Advertisement

The Impact of COVID-19 on Education: A Meta-Narrative Review
- Original Paper
- Published: 05 July 2022
- Volume 66 , pages 883–896, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Aras Bozkurt ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4520-642X 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Kadir Karakaya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3375-1532 4 ,
- Murat Turk ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5105-2578 5 ,
- Özlem Karakaya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9950-481X 6 &
- Daniela Castellanos-Reyes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0183-1549 7
14k Accesses
43 Citations
52 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The rapid and unexpected onset of the COVID-19 global pandemic has generated a great degree of uncertainty about the future of education and has required teachers and students alike to adapt to a new normal to survive in the new educational ecology. Through this experience of the new educational ecology, educators have learned many lessons, including how to navigate through uncertainty by recognizing their strengths and vulnerabilities. In this context, the aim of this study is to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the publications covering COVID-19 and education to analyze the impact of the pandemic by applying the data mining and analytics techniques of social network analysis and text-mining. From the abstract, title, and keyword analysis of a total of 1150 publications, seven themes were identified: (1) the great reset, (2) shifting educational landscape and emerging educational roles (3) digital pedagogy, (4) emergency remote education, (5) pedagogy of care, (6) social equity, equality, and injustice, and (7) future of education. Moreover, from the citation analysis, two thematic clusters emerged: (1) educational response, emergency remote education affordances, and continuity of education, and (2) psychological impact of COVID-19. The overlap between themes and thematic clusters revealed researchers’ emphasis on guaranteeing continuity of education and supporting the socio-emotional needs of learners. From the results of the study, it is clear that there is a heightened need to develop effective strategies to ensure the continuity of education in the future, and that it is critical to proactively respond to such crises through resilience and flexibility.
Similar content being viewed by others

The Impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review of Pedagogical Approaches and Challenges

