Dissertation Formatting Guidance
The following resource shares some best practice guidance for dissertation formatting.

USEFUL LINKS
Share this page.
The following resource shares some best practice guidance for dissertation formatting. Please note that some of the elements outlined below are required and will be reviewed by the FAS Registrar's Office as part of Harvard Griffin GSAS policies on formatting .
Language of the Dissertation
The language of the dissertation is ordinarily English, although some departments whose subject matter involves foreign languages may accept a dissertation written in a language other than English.
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and subdivisions.
Page and Text Requirements
- 8½ x 11 inches, unless a musical score is included
- At least 1 inch for all margins
- Body of text: double spacing
- Block quotations, footnotes, and bibliographies: single spacing within each entry but double spacing between each entry
- Table of contents, list of tables, list of figures or illustrations, and lengthy tables: single spacing may be used
Fonts and Point Size
Use 10-12 point size. Fonts must be embedded in the PDF file to ensure all characters display correctly.
Recommended Fonts
If you are unsure whether your chosen font will display correctly, use one of the following fonts:
| Arial | 10 pt |
| Century | 11 pt |
| Courier New | 10 pt |
| Garamond | 12 pt |
| Georgia | 11 pt |
| Lucida Bright | 10 pt |
| Microsoft Sans Serif | 10 pt |
| Tahoma | 10 pt |
| Times New Roman | 12 pt |
| Trebuchet MS | 10 pt |
| Verdana | 10 pt |
If fonts are not embedded, non-English characters may not appear as intended. Fonts embedded improperly will be published to DASH as is. It is the student’s responsibility to make sure that fonts are embedded properly prior to submission.
Instructions for Embedding Fonts
To embed your fonts in recent versions of Word, follow these instructions from Microsoft:
- Click the File tab and then click Options .
- In the left column, select the Save tab.
- Clear the Do not embed common system fonts check box.
For reference, below are some instructions from ProQuest UMI for embedding fonts in older file formats:
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2010:
- In the File pull-down menu, click on Options .
- Choose Save on the left sidebar.
- Check the box next to Embed fonts in the file.
- Click the OK button.
- Save the document.
Note that when saving as a PDF, make sure to go to “more options” and save as “PDF/A compliant”
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2007:
- Click the circular Office button in the upper left corner of Microsoft Word.
- A new window will display. In the bottom right corner select Word Options .
- Choose Save from the left sidebar.
Using Microsoft Word on a Mac:
Microsoft Word 2008 on a Mac OS X computer will automatically embed your fonts while converting your document to a PDF file.
If you are converting to PDF using Acrobat Professional (instructions courtesy of the Graduate Thesis Office at Iowa State University):
- Open your document in Microsoft Word.
- Click on the Adobe PDF tab at the top. Select "Change Conversion Settings."
- Click on Advanced Settings.
- Click on the Fonts folder on the left side of the new window. In the lower box on the right, delete any fonts that appear in the "Never Embed" box. Then click "OK."
- If prompted to save these new settings, save them as "Embed all fonts."
- Now the Change Conversion Settings window should show "embed all fonts" in the Conversion Settings drop-down list and it should be selected. Click "OK" again.
- Click on the Adobe PDF link at the top again. This time select Convert to Adobe PDF. Depending on the size of your document and the speed of your computer, this process can take 1-15 minutes.
- After your document is converted, select the "File" tab at the top of the page. Then select "Document Properties."
- Click on the "Fonts" tab. Carefully check all of your fonts. They should all show "(Embedded Subset)" after the font name.
- If you see "(Embedded Subset)" after all fonts, you have succeeded.
Body of Text, Tables, Figures, and Captions
The font used in the body of the text must also be used in headers, page numbers, and footnotes. Exceptions are made only for tables and figures created with different software and inserted into the document.
Tables and figures must be placed as close as possible to their first mention in the text. They may be placed on a page with no text above or below, or they may be placed directly into the text. If a table or a figure is alone on a page (with no narrative), it should be centered within the margins on the page. Tables may take up more than one page as long as they obey all rules about margins. Tables and figures referred to in the text may not be placed at the end of the chapter or at the end of the dissertation.
- Given the standards of the discipline, dissertations in the Department of History of Art and Architecture and the Department of Architecture, Landscape Architecture, and Urban Planning often place illustrations at the end of the dissertation.
Figure and table numbering must be continuous throughout the dissertation or by chapter (e.g., 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2, etc.). Two figures or tables cannot be designated with the same number. If you have repeating images that you need to cite more than once, label them with their number and A, B, etc.
Headings should be placed at the top of tables. While no specific rules for the format of table headings and figure captions are required, a consistent format must be used throughout the dissertation (contact your department for style manuals appropriate to the field).
Captions should appear at the bottom of any figures. If the figure takes up the entire page, the caption should be placed alone on the preceding page, centered vertically and horizontally within the margins.
Each page receives a separate page number. When a figure or table title is on a preceding page, the second and subsequent pages of the figure or table should say, for example, “Figure 5 (Continued).” In such an instance, the list of figures or tables will list the page number containing the title. The word “figure” should be written in full (not abbreviated), and the “F” should be capitalized (e.g., Figure 5). In instances where the caption continues on a second page, the “(Continued)” notation should appear on the second and any subsequent page. The figure/table and the caption are viewed as one entity and the numbering should show correlation between all pages. Each page must include a header.
Landscape orientation figures and tables must be positioned correctly and bound at the top so that the top of the figure or table will be at the left margin. Figure and table headings/captions are placed with the same orientation as the figure or table when on the same page. When on a separate page, headings/captions are always placed in portrait orientation, regardless of the orientation of the figure or table. Page numbers are always placed as if the figure were vertical on the page.
If a graphic artist does the figures, Harvard Griffin GSAS will accept lettering done by the artist only within the figure. Figures done with software are acceptable if the figures are clear and legible. Legends and titles done by the same process as the figures will be accepted if they too are clear, legible, and run at least 10 or 12 characters per inch. Otherwise, legends and captions should be printed with the same font used in the text.
Original illustrations, photographs, and fine arts prints may be scanned and included, centered between the margins on a page with no text above or below.
Pages should be assigned a number except for the Thesis Acceptance Certificate. Preliminary pages (abstract, table of contents, list of tables, graphs, illustrations, and preface) should use small Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.). All pages must contain text or images.
Count the title page as page i and the copyright page as page ii, but do not print page numbers on either page .
For the body of text, use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) starting with page 1 on the first page of text. Page numbers must be centered throughout the manuscript at the top or bottom. Every numbered page must be consecutively ordered, including tables, graphs, illustrations, and bibliography/index (if included); letter suffixes (such as 10a, 10b, etc.) are not allowed. It is customary not to have a page number on the page containing a chapter heading.
Check pagination carefully. Account for all pages.
Thesis Acceptance Certificate
A copy of the Thesis Acceptance Certificate should appear as the first page. This page should not be counted or numbered. The DAC will appear in the online version of the published dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
The dissertation begins with the title page; the title should be as concise as possible and should provide an accurate description of the dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
Do not print a page number on the title page. It is understood to be page i for counting purposes only.
Copyright Statement
A copyright notice should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page and include the copyright symbol ©, the year of first publication of the work, and the name of the author:
© [ year ] [ Author’s Name ] All rights reserved.
Alternatively, students may choose to license their work openly under a Creative Commons license. The author remains the copyright holder while at the same time granting up-front permission to others to read, share, and (depending on the license) adapt the work, so long as proper attribution is given. (By default, under copyright law, the author reserves all rights; under a Creative Commons license, the author reserves some rights.)
Do not print a page number on the copyright page. It is understood to be page ii for counting purposes only.
An abstract, numbered as page iii , should immediately follow the copyright page and should state the problem, describe the methods and procedures used, and give the main results or conclusions of the research. The abstract will appear in the online and bound versions of the dissertation and will be published by ProQuest. There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- double-spaced
- left-justified
- indented on the first line of each paragraph
- The author’s name, right justified
- The words “Dissertation Advisor:” followed by the advisor’s name, left-justified (a maximum of two advisors is allowed)
- Title of the dissertation, centered, several lines below author and advisor
- Table of Contents
Dissertations divided into sections must contain a table of contents that lists, at minimum, the major headings in the following order:
- Front Matter
- Body of Text
- Back Matter
Front and Back Matter
Front matter includes (if applicable):
- acknowledgements of help or encouragement from individuals or institutions
- a dedication
- a list of illustrations or tables
- a glossary of terms
- one or more epigraphs.
Back matter includes (if applicable):
- bibliography
- supplemental materials, including figures and tables
- an index (in rare instances).
Supplemental Material
Supplemental figures and tables must be placed at the end of the dissertation in an appendix, not within or at the end of a chapter. If additional digital information (including audio, video, image, or datasets) will accompany the main body of the dissertation, it should be uploaded as a supplemental file through ProQuest ETD . Supplemental material will be available in DASH and ProQuest and preserved digitally in the Harvard University Archives.
Harvard Library Office for Scholarly Communication

