
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions

Development of the idea
Overall reaction of photosynthesis.
- Basic products of photosynthesis
- Evolution of the process
- Light intensity and temperature
- Carbon dioxide
- Internal factors
- Energy efficiency of photosynthesis
- Structural features
- Light absorption and energy transfer
- The pathway of electrons
- Evidence of two light reactions
- Photosystems I and II
- Quantum requirements
- The process of photosynthesis: the conversion of light energy to ATP
- Elucidation of the carbon pathway
- Carboxylation
- Isomerization/condensation/dismutation
- Phosphorylation
- Regulation of the cycle
- Products of carbon reduction
- Photorespiration
- Carbon fixation in C 4 plants
- Carbon fixation via crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)
- Differences in carbon fixation pathways
- The molecular biology of photosynthesis

Why is photosynthesis important?
What is the basic formula for photosynthesis, which organisms can photosynthesize.

photosynthesis
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Khan Academy - Photosynthesis
- Biology LibreTexts - Photosynthesis
- University of Florida - Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences - Photosynthesis
- Milne Library - Inanimate Life - Photosynthesis
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis
- Roger Williams University Pressbooks - Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology - Photosynthesis
- BCcampus Open Publishing - Concepts of Biology – 1st Canadian Edition - Overview of Photosynthesis
- photosynthesis - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- photosynthesis - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Trusted Britannica articles, summarized using artificial intelligence, to provide a quicker and simpler reading experience. This is a beta feature. Please verify important information in our full article.
This summary was created from our Britannica article using AI. Please verify important information in our full article.
Photosynthesis is critical for the existence of the vast majority of life on Earth. It is the way in which virtually all energy in the biosphere becomes available to living things. As primary producers, photosynthetic organisms form the base of Earth’s food webs and are consumed directly or indirectly by all higher life-forms. Additionally, almost all the oxygen in the atmosphere is due to the process of photosynthesis. If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other organic matter on Earth, most organisms would disappear, and Earth’s atmosphere would eventually become nearly devoid of gaseous oxygen.
The process of photosynthesis is commonly written as: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 . This means that the reactants, six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules, are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll (implied by the arrow) into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules, the products. The sugar is used by the organism, and the oxygen is released as a by-product.
The ability to photosynthesize is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. The most well-known examples are plants, as all but a very few parasitic or mycoheterotrophic species contain chlorophyll and produce their own food. Algae are the other dominant group of eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms. All algae, which include massive kelps and microscopic diatoms , are important primary producers. Cyanobacteria and certain sulfur bacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes, in whom photosynthesis evolved. No animals are thought to be independently capable of photosynthesis, though the emerald green sea slug can temporarily incorporate algae chloroplasts in its body for food production.
Recent News
photosynthesis , the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy . During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water , carbon dioxide , and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds .
It would be impossible to overestimate the importance of photosynthesis in the maintenance of life on Earth . If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other organic matter on Earth. Most organisms would disappear, and in time Earth’s atmosphere would become nearly devoid of gaseous oxygen. The only organisms able to exist under such conditions would be the chemosynthetic bacteria , which can utilize the chemical energy of certain inorganic compounds and thus are not dependent on the conversion of light energy.

Energy produced by photosynthesis carried out by plants millions of years ago is responsible for the fossil fuels (i.e., coal , oil , and gas ) that power industrial society . In past ages, green plants and small organisms that fed on plants increased faster than they were consumed, and their remains were deposited in Earth’s crust by sedimentation and other geological processes. There, protected from oxidation , these organic remains were slowly converted to fossil fuels. These fuels not only provide much of the energy used in factories, homes, and transportation but also serve as the raw material for plastics and other synthetic products. Unfortunately, modern civilization is using up in a few centuries the excess of photosynthetic production accumulated over millions of years. Consequently, the carbon dioxide that has been removed from the air to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis over millions of years is being returned at an incredibly rapid rate. The carbon dioxide concentration in Earth’s atmosphere is rising the fastest it ever has in Earth’s history, and this phenomenon is expected to have major implications on Earth’s climate .
Requirements for food, materials, and energy in a world where human population is rapidly growing have created a need to increase both the amount of photosynthesis and the efficiency of converting photosynthetic output into products useful to people. One response to those needs—the so-called Green Revolution , begun in the mid-20th century—achieved enormous improvements in agricultural yield through the use of chemical fertilizers , pest and plant- disease control, plant breeding , and mechanized tilling, harvesting, and crop processing. This effort limited severe famines to a few areas of the world despite rapid population growth , but it did not eliminate widespread malnutrition . Moreover, beginning in the early 1990s, the rate at which yields of major crops increased began to decline. This was especially true for rice in Asia. Rising costs associated with sustaining high rates of agricultural production, which required ever-increasing inputs of fertilizers and pesticides and constant development of new plant varieties, also became problematic for farmers in many countries.

A second agricultural revolution , based on plant genetic engineering , was forecast to lead to increases in plant productivity and thereby partially alleviate malnutrition. Since the 1970s, molecular biologists have possessed the means to alter a plant’s genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA ) with the aim of achieving improvements in disease and drought resistance, product yield and quality, frost hardiness, and other desirable properties. However, such traits are inherently complex, and the process of making changes to crop plants through genetic engineering has turned out to be more complicated than anticipated. In the future such genetic engineering may result in improvements in the process of photosynthesis, but by the first decades of the 21st century, it had yet to demonstrate that it could dramatically increase crop yields.
Another intriguing area in the study of photosynthesis has been the discovery that certain animals are able to convert light energy into chemical energy. The emerald green sea slug ( Elysia chlorotica ), for example, acquires genes and chloroplasts from Vaucheria litorea , an alga it consumes, giving it a limited ability to produce chlorophyll . When enough chloroplasts are assimilated , the slug may forgo the ingestion of food. The pea aphid ( Acyrthosiphon pisum ) can harness light to manufacture the energy-rich compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP); this ability has been linked to the aphid’s manufacture of carotenoid pigments.
General characteristics
The study of photosynthesis began in 1771 with observations made by the English clergyman and scientist Joseph Priestley . Priestley had burned a candle in a closed container until the air within the container could no longer support combustion . He then placed a sprig of mint plant in the container and discovered that after several days the mint had produced some substance (later recognized as oxygen) that enabled the confined air to again support combustion. In 1779 the Dutch physician Jan Ingenhousz expanded upon Priestley’s work, showing that the plant had to be exposed to light if the combustible substance (i.e., oxygen) was to be restored. He also demonstrated that this process required the presence of the green tissues of the plant.
In 1782 it was demonstrated that the combustion-supporting gas (oxygen) was formed at the expense of another gas, or “fixed air,” which had been identified the year before as carbon dioxide. Gas-exchange experiments in 1804 showed that the gain in weight of a plant grown in a carefully weighed pot resulted from the uptake of carbon, which came entirely from absorbed carbon dioxide, and water taken up by plant roots; the balance is oxygen, released back to the atmosphere. Almost half a century passed before the concept of chemical energy had developed sufficiently to permit the discovery (in 1845) that light energy from the sun is stored as chemical energy in products formed during photosynthesis.

This equation is merely a summary statement, for the process of photosynthesis actually involves numerous reactions catalyzed by enzymes (organic catalysts ). These reactions occur in two stages: the “light” stage, consisting of photochemical (i.e., light-capturing) reactions; and the “dark” stage, comprising chemical reactions controlled by enzymes . During the first stage, the energy of light is absorbed and used to drive a series of electron transfers, resulting in the synthesis of ATP and the electron-donor-reduced nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). During the dark stage, the ATP and NADPH formed in the light-capturing reactions are used to reduce carbon dioxide to organic carbon compounds. This assimilation of inorganic carbon into organic compounds is called carbon fixation.

