- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course

Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
- NCERT Questions
- Teachoo Questions
What is Photosynthesis?
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo
Green plants make their own food (Carbohydrates) from Carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. This process is called photosynthesis

Steps of Photosynthesis
- Leaves have tiny pores called stomata .
- These help take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen .
- Green leaves have a colour pigment called chlorophyll .
- It helps to capture the sunlight .
- The chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, sunlight and water help to synthesise food . This process is called photosynthesis
- Since sunlight is required for the process, it only occurs during the day .

Maninder Singh
CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years and a teacher from the past 18 years. He teaches Science, Economics, Accounting and English at Teachoo
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
Class Notes
Free Class Notes & Study Material
Photosynthesis
Last Updated on July 3, 2023 By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
Question 1 Define the term nutrition?
Question 2 Name any two modes of nutrition?
Question 3 Name the pores through which leaves exchange gases?
Question 4 What is photosynthesis?
Question 5 Why do organisms need food?
Question 6 Why green plants are called autotrophs?
Question 7 Name the green pigment present in the leaves of plants?
Question 8 “Human being cannot make their own food”? Explain?
Question 9 Why animals are called as heterotrophs?
Question 10 Explain the process of synthesis of food in green plants?
Question 11 State the conditions necessary for the process of photosynthesis to take place?
Question 12 What is the role of chlorophyll in green plants?
Question 13 Explain how the plants obtain Carbon Dioxide for making food by photosynthesis?
Question 14 Explain how, water and minerals are transported to the leaves of a plant to be used in food making by photosynthesis?
Question 15 What is the role of sunlight in photosynthesis?
Question 16 What is the importance of photosynthesis in life?
Question 17 Name foods made by plants which are important part of our diet?
Question 18 Why are algae green?
Question 19 Why leaves of certain plants are coloured?
☛ Also Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants
- 1 Nutrition
- 2.1 Autotrophs: Autotrophic Mode of Nutrition
- 2.2 Heterotrophs: Heterotrophic Mode of Nutrition
- 3 Photosynthesis
- 4 Conditions necessary for Photosynthesis
- 5 Leaves of Various Colours
- 6 Photosynthesis by Algae
- 7.1 (1) Plants Make Starch as food
- 7.2 (2) Plants Make Oils (or Fats) as Food
- 7.3 (3) Plants make Proteins as Food
- 7.4 (4) Plants make Vitamins as Food
- 8 Importance of Photosynthesis
The organisms need to take food
(1) To obtain energy (2) To obtain materials for growth and (3) To obtain materials for the repair of damaged parts of the body.
The process of taking food by an organism as well as the utilisation of this food by the organism is called Nutrition.
Plants can make their own food but animals can not make food themselves. Human beings and animals depend on plants for their food, directly or indirectly.
Modes of Nutrition
The methods of obtaining food are called modes of nutrition. On the basis of their modes of nutrition, all the organisms can be divided into two main groups:
(1) Autotrophs (2) Heterotrophs
Autotrophs: Autotrophic Mode of Nutrition
Those organisms which can make food themselves from simple substances (like carbon dioxide and water) by the process of photosynthesis, are called autotrophs (and their mode of nutrition is called autotrophic).
All the green plants are autotrophs because green plants can make their own food from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water present in their surroundings by the process of photosynthesis.
Autotrophs contain a green pigment called chlorophyll which helps them make food by absorbing energy from sunlight. The green plants produce food for non green plants as well as for animals.
Our body cannot make food from carbon dioxide and water present around us by the process of photosynthesis (like plants do) because our body does not have the green pigment called
chlorophyll. The green pigment chlorophyll is necessary to absorb energy from sunlight required for making food by photosynthesis.
Heterotrophs: Heterotrophic Mode of Nutrition
Those organisms which can not make food themselves by the process of photosynthesis and take food from green plants or animals, are called heterotrophs (and their mode of nutrition is called heterotrophic). All the non green plants and animals (including human beings) are heterotrophs. The non green plants called fungi are heterotrophs.
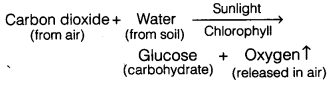
Photosynthesis
The plants use the energy in sunlight to prepare food in the presence of a green colour matter called “chlorophyll” present in the leaves of a green plant.
The process by which green plants make their own food (like glucose) from carbon dioxide and water by using sunlight energy (in the presence of chlorophyll) is called photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
The process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of a plant. Oxygen gas is produced during photosynthesis which is utilised by all the living organisms for their survival.
(1) The process of photosynthesis first produces a simple carbohydrate called ‘glucose’ as food.
(2) The glucose carbohydrate then gets converted into a complex carbohydrate called Starch.
(3) Starch gets stored as food in the various parts of plant including leaves.
(4) Some of the glucose is also converted into other types of plant foods such as fats and oils, proteins as well as vitamins.
(5) The synthesis of food (or making of food) occurs in the leaves of a plant, so leaves are the food factories of a plant. The leaves of a plant can synthesise food because they contain a green pigment chlorophyll (which is necessary for making food). Other parts of a plant usually cannot synthesise food because they do not contain chlorophyll.
Conditions necessary for Photosynthesis
The presence of carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight is necessary for the process of photosynthesis to take place.
(1) How the plants obtain Carbon Dioxide for photosynthesis – The plants take carbon dioxide gas from air through the tiny pores (called stomata) present on the surface of leaves. Each pore is surrounded by a pair of guard cells. The opening and closing of stomatal pores in the leaves is controlled by the guard cells. The carbon dioxide gas present in air enters the leaves of a plant through the stomatal pores present on their surface and utilised in photosynthesis. The oxygen gas produced in the leaves during photosynthesis goes out into air through the same stomatal pores. The stomatal pores of leaves during photosynthesis goes out into air through the same stomatal pores. The stomatal pores of leaves open only when carbon dioxide is to be taken in or oxygen is to be released otherwise they remain closed.
(2) How the plants obtain water for photosynthesis – Water present in the soil is absorbed by the roots of a plant and then transported to the leaves through the vessels which run like inter-connected pipes throughout the roots, stem, branches and leaves. The tiny, pipe-like vessels which transport water from the roots of a plant to its leaves are called xylem.
The plants also need minerals to make foods other than carohydrates. The minerals dissolve in water present in the soil and get transported with it. Water and minerals present in the soil are absorbed by the roots of a plant and transported to its leaves through interconnected pipe like xylem vessels present throughout the roots, stem, branches and leaves of the plant.
(3) Role of chlorophyll in Photosynthesis – It is the presence of chlorophyll which makes the leaves look green. Chlorophyll can absorb the energy from sunlight. The sunlight energy absorbed by chlorophyll is used to combine carbon dioxide and water in the green leaves to produce food. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and supplies this energy to the leaves to enable them to carry out photosynthesis for making food. Chlorophyll is present in every leaf of a plant in the form of hundreds of tiny structures called chloroplasts.
(4) The role of Sunlight in photosynthesis – The sunlight supplies energy for the food making process called photosynthesis. The sun’s energy is captured by plant leaves with the help of chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy of food. This chemical energy gets stored in the form of plant food. So, when plants utilise the food made by photosynthesis, they actually use the solar energy stored in it in the form of chemical energy. Since all the food on this earth is made by utilising solar energy, therefore, sun is the ultimate source of energy for all the living organisms.
Leaves of Various Colours
Most of the plants have green coloured leaves. Some of the plants, however, have leaves of other colours such as red, violet, brown etc. The leaves having colours other than green also have chlorophyll in them. Actually, the large amount of red, violet, brown or other pigments in such leaves masks the green colour of chlorophyll. So, photosynthesis also takes place in leaves having colour other than green.
Photosynthesis by Plant Parts Other Than Leaves
In some plants, photosynthesis also takes place in other parts of plants such as “green stems” and “green branches. The green stems and green branches can do photosynthesis because they contain chlorophyll.
For example: The desert plants such as cactus have tiny, spine-like leaves to reduce the loss of water by transpiration. These tiny, spine-like leaves of a cactus plant cannot do photosynthesis. The stem and branches of a cactus plant are green which contain chlorophyll . So, the green stem and green branches of a cactus plant carry out the process of photosynthesis to make food for the plant.
Photosynthesis by Algae
We see patches of slimy, green layer floating on the surface of a pond or lake, or even in the stagnant parts of a river. This green layer is formed by the growth of tiny green plant-like organisms called algae .
Algae are a large group of simple, plant-like organisms. Algae contain chlorophyll and produce food by photosynthesis just like plants. Algae differ from plants because they do not have proper roots, stems and leaves. The green colour of algae is due to the presence of chlorophyll in them.
Synthesis of Food other than simple carbohydrate
The simplest food synthesised by the plants by photosynthesis is, a simple carbohydrate called glucose.
The glucose carbohydrate is made up of three elements : carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The plants use the simple carbohydrate glucose to make many other foods such as starch, oils (or fats), proteins and vitamins.
