
- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
- Citing a Website Article or Page

Citing a Website Article (APA)
Format: Author(s). (Year, Month Day). Title of article in italics . Website Name. URL
Note: Cite an online source as a website only if no other type of source applies to it. For instance, many magazines and newspapers publish articles on their websites - in cases like this, you would cite the article as if it were an online magazines or newspaper article (not a website article). This holds true for journal articles, conference procedures, social media posts, blog posts, online videos, etc. You may need to check the APA manual or ask a librarian to see if your type of source is listed.
Note : If you're citing multiple articles or webpage from the same website, then create a reference entry for each one.
Note : If you're just mentioning a website in general but not actually pulling any specific information from it, do not created a reference list entry or use an in-text citation. Simply include the name of the website in the text of your paper, and list the URL in parenthesis after the name. For instance, the the Centers for Disease Control website (https://www.cdc.gov/) provides information on vaccines. If you pulled specific information from the website, then cite each page that you pulled information from as it's own reference entry (see note above).
Example: Harrar, S. (2007, July 5). Better heart health . CNN. http://cnn.com/better-heart-201562
Example: Smith , J. D. (2002-2023). The secret to a long life . American Cancer Society. http://americancancersociety.com/secret-long-life-356892
Group Author: Mayo Clinic. (2011, June 23). Absence seizure . http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/201569
Access Date: Smith, J. D. (n.d.). Considerations for new nurses. Career Spot. Retrieved July 3, 2023, from https://www.careerspot.org/nursing213659/
Government: National Cancer Institute . (2020). Lung cancer update (NIH Publication No. 20-6548). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/lungcancer206528/
Note : When using a government website with many layers of agencies, use the most specific agency as the author, then list the name(s) of the parent agencies as the website name, beginning with the biggest agency/parent agency and working towards more specific separating with commas (i.e. The White House, Office of the Press Secretary). Do no repeat agencies in the that were used as the author.
Helpful Information
For the website article title, capitalize only proper nouns and the first word of the article title and subtitle. Also italicize the website article title (APA considers it a standalone).
For the website name, capitalize all the significant words in the title. Do not use italics or quotation marks.
Note: If you mention a Website article title in your paper, all major words should be capitalized and it should be in italics.
When author and website name are the same, skip the website name (to avoid repetition).
Do not put a period at the end of entries with a URL.
For the URL, put the exact link to content or page where reader can easily find the cited material. For example, use https://www.nytimes.com/2020/07/28/us/politics/william-barr-house-judiciary-hearing.html?action=click&module=Top%20Stories&pgtype=Homepage instead of https://www.nytimes.com.
Some works online note last updated or edited or revised date, you would use this date if listed. If lists last reviewed as the date, you would not use as the content was not necessarily changed when reviewed. You can use copyright date(s) if exist and there is not a last updated/edited/revised date. If the website has no specific date (year or no date), but will not change over time such as an edition of a report or ebook for instance then no retrieval date is needed. Include a retrieval date only if source material could change over time like a webpage or non-published article with just year (2023) or (n.d.). See example above.
Formatting:
Double space entries. If an entry runs more than one line, use hanging indent the next line(s).
Helpful Resources
- Where to Find Citation Information on a Website This interactive guide will show you where on a website you can find the information needed to complete your citation.
- How to Cite a Website Article in APA Format This handout will break down how to cite a website article in APA format.
- << Previous: Citing Interviews, Emails, etc.
- Next: Citing a Video >>
- Formatting the Author & Title
- Citing a Book or Ebook
- Citing Part of a Book or Ebook
- Citing an Encyclopedia
- Citing a Journal Article
- Citing an Article Written for a Database
- Citing a Magazine or Newspaper Article
- Citing Interviews, Emails, etc.
- Citing a Video
- Citing Images in a Project
- In-text Citations
- Annotated Bibliography - APA
- Formatting Your Title Page and Paper in Word
- Formatting Your Reference Page in Word
- APA Handouts
- More APA Resources
- APA Workshop (Mar. 2022)
Questions? Ask a Librarian

- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 10:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/APA
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA Website Citation
How to Cite a Website in APA
This guide explains all of the important steps to referencing a website/web page in your APA research papers. The guidance below follows APA style, 7th edition.
APA format is much different than MLA format and other styles. If you need to cite websites in MLA , or you’re looking for more styles , check out the other resources on EasyBib.com!
Guide Overview
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
What is a website? Am I citing a website or a web page?
Citing a website in the text (in-text citation), citing a website on the reference page, citing a general web article without an author, titles of pages on the web, extra information, publisher information, web addresses and dois, apa format for online news articles, additional website citation examples, troubleshooting.
A website is a place on the Internet that holds a group of individual pages (called web pages).
Think of a website like a tree. A website is the tree, and the individual web pages are the branches. Use YouTube as an example. YouTube is the site, and the individual channel pages and video pages are the branches. Wikipedia is a site, and each article has its own individual web page on that site.
Most of the time, you aren’t trying to cite a whole, entire site, but actually an individual web page. If you used a YouTube video to help you with your research project, you wouldn’t cite the entire YouTube site, you would cite the specific YouTube page the video was found on.
Here’s a similar question we’re often asked when it comes to the APA citation of a web page:
Q: This page describes citing specific pages and articles. Can I cite an entire site?
A: According to the APA manual (7th edition), it is not necessary to cite a site in its entirety in a reference list. Instead, include a reference to the website in the body of your paper and cite any web page individually.
The Department of Justice has just released a new site called ReportCrime.gov at https://www.reportcrime.gov/ to help people identify and report crimes in their area.
In the above passage, the website is stated in the text rather than cited. This guide focuses on how to cite individual pages found on the web (web pages). If you used an entire website, it’s perfectly acceptable to cite the whole site in the text of your paper, as shown above, but for the most part, you want to cite the page where the information was found.
If you’re seeking out an APA citation website to take the stress away from proper referencing, try out EasyBib.com! Stop typing into the search bar, “how to cite a website APA” or “APA in-text citation website.” EasyBib.com is the answer to your referencing questions and needs!
When you include a piece of information from a site in your project, you must include two citations: a brief citation in the text and also a full citation on the reference page.
When it comes to mentions in the text, students are sometimes tempted to put the web address in the body of a project. However, URLs can be long, clunky, and distracting. They should never be written in the body of a project.
Instead of writing the full address in the text, use the last name of the author and the date the source was published. If no author is shown, write the title of the individual page and the date.
For direct quotations, you may use paragraphs to indicate the quotation’s location in the work. Count the paragraphs manually if needed and use the abbreviation “para.” for paragraph.
Check out this in-text citation APA website example:
| In-text citation | |
|---|---|
| Examples: | The ice shelves in the Antarctic Peninsula have been affected by climate change (Rasmussen, 2021).
Researchers found that “these ice shelves may break up even faster than scientists had expected due to rising air temperatures” (Rasmussen, 2021, para. 2). |
Cite your source
The above APA website in-text citation (the author’s last name and the date the information was published) corresponds to the information on the final page of the project, the reference page.
Here’s how the full APA citation for a web page looks on the final page of the project:
| Reference page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Rasmussen, C. (2021, October 12). . National Aeronautics and Space Administration. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/icy-glue-may-control-pace-of-antarctic-ice-shelf-breakup |
Need more in-text citation APA website info? Here’s more on how to build an APA parenthetical citation . You may also like our full-length guide on how to create an APA in-text citation .
If you’re looking for information on structuring other styles in the text of your paper, check out our page on MLA in-text and parenthetical citations .
In the next section of this APA citation website guide, we’re going to focus on how to format an APA website citation. If you’re wondering how to create an APA citation of a web page, the majority of web references use the structure shown below.
General structure for how to cite a website in APA
Note: A retrieval date is no longer required for online sources. It’s only needed if the content is likely to change over time (such as wikis and social media). The article or page title should be italicized. The URL is at the end and does not have a period after it.
Full reference example:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Date Published). . Site Name. URL |
| Example | Limer, E. (2013, October 1). . Gizmodo. https://gizmodo.com/heck-yes-the-first-free-wireless-plan-is-finally-here |
View Screenshot | Cite your source
Example of an in-text citation for a website in APA:
| In-text citation | |
|---|---|
| Example #1 | (Limer, 2013) |
| Example #2 | According to Limer (2013), … |
If you’re looking for an APA format website to do the work for you, try out EasyBib.com’s citation generator. Our APA citation website makes referencing a breeze!
APA citation for website structure:
Do you need to cite a source with no author in APA ? No problem. Wikipedia pages, online dictionary sites, and online encyclopedia sites are just a few examples of sites without an author. When there is no clear individual author, use the website organization (group author) as the author.
Group authors
There are plenty of times when an individual’s name isn’t listed as the author, but the information on the site is written by a group, organization, or company.
In an APA website citation, it is completely acceptable to use the group’s name in the author position. Type it out in its entirety and add a period at the end. Check out the various APA citation of web page examples at the bottom of the page to see group authors in action!
Note: If the author name and website name is the same, just list it once in as the author; leave out the website name section in the APA citation.
APA citation for website example:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Website Name. Year, Month Date of publication). . Site Name. URL |
| Examples | Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2021. (2014). . NobelPrize.org. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/peace/2014/yousafzai/lecture/ Columbia Doctors. (2016). . https://www.columbiadoctors.org/condition/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure |
| In-text citation | |
|---|---|
| Example | (Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2021, 2014) |
If you’re wondering whether to include the full date in your APA citation for web pages (month, day, and year) or just the year, we have the answer for you here.
An APA citation of web page reference includes the month, day, and year if it’s a site that is updated with new information frequently. Blog posts, newspaper articles, posts from social media profiles, and YouTube videos are just a few of the sources that would display the full date. In an APA citation for web pages, it’s written in this order in parentheses: (Year, Month Day).
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Mukherjee, S. (2016, November 17). . VICE. https://www.vice.com/en_us/article/wdj7qz/how-far-can-we-push-the-limits-of-human-life |
| In-text citation | |
|---|---|
| Example | (Mukherjee, 2016). |
If there is any information missing, simply include what is available. Also, if there is no date , indicate this by using (n.d.).
No date APA website example:
| Reference page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Chegg Inc. (n.d.). Marginal product of labor. https://www.chegg.com/learn/economics/introduction-to-economics/marginal-product-of-labor |
If you’re using the EasyBib citation generator to create an APA citation for a web page, our technology structures dates for you in their proper order. It’s the APA format website (and also the APA in-text citation website) you’ve been waiting for. Give it a whirl!
Here’s the advice we provide on many of our guides:
- If the source you are citing is a standalone source, meaning an entire book, television series, or film, the title of such sources should be in italics.
- If, however, you are citing a piece of a larger source, i.e., a journal article, a page on a site, or an episode of a show, the title should be in sentence case and not in italics.
Long story short, do not italicize an APA citation for web pages’ title in the text and on the final page of references.
For full references on the final page of the project, only include capital letters at the beginning of the title, at the beginning of each proper noun, and at the beginning of the first word in the subtitle.
The title is written in the text only when there isn’t an author listed. So, instead of showing the reference as (Author, Date), use (“Title of Page,” Date) in any APA citation for web pages. Notice the switch from sentence case to title case in the text reference.
A little extra information goes a long way when it comes to site citations. If you’re including a unique source type, include information about the medium directly after the title. This information is placed in brackets. Only the first letter is capitalized.
Here are a few examples you might see in an APA citation for a web page:
[Image attached]
[Infographic]
[Status update]
To see some of the extra information in action, scroll down to the examples towards the bottom of this page.
Speaking of extra information, it may not hurt to get some extra details on grammar topics in that brain of yours. Brush up on your adjective , pronoun , and interjection knowledge with our comprehensive guides!
Any information related to the publisher is not invited to the web citation party. In an APA citation of a web page, you do not need to include information about the company that made the site, where its offices are located, or any other similar information about the company in any web references. One thing less to worry about in your APA citation for web pages!
Other source types are much different, so before you exclude publisher information from all of your references, make sure you check out our APA citation page. While you’re at it, check out our other helpful resources, such as APA reference page and MLA works cited .
We also need a web address and DOI number in an APA citation for a web page. Including site addresses and DOIs are an absolute necessity. Addresses and DOIs (which stand for direct object identifiers) are usually the last item in an APA website citation.