Learning from a Pandemic. The Impact of COVID-19 on Education Around the World
A multimethod synthesis of Covid-19 education research: the tightrope between covidization and meaningfulness
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Education and Educational Technology
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has proven to be a massive challenge for the entire world, imposing a radical transformation in many areas of life, including education. It was rapid and unexpected; the world was unprepared and hit hard. The virus is highly contagious, having a pathogenic nature whose effects have not been limited to humans alone, but rather, includes every construct and domain of societies, including education. The education system, which has been affected at all levels, has been required to respond to the crisis, forced to transition into emergency modes, and adapt to the unprecedented impact of the global crisis. Although the beginning of 2021 will mark nearly a year of experience in living through the pandemic, the crisis remains a phenomenon with many unknowns. A deeper and more comprehensive understanding of the changes that have been made in response to the crisis is needed to survive in these hard times. Hence, this study aims to provide a better understanding by examining the scholarly publications on COVID-19 and education. In doing this, we can identify our weaknesses and vulnerabilities, be better prepared for the new normal, and be more fit to survive.
Related Literature
Though the COVID-19 pandemic is not the first major disruption to be experienced in the history of the world, it has been unique due to its scale and the requirements that have been imposed because of it (Guitton, 2020 ). The economies of many countries have greatly suffered from the lockdowns and other restrictive measurements, and people have had to adapt to a new lifestyle, where their primary concern is to survive by keeping themselves safe from contracting the deadly virus. The education system has not been exempt from this series of unfortunate events inflicted by COVID-19. Since brick-and-mortar schools had to be closed due to the pandemic, millions of students, from those in K-12 to those in higher education, were deprived of physical access to their classrooms, peers, and teachers (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020a , b ). This extraordinary pandemic period has posed arguably the most challenging and complex problems ever for educators, students, schools, educational institutions, parents, governments, and all other educational stakeholders. The closing of brick-and-mortar schools and campuses rendered online teaching and learning the only viable solution to the problem of access-to-education during this emergency period (Hodges et al., 2020 ). Due to the urgency of this move, teachers and instructors were rushed to shift all their face-to-face instruction and instructional materials to online spaces, such as learning management systems or electronic platforms, in order to facilitate teaching virtually at a distance. As a result of this sudden migration to learning and instruction online, the key distinctions between online education and education delivered online during such crisis and emergency circumstances have been obfuscated (Hodges et al., 2020 ).
State of the Current Relevant Literature
Although the scale of the impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic on education overshadows previously experienced nationwide or global crises or disruptions, the phenomenon of schools and higher education institutions having to shift their instruction to online spaces is not totally new to the education community and academia (Johnson et al., 2020 ). Prior literature on this subject indicates that in the past, schools and institutions resorted to online or electronic delivery of instruction in times of serious crises and uncertainties, including but not limited to natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes (e.g., Ayebi-Arthur, 2017 ; Lorenzo, 2008 ; Tull et al., 2017 ), local disruptions such as civil wars and socio-economic events such as political upheavals, social turmoils or economic recessions (e.g., Czerniewicz et al., 2019 ). Nevertheless, the past attempts to move learning and teaching online do not compare to the current efforts that have been implemented during the global COVID-19 pandemic, insofar as the past crisis situations were sporadic events in specific territories, affecting a limited population for relatively short periods of time. In contrast, the COVID-19 pandemic has continued to pose a serious threat to the continuity of education around the globe (Johnson et al., 2020 ).
Considering the scale and severity of the global pandemic, the impacts it has had on education in general and higher education in particular need to be explored and studied empirically so that necessary plans and strategies aimed at reducing its devastating effects can be developed and implemented. Due to the rapid onset and spread of the global pandemic, the current literature on the impact of COVID-19 on education is still limited, including mostly non-academic editorials or non-empirical personal reflections, anecdotes, reports, and stories (e.g., Baker, 2020 ; DePietro, 2020 ). Yet, with that said, empirical research on the impact of the global pandemic on higher education is rapidly growing. For example, Johnson et al. ( 2020 ), in their empirical study, found that faculty members who were struggling with various challenges adopted new instructional methods and strategies and adjusted certain course components to foster emergency remote education (ERE). Unger and Meiran ( 2020 ) observed that the pandemic made students in the US feel anxious about completing online learning tasks. In contrast, Suleri ( 2020 ) reported that a large majority of European higher education students were satisfied with their virtual learning experiences during the pandemic, and that most were willing to continue virtual higher education even after the pandemic (Suleri, 2020 ). The limited empirical research also points to the need for systematically planning and designing online learning experiences in advance in preparation for future outbreaks of such global pandemics and other crises (e.g., Korkmaz & Toraman, 2020 ). Despite the growing literature, the studies provide only fragmentary evidence on the impact of the pandemic on online learning and teaching. For a more thorough understanding of the serious implications the pandemic has for higher education in relation to learning and teaching online, more empirical research is needed.
Unlike previously conducted bibliometric analysis studies on this subject, which have largely involved general analysis of research on health sciences and COVID-19, Aristovnik et al. ( 2020 ) performed an in-depth bibliometric analysis of various science and social science research disciplines by examining a comprehensive database of document and source information. By the final phase of their bibliometric analysis, the authors had analyzed 16,866 documents. They utilized a mix of innovative bibliometric approaches to capture the existing research and assess the state of COVID-19 research across different research landscapes (e.g., health sciences, life sciences, physical sciences, social sciences, and humanities). Their findings showed that most COVID-19 research has been performed in the field of health sciences, followed by life sciences, physical sciences, and social sciences and humanities. Results from the keyword co-occurrence analysis revealed that health sciences research on COVID-19 tended to focus on health consequences, whereas the life sciences research on the subject tended to focus on drug efficiency. Moreover, physical sciences research tended to focus on environmental consequences, and social sciences and humanities research was largely oriented towards socio-economic consequences.
Similarly, Rodrigues et al. ( 2020 ) carried out a bibliometric analysis of COVID-19 related studies from a management perspective in order to elucidate how scientific research and education arrive at solutions to the pandemic crisis and the post-COVID-19 era. In line with Aristovnik et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings, Rodrigues et al. ( 2020 ) reported that most of the published research on this subject has fallen under the field of health sciences, leaving education as an under-researched area of inquiry. The content analysis they performed in their study also found a special emphasis on qualitative research. The descriptive and content analysis yielded two major strands of studies: (1) online education and (2) COVID-19 and education, business, economics, and management. The online education strand focused on the issue of technological anxiety caused by online classes, the feeling of belonging to an academic community, and feedback.
Lastly, Bond ( 2020 ) conducted a rapid review of K-12 research undertaken in the first seven months of the COVID-19 pandemic to identify successes and challenges and to offer recommendations for the future. From a search of K-12 research on the Web of Science, Scopus, EBSCOHost, the Microsoft Academic, and the COVID-19 living systematic map, 90 studies were identified and analyzed. The findings revealed that the reviewed research has focused predominantly on the challenges to shifting to ERE, teacher digital competencies and digital infrastructure, teacher ICT skills, parent engagement in learning, and students’ health and well-being. The review highlighted the need for straightforward communication between schools and families to inform families about learning activities and to promote interactivity between students. Teachers were also encouraged to develop their professional networks to increase motivation and support amongst themselves and to include opportunities for both synchronous and asynchronous interaction for promoting student engagement when using technology. Bond ( 2020 ) reported that the reviewed studies called for providing teachers with opportunities to further develop their digital technical competencies and their distance and online learning pedagogies. In a recent study that examines the impact of COVID-19 at higher education (Bozkurt, 2022 ), three broad themes from the body of research on this subject: (1) educational crisis and higher education in the new normal: resilience, adaptability, and sustainability, (2) psychological pressures, social uncertainty, and mental well-being of learners, and (3) the rise of online distance education and blended-hybrid modes. The findings of this study are similar to Mishra et al. ( 2021 ) who examined the COVID-19 pandemic from the lens of online distance education and noted that technologies for teaching and learning and psychosocial issues were emerging issues.
The aforementioned studies indicate that a great majority of research on COVID-19 has been produced in the field of health sciences, as expected. These studies nonetheless note that there is a noticeable shortage of studies dealing with the effects of the pandemic in the fields of social sciences, humanities, and education. Given the profound impact of the pandemic on learning and teaching, as well as on the related stakeholders in education, now more than ever, a greater amount of research on COVID-19 needs to be conducted in the field of education. The bibliometric studies discussed above have analyzed COVID-19 research across various fields, yielding a comparative snapshot of the research undertaken so far in different research spheres. However, despite being comprehensive, these studies did not appear to have examined a specific discipline or area of research in depth. Therefore, this bibliometric study aims to provide a focused, in-depth analysis of the COVID-19-related research in the field of education. In this regard, the main purpose of this study is to identify research patterns and trends in the field of education by examining COVID-19-related research papers. The study sought to answer the following research questions:
What are the thematic patterns in the title, abstract, and keywords of the publications on COVID-19 and education?
What are the citation trends in the references of the sampled publications on COVID-19 and education?
Methodology
This study used data mining and analytic approaches (Fayyad et al., 2002 ) to examine bibliometric patterns and trends. More specifically, social network analysis (SNA) (Hansen et al., 2020 ) was applied to examine the keywords and references, while text-mining was applied (Aggarwal & Zhai, 2012 ) to examine the titles and abstracts of the research corpus. Keywords represent the essence of an article at a micro level and for the analysis of the keywords, SNA was used. SNA “provides powerful ways to summarize networks and identify key people, [entities], or other objects that occupy strategic locations and positions within a matrix of links” (Hansen et al., 2020 , p. 6). In this regard, the keywords were analyzed based on their co-occurrences and visualized on a network graph by identifying the significant keywords which were demonstrated as nodes and their relationships were demonstrated with ties. For text-mining of the titles and abstracts, the researchers performed a lexical analysis that employs “two stages of co-occurrence information extraction—semantic and relational—using a different algorithm for each stage” (Smith & Humphreys, 2006 , p. 262). Thus, text-mining analysis enabled researchers to identify the hidden patterns and visualize them on a thematic concept map. For the analysis of the references, the researchers further used SNA based on the arguments that “citing articles and cited articles are linked to each other through invisible ties, and they collaboratively and collectively build an intellectual community that can be referred to as a living network, structure, or an ecology” (Bozkurt, 2019 , p. 498). The analysis of the references enabled the researchers to identify pivotal scholarly contributions that guided and shaped the intellectual landscape. The use of multiple approaches enables the study to present a broader view, or a meta-narrative.
Sample and Inclusion Criteria
The publications included in this research met the following inclusion criteria: (1) indexed by the Scopus database, (2) written in English, and (3) had the search queries on their title (Table 1 ). The search query reflects the focus on the impact of COVID-19 on education by including common words in the field like learn , teach , or student . Truncation was also used in the search to capture all relevant literature. Narrowing down the search allowed us to exclude publications that were not education related. Scopus was selected because it is one of the largest scholarly databases, and only publications in English were selected to facilitate identification of meaningful lexical patterns through text-mining and provide a condensed view of the research. The search yielded a total of 1150 papers (articles = 887, editorials = 66, notes = 58, conference papers = 56, letters = 40, review studies = 30, book chapters = 9, short surveys = 3, books = 1).
Data Analysis and Research Procedures
This study has two phases of analysis. In the first phase, text mining was used to analyze titles and abstracts, and SNA was applied to analyze keywords. By using two different analytical approaches, the authors were able to triangulate the research findings (Thurmond, 2001 ). In this phase, using lexical algorithms, text mining analysis enabled visualizing the textual data on a thematic concept map according to semantic relationships and co-occurrences of the words (Fig. 1 ). Text mining generated a machine-based concept map by analyzing the co-occurrences and lexical relationships of textual data. Then, based on the co-occurrences and centrality metrics, SNA enabled visualizing keywords on a network graphic called sociogram (Fig. 2 ). SNA allowed researchers to visually identify the key terms on a connected network graph where keywords are represented as nodes and their relationships are represented as edges. In the first phase of the study, by synthesizing outputs of the data mining and analytic approaches, meaningful patterns of textual data were presented as seven main research themes.