(1) Plants Make Starch as food
Some of the simple carbohydrate glucose made by the plants through photosynthesis is converted naturally into a complex carbohydrate called starch. The starch is a food which is stored in various parts of a plant such as roots, stems, leaves and seeds.
The seeds or grains of wheat and rice have a lot of starch in them. Potato and carrot plants store a lot of starch in their roots.
(2) Plants Make Oils (or Fats) as Food
Certain plants convert the simple carbohydrate glucose made during photosynthesis into oils and store them in their seeds. Such seeds are called oil-seeds and give us oil (or fats) for cooking food.
For example: the seeds of sunflower plant contain a lot of oil stored in them.
We can extract oil from sunflower seeds and use it as a food. The oils obtained from plant seeds are commonly known as vegetable oil.
(3) Plants make Proteins as Food
Plants combine some of the glucose carbohydrate made during photosynthesis with nitrate minerals(obtained from soil) to make amino acids which are then made into proteins. In this way, plants make proteins as food.
Proteins are nitrogenous substances which contain nitrogen element
Nitrogen element is present in abundance in air in the form of nitrogen gas. However, the plants cannot absorb nitrogen gas for their needs. The soil has certain bacteria which convert nitrogen gas of air into nitrogen compounds (like nitrates) and release them into soil. Nitrates are the water soluble nitrogen compounds which are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water. The plants fulfill their requirement of nitrogen. The plants also obtain nitrogen from the nitrogen fertilisers.
(4) Plants make Vitamins as Food
Vitamins are made by plants. Vitamins are contained in vegetables, fruits and cereals made by plants.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is important for the existence of life on this earth.
(1) Photosynthesis by plants provides food to animals (including human beings): The survival of animals (including human beings) depends on the food made by plants by photosynthesis. In the absence of photosynthesis, there would be no plants on this earth and hence no animals will survive.
(2) The process of photosynthesis by plants puts oxygen gas into the air:
It is this oxygen gas which the animals (including human beings) use for breathing and respiration. In the absence of photosynthesis, there would be no oxygen in air and hence no animals could exist on this earth.
About Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
Author of this website, Mrs. Shilpi Nagpal is MSc (Hons, Chemistry) and BSc (Hons, Chemistry) from Delhi University, B.Ed. (I. P. University) and has many years of experience in teaching. She has started this educational website with the mindset of spreading free education to everyone.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
NCERT Books

NCERT Books for Class 7 Science PDF Download
NCERT Books Class 7 Science : The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) publishes Science textbooks for Class 7. The NCERT Class 7th Science textbooks are well known for it’s updated and thoroughly revised syllabus. The NCERT Science Books are based on the latest exam pattern and CBSE syllabus.
NCERT keeps on updating the Science books with the help of the latest question papers of each year. The Class 7 Science books of NCERT are very well known for its presentation. The use of NCERT Books Class 7 Science is not only suitable for studying the regular syllabus of various boards but it can also be useful for the candidates appearing for various competitive exams, Engineering Entrance Exams, and Olympiads.
NCERT Class 7 Science Books in English PDF Download
NCERT Class 7 Science Books are provided in PDF form so that students can access it at any time anywhere. Class 7 NCERT Science Books are created by the best professors who are experts in Science and have good knowledge in the subject.
NCERT Books for Class 7 Science – English Medium
- Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Solutions for class 7 Science
- Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4: Heat
- Chapter 5: Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6: Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7: Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals of Climate
- Chapter 8: Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9: Soil
- Chapter 10: Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11: Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12: Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13: Motion and Time
- Chapter 14: Electric Current and its Effects
- Chapter 15: Light
- Chapter 16: Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17: Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18: Wastewater Story
NCERT Solutions for class 7 Science PDF
NCERT Books for Class 7 Science – Hindi Medium
- अध्याय 1: पादपों में पोषण
- अध्याय 2: प्राणियों में पोषण
- अध्याय 3: रेशों से वस्त्र तकग
- अध्याय 4: ऊष्मा
- अध्याय 5: अम्ल, क्षारक और लवण
- अध्याय 6: भौतिक एवं रासायनिक परिवर्तन
- अध्याय 7: मौसम, जलवायु तथा जलवायु के अनुरूप जंतुओं द्वारा अनुकूल
- अध्याय 8: पवन, तूफ़ान और चक्रवात
- अध्याय 9: मृदा
- अध्याय 10: जीवों में श्वसन
- अध्याय 11: जंतुओं और पादप में परिवहन
- अध्याय 12: पादप में जनन
- अध्याय 13: गति एवं समय
- अध्याय 14: विधुत और इसके प्रभाव
- अध्याय 15: प्रकाश
- अध्याय 16: जल: हमारी जीवन रेखा
- अध्याय 17: वन: हमारी जीवन रेखा
- अध्याय 18: अपशिष्ट जल की कहानी
NCERT Books for Class 7 Science – Urdu Medium PDF Download
The NCERT syllabus mainly focuses on this book to make it student-friendly to make it useful for both the students and the competitive exam aspirants. The book covers a detailed Science based on the syllabuses of various boards. NCERT Science Books for Class 7 is perfectly compatible with almost every Indian education state and central boards.
We hope that this detailed article on NCERT Books Class 7 Science helps you in your preparation and you crack the Class 7 exams or competitive exams with excellent scores.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants

Science Chapter 1 - Nutrition in Plants Class 7 NCERT Solutions - FREE PDF Download
Unlock the comprehensive study with Vedantu through class 7 Science Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions. This gives access to the class 7 science chapter 1 PDF elucidating fundamental principles crucial for understanding the subject's intricacies and topics such as nutrition, stomata, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, etc.

By accessing Chapter 1 nutrition in Plants Class 7, students gain comprehensive insights into the core concepts outlined in the curriculum. With a focus on clarity and depth, these resources serve as indispensable tools for students navigating through science class 7, chapter 1. Check out the revised class 7 science syllabus and start with Vedantu to embark on a journey of academic excellence.
Glance on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1
Science ch 1 class 7 embark on a fascinating journey to understand the fundamental concepts of nutrition and its various aspects.
From Class 7 Science Chapter 1, Nutrition in Plants questions and answers, students become familiar with how plants get nutrition and how they conduct photosynthesis.
Students can access class 7 science chapter 1 PDF to resolve all their doubts about class 7 science ch 1 question answer.
This chapter deals with the process of photosynthesis, other modes of nutrition in plants, the concept of saprotrophs, and how nutrients are replenished in the soil.
Class 7th Science Chapter 1 can help students analyse their level of preparation and understanding of concepts.
In Science class 7 chapter 1, students will learn about many new topics linked to plants and how they obtain nutrition for themselves.
This chapter will cover the fundamentals of plant nutrition and how plants create their food, but reading it attentively will help students comprehend botany principles at a deeper level.
As a result, it is strongly advised that students should make notes so that they may revise them while preparing this chapter for the exam.
Access Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants NCERT Solutions
Q1. Why do organisms need to take food?
Ans:
Organism needs food to:-
Gain energy
Damage repair
Maintain bodily functions
Other activities
Q2. Distinguish between a parasite and saprophyte.
Ans: Differences between parasites and saprophytes are as follows:
Parasite | Saprophyte |
Q3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Ans: When starch reacts with an iodine solution, it takes on a characteristic dark blue colour. If a few drops of iodine solution are applied to a leaf and a dark blue colour develops, the existence of starch in the leaf is confirmed.
Q4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Ans: In green plants, the synthesis of food occurs by a process called photosynthesis. During this process, chlorophyll in the cells of the leaves uses carbon dioxide and water to synthesise carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight. The process can be represented by an equation:
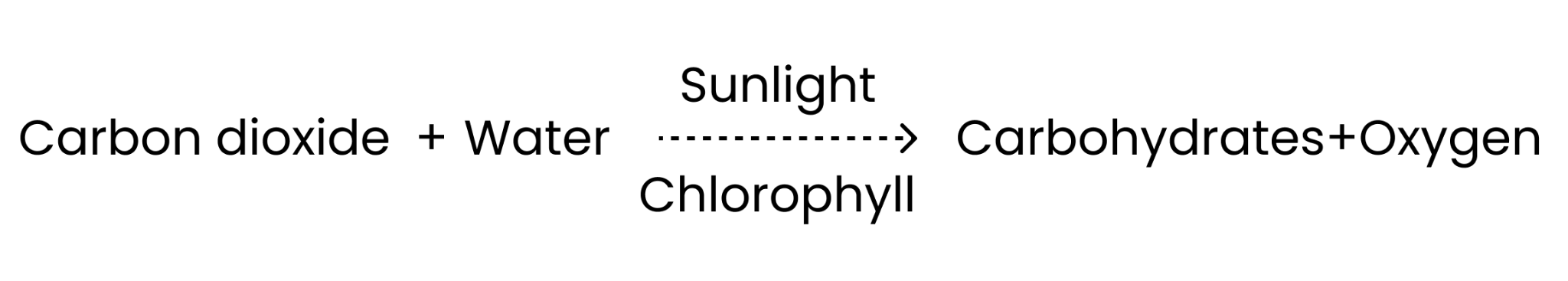
During this process, oxygen is released, and the carbohydrates generated are stored as starch.
