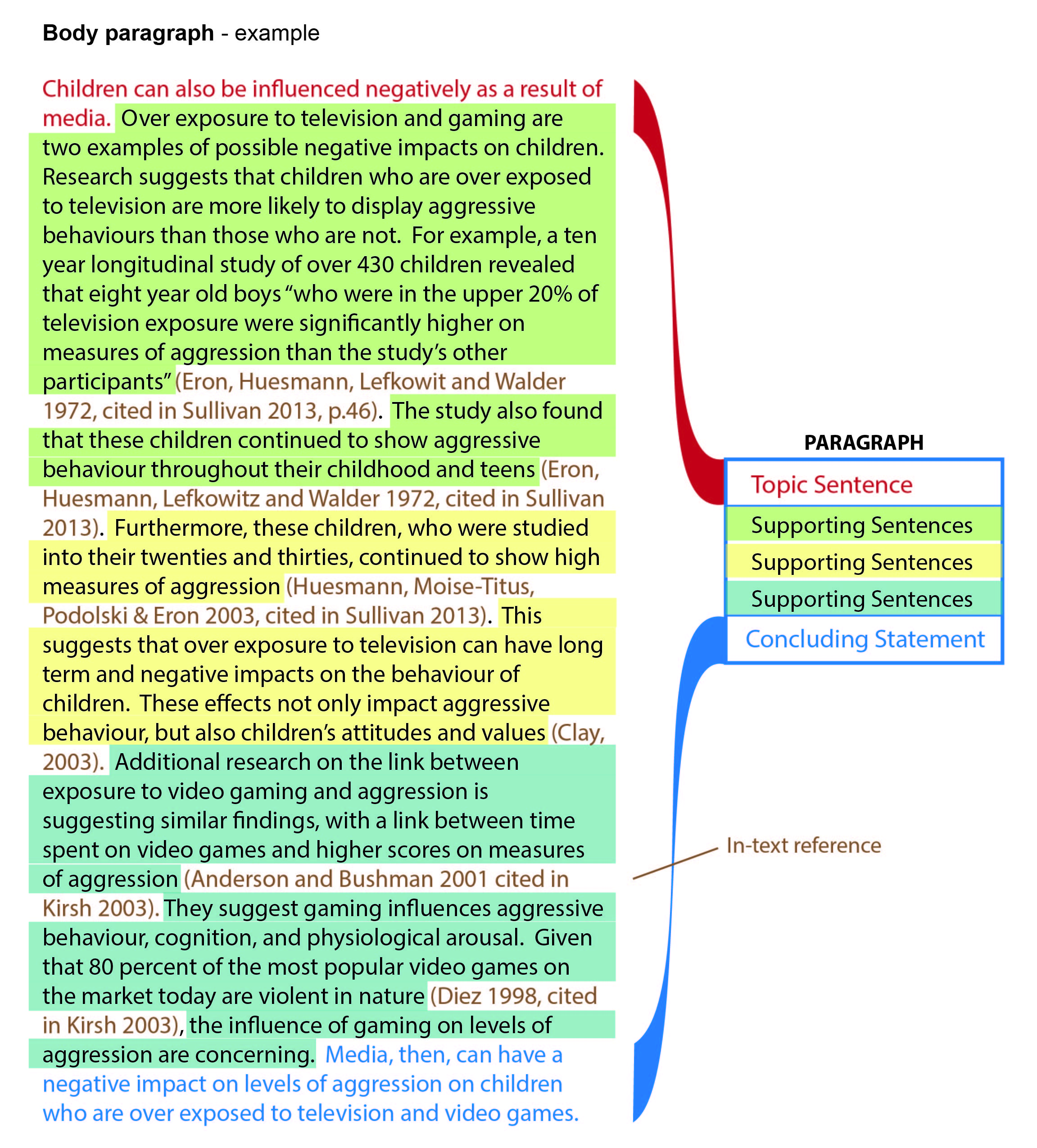
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write a Body Paragraph for a College Essay
January 29, 2024
No matter the discipline, college success requires mastering several academic basics, including the body paragraph. This article will provide tips on drafting and editing a strong body paragraph before examining several body paragraph examples. Before we look at how to start a body paragraph and how to write a body paragraph for a college essay (or other writing assignment), let’s define what exactly a body paragraph is.
What is a Body Paragraph?
Simply put, a body paragraph consists of everything in an academic essay that does not constitute the introduction and conclusion. It makes up everything in between. In a five-paragraph, thesis-style essay (which most high schoolers encounter before heading off to college), there are three body paragraphs. Longer essays with more complex arguments will include many more body paragraphs.
We might correlate body paragraphs with bodily appendages—say, a leg. Both operate in a somewhat isolated way to perform specific operations, yet are integral to creating a cohesive, functioning whole. A leg helps the body sit, walk, and run. Like legs, body paragraphs work to move an essay along, by leading the reader through several convincing ideas. Together, these ideas, sometimes called topics, or points, work to prove an overall argument, called the essay’s thesis.
If you compared an essay on Kant’s theory of beauty to an essay on migratory birds, you’d notice that the body paragraphs differ drastically. However, on closer inspection, you’d probably find that they included many of the same key components. Most body paragraphs will include specific, detailed evidence, an analysis of the evidence, a conclusion drawn by the author, and several tie-ins to the larger ideas at play. They’ll also include transitions and citations leading the reader to source material. We’ll go into more detail on these components soon. First, let’s see if you’ve organized your essay so that you’ll know how to start a body paragraph.
How to Start a Body Paragraph
It can be tempting to start writing your college essay as soon as you sit down at your desk. The sooner begun, the sooner done, right? I’d recommend resisting that itch. Instead, pull up a blank document on your screen and make an outline. There are numerous reasons to make an outline, and most involve helping you stay on track. This is especially true of longer college papers, like the 60+ page dissertation some seniors are required to write. Even with regular writing assignments with a page count between 4-10, an outline will help you visualize your argumentation strategy. Moreover, it will help you order your key points and their relevant evidence from most to least convincing. This in turn will determine the order of your body paragraphs.
The most convincing sequence of body paragraphs will depend entirely on your paper’s subject. Let’s say you’re writing about Penelope’s success in outwitting male counterparts in The Odyssey . You may want to begin with Penelope’s weaving, the most obvious way in which Penelope dupes her suitors. You can end with Penelope’s ingenious way of outsmarting her own husband. Because this evidence is more ambiguous it will require a more nuanced analysis. Thus, it’ll work best as your final body paragraph, after readers have already been convinced of more digestible evidence. If in doubt, keep your body paragraph order chronological.
It can be worthwhile to consider your topic from multiple perspectives. You may decide to include a body paragraph that sets out to consider and refute an opposing point to your thesis. This type of body paragraph will often appear near the end of the essay. It works to erase any lingering doubts readers may have had, and requires strong rhetorical techniques.
How to Start a Body Paragraph, Continued
Once you’ve determined which key points will best support your argument and in what order, draft an introduction. This is a crucial step towards writing a body paragraph. First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly. You should be looking at your thesis throughout the drafting of your body paragraphs.
Finally, make sure that your introduction indicates which key points you’ll be covering in your body paragraphs, and in what order. While this level of organization might seem like overkill, it will indicate to the reader that your entire paper is minutely thought-out. It will boost your reader’s confidence going in. They’ll feel reassured and open to your thought process if they can see that it follows a clear path.
Now that you have an essay outline and introduction, you’re ready to draft your body paragraphs.
How to Draft a Body Paragraph
At this point, you know your body paragraph topic, the key point you’re trying to make, and you’ve gathered your evidence. The next thing to do is write! The words highlighted in bold below comprise the main components that will make up your body paragraph. (You’ll notice in the body paragraph examples below that the order of these components is flexible.)
Start with a topic sentence . This will indicate the main point you plan to make that will work to support your overall thesis. Your topic sentence also alerts the reader to the change in topic from the last paragraph to the current one. In making this new topic known, you’ll want to create a transition from the last topic to this one.
Transitions appear in nearly every paragraph of a college essay, apart from the introduction. They create a link between disparate ideas. (For example, if your transition comes at the end of paragraph 4, you won’t need a second transition at the beginning of paragraph 5.) The University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center has a page devoted to Developing Strategic Transitions . Likewise, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center offers help on paragraph transitions .
How to Draft a Body Paragraph for a College Essay ( Continued)
With the topic sentence written, you’ll need to prove your point through tangible evidence. This requires several sentences with various components. You’ll want to provide more context , going into greater detail to situate the reader within the topic. Next, you’ll provide evidence , often in the form of a quote, facts, or data, and supply a source citation . Citing your source is paramount. Sources indicate that your evidence is empirical and objective. It implies that your evidence is knowledge shared by others in the academic community. Sometimes you’ll want to provide multiple pieces of evidence, if the evidence is similar and can be grouped together.