Van Niel’s proposal was important because the popular (but incorrect) theory had been that oxygen was removed from carbon dioxide (rather than hydrogen from water, releasing oxygen) and that carbon then combined with water to form carbohydrate (rather than the hydrogen from water combining with CO 2 to form CH 2 O).
By 1940 chemists were using heavy isotopes to follow the reactions of photosynthesis. Water marked with an isotope of oxygen ( 18 O) was used in early experiments. Plants that photosynthesized in the presence of water containing H 2 18 O produced oxygen gas containing 18 O; those that photosynthesized in the presence of normal water produced normal oxygen gas. These results provided definitive support for van Niel’s theory that the oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis is derived from water.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Photosynthesis
All you need to know about photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which a plant produces its food by converting light energy into chemical energy. Plants use water, carbon dioxide and sunlight in the presence of chlorophyll to produce their food or energy in the form of sugar and release oxygen as the byproduct. Understanding the process of photosynthesis means a clear concept about the different cellular and chemical activities going on in the plant body. The word photosynthesis is coined from the Greek word for meaning light along with synthesis. This implies a synthesis i.e a chemical reaction using light energy. This is not always for green plants only but certain bacteria and prokaryotes also use this process to prepare their food. In green plants or algae, the synthesis takes place within an important organelle called chloroplast where the pigment chlorophyll is present. Chlorophyll occurs in their leaves, stems, flowers, sepals and even in plastids.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Various factors influence/affect the photosynthesis process. These are:
Light Intensity: More the light, the more will be the rate of photosynthesis. Similarly, low light will lead to a low rate of photosynthesis.
The Concentration of CO 2 : A higher CO 2 concentration rate in a plant also accelerates the photosynthesis process. The required amount of CO 2 is 300-400 PPM.
Temperature: If the temperature is between the range of 25 to 35 degrees Celsius, photosynthesis takes place effectively.
Water: An essential amount of water is required for stomatal opening, and it’s a key factor in the process of photosynthesis.
Pollution: The increasing rate of polluting particles in the atmosphere block the pores of somatic cells, and the intake of carbon dioxide becomes difficult.
Photosynthesis Equation
Carbon dioxide and water are the two major factors involved in the photosynthesis reaction. It’s an endothermic reaction, and the products resulting from it are oxygen and glucose. The formula is:
\[6CO_{2} + 6H_{2}O = C_{6}H_{1}2O_{6} + 6O_{2}\]
However, some bacteria don’t produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis. They are called anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria, and those who do it are called oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria.
Photosynthetic Pigments
Four types of photosynthetic pigments are present in the leaves of the plants. They are:
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
Xanthophylls
Carotenoids
Structure of Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green colour pigment found in plants that play a vital role in photosynthesis. It allows the plants to absorb the energy coming from the sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis.
Process of Photosynthesis
The photosynthesis process occurs in plants. It takes place in chloroplasts at the cellular level that contains chlorophyll. Leaves have parts called the petiole, epidermis, and lamina that absorb sunlight.
Photosynthesis Steps:
The photosynthesis process takes place at two levels or steps. These are:
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-dependent Reaction
The process begins in the daylight, by gathering the light. The two types of photosystems convert light energy into ATP and NADPH. During their conversion, oxygen is produced, and water is used. The equation of this step is:
\[2H_{2}O + 2NADP + 3ADP + 3P_{i} = O_{2} + 2 NADPH + 3ATP\]
The Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent Reaction
This is also called carbon-fixing. It is not dependent on light and takes place in chloroplast where the products from the earlier step are used. Plants intake CO 2 and the Calvin Photosynthesis Cycle begins, where the six molecules of CO 2 are converted into sugar or glucose.
\[3CO_{2} + 6NADPH + 5H_{2}O + 9ATP = G3P + 2H + 6NADP + 9ADP + 8P_{i}\]
Importance of Photosynthesis
The photosynthesis process is very important for the survival of living beings, and to continue the food chain. It also produces oxygen, which is required for breathing.
FAQs on Photosynthesis
1. What is photosynthesis?
The process by plants, of producing nutrients essential for survival.
2. What happens in a photosynthesis process?
The nutrients and glucose required for plants, and oxygen required for the animals, is created during the process.
3. What is the photosynthesis reaction?
A reaction taking place in plants that results in the production of glucose and oxygen.
4. What is shown in a photosynthesis diagram?
The photosynthesis diagram shows how the plants take sunlight and use it to produce essential nutrients and oxygen.
5. Why is photosynthesis in plants important?
It helps in the survival of the plants, the creation of products essential for the survival of living beings, and also to maintain the environmental balance.
6. How long is the photosynthesis cycle?
The whole process of photosynthesis, right from absorbing the light up to the final stage, takes place in just 30 seconds!
7. What is included in the mechanism of photosynthesis?
The mechanism of photosynthesis is an oxidation (oxygen releasing) and reduction reaction. It produces glucose along with oxygen.
8. What are the two phases of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a synthesis reaction in which solar energy gets converted to chemical energy. However, the few steps involved in the synthesis also occur without light and based on that there are two phases of photosynthesis. The light-dependent reactions and the light-independent phase. In the light-dependent phase which is the starting phase the molecule of chlorophyll pigment absorbs one photon from the sun rays and loses electrons and ultimately after several steps generate NADPH and ATP which are used in the second phase or the light-independent phase of the reaction. In the dark phase, the atmospheric carbon dioxide is captured by a photosynthetic enzyme that uses the NADPH formed in the first phase to produce 3 carbon sugars which ultimately gets converted to starch and sucrose. Thus the two phases occur subsequently to form the end products which are the food of the plant.
9. What is the efficiency of the photosynthetic reaction?
Photosynthesis is the most important reaction or synthesis for which lives and the planet can run. It converts light to chemical energy. The efficiency of the reaction is however only 3-6% and the absorbed light cannot be used. The unused light gets dissipated to the atmosphere as heat. The efficiency of the synthesis varies with temperature, light intensity and proportion of carbon dioxide in nature which can vary the efficiency to a maximum of 8% even. The efficiency of the two phases can be separately taken into count and they both separately contribute to the total efficiency of the process.
10. Which factors can affect the process of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is affected by many factors including the corollary ones. The main factors that affect the process are as follows:
Light: Its intensity and wavelength
Carbon dioxide: Its concentration in the atmosphere
Temperature: Favorable temperature is needed
Water: Suitable quantity of water is needed
Apart from these factors photosynthesis also depends upon the factor referred to as the corollary factor which is the surface area of the leaf available to absorb the sunlight. This is why if a plant is overshadowed by other big trees it cannot efficiently photosynthesize.
11. What are the actual stages of the process of photosynthesis?
The process of photosynthesis can be divided into four essential steps. They are as follows:
Transfer of solar energy in thylakoid membranes of chlorophyll.
Transfer of the electrons in the light reaction
The synthesis of electron transport chain and ATP in the thylakoid membrane.
Absorption and fixation of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere with the formation of resulting stable plant food.
Each of these steps takes a specific time to happen with the maximum time of one second taken by the last step.
12. How is photosynthesis essential for the ecosystem?
Photosynthesis is the procedure by which plants convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of their food. Photosynthesis is an ideal process for a living organism that has not evolved the capacity to actively move around in order to obtain food. Photosynthesis is also important for the consumers of the food web and thus is the starting point of all food chains of the ecosystem. Photosynthesis is thus an essential living process for plants and the ecosystem. All life on the earth depends upon photosynthesis, not only for the food but also for the oxygen in the atmosphere which is essential for them to respire. It is the process of photosynthesis that purifies the atmosphere by removing carbon dioxide from the environment and converting it to oxygen.
Biology • Class 11
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Course: ap®︎/college biology > unit 3.
- Photosynthesis
Intro to photosynthesis
- Breaking down photosynthesis stages
- Conceptual overview of light dependent reactions
- The light-dependent reactions
- The Calvin cycle
- Photosynthesis evolution
- Photosynthesis review
Introduction
What is photosynthesis.
- Energy. The glucose molecules serve as fuel for cells: their chemical energy can be harvested through processes like cellular respiration and fermentation , which generate adenosine triphosphate— ATP , a small, energy-carrying molecule—for the cell’s immediate energy needs.
- Fixed carbon. Carbon from carbon dioxide—inorganic carbon—can be incorporated into organic molecules; this process is called carbon fixation , and the carbon in organic molecules is also known as fixed carbon . The carbon that's fixed and incorporated into sugars during photosynthesis can be used to build other types of organic molecules needed by cells.
The ecological importance of photosynthesis
- Photoautotrophs use light energy to convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds. This process is called photosynthesis.
- Chemoautotrophs extract energy from inorganic compounds by oxidizing them and use this chemical energy, rather than light energy, to convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds. This process is called chemosynthesis.
- Photoheterotrophs obtain energy from sunlight but must get fixed carbon in the form of organic compounds made by other organisms. Some types of prokaryotes are photoheterotrophs.
- Chemoheterotrophs obtain energy by oxidizing organic or inorganic compounds and, like all heterotrophs, get their fixed carbon from organic compounds made by other organisms. Animals, fungi, and many prokaryotes and protists are chemoheterotrophs.
Leaves are sites of photosynthesis
The light-dependent reactions and the calvin cycle.
- The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membrane and require a continuous supply of light energy. Chlorophylls absorb this light energy, which is converted into chemical energy through the formation of two compounds, ATP —an energy storage molecule—and NADPH —a reduced (electron-bearing) electron carrier. In this process, water molecules are also converted to oxygen gas—the oxygen we breathe!
- The Calvin cycle , also called the light-independent reactions , takes place in the stroma and does not directly require light. Instead, the Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide and produce three-carbon sugars—glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, or G3P, molecules—which join up to form glucose.
Photosynthesis vs. cellular respiration
Attribution.
- “ Overview of Photosynthesis ” by OpenStax College, Biology, CC BY 3.0 . Download the original article for free at http://cnx.org/contents/5bb72d25-e488-4760-8da8-51bc5b86c29d@8 .
- “ Overview of Photosynthesis ” by OpenStax College, Concepts of Biology, CC BY 3.0 . Download the original article for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] .
Works cited:
- "Great Oxygenation Event." Wikipedia. Last modified July 17, 2016. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Oxygenation_Event .
Additional references
Want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
Loading ...
Learning materials, instructional links.
- Photosynthesis (Google doc)
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis .The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2 ) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). Herbivores then obtain this energy by eating plants, and carnivores obtain it by eating herbivores.
The process
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen back into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
Chlorophyll
Inside the plant cell are small organelles called chloroplasts , which store the energy of sunlight. Within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast is a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll , which is responsible for giving the plant its green color. During photosynthesis , chlorophyll absorbs energy from blue- and red-light waves, and reflects green-light waves, making the plant appear green.
Light-dependent Reactions vs. Light-independent Reactions
While there are many steps behind the process of photosynthesis, it can be broken down into two major stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reaction takes place within the thylakoid membrane and requires a steady stream of sunlight, hence the name light- dependent reaction. The chlorophyll absorbs energy from the light waves, which is converted into chemical energy in the form of the molecules ATP and NADPH . The light-independent stage, also known as the Calvin cycle , takes place in the stroma , the space between the thylakoid membranes and the chloroplast membranes, and does not require light, hence the name light- independent reaction. During this stage, energy from the ATP and NADPH molecules is used to assemble carbohydrate molecules, like glucose, from carbon dioxide.
C3 and C4 Photosynthesis
Not all forms of photosynthesis are created equal, however. There are different types of photosynthesis, including C3 photosynthesis and C4 photosynthesis. C3 photosynthesis is used by the majority of plants. It involves producing a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid during the Calvin Cycle, which goes on to become glucose. C4 photosynthesis, on the other hand, produces a four-carbon intermediate compound, which splits into carbon dioxide and a three-carbon compound during the Calvin Cycle. A benefit of C4 photosynthesis is that by producing higher levels of carbon, it allows plants to thrive in environments without much light or water. The National Geographic Society is making this content available under a Creative Commons CC-BY-NC-SA license . The License excludes the National Geographic Logo (meaning the words National Geographic + the Yellow Border Logo) and any images that are included as part of each content piece. For clarity the Logo and images may not be removed, altered, or changed in any way.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
June 21, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
CBSE Class Notes Online – Classnotes123
CBSE Class Notes, Worksheets, Question Answers, Diagrams , Definitions , Diffrence between , Maths Concepts, Science Facts Online – Classnotes123
Photosynthesis – Class 10

Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that occurs in green plants and certain bacteria. It is an autotrophic mode of nutrition wherein organisms synthesise their food from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight.
Table of Contents
Definition of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the green parts of plants, such as leaves, stems, and sometimes in other green tissues. It is the primary mechanism by which plants produce their own food, using energy from sunlight to convert inorganic substances into organic compounds.
Modes of Autotrophic Nutrition
Autotrophic mode of nutrition refers to the mode of nutrition in which organisms synthesise their own food from simple inorganic substances present in the environment. Two common modes of autotrophic nutrition are- –
- Photosynthesis – Photosynthesis is the primary mode of autotrophic nutrition used by green plants and some bacteria. It is the process by which green plants synthesise organic food using carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll.
- Chemosynthesis – Chemosynthesis is another mode of autotrophic nutrition used by certain bacteria that live in extreme environments, such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents. These bacteria utilise energy obtained from chemical reactions involving inorganic compounds to produce organic food.
Significance of Photosynthesis
- Production of Organic Food – Through Photosynthesis, green plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a simple sugar that serves as their primary source of energy. This energy is utilised for various metabolic processes required for growth, reproduction, and maintenance of cellular functions.
- Energy Storage- Carbohydrates, primarily in the form of glucose, are produced during Photosynthesis. These carbohydrates provide energy to the plant for immediate use. Any excess carbohydrates that are not immediately utilised are converted into starch and stored as an internal energy reserve. This stored energy is available to the plant whenever required.
- Oxygen Release- As a byproduct of Photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere. This oxygen is essential for the survival of all living organisms, as it is used in cellular respiration to produce energy.
Also Check – Diffrence Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
Process of Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis occurs in the specialised organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in the cells of green plant tissues, particularly in leaves. The process can be divided into two main stages-
- The light-dependent reactions
- The light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle)
Light-Dependent Reactions
In the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, initiating the following steps-
- Absorption of Light Energy- Chlorophyll, the green pigment present in chloroplasts, absorbs light energy from the sun.
- Splitting of Water Molecules- The absorbed light energy is used to split water molecules (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen ions (H+).
- Generation of ATP and NADPH- The energy from the absorbed light is harnessed to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which serve as energy carriers for the subsequent reactions.
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
In the stroma of chloroplasts, the light-independent reactions occur and involve the following steps-
- Carbon Dioxide Fixation- Carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere combines with the hydrogen ions (H+) and energy carriers (ATP and NADPH) to form an intermediate molecule.
- Production of Glucose- The intermediate molecule undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions, ultimately leading to the production of glucose (C6H12O6).
- Regeneration of Reactants- Some molecules from the intermediate stage are recycled to regenerate the starting materials, ATP, NADPH, and carbon dioxide acceptors, allowing the process to continue.
Overall Equation for Photosynthesis
The process of Photosynthesis can be represented by the following simplified chemical equation-
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
In this equation, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) are the raw materials, and in the presence of light energy, glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) are produced.
The Raw Materials for Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis requires specific raw materials for the process to occur efficiently. The essential raw materials for Photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and other mineral nutrients obtained from the soil. Let’s delve into each of these raw materials and their role in Photosynthesis-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon dioxide is a colourless and odourless gas that is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of cellular respiration in living organisms.
- During cellular respiration, organisms, including plants, break down organic molecules to release energy. In turn, they release carbon dioxide as a waste product.
- For plants, carbon dioxide enters the leaves through tiny openings called stomata. Stomata are present on the surface of leaves and allow for the exchange of gases between the plant and the environment.
- Carbon dioxide diffuses into the leaf through the stomata, providing the necessary carbon source for Photosynthesis.
Also Check – Mechanism of opening and Closing of the Stomata
Water (H2O)-
- Water is another crucial raw material required for Photosynthesis. Plants absorb water through their roots from the soil.
- The root hairs, which are extensions of root cells, increase the surface area for water absorption.
- Once absorbed, water is transported upward through the plant’s vascular system, specifically through a specialised tissue called xylem.
- The xylem vessels extend from the roots all the way to the leaves. The movement of water through xylem is driven by a combination of root pressure and transpiration , the loss of water vapour through small openings on the leaf surface called stomata.
- During Photosynthesis, water molecules are split in a process called photolysis. This splitting occurs in the presence of sunlight and takes place in the chloroplasts of the plant cells.
- The photolysis of water results in the production of oxygen gas (O2) and hydrogen ions (H+). The oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of Photosynthesis, while the hydrogen ions are used in subsequent reactions.
Other Materials- Mineral Nutrients
- In addition to carbon dioxide and water, plants require various mineral nutrients obtained from the soil for optimal growth and Photosynthesis.
- These mineral nutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), iron (Fe), and magnesium (Mg), among others.
- Nitrogen is an essential nutrient that plants require for the synthesis of proteins and other vital compounds. Plants uptake nitrogen from the soil in the form of inorganic nitrates (or nitrites) or as organic compounds derived from symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
- Phosphorus is necessary for energy transfer and storage in plants. It is obtained from the soil in the form of inorganic phosphates and plays a critical role in various metabolic processes.
- Iron is a micronutrient essential for chlorophyll synthesis. It is involved in capturing light energy during Photosynthesis. Plants absorb iron in the form of inorganic ions from the soil.
- Magnesium is a central component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing light energy during Photosynthesis. Plants absorb magnesium as an inorganic ion from the soil.
- These mineral nutrients are absorbed by the plant’s roots and transported through the vascular system to the cells where Photosynthesis occurs. They are crucial for the plant’s overall growth, development, and efficient photosynthetic processes. Read More ..
The Site of Photosynthesis- Chloroplasts
Photosynthesis takes place within specialised organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in the cells of green plants. Chloroplasts play a crucial role as the primary sites of Photosynthesis. Let’s explore the structure of chloroplasts, their presence in photosynthetic cells, and the role of chlorophyll in capturing light energy.
Structure of Chloroplasts