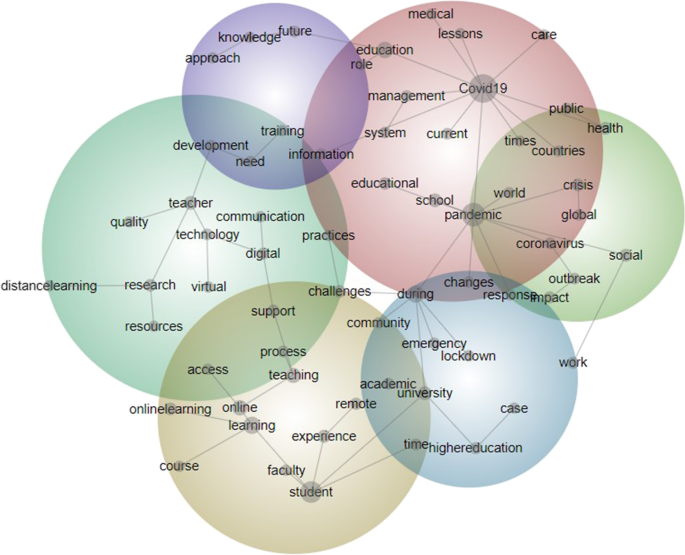
Thematic concept mapping of COVID-19 and education-related papers
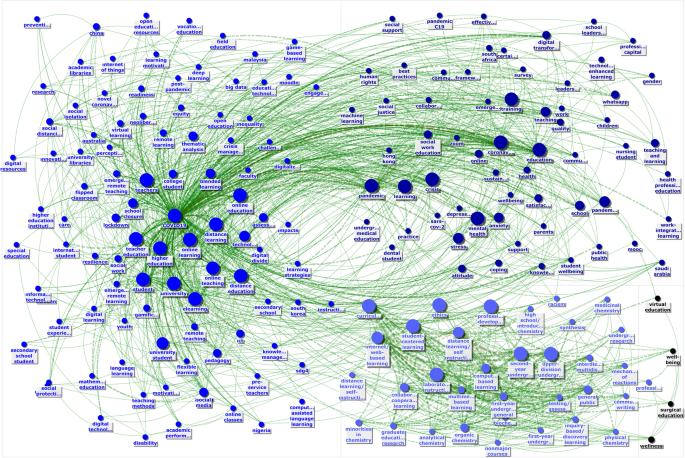
Social networks analysis of the keywords in COVID-19 and education-related papers
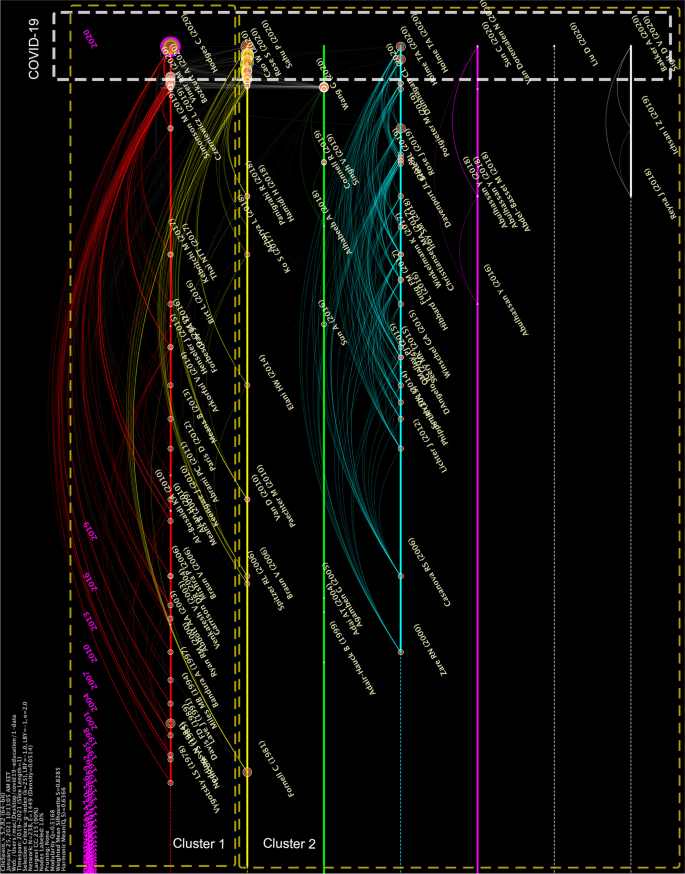
In the second phase of the study, through the examination of the references and citation patterns (e.g., citing and being cited) of the articles in the research corpus, the citation patterns were visualized on a network graphic by clusters (See Fig. 3 ) showing also chronical relationships which enabled to identify pivotal COVID-19 studies. In the second phase of the study, two new themes were identified which were in line with the themes that emerged in the first phase of the study.
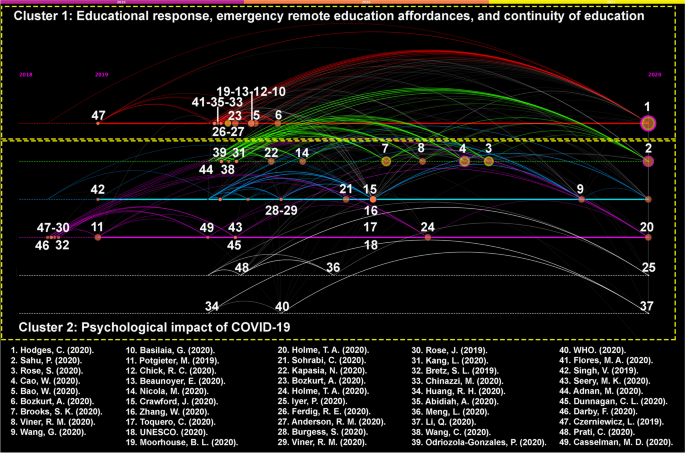
Social networks analysis of the references in COVID-19 and education-related papers 2019–2020 (Only the first authors were labeled – See Appendix Fig. 4 for SNA of references covering pre-COVID-19 period)
Strengths and Limitations
This study is one of the first attempts to use bibliometric approaches benefiting from data mining and analysis techniques to better understand COVID-19 and its consequences on published educational research. By applying such an approach, a large volume of data is able to be visualized and reported. However, besides these strengths, the study also has certain limitations. First, the study uses the Scopus database, which, though being one of the largest databases, does not include all types of publications. Therefore, the publications selected for this study offer only a partial view, as there are many significant publications in gray literature (e.g., reports, briefs, blogs). Second, the study includes only publications written in English, however, with COVID-19 being a global crisis, publications in different languages would provide a complementary view and be helpful in understanding local reflections in the field of education.
Findings and Discussion
Sna and text-mining: thematic patterns in the title, abstract, and keywords of the publications.
This section reports the findings based on a thematic concept map and network graphic that were developed through text mining (Fig. 1 —Textual data composed of 186.234 words visualized according to lexical relationships and co-occurrences) and sociograms created using SNA (Fig. 2 —The top 200 keywords with highest betweenness centrality and 1577 connections among them mapped on a network graph) to visualize the data. Accordingly, seven major themes were identified by analyzing the data through text-mining and SNA: (1) the great reset, (2) digital pedagogy, (3) shifting educational landscape and emerging educational roles, (4) emergency remote education, (5) pedagogy of care, (6) social equity, equality, and injustice, and (7) future of education.
Theme 1: The Great Reset (See path Fig. 1 : lockdown + emergency + community + challenges + during > pandemic and impact > outbreak > coronavirus > pandemic and global > crisis > pandemic > world; See nodes on Fig. 2 : Covid19, pandemic, Coronavirus, lockdown, crisis ). The first theme in the thematic concept map and network graphic is the Great Reset. It has been relatively a short time since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 a pandemic. Although vaccination had already started, the pandemic continued to have an adverse impact on the world. Ever since the start of the pandemic, people were discussing when there would be a return to normal (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020a , b ; Xiao, 2021 ); however, as time goes by, this hope has faded, and returning to normal appears to be far into the future (Schwab & Malleret, 2020 ). The pandemic is seen as a major milestone, in the sense that a macro reset in economic, social, geopolitical, environmental, and technological fields will produce multi-faceted changes affecting almost all aspects of life (Schwab & Malleret, 2020 ). The cover of an issue of the international edition of Time Magazine reflected this idea of a great reset and presented the COVID-19 pandemic as an opportunity to transform the way we live and work (Time, 2020 ). It has been argued that the pandemic will generate the emergence of a new era, and that we will have to adapt to the changes it produces (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020 ). For example, the industrial sector quickly embraced remote work despite its challenges, and it is possible that most industrial companies will not return to the on-site working model even after the pandemic ends (Hern, 2020 ). We can expect a high rate of similar responses in other fields, including education, where COVID-19 has already reshaped our educational systems, the way we deliver education, and pedagogical approaches.
Theme 2: Digital pedagogy (See path on Fig. 1 : distance learning > research > teacher > development > need > training + technology + virtual > digital > communication > support > process > teaching > online > learning > online learning + course > faculty > students > experience ; See nodes on Fig. 2 : online learning, distance learning, computer-based learning, elearning, online education, distance education, online teaching, multimedia-based learning, technology, blended learning, online, digital transformation, ICT, online classes, flexible learning, technology-enhanced learning, digitalization ). Owing to the rapid transition to online education as a result of COVID-19, digital pedagogy and teachers’ competencies in information and communication technology (ICT) integration have gained greater prominence with the unprecedented challenges teachers have faced to adapt to remote teaching and learning. The COVID-19 pandemic has unquestionably manifested the need to prepare teachers to teach online, as most of them have been forced to assume ERE roles with inadequate preparation. Studies involving the use of SNA indicate a correspondence between adapting to a digital pedagogy and the need to equip teachers with greater competency in technology and online teaching (e.g., Blume, 2020 ; König et al., 2020 ). König et al. ( 2020 ) conducted a survey-based study investigating how early career teachers have adapted to online teaching during COVID-19 school closures. Their study found that while all the teachers maintained communication with students and their parents, introduced new learning content, and provided feedback, they lacked the ability to respond to challenges requiring ICT integration, such as those related to providing quality online teaching and to conducting assessments. Likewise, Blume ( 2020 ) noted that most teachers need to acquire digital skills to implement digitally-mediated pedagogy and communication more effectively. Both study findings point to the need for building ICT-related teaching and learning competencies in initial teacher education and teacher professional development. The findings from the SNA conducted in the present study are in line with the aforementioned findings in terms of keyword analysis and overlapping themes and nodes.
Theme 3: Shifting educational landscape and emerging educational roles (See path on Fig. 1 : future > education > role > Covid19; See nodes on Fig. 2 : higher education, education, student, curriculum, university, teachers, learning, professional development, teacher education, knowledge, readiness ). The role of technology in education and human learning has been essential during the COVID-19 pandemic. Technology has become a prerequisite for learning and teaching during the pandemic and will likely continue to be so after it. In the rapid shift to an unprecedented mode of learning and teaching, stakeholders have had to assume different roles in the educational landscape of the new normal. For example, in a comprehensive study involving the participation of over 30 K higher education students from 62 countries conducted by Aristovnik et al. ( 2020 ), it was found that students with certain socio-demographic characteristics (male, lower living standard, from Africa or Asia) were significantly less satisfied with the changes to work/life balance created by the COVID-19 pandemic, and that female students who were facing financial problems were generally more affected by COVID-19 in their emotional life and personal circumstances. Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, there is likely to be carry over in the post-pandemic era of some of the educational changes made during the COVID-19 times. For example, traditional lecture-based teacher-centered classes may be replaced by more student-centered online collaborative classes (Zhu & Liu, 2020 ). This may require the development and proliferation of open educational platforms that allow access to high-quality educational materials (Bozkurt et al., 2020 ) and the adoption of new roles to survive in the learning ecologies informed by digital learning pedagogies. In common with the present study, the aforementioned studies (e.g., Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; König et al., 2020 ) call for more deliberate actions to improve teacher education programs by offering training on various teaching approaches, such as blended, hybrid, flexible, and online learning, to better prepare educators for emerging roles in the post-pandemic era.
Theme 4: Emergency remote education (see path Fig. 1 : higher education > university > student > experience > remote; See nodes on Fig. 2 : Covid19, pandemic, Coronavirus, higher education, education, school closure, emergency remote teaching, emergency remote learning ). Educational institutions have undergone a rapid shift to ERE in the wake of COVID-19 (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020a ; Bozkurt et al., 2020 ; Hodges et al., 2020 ). Although ERE is viewed as similar to distance education, they are essentially different. That is, ERE is a prompt response measure to an emergency situation or unusual circumstances, such as a global pandemic or a civil war, for a temporary period of time, whereas distance education is a planned and systematic approach to instructional design and development grounded in educational theory and practice (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020b ). Due to the urgent nature of situations requiring ERE, it may fall short in embracing the solid pedagogical learning and teaching principles represented by distance education (Hodges et al., 2020 ). The early implementations of ERE primarily involved synchronous video-conferencing sessions that sought to imitate in-person classroom instruction. It is worth noting that educators may have heavily relied on synchronous communication to overcome certain challenges, such as the lack of available materials and planned activities for asynchronous communication. Lockdowns and school closures, which turned homes into compulsory learning environments, have posed major challenges for families and students, including scheduling, device sharing, and learner engagement in a socially distanced home learning environment (Bond, 2020 ). For example, Shim and Lee ( 2020 ) conducted a qualitative study exploring university students’ ERE experiences and reported that students complained about network instability, unilateral interactions, and reduced levels of concentration. The SNA findings clearly highlight that there has been a focus on ERE due to the school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is key to adopt the best practices of ERE and to utilize them regularly in distance education (Bozkurt, 2022 ). Moreover, it is important to note that unless clear distinctions are drawn between these two different forms of distance education or virtual instruction, a series of unfortunate events in education during these COVID-19 times is very likely to take place and lead to fatal errors in instructional practices and to poor student learning outcomes.
Theme 5: Pedagogy of care (See path Fig. 1 : r ole > education > Covid19 > care ; See nodes on Fig. 2 : Stress, anxiety, student wellbeing, coping, care, crisis management, depression ). The thematic concept map and network graphic show the psychological and emotional impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on various stakeholders, revealing that they have experienced anxiety, expressed the need for care, and sought coping strategies. A study by Baloran ( 2020 ), conducted in the southern part of the Philippines to examine college students’ knowledge, attitudes, anxiety, and personal coping strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic, found that the majority of the students experienced anxiety during the lockdown and worried about food security, financial resources, social contact, and large gatherings. It was reported that the students coped with this anxiety by following protective measures, chatting with family members and friends, and motivating themselves to have a positive attitude. In a similar study, Islam et al. ( 2020 ) conducted an investigation to determine whether Bangladeshi college students experienced anxiety and depression and the factors responsible for these emotional responses. Their cross-sectional survey-based study found that a large percentage of the participants had suffered from anxiety and depression during the pandemic. Academic and professional uncertainty, as well as financial insecurity, have been documented as factors contributing to the anxiety and depression among college students. Both studies point to the need for support mechanisms to be established by higher education institutions in order to ensure student wellbeing, provide them with care, and help them to cope with stress, anxiety, and depression. Talidong and Toquero ( 2020 ) reported that, in addition to students’ well-being and care, teachers’ perceptions and experiences of stress and anxiety during the quarantine period need to be taken into account. The authors found that teachers were worried about the safety of their loved ones and were susceptible to anxiety but tended to follow the preventive policies. A pedagogy of care has been presented as an approach that would effectively allow educators to plan more supportive teaching practices during the pandemic by fostering clear and prompt communication with students and their families and taking into consideration learner needs in lesson planning (e.g., Karakaya, 2021 ; Robinson et al., 2020 ). Here it is important to stress that a pedagogy of care is a multifaceted concept, one that involves the concepts of social equity, equality, and injustice.
Theme 6: Social equity, equality, and injustice (See path on Fig. 1 : Impact > outbreak > coronavirus > pandemic > social ; See nodes on Fig. 2 : Support, equity, social justice, digital divide, inequality, social support ). One of the more significant impacts of COVID-19 has been the deepening of the existing social injustices around the world (Oldekop et al., 2020 ; Williamson et al., 2020 ). Long-term school closures have deteriorated social bonds and adversely affected health issues, poverty, economy, food insecurity, and digital divide (Van Lancker & Parolin, 2020 ). Regarding the digital divide, there has been a major disparity in access to devices and data connectivity between high-income and low-income populations increasing the digital divide, social injustice, and inequality in the world (Bozkurt et al., 2020 ). In line with the SNA findings, the digital divide, manifesting itself most visibly in the inadequacy and insufficiency of digital devices and lack of high-speed Internet, can easily result in widespread inequalities. As such, the disparities between low and high socio-economic status families and school districts in terms of digital pedagogy inequality may deepen as teachers in affluent schools are more likely to offer a wide range of online learning activities and thereby secure better student engagement, participation, and interaction (Greenhow et al., 2020 ). These findings demonstrate that social inequities have been sharpened by the unfortunate disparities imposed by the COVID-19, thus requiring us to reimagine a future that mitigates such concerns.