After providing evidence, you must provide an interpretation and analysis of this evidence. In other words, use rhetorical techniques to paraphrase what your evidence seems to suggest. Break down the evidence further and explain and summarize it in new words. Don’t simply skip to your conclusion. Your evidence should never stand for itself. Why? Because your interpretation and analysis allow you to exhibit original, analytical, and critical thinking skills.
Depending on what evidence you’re using, you may repeat some of these components in the same body paragraph. This might look like: more context + further evidence + increased interpretation and analysis . All this will add up to proving and reaffirming your body paragraph’s main point . To do so, conclude your body paragraph by reformulating your thesis statement in light of the information you’ve given. I recommend comparing your original thesis statement to your paragraph’s concluding statement. Do they align? Does your body paragraph create a sound connection to the overall academic argument? If not, you’ll need to fix this issue when you edit your body paragraph.
How to Edit a Body Paragraph
As you go over each body paragraph of your college essay, keep this short checklist in mind.
- Consistency in your argument: If your key points don’t add up to a cogent argument, you’ll need to identify where the inconsistency lies. Often it lies in interpretation and analysis. You may need to improve the way you articulate this component. Try to think like a lawyer: how can you use this evidence to your advantage? If that doesn’t work, you may need to find new evidence. As a last resort, amend your thesis statement.
- Language-level persuasion. Use a broad vocabulary. Vary your sentence structure. Don’t repeat the same words too often, which can induce mental fatigue in the reader. I suggest keeping an online dictionary open on your browser. I find Merriam-Webster user-friendly, since it allows you to toggle between definitions and synonyms. It also includes up-to-date example sentences. Also, don’t forget the power of rhetorical devices .
- Does your writing flow naturally from one idea to the next, or are there jarring breaks? The editing stage is a great place to polish transitions and reinforce the structure as a whole.
Our first body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay .” Here’s the prompt: Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.” Now let’s see how this writer builds an argument against perfection through one main point across two body paragraphs. (While this writer has split this idea into two paragraphs, one to address a problem and one to provide an alternative resolution, it could easily be combined into one paragraph.)
“Students often feel the need to be perfect in their classes, and this can cause students to struggle or stop making an effort in class. In elementary and middle school, for example, I was very nervous about public speaking. When I had to give a speech, my voice would shake, and I would turn very red. My teachers always told me “relax!” and I got Bs on Cs on my speeches. As a result, I put more pressure on myself to do well, spending extra time making my speeches perfect and rehearsing late at night at home. But this pressure only made me more nervous, and I started getting stomach aches before speaking in public.
“Once I got to high school, however, I started doing YouTube make-up tutorials with a friend. We made videos just for fun, and laughed when we made mistakes or said something silly. Only then, when I wasn’t striving to be perfect, did I get more comfortable with public speaking.”
Body Paragraph Example 1 Dissected
In this body paragraph example, the writer uses their personal experience as evidence against the value of striving for perfection. The writer sets up this example with a topic sentence that acts as a transition from the introduction. They also situate the reader in the classroom. The evidence takes the form of emotion and physical reactions to the pressure of public speaking (nervousness, shaking voice, blushing). Evidence also takes the form of poor results (mediocre grades). Rather than interpret the evidence from an analytical perspective, the writer produces more evidence to underline their point. (This method works fine for a narrative-style essay.) It’s clear that working harder to be perfect further increased the student’s nausea.
The writer proves their point in the second paragraph, through a counter-example. The main point is that improvement comes more naturally when the pressure is lifted; when amusement is possible and mistakes aren’t something to fear. This point ties back in with the thesis, that “we should value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfection.
This second body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay .” Here’s an abridged version of the prompt: Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.” Now read the body paragraph example, below.
“To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.”
Body Paragraph Example 2 Dissected
The first sentence in this body paragraph example indicates that the topic is transitioning into biblical references as a means of motivating ordinary citizens. The evidence comes as quotes taken from Obama’s speech. One is a reference to God, and the other an allusion to a story from the bible. The subsequent interpretation and analysis demonstrate that Obama’s biblical references imply a deeper, moral and spiritual significance. The concluding sentence draws together the morality inherent in equal rights with Rosa Parks’ power to spark change. Through the words “no political power or fortune,” and “moral balance,” the writer ties the point proven in this body paragraph back to the thesis statement. Obama promises that “All of us” (no matter how small our influence) “are capable of achieving greater good”—a greater moral good.
What’s Next?
Before you body paragraphs come the start and, after your body paragraphs, the conclusion, of course! If you’ve found this article helpful, be sure to read up on how to start a college essay and how to end a college essay .
You may also find the following blogs to be of interest:
- 6 Best Common App Essay Examples
- How to Write the Overcoming Challenges Essay
- UC Essay Examples
- How to Write the Community Essay
- How to Write the Why this Major? Essay
- College Essay
Kaylen Baker
With a BA in Literary Studies from Middlebury College, an MFA in Fiction from Columbia University, and a Master’s in Translation from Université Paris 8 Vincennes-Saint-Denis, Kaylen has been working with students on their writing for over five years. Previously, Kaylen taught a fiction course for high school students as part of Columbia Artists/Teachers, and served as an English Language Assistant for the French National Department of Education. Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
| {{item.snippet}} |
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback

TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
| --> |
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
|
|
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Main body How to write a good essay paragraph
As the name suggests, the main body is the main part of your essay. It is a collection of paragraphs related to your topic, and in order to understand how to write a good main body, you need to understand how to write good paragraphs. This section will help you understand the three main structural components of any good paragraph: the topic sentence , supporting sentences , and the concluding sentence . An example essay has been given to help you understand all of these, and there is a checklist at the end which you can use for editing your main body.
The topic sentence
The topic sentence is the most important sentence in a paragraph. It is usually the first sentence, though may sometimes also be placed at the end. It indicates what the paragraph is going to discuss, and thus serves as a useful guide both for the writer and the reader; the writer can have a clear idea what information to include (and what information to exclude), while the reader will have a clear idea of what the paragraph will discuss, which will aid in understanding.
The topic sentence comprises two separate parts: the topic of the paragraph, and the controlling idea, which limits the topic to one or two areas that can be discussed fully in one paragraph.
Consider the following topic sentence (from the example essay below):
The most striking advantage of the car is its convenience .
The topic of this short essay is the advantages and disadvantages of cars, as a result of which each paragraph has either the advantages or the disadvantages of cars as its topic. In this case, the topic is the advantage of cars . The controlling idea is convenience , which limits the discussion of advantages of cars to this one idea. This paragraph will therefore give supporting ideas (reasons, facts, etc.) to show why convenience is an advantage of cars.
Here is another topic sentence from the same example essay :
Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages , the most important of which is the pollution they cause.
The topic of this paragraph is the disadvantage of cars . The controlling idea is pollution . This paragraph will therefore give supporting ideas (reasons, facts, etc.) to show why pollution is a disadvantage of cars.
Here is the final topic sentence from the same example essay :
A further disadvantage is the traffic problems that they cause in many cities and towns of the world.
The topic of this paragraph is again the disadvantage of cars . The controlling idea this time is traffic problems . This paragraph will therefore give supporting ideas (reasons, facts, etc.) to show why traffic congestion is a disadvantage of cars.
The following are key points to remember about the topic sentence:
- it should be a complete sentence
- it should contain both a topic and a controlling idea
- it is the most general statement in the paragraph, because it gives only the main idea with any supporting details
Supporting sentences
Supporting sentences develop the topic sentence. They are more specific than the topic sentence, giving reasons, examples, facts, statistics, and citations in support of the main idea of the paragraph.
Below is the whole paragraph for the second topic sentence above. The supporting sentences are in bold.
Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages, the most important of which is the pollution they cause. Almost all cars run either on petrol or diesel fuel, both of which are fossil fuels. Burning these fuels causes the car to emit serious pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. Not only are these gases harmful for health, causing respiratory disease and other illnesses, they also contribute to global warming, an increasing problem in the modern world. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (2013), transportation in the US accounts for 30% of all carbon dioxide production in that country, with 60% of these emissions coming from cars and small trucks. In short, pollution is a major drawback of cars.
The paragraph above has the following support:
- burning fuels (petrol and diesel) in car engines emits pollutants - fact
- cars emit carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide - examples (of pollutants)
- the pollutants are harmful for health - fact
- the pollutants cause respiratory disease - example (of how they harm our health)
- the pollutants contribute to global warming - fact
- 30% of carbon dioxide in the US comes from transport - statistic
- 60% of the these emissions come from cars and small trucks - statistic
- this information comes from Union of Concerned Scientists (2013) - citation
The concluding sentence
The concluding sentence is an optional component of a paragraph. In other words, it is not absolutely necessary. It most useful for especially long paragraphs, as it will help the reader to remember of the main ideas of the paragraph.
Below is the concluding sentence from the paragraph above:
In short, the harm to our health and to the environment means that pollution from cars is a major drawback.
Here the concluding sentence not only repeats the controlling idea of the topic sentence , that cars cause pollution, but also summarises the information of the paragraph, which is that the pollution from cars is harmful to both our health and the environment.
The following are useful transition signals to use for the concluding sentence:
- In conclusion...
- In summary...
- In brief...
- Therefore...
- In short...
- These examples show that...
- This evidence strongly suggests that...
Example essay
Below is a discussion essay which looks at the advantages and disadvantages of car ownership. This essay is used throughout the essay writing section to help you understand different aspects of essay writing. Here it focuses on topic sentences and controlling ideas (mentioned on this page), the thesis statement and general statements of the introduction, and the summary and final comment of the conclusion. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different structural aspects in this essay.
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car. While cars have undoubted advantages , of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks , most notably pollution and traffic problems . The most striking advantage of the car is its convenience. When travelling long distance, there may be only one choice of bus or train per day, which may be at an unsuitable time. The car, however, allows people to travel at any time they wish, and to almost any destination they choose. Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages , the most important of which is the pollution they cause. Almost all cars run either on petrol or diesel fuel, both of which are fossil fuels. Burning these fuels causes the car to emit serious pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. Not only are these gases harmful for health, causing respiratory disease and other illnesses, they also contribute to global warming, an increasing problem in the modern world. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (2013), transportation in the US accounts for 30% of all carbon dioxide production in that country, with 60% of these emissions coming from cars and small trucks. In short, pollution is a major drawback of cars. A further disadvantage is the traffic problems that they cause in many cities and towns of the world. While car ownership is increasing in almost all countries of the world, especially in developing countries, the amount of available roadway in cities is not increasing at an equal pace. This can lead to traffic congestion, in particular during the morning and evening rush hour. In some cities, this congestion can be severe, and delays of several hours can be a common occurrence. Such congestion can also affect those people who travel out of cities at the weekend. Spending hours sitting in an idle car means that this form of transport can in fact be less convenient than trains or aeroplanes or other forms of public transport. In conclusion, while the car is advantageous for its convenience , it has some important disadvantages , in particular the pollution it causes and the rise of traffic jams . If countries can invest in the development of technology for green fuels, and if car owners can think of alternatives such as car sharing, then some of these problems can be lessened. References
Union of Concerned Scientists (2013). Car Emissions and Global Warming. www.ucsusa.org/clean vehicles/why-clean-cars/global-warming/ (Access date: 8 August, 2013)

