- Engineering
- Write For Us
- Privacy Policy


Business Speech: Types with Examples, Informative, Special, Persuasive

Good presentation and speaking habits may be considered soft skills in the workplace or in any type of organization. Today in this article, we have shared what is business speech and how many types of business speeches are there.
Anybody can relate to all these types of business speech because these all are equally important in social life as well. So let’s start our topic with the basics of business speech.
► What is Business Speech?
Speech refers to that action when a person stands among a great number of people and starts delivering any kind of information or statement. It may be or may not be useful for the whole audience but most of the time it is valuable for them.
A speech that is delivered in the workplace or in any business organization for some specific purpose is known as Business Speech.
This is one of the forms of Business Communication and the audience has to sit quietly while the speech is being delivered. Most of the time audience knows very well that the speech must contain anything that will be beneficial for them.
► Types of Business Speech:

There are mainly three types of speech that are as follow;
- Informative Speech
- Persuasive Speech
- Special Occasion Speech
◉ Informative Speech
Informative business speech can be defined as speech that comprises the purpose to deliver useful information to the audience.
For Example – In any organization, an Executive Coach or Trainer speaking about the new trends in the market to his trainees. It can be hard to understand for few trainees, but the fact is that he is delivering something informative that is beneficial for them.
Informative Speech is further divided into four types;
- Speeches about Objects
- Speeches about Events
- Speeches about Processes
- Speeches about Concepts
The following are known kinds of informative speech.
✔ Speeches about Objects :
It can be about any object related to that particular organization where the speech is being delivered.
For Example – how various wildlife animals look, what is the smell of medicine, information about any product.
✔ Speeches about Events :
Those speeches that inform the audience about any events like historical incidents or about any situations are called speeches about the event.
For Example – New President’s speech about future goals after the oath-taking ceremony.
✔ Speeches about Processes :
The main purpose of this type of informative speech is to inform the audience about anything which is currently happening or about how to do any particular task or work.
For Example – a Yoga teacher explaining how to perform specific yoga poses.
✔ Speeches about Concepts :
Speeches about concepts are those speeches that inform the audience about any concept such as the peace of the world, freedom of rights, or love, fundamentals of any study topic.
For Example – a Science teacher explains Einstein’s theory of general relativity to his students in the class.
Must Read : Skills of HR Manager
◉ Persuasive Speech
Persuasive Speech refers to those speeches where the intention of the speech is to convince the audience to accept the particular opinion or fact and create influence on the audience to do anyhow.
In short, the speech which influences the listeners or audience to follow a certain idea is called a persuasive speech.
Persuasive speech is also an informative speech. because here speaker gives information in a lucrative manner to influence others.
For Example – in any debate, every person is try to persuade others to follow their given point of view. It is a form of persuasive speech.
In another example, During the advertising and promotional functions of any business, the sales manager or speaker uses his persuasion skills to influence the audience. Here the main purpose of speech is to change the thinking, beliefs, or behaviors of the audience towards his product.
Persuasive speech can be divided into three types that are as follows:
- Factual Persuasive Speech
- Value Persuasive Speech
- Policy Persuasive Speech
✔ Factual Persuasive Speech:
The Factual Persuasive Speech is such a speech that contains facts and it is based on a concrete proof about the certainty of anything that had happened.
The main purpose of this factual persuasive speech is to persuade the listeners whether the certain thing happened or not, exists or doesn’t exist.
For Example – If a student is giving a speech about the first man, who landed on the surface of the Moon. Nobody in the class knows whether it did happen or not, yet it possesses concrete proof.
✔ Value Persuasive Speech:
A Value Persuasive Speech is such a speech that tells the listeners about anything, whether it is wrong or right. The purpose of this speech is to challenge the ethical or moral aspects of a certain issue.
For Example – If someone is giving a speech about capital punishment, whether it is moral or immoral, right or wrong, done or prevented. this type of speech is a value persuasive speech.
✔ Policy Persuasive Speech:
The policy persuasive speech refers to that speech where the speaker is trying to persuade the audience to either following a policy or rejecting it. It is not limited to just a policy, but it can be about accepting or rejecting a rule or a candidate is also a policy persuasive speech.
For Example – Suppose If the President of a country is not satisfied with the present foreign policy and wants to change it. The president gives a speech to higher authorities for convincing them to change the current foreign policy and support the new policy then it is known as policy persuasive speech.
Must Read : Types of Communication
◉ Special Occasion Speech:
Special Occasion speech refers to that speech which is given on the special occasion like; A speech of farewell allows someone to say good-bye to one part of his or her life as he or she is moving on to the next part of life. Maybe you’ve accepted a new job and are leaving your current job.
Special occasion business speech is something which anyone can face at some point in their lives.
For example – If your company won an award of the year for excellence. And you are receiving that award on the behalf of your company. The speech given by you after getting the award can be considered as a special occasion business speech.
In another example, If you are getting retirement from your job and want to thank your subordinates, superiors, and top management at the farewell party.
Related Articles More From Author
Factors influencing consumer behaviour, what is consumer behaviour, what is market segmentation, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The Purpose of Speech Explained
If you ever find it unnecessary, out of fashion, dull, or even have no idea what speeches are for, this article is undoubtedly for you. With each word of this article, you will understand the real purpose of the speeches, how they arose, and what usefulness they bring to our day-to-day lives.
What is a Speech?
Professionals from the most diverse areas have increasingly sought this capacity. For some, this may be an innate ability, but it is an aptitude that can and must be developed continuously for most.
The purpose of Speech depends on the context in which a person speaks, it can be informative, expressive, instructive, and motivational and, mainly, to convince and influence people, regardless of the environment in which they are inserted.
There were also several cases in which oratory was adopted in a pernicious manner, motivating war and discord. Many dictators and heads of state took advantage of their discursive ability to call populations to hatred against their equals.
Activist and pastor Martin Luther King Jr. is an example of a leader that used a speech to spread a message of equal rights in the United States.
He won worldwide fame for speeches such as the “I Have a Dream” speech , being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 for his significant contribution to combating racism without resorting to violence.
| We make others believe something that we hold in their appreciation. | Speaking to convince Parliament to legislate on fundamental importance or when we want someone to lend us their car. | |
| The speaker carefully prepares a short speech that stages and interprets recurring mechanisms usually humorous and alluding to unusual situations. | Stand-Up comedy is one of the best examples of a speech aimed at entertaining the audience. | |
| The speeches of football coaches to their teams, for example, may involve a motivating dimension capable of changing the way the squad looks at itself and ultimately leading it to overcome. So it was with Martin Luther King or Nelson Mandela they inspired and simultaneously motivated the audience to think or act differently. | ||
| Delivering a message to the public to be aware or acknowledge a group about it. In these speeches, it is notified, clarified, and made known. | So it is with press conferences or news that seek to enlighten citizens/supporters/consumers about any event. | |
| Some speeches defend a cause, be it a social, environmental, political, or cultural cause; in speeches advocating a topic, we find persuasive communication that focuses specifically on convincing the audience from the speaker’s point of view. | An example is Al Gore at the Web Summit held in 2017 in Lisbon. Al Gore is an environmental activist invited worldwide to address global warming and warn of the need to change environmental policies for the planet’s sustainable future. Not only is it a form of standing up for yourself, but those who need a voice, one of which is to defend a cause, allows us to change social reality and inspire people. | |
The Importance of Speech
The ability to effectively use a speech is critical because it opens doors of opportunities for most individuals in their lives. Common examples are: standing out in work meetings, job interviews, inspiring people with graduation speeches, closing negotiations, sales, among many others.
“Of all the talents bestowed upon men, none is so precious as the gift of oratory.” Winston Churchill
It is impossible to predict when a presentation situation will happen; often, a potential customer or partner does not warn you before appearing. A critical work opportunity can arise at unexpected times.
When these occasions occur, it is best to be prepared; letting the stomach chill, excessive sweating, and shivering get in the way of a presentation is a choice.
Anyone can use oratory to their advantage. And it all starts with a change of attitude: it is necessary to see the presentation situations as opportunities and no longer punishments.
The Use of Speech in History
Throughout history, speeches have influenced people to combat injustice or show solidarity with others, comfort mourners, honor those who deserve it, and many other situations.
In short, addressing the public is an effective means of inducing it to virtuous action. It is in moments of tragedy and crisis that this characteristic stands out the most.
The purpose of giving a speech is unique and, at the same time Versatile, it has the role of conveying a message in various ways, whether it is entrenched, persuading, informing, or combining multiple forms.
AcethePresentation. AmadeBai, Emidio 15 Ideas To Make A Speech Unique, Memorable & Inspiring
AcethePresentation. AmadeBai, Emidio. 14 Types of Speech and Easy Tips to Master Them.
Similar Posts
Types of public speaking and pitching – 3 types of speech vs pitching, 80+ impromptu speech topics & 7 ways to nail one, what makes a great presenter 9 key qualities to look for, the 7 best apps for developing communication skills, 10 best tips on how to become a public speaker, the importance of public speaking – 10 ways in which it furthers your career and business growth.
Module 7: Public Speaking
What is public speaking, learning outcomes.
- Discuss key characteristics of public speaking
Public speaking is, simply, an oral presentation or speech delivered to a live audience. It is generally a formal or staged event— although impromptu speeches are a common occurrence—and can be a defining career moment. For example, you may think you’re attending a client meeting only to find yourself called on to explain a procedural or technical point being discussed. Or you may be sitting in a management meeting thinking you are just there to observe when you are asked to elaborate on an aspect of the supporting research and analysis or defend your recommendations.
Impromptu Speaking
Although impromptu speaking isn’t the focus of this module, it is worth noting that this type of speaking is something Toastmaster members train for on an ongoing basis using a technique called “Table Topics.” For more on this technique, read A Table Topics Workout: The Power Packed Exercise for Stretching Your Brain .
Executive presentation coach Peter Khoury has reverse-engineered the characteristics of great speakers for over fifteen years. Combining his findings with scientific research on leadership, he’s distilled this research into the following 9 characteristics of effective public speakers: [1]
Confidence Passion Practice, don’t memorize Speak in a natural voice Authenticity Keep it Short and Sweet Connect with your Audience Paint a Picture through Storytelling Repetition
Like computer failure and natural disasters, finding yourself in a situation requiring public speaking skills is not a matter of whether it will happen but when it will happen. Given the potential career impact, you need to prepare accordingly.
Practice Question
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/9-characteristics-highly-effective-public-speakers-peter-khoury/ ↵
- What is Public Speaking?. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

