Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
| Exploratory | Explores a previously unstudied topic, issue, or phenomenon; aims to generate ideas or hypotheses |
| Descriptive | Describes the characteristics and features of a particular population or group |
| Explanatory | Explains the relationships between variables; seeks to identify cause-and-effect relationships |
| Predictive | Predicts future outcomes or events based on existing data samples or trends |
| Diagnostic | Identifies factors contributing to a particular problem |
| Comparative | Compares two or more groups or phenomena to identify similarities and differences |
| Historical | Examines past events and trends to understand their significance and impact |
| Methodological | Develops and improves research methods and techniques |
| Theoretical | Tests and refines existing theories or helps develop new theoretical perspectives |
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
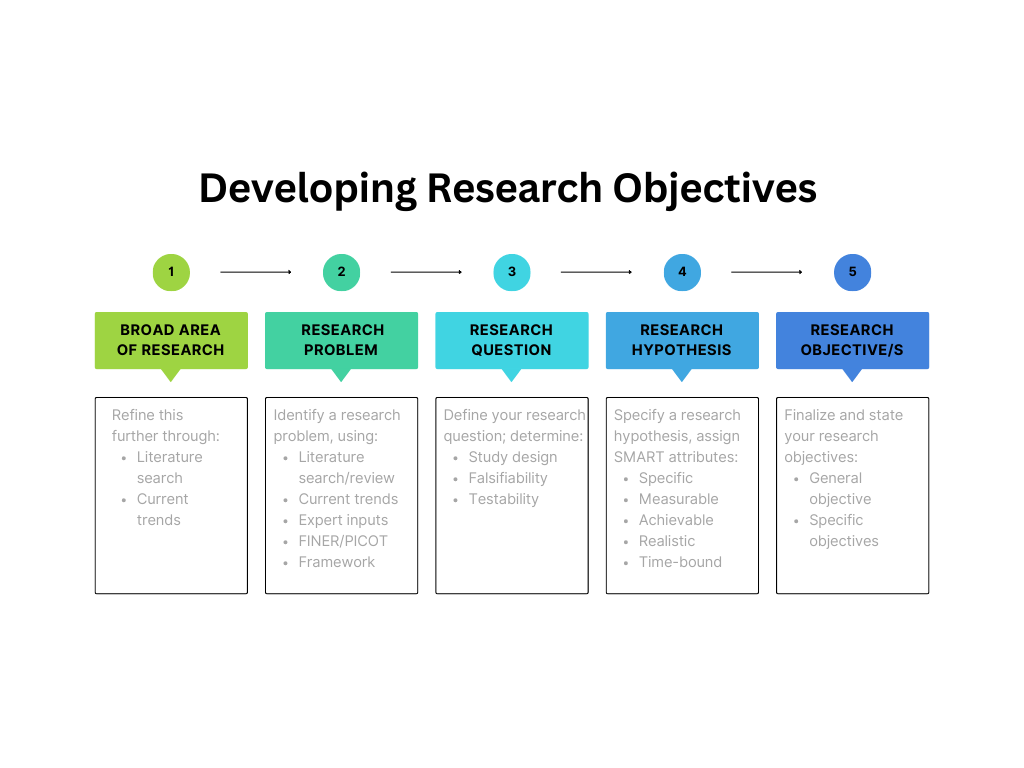
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
| Broad statement; guide the overall direction of the research | Specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve |
| Identify the main problem | Define the specific outcomes the study aims to achieve |
| Used to generate hypotheses or identify gaps in existing knowledge | Used to establish clear and achievable targets for the research |
| Not mutually exclusive with research objectives | Should be directly related to the research question |
| Example: | Example: |
Q: Are research objectives the same as hypotheses?
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

Research in Shorts: R Discovery’s New Feature Helps Academics Assess Relevant Papers in 2mins

How Does R Discovery’s Interplatform Capability Enhance Research Accessibility

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
| (Understanding and organising information) | (Solving problems using information) | (reaching conclusion from evidence) | (Breaking down into components) | (Judging merit) |
| Review Identify Explore Discover Discuss Summarise Describe | Interpret Apply Demonstrate Establish Determine Estimate Calculate Relate | Analyse Compare Inspect Examine Verify Select Test Arrange | Propose Design Formulate Collect Construct Prepare Undertake Assemble | Appraise Evaluate Compare Assess Recommend Conclude Select |
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Research Objectives: The Compass of Your Study
Table of contents
- 1 Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
- 2 How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
- 3 Types of Research Objectives
- 4 Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
- 5 Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
- 6.1 Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
- 6.2 Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
- 6.3 How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
- 7 Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
- 8 Conclusion
Embarking on a research journey without clear objectives is like navigating the sea without a compass. This article delves into the essence of establishing precise research objectives, serving as the guiding star for your scholarly exploration.
We will unfold the layers of how the objective of study not only defines the scope of your research but also directs every phase of the research process, from formulating research questions to interpreting research findings. By bridging theory with practical examples, we aim to illuminate the path to crafting effective research objectives that are both ambitious and attainable. Let’s chart the course to a successful research voyage, exploring the significance, types, and formulation of research paper objectives.
Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
Defining the research objectives includes which two tasks? Research objectives are clear and concise statements that outline what you aim to achieve through your study. They are the foundation for determining your research scope, guiding your data collection methods, and shaping your analysis. The purpose of research proposal and setting clear objectives in it is to ensure that your research efforts are focused and efficient, and to provide a roadmap that keeps your study aligned with its intended outcomes.
To define the research objective at the outset, researchers can avoid the pitfalls of scope creep, where the study’s focus gradually broadens beyond its initial boundaries, leading to wasted resources and time. Clear objectives facilitate communication with stakeholders, such as funding bodies, academic supervisors, and the broader academic community, by succinctly conveying the study’s goals and significance. Furthermore, they help in the formulation of precise research questions and hypotheses, making the research process more systematic and organized. Yet, it is not always easy. For this reason, PapersOwl is always ready to help. Lastly, clear research objectives enable the researcher to critically assess the study’s progress and outcomes against predefined benchmarks, ensuring the research stays on track and delivers meaningful results.
How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
Research objectives are integral to the research framework as the nexus between the research problem, questions, and hypotheses. They translate the broad goals of your study into actionable steps, ensuring every aspect of your research is purposefully aligned towards addressing the research problem. This alignment helps in structuring the research design and methodology, ensuring that each component of the study is geared towards answering the core questions derived from the objectives. Creating such a difficult piece may take a lot of time. If you need it to be accurate yet fast delivered, consider getting professional research paper writing help whenever the time comes. It also aids in the identification and justification of the research methods and tools used for data collection and analysis, aligning them with the objectives to enhance the validity and reliability of the findings.
Furthermore, by setting clear objectives, researchers can more effectively evaluate the impact and significance of their work in contributing to existing knowledge. Additionally, research objectives guide literature review, enabling researchers to focus their examination on relevant studies and theoretical frameworks that directly inform their research goals.
Types of Research Objectives
In the landscape of research, setting objectives is akin to laying down the tracks for a train’s journey, guiding it towards its destination. Constructing these tracks involves defining two main types of objectives: general and specific. Each serves a unique purpose in guiding the research towards its ultimate goals, with general objectives providing the broad vision and specific objectives outlining the concrete steps needed to fulfill that vision. Together, they form a cohesive blueprint that directs the focus of the study, ensuring that every effort contributes meaningfully to the overarching research aims.
- General objectives articulate the overarching goals of your study. They are broad, setting the direction for your research without delving into specifics. These objectives capture what you wish to explore or contribute to existing knowledge.
- Specific objectives break down the general objectives into measurable outcomes. They are precise, detailing the steps needed to achieve the broader goals of your study. They often correspond to different aspects of your research question , ensuring a comprehensive approach to your study.
To illustrate, consider a research project on the impact of digital marketing on consumer behavior. A general objective might be “to explore the influence of digital marketing on consumer purchasing decisions.” Specific objectives could include “to assess the effectiveness of social media advertising in enhancing brand awareness” and “to evaluate the impact of email marketing on customer loyalty.”
Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
The harmony between what research objectives should be, questions, and hypotheses is critical. Objectives define what you aim to achieve; research questions specify what you seek to understand, and hypotheses predict the expected outcomes.
This alignment ensures a coherent and focused research endeavor. Achieving it necessitates a thoughtful consideration of how each component interrelates, ensuring that the objectives are not only ambitious but also directly answerable through the research questions and testable via the hypotheses. This interconnectedness facilitates a streamlined approach to the research process, enabling researchers to systematically address each aspect of their study in a logical sequence. Moreover, it enhances the clarity and precision of the research, making it easier for peers and stakeholders to grasp the study’s direction and potential contributions.
Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
Throughout the research process, objectives guide your choices and strategies – from selecting the appropriate research design and methods to analyzing data and interpreting results. They are the criteria against which you measure the success of your study. In the initial stages, research objectives inform the selection of a topic, helping to narrow down a broad area of interest into a focused question that can be explored in depth. During the methodology phase, they dictate the type of data needed and the best methods for obtaining that data, ensuring that every step taken is purposeful and aligned with the study’s goals. As the research progresses, objectives provide a framework for analyzing the collected data, guiding the researcher in identifying patterns, drawing conclusions, and making informed decisions.
Crafting Effective Research Objectives

The effective objective of research is pivotal in laying the groundwork for a successful investigation. These objectives clarify the focus of your study and determine its direction and scope. Ensuring that your objectives are well-defined and aligned with the SMART criteria is crucial for setting a strong foundation for your research.
Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
Well-defined research objectives are characterized by the SMART criteria – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Specific objectives clearly define what you plan to achieve, eliminating any ambiguity. Measurable objectives allow you to track progress and assess the outcome. Achievable objectives are realistic, considering the research sources and time available. Relevant objectives align with the broader goals of your field or research question. Finally, Time-bound objectives have a clear timeline for completion, adding urgency and a schedule to your work.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
So lets get to the part, how to write research objectives properly?
- Understand the issue or gap in existing knowledge your study aims to address.
- Gain insights into how similar challenges have been approached to refine your objectives.
- Articulate the broad goal of research based on your understanding of the problem.
- Detail the specific aspects of your research, ensuring they are actionable and measurable.
How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
Your objectives of research may require refinement if they lack clarity, feasibility, or alignment with the research problem. If you find yourself struggling to design experiments or methods that directly address your objectives, or if the objectives seem too broad or not directly related to your research question, it’s likely time for refinement. Additionally, objectives in research proposal that do not facilitate a clear measurement of success indicate a need for a more precise definition. Refinement involves ensuring that each objective is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, enhancing your research’s overall focus and impact.
Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
The application of research objectives spans various academic disciplines, each with its unique focus and methodologies. To illustrate how the objectives of the study guide a research paper across different fields, here are some research objective examples:
- In Health Sciences , a research aim may be to “determine the efficacy of a new vaccine in reducing the incidence of a specific disease among a target population within one year.” This objective is specific (efficacy of a new vaccine), measurable (reduction in disease incidence), achievable (with the right study design and sample size), relevant (to public health), and time-bound (within one year).
- In Environmental Studies , the study objectives could be “to assess the impact of air pollution on urban biodiversity over a decade.” This reflects a commitment to understanding the long-term effects of human activities on urban ecosystems, emphasizing the need for sustainable urban planning.
- In Economics , an example objective of a study might be “to analyze the relationship between fiscal policies and unemployment rates in developing countries over the past twenty years.” This seeks to explore macroeconomic trends and inform policymaking, highlighting the role of economic research study in societal development.
These examples of research objectives describe the versatility and significance of research objectives in guiding scholarly inquiry across different domains. By setting clear, well-defined objectives, researchers can ensure their studies are focused and impactful and contribute valuable knowledge to their respective fields.
Defining research studies objectives and problem statement is not just a preliminary step, but a continuous guiding force throughout the research journey. These goals of research illuminate the path forward and ensure that every stride taken is meaningful and aligned with the ultimate goals of the inquiry. Whether through the meticulous application of the SMART criteria or the strategic alignment with research questions and hypotheses, the rigor in crafting and refining these objectives underscores the integrity and relevance of the research. As scholars venture into the vast terrains of knowledge, the clarity, and precision of their objectives serve as beacons of light, steering their explorations toward discoveries that advance academic discourse and resonate with the broader societal needs.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Handy Tips To Write A Clear Research Objectives With Examples
Introduction.
Research objectives play a crucial role in any research study. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the research, guiding the researcher in their investigation. Understanding research objectives is essential for conducting a successful study and achieving meaningful results.
In this comprehensive review, we will delve into the definition of research objectives, exploring their characteristics, types, and examples. We will also discuss the relationship between research objectives and research questions , as well as provide insights into how to write effective research objectives. Additionally, we will examine the role of research objectives in research methodology and highlight the importance of them in a study. By the end of this review, you will have a comprehensive understanding of research objectives and their significance in the research process.
Definition of Research Objectives: What Are They?