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for the main body of an essay. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
| Each paragraph has a | ||
| Each topic sentence has a suitable topic and controlling idea | ||
| Each paragraph has detailed (facts, reasons, examples, citations, etc.) | ||
| Long paragraphs include a to make the paragraph clearer | ||
| Any concluding sentences are introduced using clear |
Next section
Find out how to structure the conclusion of an essay in the next section.
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about the essay introduction .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 26 January 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub
How to Write a Body Paragraph
Last Updated: June 4, 2023
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been viewed 27,332 times.
Writing a paragraph might seem simple on the surface—it just needs a starting point, an ending point, and some related sentences in between to fill it out. However, a quality paragraph states a clear main idea, supports and analyzes this main idea based on strong evidence, and ties it all into the overall focus of your essay. This is especially true of body paragraphs, which make up the heart of your essay between the introduction and conclusion.
Planning Before Writing

- As a mini essay, each paragraph needs to have a main point (or thesis), supporting evidence, analysis of that evidence, commentary, and a recap of the main point based on the evidence and analysis. Your topic sentence acts as the thesis for the paragraph, providing a road map of what you'll discuss.
- Each paragraph should feel complete if you read it on its own, but also logically connect to the other paragraphs in the essay.
- For instance, a topic sentence might look like this: "As the length of playoff games expand, baseball fans lose interest in the game."
- Supporting evidence for this topic sentence could include statistics of how many fans watched the games, results of fan polls, and quotes from reliable sports articles.

- Like that freight train, your paragraph should move in only one direction—forward toward your end point. Each sentence needs to build on the last.
- So, before you start writing, jot down the concept for the paragraph’s main idea and start thinking how the paragraph will advance it forward.

