

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
How to Start an Assignment
Last Updated: January 29, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michelle Golden, PhD . Michelle Golden is an English teacher in Athens, Georgia. She received her MA in Language Arts Teacher Education in 2008 and received her PhD in English from Georgia State University in 2015. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 111,246 times.
Getting started on an assignment or homework can often times be the hardest step. Putting off the assignment can make the problem worse, reducing the time you have to complete the task and increasing stress. By learning how to get started and overcome the urge to procrastinate, you can get your assignments done on schedule and with less stress, opening up more free time.
Restructuring Your Assignment

- For example, you might research areas of a report that you find most interesting before moving on to other areas.
- If your math assignment has different types of questions, try doing those that you enjoy the most before moving on to the others.
- You might also try tackling smaller or easier tasks first so you can cross a few items off your list. Seeing that you've already made progress may help you feel motivated to continue.

- Promise yourself that you will meet your goal of working for five minutes on the assignment.
- Once you get started, you may find that you don't want to stop working. Otherwise, you can take a break and come back to the assignment, knowing you're at least five minutes closer to finishing than you were before.

- Try to set reasonable periods of time that you know you can meet. For example, you might set aside two hours on a Friday to dedicate to your assignment. If you don't have that much time all at once, try to carve out a few 20- or 30-minute blocks.
- You may or may not wish to continue working after your time limit has gone by.
- Have a realistic understanding of how fast you can write and plan your schedule accordingly.

- It can help to read the assignment as soon as you get it and then ask any questions you might have.
- If you're not sure if you understand the assignment, try rewriting it in your own words or explaining it to someone else. If you find you can't or have a lot of questions, you may need more information.
- You should have an overview of the assignment, understand the main task, and understand the technical and stylistic requirements.
- Look for important words in the instructions to understand the assignment. These words might include define, explain, compare, relate, or prove.
- Keep your audience in mind and write a paper that would best deliver information to them.

- Goals that are too big or not well defined can be difficult to start working towards.
- Smaller and well defined goals can seem easier to achieve than larger ones.
- For example, you could break a research paper down into several smaller tasks: 1) do preliminary research, 2) write an outline, 3) draft an introduction, 4) draft body paragraphs, 5) write conclusion, 6) revise. Each of these is much more do-able on its own.
Changing Your Focus

- You might want to go for a quick walk after working for a set amount of time.
- Try reading a website or book that you enjoy for a few minutes after working.
- Alternatively, try a quick burst of exercise before setting to work. Exercise releases feel-good chemicals called endorphins and can also help boost your memory. [8] X Research source

- Instead of dreading your work, focus on how good it will feel to make progress. You won't have it hanging over your head. You can actually enjoy the weekend instead of feeling guilty.
- Keeping your eye on long-term rewards can help you stay motivated to finish your assignment.

- Avoid moving your workspace constantly.
- Don't get lost on tangential research.
- Don't take constant breaks to get a snack.

- For every hour you waste procrastinating, you can limit how much television you watch that night.
- If you waste too much time procrastinating, you might deny yourself a favorite snack later on.

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/solving-unsolvable-problems/201408/4-steps-stop-procrastinating
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/friendship-20/201405/the-surefire-first-step-stop-procrastinating
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/procrastination/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/homework.html
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/understanding-assignments/
- ↑ https://open.alberta.ca/dataset/ab22ff64-3358-4387-9761-8c58878a6b84/resource/3ee38320-17e4-46f9-b24f-c95f9f345eb9/download/ipp7.pdf
- ↑ http://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/07/how-exercise-can-help-us-learn/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/happy-life.html
About This Article

To start an assignment, try working on the most enjoyable or easiest parts of the assignment first to get the ball rolling. Even if no part of the assignment seems enjoyable or easy, set a timer and try to make yourself work for at least 5 minutes, which is usually enough time to build momentum and overcome procrastination. You can also try breaking your assignment up into smaller, more manageable tasks and scheduling yourself regular breaks so it doesn't seem as overwhelming. To learn how to stay positive and avoid procrastination while working on your homework, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Faith Wanjiku
Dec 7, 2018
Did this article help you?