Q5. Show with the help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food.

6. Fill in the blanks:
Green plants are called ----------- since they synthesize their own food.b. The food synthesized by the plants is stored as ---------------.
Ans: Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesize their own food.
The food synthesized by the plants is stored as ---------------.
Ans: The food synthesized by the plants is stored as starch.
In photosynthesis, solar energy is captured by the pigment called------------.
Ans: In photosynthesis, solar energy is captured by the pigment called chlorophyll.
During photosynthesis plants take in ------------- and release -------------.
Ans: During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
Q7. Name the following:
A Parasitic plant with a yellow, slender, and tubular stem.
Ans: Cuscuta- The Cuscuta plant is classified as a parasite since it lacks chlorophyll and feeds on the host. The host loses vital nutrients as a result of this process.
A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
Ans: Pitcher plant - The pitcher plant is an autotrophic plant that performs photosynthesis, but it also has a partly heterotrophic method of nutrition because it grows in nitrogen-deficient soil.
The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Ans: Stomata- Gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapour, and oxygen can diffuse into and out of the plant's interior tissues through stomata.
Q8. Tick the Correct Answer:
a. Amarbel is an example of:
Ans: (ii) Parasite-
Cuscuta or Dodder are other names for Amarbel. A parasite is an organism that grows on the body of another organism and feeds on its nutrition.
b. The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
Pitcher plant
Ans: (iii) Pitcher plant
The pitcher plant is a type of plant with trapping and digesting leaves. Medicine is made from the leaf and roots.
Q9. Match the item in given column I with those in column II.
Column 1 | Column 2 |
Chlorophyll | Bacteria |
Nitrogen | Heterotrophs |
Amarbel | Pitcher plant |
Animals | Leaf |
Insects | Parasite |
Column I | Column II |
Chlorophyll | Leaf |
Nitrogen | Bacteria |
Amarbel | Parasite |
Animals | Heterotrophs |
Insects | Pitcher plant |
Q10. Mark “T” if the statement is true and “F” if it is false:
Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Ans: False- Oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
Plants that synthesize their food themselves are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
Ans: False- Plants which synthesize their food themselves are called autotrophs.
The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
Ans : True- The product of photosynthesis is not a protein.
Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Ans: True- Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Q11. Choose the Correct Option From the Following:
Which part of the plant gets carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
Stomata
Sepals
Ans: (b) Stomata get carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.
Q12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
Roots
Ans: (d) Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their leaves.
13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large green houses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large green houses as it protects crops from external climatic conditions and provides optimal temperature for the growth of plants.
Topics Covered in Science Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants Class 7
S. No | List of Topics Covered in Science Chapter 1 Class 7 |
1 | Mode of Nutrition in Plants |
2 | Photosynthesis |
3 | Other Modes of Nutrition In Plants |
4 | Saprotrophs |
5 | How Nutrients are Replenished in the Soil |
Benefits of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants
Experts at Vedantu have made class 7 science chapter 1, nutrition in Plants, questions and answers in a simple and easy-to-understand format. Students can get the benefits given below:
Subject matter experts have designed the science ch 1 class 7 Solutions. That is why the NCERT Class 7th Science Chapter 1 Solutions can be considered the students' most comprehensive, easy-to-understand, and to-the-point study materials.
Students have the unique ability to ask experts whenever they face any problem.
Class 7 science chapter 1 PDF has arranged all the concepts and equations in a proper sequence, thus saving students time while studying.
The students are encouraged to perform several Science experiments to understand the concepts.
Since class 7 science ch 1 question answers can be downloaded, students can read and revise the concepts conveniently.
CBSE Science Class 7 Chapter 1 becomes more helpful when students plan for a quick revision before the examination.
Science class 7 chapter 1 question-answer solutions promise a significant increase in marks for the students.
Important Study Material Links for Class 7 Science Chapter 1
S. No | Study Material Links for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 |
1. |
|
2. |
|
3. |
|
Chapter 1, nutrition in Plants class 7, provides students with simple and detailed definitions and explanations of each concept covered in the chapter. Therefore, it is highly recommended that students download and refer to our comprehensive and expert-curated class 7 science chapter 1 question answer to get a gist of the chapter before the exam and to know how to answer the questions in the exam. Students can also refer to our plethora of other study resources related to this chapter, which are available for free on our website and mobile app.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Other Chapter-wise Link for FREE PDF
Dive into our collection of FREE PDF links offering other chapter-wise NCERT solutions prepared by Vedantu Experts to help you understand and master fundamental scientific concepts.
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter-wise Links |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Important Links for Class 7 Science
S. No | Important Links for Science Class 7 |
1. |
|
2. |
|
3. |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
1. Explain the process of how nutrients are replenished in the soil from class 7 science chapter 1 question answer.
The plants absorb mineral nutrients from the soil. The fertilizers and manures containing various nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus need to be added from time to time to enrich the soil. Nitrogen gas is available in large amounts but plants cannot use it directly from the air. The bacterium Rhizobium lives in the roots of the leguminous plants. Rhizobium bacteria convert the non-usable form of nitrogen. In this way, the nutrients are replenished in the soil by using fertilizers and manures, and by sowing leguminous plants.
2. Explain the mechanism of eating insects by a pitcher plant as a nutritious source related to NCERT class 7 science chapter 1
The leaves of the pitcher plants are tailored into a pitcher-like structure. The tip of the leaves forms a lid that can open and close the mouth of the pitcher-like structure of the leaves. There is hair inside the pitcher, which is directed downwards. When an insect lands in the pitcher, it gets entangled in the hair. The pitcher secretes some digestive juices that help the plant digest the insect. Such insects eating plants are insectivorous plants. These plants do not get all the necessary nutrients from the soil. So, they are called partial heterotrophs.
3. Summarize Science ch 1 class 7.
In Class 7 Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants, students are introduced to topics related to plants and how they get nutrition for themselves. The concepts covered in these topics include the photosynthesis process, chlorophyll and stomata. The chapter also teaches other modes of nutrition in insectivorous plants.
Students also learn how nutrients are replenished in the soil and how atmospheric nitrogen is fixed in the soil through a bacterium called Rhizobium.
4. Why should we grow crops inside greenhouses as described in class 7 science ch 1 question answer?
Factors like diseases, rodents, wind, and adverse climatic conditions cannot affect the crops grown in greenhouses. Therefore, growing crops in greenhouses is beneficial for the farmers in the long run.
5. How can I download the Solutions of Class 7th Science Chapter 1 NCERT?
The solutions are easily available on the Vedantu site.
Click on NCERT Solutions of Class 7 Science and choose Chapter 1.
The webpage with Vedantu’s solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 7th Science NCERT Textbook will open.
To download this, click on the Download PDF button and you can view the solutions offline.
For other solutions and concept-related modules on other topics or subjects, visit the Vedantu and go through the related modules. The solutions are free of cost and also available on the Vedantu Mobile app.
6. What do you understand about photosynthesis according to class 7 science chapter 1 question answer?
During photosynthesis, the light energy is converted into chemical energy by green plants and other organisms. Chloroplasts are tiny particles found inside plant cells that perform photosynthesis. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and water from the earth via their roots. The Sun gives out light energy. The leaves release the oxygen that has been generated into the air. Since it is an important topic, do understand it properly along with all its components such as chloroplasts and so on.
7. What are the different modes of Nutrition in Plants from Science Class 7 Chapter 1 question answer?
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 categorises plants into two main types:
Autotrophic Nutrition, in which plants can synthesise their own food using sunlight.
Heterotrophic Nutrition, in which plants cannot produce their own food and rely on other organisms for their nutritional needs.
8. How can I improve my understanding of the concepts covered in science class 7 chapter 1 question answer?
Here are some tips to solidify your understanding:
Relate to real-world examples
Perform experiments
Use diagrams and illustrations
Ask questions
Students can download and refer to class 7 science chapter 1 PDF to get all the solved answers related to this chapter.
9. What is the importance of nutrition for plants?
NCERT class 7 science chapter 1 explains the concepts related to nutrition and its importance. A few of the points to remember are:
Growth and development
Energy Production
Repair and maintenance
10. What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in plant leaves and plays a crucial role in photosynthesis by absorbing sunlight energy. To learn more about chapter 1, students can refer to class 7th science chapter 1 solutions provided by Vedantu.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Nutrition in Plants Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.