Academic Manual
- 4. Marking & Moderation

Section 4: Marking & Moderation
Published for 2024-25
| The Marking and Moderation regulations define the procedures for the internal marking and moderation of assessed student work. All programmes must apply these threshold standards as a minimum. |
4.1 Responsibilities
| 1. | Markers are responsible for assessing student work against the published marking criteria, assigning each student a mark according to the relevant marking scale and providing students with feedback on their work. |
| 2. | The Programme Exam Board is responsible for the planning, documenting and implementation of appropriate marking, second-marking and internal moderation processes on a programme or group of modules. |
| 3. | The Faculty Board of Examiners is responsible for ensuring that appropriate marking, second-marking and moderation systems are documented and in place on all programmes within their remit (see for further details). |
4.2 Markers
| 1. | A UCL marker may be an Internal Examiner or an Assistant Internal Examiner. |
| 2. | Markers must be formally appointed as Internal Examiners or Assistant Internal Examiners by the Board of Examiners – see for further details on the appointment process, duties and responsibilities. |
| 3. | Students may also be asked to assess each other’s work as a valuable tool in enhancing their assessment literacy. Where Peer Assessment is used in summative assessment, the Internal Examiner(s) responsible for the module/ assessment must ensure that there are clear marking criteria, which are discussed with the students in advance, and that all marks awarded by students are subject to some form of second-marking by an Internal Examiner. |
4.3 Anonymity
| 1. | All summative assessments should be carried out anonymously unless the nature of assessment makes this impossible. |
| 2. | Where anonymity is not used, programmes must ensure, to the satisfaction of the External Examiner and the Board of Examiners, that there are robust processes in place for second-marking and internal moderation (see below). |
| 3. | There is no requirement for anonymity for formative assessments. |
| 4. | Examinations and tests must be assessed against Candidate Number only. |
| 5. | For coursework submissions, wherever possible, first and second markers should assign marks and provide written feedback based on Candidate Number or Student Record Number only. |
| 6. | Where coursework assessments include formative submissions, tutorials and/ or in-class feedback, it is recognised that full anonymity will not always be possible or desirable. Where this is the case, and the first marker knows the student, second-marking and moderation must be carried out anonymously. |
| 7. | Where dissertations and research projects involve close working between the supervisor and the student it is recognised that full anonymity will not always be possible or desirable. Where the supervisor acts as a marker for the dissertation or report, the assessment must be subject to full, independent and anonymous second-marking. |
| 8. | Feedback and an indicative mark based on the first marker’s comments, but prior to second marking, can be given to facilitate prompt feedback. However, students should be aware that the mark is indicative and subject to second-marking, internal moderation and ratification by the Board of Examiners and the External Examiner. |
4.4 Marking Criteria
| 1. | For both summative and formative assessment the marking criteria should be designed to help students understand what they are expected to achieve and the knowledge and skills that will be taken into account in awarding marks. |
| 2. | For every summative assessment (i.e. assessments whose results count towards Progression, Classification and/ or the Award of a degree), at least one of the following must be made available to students in advance of the assessment: |
| a) | Grade Descriptors explaining the criteria and providing a detailed description of the qualities representative of different mark classes/grades. Where appropriate, grade descriptors can be agreed at departmental/divisional or programme level. | |
| b) | A Marking Scheme explaining how the assessment is scored, i.e. how points are associated with answers to the question set and attributed to parts of the assessment. |
| 3. | Where appropriate, the following should also be made available to all markers and second-markers: |
| a) | Indicative Answers by the question setter that outline the essential material expected to be considered by relevant answers. | |
| b) | Model Answers that show the correct answer to the question as documented by the question setter. |
| 4. | Summative assessment must be criterion-referenced i.e. the assessment evaluates the ‘absolute’ quality of a candidate’s work against the marking criteria; the same work will always receive the same mark, irrespective of the performance of other students in the cohort. |
| 5. | Further guidance for best practice in designing marking criteria, including the identification of the key skills and knowledge being tested, is available from . |
4.5 Second Marking
4.5.1 minimum requirements.
| 1. | All modules must be subject to a form of second marking. |
| 2. | All dissertations/ research projects must be subject to Full, Independent, second-marking. |
| 3. | Faculties or Department may determine and publish policies on the appropriate use of different forms of second marking within the disciplinary context over and above UCL’s minimum threshold requirements. |
| 4. | The options for second marking are: |
| a) | Second marking may be Full or Sampled: |
| i. | Full second-marking: second markers mark or check all assessments. | ||
| ii. | Sampled second-marking: Second markers mark or check a sample, based on defined criteria, of the full set of assessments. |
| b) | Second marking may be Independent or done by Check Marking: |
| i. | Independent marking (also known as double marking): Each marker assigns a mark. The two marks are subsequently reconciled to agree the mark for the assessment. | ||
| ii. | Check marking: The second marker determines whether the mark awarded by the first marker is appropriate, but does not give a separate mark. The second marker confirms the mark if appropriate, and brings it to the attention of the first marker if not. Check marking will usually only be appropriate for quantitative or multiple-choice assessments in which answers can be scored objectively rather than requiring qualitative judgement on the part of the markers. |
| c) | Second marking may be Blind or Open: |
| i. | Blind second-marking: The second marker is not informed of the first marker’s marks and/ or comments. | ||
| ii. | Open second-marking: The second marker is informed of the first marker’s marks and comments before commencing and can take these into account. |
| d) | Second marking may be Live: |
| i. | Live marking: Where an assessment is conducted ‘live’ (e.g. oral examinations, presentations, exhibitions, laboratory work, marking clinical work with patients, portfolios of work, group work etc.) the assessment should include provisions for second-marking, internal moderation and External Examiner scrutiny of either the full set of assessments or an appropriate sample. This may take the form of having two or more markers present, inviting the External Examiner to observe the event, recording the event or asking students to submit notes, slides and/ or visual material for these purposes. |
4.5.2 Parity Meetings
| 1. | Where an assessment includes multiple pairs of markers it is good practice to hold a parity meeting at the start of the marking process where markers can discuss and develop a shared understanding of the marking criteria. This can include comparing marks for a small sample of student work. |
| 2. | Parity meetings are particularly important where there is a large number of markers and where there are new markers in a team. |
4.5.3 Sampling
| 1. | Sampling may be used where a large number of students undertakes an assessment. If the second markers agree with the marks for the sampled students, it can be assumed that marking is accurate for the population. However if the second markers disagree with one or more marks, the sample must be extended (see below). |
| 2. | Where sampling is used in second-marking, the sample must include the following as a minimum: |
| a) | All Fails | |
| b) | Mid-class examples for each class (mid-forties, mid-fifties, mid-sixties, Firsts/Distinctions) | |
| c) | Examples of all upper borderlines (39, 49, 59, 69) | |
| d) | The higher of either: at least 10% of assessments, or at least five assessments. |
| 3. | The above is based on the standard UCL marking scale; programmes operating an alternate marking scale should adjust as appropriate. |
| 4. | Thresholds for the use of sampling versus full second-marking over and above UCL’s threshold standards may be set at Faculty or Departmental/Divisional level. |
| 5. | Where there is disagreement over a single mark or a group of marks within the sample, markers must not change individual student marks. Instead, the sample must be extended. i. Particular attention should be paid to students with similar marks to those being contested, and to those marks falling close to a Classification boundary. ii. Where necessary, markers may review the marks of all students in the assessment concerned. |
| 6. | Extension of the sample must demonstrate to the External Examiner and the Board of Examiners that marking across the assessment concerned is sound and fair and that no student is advantaged or disadvantaged by being included in the sample (i.e. markers must not only change the marks of students in the sample; all marks must be reviewed). |
4.5.4 Reconciliation of Marks
| 1. | All marks must be agreed by the markers. Where there is disagreement, the markers must adopt one of the following: |
| a) | For mark differences of 10% or more, or which bracket a class boundary, the marks must be reconciled through discussion of the marking criteria. Mathematical averaging should not be used. | |
| b) | For mark differences of less than 10%, the mark may be reconciled by discussion of the marking criteria or by mathematical averaging. |
4.5.5 Third Markers
| 1. | A third marker may be brought in where a first and second marker are unable to agree on a final mark. The third marker’s role is not to over-ride the two previous markers, but to contribute to resolving the discussion with reference to the marking criteria. |
| 2. | Third marking to reconcile disagreements between first and second markers must not be carried out by the External Examiner (see ). However, subsequently bringing third-marked work to the attention of the External Examiner is good practice. |
4.5.6 Documentation of Marking
| 1. | Marks and how marks are arrived at must be transparent for Programme and Faculty Boards of Examiners, External Examiners, students, and, if necessary, complaint panels. |
| 2. | The first mark, second mark (where applicable) and the agreed mark must be recorded separately. |
| 3. | Justification for marks awarded must be documented in one of the following forms: |
| a) | Examiner’s comments from both the first and, where applicable, second marker. These comments may be identical to the feedback provided to the student. | |
| b) | Model answers and evidence of the scoring of the assessment by the first and, where applicable, second marker. |
4.6 Internal Moderation
| 1. | All programmes must have internal moderation systems in place to assure the consistency of marking and the proper application of the marking criteria across markers, students and modules. |
| 2. | Internal moderation may include, but is not limited to: |
| a) | Checks to ensure that marking is comparable across marking pairs or teams | |
| b) | Checks to ensure that marking is comparable across different options and electives |
| 3. | Where the internal moderation process identifies substantial discrepancies, third-marking of a set of assessments may be required. |
| 4. | Internal moderation processes must be documented and shared with the relevant Programme and Faculty Boards of Examiners. |
Advice for Students
Further information and advice for students about assessment is available on the Examinations & Awards webpages .
Recent Changes
A guide to changes to the regulations are available from the Recent Changes page.
- Current Students
- News & Press
- Exam Technique for In-Person Exams
- Revising for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Introduction to 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Before the 24 Hour Take Home Exam
- Exam Technique for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Structuring a Literature Review
- Writing Coursework under Time Constraints
- Reflective Writing
- Writing a Synopsis
- Structuring a Science Report
- Presentations
- How the University works out your degree award
- Accessing your assignment feedback via Canvas
- Inspera Digital Exams
- Writing Introductions and Conclusions
- Paragraphing
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting
- Proofreading
- Working with a Proofreader
- Writing Concisely
- The 1-Hour Writing Challenge
- Editing strategies
- Apostrophes
- Semi-colons
- Run-on sentences
- How to Improve your Grammar (native English)
- How to Improve your Grammar (non-native English)
- Independent Learning for Online Study
- Reflective Practice
- Academic Reading
- Strategic Reading Framework
- Note-taking Strategies
- Note-taking in Lectures
- Making Notes from Reading
- Using Evidence to Support your Argument
- Integrating Scholarship
- Managing Time and Motivation
- Dealing with Procrastination
- How to Paraphrase
- Quote or Paraphrase?
- How to Quote
- Referencing
- Responsible and Ethical use of AI
- Acknowledging use of AI
- Numeracy, Maths & Statistics
- Library Search
- Search Techniques
Keeping up to date
Evaluating information, managing information.
- Understanding Artificial Intelligence
- Getting started with prompts
- Thinking Critically about AI
- Using Information generated by AI
- SensusAccess
- Develop Your Digital Skills
- Digital Tools to Help You Study