Chloroplasts are unique double-membrane organelles found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other organisms capable of Photosynthesis. These organelles contain an intricate network of membranes, enzymes, and pigments that facilitate the process of Photosynthesis.
Within the chloroplasts, there are several key structures-
- Outer Membrane- The outer membrane of the chloroplast acts as a protective barrier, separating the internal contents from the surrounding cytoplasm of the cell.
- Inner Membrane- The inner membrane is located inside the outer membrane and encloses the stroma, a gel-like substance where the light-independent reactions of Photosynthesis occur.
- Thylakoid Membranes- The thylakoid membranes are interconnected sac-like structures that are stacked on top of each other in a structure called a grana (plural- granum). These membranes contain specialised pigments, including chlorophyll, that capture light energy.
- Stroma- The stroma is the fluid-filled space within the chloroplast that surrounds the thylakoid membranes. It contains enzymes and other molecules necessary for the light-independent reactions of Photosynthesis.
Also Check – Chloroplast – Definition, Structure, Distribution, function and Diagram
Presence of Chloroplasts in Photosynthetic Cells
Chloroplasts are primarily found in the photosynthetic cells of green plants, particularly in the mesophyll cells of leaves. The mesophyll cells are specialised for Photosynthesis and contain numerous chloroplasts. This arrangement maximises the surface area available for light capture and ensures efficient photosynthetic processes.
Chlorophyll and Light Absorption
- Chlorophyll is a green pigment found within the chloroplasts that plays a vital role in capturing light energy during Photosynthesis. It is responsible for the characteristic green colour of plants.
- Chlorophyll molecules are embedded in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These molecules have a unique structure that allows them to absorb light energy from the visible spectrum, particularly in the red and blue regions, while reflecting green light.
- When light strikes chlorophyll molecules, they absorb photons of specific wavelengths. The absorbed light energy is then transferred to other chlorophyll molecules and ultimately to the reaction centres in the thylakoid membranes. This energy is used to drive the chemical reactions of Photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in the form of ATP and NADPH.
Conditions Necessary for Photosynthesis
For Photosynthesis to occur, certain conditions must be met. These conditions include the availability of sunlight and the presence of chlorophyll. Let’s explore the significance of these conditions in detail-
Sunlight is a crucial factor in Photosynthesis as it provides the energy needed for the process. The intensity, quality, and duration of sunlight all influence the rate of Photosynthesis.
- Intensity- The intensity of sunlight refers to the amount of light energy reaching a given area. Higher light intensity generally leads to increased photosynthetic activity. However, there is an optimal range of light intensity beyond which the rate of Photosynthesis plateaus. Insufficient light intensity limits the amount of energy available for the process.
- Quality – Sunlight consists of a spectrum of colours, each with a different wavelength. Plants primarily absorb light in the red and blue regions of the spectrum, while green light is reflected, giving plants their green appearance. Thus, the quality of light, specifically the presence of red and blue wavelengths, is essential for efficient Photosynthesis.
- Duration- The duration of exposure to sunlight also affects Photosynthesis. Longer periods of light availability allow for a greater accumulation of energy, leading to increased photosynthetic activity. However, plants also have mechanisms to adapt to changing light conditions, such as adjusting the opening and closing of stomata to optimise gas exchange and reduce water loss.
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a pigment found in chloroplasts, and it plays a pivotal role in capturing solar energy during Photosynthesis.
- Trapping Solar Energy- Chlorophyll molecules are responsible for absorbing light energy from the sun. Specifically, chlorophyll molecules absorb photons of light in the red and blue regions of the spectrum. This absorbed energy is then transferred to other molecules within the chloroplast, leading to the initiation of the light-dependent reactions of Photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll molecules are arranged within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, maximising their exposure to light. This organisation allows for efficient light absorption and energy transfer.
- It is important to note that other pigments, such as carotenoids, also contribute to light absorption in plants. These pigments capture light energy in different regions of the spectrum and help supplement the overall efficiency of Photosynthesis.
Events in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis involves a series of interconnected events that occur within the chloroplasts of plant cells. These events are essential for converting light energy into chemical energy and synthesise carbohydrates. Let’s explore these events in detail-
Absorption of Light Energy-
During Photosynthesis, chlorophyll, the primary pigment in chloroplasts, plays a crucial role in absorbing light energy from the sun. Chlorophyll molecules are located in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and are arranged to maximise light absorption.
When chlorophyll molecules absorb photons of specific wavelengths, they become energised. This absorbed energy is transferred to neighbouring chlorophyll molecules until it reaches specialised structures called reaction centres. These reaction centers initiate the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
Conversion of Light Energy
The absorbed light energy is utilized in the light-dependent reactions of Photosynthesis to produce energy-rich molecules such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy carriers serve as the “currency” for the subsequent synthesis of carbohydrates.
Additionally, during the light-dependent reactions, water molecules are split through a process called photolysis. The energy absorbed by chlorophyll facilitates the separation of water molecules into hydrogen ions (H+) and oxygen (O2). This release of oxygen is vital for the oxygenation of our atmosphere, while the hydrogen ions are further utilised in the synthesis of carbohydrates.
Reduction of Carbon Dioxide
In the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, the energy-rich molecules (ATP and NADPH) generated in the light-dependent reactions are used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbohydrates.
During this process, carbon dioxide molecules from the atmosphere enter the chloroplasts and undergo a series of chemical reactions. The energy from ATP and the high-energy electrons from NADPH are utilised to drive the reduction of carbon dioxide. The end result is the synthesis of simple sugars, such as glucose, which serve as a vital source of energy and building blocks for the plant.
It’s important to note that the events in Photosynthesis do not occur sequentially in a strict order. Instead, they are interconnected and continually ongoing, with various stages and reactions happening simultaneously or in response to changing environmental conditions.
Also Check – Top 10 Experiments on Photosynthesis (With Diagram)
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Temperature- Photosynthesis is temperature-sensitive, with the optimal range for most plants typically being between 20-30 degrees Celsius (68-86 degrees Fahrenheit). Higher temperatures can initially increase the rate of photosynthesis, but excessive heat can damage the enzymes involved in the process.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration- Carbon dioxide is an important raw material for photosynthesis. Higher CO2 concentrations can increase the rate of photosynthesis, up to a certain point where it becomes saturated. Insufficient CO2 can limit the photosynthetic process.
- Light intensity- Light is an essential factor for photosynthesis as it provides the energy needed to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Higher light intensity usually increases the rate of photosynthesis, but beyond a certain threshold the rate stagnates.
- Light quality- Plants absorb mainly red and blue wavelengths of light, while green light is reflected, which is why plants appear green. Different wavelengths and light spectra can affect the photosynthesis rate differently. Certain plants have specific light requirements.
- Availability of water- Water is crucial for photosynthesis as it provides the hydrogen ions necessary for the synthesis of glucose. Insufficient water supply can lead to closure of the stomata, reducing CO2 uptake and limiting the rate of photosynthesis.
- Availability of nutrients- Plants require various nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and trace elements, to carry out photosynthesis effectively. An insufficient supply of nutrients can limit the production of enzymes and other components involved in this process.
- Chlorophyll content- Chlorophyll is the most important pigment responsible for the absorption of light energy during photosynthesis. Plants with a higher chlorophyll content tend to have a greater capacity for photosynthesis.
- Environmental factors- Factors such as altitude, humidity and air pollutants can affect photosynthesis. Extreme conditions such as high altitude or pollution can affect the availability of light, temperature and CO2, thus affecting the rate of photosynthesis. Read More..
Adaptations and Additional Photosynthesis Information
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process that has evolved various adaptations to suit different environmental conditions. These adaptations allow plants to optimise their photosynthetic efficiency and ensure survival in diverse habitats. Let’s explore some of these unique adaptations and additional information related to Photosynthesis-
Desert Plants Adaptation
Desert plants, such as cacti and certain succulents, have adapted to conserve water in arid environments. To minimise water loss through transpiration, they have developed a unique adaptation known as Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). CAM plants open their stomata and take in carbon dioxide during the cooler nights when evaporation rates are lower. The carbon dioxide is then stored as an intermediate compound, typically malic acid, within the cells. During the day, when the stomata are closed to prevent water loss, the stored carbon dioxide is released and used for Photosynthesis. This adaptation allows desert plants to conserve water while still performing Photosynthesis efficiently.
Also Check- What are the Adaptations of leaf for Photosynthesis
Aquatic Plants’ Adaptation
- Aquatic plants, such as Hydrilla and Vallisneria, have adapted to living in waterlogged environments. Unlike terrestrial plants that primarily obtain carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, these plants can use dissolved carbon dioxide present in the water for Photosynthesis. They possess specialised structures that facilitate the uptake of dissolved carbon dioxide directly from their aquatic surroundings. This adaptation enables them to thrive in aquatic habitats where access to atmospheric carbon dioxide is limited.
Additional Information
Photosynthesis and oxygen production.
Photosynthesis is responsible for oxygen production, which is vital for supporting life on Earth. The oxygen released as a byproduct during the splitting of water molecules in the light-dependent reactions of Photosynthesis contributes to the oxygenation of our atmosphere, making it suitable for aerobic organisms.
Nitrogen is taken up in the form of inorganic nitrates (or nitrites) or as organic compounds prepared by symbiotic bacteria like Rhizobium from Atmospheric nitrogen .
Photosynthetic Pigments and Leaf Coloration
Besides chlorophyll, other pigments, such as carotenoids, play a role in Photosynthesis. These pigments absorb light in different regions of the spectrum, enhancing the range of light wavelengths that can be utilised for Photosynthesis. Carotenoids also provide colours like yellow, orange, and red to leaves, contributing to the vibrant autumn foliage.
Also Check- Steps of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis – frequently asked questions and answers.
What is Photosynthesis?
Answer- Photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the green parts of plants, using energy from sunlight to convert inorganic substances (carbon dioxide and water) into organic compounds (glucose) as a means of producing food.
What are the two common modes of autotrophic nutrition?
Answer- The two common modes of autotrophic nutrition are Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
How do green plants obtain their energy through Photosynthesis?
Answer- Green plants obtain their energy through Photosynthesis by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a simple sugar that serves as their primary source of energy.
What is the significance of Photosynthesis in terms of energy storage?
Answer- Photosynthesis allows plants to produce carbohydrates, primarily in the form of glucose, which provide immediate energy for the plant. Any excess carbohydrates not immediately used are converted into starch and stored as an internal energy reserve.
How does Photosynthesis contribute to the oxygen levels in the atmosphere?
Answer- As a byproduct of Photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere. This oxygen is essential for the survival of all living organisms, as it is used in cellular respiration to produce energy.
Which organelle is responsible for Photosynthesis in green plant tissues?
Answer- Photosynthesis occurs in specialised organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in the cells of green plant tissues, particularly in leaves.
What are the two main stages of Photosynthesis?
Answer- The two main stages of Photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
What happens during the light-dependent reactions of Photosynthesis?
Answer- In the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, leading to the splitting of water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions. The energy from the absorbed light is used to produce ATP and NADPH, which serve as energy carriers for the subsequent reactions.
What occurs during the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) of Photosynthesis?
Answer- During the light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere combines with hydrogen ions and energy carriers (ATP and NADPH) to form an intermediate molecule, which undergoes enzymatic reactions ultimately leading to the production of glucose. Some molecules from the intermediate stage are recycled to regenerate the starting materials, allowing the process to continue.
Provide the overall chemical equation for Photosynthesis.
Answer- The overall equation for Photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2. In this equation, carbon dioxide and water are the raw materials, and in the presence of light energy, glucose and oxygen are produced.
What are the three essential raw materials required for Photosynthesis?
Answer- The three essential raw materials required for Photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and mineral nutrients obtained from the soil.
What is the process called when water molecules are split during Photosynthesis?
Answer- The process of water molecule splitting during Photosynthesis is called photolysis.
Name two mineral nutrients required by plants for optimal growth and Photosynthesis.
Answer- Two mineral nutrients required by plants for optimal growth and Photosynthesis are nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P).
Where does Photosynthesis take place within the cells of green plants?
Answer- Photosynthesis takes place within specialised organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in the cells of green plants.
What are the key structures within chloroplasts?
Answer- The key structures within chloroplasts include the outer membrane, inner membrane, thylakoid membranes, and stroma.
Which pigment is responsible for capturing light energy during Photosynthesis?
Answer- Chlorophyll is the pigment responsible for capturing light energy during Photosynthesis.
What wavelengths of light are absorbed by chlorophyll?
Answer- Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the red and blue regions of the visible spectrum while reflecting green light.
How is the absorbed light energy used during Photosynthesis?
Answer- The absorbed light energy is used to drive the chemical reactions of Photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in the form of ATP and NADPH.
In which cells of plants are chloroplasts primarily found?
Answer- Chloroplasts are primarily found in the photosynthetic cells of green plants, particularly in the mesophyll cells of leaves.
What are the essential raw materials required for Photosynthesis?
Answer- The essential raw materials for Photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and other mineral nutrients obtained from the soil.
How does carbon dioxide enter the leaves of plants?
Answer- Carbon dioxide enters the leaves of plants through tiny openings called stomata, which are present on the surface of leaves.
Where does water absorption occur in plants?
Answer- Water is absorbed by plants through their roots from the soil.
Which specialised tissue transports water from the roots to the leaves?
Answer- The xylem, a specialised tissue, transports water from the roots to the leaves.
What is the role of chlorophyll in Photosynthesis?
Answer- Chlorophyll is a pigment that captures light energy during Photosynthesis. It absorbs photons of specific wavelengths, particularly in the red and blue regions of the spectrum.
What are the primary factors influencing the rate of Photosynthesis?
Answer- The primary factors influencing the rate of Photosynthesis are light intensity, light quality, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and the availability of water and nutrients.
How does light energy get converted into chemical energy during Photosynthesis?
Answer- Light energy is converted into chemical energy during Photosynthesis through the light-dependent reactions, where chlorophyll molecules absorb light and transfer the energy to generate energy-rich molecules such as ATP and NADPH.
What is the role of ATP and NADPH in Photosynthesis?
Answer- ATP and NADPH are energy carriers produced during the light-dependent reactions of Photosynthesis. They provide the energy and reducing power needed for the light-independent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
What are some adaptations of desert plants for Photosynthesis in arid environments?
Answer- Desert plants, such as cacti, have adapted a process called Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). They open their stomata at night to take in carbon dioxide and store it as malic acid. During the day, the stored carbon dioxide is released for Photosynthesis when the stomata are closed to minimise water loss.
How do aquatic plants obtain carbon dioxide for Photosynthesis? Answer- Aquatic plants can use dissolved carbon dioxide present in the water for Photosynthesis. They have specialised structures that facilitate the uptake of dissolved carbon dioxide from their aquatic surroundings.
Related Posts
What is a reflex action – for class 10th.
February 10, 2024 March 16, 2024

