Test: The Story of Village Palampur- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions - Class 9 MCQ
15 questions mcq test - test: the story of village palampur- assertion-reason & case based questions, directions: in the questions given below, there are two statements marked as assertion (a) and reason (r). read the statements and choose the correct option. assertion (a): the aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want. reason (r): there are four requirements for production of goods and services..
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is correct but R is wrong.
A is wrong but R is correct.
The aim of production is to produce goods and services to satisfy the needs of people as per their demand.
Four factors for production of goods and services are as follows :
Land and other natural resources such as water, forests, minerals etc.
Labour or Workers The workers provide necessary labour for production. They may be highly educated or illiterate persons (i.e. skilled and unskilled) who may do manual work.
Physical Capital It consists of various inputs which are required at different stages of production.


Directions: In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): HYV seeds promised to produce much greater amounts of grain on a single plant. Reason (R): Green revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivation of wheat and rice using high yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds.
The Green Revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivation of wheat and rice using high yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds.
Compared to the traditional seeds, the HYV seeds promised to produce much greater amounts of grain on a single plant.In Palampur, the yield of wheat grown from the traditional varieties was 1300 kg per hectare. With HYV seeds, the yield went up to 3200 kg per hectare.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Directions: In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Raw materials and money in hand are called working capital. Reason (R): Money is always required during production to make payments and buy other necessary items.
Production requires a variety of raw materials. It requires money to make payments and buy other necessary items. Raw materials and money in hand are called working capital. Production requires a variety of raw materials such as the yarn used by the weaver and the clay used by the potter. They are used up in a single act of production.
Directions: In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): Small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital.
Reason (R): They are put to great distress to repay the loan.
- i) Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village money lenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation.
ii) The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to great distress to repay the loan.
iii) In contrast to small farmers, the medium and large farmers have their own savings from farming. They are thus able to arrange for the capital.
Assertion (A): 75 percent of the people who are working are dependent on farming for their livelihood.
Reason (R): Farming is the main production activity in Palampur.
Farming activities: Farming is the main production activity in Palampur. About 75% of the people depend upon farming for their livelihood. They use methods of multiple farming and modern farming techniques for increase in their productivity. Well-developed irrigational facilities and use of HYV seeds has improved in production levels of agriculture in Palampur.
Read the text given below and answer the following questions:
Apart from farming activities in Palampur, certain non- farming activities are also carried out. Only 25 per cent of the people working in Palampur are engaged in activities other than agriculture. Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur. The milk is sold in Raiganj, the nearby large village. Two traders from Shahpur town have set up collection cum chilling centres at Raiganj from where the milk is transported to far away towns and cities.
People involved in trade (exchange of goods) are not many in Palampur. The traders of Palampur are shopkeepers who buy various goods from wholesale markets in the cities and sell them in the village. There are a variety of vehicles on the road connecting Palampur to Raiganj. Rickshaw Wallahs, tongawallah, jeep, tractor, truck drivers and people driving the traditional bullock cart and bogey are people in the transport services. They ferry people and goods from one place to another, and in return get paid for it. The number of people involved in transport has grown over the last several years.
Q. Manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and are done on a:
- A. Small scale
- B. Large scale
- C. Medium scale
- D. None of the above
Q. .............. is a common activity in many families of Palampur.
- A. Manufacturing
- B. Transport
- D. All of the above.
Q. ............... percent of the people working in Palampur are engaged in activities other than agriculture.
Shop-keepers buy goods from wholesalers in Shahpur and sell them in Palampur. Milk from the dairies in Palampur is transported daily to Raiganj. Some traders from Shahpur have set up collection centres and chilling plants at Raiganj, from where milk is supplied to other towns and cities.
Q. There are variety of vehicles on the road connecting Palampur to:
- C. Both (a) and (b)
(i) Rickshaw Wallahs, tongawallah, jeep, tractor, truck drivers and people driving the traditional bullock-cart and bogey are people in the transport services.
(ii) They ferry people and goods from one place to another, and in return get paid for it.
(iii) The number of people involved in transport has grown over the last several years.
Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur. This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper caste families own the majority of land in the village. Their houses, some of them quite large, are made of brick with cement plastering. The SCs (dalits) comprise one third of the population and live in one corner of the village and in much smaller houses some of which are of mud and straw. Most of the houses have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small business. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school. There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick are treated. The story of Palampur, an imaginary village, will take us through the different types of production activities in the village. In villages across India, farming is the main production activity. The other production activities, referred to as non- farm activities include small manufacturing, transport, shop-keeping, etc. Every production is organised by combining land, labour, physical capital and human capital, which are known as factors of production.
Q. Which of the following statement is true with respect to Palampur:
- A. Palampur has one primary school and two high schools.
- B. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school.
- C. Dairy is the main production activity.
- D. The village has about 600 families belonging to several different castes.
Q. The variety of inputs required at every stage during production is known as_________.
- A. Physical capital
- C. Human capital
Q. Raiganj, a big village, is __________ kms from Palampur.
Q. Raw materials and money in hand are called:
- A. Working capital
- B. Fixed capital
Farming is the main production activity in Palampur. 75 percent of the people who are working are dependent on farming for their livelihood. All land is cultivated in Palampur. No land is left idle. During the rainy season (kharif) farmers grow jowar and bajra. These plants are used as cattle feed. It is followed by cultivation of potatoes between October and December. In the winter season (rabi), fields are sown with wheat. The main reason why farmers are able to grow three different crops in a year in Palampur is due to the well-developed system of irrigation.
To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping. One way of increasing production from the same land is by multiple cropping. The other way is to use modern farming methods for higher yield. Yield is measured as crop produced on a given piece of land during a single season. Till the mid1960s, the seeds used in cultivation were traditional ones with relatively low yields. Traditional seeds needed less irrigation. Farmers used cow-dung and other natural manure as fertilizers. All these were readily available with the farmers who did not have to buy them.
The Green Revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivation of wheat and rice using high yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds. Farmers of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh were the first to try out the modern farming method in India. In Palampur, the yield of wheat grown from the traditional varieties was 1,300 kg per hectare. With HYV seeds, the yield went up to 3,200 kg per hectare. There was a large increase in the production of wheat. Farmers now had greater amounts of surplus wheat to sell in the markets.
Q. The Green revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivation of:
- A. Wheat and rice
- B. Wheat and jowar
- C. Rice and bajra
- D. Rice and jowar
Q. Which of the following statements is true with respect to traditional farming?
- A. Traditional seeds needed less irrigation.
- B. Farmers used cow-dung
- C. Farmers used other natural manure as fertilizers.
- D. All of the above
Top Courses for Class 9

Important Questions for The Story of Village Palampur- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions
The story of village palampur- assertion-reason & case based questions mcqs with answers, online tests for the story of village palampur- assertion-reason & case based questions.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science Economics
- Chapter 1 The Story Of Village Palampur

NCERT Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Questions and Answers - FREE PDF Download
Get a comprehensive study with Vedantu through the Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions. This resource provides access to The Story of Village Palampur - Class 9 PDF, elucidating fundamental principles for understanding the subject's intricacies. Enhance your learning experience with Class 9 Economics NCERT Solutions .

The story's purpose is to introduce some basic concepts relating to production, which we do through a story of a hypothetical village called Palampur. As you read the story of Palampur, you will learn how various resources combine to produce the desired goods and services in the village. Check out the revised class 9 social science syllabus and the NCERT Solutions, and start with Vedantu to embark on a journey of academic excellence.
Glance on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1- The Story of Village Palampur
NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 introduces the concept of an economy through the fictional village of Palampur, highlighting the various aspects of rural life and agricultural activities.
CBSE Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 introduces students to the organisation of production, land distribution, capital for farming, and other production activities through an exciting story of the village of Palampur.
Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 questions and answers PDF further tries to develop knowledge about various methods to produce more from the same piece of land.
This chapter introduces students to the village of Palampur and its various economic activities, including farming, non-farming activities, and modern technology.
Understand the factors of production, including land, labour, physical capital, and human capital.
Economics class 9, chapter 1, teaches about modern and traditional farming methods, crop patterns, and the importance of irrigation.
Explore various non-farming activities such as dairy, small-scale manufacturing, transport, and shop-keeping.
This Chapter helps students grasp the fundamentals of economics through a relatable and practical example, laying the foundation for more advanced economic studies.

Access NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
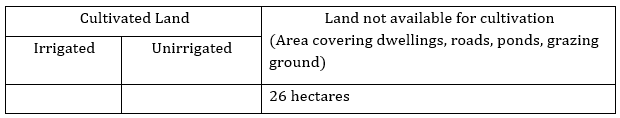
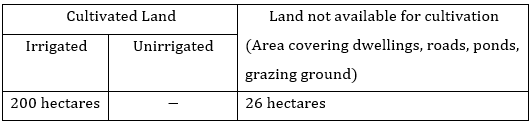
1. Every village in India is surveyed once in ten years during the Census and some of details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur.
(a) Location
Ans: Bulandshahr district, Western Uttar Pradesh
(b) Total Area of the Village
Ans: 226 hectares
(c) Land Use(in hectares)
Cultivated Land | Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing ground) | |
Irrigated | Unirrigated | |
200 hectares | - | 26 hectares |
(d) Facilities:
Educational |
Medical |
Market |
Electricity Supply |
Communication |
Nearest Town |
Educational: There are two primary schools and one high school in Palampur.
Medical: A primary health centre was run by the government, also there was a private dispensary to treat sick people.
Market: Raiganj and Shahpur
Communication: Well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. 3 kms from Palampur.
Electricity Supply: Most of the houses had electric connections and it was also used to run the tube wells in fields.
Nearest Town: Raiganj, because many roads are connected to the Raiganj and to Shahpur.
2. Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree?
Ans: Yes, modern farming methods make use of a greater number of industrial outputs as compared to traditional farming methods. Modern farming methods make use of high-yielding seeds. These seeds require pesticides and chemical fertilisers, equipment of agriculture which are manufactured in industries like tractors, and advanced irrigation facilities like electric tube wells in order to produce the best results.
3. How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
Ans: The spread of electricity has helped the farmers of Palampur:
Almost every household has an electric supply.
Electric supply was used for tube wells to run it in agricultural fields.
Electricity is also used in small business’s activities.
4. Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Ans: In India, nearly two-thirds of the people are dependent on farming. From that total cultivated area in the country, less than 40% is irrigated. In the other areas, farming is dependent on rainfall which is not regular. Modern farming methods are really difficult to apply in the presence of inadequate water supplies. India cannot achieve self- sufficiency in food grains until land is increased for the use of irrigation.
5. Construct a table on the distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
No. of Families of Palampur | Land in hectares |
150 Families | No land |
240 Families | Less than 2 hectares |
60 Families | More than 2 hectares |
Total: 450 Families |
6. Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages?
Ans: In Palampur farm workers used to get less wages than the minimum wages fixed by the government. The minimum wages for a farm labourer are fixed at Rs 115 per day, but the farm labourers only get Rs. 70 – 80, since there was heavy competition for work among the farm labourers.
7. In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid in cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
Ans: The labourers working at construction sites, get daily wages Rs. 600 per day. They are paid in cash, for regular work. They don’t have any debt.
8. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
Ans: The different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land are:
Multiple Cropping: The most common method of growing the production on a given piece of land. Here, more than one crop is grown on the same piece of land. Indian farmers grow at least more than two main crops in a year.
Modern Farming Methods: Modern farming consists of cultivable areas where HYV seeds and irrigation are used there. The use of simple wooden plough is replaced by tractors and fertilizers or pesticides are used.
9. Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land.
Ans: A farmer with one hectare of land is in the category of small farmer. Most of the work is done by the farmer and his family members. The farmer will use a pair of bullocks to plough the field. His family members will assist him in sowing the seeds. During harvest time, he may need a few labourers.
10. How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers?
Ans: By selling farm produce medium and large farmers usually produce surplus cash. Because they have land and a house, getting a loan from banks is very easy. Small farmers may not be able to get bank loans. They have to depend on the moneylender and local merchant for a loan.
11. On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tajpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Ans: Savita needed money for buying pesticides, seeds and fertilisers, and water for irrigation. She required money for the repairing of her farm instruments. Hence, she decided to borrow money from Tejpal Singh, who was a large farmer in her village. Tejpal Singh convinced to give the loan of Rs. 3000 at an interest rate of 24% for four months. He agreed with Savita to work on his field during the harvest season for Rs. 35 a day.
If Savita would have borrowed the loan from the bank, then her condition would have been better. Banks provide loans at low interest rates. Moreover, Savita should have devoted more time to her own field instead of working for Tejpal Singh as farm labourer.
12. Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years.
Ans: In the past 30 years, there were many changes in terms of irrigation and production methods. For irrigation, instead of canals, tube wells are being used for water supply. Many electric pumps replaced other old systems. Instead of bullocks, now tractors are being used for larger farms.
13. What are the non-farm production activities taking place in your region? Make a short list.
Ans: The non-farm production activities taking place in our region are:
General Stores
Transportation
14. What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
Ans: Three things that need to be done to encourage non-farm production activities in villages:
The government can bring new schemes to landless labourers and small farmers, who are able to get loans at cheaper rates to start small individual/community businesses.
From financial assistance, the government should set up rural workshops to enable the villagers to build on their skill levels.
The government needs to work towards improving the infrastructure of villages, this will help the rural parts of the country to get connected with urban parts.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
Economics Chapter 1 Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur Topics |
1. Organisation of Production |
2. Factors affecting production, such as |
3. Non-farming activities |
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science The Story Of Village Palampur Chapter 1
The NCERT solutions provide a detailed and clear explanation of the economic activities in a rural setting, helping students thoroughly understand the chapter's concepts.
Expert teachers in Economics have designed the story of the village Palampur NCERT Solutions PDF for easy comprehension.
The Economic Class 9 Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers are included here to assist students with their assignments.
Economics class 9 Chapter 1 solutions are a great resource for improving writing skills and preparing for school exams.
Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 questions and answers help students comprehend the factors of production, such as land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship, and how these elements contribute to the village's economy.
By breaking down complex topics such as factors of production, farming practices, and non-farming activities, these solutions ensure that students grasp and retain key economic principles.
The solutions help students apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios by using the fictional village of Palampur as a case study, making learning more relatable and engaging.
Economics class 9, chapter 1 offers well-structured answers to textbook questions, which are beneficial for exam preparation.
Along with the NCERT Solutions, you can learn more about this chapter through Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur Revision Notes .
Conclusion
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1, "The Story of Village Palampur," provides an invaluable resource for students to understand the basic economics concepts in a rural setting. These solutions offer detailed explanations of the various economic activities, including farming and non-farming practices, which help students grasp the factors of production and their applications. Students can rely on Vedantu's NCERT Solutions to enhance their knowledge, clarify doubts, and confidently prepare for exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics - Other Chapter-wise Links for FREE PDF
Dive into our FREE PDF links, which offer chapter-wise NCERT solutions prepared by Vedantu Experts to help you understand and master social concepts.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science (Economics) Chapter-wise List |
|
|
|
Related Important Links for Class 9 Economics
S. No | Important Links for Class 9 Economics |
1. |
|
2. |
|
3. |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
1. Did the Spread of Electricity Help the Farmers in Palampur in Their Agricultural Activities?
The flow of electric current in villages succumbed by darkness helped the farmers in Palampur extensively in their agricultural activities. It has bestowed power to the powerless farmers. Here is the list of benefits the farmers derived from the spread of electricity.
Powered tube wells efficiently irrigate extensive farmland. Earlier farmers found it difficult to water their large area of the agricultural field with the complex Persian wheel.
Electricity is pivotal in increasing production in villages.
Electricity in houses could provide a comfortable life for farmers.
Electricity facilitated small-scale industries in processing.
2. Farm Labourer’s Wages are Less than Minimum Wages. Explain.
Farmers put forth a lot of effort to develop crops, yet they are not adequately paid. Agricultural labourers are considered impoverished. Their daily minimum salary for working under severe conditions is Rs-60, far less than the mandated minimum wage. A large population is to blame for this. The hamlet of Palampur has more labourers but less job prospects. The intense rivalry among labourers for a single position drives down pay. As a result, farm labourers in Palampur village are willing to work for cheap rates.
3. What are the important topics discussed in Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics?
Following are the important topics discussed in Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics:
Organisation of production
Fixed capital and working capital
Factors of production
The types of farming in Palampur
Non-farming activities in Palampur
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 include answers to every question of the Class 9 NCERT Economics book in an easy way. These solutions will help the students to write answers in exams in an efficient manner.
4. Where can I get the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 PDF online?
By clicking on the download link, you can get the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 PDF for free from Vedantu's official website. The solutions are written by subject-matter specialists who construct the answers to achieve high exam scores. The solutions efficiently explain every topic of the Class 9 Economics syllabus so that students may readily comprehend them.
5. What is Economics according to class 9?
In CBSE Class 9, Economics is a branch of Social Science that is the fundamental step to understand how an economy functions. It is essential to refer to reliable study resources for your understanding and exam preparation. Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Economics Solutions are prepared by subject experts who follow the CBSE curriculum and provide every answer to the questions in the NCERT Economics book in a simple way.
6. What type of village is Palampur?
Palampur is a made-up town where farming is the primary source of revenue. The town is involved in activities such as dairy and transportation. The story emphasises fundamental agricultural and production concepts including crop production, capital, work, creation, and transportation. These concepts are presented properly in Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 so that students may understand them. Students may also access the resources using Vedantu's app. All resources are free to use.
7. What is the area of Palampur?
The total area of Palampur is 226 hectares. The hypothetical village is located in the Bulandshahar district of Uttar Pradesh. This chapter explains the different economic aspects of farming that provide the majority of occupation for people in India. You need to prefer reliable resources to study the chapter. Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Economics Solutions explain every concept comprehensively and efficiently for students to understand.
8. What is the theme of the story of village Palampur?
The theme of the story of village Palampur revolves around understanding the basics of production and economic activities in a rural Indian setting. It introduces concepts like:
Farming and crop cultivation
Land and labor
Capital and infrastructure
Production process
Market and exchange
9. What are the five features of village Palampur?
The five features of Village Palampur are:
Agriculture-based economy: Farming is the primary occupation in Palampur, with a majority of the population involved in cultivating crops and raising livestock.
Diverse occupations: While farming is dominant, other activities like dairy, small-scale manufacturing, and transport contribute to the village economy.
Social diversity: The story mentions Palampur has around 450 families belonging to different castes and creeds, reflecting a mix of social groups.
Developing infrastructure: The village has basic infrastructure like electricity, transportation (roads, bullock carts, tractors), a primary health center, and schools.
Market connectivity: Palampur is connected to nearby towns, suggesting it participates in buying and selling goods, essential for any economy.
10. What is the main focus of economics class 9, Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur?
The main focus of economics class 9, chapter 1 is to introduce students to the basic concepts of an economy through the example of a fictional village, Palampur. It covers various aspects of rural life and economic activities.
11. What key economic activities are discussed in the class 9 economics chapter 1 questions and answers?
Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 question answer discusses both farming and non-farming activities. Farming includes traditional and modern agricultural practices, while non-farming activities cover dairy, small-scale manufacturing, transport, and shop-keeping.
12. What are the factors of production explained in class 9th economics chapter 1 question answer?
The factors of production include land, labour, physical capital, and human capital, as discussed in class 9th economics chapter 1 question answer. These are essential inputs required to produce goods and services.
13. How does the class 9th Economics chapter 1 explain the concept of modern farming methods?
The story of village Palampur class 9 questions answers explains modern farming methods such as the use of HYV (High Yielding Variety) seeds, chemical fertilisers, and modern irrigation techniques, highlighting their impact on productivity and sustainability.
14. Why is it important to understand the rock cycle in the chapter The Story of Village Palampur class 9 questions answers?
The rock cycle is not directly relevant to the story of village palampur questions and answers, which focuses on economic activities in a rural setting. However, understanding the interdependence of natural resources and economic activities can provide a broader perspective.
15. How do the story of village palampur questions and answers help in exam preparation?
The NCERT solutions of the story of village palampur questions and answers provide clear and structured answers to textbook questions, making it easier for students to understand and revise key concepts. They are designed to help students prepare effectively for exams by offering concise explanations and relevant examples.
NCERT Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter wise Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 9 social science, cbse study materials.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Social Science
- The Story of Village Palampur
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
9th Class Social Science The Story of Village Palampur Question Bank
Done case based (mcqs) - the story of village palampur total questions - 20.