For sites, after adding the full URL to the APA citation for a web page, do not end it with a period. If the address is very long, it is acceptable to roll it onto the next line, but break it up so that a type of punctuation mark or symbol is the first item closest to the left margin. Check out the APA citation of a webpage URL below.
APA citation of a webpage example of a properly structured URL:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | https://books.google.com/books?id=Oa0JAgAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=sports+ medicine&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi1l-jy-fPiAhVLMY8KHQD6BfUQ6AEIWjAJ#v=onepage&q=sports %20medicine&f=false |
DOI numbers are assigned by publishers to electronic sources such as journal articles, e-books, datasets, and more. They’re a string of numbers and sometimes other characters. If the source you’re using has a DOI number assigned to it, place it at the end of the APA website citation, instead of the URL, in this format: https://doi.org/10.XXXXXXXXX. Place the DOI string in place of the X’s shown above.
DOIs were created to combat the problem of broken links and 404 errors (pages taken down). Think about it: if a webpage is taken off of the Internet, it can be pretty difficult to find a copy of it. If you’re lucky, an archive site may have a copy stored somewhere, but for the most part, when sites are gone, they’re gone. DOIs are permanent, making them the ideal choice to include in any APA citation for webpages.
APA properly structured DOI:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04043-8 |
APA differentiates between traditional newspapers that are online versus news websites with no daily/weekly/monthly newspaper or magazine edition. Unsure what you’re citing? Follow this decision tree:
- YES –> Cite it as a newspaper article.
- NO –> Cite it as a web page or a news site article.
- NO –> Cite it as a web page or news site article.
Online news article APA example:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Nicholls, P., & Young, S. (2021, August 14). Reuters. https://www.reutersagency.com/en/coverage/a-great-british-spraycation-banksys-new-seaside-murals/ |
News sites with no associated daily/weekly/monthly publication should be cited like a web page. That means the article title is italicized and the publisher/site name is in plan font. This format applies to articles from these sites:
- MSNBC Fox News
Newspaper article online APA example:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Nunn, G. (2019, April 2). Don’t ditch the adverb, the emoji of writing. . https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2019/apr/29/dont-ditch-the-adverb-the-emoji |
Sites associated with a daily/weekly/monthly publication should be cited as a newspaper article. That means the article title is in plain font and the publisher/site name is italicized. This format applies to articles from these sites:
- The New York Times
- The Guardian
- The Times of India
- The Wall Street Journal
- The Washington Post
- Yomiuri Shimbun
Below are various web reference examples to give you a quick visual of how pages are structured and organized. Quick reminder that if you’re trying to create a reference for an e-book found on the web, use the APA book citation page. In addition, if it’s an online article from journal, use our APA journal page.
If you’re looking for a quick and easy way to build your references, EasyBib.com is an APA citation website that does the work for you. Try it out and say hello to stress-free referencing and goodbye to constantly searching for “how to cite a website APA” or “how to cite APA” on search engines. The APA offers more information here .
How to cite a group/organization/company:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Columbia Doctors. (2016). . https://www.columbiadoctors.org/condition/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure |
How to Cite a Blog Post in APA:
The structure is the same, but the format is slightly different: The blog article title is in plain text, and the name of the blog is italicized.
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Last, F. M. (Year, Month Date Published). Article title. . URL |
| Example | Schonfeld, E. (2010, May 3). Google throws $38.8 million to the wind. https://techcrunch.com/2010/05/03/google-38-8-million-wind/ |
APA citation of a web page example for Facebook:
The text of the post is italicized, while the site name (Facebook) is in plain text.
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Kaku, M. (2019, April 10). [Status update]. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/michiokaku/ |
APA citation of a web page example for Twitter:
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Kaku, M. [michiokaku]. (2019, May 31). [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/michiokaku/status/1134489848994258945 |
Cite your source
If the name of the author is unknown, start the APA citation of a web page for Twitter with the username.
| Reference Page | |
|---|---|
| Example | Rdjquotes. (2019, June 19). “I think that we all do heroic things, but hero is not a noun, it’s a verb. #RDJ [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/rdjquotes/status/1141344520535252993 |
Need another set of eyes to check your paper for grammar and spelling edits? Not quite sure if every determiner , preposition , or conjunction is where it belongs? Check out our grammar and plagiarism checker . It’s the answer to all of your grammar questions!
If you’re still confused and typing into the search bar, “how to cite APA” or “how to cite a website APA,” try out EasyBib.com’s reference generator. It’s fast, easy, and allows you to focus on your writing and research, and less on your references. The best part? It creates both types of references. It has an in-text citation website APA generator and also a full reference generator! What are you waiting for? Go see the magic happen!
Here’s a quick video overview of how to cite a website in APA:
Solution #1: Determining the website company, the author, the publisher, or both (APA)
A website citation included in an APA-format bibliography doesn’t need a publisher, so you do not need to worry whether the website company is the publisher of a page you want to cite!
If an author isn’t credited on a given webpage, the website company should be listed as the author. This also goes for online encyclopedias, dictionaries, etc.
Here’s an example for a full bibliography:
Roman empire. (2022, February 6). In Wikipedia . https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roman_Empire
Here is an example for an in-text citation:
(“Roman Empire,” 2022)
Solution #2: How to cite images and videos from social media in APA format
Making a bibliographic citation for a photo or video from social media is similar to making a citation for any website. Examples that fall into this category include photos, videos, or social media-specific mediums like highlights, reels, moments, or lives.
For your full citation in your bibliography, use the caption of the photo or video, up to 20 words, as the title. Denote the style of media in brackets, following the title.
For sources like Instagram Reels, Highlights, and other media whose exact date of posting is hard to discern, include the date you found and cited the photo or video rather than the original date the media was shared.
Here are examples of bibliographic citations:
World Wildlife Foundation [wwf]. (2021, October 20). This year marks our 60 years of action for people and nature. Together, we’ve done so much… [Photo]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/CVQQbF_KmA6/
New York Times [nytimes]. (n.d.) NYC Marathon 2021 [Highlight]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/stories/highlights/17928514339867051/
Here are the corresponding in-text citations:
(World Wildlife Foundation, 2021)
(New York Times, 2021)
Solution #3: How emojis are cited in APA format
If the website or social media post you are citing contains an emoji, keep the emoji in your full bibliographic citation without altering it.
Reference list example:
Grande, A [arianagrande]. (2021, October 18) the final #voicebattles begin tonight @nbcthevoice.🧚🏼♂️ thank you @kchenoweth, i love you. [Photo]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/CVLfY_vv_3c/
In-text citation example:
(Grande, 2021)
If you have trouble pasting the emoji into your full citation, put the emoji’s name followed by the word “emoji” all in brackets within your citation instead. Use Unicode’s Emoji Charts to look up the widely accepted, technical name of the emoji you want to cite.
Grande, A [arianagrande]. the final the final #voicebattles begin tonight @nbcthevoice . [woman fairy emoji] thank you @kchenoweth , i love you. [Photo]. Instagram. https://www.instagram.com/p/CVLfY_vv_3c/
This guide is not officially associated with the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, but it does provide information in line with the manual.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
You will need the webpage’s author’s name, publication date, title of the page, website name, and the URL.
Here is an example with an author:
Geggel, L. (2021, July 6). A brief history of dinosaurs . LiveScience. https://www.livescience.com/3945-history-dinosaurs.html
Usually, if no author is shown the website is assumed to be the author. In these cases, the website name replaces the author name in the beginning of the reference.
For example:
National Park Service. (2018, July 23). Night skies as a cultural-historical resource . https://www.nps.gov/subjects/nightskies/cultural.htm
The URL of a website is mandatory if you cite a website or a webpage. Where you include the URL depends on the type of citation. To cite a website as a general reference without any reference to a specific page or particular details, simply add the name of the website in the text and include the URL in parentheses. There is no need to add a reference list entry. However, to cite a webpage on a website, you need to provide both an in-text citation and a reference list entry. Do not add the URL in the in-text citation. Just add the author’s name and year. The URL is given only in the reference list entry. Templates for in-text citations and reference list entries of a website or webpage along with examples are given below.
Website as a general reference
In-text style:
We took the data from the Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India (https://censusindia.gov.in/).
Webpage of a website
In-text citation templates and examples:
Author Surname (publication year)
Skelton (2017)
Parenthetical:
(Author Surname, publication year)
(Skelton, 2017)
Note that month and day are not mentioned in in-text citations.
Reference list entry template and example:
Author Surname, F. M. (Year, Month Day). Title of the webpage. Name of the Site. URL
Skelton, R. (2017, February 16). Fact check’s return perfect timing in ‘post truth’ age. ABC Opinion. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-02-16/fact-check-return-perfect-timing-in-post-truth-age/8277268
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Cite a Research Paper in APA
Last Updated: October 19, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 162,186 times.
If you’re citing a research article or paper in APA style, you’ll need to use a specific citation format that varies depending on the source. Assess whether your source is an article or report published in an academic journal or book, or whether it is an unpublished research paper, such as a print-only thesis or dissertation. Either way, your in-text citations will need to include information about the author (if available) and the date when your source was published or written.
Sample Citations