Dissertations & Theses
Explore tools and support to help you complete your dissertation or thesis.
- Dissertations & Theses
- Newcastle University
- Academic Skills Kit
What is a dissertation or thesis?
A dissertation is an extended piece of academic writing on a question or problem related to particular subject. Usually done at the end of an undergraduate or master’s degree, this type of research project can take several months to complete.
A thesis is usually completed as part of a PhD. While similar in nature to a dissertation, a thesis is a longer project that tackles a question or problem in-depth and will take a number of years to write and research.
Whether you’re beginning a dissertation, or embarking on your PhD thesis, you’ll find it can be a different challenge to other assignments you’ve completed. These projects require you to bring together all the skills that you will have developed in your studies including: finding and evaluating literature, critical analysis, developing an argument, academic writing and referencing.
Your dissertation or thesis might also include things that you have not done before, for example developing a research question, analysing data or writing an abstract.
Process of writing a dissertation or thesis
Dissertations and theses are long and complicated projects. The processes you need to go through are likely to be iterative, non-linear and dynamic. However, it can be helpful to start by breaking the project down into the different stages, and approach each section of the planning, researching and writing process in turn. You then need to bring the stages together into a single piece of research.
A dissertation or thesis is an excellent opportunity for you to immerse yourself in your subject and a topic that you are passionate about. On the other hand, if you’re allocated a project, you’ll need to make the research your own and learn to understand why it’s worthwhile.
Your project proposal allows you to explore these initial research ideas, identify your aims, think around the context of your potential research and get ahead of any pitfalls by thinking about the feasibility and limitations involved.
Thinking about what you want to achieve with your research at this stage, will help inform how you approach your project.
Research Proposal Planning Tool
Literature review.
The nature of the research you do will likely depend on your subject area and research question. This may involve conducting interviews, gathering statistics, carrying out experiments or exploring texts and documents.
Most dissertations and theses will, however, involve a literature review as part of the research process.
What is a literature review?
A literature review sets the scene for your work. It places your research in context, and shows how it relates to and builds upon the work of others. It’s also your chance to tell people why your work matters, why it’s relevant, and how it contributes original research to your field.
In your literature review, you’ll discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the information you’ve found, and describe why you think it’s important. You might also want to discuss gaps in the literature that your own research will attempt to fill.

Literature Searching and Reading
Compiling a literature review involves rigorous literature searching, critical reading of information and combining ideas and research from different sources. You’ll need to develop an effective search strategy to ensure you find all the key information relevant to your topic.
New research is published every day, and your work is likely to take you down paths you hadn’t thought about initially so you’ll need to frequently return to and adapt your search, and then update your literature review as you go. As part of your search strategy, it's important that you consider how you'll keep your research up to date, and how you'll manage all the information you'll find.
There are different types of literature review too, so check with your supervisor to make sure you know what is expected. If you’ve been asked to take a systematic approach, our systematic review guide can help you understand the systematic process.

Search strategy planning tool
Build your search strategy with our Search Planner tool. **Online planner**

Finding Information
Discover tips and advice for starting your search, selecting information types and using advanced search techniques.

Systematic Review guide
Find out about the systematic process and types of systematic review.