| Read the source and answer the following. |
| Tools, Machines, Buildings: Tools and machines range from very simple tools such as a fanciers plough to sophisticated machines such as generators, turbines, computers, etc. Tools, machines, buildings can be used in production over many years, and are called fixed capital. |
| Raw Materials and Money in Hand |
| Production requires a variety of raw materials such as the yarn used by the weaver and the clay used by the potter. Also, some money is always required during production to make payments and buy other necessary items. Raw materials and money in hand are called working capital. Unlike tools, machines and buildings, these are used up in production. |
| A small farmer has 2 hectares of land to cultivate wheat crop his land comes under which type of factor of production? |
A) Fixed capital done clear
B) Working capital done clear
C) Natural resource done clear
D) Human capital done clear
question_answer 2) For a sugarcane farmer the sugarcane seeds sown in the agricultural field is
C) Human capital done clear
D) All of the above done clear
question_answer 3) If a farmer wants to cultivate his field, then which kind of factors of production he may need?
A) Working capital done clear
B) Natural resources done clear
C) Fixed capital done clear
question_answer 4) If a manufacturer wants to establish his factory at a place what he would need to do so?
A) Labour done clear
B) Money and raw material done clear
C) Land done clear
| Read the source and answer the following. |
| We have learnt about farming as the main production activity in Palampur. We shall now take a look at some of the non-farm production activities. Only 25 per cent of the people working in Palampur are engaged in activities other than agriculture. |
| Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur. People feed their buffalos on various kinds of grass and the jowar and bajra that grows during the rainy season. The milk is sold in Raiganj, the nearby large village. Two traders from Shahpur town have set up collection cum chilling centres at Raiganj from where the milk is transported to far away towns and cities. |
| At present, less than fifty people are engaged in manufacturing in Palampur. Unlike the manufacturing that takes place in the big factories in the towns and cities, manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and are done on a small scale. They are carried out mostly at home or in the fields with the help of family labour. Rarely are labourers hired. |
| Why are most of the families engaged in farming activity in Palampur village? |
A) People have much area for agricultural activities. done clear
B) People have become well-off due to farming activities. done clear
C) Farming has become a passion for people. done clear
D) Other non-farm activities have not much developed. done clear
question_answer 6) Which of the following is an example of non-farm production activities?
A) Transportation done clear
B) Weaving done clear
C) Handicrafts done clear
question_answer 7) How dairy is dependent on farming in Palampur?
A) Dairy is a farming activity. done clear
B) Dairy is done by farmers. done clear
C) Buffaloes are fed on agricultural produce. done clear
D) Dairy gives more money to farmers. done clear
question_answer 8) Which of the following steps can be taken in order to increase manufacturing sector in Palampur?
A) Provide incentive to people who are engaged in manufacturing. done clear
B) Establish factories in Palampur. done clear
C) Provide skill training to people of Palampur. done clear
| Read the source and answer the following. |
| The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want. There are four requirements for production of goods and services. These are |
| The first requirement is land and other natural resources such as water, forests, minerals, etc. |
| The second requirement is labour i.e. people who will do the work. Some production activities require highly educated workers to perform the necessary tasks. Other activities require workers who can do manual work. Each worker is providing the labour necessary for production. |
| The third requirement is physical capital i.e. the variety of inputs required at every stage during production. There is a fourth requirement too. You will need knowledge and enterprise to be able to put together land, labour and physical capital and produce an output either to use yourself or to sell in the market. |
| This these days is called human capital. |
| There are four requirements which are needed always to produce ...... and........ |
A) land, labour done clear
B) inputs, knowledge done clear
C) goods, services done clear
D) goods, physical capital done clear
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | Land | 1. | Work |
| B. | Labour | 2. | Enterprise |
| C. | Physical capital | 3. | Inputs |
| D. | Human capital | 4. | Natural resources |
| A-3 | B-2 | C-4 | D-1 |
| A-1 | B-3 | C-2 | D-4 |
| A-2 | B-4 | C-1 | D-3 |
| A-4 | B-1 | C-3 | D-2 |
question_answer 11) An economic activity is always based on:
A) People/Labour done clear
B) Money done clear
D) All of these done clear
question_answer 12) Which of the following is not a physical capital that is required in agricultural practices?
A) Farm equipment done clear
B) Seeds done clear
C) Turbines done clear
D) Tractors done clear
| Read the source and answer the following. |
| Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to great distress to repay the loan. In contrast to the small farmers, the medium and large farmers have their own savings from farming. They are thus able to arrange for the capital needed. |
| Why small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital? |
A) To pay high rate of interest. done clear
B) Their savings are less. done clear
C) Farm inputs are high priced. done clear
D) To maintain good relations with moneylenders. done clear
question_answer 14) What could be the other source of credit for small farmers in a village?
A) Banks done clear
B) Cooperatives done clear
C) Self-help groups done clear
question_answer 15) Why medium and large farmers can arrange their capital whenever needed?
A) Their income from farming is high. done clear
B) They do not pay high interest rates. done clear
C) They can do savings. done clear
D) Both (a) and (c) done clear
question_answer 16) What role do medium and large farmers play in the market place?
A) They provide jobs to people. done clear
B) They donate to the market places. done clear
C) They sell their surplus crops in the market done clear
D) None of these done clear
| Read the source and answer the following. |
| Land being a natural resource, it is necessary to be careful in its use. Scientific reports indicate that the modern farming methods have overused the natural resource base. |
| In many areas, Green Revolution is associated with the loss of soil fertility due to increased use of chemical fertilisers. Also, continuous use of groundwater for tubewell irrigation has led to the depletion of the water table. |
| Environmental resources, like soil fertility and groundwater, are built up over years. Once destroyed it is very difficult to restore them. We must take care of the environment to ensure future development of agriculture. |
| Modern farming methods have increased the agricultural productivity. |
| These methods refer to |
A) farming on small piece of land. done clear
B) developed farms in urban areas. done clear
C) farms using only machines, no labour. done clear
D) use of HYV seeds, machines and fertilisers. done clear
question_answer 18) Green Revolution is associated with which of the following?
A) High productivity done clear
B) Reduction in soil fertility done clear
C) Environmental degradation done clear
question_answer 19) Which freshwater resource has been depleted due to over irrigation practice?
A) Rainwater done clear
B) Canals done clear
C) Groundwater done clear
D) Lakes done clear
question_answer 20) Being a farmers what measure would you use to conserve environmental resources?
A) Built rainwater harvesting system in order to minimise the load on groundwater resources. done clear
B) Less use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides to reduces land degradation. done clear
C) Use organic manure in order to increase soil fertility. done clear
Study Package

Case Based (MCQs) - The Story of Village Palampur
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 1 Class 9 Economics - The Story of Village Palampur
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
MCQ Questions - 1 Mark
Assertion reasoning, picture based questions (mcq), match the following, fill in the blanks (mcq), complete the table, correct and rewrite the sentences, ncert questions, past year questions - 2 marks, past year questions - 3 marks, past year questions - 5 marks, case based questions, hi, it looks like you're using adblock :(, please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur contain answers to the textbook exercise questions. The NCERT solutions are easy and accurate that helps with the questions asked in the examinations. These solutions cover all the questions of the chapter in detail. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 are prepared by our subject experts in very easy language. All our solutions are updated as per the latest CBSE Syllabus and Guidelines.
Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions
Let’s Discuss Page No. 3
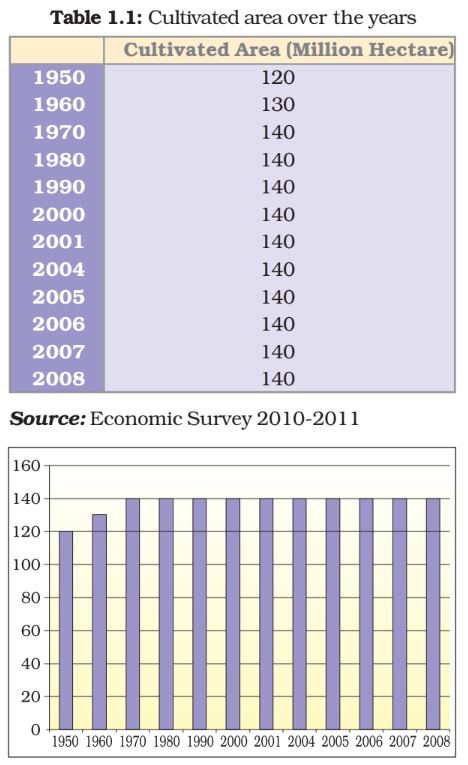
Question 1: The following Table 1.1 shows the land under cultivation in India in units of million hectares. Plot this on the graph provided. What does the graph show? Discuss in class.
Table 1.1: Cultivated area over the years
| 1950-51 | 129 |
| 1990-91 | 157 |
| 2000-01 | 156 |
| 2010-11 | 156 |
| 2011-12 | 156 |
| 2012-13 | 155 |
| 2013-14 | 156 |
| 2014-15 | 155 |
Answer: The above graph shows the land under cultivation in India in units of million hectares.
The graph shows that the land under cultivation in India was 120 million hectares in 1950 which rose to 140 million hectares in 1970 and remained constant at 140 million hectares till 2000.
Question 2: Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Answer: Yes, it is important to increase the land area under irrigation firstly so that the farmers can do multiple cropping and grow more than one crop in a year and increase their production and earning. Secondly, use of HYV seeds need of plenty of water to give best results.
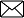
Question 3: You have read about the crops grown in Palampur. Fill the following table based on information on the crops grown in your region
Let’s Discuss Page No. 5
Question 1: What is the difference between multiple cropping and modern farming method?
Answer: Multiple Cropping To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land Modern Farming Method The farmers of Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh use HYV seeds, tube wells for irrigation, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as machinery like tractors and threshers to increase production. All these measures comprise what are known as modem farming methods
Question 2: The following table shows the production of wheat and pulses in India after the Green Revolution in units of million tonnes. Plot this on a graph. Was the Green Revolution equally successful for both the crops? Discuss.
| 1965 – 66 | 10 | 10 |
| 1970 – 71 | 12 | 24 |
| 1980 – 81 | 11 | 36 |
| 1990 – 91 | 14 | 55 |
| 2000 – 01 | 11 | 70 |
| 2010 – 11 | 18 | 87 |
| 2012 – 13 | 18 | 94 |
| 2013 – 14 | 19 | 96 |
| 2014 – 15 | 17 | 87 |
| 2015 – 16 | 17 | 94 |
| 2016 – 17 | 23 | 99 |
| 2017 – 18 | 24 | 97 |
Answer: Between 1965 and 2001, the production of pulses has increased negligibly whereas the production of wheat increased greatly. Thus, we can say that the Green Revolution was more successful in increasing the production of wheat as compared to pulses.
Question 3: What is the working capital required by the farmer using modern farming methods?
Answer: The working capital required by the farmer using modern farming methods are raw material and money. Money is always required during production to make payments and buy other necessary items.
Question 4: Modern farming methods require the farmer to start with more cash than before. Why?
Answer: Modern farming methods require the use of HYV seeds which needs chemical fertilizers and pesticides to produce best results and increased production. However, for buying all these inputs a lot of money is needed so a farmer needs to have more cash to start farming.
Let’s Discuss Page No. 7
Question 1: In the Picture 1.5, can you shade the land cultivated by the small farmers?