Theme 7: Future of education (See word path on Fig. 1 : Future > education > Covid19 > pandemic > changes and pandemic > coronavirus, outbreak, impact > world ; See nodes on Fig. 2 : Sustainability, resilience, uncertainty, sdg4). Most significantly, COVID-19 the pandemic has shown the entire world that teachers and schools are invaluable resources and execute critical roles in society. Beyond that, with the compulsory changes resulting from the pandemic, it is evident that teaching and learning environments are not exclusive to brick-and-mortar classrooms. Digital technologies, being at the center of teaching and learning during the pandemic period, have been viewed as a pivotal agent in leveraging how learning takes place beyond the classroom walls (Quilter-Pinner & Ambrose, 2020 ). COVID-19 has made some concerns more visible. For example, the well-being of students, teachers, and society at large has gained more importance in these times of crisis. Furthermore, the need for educational technology and digital devices has compounded and amplified social inequities (Pelletier et al., 2021 ; West & Allen, 2020 ). Despite its global challenges, the need for technology and digital devices has highlighted some advantages that are likely to shape the future of education, particularly those related to the benefits of educational technology. For example, online learning could provide a more flexible, informal, self-paced learning environment for students (Adedoyin & Soykan, 2020 ). However, it also bears the risk of minimizing social interaction, as working in shared office environments has shifted to working alone in home-office settings. In this respect, the transformation of online education must involve a particular emphasis on sustaining interactivity through technology (Dwivedi et al., 2020 ). In view of the findings of the aforementioned studies, our text-mining and SNA findings suggest that the COVID-19 impositions may strongly shape the future of education and how learning takes place.
In summary, these themes extracted from the text-mining and SNA point to a significant milestone in the history of humanity, a multi-faceted reset that will affect many fields of life, from education and economics to sociology and lifestyle. The resulting themes have revealed that our natural response to an emerging worldwide situation shifted the educational landscape. The early response of the educational system was emergency-based and emphasized the continuance of in-person instruction via synchronous learning technologies. The subsequent response foregrounded the significance of digitally mediated learning pedagogy, related teacher competencies, and professional development. As various stakeholders (e.g., students, teachers, parents) have experienced a heightened level of anxiety and stress, an emerging strand of research has highlighted the need for care-based and trauma-informed pedagogies as a response to the side effects of the pandemic. In addition, as the global pandemic has made systemic impairments, such as social injustice and inequity, more visible, an important line of research has emerged on how social justice can be ensured given the challenges caused by the pandemic. Lastly, a sizable amount of research indicates that although the COVID-19 pandemic has imposed unprecedented challenges to our personal, educational, and social lives, it has also taught us how to respond to future crises in a timely, technologically-ready, pedagogically appropriate, and inclusive manner.
SNA: Citation Trends in the References of the Sampled Publications
The trends identified through SNA in citation patterns indicate two lines of thematic clusters (see Fig. 3 -A network graph depicting the citing and being cited patterns in the research corpus. Node sizes were defined by their citation count and betweenness centrality.). These clusters align with the results of the analysis of the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the sampled publications and forge the earlier themes (Theme 4: Emergency remote education and Theme 5: Pedagogy of care).
Thematic Cluster 1: The first cluster centers on the abilities of educational response, emergency remote education affordances, and continuity of education (Bozkurt & Sharma, 2020a ; Crawford et al., 2020 ; Hodges et al., 2020 ) to mitigate the impact of COVID-19 on education, especially for more vulnerable and disadvantaged groups (UNESCO, 2020 ; Viner et al., 2020 ). The thematic cluster one agrees with the theme four emergency remote education . The first trend line (See red line in Fig. 3 ) shows that the education system is vulnerable to external threats. Considering that interruption of education is not exclusive to pandemics – for example, political crises have also caused disruptions (Rapp et al., 2016 ) – it is clear that coping mechanisms are needed to ensure the continuity of education under all conditions. In this case, we need to reimagine and recalibrate education to make it resilient, flexible, and adaptive, not only to ensure the continuity of education, but also to ensure social justice, equity, and equality. Given that online education has its own limitations (e.g., it is restricted to online tools and infrastructures), we need to identify alternative entry points for those who do not have digital devices or lack access to the internet.
Thematic Cluster 2: The second cluster centers on the psychological impact of COVID-19 on learners, who during these times suffered a sense of uncertainty (Bozkurt, & Sharma, 2021 ; Cao et al., 2020 ; Rose, 2020 ; Sahu, 2020 ) which suggest that learners are experiencing difficult times that can result in psychological and mental problems. The thematic cluster two agrees with theme five which is pedagogy of care . Therefore, it can be argued that learners' psychological and emotional states should be a top priority. Brooks et al. ( 2020 ) reported the potential of post-traumatic issues with long-lasting effects, on top of the trauma that has already been suffered during the COVID-19 pandemic. In other words, the effects of the COVID-19 crisis may prove to extend beyond their current state and add long-term challenges. Additionally, it has further been reported that the socio-economic effects of the pandemic (Nicola et al., 2020 ) may cause inequality and inequity in educational communities (Beaunoyer et al., 2020 ). The research also shows that learners’ achievement gaps are positively associated with psychological issues, while support and care are negatively associated with their traumatic states (Cao et al., 2020 ). In this context, the second thematic cluster reveals that researchers have seriously considered the psychological and emotional needs of learners in their publications. Care (Noddings, 1984 ) and that trauma-informed pedagogy (Imad, 2020 ) can be a guideline during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. It is quite clear that learners have experienced educational loss (e.g., drop-outs, achievement gaps, academic procrastination, etc.), as well as social and emotional impairments (e.g., fear, frustration, confusion, anxiety, sense of isolation, death of loved ones, etc.). Therefore, we need to critically approach the situation, focusing first on healing our social and emotional losses, and then, on the educational losses. As Bozkurt and Sharma ( 2020a ) put it:
“What we teach in these times can have secondary importance. We have to keep in mind that students will remember not the educational content delivered, but how they felt during these hard times. With an empathetic approach, the story will not center on how to successfully deliver educational content, but it will be on how learners narrate these times” (p. iv).
Conclusion and Suggestions
The results from this study indicate that quick adaptability and flexibility have been key to surviving the substantial challenges generated by COVID-19. However, extreme demands on flexibility have taken a toll on human well-being and have exacerbated systemic issues like inequity and inequality. Using data mining that involved network analysis and text mining as analytical tools, this research provides a panoramic picture of the COVID-19-related themes educational researchers have addressed in their work. A sample of 1150 references yielded seven themes, which served to provide a comprehensive meta-narrative about COVID-19 and its impact on education.
A portion of the sampled publications focused on what we refer to as the great reset , highlighting the challenges that the emergency lockdown brought to the world. A publication pattern centered around digital pedagogy posited distance and online learning as key components and identified the need for teacher training. Given the need for adaptability, a third theme revealed the demand for professional development in higher education and a future shift in educational roles. It can be recommended that future research investigate institutional policy changes and the adaptation to these changes in renewed educational roles. The ERE theme centered on the lack of preparation in instituting the forced changes brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. The publications related to this theme revealed that the COVID-19 pandemic uncovered silent threads in educational environments, like depression, inequality, and injustice. A pedagogy of care has been developed with the aim of reducing anxiety and providing support through coping strategies. These research patterns indicate that the future of education demands sustainability and resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Results of the thematic analysis of citation patterns (Fig. 3 ) overlapped with two of the themes found in our thematic concept map (Fig. 1 ) and network graphic (Fig. 2 ). It was shown that researchers have emphasized the continuity of education and the psychological effects of the COVID-19 crisis on learners. Creating coping strategies to deal with global crises (e.g., pandemics, political upheavals, natural disasters) has been shown to be a priority for educational researchers. The pedagogy of resilience (Purdue University Innovative learning, n.d. ) provides governments, institutions, and instructors with an alternative tool to applying to their contexts in the face of hardship. Furthermore, prioritizing the psychological long-term effects of the crisis in learners could alleviate achievement gaps. We recommend that researchers support grieving learners through care (Noddings, 1984 ) and trauma-informed pedagogy (Imad, 2020 ). Our resilience and empathy will reflect our preparedness for impending crises. The thematic analysis of citation patterns (1: educational response, emergency remote education affordances, and continuity of education; 2: psychological impact of COVID-19) further indicates suggestions for future instructional/learning designers. Freire ( 1985 ) argues that to transform the world we need to humanize it. Supporting that argument, the need for human-centered pedagogical approaches (Robinson et al., 2020 ) by considering learning a multifaceted process (Hodges et al., 2021 ) for well-designed learning experiences (Moore et al., 2021 ) is a requirement and instructional/learning designers have an important responsibility not only to design courses but an entire learning ecosystem where diversity, sensitivity, and inclusivity are prioritized.
ERE is not a representative feature in the field of online education or distance education but rather, a forced reaction to extraordinary circumstances in education. The increasing confusion between the practice of ERE and online learning could have catastrophic consequences in learners' outcomes, teachers' instructional practices, and institutional policies. Researchers, educators, and policymakers must work cooperatively and be guided by sound work in the field of distance learning to design nourishing educational environments that serve students’ best interests.
In this study, text mining and social network analysis were demonstrated to be powerful tools for exploring and visualizing patterns in COVID-19-related educational research. However, a more in-depth examination is still needed to synthesize effective strategies that can be used to support us in future crises. Systematic reviews that use classical manual coding techniques may take more time but increase our understanding of a phenomenon and help us to develop specific action plans. Future systematic reviews can use the seven themes identified in this study to analyze primary studies and find strategies that counteract the survival of the fittest mindset to ensure that no student is left behind.
Data Availability
The dataset is available from the authors upon request.
Adedoyin, O. B., & Soykan, E. (2020). Covid-19 pandemic and online learning: The challenges and opportunities. Interactive Learning Environments . https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1813180
Article Google Scholar
Aggarwal, C. C., & Zhai, C. (Eds.). (2012). Mining text data. Springer Science & Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3223 -4
Aristovnik, A., Keržič, D., Ravšelj, D., Tomaževič, N., & Umek, L. (2020). Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on life of higher education students: A global perspective. Sustainability, 12 (20), 8438. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208438
Ayebi-Arthur, K. (2017). E-learning, resilience and change in higher education: Helping a university cope after a natural disaster. E-Learning and Digital Media, 14 (5), 259–274. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042753017751712
Baker, V. L. (2020, March 25). How colleges can better help faculty during the pandemic . Inside Higher Ed. https://www.insidehighered.com/views/2020/03/25/recommendations-how-colleges-can-better-support-their-faculty-during-covid-19 . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Baloran, E. T. (2020). Knowledge, attitudes, anxiety, and coping strategies of students during COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Loss and Trauma, 25 (8), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2020.1769300
Beaunoyer, E., Dupéré, S., & Guitton, M. J. (2020). COVID-19 and digital inequalities: Reciprocal impacts and mitigation strategies. Computers in Human Behavior, 111 , 106424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106424
Blume, C. (2020). German Teachers’ Digital Habitus and Their Pandemic Pedagogy. Postdigital Science and Education, 2 (3), 879–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42438-020-00174-9
Bond, M. (2020). Schools and emergency remote education during the COVID-19 pandemic: A living rapid systematic review. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 15 (2), 191–247. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4425683
Bozkurt, A. (2019). Intellectual roots of distance education: A progressive knowledge domain analysis. Distance Education, 40 (4), 497–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587919.2019.1681894
Bozkurt, A. (2022). Resilience, adaptability, and sustainability of higher education: A systematic mapping study on the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the transition to the new normal. Journal of Learning for Development (JL4D), 9 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6370948
Bozkurt, A., & Sharma, R. C. (2020a). Emergency remote teaching in a time of global crisis due to CoronaVirus pandemic. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 15 (1), i–vi. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3778083
Bozkurt, A., & Sharma, R. C. (2020b). Education in normal, new normal, and next normal: Observations from the past, insights from the present and projections for the future. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 15 (2), i–x. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4362664
Bozkurt, A., & Sharma, R. C. (2021). On the verge of a new renaissance: Care and empathy oriented, human-centered pandemic pedagogy. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 16 (1), i–vii. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5070496