Winnie Wong
May 18, 2016
Turab Ahamad
Oct 23, 2016
Sofia Madrid
Sep 5, 2016
Doha Elabbasi
Sep 27, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to Write a Perfect Assignment: Step-By-Step Guide
Table of contents
- 1 How to Structure an Assignment?
- 2.1 The research part
- 2.2 Planning your text
- 2.3 Writing major parts
- 3 Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
- 4 Will I succeed with my assignments?
- 5 Conclusion
How to Structure an Assignment?
To cope with assignments, you should familiarize yourself with the tips on formatting and presenting assignments or any written paper, which are given below. It is worth paying attention to the content of the paper, making it structured and understandable so that ideas are not lost and thoughts do not refute each other.
If the topic is free or you can choose from the given list — be sure to choose the one you understand best. Especially if that could affect your semester score or scholarship. It is important to select an engaging title that is contextualized within your topic. A topic that should captivate you or at least give you a general sense of what is needed there. It’s easier to dwell upon what interests you, so the process goes faster.
To construct an assignment structure, use outlines. These are pieces of text that relate to your topic. It can be ideas, quotes, all your thoughts, or disparate arguments. Type in everything that you think about. Separate thoughts scattered across the sheets of Word will help in the next step.
Then it is time to form the text. At this stage, you have to form a coherent story from separate pieces, where each new thought reinforces the previous one, and one idea smoothly flows into another.
Main Steps of Assignment Writing
These are steps to take to get a worthy paper. If you complete these step-by-step, your text will be among the most exemplary ones.
The research part
If the topic is unique and no one has written about it yet, look at materials close to this topic to gain thoughts about it. You should feel that you are ready to express your thoughts. Also, while reading, get acquainted with the format of the articles, study the details, collect material for your thoughts, and accumulate different points of view for your article. Be careful at this stage, as the process can help you develop your ideas. If you are already struggling here, pay for assignment to be done , and it will be processed in a split second via special services. These services are especially helpful when the deadline is near as they guarantee fast delivery of high-quality papers on any subject.
If you use Google to search for material for your assignment, you will, of course, find a lot of information very quickly. Still, the databases available on your library’s website will give you the clearest and most reliable facts that satisfy your teacher or professor. Be sure you copy the addresses of all the web pages you will use when composing your paper, so you don’t lose them. You can use them later in your bibliography if you add a bit of description! Select resources and extract quotes from them that you can use while working. At this stage, you may also create a request for late assignment if you realize the paper requires a lot of effort and is time-consuming. This way, you’ll have a backup plan if something goes wrong.
Planning your text
Assemble a layout. It may be appropriate to use the structure of the paper of some outstanding scientists in your field and argue it in one of the parts. As the planning progresses, you can add suggestions that come to mind. If you use citations that require footnotes, and if you use single spacing throughout the paper and double spacing at the end, it will take you a very long time to make sure that all the citations are on the exact pages you specified! Add a reference list or bibliography. If you haven’t already done so, don’t put off writing an essay until the last day. It will be more difficult to do later as you will be stressed out because of time pressure.
Writing major parts
It happens that there is simply no mood or strength to get started and zero thoughts. In that case, postpone this process for 2-3 hours, and, perhaps, soon, you will be able to start with renewed vigor. Writing essays is a great (albeit controversial) way to improve your skills. This experience will not be forgotten. It will certainly come in handy and bring many benefits in the future. Do your best here because asking for an extension is not always possible, so you probably won’t have time to redo it later. And the quality of this part defines the success of the whole paper.
Writing the major part does not mean the matter is finished. To review the text, make sure that the ideas of the introduction and conclusion coincide because such a discrepancy is the first thing that will catch the reader’s eye and can spoil the impression. Add or remove anything from your intro to edit it to fit the entire paper. Also, check your spelling and grammar to ensure there are no typos or draft comments. Check the sources of your quotes so that your it is honest and does not violate any rules. And do not forget the formatting rules.
with the right tips and guidance, it can be easier than it looks. To make the process even more straightforward, students can also use an assignment service to get the job done. This way they can get professional assistance and make sure that their assignments are up to the mark. At PapersOwl, we provide a professional writing service where students can order custom-made assignments that meet their exact requirements.
Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
Want to write like a pro? Here’s what you should consider:
- Save the document! Send the finished document by email to yourself so you have a backup copy in case your computer crashes.
- Don’t wait until the last minute to complete a list of citations or a bibliography after the paper is finished. It will be much longer and more difficult, so add to them as you go.
- If you find a lot of information on the topic of your search, then arrange it in a separate paragraph.
- If possible, choose a topic that you know and are interested in.
- Believe in yourself! If you set yourself up well and use your limited time wisely, you will be able to deliver the paper on time.
- Do not copy information directly from the Internet without citing them.
Writing assignments is a tedious and time-consuming process. It requires a lot of research and hard work to produce a quality paper. However, if you are feeling overwhelmed or having difficulty understanding the concept, you may want to consider getting accounting homework help online . Professional experts can assist you in understanding how to complete your assignment effectively. PapersOwl.com offers expert help from highly qualified and experienced writers who can provide you with the homework help you need.
Will I succeed with my assignments?
Anyone can learn how to be good at writing: follow simple rules of creating the structure and be creative where it is appropriate. At one moment, you will need some additional study tools, study support, or solid study tips. And you can easily get help in writing assignments or any other work. This is especially useful since the strategy of learning how to write an assignment can take more time than a student has.
Therefore all students are happy that there is an option to order your paper at a professional service to pass all the courses perfectly and sleep still at night. You can also find the sample of the assignment there to check if you are on the same page and if not — focus on your papers more diligently.
So, in the times of studies online, the desire and skill to research and write may be lost. Planning your assignment carefully and presenting arguments step-by-step is necessary to succeed with your homework. When going through your references, note the questions that appear and answer them, building your text. Create a cover page, proofread the whole text, and take care of formatting. Feel free to use these rules for passing your next assignments.
When it comes to writing an assignment, it can be overwhelming and stressful, but Papersowl is here to make it easier for you. With a range of helpful resources available, Papersowl can assist you in creating high-quality written work, regardless of whether you’re starting from scratch or refining an existing draft. From conducting research to creating an outline, and from proofreading to formatting, the team at Papersowl has the expertise to guide you through the entire writing process and ensure that your assignment meets all the necessary requirements.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
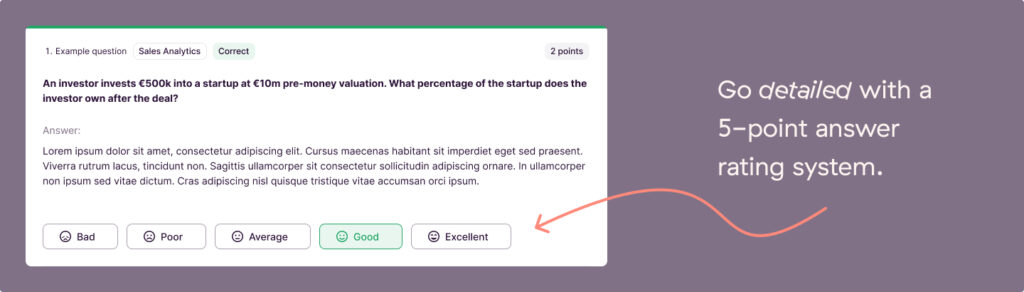
5 Examples of Take-Home Tasks for Different Roles
Assigning take-home tasks when hiring is much like marmite, coriander, or Hawaiian pizza. Your candidates will either love it or hate it.
The ‘love it’ camp likely welcomes the opportunity to showcase their skills and appreciate the time to think it through versus answering questions on the spot in an interview.
However, the ‘hate it’ group sees it as doing work for free, might already have portfolios of work that give a much fairer picture of their experience level, and resent the infringement on their personal time (regardless of how this might be their dream job).
What we can learn from this dichotomy is that while a take-home assignment is not right for every role, it’s still worth it for some. To figure out if it’s a fit for the role you’re hiring for, let’s look at five good examples of take-home tasks that your candidates will (hopefully) love.
TL;DR — Key Takeaways
A take-home assignment is an important part of the interview process that focuses on candidates crafting and completing real-world tasks .
Incorporating a take-home assignment will give your organization better insight and skill observation over candidates. However, job seekers may see take-home tests as time-consuming, exploitative, or manipulative.
The perfect take-home assignment should be structured around providing the candidate with clarity about the role, respecting their time, and ensuring consistent testing criteria.
Toggl Hire introduced homework tasks in our skills assessment library! It’s never been easier to raise the quality of your hires with reliable proof of competence.