Nutrition in Plants Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Fungi is a (a) parasite (b) autotroph (c) saprotroph (d) insectivore
Answer: (c) saprotroph

Question 2. Human beings can be categorised as (a) parasite (b) heterotrophs (c) saprotrophs (d) autotrophs
Answer: (b) heterotrophs

Question 3. Human beings get food from (a) plants (b) animals (c) neither (a) or (b) (d) both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) both (a) and (b)
Question 4. Parasites obtain their food from (a) insects (b) plants (c) animals (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
Question 5. Which part of plant is called food factory? (a) Fruits (b) Seeds (c) Leaves (d) Flowers
Answer: (c) Leaves
Question 6. The green pigment that is present in the leaves are called (a) haemoglobin (b) globulin (c) albumin (d) chlorophyll
Answer: (d) chlorophyll
Question 7. Which of the following is an insectivorous plant? (a) Pitcher plant (b) Cuscuta (c) Algae (d) Lichens
Answer: (a) Pitcher plant
Question 8. Which of the following is a nutrient? (a) Fats (b) Vitamins (c) Proteins (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 9. The organisms which prepare their own food are known as (a) saprotrophs (b) autotrophs (c) heterotrophs (d) none of these
Answer: (b) autotrophs
Question 10. ________ is essential for all living organisms. (a) Protein (b) Fat (c) Food (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Food
Question 11. Photosynthesis will not occur in leaves in the absence of (a) guard cells (b) chlorophyll (c) vacuole (d) space between cells
Answer: (b) chlorophyll
Question 12. The raw materials used for photosynthesis are: (a) CO 2 , O 2 H 2 (b) CO 2 , water (c) N 2 , water (d) O 2 water
Answer: (b) CO 2 , water
Question 13. The process by which green plants prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight is called (a) saprophytic nutrition (b) photosynthesis (c) cellular nutrition (d) nutrition
Answer: (b) photosynthesis
Question 14. Ultimate source of energy is (a) chemical energy (b) wind energy (c) solar energy (d) water energy
Answer: (c) solar energy
Question 15. Which one of the following is an autotroph? (a) Lichens (b) Algae (c) Fungus (d) Cuscuta
Answer: (b) Algae
Question 16. Which of the following statements is/are correct? (i) All green plants can prepare their own food. (ii) Most animals are autotrophs. (iii) Carbon dioxide is not required for photosynthesis. (iv) Oxygen is liberated during photosynthesis. Choose the correct answer from the options below (a) (i) and (iv) (b) (ii) only (c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (ii)
Answer: (a) (i) and (iv)
Question 17. Pitcher plant traps insects because it (a) is a heterotroph (b) grows in soils which lacks nitrogen (c) does not have chlorophyll (d) has a digestive system like human beings
Answer: (b) grows in soils which lacks nitrogen
Question 18. Yeast, mushroom and bread-mould are (a) autotrophic (b) insectivorous (c) saprophytic (d) parasitic
Answer: (c) saprophytic
Question 19. Numerous small openings observed under the lower surface of a leaf through a magnifying lens are: (a) stomata (b) lamina (c) midrib (d) veins
Answer: (a) stomata
Question 20. When two organisms are good friends and live together and they benefit each other. Such an association of organisms is termed as (a) saprophyte (b) parasite (c) autotroph (d) symbiosis
Answer: (d) symbiosis
Question 21. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere generally through (a) flowers (b) stem (c) root (d) leaves
Answer: (d) leaves
Question 22. Insectivorous plants are found in (a) marshy areas (b) deserts areas (c) aquatic areas (d) mesophytes
Answer: (a) marshy areas
Question 23. Which one of the following is an autotrophic organism? (a) Mango (b) Dog (c) Human (d) Cuscuta
Answer: (a) Mango
Question 24. Guard cell in dicots are (a) dumbbell-shaped (b) biconcave (c) biconvex (d) bean-shaped
Answer: (d) bean-shaped
Question 25. All animals are dependent on plants for (a) food (b) water (c) minerals (d) fat
Answer: (a) food
Question 26. The study of the role of different components of the diet of living organism is called (a) science of nutrition (b) science of diet (c) science of food (d) science of minerals
Answer: (a) science of nutrition
Question 27. Most of the plants are (a) omnivores (b) herbivores (c) heterotrophs (d) autotrophs
Answer: (d) autotrophs
Question 28. Photosynthesis occurs only in (a) green plants (b) fungi (c) all plants (d) aquatic plants
Answer: (a) green plants
Question 29. Which one of the following is an omnivorous organism? (a) Lion (b) Crow (c) Horse (d) Cow
Answer: (b) Crow
Question 30. Food is used as source of (a) cohesive (b) water (c) adhesive (d) nourishment
Answer: (d) nourishment
Question 31. Opening and closing of stomata is controlled by (a) nucleus (b) accessory cells (c) stoma (d) guard cells
Answer: (d) guard cells
Question 32. Which material is not required for photosynthesis? (a) Water (b) Carbon dioxide (c) Chlorophyll (d) Oxygen
Answer: (d) Oxygen
Question 33. traps the energy from sunlight. (a) Stomata (b) Guard cells (c) Chlorophyll (d) Xanthophylls
Answer: (c) Chlorophyll
Question 34. Which of the following is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms? (a) Plants (b) Animals (c) Water (d) Sun
Answer: (d) Sun
Question 35. The substance synthesised during photosynthesis is (a) protein (b) maltose (c) fructose (d) glucose
Answer: (d) glucose
Question 36. Which one of the following is a parasite? (a) Lichens (b) Algae (c) Cuscuta (d) Fungus
Answer: (c) Cuscuta
Question 37. Pitcher plant is an example of (a) autotroph (b) heterotroph (c) saprotroph (d) partial heterotroph
Answer: (d) partial heterotroph
Question 38. Fungi can grow on (a) pickles (b) leather and clothes (c) dead and decaying matter (d) all of these
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Solar energy is stored in leaves with the help of ………………
Answer: chlorophyll
Question 2. All green plants are called ………………
Answer: autotrophs
Question 3. Plants and animals which depend on others for their food are called ………………
Answer: heterotrophs
Question 4. The ……………… help in the opening and closing of the stomata.
Answer: guard cell
Question 5. Plants can synthesise components of food other than carbohydrates such as ……………… and ……………….
Answer: proteins, fats
Question 6. In ……………… nutrition organisms prepare their food themselves.
Answer: autotrophic
Question 7. During photosynthesis plants take in ……………… and release ………………
Answer: carbon dioxide, oxygen
Question 8. The food that is synthesised by plant is stored as ………………
Answer: starch
Question 9. ……………… plants traps insect and feed on them.
Answer: Insectivorous
Question 10. ……………… feed on dead and decaying matters.
Answer: Saprotrophs
Question 11. The organisms that provides nutrients to parasitic organisms are known as ………………
Answer: hosts
Question 12. ……………. are the components of food which are essential for any organism for growth and development.
Answer: Nutrients
Question 13. ……………… derives nutrients from other organisms without benefiting them.
Answer: Parasites
Question 14. ……………… are tiny pores on the surface of leaves.
Answer: Stomata
Question 15. ……………… is a symbiotic association between an alga and a fungus.
Answer: Lichen
Question 16. In photosynthesis, solar energy is captured by the pigment called …………………….
Question 17. During photosynthesis, plants take in and release …………………….
Question 18. ……………………. in plant, take in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.
Question 19. Carbohydrates are the products of …………………….
Answer: photosynthesis
Question 20. ……………………. grow in warm and humid climate.
Answer: Fungus
Question 21. Fungi like ……………………. and ……………………. are useful.
Answer: mushroom, yeast
Question 22. The food synthesised by plants is stored as …………………….
Question 23. ……………………. are formed by a symbiotic relationship between alga and fungus.
Answer: Lichens
Question 24. Plant on which another plant grows and derives nutrients from is called a …………………….
Answer: Host
Question 25. Plants that take in living insects and digest them are called ……………………. plants.
Answer: insectivorous
True or False
Question 1. Green plants are autotrophs.
Answer: True
Question 2. Oxygen is not released during photosynthesis.
Answer: False
Question 3. Yeast and mushrooms are useful for us.
Question 4. Food is essential for all living organisms.
Question 5. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living beings.
Question 6. The cell is enclosed by a thin outer boundary called cytoplasm.
Question 7. The tiny pores on the leaves is called stomata.
Question 8. Certain fungi lives in symbiotic association with the roots of trees.
Question 9. Heterotrophs prepare their own food.
Question 10. Water and minerals are transported to the leaves by the vessels which run like pipes throughout the plant.
Question 11. The process by which plant prepare their own food with the help of sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Question 12. In the absence of photosynthesis there would not be any food.
Question 13. Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Question 14. Crop require a lot of carbohydrate to make protein.
Question 15. Plants other than green do not contain chlorophyll.
Question 16. Non-green parts of a plant can also perform photosynthesis.
Question 17. Fungi are heterotrophs.
Question 18. Mushroom is not a fungus.
Question 19. Lichens are an example of a parasite.
Question 20. Pitcher plant grows in soil deficient in nitrogen.
Question 21. Oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
Question 22. All living organisms are made up of cells.
Question 23. Rhizobium bacteria is a parasite of plants.
Question 24. Fertilisers replenish the soil with nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Question 25. Carnivores are not affected by photosynthesis in nature.