Bozkurt, A., Jung, I., Xiao, J., Vladimirschi, V., Schuwer, R., Egorov, G., Lambert, S. R., Al-Freih, M., Pete, J., Olcott, D., Jr., Rodes, V., Aranciaga, I., Bali, M., Alvarez, A. V., Jr., Roberts, J., Pazurek, A., Raffaghelli, J. E., Panagiotou, N., de Coëtlogon, P., … Paskevicius, M. (2020). A global outlook to the interruption of education due to COVID-19 pandemic: Navigating in a time of uncertainty and crisis. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 15 (1), 1–126. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3878572
Brooks, S. K., Webster, R. K., Smith, L. E., Woodland, L., Wessely, S., Greenberg, N., & Rubin, G. J. (2020). The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. The Lancet, 395 (10227), 912–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8
Cao, W., Fang, Z., Hou, G., Han, M., Xu, X., Dong, J., & Zheng, J. (2020). The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on college students in China. Psychiatry Research, 287 , 112934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112934
Crawford, J., Butler-Henderson, K., Rudolph, J., Malkawi, B., Glowatz, M., Burton, R., ... & Lam, S. (2020). COVID-19: 20 countries' higher education intra-period digital pedagogy responses. Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 3 (1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2020.3.1.7
Czerniewicz, L., Trotter, H., & Haupt, G. (2019). Online teaching in response to student protests and campus shutdowns: Academics’ perspectives. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16 (1), 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0170-1
DePietro, A. (2020). Here’s a look at the impact of coronavirus (COVID-19) on colleges and universities in the U.S. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/andrewdepietro/2020/04/30/impact-coronavirus-covid-19-colleges-universities/?sh=20a7121461a6 . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, D. L., Coombs, C., Constantiou, I., Duan, Y., Edwards, J. S., Gupta, B., Lal, B., Misra, S., Prashant, P., Raman, R., Rana, N. P., Sharma, S. K., & Upadhyay, N. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on information management research and practice: Transforming education, work and life. International Journal of Information Management, 55 , 102211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102211
Fayyad, U., Grinstein, G. G., & Wierse, A. (Eds.). (2002). Information visualization in data mining and knowledge discovery . Morgan Kaufmann.
Google Scholar
Freire, P. (1985). The politics of education: Culture, power and liberation . Bergin & Garvey.
Book Google Scholar
Greenhow, C., Lewin, C., & Staud Willet, K. B. (2020). The educational response to Covid-19 across two countries: A critical examination of initial digital pedagogy adoption. Technology, Pedagogy and Education . https://doi.org/10.1080/1475939X.2020.1866654
Guitton, M. J. (2020). Cyberpsychology research and COVID-19. Computers in Human Behavior, 111 , 106357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106357
Hansen, D. L., Shneiderman, B., Smith, M. A., & Himelboim, I. (2020). Analyzing social media networks with NodeXL: Insights from a connected world (2nd ed.). Morgan Kaufmann.
Hern, A. (2020). Covid19 could cause permanent shift towards home working. The Guardian. http://www.miamidadetpo.org/library/2020-03-13-uk-covid19-could-cause-permanent-shift-towards-home-working.pdf . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T., & Bond, A. (2020). The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning . EDUCAUSE Review. https://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Hodges, C. B., Moore, S. L., Lockee, B. B., Aaron Bond, M., Jewett, A. (2021). An Instructional Design Process for Emergency Remote Teaching. In Burgos, D., Tlili, A., Tabacco, A. (Eds), Radical Solutions for Education in a Crisis Context. Lecture Notes in Educational Technology (pp. 37–51). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7869-4_3
Imad, M. (2020). Leveraging the neuroscience of now. Inside Higher Ed . https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2020/06/03/seven-recommendations-helping-students-thrive-times-trauma . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Islam, M. A., Barna, S. D., Raihan, H., Khan, M. N. A., & Hossain, M. T. (2020). Depression and anxiety among university students during the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh: A web-based cross-sectional survey. PLoS One, 15 (8), e0238162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238162
Johnson, N., Veletsianos, G., & Seaman, J. (2020). U.S. faculty and administrators’ experiences and approaches in the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic. Online Learning, 24 (2), 6–21. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v24i2.2285
Karakaya, K. (2021). Design considerations in emergency remote teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: A human-centered approach. Education Technology Research and Development, 69 , 295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-020-09884-0
König, J., Jäger-Biela, D. J., & Glutsch, N. (2020). Adapting to online teaching during COVID-19 school closure: Teacher education and teacher competence effects among early career teachers in Germany. European Journal of Teacher Education, 43 (4), 608–622. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2020.1809650
Korkmaz, G., & Toraman, Ç. (2020). Are we ready for the post-COVID-19 educational practice? An investigation into what educators think as to online learning. International Journal of Technology in Education and Science, 4 (4), 293–309. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijtes.v4i4.110
Lorenzo, G. (2008). The Sloan Semester. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 12 (2), 5–40. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v12i2.1693
Mishra, S., Sahoo, S., & Pandey, S. (2021). Research trends in online distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Distance Education, 42 (4), 494–519. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587919.2021.1986373
Moore, S., Trust, T., Lockee, B. B., Bond, A., & Hodges, C. (2021). One year later... and counting: Reflections on emergency remote teaching and online learning. EDUCAUSE Review. https://er.educause.edu/articles/2021/11/one-year-later-and-counting-reflections-on-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., ... & Agha, R. (2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus and COVID-19 pandemic: A review. International Journal of Surgery, 78 , 185-193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018
Noddings, N. (1984). Caring: A feminine approach to ethics . Moral Education.
Oldekop, J. A., Horner, R., Hulme, D., Adhikari, R., Agarwal, B., ... Zheng, Y. (2020). Covid-19 and the case for global development. World Development, 134 , 105044.
Pelletier, K., Brown, M., Brooks, D. C., McCormack, M., Reeves, J., Arbino, N., Bozkurt, A., Crawford, S., Czerniewicz, L., Gibson, R., Linder, K., Mason, J., & Mondelli, V. (2021). 2021 EDUCAUSE Horizon Report Teaching and Learning Edition . EDUCAUSE. https://www.learntechlib.org/p/219489/ . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Purdue University Innovative Learning. (n.d.). Hy-flex and resilient pedagogy resources. https://www.purdue.edu/innovativelearning/teaching-remotely/pedagogy.aspx . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Quilter-Pinner, H., & Ambrose, A. (2020). The new normal: The future of education after Covid-19 . The Institute for Public Policy Research.
Rapp, C., Gülbahar, Y., & Adnan, M. (2016). e-Tutor: A multilingual open educational resource for faculty development to teach online. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 17 (5), 284–289. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v17i5.2783
Robinson, H., Al-Freih, M., & Kilgore, W. (2020). Designing with care: Towards a care-centered model for online learning design. The International Journal of Information and Learning Technology, 37 (3), 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-10-2019-0098
Rodrigues, M., Franco, M., & Silva, R. (2020). COVID-19 and Disruption in Management and Education Academics: Bibliometric Mapping and Analysis. Sustainability, 12 (18), 7362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187362
Rose, S. (2020). Medical student education in the time of COVID-19. JAMA, 323 (21), 2131–2132. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.5227
Sahu, P. (2020). Closure of universities due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): impact on education and mental health of students and academic staff. Cureus, 12 (4). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7541
Schwab, M., & Malleret, T. (2020). Covid-19: The great reset . World Economic Forum.
Shim, T. E., & Lee, S. Y. (2020). College students’ experience of emergency remote teaching due to COVID-19. Children and Youth Services Review, 119 , 105578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105578
Smith, A. E., & Humphreys, M. S. (2006). Evaluation of unsupervised semantic mapping of natural language with Leximancer concept mapping. Behavior Research Methods, 38 (2), 262–279. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03192778
Suleri, J. (2020). Learners’ experience and expectations during and post COVID-19 in higher education. Research in Hospitality Management, 10 (2), 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/22243534.2020.1869463
Talidong, K. J. B., & Toquero, C. M. D. (2020). Philippine teachers’ practices to deal with anxiety amid COVID-19. Journal of Loss and Trauma, 25 (6–7), 573–579. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2020.1759225
Thurmond, V. A. (2001). The point of triangulation. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 33 (3), 253–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2001.00253.x
Time (2020). The great reset: cover image. https://time.com/collection/great-reset/ . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Tull, S., Dabner, N., & Ayebi-Arthur, K. (2017). Social media and e-learning in response to seismic events: Resilient practices. Journal of Open, Flexible & Distance Learning , 21 (1), 63–76. http://www.jofdl.nz/index.php/JOFDL/article/view/405 . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
UNESCO. (2020). COVID-19 education response. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse/ . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Unger, S., & Meiran, W. R. (2020). Student attitudes towards online education during the COVID-19 viral outbreak of 2020: Distance learning in a time of social distance. International Journal of Technology in Education and Science, 4 (4), 256–266. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijtes.v4i4.107
Van Lancker, W., & Parolin, Z. (2020). COVID-19, school closures, and child poverty: A social crisis in the making [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 7]. T he Lancet Public Health, 5 (5), e243–e244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30084-0
Viner, R. M., Russell, S. J., Croker, H., Packer, J., Ward, J., Stansfield, C., ... & Booy, R. (2020). School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: A rapid systematic review. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, 4 (5), 397-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30095-X
West, D., & Allen, J. (2020). How to address inequality exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Tech Crunch . https://techcrunch.com/2020/10/27/how-to-address-inequality-exposed-by-the-covid-19-pandemic/ . Accessed 15 Apr 2022
Williamson, B., Eynon, R., & Potter, J. (2020). Pandemic politics, pedagogies and practices: Digital technologies and distance education during the coronavirus emergency. Learning, Media and Technology, 45 (2), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439884.2020.1761641
Xiao, J. (2021). From equality to equity to justice: Should online education be the new normal in education?. In Bozkurt, A. (Eds.), Handbook of research on emerging pedagogies for the future of education: Trauma-informed, care, and pandemic pedagogy (pp. 1–15). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-7275-7.ch001
Zhu, X., & Liu, J. (2020). Education in and after Covid-19: Immediate responses and long-term visions. Postdigital Science and Education, 2 , 695–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42438-020-00126-3
Download references
Acknowledgements
This paper is dedicated to all educators and instructional/learning designers who ensured the continuity of education during the tough times of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This article is produced as a part of the 2020 AECT Mentoring Program.
This paper is supported by Anadolu University, Scientific Research Commission with grant no: 2106E084.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Distance Education Department, Anadolu University, Eskişehir, Turkey
Aras Bozkurt
Department of English Studies, University of South Africa, Pretoria, South Africa
Anadolu Üniversitesi, Açıköğretim Fakültesi, Kat:7, Oda:702, 26470, Tepebaşı, Eskişehir, Turkey
Applied Linguistics & Technology Department, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA
Kadir Karakaya
Educational Psychology, Learning Sciences, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA
Educational Technology & Human-Computer Interaction, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA
Özlem Karakaya
Curriculum and Instruction, Learning Design and Technology, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA
Daniela Castellanos-Reyes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing, Visualization, Funding acquisition.; KK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing.; MT: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing.; ÖK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing.; DCR: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Aras Bozkurt .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This is a systematic review study and exempt from ethical approval.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
SNA of references covering pre-COVID-19 period (Only the first authors were labeled)
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bozkurt, A., Karakaya, K., Turk, M. et al. The Impact of COVID-19 on Education: A Meta-Narrative Review. TechTrends 66 , 883–896 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-00759-0
Download citation
Accepted : 22 June 2022
Published : 05 July 2022
Issue Date : September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-00759-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coronavirus pandemic
- Education during the pandemic
- Teaching and learning in the new normal
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Global Education Coalition
- Stories & Ideas
- Explore initiatives & stories from UNESCO networks
- COVID-19 Impact on education
- School meals during school closures
- Open access to facilitate research and information on COVID-19
- Visual to combat COVID-19
- Media support
- UNESCO-WHO audio resources
- Audio resources to fight disinformation
- Resources for documentary heritage professionals
Education: From COVID-19 school closures to recovery
After the historic disruption of the COVID-19 pandemic, most schools are back open worldwide but education is still in recovery assessing the damage done and lessons learned. Education: The pandemic affected more than 1.6 billion students and youth globally, with the most vulnerable learners being hit hardest. Some gains already made towards the goals of the 2030 Education Agenda were lost.
From the outset UNESCO's Education Sector worked with ministries of education, public and private partners and civil society to ensure continued learning for all children and youth. The Sector's work is now focused on prioritizing education as a public good for everyone in order to avoid a generational catastrophe and drive sustainable recovery.
- Read more on UNESCO's initiatives during and after the pandemic