What are take-home tasks?
A take-home assignment is given to candidates during the interview process to complete in their own time and shows the hiring manager how the job seeker is able to complete a task.
These assignments generally consist of coding tests for developers , presentations for upper-level management, and campaigns for marketers. They’re given to candidates after the first interview round. The success will determine if the candidate makes it to the second round.
| Take-home task type | Description | Roles |
|---|---|---|
| A coding challenge is a test designed to test the skills of developers. (Get more info on ) | Developers, Coders, Engineers | |
| A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific situation, problem, or scenario in order to understand and evaluate its complexities, factors, and potential solutions. | Researchers, Analysts, Consultants, Academics, Business Professionals | |
| Used to test if a candidate can construct long form, short form, news articles, or marketing copy. | Copywriters, Marketers, Journalists | |
| Showcase how an individual would communicate a concept or idea to a group of people. | Managers, C-level Execs, Customer Success | |
| A sales pitch is a persuasive approach used to promote and market a product or service. It focuses on highlighting the item’s unique features, advantages, and benefits to convince potential buyers and clients that the offering is worth their time and money. | Sales Representatives, Business Development Professionals | |
| A marketing campaign is a structured effort created by a business or entity to advertise, promote, and gain recognition for a product, service, or brand among a specific group of people. | Marketing Managers, Marketing Specialists, Creative Designers |