Mapping the literature
Downloadable resource to help you get an overview of your literature review reading. **PDF Download**

Three domains of critical reading study guide
A downloadable resource to guide your literature review reading. **PDF download**

An audio-visual guide to in-depth critical reading, for literature reviews. **Guide with audio**
Discover ways to critically evaluate the information you find.
Explore methods for effectively managing your documents and references.
Discover simple ways to keep up to date with information in your field.
Structuring a literature review
Explore different methods on how to structure your literature review.
Dissertation Structure
As this will be one of the longest academic documents you'll create, it can be helpful to start thinking about the overall shape of your dissertation early on, considering how many chapters there will be and how they'll relate to each other. This will be a provisional guide at first but having an idea of the structure can give you a way forward, help you to stay focused, and help manage your word count.

Sorry, you need JavaScript to view this video
Where to go for support
You will be given a supervisor for your dissertation or thesis by your academic school or institute. Your supervisor is there to give you advice and guidance about all aspects of your research project.
There is also support and advice available to you at each stage of your project from the services below:

University Library
For advice on planning your search strategy, finding and evaluating information, and managing your references.

Academic Skills Team
For help with managing your project, academic writing strategies, critiquing and reviewing literature, and developing a clear authorial voice.

Support for undergraduates and postgraduates with SPSS and data analysis.
Recommended books and e-books
For further reading related to dissertations and projects, browse our specially curated list of resources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

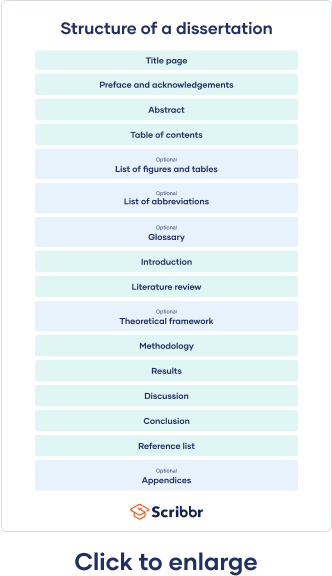
Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Theses and Dissertations
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
- Academic Writing
- From Research to Writing
- GSD Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
- Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
What is a thesis?
What is a dissertation, getting started, staying on track.
A thesis is a long-term project that you work on over the course of a semester or a year. Theses have a very wide variety of styles and content, so we encourage you to look at prior examples and work closely with faculty to develop yours.
Before you begin, make sure that you are familiar with the dissertation genre—what it is for and what it looks like.
Generally speaking, a dissertation’s purpose is to prove that you have the expertise necessary to fulfill your doctoral-degree requirements by showing depth of knowledge and independent thinking.
The form of a dissertation may vary by discipline. Be sure to follow the specific guidelines of your department.
- PhD This site directs candidates to the GSAS website about dissertations , with links to checklists, planning, formatting, acknowledgments, submission, and publishing options. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus . Consult with your committee chair about specific requirements and standards for your dissertation.
- DDES This document covers planning, patent filing, submission guidelines, publishing options, formatting guidelines, sample pages, citation guidelines, and a list of common errors to avoid. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus .
- Scholarly Pursuits (GSAS) This searchable booklet from Harvard GSAS is a comprehensive guide to writing dissertations, dissertation-fellowship applications, academic journal articles, and academic job documents.
Finding an original topic can be a daunting and overwhelming task. These key concepts can help you focus and save time.
Finding a topic for your thesis or dissertation should start with a research question that excites or at least interests you. A rigorous, engaging, and original project will require continuous curiosity about your topic, about your own thoughts on the topic, and about what other scholars have said on your topic. Avoid getting boxed in by thinking you know what you want to say from the beginning; let your research and your writing evolve as you explore and fine-tune your focus through constant questioning and exploration.
Get a sense of the broader picture before you narrow your focus and attempt to frame an argument. Read, skim, and otherwise familiarize yourself with what other scholars have done in areas related to your proposed topic. Briefly explore topics tangentially related to yours to broaden your perspective and increase your chance of finding a unique angle to pursue.
Critical Reading
Critical reading is the opposite of passive reading. Instead of merely reading for information to absorb, critical reading also involves careful, sustained thinking about what you are reading. This process may include analyzing the author’s motives and assumptions, asking what might be left out of the discussion, considering what you agree with or disagree with in the author’s statements and why you agree or disagree, and exploring connections or contradictions between scholarly arguments. Here is a resource to help hone your critical-reading skills:
http://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/criticalread.pdf
Conversation
Your thesis or dissertation will incorporate some ideas from other scholars whose work you researched. By reading critically and following your curiosity, you will develop your own ideas and claims, and these contributions are the core of your project. You will also acknowledge the work of scholars who came before you, and you must accurately and fairly attribute this work and define your place within the larger discussion. Make sure that you know how to quote, summarize, paraphrase , integrate , and cite secondary sources to avoid plagiarism and to show the depth and breadth of your knowledge.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have.
The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed. The project can feel daunting or even overwhelming unless you break it down into manageable pieces and create a timeline for completing each smaller task. Be realistic but also challenge yourself, and be forgiving of yourself if you miss a self-imposed deadline here and there.
Your program will also have specific deadlines for different requirements, including establishing a committee, submitting a prospectus, completing the dissertation, defending the dissertation, and submitting your work. Consult your department’s website for these dates and incorporate them into the timeline for your work.
Accountability
Sometimes self-imposed deadlines do not feel urgent unless there is accountability to someone beyond yourself. To increase your motivation to complete tasks on schedule, set dates with your committee chair to submit pre-determined pieces of a chapter. You can also arrange with a fellow doctoral student to check on each other’s progress. Research and writing can be lonely, so it is also nice to share that journey with someone and support each other through the process.
Common Pitfalls
The most common challenges for students writing a dissertation are writer’s block, information-overload, and the compulsion to keep researching forever.
There are many strategies for avoiding writer’s block, such as freewriting, outlining, taking a walk, starting in the middle, and creating an ideal work environment for your particular learning style. Pay attention to what helps you and try different things until you find what works.
Efficient researching techniques are essential to avoiding information-overload. Here are a couple of resources about strategies for finding sources and quickly obtaining essential information from them.
https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_in_literature_detailed_discussion/reading_criticism.html
https://students.dartmouth.edu/academic-skills/learning-resources/learning-strategies/reading-techniques
Finally, remember that there is always more to learn and your dissertation cannot incorporate everything. Follow your curiosity but also set limits on the scope of your work. It helps to create a folder entitled “future projects” for topics and sources that interest you but that do not fit neatly into the dissertation. Also remember that future scholars will build off of your work, so leave something for them to do.
Browsing through theses and dissertations of the past can help to get a sense of your options and gain inspiration but be careful to use current guidelines and refer to your committee instead of relying on these examples for form or formatting.
DASH Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard.
HOLLIS Harvard Library’s catalog provides access to ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global .
MIT Architecture has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Rhode Island School of Design has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
University of South Florida has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Harvard GSD has a list of projects, including theses and professors’ research.
- << Previous: Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
- Next: Publishing >>
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 4:05 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.

Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
| & | An author–date citation in brackets in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end. |
|---|---|---|
| A superscript or bracketed reference number in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the numbered reference list at the end. | |
| A footnote in the text that gives full source information… | …and an alphabetised bibliography at the end listing all sources. |
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
Browser does not support script.
We use cookies on this site. By browsing our site you agree to our use of cookies. Close this message Find out more

- Find your course
- The Principal
- Our experts
- Our history
- Facts & figures
- Art Collections & Picture Gallery
- Exhibitions
- Online shop
- Organisation of the College
- Charitable status
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research degrees
- Scholarships
- Accommodation
- Guide for parents
- Schools & colleges
- Lifelong learning
- Passport Award
- Discover Arts
- Discover Science
- Careers & Employability
- Departments and Schools
- Biological Sciences
- Comparative Literature & Culture
- Computer Science
- Drama,Theatre & Dance
- Earth Sciences
- Electronic Engineering
- European Studies
- Information Security
- Liberal Arts
- Mathematics
- Modern Languages, Literatures & Cultures
- Politics & International Relations
- Professional Studies
- Social Work
- Student life
- Campus & facilities
- Social life
- Royal Holloway and Me
- What our students say
- Student media
- Students' Union
- Active lifestyle & sport
- Volunteering
- Support, health & welfare
- Jobs while you study
- Sustainability
- International
- Why Royal Holloway?
- English language & university preparation
- Study abroad & exchanges
- Immigration & visas
- Your country
- Fees & scholarships
- After applying
- Support for international students
- Information for agents
- Virtual Open Day
- Current research
- Doctoral School
- Impact case studies
- Research support
- Funding opportunities
- Departments & Groups
- Pure support
- Commercialisation seed funds
- Research data management
- For business
- The Institute for Cyber Security Innovation
- Conferences & hospitality
- Consultancy
- Enterprise centre / incubation
- Licensing / commercialisation
- Research & business
- Recruiting our students
- Proof of award
- Get involved
- Benefits & services
- Events & reunions
- Higher magazine
- Why support the College?
- Our priorities
- A gift in your will
- American Foundation
- Tax efficient giving
Dissertation - Marking Criteria
The text below is an extract from the MSc handbook for students
Each dissertation is independently marked by two examiners; one of these is normally the supervisor. An external examiner moderates the assessment. The examiners may conduct an oral examination if they wish to check the depth of the student's understanding and to ensure that the dissertation is the student's own work. Students must obtain a pass grade on the dissertation to pass the MSc degree. The examiners give up to 100 points where the points translate to the following categories:
85 − 100: An exceptionally high level of understanding and outstanding research potential.
70 − 84.99: Very high competence and excellent research potential.
60 − 69.99: Evidence of some creativity and independence of thought.
50 − 59.99: Sound understanding of the literature, but lack of accuracy or originality.
0 − 49.99: Insufficient or no understanding of the topic, poor quality of work.
The points are given according to the following guidelines:
Knowledge of subject (25)
21 − 25: Deep understanding and near-comprehensive knowledge.
18 − 20: Deep understanding.
15 − 17: Very good understanding.
12 − 14: Sound knowledge of relevant information.
10 − 11: Basic understanding of the main issues.
0 − 9: Little or no understanding of the main issues.
Organisation of material (25)
21 − 25: Of publishable quality.
18 − 20: Arguments clearly constructed; material very well-organised.
15 − 17: Well-organised; aims met with no significant errors or omissions.
12 − 14: Coherent and competent organisation.
10 − 11: Lack of clarity in written presentation or aims only partially met.
6 − 9: Major flaws in arguments; aims of project not met.
0 − 5: Arguments are missing/deficient. Disorganised or fragmentary.
Originality, interpretation and analysis (20)
17 − 20: Significant originality in the interpretation and/or analysis; project aims challenging.
14 − 16: Some originality; evidence of excellent analytical and problem- solving skills.
12 − 13: Good attempt to interpret and analyse existing literature.
10 − 11: Minor flaws in interpretation/analysis of existing literature.
5 − 9: Poor interpretation/analysis or project aims too simple.
0 − 4: Little or no interpretation or analysis; project aims trivial.
Evidence of reading (10)
8 − 10: Independent reading including research papers.
6 − 7: Good use of outside reading.
4 − 5: Some evidence of outside reading.
0 − 3: Little or no evidence of outside reading.
Bibliography and referencing (10)
9 − 10: Of publishable quality.
7 − 8: Good referencing and bibliography.
5 − 6: Either poor bibliography or poor referencing.
3 − 4: Poor bibliography and little or no referencing.
0 − 2: No bibliography and little or no referencing.
Style, spelling, punctuation and grammar (10)
9 − 10: Incisive and fluent, no errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
7 − 8: Very minor errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
4 − 6: Some errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
0 − 3: Many errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
Find your Mathematics course
- Mathematical Studies BSc
- Mathematics BSc
- Mathematics MSci
- Mathematics and Management BSc
- Mathematics and Music BA
- Mathematics and Physics BSc
- Mathematics and Physics MSci
- Mathematics with French BSc
- Mathematics with German BSc
- Mathematics with Italian BSc
- Mathematics with Management BSc
- Mathematics with Philosophy BSc
- Mathematics with Spanish BSc
- Mathematics with Statistics BSc
- Computer Science and Mathematics BSc
- Economics and Mathematics BSc
- Economics and Mathematics with a Year in Business BSc
- Finance and Mathematics BSc
- Finance and Mathematics with a Year in Business BSc
- Management with Mathematics BSc
- Modern Languages with Mathematics BA
- Mathematics for Applications MSc
- Mathematics of Cryptography and Communications MSc
- settings Undergraduate Postgraduate taught Postgraduate research Search Mathematics All departments View all undergraduate courses for 2018 View all undergraduate courses for 2019 View all postgraduate courses for 2018
- Mobile site view
- Desktop site view
- Media enquiries
- Modern Slavery Act
- IT Services
- Social media
- CampusAnywhere
- Terms and conditions
Comment on this page
Did you find the information you were looking for? Is there a broken link or content that needs updating? Let us know so we can improve the page.
Note: If you need further information or have a question that cannot be satisfied by this page, please call our switchboard on +44 (0)1784 434455.
This window will close when you submit your comment.

Finish Your Dissertation, Fast
Stop going in circles trying to figure it all out on your own. Get hands-on help from a certified coach, today.

Clients Passed
Client Pass Rate
Trustpilot Score
Facebook Rating
How 1:1 Coaching Works
Our private coaching service gets you across the finish line as quickly as ethically possible.
Step 1: Initial Chat
We’ll have a free, no-obligation consultation to understand your unique situation and needs.
Step 2: Engage
Your dedicated coach will support you through every stage and help you fast-track the process.
Step 3: Finish
Submit your project with confidence and get your life back – or jump into the next degree!
Why Grad Coach?

It's all about you
We take the time to understand your unique challenges and work with you to achieve your specific academic goals . Whether you're aiming to earn top marks or just need to cross the finish line, we're here to help.

An insider advantage
Our award-winning Dissertation Coaches all hold doctoral-level degrees and share 100+ years of combined academic experience. Having worked on "the inside", we know exactly what markers want .

Any time, anywhere
Getting help from your dedicated Dissertation Coach is simple. Book a live video /voice call, chat via email or send your document to us for an in-depth review and critique . We're here when you need us.

A track record you can trust
Over 10 million students have enjoyed our online lessons and courses, while 5000+ students have benefited from 1:1 Private Coaching. The plethora of glowing reviews reflects our commitment.
Chat With A Friendly Coach