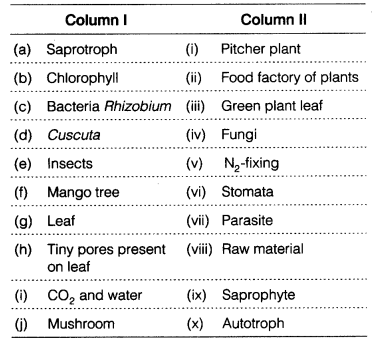
Match the Following
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Parasite | (a) green pigment in leaves |
| 2. Autotrophs | (b) proteins, vitamins, fats, etc. |
| 3. Chlorophyll | (c) prepare their own food |
| 4. Stomata | (d) depends on host |
| 5. Nutrients | (e) tiny pores on leaves |
| 6. Heterotrophs | (f) food factory |
| 7. Leaves | (g) parasitic plant |
| 8. Saprotrophs | (h) Rhizobium |
| 9. Nitrogen fixation | (i) depends on other for food |
| 10. Dodder | (j) dead and decaying matters |
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Parasite | (d) depends on host |
| 2. Autotrophs | (c) prepare their own food |
| 3. Chlorophyll | (a) green pigment in leaves |
| 4. Stomata | (e) tiny pores on leaves |
| 5. Nutrients | (b) proteins, vitamins, fats, etc. |
| 6. Heterotrophs | (i) depends on other for food |
| 7. Leaves | (f) food factory |
| 8. Saprotrophs | (j) dead and decaying matters |
| 9. Nitrogen fixation | (h) Rhizobium |
| 10. Dodder | (g) parasitic plant |
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Photosynthesis | (a) Symbiotic relationship |
| 2. Cuscuta | (b) Carbon dioxide, water |
| 3. Rhizobium | (c) Heterotrophic nutrition |
| 4. Green pigment | (d) Nitrogen fixation |
| 5. Lichen | (e) Chlorophyll |
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Photosynthesis | (b) Carbon dioxide, water |
| 2. Cuscuta | (c) Heterotrophic nutrition |
| 3. Rhizobium | (d) Nitrogen fixation |
| 4. Green pigment | (e) Chlorophyll |
| 5. Lichen | (a) Symbiotic relationship |
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
NCERT Books Class 7 Science PDF Download
NCERT Books Class 7 Science in English and Hindi Medium with NCERT solutions free pdf download . Download Science, Physics, Chemistry, Biology exam support material for the students studying in Class 7. PDF download NCERT Science books Class 7.
NCERT Books Class 7 Science Free PDF Download
PDF Download official prescribed Science Class 7 NCERT textbook below. Book based on Latest Science Class 7 Syllabus . Class VII Science, Physics, Chemistry, NCERT Biology Books are easy to understand with fundamental explanations.
NCERT Science, Physics, Chemistry, Biology Class 7 Books
Ncert science, physics, chemistry, biology class 7 books free pdf download.
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
NCERT विज्ञान, भौतिकी, रसायन विज्ञान, जीवविज्ञान Class 7th Books All Chapters in Hindi Medium
Ncert books class 7 free pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Extra Questions Science Chapter 1
June 1, 2019 by Bhagya
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. Potato and ginger are both underground parts that store food. Where is the food prepared in these plants? [NCERT Exemplar] Anwer: In both the plants, shoot system and leaves are above ground. They prepare food through photosynthesis and transport it to the underground part for storage.
Question 2. Plants prepare their food using a different mode of nutrition than us. What is it? Answer: The mode of nutrition in plant is autotrophic, i.e. they synthesise their own food.
Question 3. Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll and a few other raw materials. Add the missing raw materials to the list given below: Water, minerals, (a) …… (b) ……. Answer: (a) Sunlight (b) Carbon dioxide
Question 4. The tiny openings present on the leaf surface. What are they called? Answer: Stomata are the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves through which gaseous exchange takes place in plants.
Question 5. What is the function of guard cells of stomata? Answer: Guard cells help in controlling the opening and closing of stomata for gaseous exchange.
Question 6. Which parts of the plant are called food factories of the plant? Answer: Leaves are referred to as food factories of plants. This is because, leaves synthesise food by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 7. A carbohydrate is produced by plants as food source. It is constituted from which molecules? Answer: Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Question 8. Why do some plants feed on insects? Answer: Insectivorous plants grow in soil which lack nitrogen, therefore they eat insects to fulfill their need of nitrogen.
Question 9. Define parasites. Answer: Parasites they are those organisms which grow on other plants or animals for their food, e.g. Cuscuta.
Question 10. Name the bacteria that can fix atmospheric nitrogen. Answer: Rhizobium is the bacterium which can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 11. Except plants, why can’t other living organisms prepare their food using CO 2 , water and minerals? [HOTS] Answer: Our body does not contain chlorophyll for absorbing solar energy which is necessary for preparing food using air, water, etc.
Question 12. A leguminous plant can restore the soil’s concentration of mineral nutrients. Can you give examples of some such plants? Answer: Plants such as gram, pulses and beans are leguminous.
Question 13. Algae are green in colour. Why? Answer: Algae contain chlorophyll which imparts green colour to them.
Question 14. what do you understand by nutrition? Answer: The process of utilising nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc., to generate energy is called nutrition.
Question 15. Fungus can be harmful and useful. Give an example showing both of these traits of fungus. Answer: Fungus produces antibiotics like penicillin used to treat diseases and fungus can also harm us by causing fungal infections on skin and hair.
Question 16. A unique feature in leaves allows them to prepare the food while other parts of plants cannot. Write the possible reason for this. [HOTS] Answer: Leaves contain chlorophyll which is essential for food preparation and is absent in other parts of plant.
Question 17. Algae and fungi form a unique association sharing benefits from each other. What is the name of association between them? Answer: Lichens.
Question 18. In a plant, photosynthesis occurs in a part other than leaf. Name that plant and the part where photosynthesis occurs. Answer: Cactus, the part where photosynthesis occurs are stem and branches which are green.
Question 19. Why is Cuscuta, categorised as a parasite? Answer: Cuscuta derives its nutrition using an association where it deprives its host of all valuable nutrients and absorbs them itself. Hence, it is called a parasitic plant.
Question 20. Plant cannot use the nitrogen present in the soil directly. Why? Answer: Plants can use nitrogen only in soluble form while in soil nitrogen is present in inorganic form.
Question 21. Why are insectivorous plants called partial heterotrophs? Answer: Insectivorous plants are autotrophs, i.e. they prepare their own food. They are partial heterotrophs as they eat insects for obtaining nitrogen.
Question 22. What is the stored food form in sunflower seeds? Answer: In sunflower seeds, glucose is stored in the form of oils (fats).
Question 23. What do you understand by saprotrophic mode of nutrition? Answer: The mode of nutrition in which organisms take their nutrients from dead and decaying matter is called saprotrophic mode of nutrition.
Question 24. A mutually beneficial relationship that occurs between two plants. It is known by what name? Give an example. Answer: Symbiosis is the mutually benefitting association between two plants, e.g. lichens.
Question 25. For testing the presence of starch in leaves, a boiled leaf is used. Why? Answer: Boiling the leaf remove chlorophyll/green colour from the leaves.
Question 26. Mosquitoes, bed bugs, lice and leeches suck our blood. Can they be called as parasites? [HOTS] Answer: Yes, these animals/insects are parasites as they harm the hosts while they suck blood.
Question 27. Insectivorous plants have one or the other specialised organs to catch their prey. What is that organ? Answer: Leaves of insectivorous plants catches the prey.
Question 28. Farmers spread manure of fertilisers in the field or in gardens, etc. Why are these added to the soil? Answer: Plants absorb mineral nutrients from soil. Thus, declining their concentration in soil fertilisers and manures enhance or add these essential nutrients back in soil.
Question 29. A cell is formed of many sub-components. Identify different constituents of the cell. Are animal and plant cells similar? Answer: A cell contains nucleus, cytoplasm, vacuole, cell organelles like chloroplast, mitochondria, etc. No, animal cells are different from plant cells.
Question 30. A goat eats away all the leaves of a small plant (balsam). However, in a few days, new leaves could be seen sprouting in the plant again. How did the plant survive without leaves? [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: The plant of balsam survived on the food stored in the stem and roots.
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1. Different modes of nutrition has been observed in plants. What are they? Give example of each. Answer: Plants show two major modes of nutrition, i.e. (i) Autotrophs are those which can synthesise their own food. (ii) Heterotrophs are those which are dependent on other plants and animals for their food. They are of following types: (a) Parasites, e.g. Cuscuta (b) Saprotrophs, e.g. fungi.
Question 2. Sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water and minerals are raw materials essential for photosynthesis. Do you know where they are available? Fill in the blanks with the appropriate raw materials. (a) Available in the plant: ……… (b) Available in the soil: ……… (c) Available in the air: ……… (d) Available during day : ……… [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) Available in the plant: chlorophyll (b) Available in the soil : water, minerals (c) Available in the air : carbon dioxide (d) Available during day : sunlight
Question 3. Plants are considered an essential part of earth as they keep a check on lot of process occurring all over. What would happen if all the green plants are wiped from earth? [HOTS] Answer: Green plants are the source of energy for all the living organisms so that they can perform their normal functions. If all green plants and trees disappear, all the organism depending on them for food and shelter will also die.