9 Ways For Preparing Effective Speech In Business Communication
Business executives, social activists, political and religion leaders deliver speeches on a regular basic on their respective areas of works. Though speech, they try to communicate information, ideas, wishes and opinions to their colleagues and peers. Hence, delivering effective and convincing speech is very essential.
Table of Contents
For the purpose of delivering effective speech, the following steps or ways should be followed.
Determining the purpose
Before delivering speech, the speaker should determine the objective clearly. The objective of speech may be to inform, to persuade or to convince others.
Analyzing the audience and occasion
Success of any speech depends on proper understanding of the meaning of speech by the audience. Therefore, the speaker must consider the age, education, profession, interest, attitude, likings and disliking as well as the nature of occasion at the time of delivering of speech.
Selecting the main idea of speech
In this stage, the speaker selects the main theme of the speech. Moreover, in order to present the main theme, the speaker can include other relevant subjects or topics.
Enquiring the information
Arranging data and writing draft.
After collecting relevant information, a draft of speech should be developed. The speaker should read the drafted speech over and over again and then develop the final speech. A well-organized speech is make up of three elements such as (a) introduction, (b) body and (c) conclusion.
Selecting the methods of delivering speech
In this stage, the speaker selects the proper method of delivering the speech. Murphy and others have suggested the following four alternative methods of delivering speech:
Arranging visual aids
Rehearsing the speech.
An important way to increase the effectiveness of speech is to rehearse it at any convenient place before delivering it to the audience. It helps the speaker to remove his shyness, confusion and nervousness.
Delivering the final speech
Moreover, the speaker should deliver the speech clearly, slowly, courteously and confidently by using simple language. For making the speech effective, speaker can also use any relevant non-verbal cues.
LET’S KEEP IN TOUCH!
You're on the list!! Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.
Reader Interactions
I agree, preparation is key to delivering effective speech. Particularly love your advice to analyze the audience so you can speak directly to them. Thanks for this post!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 18: Business Presentations
Venecia Williams and Olds College
Learning Objectives
- Understand how to use effective interpersonal communication skills in professional presentations
- Learn how to organize a presentation
- Examine how to use visual aids effectively
- Discuss the effective integration of communication and presentation techniques in the delivery of professional presentations
Along with good writing skills, the ability to communicate verbally is vital to many employers today. It is an integral part of the modern business world. People in the workplace spend the majority of their time communicating. Verbal communication in the workplace takes many forms such as staff meetings, discussions, speeches, presentations, informal conversations, and telephone and video conferences. Communicating verbally is more personal and flexible than writing. It allows workers to exchange ideas, information, and feedback more quickly. Verbal communication tends to occur in person, making it easier to negotiate, express emotions, outline expectations, and build trust, all of which are important in today’s workplace. Communication can also occur between people who are not together in person. In these situations, unique skills are necessary to achieve success. Simple conversation skills are also valued in the workplace, but this does not mean using casual or informal language. Rather, what is prized by many employers is the ability to communicate important information professionally but in a meaningful and understandable way. This can be important when making spontaneous presentations as well as more elaborate formal group presentations, which are a part of many work roles today.
What Makes a Successful Speaker?
According to longtime Toastmasters member Bob Kienzle, there are a few key elements that tend to make a successful speaker:
- Voice : Can the person be easily understood?
- Body Language : Does their body support what they’re saying? Are they confident?
- Coherent Structure: Does what they’re presenting make sense? Is it logical?
- Enthusiasm : Do they care about what they’re presenting?
- Expertise: Do they know what they’re talking about? Are they credible?
- Practice : If they haven’t practised or sufficiently prepared, it will likely show up in one or more of the above.
A successful speaker can be inspired by other speeches or speakers but may fall flat if they try to copy someone else. Authenticity and passion can resonate so much with an audience that it can outweigh elements otherwise considered pitfalls. The techniques, tools, and best practices are a guideline, and it’s important to note there is no such thing as “perfection” in public speaking. “Failure” can happen in myriad ways, but it’s more helpful to see them as learning opportunities, or opportunities to make a stronger connection to your audience. The biggest failure, according to Kienzle, is to pass up opportunities to practise your skills in presenting or public speaking.
Preparing a Presentation
Develop your message while keeping in mind the format, audience, style , and tone . First, you’ll need to think about the format of your presentation. This is a choice between presentation types. In your professional life, you’ll encounter the verbal communication channels in Figure 18.1. The purpose column labels each channel with a purpose (I=Inform, P=Persuade, or E=Entertain) depending on that channel’s most likely purpose.
| One-to-many | Formal | Low. One-sided | I, P, E | |
| One/ Few-to-many | Formal | Variable. Often includes Q&A | I, P, E | |
| Few-to-many | Formal | High. Q&A-based. | I, P | |
| Group | Informal | High. | I, P | |
| Group | Informal | High. | I, P | |
| One-to-many | Informal | High. Collaborative. | I (Educate) | |
| One-to-many | Formal | Low. | I | |
| One-to-many | Formal | Low. Recorded | I, P, E |
Figure 18.1 | Presentation Communication Channels
There are some other considerations to make when you are selecting a format. For example, the number of speakers may influence the format you choose. Panels and Presentations may have more than one speaker. In Meetings and Teleconferences, multiple people will converse. In a Workshop setting, one person will usually lead the event, but there is often a high-level of collaboration between participants. The location of participants will also influence your decision. For example, if participants cannot all be in the same room, you might choose a teleconference or webinar. If asynchronous delivery is important, you might record a podcast. When choosing a technology-reliant channel, such as a teleconference or webinar, be sure to test your equipment and make sure each participant has access to any materials they need before you begin.
Once you have chosen a format, make sure your message is right for your audience. You’ll need to think about issues such as the following:
- What expectations will the audience have?
- What is the context of your communication?
- What does the audience already know about the topic?
- How is the audience likely to react to you and your message?
Next, you’ll consider the style of your presentation. Analyze your specific presentation styles. Perhaps you prefer to present formally, limiting your interaction with the audience, or perhaps you prefer a more conversational, informal style, where discussion is a key element. You may prefer to cover serious subjects, or perhaps you enjoy delivering humorous speeches. Style is all about your personality!
Finally, you’ll select a tone for your presentation. Your voice, body language, level of self-confidence, dress, and use of space all contribute to the mood that your message takes on. Consider how you want your audience to feel when they leave your presentation and approach it with that mood in mind.
Presentation Purpose
Your presentation will have a general and specific purpose. Your general purpose may be to inform, persuade, or entertain. It’s likely that any speech you develop will have a combination of these goals. Most presentations have a little bit of entertainment value, even if they are primarily attempting to inform or persuade. For example, the speaker might begin with a joke or dramatic opening, even though their speech is primarily informational. Your specific purpose addresses what you are going to inform, persuade, or entertain your audience with the main topic of your speech.
Incorporating Backchannels
Technology has given speakers new ways to engage with an audience in real-time, and these can be particularly useful when it isn’t practical for the audience to share their thoughts verbally—for example, when the audience is very large, or when they are not all in the same location. These secondary or additional means of interacting with your audience are called backchannels, and you might decide to incorporate one into your presentation, depending on your aims. They can be helpful for engaging more introverted members of the audience who may not be comfortable speaking out verbally in a large group. Using publicly accessible social networks, such as a Facebook Page or Twitter feed, can also help to spread your message to a wider audience, as audience members share posts related to your speech with their networks. Because of this, backchannels are often incorporated into conferences; they are helpful in marketing the conference and its speakers both during and after the event.
Developing the Content
As with any type of messaging, it helps if you create an outline of your speech or presentation before you create it fully. This ensures that each element is in the right place and gives you a place to start to avoid the dreaded blank page. Figure 18.2 is an outline template that you can adapt for your purpose. Replace the placeholders in the Content column with your ideas or points.
| Introduction | |
|
Body |
|
| Conclusion |
Figure `18.2 | Presentation Outline
Introduction
The beginning of your speech needs an attention-grabber to get your audience interested right away. Choose your attention-grabbing device based on what works best for your topic. Your entire introduction should only be around 10 to 15 percent of your total speech, so be sure to keep this section short. Here are some devices that you could try:
| – to the point, but not the most interesting choice. | |
| – highlights something common to the audience that will make them interested in the topic. | |
| – wise words of another person. You can find quotations online that cover just about any topic. | |
| – refer to a current event in the news that demonstrates the relevance of your topic to the audience. | |
| – Compare or contrast your topic with an occasion in history. | |
| – An anecdote is a brief account or story of an interesting or humorous event, while a parable or fable is a symbolic tale designed to teach a life lesson. | |
| – A strange fact or statistic related to your topic that startles your audience. | |
| – You could ask either a question that asks for a response from your audience, or a rhetorical question, which does not need a response but is designed to get them thinking about the topic. | |
| – A joke or humorous quotation can work well, but to use humour you need to be sure that your audience will find the comment funny. You run the risk of insulting members of the audience, or leaving them puzzled if they don’t get the joke, so test it out on someone else first! | |
| – Refer to a story about yourself that is relevant to the topic. |
After the attention-getter comes the rest of your introduction. It needs to do the following:
- Capture the audience’s interest
- State the purpose of your speech
- Establish credibility
- Give the audience a reason to listen
- Signpost the main ideas
Once you have identified an attention-getting, it is time to develop the body of your presentation or speech. In your body, you will focus on the specific points you would like to communicate to your audience.
Rhetoric and Argument: Your audience will think to themselves, Why should I listen to this speech? What’s in it for me? One of the best things you can do as a speaker is to answer these questions early in your body, if you haven’t already done so in your introduction. This will serve to gain their support early and will fill in the blanks of who, what, when, where, why, and how in their minds.
Organization: An organized body helps your audience to follow your speech and recall your points later. When developing the body of your speech, recall the specific purpose you decided on, then choose main points to support it. Just two or three main points are usually sufficient, depending on the length of your speech. Anticipate one main point per two to three minutes of speaking.
Concluding on a High Note
You’ll need to keep your energy up until the very end of your speech. In your conclusion, your job is to let the audience know you are finished, help them remember what you’ve told them, and leave them with a final thought or call-to-action, depending on the general purpose of your message.
Presentation Aids
Presentations can be enhanced by the effective use of visual aids. These include handouts, overhead transparencies, drawings on the whiteboard, PowerPoint slides, and many other types of props. Once you have chosen a topic, consider how you are going to show your audience what you are talking about. Visuals can provide a reference, illustration, or image to help the audience to understand and remember your point.
Visual aids accomplish several goals:
- Make your speech more interesting
- Enhance your credibility as a speaker
- Guide transitions, helping the audience stay on track
- Communicate complex information in a short time
- Reinforce your message
- Encourage retention
Methods and Materials
There are many different presentation aids available. Before you decide on a presentation aid, think carefully about how you plan on using it and how it will enhance your presentation.
|
| The most common visual aid used in presentations, slide decks may be developed using software such as PowerPoint, Keynote, Prezi, or Google Slides. These tools allow you to show text, images, and charts and even to play audio or video files. They are an excellent enhancement to your presentation, | |
|
| Flip charts and whiteboards are a good choice when you don’t have access to a computer and projector. Alternatively, you can print some visual aids like charts and graphs in large sizes and show them during your presentation. If you plan to get a lot of audience input and want to write or draw things out, then a whiteboard is an ideal choice. | |
|
| If it will be helpful for your audience to refer to the information you’re sharing at a later date, they’ll appreciate it if you leave them with a handout. But never give handouts to the audience at the beginning of your speech. They will be distracted by reading and tune you out. | |
|
| If your presentation is about how to do something, for example, how to cook a particular dish or how to use a tool, you will want to show the audience a demonstration. Sometimes it is helpful to pass around a tactile aid, for example, a model. These can be very helpful if you want your audience to learn by doing |
Using Visual Aids
Visual aids can be a powerful tool when used effectively but can run the risk of dominating your presentation. Consider your audience and how the portrayal of images, text, graphic, animated sequences, or sound files will contribute or detract from your presentation. Here are some tips to keep in mind as you prepare yours.
Designing Slide Decks
When you design your slide decks, you might be overwhelmed by the possibilities, and you might be tempted to use all the bells, whistles, and sounds, not to mention the flying, and animated graphics. If used wisely, a simple transition can be effective, but if used indiscriminately, it can annoy the audience to the point where they cringe in anticipation of the sound effect at the start of each slide.
Stick to one main idea per slide. The presentation is for the audience’s benefit, not yours. Pictures and images can be understood more quickly and easily than text, so you can use this to your advantage as you present.
If you develop a slide deck for your presentation, test these out in the location beforehand, not just on your own computer screen, as different computers and software versions can make your slides look different than you expected. Allow time for revision based on what you learn.
Your visual aids should meet the following criteria:
- Big: legible for everyone, even the back row
- Clear: easy for audience to understand
- Simple: simplify concepts rather than complicating them
- Consistent: use the same visual style throughout