Answer: The shaded rectangles with boundaries show the land cultivated by small farmers. Question 2: Why do so many families of farmers cultivate such small plots of land?
Answer: Land in Palampur is fixed and 75% of the people who are working are dependent on farming for their livelihood. Since land is fixed and maximum people are dependent on land they are forced to cultivate small plots of land.
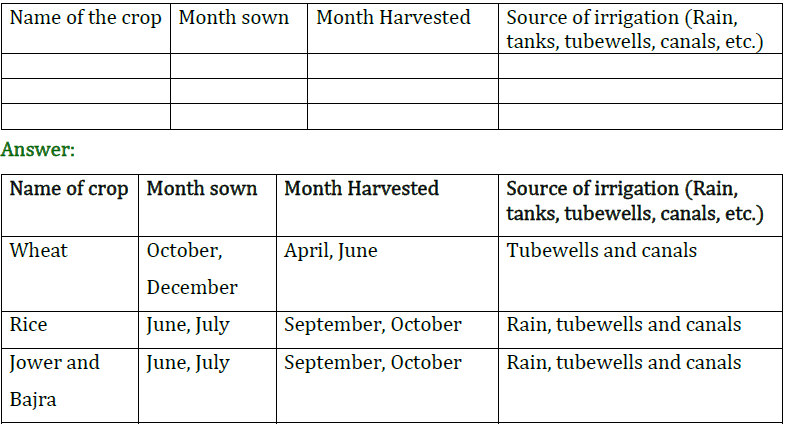
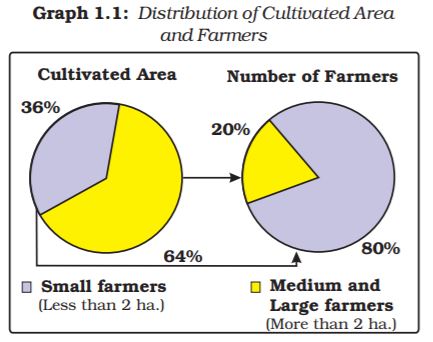
Question 3: The distribution of farmers in India and the amount of land they cultivate is given in the following Graph Discuss in the classroom.
Answer: Yes, I agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in Palampur because out of the 450 families, 150 families are landless, 240 families cultivate small plots of land less than 2 hectares in size whereas 60 medium and large farmers cultivate more than 2 hectares of land, a few of them have land extending over 10 hectares or more, which shows that medium and large farmers have more land though they are numerically Smaller. This clearly shows the inequality in the distribution of cultivated land. According to the graph, a similar situation exists for India also which means that 80% of the small farmers cultivate only 36% of the cultivated area whereas 20% of the big farmers cultivate 64% of the cultivated area
Question 4: Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in Palampur? Do you find a similar situation for India? Explain.
Answer: Do it yourself.
Question 5: Identify the work being done on the field in the Pictures 1.6 and arrange them in a proper sequence.