A multi-sector Coalition to protect the right to education during unprecedented disruption from response to recovery #LearningNeverStops
Monitoring of school closures
Throughout the pandemic, in close cooperation with ministers of education, UNESCO monitored the evolution of school closures around the world. Data presented in the interactive map show the evolution from February 2020 to June 2022. Download the data here .

UNESCO's campaigns
Everyone can play a role in supporting girls’ education
Two years into the COVID-19 crisis: Students and teachers share their stories
Evidence of good practices, practical tips and references to mitigate the impact of school closures
Explore UNESCO database for useful resources.
Video messages from the first group of partners who joined UNESCO’s Global Education Coalition.
Latest publications

Related items
- Programme implementation
- UN & International cooperation
- SDG: SDG 4 - Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- See more add
COVID-19 and education: The lingering effects of unfinished learning
As this most disrupted of school years draws to a close, it is time to take stock of the impact of the pandemic on student learning and well-being. Although the 2020–21 academic year ended on a high note—with rising vaccination rates, outdoor in-person graduations, and access to at least some in-person learning for 98 percent of students—it was as a whole perhaps one of the most challenging for educators and students in our nation’s history. 1 “Burbio’s K-12 school opening tracker,” Burbio, accessed May 31, 2021, cai.burbio.com. By the end of the school year, only 2 percent of students were in virtual-only districts. Many students, however, chose to keep learning virtually in districts that were offering hybrid or fully in-person learning.
Our analysis shows that the impact of the pandemic on K–12 student learning was significant, leaving students on average five months behind in mathematics and four months behind in reading by the end of the school year. The pandemic widened preexisting opportunity and achievement gaps, hitting historically disadvantaged students hardest. In math, students in majority Black schools ended the year with six months of unfinished learning, students in low-income schools with seven. High schoolers have become more likely to drop out of school, and high school seniors, especially those from low-income families, are less likely to go on to postsecondary education. And the crisis had an impact on not just academics but also the broader health and well-being of students, with more than 35 percent of parents very or extremely concerned about their children’s mental health.
The fallout from the pandemic threatens to depress this generation’s prospects and constrict their opportunities far into adulthood. The ripple effects may undermine their chances of attending college and ultimately finding a fulfilling job that enables them to support a family. Our analysis suggests that, unless steps are taken to address unfinished learning, today’s students may earn $49,000 to $61,000 less over their lifetime owing to the impact of the pandemic on their schooling. The impact on the US economy could amount to $128 billion to $188 billion every year as this cohort enters the workforce.
Federal funds are in place to help states and districts respond, though funding is only part of the answer. The deep-rooted challenges in our school systems predate the pandemic and have resisted many reform efforts. States and districts have a critical role to play in marshaling that funding into sustainable programs that improve student outcomes. They can ensure rigorous implementation of evidence-based initiatives, while also piloting and tracking the impact of innovative new approaches. Although it is too early to fully assess the effectiveness of postpandemic solutions to unfinished learning, the scope of action is already clear. The immediate imperative is to not only reopen schools and recover unfinished learning but also reimagine education systems for the long term. Across all of these priorities it will be critical to take a holistic approach, listening to students and parents and designing programs that meet academic and nonacademic needs alike.
What have we learned about unfinished learning?
As the 2020–21 school year began, just 40 percent of K–12 students were in districts that offered any in-person instruction. By the end of the year, more than 98 percent of students had access to some form of in-person learning, from the traditional five days a week to hybrid models. In the interim, districts oscillated among virtual, hybrid, and in-person learning as they balanced the need to keep students and staff safe with the need to provide an effective learning environment. Students faced multiple schedule changes, were assigned new teachers midyear, and struggled with glitchy internet connections and Zoom fatigue. This was a uniquely challenging year for teachers and students, and it is no surprise that it has left its mark—on student learning, and on student well-being.
As we analyze the cost of the pandemic, we use the term “unfinished learning” to capture the reality that students were not given the opportunity this year to complete all the learning they would have completed in a typical year. Some students who have disengaged from school altogether may have slipped backward, losing knowledge or skills they once had. The majority simply learned less than they would have in a typical year, but this is nonetheless important. Students who move on to the next grade unprepared are missing key building blocks of knowledge that are necessary for success, while students who repeat a year are much less likely to complete high school and move on to college. And it’s not just academic knowledge these students may miss out on. They are at risk of finishing school without the skills, behaviors, and mindsets to succeed in college or in the workforce. An accurate assessment of the depth and extent of unfinished learning will best enable districts and states to support students in catching up on the learning they missed and moving past the pandemic and into a successful future.
Students testing in 2021 were about ten points behind in math and nine points behind in reading, compared with matched students in previous years.
Unfinished learning is real—and inequitable
To assess student learning through the pandemic, we analyzed Curriculum Associates’ i-Ready in-school assessment results of more than 1.6 million elementary school students across more than 40 states. 2 The Curriculum Associates in-school sample consisted of 1.6 million K–6 students in mathematics and 1.5 million in reading. The math sample came from all 50 states, but 23 states accounted for 90 percent of the sample. The reading sample came from 46 states, with 21 states accounting for 90 percent of the sample. Florida accounted for 29 percent of the math and 30 percent of the reading sample. In general, states that had reopened schools are overweighted given the in-school nature of the assessment. We compared students’ performance in the spring of 2021 with the performance of similar students prior to the pandemic. 3 Specifically, we compared spring 2021 results to those of historically matched students in the springs of 2019, 2018, and 2017. Students testing in 2021 were about ten points behind in math and nine points behind in reading, compared with matched students in previous years.
To get a sense of the magnitude of these gaps, we translated these differences in scores to a more intuitive measure—months of learning. Although there is no perfect way to make this translation, we can get a sense of how far students are behind by comparing the levels students attained this spring with the growth in learning that usually occurs from one grade level to the next. We found that this cohort of students is five months behind in math and four months behind in reading, compared with where we would expect them to be based on historical data. 4 The conversion into months of learning compares students’ achievement in the spring of one grade level with their performance in the spring of the next grade level, treating this spring-to-spring difference in historical scores as a “year” of learning. It assumes a ten-month school year with a two-month summer vacation. Actual school schedules vary significantly, and i-Ready’s typical growth numbers for a “year” of learning are based on 30 weeks of actual instruction between the fall and the spring rather than on a spring-to-spring calendar-year comparison.
Unfinished learning did not vary significantly across elementary grades. Despite reports that remote learning was more challenging for early elementary students, 5 Marva Hinton, “Why teaching kindergarten online is so very, very hard,” Edutopia, October 21, 2020, edutopia.org. our results suggest the impact was just as meaningful for older elementary students. 6 While our analysis only includes results from students who tested in-school in the spring, many of these students were learning remotely for meaningful portions of the fall and the winter. We can hypothesize that perhaps younger elementary students received more help from parents and older siblings, and that older elementary students were more likely to be struggling alone.
It is also worth remembering that our numbers capture the “average” progress by grade level. Especially in early reading, this average can conceal a wide range of outcomes. Another way of cutting the data looks instead at which students have dropped further behind grade levels. A recent report suggests that more first and second graders have ended this year two or more grade levels below expectations than in any previous year. 7 Academic achievement at the end of the 2020–2021 school year , Curriculum Associates, June 2021, curriculumassociates.com. Given the major strides children at this age typically make in mastering reading, and the critical importance of early reading for later academic success, this is of particular concern.
While all types of students experienced unfinished learning, some groups were disproportionately affected. Students of color and low-income students suffered most. Students in majority-Black schools ended the school year six months behind in both math and reading, while students in majority-white schools ended up just four months behind in math and three months behind in reading. 8 To respect students’ privacy, we cannot isolate the race or income of individual students in our sample, but we can look at school-level demographics. Students in predominantly low-income schools and in urban locations also lost more learning during the pandemic than their peers in high-income rural and suburban schools (Exhibit 1).
In fall 2020, we projected that students could lose as much as five to ten months of learning in mathematics, and about half of that in reading, by the end of the school year. Spring assessment results came in toward the lower end of these projections, suggesting that districts and states were able to improve the quality of remote and hybrid learning through the 2020–21 school year and bring more students back into classrooms.
Indeed, if we look at the data over time, some interesting patterns emerge. 9 The composition of the fall student sample was different from that of the spring sample, because more students returned to in-person assessments in the spring. Some of the increase in unfinished learning from fall to spring could be because the spring assessment included previously virtual students, who may have struggled more during the school year. Even so, the spring data are the best reflection of unfinished learning at the end of the school year. Taking math as an example, as schools closed their buildings in the spring of 2020, students fell behind rapidly, learning almost no new math content over the final few months of the 2019–20 school year. Over the summer, we assume that they experienced the typical “summer slide” in which students lose some of the academic knowledge and skills they had learned the year before. Then they resumed learning through the 2020–21 school year, but at a slower pace than usual, resulting in five months of unfinished learning by the end of the year (Exhibit 2). 10 These lines simplify the pattern of typical learning through the year. In a typical year, students learn more in the fall and less in the spring, and only learn during periods of instruction (the chart includes the well-documented learning loss that happens during the summer, but does not include shorter holidays when students are not in school receiving instruction).
In reading, however, the story is somewhat different. As schools closed their buildings in March 2020, students continued to progress in reading, albeit at a slower pace. During the summer, we assume that students’ reading level stayed roughly flat, as in previous years. The pace of learning increased slightly over the 2020–21 school year, but the difference was not as great as it was in math, resulting in four months of unfinished learning by the end of the school year (Exhibit 3). Put another way, the initial shock in reading was less severe, but the improvements to remote and hybrid learning seem to have had less impact in reading than they did in math.
Before we celebrate the improvements in student trajectories between the initial school shutdowns and the subsequent year of learning, we should remember that these are still sobering numbers. On average, students who took the spring assessments in school are half a year behind in math, and nearly that in reading. For Black and Hispanic students, the losses are not only greater but also piled on top of historical inequities in opportunity and achievement (Exhibit 4).
Furthermore, these results likely represent an optimistic scenario. They reflect outcomes for students who took interim assessments in the spring in a school building 11 Students who took the assessment out of school are not included in our sample because we could not guarantee fidelity and comparability of results, given the change in the testing environment. Out-of-school students represent about a third of the students taking i-Ready assessments in the spring, and we will not have an accurate understanding of the pandemic’s impact on their learning until they return to school buildings, likely in the fall. —and thus exclude students who remained remote throughout the entire school year, and who may have experienced the most disruption to their schooling. 12 Initial results from Texas suggest that districts with mostly virtual instruction experienced more unfinished learning than those with mostly in-person instruction. The percent of students meeting math expectations dropped 32 percent in mostly virtual districts but just 9 percent in mostly in-person ones. See Reese Oxner, “Texas students’ standardized test scores dropped dramatically during the pandemic, especially in math,” Texas Tribune , June 28, 2021, texastribune.org. The Curriculum Associates data cover a broad variety of schools and states across the country, but are not fully representative, being overweighted for rural and southeastern states that were more likely to get students back into the classrooms this year. Finally, these data cover only elementary schools. They are silent on the academic impact of the pandemic for middle and high schoolers. However, data from school districts suggest that, even for older students, the pandemic has had a significant effect on learning. 13 For example, in Salt Lake City, the percentage of middle and high school students failing a class jumped by 60 percent, from 2,500 to 4,000, during the pandemic. To learn about increased failure rates across multiple districts from the Bay Area to New Mexico, Austin, and Hawaii, see Richard Fulton, “Failing Grades,” Inside Higher Ed , March 8, 2021, insidehighered.com.
The harm inflicted by the pandemic goes beyond academics
Students didn’t just lose academic learning during the pandemic. Some lost family members; others had caregivers who lost their jobs and sources of income; and almost all experienced social isolation.
These pressures have taken a toll on students of all ages. In our recent survey of 16,370 parents across every state in America, 35 percent of parents said they were very or extremely concerned about their child’s mental health, with a similar proportion worried about their child’s social and emotional well-being. Roughly 80 percent of parents had some level of concern about their child’s mental health or social and emotional health and development since the pandemic began. Parental concerns about mental health span grade levels but are slightly lower for parents of early elementary school students. 14 While 30.7% percent of all K–2 parents were very or extremely concerned, a peak of 37.6% percent of eighth-grade parents were.
Parents also report increases in clinical mental health conditions among their children, with a five-percentage-point increase in anxiety and a six-percentage-point increase in depression. They also report increases in behaviors such as social withdrawal, self-isolation, lethargy, and irrational fears (Exhibit 5). Despite increased levels of concern among parents, the amount of mental health assessment and testing done for children is 6.1 percent lower than it was in 2019 —the steepest decline in assessment and testing rates of any age group.
Broader student well-being is not independent of academics. Parents whose children have fallen significantly behind academically are one-third more likely to say that they are very or extremely concerned about their children’s mental health. Black and Hispanic parents are seven to nine percentage points more likely than white parents to report higher levels of concern. Unaddressed mental-health challenges will likely have a knock-on effect on academics going forward as well. Research shows that trauma and other mental-health issues can influence children’s attendance, their ability to complete schoolwork in and out of class, and even the way they learn. 15 Satu Larson et al., “Chronic childhood trauma, mental health, academic achievement, and school-based health center mental health services,” Journal of School Health , 2017, 87(9), 675–86, escholarship.org.
In our recent survey of 16,370 parents across every state in America, 35 percent of parents said they were very or extremely concerned about their child’s mental health.
The impact of unfinished learning on diminished student well-being seems to be playing out in the choices that students are making. Some students have already effectively dropped out of formal education entirely. 16 To assess the impact of the pandemic on dropout rates, we have to look beyond official enrollment data, which are only published annually, and which only capture whether a child has enrolled at the beginning of the year, not whether they are engaged and attending school. Chronic absenteeism rates provide clues as to which students are likely to persist in school and which students are at risk of dropping out. Our parent survey suggests that chronic absenteeism for eighth through 12th graders has increased by 12 percentage points, and 42 percent of the students who are new to chronic absenteeism are attending no school at all, according to their parents. Scaled up to the national level, this suggests that 2.3 million to 4.6 million additional eighth- to 12th-grade students were chronically absent from school this year, in addition to the 3.1 million who are chronically absent in nonpandemic years. State and district data on chronic absenteeism are still emerging, but data released so far also suggest a sharp uptick in absenteeism rates nationwide, particularly in higher grades. 17 A review of available state and district data, including data released by 14 states and 11 districts, showed increases in chronic absenteeism of between three and 16 percentage points, with an average of seven percentage points. However, many states changed the definition of absenteeism during the pandemic, so a true like-for-like comparison is difficult to obtain. According to emerging state and district data, increases in chronic absenteeism are highest among populations with historically low rates. This is reflected also in our survey results. Black students, with the highest historical absenteeism rates, saw more modest increases during the pandemic than white or Hispanic students (Exhibit 6).
It remains unclear whether these pandemic-related chronic absentees will drop out at rates similar to those of students who were chronically absent prior to the pandemic. Some students could choose to return to school once in-person options are restored; but some portion of these newly absent students will likely drop out of school altogether. Based on historical links between chronic absenteeism and dropout rates, as well as differentials in absenteeism between fully virtual and fully in-person students, we estimate that an additional 617,000 to 1.2 million eighth–12th graders could drop out of school altogether because of the pandemic if efforts are not made to reengage them in learning next year. 18 The federal definition of chronic absenteeism is missing more than 15 days of school each year. According to the Utah Education Policy Center’s research brief on chronic absenteeism, the overall correlation between one year of chronic absence between eighth and 12th grade and dropping out of school is 0.134. For more, see Utah Education Policy Center, Research brief: Chronic absenteeism , July 2012, uepc.utah.edu. We then apply the differential in chronic absenteeism between fully virtual and fully in-person students to account for virtual students reengaging when in-person education is offered. For students who were not attending school at all, we assumed that 50 to 75 percent would not return to learning. This estimation is partly based on The on-track indicator as a predictor of high school graduation from the UChicago Consortium on School Research, which estimates that up to 75 percent of high school students who are “off track”—either failing or behind in credits—do not graduate in five years. For more, see Elaine Allensworth and John Q. Easton, The on-track indicator as a predictor of high school graduation , UChicago Consortium on School Research, 2005, consortium.uchicago.edu.