In Figure 18.3 the slide deck on the left has a colour combination which makes the information difficult to understand. The list is not parallel and the slide contains a grammatical error. The slide deck on the right is an improved and more professional version.
Another consideration that you’ll need to make when designing your slide decks is font. As previously mentioned, think about the people at the back of the room when choosing the size of your text, to make sure it can be read by everyone. A common mistake that presenters make is to use decorative fonts or to incorporate many different fonts in their slides. This not only creates a mixed message for the audience but also makes your message difficult to read. Choose legible, common fonts that do not have thin elements that may be difficult to see.
When considering your choice of colours to use, legibility must be your priority. Contrast can help the audience read your key terms more easily. Make sure the background colour and the images you plan to use complement each other. Repeat colours, from your graphics to your text, to help unify each slide. To reduce visual noise, try not to use more than two or three colours. Blue-green colour blindness, and red-green colour blindness are fairly common, so avoid using these colour combinations if it is important for the audience to differentiate between them. If you are using a pie chart, for example, avoid putting a blue segment next to a green one. Use labelling so that even if someone is colour blind, they will be able to tell the relative sizes of the pie segments and what they signify.
Colour is also a matter of culture. Some colours may be perceived as formal or informal, or masculine or feminine. Certain colours have understood meanings; for example, red is usually associated with danger, while green signals “go.” Make sure the colours you use align with your message. If you are discussing climate change or the natural world, for example, you’d be more likely to use blues and greens rather than metallic colours to avoid confusing the audience.
Once you have prepared your visual aid, do not forget to revise. There is nothing more uncomfortable than seeing a typo or grammatical error on your screen in the middle of your presentation. These errors can create a bad impression and affect your credibility with the audience. You want your audience to focus on your message so be sure to revise to maintain the audience’s attention and keep your credibility.
Preparing to Present
You are almost ready to deliver your presentation. What are some final elements you can focus on to ensure a smooth delivery?
To deliver your presentation to the best of your ability, and to reduce your nerves once you take the stage, you need to practise by rehearsing. As you do, try to identify the weaknesses in your delivery to improve on them. For example, do you often misspeak the same words (e.g., pacific for specific; ax for ask) or do your hands or feet fidget? Use your practice time to focus on correcting these issues. These sessions should help you get comfortable and help you remember what you want to say without having to constantly refer to notes. Try practising in front of a mirror, or even recording yourself speaking to a camera and playing it back. It’s also helpful to get feedback from a supportive audience at this stage. Perhaps a few family members or friends could watch you give your presentation and provide some feedback.
Dress for Success
While there are no definitive guidelines for how you should dress for your presentation, your appearance is an important part of your audience’s first impression. If you want them to take you seriously, you’ll need to look the part. While you don’t have to wear a suit each time you present, there are some scenarios where this would be expected; for example, if you are presenting to a corporate audience who wear suits to work, you should do the same. You should dress one step above your audience. If your audience is going to be dressed casually in shorts and jeans, then wear nice casual clothing such as a pair of pressed slacks and a collared shirt or blouse. If your audience is going to be wearing business casual attire, then you should wear a dress or a suit. The general rule is to avoid any distractions in your appearance that can distract your audience’s attention from your message.
Set Up Your Environment
Depending on the circumstances of your speech or presentation, you may have some choices to make about the environment. Perhaps you have a choice of meeting rooms that you can use, or, perhaps you have only one option. If you have some flexibility, it is helpful to think about what sort of environment would best help you get your message across. For example, if you are running a workshop, you might want to assemble participants in a circle to encourage collaboration and discussion. If you are holding a webinar, you’ll need a quiet location with a strong Internet connection and a computer system. It is imperative that you think about what facilities you need well before the day of your presentation arrives. Arriving to find that the equipment you expected isn’t available is not a nice surprise for even the most experienced speaker!
If you have access to the location beforehand, you may need to move tables or chairs around to get things just the way you want them. You might choose to have a podium brought in, if you are aiming for a formal feel, for example, or you may need to position your flip chart. Double-check that you have all the equipment you need, from whiteboard markers to speakers. It is far better if you can get comfortable with the room before your audience arrives, as this will make you feel more prepared and less nervous.
If you are using technology to support your presentation (i.e., PowerPoint slides or a projector), test everything before you begin. Do a microphone check and test its volume, view your slides on the computer you will be using, check any weblinks, play videos to test their sound, or make a call to test the phone connection prior to your teleconference. Your audience will get restless quickly if they arrive and are expected to wait while you fix a technical problem. This will also make you seem disorganized and hurt your credibility as an authoritative speaker.
During the Presentation
You’ve organized your presentation with great visuals and you are ready to present. You now have to deliver your presentation. How do you effectively deliver your presentation calmly and clearly?
Managing Anxiety
Studies have been done to assess how nervous or stressful people typically get during presentations, by examining people’s physiological responses at three intervals: one minute before the presentation, the first minute of the speech, and the last minute of the speech. They discovered that nervousness usually peaked at the anticipation stage that occurs one minute before the presentation. They further found that as the speech progresses, nervousness tends to go down. Here are some things you can do to help you manage your anxiety before the presentation:
- Practice/rehearse in similar conditions/setting as your speech
- Be organized
- Think positively
- Analyze your audience
- Adapt your language to speaking style
During the presentation, there are four main areas where you can focus attention in order to manage your anxiety:
- Your body’s reaction
- Attention to the audience
- Keeping a sense of humour
- Common stress management techniques
Your Body’s Reaction
Physical movement helps to channel some of the excess energy that your body produces in response to anxiety. If at all possible, move around the front of the room rather than remaining behind the lectern or gripping it for dear life (avoid pacing nervously from side to side, however). Move closer to the audience and then stop for a moment. If you are afraid that moving away from the lectern will reveal your shaking hands, use note cards rather than a sheet of paper for your outline. Note cards do not quiver like paper, and they provide you with something to do with your hands. Other options include vocal warm-ups right before your speech, having water (preferably in a non-spillable bottle with a spout) nearby for dry mouth, and doing a few stretches before going on stage. Deep breathing will help to counteract the effects of excess adrenaline. You can place cues or symbols in your notes, such as “slow down” or “smile”, that remind you to pause and breathe during points in your speech. It is also a good idea to pause a moment before you get started to set an appropriate pace from the onset. Look at your audience and smile. It is a reflex for some of your audience members to smile back. Those smiles will reassure you that your audience members are friendly.
Attention to the Audience
During your speech, make a point of establishing direct eye contact with your audience members. By looking at individuals, you establish a series of one-to-one contacts similar to interpersonal communication. An audience becomes much less threatening when you think of them not as an anonymous mass but as a collection of individuals.
Keeping a Sense of Humour
No matter how well we plan, unexpected things happen. That fact is what makes the public speaking situation so interesting. If things go wrong, try to have a sense of humour and stay calm. The audience will respond better if you stay calm than if you get upset or have a breakdown.
Stress Management Techniques
Even when we use positive thinking and are well prepared, some of us still feel a great deal of anxiety about public speaking. When that is the case, it can be more helpful to use stress management than to try to make the anxiety go away. Here are two main tools that can help:
- Visualization: imagining the details of what a successful speech would look and sound like from beginning to end; a way of hypnotizing yourself into positive thinking by using your mind’s eye to make success real.
- Systematic desensitization: Gradual exposure to the thing that causes fear—in this case, giving a speech—can ultimately lead to decreased anxiety. Basically, the more practice you get speaking in front of people, the less fear and anxiety you’ll have about public speaking. Organizations like Toastmasters that help people confront their fears by providing a supportive environment to learn and practise is a good option if you have a true phobia around presenting or public speaking.
Focus on Verbal Communication Techniques
- Pitch : Use pitch inflections to make your delivery more interesting and emphatic. If you don’t change pitch at all, your delivery will be monotone, which gets boring for the audience very quickly.
- Volume : Adjust the volume of your voice to your environment and audience. If you’re in a large auditorium, speak up so that people in the back row can hear you. But if you’re in a small room with only a few people, you don’t want to alarm them by shouting!
- Emphasis : Stress certain words in your speech to add emphasis to them, that is, to indicate that they are particularly important.
- Pronunciation : Make sure that you know the appropriate pronunciation of the words you choose. If you mispronounce a word, it could hurt your credibility or confuse your audience. Your pronunciation is also influenced by your accent. If your accent is quite different from the accent you expect most members of your audience to have, practise your speech in front of someone with the same accent that your audience members will have, to ensure you are pronouncing words in a clear, understandable way.
- Fillers : Avoid the use of “fillers” as placeholders for actual words (like, er, um, uh, etc.). If you have a habit of using fillers, practise your speech thoroughly so that you remember what you want to say. This way, you are less likely to lose your place and let a filler word slip out.
- Rate : The pace that you speak at will influence how well the audience can understand you. Many people speak quickly when they are nervous. If this is a habit of yours, practice will help you here, too. Pause for breath naturally during your speech. Your speaking rate should be appropriate for your topic. A rapid, lively rate communicates enthusiasm, urgency, or humour. A slower, moderated rate conveys respect and seriousness.
Focus on Non-verbal Communication Techniques
- Gestures : You can use your hands or head to help you express an idea or meaning, or reinforce important points, but they can be distracting if overused. If the audience is busy watching your hands fly around, they will not be able to concentrate on your words.
- Facial Expression : Rehearse your speech in front of a mirror to see what facial expressions come across. If you are speaking about an upbeat topic, smile! Conversely, if your topic is serious or solemn, avoid facial expressions that are overtly cheerful, because the audience will be confused by the mixed message. In North American culture, the most important facial expression you can use is eye contact. Briefly catch the eye of audience members as you move through your speech. If you can’t look your audience members in the eye, they may view you as untrustworthy. You’ll want to avoid holding eye contact for too long with any one person, as too much can be unnerving.
- Posture : Try to stay conscious of your posture and stand up straight. This gives the audience the perception that you are authoritative and take your position seriously. If you are slouching, hunched over, or leaning on something, this gives the impression that you are anxious, lacking in credibility, or not serious about your message.
- Silence : Silence is a powerful technique if used well. Pauses are useful for emphasis and dramatic effect when you are speaking. Some speakers are reluctant to pause or use silence because they become uncomfortable with the dead air, but sometimes your audience needs a moment to process information and respond to you.
- Movement : You can use your body movements to communicate positively with the audience. Leaning in or moving closer to the audience helps to bridge the space of separation. Moving from one side of the room to the other in a purposeful way that supports your content is a useful way to keep your audience engaged; their eyes will track your movements. However, pacing rapidly with no purpose and no support to your message may quickly distract from your message.
Coping with Mistakes and Surprises
Even the most prepared speaker will encounter unexpected challenges from time to time. Here are a few strategies for combating the unexpected in your own presentations.
Speech Content Issues
What if a notecard goes missing or you skip important information from the beginning of your speech? Pause for a moment to think about what to do. Is it important to include the missing information, or can it be omitted without hindering the audience’s ability to understand your speech? If it needs to be included, does the information fit better now or in a later segment? If you can move on without the missing element, that is often the best choice, but pausing for a few seconds to decide will be less distracting to the audience than sputtering through a few “ums” and “uhs.” Situations like these demonstrate why it’s a good idea to have a glass of water with you when you speak. Pausing for a moment to take a sip of water is a perfectly natural movement, so the audience may not even notice that anything is amiss.
Technical Difficulties
Technology has become a very useful aid in public speaking, allowing us to use audio or video clips, presentation software, or direct links to websites. But it does break down occasionally! Web servers go offline, files will not download, or media contents are incompatible with the computer in the presentation room. Always have a backup plan in case of technical difficulties. As you develop your speech and visual aids, think through what you will do if you cannot show a particular graph or if your presentation slides are garbled. Your beautifully prepared chart may be superior to the verbal description you can provide. However, your ability to provide a succinct verbal description when technology fails will give your audience the information they need and keep your speech moving forward.
External Distractions
Unfortunately, one thing that you can’t control during your speech is audience etiquette, but you can decide how to react to it. Inevitably, an audience member will walk in late, a cell phone will ring, or a car alarm will go off outside. If you are interrupted by external events like these, it is often useful and sometimes necessary to pause and wait so that you can regain the audience’s attention. Whatever the event, maintain your composure. Do not get upset or angry about these glitches. If you keep your cool and quickly implement a “plan B” for moving forward, your audience will be impressed.
Reading Your Audience
Recognizing your audience’s mood by observing their body language can help you adjust your message and see who agrees with you, who doesn’t, and who is still deciding. With this information, you can direct your attention—including eye contact and questions—to the areas of the room where they can have the most impact. As the speaker, you are conscious that you are being observed. But your audience members probably don’t think of themselves as being observed, so their body language will be easy to read.
Handling Q&A
Question-and-answer sessions can be trickier to manage than the presentation itself. You can prepare for and rehearse the presentation, but audience members could ask a question you hadn’t considered or don’t know how to answer. There are three important elements to think about when incorporating Q&As as part of your presentation:
1. Audience Expectations
At the beginning of your speech, give the audience a little bit of information about who you are and what your expertise on the subject is. Once they know what you do (and what you know), it will be easier for the audience to align their questions with your area of expertise—and for you to bow out of answering questions that are outside of your area.
2. Timing of Q&As
Questions are easier to manage when you are expecting them. Unless you are part of a panel, meeting, or teleconference, it is probably easier to let the audience know that you will take questions at the end of your presentation. This way you can avoid interruptions to your speech that can distract you and cause you to lose time. If audience members interrupt during your talk, you can then ask them politely to hold on to their questions until the Q&A session at the end.
3. Knowing How to Respond
Never pretend that you know the answer to a question if you don’t. The audience will pick up on it! Instead, calmly apologize and say that the question is outside of the scope of your knowledge but that you’d be happy to find out after the presentation (or, suggest some resources where the person could find out for themselves). If you are uncertain about how to answer a question, say something like “That’s really interesting. Could you elaborate on that?” This will make the audience member feel good because they have asked an interesting question, and it will give you a moment to comprehend what they are asking. Sometimes presenters rush to answer a question because they are nervous or want to impress. Pause for a moment, before you begin your answer, to think about what you want to say. This will help you to avoid misinterpreting the question or taking offense to a question that is not intended that way.
A final tip is to be cautious about how you answer so that you don’t offend your audience. You are presenting on a topic because you are knowledgeable about it, but your audience is not. It is important not to make the audience feel inferior because there are things that they don’t know. Avoid comments such as “Oh, yes, it’s really easy to do that…” Instead, say something like “Yes, that can be tricky. I would recommend…” Also, avoid a bossy tone. For example, phrase your response with “What I find helpful is…” rather than “What you should do is…”
Good presentation skills are important to successfully communicate ideas in business. Make sure your presentation has a clear topic with relevant supporting details. Use verbal and non-verbal communication techniques to make your presentation engaging, and don’t forget to practice!
End of Chapter Activities
18a. thinking about the content.
What are your key takeaways from this chapter? What is something you have learned or something you would like to add from your experience?
18b. Discussion Questions
Discussion Questions
- How can a speaker prepare a presentation for a diverse audience? Explain and give some specific examples.
- How can an audience’s prior knowledge affect a presentation?
- Think of someone you have met but do not know very well. What kinds of conversations have you had with this person? How might you expect your conversations to change if you have more opportunities to get better acquainted? Discuss your thoughts with a classmate.
- While managing a Q&A session following a presentation, if you find yourself unable to answer a question posed by one of the audience members which tactics can you use to maintain control of the session?
18c. Applying chapter concepts to a situation
Presenting for success
Akhil works at a software development company in White Rock called Blackball Technologies. It is a medium-sized company that allows its employees to dress casually and occasionally work from home. Akhil likes this because his preference is to wear t-shirts and jeans to the office or work from home in his pyjamas.
Blackball recently created a new software program that has the potential to make a huge profit. However, they need investors to fund their latest innovation. The new software was developed using one of Akhil’s ideas; therefore, the company chooses him to present their proposal to a diverse group of investors from several countries.
Some of the investors are not fluent in English as it is their second language. Additionally, they each have a busy day ahead as they have to listen to proposals from multiple companies. Akhil fears that the investors will not understand him. He is also nervous about the presentation due to its significance to his career. If he is successful, he will get the promotion that he has wanted for the past two years and a pay raise.
What are some of the things that Akhil should consider when presenting to the investors?