The lack of gaseous exchange will lead to increase in amount of CO 2 , causing death in humans and other animals also. The cycle of life will gradually disappear.
Question 4. Autotrophs and heterotrophs are two different organisms with distinct modes of nutrition state. How are they different from each other? Answer: The difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs are as follows:
| Autotrophs | Heterotrophs |
| They can prepare their own food. | They cannot prepare their own food. |
| Autotrophs take simple inorganic substances and change it into complex organic food, e.g. green plants. | They take in complex food and breakdown it into simple compounds, e.g. all animals, fungi and non-green plants. |
Question 5. Wheat dough if left in the open, after a few days, starts to emit a foul smell and becomes unfit for use. Give reason. [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: Carbohydrates in wheat dough encourage the growth of yeast and other saprophytic fungi which breakdown carbohydrates into simpler compounds like CO 2 and alcohol and emit a foul smell.
Question 6. What are the various raw materials for photosynthesis? Answer: Plants utilise carbon dioxide from air and water and minerals are derived from soil (through roots) as raw material for photosynthesis. Besides these chlorophyll present in green leaf is necessary for the process and sunlight is the source of energy which is converted into chemical energy during the process of photosynthesis.
Question 8. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants growth. But farmers who cultivate pulses as crops like green gram, bengal gram, black gram, etc., do not apply nitrogenous fertilisers during t cultivation. Why? [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: Roots of pulses (leguminous plants) have a symbiotic association with a bacterium called Rhizobium. This bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen of air into water soluble nitrogen compounds and give them to the leguminous plants for their growth. Hence, farmers need not use nitrogenous fertilisers.
Question 9. Pooja is worried about her new shoes which she wore on special occassions that they were spoiled by fungus during rainy season. Is she right to worry, if yes, then tell why does fungi suddenly appears during the rainy season? [HOTS] Answer: Yes, the fungi reproduces by spores which are generally present in the air and grow on any article that are left in hot and humid weather for a long time. During rainy season they land on wet and warm things and begin to germinate and grow.
Question 10. In what unique manner does a pitcher plant derive its nutrition? Answer: Nepenthes or pitcher plant modifies its leaf axis into a long tubular pitcher to form a pitfall trap. Inside the pitcher sticky liquid is present. When any insect comes in contact with the leaf, the lid present on it is closed and insect is trapped. The liquid contains digestive enzymes which slowly digest the trapped insects.
Question 11. Water and minerals are absorbed by the roots and then transported to leaves. How? Answer: Water and minerals are transported to the leaves by the vessels which run like pipes throughout the root, stem, branches and the leaves. These vessels are xylem and phloem, forming a continuous path or passage for the nutrients to make them reach the leaf.
Question 12. Some plants have deep red, violet or brown coloured leaves. Can these leaves perform the photosynthesis process? [HOTS] Answer: Yes, plants having deep red, violet or brown coloured leaves can also carry out photosynthesis because they contain chlorophyll. But their green colour of chlorophyll is masked by the large amount of all other coloured pigments.
Question 13. If plant has a requirement for nitrogen, then from where will they obtain it? Answer: Soil contains nitrogen in the form that is not usable by plants. Bacteria like Rhizobium converts nitrogen into soluble form that can be easily used by plants. So, if plant has a requirement for nitrogen, then it will obtain that which the help of bacteria.
Question 14. In the absence of photosynthesis, life would be impossible on earth. Is it true or false? Answer: True, because photosynthesis is important for the existence of life on the earth. Photosynthesis is important process as it is provides food to all living organisms and maintains CO 2 – O 2 balance of nature.
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 2. Describe the method for replinishing the soils with minerals and other essential constituents used by plants growing in those soil by farmers. Answer: Replenishment of Nutrients in Soil
Crops require a lot of nitrogen to make proteins. After the harvest, the soil becomes deficient in nitrogen. Plants cannot use the nitrogen gas available in atmosphere directly. Action of certain bacteria can convert this nitrogen into form readily used by plants. Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants. These bacteria take nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and convert it into water soluble nitrogen compounds making it available to the leguminous plants for their growth.
In return, leguminous plants provide food and shelter to the bacteria as Rhizobium cannot prepare its food. They, thus have a symbiotic relationship. This association is very important for the farmers, as they do not need to add nitrogen fertilisers to the soil in which leguminous plants are grown.
Question 3. Harish went to visit his grandfather in village where he saw that his grandfather’s field of wheat are infected with fungus but no one is aware of this. Harish rushed to his grandfather’s side and told him that the field have been infected with fungi. He should use an antifungal agent in his fields to stop this infection. (a) What is fungus? (b) Can fungus only cause diseases or can it be helpful also? (c) What values are shown by Harish? [Value Based Question] Answer: (a) Fungus are saprophytic organisms usually present as spores in atmosphere which can germinate on any substrate in optimal conditions. (b) Fungus are also useful in that they produce many antibiotics which can cure different types of infections like penicillin. (c) Harish is sincere, curious and knowledgeable with a keen sense of applying it where necessary.
Question 4. Wild animals like tiger, wolf, lion and leopard do not eat plants. Does this mean that they can survive without plants? Can you provide a suitable explanation? [HOTS] Answer: Animals like tiger, wolf, lion and leopard are carnivores and do not eat plants. They hunt and eat herbivorous animals like deer, gaur, bison, zebra, giraffe, etc., which are dependent on plants for food.
If there are no plants, herbivorous animals will not survive and ultimately animals like tiger, wolf, lion and leopard will have nothing to eat.
Question 5. Asha went to visit her grandfather in his village. He was having a serious discussion with his fellow members regarding the productivity level of crops for present year. They all were worried about how to increase the productivity of crop Asha listened to this and then suggested to the group that the reason may be decreased level of minerals in soil. She told her grandfather to plant crops like pulses, gram, beans, etc., for a year then follow with regular crops. This will increase the crop productivity? (a) What will you name the process suggested by Asha? Why is there decrease in crop productivity? (b) What are noted benefits of this process? Will the results be as what Asha expressed? (c) What values are shown by Asha? [Value Based Question] Answer: (a) This process is known as crop rotation. All the plants/crops grown in soil use the minerals present in soil for their own use. This continuous usage depletes the concentration of mineral in soil. (b) After growing leguminous plants, the mineral content of soil is restored and enriched to new level. Yes, the benefit of leguminous plant is the re-enrichment of soil minerals. (c) Asha is observant, sincere and interested in applying her knowledge to situations.
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Extra Questions Miscellaneous
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Organisms which prepare food for themselves using simple naturally available raw materials are referred to as [NCERT Exemplar] (a) heterotrophs (b) autotrophs (c) parasites (d) saprophytes Answer: (b) autotrophs
Question 2. In the process of photosynthesis, which of the following energy conversions occur? (a) Solar energy is changed into chemical energy. (b) Solar energy is changed into mechanical energy. (c) Bioenergy is converted into chemical energy. (d) Chemical energy is changed into light energy. Answer: (a) Solar energy is changed into chemical energy.
Question 3. The raw material used by plants during photosynthesis (a) N 2 and O 2 (b) O 2 , H 2 and CO 2 (c) CO 2 and water (d) water and minerals Answer: (c) CO 2 and water
Question 4. Which of the following statements is/are correct? (i) All green plants can prepare their own food. (ii) Most animals are autotrophs. (iii) Carbon dioxide is not required for photosynthesis. (iv) Oxygen is liberated during photosynthesis. choose the correct answer from the options below: [NCERT Examplar] (a) (i) and (iv) (b) only (ii) (c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (ii) Answer: (a) (i) and (iv) are correct statements and (ii) and (iii) are incorrect. Because (ii) animals are heterotrophs and (iii) CO 2 is necessary for photosynthesis. Green plants prepare their own food from CO 2 and H 2 O.