Pros and cons of a take-home assignment
Obviously, there are pros and cons to using a take-home assignment, right? Of course! So let’s go over the big ones.
• Skill observation : It allows the hiring company to understand the candidate’s skills in action and their thought process.
• Insight : The take-home interview assignment will allow the candidate to have a better understanding of the position, break any key assumptions, and what the company expects of them.
• Supplemental information : If done early in the interview process, an interview assignment allows the candidate’s skills to do the talking as opposed to the hiring manager only relying on the resume.
• Less pressure : Because a Q&A interview can be a pressure cooker, the take-home assignment makes the interviewing candidate feel more at ease.
• Time-consuming : A hiring team may claim the assignment will only take several hours to prepare and complete, but any interview assignment over more than an hour is cutting into the candidate’s personal time and current job.
• Ethical concerns and lost earnings : Asking a candidate to complete an unpaid work assignment can be seen as unethical and equivalent to unpaid labor. Some companies may even go so far as to steal the ideas of the candidate, use them, and not give credit or compensate the candidate.
• Limited personal evaluation : While the interview take-home assignment can assess a candidate’s skill set, it may not capture important aspects such as personality and behavior.
How to structure a take-home task
Creating a take-home assignment that strikes the perfect balance of helpful but not exploitative can be tricky. Regardless of what kind of take-home task or homework assignment you’re creating for hiring, it’s crucial for hiring managers to approach their creation with careful thought and attention.
Your hiring team will need to consider all of the following:
| What to consider | Why? |
|---|---|
| Assign the task after the interview to provide candidates with sufficient context about the role and the organization. | |
| Maintain a consistent structure for all examples to ensure fairness and enable a fair comparison between candidates. (hint, this is especially relevant if you want to establish in your organization) | |
| Create comprehensive and unambiguous instructions, ensuring candidates understand the task requirements fully. | |
| Provide a concise yet detailed task description, outlining the goals, objectives, and specific deliverables expected from the candidate’s work. Basically, make sure it makes sense. | |
| Clearly communicate the anticipated time needed to complete the task, allowing candidates to manage their time effectively and not spend hours on the take-home assignment. | |
| Specify the preferred format for the deliverable and offer any necessary guidelines. | |
| Enhance a candidate’s chances of success by including helpful resources such as internal insights, reference materials, datasets, or relevant links. | |
| Establish a reasonable deadline for completing the task, enabling candidates to plan and allocate their time accordingly. Keep in mind that a candidate might have other commitments that prevent them from completing the task in one sitting. | |
| Communicate the level of prior knowledge expected from candidates, distinguishing between information they should possess beforehand and details that can be withheld until the task is assigned or until a candidate asks follow-up questions. | |
| Pre-determine the criteria and weightage for evaluating different aspects of the task, ensuring a fair and consistent assessment. | |
| When creating the take-home task, it’s vital to design it around authentic real-world scenarios that will take place in the potential candidate’s new job. |
What are the common mistakes?
It’s normal to make mistakes, and learning from them can help you hire better, faster, and more fair.
So, let’s explore common blunders to steer clear of when designing and implementing a take-home assignment during the interview process, ensuring fairness and an effective evaluation process that respects candidates’ time and effort.
• Appropriate Task Alignment : Avoid assigning tasks that aren’t directly relevant to the role.
• Reasonable Task Length : Create a take-home assignment that can be completed within a reasonable timeframe.
• Providing Sufficient Context : Avoid requesting candidates to answer or solve company-specific problems without providing adequate information.
• Ethical Treatment of Work Requests : Refrain from asking candidates to produce work for free that the company may later exploit, such as writing a blog post for publication.
• Timely Introduction of Tasks : Including a take-home assignment as an early screening requirement can discourage candidates. Do this after their first interview.
• Constructive Feedback : Don’t miss the opportunity to provide candidates with constructive feedback on their completed tasks.
• Balancing Mandatory and Optional Tasks : Avoid making the take-home assignment mandatory for all applicants, as circumstances may prevent some candidates from completing it.
• Conduct post-assignment interviews : Once you have received a few tasks back from candidates, we highly recommend that you schedule a take-home assignment interview to better understand any pain points the job seeker may have had.
5 thorough examples of great take-home assignments
Now that you better understand the how , the when , and the why of take-home assignments, we’ll show you five examples. The example take-home assignments will cover tasks for:
- Developer – fixing a broken site
- Product manager – redesigning a feature
- Marketing lead – creating a marketing campaign
- Designer – redesigning the onboarding flow
- Customer success executive – running a mock QBR
Example #1: Take-home task for a developer role
This challenge is geared towards a mid-level developer who can identify and fix errors and optimize the code of an eCommerce website. The goal here is to see how well the candidates understand debugging techniques, approach problem-solving, and how they will communicate with the rest of their team.
Task: Fixing a Broken E-commerce Site
Introduction
Your mission is to debug the broken e-commerce site, fix errors, and ensure it runs smoothly. Customers are unable to place orders due to the significant increase in errors.
Requirements
- Identify and fix all of the errors on the site.
- Ensure that customers can place orders without any problems.
- Optimize the site to improve its performance.
- Document your approach and explain your reasoning behind your changes.
Instructions
- Clone the repository from the following Github URL: https://github.com/debugging-challenge/e-commerce-site.git .
- Install all the dependencies by running npm install .
- Start the development server by running npm start .
- Debug and fix all errors.
- Document your approach and explain your reasoning in a README file.
Your submission will be evaluated based on the following criteria:
- Identification and fixing of all errors
- Site optimization
- Completeness of documentation and reasoning
- Code cleanliness and adherence to best practices
- Clarity and organization of documentation
- Submit your code as a ZIP file.
- Include the README file that explains your approach and reasoning.
- Send the ZIP file to the hiring manager by email.
Example #2: Challenge for a product manager
Our next example focuses on testing product manager candidates on how they approach problem-solving, communicate with customers, and conduct user research while implementing open-ended questions.
In a sense, how well they’ll actually do their jobs in a product management role. This assignment is bound to produce better product management interviews for your organization.
Task: Redesigning Filma’s Collaboration Features
You are the Product Manager for collaboration features at Filma, a leading collaborative design platform. Recent feedback from customers has shown that they are not happy with how collaboration features work on the site. Your mission in this product management task is to redesign the collaboration features to better meet customer needs and preferences.
- Review the problem statement and develop a list of open-ended questions to better understand the issue.
- Conduct user research to validate assumptions and identify pain points and user needs.
- Develop a new design for collaboration features.
- Prioritize features and functionality based on customer needs and business goals.
- Outline the implementation plan.
- Document your approach and explain your reasoning.
- Review the problem statement and develop a list of open-ended questions to better understand the issue and customer needs.
- Conduct (mock) user research to validate assumptions and identify pain points and user needs. Schedule a call with a team member to role-play a customer interview. Include data points such as user feedback, user behaviour, and competitor analysis in your research.
- Develop a new design for collaboration features. Identify the key features and functionality of the new design, and prioritize them based on customer needs and business goals.
- Outline the implementation plan. Include a timeline, resources required, and technical feasibility.
- Document your approach and explain your reasoning in a presentation or document.
- Quality of open-ended questions and user research.
- Soundness of the new design and prioritization of features and functionality.
- Clarity and feasibility of the product management implementation plan.
- Completeness of documentation and reasoning.
- Clarity and organization of presentation or document.
- Submit your open-ended questions, presentation, or document as a PDF or PowerPoint file.
- Send the file to the hiring manager by email.
Example #3: Testing marketing managers
Let’s now explore an exciting marketing challenge that aims to find a candidate who can skillfully design an innovative user acquisition growth loop. This task involves leveraging valuable market research insights to craft a robust strategy that showcases a deep understanding of growth concepts.
Task: Designing a User Acquisition Growth Loop
You are the Marketing Lead at a Product-Led Growth (PLG) company that provides a collaboration tool for remote teams. Your team has conducted market research to identify target customer segments. Your mission is to design a new user acquisition growth loop based on the insights gained.
- Review the market research insights provided by your team.
- Design a new user acquisition growth loop, with a structured approach, based on the insights gained.
- Identify metrics to measure the effectiveness of the growth loop.
- Review the market research insights provided by your team. Use the insights to identify areas where a new user acquisition growth loop can be designed.
- Design a new user acquisition growth loop based on the insights gained. The growth loop should identify key stages, such as awareness, interest, and activation, and prioritize them based on customer needs and business goals.
- Identify metrics to measure the effectiveness of the growth loop. The metrics should be tied to the key stages of the growth loop and should be used to track progress and optimize the loop over time.
- Soundness of the new user acquisition growth loop and prioritization of key stages
- Creativity and effectiveness of the growth loop design
- Identification and feasibility of metrics to measure the effectiveness of the growth loop
- Clarity and organization of presentation or document
- Submit your presentation or document as a PDF or PowerPoint file.