Take A Peak Inside…
Here’s a snippet from one of our client sessions (thanks, Michelle!)
What Our Clients Say...
We've worked 1:1 with 5000+ students . Here's what some of them have to say:
David's depth of knowledge in research methodology was truly impressive. He demonstrated a profound understanding of the nuances and complexities of my research area, offering insights that I hadn't even considered. His ability to synthesize information, identify key research gaps, and suggest research topics was truly inspiring. I felt like I had a true expert by my side, guiding me through the complexities of the proposal.
Cyntia Sacani (US)
I had been struggling with the first 3 chapters of my dissertation for over a year. I finally decided to give GradCoach a try and it made a huge difference. Alexandra provided helpful suggestions along with edits that transformed my paper. My advisor was very impressed.
Tracy Shelton (US)
Working with Kerryn has been brilliant. She has guided me through that pesky academic language that makes us all scratch our heads. I can't recommend Grad Coach highly enough; they are very professional, humble, and fun to work with. If like me, you know your subject matter but you're getting lost in the academic language, look no further, give them a go.
Tony Fogarty (UK)
So helpful! Amy assisted me with an outline for my literature review and with organizing the results for my MBA applied research project. Having a road map helped enormously and saved a lot of time. Definitely worth it.
Jennifer Hagedorn (Canada)
Everything about my experience was great, from Dr. Shaeffer’s expertise, to her patience and flexibility. I reached out to GradCoach after receiving a 78 on a midterm paper. Not only did I get a 100 on my final paper in the same class, but I haven’t received a mark less than A+ since. I recommend GradCoach for everyone who needs help with academic research.
Antonia Singleton (Qatar)
I started using Grad Coach for my dissertation and I can honestly say that if it wasn’t for them, I would have really struggled. I would strongly recommend them – worth every penny!
Richard Egenreider (South Africa)
Have A Question?
Here are some of the most popular questions we get asked.
Dissertation Coaching
How does coaching work.
Working with Grad Coach means you get a dedicated, highly-qualified research specialist to help you through any stage of your research.
Whether you just want a little initial guidance to make sure you're headed in the right direction, or you want hands-on, ongoing support throughout your entire research journey, your coach will be there for you whenever you need help.
Your dedicated coach will work with you using three channels: live sessions, content reviews and email support.
Live Coaching Sessions
A live coaching session is a real-time online meeting (audio or video) with your coach. In these sessions, you can discuss anything you need assistance with. For example, you might discuss topic ideas, how to structure your next chapter, how to undertake a specific analysis, etc.
Content Reviews
A content review is an offline review, where you send your document to your coach and they’ll meticulously review it at the scheduled time. They will provide extensive commentary within the document (including what’s wrong, why it’s problematic and how to correct it), and then email it back to you (see an example here ). If you want to have a call in addition to the content review, you can do that too.
Email Support
In addition to these two options, you can also email your coach at any time to ask any questions you have, so you'll never be left feeling unsure.
How is coaching different from a university-allocated supervisor?
There are a few key differences:
On-demand access
A university-allocated supervisor can only spend a limited amount of time with each student and their support is usually limited to a certain amount of time per section of content. Also, support is often limited to one or two formats (e.g., email).
Conversely, we provide unlimited , multi-channel, on-demand support . You can book a live coaching session anytime you need to, get your work reviewed as many times as you like (see an example here ) and drop us an email whenever you have a question or concern.
Plain-language advice
Supervisors often communicate in complex “ivory tower academic-speak” that is difficult to understand and not particularly actionable. Students often struggle to make sense of their supervisor’s advice and feedback, due to this language barrier and experience gap.
Conversely, we provide you with plain language, actionable advice and feedback, with lots of examples and analogies to help you grasp concepts as quickly and easily as possible.
A safe, confidential space
The supervisor-student relationship is a tricky one to navigate, as the supervisor is often the first/primary marker or will be assessing you in some way. This creates an awkward dynamic, where it can feel somewhat risky to ask certain questions or propose ideas.
Conversely, your dedicated coach is your “partner in research” and there are no power dynamics. We create a 100% safe, comfortable space for you to ask questions, learn and grow. No question is a "stupid question".
Combined research expertise
Your supervisor will generally be allocated based on your area of research (your topic), not your methodology. This means that oftentimes (not always) they are not methodology experts and cannot provide the best possible guidance regarding your research design.
Conversely, the Grad Coach team consists of methodology experts across the spectrum of qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods. While you'll usually only work with one dedicated coach, you'll have access to the combined knowledge pool, which means you'll get the best possible advice.
How is coaching different from editing and proofreading?
Editing and proofreading services focus purely on language, formatting and technical presentation requirements, such as referencing. In other words, the focus is on the language , not the content itself. As a result, a dissertation can be perfectly edited and proofread but still fail, as the content itself is poor.
With coaching, on the other hand, the focus is on content . In other words, we focus on the quality of the research itself. For example, we look at things like:
- Is the research topic well-defined and justified?
- Are the research aims, objectives and research questions well-articulated and aligned?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, integrative and well-structured?
- Is the methodology well-considered and executed?
- Is the analysis sound and do the conclusions make sense?
Simply put – coaching focuses on the things that earn the majority of the marks . Additionally, we do offer a separate editing and proofreading service to polish the document, once the content is finalised.
Is coaching allowed by universities?
Yes . In fact, many universities refer students to us and some institutions even use our content (articles and videos) as part of their curriculum.
We provide dissertation coaching to help you improve the quality of your work. Importantly, all work must be your own – we do not write for you . While there are organisations that will cross this ethical boundary, we refuse to engage in any activity which may be considered as academic misconduct.
WARNING - If you are considering any academic writing service, please be aware that the use of such services can lead to expulsion or even revocation of your degree years after the fact. Many websites offering such services provide extremely low-quality work that is unlikely to pass and some websites are outright scams preying on desperate students.
What's included in the (free) initial consultation?
The purpose of the initial consultation is for us to assess your specific situation , needs and wants, and then e xplain how we can help you .
Please note that the initial consultation is not a coaching session. Naturally, we cannot provide accurate guidance without first having a sound understanding of your project, and we need to charge for such services.
Why should I work with Grad Coach specifically?
There are a few factors that distinguish Grad Coach from the alternatives:
On-demand, online service
Grad Coach was built to give you the help you need, whenever you need it, wherever you are. You can book live audio/video sessions, get your written work reviewed and sent back to you, or just drop your coach an email whenever you have a question. 1-on-1, hands-on help is always just a click away.
Friendly, plain-language coaches
At Grad Coach, our goal is to bring academia "back down to earth". While our coaches have over 100 years of combined experience within academia (including dissertation supervision, marking and lecturing), we always aim to simplify the content as much as possible, using plain language, actionable advice and feedback. You can download a sample content review here to see this in practice.
More than just coaching - a one-stop-shop
In addition to our flagship dissertation coaching service, we also provide a suite of time-saving services such as interview transcription, qualitative coding, survey design, statistical testing, and editing and proofreading. This means you get everything you need under one trusted roof. You can visit the services page to learn more about our full offering.
An accredited, award-winning operation
We take our work seriously, which is why we're accredited by the Tutors' Association UK and subscribe to their extensive code of ethics. We've also won multiple awards, including " Best Dissertation Coaching Service 2021 " (AI International), " Best Dissertation & Thesis Coaching Specialists 2020 " (MEA) and " Top 50 Student Blog " (Feedspot). To date, we've supported over 3000 students with private dissertation coaching and approximately 7 million students with video lessons.
To learn more about Grad Coach and the team behind it, visit the “About Us” page .
Which universities and degrees do you support?
We can provide coaching for a wide range of dissertations, theses and research projects/assignments at Bachelors , Honours , Master's and Doctoral -level degrees, especially (but not limited to) those within the social sciences.
Importantly, our expertise lies in the research process itself , especially research design, methodologies and academic writing – rather than specific research areas/topics (e.g. psychology, management, etc.). In other words, the support we provide is topic-agnostic , which allows us to support students across a very broad range of research topics.
If you’re unsure about whether we’re the right fit, feel free to drop us an email or book a free initial consultation .
Can I get a coach that specialises in psychology/marketing/etc.?
As we mentioned previously, our expertise lies in the research process itself , especially research design, methodologies and academic writing – rather than specific research areas/topics (e.g., psychology, management, etc.).
Simply put, the support we provide is topic-agnostic , which allows us to support students across a very broad range of research topics. That said, if there is a coach on our team that has experience in your area of research, as well as your chosen methodology, we can allocate them to your project (depending on availability).
Can I work with multiple coaches at once?
No. We work on a 1-on-1 basis, where each client has a dedicated coach assigned to their project, to ensure that they receive the highest possible quality of service.
How much does coaching cost?
Since our coaching services are completely custom-tailored for each student, they are billed on a time basis (as opposed to a project basis). This allows you to engage as much or as little as you want, with no long-term commitments or tie-downs.
The hourly rate itself depends on whether you purchase single hours or a discounted package. Please visit the pricing page for more information.
Do you have any testimonials or reviews?
Yes - you can view our Facebook and Trustpilot reviews here . You can also read about our accreditations and awards here .
Will my work be treated confidentially?
Absolutely. Your work will be treated completely confidentially and will not be shared with any third parties, nor published anywhere. We can sign a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) if you wish. Once you have completed your project, we can delete all content from our servers.
Do you offer other services?
Yes, in addition to dissertation coaching, we provide a suite of time-saving services , including:
- Interview transcription
- Qualitative data coding
- Survey design and hosting
- Statistical testing (SPSS & R)
- Editing and proofreading
If you have any other requirements, feel free to contact us to discuss them.
Can you write (or rewrite) sections for me?
No - all writing must be your own. We can hold your hand throughout the research process, but we cannot write for you as that would constitute academic misconduct.
WARNING - If you are considering any academic writing service, please be aware that the use of such services can lead to expulsion or even revocation of your degree years after the fact. Many websites offering such services provide extremely low-quality work that is unlikely to pass, and some websites are outright scams preying on desperate students.
English is not my first language (ESL student). Can you help me?
Yes , we can. In fact, many of our students are international ESL students. We can assist both with the academic aspects (e.g., coaching) and the English communication aspects (e.g., editing and proofreading).
My work is due in the next few days. Can you help me?
It’s not ideal, but we will do our best to help. Please email us or book an initial consultation as soon as possible.
Can you help me apply for a degree programme?
If your application requires a research topic or proposal (as is common for Master's and PhD applications), we can assist with that aspect of the application. However, if you require admissions-specific advice and guidance, that is not our area of expertise.
Please book a free initial consultation with us to discuss.
I still have questions…
No problem. Feel free to email us or book an initial consultation to discuss.
Kickstart Your Dissertation, Today
Enter your details below, pop us an email, or book an introductory consultation .