Even among students who complete high school, many may not fulfill their dreams of going on to postsecondary education. Our survey suggests that 17 percent of high school seniors who had planned to attend postsecondary education abandoned their plans—most often because they had joined or were planning to join the workforce or because the costs of college were too high. The number is much higher among low-income high school seniors, with 26 percent abandoning their plans. Low-income seniors are more likely to state cost as a reason, with high-income seniors more likely to be planning to reapply the following year or enroll in a gap-year program. This is consistent with National Student Clearinghouse reports that show overall college enrollment declines, with low-income, high-poverty, and high-minority high schools disproportionately affected. 19 Todd Sedmak, “Fall 2020 college enrollment update for the high school graduating class of 2020,” National Student Clearinghouse, March 25, 2021, studentclearinghouse.org; Todd Sedmak, “Spring 2021 college enrollment declines 603,000 to 16.9 million students,” National Student Clearinghouse, June 10, 2021, studentclearinghouse.org.
Unfinished learning has long-term consequences
The cumulative effects of the pandemic could have a long-term impact on an entire generation of students. Education achievement and attainment are linked not only to higher earnings but also to better health, reduced incarceration rates, and greater political participation. 20 See, for example, Michael Grossman, “Education and nonmarket outcomes,” in Handbook of the Economics of Education, Volume 1 , ed. Eric Hanushek and Finis Welch (Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006), 577–633; Lance Lochner and Enrico Moretti, “The effect of education on crime: Evidence from prison inmates, arrests, and self-reports,” American Economic Review , 2004, Volume 94, Number 1, pp. 155–89; Kevin Milligan, Enrico Moretti, and Philip Oreopoulos, “Does education improve citizenship? Evidence from the United States and the United Kingdom,” Journal of Public Economics , August 2004, Volume 88, Number 9–10, pp. 1667–95; and Education transforms lives , UNESCO, 2013, unesdoc.unesco.org. We estimate that, without immediate and sustained interventions, pandemic-related unfinished learning could reduce lifetime earnings for K–12 students by an average of $49,000 to $61,000. These costs are significant, especially for students who have lost more learning. While white students may see lifetime earnings reduced by 1.4 percent, the reduction could be as much as 2.4 percent for Black students and 2.1 percent for Hispanic students. 21 Projected earnings across children’s lifetimes using current annual incomes for those with at least a high school diploma, discounting the earnings by a premium established in Murnane et al., 2000, which tied cognitive skills and future earnings. See Richard J. Murnane et al., “How important are the cognitive skills of teenagers in predicting subsequent earnings?,” Journal of Policy Analysis and Management , September 2000, Volume 19, Number 4, pp. 547–68.
Lower earnings, lower levels of education attainment, less innovation—all of these lead to decreased economic productivity. By 2040 the majority of this cohort of K–12 students will be in the workforce. We anticipate a potential annual GDP loss of $128 billion to $188 billion from pandemic-related unfinished learning. 22 Using Hanushek and Woessmann 2008 methodology to map national per capita growth associated with decrease in academic achievement, then adding additional impact of pandemic dropouts on GDP. For more, see Eric A. Hanushek and Ludger Woessmann, “The role of cognitive skills in economic development,” Journal of Economic Literature , September 2008, Volume 46, Number 3, pp. 607–68.
This increases by about one-third the existing hits to GDP from achievement gaps that predated COVID-19. Our previous research indicated that the pre-COVID-19 racial achievement gap was equivalent to $426 billion to $705 billion in lost economic potential every year (Exhibit 7). 23 This is the increase in GDP that would result if Black and Hispanic students achieved the same levels of academic performance as white students. For more information on historical opportunity and achievement gaps, please see Emma Dorn, Bryan Hancock, Jimmy Sarakatsannis, and Ellen Viruleg, “ COVID-19 and student learning in the United States: The hurt could last a lifetime ,” June 1, 2020.
What is the path forward for our nation’s students?
There is now significant funding in place to address these critical issues. Through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act); the Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act (CRRSAA); and the American Rescue Plan (ARP), the federal government has already committed more than $200 billion to K–12 education over the next three years, 24 The CARES Act provided $13 billion to ESSER and $3 billion to the Governor’s Emergency Education Relief (GEER) Fund; CRRSAA provided $54 billion to ESSER II, $4 billion to Governors (GEER II and EANS); ARP provided $123 billion to ESSER III, $3 billion to Governors (EANS II), and $10 billion to other education programs. For more, see “CCSSO fact sheet: COVID-19 relief funding for K-12 education,” Council of Chief State School Officers, 2021, https://753a0706.flowpaper.com/CCSSOCovidReliefFactSheet/#page=2. a significant increase over the approximately $750 billion spent annually on public schooling. 25 “The condition of education 2021: At a glance,” National Center for Education Statistics, accessed June 30, 2021, nces.ed.gov. The majority of these funds are routed through the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief Fund (ESSER), of which 90 percent flows to districts and 10 percent to state education agencies. These are vast sums of money, particularly in historical context. As part of the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA), the Obama administration committed more than $80 billion toward K–12 schools—at the time the biggest federal infusion of funds to public schools in the nation’s history. 26 “The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009: Saving and Creating Jobs and Reforming Education,” US Department of Education, March 7, 2009, ed.gov. Today’s funding more than doubles that previous record and gives districts much more freedom in how they spend the money. 27 Andrew Ujifusa, “What Obama’s stimulus had for education that the coronavirus package doesn’t,” Education Week , March 31, 2020, www.edweek.org.
However, if this funding can mitigate the impact of unfinished learning, it could prevent much larger losses to the US economy. Given that this generation of students will likely spend 35 to 40 years in the workforce, the cumulative impact of COVID-19 unfinished learning over their lifetimes could far exceed the investments that are being made today.
Furthermore, much of today’s federal infusion will likely be spent not only on supporting students in catching up on the unfinished learning of the pandemic but also on tackling deeper historical opportunity and achievement gaps among students of different races and income levels.
As districts consider competing uses of funding, they are juggling multiple priorities over several time horizons. The ARP funding needs to be obligated by September 2023. This restricts how monies can be spent. Districts are balancing the desire to hire new personnel or start new programs with the risk of having to close programs because of lack of sustained funds in the future. Districts are also facing decisions about whether to run programs at the district level or to give more freedom to principals in allocating funds; about the balance between academics and broader student needs; about the extent to which funds should be targeted to students who have struggled most or spread evenly across all students; and about the balance between rolling out existing evidence-based programs and experimenting with innovative approaches.
It is too early to answer all of these questions decisively. However, as districts consider this complex set of decisions, leading practitioners and thinkers have come together to form the Coalition to Advance Future Student Success—and to outline priorities to ensure the effective and equitable use of federal funds. 28 “Framework: The Coalition to Advance Future Student Success,” Council of Chief State School Officers, accessed June 30, 2021, learning.ccsso.org.
These priorities encompass four potential actions for schools:
- Safely reopen schools for in-person learning.
- Reengage students and reenroll them into effective learning environments.
- Support students in recovering unfinished learning and broader needs.
- Recommit and reimagine our education systems for the long term.
Across all of these actions, it is important for districts to understand the changing needs of parents and students as we emerge from the pandemic, and to engage with them to support students to learn and to thrive. The remainder of this article shares insights from our parent survey of more than 16,000 parents on these changing needs and perspectives, and highlights some early actions by states and districts to adapt to meet them.
1. Safely reopen schools for in-person learning
The majority of school districts across the country are planning to offer traditional five-days-a-week in-person instruction in the fall, employing COVID-19-mitigation strategies such as staff and student vaccination drives, ongoing COVID-19 testing, mask mandates, and infrastructure updates. 29 “Map: Where Were Schools Required to Be Open for the 2020-21 School Year?,” Education Week , updated May 2021, edweek.org. The evidence suggests that schools can reopen buildings safely with the right protocols in place, 30 For a summary of the evidence on safely reopening schools, see John Bailey, Is it safe to reopen schools? , CRPE, March 2021, crpe.org. but health preparedness will likely remain critical as buildings reopen. Indeed, by the end of the school year, a significant subset of parents remain concerned about safety in schools, with nearly a third still very or extremely worried about the threat of COVID-19 to their child’s health. Parents also want districts to continue to invest in safety—39 percent say schools should invest in COVID-19 health and safety measures this fall.
2. Reengage and reenroll students in effective learning environments
Opening buildings safely is hard enough, but encouraging students to show up could be even more challenging. Some students will have dropped out of formal schooling entirely, and those who remain in school may be reluctant to return to physical classrooms. Our survey results suggest that 24 percent of parents are still not convinced they will choose in-person instruction for their children this fall. Within Black communities, that rises to 34 percent. But many of these parents are still open to persuasion. Only 4 percent of parents (and 6 percent of Black parents) say their children will definitely not return to fully in-person learning—which is not very different from the percentage of parents who choose to homeschool or pursue other alternative education options in a typical year. For students who choose to remain virtual, schools should make continual efforts to improve virtual learning models, based on lessons from the past year.
For parents who are still on the fence, school districts can work to understand their needs and provide effective learning options. Safety concerns remain the primary reason that parents remain hesitant about returning to the classroom; however, this is not the only driver. Some parents feel that remote learning has been a better learning environment for their child, while others have seen their child’s social-emotional and mental health improve at home.
Still, while remote learning may have worked well for some students, our data suggest that it failed many. In addition to understanding parent needs, districts should reach out to families and build confidence not just in their schools’ safety precautions but also in their learning environment and broader role in the community. Addressing root causes will likely be more effective than punitive measures, and a broad range of tactics may be needed, from outreach and attendance campaigns to student incentives to providing services families need, such as transportation and childcare. 31 Roshon R. Bradley, “A comprehensive approach to improving student attendance,” St. John Fisher College, August 2015, Education Doctoral, Paper 225, fisherpub.sjfc.edu; a 2011 literature review highlights how incentives can effectively be employed to increase attendance rates. Across all of these, a critical component will likely be identifying students who are at risk and ensuring targeted outreach and interventions. 32 Elaine M. Allensworth and John Q. Easton, “What matters for staying on-track and graduating in Chicago Public Schools: A close look at course grades, failures, and attendance in the freshman year,” Consortium on Chicago School Research at the University of Chicago, July 2007, files.eric.ed.gov.
Chicago Public Schools, in partnership with the University of Chicago, has developed a student prioritization index (SPI) that identifies students at highest risk of unfinished learning and dropping out of school. The index is based on a combination of academic, attendance, socio-emotional, and community vulnerability inputs. The district is reaching out to all students with a back-to-school marketing campaign while targeting more vulnerable students with additional support. Schools are partnering with community-based organizations to carry out home visits, and with parents to staff phone banks. They are offering various paid summer opportunities to reduce the trade-offs students may have to make between summer school and summer jobs, recognizing that many have found paid work during the pandemic. The district will track and monitor the results to learn which tactics work. 33 “Moving Forward Together,” Chicago Public Schools, June 2021, cps.edu.
In Florida’s Miami-Dade schools, each school employee was assigned 30 households to contact personally, starting with a phone call and then showing up for a home visit. Superintendent Alberto Carvalho personally contacted 30 families and persuaded 23 to return to in-person learning. The district is starting the transition to in-person learning by hosting engaging in-person summer learning programs. 34 Hannah Natanson, “Schools use home visits, calls to convince parents to choose in-person classes in fall,” Washington Post , July 7, 2021, washingtonpost.com.
3. Support students in recovering unfinished learning and in broader needs
Even if students reenroll in effective learning environments in the fall, many will be several months behind academically and may struggle to reintegrate into a traditional learning environment. School districts are therefore creating strategies to support students as they work to make up unfinished learning, and as they work through broader mental health issues and social reintegration. Again, getting parents and students to show up for these programs may be harder than districts expect.
Our research suggests that parents underestimate the unfinished learning caused by the pandemic. In addition, their beliefs about their children’s learning do not reflect racial disparities in unfinished learning. In our survey, 40 percent of parents said their child is on track and 16 percent said their child is progressing faster than in a usual year. Black parents are slightly more likely than white parents to think their child is on track or better, Hispanic parents less so. However, across all races, more than half of parents think their child is doing just fine. Only 14 percent of parents said their child has fallen significantly behind.
Even if programs are offered for free, many parents may not take advantage of them, especially if they are too academically oriented. Only about a quarter of parents said they are very likely to enroll their child in tutoring, after-school, or summer-school programs, for example. Nearly 40 percent said they are very likely to enroll their students in enrichment programs such as art or music. Districts therefore should consider not only offering effective evidence-based programs, such as high-dosage tutoring and vacation academies, but also ensuring that these programs are attractive to students.
In Rhode Island, for example, the state is taking a “Broccoli and Ice Cream” approach to summer school to prepare students for the new school year, combining rigorous reading and math instruction with fun activities provided by community-based partners. Enrichment activities such as sailing, Italian cooking lessons, and Olympic sports are persuading students to participate. 35 From webinar with Angélica Infante-Green, Rhode Island Department of Education, https://www.ewa.org/agenda/ewa-74th-national-seminar-agenda. The state-run summer program is open to students across the state, but the Rhode Island Department of Education has also provided guidance to district-run programs, 36 Learning, Equity & Accelerated Pathways Task Force Report , Rhode Island Department of Education, April 2021, ride.ri.gov. encouraging partnerships with community-based organizations, a dual focus on academics and enrichment, small class sizes, and a strong focus on relationships and social-emotional support.
In Louisiana, the state has provided guidance and support 37 Staffing and scheduling best practices guidance , Louisiana Department of Education, June 3, 2021, louisianabelieves.com. to districts in implementing recovery programs to ensure evidence-based approaches are rolled out state-wide. The guidance includes practical tips on ramping up staffing, and on scheduling high-dosage tutoring and other dedicated acceleration blocks. The state didn’t stop at guidance, but also flooded districts with support and two-way dialogue through webinars, conferences, monthly calls, and regional technical coaching. By scheduling acceleration blocks during the school day, rather than an add-on after school, districts are not dependent on parents signing up for programs.
For students who have experienced trauma, schools will likely need to address the broader fallout from the pandemic. In southwest Virginia, the United Way is partnering with five school systems to establish a trauma-informed schools initiative, providing teachers and staff with training and resources on trauma recovery. 38 Mike Still, “SWVA school districts partner to help students in wake of pandemic,” Kingsport Times News, June 26, 2021, timesnews.net. San Antonio is planning to hire more licensed therapists and social workers to help students and their families, leveraging partnerships with community organizations to place a licensed social worker on every campus. 39 Brooke Crum, “SAISD superintendent: ‘There are no shortcuts’ to tackling COVID-related learning gaps,” San Antonio Report, April 12, 2021, sanantonioreport.org.
4. Recommit and reimagine our education systems for the long term
Opportunity gaps have existed in our school systems for a long time. As schools build back from the pandemic, districts are also recommitting to providing an excellent education to every child. A potential starting point could be redoubling efforts to provide engaging, high-quality grade-level curriculum and instruction delivered by diverse and effective educators in every classroom, supported by effective assessments to inform instruction and support.
Beyond these foundational elements, districts may consider reimagining other aspects of the system. Parents may also be open to nontraditional models. Thirty-three percent of parents said that even when the pandemic is over, the ideal fit for their child would be something other than five days a week in a traditional brick-and-mortar school. Parents are considering hybrid models, remote learning, homeschooling, or learning hubs over the long term. Even if learning resumes mostly in the building, parents are open to the use of new technology to support teaching.
Edgecombe County Public Schools in North Carolina is planning to continue its use of learning hubs this fall to better meet student needs. In the district’s hub-and-spoke model, students will spend half of their time learning core content (the “hub”). For the other half they will engage in enrichment activities aligned to learning standards (the “spokes”). For elementary and middle school students, enrichment activities will involve interest-based projects in science and social studies; for high schoolers, activities could include exploring their passions through targeted English language arts and social studies projects or getting work experience—either paid or volunteer. The district is redeploying staff and leveraging community-based partnerships to enable these smaller-group activities with trusted adults who mirror the demographics of the students. 40 “District- and community-driven learning pods,” Center on Reinventing Public Education, crpe.org.
In Tennessee, the new Advanced Placement (AP) Access for All program will provide students across the state with access to AP courses, virtually. The goal is to eliminate financial barriers and help students take AP courses that aren’t currently offered at their home high school. 41 Amy Cockerham, “TN Department of Education announces ‘AP Access for All program,’” April 28, 2021, WJHL-TV, wjhl.com.
The Dallas Independent School District is rethinking the traditional school year, gathering input from families, teachers, and school staff to ensure that school communities are ready for the plunge. More than 40 schools have opted to add five additional intercession weeks to the year to provide targeted academics and enrichment activities. A smaller group of schools will add 23 days to the school year to increase time for student learning and teacher planning and collaboration. 42 “Time to Learn,” Dallas Independent School District, dallasisd.org.
It is unclear whether all these experiments will succeed, and school districts should monitor them closely to ensure they can scale successful programs and sunset unsuccessful ones. However, we have learned in the pandemic that some of the innovations born of necessity met some families’ needs better. Continued experimentation and fine-tuning could bring the best of traditional and new approaches together.
Thanks to concerted efforts by states and districts, the worst projections for learning outcomes this past year have not materialized for most students. However, students are still far behind where they need to be, especially those from historically marginalized groups. Left unchecked, unfinished learning could have severe consequences for students’ opportunities and prospects. In the long term, it could exact a heavy toll on the economy. It is not too late to mitigate these threats, and funding is now in place. Districts and states now have the opportunity to spend that money effectively to support our nation’s students.
Emma Dorn is a senior expert in McKinsey’s Silicon Valley office; Bryan Hancock and Jimmy Sarakatsannis are partners in the Washington, DC, office; and Ellen Viruleg is a senior adviser based in Providence, Rhode Island.
The authors wish to thank Alice Boucher, Ezra Glenn, Ben Hayes, Cheryl Healey, Chauncey Holder, and Sidney Scott for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Teacher survey: Learning loss is global—and significant