Example #4: Take-home test for designers
This challenge is centered around an intriguing product design assessment designed to narrow down a candidate who excels in analyzing user recording sessions and crafting an improved onboarding flow design.
Task: Redesigning the Onboarding Flow Introduction
You are a Product Designer at a web-based Product-Led Growth (PLG) company that provides a collaboration tool for remote teams. Your team has recorded user sessions for the past 3 months to help identify areas of improvement for the onboarding flow. Your mission is to redesign the onboarding flow to improve user engagement and activation based on the insights gathered.
- Analyze the user recording sessions to identify user needs and preferences.
- Develop a new design for the onboarding flow.
- Prioritize design features based on user needs and business goals.
- Ensure that the design aligns with the company’s minimalist, intuitive design philosophy.
- Analyze the user recording sessions to identify user needs and preferences. Use the insights gathered to identify areas for improvement in the onboarding flow.
- Develop a new design for the onboarding flow. Identify the key stages of the flow, and prioritize them based on user needs and business goals. Ensure that the design aligns with the company’s minimalist, intuitive design philosophy.
- Prioritize design features based on user needs and business goals. Identify the most important design features that will enhance user engagement and activation.
- Quality of analysis of user recording sessions and identification of user needs and preferences
- The soundness of the new onboarding flow design and prioritization of key stages
- Alignment with the company’s minimalist, intuitive design philosophy
- Creativity and effectiveness of the prioritized design features

Example #5: Testing customer succes
Our final challenge example focuses on a customer success assignment. The perfect candidate will showcase their expertise in defining success metrics for a simulated account, devising impactful tactics to drive feature adoption and enhance metrics, and effectively presenting their approach and results in a mock Quarterly Business Review (QBR) presentation.
Task: Driving Feature Adoption and Improving Metrics
You are a Customer Success Manager at a PLG company that provides a project management tool for remote teams. Your mission is to work with a mock account to define success metrics, develop tactics to drive feature adoption and improve metrics for Q2, culminating in a mock QBR presentation.
- Define success metrics for the mock account.
- Develop tactics to drive feature adoption and improve metrics.
- Document your approach and results in a mock QBR presentation.
- Define success metrics for the mock account. Assume that the mock account is a remote team of 20 people that uses your project management tool for all their projects. Assume that they have been using the tool for 6 months, and that they have expressed interest in increasing feature adoption and improving metrics related to on-time delivery, collaboration, and budget management. Use your own assumptions to define success metrics that measure the impact of the product on their business.
- Develop tactics to drive feature adoption and improve metrics. Use the success metrics to identify the actions needed to increase feature adoption and improve metrics, and assign responsibilities to your team. Use customer success best practices, such as regular check-ins and training sessions, to ensure that the tactics are on track and that the mock account is engaged and satisfied.
- Document your approach and results in a mock QBR presentation. Create a deck that’s less than 10 slides, with consistent title and object placement, fonts, font colors, and different ways of visualizing insights. Use the mock QBR presentation to realign on the mock account’s goals, review their performance, present the tactics and their impact on the success metrics, and recommend the next steps to improve product performance next quarter.
- Quality of success metrics defined for the mock account.
- Soundness of the tactics to drive feature adoption and improve metrics.
- Collaborative execution of the tactics with your team.
- Clarity, organization, and persuasiveness of the mock QBR presentation.
- Submit your mock QBR presentation as a PDF or PowerPoint file.