18d. Writing Activity
Watch this video from TED.com on The Secret Structure of Great Talks . Summarize the video. What is the most interesting point made by Nancy Duarte in your opinion?
Attribution
Content attribution.
This chapter contains information from Professional Communications OER by the Olds College OER Development Team used under a CC-BY 4.0 international license.
This chapter contains information from Business Communication for Success which is adapted from a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-SA) in 2010 by a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution. This adapted edition is produced by the University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing through the eLearning Support Initiative .
Media Attribution
Presentation icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com .
Whiteboard icon made by Phatplus from www.flaticon.com .
Handout icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com .
Demonstration icon made by Ultimatearm from www.flaticon.com .
Chapter 18: Business Presentations Copyright © 2020 by Venecia Williams and Olds College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- List of Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Opt-out preferences
The 7 C’s of Effective Communication – Explained with Examples
An effective communication takes place when the message sent across by the conveyer is clear and easily comprehended by the receiver and relevant response is fed back to the one who conveyed the message and the flow continues similarly.

Source: Kurhan/Adobe Stock
Although communication takes place at all times, if it is done effectively is a matter of dispute. For the most part, people don’t communicate efficiently, and this has been one of the predominant contributors to interpersonal conflicts.
Lack of proper listening, psychological conditions, poor comprehension skills, absence of mind, ambiguity in the message conveyed, and improper usage of words are some of the most frequently occurring mistakes during conversations.
So what makes communication effective? What are some of the tips and strategies that can be applied when communicating in general?
We are constantly in touch with people, texting, sending emails, creating reports, attending conferences and whatnot. So how can we scale up our communication game? What would make us stand out and seem distinctive in this world swarming with competitors?
The 7 C’s of Effective Communication
The 7 C’s of communication is an excellent strategy formulated by Scott Cutlip and Allen Center in the year 1952 in his book “Effective public relations”. This came to be utilized by people across the globe and is one of the most operative strategies used to date.
It involves the following C’s:
- Completeness
- Correctness
- Conciseness
- Consideration
- Concreteness
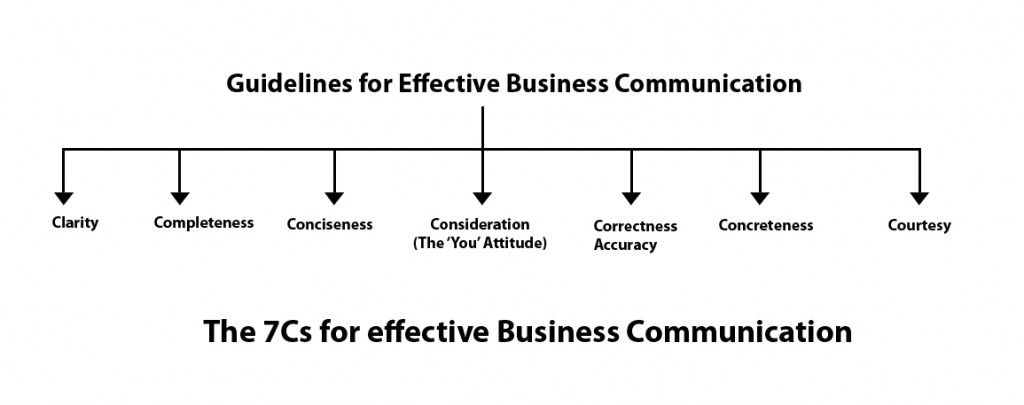
These strategies apply to both written and oral communication . The one who is aware of and makes use of these 7C’s in a sensible manner can become a good and effective communicator.
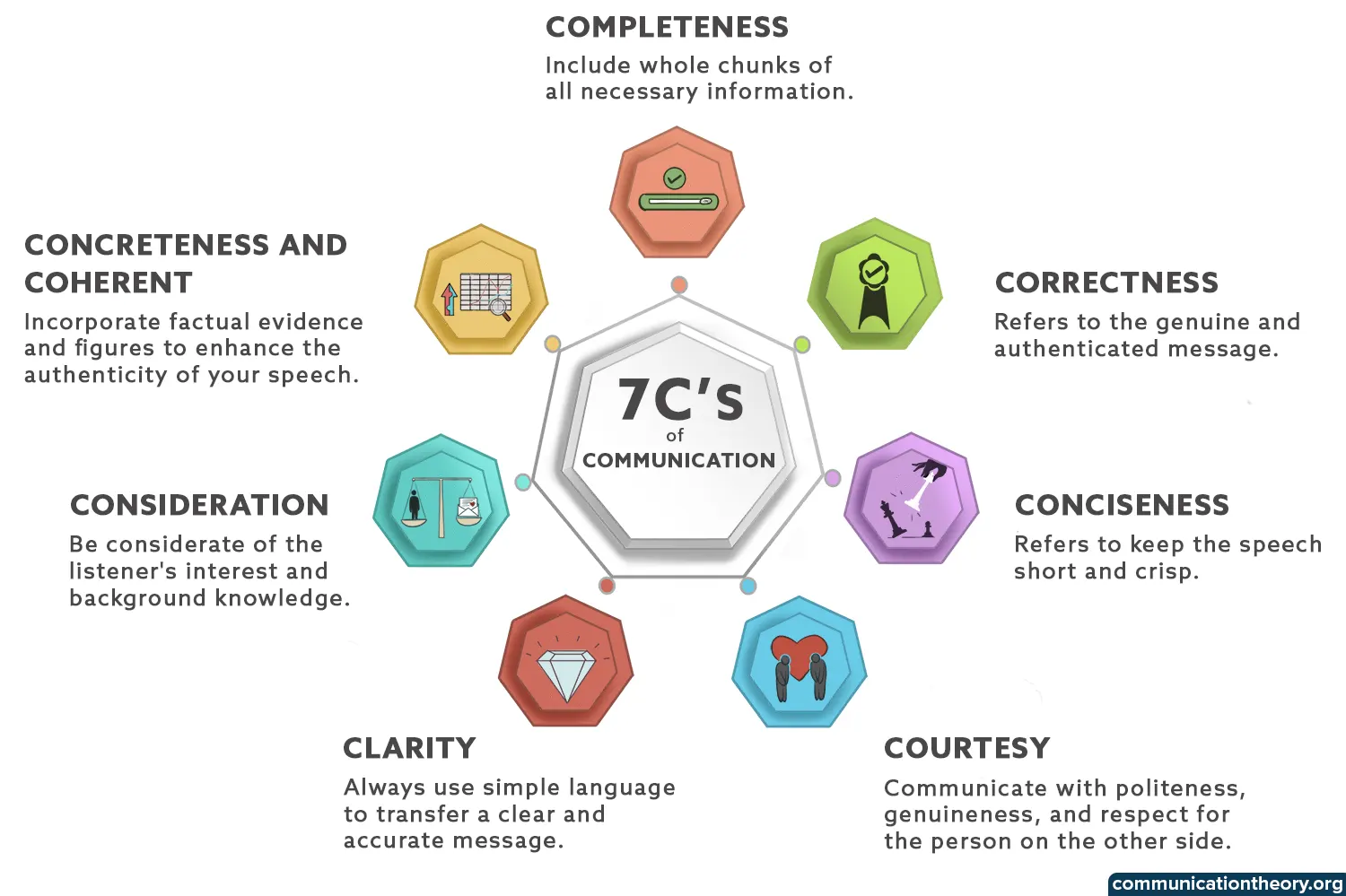
1. Completeness
This is one of the most significant aspects of effective communication . Completeness refers to giving full information about something rather than just saying it in bits and pieces. It’s the right of the recipient to receive access to the whole chunk of information to be able to follow the sender’s line of reasoning in regards to the matter being discussed.
For example, when Peter told “write a short passage on data science and send me”, Shawn couldn’t understand the context whatsoever. He had too many questions in his head about the topic, its length and the style of writing, where this piece of writing go etc.
Instead, Peter could frame his instructions as “Shawn I want you to write a 100-200 word short essay on the recent trends in data science. Submit it to me by the end of this day. I need it for our blog.”
Completeness holds much higher salience during the delegation of tasks when the subordinates need detailed instructions to pursue a task at hand.
2. Correctness
The genuineness and the value of your speech lie in its correctness and authenticity. It’s better to keep quiet rather than talk about something that you aren’t so sure of. The correctness of the speech would reflect directly on your personality and so it should be given utmost prominence.
The legitimacy of the factual information, the language used and grammar are some of the aspects of correctness amongst others.
If your audience spots any errors or blunders in your speech, it is no longer valued and they are likely to be distracted. The credibility of the speaker would also receive a massive hit and therefore the effectiveness of the communication will be compromised.
Related: Language Barriers
3. Conciseness
Conciseness is to keep the speech short and crisp. Nobody likes listening to someone who delivers long and draggy speeches because people lose interest and attention very easily. When interacting or delivering the speech, the ultimate objective is to make sure that the message is received in its intended form. Lack of conciseness will lead to the loss of essence in the content. Make sure to keep your speech brief and precise.
For example,
Intended message: “could you please receive Amanda from the airport?”
Delivered method: “Yesterday was a tiring day. Last night I couldn’t sleep properly. My wife has severe migraine and she’s down. I couldn’t have breakfast in the morning and I am tired. Amanda has taken her flight from Indonesia last night. She would reach here in some time. It would be nice if someone could pick her up from the airport.”
In this example, the message was simple. Yet, the sender makes it seem complicated and leaves the recipient feeling puzzled, irritated or exhausted. Also, he may deny the request. Such delivery of a message makes the message lose its value.
Related: Semantic Barriers
4. Courtesy
Courtesy refers to communicating with politeness, genuineness and respect for the person on the other side of the conversation. It will naturally scale up the value of communication. Courtesy is a tendency which stems out of empathy for people.
To be courteous doesn’t mean just use polite, magical phrases like “thank you”, “sorry”, “please” and “excuse me”. It also means to be honest, respectful and empathetic of people and not make sarcastic or any other form of passive-aggressive remarks.
One classic example would be from the infamous movie “Mean Girls” where Regina would tell a fellow classmate about how she loves the skirt she was wearing. As the girl leaves, Regina would tell her friend Cady how that was the ugliest skirt she has ever seen. This is an example of how you should not communicate.
In many instances, people use the power of their intellect and status to belittle the plight of others. This is so especially among those who bully the perceivably weaker ones for their timidity, racial backgrounds, gender, and color among many other aspects.
The global star Priyanka Chopra narrates in an interview about her high school days when she was severely bullied by her schoolmates. She was called names like “brownie” for her skin color and her ethnicity so much so that she was forced to have lunch inside a toilet cubicle.
Related: Assertive Communication
Clarity is to transfer accurate and easily comprehendible messages to the receiver. Before choosing to talk, be clear about your goals for the conversation. Let the other person know what your objective is for the interaction. To make your speech clear, always use simple language rather than using intricate phrases that would make comprehension difficult.
The recipient shouldn’t be made to “read between the lines”. Even if the content is complicated in nature, try to divide your ideas, distill it and make it as simple and clear as possible as that would make it easy for the receiver to grasp the information well.
6. Consideration
Consideration is quite similar to that of courtesy. It means to consider the other person and to address them putting you in their place. In other words, you talk to someone in a way you would want someone to talk to you.
For example, if you prefer someone to talk to you with respect and politeness, you would exhibit the same behaviors towards others. Just as that of courtesy, one should be inherently empathetic to be able to show consideration for the other person. When you are considerate, you sincerely regard people’s interests and benefits.
To be considerate also means to acknowledge the situational factors of the audience that you address. If you are going to give a talk on astrophysics amongst a bunch of seven-year-olds, the only response you would receive would be the sound of yawning and snoring; maybe even a giggle here and there if you’re lucky.
So when you talk to someone, remember to acknowledge their background such as their age, language proficiency, culture, literacy level, mental state, character, interests etc. so that you may be relatable to your audience and your intended message reaches them successfully.
7. Concreteness
Concrete communication denotes your message being specific, meaningful and focused. You don’t beat around the bush to get to a point. Rather it is solid and concise. You avoid vague and ambiguous messages and only strive toward making your information well received by the recipient. Your speech is crisp yet brimming with beneficial information. You incorporate factual evidence and figures to enhance the authenticity of your speech.
For example, when you say “Depression is a global issue”, you don’t just bluntly make that claim but also pitch in the statistical values and empirical evidence to support your statement.
And now, for your upcoming presentations make sure to follow these strategies and show up your confidence. These effective strategies may take you to the place of success at your workplace.
Best of luck!
Related Posts:
- Various Types Of Communication Styles - Examples
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Conflict Management - Skills, Styles And Models
- Active Listening Skills - Techniques And Tips To Practice It
- Most Important Social Skills - Explained With Examples
- Kinds (Types) of Communication employed by Business…
these are the best or very good note that helps me in hawassa university while learning the business communication.
Assalamaoalikum ! Sir please give me full detail in one by one …thankyou
do you have complete intodution to 7Cs of effective bussiness communication?
I want to get detail of these seven c’s .Thank you
please whould you like to send thise cs in detail
please so the detail of 7c’s thanks …………………………………………………..
plz give me more detail
give more detail but notes is best
plz give me defination of each c’s
kindly give the explanation of these C’s.
Good post thank
I want to know more about the seven c’s
This is very very helpfull in my exam Thank you so much for all your efforts. This is best and very simple to understand.
This is very helpful, thanks for your post.
Ma sha Allah very gud and informative…
Leave a Comment
Next post: Clarity/Clearness for effective business Communication
Previous post: Features of Business Communication
- Advertising, Public relations, Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- Business Communication
- Communication / General
- Communication Barriers
- Communication in Practice
- Communication Models
- Cultural Communication
- Development Communication
- Group Communication
- Intercultural Communication
- Interpersonal Communication
- Mass Communication
- Organisational Communication
- Political Communication
- Psychology, Behavioral And Social Science
- Technical Communication
- Visual Communication
Communication Theory