A research objective is defined as a clear and concise statement that outlines the specific goals and aims of a research study. These objectives are designed to be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), ensuring they provide a structured pathway to accomplishing the intended outcomes of the project. Each objective serves as a foundational element that summarizes the purpose of your study, guiding the research activities and helping to measure progress toward the study’s goals. Additionally, research objectives are integral components of the research framework , establishing a clear direction that aligns with the overall research questions and hypotheses. This alignment helps to ensure that the study remains focused and relevant, facilitating the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Characteristics of Effective Research Objectives
Characteristics of research objectives include:
- Specific: Research objectives should be clear about the what, why, when, and how of the study.
- Measurable: Research objectives should identify the main variables of the study that can be measured or observed.
- Relevant: Research objectives should be relevant to the research topic and contribute to the overall understanding of the subject.
- Feasible: Research objectives should be achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and expertise available.
- Logical: Research objectives should follow a logical sequence and build upon each other to achieve the overall research goal.
- Observable: Research objectives should be observable or measurable in order to assess the progress and success of the research project.
- Unambiguous: Research objectives should be clear and unambiguous, leaving no room for interpretation or confusion.
- Measurable: Research objectives should be measurable, allowing for the collection of data and analysis of results.
By incorporating these characteristics into research objectives, researchers can ensure that their study is focused, achievable, and contributes to the body of knowledge in their field.
Types of Research Objectives
Research objective can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives. General objectives are broad statements that define the overall purpose of the research. They provide a broad direction for the study and help in setting the context. Specific objectives, on the other hand, are detailed objectives that describe what will be researched during the study. They are more focused and provide specific outcomes that the researcher aims to achieve. Specific objectives are derived from the general objectives and help in breaking down the research into smaller, manageable parts. The specific objectives should be clear, measurable, and achievable. They should be designed in a way that allows the researcher to answer the research questions and address the research problem.
In addition to general and specific objectives, research objective can also be categorized as descriptive or analytical objectives. Descriptive objectives focus on describing the characteristics or phenomena of a particular subject or population. They involve surveys, observations, and data collection to provide a detailed understanding of the subject. Analytical objectives, on the other hand, aim to analyze the relationships between variables or factors. They involve data analysis and interpretation to gain insights and draw conclusions.
Both descriptive and analytical objectives are important in research as they serve different purposes and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Examples of Research Objectives
Here are some examples of research objectives in different fields:
1. Objective: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
This objective focuses on exploring the characteristics and styles of art during the Renaissance period. The research may involve analyzing various artworks, studying historical documents, and interviewing experts in the field.
2. Objective: To analyze modern art trends and their impact on society.
This objective aims to examine the current trends in modern art and understand how they influence society. The research may involve analyzing artworks, conducting surveys or interviews with artists and art enthusiasts, and studying the social and cultural implications of modern art.
3. Objective: To investigate the effects of exercise on mental health.
This objective focuses on studying the relationship between exercise and mental health. The research may involve conducting experiments or surveys to assess the impact of exercise on factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression.
4. Objective: To explore the factors influencing consumer purchasing decisions in the fashion industry.
This objective aims to understand the various factors that influence consumers’ purchasing decisions in the fashion industry. The research may involve conducting surveys, analyzing consumer behavior data, and studying the impact of marketing strategies on consumer choices.
5. Objective: To examine the effectiveness of a new drug in treating a specific medical condition.
This objective focuses on evaluating the effectiveness of a newly developed drug in treating a particular medical condition. The research may involve conducting clinical trials, analyzing patient data, and comparing the outcomes of the new drug with existing treatment options.
These examples demonstrate the diversity of research objectives across different disciplines. Each objective is specific, measurable, and achievable, providing a clear direction for the research study.
Aligning Research Objectives with Research Questions
Research objectives and research questions are essential components of a research project. Research objective describe what you intend your research project to accomplish. They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and provide a clear direction for the research. Research questions, on the other hand, are the starting point of any good research. They guide the overall direction of the research and help identify and focus on the research gaps .
The main difference between research questions and objectives is their form. Research questions are stated in a question form, while objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. Research questions are broad statements that provide a roadmap for the research, while objectives break down the research aim into smaller, actionable steps.
Research objectives and research questions work together to form the ‘golden thread’ of a research project. The research aim specifies what the study will answer, while the objectives and questions specify how the study will answer it. They provide a clear focus and scope for the research project, helping researchers stay on track and ensure that their study is meaningful and relevant.
When writing research objectives and questions, it is important to be clear, concise, and specific. Each objective or question should address a specific aspect of the research and contribute to the overall goal of the study. They should also be measurable, meaning that their achievement can be assessed and evaluated. Additionally, research objectives and questions should be achievable within the given timeframe and resources of the research project. By clearly defining the objectives and questions, researchers can effectively plan and execute their research, leading to valuable insights and contributions to the field.
Guidelines for Writing Clear Research Objectives
Writing research objective is a crucial step in any research project. The objectives provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, guiding the researcher in their data collection and analysis. Here are some tips on how to write effective research objective:
1. Be clear and specific
Research objective should be written in a clear and specific manner. Avoid vague or ambiguous language that can lead to confusion. Clearly state what you intend to achieve through your research.
2. Use action verbs
Start your research objective with action verbs that describe the desired outcome. Action verbs such as ‘investigate’, ‘analyze’, ‘compare’, ‘evaluate’, or ‘identify’ help to convey the purpose of the study.
3. Align with research questions or hypotheses
Ensure that your research objectives are aligned with your research questions or hypotheses. The objectives should address the main goals of your study and provide a framework for answering your research questions or testing your hypotheses.
4. Be realistic and achievable
Set research objectives that are realistic and achievable within the scope of your study. Consider the available resources, time constraints, and feasibility of your objectives. Unrealistic objectives can lead to frustration and hinder the progress of your research.
5. Consider the significance and relevance
Reflect on the significance and relevance of your research objectives. How will achieving these objectives contribute to the existing knowledge or address a gap in the literature? Ensure that your objectives have a clear purpose and value.
6. Seek feedback
It is beneficial to seek feedback on your research objectives from colleagues, mentors, or experts in your field. They can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improving the clarity and effectiveness of your objectives.
7. Revise and refine
Research objectives are not set in stone. As you progress in your research, you may need to revise and refine your objectives to align with new findings or changes in the research context. Regularly review and update your objectives to ensure they remain relevant and focused.
By following these tips, you can write research objectives that are clear, focused, and aligned with your research goals. Well-defined objectives will guide your research process and help you achieve meaningful outcomes.
The Role of Research Objectives in Research Methodology
Research objectives play a crucial role in the research methodology . In research methodology, research objectives are formulated based on the research questions or problem statement. These objectives help in defining the scope and focus of the study, ensuring that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner.
The research objectives in research methodology act as a roadmap for the research project. They help in identifying the key variables to be studied, determining the research design and methodology, and selecting the appropriate data collection methods .
Furthermore, research objectives in research methodology assist in evaluating the success of the study. By setting clear objectives, researchers can assess whether the desired outcomes have been achieved and determine the effectiveness of the research methods employed. It is important to note that research objectives in research methodology should be aligned with the overall research aim. They should address the specific aspects or components of the research aim and provide a framework for achieving the desired outcomes.
Understanding The Dynamic of Research Objectives in Your Study
The research objectives of a study play a crucial role in guiding the research process, ensuring that the study is focused, purposeful, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field. It is important to note that the research objectives may evolve or change as the study progresses. As new information is gathered and analyzed, the researcher may need to revise the objectives to ensure that they remain relevant and achievable.
In summary, research objectives are essential components in writing an effective research paper . They provide a roadmap for the research process, guiding the researcher in their investigation and helping to ensure that the study is purposeful and meaningful. By understanding and effectively utilizing research objectives, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their research endeavors.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

How to Formulate Research Questions in a Research Proposal? Discover The No. 1 Easiest Template Here!

7 Easy Step-By-Step Guide of Using ChatGPT: The Best Literature Review Generator for Time-Saving Academic Research

Writing Engaging Introduction in Research Papers : 7 Tips and Tricks!

Understanding Comparative Frameworks: Their Importance, Components, Examples and 8 Best Practices

Revolutionizing Effective Thesis Writing for PhD Students Using Artificial Intelligence!

3 Types of Interviews in Qualitative Research: An Essential Research Instrument and Handy Tips to Conduct Them

Highlight Abstracts: An Ultimate Guide For Researchers!

Crafting Critical Abstracts: 11 Expert Strategies for Summarizing Research
Crafting Clear Pathways: Writing Objectives in Research Papers
Struggling to write research objectives? Follow our easy steps to learn how to craft effective and compelling objectives in research papers.
Are you struggling to define the goals and direction of your research ? Are you losing yourself while doing research and tend to go astray from the intended research topic? Fear not, as many face the same problem and it is quite understandable to overcome this, a concept called research objective comes into play here.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of the objectives in research papers and why they are essential for a successful study. We will be studying what they are and how they are used in research.
What is a Research Objective?
A research objective is a clear and specific goal that a researcher aims to achieve through a research study. It serves as a roadmap for the research, providing direction and focus. Research objectives are formulated based on the research questions or hypotheses, and they help in defining the scope of the study and guiding the research design and methodology . They also assist in evaluating the success and outcomes of the research.
Types of Research Objectives
There are typically three main types of objectives in a research paper:
- Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are focused on gaining a deeper understanding of a particular phenomenon, topic, or issue. Exploratory research objectives aim to explore and identify new ideas, insights, or patterns that were previously unknown or poorly understood. This type of objective is commonly used in preliminary or qualitative studies.
- Descriptive Objectives: Descriptive objectives seek to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or attributes of a specific population, event, or phenomenon. The purpose is to provide a comprehensive and accurate account of the subject of study. Descriptive research objectives often involve collecting and analyzing data through surveys, observations, or archival research.
- Explanatory or Causal Objectives: Explanatory objectives aim to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between variables or factors. These objectives focus on understanding why certain events or phenomena occur and how they are related to each other.
Also Read: What are the types of research?
Steps for Writing Objectives in Research Paper
1. identify the research topic:.
Clearly define the subject or topic of your research. This will provide a broad context for developing specific research objectives.
2. Conduct a Literature Review
Review existing literature and research related to your topic. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge, identify any research gaps, and refine your research objectives accordingly.
3. Identify the Research Questions or Hypotheses
Formulate specific research questions or hypotheses that you want to address in your study. These questions should be directly related to your research topic and guide the development of your research objectives.
4. Focus on Specific Goals
Break down the broader research questions or hypothesis into specific goals or objectives. Each objective should focus on a particular aspect of your research topic and be achievable within the scope of your study.
5. Use Clear and Measurable Language
Write your research objectives using clear and precise language. Avoid vague terms and use specific and measurable terms that can be observed, analyzed, or measured.
6. Consider Feasibility
Ensure that your research objectives are feasible within the available resources, time constraints, and ethical considerations. They should be realistic and attainable given the limitations of your study.
7. Prioritize Objectives
If you have multiple research objectives, prioritize them based on their importance and relevance to your overall research goals. This will help you allocate resources and focus your efforts accordingly.
8. Review and Refine
Review your research objectives to ensure they align with your research questions or hypotheses, and revise them if necessary. Seek feedback from peers or advisors to ensure clarity and coherence.
Tips for Writing Objectives in Research Paper
1. be clear and specific.
Clearly state what you intend to achieve with your research. Use specific language that leaves no room for ambiguity or confusion. This ensures that your objectives are well-defined and focused.
2. Use Action Verbs
Begin each research objective with an action verb that describes a measurable action or outcome. This helps make your objectives more actionable and measurable.
3. Align with Research Questions or Hypotheses
Your research objectives should directly address the research questions or hypotheses you have formulated. Ensure there is a clear connection between them to maintain coherence in your study.
4. Be Realistic and Feasible
Set research objectives that are attainable within the constraints of your study, including available resources, time, and ethical considerations. Unrealistic objectives may undermine the validity and reliability of your research.
5. Consider Relevance and Significance
Your research objectives should be relevant to your research topic and contribute to the broader field of study. Consider the potential impact and significance of achieving the objectives.
SMART Goals for Writing Research Objectives
To ensure that your research objectives are well-defined and effectively guide your study, you can apply the SMART framework. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Here’s how you can make your research objectives SMART:
- Specific : Clearly state what you want to achieve in a precise and specific manner. Avoid vague or generalized language. Specify the population, variables, or phenomena of interest.
- Measurable : Ensure that your research objectives can be quantified or observed in a measurable way. This allows for objective evaluation and assessment of progress.
- Achievable : Set research objectives that are realistic and attainable within the available resources, time, and scope of your study. Consider the feasibility of conducting the research and collecting the necessary data.
- Relevant : Ensure that your research objectives are directly relevant to your research topic and contribute to the broader knowledge or understanding of the field. They should align with the purpose and significance of your study.
- Time-bound : Set a specific timeframe or deadline for achieving your research objectives. This helps create a sense of urgency and provides a clear timeline for your study.
Examples of Research Objectives
Here are some examples of research objectives from various fields of study:
- To examine the relationship between social media usage and self-esteem among young adults aged 18-25 in order to understand the potential impact on mental well-being.
- To assess the effectiveness of a mindfulness-based intervention in reducing stress levels and improving coping mechanisms among individuals diagnosed with anxiety disorders.
- To investigate the factors influencing consumer purchasing decisions in the e-commerce industry, with a focus on the role of online reviews and social media influencers.
- To analyze the effects of climate change on the biodiversity of coral reefs in a specific region, using remote sensing techniques and field surveys.
Importance of Research Objectives
Research objectives play a crucial role in the research process and hold significant importance for several reasons:
- Guiding the Research Process: Research objectives provide a clear roadmap for the entire research process. They help researchers stay focused and on track, ensuring that the study remains purposeful and relevant.
- Defining the Scope of the Study: Research objectives help in determining the boundaries and scope of the study. They clarify what aspects of the research topic will be explored and what will be excluded.
- Providing Direction for Data Collection and Analysis: Research objectives assist in identifying the type of data to be collected and the methods of data collection. They also guide the selection of appropriate data analysis techniques.
- Evaluating the Success of the Study: Research objectives serve as benchmarks for evaluating the success and outcomes of the research. They provide measurable criteria against which the researcher can assess whether the objectives have been met or not.
- Enhancing Communication and Collaboration: Clearly defined research objectives facilitate effective communication and collaboration among researchers, advisors, and stakeholders.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Writing Research Objectives
When writing research objectives, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes and pitfalls that can undermine the effectiveness and clarity of your objectives. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Vague or Ambiguous Language: One of the key mistakes is using vague or ambiguous language that lacks specificity. Ensure that your research objectives are clearly and precisely stated, leaving no room for misinterpretation or confusion.
- Lack of Measurability: Research objectives should be measurable, meaning that they should allow for the collection of data or evidence that can be quantified or observed. Avoid setting objectives that cannot be measured or assessed objectively.
- Lack of Alignment with Research Questions or Hypotheses: Your research objectives should directly align with the research questions or hypotheses you have formulated. Make sure there is a clear connection between them to maintain coherence in your study.
- Overgeneralization : Avoid writing research objectives that are too broad or encompass too many variables or phenomena. Overgeneralized objectives may lead to a lack of focus or feasibility in conducting the research.
- Unrealistic or Unattainable Objectives: Ensure that your research objectives are realistic and attainable within the available resources, time, and scope of your study. Setting unrealistic objectives may compromise the validity and reliability of your research.
In conclusion, research objectives are integral to the success and effectiveness of any research study. They provide a clear direction, focus, and purpose, guiding the entire research process from start to finish. By formulating specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives, researchers can define the scope of their study, guide data collection and analysis, and evaluate the outcomes of their research.
Turn your data into easy-to-understand and dynamic stories
When you wish to explain any complex data, it’s always advised to break it down into simpler visuals or stories. This is where Mind the Graph comes in. It is a platform that helps researchers and scientists to turn their data into easy-to-understand and dynamic stories, helping the audience understand the concepts better. Sign Up now to explore the library of scientific infographics.

Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
- Defining Research Objectives: How To Write Them

Almost all industries use research for growth and development. Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche.
Research objectives provide a clear and concise statement of what the researcher wants to find out. As a researcher, you need to clearly outline and define research objectives to guide the research process and ensure that the study is relevant and generates the impact you want.
In this article, we will explore research objectives and how to leverage them to achieve successful research studies.
What Are Research Objectives?
Research objectives are what you want to achieve through your research study. They guide your research process and help you focus on the most important aspects of your topic.
You can also define the scope of your study and set realistic and attainable study goals with research objectives. For example, with clear research objectives, your study focuses on the specific goals you want to achieve and prevents you from spending time and resources collecting unnecessary data.
However, sticking to research objectives isn’t always easy, especially in broad or unconventional research. This is why most researchers follow the SMART criteria when defining their research objectives.
Understanding SMART Criteria in Research
Think of research objectives as a roadmap to achieving your research goals, with the SMART criteria as your navigator on the map.
SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These criteria help you ensure that your research objectives are clear, specific, realistic, meaningful, and time-bound.
Here’s a breakdown of the SMART Criteria:
Specific : Your research objectives should be clear: what do you want to achieve, why do you want to achieve it, and how do you plan to achieve it? Avoid vague or broad statements that don’t provide enough direction for your research.
Measurable : Your research objectives should have metrics that help you track your progress and measure your results. Also, ensure the metrics are measurable with data to verify them.
Achievable : Your research objectives should be within your research scope, timeframe, and budget. Also, set goals that are challenging but not impossible.
Relevant: Your research objectives should be in line with the goal and significance of your study. Also, ensure that the objectives address a specific issue or knowledge gap that is interesting and relevant to your industry or niche.
Time-bound : Your research objectives should have a specific deadline or timeframe for completion. This will help you carefully set a schedule for your research activities and milestones and monitor your study progress.
Characteristics of Effective Research Objectives
Clarity : Your objectives should be clear and unambiguous so that anyone who reads them can understand what you intend to do. Avoid vague or general terms that could be taken out of context.
Specificity : Your objectives should be specific and address the research questions that you have formulated. Do not use broad or narrow objectives as they may restrict your field of research or make your research irrelevant.
Measurability : Define your metrics with indicators or metrics that help you determine if you’ve accomplished your goals or not. This will ensure you are tracking the research progress and making interventions when needed.
Also, do use objectives that are subjective or based on personal opinions, as they may be difficult to accurately verify and measure.
Achievability : Your objectives should be realistic and attainable, given the resources and time available for your research project. You should set objectives that match your skills and capabilities, they can be difficult but not so hard that they are realistically unachievable.
For example, setting very difficult make you lose confidence, and abandon your research. Also, setting very simple objectives could demotivate you and prevent you from closing the knowledge gap or making significant contributions to your field with your research.
Relevance : Your objectives should be relevant to your research topic and contribute to the existing knowledge in your field. Avoid objectives that are unrelated or insignificant, as they may waste your time or resources.
Time-bound : Your objectives should be time-bound and specify when you will complete them. Have a realistic and flexible timeframe for achieving your objectives, and track your progress with it.
Steps to Writing Research Objectives
Identify the research questions.
The first step in writing effective research objectives is to identify the research questions that you are trying to answer. Research questions help you narrow down your topic and identify the gaps or problems that you want to address with your research.
For example, if you are interested in the impact of technology on children’s development, your research questions could be:
- What is the relationship between technology use and academic performance among children?
- Are children who use technology more likely to do better in school than those who do not?
- What is the social and psychological impact of technology use on children?
Brainstorm Objectives
Once you have your research questions, you can brainstorm possible objectives that relate to them. Objectives are more specific than research questions, and they tell you what you want to achieve or learn in your research.
You can use verbs such as analyze, compare, evaluate, explore, investigate, etc. to express your objectives. Also, try to generate as many objectives as possible, without worrying about their quality or feasibility at this stage.
Prioritize Objectives
Once you’ve brainstormed your objectives, you’ll need to prioritize them based on their relevance and feasibility. Relevance is how relevant the objective is to your research topic and how well it fits into your overall research objective.
Feasibility is how realistic and feasible the objective is compared to the time, money, and expertise you have. You can create a matrix or ranking system to organize your objectives and pick the ones that matter the most.
Refine Objectives
The next step is to refine and revise your objectives to ensure clarity and specificity. Start by ensuring that your objectives are consistent and coherent with each other and with your research questions.
Make Objectives SMART
A useful way to refine your objectives is to make them SMART, which stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Specific : Objectives should clearly state what you hope to achieve.
- Measurable : They should be able to be quantified or evaluated.
- Achievable : realistic and within the scope of the research study.
- Relevant : They should be directly related to the research questions.
- Time-bound : specific timeframe for research completion.
Review and Finalize Objectives
The final step is to review your objectives for coherence and alignment with your research questions and aim. Ensure your objectives are logically connected and consistent with each other and with the purpose of your study.
You also need to check that your objectives are not too broad or too narrow, too easy or too hard, too many or too few. You can use a checklist or a rubric to evaluate your objectives and make modifications.
Examples of Well-Written Research Objectives
Example 1- Psychology
Research question: What are the effects of social media use on teenagers’ mental health?
Objective : To determine the relationship between the amount of time teenagers in the US spend on social media and their levels of anxiety and depression before and after using social media.
What Makes the Research Objective SMART?
The research objective is specific because it clearly states what the researcher hopes to achieve. It is measurable because it can be quantified by measuring the levels of anxiety and depression in teenagers.
Also, the objective is achievable because the researcher can collect enough data to answer the research question. It is relevant because it is directly related to the research question. It is time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Example 2- Marketing
Research question : How can a company increase its brand awareness by 10%?
Objective : To develop a marketing strategy that will increase the company’s sales by 10% within the next quarter.
How Is this Research Objective SMART?
The research states what the researcher hopes to achieve ( Specific ). You can also measure the company’s reach before and after the marketing plan is implemented ( Measurable ).
The research objective is also achievable because you can develop a marketing plan that will increase awareness by 10% within the timeframe. The objective is directly related to the research question ( Relevant ). It is also time-bound because it has a specific deadline for completion.
Research objectives are a well-designed roadmap to completing and achieving your overall research goal.
However, research goals are only effective if they are well-defined and backed up with the best practices such as the SMART criteria. Properly defining research objectives will help you plan and conduct your research project effectively and efficiently.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- research goals
- research objectives
- research roadmap
- smart goals
- SMART research objectives
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...

Subgroup Analysis: What It Is + How to Conduct It
Introduction Clinical trials are an integral part of the drug development process. They aim to assess the safety and efficacy of a new...
Desk Research: Definition, Types, Application, Pros & Cons
If you are looking for a way to conduct a research study while optimizing your resources, desk research is a great option. Desk research...
Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Writing the Research Objectives: 5 Straightforward Examples
The research objective of a research proposal or scientific article defines the direction or content of a research investigation. Without the research objectives, the proposal or research paper is in disarray. It is like a fisherman riding on a boat without any purpose and with no destination in sight. Therefore, at the beginning of any research venture, the researcher must be clear about what he or she intends to do or achieve in conducting a study.
How do you define the objectives of a study? What are the uses of the research objective? How would a researcher write this essential part of the research? This article aims to provide answers to these questions.
Table of Contents
Definition of a research objective.
A research objective describes, in a few words, the result of the research project after its implementation. It answers the question,
The research objective provides direction to the performance of the study.
What are the Uses of the Research Objective?
The research design serves as the “blueprint” for the research investigation. The University of Southern California describes the different types of research design extensively. It details the data to be gathered, data collection procedure, data measurement, and statistical tests to use in the analysis.
The variables of the study include those factors that the researcher wants to evaluate in the study. These variables narrow down the research to several manageable components to see differences or correlations between them.
How is the Research Objective Written?
A research objective must be achievable, i.e., it must be framed keeping in mind the available time, infrastructure required for research, and other resources.
5 Examples of Research Objectives
The following examples of research objectives based on several published studies on various topics demonstrate how the research objectives are written:
Finally, writing the research objectives requires constant practice, experience, and knowledge about the topic investigated. Clearly written objectives save time, money, and effort.
Evans, K. L., Rodrigues, A. S., Chown, S. L., & Gaston, K. J. (2006). Protected areas and regional avian species richness in South Africa. Biology letters , 2 (2), 184-188.
Yeemin, T., Sutthacheep, M., & Pettongma, R. (2006). Coral reef restoration projects in Thailand. Ocean & Coastal Management , 49 (9-10), 562-575.
© 2020 March 23 P. A. Regoniel Updated 17 November 2020 | Updated 18 January 2024
Related Posts
How to write a thesis statement, mango pulp weevil: a pest control problem in palawan island, how to conduct a focus group discussion, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a hobbyist writer, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy
Frequently asked questions
What is a research objective.
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Frequently asked questions: Dissertation
The acknowledgements are generally included at the very beginning of your thesis or dissertation, directly after the title page and before the abstract .
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A list of figures and tables compiles all of the figures and tables that you used in your thesis or dissertation and displays them with the page number where they can be found.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 150–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract appears on its own page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.

Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Chat with us
- Email [email protected]
- Call +44 (0)20 3917 4242
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
Read more about how the sample edit works
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service , which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
| Types of editing | Available at Scribbr? |
|---|---|
| | This is the “proofreading” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with editing. |
| | This is the “editing” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with proofreading. |
| | Select the Structure Check and Clarity Check to receive a comprehensive edit equivalent to a line edit. |
| | This kind of editing involves heavy rewriting and restructuring. Our editors cannot help with this. |
View an example
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours , 3 days or 1 week . These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
Calculate the costs
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between four deadlines:
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English .
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.
21 Research Objectives Examples (Copy and Paste)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve.
These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or quantitative study.
Research objectives are typically nested under one overarching research aim. The objectives are the steps you’ll need to take in order to achieve the aim (see the examples below, for example, which demonstrate an aim followed by 3 objectives, which is what I recommend to my research students).
Research Objectives vs Research Aims
Research aim and research objectives are fundamental constituents of any study, fitting together like two pieces of the same puzzle.
The ‘research aim’ describes the overarching goal or purpose of the study (Kumar, 2019). This is usually a broad, high-level purpose statement, summing up the central question that the research intends to answer.
Example of an Overarching Research Aim:
“The aim of this study is to explore the impact of climate change on crop productivity.”
Comparatively, ‘research objectives’ are concrete goals that underpin the research aim, providing stepwise actions to achieve the aim.
Objectives break the primary aim into manageable, focused pieces, and are usually characterized as being more specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Examples of Specific Research Objectives:
1. “To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.” 2. “To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).” 3. “To analyze the impact of changing weather patterns on crop diseases within the same timeframe.”
The distinction between these two terms, though subtle, is significant for successfully conducting a study. The research aim provides the study with direction, while the research objectives set the path to achieving this aim, thereby ensuring the study’s efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Write Research Objectives
I usually recommend to my students that they use the SMART framework to create their research objectives.
SMART is an acronym standing for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a clear method of defining solid research objectives and helps students know where to start in writing their objectives (Locke & Latham, 2013).
Each element of this acronym adds a distinct dimension to the framework, aiding in the creation of comprehensive, well-delineated objectives.
Here is each step:
- Specific : We need to avoid ambiguity in our objectives. They need to be clear and precise (Doran, 1981). For instance, rather than stating the objective as “to study the effects of social media,” a more focused detail would be “to examine the effects of social media use (Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter) on the academic performance of college students.”
- Measurable: The measurable attribute provides a clear criterion to determine if the objective has been met (Locke & Latham, 2013). A quantifiable element, such as a percentage or a number, adds a measurable quality. For example, “to increase response rate to the annual customer survey by 10%,” makes it easier to ascertain achievement.
- Achievable: The achievable aspect encourages researchers to craft realistic objectives, resembling a self-check mechanism to ensure the objectives align with the scope and resources at disposal (Doran, 1981). For example, “to interview 25 participants selected randomly from a population of 100” is an attainable objective as long as the researcher has access to these participants.
- Relevance : Relevance, the fourth element, compels the researcher to tailor the objectives in alignment with overarching goals of the study (Locke & Latham, 2013). This is extremely important – each objective must help you meet your overall one-sentence ‘aim’ in your study.
- Time-Bound: Lastly, the time-bound element fosters a sense of urgency and prioritization, preventing procrastination and enhancing productivity (Doran, 1981). “To analyze the effect of laptop use in lectures on student engagement over the course of two semesters this year” expresses a clear deadline, thus serving as a motivator for timely completion.
You’re not expected to fit every single element of the SMART framework in one objective, but across your objectives, try to touch on each of the five components.
Research Objectives Examples
1. Field: Psychology
Aim: To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.
- Objective 1: To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.
- Objective 2: To investigate the relationship between class grades and reported sleep duration.
- Objective 3: To survey student perceptions and experiences on how sleep deprivation affects their cognitive capabilities.
2. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To understand the effects of urban green spaces on human well-being in a metropolitan city.
- Objective 1: To assess the physical and mental health benefits of regular exposure to urban green spaces.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the social impacts of urban green spaces on community interactions.
- Objective 3: To examine patterns of use for different types of urban green spaces.
3. Field: Technology
Aim: To investigate the influence of using social media on productivity in the workplace.
- Objective 1: To measure the amount of time spent on social media during work hours.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the perceived impact of social media use on task completion and work efficiency.
- Objective 3: To explore whether company policies on social media usage correlate with different patterns of productivity.
4. Field: Education
Aim: To examine the effectiveness of online vs traditional face-to-face learning on student engagement and achievement.
- Objective 1: To compare student grades between the groups exposed to online and traditional face-to-face learning.
- Objective 2: To assess student engagement levels in both learning environments.
- Objective 3: To collate student perceptions and preferences regarding both learning methods.
5. Field: Health
Aim: To determine the impact of a Mediterranean diet on cardiac health among adults over 50.
- Objective 1: To assess changes in cardiovascular health metrics after following a Mediterranean diet for six months.
- Objective 2: To compare these health metrics with a similar group who follow their regular diet.
- Objective 3: To document participants’ experiences and adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
6. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To analyze the impact of urban farming on community sustainability.
- Objective 1: To document the types and quantity of food produced through urban farming initiatives.
- Objective 2: To assess the effect of urban farming on local communities’ access to fresh produce.
- Objective 3: To examine the social dynamics and cooperative relationships in the creating and maintaining of urban farms.
7. Field: Sociology
Aim: To investigate the influence of home offices on work-life balance during remote work.
- Objective 1: To survey remote workers on their perceptions of work-life balance since setting up home offices.
- Objective 2: To conduct an observational study of daily work routines and family interactions in a home office setting.
- Objective 3: To assess the correlation, if any, between physical boundaries of workspaces and mental boundaries for work in the home setting.
8. Field: Economics
Aim: To evaluate the effects of minimum wage increases on small businesses.
- Objective 1: To analyze cost structures, pricing changes, and profitability of small businesses before and after minimum wage increases.
- Objective 2: To survey small business owners on the strategies they employ to navigate minimum wage increases.
- Objective 3: To examine employment trends in small businesses in response to wage increase legislation.
9. Field: Education
Aim: To explore the role of extracurricular activities in promoting soft skills among high school students.
- Objective 1: To assess the variety of soft skills developed through different types of extracurricular activities.
- Objective 2: To compare self-reported soft skills between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not.
- Objective 3: To investigate the teachers’ perspectives on the contribution of extracurricular activities to students’ skill development.
10. Field: Technology
Aim: To assess the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on the tourism industry.
- Objective 1: To document the types and popularity of VR experiences available in the tourism market.
- Objective 2: To survey tourists on their interest levels and satisfaction rates with VR tourism experiences.
- Objective 3: To determine whether VR tourism experiences correlate with increased interest in real-life travel to the simulated destinations.
11. Field: Biochemistry
Aim: To examine the role of antioxidants in preventing cellular damage.
- Objective 1: To identify the types and quantities of antioxidants in common fruits and vegetables.
- Objective 2: To determine the effects of various antioxidants on free radical neutralization in controlled lab tests.
- Objective 3: To investigate potential beneficial impacts of antioxidant-rich diets on long-term cellular health.
12. Field: Linguistics
Aim: To determine the influence of early exposure to multiple languages on cognitive development in children.
- Objective 1: To assess cognitive development milestones in monolingual and multilingual children.
- Objective 2: To document the number and intensity of language exposures for each group in the study.
- Objective 3: To investigate the specific cognitive advantages, if any, enjoyed by multilingual children.
13. Field: Art History
Aim: To explore the impact of the Renaissance period on modern-day art trends.
- Objective 1: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
- Objective 2: To analyze modern art pieces for the influence of the Renaissance style.
- Objective 3: To survey modern-day artists for their inspirations and the influence of historical art movements on their work.
14. Field: Cybersecurity
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of two-factor authentication (2FA) in preventing unauthorized system access.
- Objective 1: To measure the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after the introduction of 2FA.
- Objective 2: To survey users about their experiences and challenges with 2FA implementation.
- Objective 3: To evaluate the efficacy of different types of 2FA (SMS-based, authenticator apps, biometrics, etc.).
15. Field: Cultural Studies
Aim: To analyze the role of music in cultural identity formation among ethnic minorities.
- Objective 1: To document the types and frequency of traditional music practices within selected ethnic minority communities.
- Objective 2: To survey community members on the role of music in their personal and communal identity.
- Objective 3: To explore the resilience and transmission of traditional music practices in contemporary society.
16. Field: Astronomy
Aim: To explore the impact of solar activity on satellite communication.
- Objective 1: To categorize different types of solar activities and their frequencies of occurrence.
- Objective 2: To ascertain how variations in solar activity may influence satellite communication.
- Objective 3: To investigate preventative and damage-control measures currently in place during periods of high solar activity.
17. Field: Literature
Aim: To examine narrative techniques in contemporary graphic novels.
- Objective 1: To identify a range of narrative techniques employed in this genre.
- Objective 2: To analyze the ways in which these narrative techniques engage readers and affect story interpretation.
- Objective 3: To compare narrative techniques in graphic novels to those found in traditional printed novels.
18. Field: Renewable Energy
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of solar energy as a primary renewable resource within urban areas.
- Objective 1: To quantify the average sunlight hours across urban areas in different climatic zones.
- Objective 2: To calculate the potential solar energy that could be harnessed within these areas.
- Objective 3: To identify barriers or challenges to widespread solar energy implementation in urban settings and potential solutions.
19. Field: Sports Science
Aim: To evaluate the role of pre-game rituals in athlete performance.
- Objective 1: To identify the variety and frequency of pre-game rituals among professional athletes in several sports.
- Objective 2: To measure the impact of pre-game rituals on individual athletes’ performance metrics.
- Objective 3: To examine the psychological mechanisms that might explain the effects (if any) of pre-game ritual on performance.
20. Field: Ecology
Aim: To investigate the effects of urban noise pollution on bird populations.
- Objective 1: To record and quantify urban noise levels in various bird habitats.
- Objective 2: To measure bird population densities in relation to noise levels.
- Objective 3: To determine any changes in bird behavior or vocalization linked to noise levels.
21. Field: Food Science
Aim: To examine the influence of cooking methods on the nutritional value of vegetables.
- Objective 1: To identify the nutrient content of various vegetables both raw and after different cooking processes.
- Objective 2: To compare the effect of various cooking methods on the nutrient retention of these vegetables.
- Objective 3: To propose cooking strategies that optimize nutrient retention.
The Importance of Research Objectives
The importance of research objectives cannot be overstated. In essence, these guideposts articulate what the researcher aims to discover, understand, or examine (Kothari, 2014).
When drafting research objectives, it’s essential to make them simple and comprehensible, specific to the point of being quantifiable where possible, achievable in a practical sense, relevant to the chosen research question, and time-constrained to ensure efficient progress (Kumar, 2019).
Remember that a good research objective is integral to the success of your project, offering a clear path forward for setting out a research design , and serving as the bedrock of your study plan. Each objective must distinctly address a different dimension of your research question or problem (Kothari, 2014). Always bear in mind that the ultimate purpose of your research objectives is to succinctly encapsulate your aims in the clearest way possible, facilitating a coherent, comprehensive and rational approach to your planned study, and furnishing a scientific roadmap for your journey into the depths of knowledge and research (Kumar, 2019).
Kothari, C.R (2014). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Delhi: New Age International.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners .New York: SAGE Publications.
Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Management review, 70 (11), 35-36.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2013). New Developments in Goal Setting and Task Performance . New York: Routledge.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.1 The Purpose of Research Writing
Learning objectives.
- Identify reasons to research writing projects.
- Outline the steps of the research writing process.
Why was the Great Wall of China built? What have scientists learned about the possibility of life on Mars? What roles did women play in the American Revolution? How does the human brain create, store, and retrieve memories? Who invented the game of football, and how has it changed over the years?
You may know the answers to these questions off the top of your head. If you are like most people, however, you find answers to tough questions like these by searching the Internet, visiting the library, or asking others for information. To put it simply, you perform research.
Whether you are a scientist, an artist, a paralegal, or a parent, you probably perform research in your everyday life. When your boss, your instructor, or a family member asks you a question that you do not know the answer to, you locate relevant information, analyze your findings, and share your results. Locating, analyzing, and sharing information are key steps in the research process, and in this chapter, you will learn more about each step. By developing your research writing skills, you will prepare yourself to answer any question no matter how challenging.
Reasons for Research
When you perform research, you are essentially trying to solve a mystery—you want to know how something works or why something happened. In other words, you want to answer a question that you (and other people) have about the world. This is one of the most basic reasons for performing research.
But the research process does not end when you have solved your mystery. Imagine what would happen if a detective collected enough evidence to solve a criminal case, but she never shared her solution with the authorities. Presenting what you have learned from research can be just as important as performing the research. Research results can be presented in a variety of ways, but one of the most popular—and effective—presentation forms is the research paper . A research paper presents an original thesis, or purpose statement, about a topic and develops that thesis with information gathered from a variety of sources.
If you are curious about the possibility of life on Mars, for example, you might choose to research the topic. What will you do, though, when your research is complete? You will need a way to put your thoughts together in a logical, coherent manner. You may want to use the facts you have learned to create a narrative or to support an argument. And you may want to show the results of your research to your friends, your teachers, or even the editors of magazines and journals. Writing a research paper is an ideal way to organize thoughts, craft narratives or make arguments based on research, and share your newfound knowledge with the world.
Write a paragraph about a time when you used research in your everyday life. Did you look for the cheapest way to travel from Houston to Denver? Did you search for a way to remove gum from the bottom of your shoe? In your paragraph, explain what you wanted to research, how you performed the research, and what you learned as a result.
Research Writing and the Academic Paper
No matter what field of study you are interested in, you will most likely be asked to write a research paper during your academic career. For example, a student in an art history course might write a research paper about an artist’s work. Similarly, a student in a psychology course might write a research paper about current findings in childhood development.
Having to write a research paper may feel intimidating at first. After all, researching and writing a long paper requires a lot of time, effort, and organization. However, writing a research paper can also be a great opportunity to explore a topic that is particularly interesting to you. The research process allows you to gain expertise on a topic of your choice, and the writing process helps you remember what you have learned and understand it on a deeper level.
Research Writing at Work
Knowing how to write a good research paper is a valuable skill that will serve you well throughout your career. Whether you are developing a new product, studying the best way to perform a procedure, or learning about challenges and opportunities in your field of employment, you will use research techniques to guide your exploration. You may even need to create a written report of your findings. And because effective communication is essential to any company, employers seek to hire people who can write clearly and professionally.
Writing at Work
Take a few minutes to think about each of the following careers. How might each of these professionals use researching and research writing skills on the job?
- Medical laboratory technician
- Small business owner
- Information technology professional
- Freelance magazine writer
A medical laboratory technician or information technology professional might do research to learn about the latest technological developments in either of these fields. A small business owner might conduct research to learn about the latest trends in his or her industry. A freelance magazine writer may need to research a given topic to write an informed, up-to-date article.
Think about the job of your dreams. How might you use research writing skills to perform that job? Create a list of ways in which strong researching, organizing, writing, and critical thinking skills could help you succeed at your dream job. How might these skills help you obtain that job?
Steps of the Research Writing Process
How does a research paper grow from a folder of brainstormed notes to a polished final draft? No two projects are identical, but most projects follow a series of six basic steps.
These are the steps in the research writing process:
- Choose a topic.
- Plan and schedule time to research and write.
- Conduct research.
- Organize research and ideas.
- Draft your paper.
- Revise and edit your paper.
Each of these steps will be discussed in more detail later in this chapter. For now, though, we will take a brief look at what each step involves.
Step 1: Choosing a Topic
As you may recall from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , to narrow the focus of your topic, you may try freewriting exercises, such as brainstorming. You may also need to ask a specific research question —a broad, open-ended question that will guide your research—as well as propose a possible answer, or a working thesis . You may use your research question and your working thesis to create a research proposal . In a research proposal, you present your main research question, any related subquestions you plan to explore, and your working thesis.
Step 2: Planning and Scheduling
Before you start researching your topic, take time to plan your researching and writing schedule. Research projects can take days, weeks, or even months to complete. Creating a schedule is a good way to ensure that you do not end up being overwhelmed by all the work you have to do as the deadline approaches.
During this step of the process, it is also a good idea to plan the resources and organizational tools you will use to keep yourself on track throughout the project. Flowcharts, calendars, and checklists can all help you stick to your schedule. See Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” for an example of a research schedule.
Step 3: Conducting Research
When going about your research, you will likely use a variety of sources—anything from books and periodicals to video presentations and in-person interviews.
Your sources will include both primary sources and secondary sources . Primary sources provide firsthand information or raw data. For example, surveys, in-person interviews, and historical documents are primary sources. Secondary sources, such as biographies, literary reviews, or magazine articles, include some analysis or interpretation of the information presented. As you conduct research, you will take detailed, careful notes about your discoveries. You will also evaluate the reliability of each source you find.
Step 4: Organizing Research and the Writer’s Ideas
When your research is complete, you will organize your findings and decide which sources to cite in your paper. You will also have an opportunity to evaluate the evidence you have collected and determine whether it supports your thesis, or the focus of your paper. You may decide to adjust your thesis or conduct additional research to ensure that your thesis is well supported.
Remember, your working thesis is not set in stone. You can and should change your working thesis throughout the research writing process if the evidence you find does not support your original thesis. Never try to force evidence to fit your argument. For example, your working thesis is “Mars cannot support life-forms.” Yet, a week into researching your topic, you find an article in the New York Times detailing new findings of bacteria under the Martian surface. Instead of trying to argue that bacteria are not life forms, you might instead alter your thesis to “Mars cannot support complex life-forms.”
Step 5: Drafting Your Paper
Now you are ready to combine your research findings with your critical analysis of the results in a rough draft. You will incorporate source materials into your paper and discuss each source thoughtfully in relation to your thesis or purpose statement.
When you cite your reference sources, it is important to pay close attention to standard conventions for citing sources in order to avoid plagiarism , or the practice of using someone else’s words without acknowledging the source. Later in this chapter, you will learn how to incorporate sources in your paper and avoid some of the most common pitfalls of attributing information.
Step 6: Revising and Editing Your Paper
In the final step of the research writing process, you will revise and polish your paper. You might reorganize your paper’s structure or revise for unity and cohesion, ensuring that each element in your paper flows into the next logically and naturally. You will also make sure that your paper uses an appropriate and consistent tone.
Once you feel confident in the strength of your writing, you will edit your paper for proper spelling, grammar, punctuation, mechanics, and formatting. When you complete this final step, you will have transformed a simple idea or question into a thoroughly researched and well-written paper you can be proud of!
Review the steps of the research writing process. Then answer the questions on your own sheet of paper.
- In which steps of the research writing process are you allowed to change your thesis?
- In step 2, which types of information should you include in your project schedule?
- What might happen if you eliminated step 4 from the research writing process?
Key Takeaways
- People undertake research projects throughout their academic and professional careers in order to answer specific questions, share their findings with others, increase their understanding of challenging topics, and strengthen their researching, writing, and analytical skills.
- The research writing process generally comprises six steps: choosing a topic, scheduling and planning time for research and writing, conducting research, organizing research and ideas, drafting a paper, and revising and editing the paper.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
| Quantitative research questions | Quantitative research hypotheses |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research questions | Simple hypothesis |
| Comparative research questions | Complex hypothesis |
| Relationship research questions | Directional hypothesis |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| Hypothesis-testing | |
| Qualitative research questions | Qualitative research hypotheses |
| Contextual research questions | Hypothesis-generating |
| Descriptive research questions | |
| Evaluation research questions | |
| Explanatory research questions | |
| Exploratory research questions | |
| Generative research questions | |
| Ideological research questions | |
| Ethnographic research questions | |
| Phenomenological research questions | |
| Grounded theory questions | |
| Qualitative case study questions |
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
| Quantitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Measures responses of subjects to variables | |
| - Presents variables to measure, analyze, or assess | |
| What is the proportion of resident doctors in the hospital who have mastered ultrasonography (response of subjects to a variable) as a diagnostic technique in their clinical training? | |
| Comparative research question | |
| - Clarifies difference between one group with outcome variable and another group without outcome variable | |
| Is there a difference in the reduction of lung metastasis in osteosarcoma patients who received the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group with outcome variable) compared with osteosarcoma patients who did not receive the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group without outcome variable)? | |
| - Compares the effects of variables | |
| How does the vitamin D analogue 22-Oxacalcitriol (variable 1) mimic the antiproliferative activity of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D (variable 2) in osteosarcoma cells? | |
| Relationship research question | |
| - Defines trends, association, relationships, or interactions between dependent variable and independent variable | |
| Is there a relationship between the number of medical student suicide (dependent variable) and the level of medical student stress (independent variable) in Japan during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
| Quantitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Simple hypothesis | |
| - Predicts relationship between single dependent variable and single independent variable | |
| If the dose of the new medication (single independent variable) is high, blood pressure (single dependent variable) is lowered. | |
| Complex hypothesis | |
| - Foretells relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables | |
| The higher the use of anticancer drugs, radiation therapy, and adjunctive agents (3 independent variables), the higher would be the survival rate (1 dependent variable). | |
| Directional hypothesis | |
| - Identifies study direction based on theory towards particular outcome to clarify relationship between variables | |
| Privately funded research projects will have a larger international scope (study direction) than publicly funded research projects. | |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| - Nature of relationship between two variables or exact study direction is not identified | |
| - Does not involve a theory | |
| Women and men are different in terms of helpfulness. (Exact study direction is not identified) | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| - Describes variable interdependency | |
| - Change in one variable causes change in another variable | |
| A larger number of people vaccinated against COVID-19 in the region (change in independent variable) will reduce the region’s incidence of COVID-19 infection (change in dependent variable). | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| - An effect on dependent variable is predicted from manipulation of independent variable | |
| A change into a high-fiber diet (independent variable) will reduce the blood sugar level (dependent variable) of the patient. | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| - A negative statement indicating no relationship or difference between 2 variables | |
| There is no significant difference in the severity of pulmonary metastases between the new drug (variable 1) and the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| - Following a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis predicts a relationship between 2 study variables | |
| The new drug (variable 1) is better on average in reducing the level of pain from pulmonary metastasis than the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory | |
| Dairy cows fed with concentrates of different formulations will produce different amounts of milk. | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| - Assumption about the value of population parameter or relationship among several population characteristics | |
| - Validity tested by a statistical experiment or analysis | |
| The mean recovery rate from COVID-19 infection (value of population parameter) is not significantly different between population 1 and population 2. | |
| There is a positive correlation between the level of stress at the workplace and the number of suicides (population characteristics) among working people in Japan. | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| - Offers or proposes an explanation with limited or no extensive evidence | |
| If healthcare workers provide more educational programs about contraception methods, the number of adolescent pregnancies will be less. | |
| Hypothesis-testing (Quantitative hypothesis-testing research) | |
| - Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves the formation of a hypothesis, collection of data in the investigation of the problem, analysis and use of the data from the investigation, and drawing of conclusions to validate or nullify the hypotheses. | |
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
| Qualitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Contextual research question | |
| - Ask the nature of what already exists | |
| - Individuals or groups function to further clarify and understand the natural context of real-world problems | |
| What are the experiences of nurses working night shifts in healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic? (natural context of real-world problems) | |
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Aims to describe a phenomenon | |
| What are the different forms of disrespect and abuse (phenomenon) experienced by Tanzanian women when giving birth in healthcare facilities? | |
| Evaluation research question | |
| - Examines the effectiveness of existing practice or accepted frameworks | |
| How effective are decision aids (effectiveness of existing practice) in helping decide whether to give birth at home or in a healthcare facility? | |
| Explanatory research question | |
| - Clarifies a previously studied phenomenon and explains why it occurs | |
| Why is there an increase in teenage pregnancy (phenomenon) in Tanzania? | |
| Exploratory research question | |
| - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated to have a deeper understanding of the research problem | |
| What factors affect the mental health of medical students (areas that have not yet been fully investigated) during the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
| Generative research question | |
| - Develops an in-depth understanding of people’s behavior by asking ‘how would’ or ‘what if’ to identify problems and find solutions | |
| How would the extensive research experience of the behavior of new staff impact the success of the novel drug initiative? | |
| Ideological research question | |
| - Aims to advance specific ideas or ideologies of a position | |
| Are Japanese nurses who volunteer in remote African hospitals able to promote humanized care of patients (specific ideas or ideologies) in the areas of safe patient environment, respect of patient privacy, and provision of accurate information related to health and care? | |
| Ethnographic research question | |
| - Clarifies peoples’ nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes of their actions in specific settings | |
| What are the demographic characteristics, rehabilitative treatments, community interactions, and disease outcomes (nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes) of people in China who are suffering from pneumoconiosis? | |
| Phenomenological research question | |
| - Knows more about the phenomena that have impacted an individual | |
| What are the lived experiences of parents who have been living with and caring for children with a diagnosis of autism? (phenomena that have impacted an individual) | |
| Grounded theory question | |
| - Focuses on social processes asking about what happens and how people interact, or uncovering social relationships and behaviors of groups | |
| What are the problems that pregnant adolescents face in terms of social and cultural norms (social processes), and how can these be addressed? | |
| Qualitative case study question | |
| - Assesses a phenomenon using different sources of data to answer “why” and “how” questions | |
| - Considers how the phenomenon is influenced by its contextual situation. | |
| How does quitting work and assuming the role of a full-time mother (phenomenon assessed) change the lives of women in Japan? | |
| Qualitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Hypothesis-generating (Qualitative hypothesis-generating research) | |
| - Qualitative research uses inductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves data collection from study participants or the literature regarding a phenomenon of interest, using the collected data to develop a formal hypothesis, and using the formal hypothesis as a framework for testing the hypothesis. | |
| - Qualitative exploratory studies explore areas deeper, clarifying subjective experience and allowing formulation of a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach. | |
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion? | “Moreover, regarding smoke moxibustion versus smokeless moxibustion, it remains unclear which is more effective, safe, and acceptable to pregnant women, and whether there is any difference in the amount of heat generated.” | 1) Vague and unfocused questions |
| 2) Closed questions simply answerable by yes or no | |||
| 3) Questions requiring a simple choice | |||
| Hypothesis | The smoke moxibustion group will have higher cephalic presentation. | “Hypothesis 1. The smoke moxibustion stick group (SM group) and smokeless moxibustion stick group (-SLM group) will have higher rates of cephalic presentation after treatment than the control group. | 1) Unverifiable hypotheses |
| Hypothesis 2. The SM group and SLM group will have higher rates of cephalic presentation at birth than the control group. | 2) Incompletely stated groups of comparison | ||
| Hypothesis 3. There will be no significant differences in the well-being of the mother and child among the three groups in terms of the following outcomes: premature birth, premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at < 37 weeks, Apgar score < 7 at 5 min, umbilical cord blood pH < 7.1, admission to neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and intrauterine fetal death.” | 3) Insufficiently described variables or outcomes | ||
| Research objective | To determine which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion. | “The specific aims of this pilot study were (a) to compare the effects of smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion treatments with the control group as a possible supplement to ECV for converting breech presentation to cephalic presentation and increasing adherence to the newly obtained cephalic position, and (b) to assess the effects of these treatments on the well-being of the mother and child.” | 1) Poor understanding of the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Insufficient description of population, variables, or study outcomes |
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania? | How does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur and what are the types of physical and psychological abuses observed in midwives’ actual care during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania? | 1) Ambiguous or oversimplistic questions |
| 2) Questions unverifiable by data collection and analysis | |||
| Hypothesis | Disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania. | Hypothesis 1: Several types of physical and psychological abuse by midwives in actual care occur during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 1) Statements simply expressing facts |
| Hypothesis 2: Weak nursing and midwifery management contribute to the D&A of women during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 2) Insufficiently described concepts or variables | ||
| Research objective | To describe disrespect and abuse (D&A) in childbirth in Tanzania. | “This study aimed to describe from actual observations the respectful and disrespectful care received by women from midwives during their labor period in two hospitals in urban Tanzania.” | 1) Statements unrelated to the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Unattainable or unexplorable objectives |
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, what is your plagiarism score.