- A body paragraph is only as good as its evidence. Your main idea will fall flat if you have flimsy evidence—or no evidence—to advance it forward.
- If you don’t have adequate evidence to support your proposed main idea for the paragraph, you’ll either have to do additional research or adjust your claim to suit your evidence.
- Great sources of evidence include books, journal articles, reliable websites, and newspaper articles.
Writing the Paragraph

- For instance, if your previous paragraph focused on revealing how exciting baseball’s World Series has been in recent years, you might start by writing, “While there’s no doubt the World Series has provided numerous exciting moments recently,...”
- Repeating a key phrase can also make a good transition. To keep with the baseball theme, you might repeat the phrase “big hit” in the last sentence of the previous paragraph and the first sentence of the current one.

- The main idea should be a claim that you can make a convincing argument to support, not a statement of fact.
- For instance: “While there’s no doubt the World Series has provided numerous exciting moments recently, the increasing amount of time it takes to complete each game likely decreases overall interest.”

- For example: “The average Major League Baseball playoff game (as of 2017) takes over three-and-a-half hours to complete, an increase in more than thirty minutes from the average length of World Series games in 1988.” [5] X Research source
- Also: “Since World Series games start after 8 pm in the Eastern Time Zone, they often don’t end until midnight or later for many viewers in the U.S.”

- While including longer quotes can sometimes be helpful, it’s usually best to incorporate smaller snippets from quotations into your own sentence.
- Introduce the quote with “asserts,” “claims,” “proposes,” or similar: “As 12-year old Boston Red Sox fan Tim Green bemoans, ‘I haven’t been able to watch the end of a single game of the World Series,’ due to the length of the games.”
- Make sure to provide a citation with the source of the quotation, according to the citation style you’re using.

- Your analysis might include anticipating counter-perspectives to your evidence: “While many baseball fans embrace the notion that it’s one of few sports without a game clock, it’s hard to imagine that anyone finds it easy to stay engaged and enthused—if tuned in at all—to a four-plus hour game.”

- Imagine that you're answering the question, "So what?" What should people take from your paragraph? How should they feel about your topic?
- For instance: “The long games and late conclusions during baseball’s showcase time of year threaten to alienate fans, especially the younger ones who are essential to the sport’s future.”
- Closing the current paragraph with an enhancement of your main idea provides a solid transition into the next paragraph, without having to write an actual transition (as you did at the start of the paragraph).

Revising Your Work

- Try having a friend or family member read the paragraph, then ask them, “What’s it about?” They should answer with some version of your main idea.

- Try cutting sentences or sections you’re not sure about and see if they are missed—if not, get rid of them permanently.

- Make sure each sentence builds logically from the one before it, and leads logically into the one after it. Try rearranging content if necessary.
- Verbal bridges can be transitions (“Also,” “However,” “So,” etc.), or you can use strategies like repetition or synonyms to link each sentence to the next.

- It’s very easy to miss mistakes in your own writing, so have a fresh set of eyes look over your work whenever possible.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://slc.berkeley.edu/some-tips-writing-efficient-effective-body-paragraphs
- ↑ https://ctl.yale.edu/sites/default/files/basic-page-supplementary-materials-files/body_paragraph_analysis_0.pdf
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://www.usatoday.com/story/sports/mlb/2017/10/23/pace-of-play-playoffs/791927001/
About this article

Reader Success Stories
Sep 29, 2023
Did this article help you?

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
Suddenly Trump Looks Older and More Deranged
Now the Republicans are the ones saddled with a candidate who can’t make a clear argument or finish a sentence.