5 reasons “Clarity” is most important component of communication

What’s the cost of unclear communication?
If you asked this question to Pepsi executives in 1996, they would have said $33 million.
Yes, in 1996, a man named John Leonard sued Pepsi over a commercial that promised a harrier jet worth 33 million US dollars.
Well, the whole lawsuit was based on a lack of clarity in Pepsi’s commercial tagline.

When it comes to effective communication, one aspect that stands above all: clarity.
Clarity is incredibly important in business communication.
You need to make sure your message is clear and easy to understand while communicating with colleagues, clients, or customers. Clarity in communication helps to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts that can be costly in terms of time, money, and reputation.
In this blog, we will explore five reasons why clarity is the most important aspect of effective communication. And how it can make a significant difference in our lives.
So, let’s dive in.

5 Reasons Why Clarity Is Important in Communication? 1. Provides Guidance 2. Defines Purpose 3. Engages Listeners 4. Enables Persuasion 5. Avoids Misinterpretations
What is Clarity in Communication?
Clarity in communication means ensuring what you say is easy to understand for others. Clear communication encompasses not only clarity of speech but also clarity of message, intent, and context.
It means that the language, vocabulary , tone, and context are clear and straightforward, without any confusion or ambiguity among listeners.
By following the principle of clarity, we can build better relationships, foster understanding, and achieve success in our communication.
“If you can’t explain it to a six-year-old, you don’t understand it yourself.” – Albert Einstein

There are many factors that can make clear & concrete communication hard, such as:
- Language barriers: It’s difficult to convey your message accurately if your listener speaks a different language.
- Cultural differences: Different communication styles and norms across cultures make achieving clarity difficult.
- Emotional factors: Our emotions affect how we communicate. You may find it hard to express yourself clearly when you are upset or angry.
- Technical jargon : In some fields, there is a lot of technical jargon that makes it hard for non-experts to understand.
- Distractions: Digital distractions, such as notifications and social media, can interfere with our ability to focus on communication.
- Poor Communication skills: Lack of clarity can also result from poor communication skills, such as speaking too fast, using too many filler words , or failing to organize our thoughts before speaking or writing.
Now that we understand the meaning of clarity let’s see why it is the number one aspect among the 7 c’s of communication.
1. Clarity Provides Guidance
The term “clarity” is derived from the Latin word “clarus,” which means “clear,” and this is precisely what clear communication aims to achieve.

In today’s communication environments, there is often an overload of information. People are bombarded with messages from various sources, including social media, email, and text messages.
But communication can often be meaningless if it’s not clear. Additionally, there is often incorrect information, news, and data being circulated via social media platforms.
People will ignore messages that are ambiguous or confusing, and as a result, the intended message can be lost. If you can’t hold people’s attention, you can’t be a good presenter.
The clarity in your message ensures it stands out and is understood.
This allows the listener to make informed decisions based on the information provided, leading to better outcomes.
For example, if the manager communicates the project goals clearly to the team, the team will have a clear understanding of what is expected of them.
This clarity provides guidance and direction for the team, allowing them to work towards the project’s objectives more efficiently.
2. Clarity Defines Purpose
When you communicate with clarity, you can clearly convey your goals and intentions to your listeners. This is particularly important in business, where your purpose is defined by your ambitions, actions, plans, and principles.
Clarity of speech ensures that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same objectives.

For example, if your ambition is to make your company a leader in our industry, then you need to be clear in communicating this ambition to your employees, customers, and partners. You need to explain how you plan to achieve it and what actions you will take to make it a reality.
Now, this requires clear and effective communication that aligns with your values and principles.
If the message is not clear, team members may not fully comprehend the company’s objectives, leading to confusion.
Finally, our principles and values play a key role in defining our purpose and communicating it to others. We need to be clear in communicating our values, such as integrity, honesty, and transparency, to ensure that we build trust and credibility with our stakeholders.
3. Clarity Engages Listeners
Clear communication captures the attention of your audience . It makes it easy for them to follow along with your message.

This is crucial when you are presenting complex information. People lose interest and stop caring if they find themselves struggling to understand your speech. They will tune out.
Clarity and simplicity in communication relieve your listeners of the burden of interpretation.
Imagine you are attending a lecture on a complex topic like quantum physics.
If the speaker uses jargon and technical terms that you are not familiar with, it can be difficult to follow along with their message. However, if they use clear, concise language that explains the concepts in simple terms, it becomes easier to understand and engage with the topic.
And when you engage your listeners, they are more likely to remember your message and act on it.
Simplicity is a powerful tool that helps to enhance the effectiveness of communication.
4. Clarity Enables Persuasion
Persuasion is an important principle of business communication. **Clear and concise communication plays a huge role in acquiring the ability to persuade others.

Whether it’s convincing your team members to meet deadlines, negotiating a deal, or convincing customers to buy a product or service. Clear and concise messaging is key to achieving your objectives.
Clarity helps to ensure that your message is understood. And your audience can see the benefits of taking action.
Trust and credibility are critical for effective persuasion. People will trust you if they believe in your speech. And people will believe you if they clearly understand your arguments.
A confusing message makes persuasion difficult. This can result in missed opportunities, lost sales, and other negative consequences for our business.
On the other hand, better persuasion with clear communication can lead to greater productivity, improved morale, and better results for our business.
5. Clarity Avoids Misinterpretations
Unclear communication has a greater risk that your message will be misunderstood or misinterpreted, which can lead to mistakes, conflicts, or even failures.
Your audience may make assumptions and draw their own conclusion, as happened in the Pepsi lawsuit mentioned in the beginning.

For example, imagine that you are giving instructions to a colleague at work. If your instructions are not clear, your colleague may not understand and may end up doing the task incorrectly. This can result in wasted time and resources, as well as frustration for both you and your colleague.
There are higher chances of misunderstanding while communicating under stress.
One way to test the clarity of our message is to use a simple exercise.
First, share one sentence with no less than ten words and no more than 15 with a person or group.
Then ask them to repeat it back to you verbatim.
If they can recall the message exactly, then your message was clear and easy to understand.
If not, try to simplify and bring more clarity to your message, still keeping it concise.
This helps to reduce misinterpretation and failure in communication, leading to better outcomes and more effective communication.
Final Thoughts
Clear communication is essential in every aspect of life, from personal relationships to business transactions. Without clarity, misunderstandings can occur, trust can be lost, and resources can be wasted.
Therefore, it is important to make a conscious effort to communicate clearly in all situations. This means taking the time to choose the right words, providing context and background information where necessary, and checking for understanding.
Though the responsibility for clarity in communication is always on the communicator, it is equally important for a listener to ensure clarity in communication.
It’s essential to actively engage in the communication process and seek clarification when needed. This means asking questions, paraphrasing the message, and seeking feedback.
Lastly, it’s essential to work on improving your communication and language skills, including public speaking , to communicate clearly. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you will become in expressing your thoughts and ideas clearly and concisely.
One way to improve your communication skills is to get a personal coach.
A personal communication expert helps you target your specific issues, such as grammar, vocabulary, public speaking, confidence, tonality, etc.
BBR English is a great platform to ensure personalized learning through live 1:1 interactive sessions. You’ll learn and practice techniques of effective communication from experts with corporate experience. A supportive environment and timely feedback help you accelerate your learning process and feel more confident.
Start your journey to clear communication by booking a counseling session with us today.
And join the hundreds of effective communicators who wrote their own success stories.
Thank you for reading.
who needs to see our story? Share this content
- Opens in a new window
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- 🌟 Expert advice on improving your spoken skills
- 📚 Engaging language learning resources
- 📆 Weekly tips to boost your spoken English
- 🎉 Exciting updates about our courses and events
- I agree to receiving marketing emails and special deals
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Communicate Your Company’s Strategy Effectively
- David Lancefield