Writing an In-Text Citation

- For example, you may write, “Gardener (2008) notes, ‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (p. 199).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (Meek & Hill, 2015, p.13-14).”
- For articles with 3-5 authors, write out the names of all the authors the first time you cite the source. For example: (Hammett, Wooster, Smith, & Charles, 1928). In subsequent citations, write only the first author’s name, followed by et al.: (Hammett et al., 1928).
- If there are 6 or more authors for the paper, include the last name of the first author listed and then write "et al." to indicate that there are more than 5 authors.
- For example, you may write, "'This is a quote' (Minaj et al., 1997, p. 45)."

- For example, you may write, “‘The risk of cervical cancer in women is rising’ (American Cancer Society, 2012, p. 2).”

- For example, you may write, “‘Shakespeare may have been a woman’ (“Radical English Literature,” 2004, p. 45).” Or, “The paper notes, ‘There is a boom in Virgin Mary imagery’ (“Art History in Italy,” 2011, p. 32).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.13-14).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.145-146).”

- For example, you may write, “‘The effects of food deprivation are long-term’ (Mett, 2005, para. 18).”
Creating a Reference List Citation for a Published Source
- Material on websites is also considered “published,” even if it’s not peer-reviewed or associated with a formal publishing company.
- While academic dissertations or theses that are print-only are considered unpublished, these types of documents are considered published if they’re included in an online database (such as ProQuest) or incorporated into an institutional repository.

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M.” Or, “Meek, P. Q., Kendrick, L. H., & Hill, R. W.”
- If there is no author, you can list the name of the organization that published the research paper. For example, you may write, “American Cancer Society” or “The Reading Room.”
- Formally published documents that don’t list an author or that have a corporate author are typically reports or white papers .

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008).” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015).”

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data.” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015). Cervical cancer rates in women ages 20-45.”

- For example, for a journal article, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data. Modern Journal of Malacostracan Research, 25, 150-305.”
- For a book chapter, you could write: “Wooster, B. W. (1937). A comparative study of modern Dutch cow creamers. In T. E. Travers (Ed.), A Detailed History of Tea Serviceware (pp. 127-155). London: Wimble Press."

- For example, you may write, “Kotb, M. A., Kamal, A. M., Aldossary, N. M., & Bedewi, M. A. (2019). Effect of vitamin D replacement on depression in multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders, 29, 111-117. Retrieved from PubMed, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30708308.
- If you’re citing a paper or article that was published online but did not come from an academic journal or database, provide information about the author (if known), the date of publication (if available), and the website where you found the article. For example: “Hill, M. (n.d.). Egypt in the Ptolemaic Period. Retrieved from https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/ptol/hd_ptol.htm”
Citing Unpublished Sources in Your Reference List

- Print-only dissertations or theses.
- Articles or book chapters that are in press or have been recently prepared or submitted for publication.
- Papers that have been rejected for publication or were never intended for publication (such as student research papers or unpublished conference papers).

- If the paper is currently being prepared for publication, include the author’s name, the year when the current draft was completed, and the title of the article in italics, followed by “Manuscript in preparation.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript in preparation.
- If the paper has been submitted for publication, format the citation the same way as if it were in preparation, but instead follow the title with “Manuscript submitted for publication.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript submitted for publication.
- If the paper has been accepted for publication but is not yet published, replace the date with “in press.” Do not italicize the paper title, but do include the title of the periodical or book in which it will be published and italicize that. For example: Wooster, B. W. (in press). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Milady’s Boudoir.

- If the paper was written for a conference but never published, your citation should look like this: Riker, W. T. (2019, March). Traditional methods for the preparation of spiny lobe-fish. Paper presented at the 325th Annual Intergalactic Culinary Conference, San Francisco, CA.
- For an unpublished paper written by a student for a class, include details about the institution where the paper was written. For example: Crusher, B. H. (2019). A typology of Cardassian skin diseases. Unpublished manuscript, Department of External Medicine, Starfleet Academy, San Francisco, CA.