What is Reflex Arc for Class 10
February 9, 2024 February 10, 2024

What is Interstitial Fluid and its Vital Role in Cellular Health and Function
February 9, 2024 February 9, 2024
About Jaishree Gorane
19 comments on “photosynthesis – class 10”.
- Pingback: SIGNIFICANCE OF TRANSPIRATION - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: How are Water and Minerals Transported in Plants ? - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: How do the Guard cells Regulate Opening and Closing of Stomatal Pores - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Name the Factors Which Affect Photosynthesis - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Cross Section of Leaf Class 10 - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: What are the Adaptations of leaf for Photosynthesis - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Difference between Potosynthesis and Respiration - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: What is Photosynthesis? Explain the mechanism. - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Autotrophic Nutrition - Class 10 - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Life Processes Class 10 Notes - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: What is the Function of the Stomata ? - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: What is Photosynthesis Short Answer - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Nutrition in Plants Class 10 - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Diagram of a Chloroplast - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Transverse Section of Leaf - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: What are the Components of Transport System in Highly Organised Plants - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Transportation in Plants Class 10 - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: How is Food Transported in Plants -Class 10 - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
- Pingback: Chloroplast - Definition, Structure, Distribution, function and Diagram - CBSE Class Notes Online - Classnotes123
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Make Waves in Learning! 25% off
for World Oceans Day
Use code OCEAN25

Share this article

Table of Contents
Latest updates.