Listen to more stories on hark
Four days after the end of the Republican National Convention, it suddenly looks like a very different event. I watched it intermittently, on television, along with perhaps 25 million other Americans (a relatively small number, though enough to matter). I focused on the highlights, like most viewers did. I read the analysis and thought I understood what had happened. But in the light of President Joe Biden’s brave and unprecedented decision to drop out of the race, my memory of what Donald Trump and his party were doing and saying has permanently shifted. I suspect this will be true for at least some of the other 25 million of us too.
Whatever happens next, the frame has altered. Now it is the Republicans who are saddled with the elderly candidate, the one who can’t make a clear argument or finish a sentence without veering off into anecdote. Now the Democrats are instead proposing something new. Now it is the many pundits who were already bored by the race and ready to wrap it up who look foolish.
Remember, if you still can: The Republican convention was a carefully curated, meticulously planned presentation. As my colleague Tim Alberta has said, the theme was “strength.” Strength was expressed by exaggerated, absurd, comic-book figures: Hulk Hogan, Kid Rock. The latter chanted “Fight, fight!” and “Trump, Trump!” while pumping his fist. Then he sang “American Bad Ass,” an unlistenable work of profound dissonance. Trump himself walked into the convention hall to the strains of James Brown’s famously misogynistic anthem “It’s a Man’s Man’s Man’s World.”
Read: This is exactly what the Trump team feared
Strength was implied by the equally choreographed demonstrations of debasement. Nikki Haley, who had repeatedly questioned whether Trump is “mentally fit” to be president—and had declared that “the first party to retire its 80-year-old candidate” will win the election—offered her “strong endorsement.” The vice-presidential nominee, J. D. Vance, who had previously compared Trump to Hitler and described him as “ cultural heroin ,” performed a kind of kowtow, appearing at the convention in the form of supplicant, acolyte, prodigal son. Like so many other Republicans, he bowed to the power of Trump, to the vulgarity of Hulk Hogan, to a whole host of things he used to say he didn’t like, and maybe still doesn’t like. He even made a peculiar, strained attempt to link his children and his wife, the daughter of South Asian immigrants, to a cemetery in East Kentucky where he said they will be buried, as if none of this will make sense until all of us are dead.
But then Trump himself appeared, and it was as if the emperor with no clothes had taken the stage. There was nothing strong about an overweight, heavily made up yet nevertheless shiny-faced elderly man who rambled and babbled for an hour and a half, completely undermining the slick image created in the previous four days. He began by sticking to his script, solemnly referencing the failed assassination attempt against him days before. But even when telling that story, he could not master the appropriate tone and almost immediately changed the subject. “And there’s an interesting statistic,” he said: “The ears are the bloodiest part. If something happens with the ears, they bleed more than any other part of the body. For whatever reason, the doctors told me that.”
Eventually, instead of sounding like an “American Bad Ass,” he digressed into pure gibberish . One example:
They’re coming from prisons. They’re coming from jails. They’re coming from mental institutions and insane asylums. I—you know the press is always on because I say this. Has anyone seen The Silence of the Lambs ? The late, great Hannibal Lecter. He’d love to have you for dinner. That’s insane asylums. They’re emptying out their insane asylums. And terrorists at numbers that we’ve never seen before. Bad things are going to happen.
In Venezuela, Caracas, high crime, high crime. Caracas, Venezuela, really a dangerous place. But not anymore, because in Venezuela, crime is down 72 percent. In fact, if they would ever in this election, I hate to even say that, we will have our next Republican convention in Venezuela because it will be safe. Our cities, our cities will be so unsafe, we won’t be able—we will not be able to have it there.
On Thursday evening, this performance seemed deranged, sinister, and frightening. Now, following Biden’s decision to halt his own campaign, it just looks deranged. On the one hand, we have a sitting president who understood his limitations and, in an act of patriotism, selflessness, and party unity, decided to step away from power. On the other hand, we have a former president clinging to power, holding on desperately to the myth of a lost election, evoking the same predictable descriptions of carnage and disaster he served up eight years ago. Today, he is still attacking Biden, who is no longer his opponent.
Read: A searing reminder that Trump is unwell
In retrospect, the Republican Party’s convention looks not just staged but also hollow and false. By contrast, the Democratic Party’s convention will be substantive and maybe even spontaneous. In the hours that have passed since Biden’s announcement, a million different Kamala Harris memes, music mixes, and clips have appeared online, not orchestrated by her campaign or by any campaign, just put together by random people, some of whom like her and some of whom do not. One mash-up of her wackier speeches, her laugh, and a Charli XCX soundtrack had 3.4 million views by this morning. We don’t know yet whether Harris will be the candidate or, if she is, whether she will be a good one, but the energy has already shifted from the men trying to impose their image of their party on the country to online Gen Zers who can flip the script any way they want.
I don’t know what will happen next, and that’s the point. The heavy sense of inevitability that surrounded the RNC has lifted. The cadres of people organized by the Heritage Foundation and a dozen offshoots, all quietly preparing to dismantle the rights of American women, to replace civil servants with loyalists, to take apart pollution controls, and to transfer more money into the hands of Trump-friendly billionaires—they are no longer marching inexorably toward the halls of power. The people who spent a week trying to bend reality to fit their flawed, vengeful candidate became too confident too soon.
About the Author

More Stories
How Labour Defeated Populism
Time to Roll the Dice
Kamala Harris said 19 words in 2018 that taught us all we need to know
Curious about what kind of candidate she’ll be? Her dismantling of Justice Brett Kavanaugh at his confirmation hearing is worth a rewatch.
Key takeaways
Summary is AI-generated, newsroom-reviewed.
- Kamala Harris's sharp questioning of Kavanaugh highlighted in article
- Harris's approach in 2018 hearings showcased her prosecutorial skills
- Article suggests Harris's candidacy benefits from her assertive questioning style