Try a Homework Assignment by Toggl Hire
Ready to add homework assignments to your hiring process? Our homework assessments provide invaluable insights for hiring managers evaluating candidates ‘ ability to solve job-specific assignments.
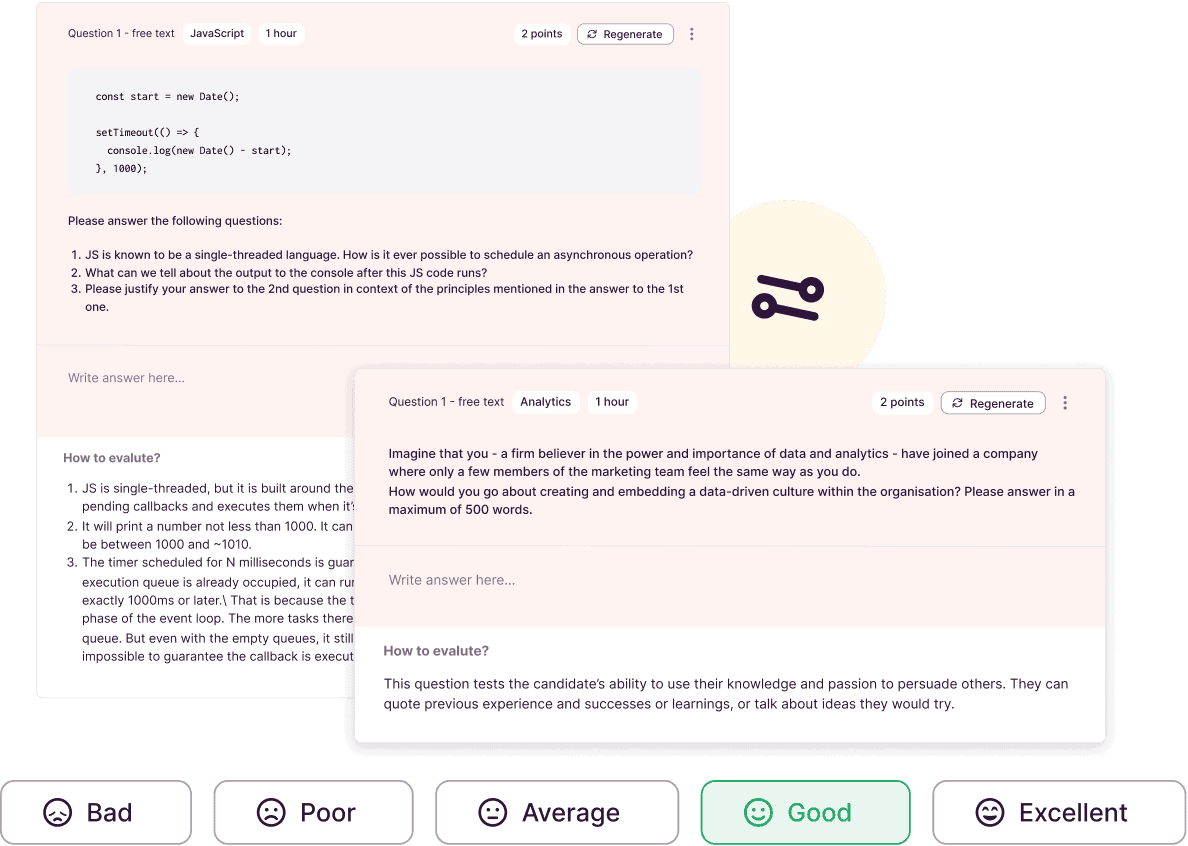
Designed to test the hands-on skills necessary for day-to-day work, these assessments offer a glimpse into a candidate’s potential future job performance . With over 500 pre-built tasks available in Toggl Hire’s library, you can quickly implement comprehensive tests that align with your hiring needs.
Toggl Hire’s homework assessments are highly flexible, allowing for either integration with other assessments or standalone use. Create your free account now to explore a few examples!
Juste loves investigating through writing. A copywriter by trade, she spent the last ten years in startups, telling stories and building marketing teams. She works at Toggl Hire and writes about how businesses can recruit really great people.
Subscribe to On The Clock.
Insights into building businesses better, from hiring to profitability (and everything in between). New editions drop every two weeks.
You might also like...
Related to Talent Assessments
What is Pre-Employment Skills Testing? A Full Guide for 2024
4 Benefits of Using an Online Coding Test to Hire Great Developers
How to Design an Effective Writing Skills Assessment Test
Take a peek at our most popular categories:
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
And #11 Successful Students Learn Independently
16 Dealing With Assignments
Understanding your first assignment.
The number of assignments you will receive in a semester often surprises students. For some students, figuring out how to manage assignments is a new experience. For others who have had assignments in the past, the amount of work needed to complete assignments at the college level is what is unexpected. Most of the assignments you will receive will take longer than one session of study to complete. You will likely need to work on your assignment over several days or weeks. In this section, we will provide you with advice on how to understand the requirements of your assignment, and how to manage and track the tasks you will need to complete. We will provide you with some time management tips and an assignment tracker to try.
Assignment Terms
Assignment questions, outlines and marking schemes, breaking down large assignments.
How to breakdown assignments into tasks
- Understand the assignment: Read the assignment instructions carefully, and make sure you understand what is required. If you do not understand what you need to do, ask your professor as soon as possible.
- Create a task list: What are the smaller tasks you need to do to complete this assignment? Smaller tasks are activities like conducting research at the library or setting up group meetings for a group project.
- Create a timeline: Create a timeline that includes all the tasks that need to be completed. Consider how much time you will need to complete that task and when you will work on it. Set due dates for each task.
- Brainstorm ideas: Before you start writing, brainstorm ideas for the assignment. Think about the main points you want to cover, any research you need to do, and any supporting evidence you might need.
- Create an outline: Once you have a list of ideas, create an outline for your assignment. An outline can help you organize your thoughts and make sure you cover all the necessary points.
- Schedule time for research: Do your research before you begin writing. As you find sources, gather the information you will need to create a reference and take notes about essential information the source will provide and where this information fits in with your outline.
- Schedule time for revision: Plan to review your work before you submit. This can include checking your work against the assignment instructions or rubric, making changes to the content, and proofreading.
Here is an example of this process:
Key Takeaway from video
- Breaking down a large or medium-sized assignment into smaller pieces can help reduce stress, ensure completion of all parts of the assignment, and allow you to get other important tasks done too.
Using an Assignment Tracker
Time Management Considerations

Time management is the practice of organizing and prioritizing one’s activities and tasks effectively in order to maximize productivity and achieve one’s goals. For college students, time management involves creating a plan for allocating their time efficiently and balancing academic responsibilities with social activities, work, and personal obligations. It requires identifying tasks and goals, setting realistic deadlines, and using tools such as schedules, to-do lists, and reminders to stay on track. Effective time management helps students to reduce stress, increase productivity, and achieve academic success while still enjoying a balanced lifestyle.
- Procrastination: Students tend to put off starting a large writing assignment until the last minute, leaving themselves with insufficient time to complete the assignment.
- Lack of Planning: Many students do not adequately plan their time for the writing process, which can result in poor time management and a lower quality of work.
- Perfectionism: Students may spend too much time trying to perfect every aspect of their writing, which can lead to time wastage and increased stress.
- Break the Task into Smaller Parts: Instead of attempting to complete the entire assignment in one sitting, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts, and set specific deadlines for each.
- Create a Schedule: Create a schedule for the writing process and stick to it. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you have enough time to complete the assignment.
- Avoid Distractions: Avoid any distractions that can lead to time wastage, such as social media, television, and video games.
- Set Priorities: Set priorities for your writing tasks, focusing on the most critical aspects of the assignment first.
- Use Writing Tools : Utilize writing tools such as spell check, grammar check, and citation generators to save time and reduce the need for extensive revisions.
- Take Breaks: Taking regular breaks can help you stay focused and prevent burnout, ensuring that you produce your best work.
Avoiding Procrastination
Key Takeaways

Want more? The Learning Portal has more ideas for Managing Assignments.
A Guide for Successful Students 2nd ed. Copyright © 2023 by Irene Stewart, Aaron Maisonville, and Nicolai Zriachev, St. Clair College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Privacy Policy

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

References in Research – Types, Examples and...