King's College London
- Postgraduate Taught Dissertation Framework
Document profile
Framework outlining key principles and good practice for postgraduate taught dissertations and equivalent major projects. This framework aims to ensure that students are effectively supported and supervised throughout the process and are able to develop their academic skills and research practice.
The previous Postgraduate Taught Students Core Code of Practice applies to students completing dissertations in the 2023-24 academic year.
- Core Code of Practice for PGT Research Governance and Dissertation Framework
Relevant links
- FindAMasters
- Researching and Writing a Masters Dissertation
Written by Mark Bennett
All Masters programmes include some form of extended individual project. Research-focussed programmes, such as an MRes , may include multiple independent research components. Taught courses usually culminate with a substantial research task, referred to as the Masters dissertation or thesis.
This article talks about how long a Masters dissertation is and the structure it follows.Before you get started on your dissertation, you'll usually need to write a proposal. Read our full guide to Masters dissertation proposals for more information on what this should include!
| Length | 15,000 - 20,000 words |
| Structure | Abstract (300 words) Introduction (1,000 words) Literature review (1,000 words) Research methodology (1,500 words) Results Discussion (12,000 words) Conclusion (1,500 words) References/Bibliography Appendices |
| Supervision | Yes, you’ll be paired with an academic from your own university |
| Assessment | External examiner along with additional members of faculty. There is not usually a viva at Masters level. |
On this page
What’s the difference between a masters dissertation and an undergraduate dissertation.
The Masters thesis is a bridge between undergraduate study and higher level postgraduate degrees such as the PhD .
A postgraduate dissertation may not look that different to its undergraduate equivalent. You’ll likely have to produce a longer piece of work but the foundations remain the same.
After all, one of the purposes of an undergraduate dissertation or final year project is to prepare you for more in-depth research work as a postgraduate. That said, there are some important differences between the two levels.
So, how long is a Masters dissertation? A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent – usually it’ll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries.
To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you’ll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic. This can be like producing a series of shorter pieces of work, similar to those required by individual modules. However, there’s the additional requirement that they collectively support a broader set of conclusions.
This more involved Masters dissertation structure will:
- Give you the scope to investigate your subject in greater detail than is possible at undergraduate level
- Challenge you to be effective at organising your work so that its individual components function as stages in a coherent and persuasive overall argument
- Allow you to develop and hone a suitable research methodology (for example, choosing between qualitative and quantitative methods)
If the individual topics within your overall project require you to access separate sources or datasets, this may also have an impact on your research process.
As a postgraduate, you’ll be expected to establish and assert your own critical voice as a member of the academic community associated with your field .
During your Masters thesis you’ll need to show that you are not just capable of analysing and critiquing original data or primary source material. You should also demonstrate awareness of the existing body of scholarship relating to your topic .
So, if you’ll excuse the pun, a ‘Masters’ degree really is about achieving ‘mastery’ of your particular specialism and the dissertation is where you’ll demonstrate this: showing off the scholarly expertise and research skills that you’ve developed across your programme.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
A dissertation is a long piece of (usually) written work on the same topic. A thesis is a little more specific: it usually means something that presents an original argument based on the interpretation of data, statistics or content.
So, a thesis is almost always presented as a dissertation, but not all dissertations present a thesis.
Masters dissertation structure
As you can probably imagine, no two dissertations follow the exact same structure, especially given the differences found between Masters programmes from university to university and country to country .
That said, there are several key components that make up the structure of a typical Masters dissertation
How long is a Masters dissertation?
Most dissertations will typically be between 15,000 and 20,000 words long, although this can vary significantly depending on the nature of the programme.
You should also check with your university exactly which sections of the dissertation count towards the final word count (the abstract, bibliography and appendices won’t usually be included in the total).
Usually around 300 words long, the abstract is meant to be a concise summary of your dissertation. It should briefly cover the question(s) you aim to answer, your primary argument and your conclusion.
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to provide context for the rest of the dissertation, setting out your aims and the scope of what you want to achieve with your research. The introduction should give a clear overview of the dissertation’s chapters and will usually be around 1,000 words long.
Literature review
This part of the dissertation should examine the scholarship that has already been published in your field, presenting various arguments and counter-arguments while situating your own research within this wider body of work.
You should analyse and evaluate other publications and explain how your dissertation will contribute to the existing literature in your subject area. The literature review sometimes forms part of the introduction or follows immediately on from it. Most literature reviews are up to 1,000 words long.
Research methodology
Not all dissertations will require a section covering research methodology (Arts and Humanities dissertations won’t normally undertake the kind of research that involves a set methodology). However, if you are using a particular method to collect information for your dissertation, you should make sure to explain the rationale behind your choice of methodology. The word count for this part of the dissertation is usually around the 1,500 mark.
Those in the Arts and Humanities will usually outline their theoretical perspectives and approaches as part of the introduction, rather than requiring a detailed explanation of the methodology for their data collection and analysis.
Results / findings
If your research involves some form of survey or experiment, this is where you’ll present the results of your work. Depending on the nature of the study, this might be in the form of graphs, tables or charts – or even just a written description of what the research entailed and what the findings were.
This section forms the bulk of your dissertation and should be carefully structured using a series of related chapters (and sub-chapters). There should be a logical progression from one chapter to the next, with each part building on the arguments of its predecessor.
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
Here you should draw together the threads of the previous discussion chapters and make your final concluding statements, drawing on evidence and arguments that you’ve already explored over the course of the dissertation. Explain the significance of your findings and point towards directions that future research could follow. This section of the Masters thesis will be around 1,500 words long.
References / bibliography
While planning and writing your dissertation, you should keep an extensive, organised record of any papers, sources or books you’ve quoted (or referred to). This will be a lot easier than leaving all of it until the end and struggling to work out where a particular quotation is from!
Appendices won’t be necessary in many dissertations, but you may need to include supplementary material to support your argument. This could be interview transcripts or questionnaires. If including such content within the body of the dissertation won’t be feasible – i.e. there wouldn’t be enough space or it would break the flow of your writing – you should consult with your supervisor and consider attaching it in an appendix.
It’s worth bearing in mind that these sections won’t always be discretely labelled in every dissertation. For example, everything up to ‘discussion’ might be covered in introductory chapter (rather than as distinct sections). If you’re unsure about the structure of your Masters dissertation, your supervisor will be able to help you map it out.
How does supervision work for a Masters dissertation?
As a Masters student at the dissertation stage you’ll usually be matched with an academic within your institution who will be tasked with guiding your work. This might be someone who has already taught you, or it may be another scholar whose research interests and expertise align well with what you want to do. You may be able to request a particular supervisor, but taught postgraduates are more likely to be assigned them by their department.
Specific arrangements with your supervisor will vary depending on your institution and subject area. They will usually meet with you at the beginning of the dissertation period to discuss your project and agree a suitable schedule for its undertaking. This timetable will probably set dates for:
- Subsequent discussions and progress checks
- The submission of draft chapters or sections
- Feedback appointments
Though your supervisor is there to help and advise you, it is important to remember that your dissertation is a personal research project with associated expectations of you as an independent scholar.
As a rule of thumb, you can expect your supervisor to read each part of your dissertation once at the draft stage and to offer feedback. Most will not have time to look at lots of subsequent revisions, but may respond favourably to polite requests for exceptions (provided their own workload permits it).
Inundating your supervisor with emails or multiple iterations of draft material is best avoided; they will have their own research to manage (as well as other supervision assignments) and will be able to offer better quality feedback if you stick to an agreed schedule.
How is a Masters dissertation assessed and examined?
On most courses your dissertation will be assessed by an external examiner (as well as additional members of faculty within your university who haven’t been responsible for supervising you), but these will read and critique the work you submit without personally questioning and testing you on it.
Though this examination process is not as challenging as the oral defence or ‘ viva voce ’ required for a PhD thesis, the grading of your Masters dissertation is still a fundamental component of your degree.
On some programmes the result awarded to a student’s dissertation may determine the upper grade-band that can be awarded to their degree.
Search for a Masters
Ready to start looking for your ideal postgraduate opportunity? Browse and compare Masters degrees on FindAMasters.com.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