Question 5. The symbiotic association is seen in which of the following? (a) Lichens (b) Algae (c) Fungi (d) Bacteria Answer: (a) Lichens
Question 6. Pitcher plant traps insects because it (a) is a heterotroph (b) grows in soils which lack in nitrogen (c) does not have chlorophyll (d) has a digestive system like human beings Answer: (b) grows in soils which lack in nitrogen
Question 7. Insectivorous plant among the following is (a) lichen (b) Cuscuta (c) pitcher plant (d) bread mould Answer: (c) pitcher plant
Question 8. In the plant of cactus leaves are modified into (a) branches (b) spines (c) leaf vein (d) pitcher Answer: (b) spines
Question 9. If iodine is dropped on the boiled leaf it gives blue-black colour due to the presence of (a) starch (b) protein (c) fat (d) vitamin Answer: (a) starch
Question 10. When we observe the lower surface of a leaf through a magnifying lens, we see numerous small openings. Which of the following is the term given to such openings (a) Stomata (b) Lamina (c) Midrib (d) Veins Answer: (a) Stomata
Question 11. Two organisms are good friends and live together. One provide? shelter, water and nutrients while the other prepares and provides food. Such an association of organisms is termed as (a) saprophyte (b) parasite (c) autotroph (d) symbiosis Answer: (d) symbiosis
Question 12. In the process of photosynthesis, plants (a) take O 2 and release CO 2 (b) take CO 2 and release O 2 (c) take and release O 2 (d) take O 2 and release water Answer: (b) take CO 2 and release O 2
Question 13. Which of the following raw material is available in the air for photosynthesis? [NCERT Exemplar] (a) Oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide (c) Nitrogen (d) Hydrogen Answer: (b) Carbon dioxide
Question 14. The ultimate source of food on earth is (a) plants (b) sunlight (c) animals (d) proteins Answer: (a) plants
Question 15. Farmers use manure and fertilisers to (a) replenish plant (b) replenish soil (c) replenish air (d) replenish fungi Answer: (b) replenish soil
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. The association where two participating plants mutually benefit each other is called ……. Answer: symbiosis
Question 2. ……. plants derive their nutrient from dead and decaying animals or plants. Answer: Saprophytic
Question 3. The openings present on the surface of leaves are protected by cells called ……. Answer: guard cells
Question 4. Leaves are called the ……. of plants. Answer: food factory
Question 5. All green plants possess ……. in their leaves. Answer: chlorophyll
Question 6. Cuscuta is a ……. plant. Answer: parasitic
Question 7. The plants that provide nutrition to the parasitic plant are called ……. Answer: host
Question 1. Food is necessary for plants only. Answer: False, food is necessary for all the living organisms as all of them grow and require maintenance from time to time
Question 2. Animals are heterotrophs. Answer: True
Question 3. Cells are called building block of a body. Answer: True
Question 4. Chlorophyll is present in an animal cell. Answer: False, chlorophyll is present in leaf of plants not in animal cells.
Question 5. Fungi are green plants that can synthesise their own food. Answer: False, fungi are not green and they are not classified as plants. They are saprophytic organisms which derive nutrition from dead and decaying matter.
Question 6. Pitcher plant eats insects. Answer: True
Question 7. Lichen is a saprophytic plant. Answer: False, lichen is a symbiotic association between an alga and a fungi. It is not a plant.
Question 8. Rhizobium can fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compound. Answer: True
Match the Columns
Extra Questions for Class 7 Science
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
LIVE Course for free
- Ask a Question

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
Comprehensive Guide to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology:
Biology, the study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment, is a crucial subject in the Class 11 curriculum. The NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology provide a structured and detailed approach to understanding complex biological concepts. This article will explore the significance of these solutions, the structure of the Class 11 Biology syllabus, and how to effectively use NCERT solutions to excel in your studies.
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) books are prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and form the foundation of the Class 11 curriculum. The NCERT Solutions are meticulously crafted to provide clear and concise answers to the questions in the NCERT textbooks.
Advantages of Using NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology:
Clarity and Accuracy: The solutions are prepared by subject matter experts and provide accurate answers.
Exam-Oriented Approach: The solutions are aligned with the CBSE syllabus and exam pattern, making them an effective tool for exam preparation. They help students practice the types of questions likely to appear in the exams.
Time Management: With detailed step-by-step solutions, students can learn to solve questions efficiently, which is crucial during exams.
Self-Assessment: The solutions allow students to self-assess their understanding and identify areas that need more focus, facilitating targeted revision.
Accessibility: NCERT Solutions are readily available online, making it easy for students to access them anytime and anywhere.
Tips for Using NCERT Solutions Effectively:
Read the Textbook Thoroughly: Before referring to the solutions, ensure you have read and understood the corresponding chapters in the NCERT textbook.
Practice Regularly: Regular practice using NCERT Solutions helps reinforce learning and improves retention.
Clarify Doubts: Use the solutions to clarify any doubts and strengthen your grasp of challenging topics.
Revise Systematically: Periodic revision using NCERT Solutions can help keep the information fresh in your mind.
With just a click, you have immediate access to all the solutions and practice questions at your fingertips.
- ncert solutions
- ncert solutions class 11
- ncert solutions class 11 biology
Please log in or register to add a comment.
Please log in or register to answer this question..
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology are an invaluable resource for students aiming to excel in their studies. By offering clear explanations, practice exercises, and a structured approach, these solutions not only help in mastering the subject but also in building a strong foundation for future studies in biology. Make the most of these solutions by integrating them into your study routine and addressing any difficulties with perseverance and practice.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology:
Chapter : The Living World
Chapter : Biological Classification
Chapter : Plant Kingdom
Chapter : Animal Kingdom
Chapter : Morphology of Flowering Plants
Chapter : Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Chapter : Structural Organisation in Animals
Chapter : Cell The Unit of Life
Chapter : Biomolecules
Chapter : Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Chapter : Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Chapter : Respiration in Plants
Chapter : Plant Growth and Development
Chapter : Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Chapter : Body Fluids and Circulation
Chapter : Excretory Products and their Elimination
Chapter : Locomotion and Movement
Chapter : Neural Control and Coordination
Chapter : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Find MCQs & Mock Test
- JEE Main 2025 Test Series
- NEET Test Series
- Class 12 Chapterwise MCQ Test
- Class 11 Chapterwise Practice Test
- Class 10 Chapterwise MCQ Test
- Class 9 Chapterwise MCQ Test
- Class 8 Chapterwise MCQ Test
- Class 7 Chapterwise MCQ Test
Related questions
- chemical coordination and integration
- neural control and coordination
- locomotion-and-movement
- excretory-products-and-their-elimination
- body-fluids-and-circulation
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect: A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. Students (upto class 10+2) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam , ICSE Board Exam , State Board Exam, JEE (Mains+Advance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers by subject teachers/ experts/mentors/students.
- All categories
- JEE (36.7k)
- NEET (9.4k)
- Physics (267k)
- Chemistry (264k)
- Biology (222k)
- Mathematics (256k)
- Statistics (3.0k)
- Environmental Science (5.4k)
- Biotechnology (704)
- Social Science (126k)
- Commerce (74.9k)
- Electronics (3.9k)
- Computer (21.7k)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) (3.3k)
- Information Technology (21.5k)
- Programming (13.1k)
- Political Science (10.5k)
- Home Science (8.1k)
- Psychology (4.4k)
- Sociology (7.1k)
- English (68.1k)
- Hindi (30.8k)
- Aptitude (23.7k)
- Reasoning (14.8k)
- Olympiad (535)
- Skill Tips (91)
- RBSE (49.1k)
- General (72.9k)
- MSBSHSE (1.8k)
- Tamilnadu Board (59.3k)
- Kerala Board (24.5k)
- Send feedback
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refund Policy
- CBSE Notes For Class 7
- CBSE Class 7 Science Notes
- Chapter 1: Nutrition In Plants
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Notes - Chapter 1
Introduction to nutrition in plants, living and non-living organisms.
- Living organisms like human beings, plants and animals need food to survive and exist.
- Living organisms reproduce, respond to the environment and also adapt.
- Living organisms respire and excrete as well.
Cells are tiny units that help make up a living organism. Hence, they are also called building blocks of an organism.
- A cell is constituted of three major parts :
- A thin outer layer is called the cell membrane .
- A spherical structure located at the centre of the cell is called a nucleus .
- A jelly-like substance that surrounds a nucleus called the cytoplasm .
To know more about Cell, visit here .
Single and Multi-Cellular Organisms
- Organisms that are made up of just one cell are called single-celled or Unicellular organisms. E.g. Amoeba
- Organisms with more than one cell in their body are called multicellular organisms.
- All human beings, plants and animals are multicellular organisms.
To know the difference between Unicellular and Muti-Cellular Organisms, visit here .
Nutrition is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
- Nutrition is very important as the nutrients from the food consumed enable living organisms to build their bodies and grow.
- Nutrition helps to repair damaged parts and organs.
- Nutrition also provides energy for carrying out various functions.
For more information on How Plants Get Their Nutrition, watch the below video

To know more about Nutrition, visit here .
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Organisms that make food themselves are called autotrophs .
- Plants are an example of autotrophs as they make their own food using carbon dioxide, water and light energy.
Organisms that rely on others and usually take in ready-made food made by the autotrophs are called heterotrophs.
- Animals and human beings are an example of heterotrophs as they depend on plants in many ways for their food.
To know the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs, visit here .
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process of synthesis of food by green plants.
- This process usually takes place in the leaves of plants.
- The process requires chlorophyll (green-coloured pigment), sunlight, carbon dioxide and water.
For more information on Photosynthesis, watch the below videos:

To know more about Photosynthesis, visit here .
- Organelles are tiny cellular structures inside a cell and perform specific functions that are important for the cell.
- They are found in the cytoplasm of a cell.
- E.g. Chloroplast is the cell organelle that carries out photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts
- The chloroplast is a type of organelle that exists in plants.
- These organelles contain chlorophyll , the green-coloured pigment that is responsible for carrying out the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Chlorophyll
- Chlorophyll is the pigment that is responsible for the synthesis of food in green plants.
- This pigment green colour to its bearers and is abundantly found in leaves.