1 Million Means: 1 Million in Rupees, Lakhs and Crores

Ways To Improve Learning Outcomes: Learn Tips & Tricks

Visual Learning Style for Students: Pros and Cons

NCERT Books for Class 6 Social Science 2024 – Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 9 Social Science 2023-24: Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2024: Download PDF

NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths 2025: Download Latest PDF

CBSE Class 10 Study Timetable 2024 – Best Preparation Strategy

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2025 – Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 2025: Download PDF
Tag cloud :.
- entrance exams
- engineering
- ssc cgl 2024
- Written By Manisha Minni
- Last Modified 25-01-2023
Photosynthesis: Process, Equation and Factors
Photosynthesis Process: Photosynthesis is the process by which a plant converts light energy into chemical energy for the production of food. A plant uses water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight in the presence of chlorophyll to produce food or energy in the form of sugar and releases oxygen as a by-product. The word “Photosynthesis” is broken into two words, Photo means ‘ Light ‘ and Synthesis means ‘To Put Together. Humans, along with other animals, are dependent on plants for survival. Plants and algae produce the oxygen we need for survival, as well as the carbohydrates we need for energy. These things are all produced through photosynthesis.
In this article, we will talk about the process of Photosynthesis, factors and the equation of Photosynthesis. Let us know more about the process of Photosynthesis that helps sustain life on earth with the help of sunlight, water and carbon dioxide.

Photosynthesis: Definition
Photosynthesis is a physicochemical process in which autotrophs convert light energy into chemical energy to synthesise organic compounds, which are stored in the form of sugar and later used to complete cellular activities. In this process, carbohydrates and oxygen are synthesized by using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. The word Photosynthesis is derived from the Greek word, “Photo” means “light”, and “Synthesis” means “putting together”. To sum up, this word means “combining together with the help of light.”
Diagram of Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis Equation

Fig: Chemical Reaction of Photosynthesis
Sites of Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are the cell organelle that carries out Photosynthesis in plants. Every green part of a plant, including the green stems, green leaves, take part in Photosynthesis. The mesophyll cells of leaves have many chloroplasts that hold specialised light-absorbing green pigments called chlorophyll. The chloroplasts are known as the kitchen of the cell because complete food synthesis takes place here.

Fig: Chloroplast
Photosynthetic Pigments
Photosynthetic pigments are light-absorbing molecules, which absorb only specific wavelengths of visible light but reflect others. The photosynthetic pigments are of two types based on their significance.
1. Primary Pigments: The pigment forms the main molecule of the photosystem , e.g., Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll b . 2. Accessory Pigments: These support the function of primary pigments , e.g., Xanthophylls and Carotenoids .
The reaction centre contains Chlorophyll a molecule where the energy is trapped. The antenna pigments are mainly chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenoid molecules, which absorb photons and transfer their energy to the reaction centre.

Fig: Photosynthetic Pigments
Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two main phases. These are light-dependent and light-independent phases.
A. Light-dependent Phase
- In this phase, light plays the main role.
- The light reaction takes place in the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
- Activation of chlorophyll- The chlorophyll on exposure to light energy becomes activated by absorbing photon particles.
- Splitting of water- In the activated chlorophyll in the presence of sunlight, \({{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\) breaks down into \({{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}\) and \({\rm{O}}{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ – }}}\) and releases electrons. This reaction is known as photolysis of water which means splitting by light.
- Formation of NADPH- NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) is known as Hill reagent. The hydrogen ions \(\left( {{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}} \right)\) are picked up by a compound NADP to form NADPH.
- Evolution of oxygen- The oxygen \(\left( {\rm{O}} \right)\) component is given out as molecular oxygen \(\left( {{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right){\rm{.}}\)
- Photophosphorylation- In the activated chlorophyll, in the presence of sunlight, ADP and Pi combine together to form energy-rich compound ATP . This is called photophosphorylation. These can be of two types cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
- So, the net production of light reaction will be ATP, \({\rm{NADPH + }}{{\rm{H}}^{\rm{ + }}}\) and \({{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{.}}\)
B. Light-independent Reaction or Dark Reaction or Biosynthetic Phase
- In this phase, light is not required.
- This occurs simultaneously with the light reaction.
- This occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast.
- The hydrogen of NADPH is used to combine with \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\) by utilising ATP energy to ultimately produce glucose \(\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}} \right){\rm{.}}\)
- This fixation of \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\) is catalysed by the enzyme Rubisco (Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase).
- This fixation of \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\) occurs in a number of steps using a special \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\) acceptor compound RUBP (Ribulose bisphosphate).
- During the dark reaction of photosynthesis carbon of \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\) is absorbed and assimilated into glucose. So the process of dark reaction is known as carbon assimilation.

Fig: Light Dependent and Light-Independent Phase

Factors of Photosynthesis
There are many external and internal factors that affect Photosynthesis. 1. External Factors a. Light – The rate of Photosynthesis is directly proportional to the intensity of light. b. Carbon dioxide – Initially, carbon dioxide increases the rate of Photosynthesis, but after optimum level, it acts as a reducing factor. c. Water – Increased water availability causes a steady increase in the rate of Photosynthesis. d. Temperature – The rate of Photosynthesis increases with an increase in temperature. The optimum temperature for Photosynthesis is \({\rm{35 – 4}}{{\rm{0}}^{\rm{0}}}{\rm{C}}{\rm{.}}\) After that, the rate decreases with the increase in temperature.
2. Internal Factors a. Chlorophyll – The rate of Photosynthesis increases with increased chlorophyll content. b. Structure of leaf – The thickness of the cuticle, the distribution of stomata, and the size of the leaf influence the rate of Photosynthesis.
Significance
The significance of Photosynthesis are mentioned below: 1. Photosynthesis is a physicochemical process that is an utmost source of breathable oxygen in the air. 2. In the food chain, plants are the primary producer, and they create their food using Photosynthesis. 3. Photosynthesis helps in the purification of air. 4. The relationship of photosynthesis to man is important not only from the standpoint of food but also from the point of economic existence and civilization.
Photosynthesis is the process by which a plant converts light energy into chemical energy for the production of food. A plant uses water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight in the presence of chlorophyll to produce food or energy in the form of sugar and releases oxygen as a by-product. Chloroplasts include chlorophyll and other light-sensitive pigments that catch solar energy. The photosynthetic cells can transform this solar energy into organic molecules that carry energy, such as glucose, in the presence of carbon dioxide. These cells not only maintain the global carbon cycle but also generate much of the oxygen present in the atmosphere.