The Importance Of Research Objectives
Imagine you’re a student planning a vacation in a foreign country. You’re on a tight budget and need to draw…

Imagine you’re a student planning a vacation in a foreign country. You’re on a tight budget and need to draw up a pocket-friendly plan. Where do you begin? The first step is to do your research.
Before that, you make a mental list of your objectives—finding reasonably-priced hotels, traveling safely and finding ways of communicating with someone back home. These objectives help you focus sharply during your research and be aware of the finer details of your trip.
More often than not, research is a part of our daily lives. Whether it’s to pick a restaurant for your next birthday dinner or to prepare a presentation at work, good research is the foundation of effective learning. Read on to understand the meaning, importance and examples of research objectives.
Why Do We Need Research?
What are the objectives of research, what goes into a research plan.
Research is a careful and detailed study of a particular problem or concern, using scientific methods. An in-depth analysis of information creates space for generating new questions, concepts and understandings. The main objective of research is to explore the unknown and unlock new possibilities. It’s an essential component of success.
Over the years, businesses have started emphasizing the need for research. You’ve probably noticed organizations hiring research managers and analysts. The primary purpose of business research is to determine the goals and opportunities of an organization. It’s critical in making business decisions and appropriately allocating available resources.
Here are a few benefits of research that’ll explain why it is a vital aspect of our professional lives:
Expands Your Knowledge Base
One of the greatest benefits of research is to learn and gain a deeper understanding. The deeper you dig into a topic, the more well-versed you are. Furthermore, research has the power to help you build on any personal experience you have on the subject.
Keeps You Up To Date
Research encourages you to discover the most recent information available. Updated information prevents you from falling behind and helps you present accurate information. You’re better equipped to develop ideas or talk about a topic when you’re armed with the latest inputs.
Builds Your Credibility
Research provides you with a good foundation upon which you can develop your thoughts and ideas. People take you more seriously when your suggestions are backed by research. You can speak with greater confidence because you know that the information is accurate.
Sparks Connections
Take any leading nonprofit organization, you’ll see how they have a strong research arm supported by real-life stories. Research also becomes the base upon which real-life connections and impact can be made. It even helps you communicate better with others and conveys why you’re pursuing something.
Encourages Curiosity
As we’ve already established, research is mostly about using existing information to create new ideas and opinions. In the process, it sparks curiosity as you’re encouraged to explore and gain deeper insights into a subject. Curiosity leads to higher levels of positivity and lower levels of anxiety.
Well-defined objectives of research are an essential component of successful research engagement. If you want to drive all aspects of your research methodology such as data collection, design, analysis and recommendation, you need to lay down the objectives of research methodology. In other words, the objectives of research should address the underlying purpose of investigation and analysis. It should outline the steps you’d take to achieve desirable outcomes. Research objectives help you stay focused and adjust your expectations as you progress.
The objectives of research should be closely related to the problem statement, giving way to specific and achievable goals. Here are the four types of research objectives for you to explore:
General Objective
Also known as secondary objectives, general objectives provide a detailed view of the aim of a study. In other words, you get a general overview of what you want to achieve by the end of your study. For example, if you want to study an organization’s contribution to environmental sustainability, your general objective could be: a study of sustainable practices and the use of renewable energy by the organization.
Specific Objectives
Specific objectives define the primary aim of the study. Typically, general objectives provide the foundation for identifying specific objectives. In other words, when general objectives are broken down into smaller and logically connected objectives, they’re known as specific objectives. They help define the who, what, why, when and how aspects of your project. Once you identify the main objective of research, it’s easier to develop and pursue a plan of action.
Let’s take the example of ‘a study of an organization’s contribution to environmental sustainability’ again. The specific objectives will look like this:
To determine through history how the organization has changed its practices and adopted new solutions
To assess how the new practices, technology and strategies will contribute to the overall effectiveness
Once you’ve identified the objectives of research, it’s time to organize your thoughts and streamline your research goals. Here are a few effective tips to develop a powerful research plan and improve your business performance.
Set SMART Goals
Your research objectives should be SMART—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time-constrained. When you focus on utilizing available resources and setting realistic timeframes and milestones, it’s easier to prioritize objectives. Continuously track your progress and check whether you need to revise your expectations or targets. This way, you’re in greater control over the process.
Create A Plan
Create a plan that’ll help you select appropriate methods to collect accurate information. A well-structured plan allows you to use logical and creative approaches towards problem-solving. The complexity of information and your skills are bound to influence your plan, which is why you need to make room for flexibility. The availability of resources will also play a big role in influencing your decisions.
Collect And Collate
After you’ve created a plan for the research process, make a list of the data you’re going to collect and the methods you’ll use. Not only will it help make sense of your insights but also keep track of your approach. The information you collect should be:
Logical, rigorous and objective
Can be reproduced by other people working on the same subject
Free of errors and highlighting necessary details
Current and updated
Includes everything required to support your argument/suggestions
Analyze And Keep Ready
Data analysis is the most crucial part of the process and there are many ways in which the information can be utilized. Four types of data analysis are often seen in a professional environment. While they may be divided into separate categories, they’re linked to each other.
Descriptive Analysis:
The most commonly used data analysis, descriptive analysis simply summarizes past data. For example, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) use descriptive analysis. It establishes certain benchmarks after studying how someone has been performing in the past.
Diagnostic Analysis:
The next step is to identify why something happened. Diagnostic analysis uses the information gathered through descriptive analysis and helps find the underlying causes of an outcome. For example, if a marketing initiative was successful, you deep-dive into the strategies that worked.
Predictive Analysis:
It attempts to answer ‘what’s likely to happen’. Predictive analysis makes use of past data to predict future outcomes. However, the accuracy of predictions depends on the quality of the data provided. Risk assessment is an ideal example of using predictive analysis.
Prescriptive Analysis:
The most sought-after type of data analysis, prescriptive analysis combines the insights of all of the previous analyses. It’s a huge organizational commitment as it requires plenty of effort and resources. A great example of prescriptive analysis is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which consumes large amounts of data. You need to be prepared to commit to this type of analysis.
Review And Interpret
Once you’ve collected and collated your data, it’s time to review it and draw accurate conclusions. Here are a few ways to improve the review process:
Identify the fundamental issues, opportunities and problems and make note of recurring trends if any
Make a list of your insights and check which is the most or the least common. In short, keep track of the frequency of each insight
Conduct a SWOT analysis and identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
Write down your conclusions and recommendations of the research
When we think about research, we often associate it with academicians and students. but the truth is research is for everybody who is willing to learn and enhance their knowledge. If you want to master the art of strategically upgrading your knowledge, Harappa Education’s Learning Expertly course has all the answers. Not only will it help you look at things from a fresh perspective but also show you how to acquire new information with greater efficiency. The Growth Mindset framework will teach you how to believe in your abilities to grow and improve. The Learning Transfer framework will help you apply your learnings from one context to another. Begin the journey of tactful learning and self-improvement today!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics related to the THINK Habit such as Learning From Experience , Critical Thinking & What is Brainstorming to think clearly and rationally.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications
Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications
Table of Contents