- Chlorophyll is locked inside the chloroplast.
Process of Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves, the “food factory” of the plants.
- Carbon dioxide is taken in through tiny pores on the leaves called stomata.
- Water and minerals that are required for the process are transported to the leaves from the roots through the stem.
- Chlorophyll helps the leaves use the energy from the sunlight to prepare food using carbon dioxide, water and minerals.
- Oxygen is released as a by-product of this process.
- The equation can be given as follows:
To know more about Photosynthesis Process, visit here .
Nutrients Being Replenished in Soil
- Plants absorb mineral nutrients from the soil in order to make their own food and for other important processes.
- Soils need to be enriched with nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium etc regularly.
- Only then can we grow plants and keep them healthy.
- There are 17 most important nutrients for plants.
- 6 are called macronutrients, and the rest are called micronutrients.
- Macronutrients are required in large quantities, while micronutrients are required in very small quantities.
To know more about Soil Fertility: Replenishment of Nutrients, visit here .
Other Modes of Nutrition
Symbiotic relationship.
Organisms that live together and share their shelter and nutrients are said to be in a symbiotic relationship.
- Certain fungi live in the roots of trees.
- The tree provides nutrients to the fungus and, in return, receives help from it to take up water and nutrients from the soil.
- This association works well for both the fungi and the tree.
- Another common example is Rhizobium bacteria .
- They reside in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
- The bacteria provide a plant with nitrogen that they fix, and in turn, they get shelter and food from the plant.
- Rhizobium is a type of bacteria that converts atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form that can be utilised by plants (nitrogen fixation) .
- It usually resides in the roots of leguminous plants like peas, gram, moong etc., and is instrumental in providing these plants with a rich source of nitrogen.
To know more about Rhizobium, visit here .
Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen is an important nutrient required for soil and for plants.
- However, nitrogen in the atmosphere is not easily accessible.
The process by which nitrogen is converted into a form that can be used by plants and other living organisms is called nitrogen fixation .
To know more about Nitrogen Fixation, visit here .
A parasite is a heterotroph that completely depends on another organism for its food.
- The organism to which the parasite latches onto is called the host .
- The host, in the process, is deprived of all nutrients for its own growth as they are consumed by the parasite.
- For example, Cuscuta (Amarbel) is a nongreen plant that takes readymade food from the plant on which it is growing.
To know more about Parasites, visit here .
Saprotrophs
Organisms which rely on dead and decaying matter for their food are called Saprotrophs .
- This mode of nutrition is called saprotrophic nutrition .
- For example, Fungi.
- Fungi secrete digestive juices on the dead and decaying matter and convert it into a solution.
- Then they absorb the nutrients from it.
To know the difference between Parasites and Saprotrophs, visit here .
Insectivorous Plants
Plants that feed on insects are called Insectivorous plants.
- These plants are green and carry out photosynthesis.
- But, they grow in nitrogen-deficient soils.
- So, in order to get nitrogen, they feed on insects.
- These insectivorous plants have their parts modified for attracting and catching insects.
- For example, The pitcher plant, Venous flytrap
To know more about Insectivorous plants, visit here .
Did You Know?
Cactus plants.
- Most of the photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of green plants.
- However, in the case of some desert plants, it takes place in their stem and even branches.
- Cacti are found in the desert, and their leaves are modified to spines to avoid loss of water due to transpiration.
- Therefore, their green stems enable them to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
What are micronutrients.
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals required by the plant in very small amounts.
What is nutrient density?
The nutrient density of a food is the ratio of beneficial ingredients to the food’s energy content for the amount that is commonly consumed.
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients are vitamins and minerals required by the plant in large amounts.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It resembles roughly the absorption spectra of chlorophyll a and b (discussed in section 13.4). By the middle of the nineteenth century the key features of plant photosynthesis were known, namely, that plants could use light energy to make carbohydrates from CO and water. The empirical equation. 2.
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide. 3,12,343.
If there is any trouble in grasping the topics related to Science, students can refer to the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions covered in CBSE Class 7 Science. Students can check out chapter-wise solutions from the links given below: Chapter 1 - Nutrition in Plants. Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals. Chapter 3 - Heat.
Chapter 1 Class 7 - Nutrition in Plants. Green plants make their own food (Carbohydrates)from Carbon dioxideandwaterin the presence ofsunlightandchlorophyll.This processis calledphotosynthesisSteps of PhotosynthesisLeaves havetiny pores called stomata.These helptake in carbon dioxideandgive out oxygen.Green leaves have acolour pigment calle.
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen. The process of photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of a plant. Oxygen gas is produced during photosynthesis which is utilised by all the living organisms for their survival. (1) The process of photosynthesis first produces a simple carbohydrate called 'glucose' as food.
This solution also covers questions on the mode of nutrition in saprophytes, which proves to be an extension of learning nutrition in different organisms. Sub-topics of Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants. 1.1 - Mode of Nutrition in Plant. 1.2 - Photosynthesis - Food Making Process in Plants. 1.3 - Other Modes of Nutrition in ...
NCERT, Sri Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi-110016. [email protected]. +91 8800440559
Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants. NCERT Solutions for class 7 Science. Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals. Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4: Heat. Chapter 5: Acids, Bases and Salts. Chapter 6: Physical and Chemical Changes. Chapter 7: Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals of Climate. Chapter 8: Winds, Storms and Cyclones.
Students can access class 7 science chapter 1 PDF to resolve all their doubts about class 7 science ch 1 question answer. This chapter deals with the process of photosynthesis, other modes of nutrition in plants, the concept of saprotrophs, and how nutrients are replenished in the soil. Class 7th Science Chapter 1 can help students analyse ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science. Please go throrugh the list of chapters and click on the desired chapters. Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants. Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Heat. Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts. Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes. Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals ...
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science with Answers on ... Photosynthesis will not occur in leaves in the absence of (a) guard cells (b) chlorophyll (c) vacuole (d) space between cells ...
2. drive the processes leading to the synthesis of food, more accurately, sugars. This is the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis. This process does not directly depend on the presence of light but is dependent on the products of the light reaction, i.e., ATP and NADPH, besides CO 2 and H2O.
Q.7. Name the following: (i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and tubular stem. (ii) A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition. (iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases. Ans. (i) cuscuta (ii) Insectivorous plant (iii) Stomata. Q.8. Tick the correct answer:
Take two strips of black paper and cut out a small square in the centres. Cover a part of two leaves with these papers and secure them with paper clips (Fig. 1.9). Keep the plant in sunlight for 2-5 days. Observe the difference in the colour of the covered and the uncovered portions on the leaf.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants. Multiple Choice Questions. Question 1. Organisms which prepare food for themselves using simple naturally available raw materials are referred to as. (a) heterotrophs. (b) autotrophs. (c) parasites. (d) saprophytes.
Solution: (a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their food. (b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as starch. (c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll. (d) During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen gas. 7.
NCERT Science, Physics, Chemistry, Biology Class 7 Books Free PDF Download. Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants. Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Heat. Chapter 5 Acids Bases and Salts. Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes. Chapter 7 Weather Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate.
Learning Outcomes already developed by the NCERT across classes had been taken into consideration in this exercise. Contents of the textbooks had been rationalised in view of the following: Content based on genres of literature in the textbooks and supplementary readers at different stages of school education ;
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science Extra Questions Long Answer Type. Question 1. Describe the process by which plants prepare their food using different raw materials. Answer: The process by which green plants can prepare their own food is called photosynthesis. Green plants possess chlorophyll in their leaf and utilises carbon dioxide (from ...
CBSE Class 11 Biology 2025 Deleted Syllabus: This is the 2024-25 academic year, and it's been a long time since CBSE has reduced its syllabus by approximately 30% (not for all subjects). Following ...
Comprehensive Guide to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology: Biology, the study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment, is a crucial subject in the Class 11 curriculum. The NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology provide a structured and detailed approach to understanding complex biological concepts. This article will ...
The NCERT Class 7 Books provide students with the best study resource for exam preparations, and they can score good marks in the annual examinations by referring to them. Moreover, these NCERT books can be used for a thorough understanding of topics and concepts which are covered under the syllabus of CBSE. We, at BYJU'S, provide NCERT Books for CBSE Class 7 for all subjects.
The food passes through a continuous canal (Fig. 2.2) which begins at the buccal cavity and ends at the anus. The canal can be divided into various compartments: (1) the buccal cavity, (2) foodpipe or. oesophagus, (3) stomach, (4) small intestine, (5) large intestine ending in the rectum and (6) the anus.
The Class 7 Science NCERT Solutions for Chapter 17 are provided here for the students to learn the concept covered in this chapter in an interactive manner. The solutions are prepared by expert teachers in a unique manner to help students understand the concepts easily. NCERT Solutions will help students to get familiar with the exam pattern ...
Plants absorb mineral nutrients from the soil in order to make their own food and for other important processes. Soils need to be enriched with nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium etc regularly. Only then can we grow plants and keep them healthy. There are 17 most important nutrients for plants.