FAQs About Photosynthesis
Let’s look at some of the commonly asked questions about Photosynthesis:
Q.1. What are the different stages of Photosynthesis? Ans: There are two stages of Photosynthesis: i) Light-dependent or photochemical reaction ii) Light-independent or Dark reaction or Biosynthetic Phase
Q.2. What is photosynthesis? Ans: Photosynthesis is the process by which carbohydrates (glucose or other sugar) and oxygen are synthesized by using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight.
Q.3. What is Calvin Cycle? Ans: Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. This is also referred to as the light-independent reaction.
Q.4. Mention different types of photosynthetic pigments? Ans: There are 4 major photosynthetic pigments present in chloroplasts. These are Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b, Xanthophylls and Carotenoids.
Q.5. Where do the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of Photosynthesis take place? Ans: Light-dependent reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts , and the light-independent reaction takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
We hope this detailed article on Photosynthesis helps you in your preparation. If you get stuck do let us know in the comments section below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Related Articles
1 Million Means: 1 million in numerical is represented as 10,00,000. The Indian equivalent of a million is ten lakh rupees. It is not a...
Ways To Improve Learning Outcomes: With the development of technology, students may now rely on strategies to enhance learning outcomes. No matter how knowledgeable a...
Visual Learning Style: We as humans possess the power to remember those which we have caught visually in our memory and that too for a...
NCERT Books for Class 6 Social Science 2024: Many state education boards, including the CBSE, prescribe the NCRET curriculum for classes 1 to 12. Thus,...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 9 Social Science: The Central Board of Secondary Education releases the revised CBSE Class 9 Social Science syllabus. The syllabus is...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2023-24: Students in CBSE Class 8 need to be thorough with their syllabus so that they can prepare for the...
NCERT Books for Class 6 Maths 2025: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) textbooks are the prescribed set of books for schools...
CBSE Class 10 Study Timetable: The CBSE Class 10 is the board-level exam, and the Class 10th students will appear for the board examinations for...
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducts the Class 10 exams every year. Students in the CBSE 10th Class...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has published the Class 11 syllabus for all streams on its official...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water – A Precious Resource
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Water – A Precious Resource: In this chapter, students will study about the importance of water. There are three...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 2024: Respiration in Organisms
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms: NCERT solutions are great study resources that help students solve all the questions associated...
Factors Affecting Respiration: Definition, Diagrams with Examples
In plants, respiration can be regarded as the reversal of the photosynthetic process. Like photosynthesis, respiration involves gas exchange with the environment. Unlike photosynthesis, respiration...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants: The chapter 'Reproduction' in Class 7 Science discusses the different modes of reproduction in...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11: Chapter 11 of Class 7 Science deals with Transportation in Animals and Plants. Students need to ensure...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15: Light
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15: The NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 15 is Light. It is one of the most basic concepts. Students...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13: Chapter 13 in class 7 Science is Motion and Time. The chapter concepts have a profound impact...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14: Electric Current and its Effects
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 14: One of the most important chapters in CBSE Class 7 is Electric Current and its Effects. Using...
General Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
General terms related to spherical mirrors: A mirror with the shape of a portion cut out of a spherical surface or substance is known as a...
Animal Cell: Definition, Diagram, Types of Animal Cells
Animal Cell: An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell with membrane-bound cell organelles without a cell wall. We all know that the cell is the fundamental...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science 2024 – Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) publishes NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science as a comprehensive...
NCERT Books for Class 12 Chemistry 2024: Download PDF
NCERT Books for class 12 Chemistry: NCERT publishes chemistry class 12 books every year. The NCERT chemistry class 12 books are essential study material for...
CBSE Class 9 Mock Tests 2025: Attempt Online Mock Test Series (Subject-wise)
We all have heard at least once that the secret to success is practice. Some of you could say it's a cliché, but those who...
NCERT Books for Class 10 Maths 2025: Download Latest PDF
NCERT Books for Class 10 Maths: The NCERT Class 10 Maths Book is a comprehensive study resource for students preparing for their Class 10 board exams....
Arc of a Circle: Definition, Properties, and Examples
Arc of a circle: A circle is the set of all points in the plane that are a fixed distance called the radius from a fixed point...
CBSE Class 10 Mock Test 2025: Practice Latest Test Series
CBSE Class 10 Mock Test 2025: Students' stress is real due to the mounting pressure of scoring good marks and getting into a renowned college....
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 2024: Science and Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 2024: Students appearing for the CBSE Class 10 board exam must go through NCERT Solutions to prepare for the exams...

39 Insightful Publications

Embibe Is A Global Innovator

Innovator Of The Year Education Forever

Interpretable And Explainable AI

Revolutionizing Education Forever

Best AI Platform For Education

Enabling Teachers Everywhere

Decoding Performance

Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider

Auto Generation Of Tests

Disrupting Education In India

Problem Sequencing Using DKT

Help Students Ace India's Toughest Exams

Best Education AI Platform

Unlocking AI Through Saas

Fixing Student’s Behaviour With Data Analytics

Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results

Brave New World Of Applied AI

You Can Score Higher

Harnessing AI In Education

Personalized Ed-tech With AI

Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education

Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact

Top 20 AI Influencers In India

Proud Owner Of 9 Patents

Innovation in AR/VR/MR

Best Animated Frames Award 2024
Trending Searches
Previous year question papers, sample papers.
Practice Photosynthesis Questions with Hints & Solutions

Practice Photosynthesis Questions with Solutions & Ace Exam
Enter mobile number.
By signing up, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions
Explain the mechanism of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare their food in the presence of sunlight. green plants utilize carbon dioxide and water to make carbohydrate. the reaction of photosynthesis can be depicted in the following equation: $$6co_2+12h_2o\xrightarrow{chlorophyll+sunlight}c_6h_12o_6+6o_2+6h_2o$$ the process of photosynthesis is composed of following step: (a) absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. (b) conversion of light energy into chemical energy (c) splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. (d) reduction of carbon dioxide to form carbohydrate these steps need not take place one after another immediately. for example; desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night to make an intermediate. during daytime. they make carbohydrate. after photosynthesis, carbohydrate is converted into starch and starch is stored in different plant organs..
explain the mechanism of photosynthesis?
Question 79 Explain the mechanism of photosynthesis.
- Biology Article
- Light Reaction Vs Dark Reaction
Light reaction And Dark reaction
Table of Contents
Difference between Light and Dark Reaction
|
|
| – Discover its definition and significance |
| – Explore its meaning and implications |
| – Learn how these two processes vary from each other |
Photosynthesis is the process of conversion of light energy into chemical energy which can then be utilized by living organisms. It is a rather complex process which is carried out through various stages.
Photosynthesis comprises two phases:
- The first phase is the photochemical phase or light-dependent process . This phase is commonly known as the light reaction.
- The second phase is the biosynthetic phase of the dark reaction of photosynthesis. This phase is the light-independent process.
The whole process of photosynthesis takes place within the chloroplast.
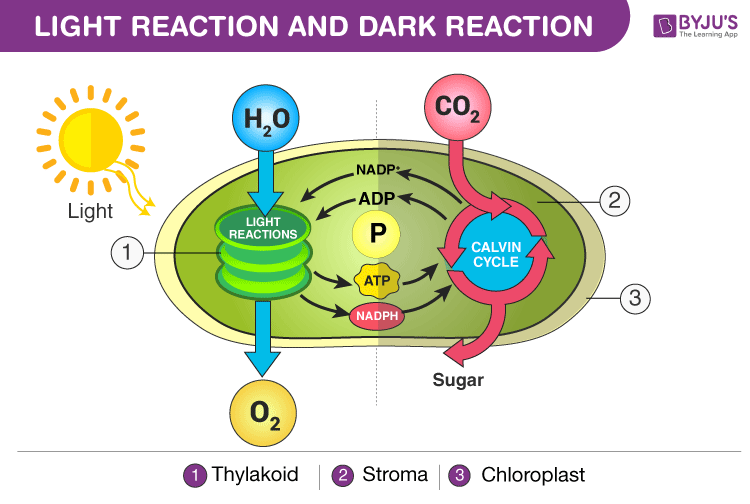
Steps Carried out in Light Reaction and Dark Reaction
As stated above, photosynthesis occurs in two phases – light reaction and dark reaction.
Light Reaction
The light reaction is a light-dependent process which includes a series of events such as light absorption, hydrolysis, the release of oxygen, formation of ATP and NADPH.
The light reaction of photosynthesis initiates only when it is supplied with light energy.
The photosystem is the arrangement of pigments, including chlorophyll within thylakoids.
There are two photosystems in plants:
- Photosystem I (PS-I)
- Photosystem II (PS-II)
Photosystem I absorbs light at a wavelength of 700 nm, whereas Photosystem II absorbs light at a wavelength of 680 nm.
The light reaction occurs in the thylakoids of the chloroplast. When the light hits, chlorophyll- a gets excited to a higher energy state followed by a series of reactions. This energy is converted into energy molecules ATP and NADPH by using PS I and PS II. Also, hydrolysis occurs and releases oxygen.
Also Read: Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Dark Reaction
Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction. It is a light-independent process in which sugar molecules are formed from the carbon dioxide and water molecules.
The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast, where they utilize the products of the light reaction.
Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin cycle .
In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drives the reaction and convert six molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule, i.e. glucose.
Also Refer: Photosynthesis in Higher plants
Following are the important differences between light and dark reaction:
|
|
|
| It takes place only in the presence of light. | It can take place in the or of sunlight. |
| It is a photochemical phase. | It is a biochemical phase. |
| It takes place in the grana of the chloroplast. | It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. |
| NADP utilizes H+ ions to form NADPH. | The hydrogen of NADPH combines with CO2. |
| The end products are ATP and NADPH. | Glucose is the end product. ATP and NADPH help in the formation of glucose. |
| The water molecules split into hydrogen and oxygen. | Glucose is produced. Co2 is utilized in the dark reaction. |
| Photolysis occurs in PS-II. | Photolysis does not occur. |
Also Read: Difference between Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
For more details on light reaction, dark reaction and the difference between light and dark reaction, keep visiting BYJU’S or download the BYJU’S app for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a light reaction.
The light reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes. In the light reaction, the light is absorbed and energy is used to drive electrons from water to generate NADPH and to drive protons across the membrane.
What is a dark reaction?
In the dark reaction, plants use carbon dioxide with ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to produce glucose. It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
What are the end products of light reactions?
The end products of the light reaction are ATP and NADPH, also known as assimilatory powers.
What is the end product of the dark reaction?
Glucose is the end product of the dark reaction.
What is the difference between light and dark reaction?
The light reaction is the initial stage of photosynthesis which traps light energy to produce ATP and NADPH, whereas dark reaction is the second step of photosynthesis which utilizes the energy from ATP and NADPH to produce glucose.
Does the dark reaction occur at night?
No, the dark reaction does not occur at night. It occurs during the day, but the reaction does not use the light directly. Therefore, it is known as the dark reaction.
How does a plant make energy without light?
Plants make ATP from other sources such as metal ions and turn carbon dioxide into glucose. The anaerobic photosynthetic bacteria use light energy but do not have the light reactions as in plants and produce no oxygen.
How does light affect the growth of plants?
Light provides energy to plants through a process called photosynthesis. This energy helps the plant to grow. This is how plant growth is affected by light.
Also Read: Light-dependent reaction