Purpose of Research
Definition:
The purpose of research is to systematically investigate and gather information on a particular topic or issue, with the aim of answering questions, solving problems, or advancing knowledge.
The purpose of research can vary depending on the field of study, the research question, and the intended audience. In general, research can be used to:
- Generate new knowledge and theories
- Test existing theories or hypotheses
- Identify trends or patterns
- Gather information for decision-making
- Evaluate the effectiveness of programs, policies, or interventions
- Develop new technologies or products
- Identify new opportunities or areas for further study.
Objectives of Research
The objectives of research may vary depending on the field of study and the specific research question being investigated. However, some common objectives of research include:
- To explore and describe a phenomenon: Research can be conducted to describe and understand a phenomenon or situation in greater detail.
- To test a hypothesis or theory : Research can be used to test a specific hypothesis or theory by collecting and analyzing data.
- To identify patterns or trends: Research can be conducted to identify patterns or trends in data, which can provide insights into the behavior of a system or population.
- To evaluate a program or intervention: Research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or intervention, such as a new drug or educational intervention.
- To develop new knowledge or technology : Research can be conducted to develop new knowledge or technologies that can be applied to solve practical problems.
- To inform policy decisions: Research can provide evidence to inform policy decisions and improve public policy.
- To improve existing knowledge: Research can be conducted to improve existing knowledge and fill gaps in the current understanding of a topic.
Applications of Research
Research has a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
- Medicine : Research is critical in developing new treatments and drugs for diseases. Researchers conduct clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of new medications and therapies. They also study the underlying causes of diseases to find new ways to prevent or treat them.
- Technology : Research is crucial in developing new technologies and improving existing ones. Researchers work to develop new software, hardware, and other technological innovations that can be used in various industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and telecommunications.
- Education : Research is essential in the field of education to develop new teaching methods and strategies. Researchers conduct studies to determine the effectiveness of various educational approaches and to identify factors that influence student learning.
- Business : Research is critical in helping businesses make informed decisions. Market research can help businesses understand their target audience and identify trends in the market. Research can also help businesses improve their products and services.
- Environmental Science : Research is crucial in the field of environmental science to understand the impact of human activities on the environment. Researchers conduct studies to identify ways to reduce pollution, protect natural resources, and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Goal of Research
The ultimate goal of research is to advance our understanding of the world and to contribute to the development of new theories, ideas, and technologies that can be used to improve our lives. Some more common Goals are follows:
- Explore and discover new knowledge : Research can help uncover new information and insights that were previously unknown.
- Test hypotheses and theories : Research can be used to test and validate theories and hypotheses, allowing researchers to refine and develop their ideas.
- Solve practical problems: Research can be used to identify solutions to real-world problems and to inform policy and decision-making.
- Improve understanding : Research can help improve our understanding of complex phenomena and systems, such as the human body, the natural world, and social systems.
- Develop new technologies and innovations : Research can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and innovations that can improve our lives and society.
- Contribute to the development of academic fields : Research can help advance academic fields by expanding our knowledge and understanding of important topics and areas of inquiry.
Importance of Research
The importance of research lies in its ability to generate new knowledge and insights, to test existing theories and ideas, and to solve practical problems.
Some of the key reasons why research is important are:
- Advancing knowledge: Research is essential for advancing knowledge and understanding in various fields. It enables us to explore and discover new concepts, ideas, and phenomena that can contribute to scientific and technological progress.
- Solving problems : Research can help identify and solve practical problems and challenges in various domains, such as health care, agriculture, engineering, and social policy.
- Innovation : Research is a critical driver of innovation, as it enables the development of new products, services, and technologies that can improve people’s lives and contribute to economic growth.
- Evidence-based decision-making : Research provides evidence and data that can inform decision-making in various fields, such as policy-making, business strategy, and healthcare.
- Personal and professional development : Engaging in research can also contribute to personal and professional development, as it requires critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
When to use Research
Research should be used in situations where there is a need to gather new information, test existing theories, or solve problems. Some common scenarios where research is often used include:
- Scientific inquiry : Research is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and understanding, and for exploring new concepts, theories, and phenomena.
- Business and market analysis: Research is critical for businesses to gather data and insights about the market, customer preferences, and competition, to inform decision-making and strategy development.
- Social policy and public administration: Research is often used in social policy and public administration to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies, and to identify areas where improvements are needed.
- Healthcare: Research is essential in healthcare to develop new treatments, improve existing ones, and to understand the causes and mechanisms of diseases.
- Education : Research is critical in education to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching methods and programs, and to develop new approaches to learning.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
- Open access
- Published: 28 August 2024
Perspectives of midwives on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for induction of labour among pregnant women in the government hospitals in Tamale
- Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan 1 ,
- Shivera Dakurah 2 &
- Joseph Lasong 1
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 24 , Article number: 561 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The use of herbal medicine and/or its products is common throughout the world. In Tamale Metropolis, pregnant women frequently use local oxytocin to induce labour, as shown by the fact that 90% of midwives reported managing patients who used kaligutim (local oxytocin) to speed up labour. Early career midwives are also aware of this and have personally observed it being used by their clients. The purpose of the study was to assess midwives’ opinions on pregnant women’s use of the well-known kaligutim (local oxytocin) for labour induction in the Tamale Metropolis.
A facility-based, quantitative, cross-sectional research design was used for the study. A total of 214 working midwives from Tamale’s three main public hospitals participated. Data for the study were gathered through a standardized questionnaire. For the analysis and presentation of the data, descriptive and analytical statistics, such as basic frequencies, percentages, Fisher’s exact test, chi square test and multivariate analysis, were employed.
According to the findings of this study, the safety, dosages, and contraindications of kaligutim during pregnancy and labour are unknown. The cessation of contractions was reported by 44 (22.4%) of the respondents whose clients used local oxytocin. The study also revealed that women in Tamale metropolis use “walgu”, a spiritual form of oxytocin, to induce and augment labour. Respondents who responded, “yes” to baby admission to the new-born care unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded, “no” to baby admission to the new-born care unit (AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021).
Conclusions
It can be concluded that using kaligutim to start labour has negative effects on both the mother and the foetus. Additional research is required to evaluate the efficacy, effectiveness, biochemical makeup, and safety of these herbal medicines, particularly during pregnancy and delivery, as well as the spiritual significance of kaligutim (Walgu) and its forms.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Herbal medicines, traditional treatments, and traditional practitioners are the main source of health care for many millions of people, and sometimes the only source of care [ 1 ]. Herbal medicines include herbs, herbal materials, herbal preparations and finished herbal products, that contain as active ingredients parts of plants, or other plant materials, or combinations [ 1 , 2 ]. Women in both developed and developing countries use herbal medicine before pregnancy and during pregnancy and delivery, which has several consequences [ 3 ]. The use of herbal medicine has a long history, tracing its roots back to ancient and biblical days when there was no Orthodox medicine. Currently, both developed and developing countries use herbal medicine due to the presence of many traditional medicine practitioners [ 4 ].
Many cultures worldwide use herbal medicine to induce or accelerate labour, and the incidence of labour induction to shorten the duration of labour is on the rise. Most herbal medicine users are pregnant women who have no formal education, who have a low level of income and who mostly stay far from health facilities [ 5 ]. The majority of pregnant women use herbal medicine through the oral route and have confidence in its efficacy, safety and effectiveness [ 6 ]. Herbal medicine is used by women for maternal health-related issues, such as to induce abortion and labour, to correct infertility, for the treatment of pregnancy-related issues, for breast milk secretion and for general wellbeing during pregnancy [ 5 ].
Women who use herbal medicine during pregnancy and/or labour usually have a high risk of postpartum complications [ 7 ]. The use of herbal uterotonics can lead to hyperstimulation of the uterus, foetal asphyxia and several other adverse effects of labour [ 8 ]. Moreover, traditional medicine used by pregnant women is associated with several complications, including a ruptured uterus, a fresh still birth, a macerated still birth, a caesarean section and even death [ 9 ]. These herbal medicines have both uterotonic and nonuterotonic effects on labour and delivery and are mostly used to induce or augment labour in prolonged labour or postdate or to relax or widen the pelvis for delivery [ 8 ].
Maternal and neonatal deaths are still major challenges for most developing countries, with obstetric complications, especially postpartum haemorrhage (P.P.H.) being the major cause of maternal mortality [ 10 ]. The delivery of healthcare services is still poor quality in developing nations [ 11 ]. Maternal and foetal mortality and morbidity have remained high due to inadequate health services and inadequate emergency obstetric treatment. Childbirth is accompanied by numerous customs that are subject to ethnological research and are often rooted in traditional medicine or religion. Cultural influences and sociodemographic characteristics play an important role in a woman’s decision to seek maternal and child health services.
The induction of labour is the process of artificially starting labour by stimulating the uterus with oxytocin or manually through the rupture of amniotic membranes. This process is usually not risk free, and most women find it to be uncomfortable [ 12 ]. The induction of labour is an obstetric procedure recommended when the benefits to the baby and mother outweigh the benefits of continuing the pregnancy. The procedure usually involves complications and failures and must be performed under close monitoring, proper selection of clients and good preparation [ 13 ].
Labour induction also changes the normal physiological processes that accompany childbirth and increases the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes such as postpartum haemorrhage, neonatal mortality, foetal distress, uterine rapture and premature birth [ 14 ]. Oxytocin is a natural hormone produced by the hypothalamus and is responsible for the activation of sensory nerves during labour and breastfeeding [ 15 ]. Clinically, commercially manufactured synthetic oxytocin is administered to commence or increase uterine activity to reduce the duration of labour [ 16 ].
The induction of labour is not free from risk and must be performed with caution because the procedure involves hyperstimulation of the uterus and foetal distress. Herbal medicine used by pregnant women has long-term effects on both mothers and babies [ 17 ]. Many pregnant women in the Tamale Metropolis use prepackaged herbal medicine before and during pregnancy [ 18 ]. Health-related factors such as cost, distance, access and unavailability of medications influence the utilization of herbal medicine by pregnant women [ 17 ].
All women should be given a prophylactic dose of oxytocin as soon as they give birth. If they start to haemorrhage, they should also be given a treatment dose of oxytocin, which is greater than the prophylactic dose [ 19 ]. There is also a traditional manufactured form of oxytocin (kaligutim) that pregnant women use to start labour. Kaligutim is the local name for the mixture of some special plant parts or a combination of plants prepared and given to pregnant women to start or accelerate the process of labour in the northern part of Ghana [ 17 ].
Ideally, women should take medical drugs during pregnancy (folic acid and fersolate) to help prevent birth defects and congenital malformations such as neural tube defects of the foetus and spinal bifida during pregnancy [ 20 ]. However, in recent decades, women worldwide have used herbal medications during pregnancy and labour, with some taking both herbal medicine and orthodox medicine at the same time [ 21 ]. However, little is known about the use and safety of these medicines, especially during pregnancy, and their dosages, indications and contraindications are not known [ 22 ].
There are studies on herbal medicine use by women during pregnancy and labour, but there is currently no literature on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for labour induction among pregnant women in Ghana, but similar studies have been conducted in Uganda, Malawi, Tanzania, and Nigeria. Despite the efforts of the government and other nongovernmental organizations to ensure maximum coverage of skilled delivery to help reduce maternal and neonatal mortalities, women still use locally prepared oxytocin to induce labour. Although herbal medicine is commonly used by pregnant women, healthcare providers, especially midwives, are often unprepared to communicate effectively with patients or make proper decisions concerning complementary and alternative medicine use, especially during pregnancy and labour [ 23 ].
It is well known that herbs have played a vital role since the precolonial era during pregnancy, delivery and postpartum care in many parts of the country, but there are still few data on the use of herbs among pregnant women in Ghana [ 24 ]. Towards the end of pregnancy, many women are tired and eager to welcome their babies into the world. Moreover, as the expected date of delivery approaches, these women are given local oxytocin by their mothers’ in-laws, grandmothers, mothers, or TBAs or even by the women themselves to start labour at home before going to the health facility [ 25 ].
Medicinal plants that are used to hasten or speed up labour are mostly taken towards the end of pregnancy or the beginning of labour [ 26 ]. Even after delivery, these herbs may be found in small amounts in the mother’s breast, and some may cross the placental barrier and have harmful effects on the baby. The use of herbal medication by pregnant women is inevitable given that up to 80% of people who live in developing nations rely on traditional medicine for their healthcare needs [ 18 ].
The situation in Ghana, especially Northern Ghana, is not different, as pregnant women continue to use herbs despite the availability of health facilities [ 24 ]. The use of herbal medicine (kaligutim) among the Ghanaian population is alarming. Pregnant women in Tamale use herbal products at a rate of 42.5% prior to pregnancy and 52.7% during pregnancy [ 27 ]. Residents of Tamales who seek healthcare services in hospitals or herbal clinics are therefore at a greater risk of experiencing adverse consequences from drug-herb interactions [ 28 ].
Herbal product manufacturers should clearly state that pregnancy is a contraindication, and vendors should use caution when selling these items to pregnant women [ 27 ]. The use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) by pregnant women is a maternal and child health problem. Herbal medicine used by pregnant women has long-term effects on both mothers and babies [ 17 ]. Unfortunately, maternal, and neonatal deaths may occur, and hence, there is a need to examine midwives’ perspectives on local oxytocin use during labour, its effects on the progress and outcome of labour, and the relationship between kaligutim use and birth outcomes among pregnant women in the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis.
Theoretical foundation
This study adopted and adapted Andersen’s (1968) behavioural model of healthcare service utilization (use and nonuse of health services [ 29 ]. Andersen’s healthcare utilization model is a conceptual model aimed at demonstrating the factors that lead to the use/nonuse of health services [ 29 ]. This study was guided by Andersen’s behavioural model of health service use as a theoretical framework to identify the effects of Kaligutim on the progress and outcome of labour and to establish the relationship between the use of Kaligutim and nonuse of kaligutim and birth outcomes. The behavioural model is a multilevel model that incorporates both individual and contextual determinants of health service use.
Conceptual framework
Many people rely on products made from medicinal plants to maintain their health or treat illness, and current general development trends in developing and developed countries suggest that the consumption of medicinal plants is unlikely to decline in the short to medium term because of the benefits to consumers, producers, and society as a whole [ 29 ]. Therefore, there is a need to increase our understanding of what motivates the consumption of medicinal plants, despite the barriers to the establishment of solid evidence on the safety and efficacy of herbal medicines and related products [ 29 ].
This unified conceptual framework offers a step towards establishing a comprehensive approach to understanding the experiences midwives encounter when their clients use herbal medicine to induce their labour. The exposure variable in this study refers to kaligutim (local oxytocin) used by pregnant women in the three major government hospitals to induce labour through several routes, including oral, rectal, and vaginal routes, among others. When oxytocin is used by pregnant women, it can produce several results that can be immediate or late.
The results elicited on labour are termed the outcome variables, which can be immediate outcomes (the progress of labour) or outcomes after delivery (the outcome of labour). The progression of labour includes three stages: progressive dilatation of the cervix from 1 cm to 10 cm, delivery of the baby and expulsion of the placenta. Several factors can be used to determine the progress of labour (obstructed labour, prolonged labour, nature of uterine contractions, precipitated labour, foetal distress, and poor progress of labour).