- For example, you may write, “Pendlebottom, R. H. (2011). Iconography in Italian Frescos (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). New York University, New York, United States.”
Community Q&A
- If you want certain information to stand out in the research paper, then you can consider using a block quote. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/7JournalArticles
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_author_authors.html
- ↑ https://bowvalleycollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=714519&p=5093747
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://libguides.southernct.edu/c.php?g=7125&p=34582#1951239
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_articles_in_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_books.html
- ↑ https://morlingcollege.libguides.com/apareferencing/unpublished-or-informally-published-work
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_apa_faqs.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_other_print_sources.html
About This Article

To cite a research paper in-text in APA, name the author in the text to introduce the quote and put the publication date for the text in parentheses. At the end of your quote, put the page number in parentheses. If you don’t mention the author in your prose, include them in the citation. Start the citation, which should come at the end of the quote, by listing the author’s last name, the year of publication, and the page number. Make sure to put all of this information in parentheses. If there’s no author, use the name of the organization that published the paper or the first few words from the title. To learn how to cite published and unpublished sources in your reference list, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World

Effective ways to communicate research in a journal article

Oxford Academic: Journals
We publish over 500 high-quality journals, with two-thirds in partnership with learned societies and prestigious institutions. Our diverse journal offerings ensure that your research finds a home alongside award-winning content, reaching a global audience and maximizing impact.
- By Megan Taphouse , Anne Foster , Eduardo Franco , Howard Browman , and Michael Schnoor
- August 12 th 2024
In this blog post, editors of OUP journals delve into the vital aspect of clear communication in a journal article. Anne Foster (Editor of Diplomatic History ), Eduardo Franco (Editor-in-Chief of JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute and JNCI Monographs ), Howard Browman (Editor-in-Chief of ICES Journal of Marine Science ), and Michael Schnoor (Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Leukocyte Biology ) provide editorial recommendations on achieving clarity, avoiding common mistakes, and creating an effective structure.
Ensuring clear communication of research findings
AF : To ensure research findings are clearly communicated, you should be able to state the significance of those findings in one sentence—if you don’t have that simple, clear claim in your mind, you will not be able to communicate it.
MS : The most important thing is clear and concise language. It is also critical to have a logical flow of your story with clear transitions from one research question to the next.
EF : It is crucial to write with both experts and interested non-specialists in mind, valuing their diverse perspectives and insights.
Common mistakes that obscure authors’ arguments and data
AF : Many authors do a lovely job of contextualizing their work, acknowledging what other scholars have written about the topic, but then do not sufficiently distinguish what their work is adding to the conversation.
HB : Be succinct—eliminate repetition and superfluous material. Do not attempt to write a mini review. Do not overinterpret your results or extrapolate far beyond the limits of the study. Do not report the same data in the text, tables, and figures.
The importance of the introduction
AF : The introduction is absolutely critical. It needs to bring them straight into your argument and contribution, as quickly as possible.
EF : The introduction is where you make a promise to the reader. It is like you saying, “I identified this problem and will solve it.” What comes next in the paper is how you kept that promise.
Structural pitfalls
EF : Remember, editors are your first audience; make sure your writing is clear and compelling because if the editor cannot understand your writing, chances are that s/he will reject your paper without sending it out for external peer review.
HB : Authors often misplace content across sections, placing material in the introduction that belongs in methods, results, or discussion, and interpretive phrases in results instead of discussion. Additionally, they redundantly present information in multiple sections.
Creating an effective structure
AF : I have one tip which is more of a thinking and planning strategy. I write myself letters about what I think the argument is, what kinds of support it needs, how I will use the specific material I have to provide that support, how it fits together, etc.
EF : Effective writing comes from effective reading—try to appreciate good writing in the work of others as you read their papers. Do you like their writing? Do you like their strategy of advancing arguments? Are you suspicious of their methods, findings, or how they interpret them? Do you see yourself resisting? Examine your reactions. You should also write frequently. Effective writing is like a physical sport; you develop ‘muscle memory’ by hitting a golf ball or scoring a 3-pointer in basketball.
The importance of visualizing data and findings
MS : It is extremely important to present your data in clean and well-organized figures—they act as your business card. Also, understand and consider the page layout and page or column dimensions of your target journal and format your tables and figures accordingly.
EF : Be careful when cropping gels to assemble them in a figure. Make sure that image contrasts are preserved from the original blots. Image cleaning for the sake of readability can alter the meaning of results and eventually be flagged by readers as suspicious.
The power of editing
AF : Most of the time, our first draft is for ourselves. We write what we have been thinking about most, which means the article reflects our questions, our knowledge, and our interests. A round or two of editing and refining before submission to the journal is valuable.
HB : Editing does yourself a favour by minimizing distractions-annoyances-cosmetic points that a reviewer can criticize. Why give reviewers things to criticize when you can eliminate them by submitting a carefully prepared manuscript?
Editing mistakes to avoid
AF : Do not submit an article which is already at or above the word limit for articles in the journal. The review process rarely asks for cuts; usually, you will be asked to clarify or add material. If you are at the maximum word count in the initial submission, you then must cut something during the revision process.
EF : Wait 2-3 days and then reread your draft. You will be surprised to see how many passages in your great paper are too complicated and inscrutable even for you. And you wrote it!
Featured image by Charlotte May via Pexels .
Megan Taphouse , Marketing Executive
Anne Foster , (Editor of Diplomatic History)
Eduardo Franco , (Editor-in-Chief of JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer institute and JNCI Monographs)
Howard Browman , (Editor-in-Chief of ICES Journal of Marine Science)
Michael Schnoor , (Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Leukocyte Biology)
- Publishing 101
- Series & Columns
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:

Recent Comments
There are currently no comments.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.

Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
- Introduction
- Article Information
OR indicates odds ratio. Comparing extreme quintiles of intake, artificially sweetened beverages, and artificial sweeteners were associated with greater risk of depression (strict definition) after multivariable regression.
Data Sharing Statement
- Errors in the Table JAMA Network Open Correction October 18, 2023
See More About
Sign up for emails based on your interests, select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Get the latest research based on your areas of interest.
Others also liked.
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Samuthpongtorn C , Nguyen LH , Okereke OI, et al. Consumption of Ultraprocessed Food and Risk of Depression. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(9):e2334770. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34770
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Consumption of Ultraprocessed Food and Risk of Depression
- 1 Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston
- 2 Division of Gastroenterology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston
- 3 Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston
- 4 Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- 5 Channing Division of Network Medicine, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts
- 6 Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- 7 Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts
- 8 Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts
- Correction Errors in the Table JAMA Network Open
Increasing evidence suggests that diet may influence risk of depression. 1 - 3 Despite extensive data linking ultraprocessed foods (UPF; ie, energy-dense, palatable, and ready-to-eat items) with human disease, 4 evidence examining the association between UPF consumption and depression is scant. Prior studies have been hampered by short-term dietary data 1 , 2 and a limited ability to account for potential confounders. 1 , 3 Additionally, no study has identified which UPF foods and/or ingredients that may be associated with risk of depression or how the timing of UPF consumption may be associated. Therefore, we investigated the prospective association between UPF and its components with incident depression.
This cohort study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The return of a completed questionnaire was accepted by the IRB as implied informed consent. The study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology ( STROBE ) reporting guideline.
We conducted a prospective study in the Nurses’ Health Study II between 2003 and 2017 among middle-aged females free of depression at baseline. Diet was assessed using validated food frequency questionnaires (FFQs) every 4 years. We estimated UPF intake using the NOVA classification, 2 which groups foods according to the degree of their processing. In secondary analyses, we classified UPF into their components, including ultraprocessed grain foods, sweet snacks, ready-to-eat meals, fats and sauces, ultraprocessed dairy products, savory snacks, processed meat, beverages, and artificial sweeteners. 4 We used 2 definitions for depression: (1) a strict definition requiring self-reported clinician–diagnosed depression and regular antidepressant use and (2) a broad definition requiring clinical diagnosis and/or antidepressant use.
We estimated hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs for depression according to quintiles of UPF intake using Cox proportional hazards models, with adjustment for known and suspected risk factors for depression, including age, total caloric intake, body mass index (BMI; calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), physical activity, smoking status, menopausal hormone therapy, total energy intake, alcohol, comorbidities (eg, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia), median family income, social network levels, marital status, sleep duration, and pain. In an exploratory analysis, we examined the association between changes in UPF consumption updated every 4 years with incident depression. All analyses were performed using 2-sided tests from SAS (version 9.4). Data were analyzed from September 2022 to January 2023.
Our cohort included 31 712 females, aged 42 to 62 years at baseline (mean [SD] age, 52 [4.7] years; 30 190 [95.2%] non-Hispanic White females). Participants with high UPF intake had greater BMI, higher smoking rates, and increased prevalence of comorbidities like diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia and were less likely to exercise regularly. We identified 2122 incident cases of depression using the strict definition and 4840 incident cases using the broad definition. Compared with those in the lowest quintile of UPF consumption, those in the highest quintile had an increased risk of depression, noted for both strict definition (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.26-1.76; P < .001) and broad definition (HR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.20-1.50; P < .001) ( Table ). Models were not materially altered after inclusion of potential confounders. We did not observe differential associations in subgroups defined by age, BMI, physical activity, or smoking. In a 4-year lag analysis, associations were not materially altered (strict definition: HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.13-1.54; P < .001), arguing against reverse causation.
Next, we examined the association of specific UPF components with risk of depression. Comparing extreme quintiles, only artificially sweetened beverages (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.19-1.57; P < .001) and artificial sweeteners (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.10-1.43; P < .001) were associated with greater risk of depression and after multivariable regression ( Figure ). In an exploratory analysis, those who reduced UPF intake by at least 3 servings per day were at lower risk of depression (strict definition: HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.71-0.99) compared with those with relatively stable intake in each 4-year period.
These findings suggest that greater UPF intake, particularly artificial sweeteners and artificially sweetened beverages, is associated with increased risk of depression. Although the mechanism associating UPF to depression is unknown, recent experimental data suggests that artificial sweeteners elicit purinergic transmission in the brain, 5 which may be involved in the etiopathogenesis of depression. 6 Strengths of our study include the large sample, prospective design, high follow-up rate, ability to adjust for multiple confounders, and extensively validated dietary assessment tools. This study had limitations. The cohort primarily included non-Hispanic White females. Additionally, without structured clinical interviews, misclassification of the outcome may be considered.
Accepted for Publication: August 15, 2023.
Published: September 20, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34770
Correction: This article was corrected on October 18, 2023, to fix transcription errors in the Table.
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2023 Samuthpongtorn C et al. JAMA Network Open .
Corresponding Authors: Raaj S. Mehta, MD, MPH ( [email protected] ), and Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH ( [email protected] ), Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, 100 Cambridge St, Ste 1580 Boston, MA 02114.
Author Contributions: Drs Samuthpongtorn and Mehta had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Samuthpongtorn, Chan, Mehta.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Samuthpongtorn, Chan, Mehta.
Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors.
Statistical analysis: Samuthpongtorn, Chan, Mehta.
Obtained funding: Chan.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Samuthpongtorn, Okereke, Song, Chan, Mehta.
Supervision: Chan, Mehta.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Okereke reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and royalties from Springer Publishing outside the submitted work. Dr Chan reported receiving grants from Bayer Pharma AG and Zoe and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Freenome outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Funding/Support: The Nurses’ Health Study II was funded by grant U01 CA176726 from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Disclaimer: The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Data Sharing Statement: See the Supplement .
Additional Contributions: We thank the participants and staff of the Nurses’ Health Study II for their valuable contributions. They received no compensation for their contributions.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
3 Questions: How to prove humanity online
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
As artificial intelligence agents become more advanced, it could become increasingly difficult to distinguish between AI-powered users and real humans on the internet. In a new white paper , researchers from MIT, OpenAI, Microsoft, and other tech companies and academic institutions propose the use of personhood credentials, a verification technique that enables someone to prove they are a real human online, while preserving their privacy.
MIT News spoke with two co-authors of the paper, Nouran Soliman, an electrical engineering and computer science graduate student, and Tobin South, a graduate student in the Media Lab, about the need for such credentials, the risks associated with them, and how they could be implemented in a safe and equitable way.
Q: Why do we need personhood credentials?
Tobin South: AI capabilities are rapidly improving. While a lot of the public discourse has been about how chatbots keep getting better, sophisticated AI enables far more capabilities than just a better ChatGPT, like the ability of AI to interact online autonomously. AI could have the ability to create accounts, post content, generate fake content, pretend to be human online, or algorithmically amplify content at a massive scale. This unlocks a lot of risks. You can think of this as a “digital imposter” problem, where it is getting harder to distinguish between sophisticated AI and humans. Personhood credentials are one potential solution to that problem.
Nouran Soliman: Such advanced AI capabilities could help bad actors run large-scale attacks or spread misinformation. The internet could be filled with AIs that are resharing content from real humans to run disinformation campaigns. It is going to become harder to navigate the internet, and social media specifically. You could imagine using personhood credentials to filter out certain content and moderate content on your social media feed or determine the trust level of information you receive online.
Q: What is a personhood credential, and how can you ensure such a credential is secure?
South: Personhood credentials allow you to prove you are human without revealing anything else about your identity. These credentials let you take information from an entity like the government, who can guarantee you are human, and then through privacy technology, allow you to prove that fact without sharing any sensitive information about your identity. To get a personhood credential, you are going to have to show up in person or have a relationship with the government, like a tax ID number. There is an offline component. You are going to have to do something that only humans can do. AIs can’t turn up at the DMV, for instance. And even the most sophisticated AIs can’t fake or break cryptography. So, we combine two ideas — the security that we have through cryptography and the fact that humans still have some capabilities that AIs don’t have — to make really robust guarantees that you are human.
Soliman: But personhood credentials can be optional. Service providers can let people choose whether they want to use one or not. Right now, if people only want to interact with real, verified people online, there is no reasonable way to do it. And beyond just creating content and talking to people, at some point AI agents are also going to take actions on behalf of people. If I am going to buy something online, or negotiate a deal, then maybe in that case I want to be certain I am interacting with entities that have personhood credentials to ensure they are trustworthy.
South: Personhood credentials build on top of an infrastructure and a set of security technologies we’ve had for decades, such as the use of identifiers like an email account to sign into online services, and they can complement those existing methods.
Q: What are some of the risks associated with personhood credentials, and how could you reduce those risks?
Soliman: One risk comes from how personhood credentials could be implemented. There is a concern about concentration of power. Let’s say one specific entity is the only issuer, or the system is designed in such a way that all the power is given to one entity. This could raise a lot of concerns for a part of the population — maybe they don’t trust that entity and don’t feel it is safe to engage with them. We need to implement personhood credentials in such a way that people trust the issuers and ensure that people’s identities remain completely isolated from their personhood credentials to preserve privacy.
South: If the only way to get a personhood credential is to physically go somewhere to prove you are human, then that could be scary if you are in a sociopolitical environment where it is difficult or dangerous to go to that physical location. That could prevent some people from having the ability to share their messages online in an unfettered way, possibly stifling free expression. That’s why it is important to have a variety of issuers of personhood credentials, and an open protocol to make sure that freedom of expression is maintained.
Soliman: Our paper is trying to encourage governments, policymakers, leaders, and researchers to invest more resources in personhood credentials. We are suggesting that researchers study different implementation directions and explore the broader impacts personhood credentials could have on the community. We need to make sure we create the right policies and rules about how personhood credentials should be implemented.
South: AI is moving very fast, certainly much faster than the speed at which governments adapt. It is time for governments and big companies to start thinking about how they can adapt their digital systems to be ready to prove that someone is human, but in a way that is privacy-preserving and safe, so we can be ready when we reach a future where AI has these advanced capabilities.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Nouran Soliman
- Tobin South
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- School of Architecture and Planning
Related Topics
- Artificial intelligence
- Cybersecurity
- Social media
- Social networks
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

3 Questions: What you need to know about audio deepfakes

MIT group releases white papers on governance of AI

What does the future hold for generative AI?