Listen, nearly everything you need to know about the presidential candidacy of Kamala Harris can be summed up by 19 words she uttered at the 2018 confirmation hearings of Supreme Court Justice Brett M. Kavanaugh.
Harris, then a senator from California serving on the Judicial Committee, had used up several minutes trying to pin down Kavanaugh’s opinion on Roe v. Wade . Like nearly every senator on the topic, she was mostly unsuccessful. “I have not articulated a position on that,” Kavanaugh told her at one point, sidestepping the fact that articulating a position is precisely what she’d been asking him to do. Finally, in a cool and deliciously patient voice, Harris changed tactics:
“Can you think of any laws,” she asked the nominee, “that give the government the power to make decisions about the male body?”
“Um,” Kavanaugh replied, furrowing his brow. “I am happy to answer a more specific question, but — ”
“Male versus female,” Harris offered, smiling, and when Kavanaugh still expressed confusion, she repeated her 19-word question: “Can you think of any laws that give the government the power to make decisions about the male body?”
Kavanaugh responded, “I am not thinking of any right now.”
Shortly thereafter, Harris’s questioning moved on to other topics, but that moment is what the women in my life spent the rest of the day talking about. It was obvious that Kavanaugh was not planning to reveal his professional opinion on the legality of abortion , so Harris had instead gone straight to the heart of the matter.
Laws related to reproductive health care only impact female bodies. Overturning Roe v. Wade would primarily hurt women. The health and personal choices of women were monitored, restricted and regulated by the government in ways that men could not begin to imagine — in a way that Kavanaugh himself had clearly not begun to imagine, considering how long it took him to grasp Harris’s question. And if he would not articulate a position, then she would at least make him articulate the injustice.
Yeah, he would go on to secure the seat on the bench. And four years later he would vote to overturn Roe v. Wade . But at least Kamala Harris made it clear that she was going into this goat rodeo with her eyes wide open.
In the early hours since President Biden announced on Sunday that he would be endorsing Harris as the Democratic nominee, everyone and their MSNBC-loving nana seems to have an opinion on how Harris should campaign. Should she remind the voting public that she was a former prosecutor who would know exactly what to do with a felon like Donald Trump ? Should she go full coconuts and lean into the memes? Within hours of Biden’s announcement, the pop star Charli XCX posted on X that “Kamala is brat,” which refers to — you know what, just Google it, and trust that it’s the kind of approval seal that will turn out more 20-something votes than a whole army of endorsements from Nancy Pelosi.
The answer is, probably, all of the above. Harris is going to need a powerhouse coalition that includes church ladies and hard-working stepmoms as well as Fire Island gays. But the version of Harris that always struck me as the most authentic and the most reassuring was the one we were introduced to in 2018, when Donald Trump’s Supreme Court pick turned up on Capitol Hill with the confidence of an altar boy who’d never before had to account for some missing Communion wine.
On the second day of his confirmation hearings, Kamala pressed Kavanaugh to share whether he thought that Obergefell v. Hodges , the 2015 case that essentially legalized same-sex marriage, had been “correctly decided.” When he would not answer, she reframed the question: “You have said that Brown v. Board of Education was one of the greatest moments in the court’s history,” she told Kavanaugh. “Do you believe that Obergefell was also one of those moments?”
Note how the second version of the question is slightly different than the first. She is no longer simply asking for the opinion of a legal scholar. She is also asking for the opinion of a human. Civil rights protection had been expanded to gay couples — and how did that make him feel? If he’d been willing to share vocal support for one kind of equality, why not the other? What were his values, and how were they going to inform his work on the court? (Kavanaugh responded to her question not by sharing his own opinion but by quoting someone else, which Harris noted.)
Later, the confirmation process took an unexpected turn, following Christine Blasey Ford’s allegations that Kavanaugh had attempted to assault her when they both were teens. The truth of those allegations proved impossible to litigate in the context of the Senate Judiciary Committee. The alleged events were decades old. But in the middle of that hearing, Harris asked Kavanaugh — whose defense somehow involved a global conspiracy and “revenge on behalf of the Clintons” — what outwardly appeared to be a softball: “Do you agree that it is possible for men to both be friends with some women and treat other women badly?”
It was a philosophical question more than a legal one, but man if it didn’t encapsulate everything that feminists had been trying to point out: that people were complicated. That powerful men might have hired female law clerks and coached girls basketball, as Kavanaugh did, but that didn’t mean we should assume they couldn’t have also abused women. That it was possible for good men to do bad things, and until we understood that, we weren’t going to get anywhere as a country.
I was riveted by those hearings at the time, and the fact that they happened six long years ago is why I’m refreshing your memory now. It’s worth going back to watch them. Kamala the prosecutor is present there, and, to a lesser extent, so is Kamala the meme.
But the most compelling version of Kamala is that of a savvy practitioner at the top of her game, asking the right questions even when the answers never arrived. Clear-eyed. Laser-focused. Take no prisoners. Accept no B.S.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, what is your plagiarism score.
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
- TODAY Plaza
I kept my first marriage a secret from my kids. I wish I'd just told them truth

“Mom!” My son Chris, then 16, was summoning me to the basement. The concern in his voice made me think he’d seen a spider. Or maybe there was another baby squirrel in the furnace. What he’d found was more jarring: an old photo from a box of items my parents were temporarily storing at our house. In it, I was wearing a white suit, a man in military dress blues was putting a ring on my finger, and a woman holding a book was standing between us.
“Were you going to a dance?” he asked, his face confused.
It wasn’t a dance. The photo was of my wedding day — my first wedding day, the one that didn’t include his father.
“No,” I said quietly. “I was married to someone else before I met your dad.”
Chris looked at the photo and then at me. “The marriage was short and annulled,” I continued. “I never told you because it never came up. It was so long ago and honestly feels like it never happened.”
Then, in a strange need to redeem myself, I blurted out, “Your dad was married to someone else before me, too.”
Chris dropped the photo back into the box, touched his fingers to his temples, and gestured that his mind had been blown.

I never set out to keep my first marriage a secret; it just happened. The truth is it was a period of my life I wanted to forget. I was in my early 20s when I met him, and our relationship was rocky from the start. He was impulsive and proposed on a whim, and we married quickly — and then got it annulled almost as fast.
It took me about a year, but I finally put that part of my life behind me when I met David, my kids’ father. Ironically, he’d had a short-lived first marriage, too, and the shared experience made us appreciate each other even more. When we married and had a family, I told myself that my first marriage didn’t count. It was a blip in my life. No children. No ties. Our kids didn’t need to know because it wasn’t relevant to them. It was a mistake in judgment I could simply erase, as if it had never happened at all.
I decided that if they never ask — and why would they? — I didn’t need to bring it up, either. But I didn’t quite follow that plan. A couple of years before he discovered the photo, Chris asked me, “How old were you when you got married?” Without thinking, I responded, “To your dad?” He missed my need to clarify, and I let a perfect opportunity go by.