The outcome of labour on the hand refers to what happens during the delivery of the baby, how the baby was delivered, foetal conditions and maternal conditions. The following factors were used for the purpose of this study to determine the outcome of labour (mode of delivery, postpartum haemorrhage, ruptured uterus, cervical tear, birth asphyxia, uterine atony, maternal mortality, and neonatal mortality). This study focused on the immediate effects of Kaligutim (on labour progress) and the effects of Kaligutim after delivery (on labour outcomes) and the relationship between the use of Kaligutim and birth outcomes.
The study was carried out in Tamale, which is the capital city of the northern region of Ghana. According to the 2021 World Urbanization Review, Tamales has an estimated population of 671,812 people. Tamale still has a blend of typical rural and urban communities, although it has attained the status of a metropolitan area. There are three major government hospitals in Tamale: Tamale Central Hospital, Tamale West Hospital and Tamale Teaching Hospital. The Tamale Teaching Hospital is the only tertiary facility in the northern region and serves as the main reference centre for the five regions of the north.
Study population
The main study population was midwives working in Tamale Metropolis. The sampling frame was all midwives practicing in the three major hospitals in Tamale Metropolis who were willing to participate in the study.
Study design
A facility-based cross-sectional research design was used for this study. A cross-sectional study is a type of observational study design carried out at one point in time or over a short period of time to estimate the prevalence of the outcome of interest for a given population for the purpose of public health planning [ 30 ]. This study adopted a quantitative research approach to obtain information.
Sampling technique
A purposive sampling technique was used for this study. Purposive sampling is a nonprobability sampling method in which participants are selected for inclusion in the sample based on their characteristics, knowledge, or experiences. This is because of the midwives’ knowledge, experiences, and objective of the study.
Sample size calculation
Total number of midwives = 458
Yamane formula (1967) was used with a confidence interval of 95% and a margin of error of 5%.
N = population size (458).
n = the sample size (?)
e = margin of error (5%).
n \(\:=\frac{N}{1\:+N\left(e\right)2}\)
n= \(\:\frac{458}{1\:+458\left(0.05\right)2}\)
n = 214.01 = 214.
Sample size = 214 midwives.
Inclusion criteria
All midwives practicing in the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis who were willing to participate in the study were included.
All midwives in the three-government hospital with experience with kaligutim use during labour were also included in the study.
Exclusion criteria
All midwives who were not practising at the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis were excluded from the study.
Midwives who were practicing at the three major government hospitals in Tamale and who were not willing to participate in the study were also excluded from the study.
All midwives who did not have experience with kaligutim use for the induction of labour were excluded from the study.
Data collection instrument
The data collection tool that was used for the study was a standardized questionnaire. The questionnaire was constructed by reviewing various documents, including existing questionnaires that have been used in previous research. Close-ended questions with few open-ended questions were used as the question format. It was designed in line with the objectives of the study to help obtain the necessary information needed for the study. The questionnaire was pretested with midwives before the actual data collection took place.
Data management and analysis
Data collected from the field were coded, cleaned, and entered into the Statistical Package for Social Services (SPSS) version 21.0. Descriptive and analytical statistics, including simple frequencies and percentages, were used for the analysis and presentation of the data. The relationships between predictor and outcome variables were assessed by means of bivariate (chi-square test) analysis to determine potential predictors of kaligutim (local oxytocin) at p values less than 0.05. Adjusted odds ratios were reported, and p values less than 0.05 were deemed to indicate statistical significance at the 95% confidence level after multivariate analysis.
Ethical consideration
The following ethical principles guided this study: respect for persons, beneficence, and justice for all. These principles are based on the human rights that must be protected during any research project, including the right to self-determination, privacy, anonymity, confidentiality, fair treatment and protection from discomfort and harm. First, an introductory letter was obtained from the University for Development Studies authorities. This letter was then presented to the authorities of the three major government hospitals in Tamale, namely, Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H.), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H.) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH.), to seek permission to undertake the study. Ethical clearance was also obtained from the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) (CHRPE/AP/332/22).
Permission was once sought through a consent form to which participants were asked to consent if they were willing to participate in the study. The participants were assured of the confidentiality of all the information they were going to provide. They were also encouraged to participate in the study as much as they could but were also made aware that the study was voluntary and that they could withdraw at any point in time during the process if needed. There was no compensation for the study participants.
The study revealed that 45% of the respondents were between the ages of 20 and 30. Most of the respondents were in their twenties or thirties. Those who were in the first half of their work life constituted 73% of the respondents, while 17% were in the second half of their working life. The majority of the respondents were diploma midwives, representing 48% of the respondents; post basic midwives, constituting 32%; and degree and master’s holders, representing 19% and 1%, respectively. Staff midwives composed the largest group of respondents, while Principal Midwifery officers composed the group with the lowest participation in the study. The lowest rank in midwifery practice in the study was staff midwives, and the highest was principal midwifery officers. This is presented in Table 1 .
The experience of using local oxytocin to induce labour
Approximately 90% of the respondents have prior knowledge or heard that some of their clients take local oxytocin at home to start labour, and only 10% of respondents have no prior knowledge of that. Approximately 63.4% of the respondents encountered local oxytocin cases more than three times every week. This is presented in Fig. 1 .
Average number of local oxytocin cases per week
Approximately 72.9% of the respondents said that their clients had ever induced labour during the previous C/S, and 59.6% of the respondents said that they met clients who also induced their labour during twin pregnancy. Another 64.5% of the respondents said that they also met clients with large babies who also induced labour using local oxytocin, while 86.2% of the respondents said that they also met clients who induced labour with local oxytocin even when they had grand multiparity. Another 11.3% of the respondents said that they met clients who used local oxytocin to induce labour during transverse lies, and 15.3% of the respondents said that they had experienced when clients with mal presentations used local oxytocin to induce labour. This is presented in Fig. 2 .
Induction of labour by clients through local oxytocin under certain conditions
The study additionally asked midwives to report on how pregnant women who had taken local oxytocin to induce labour coped during their care. Midwives were expected to respond whether the women they cared for experienced good, difficult, bad, painful, life-threatening, terrible, or normal labour. As shown in Fig. 3 , generally, the experience that pregnant women experience when they use local oxytocin to induce labour is not good. A total of 93.5% of the respondents said that the women who used local oxytocin had very bad experiences.
Experience of using local oxytocin to induce labour
The study further revealed that 15.2% of the respondents had experienced situations where some pregnant women died because of the use of local oxytocin.
Effects of local oxytocin on the progress of labour
The effects of local oxytocin (Kaligutim) on the progress of labour were diverse. The study revealed that the effects of Kaligutim on the progress of labour are negative, as it causes prolonged labour for some, obstructed labour for others, precipitated labour, and poor progress of labour for others. With obstructed labour being the leading effect of kaligutim on the progress of labour, most of the respondents chose caesarean section as the preferred delivery for most clients who used kaligutim at birth. The use of local oxytocin also has some effect on the amniotic fluid of pregnant women, as 99% of the midwives who responded to the study said that there were some levels of stain of the amniotic fluid, and only 1% said it was clear. It is evident from the study that for most pregnant women who use local oxytocin, there is hyperstimulation of the uterus, as most of the midwives confirmed this for the study. Most pregnant women who use kaligutim suffer excessive contractions, which could have an effect on both mothers and babies. Again, more than half (53.75) of the respondents also said that their foetal heart rate was above 160 bpm. The majority (77.65) of the respondents said that there was no cessation of the contractions for those who took the local oxytocin. The results are presented in Table 2 .
Impact of local oxytocin on the outcome of labour
To understand how local oxytocin impacts labour, the study went further to ask participants what the mode of delivery was for those who used Kaligutim. According to the data, caesarean section is the mode of delivery for most women (56.5%) who use local oxytocin, and most are unable to achieve spontaneous delivery. This has contributed to the increasing number of caesarean sections recorded daily. Most of the babies had an Apgar score of 4/10 to 6/10. Many babies born to mothers who used herbal oxytocin were born with moderate birth asphyxia (69.6%) and severe birth asphyxia (24%). The study also reported that 20.8% of midwives reported that hysterectomy was carried out on their clients who had used herbal preparations to induce or hasten labour. This is alarming because many women have their uterus removed as a result of herbal oxytocin (kaligutm) usage. Most clients who used Kaligutim experienced postpartum haemorrhage after delivery. It was also evident that some pregnant women (34.5%) had uterine atony, although it cannot be said that Kaligutim was the cause of uterine atony. Several pregnant women (65.3 years old) who used Kaligutim also developed a ruptured uterus. See Table 3 .
Relationship between kaligutim (local oxytocin) use and birth outcome
Table 4 shows the associations between kaligutim (local oxytocin) use and birth outcomes among the respondents. Fisher’s exact test and the chi-square test showed that several birth outcome variables were significantly associated with kaligutim (local oxytocin). Do women who go through the normal process of labour and those who use kaligutim to induce their labour have the same birth outcome? (P value = 0.021), what was the foetal wellbeing? (P value = 0.041), When do most neonates whose mothers have taken Kaligutim die? (P value = 0.038), was baby admitted at the Newborn Care Unit? (P value = 0.001), were significantly associated with kaligutim. Additionally, having recorded a maternal death because of the use of Kaligutim (p value = 0.002) was also significantly associated with kaligutim, as presented in Table 4 .
Multivariate analysis of birth outcome predictors of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) among pregnant women in three major government hospitals in Tamale metropolis
In Table 5 , three birth outcome variables strongly depicted kaligutim use among the respondents: foetal wellbeing, admission to the new-born care unit, and death of most neonates because of the use of Kaligutim by their mothers. Respondents who responded, “yes” to baby admission to the Newborn Care Unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded “no” to baby admission to the Newborn Care Unit [(AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021)].
Discussions
Although the respondents cut across with regard to the number of years of experience, most of the respondents were early career midwives. The fact that these early career midwives are familiar with and have experienced the use of local oxytocin by their clients shows that it is widely used by pregnant women in the Tamale metropolis. Approximately 90% of respondents were aware of the usage of kaligutim (local oxytocin) for inducing labour at home before going to the hospital for delivery. However, a study conducted in the Ashanti region of Ghana revealed that midwives and other healthcare professionals lack proper knowledge about herbal medicine usage among pregnant women, even though this information is urgently needed so that appropriate action may be taken to address the issue [ 31 ]. The study findings also demonstrated that pregnant women frequently utilize local oxytocin and that many of them are unaware of the potential negative effects that these herbs may have on them in certain circumstances. Figure 2 shows that the use of local oxytocin was not limited to only one condition. These findings further show that the use of local oxytocin by pregnant women is widespread and that pregnant women do not know the effect that local oxytocin can have on them when they have certain conditions. Additionally, pregnant women are ignorant of the fact that local oxytocin can be contraindicated under certain conditions and must be avoided. Hence, it may put the life of the pregnant mother and her baby in danger.
Although herbal medicines are natural, not all herbs are safe to use while pregnant. Thus, expectant mothers should consult their midwives for guidance before taking herbal remedies. The experience that pregnant women have when they use local oxytocin to induce labour is not a positive one. A total of 188 respondents, or 93.5% of the respondents, stated that the women who used local oxytocin had a very unpleasant experience. This is supported by additional research results showing that between 50 and 80% of pregnant women use traditional plant remedies, which could have adverse perinatal effects [ 32 ]. The statistics indicate that local oxytocin is frequently used by pregnant women in the Tamale Metropolis. Most of the midwives reported seeing these cases virtually daily. This finding supports a study conducted in Ghana’s Ashanti region (Kumasi), which revealed that knowledge of herbal medicine is widely shared and that there is evidence of an increase in the usage of herbs [ 33 ].
The study revealed that local oxytocin (Kaligutim) has a diverse range of effects on the progress of labour, including precipitating labour, prolonging labour, obstructing labour, and slowing labour. The partograph is a great tool for keeping track of labour progress and serving as a warning system for abnormalities in normal labour, which helps to prevent obstructed labour and improves maternal and foetal outcomes [ 34 ]. This is supported by the study’s findings, which indicate that using a partograph to monitor labour progress and identify any deviations is essential [ 34 ].
According to this study, most midwives, who make up 65.2% of the respondents, also claimed that pregnant women who use local oxytocin (Kaligutim) have excessive contractions, while only 71 of them, or 34.8% of the respondents, claimed that they do not notice excessive contractions in their clients. This is supported by research performed in Zambia, which revealed that these herbal medicines also elicit greater than normal uterine contractions [ 26 ].
Most pregnant women who use kaligutim experience excessive contractions, which may have an impact on both the mother and the unborn child. Similarly, other authors have also claimed that using herbal remedies during labour causes stronger and more frequent uterine contractions, which do not necessarily result in cervical dilatation [ 35 ]. This was confirmed in the study’s findings, which also noted that herbal oxytocin not only produces excessive uterine contractions but also may cause contractions to cease, as 44 (22.4%) of the respondents reported that those who took local oxytocin had a halt in contractions. Intravenous fluids such as normal saline and Ringer’s lactate are used to flush out the local oxytocin in the system and CS in the case of an emergency. Nifedipine is also given in certain circumstances to prevent contractions.
According to the study, 121 midwives, or 59.6% of the respondents, stated that caesarean sections were the preferred method of delivery for women who used kaligutim to induce labour. Both [ 36 ] in South Africa and [ 34 ] in Western Uganda reported these findings. Moderate birth asphyxia (69.6%) and severe birth asphyxia (23%) are common in newborns whose mothers utilize herbal oxytocin. According to the survey, 20.8% of midwives said they had performed hysterectomy procedures on clients who had utilized herbal induction or hastening methods to induce labour.
One of the main causes of maternal deaths worldwide, including in Ghana, is postpartum haemorrhage [ 10 ]. 91% of midwives said that when their patients use herbal oxytocin during labour, more of them suffer from postpartum haemorrhage. This is corroborated by research by Frank (2018), who found a connection between postpartum haemorrhage and the use of herbal medications during labour [ 37 ]. In contrast, other studies [ 38 ] have shown that using herbal medication during childbirth is linked to a lower risk of postpartum haemorrhage. Individuals who experienced postpartum haemorrhage were managed with uterine massage, intravenous fluids, Cytotec, repairs to tears, expulsion of retained products, blood transfusions, cervical repairs, and catheter use.
This report supports the findings of a study conducted in the Ugandan village of Kiganda, where the researcher [ 37 ] reported that the use of herbal medicines has been linked to labour induction, which can cause significant birth canal tearing, postpartum haemorrhage, uterine atony, a raptured uterus, and, if untreated, maternal mortality. Medical experts who are aware of the dangers of herbal remedies and who are obliged to advise patients against using them do so themselves. The majority of women who use herbal preparations during pregnancy have a high school education or higher, according to evidence showing that more than 57.5% of pregnant women who use herbs have a high school diploma or higher, which is consistent with findings from Saudi Arabia by [ 39 ] that show that formal education cannot even prevent women from taking herbs during pregnancy and labour.
Kaligutim also causes excessive uterine contractions, foetal discomfort, excessive uterine stimulation, uterine atony, PPH, birth hypoxia, and premature bearing down, claims this study. This is supported by the results of a study carried out in Europe, where researchers [ 40 ] found that the majority of herbal drugs taken by pregnant women have undesirable side effects. An Iranian study, however, revealed that utilizing herbal treatments during labour can lessen discomfort, speed up the process, and enhance both the quality of a woman’s delivery experience and her odds of having a healthy baby [ 41 ].
According to the study’s findings, three birth outcome variables strongly affected kaligutim (local oxytocin) use among the respondents: foetal wellbeing, admission to the newborn care unit, and death of most neonates as a result of the use of Kaligutim by their mothers. Respondents who responded, “yes to baby” and were admitted to the new-born care unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded, “no to baby” and were admitted to the new-born care unit (AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021). This is probably one of the effects of taking local oxytocin. These infants were hospitalized for a variety of reasons, including asphyxia, respiratory distress, and low Apgar scores.
Additionally, the study results indicated that respondents who responded that a still birth outcome affected foetal wellbeing were 1.9 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those who responded no to having live births were (AOR = 1.9 95% CI (0.01, 1.21), P = 0.047)]. This finding is consistent with findings from a sub-Saharan African study that showed that herbal medications used to speed up and induce labour have uterotonic effects and increase the risk of neonatal asphyxia attributable to uterine hyperstimulation [ 42 ]. This could be ascribed to the fact that the respondents wanted fast and easy delivery, which subsequently caused this effect.