Ditch the lofty purpose statements and lengthy slide decks.
For too long, communicating strategy has been an afterthought. Executives have shared long, bombastic documents or withheld critical information and expected people to just “get it.” And it hasn’t worked. Greater external uncertainty, collaboration, employee anxiety, and organizational openness demands a change of approach. The author presents five actions that will improve the clarity and quality of communication, enabling stakeholders to make a more substantive and meaningful contribution to the strategy.
Most people can’t recall the strategy of the organization they work for. Even the executives and managers responsible for strategy struggle, with one study reporting that only 28% of them could list three strategic priorities.
- David Lancefield is a catalyst, strategist, and coach for leaders. He’s advised more than 40 CEOs and hundreds of executives, was a senior partner at Strategy&, and is a guest lecturer at the London Business School. Find him on LinkedIn (@davidclancefield) or at davidlancefield.com , where you can sign up for his free “Mastering Big Moments” workbook .
Partner Center
What Is Speech Analytics?
Speech analytics records and analyzes conversations to understand the content and sentiment of business communication.
Speech analytics is a combination of technologies that capture and analyze spoken language to extract business insights. It focuses on what is said and how it’s said, offering a comprehensive understanding of both the content and context of the conversations.
In today’s business landscape, speech analytics enables organizations to improve customer service , minimize costs, ensure compliance and gain a competitive edge by better understanding customer needs and sentiments.
As businesses increasingly adopt digital communication channels, speech analytics is evolving to provide real-time insights across different ways consumers interact with a business.
What Industries Use Speech Analytics?
Speech analytics traditionally occurs in contact centers, where customer interactions are recorded and analyzed to improve service quality. Recently, though, it’s expanding to industries such as sales, marketing and even internal communications.
More on AI Everything to Know About Artificial Intelligence
How Does Speech Analytics Work?
Core technologies.
The core technologies behind speech analytics include the following.
- Automatic speech recognition : Converts spoken language into text.
- Natural language processing : Analyzes and interprets the meaning and context of the transcribed text.
- Machine learning algorithms : Identify patterns, trends and anomalies in the data they collect.
Speech analytics typically follow these steps.
- Audio capture : Recording of conversations through various channels such as phone calls, video calls and face-to-face interactions.
- Transcription : Converting the audio recordings into text using automatic speech recognition.
- Embedding acoustic data : Pairing the acoustic data with the timings from the recognized transcript to capture how something is said.
- Text analysis : Applying NLP to understand the sentiment, keywords and context.
- Data analysis and visualization : Analyzing the combined data and presenting it in a user-friendly format, often through dashboards and reports, to derive business insights.
Features of Speech Analytics
The core feature of any speech analytics system is the speech-to-text engine or recognizer, which is responsible for converting spoken language into a text transcript.
This transcript is the foundation for building further analysis, allowing natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to process the content and context of the conversation.
Speech analytics is essentially text analytics applied to the recognized text of a conversation. It goes beyond mere text analysis, though, by incorporating conversation data such as pace, tone and volume, adding layers of context that provide a richer understanding of the interaction.
The outputs of speech analytics are multi-faceted and highly valuable to businesses, including the following.
- Transcripts : Accurate renderings of the spoken conversation into text form, which can be stored, searched and analyzed.
- Call scores : Evaluations based on targeted sentiments such as satisfaction, experience, participation, engagement, responsiveness, complexity and effort.
- Notable events : Key moments in the conversation, such as agreement, dissatisfaction or escalation, that require attention or action.
- Reasons for interaction : Insights into why the conversation took place, identifying the underlying motivations or issues.
- Topics and segments : Identification of the main topics discussed and the segmentation of the conversation into relevant parts for more focused analysis.
These features collectively allow businesses to extract actionable insights from spoken interactions, driving improvements in customer service, compliance and overall operational efficiency.
Speech Analytics Tools
In the rapidly evolving field of speech analytics, we can categorize tools based on their primary focus and capabilities. Here are some key categories.
Integration-Focused Tools
These tools emphasize seamless integration with existing business systems, such as customer relationship management platforms , enterprise resource planning systems and contact center infrastructure. They are designed to plug into existing workflows with minimal disruption, allowing businesses to quickly implement speech analytics without overhauling their systems.
Real-Time Analytics Tools
Real-time analytics tools offer immediate insights during customer interactions, enabling on-the-fly adjustments in response to customer sentiment, tone and context. These tools are critical in contact centers and sales organizations where instant feedback can directly influence outcomes.
Feature-Rich Tools
Some tools are distinguished by their robust feature sets, which may include the following.
- Query engine : Allows users to perform complex searches across large conversational data sets to uncover specific patterns or insights.
- Quality assurance : Ensures that interactions meet predefined standards by monitoring and scoring calls based on key performance indicators.
- Data streams : Facilitates the real-time or near-real-time processing of voice data, ensuring that insights are as current as possible.
- Applications and plug-ins : These tools often support various applications or plug-ins, allowing businesses to customize their speech analytics environment to meet specific needs, such as sentiment analysis , keyword spotting or automated call summaries.
Applications of Speech Analytics
Industries using speech analytics tools.
Speech analytics tools are critical in industries with frequent customer interaction.
- Contact centers : These are the primary users of speech analytics, using it to enhance customer service, monitor agent performance and ensure compliance.
- Sales organizations : Speech analytics helps in analyzing sales calls to identify successful strategies and improve overall sales effectiveness.
- Healthcare : In healthcare, speech analytics can be used to improve patient interactions, monitor compliance with regulations and provide better training for patient-facing staff.
- Financial services : Financial institutions use these tools for compliance monitoring, fraud detection and improving customer service.
Real-Time and Post-Call Analytics
- Real-time analytics : Provides immediate insights during a call, allowing agents to adjust their approach based on customer sentiment and context.
- Post-call analytics : Analyzes recorded calls to identify trends, measure performance and develop strategies for improvement.
Benefits of Using Speech Analytics
Improving customer service.
Speech analytics helps in understanding customer needs and sentiments, enabling organizations to provide personalized service. It can identify frequent issues and provide insights into customer expectations, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
By analyzing the tone and emotion in customer interactions, businesses can also address problems more proactively, leading to a better overall customer experience.
Saving Resources
By automating the analysis of customer interactions, speech analytics reduces the need for manual call monitoring, saving time and resources. It helps identify areas where you can optimize processes, leading to cost savings.
Additionally, speech analytics can pinpoint areas where you can improve self-service options, further reducing the workload on customer service representatives and lowering operational costs.
Enhancing Compliance and Risk Management
Speech analytics ensures compliance with industry regulations by monitoring all interactions for specific keywords and phrases. It can alert management to potential compliance breaches, reducing the risk of fines and legal issues. This proactive monitoring helps maintain high standards of compliance and minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Retaining Talent and Training Agents Faster
Speech analytics can be instrumental in employee training and development. By analyzing interactions, managers can identify areas where agents need improvement and provide targeted coaching.
This leads to faster training times and helps in retaining talent by continuously developing their skills and enhancing their job satisfaction. Effective training and coaching also lead to higher performance levels and reduced turnover rates.
Process Optimization and Self-Service Improvement
Identifying areas for self-service improvement is another significant benefit. Speech analytics can reveal common customer inquiries and issues that could be resolved through automated systems. By enhancing self-service options, businesses can reduce the volume of calls handled by human agents, allowing them to focus on more complex and value-added interactions.
Enhancing Customer Insights
Speech analytics provides insights into customer preferences, behavior and emerging trends. You can use this data to tailor products, services and marketing strategies to better meet customer needs. Understanding customer sentiment and feedback helps in making informed business decisions and improving overall customer engagement.
Improving Agent Performance and Customer Interactions
By providing real-time feedback to agents during calls, speech analytics can improve the quality of customer interactions. It can alert agents to use certain phrases or avoid specific words, leading to more positive customer experiences. Continuous monitoring and feedback help agents refine their communication skills and handle interactions more effectively.
Reducing Churn and Increasing Customer Retention
Speech analytics can identify patterns and warning signs of customer dissatisfaction, enabling businesses to take proactive measures to address issues before they lead to churn . By understanding and addressing the root causes of dissatisfaction, businesses can improve customer retention rates and build long-term loyalty .
Enhancing Strategic Planning
The insights gained from speech analytics can inform strategic planning and decision-making processes. By understanding customer needs and market trends, businesses can develop better strategies for growth and competitive advantage. Speech analytics provides a wealth of data that businesses can use to guide product development, marketing and customer service initiatives.
More on Voice Recognition Technology Voice Cloning: What It Is and Why It’s Scary
Limitations of Using Speech Analytics
Technical challenges.
Implementing speech analytics can be technically challenging, requiring robust infrastructure and integration with existing systems. Ensuring the accuracy of transcriptions and interpretations, especially with diverse accents and languages , can also be difficult.
Privacy Concerns
The use of speech analytics raises privacy concerns, as it involves recording and analyzing customer interactions. Organizations must comply with data protection regulations and obtain necessary consent from customers. This is particularly important in industries where recording conversations is not a standard practice.
For instance, general contact centers that handle routine inquiries or sales transactions typically require a notification at the beginning of a call, informing the customer that calls may be monitored for quality assurance or similar purposes. This notice is a legal requirement in many jurisdictions to ensure transparency and obtain implicit consent for recording.
In contrast, certain types of contact centers, such as emergency services (e.g., 911 centers), may not require explicit consent to record interactions. These centers operate under different regulatory frameworks where the primary focus is on public safety, and recording is deemed essential for operational effectiveness.
Even in these cases, though, organizations must still adhere to relevant privacy laws and securely store recordings, accessed only by authorized personnel.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the role of a speech analyst.
A speech analyst is a specialist responsible for interpreting the data generated by speech analytics tools. Their primary tasks include analyzing call recordings, identifying trends and providing actionable insights to help businesses improve customer service, ensure compliance and optimize operational efficiency.
How does speech analytics differ from text analytics?
While text analytics focuses on analyzing written content, speech analytics starts with spoken language, converting it to text and then applying similar analytical techniques. Speech analytics adds a layer of complexity by considering factors like tone, pace and volume.
What are challenges in implementing speech analytics?
Implementing speech analytics can be challenging due to technical requirements and the need for integration with existing systems. For real-time analytics, integration with computer-telephony integration systems is crucial, allowing data capture and analysis during live interactions. Ensuring that speech analytics tools work smoothly within the same environment as telephony and CRM systems can be complex and require additional customization.
Recent Natural Language Processing Articles