Answer: The proper sequence of the activities is given below (the numbers are marked alongside each picture). (1) Plowing by bullocks (2) Sowing (3) Spraying of insecticides (4) Cultivation by traditional methods (5) Cultivation by modern methods (6) Cutting of crops
Let’s Discuss Page No. 9
Question 1: Why are farm labourers like Dala and Ramkali poor?
Answer: (a) Dala and Ramkali are landless farm labourers who work on daily wages in Palampur. (b) Though, minimum wages for farm labourers set by the government is 60 per day, they get only 35-40 (c) There is heavy competition for work among the farm labourers in Palampur, so people agree to work for low wages. (d) They remain out of work for most parts of the year and have to take loans from the moneylender to fulèll their needs. Due to this seasonal unemployment, they remain poor and are unable to repay the loan and fall into a debt trap.
Question 2: Gosaipur and Majauli are two villages in North Bihar. Out of a total of 850 households in the two villages, there are more than 250 men who are employed in rural Punjab and Haryana or in Delhi, Mumbai, Surat, Hyderabad or Nagpur. Such migration is common in most villages across India. Why do people migrate? Can you describe (based on your imagination) the work that the migrants of Gosaipur and Majauli might do at the place of destination?
Answer: Mostly people migrate in search of employment or better job Opportunities to the cities like Mumbai, Delhi etc or to the prosperous agricultural regions like Punjab and Haryana to work as farm labourers. (a) This migration usually takes place when a person is unemployed or in extreme poverty, which may be due to lack of land, displacements, negative impact of natural disasters like drought or floods, etc. (b) The migrants from Gosaipur and Majauli who went to cities will probably find work as casual labourers, industrial workers, street hawkers, rickshaw pullers, headload workers or as servants in homes and hotels, etc (c) Those who went to rural areas of Punjab and Haryana will probably work as farm labourers since agriculture is the main occupation of the rural people in these states.
Let’s Discuss Page No. 11
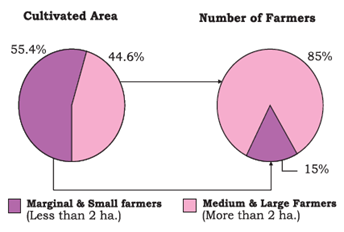
Question 1: Let us take three farmers. Each has grown wheat on his èeld though the production is different (see Column 2). The consumption of wheat by each farmer family is the same (Column 3). Me whole of surplus wheat this year is used as capital for next year’s production. Also suppose, production is twice the capital used in production. Complete the tables.
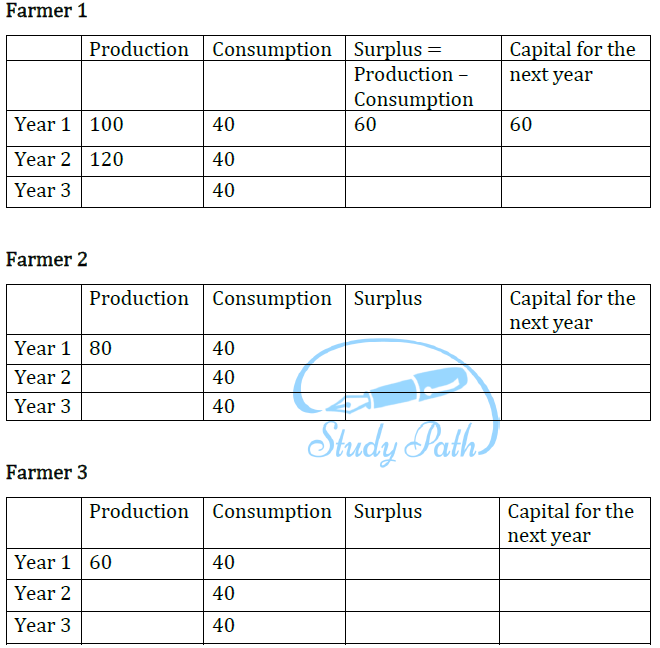
Question 2: Compare the Production of wheat by the three farmers over the years.
| Farmer 1 | Farmer 2 | Farmer 3 | |
| Year 1 | 100 | 80 | 60 |
| Year 2 | 120 | 80 | 40 |
| Year 3 | 160 | 80 | 0 |
• The production of wheat of the first farmer increased from 100 to 16CL • The production of wheat of the second farmer was constant at 8CL • The production of wheat of the third farmer declined from 60 to 0
Question 3: What happens to Farmer 3 in Year 3? Can he continue production? What will he have to do to continue production?
Answer: In the third year, the third farmer did not produce any wheat and had to buy it from the market. He cannot continue production any longer unless he arranges capital, as he has no surplus to invest as capital.
Let’s Discuss Page No. 12
Question 1: What capital did Mishrilal need to set up his jaggery manufacturing unit?
Answer: To set up his manufacturing unit Mishrilal needed the following capital (a) Fixed Capital in the form of the sugarcane crushing machine. Working Capital in the form of money for buying sugarcane from other farmers for crushing and for paying the electricity bill of running the (b) crushing machine.
Question 2: Who provides the labour in this case?
Answer: The labour is provided by him and his family. Otherwise he will employ landless labourers
Question 3: Can you guess why Mishrilal is unable to increase his profit?
Answer: (a) Mishrilal has set up a small scale unit. (b) The farm holdings in the village are very small of about 2 hectares in size and production of sugarcane is low as more area is under wheat, so raw material is also less (c) He has to pay for the electricity to run the machine. (d) Since the industry is small scale, production is less and therefore, he is unable to increase his profit.
Question 4: Could you think of any reasons when he might face a loss?
Answer: Conditions under which he may face a toss can be any of the following
(a) If his crushing machine becomes defective, his production will reduce or totally stop.
(b) If due to drought or other calamity, the production of sugarcane in nearby areas reduces; his jaggery production will come down leading to a loss for him.
(c) If the demand for jaggery decreases, ne will not be able to sell enough to break even.
(d) If any other costs like electricity, labour or transportation costs increase, he may face a loss.
Question 5: Why does Mishrilal sell his jaggery to traders in Shahpur and not in his village?
Answer: (a) Palampur is a small village with 450 families and there is not a big demand for jaggery there.
(b) Shahpur is a town where people come from different surrounding villages to buy things and there is more demand of jaggery there, so Mishrilal sells his jaggery traders in Shahpur and not in his village.
Question 1: In what ways is Kareem’s capital and labour different from Mishrilal?
Answer: 80th have fixed capital in the form of machines, but Kareem has a larger fixed capital because he has assets in the form of computers which are more expensive than the sugarcane crushing machine. Kareem has also employed educated and qualified computer teachers, whereas Mishrilal labour is mainly unskilled labour Question 2: Why didn’t someone start a computer centre earlier? Discuss the possible reasons
Answer: Reasons why someone didn’t start a computer centre may be any of the following (a) As very few educated people were there in the village, there was not any demand for computer courses. (b) The villagers were not aware of the employment potential of computer courses and so nobody thought that such a business could be successful. (c) Teaching faculty for computer courses was not available
Let’s Discuss Page No. 13
Question 1: What is Kishora’s fixed capital?
Answer: Kishora’s fixed capital is the buffalo and wooden-cart which he has purchased with the bank loathe Question 2: What do you think would be his working capital?
Answer: The money that he earns from selling the milk and transporting goods an his bullock-cart minus his own living expenses are his working capital.
Question 3: In how many production activities is Kishora involved?
Answer: Kishora is involved in the following production activities. (a) Selling of buffalo’s milk. (b) Transporting of various items. (c) Bringing clay from the river Ganga for the potter (d) Transporting jaggery etc to Shahpur. Question 4: Would you say that Kishora has benefitted from better roads in Palampur?
Answer: Kishora has certainly benefitted from better roads in Palampur because he is involved in the transport business; better roads enable him to easily transport goods from one place to another, run his business successfully and earn profits, which would have been very difficult in the absence of proper roads.
Questions 1: Every village in India is surveyed once in ten years during the Census and some of details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur.
(a) LOCATION:
(b) TOTAL AREA OF THE VILLAGE:
(c) LAND USE (in hectares):
(d) FACILITIES:
| Educational | |
| Medical | |
| Market | |
| Electricity Supply | |
| Communication | |
| Nearest Town |
(a) LOCATION: Bulandshahar district, Western Uttar Pradesh
(b) TOTAL AREA OF THE VILLAGE: 226 hectares
| Educational | 2 primary schools and 1 high school |
| Medical | 1 primary health centre and 1 private dispensary |
| Market | Raiganj and Shahpur |
| Electricity Supply | Most of the houses have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small businesses. |
| Communication | Well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. 3 kms from Raiganj. All-weather road connects it to Raiganj and further on toShahpur. Many kinds of transport like bullock carts,tongas, bogeys, motorcycles, jeeps, tractors and trucks are present. |
| Nearest Town | Shahpur |
Question 2: Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree?
Answer: Modern farming methods involve the use of high-yielding variety seeds. These seeds require a combination of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, agricultural implements like tractors, and proper irrigation facilities like electric tube wells to produce the best results. All these elements are manufactured in industries. Hence, it would be right to say that modern farming methods make use of a greater number of industrial outputs as compared to traditional farming methods.
Question 3: How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
Answer: The spread of electricity has helped the farmers of Palampur village in the following ways:
- Most of the houses have electric connections.
- Electricity is used to run tubewells in the fields.
- Electricity is used in various types of small business.
Question 4: Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Answer: India is an agricultural country. Of the total cultivated area in the country a little less than 40 per cent is irrigated even today. In the remaining areas, farming is largely dependent on rainfall. In India, rainfall is not regular and irrigation is important to get better crop yield and hence it is important to increase the area under irrigation.
Question 5: Construct a table on the distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
Answer: Number of families Land (hectare)
| Number of families | Land (hectare) |
| 150 | 0 |
| 240 | Less than 2 |
| 60 | More than 2 |
Question 6: Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages?
Answer: Farm workers at Palampur village get lower wages than the minimum wages fixed by the government. The minimum wages for a farm labourer is fixed at Rs 115 per day. But farm labourers get only Rs. 70 – 80. This happens because of heavy competition for work among the farm labourers at Palampur village.
Question 7: In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid in cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
Answer: Do it yourself.
Question 8: What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
Answer: The different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land are:
- Multiple Cropping: It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land. Under it, more than one crop is grown on the same piece of land during the year. Indian farmers should grow at least two main crops in a year. In India, some farmers are growing a third crop also over the past 20 years.
- Modern Farming Methods: Production on the same piece of land can also be increased by adopting modern farming methods. The Green Revolution in India is a remarkable example of it. Under modern farming, more cultivable areas should be brought under HYV seeds and irrigation. The use of simple wooden plough must be replaced by tractors. The increasing use of farm machinery like tractors, threshers, harvesters, etc. make cultivation faster.
Question 9: Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land.
Answer: A farmer with 1 hectare of land shall put under the category of small farmer. Most of the work would be done by the farmer and his family members. The farmer will normally use a pair of bullocks to plough the field. His family members would assist him in sowing the seeds. During harvest time, he may require to hire some labourers.
Question 10: How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers?
Answer: Medium and large farmers usually have surplus cash by selling their farm produce. Since they have land and house, they easily get loan from banks. Small farmers, on the other hand, may not be able to get bank loans. They have to depend on the local merchant and moneylender for loan.
Question 11: On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tajpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Answer: Savita required money for buying seeds, fertilisers and pesticides, and water for irrigation. She also needed money for repairing her farm instruments. So, she decided to borrow money from Tejpal Singh, a large farmer in her village. Tejpal Singh agreed to give the loan of Rs. 3000 at an interest rate of 24 per cent for four months. He also got her to agree to work on his field during the harvest season for Rs. 35 a day.
Savita’s condition would have been better if she could get a loan from the bank. The bank would have provided her the loan at a low rate of interest. Moreover, Savita could have devoted more time on her own field instead of working for Tejpal Singh as farm labourer.
Question 12: Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years. (Optional)
Answer: Attempt this question on your own.
Question 13: What are the non-farm production activities taking place in your region? Make a short list.
Answer: Cycle repair shop, carpenter, ironsmith, general store, tea stall, stationary shop, computer training institute, etc.
Question 14: What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
Answer: The government should improve electricity supply in the villages. It should open more schools so that children can grow to become educated adults. Moreover, government can also provide vocational training to the rural youths. These activities would help in increasing non-farm production activities in a village.
Three things that need to be done to encourage non-farm production activities in villages:
- The government should set up schemes whereby landless labourers and small farmers are able to get cheap loans to start small individual/community businesses.
- In addition to financial assistance, the government should set up rural workshops to enable the villagers to build on their skill levels.
- The government should also work towards improving the infrastructure of villages so that the rural parts of the country are well connected to the urban areas.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
Class Notes
Free Class Notes & Study Material
Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of the village Palampur
Last Updated on July 3, 2023 By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
NCERT Solutions for Economics , Chapter 1 – The Story of the village Palampur
☛ Notes and Study Material – Chapter 1 The story of Village Palampur
Intext Questions
Question 1. The following table 1.1 shows that the land under cultivation in India in units of million hectares. Plot this on the graph provided.
(i) What does the graph show?
(ii) Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
(iii) You have read about the crops grown in Palampur. Fill the following table based on the information on the crops grown in your region.
(i) The above graph shows the land under cultivation in India in units of million hectares.
The graph shows that the land under cultivation in India was 120 million hectares in 1950 which rose to 140 million hectares in 1970 and remained constant at 140 million hectares till 2000.
(ii) Yes, it is important to increase the land area under irrigation firstly so that the farmers can do multiple cropping and grow more than one crops in a year and increase their production and earning. Secondly, use of HYV seeds need of plenty of water to give best results.
| Wheat | October, December | April, July | Tubewells and canals |
| Rice | June, July | September, October | Rain, canals and tubewells |
| Jower and Bajra | June, July | September, October | Rain, canals and tubewells |
Question 1. What is the difference between multiple cropping and modern farming method?
Answer Multiple Cropping To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping. It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land.
Modern Farming Method The farmers of Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh use HYV seeds, tube wells for irrigation, chemical fertilisers and pesticides, as well as machinery like tractors and threshers to increase production. All these measures comprise what are known as modern farming methods.
Question 2. The following table shows the production of wheat and pulses in India after the Green Revolution in units of million tonnes. Plot this on a graph. Was the Green Revolution equally successful for both the crops? Discuss.
| 1965-66 | 10 | 10 |
| 1970-71 | 12 | 24 |
| 1980-81 | 11 | 36 |
| 1990-91 | 14 | 55 |
| 2000-01 | 11 | 70 |
Answer Between 1965 and 2001, the production of pulses has increased negligibly whereas the production of wheat increased greatly.
Thus, we can say that the Green Revolution was more successful in increasing the production of wheat as compared to pulses.
Question 3. What is the working capital required by the farmer using modern farming methods?
Answer The working capital required by the farmer using modern farming methods are raw material and money. Money is always required during production to make payments and buy other necessary items.
Question 4. Modern farming methods require the farmers to start with more cash than before. Why?
Answer Modern farming methods require the use of HYV seeds which needs chemical fertilisers and pesticides to produce best results and increased production. However, for buying all these inputs a lot of money is needed so a farmer needs to have more cash to start farming.
Question 1. In the picture 1.5 can you shade the land cultivated by the small farmers?
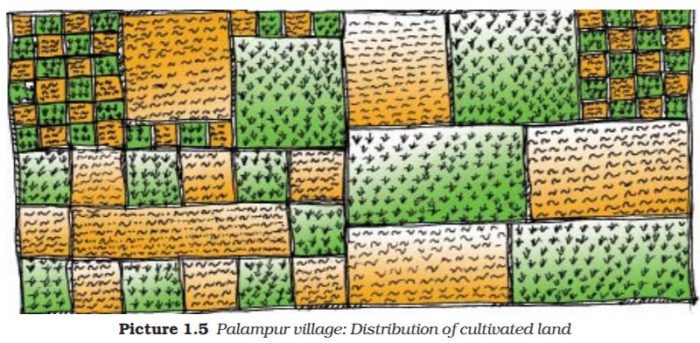
Answer The shaded rectangles with boundaries show the land cultivated by small farmers.
Question 2. Why do so many families of farmers cultivate such small plots of land?
Answer Land in Palampur is fixed and 75% of the people who are working are dependent on farming for their livelihood. Since land is fixed and maximum people are dependent on land they are forced to cultivate small plots of land.
Question 3. The distribution of farmers in India and the amount of land their cultivate is given in the following graph 1.1.
Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in Palampur? Do you find a similar situation for India? Explain.
Answer Yes, I agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in Palampur because out of the 450 families, 150 families are landless, 240 families cultivate small plots of land less than 2 hectares in size whereas 60 medium and large farmers cultivate more than 2 hectares of land, a few of them have land extending over 10 hectares or more, which shows that medium and large farmers have more land though they are numerically smaller. This clearly shows the inequality in the distribution of cultivated land.
According to the graph, a similar situation exits for India also which means that 80% of the small farmers cultivate only 36% of the cultivated area whereas 20% of the big farmers cultivate 64% of the cultivated area which again shows that there is inequality in the distribution of cultivated area in the case of India also as was in Palampur.
Question 4. Identify the work being done on the field in the picture 1.6 and arrange them in proper sequence.
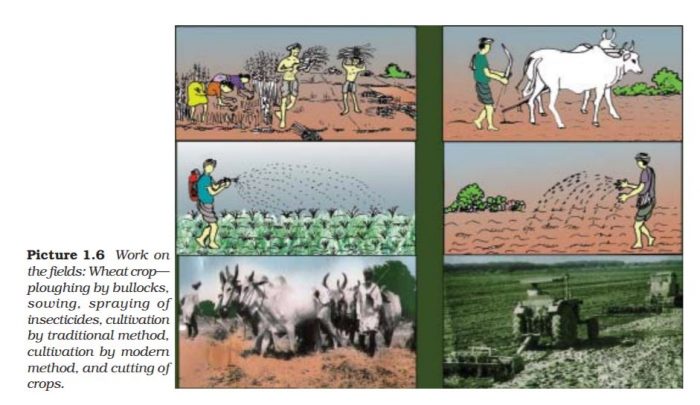
Answer The proper sequence of the activities is given below (the numbers are marked alongside each picture).
1) Plowing by bullocks
3) Spraying of insecticides
4) Cultivation by traditional methods
5) Cultivation by modern methods
6) Cutting of crops
Question 1. Why are farm labourers like Dala and Ramkali poor?
(a) Dala and Ramkali are landless farm labourers who work on daily wages in Palampur.
(b) Though, minimum wages for farm labourers set by the government is Rs 60 per day, they get only Rs 35-40.
(c) There is heavy competition for work among the farm labourers in Palampur, so people agree to work for low wages.
(d) They remain out of work for most parts of the year and have to take loans from the moneylender to fulfill their needs. Due to this seasonal unemployment, they remain poor and are unable to repay the loan and fall into a debt trap.
Question 2. Gosaipur and Majauli are two villages in North Bihar. Out of the 850 households in the two villages there are more than 250 men who are employed in rural Punjab and Haryana or in Delhi, Mumbai, Surat, Nagpur etc.
Why do people migrate? Can you describe based on your imagination the work the migrants of Gosaipur and Majauli might do at the place of destination.
Answer Mostly people migrate in search of employment or better job opportunities to the cities like Mumbai, Delhi etc or to the prosperous agricultural regions-hike Punjab and Haryana to work as farm labourers.
(a) This migration usually takes place when a person is unemployed or in extreme poverty, which may be due to lack of land, displacement, negative impact of natural disasters like drought or floods, etc.
(b) The migrants from Gosaipur and Majauli who went to cities will probably find work as casual labourers, industrial workers, street hawkers, rickshaw pullers, headload workers or as servants in homes and hotels, etc.
(c) Those who went to rural areas of Punjab and Haryana will probably work as farm labourers since agriculture is the main occupation of the rural people in these states.
Question 3. Let us fill in the blanks given below.
Among the three factors of production, we found that labour is the most abundant factor of production. There are many people who are willing to work as farm labourers in the villages, whereas the opportunities of work are limited. They belong to either landless families or life.
In contrast to labour,_________ is a scarce factor of production. Cultivated land area is _____ . Moreover, even the existing land is distributed ______(equally/unequally) among the people engaged in farming. There are a large number of small farmers who cultivate small plots of land and live in conditions not much better than the landless farm labourer. To make the maximum use of the existing land, farmers use ____ and ____.Both these have led to increase in production of crops.
Modern farming methods require a great deal of _____.Small farmers usually need to borrow money to arrange for the capital, and are put to great distress to repay the loan. Therefore, capital too is a scarce factor of production, particularly for the small farmers.
Though both land and capital are scarce, there is a basic difference between the two factors of production.
______ is a natural resource, whereas ________ is man-made.
It is possible to increase capital, whereas land is fixed. Therefore, it is very important that we take good care of land and other natural resources used in farming.
Answer The blanks should be filled up with the following words in succession
small farmers, land, fixed, unequally, chemical fertilizers and pesticides, multiple cropping technique, capital, Land, capital.
Question 1. Let us take 3 farmers. Each has grown wheat on his field though the production is different (see column 2). The consumption of wheat by each family is the same (column 3). The whole of surplus wheat this year is used as capital for next years production. Also suppose, production is twice the capital used in production.
(i) Complete the tables.
| Year 1 | 100 | 40 | 60 | 60 |
| Year 2 | 120 | 40 | ||
| Year 3 | 40 |
| Year 1 | 80 | 40 | ||
| Year 2 | 40 | |||
| Year 3 | 40 |
| Year 1 | 60 | 40 | ||
| Year 2 | 40 | |||
| Year 3 | 40 |
(ii) Compare the production of wheat by the three farmers over the years.
(iii) What happens to farmer 3 in year 3? Can he continue production? What will he have to do to continue production.
Answer (i)
| Year 1 | 100 | 40 | 60 | 60 |
| Year 2 | 120 | 40 | 80 | 80 |
| Year 3 | 160 | 40 | 120 | 120 |
| Year 1 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Year 2 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Year 3 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Year 1 | 60 | 40 | 20 | 20 |
| Year 2 | 40 | 40 | 00 | 00 |
| Year 3 | 00 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
(ii) Comparison of wheat production of the 3 farmers over the year was as follows
| Year 1 | 100 | 80 | 60 |
| Year 2 | 120 | 80 | 40 |
| Year 3 | 160 | 80 | 00 |
The production of wheat of the first farmer increased from 100 to 160.
The production of wheat of the second farmer was constant at 80.
The production of wheat of the third farmer declined from 60 to 00.
(iii) In the third year, the third farmer did not produce any wheat and had to buy it from the market. He cannot continue production any longer unless he arranges capital, as he has no surplus to invest as capital.
Question 1. Mishrilal has purchased a mechanical crushing machine run on electricity and has set up on his field. Sugarcane crushing was earlier done with the help of bullock, but people prefer to do it by machines these days. Mishrilal also buys sugarcane from other farmers and processes it into jaggery. The jaggery is then sold to traders as Shahpur. In this process, Mishrilal makes a small profit.
(i) What capital did Mishrilal need to set up his jaggery sugarcane manufacturing unit?
Answer To set up his manufacturing unit Mishrilal needed the following capital
(a) Fixed Capital in the form of the sugarcane crushing machine.
(b) Working Capital in the form of money for buying sugarcane from other farmers for crushing and for paying the electricity bill of running the crushing machine.
(ii) Who provides the labour in this case?
Answer The labour is provided by him and his family. Otherwise he will employ landless labourers.
(iii) Can you guess why Mishrilal is unable to increase his profit?
(a) Mishrilal has set up a small scale unit.
(b) The farm holdings in the village are very small of about 2 hectares in size and production of sugarcane is low as more area is under wheat, so raw material is also less.
(c) He has to pay for the electricity to run the machine.
(d) Since the industry is small scale, production is less and therefore, he is unable to increase his profit.
(iv) Could you think of any reasons when he might face a loss?
Answer Conditions under which he may face a loss can be any of the following
(a) If his crushing machine becomes defective, his production will reduce or totally stop.
(b) If due to drought or other calamity, the production of sugarcane nearby areas reduces, his jaggery production will come do leading to a loss for him.
(c) It the demand for jaggery decreases, he will not be able to sell enough to break even.
(d) It any other costs like electricity, labour or transportation costs increase, he may face a loss.
(v) Why does Mishrilal sells his jaggery to traders in Shahpur and not in his village?
(a) Palampur is a small village with 450 families and there is not a big demand for jaggery there.
(b) Shahpur is a town where people come from different surrounding villages to buy things and there is more demand of jaggery there, so Mishrilal sells his jaggery to traders in Shahpur and not in his village.
Question 2. Kareem has opened a computer class centre in the village. In recent years, a large number of students have been attending college in Shahpur town. Kareem found that a number students from the village are also attending computer classes in the town. There were two women in the village who had a degree in computer applications. He decided to employ them. He bought computers and set up the classes in the front room of their house overlooking the market. High school students have started attending them in good numbers.
(i) In what way is Kareem’s capital and labour different from Mishrilal?
Answer Both have fixed capital in the form of machines, but Kareem has a larger fixed capital because he has assets in the form of computers which are more expensive then the sugarcane crushing machine. Kareem has also employed educated and qualified computer teachers, whereas Mishrilal’s labour is mainly unskilled labour.
(ii) Why didn’t someone start a computer centre earlier? Discuss the possible reasons.
Answer Reasons why someone didn’t start a computer centre may be any of the following
(a) As very few educated people were there in the village, there was not any demand for computer courses.
(b) The villagers were not aware of the employment potential of computer courses and so nobody thought that such a business could be successful.
(c) Teaching faculty for computer courses was not available in the village earlier.
Question 3. Kishora is a farm labourer. Like other such labourers, Kishora found it difficult to meet his family’s needs from the wages he received. A few years back Kishora took a loan from the bank was under a government programme which was giving cheap loans to the poor landless households. Kishora bought a buffalo with this money. He now sells the buffalo’s milk.
Further he has attached a wooden cart to his buffalo and uses it to transport various items. Once a week he goes to the river Ganga to bring back clay for the potter. 0r sometimes he goes to Shahpur with a load of jaggery or other commodities. Every month he gets some work in transport. As a result, Kishora is able to earn more than what he used to do some years back.
(i) What is Kishora’s fixed capital?
Answer Kishora’s fixed capital is the buffalo and wooden-cart which he has purchased with the bank loan.
(ii) What do you think would be his working capital?
Answer The money that he earns from selling the milk and transporting goods on his bullock-cart minus his own living expenses are his working capital.
(iii) In how many production activities is Kishora involved?
Answer Kishora is involved in the following production activities.
(a) Selling of buffalo’s milk.
(b) Transporting of various items.
(c) Bringing clay from the fiver Ganga for the potter.
(d) Transporting jaggery etc to Shahpur.
(iv) Would you say that Kishora has benefited from better roads in Palampur?
Answer Kishora has certainly benefited from better roads in Palampur because he is involved in the transport business; better roads enable him to easily transport goods from one place to another, run his business successfully and earn profits, which would have been very difficult in the absence of proper roads.
Exercises Page 14
Question 1. Every village in India is surveyed once in ten years during the census and some of the details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur.
(a) LOCATION
(c) LAND USE (in hectares)
(b) TOTAL AREA OF THE VILLAGE
| Cultivated Land | Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing, ground) | |
| Irrigated | Unirrigated | |
| 26 hectares | ||
(d) FACILITIES
| Educational | |
| Medical | |
| Market | |
| Electricity supply | |
| Communication | |
| Nearest town |
(a) Location Palampur is located 3 km from Raiganj which is a big village. The nearest town is Shahpur.
a) It is well connected with neighbouring villages and towns.
b) An all weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further to the nearest small town of Shahpur.
(b) Total Area of the Village
The total area of the Palampur village is 246 hectares.
(c) Land Use (in hectares)
| Cultivated Land | Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing, ground) | |
| Irrigated | Unirrigated | |
| 200 hectares | 20 hectares | 26 hectares |
(d) Facilities
| Educational | Palampur has two primary schools and one high school |
| Medical | There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary |
| Market | Market has some general stores and shops selling eatables |
| Electricity supply | Most of the houses have electric connections. It powers the tube wells and is used in various small businesses |
| Communication | A well developed system of roads and transport |
| Nearest town | Shahpur |
Question 2. Modern farming methods require more input which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree?
Answer Yes, it is true that modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industry. For example
(i) HYV seeds, insecticides, pesticides and chemical fertilisers needed for increasing the yield per hectare are all manufactured in industries
(ii) Farmers use farm machinery like tractors, threshers and also combined harvestors which are also manufactured in industries
(iii) Tubewell equipment and water pumps used for irrigation are also manufactured in industries.
Question 3. How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
(i) Most of the houses in Palampur have electric connections.
(ii) Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields that help to irrigate much larger areas of land more effectively as compared to the traditional Persian wheel drawn by bullocks. Since the entire cultivated area of 200 hectares had come under irrigation farmers did not have to depend on ‘rainfall and could grow multiple crops.
(iii) It helps small businesses run their machinery like Mishrilal’s sugarcane crushing machine.
Question 4. Is it important to increase the area under irrigation ? why?
Answer Yes, it is important to increase the area under irrigation because water is very essential for agriculture. In India, the rainfall is unevenly distributed in the country and if rainfall is less, then production will be low, and they will be only able to grow one crop in a season.
With good irrigation it will be possible to do multiple cropping, helping to increase the yield per hectare.
Question 5. Construct a table on the distribution of land among 450 families of Palampur.
Answer Distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
| Families with no land (mainly dalits) | 150 Families |
| Families with less than 2 hectares | 240 Families |
| Families with more than 2 hectares | 60 Families |
| Total | 450 families |
Question 6) Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages?
Answer The minimum wages for a farm labourer set by the government are 60 per day, but wages of farm labourers in Palampur are less than minimum wages because there is heavy competition for work among the farm labourers in Palampur, so people agree to work for lower wages.
Question 7. In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
(i) In our region, there are two labourers namely Ram Khilawan and Basanti, who are husband and wife working as casual constructing labourers. Due to drought, they had to leave their village in search of employment, They get approximately 50 to 60 rupees per day which they are paid in cash.
(ii) They do not get work regularly because there are a large number of workers seeking employment, due to which they agree to work for low wages. Because of irregular work and low wages they are unable to fulfill their needs and are in debt.
Question 8. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
Answer Multiple cropping and use of modern farming methods are two different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land. e.g.,
(i) Multiple Cropping When more than one crop is grown on a piece of land during the year it is known as multiple cropping.
(a) It is the most common way to increase production on a given piece of land.
(b) All farmers in Palampur grow atleast two main crops, many are growing potato as the third crop in the past fifteen to twenty years.
(ii) Use of Modern Farming Methods
Modern farming methods also help to increase the yield per hectare.
(a) Farmers of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh were the first to try modern farming methods in India.
(b) The farmers in these regions set up tube wells for irrigation and made use of HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers and pesticides in farming.
(c) Some also used farm machinery like tractors and threshers, which made ploughing and harvesting faster. They were rewarded with high yields of wheat, increasing from 1300 kg per hectare to 3200 kg per hectare with HYV seeds.
Question 9. Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land?
(i) A farmer having 1 hectare of land for farming is called a subsistence farmer because 1 hectare of land is too less for even the sustenance of a small family.
(ii) Production is very low and it is very difficult for the farmer to provide for his family.
(iii) Apart from working on his own field he has to work on the field of the rich farmers or work as a casual labourer to survive.
(iv) The small farmer has no irrigation facilities.
(v) He has no working capital so he is also not able to buy modern machinery, HYV seeds or insecticides and pesticides.
(vi) In the absence of capital, he has to take loan from moneylender who charges a high interest rate. He is rarely able to repay the loan and eventually falls into a debt trap.
Question 10. How did the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? how is it different from the small farmers?
Answer Modern farming methods such as use of HYV insecticides pesticides etc require a great deal of capital so the farmer needs more money than before.
(i) The medium and large farmers have their own savings from farming.They are thus able to arrange for the capital needed.
(ii) In contrast, the small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation.
(iii) The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to great distress to repay the loan, which is not so in the case of medium and large farmers.
Question 11. On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tejpal Singh?Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Answer Savita, a small farmer, in order to cultivate wheat on her 1 hectare of land, decides to borrow money from Tejpal Singh a large farmer on the following terms
(i) Tejpal Singh agrees to give Savita the loan at an interest rate of 24 per cent for four months which is a very high interest rate. Savita also has to promise to work on his field as farm labourer during the harvest season at Rs 35 per day.
(ii) The rate of interest charged by Tejpal Singh was higher than that of banks. If Savita had taken the loan from the bank, interest would have been lower and she could have easily repaid the loan and her condition would have been far better.
Question 12. Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years.
(i) On talking to two old residents Ramlal and Dharam Singh I came to know about the irrigation methods that were traditionally in use in our area. They told me that earlier they were dependent on rainfall and later on they started to use the Persian wheel to draw water from the wells. With development of technology, tube wells were used for more better and effective irrigation.
(ii) In the farming methods, traditionally they ploughed the field with ploughs drawn by bullocks which was a very difficult and time consuming process. They used ordinary seeds and cow dung manure for fertilisation.
(iii) However with changes in technology the farmers started using HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides and modern machinery like tractors and threshers which has led to an increase in yield per hectare and improved the lives of the farmers.
Question 13. What are the non farm activities taking place in your region (or Palampur)? Make a short list.
(i) Dairy is a common activity in many families of our region.
(ii) Some people are involved in small scale manufacturing in their homes or in the field like production of jaggery by Mishrilal.
(iii) A few people are involved as shopkeepers and traders who buy various goods from the wholesale market in the cities and sell them in the villages.
(iv) Some people near the bus stand have opened shops selling eatables.
(v) Some people are in the transportation sector ferrying people and carrying goods from one place to another in different types of vehicles.
(vi) People like Kareem opened a computer class centre and also provided employment to two women who had a diploma in computer application.
Question 14. What can be done so that non-farm production activities can be started in villages.
(i) Banks should provide loans at low interest rates so that the poor villagers can start some business to help them earn a living.
(ii) Government should be more active and start and effective employment generating schemes.
(iii) Government should provide training to the villagers in different small crafts.
(iv) Government should proVide facilities for transportation and selling of locally manufactured goods of the villagers in the cities.
(v) Industries can be set up in rural areas.
About Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
Author of this website, Mrs. Shilpi Nagpal is MSc (Hons, Chemistry) and BSc (Hons, Chemistry) from Delhi University, B.Ed. (I. P. University) and has many years of experience in teaching. She has started this educational website with the mindset of spreading free education to everyone.
Reader Interactions
June 5, 2020 at 5:47 am
Mam you are so nice , thank you mam I get many questions in this website
June 17, 2020 at 1:14 pm
Thank you mam it was too good and I had got many answers and it cleared my all douts thank you mam
August 9, 2020 at 9:16 pm
thank you ma’am for making this website as I got cleared with many questions from this website..
October 16, 2020 at 5:22 pm
Thanks for free education….
January 30, 2021 at 5:30 pm
It is very good website It really helps me for studying at home It cleared many doubt and have all answers…
February 11, 2021 at 3:57 pm
thanks for your explanation maam
June 11, 2021 at 2:50 pm
Thank you so much mam This website helps me a lot Mam one suggestion please make a pdf available of these notes as I don’t have internet everytime Thank you mam
July 17, 2021 at 3:59 pm
Thanks a lot …it is a very good website ..it helps me in a very good way .actually it is an excellent website for students to study……. I my cleared doubts in an very good way…………..
August 11, 2021 at 11:05 am
Ma’am this website is an excellent way to read the entire chapter . Thanks for solving our problems.
April 8, 2022 at 8:00 pm
Thanks mam this site helps us to write notes and right answers
September 10, 2022 at 9:32 pm
Thank you so much mam I was looking for this answers only… Helped a lot thanks
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The story of village palampur
Ncert solutions for class 9 social science economics chapter 1 the story of village palampur, economics class 9 ncert solutions chapter 1 the story of village palampur.
Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Question-1 Modern farming methods require more inputs, which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree? Solution: No doubt, modern farming requires more inputs than traditional farming. These are:
- chemical fertilizers
- farm machinery
- electricity
- water supply
Most of these inputs like fertilizers, tools, and implements are manufactured in industry. HYV seeds are developed in agriculture research laboratories. Machine industry provides various kinds of implements, irrigation pumps, and farming machinery to improve productivity and minimize farming efforts. Chemical and soil engineering-based industries provide fertilizers and pesticides to boost agriculture. Water supply is done by canals and tanks. Electricity is supplied by powerhouses.
Formulae Handbook for Class 9 Maths and Science Educational Loans in India
Question-2 How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur? Solution: The spread of electricity helped the farmers in Palampur in the following ways:
- Most of the houses have electricity connections.
- It is used to run tubewells in the fields.
- It is used in various types of small businesses.
More Resources for NCERT Solutions Class 9

NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 IT
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
Question-3 Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why? Solution: Irrigation facilities are available only to about 40% of the cultivated land area in the country. The rest of the land, i.e., 60% of the cultivated area, is still dependent on rainfall for irrigation. It means that the benefit of multiple cropping cannot be achieved by 60% of the farmers in the country. They produce less and so their income is also low. Thus, they live in poverty.
Therefore, if these farmers are to be brought out of poverty, farm productivity has to increase. This is only possible when they use modern farming methods and dependable irrigation facilities. Hence, it is important to increase the area under irrigation.
Question-4 Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages? Solution: A waged labourer might be employed on a daily basis, or for one particular farm activity like harvesting, or for the whole year. Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to great distress to repay the loan. Hence they pay very low wages to the farm labourers.
Question-5 What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to Explain. Solution: To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping. It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land. All farmers in Palampur grow at least two main crops; many are growing potato as the third crop in the past fifteen to twenty years.
Question-6 How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers? Solution: In contrast to the small farmers, the medium and large farmers have their own savings from farming. They are thus able to arrange for the capital needed.
Question-7 On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tajpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest? Solution: Savita was a small farmer. She planed to cultivate wheat on her 1-hectare land. Besides seeds, fertilizers and pesticides, she needed cash to buy water and repair her farm instruments. She estimated that his working capital itself would cost a minimum of Rs 3,000. She didn’t have the money, so she decided to borrow from Tejpal Singh, a large farmer. Tejpal Singh agreed to give Savita the loan at an interest rate of 24 percent for four months, which was a very high-interest rate.
Savita also had to promise to work on his field as a farm labourer during the harvest season at Rs 35 per day. Savita knew that this wage is quite low and she will have to work very hard to complete harvesting on her own field, and then work as a farm labourer for Tejpal Singh. Savita agreed to those tough conditions, as she knew, that getting a loan is difficult for a small farmer. Yes, Savita’s condition would have been different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest.
Question-8 What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages? Solution: The villagers must be made aware of the non-farm production activities and their benefits. They must also be taught the methods of doing such activities. The villagers who have the impression that they can earn only by farming, must be given proper guidance and help to do such activities.
Free Resources
Quick Resources

NCERT Solutions for Class 9th: Ch 1 The Story of Village Palampur Economics
Ncert solutions for class 9th: ch 1 the story of village palampur economics social studies (s.st).
| Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing ground) | ||
| Educational | |
| Medical | |
| Market | |
| Electricity Supply | |
| Communication | |
| Nearest Town |
| Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing ground) | ||
| 200 hectares | 26 hectares | |
| Educational | 2 primary schools and 1 high school |
| Medical | 1 primary health centre and 1 private dispensary |
| Market | Raiganj and Shahpur |
| Electricity Supply | Most of the houses have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small businesses. |
| Communication | Well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. 3 kms from Raiganj. All-weather road connects it to Raiganj and further on to Shahpur. Many kinds of transport like bullock carts, , bogeys, motorcycles, jeeps, tractors and trucks are present. |
| Nearest Town | Shahpur |
| Number of families | Land (hectare) |
| 150 | 0 |
| 240 | Less than 2 |
| 60 | More than 2 |
Contact Form

- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Free Video Lectures
- CBSE Important Questions
- CBSE Objective (MCQs)
- Assertation & Reasoning Questions
- Case Study Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample paper
- CBSE Mock Test Paper
- Question Bank
- Previous Year Board Exam Papers
- Project, Practical & Activities
- ICSE Free Video Lectures
- Class 6 ICSE Revision Notes
- CLASS 7 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 8 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 9 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 10 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- Class 6 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 7 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 8 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 9 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Solutions
- Class 6 ICSE Important Questions
- CLASS 7 ICSE Important Question
- CLASS 8 ICSE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
- CLASS 9 ICSE Important Questions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Important Question
- Class 6 ICSE Mcqs Question
- Class 7 ICSE Mcqs Question
- CLASS 8 ICSE MCQS QUESTION
- CLASS 9 ICSE Mcqs Questions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Mcqs Question
- ICSE Syllabus
- Class 6th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 7th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 8th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 9th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 10th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 11th Quick revision Notes
- Class 12th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 6th NCERT Solution
- Class 7th NCERT Solution
- Class 8th – NCERT Solution
- Class 9th NCERT Solution
- Class 10th NCERT Solution
- Class 11th NCERT Solution
- Class 12th NCERT Solution
- Class 6th Most Important Questions
- Class 7th Important Questions
- Class 8th Important Questions
- Class 9th Most Important Questions
- Class 10th Most Important Questions
- Class 11th important questions
- Class 12th important questions
- Class 6th MCQs
- Class 7th MCQs
- Class 8th MCQs
- Class 9th MCQs
- Class 10th MCQs
- Class 11th MCQs questions
- Class 12th Important MCQs
- Case Study Based Questions
- NCERT Books in Pdf
- NCERT Chapter Mind Maps
- OliveTree Books Study Materials
- Forever With Books Study Material
- Rs Aggrawal Solutions
- RD Sharma Solution
- HC Verma Solution
- Lakhmir Singh Solution
- T.R Jain & V.K ohri Solution
- DK Goel Solutions
- TS Grewal Solution
- Our Products
- Edugrown-Candy Notes & Solution
- Online Tuition Services
- Career Advisor Booking
- Skill Development Courses
- Free Video Lectures
Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science
- Chapter 1 The Story of…
In the questions given below, there are two Statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the Statements and Choose the correct option: Options are: (A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). (B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). (C) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong. (D) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Q.1. Assertion: Agriculture is the main economic activity in Palampur. Reason: More than 75% of the people in Palampur are engaged in farming.
➤ Show AnswerAnswer: (A)
Q.2. Assertion: Palampur has well-developed transportation facilities. Reason: The village is well-connected to the nearest town by a network of roads and railways.
Q.3. Assertion: Education and healthcare are neglected in Palampur. Reason: The government has not invested in these areas in the village.
➤ Show AnswerAnswer: (D)
Q.4. Assertion: The labourers in Palampur are paid very high wages. Reason: The competition for labour is very high in the village.
Q.5. Assertion: The use of modern farming methods has increased the productivity of crops in Palampur. Reason: The farmers in Palampur have adopted multiple cropping to increase productivity.
Q.6. Assertion: Palampur has a well-developed irrigation system. Reason: The village is located near a perennial river, and the farmers use tube wells for irrigation.
➤ Show AnswerAnswer: (C) The assertion is true, but the reason is false. Palampur does not have a well-developed irrigation system. Although the village is located near a perennial river, the farmers do not have access to canal irrigation, and they depend on tube wells for irrigation.
Q.7. Assertion: Palampur has a diverse range of crops grown throughout the year. Reason: The village has a favourable climate for growing multiple crops.
Q.8. Assertion: The Green Revolution had no impact on agriculture in Palampur. Reason: Palampur farmers have not adopted high-yielding variety seeds.
➤ Show AnswerAnswer: (D) The assertion is false, but the reason is true. The Green Revolution had a significant impact on agriculture in Palampur, as farmers adopted modern farming methods and high-yielding variety seeds. However, not all farmers in Palampur have adopted these methods.
Q.9. Assertion: The villagers in Palampur have no access to formal credit. Reason: The village does not have any banks or other financial institutions.
➤ Show AnswerAnswer: (D) The assertion is false, but the reason is true. The villagers in Palampur do have access to formal credit, as there is a primary agricultural credit society in the village. However, the village does not have any banks or other financial institutions.
Q.10. Assertion: Palampur has a high level of economic inequality. Reason: There is a wide disparity in the ownership of land in the village.
Author: school
Related posts.
Chapter 4 Food Security in India Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Chapter 2 People as Resource Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Chapter 4 Climate Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Chapter 5 Democratic Rights Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Chapter 4 Working of Institutions Assertation & Reasoning Questions Class 9th Social Science May 20, 2023
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post comment

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ Test (Online Available)
Free mcq test, table of content, the story of village palampur test - 9.
Duration: 10 Mins
Maximum Marks: 10
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. The test contains 10 total questions.
2. Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct .
3. You have to finish the test in 10 minutes.
4. You will be awarded 1 mark for each correct answer.
5. You can view your Score & Rank after submitting the test.
6. Check detailed Solution with explanation after submitting the test.
7. Rank is calculated on the basis of Marks Scored & Time
The Story of Village Palampur Test - 8
The story of village palampur test - 7, the story of village palampur test - 6, the story of village palampur test - 5, the story of village palampur test - 4, the story of village palampur test - 3, the story of village palampur test - 2, the story of village palampur test - 1.
In the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ, students need to make an accurate decision between alternatives. As this process is never considered to be an easy one as the options need to be analysed based on the concepts and topics of the chapter The Story of Village Palampur. To have a proper analysation process students need to complete the chapter The Story of Village Palampur in a proper way.
The The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ can be helpful for both teachers and students for better learning as well as teaching. With the help of multiple choice questions, teachers don’t need to waste the unnecessary time in searching for questions, they can utilise their precious time in teaching the The Story of Village Palampur concepts. Students can practise a vast amount of questions so that they can make the preparation process of the chapter The Story of Village Palampur easier.
The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ Online
The The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ Online can be accessed quickly as the website provides the questions to practise for all students. The Online Test of the Class 9 MCQ provides prompt feedback to students, accordingly they can improve their grip on the chapter The Story of Village Palampur so that they can score well.
How to Attempt the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ?
Students need to follow some given steps to attempt the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ, steps are discussed below:
- Visit the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar/ button.
- A drop down menu will appear, select MCQ Test from the list.
- New page will appear, select Class 9th from the list of classes.
- Click Social Science from the list of subjects.
- A pop-up menu will appear, select the chapter The Story of Village Palampur.
- Again a new page will appear and one can easily start the test.
Everything You Need to Know About the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ
Here are some things that every student need to know before solving the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ, those features are:
- Objective Assessment: The The Story of Village Palampur MCQ is an objective assessment that students need to select the accurate option from the given four options.
- Variety of Questions: In the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur Class 9, it may include all sorts of questions: easy, moderate, advanced so that students upgrade their preparation in each test.
- Concept Based: The MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur are generally concept based so that students can understand all concepts and topics without any complexity.
- Instructions are Given: Some instructions are given, these guidelines need to be followed and taken care of while solving the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur.
- Solutions are Given: In the MCQ The Story of Village Palampur, solutions are given so that students can refer to whenever they need any help in solving objective questions.
- Re Attempt Option is Given: Students can solve the same set of MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 number of times as a re-attempt option is given.
Top 6 Benefits of the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ
One of the prominent reasons of solving the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ is that by looking through the options, students can recollect the facts and important concepts, this is one of the important benefit, other benefits are:
- Easy to Answer: The The Story of Village Palampur MCQ are easy to answer, that is students just need to select the accurate option within secs. For this, students need to complete the topics and concepts of the The Story of Village Palampur in a better way.
- Quicker to Evaluate: The MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 are quicker to evaluate as compared to essay type questions.
- Enhances Thinking Skills: To attempt the MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur, students need to analyse and evaluate the options given, this enhances the thinking skills.
- Helps to Identify the Area of Strengths and Weaknesses: By practising MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur Class 9, students can identify their strengths as well as weaknesses and accordingly they can improve.
- Device Friendly: This MCQ The Story of Village Palampur is considered to be mobile friendly, that is it can be downloaded from anywhere without any complexity and can practise objective questions.
- Acts as a Revision Tool: The Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur MCQ acts as a revision tool that is it can be used to revise all the key concepts of the chapter.
Steps to Master in the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ
Mastering in the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ requires systematic and focused approach, below are some steps to master in the objective questions:
- Understand the Concepts: Students need to first understand the topics and concepts of the chapter The Story of Village Palampur, so that they can build a strong foundation and accordingly they can solve multiple choice questions in a better way.
- Practise Sample MCQs: Students are advised to practise the sample The Story of Village Palampur MCQ so that they can get familiarised about the format of questions.
- Analyse the Mistakes: Students need to analyse the mistakes while practising MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 so that they can analyse the weak points and accordingly they can progress.
- Recall on a Regular Basis: It is a must for students to recall the topics and concepts of the The Story of Village Palampur so that they can master multiple choice questions and score well.
- Stay Focused: Students need to be focused while preparing for MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur accordingly they can enhance their knowledge as well as can master in the MCQ.
- Maintain a Positive Attitude: Students need to maintain a positive attitude: feel relaxed while marking the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 so that they can mark the accurate answers.
When to Start Solving the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ?
Students can start solving the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ according to their preference and study schedule, they can follow general guidelines to practise the multiple choice questions:
- After Completing the Chapter: It is generally recommended for students to start solving the The Story of Village Palampur MCQ as soon as they complete the chapter accordingly they can reinforce their understanding for the chapter.
- Before Final Exams: Students can start solving the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 before the final exams so that they can identify the gaps in the understanding of the concepts.
- During Classroom Study: Students can solve the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur during classroom study and can seek help from their teachers to solve confusions.
- To Solve Doubts: Students can also start solving the MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 to solve doubts and confusions regarding the chapter.
- To Understand the Pattern: Students can solve the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur so that they can understand the pattern of objective questions.
How Mark Right Answers in The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ?
It is very important for students to marks the accurate answers in The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ so they can score good marks in it, tips to mark the right answer are:
- Read the Entire Question Carefully: Students are advised to read the entire question carefully so that they can develop a logical thinking to mark the accurate answers.
- Read Every Option: Prior to choosing the right answer in MCQ The Story of Village Palampur, students need to read each and every option thoroughly otherwise they can end up selecting the wrong answer.
- Try to Answer it in Mind First: Firstly, students need to answer the MCQ on The Story of Village Palampur in their mind so that they can prevent silly mistakes.
- Try to Use the Process of Elimination: Students need to use the process of elimination by crossing out all the wrong answers while attempting Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur MCQ.
- Select the Best Answer: Some answers can seem right but it may not be accurate so students need to be very careful while marking the answer in the MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur.
- Double Check the Answers: Students need to double check the all answers before submitting the Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur MCQ so that they can have a surety of marking the right answers.
How to Analyse the Wrong Answers in the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ?
Analysing the wrong answers in the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ is very important for students as it helps them to identify the skills and flaws, tips to analyse the mistakes are:
- Identify the Incorrect Ones: Students are advised to ident/ify the incorrect ones and compare it with the right ones while attempting The Story of Village Palampur MCQ.
- Understand the Reason for Incorrect Ones: Students need to understand the reason for incorrect MCQs of The Story of Village Palampur so that they can focus on the weak concepts.
- Seek Clarification: Students need to seek clarification from the teachers so that they don’t repeat the same set of mistakes while attempting MCQ of The Story of Village Palampur.
- Practise Different Levels of Questions: Students need to practise different levels of multiple choice questions of The Story of Village Palampur: easy, moderate, advance so that they can understand weak parts and work accordingly.
- Note Down the Mistakes: It is a must for students to note down the mistakes made while attempting the Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur MCQ so that they can easily rectify the mistakes.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 Economics
- Chapter 1 The Story Of Village Palampur
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Economics Social Science Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur
Ncert book solutions for class 9 economics chapter 1 – cbse free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 – The Story of Village Palampur contains the solutions to the exercises given in the economics book. NCERT Solutions of the exercises are provided, which will help Class 9 students to develop a skill for writing answers in an effective way. These NCERT Solutions will be useful for school exams as the source of these is from the NCERT textbooks.
The NCERT Solutions are easy and accurate, which will align school students’ preparation as per the questions asked in the CBSE exams. Practising NCERT Solutions is the ultimate need for students who intend to score good marks in the examination. Students facing trouble in solving questions from the Class 9 NCERT textbook can refer to our free NCERT Solutions for Class 9 provided below.
- Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
- Chapter 2 People as Resource
- Chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge
- Chapter 4 Food Security in India
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Studies (Economics) Chapter 1 – The Story of Village Palampur
The Solutions for Chapter 1 of Economics are given below. Students should also check NCERT Solutions for Class 9 for other subjects.
Exercises Page No 14
1. Every village in India is surveyed once in ten years during the Census and some of the details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur.
- TOTAL AREA OF THE VILLAGE:
- LAND USE (in hectares):
|
| ||
d) FACILITIES:
- LOCATION: Bulandshahr District, Western Uttar Pradesh
- TOTAL AREA OF THE VILLAGE: 226 hectares
| Cultivated Land | Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing ground) | |
| Irrigated | Unirrigated | |
| 200 hectares | — | 26 hectares |
- FACILITIES:
| Educational | 1 high school, 2 primary schools |
| Medical | 1 private dispensary, 1 primary health care centre run by the Government |
| Market | 2 markets: Raiganj and Shahpur |
| Electricity Supply | Most of the houses have electricity connections. Electricity powers all the tubewells in the fields and is used for various small business. |
| Communication | Well-connected neighbouring villages, with Raiganj located within 3 kms. Proper transportation including bullock carts, tongas and bogeys carrying jaggery. Also, motor vehicles like motorcycles, jeeps, tractors and trucks are available for easy transportation. |
| Nearest Town | Shahpur |
2. Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industries. Do you agree?
Yes, it is correct to say that modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industries. It is because modern farming methods use high-yielding varieties of seeds. These seeds require both chemical fertilisers and pesticides, agricultural implementations like tractors and proper irrigation facilities like electric tube wells, and all these elements are manufactured in industries. However, on the other hand, traditional farming methods use a relatively low-yielding variety of seeds and use cow dung and other natural manures as fertiliser, which is why they are less dependent on industrial outputs.
3. How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
The spread of electricity helped the farmers of Palampur as it aided in the transformation of the irrigation system of the village. The farmers earlier used Persian wheels to draw water from wells and irrigate small fields. But after the spread of electricity, electric tube wells replaced these Persian wheels. The first tube well was installed by the Government, but later, private tube wells were also set up by the farmers, resulting in the cultivation of the entire 200 hectares of irrigated land by the 1970s.
4. Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
It is important to increase the land under irrigation because farming is the main source of income for the maximum part of the population in India and only less than 40 per cent of the land is cultivable in the country. Farmers are dependent on the erratic monsoon season, and if the rainfall is less, farmers are bound to suffer a major loss. So if the water is provided for irrigation to the farmers for a larger portion of land, it would give better output and make more land cultivable in India and also encourage farmers to take up newer farming methods without the fear of suffering loss.
5. Construct a table on the distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
The distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur is as given below:
| Area of land Cultivated | Number of Families |
| 0 | 150 |
| Less than 2 hectares | 240 |
| More than 2 hectares | 60 |
6. Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages?
There are many landless farm labourers who are paid less than the minimum wages in Palampur. The Government-declared wage for a farm labourer is Rs 300 per day, but the competition for work among the farm labourers is very high, which is why people agree to work for lower wages.
7. In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid in cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
Students must do this activity themselves and answer the question based on their survey.
8. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping. It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land. The best example of this is the cultivation in Palampur. In Palampur, jowar and bajra grow during the rainy season, followed by potato between October and December, and during the winter season, wheat is sown in the fields. The main reason for this is the well-developed system of irrigation.
9. Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land.
A farmer with 1 hectare of land will be called a small farmer. Since the area for cultivation is small, the outcome may also not be high. So, in order to be able to get the best possible yield, the farmer needs money. This money is borrowed from a moneylender at a high interest rate and at times may also have to work as a farm labourer for the moneylender. Once the farm is cultivated, the produce has to be divided for personal use and for selling in the market. Whatever profit is earned, the farmer has to usually give it away to the moneylender, and little money is left for the use of the farmer himself. The only help a small farmer gets is that of his family members.
10. How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers?
Large and medium farmers sell surplus farm products from a part of their produce. A part of the earnings is saved and kept for buying capital for the next season. A few of them give away the savings to small farmers and loans at high interest rates and get back the amount by the next season. Thus, they are able to arrange for the capital for farming from their own savings. Some farmers might also use the savings to buy cattle, trucks, or to set up shops.
11. On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tejpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Savita got a loan from Tejpal Singh at the rate of interest of 24 per cent for four months and also had to work for Tejpal Singh as a farm labourer at the wage of Rs 100 per day during the harvest season.
The case would have been different if Savita had taken the loan from a bank. The rate of interest would have been lesser than what was asked by Tejpal Singh and also she would have been able to pay complete attention to her own field during the time of harvest.
12. Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years.
Answer: Students must do this activity and write an answer based on their own observation.
13. What are the non-farm production activities taking place in your region? Make a short list.
The non-farm production activities taking place in our region are as follow:
- Transportation
- General Stores
14. What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
To promote more non-farm production activities in villages, the following steps can be taken:
- Loans must be available for people at lower interest rates so that they can start the non-farm production activities.
- Proper markets should be set up so that the produced goods can be sold.
- The concerned authorities must set up better transportation between cities and villages so that the produced goods can be transported to cities and more money can be earned through the non-farming activities.
The Story of Village Palampur Summary
Chapter 1 of NCERT Economics book, The Story of Village Palampur is used as a medium to teach students how the production of crops and other non-farm activities takes place in villages. The need for capital and human power for the production of various products has also been discussed in detail in this chapter.
Students will also study:
1. Organisation of Production
- Fixed capital and working capital
- Factors of Production
2. The type of farming in Palampur. The crops grown and the techniques used to grow crops. Factors like the distribution of land, labour, land sustainability and the capital needed.
3. Non-Farming Activities
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1
What are the important topics discussed in chapter 1 of ncert solutions for class 9 economics, where can i get the ncert solutions for class 9 economics chapter 1 pdf online, how does the ncert solutions for class 9 economics chapter 1 aid students with their cbse exam preparations, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very easy answers better to learn very elegant solutions. Byju’s is best.
Thanks, it was very helpful for me.
Thank you 😊Very helpful for me
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Economics Social Science Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur

Table of Contents
NCERT Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Important Questions
The Story of Village Palampur is one of the most important topics in class 9 Social Science Economics. To score well in this chapter, students need to understand the topic better. To help them effectively prepare for the exam, we have collated a few important questions on The Story of Village Palampur in this article.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
The Story of Village Palampur Important Questions provided here include short answer, long answer type, and a few questions from previous year papers as well. For easy reference, a PDF of Important Question for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur is made available here. Students can download this PDF for free and get started with their exam preparation. Also Enhance your knowledge with CBSE notes class 9 and syllabus for Class 9 .
Don’t Miss:
- Important Questions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur .
- Most Scoring Chapters in Class 9 Social Science
- CBSE Class 9 Social Science Syllabus for 2024-25
- NCERT Book Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 – CBSE Term I Free PDF
- Class 9 Economics NCERT Solutions – Free PDF Download
- NCERT Books for Class 9 – Free PDF Download for 2023-24

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 All Subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English
The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: What are the factors of production?
Answer: The essential inputs required for producing goods and services are known as factors of production. For example, for the production of cloth, cotton-machine, labour and technology are required.
Question: Name the main production activity of Palampur.
Answer: Farming.
Question: What capital is needed as a priority to set up a jaggery manufacturing unit?
Answer: Fixed capital.
Question: Give a few examples of fixed capital.
Answer: Tools, machines, and building.
Question: Name any one item of working capital.
Answer: Money.
Question: Give an example of an entity not part of fixed capital.
Answer: Cash amount.
Question: Give two examples of the working capital.
Raw materials, Money in hand.
Question: What do raw materials and money in hand call?
Answer: The working capital.
Question: The clay used by a potter is an example of which type of capital?
Answer: Working capital.
Question: Why is it important to use land very carefully?
Answer: Land is a natural resource; it is difficult to restore once destroyed.
Question: What are rabi crops?
Answer: The crops are grown in the winter, i.e., November or December, and harvested in summer, i.e., April or May. For example, wheat.
Question: What are Kharif crops?
Answer: The crops are grown in the rainy season, i.e., June or July, and harvested in October or November. For example, rice.
Question: Farmer’s plough is an example of which factors of production?
Answer: Capital.
Question: Which is the most abundant factor of production?
Answer: Labour.
Question: What is physical capital?
Answer: Physical capital includes a variety of inputs required at every stage during production like machines, raw materials, etc.
Question: What are the different categories of physical capital?
- Fixed capital,
- Working capital.
Question: Categorize the following as fixed capital or working capital:
Cotton, Machine
- Cotton — Working capital,
- Machine — Fixed capital.
Question: Which term is used for production for self-consumption?
Answer: Subsistence farming.
Question: Enumerate a few effects of the modem farming method.
Answer: Soil degradation reduces the water table below the ground and water pollution.
Question: Mention any two natural factors of production.
Answer: Land, forests, water, minerals, etc.
Question: What is a market?
Answer: It is a place where goods and services can be sold.
Question: Define yield.
Answer: The crop is produced on land during a single season.
Question: Who provides capital to the small farmers at a high-interest rate?
Answer: Large farmers, village moneylenders,s or traders.
Question: What does HYV stand for?
Answer: High Yielding Varieties (HYV).
Question: “The yield of food grains hectare is high in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.” Give two reasons. HOTS
- Use of HYV seeds.
- Use of tubewells for irrigation.
Question: Which are the prime requirements for producing goods and services?
Answer: Market.
Question: Write down the names of the crops promoted by the Green Revolution.
Answer: Cultivation of wheat and rice.
Question: During which season do farmers of Palampur grow jo war and bajra?
Answer: Rainy season.
Question: At present, what percentage of people engaged in the rural areas in non-farming activities in India?
Answer: 24%.
Question: What is the basic constraint in raising farm production?
Answer: The basic constraint in raising farm production land is a fixed factor of production.
Question: What is Green Revolution? HOTS
Answer: The great increase in the production of food grains in our country during the last 40 years due to the use of high-yielding variety (HYV) of seeds and other inputs is known as the Green Revolution.
Question: What was the production of pulses and wheat in 2010-11?
Answer: Pulses – 18 MT, Wheat – 86 MT.
Question: Mention any two non-farm activities.
Answer: Dairy and transport.
Question: Name any two states which benefited from the Green Revolution.
Question: Mention any two factors responsible for India’s low yield of foodgrains.
- Old technology,
- Small land holdings.
Question: Which of the following is not used in modem farming?
Answer: Ploughs.
Question: Which best way to expand non-farm activities in a village?
Answer: Better transportation, availability of loans at low interest, and availability of markets where goods can be sold are the best way to expand non-farming activities.
Question: In which period is the cultivation of potatoes done?
Answer: October to December.
Question: In which type of activity is dairy farming included?
Answer: Primary activity.
Question: Which state in India has the highest consumption of chemical fertilizers?
Answer: Punjab.
Question: Scientific reports indicate that the modem farming methods have overused the land. Explain by giving examples.
- The soil is losing fertility due to the increased use of chemical fertilizers,
- The continuous use of groundwater from tubewell irrigation has reduced the water table.
Question: What is multiple cropping?
Answer: To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping.
Question: Name any two methods to increase production in agriculture.
- By using HYV seeds,
- By irrigation.
Question: Which capital is known as working capital?
Answer: Raw materials and money in hand are called the working capital.
Question: Which is the most important economic activity of the people of rural India?
Question: Mention the standard unit for measuring the area of land.
Answer: Hectare.
Question: “Many people belonging to SCs (Dalits) are discriminated against in the village.” Justify giving a reason.
Answer: SCs live in one corner of the village and have much smaller houses.
Question: What is production? Give an example.
Answer: Production is the creation of value in a commodity. For example, we are manufacturing a car from steel.