Another interesting finding was that respondents who responded that having a birth asphyxia outcome to foetal wellbeing were 0.16 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded no to having live births (AOR = 0.16, 95% CI (0.08, 3.08), P = 0.047). This result is similar to that of [ 42 ], who conducted their study in sub-Saharan Africa. This could be a result of the effects of kaligutim on foetal well-being, which results in birth asphyxia.
Furthermore, newborns whose mothers used kaligutim during labour and who died within the first hour of birth were 3.4 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those whose mothers used kaligutim during labour [AOR = 3.4 95% CI (0.74, 1.5), P = 0.045]. In support of the findings from this study, a study on the consumption of herbal drugs among pregnant women in rural Malawi revealed that consumption was linked to pregnancy-related issues and that users had a greater risk of neonatal mortality/morbidity within the first hour of life than nonusers [ 14 ]. This could be attributed to the dangers this herb poses to the foetus during delivery.
Newborns whose mothers used kaligutim during labor and who died within the first week of life were 2.23 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those whose mothers used intrauterine kaligutim [(AOR = 2.23 95% CI (0.00, 0.02), P = 0.045)]. This is supported by findings from a Malawian study that revealed that the use of labour-inducing plants during pregnancy has negative effects on obstetric and labour outcomes, such as uterine rapture, which can cause neonatal mortality and morbidity [ 35 ]. This could be attributed to the fact that PPH, uterine rapture, cervical tear, DIC, and hypoxia were the main causes of death.
Every life matter, which is why mothers’ lives and that of their newborn babies must be safeguarded at all costs. A sufficient level of knowledge is always vital since it exacerbates doubt. Therefore, it is crucial that people are informed of their rights, their health, and the services they can utilize to maintain and improve health to have a healthy increasing population. Although herbal medicine could be effective in treating certain ailments associated with pregnancy and delivery and is easily accessible to pregnant women, especially in rural communities, the possibility of overdose, drug-herb interactions, contraindications, and the unhygienic conditions under which they are prepared may influence both maternal and neonatal conditions.
The results showed that the use of kaligutim by pregnant women in Tamale Metropolis is on the rise. This means that much needs to be done to do away with the use of kaligutim, and this must start with midwives. Pregnancies and births can be improved with a healthy and qualified midwifery care model in improving and protecting women’s and newborn health in Tamale.
It can be concluded that the use of this herbal medicine (Kaligutim) poses a greater long-term health challenge for mothers and their babies. Midwives and other healthcare workers in the Tamale Metropolis must therefore intensify their public health campaigns against the use of Kaligutim for labour induction.
Recommendations
The findings of the study have important implications for maternal and child health. The nonuse of kaligutim (local oxytocin) for the induction of labour is the best option for pregnant women. Pregnant women should visit the hospital for all their health needs during the entire pregnancy. This will help prevent adverse pregnancy and labour outcomes as well as maternal and neonatal mortalities and morbidities.
Future researchers should perform further studies on the spiritual aspects of kaligutim (Walgu) and its types. Like synthetic oxytocin, an Islamic form of oxytocin is prepared by Mallams and causes uterine contractions and dilates the cervix.
However, studies should also be conducted on the efficiency, effectiveness and biochemical composition of these herbal preparations and their safety, especially during pregnancy and delivery. Samples of these herbal preparations should be taken for laboratory investigations.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information files are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organization. WHO traditional medicine strategy: 2014–2023. World Health Organization;2013. Accessed 20 Nov 2023.
Fokunang CN, Ndikum V, Tabi OY, Jiofack RB, Ngameni B, Guedje NM et al. Traditional medicine: past, present and future research and development prospects and integration in the National Health System of Cameroon. Afr J Trad Complement Alt Med. 2011;8(3).
John LJ, Shantakumari N. Herbal medicines use during pregnancy: a review from the Middle East. Oman Med J. 2015;30(4):229.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mekuria AB, Erku DA, Gebresillassie BM, Birru EM, Tizazu B, Ahmedin A. Prevalence and associated factors of herbal medicine use among pregnant women on antenatal care follow-up at University of Gondar referral and teaching hospital, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–7.
Google Scholar
Shewamene Z, Dune T, Smith CA. The use of traditional medicine in maternity care among African women in Africa and the diaspora: a systematic review. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–6.
Nyeko R, Tumwesigye NM, Halage AA. Prevalence and factors associated with use of herbal medicines during pregnancy among women attending postnatal clinics in Gulu district, Northern Uganda. BMC Preg Childbirth. 2016;1–12.
Fukunaga R, Morof D, Blanton C, Ruiz A, Maro G, Serbanescu F. Factors associated with local herb use during pregnancy and labor among women in Kigoma region, Tanzania, 2014–2016. BMC Preg Childbirth. 2020;20:1–1.
Article Google Scholar
Tripathi V, Stanton C, Anderson FW. Traditional preparations used as uterotonics in Sub-saharan Africa and their pharmacologic effects. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2013;120(1):16–22.
Maliwichi-Nyirenda CP, Maliwichi LL. Medicinal plants used to induce labour and traditional techniques used in determination of onset of labour in pregnant women in Malawi: a case study of Mulanje district. J Med Plants Res. 2010;4(24):2609.
Amanuel T, Dache A, Dona A. Postpartum Hemorrhage and its Associated factors among women who gave birth at Yirgalem General Hospital, Sidama Regional State, Ethiopia. Health Res Serv Manag Epidemiol. 2021;8:1–7.
James PB, Wardle J, Steel A, Adams J. Traditional, complementary and alternative medicine use in Sub-saharan Africa: a systematic review. BMJ Glob Health. 2018;3(5).
Coates D, Homer C, Wilson A, Deady L, Mason E, Foureur M, et al. Induction of labour indications and timing: a systematic analysis of clinical guidelines. Women Birth. 2020;33(3):219–30.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lawani OL, Onyebuchi AK, Iyoke CA, Okafo CN, Ajah LO. Obstetric outcome and significance of labour induction in a health resource poor setting. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2014;2014(1):419621.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zamawe C, King C, Jennings HM, Fottrell E. Associations between the use of herbal medicines and adverse pregnancy outcomes in rural Malawi: a secondary analysis of randomised controlled trial data. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2018;18:1–8.
Roopasree B, Joseph J, Mukkadan JK. Oxytocin-functions: an overview. MOJ Anat Physiol. 2019;6:128–33.
Espada-Trespalacios X, Ojeda F, Perez-Botella M, Milà Villarroel R, Bach Martinez M, Figuls Soler H, et al. Oxytocin administration in low-risk women, a retrospective analysis of birth and neonatal outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8):4375.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ayelyini B, Yidana A, Ziblim SD. The Use of Indigenous Medicine among women during pregnancy and labour in rural Ghana. Cent Afr J Public Health. 2019;5(3):120–8. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.cajph.20190503.14 .
Kwame Ameade EP, Zakaria AP, Abubakar L, Sandow R. Herbal medicine usage before and during pregnancy – a study in Northern Ghana. Int J Complement Alt Med. 2018;11(4).
Jhpiego. Business Case: Investing in production of high-quality oxytocin for low-resource settings–Final report December 2014. 2014. http://www.conceptfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/BusinessCase_Oxytocin_web.pdf . Accesed 25 Jan 2024.
Barišić T, Pecirep A, Milićević R, Vasilj A, Tirić D. What do pregnant women know about harmful effects of medication and herbal remedies use during pregnancy? Psychiatr Danub. 2017;29(1):804–11.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ameade EPK, Ibrahim M, Ibrahim HS, Habib RH, Gbedema SY. Concurrent Use of Herbal and Orthodox Medicines among Residents of Tamale, Northern Ghana, Who Patronize Hospitals and Herbal Clinics. Evidence-based Complement Alt Med. 2018;2018(2002).
Illamola SM, Amaeze OU, Krepkova LV, Birnbaum AK, Karanam A, Job KM, et al. Use of herbal medicine by pregnant women: what physicians need to know. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10:1483.
Bahall M, Legall G. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices among health care providers regarding complementary and alternative medicine in Trinidad and Tobago. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–9.
Peprah P, Agyemang-duah W, Arthur-holmes F, Budu HI, Abalo EM, Okwei R et al. ‘ we are nothing without herbs ’ : a story of herbal remedies use during pregnancy in rural Ghana. BMC Complement Altern Med.2019;1–12.
Kamatenesi-Mugisha M, Oryem-Origa H. Medicinal plants used to induce labour during childbirth in western Uganda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;109(1):1–9.
Ngoma CM. Use of Herbal Medicines to induce labour by pregnant women: a systematic review of literature. JOJ Nurs Heal Care. 2017;2(3):7–12.
Ameade EK, Zakaria AP, Abubakar L, Sandow R. Herbal medicine usage before and during pregnancy—a study in Northern Ghana. Int J Complement Alt Med. 2018;11(4):235–42.
Ameade EP, Ibrahim M, Ibrahim HS, Habib RH, Gbedema SY. Concurrent use of herbal and orthodox medicines among residents of Tamale, Northern Ghana, who patronize hospitals and herbal clinics. Evidence-Based Complement Alt Med. 2018;2018(1):1289125.
Andersen RM. Revisiting the behavioral Model and Access to Medical Care: does it Matter? J Health Soc Behav. 1995;1–10. https://doi.org/10.2307/2137284 .
Smith-Hall C, Larsen HO, Pouliot M. People, plants and health: a conceptual framework for assessing changes in medicinal plant consumption. J Ethnobiolo Ethnomed. 2012;8:1–1.
Levin KA. Study design III: cross-sectional studies. Evid-Based Dent. 2006;7(1):24–5.
Beste J, Asanti D, Nsabimana D, Anastos K, Mutimura E, Merkatz I, et al. Use of Traditional Botanical Medicines during pregnancy in Rural Rwanda. J Glob Health Perspect. 2015;2015:1–10.
Adusi-Poku Y, Vanotoo L, Detoh E, Oduro J, Nsiah R, Natogmah A. Type of herbal medicines utilized by pregnant women attending ante-natal clinic in Offinso North district: are orthodox prescribers aware? Ghana Med J. 2016;49(4):227.
Agyei-Baffour P, Kudolo A, Quansah DY, Boateng D. Integrating herbal medicine into mainstream healthcare in Ghana: clients’ acceptability, perceptions and disclosure of use. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Mukasa PK, Kabakyenga J, Senkungu JK, Ngonzi J, Kyalimpa M, Roosmalen VJ. Uterine rupture in a teaching hospital in Mbarara, western Uganda, unmatched case-control study. Reprod Health. 2013;10(1):1–6.
Lampiao F, Maliwichi-Nyirenda C, Mponda J, Tembo L, Clements C. A preliminary investigation of the effects of labour inducing plant, cissampelos mucronata, on the outcomesof pregnancy using rat models. Malawi Med J. 2018;30(3):159–61.
Kekana LS, Sebitloane MH. Ingestion of herbal medication during pregnancy and adverse perinatal outcomes. S Afr J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;26(2):1–5.
Buyondo BF. Use of Herbal Medicines in Preparation for Labour and its determinants among pregnant women at Kiganda Health Centre Iv-Mubende District. Angew Chemie Int Edu. 2018;6(11):951–2.
Koh LM, Percival B, Pauley T, Pathak S. Complementary therapy and alternative medicine: effects on induction of labour and pregnancy outcome in low risk post-dates women. Heliyon. 2019;5(11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02787 .
Al-Ghamdi S, Aldossari K, Al-Zahrani J, Al-Shaalan F, Al-Sharif S, Al-Khurayji H, et al. Prevalence, knowledge and attitudes toward herbal medication use by Saudi women in the central region during pregnancy, during labor and after delivery. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Gruber CW, O’Brien M. Uterotonic plants and their bioactive constituents. Planta Med. 2011;77(03):207–20.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zahra A. Lavender aromatherapy massages in reducing labor pain and duration of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;7(8):456–430.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the Management and Healthcare Staff of the Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH) for their support throughout the data collection process. We acknowledge the contributions of all the midwives who shared their knowledge and experiences with us, your efforts are well appreciated.
No funding was available for the study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Population and Reproductive Health, School of Public Health, University for Development Studies, P. O. Box 1883, Tamale, Northern Region, Ghana
Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan & Joseph Lasong
Nandom Nursing and Midwifery Training College, Upper West Region, Nandom, Ghana
Shivera Dakurah
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ASA and SD conceptualised and drafted the research proposal. ASA, SD, and JL performed the statistical analysis, assisted with interpretation of the results, and co-drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussion of the paper, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
An introductory letter from the University for Development Studies was presented to the three government hospitals, Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH) to seek for permission to undertake the study. Ethical clearance was also obtained from the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) with reference number (CHRPE/AP/332/22). Permission was also sought through a consent form of which participants were asked to consent to if they were willing to participate in the study. They were assured of confidentiality of every information they were going to provide. All other methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations on subject selection and participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alhassan, A.S., Dakurah, S. & Lasong, J. Perspectives of midwives on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for induction of labour among pregnant women in the government hospitals in Tamale. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24 , 561 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06745-z
Download citation
Received : 15 April 2024
Accepted : 08 August 2024
Published : 28 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06745-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Local oxytocin
- Herbal medicine
- Traditional medicine
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Characteristics of research objectives. Research objectives must start with the word "To" because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6. A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives): Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
Purpose of Research Objectives. Some of the main purposes of research objectives include: To clarify the research question or problem: Research objectives help to define the specific aspects of the research question or problem that the study aims to address. This makes it easier to design a study that is focused and relevant.
Summary. One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and ...
Let's chart the course to a successful research voyage, exploring the significance, types, and formulation of research paper objectives. Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives. ... Constructing these tracks involves defining two main types of objectives: general and specific. Each serves a unique purpose in guiding the ...
A research objective is defined as a clear and concise statement of the specific goals and aims of a research study. It outlines what the researcher intends to accomplish and what they hope to learn or discover through their research. Research objectives are crucial for guiding the research process and ensuring that the study stays focused and ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
The objectives provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, guiding the researcher in their data collection and analysis. Here are some tips on how to write effective research objective: 1. Be clear and specific. Research objective should be written in a clear and specific manner.
This step in your research journey is usually the first written method used to convey your research idea to your tutor. Therefore, aims and objectives should clearly convey your topic, academic foundation, and research design. In order to write effective research aims and objectives, researchers should consider all aspects of their proposed work.
There are typically three main types of objectives in a research paper: Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are focused on gaining a deeper understanding of a particular phenomenon, topic, or issue. Exploratory research objectives aim to explore and identify new ideas, insights, or patterns that were previously unknown or poorly understood.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
Research objectives are how researchers ensure that their study has direction and makes a significant contribution to growing an industry or niche. Research objectives provide a clear and concise statement of what the researcher wants to find out. As a researcher, you need to clearly outline and define research objectives to guide the research ...
Writing the Research Objectives: 5 Straightforward Examples. The research objective of a research proposal or scientific article defines the direction or content of a research investigation. Without the research objectives, the proposal or research paper is in disarray. It is like a fisherman riding on a boat without any purpose and with no ...
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish. They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research. Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Examples of Specific Research Objectives: 1. "To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.". 2. "To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).". 3.
Step 4: Organizing Research and the Writer's Ideas. When your research is complete, you will organize your findings and decide which sources to cite in your paper. You will also have an opportunity to evaluate the evidence you have collected and determine whether it supports your thesis, or the focus of your paper.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. ... The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above.
Answer: Research objectives describe concisely what the research is trying to achieve. They summarize the accomplishments a researcher wishes to achieve through the project and provides direction to the study. A research objective must be achievable, i.e., it must be framed keeping in mind the available time, infrastructure required for ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
A purpose statement clearly defines the objective of your qualitative or quantitative research. Learn how to create one through unique and real-world examples.
The main objective of research is to explore the unknown and unlock new possibilities. It's an essential component of success. Over the years, businesses have started emphasizing the need for research. You've probably noticed organizations hiring research managers and analysts. The primary purpose of business research is to determine the ...
The purpose of research can vary depending on the field of study, the research question, and the intended audience. In general, research can be used to: Generate new knowledge and theories. Test existing theories or hypotheses. Identify trends or patterns. Gather information for decision-making. Evaluate the effectiveness of programs, policies ...
Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion. "When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated," said Chartier.
The purpose of the study was to assess midwives' opinions on pregnant women's use of the well-known kaligutim (local oxytocin) for labour induction in the Tamale Metropolis. A facility-based, quantitative, cross-sectional research design was used for the study. ... A total of 214 working midwives from Tamale's three main public hospitals ...