More From Forbes
3 essential communication skills for skills-based organizations.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Business leaders discussing new business ideas in the office at a skills-based organization
In skills-based organizations, effective communication is the meta-skill.
Communication skills have always been vital to the success of high-performing organizations. That’s why learning and development leaders in such companies ensure that programs on, for example, active listening, feedback, and clear, concise communication are among the essential offerings for their employees’ personal and professional growth.
Recent data from top-tier research firms, such as Deloitte and Bain & Company , indicate a significant shift towards skills-based organizational models. This requires an equally important shift towards a learning mindset. According to Deloitte's research , a substantial majority of corporate leaders recognize the importance of skills in defining work and managing talent. Specifically, around 90% of executives are actively experimenting with or moving towards a skills-based approach, indicating a strong belief in its potential to improve organizational outcomes.
This development has raised the bar on communication skills.
Especially in a skills-based organization, where the focus shifts from rigidly defined job descriptions and roles to the specific skills and competencies of individuals, high levels of coordination and collaboration among team members with diverse skill sets makes effective communication the critical differentiator for leadership roles in a company.
Reasons abound why a focus on communication skills is crucial in such a model:
Coordination and Flexibility : Skills-based organizations often involve dynamic team structures where individuals are brought together based on their skills to work on specific projects or tasks. Effective communication is necessary to coordinate these efforts, ensure that everyone understands their roles, and adapt quickly to changes.
Cross-functional Collaboration : In this model, communication across different functions and departments is vital to leveraging diverse skills and knowledge. This cross-functional communication fosters innovation and problem-solving by breaking down silos and encouraging the exchange of ideas.
Election 2024 Swing State Polls: Harris Leads Or Ties Trump In All Battleground States, Latest Survey Finds
Kamala harris defends biden admin’s economic record in first big interview—but says ‘more to do’, ‘the rings of power’ season 2 premiere review: a dreadful, jumbled mockery of tolkien’s ‘the lord of the rings’.
Transparency and Trust : As roles and tasks are not strictly defined by job titles, clear and transparent communication helps build trust among team members. It ensures that everyone is aware of the organization's goals, the purpose of their tasks, and how their contributions fit into the larger picture.
Continuous Learning and Development : Skills-based organizations emphasize continuous learning and development. Effective communication is crucial for providing feedback, sharing knowledge, and identifying skill gaps that need to be addressed through training and development initiatives.
Empowerment and Engagement : By focusing on skills, organizations aim to empower employees to take ownership of their work and contribute meaningfully. Strong communication skills help articulate expectations, provide recognition, and engage employees in decision-making processes, leading to higher motivation and job satisfaction.
So, where should skills-based organizations focus the attention of their future leaders so they can elevate their communications skills?
I recommend three foundational focus areas:
Clarifying Expectations
This relatively unassuming concept doesn’t have the cachet of, say, strategic storytelling—the domain of visionary leaders—or negotiation skills. But it is increasingly important in everyday workplace communication. It is hard to overstate its value in organizations transitioning to skills-based frameworks that prioritize adaptability, continuous learning, and talent agility.
As these models gain momentum, leaders must learn and leverage requisite communication skills, to effectively navigate and manage this new environment, to enable alignment, engagement, and innovation within their teams.
Even Gallup has emphasized the significance of clarifying expectations as a key driver of employee engagement and inspiration. When managers clearly define and communicate expectations, employees understand their roles better and align their efforts with organizational goals.
This clarity enables employees to perform effectively and reduces confusion that can lead to disengagement, especially in organizations where predefined jobs with specific roles and responsibilities are a thing of the past. Employees who know what is expected of them are more likely to be engaged, which Gallup has linked to better business outcomes, such as increased productivity and profitability.
The process of clarifying expectations involves ongoing communication, alignment on outcomes, and frequent feedback. This helps employees prioritize their tasks, calibrate their approach, and measure their contributions, ultimately inspiring them to perform at their best.
Communicating Across Cultural Barriers
Cultural differences can significantly impact communication in skills-based organizations, often leading to misunderstandings and barriers to collaboration and innovation.
Leaders and their teams should take note of different cultures’ distinct communication styles, which can affect how messages are conveyed and interpreted. For example, some cultures may prefer direct communication, while others rely on indirect or nuanced expressions. Miscommunication and emotional friction can result if team members are not sensitive to these often-subtle differences.
Other cultural norms, such as attitudes towards hierarchy, authority, and teamwork, can also influence how communication is perceived and conducted. In some cultures, for instance, it is considered inappropriate to openly challenge a manager, which can stifle open dialogue and feedback in a North American environment.
Team members from such cultures sometimes don’t find it psychologically safe to challenge their more senior colleagues in meetings and in innovation discussions . In such cases, leaders and peers need to adapt their communication styles to more effectively engage those whose ingrained behaviors default to humility and conformity. This enables them to contribute fully to the organization’s success and makes having a diverse and culturally mixed team a strength rather than a potential vulnerability.
Influencing Up and Across
A critical differentiator for emerging leaders when engaging senior executives is the ability to simplify complexity, especially in skills-based organizations. They distill complex strategies into clear, understandable choice points and goals that align with the organization's skills-centric approach. In this way, leaders demonstrate their next-level potential and effectively communicate their outcome-focused strategies to both superiors and peers.
Trust is another foundational element for influencing others, especially in skills-based organizations where stakeholders and team members can change from one project to the next. Networks are in constant flux, so self-awareness is key in understanding the impact we have on those we’re partnered with. Emerging leaders should engage in self-reflection to understand their strengths and weaknesses and make the adjustments needed to foster trust and respect among peers and superiors. This is crucial for influencing decisions and driving change.
Building a strong network will become even more important to building influence in skills-based models. Leaders should cultivate relationships across the organization and leverage these connections to gather support for initiatives. In a skills-based organization, where cross-functional collaboration is key, having a robust network goes a long way in facilitating the sharing of skills and resources.
By leveraging organizational intelligence and understanding both the formal and informal structures of the skills-based organization, emerging leaders can better navigate organizational politics. Thus, they can position themselves strategically to influence decisions and initiatives.
Finally, future leaders of a skills-based organization can increase their positive impact on the business by actively fostering a skills-centric culture. By embracing skill development initiatives and promoting a culture that values continuous learning and skill enhancement, they can influence the organization's strategic direction and ability to meet new challenges.
Bottom Line
There are innumerable aspects to effective communication, each one subject to the complexity of human perception and behavior. Nonetheless, in today’s rapidly evolving business environment clear and effective communication is becoming increasingly important for employees to build followership and move up to higher levels, especially in skills-based organizations.
As companies continue to pivot from traditional job roles to skill-centric models, the leaders who will make the biggest impact are those who can master the art of clear, cross-functional, and culturally aware communication. By honing these critical communication skills, they not only ensure alignment and collaboration but also drive innovation and agility.
In doing so, emerging leaders position their teams—and themselves—for long-term success in a future that rewards agility and expertise.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.4 Visual Aids
Learning objective.
- Demonstrate how to use visual aids effectively in your presentation.
Almost all presentations can be enhanced by the effective use of visual aids. These can include handouts, overhead transparencies, drawings on the whiteboard, PowerPoint slides, and many other types of props. Visual aids are an important nonverbal aspect of your speech that you can control. Once you have chosen a topic, you need to consider how you are going to show your audience what you are talking about.
Have you ever asked for driving directions and not understood someone’s response? Did the person say, “Turn right at Sam’s Grocery Store, the new one” or “I think you will turn at the second light, but it might be the third one”? Chances are that unless you know the town well or have a map handy, the visual cue of a grocery store or a traffic light might be insufficient to let you know where to turn. Your audience experiences the same frustration, or sense of accomplishment, when they get lost or find their way during your speech. Consider how you can express yourself visually, providing common references, illustrations, and images that lead the audience to understand your point or issue.
Visual aids accomplish several goals:
- Make your speech more interesting
- Enhance your credibility as a speaker
- Serve as guides to transitions, helping the audience stay on track
- Communicate complex or intriguing information in a short period of time
- Reinforce your verbal message
- Help the audience use and retain the information
Purpose, Emphasis, Support, and Clarity
When you look at your own presentation from an audience member’s perspective, you might consider how to distinguish the main points from the rest of the information. You might also consider the relationships being presented between ideas or concepts, or how other aspects of the presentation can complement the oral message.
Your audience naturally will want to know why you are presenting the visual aid. The purpose for each visual aid should be clear, and almost speak for itself. If you can’t quickly grasp the purpose of a visual aid in a speech, you have to honestly consider whether it should be used in the first place. Visual aids can significantly develop the message of a speech, but they must be used for a specific purpose the audience can easily recognize.
Perhaps you want to highlight a trend between two related issues, such as socioeconomic status and educational attainment. A line graph might show effectively how, as socioeconomic status rises, educational attainment also rises. This use of a visual aid can provide emphasis, effectively highlighting key words, ideas, or relationships for the audience.
Visual aids can also provide necessary support for your position. Audience members may question your assertion of the relationship between socioeconomic status and educational attainment. To support your argument, you might include on the slide, “According to the U.S. Department of Education Study no. 12345,” or even use an image of the Department of Education Web page projected on a large screen. You might consider showing similar studies in graphic form, illustrating similarities across a wide range of research.
Figure 11.4
Visual aids provide necessary support for your position, illustrate relationships, and demonstrate trends.
Austin Kleon – powerpoint as a comic – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Clarity is key in the use of visual aids. One way to improve clarity is to limit the number of words on a PowerPoint slide. No more than ten words per slide, with a font large enough to be read at the back of the room or auditorium, is a good rule of thumb. Key images that have a clear relationship to the verbal message can also improve clarity. You may also choose to illustrate the same data successively in two distinct formats, perhaps a line graph followed by two pie graphs. Your central goal is to ensure your visual aid is clear.
Methods and Materials
If you have been asked to give a presentation on a new product idea that a team within your organization is considering, how might you approach the challenge? You may consider a chronological organization pattern, starting with background, current market, and a trend analysis of what is to come—fair enough, but how will you make it vivid for your audience? How to represent information visually is a significant challenge, and you have several options.
You may choose to use a chart or diagram to show a timeline of events to date, from the first meeting about the proposed product to the results from the latest focus group. This timeline may work for you, but let’s say you would like to get into the actual decision-making process that motivated your team to design the product with specific features in the first place. You may decide to use decision trees (or tree diagrams) showing the variables and products in place at the beginning of your discussions, and how each decision led to the next, bringing you to the decision-making point where you are today.
Figure 11.5

Visual aids make it vivid for your audience.
Gareth Saunders – Welcome to Powerpoint – CC BY-SA 2.0.
To complement this comprehensive guide and help make a transition to current content areas of questions, you may use a bar or pie graph to show the percentage of competing products in the market. If you have access to the Internet and a projector, you may use a topographical map showing a three-dimensional rendering of the local areas most likely to find your product attractive. If actual hills and valleys have nothing to do with your project, you can still represent the data you have collected in three dimensions. Then you may show a comparable graph illustrating the distribution of products and their relative degree of market penetration.
Figure 11.6
Bar and pie graphs can clearly demonstrate results.
Christopher Porter – EuroTrip2006 – Total Expenses – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Finally, you may move to the issue of results, and present the audience with a model of your product and one from a competitor, asking which they prefer. The object may be just the visual aid you need to make your point and reinforce the residual message. When we can see, feel, touch, or be in close proximity to an object it often has a greater impact. In a world of digital images and special effects, objects presented in real time can still make a positive effect on the audience.
Additional visual aids you may choose include—but are not limited to—sound and music, video, and even yourself. If your speech is about how to use the product, your demonstration may just be the best visual aid.
You will want to give some thought to how to portray your chart, graph, or object when it’s time to use your visual aids. The chalk or white board is common way of presenting visual aids, but it can get messy. Your instructor may write key words or diagrams on the boards while discussing a textbook chapter, but can you read his or her writing? The same lesson holds true for you. If you are going to use a white board and have a series of words on it, write them out clearly before you start your presentation.
Flip charts on a pedestal can also serve to show a series of steps or break a chart down into its basic components. A poster board is another common way of organizing your visual aids before a speech, but given its often one-time use, it is losing out to the computer screen. It is, however, portable and allows you a large “blank page” with which to express your ideas.
Handouts may also serve to communicate complex or detailed information to the audience, but be careful never to break handout rule number one: never give handouts to the audience at the beginning of your speech. Where do you want the audience to look—at you or at the handout? Many novice speakers might be tempted to say the handout, but you will no doubt recognize how that diverts and divides the audience’s attention. People will listen to the words from the handout in their minds and tune you out. They will read at their own pace and have questions. They may even be impolite enough to use them as fans or paper airplanes. Handouts can be your worst enemy. If you need to use one, state at the beginning of the speech that you will be providing one at the conclusion of your presentation. This will alleviate the audience’s worry about capturing all your content by taking notes, and keep their attention focused on you while you speak.
Transparencies and slides have been replaced by computer-generated slide show programs like PowerPoint by Microsoft, which we will discuss in greater detail later in this section. These programs can be very helpful in presenting visual information, but because computers and projectors sometimes break down and fail to work as planned, you need a plan B. You may need a poster board, or to write on the whiteboard or to have a handout in reserve, but a Plan B is always a good idea when it comes to presentations that integrate technology. You may arrive at your destination and find the equipment is no longer available, is incompatible with your media storage device, or is simply not working, but the show must go on.
Video clips, such as those you might find on YouTube, can also be effective visual aids. However, as with handouts, there is one concern: You don’t want the audience to want to watch the video more than they want to tune into your presentation. How do you prevent this? Keep the clip short and make sure it reinforces the central message of your presentation. Always stop speaking before the audience stops listening, and the same holds true for the mesmerizing force of moving images on a screen. People are naturally attracted to them and will get “sucked into” your video example rather quickly. Be a good editor, introduce the clip and state what will happen out loud, point out a key aspect of it to the audience while it plays (overlap), and then make a clear transitional statement as you turn it off. Transitions are often the hardest part of any speech as the audience can get off track, and video clips are one of the most challenging visual aids you can choose because of their power to attract attention. Use that power wisely.
Preparing Visual Aids
Get started early so that you have time to create or research visual aids that will truly support your presentation, not just provide “fluff.” Make sure you use a font or image large enough to be legible for those in the back of the room, and that you actually test your visual aids before the day of your presentation. Ask a friend to stand at the back of the room and read or interpret your visual aid. If you are using computer-generated slides, try them out in a practice setting, not just on your computer screen. The slides will look different when projected. Allow time for revision based on what you learn.
Your visual aids should meet the following criteria:
- Big . They should be legible for everyone, and should be “back row certified.”
- Clear . Your audience should “get it” the first time they see it.
- Simple . They should serve to simplify the concepts they illustrate.
- Consistent . They should reinforce continuity by using the same visual style.
Using Visual Aids
Here are three general guidelines to follow when using visual aids (McLean, S., 2003). Here are some do s and don’t s:
- Do make a clear connection between your words and the visual aid for the audience.
- Do not distract the audience with your visual aid, blocking their view of you or adjusting the visual aid repeatedly while trying to speak.
- Do speak to your audience—not to the whiteboard, the video, or other visual aids.
The timing of your presentation, and of your visual aids, can also have good or bad consequences. According to a popular joke, a good way to get your boss to approve just about anything is to schedule a meeting after lunch, turn the lights down, and present some boring PowerPoint slides. While the idea of a drowsy boss signing off on a harebrained project is amusing, in reality you will want to use visual aids not as a sleeping potion but as a strategy to keep your presentation lively and interesting.
Becoming proficient at using visual aids takes time and practice, and the more you practice before your speech, the more comfortable you will be with your visual aids and the role they serve in illustrating your points. Planning ahead before speaking will help, but when it comes time to actually give your speech, make sure they work for the audience as they should. Speaking to a visual aid (or reading it with your back to the audience) is not an effective strategy. You should know your material well enough that you refer to a visual aid, not rely on it.
Using PowerPoint as a Visual Aid
PowerPoint and similar visual representation programs can be an effective tool to help audiences remember your message, but they can also be an annoying distraction to your speech. How you prepare your slides and use the tool will determine your effectiveness.
PowerPoint is a slideware program that you have no doubt seen used in class, presentation at work, or perhaps used yourself to support a presentation. PowerPoint and similar slideware programs provide templates for creating electronic slides to present visual information to the audience, reinforcing the verbal message. You’ll be able to import, or cut and paste, words from text files, images, or video clips to create slides to represent your ideas. You can even incorporate Web links. When using any software program, it’s always a good idea to experiment with it long before you intend to use it, explore its many options and functions, and see how it can be an effective tool for you.
Intercultural Communication
(click to see video)
PowerPoint slides can connect words with images.
At first, you might be overwhelmed by the possibilities, and you might be tempted to use all the bells, whistles, and sound effects, not to mention the tumbling, flying, and animated graphics. If used wisely, a dissolve or key transition can be like a well-executed scene from a major motion picture film and lead your audience to the next point. But if used indiscriminately, it can annoy the audience to the point where they cringe in anticipation of the sound effect at the start of each slide. This danger is inherent in the tool, but you are in charge of it and can make wise choices that enhance the understanding and retention of your information.
The first point to consider is what is the most important visual aid? The answer is you, the speaker. You will facilitate the discussion, give life to the information, and help the audience correlate the content to your goal or purpose. You don’t want to be in a position where the PowerPoint presentation is the main focus and you are on the side of the stage, simply helping the audience follow along. It should support you in your presentation, rather than the other way around. Just as there is a number one rule for handouts, there is also one for PowerPoints: do not use PowerPoints as a read-aloud script for your speech. The PowerPoints should amplify and illustrate your main points, not reproduce everything you are going to say.
Your pictures are the second area of emphasis you’ll want to consider. The tool will allow you to show graphs, charts and illustrate relationships that words may only approach in terms of communication, but your verbal support of the visual images will make all the difference. Dense pictures or complicated graphics will confuse more than clarify. Choose clear images that have an immediate connection to both your content and the audience, tailored to their specific needs. After images, consider only key words that can be easily read to accompany your pictures. The fewer words the better: try to keep each slide to a total word count of less than ten words. Do not use full sentences. Using key words provides support for your verbal discussion, guiding you as well as your audience. The key words can serve as signposts or signal words related to key ideas.
A natural question at this point is, “How do I communicate complex information simply?” The answer comes with several options. The visual representation on the screen is for support and illustration. Should you need to communicate more technical, complex, or in-depth information in a visual way, consider preparing a handout to distribute at the conclusion of your speech. You may also consider using a printout of your slide show with a “notes” section, but if you distribute it at the beginning of your speech, you run the risk of turning your presentation into a guided reading exercise and possibly distracting or losing members of the audience. Everyone reads at a different pace and takes notes in their own way. You don’t want to be in the position of going back and forth between slides to help people follow along.
Another point to consider is how you want to use the tool to support your speech and how your audience will interpret its presentation. Most audiences wouldn’t want to read a page of text—as you might see in this book—on the big screen. They’ll be far more likely to glance at the screen and assess the information you present in relation to your discussion. Therefore, it is key to consider one main idea, relationship, or point per slide. The use of the tool should be guided with the idea that its presentation is for the audience’s benefit, not yours. People often understand pictures and images more quickly and easily than text, and you can use this to your advantage, using the knowledge that a picture is worth a thousand words.
Use of Color
People love color, and understandably your audience will appreciate the visual stimulation of a colorful presentation. If you have ever seen a car painted a custom color that just didn’t attract you, or seen colors put together in ways that made you wonder what people were thinking when they did that, you will recognize that color can also distract and turn off an audience.
Color is a powerful way to present information, and the power should be used wisely. You will be selecting which color you want to use for headers or key words, and how they relate the colors in the visual images. Together, your images, key words, and the use of color in fonts, backgrounds, table, and graphs can have a significant impact on your audience. You will need to give some thought and consideration to what type of impact you want to make, how it will contribute or possibly distract, and what will work well for you to produce an effective and impressive presentation.
There are inherent relationships between colors, and while you may have covered some of this information in art classes you have taken, it is valuable to review here. According to the standard color wheel, colors are grouped into primary, secondary, and tertiary categories. Primary colors are the colors from which other colors are made through various combinations. Secondary colors represent a combination of two primary colors, while tertiary colors are made from combinations of primary and secondary colors.
Figure 11.7 Color Wheel
Michael Hernandez – color wheel – CC BY 2.0.
- Primary colors . Red, blue and yellow
- Secondary colors . Green, violet, and orange
- Tertiary colors . Red-orange, red-violet, blue-violet, blue-green, yellow-orange, and yellow-green
Colors have relationships depending on their location on the wheel. Colors that are opposite each other are called complementary and they contrast, creating a dynamic effect. Analogous colors are located next to each other and promote harmony, continuity, and sense of unity.
Your audience comes first: when considering your choice of colors to use, legibility must be your priority. Contrast can help the audience read your key terms more easily. Also, focus on the background color and its relation to the images you plan to incorporate to insure they complement each other. Consider repetition of color, from your graphics to your text, to help unify each slide. To reduce visual noise, try not to use more than two or three additional colors. Use colors sparingly to make a better impact, and consider the use of texture and reverse color fonts (the same as a background or white) as an option.
Be aware that many people are blue-green colorblind, and that red-green colorblindness is also fairly common. With this in mind, choose colors that most audience members will be able to differentiate. If you are using a pie chart, for example, avoid putting a blue segment next to a green one. Use labeling so that even if someone is totally colorblind they will be able to tell the relative sizes of the pie segments and what they signify.
Color is also a matter of culture. Some colors may be perceived as formal or informal, or masculine or feminine. Recognize that red is usually associated with danger, while green signals “go.” Make sure the color associated with the word is reflected in your choice. If you have a key word about nature, but the color is metallic, the contrast may not contribute to the rhetorical situation and confuse the audience.
Seeking a balance between professionalism and attractiveness may seem to be a challenge, but experiment and test your drafts with friends to see what works for you. Also consider examining other examples, commonly available on the Internet, but retain the viewpoint that not everything online is effective nor should it be imitated. There are predetermined color schemes already incorporated into PowerPoint that you can rely on for your presentation.
We’ve given consideration to color in relation to fonts and the representation of key words, but we also need to consider font size and selection. PowerPoint will have default settings for headlines and text, but you will need to consider what is most appropriate for your rhetorical situation. Always think about the person sitting in the back of the room. The title size should be at least forty points, and the body text (used sparingly) should be at least thirty-two points.
Figure 11.8