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| BIOLOGY Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
nice chapter
Nice chapter
Very informative.
Best document
Can i get relation between light reaction and dark reaction with help of scymatic presentation
What is glycolisis?
A process in which glucose (sugar) is partially broken down by cells
Sir I AM so happy in by jis class
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide. 3,12,343.
Significance of Photosynthesis are as follows:-1. Provide food:- Photosynthesis helps to prepare food in plants and they prepare their food not only for themselves but all living beings which are lived on this earth because each and every organism is dependent on plants, either directly or indirectly.
photosynthesis, the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.. It would be impossible to overestimate the importance of photosynthesis in the maintenance of life on Earth.
What Is Photosynthesis? "Photosynthesis is the process used by green plants and a few organisms that use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to prepare their food.". The process of photosynthesis is used by plants, algae and certain bacteria that convert light energy into chemical energy. The glucose formed during the process of ...
Photosynthesis is affected by many factors including the corollary ones. The main factors that affect the process are as follows: Light: Its intensity and wavelength Carbon dioxide: Its concentration in the atmosphere Temperature: Favorable temperature is needed Water: Suitable quantity of water is needed Apart from these factors photosynthesis also depends upon the factor referred to as the ...
Pretty Good Question, Photosynthesis is one of the processes Which plants do to make Glucose. Plants get proteins from nitrates (a form of nitrogen).This process is called nitrification and fats are made from a process called fatty acid biosynthesis which uses excess energy.The Hormones and enzymes are made from different parts of the plant like for example Auxin is a plant hormone produced in ...
Photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. In a process driven by light energy, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are constructed from water and carbon dioxide, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. The glucose molecules provide organisms with two crucial resources: energy and ...
The process. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO 2) and water (H 2 O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose.
Photosynthesis ( / ˌfoʊtəˈsɪnθəsɪs / FOH-tə-SINTH-ə-sis) [1] is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism.
Photosynthesis is defined as a process that occurs primarily in chloroplasts and is mediated by photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene, and xanthophyll. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunshine to create nutrition in green plants and a few other autotrophic species.
1) Photosynthesis is a physiological process which serves as the driving and vital force to obtain food and fuel for all non-photosynthetic organisms in universe. 3) Carbohydrates synthesised during dark reaction of photosynthesis become structural parts of the organisms. 4) In the process, solar energy is converted into chemical energy by ...
🟢 Life Processes Class 10 One Shot 👉 https://www.youtube.com/live/oZbunizPfz4In this free YouTube class, Vedantu Biology expert Khusboo will discuss "Photo...
This is defined as "combining with the aid of light.". Photosynthesis is the conversion of sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water into food (sugars) and oxygen by plants, algae, and some microorganisms. Light energy is collected and used by green plants during the process to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and ...
Photosynthesis uses solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water to release oxygen and to produce energy-storing sugar molecules. The complex reactions of photosynthesis can be summarized by the chemical equation shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. The process of photosynthesis can be represented by an equation, wherein carbon dioxide and water produce ...
Photosynthesis, the vital process in plants, converts raw materials—carbon dioxide and water—into glucose, releasing oxygen. It occurs within chloroplasts, the site of photosynthesis. The process involves interconnected events, including light absorption, energy conversion, and carbon dioxide reduction. Factors like light intensity, temperature, and nutrient availability influence ...
what is photosynthesis? Class -10th science bbiology chapter - 6| Definition of photosynthesis |Prakash sanshleshan kya hai?biology class 10th photosynthes.P...
The significance of Photosynthesis are mentioned below: 1. Photosynthesis is a physicochemical process that is an utmost source of breathable oxygen in the air. 2. In the food chain, plants are the primary producer, and they create their food using Photosynthesis. ... CBSE Class 10 Study Timetable: The CBSE Class 10 is the board-level exam, and ...
Contributors and Attributions. Study Guide: Photosynthesis. Authored by: Wendy Riggs. Provided by: College of the Redwoods. Project: Kaleidoscope. License: CC BY: Attribution. 10.1: Study Guide- Photosynthesis is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Photosynthesis Equation. Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants use light energy, carbon dioxide, and water. And it produces glucose, oxygen, and water. Therefore it converts light energy into chemical energy i.e. the glucose for use in the plants. The reaction for photosynthesis is as given as follows:
Process of Photosynthesis Step by Step. The sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll in the leaves of the plants. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through structures called the stomata, which are usually found on the underside of the leaves. Water is absorbed through the roots of the plant. The light-dependent reaction occurs during the day.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare their food in the presence of sunlight. Green plants utilize carbon dioxide and water to make carbohydrate. The reaction of photosynthesis can be depicted in the following equation: (a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. (c) splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
Curriculum on plants in primary school. The early primary school biology curriculum covers the topic of humans, animals and plants. Plants appear to receive less emphasis in the science curriculum and biology textbooks with regards to these three issues as compared to animals (Schussler et al. Citation 2010).As a result, children may have a greater interest in animals than plants and tend to ...
Q. Write two differences between photosynthesis and respiration. (i) Give the overall chemical equation of photosynthesis in green plants. (ii) Mention two significant advantages of photosynthesis to the living world as a whole. Q. Write any five significances of photosynthesis. Q. Explain the significance of photosynthesis.
Laboratory animal studies have reported the biliary excretion of chemicals following exposure. Nevertheless, feces are rarely used as a matrix in biomonitoring of chemical exposures. In this study, feces and urine from pet dogs and cats were analyzed for the presence of 45 plasticizers, 45 environmental phenols, and 31 pesticides. Thirty-two analytes were detected in ≥70% pet feces, while up ...
Following are the important differences between light and dark reaction: Light Reaction. Dark Reaction. It takes place only in the presence of light. It can take place in the presence or absence of sunlight. It is a photochemical phase. It is a biochemical phase. It takes place in the grana of the chloroplast.