The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 Important Questions Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Define the meaning and aim of production.
Answer: Production creates value in a commodity, e.g., manufacturing a car from steel. Aim: Production aims to produce the goods and services that we want. There are four requirements for the production of goods and services: Land, labour, physical capital, and human capital.
Question: Mention three characteristics of the traditional method of farming,
- Traditional seeds with low yield were used.
- Cow dung and natural manures were used.
- Less irrigation was required.
Question: Explain the problems which arise due to unequal distribution of land.
Economic Inequality: Unequal distribution of land leads to economic inequality. Unemployment: It leads to unemployment. Poverty and Hunger: Lack of economic opportunities leads to poverty and hunger.
Question: Describe the role of human capital in the production process. Name two investments that can improve the quality of human capital.
- Education and training can only build human capital in the long run.
- Human capital includes competent and trained people who put together land, capital, and other factors of production to produce goods.
Question: Farmers of which two states were the first to use modem farming methods in India? Mention any four positive effects of it. MOTS
(i) Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh farmers were India’s first to use modem farming methods.
(ii) Modern farming methods increased the productivity of the land.
- It increases foodgrain production in the country.
- It brought the Green Revolution in the 1960s, which resulted in the high production of cereal grains, particularly wheat and rice.
- It has played a very important role in food security.
- It has led to the growth of agro-based industries.
Question: Write any three differences between land and capital.
| (i) It is a fixed factor of production. | It is a man-made factor of production. |
| (ii) It is a gift of nature. | It is a man-made source of production. |
| (iii) Land varies in fertility. | It is of two types, i.e., fixed and working capital. |
Question: ‘Capital is a basic need in agriculture.’ How do Indian farmers arrange it? Explain.
- Most small farmers borrow money from moneylenders or traders to arrange the capital.
- The moneylenders and traders charge a high rate of interest from the farmers.
- Medium and large farmers have their savings from farming.
- They also get loans from banks.
Question: What problems do farm labourers face in terms of unemployment? Explain any three problems. HOTS
Answer: Problems of Farm Labourers:
- They come either from landless families or families cultivating small plots of land.
- They do not have a right over the crops grown on the land.
- They got wages in cash or kind.
- Wages vary widely from region to region and from crop to crop etc.
- Wide variation in the duration of employment was also seen (any three)
Question: Mention any four characteristics of an entrepreneur or human capital as a factor of production.
- It is a factor of production that combines or arranges all the factors of production to produce.
- It is an active factor of production.
- It produces goods and services for self-consumption or to sell in the market.
- It is the most important factor of production.
Question: How do small farmers obtain capital for farming? What is its consequence? Explain.
Answer: Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the capital. They borrow from large farmers, moneylenders, or traders who supply various inputs for cultivation.
Consequence: The rate of interest on such loans is very high. The small farmers are put in great distress to repay the loan.
Question: Describe any three features of small-scale manufacturing as a non-farm activity in Palampur.
- Less than 50 people are engaged in manufacturing in Palampur.
- Manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and is done on a small scale.
- Manufacturing activities are carried out mostly at home or in the fields with the help of family labour. Labourers are hired rarely.
Question: How do the medium and large farmers make their savings, and how do they utilize them? Explain.
Answer: The medium and large farmers have surplus production even after keeping a substantial part for their own family needs. They sell it in the market, have good earnings, and save it in their bank accounts. They utilize their savings:
- By lending to small farmers who are in need of a loan.
- As working capital for farming in the next season.
- As fixed capital for buying tractors etc.
Question: What factors have led to the reduction of water levels in Palampur?
- Continuous groundwater use for tubewell irrigation has reduced the water table below the ground.
- While environmental resources like soil fertility and groundwater are built-up over many years, so, once destroyed, it isn’t easy to restore them.
- Misuse of groundwater is another important factor in lowering the water table.
Question: Describe any three sources of irrigation in Palampur.
- The Persian wheel is the main source of irrigation in Palampur.
- Well is also a source of irrigation.
- Tubewells are also important sources of irrigation. These are run by electric supply.
Question: State any two features of the modem farming method.
Answer: Its main features were:
- Use of tube wells for irrigation.
- Chemical fertilizers.
- Pesticides.
- Farm machinery such as tractors, threshers, etc. (any two)
Question: Explain any two differences between physical capital and human capital.
Answer: Differences:
- Physical capital has a variety of inputs, while human capital is labours, using those inputs.
- Physical capital includes tools and machines that can be used over the years, while human capital can produce output only if they have experience.
Question: What are modem farming methods? Explain its drawbacks.
Answer: It is a scientific way of increasing production. Under this, production is increased by using HYV seeds and other inputs.
- Rich farmers use it as it requires more inputs.
- Loss of soil fertility due to increased use of chemical fertilizers.
Question: Describe the role of the farmers after the crops are harvested and production is complete.
Answer: Role of the Farmer:
- The farmers retain a part of the crop for their family consumption and sell the surplus in the market.
- The small farmers grow the crops just to fulfill the family’s needs. So, they do not have any surplus to sell in the market.
- The big farmers make big earnings by selling main crops in the market.
- They sell the crops and earn huge profits from them.
Question: How many crops are grown by the farmers in Palampur? How are they able to grow these different crops in a year?
(i) The farmers in Palampur grow jowar and bajra during the rainy season, potatoes between October and December, and wheat in winter. (ii)
- A well-developed irrigation system in Palampur enables the farmers to grow three different crops in a year.
- Electricity came early to Palampur. Its major impact was to transform the system of irrigation in the village.
- By the mid-1970s, the entire area of 200 hectares was irrigated.
- Modern farming methods and the Green Revolution introduced HYV seeds.
Question: Why was the initial impact of the Green Revolution limited to wheat and only to a few regions?
- It was limited to wheat because HYV seeds were available only for wheat.
- Its impact was limited only to a few regions as the HYV seeds need higher inputs which only the rich farmers can afford.
- HYV seeds need assured means of irrigation available only in northern parts of India.
Question: How are traditional seeds different from HYV seeds?
| (i) HYV seeds produce more output per hectare. | Traditional seeds produce less output per hectare. |
| (ii) HYV seeds need irrigation. | Traditional seeds needed less irrigation |
| (iii) HYV seeds need modem inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, etc. | Traditional seeds needed readily available inputs from the farmers who did not have to buy these from the market. |
Question: “Most of our villages have good infrastructure.” Justify. VSQ
- Most villages are well connected with neighboring villages or towns through all weathered roads.
- Most Indian villages have primary schools, health centers, etc.
- Many means of transport are available like motorcycles, jeeps, tractors, tongas, etc.
Question: Why do people migrate? Explain.
Answer: People migrate from one region to another:
- In search of better jobs.
- For better living conditions.
- For higher education.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science: Economics
- Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
- Chapter 2 People as Resource
- Chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge
- Chapter 4 Food Security in India
The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 Important Questions Long Answer Type Questions
Question: Explain the meaning of ‘Physical Capital.’ Explain its two types with the help of suitable examples. (Or) What is physical capital? What are its different types?
Answer: Physical capital is the variety of inputs required at every stage during production. Its two different types are as follows:
Fixed Capital: It can be used in production over many years—for example, tools, generators, turbines, buildings, computers, etc. World Capital: Raw materials and money in hand are called Working Capital. Production requires various raw materials such as yarn used by the weaver and clay used by the potter. Some money is always needed during production to make payments and buy other necessary items.
Question: What is the land? Suggest any three ways to sustain the land.
(i) Land is the basic natural resource required as a factor or an input in any production activity. Various activities or human activities take place on land, a fixed asset. (ii)
- The land is a gift of nature. So, we must be very careful in its use. We must avoid the pollution of land.
- Soil is a vital part of the land and the basis of agricultural activities. So, it becomes necessary that we should use bio-compost and eco-friendly methods in place of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- We have to see that Modern Farming Methods are used scientifically to save the natural resource base that the land provides from further damage.
- If used carefully and judiciously, some farming practices can help make land sustainable. Such practices include the intensity of cropping, rotation of crops, multiple cropping, following, etc.
- We should encourage the community agriculture system or cooperative farming instead of individual farming, which is often exploitative. This could be another sustaining land productivity.
Question: How do large farmers utilize surplus farm products to arrange the capital needed for farming?
- The large farmers generally sell the surplus farm products and have good earnings.
- They put most of their earnings or money in their bank accounts and get adequate interest.
- A part of their earnings is saved and kept to arrange for the working capital for farming in the next season.
- They also use savings for lending to small farmers and other persons in the village.
- A part of their earnings is used to increase their fixed capital like tractors, threshers, cattle, etc.
Question: Distinguish between Fixed, Working, and Human Capital.
| (i) Tools, machines, buildings, etc., which can be used in production over many years, are called fixed capital. | (ii) Fixed capital cannot be changed or built-in short period of time. | Human capital includes competent and trained people who put together land, capital, and other factors of production to produce goods. |
| The production factors used in the production process are known as working capital. | Working capital can be changed or built-in short period. | Education and training can only build human capital in the long run. |
Question: What is the difference between Rabi crops and Kharif crops? When are they sown and harvested? Mention some necessary conditions for multiple cropping.
- Kharif crops are grown in the rainy season. They are sown in June-July and harvested in October-November. Farmers in Palampur mainly grow jowar and bajra, used as cattle feed.
- Rabi crops are grown in the winter season. They are sown in. October-November and harvested mainly in March-April. Wheat is the main crop grown in this season.
- Necessary Conditions for Multiple Cropping: Adequate irrigation facilities should be available on land. Farmers should also have sufficient capital to invest and meet farm expenses.
Question: Explain the distribution of the workforce engaged in non-farming activities in the rural areas. Suggest some measures to increase non-farming activities. (Or) Explain any four efforts which can be made to increase non-farming production activities in villages.
Answer: 25% of the total workforce is engaged in non-farming activities. Measures to Increase Non-farming Activities:
- Infrastructure: Infrastructure includes building roads, establishing banks, and improving communication. All these are basic inputs for economic development.
- Expansion of Market: To increase non-farming activities, rural markets should be linked to urban markets.
- Education and Health: Improvement in education will lead to human capital formation.
- Cheap Loan: Non-farming activities can be promoted by providing cheap and affordable loans to the farmers.
Question: State any five reasons why farm labourers are considered poor.
Farm labourers are generally landless. They have no permanent jobs. They have to look for work daily. They are not even paid minimum wages. The minimum wage for a farm labourer set by the government is ₹ 60 per day, but they get only? They have a large family. They are illiterate, unhealthy, and unskilled.
Question: Why do modern farming methods require more capital? Explain.
Modem farming methods need inputs like chemical fertilizers, pesticides, tractors, etc., manufactured in industry. So, they require the farmer to start with more cash than before. In modem farming methods, HYV seeds are used, which require more irrigation. In the traditional method, the farmers use cow dung as natural fertilizer, which they do not need to buy, while chemical fertilizers need more cash from the market. Modem farming is machine-oriented. Hence, farmers need more capital to purchase them. To operate the machines, semi-skilled or skilled manpower is required, which needs more investments.
Question: State three reasons for the variation in the wages of farm laboures all over India.
Answer: There is a wide variation in the wages of farm laboures in the country. They generally get wages less than the minimum wages set by the government. The reasons for the variation in the farm wages are as follows.:
The farm labourers come from landless families or families cultivating small plots of land. They are poor and helpless. They work on daily wages. They regularly have to look for work. Since there is heavy competition for work among the farm labourers in the country, these labourers agree to work for less than the minimum wages. Most agricultural labourers are from low castes and the depressed classes. They have little courage to challenge the upper caste people. Farm labourers are generally illiterate and ignorant. They are not organized in unions. So, it is difficult for them to bargain with the landowners and secure good wages.
Question: Explain the basic requirements for the production of goods and services. Which one is the most important?
Land: Land is the most important factor of production. It is required for growing crops and building factories and infrastructure. The first requirement is land. We also need other natural resources such as water, forests, minerals, etc. Labour: The second requirement is labour, i.e., people who will do the work. Different production activities require different types of workers, such as highly educated, skilled, or those doing some manual work. Each worker provides labour necessary for production. Physical Capital: The third requirement comprises various inputs required during production. It has two components. Tools, machines, and buildings fall under ‘fixed capital.’ They can be used in production for many years. Raw materials and money in hand are called working capital. These are used up in production. Human Capital: The fourth requirement is human capital. Knowledge and enterprise must combine land, labour, and physical capital to produce an output.
Question: Define Green Revolution. How is Green Revolution different from traditional farming?
Answer: The large increase in agriculture production after 1967-68 resulted from adopting a new agriculture strategy that implied a simultaneous use of better and modem agriculture inputs. Green Revolution involves the introduction of high-yielding varieties of seeds. It also encompasses using fertilizers and irrigation techniques that increase production and make countries like India self-sufficient in food grains. So, this technique is mainly used to improve the status of agriculture. It was brought to India by the initiative of the Indian government. Dr. Norman Borlaug brought high-yielding wheat to India. M.S. Swaminathan and his team also contributed to the success of the Green Revolution in India. The main regions where Green Revolution was started are Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
Difference between Green Revolution and Traditional Farming: Green Revolution refers to using artificial fertilizers and technology and high yielding a variety of genetically engineered seeds. Traditional farming emphasizes the use of natural seeds and fertilizers.
Until the mid-1960s, the cultivated seeds were traditional ones with relatively low yields. Traditional seeds needed less irrigation. Farmers used cow dung and other natural manure as fertilizers. All these were readily available to the farmers who did not have to buy them. The Green Revolution in the late 1960s introduced the Indian farmer to cultivate wheat and rice using High Yielding Varieties (HYVs) of seeds. Compared to the traditional seeds, the HYV seeds promised to produce much greater amounts of grain on a single plant. As a result, the same piece of land would now produce far larger quantities of foodgrains than was possible earlier. HYV seeds, however, needed plenty.
Question: Describe the significance of the Green Revolution in the Indian economy.
Answer: The Green Revolution has two types of effects on the Indian economy, namely
(i) Economic Effects:
Increase in Agricultural Production and Productivity: Due to the adoption of HYV technology, the production of foodgrains increased considerably in the country. The wheat production increased from 8.8 million tonnes in 1965-66 to 184 million tons in 1991-92. The productivity of other food grains has increased considerably. It was 71% for cereals, 104% for wheat, and 52% for paddy over the period 1965-66 and 1989-90. Employment: The new agricultural technology has created more employment opportunities in the agricultural sector. The new technology is early maturing and makes multiple cropping possible. Market Orientation: The new technology has made the farmer market-oriented. Due to excess production, the farmers have to go to the market to sell their surplus production.
(ii) Sociological Effects:
Personal Inequalities: Due to Green Revolution, the income of rich farmers increased considerably, whereas the poor farmers couldn’t reap any benefit. This led to a class conflict between the rich and the poor farmers. The small and marginal farmers were deprived of the gains of new technology. Regional Inequality: The new technology was successfully implemented in the wheat-producing belt of the country, whereas the rice-producing zones were not at all affected by this Green Revolution. Hence, the disparity between the two regions increased considerably. Further Green Revolution became successful in irrigated areas whereas, in the rained belt, the new technology couldn’t be implemented appropriately.
Question: Where and why has the Green Revolution started in India? Give advantages and disadvantages of the Green Revolution.
Answer: Green Revolution involves the introduction of high-yielding varieties of seeds. It also encompasses fertilizers and irrigation techniques that increase production and make countries like India self-sufficient in foodgrains. So, this technique is mainly used to improve the status of agriculture. It was brought to India by the initiative of the Indian government. Dr. Norman Borlaug brought high-yielding wheat to India.
M.S. Swaminathan and his team also contributed to the success of the Green Revolution in India. Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh are; the main regions where the green Revolution was started.
Advantages / Merits of Green Revolution:
- The HYV seeds produce a much greater amount of grains in comparison to the normal seeds.
- It has increased the production on the same pieces of land, which produces large quantities of food grains than it was produced earlier.
Disadvantages / Demerits of Green Revolution:
- Poor farmers are unable to afford HYV seeds, fertilizers, and machinery.
- This may lead to an end with large debts.
- HYV seeds need more fertilizers and water, and they are expensive.
- Since Green Revolution introduced new machinery, it replaced labour, leading to unemployment and rural-urban migration.
- It was limited to rice and wheat only.
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.
- No category
Ch- 1 Source based questions eco
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur. This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper caste families own the majority of land ...
The Test: The Story of Village Palampur- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions questions and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus.The Test: The Story of Village Palampur- Assertion-Reason & Case Based Questions MCQs are made for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples ...
Important Questions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur. The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions. Question 1. ... It was 71% in case of cereals, 104% for i wheat and 52% for paddy over the period 1965-66 and 1989-90. ...
Answer: (a) Farming at Palampur: Farming is the main activity in village Palampur. Land area available for farming is fixed. Expansion in production is done due to methods of multiple cropping and use of modern farming methods. (b) Dairy farming: Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur.
14. Name the main and other activities of the village of Palampur. Answer: Farming is the main activity in Palampur. Other activities are small -scale manufacturing, dairy, transport, etc. They also have small shops selling a wide range of items like rice, wheat, sugar, tea, oil, biscuits, soaps, etc. 15.
The solutions help students apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios by using the fictional village of Palampur as a case study, making learning more relatable and engaging. Economics class 9, chapter 1 offers well-structured answers to textbook questions, which are beneficial for exam preparation.
Free Question Bank for 9th Class Social Science The Story of Village Palampur Case Based (MCQs) - The Story of Village Palampur. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 . Railways; ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Rajasthan State Exams ; Videos Sample Papers Study Packages Question Bank Online Test
Chapter 1 Class 9 Economics - The Story of Village Palampur. Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ... Learn Maths, Science, GST and Finance at Teachoo. Important. Teachoo Ad free version. Maths 1-to-1 Classes. Skillistan. GST Simulation Portal. Sample Paper Solutions.
Answer: (a) Palampur is a small village with 450 families and there is not a big demand for jaggery there. (b) Shahpur is a town where people come from different surrounding villages to buy things and there is more demand of jaggery there, so Mishrilal sells his jaggery traders in Shahpur and not in his village. Let's Discuss Page No. 12.
rity of the landless farmers are Dalits. In Palampur, there are 60 families of medium and large farmers wh. cultivate more than 2 hectares of land. A few of the large farmers have. 10 or more hectares. CASE STUDY- I Taking the case of Gobind, who started farming with 2.25 hectares of unirrigated land, managed to feed his family with a little bit.
NCERT Solutions for Economics, Chapter 1 - The Story of the village Palampur Intext Questions Page 3 Question 1. The following table 1.1 shows that the land under cultivation in India in units of million hectares. Plot this on the graph provided. (i) What does the graph show? (ii) Is it important to increase the […]
Economics Class 9 Ncert Solutions Chapter 1 The story of village Palampur. Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Question-1. Modern farming methods require more inputs, which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree? Solution: No doubt, modern farming requires more inputs than traditional farming.
Farm workers at Palampur village get lower wages than the minimum wages fixed by the government. The minimum wages for a farm labourer is fixed at Rs 115 per day. But farm labourers get only Rs 70 - 80. This happens because of heavy competition for work among the farm labourers at Palampur village. 8.
Q.6. Assertion: Palampur has a well-developed irrigation system. Reason: The village is located near a perennial river, and the farmers use tube wells for irrigation. Show AnswerAnswer: (C) The assertion is true, but the reason is false. Palampur does not have a well-developed irrigation system.
The Story of Village Palampur 1 Chapter Picture 1.1 Scene of a village * The narrative is partly based on a research study by Gilbert Etienne of a village in Bulandshahr district in Western Uttar Pradesh. 2015-16. 2 Economics Organisation of Production The aim of production is to produce the
Chapter 1 of CBSE Class 9 Economics introduces some basic concepts relating to production, and this is done through a story of a hypothetical village called Palampur, where farming is the primary activity. Other activities such as small scale manufacturing, dairy, transport, and so on are also carried out on a limited scale. From this chapter, students learn how various resources combine to ...
Read and download free pdf of Class 9 Social Science The Story of Village Palampur Exam Notes. Students and teachers of Class 9 Social Science can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 9 Social Science prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 9 ...
The Story of Village Palampur Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Practice TestsTimed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: Instructions. Keep paper and pencil ready but keep your books away. Click the "Begin Test" button to start the test.
Students need to follow some given steps to attempt the The Story of Village Palampur Class 9 MCQ, steps are discussed below: Visit the Selfstudys website. Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar/ button. A drop down menu will appear, select MCQ Test from the list. New page will appear, select Class 9th from the ...
Economics - Chapter 01 The Story of Village Palampur (Only for Periodic Assessment) SUBJECT: SOCIAL SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 40 CLASS : IX DURATION : 1½ hrs ... SECTION - E (Case Study Based Questions) Questions 18 carry 4 marks each. 18. The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want. There are four
Chapter 1 of NCERT Economics book, The Story of Village Palampur is used as a medium to teach students how the production of crops and other non-farm activities takes place in villages. The need for capital and human power for the production of various products has also been discussed in detail in this chapter. Students will also study: 1.
For easy reference, a PDF of Important Question for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur is made available here. Students can download this PDF for free and get started with their exam preparation. Also Enhance your knowledge with CBSE notes class 9 and syllabus for Class 9. Don't Miss:
ManavRachna International School Session: 2021 - 22 Economics(Objective) Ch- The story of village palampur SOURCE BASED QUESTIONS 1. The new ways of farming need less land, but much more of capital. The medium and large farmers are able to use their own savings from production to arrange for capital during the next season.
The Story of Village Palampur - Important Questions | Class 9 Economics - Toppers Study. CBSE board students who preparing for class 9 ncert solutions maths and Economics solved exercise chapter 1. The Story of Village Palampur available and this helps in upcoming exams 2024-2025. You can Find Economics solution Class 9 Chapter 1.