Visual aids should be clear from the back of the room.
Martin Roell – Powerpoint + Sonne = … – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In Designing Visual Language: Strategies for Professional Communicators (Kostelnick, C., and Roberts, D., 1998), Charles Kostelnick and David Roberts provide a valuable discussion of fonts, font styles, and what to choose to make an impact depending on your rhetorical situation. One good principle they highlight is that sans serif fonts such as Arial work better than serif fonts like Times New Roman for images projected onto a screen. The thin lines and extra aspects to serif the font may not portray themselves well on a large screen or contribute to clarity. To you this may mean that you choose Arial or a similar font to enhance clarity and ease of reading. Kostelnick and Roberts also discuss the use of grouping strategies to improve the communication of information (Kostelnick, C., and Roberts, D., 1998). Bullets, the use of space, similarity, and proximity all pertain to the process of perception, which differs from one person to another.
Helpful Hints for Visual Aids
As we’ve discussed, visual aids can be a powerful tool when used effectively, but can also run the risk of dominating your presentation. As a speaker, you will need to consider your audience and how the portrayal of images, text, graphic, animated sequences, or sound files will contribute or detract from your presentation. Here is a brief list of hints to keep in mind as you prepare your presentation.
- Keep visual aids simple.
- Use one key idea per slide.
- Avoid clutter, noise, and overwhelming slides.
- Use large, bold fonts that the audience can read from at least twenty feet from the screen.
- Use contrasting colors to create a dynamic effect.
- Use analogous colors to unify your presentation.
- Use clip art with permission and sparingly.
- Edit and proofread each slide with care and caution.
- Use copies of your visuals available as handouts after your presentation.
- Check the presentation room beforehand.
- With a PowerPoint presentation, or any presentation involving technology, have a backup plan, such as your visuals printed on transparencies, should unexpected equipment or interface compatibility problems arise
Becoming proficient at using visual aids takes time and practice. The more you practice before your speech, the more comfortable you will be with your visual aids and the role they serve in illustrating your message. Giving thought to where to place visual aids before speaking helps, but when the time comes to actually give your speech, make sure you reassess your plans and ensure that they work for the audience as they should. Speaking to a visual aid (or reading it to the audience) is not an effective strategy. Know your material well enough that you refer to your visual aids, not rely on them.
Key Takeaway
Strategically chosen visual aids will serve to illustrate, complement, and reinforce your verbal message.
- Look at the picture of the blankets above. Write copy for the left part of the slide and decide what colors would best complement the message. Share your results with the class.
- Create your own presentation of three to five slides with no less than three images and three words per slide. Share the results with the class.
- Explore PowerPoint or a similar slideware program and find your favorite feature. Write a series of steps on how to access and use it. Share your results with the class.
- Create a slide presentation that defines and explains your favorite feature in the program and include at least one point on its advantage for the audience. Share the results with the class.
Kostelnick, C., & Roberts, D. (1998). Designing visual language: Strategies for professional communicators . Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
McLean, S. (2003). The basics of speech communication . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Business Communication for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, and speech is one of its most powerful tools. Speech allows individuals to convey ideas, emotions, intentions, and information effectively. Different types of speech are used depending on the context, audience, and purpose of communication. Understanding these
Technically speaking, a purpose can be defined as why something exists, how we use an object, or why we make something. For the purposes of public speaking, all three can be applicable. For example, when we talk about a speech's purpose, we can question why a specific speech was given; we can question how we are supposed to use the ...
The purpose of the introduction is to acquaint the audience with the topic of your speech and prepare the audience for the main points you will make in the body. The introduction of a speech should accomplish the following things: Capture the audience's attention in the very first sentence with an attention getting device.Choose an attention getting device that is relevant to the topic of ...
Figure 12.1. The rhetorical situation involves where we are, who we are with, and why we are communicating. photolibrarian - Red Oak, Iowa, Courtroom, Judge Hayzlett - CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. The rhetorical situation involves three elements: the set of expectations inherent in the context, audience, and the purpose of your speech or presentation ...
Here's a brief review of the five general purposes for speaking in public: Speech to inform. Increase the audience's knowledge, teach about a topic or issue, and share your expertise. Speech to demonstrate. Show the audience how to use, operate, or do something. Speech to persuade. Influence the audience by presenting arguments intended to ...
Speaking in public is especially important for businesses to market their offers. This allows them to get their message in front of potential customers. Salespeople and executives are often expected to have good public speaking skills. To learn more about some of the benefits of speaking in public, review this article.
State your topic and specific purpose: "My speech today will inform you on genetically modified foods that are increasingly part of our food supply.". Introduce your credibility and the topic: "My research on this topic has shown me that our food supply has changed but many people are unaware of the changes.".
A speech that is delivered in the workplace or in any business organization for some specific purpose is known as Business Speech. This is one of the forms of Business Communication and the audience has to sit quietly while the speech is being delivered. Most of the time audience knows very well that the speech must contain anything that will ...
Conclusion. The purpose of giving a speech is unique and, at the same time Versatile, it has the role of conveying a message in various ways, whether it is entrenched, persuading, informing, or combining multiple forms. What differentiates one speech from the other is how we decide to convey a message, and some are more appropriate than others ...
Informative Speakers Are Objective. Most public speaking texts discuss three general purposes for speeches: to inform, to persuade, and to entertain. Although these general purposes are theoretically distinct, in practice, they tend to overlap. Even in situations when the occasion calls for an informative speech (one which enhances ...
An informative speech is a type of speech that teaches new information to an audience without any persuasive undertones. Its sole purpose is to teach something to a group of people. Informative ...
Public speaking is, simply, an oral presentation or speech delivered to a live audience. It is generally a formal or staged event— although impromptu speeches are a common occurrence—and can be a defining career moment. For example, you may think you're attending a client meeting only to find yourself called on to explain a procedural or ...
Reading speech: In this method, speech is delivered by reading written documents. Memorized speech: In this method, the speaker memorizes the written speech and then delivers to the audience. Arranging visual aids. Various visual aids such as chart, graph, diagram, picture, model etc. can be used for presenting the speech effectively.
State your topic and specific purpose: "My speech today will inform you on genetically modified foods that are increasingly part of our food supply.". Introduce your credibility and the topic: "My research on this topic has shown me that our food supply has changed but many people are unaware of the changes.".
Preparing a Presentation. Develop your message while keeping in mind the format, audience, style, and tone. First, you'll need to think about the format of your presentation. This is a choice between presentation types. In your professional life, you'll encounter the verbal communication channels in Figure 18.1.
Using effective communication skills can benefit a business and its employees in a variety of ways, including: 1. Building better teams. Effective communication builds a positive atmosphere where teams can flourish. When communication is positive and encouraging, team members become stronger and work better together.
Courtesy. Clarity. Consideration. Concreteness. These strategies apply to both written and oral communication. The one who is aware of and makes use of these 7C's in a sensible manner can become a good and effective communicator. 1. Completeness. This is one of the most significant aspects of effective communication.
Clarity Defines Purpose. When you communicate with clarity, you can clearly convey your goals and intentions to your listeners. This is particularly important in business, where your purpose is defined by your ambitions, actions, plans, and principles. Clarity of speech ensures that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same ...
The purpose of this speech is to educate the audience regarding the main points of the topic. Explain: Explanatory speeches provide a depiction of the state of a given topic. The information ...
Buy Copies. Summary. For too long, communicating strategy has been an afterthought. Executives have shared long, bombastic documents or withheld critical information and expected people to just ...
Persuasion is an act or process of presenting arguments to move, motivate, or change your audience. Aristotle taught that rhetoric, or the art of public speaking, involves the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion (Covino, W. A. and Jolliffe, D. A., 1995). In the case of President Obama, he may have appealed ...
Speech analytics is a combination of technologies that capture and analyze spoken language to extract business insights. It focuses on what is said and how it's said, offering a comprehensive understanding of both the content and context of the conversations.
Business leaders discussing new business ideas in the office at a skills-based organization. getty. In skills-based organizations, effective communication is the meta-skill.
Figure 11.4. Visual aids provide necessary support for your position, illustrate relationships, and demonstrate trends. Austin Kleon - powerpoint as a comic - CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. Clarity is key in the use of visual aids. One way to improve clarity is to limit the number of words on a PowerPoint slide.