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Data Interpretation – Process, Methods and...
NCI LIBRARY
Academic writing skills guide: structuring your assignment.
- Key Features of Academic Writing
- The Writing Process
- Understanding Assignments
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Planning Your Assignments
- Thesis Statements
- Writing Drafts
- Structuring Your Assignment
- How to Deal With Writer's Block
- Using Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Introductions
- Revising & Editing
- Proofreading
- Grammar & Punctuation
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting, Transitions & Linking Words/Phrases
- Using Lecturers' Feedback
|
Organising and structuring your assignment can be as important as the content itself as it helps you present your arguments in a logical way. A good, logical structure to your assignment is key to ensuring your lecturer can follow your argument, making it easier to read and understand. You should take them on a journey to your conclusion, so that they can see how your case builds up through your assignment. An effective structure not only improves the flow of your writing but also demonstrates that you thought about and planned your work before you started writing. This is important as it is obvious to any lecturer if you have not planned your work before you start. Not only does this demonstrate poor thinking, it makes your work harder to understand, which will inevitably harm your grades. If you work on the structure before you write your first draft, you will not have to do so much reorganisation and rewriting when it is completed. Time spent organising the structure of the main body of your assignment is valuable as it gives you the chance to link paragraphs together into a logical sequence. It will also make the writing process easier as adopting a structured approach helps you break down each part of the process into manageable chunks. |
| Planning the structure of an assignment is important and will help you to feel more in control of your writing as it begins to take shape. Good planning is key for a well-structured assignment – you should not launch into writing with no idea of what you are going to write. Think carefully about how to structure your assignment before you start to write. Having a well-structured plan will help you considerably in producing a cohesive assignment and will also allow you to write your assignment in stages since it will clearly map out the direction you should proceed in. Before you begin writing, check the structure to make sure it matches the assignment requirements and repeat these checks as you draft and redraft your assignments. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Keep referring back to the question and assignment brief and make sure that your structure matches what you have been asked to do and check to see if you have appropriate and sufficient evidence to support all of your points. Plans can be structured/restructured at any time during the writing process. Once you have decided on your key point(s), draw a line through any points that no longer seem to fit. This will mean you are eliminating some ideas and potentially letting go of one or two points that you wanted to make. However, this process is all about improving the relevance and coherence of your writing. Writing involves making choices, including the tough choice to sideline ideas that, however promising, do not fit into your main discussion. Eventually, you will have a structure that is detailed enough for you to start writing. You will know which ideas go into each section and, ideally, each paragraph and in what order. You will also know which evidence for those ideas from your notes you will be using for each section and paragraph. Once you have a map/framework of the proposed structure, this forms the skeleton of your assignment and if you have invested enough time and effort into researching and brainstorming your ideas beforehand, it should make it easier to flesh it out. Ultimately, you are aiming for a final draft where you can sum up each paragraph in a couple of words as each paragraph focuses on one main point or idea.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

























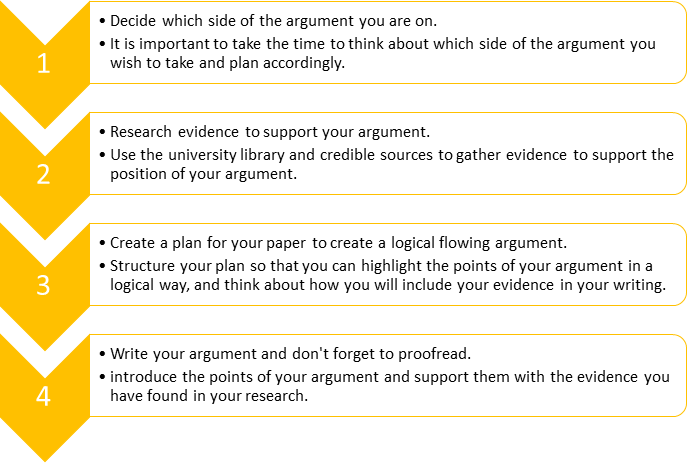
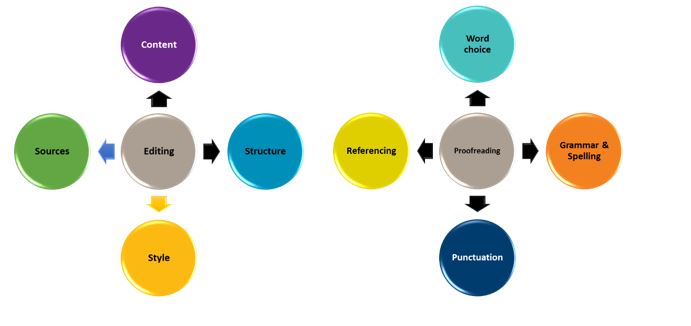





IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment. Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand.
Look over your assignment and discover the steps it will require you to take in order to complete it. Find the most appealing and personally interesting steps and work on those first. By doing the parts of your assignment that you like the most, you will be more inclined to get started and see the rewards of working rather than procrastinating. [1]
Put It in Writing: While you'll want to present your assignment orally in class, be sure to give your students a written copy, too, so they can refer to it as they work. Putting it down on paper may also help you clarify your own expectations about the assignment. Anticipate the Inevitable: You're enthusiastically explaining the limitless ...
Planning your assignment carefully and presenting arguments step-by-step is necessary to succeed with your homework. When going through your references, note the questions that appear and answer them, building your text. Create a cover page, proofread the whole text, and take care of formatting.
A take-home assignment is an important part of the interview process that focuses on candidates crafting and completing real-world tasks. Incorporating a take-home assignment will give your organization better insight and skill observation over candidates. However, job seekers may see take-home tests as time-consuming, exploitative, or ...
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
By sequencing a large assignment, or essentially breaking it down into a systematic approach consisting of interconnected smaller elements (such as a project proposal, an annotated bibliography, or a rough draft, or a series of mini-assignments related to the longer assignment), you can encourage thoughtfulness, complexity, and thoroughness in ...
Most of the assignments you will receive will take longer than one session of study to complete. You will likely need to work on your assignment over several days or weeks. In this section, we will provide you with advice on how to understand the requirements of your assignment, and how to manage and track the tasks you will need to complete ...
Types of Assignments Cristy Bartlett and Kate Derrington. Figure 20.1 By recognising different types of assignments and understanding the purpose of the task, you can direct your writing skills effectively to meet task requirements. Image by Armin Rimoldi used under CC0 licence. Introduction. As discussed in the previous chapter, assignments are a common method of assessment at university.
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class ...
Stage #3 - Assignment Framework: Take the information gathered in Stage #2 and organise it into the assignment framework chart to finalise your structure. Stage #4 - Assignment Checklist: Go through the Assignment check list to check that you have included everything that is required for each section. Writing Drafts
Set Goals: - Establish daily or weekly goals for completing portions of your assignments. Setting achievable milestones will help you stay on track and motivated. 5. Minimize Distractions: - Find a quiet and focused workspace to minimize distractions. Turn off social media notifications and other distractions while working on assignments.
Create an assignment (details above). Under Due, click the Down arrow . Next to No due date, click the Down arrow . Click a date on the calendar. (Optional) To set a due time, click Time enter a time and specify AM or PM. Note: Work is marked Missing or Turned in late as soon as the due date and time arrive.
Writing Assignments Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine. Figure 19.1 Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Image by Kampus Production used under CC0 licence. Introduction. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research.
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment. the act of assigning something; a position, post, or office to which one is assigned… See the full definition. Games & Quizzes; Games & Quizzes; Word of the Day; Grammar; Wordplay; Word Finder ...
A take-home assignment is a hands-on task they can do on their own time in the comfort of their home. This can take some of the pressure off and let the candidate showcase their skills well. Cons of a take-home assignment. Before you decide to implement take-home assignments, consider the following challenges: 1. Time-consuming
In fact, the take-home assignment should actually be a huge boost to your confidence. When you're asked to complete one, it's a clear indication that the hiring manager's excited to see how you'd tackle a problem similar to one the organization's been dealing with. In other words, the company's struggled with the issue in the past ...
Interviewing for a new job requires you to prove your skills, qualifications and personality aligns with what a company wants. Many hiring managers now look for ways to assess a candidate's technical abilities before giving them a job offer.In this article, we discuss what a job interview assignment is, the do's and don'ts of completing a job interview assignment and examples of job interview ...
from inspiring English sources. "take an assignment" is correct and usable in written English. You would use this phrase when someone is being asked to accept an assignment or task. For example, "The professor asked us to take an assignment to write a research paper by the end of the month.". Upon turning sixty-five, when asked to take an ...
on assignment one of our reporters on assignment in China; Extra Examples. The students handed in their assignments. The teacher gave us an assignment on pollution. Why did you take on this assignment if you're so busy? He refused to accept the assignment. Topics Education b1.
In regards to a math(s) assignment, "doing" is a better word choice. As used in your question, "working on" is also appropriate. You could also simply say, "I need to finish my homework."
Work assignments are most common in creative and technical fields of work. For example, writers may need to complete a trial piece before being hired, and marketing professionals may have to create a campaign pitch and outline as part of their interview process. For more technical work, like information technology or computer science, the ...
The New York Times. He had taken the assignment because it was special. 4. The New York Times. He took the assignment and contacted his friend Steve Wozniak for help. 5. The New Yorker. Show more... High quality example sentences with "take the assignment" in context from reliable sources - Ludwig is the linguistic search engine that helps ...
Synonyms for ASSIGNMENT: task, job, duty, project, mission, chore, responsibility, function; Antonyms of ASSIGNMENT: dismissal, discharge, firing, expulsion ...
Economics will attempt something very few have managed, with William Haggas keen to take on the Royal Bahrain Irish Champion Stakes and Qipco Champion Stakes double this autumn with a colt he described as having "great potential".. To outline the size of the task, in the 48 years since the inception of the Irish Champion Stakes in 1976 just six horses - Triptych (1987), Indian Skimmer (1988 ...
Answer "yes" to the question at the beginning of the form that asks if you need to change the owner's name or entity information. Enter the new name in the "Owner" field in the "Owner Information" section of the form. Your request to update the owner information will be reviewed by a USPTO employee and entered, if appropriate.
The class will include programming assignments, and a one-month short project chosen by the student. The project will be designed to compare the scalability of variant learning algorithms on datasets. An introductory course in machine learning, like 10-601 or 10-701, is a prerequisite or a co-requisite. If you plan to take this course and 10 ...
Next up, Olson could begin a rehab assignment. "The next 24 hours, always key," manager A.J. Hinch said of Olson's status. "It was another test that it looks like he passed, as of right afterwards.