Once Chris knew, I wanted to be more proactive with my younger son, Nick, who was 13. A few months later, we were in the car, talking about someone we knew who was getting a divorce . I took a deep breath. “Did you know I was married to someone else before your dad?” I asked.
“Wait, what?” he said, looking up from his phone and turning to me in disbelief. I told him an abbreviated version of the story, proud of myself for seizing the moment. Nick was speechless, which was unusual for him, and finally shrugged his shoulders and said, “Well, I didn’t see that coming.”
Keeping my first marriage hidden gave it more meaning and power than it deserved, and I regret the way Chris found out. He was just a teenager spending a rainy afternoon perusing a box of old family photos. He didn’t expect to discover his mom’s “secret” past. Fortunately for me, he shrugged it off, later telling me that he could have gone his entire life without knowing and it wouldn’t have impacted him at all. And that’s true.
“There are always parts of your past that make you wonder, ‘Should I tell, or shouldn’t I tell?’” Dr. Michele Borba , an author and child psychologist, tells TODAY.com. “It’s always up to you.”
But that decision isn’t always so easy, so Borba suggests that parents ask themselves if their child is developmentally mature enough to learn the information, and assess whether the information would fortify their relationship with their child, or cause harm. And she recommends parents always end the conversation by saying, “You probably have other questions about this. Remember, I’m always here for you.”
While it may feel awkward, divulging parts of your past can have a surprise benefit. “There’s going to come a time when your child will go through something,” says Borba. “When you choose to be open, your child is more likely to come to you. He’s going to think, ‘Mom’s going to get this.’”
After talking about my first marriage, I noticed my sons asked for my advice a little more than before. One came to me about a breakup from a girlfriend. I don’t know if he would have done this before realizing I’d had breakups of my own.
Both of my boys have confessed that they’d never thought of me having a life before their dad. The revelation gave them a different perspective. Now, I’m more than just their mom; I’m a woman with life experience, and I like that. Finally, there are no skeletons in the closet — or photos in a box — to scare anyone, including me.
Stephanie Vozza is a Nashville-based writer who covers work/life topics for Fast Company. She’s on a mission to put more wow moments into her life and blogs about her adventures at wow-moments.com .

I’m child-free by choice. It’s time to change the narrative of what that means

Seven minutes to grieve with ‘Bluey’

I make my kids bring gifts for the flight crew when we travel. Here’s why

My wife is the default parent. When I asked her to do less, it didn’t go very well

I’m a happy mom but my favorite stories are about child-free women

I refuse to play with my kids — and it makes me a better mom

I got through breast cancer treatment by hiding it from my young children

Disney-ish: How we embraced Disney magic without setting foot inside the park

I took my kids on the vacation I hated as a girl. Now I understand my parents more than ever

I hid my postpartum depression ... until a friend got me to find help

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together. This article gives you some practical tips ...
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project.
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly. Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence. This lets the reader know what the ...
First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly. You should be looking at your thesis throughout the drafting of your body paragraphs.
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is connected to the larger argument in your paper. Below is an example of a topic sentence from a paper by Laura Connor '23 that analyzes rhetoric used by ...
Step 1: Write a Topic Sentence. Consider the first sentence in a body paragraph a mini-thesis statement for that paragraph. The topic sentence should establish the main point of the paragraph and bear some relationship to the essay's overarching thesis statement. In theory, by reading only the topic sentence of every paragraph, a reader should ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
As the name suggests, the main body is the main part of your essay. It is a collection of paragraphs related to your topic, and in order to understand how to write a good main body, you need to understand how to write good paragraphs. This section will help you understand the three main structural components of any good paragraph: the topic ...
Writing Body Paragraphs. Follow these steps below to write good body paragraphs. Step 1: Develop a Topic Sentence. Step 2: Provide Evidence to Support your Topic Sentence and Overall Argument. Step 3: Add your Own Analysis and Interpretation. Step 4: Conclude. Step 5: Revise and Proofread. A P.I.E. Paragraph. For Example.
2. Express the paragraph's main idea very early on. Typically you should present this main idea in the first sentence, right after the brief transition from the last paragraph. Aim for a clear, concise claim that you can further develop and support with the evidence you've collected.
In the body section of your essay, you make arguments, explain ideas, and give evidence. This video will show you how to write a strong paragraph in just 3 s...
Learn to write the body paragraphs of an essay. Use this worksheet to take notes:https://www.englishunits.com/wp-content/uploads/Essay-Part-2.pdfTo introduce...
The body of the essay is where you fully develop your argument. Each body paragraph should contain one key idea or claim, which is supported by relevant examples and evidence from the body of scholarly work on your topic (i.e. academic books and journal articles). Together, the body paragraphs form the building blocks of your argument.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Introduction. After writing a great introduction to our essay, let's make our case in the body paragraphs. These are where we will present our arguments, back them up with evidence, and, in most cases, refute counterarguments.
In your writing, the key to developing your body paragraphs is to use supporting details and examples as you discuss your main points. In other words, you need to be specific in your explanations ...
How to Write the Main Body of an Essay in 5 Steps. 1. Analyze the thesis statement to identify three subjects or ideas in it. An effective thesis will touch on several subjects or ideas, including ...
Learn to write essay body paragraphs step by step. Use this worksheet to take notes:https://www.englishunits.com/wp-content/uploads/Essay-Part-2.pdfThis vide...
If something happens with the ears, they bleed more than any other part of the body. For whatever reason, the doctors told me that." Eventually, instead of sounding like an "American Bad Ass ...
On day two of Judge Brett Kavanaugh's Supreme Court confirmation hearing in September 2018, Sen. Kamala Harris (D-Calif.) asked about law and the "male body." (Video: C-SPAN)
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Human body needs carbohydrates for energy; proteins for growth and repair; fats for warmth, energy, and healthy body functioning; vitamins and minerals for general health and well-being. Therefore, the purpose of writing this paper is to analyze diet and to state what are the strengths and weakness of the unique course of food taken by me. The ...
"Mom!" My son Chris, then 16, was summoning me to the basement. The concern in his voice made me think he'd seen a spider. Or maybe there was another baby squirrel in the furnace.