Applying for a Masters can feel a bit daunting. Here is a checklist of all the things you need to do to make sure you have everything covered in your Masters application.

Postgraduate study is often very flexible, with the option to study a Masters degree or other qualification part-time, online or through blended learning.

How do Bachelors and Masters courses differ? We’ve covered the main differences you’ll encounter when making the transition from undergrad to postgrad study.

Our guide explains how online Masters degree work, what the benefits of online learning are and how to choose what to study online.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in Italy.
Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in the USA.
FindAMasters. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about Masters study?
Select your nearest city
- Aberystwyth
- Beaconsfield
- Bishop Burton
- Bournemouth
- Bridlington
- Chatham Maritime
- Cirencester
- East Malling
- Hemel Hempstead
- High Wycombe
- Huddersfield
- Isle of Man
- Jordanstown
- London Central
- London East
- London South
- London West
- Londonderry
- Loughborough
- Middlesbrough
- Milton Keynes
- Musselburgh
- Northampton
- Potters Bar
- Saffron Waldon
- Scarborough
- Southampton
- St Leonards on Sea
- Stoke on Trent
- Wolverhampton
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAMasters, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, application tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAMasters account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest Masters news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite courses, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your Masters courses? Log in here .

Let us help you find a Masters
Never miss a course
Enter our ambassador competition
Get funding news, tips and advice
Hear about upcoming events
Sign up to our newsletter today
We've been helping students find the right postgraduate course for over a decade.
Login to your account
Enter your username below to login to your account.

COMMENTS
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and subdivisions. Page and Text Requirements Page Size. 8½ x 11 inches, unless a musical score is included; Margins. At least 1 inch for all margins; Spacing. Body of text ...
the mark awarded for Analysis would be 27% of the total mark for the work. Dissertation Marking Criteria - Level 7 N.B. These marking criteria are based on the QAA Framework for higher education qualification in England, Wales and Northern Ireland (2008) Structure & organisation Knowledge Application of knowledge & understanding (incl.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
All dissertations/ research projects must be subject to Full, Independent, second-marking. 3. Faculties or Department may determine and publish policies on the appropriate use of different forms of second marking within the disciplinary context over and above UCL's minimum threshold requirements.
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
A first class dissertation should demonstrate professional standards of research design and management, and give confidence that the student could undertake professional work in a similar ... This mark is usually reserved for cases where there is no serious attempt to complete the dissertation (as defined in College Regulations). It may also be ...
dissertation—that is,precursor of what is to come, with each element being more fully developed and explained fu. ther along in the book.For each key element, explain reason for inclusion, quality markers, and fr. OVERVIEWFRONT MATTERFollowing is a road map that briefly outlines the contents of. an enti.
Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. A Practical Guide to Dissertation and Thesis Writing. By Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. This book first published 2019. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. Lady Stephenson Library, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE6 2PA, UK. British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data. A catalogue record for this book is available from ...
A dissertation is an extended piece of academic writing on a question or problem related to particular subject. Usually done at the end of an undergraduate or master's degree, this type of research project can take several months to complete. A thesis is usually completed as part of a PhD. While similar in nature to a dissertation, a thesis ...
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have. The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed.
Dissertation topic allocation and supervision arrangements There are some variations in dissertation topic allocation process and supervision arrangements across different divisions and programmes. However, in all cases, AMBS ensures that the dissertation topic allocation process is robust and consistent, and that each ...
ontents and appendices is 10,000 words. The maximum length of the dissertation, including footnotes/endnotes, but excluding bibliography, table of. ontents and appendices is 12,000 words.NB: The section word-lengths below are suggestions only. and assume a 10,000 word dissertation. They can be adjusted pro rata for 12,000 word dissertations ...
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
Dissertation - Marking Criteria. The text below is an extract from the MSc handbook for students. Each dissertation is independently marked by two examiners; one of these is normally the supervisor. An external examiner moderates the assessment. The examiners may conduct an oral examination if they wish to check the depth of the student's ...
Dissertation Marking Criteria 2 Marks are based on a total of 100% The three basic elements should be considered while assessing the value of the dissertation are: Content. The dissertation needs to comply with the subject matter as approved by the BOS and rooted in academic literature. The dissertation should be thorough and provide details
marking policy and marking models, marking schemes (with specific reference to the new Step-Marking Scheme), and marking criteria. Guidance on the marking ... example for supervised dissertations, performances, laboratory work, etc., and must be agreed with the Assessment Sub-Board Chair and the External Examiner. Where anonymity is not ...
Kickstart Your Dissertation, Today. Enter your details below, pop us an email, or book an introductory consultation. Get 1-on-1 thesis and dissertation coaching from seasoned PhDs, including research supervisors and markers. Book a free consultation today.
The previous Postgraduate Taught Students Core Code of Practice applies to students completing dissertations in the 2023-24 academic year. ... King's Academic Manual. Marking, College Framework. Document profile. Status: Current. Category: Teaching. Owner: Academic Regulations, Quality & Standards (Students & Education) Approval date: 26 June ...
A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent - usually it'll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries. To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you'll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic.
48-49 (final mark): The dissertation is borderline, the Board of Examiners will consider whether to award an MSc. 45-49: According to Taught Assessment Regulations (number 58), with a mark in this range the student may re-submit the thesis within 3 months, and both markers will need to re-mark the new submission. 50-52:
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
Students who fail the dissertation with a mark below 50% but higher than 30% (30-49) will be granted one opportunity to resubmit. Students who fail the dissertation with a mark below 30% will not be permitted to resubmit.1 1.4 Assessment Arrangements Once submitted, dissertations are assessed and the marking moderated by a minimum of two internal
The following Level and Mark Descriptors are to be used for the academic year 2021/22 onwards. The Level Descriptors are those developed by SEEC (2016). These descriptors are aligned with the England, Wales and Northern Ireland (EWNI) Credit Level Descriptors. Note: minor amendments to the terminology of the SEEC and EWNI descriptors have been ...