MIT professor to Congress: “We are at an inflection point” with AI
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

When the lights turned on in the universe
Read full story →

Lincoln Laboratory and National Strategic Research Institute launch student research program to tackle biothreats to national security

Christine Ortiz named director of MIT Technology and Policy Program
MIT engineers design tiny batteries for powering cell-sized robots
New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain
LLMs develop their own understanding of reality as their language abilities improve
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Journal
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing journal articles in apa.
A journal is a scholarly periodical that presents research from experts in a certain field. Typically, but not always, these journals are peer-reviewed in order to ensure that published articles are of the highest quality. That is one reason why journals are a highly credible source of information.
Journal articles in print:
Author Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). Title of article. Title of Periodical, Volume (Issue), page range.
Gleditsch, N. P., Pinker, S., Thayer, B. A., Levy, J. S., & Thompson, W. R. (2013). The forum: The decline of war. International Studies Review, 15 (3), 396-419.
Journal articles online:
- If your source is found online, but there is no DOI provided, you can include the URL instead.
- A DOI (digital object identifier) is basically a number that links a source to its location on the Internet. This number isn’t always provided, but if it is, you should include it in your citation rather than including a URL.
- Unlike previous editions, the current edition does not require including a retrieval date or date accessed for online sources. A retrieval date is only necessary if the source is likely to change (ex. Wikipedia, encyclopedia entry, Facebook homepage, etc.).
Author Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). Title of article. Title of Periodical, Volume (Issue), page range. https://doi.org/xxxx or URL
Burnell, K. J., Coleman, P. G., & Hunt, N. (2010). Coping with traumatic memories: Second World War veterans’ experiences of social support in relation to the narrative coherence of war memories. Ageing and Society, 30 (1), 57-78. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0144686X0999016X
If you need additional help, the Citation Machine APA reference generator will cite your sources automatically for you.
Featured links:
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDF
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

How to cite ChatGPT

Use discount code STYLEBLOG15 for 15% off APA Style print products with free shipping in the United States.
We, the APA Style team, are not robots. We can all pass a CAPTCHA test , and we know our roles in a Turing test . And, like so many nonrobot human beings this year, we’ve spent a fair amount of time reading, learning, and thinking about issues related to large language models, artificial intelligence (AI), AI-generated text, and specifically ChatGPT . We’ve also been gathering opinions and feedback about the use and citation of ChatGPT. Thank you to everyone who has contributed and shared ideas, opinions, research, and feedback.
In this post, I discuss situations where students and researchers use ChatGPT to create text and to facilitate their research, not to write the full text of their paper or manuscript. We know instructors have differing opinions about how or even whether students should use ChatGPT, and we’ll be continuing to collect feedback about instructor and student questions. As always, defer to instructor guidelines when writing student papers. For more about guidelines and policies about student and author use of ChatGPT, see the last section of this post.
Quoting or reproducing the text created by ChatGPT in your paper
If you’ve used ChatGPT or other AI tools in your research, describe how you used the tool in your Method section or in a comparable section of your paper. For literature reviews or other types of essays or response or reaction papers, you might describe how you used the tool in your introduction. In your text, provide the prompt you used and then any portion of the relevant text that was generated in response.
Unfortunately, the results of a ChatGPT “chat” are not retrievable by other readers, and although nonretrievable data or quotations in APA Style papers are usually cited as personal communications , with ChatGPT-generated text there is no person communicating. Quoting ChatGPT’s text from a chat session is therefore more like sharing an algorithm’s output; thus, credit the author of the algorithm with a reference list entry and the corresponding in-text citation.
When prompted with “Is the left brain right brain divide real or a metaphor?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that although the two brain hemispheres are somewhat specialized, “the notation that people can be characterized as ‘left-brained’ or ‘right-brained’ is considered to be an oversimplification and a popular myth” (OpenAI, 2023).
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
You may also put the full text of long responses from ChatGPT in an appendix of your paper or in online supplemental materials, so readers have access to the exact text that was generated. It is particularly important to document the exact text created because ChatGPT will generate a unique response in each chat session, even if given the same prompt. If you create appendices or supplemental materials, remember that each should be called out at least once in the body of your APA Style paper.
When given a follow-up prompt of “What is a more accurate representation?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that “different brain regions work together to support various cognitive processes” and “the functional specialization of different regions can change in response to experience and environmental factors” (OpenAI, 2023; see Appendix A for the full transcript).
Creating a reference to ChatGPT or other AI models and software
The in-text citations and references above are adapted from the reference template for software in Section 10.10 of the Publication Manual (American Psychological Association, 2020, Chapter 10). Although here we focus on ChatGPT, because these guidelines are based on the software template, they can be adapted to note the use of other large language models (e.g., Bard), algorithms, and similar software.
The reference and in-text citations for ChatGPT are formatted as follows:
- Parenthetical citation: (OpenAI, 2023)
- Narrative citation: OpenAI (2023)
Let’s break that reference down and look at the four elements (author, date, title, and source):
Author: The author of the model is OpenAI.
Date: The date is the year of the version you used. Following the template in Section 10.10, you need to include only the year, not the exact date. The version number provides the specific date information a reader might need.
Title: The name of the model is “ChatGPT,” so that serves as the title and is italicized in your reference, as shown in the template. Although OpenAI labels unique iterations (i.e., ChatGPT-3, ChatGPT-4), they are using “ChatGPT” as the general name of the model, with updates identified with version numbers.
The version number is included after the title in parentheses. The format for the version number in ChatGPT references includes the date because that is how OpenAI is labeling the versions. Different large language models or software might use different version numbering; use the version number in the format the author or publisher provides, which may be a numbering system (e.g., Version 2.0) or other methods.
Bracketed text is used in references for additional descriptions when they are needed to help a reader understand what’s being cited. References for a number of common sources, such as journal articles and books, do not include bracketed descriptions, but things outside of the typical peer-reviewed system often do. In the case of a reference for ChatGPT, provide the descriptor “Large language model” in square brackets. OpenAI describes ChatGPT-4 as a “large multimodal model,” so that description may be provided instead if you are using ChatGPT-4. Later versions and software or models from other companies may need different descriptions, based on how the publishers describe the model. The goal of the bracketed text is to briefly describe the kind of model to your reader.
Source: When the publisher name and the author name are the same, do not repeat the publisher name in the source element of the reference, and move directly to the URL. This is the case for ChatGPT. The URL for ChatGPT is https://chat.openai.com/chat . For other models or products for which you may create a reference, use the URL that links as directly as possible to the source (i.e., the page where you can access the model, not the publisher’s homepage).
Other questions about citing ChatGPT
You may have noticed the confidence with which ChatGPT described the ideas of brain lateralization and how the brain operates, without citing any sources. I asked for a list of sources to support those claims and ChatGPT provided five references—four of which I was able to find online. The fifth does not seem to be a real article; the digital object identifier given for that reference belongs to a different article, and I was not able to find any article with the authors, date, title, and source details that ChatGPT provided. Authors using ChatGPT or similar AI tools for research should consider making this scrutiny of the primary sources a standard process. If the sources are real, accurate, and relevant, it may be better to read those original sources to learn from that research and paraphrase or quote from those articles, as applicable, than to use the model’s interpretation of them.
We’ve also received a number of other questions about ChatGPT. Should students be allowed to use it? What guidelines should instructors create for students using AI? Does using AI-generated text constitute plagiarism? Should authors who use ChatGPT credit ChatGPT or OpenAI in their byline? What are the copyright implications ?
On these questions, researchers, editors, instructors, and others are actively debating and creating parameters and guidelines. Many of you have sent us feedback, and we encourage you to continue to do so in the comments below. We will also study the policies and procedures being established by instructors, publishers, and academic institutions, with a goal of creating guidelines that reflect the many real-world applications of AI-generated text.
For questions about manuscript byline credit, plagiarism, and related ChatGPT and AI topics, the APA Style team is seeking the recommendations of APA Journals editors. APA Style guidelines based on those recommendations will be posted on this blog and on the APA Style site later this year.
Update: APA Journals has published policies on the use of generative AI in scholarly materials .
We, the APA Style team humans, appreciate your patience as we navigate these unique challenges and new ways of thinking about how authors, researchers, and students learn, write, and work with new technologies.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Related and recent
Comments are disabled due to your privacy settings. To re-enable, please adjust your cookie preferences.
APA Style Monthly
Subscribe to the APA Style Monthly newsletter to get tips, updates, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Welcome! Thank you for subscribing.
APA Style Guidelines
Browse APA Style writing guidelines by category
- Abbreviations
- Bias-Free Language
- Capitalization
- In-Text Citations
- Italics and Quotation Marks
- Paper Format
- Punctuation
- Research and Publication
- Spelling and Hyphenation
- Tables and Figures
Full index of topics
Scribbr Citation Generator
Accurate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions
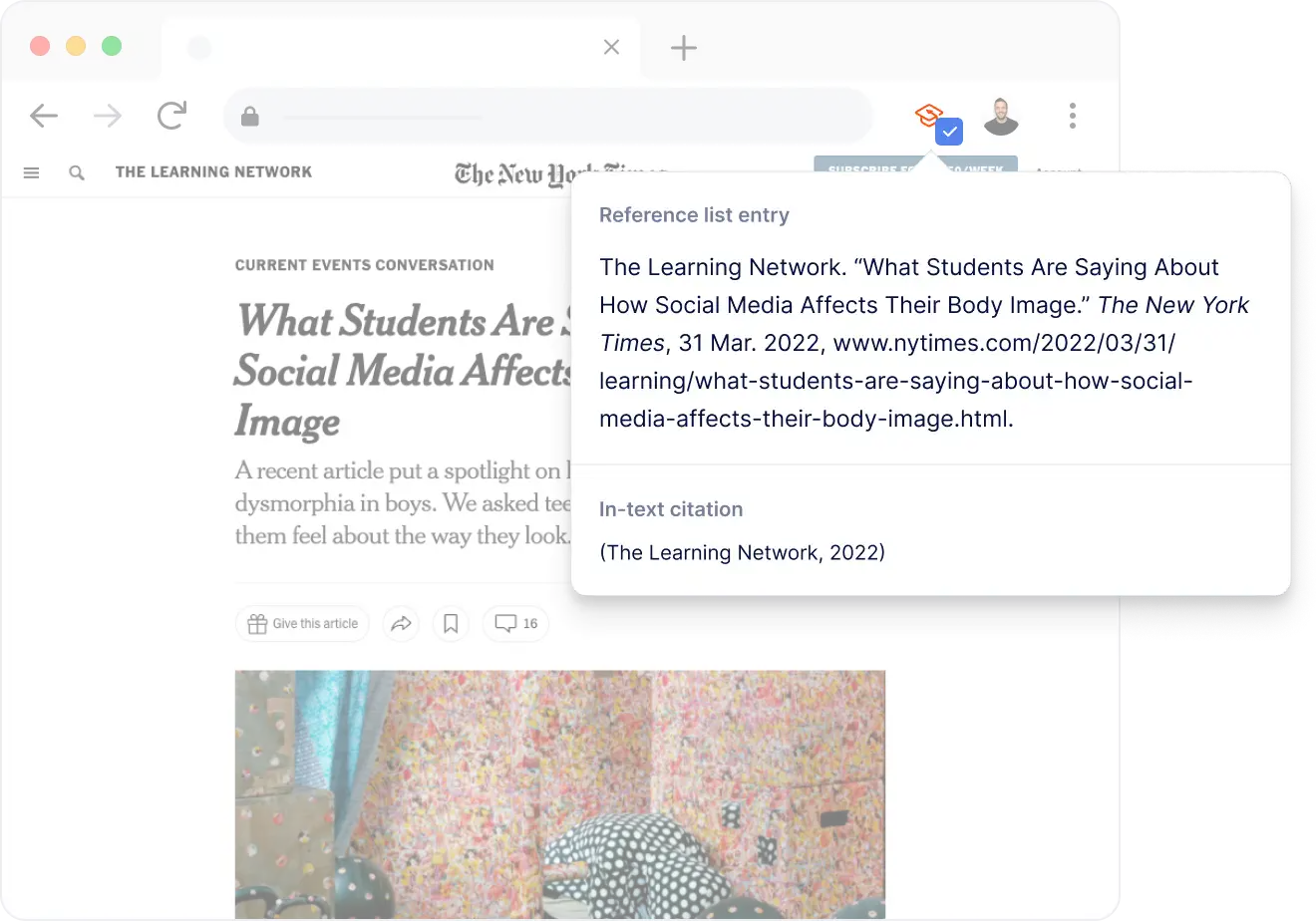
Scribbr for Chrome: Your shortcut to citations
Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser. The extension does the hard work for you by automatically grabbing the title, author(s), publication date, and everything else needed to whip up the perfect citation.
| ⚙️ Styles | APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard |
|---|---|
| 📚 Source types | Websites, books, articles |
| 🔎 Autocite | Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN |

Perfectly formatted references every time
Inaccurate citations can cost you points on your assignments, so our seasoned citation experts have invested countless hours in perfecting Scribbr’s citation generator algorithms. We’re proud to be recommended by teachers and universities worldwide.
Enjoy a citation generator without flashy ads
Staying focused is already difficult enough, so unlike other citation generators, Scribbr won’t slow you down with flashing banner ads and video pop-ups. That’s a promise!
Citation Generator features you'll love
Look up your source by its title, URL, ISBN, or DOI, and let Scribbr find and fill in all the relevant information automatically.
APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard
Generate flawless citations according to the official APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard style, or many other rules.
Export to Word
When your reference list is complete, export it to Word. We’ll apply the official formatting guidelines automatically.
Lists and folders
Create separate reference lists for each of your assignments to stay organized. You can also group related lists into folders.
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Are you using a LaTex editor like Overleaf? If so, you can easily export your references in Bib(La)TeX format with a single click.
Custom fonts
Change the typeface used for your reference list to match the rest of your document. Options include Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr’s Citation Generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Describe or evaluate your sources in annotations, and Scribbr will generate a perfectly formatted annotated bibliography .
Citation guides
Scribbr’s popular guides and videos will help you understand everything related to finding, evaluating, and citing sources.
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Finding sources
Evaluating sources
- Integrating sources
Citing sources
Tools and resources, a quick guide to working with sources.
Working with sources is an important skill that you’ll need throughout your academic career.
It includes knowing how to find relevant sources, assessing their authority and credibility, and understanding how to integrate sources into your work with proper referencing.
This quick guide will help you get started!
Finding relevant sources
Sources commonly used in academic writing include academic journals, scholarly books, websites, newspapers, and encyclopedias. There are three main places to look for such sources:
- Research databases: Databases can be general or subject-specific. To get started, check out this list of databases by academic discipline . Another good starting point is Google Scholar .
- Your institution’s library: Use your library’s database to narrow down your search using keywords to find relevant articles, books, and newspapers matching your topic.
- Other online resources: Consult popular online sources like websites, blogs, or Wikipedia to find background information. Be sure to carefully evaluate the credibility of those online sources.
When using academic databases or search engines, you can use Boolean operators to refine your results.
Generate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations in seconds
Get started
In academic writing, your sources should be credible, up to date, and relevant to your research topic. Useful approaches to evaluating sources include the CRAAP test and lateral reading.
CRAAP is an abbreviation that reminds you of a set of questions to ask yourself when evaluating information.
- Currency: Does the source reflect recent research?
- Relevance: Is the source related to your research topic?
- Authority: Is it a respected publication? Is the author an expert in their field?
- Accuracy: Does the source support its arguments and conclusions with evidence?
- Purpose: What is the author’s intention?
Lateral reading
Lateral reading means comparing your source to other sources. This allows you to:
- Verify evidence
- Contextualize information
- Find potential weaknesses
If a source is using methods or drawing conclusions that are incompatible with other research in its field, it may not be reliable.
Integrating sources into your work
Once you have found information that you want to include in your paper, signal phrases can help you to introduce it. Here are a few examples:
| Function | Example sentence | Signal words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| You present the author’s position neutrally, without any special emphasis. | recent research, food services are responsible for one-third of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. | According to, analyzes, asks, describes, discusses, explains, in the words of, notes, observes, points out, reports, writes |
| A position is taken in agreement with what came before. | Recent research Einstein’s theory of general relativity by observing light from behind a black hole. | Agrees, confirms, endorses, reinforces, promotes, supports |
| A position is taken for or against something, with the implication that the debate is ongoing. | Allen Ginsberg artistic revision … | Argues, contends, denies, insists, maintains |
Following the signal phrase, you can choose to quote, paraphrase or summarize the source.
- Quoting : This means including the exact words of another source in your paper. The quoted text must be enclosed in quotation marks or (for longer quotes) presented as a block quote . Quote a source when the meaning is difficult to convey in different words or when you want to analyze the language itself.
- Paraphrasing : This means putting another person’s ideas into your own words. It allows you to integrate sources more smoothly into your text, maintaining a consistent voice. It also shows that you have understood the meaning of the source.
- Summarizing : This means giving an overview of the essential points of a source. Summaries should be much shorter than the original text. You should describe the key points in your own words and not quote from the original text.
Whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize a source, you must include a citation crediting the original author.
Citing your sources is important because it:
- Allows you to avoid plagiarism
- Establishes the credentials of your sources
- Backs up your arguments with evidence
- Allows your reader to verify the legitimacy of your conclusions
The most common citation styles are APA, MLA, and Chicago style. Each citation style has specific rules for formatting citations.
Generate APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard citations in seconds
Scribbr offers tons of tools and resources to make working with sources easier and faster. Take a look at our top picks:
- Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator , Harvard Referencing Generator , and Chicago Citation Generator .
- Plagiarism Checker : Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to students.
- AI Proofreader: Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Have a human editor improve your writing.
- Citation checker: Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Knowledge Base : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
Grab your spot at the free arXiv Accessibility Forum
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: 3d gaussian editing with a single image.
Abstract: The modeling and manipulation of 3D scenes captured from the real world are pivotal in various applications, attracting growing research interest. While previous works on editing have achieved interesting results through manipulating 3D meshes, they often require accurately reconstructed meshes to perform editing, which limits their application in 3D content generation. To address this gap, we introduce a novel single-image-driven 3D scene editing approach based on 3D Gaussian Splatting, enabling intuitive manipulation via directly editing the content on a 2D image plane. Our method learns to optimize the 3D Gaussians to align with an edited version of the image rendered from a user-specified viewpoint of the original scene. To capture long-range object deformation, we introduce positional loss into the optimization process of 3D Gaussian Splatting and enable gradient propagation through reparameterization. To handle occluded 3D Gaussians when rendering from the specified viewpoint, we build an anchor-based structure and employ a coarse-to-fine optimization strategy capable of handling long-range deformation while maintaining structural stability. Furthermore, we design a novel masking strategy to adaptively identify non-rigid deformation regions for fine-scale modeling. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method in handling geometric details, long-range, and non-rigid deformation, demonstrating superior editing flexibility and quality compared to previous approaches.
| Comments: | 10 pages, 12 figures |
| Subjects: | Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM) |
| Cite as: | [cs.CV] |
| (or [cs.CV] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
QuillBot helps you generate bibliographies and citations in MLA, APA, and Chicago style. Citation Generator: generate citations in any style with our easy-to-use platform.
However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs. Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL. Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a "permalink," which is a shortened, stable ...
Revised on January 17, 2024. APA website citations usually include the author, the publication date, the title of the page or article, the website name, and the URL. If there is no author, start the citation with the title of the article. If the page is likely to change over time, add a retrieval date. If you are citing an online version of a ...
Citing a website in APA Style. An APA reference for a webpage lists the author's last name and initials, the full date of publication, the title of the page (in italics), the website name (in plain text), and the URL.. The in-text citation lists the author's last name and the year. If it's a long page, you may include a locator to identify the quote or paraphrase (e.g. a paragraph number ...
The term "website" can cause confusion because people use it to refer to both a reference category (see Section 10.16 in the Publication Manual and Section 10.14 in the Concise Guide) and a method of retrieval (i.e., online).. When you are citing something on a website, ensure you are thinking about its reference type and not its method of retrieval.
Download Article. 1. Start your full citation with the name of the author. If the article has an identified author, provide their last name followed by a comma, then their first name. Place a period after the author's name. If no author is identified, start your citation with the title. [1] Example: Bernstein, Mark.
Access the archived version by clicking "View History," then clicking the date/timestamp of the version you'd like to cite. Online Scholarly Journal Article: Citing DOIs. Please note: Because online materials can potentially change URLs, APA recommends providing a Digital Object Identifier (DOI), when it is available, as opposed to the URL.
Citing a Website Article (APA) Format: Author(s).(Year, Month Day). Title of article in italics.Website Name. URL . Note: Cite an online source as a website only if no other type of source applies to it. For instance, many magazines and newspapers publish articles on their websites - in cases like this, you would cite the article as if it were an online magazines or newspaper article (not a ...
Provide the name of the news website in the source element of the reference. Link to the comment itself if possible. Otherwise, link to the webpage on which the comment appears. Either a full URL or a short URL is acceptable. 3. Webpage on a website with a government agency group author.
Q: This page describes citing specific pages and articles. Can I cite an entire site? A: According to the APA manual (7th edition), it is not necessary to cite a site in its entirety in a reference list. Instead, include a reference to the website in the body of your paper and cite any web page individually. Example:
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats. Basic Rules Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the ...
In an MLA Works Cited entry for a journal article, the article title appears in quotation marks, the name of the journal in italics—both in title case. List up to two authors in both the in-text citation and the Works Cited entry. For three or more, use "et al.". MLA format. Author last name, First name.
If you're wondering how to cite a website in APA, use the structure below. Structure: Author Last Name, First initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Title of web page. Name of Website. URL. Example of an APA format website: Austerlitz, S. (2015, March 3).
1. Name the author and the publication date in-text before a quote. To simplify the in-text citation, place the last name of the author in the text to introduce the quote and then the publication date for the text in parentheses. You can then leave the author's name and the publication date out of the quote itself. [1]
If using our APA Citation Machine, our citation generator will add the correct format for you automatically. Giving a retrieval date is not needed unless the online content is likely to be frequently updated and changed (e.g., encyclopedia article, dictionary entry, Twitter profile, etc.).
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog. Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free.
Narrative citation: Grady et al. (2019) If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference. Always include the issue number for a journal article. If the journal article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range (for an explanation of why, see the database information ...
Related Read: How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion. 6. Cite your sources. The key to learning how to write a research paper is learning how to cite sources. Depending on the style guide you're following, you may need to create in-text citations, a Works Cited page, a reference list, a bibliography, or footnotes. Pay close attention to ...
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required. Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format.
In this blog post, editors of OUP journals delve into the vital aspect of clear communication in a journal article. Anne Foster (Editor of Diplomatic History), Eduardo Franco (Editor-in-Chief of JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer institute and JNCI Monographs), Howard Broman (Editor-in-Chief of ICES Journal of Marine Science), and Michael Schnoor (Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Leukocyte ...
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Increasing evidence suggests that diet may influence risk of depression. 1-3 Despite extensive data linking ultraprocessed foods (UPF; ie, energy-dense, palatable, and ready-to-eat items) with human disease, 4 evidence examining the association between UPF consumption and depression is scant. Prior studies have been hampered by short-term dietary data 1,2 and a limited ability to account for ...
One of the grand challenges of artificial general intelligence is developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. While frontier models have already been used as aides to human scientists, e.g. for brainstorming ideas, writing code, or prediction tasks, they still conduct only a small part of the scientific process. This paper presents the first ...
This paper introduces rStar, a self-play mutual reasoning approach that significantly improves reasoning capabilities of small language models (SLMs) without fine-tuning or superior models. rStar decouples reasoning into a self-play mutual generation-discrimination process. First, a target SLM augments the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with a rich set of human-like reasoning actions to ...
In a new white paper, researchers from MIT, OpenAI, Microsoft, and other tech companies and academic institutions propose the use of personhood credentials, a verification technique that enables someone to prove they are a real human online, while preserving their privacy.
Citing journal articles in APA. A journal is a scholarly periodical that presents research from experts in a certain field. Typically, but not always, these journals are peer-reviewed in order to ensure that published articles are of the highest quality. That is one reason why journals are a highly credible source of information.
In this short piece, researchers at the Cross-Strait Institute of Urban Planning at Xiamen University lay out recommendations for Beijing on how to prepare for post-"reunification" governance of Taiwan. The unnamed authors of a now-deleted article recommend Beijing create a "shadow government" that will be ready to take over in Taipei in the case of "reunification," and prepare policies for ...
In this post, I discuss situations where students and researchers use ChatGPT to create text and to facilitate their research, not to write the full text of their paper or manuscript. We know instructors have differing opinions about how or even whether students should use ChatGPT, and we'll be continuing to collect feedback about instructor ...
Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr's APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator, Harvard Referencing Generator, and Chicago Citation Generator. Plagiarism Checker: Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to ...
The modeling and manipulation of 3D scenes captured from the real world are pivotal in various applications, attracting growing research interest. While previous works on editing have achieved interesting results through manipulating 3D meshes, they often require accurately reconstructed meshes to perform editing, which limits their application in 3D content generation. To address this gap, we ...
We then propose a taxonomy of theoretical contributions typically observed in Information Systems Research (ISR). Based on this taxonomy of contributions, the typical critiques observed in empirical Econ-IS papers, and a set of published papers, we provide some broad guidelines for how authors may craft an effective theoretical contribution for ...