COVID-19 and learning loss—disparities grow and students need help

Reimagining a more equitable and resilient K–12 education system
Coronavirus and schools: Reflections on education one year into the pandemic
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, daphna bassok , daphna bassok nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy lauren bauer , lauren bauer fellow - economic studies , associate director - the hamilton project stephanie riegg cellini , stephanie riegg cellini nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy helen shwe hadani , helen shwe hadani former brookings expert michael hansen , michael hansen senior fellow - brown center on education policy , the herman and george r. brown chair - governance studies douglas n. harris , douglas n. harris nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy , professor and chair, department of economics - tulane university brad olsen , brad olsen senior fellow - global economy and development , center for universal education richard v. reeves , richard v. reeves president - american institute for boys and men jon valant , and jon valant director - brown center on education policy , senior fellow - governance studies kenneth k. wong kenneth k. wong nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy.
March 12, 2021
- 11 min read
One year ago, the World Health Organization declared the spread of COVID-19 a worldwide pandemic. Reacting to the virus, schools at every level were sent scrambling. Institutions across the world switched to virtual learning, with teachers, students, and local leaders quickly adapting to an entirely new way of life. A year later, schools are beginning to reopen, the $1.9 trillion stimulus bill has been passed, and a sense of normalcy seems to finally be in view; in President Joe Biden’s speech last night, he spoke of “finding light in the darkness.” But it’s safe to say that COVID-19 will end up changing education forever, casting a critical light on everything from equity issues to ed tech to school financing.
Below, Brookings experts examine how the pandemic upended the education landscape in the past year, what it’s taught us about schooling, and where we go from here.

In the United States, we tend to focus on the educating roles of public schools, largely ignoring the ways in which schools provide free and essential care for children while their parents work. When COVID-19 shuttered in-person schooling, it eliminated this subsidized child care for many families. It created intense stress for working parents, especially for mothers who left the workforce at a high rate.
The pandemic also highlighted the arbitrary distinction we make between the care and education of elementary school children and children aged 0 to 5 . Despite parents having the same need for care, and children learning more in those earliest years than at any other point, public investments in early care and education are woefully insufficient. The child-care sector was hit so incredibly hard by COVID-19. The recent passage of the American Rescue Plan is a meaningful but long-overdue investment, but much more than a one-time infusion of funds is needed. Hopefully, the pandemic represents a turning point in how we invest in the care and education of young children—and, in turn, in families and society.

Congressional reauthorization of Pandemic EBT for this school year , its extension in the American Rescue Plan (including for summer months), and its place as a central plank in the Biden administration’s anti-hunger agenda is well-warranted and evidence based. But much more needs to be done to ramp up the program–even today , six months after its reauthorization, about half of states do not have a USDA-approved implementation plan.

In contrast, enrollment is up in for-profit and online colleges. The research repeatedly finds weaker student outcomes for these types of institutions relative to community colleges, and many students who enroll in them will be left with more debt than they can reasonably repay. The pandemic and recession have created significant challenges for students, affecting college choices and enrollment decisions in the near future. Ultimately, these short-term choices can have long-term consequences for lifetime earnings and debt that could impact this generation of COVID-19-era college students for years to come.

Many U.S. educationalists are drawing on the “build back better” refrain and calling for the current crisis to be leveraged as a unique opportunity for educators, parents, and policymakers to fully reimagine education systems that are designed for the 21st rather than the 20th century, as we highlight in a recent Brookings report on education reform . An overwhelming body of evidence points to play as the best way to equip children with a broad set of flexible competencies and support their socioemotional development. A recent article in The Atlantic shared parent anecdotes of children playing games like “CoronaBall” and “Social-distance” tag, proving that play permeates children’s lives—even in a pandemic.

Tests play a critical role in our school system. Policymakers and the public rely on results to measure school performance and reveal whether all students are equally served. But testing has also attracted an inordinate share of criticism, alleging that test pressures undermine teacher autonomy and stress students. Much of this criticism will wither away with different formats. The current form of standardized testing—annual, paper-based, multiple-choice tests administered over the course of a week of school—is outdated. With widespread student access to computers (now possible due to the pandemic), states can test students more frequently, but in smaller time blocks that render the experience nearly invisible. Computer adaptive testing can match paper’s reliability and provides a shorter feedback loop to boot. No better time than the present to make this overdue change.

A third push for change will come from the outside in. COVID-19 has reminded us not only of how integral schools are, but how intertwined they are with the rest of society. This means that upcoming schooling changes will also be driven by the effects of COVID-19 on the world around us. In particular, parents will be working more from home, using the same online tools that students can use to learn remotely. This doesn’t mean a mass push for homeschooling, but it probably does mean that hybrid learning is here to stay.

I am hoping we will use this forced rupture in the fabric of schooling to jettison ineffective aspects of education, more fully embrace what we know works, and be bold enough to look for new solutions to the educational problems COVID-19 has illuminated.

There is already a large gender gap in education in the U.S., including in high school graduation rates , and increasingly in college-going and college completion. While the pandemic appears to be hurting women more than men in the labor market, the opposite seems to be true in education.

Looking through a policy lens, though, I’m struck by the timing and what that timing might mean for the future of education. Before the pandemic, enthusiasm for the education reforms that had defined the last few decades—choice and accountability—had waned. It felt like a period between reform eras, with the era to come still very unclear. Then COVID-19 hit, and it coincided with a national reckoning on racial injustice and a wake-up call about the fragility of our democracy. I think it’s helped us all see how connected the work of schools is with so much else in American life.
We’re in a moment when our long-lasting challenges have been laid bare, new challenges have emerged, educators and parents are seeing and experimenting with things for the first time, and the political environment has changed (with, for example, a new administration and changing attitudes on federal spending). I still don’t know where K-12 education is headed, but there’s no doubt that a pivot is underway.

- First, state and local leaders must leverage commitment and shared goals on equitable learning opportunities to support student success for all.
- Second, align and use federal, state, and local resources to implement high-leverage strategies that have proven to accelerate learning for diverse learners and disrupt the correlation between zip code and academic outcomes.
- Third, student-centered priority will require transformative leadership to dismantle the one-size-fits-all delivery rule and institute incentive-based practices for strong performance at all levels.
- Fourth, the reconfigured system will need to activate public and parental engagement to strengthen its civic and social capacity.
- Finally, public education can no longer remain insulated from other policy sectors, especially public health, community development, and social work.
These efforts will strengthen the capacity and prepare our education system for the next crisis—whatever it may be.
Higher Education K-12 Education
Brookings Metro Economic Studies Global Economy and Development Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy Center for Universal Education
Douglas N. Harris
August 13, 2024
Rachel M. Perera, Jon Valant, Katharine Meyer
August 12, 2024
Kelly Rosinger, Robert Kelchen, Justin Ortagus, Dominique J. Baker, Mitchell Lingo
August 9, 2024

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
12 COVID-19’s Effect on Higher Education and What is Being Done
Jack Klinge
Introduction
Since the beginning of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, the global population has been going through a whirlpool of side effects. This chapter will discuss major challenges facing the college education system of the United States and the start of global school closures. COVID-19 has greatly impacted the industry of college education. More specifically, engagement, interaction, and communication between college students and their peers have been changed, improved, and altered in response to the pandemic. It’s pertinent throughout this discussion to include not only the impacts of COVID-19 on the college education system, but also to mention many of the adaptations and solutions that are being provided in response to the abnormal hindrances to education during the pandemic. How these alterations relate to the studies of science, technology, and society (STS), how they create major differentiations in the outcomes of college students’ futures and the connection between these alterations to the STS paradigm of path dependency will also be discussed. The importance of this topic has led to reform and deeper consideration of the system of higher education. The topic has also been the main focus of hea dlines around the world because education is the foundation for many countries, governments, and economies.
COVID-19’s Impacts on Education
To begin, the impacts of COVID-19 on higher education are many, but the most important ones fall between two categories: physical (or structural) and psychological (people). These two categories are relevant because higher education can be described in two separate entities. The physical or structural is the location that teaching takes place and how teaching is organized and provided. The psychological or people are the individual who are involved in running that system and learning from it (ie. teachers and students). Now that some background information has been laid out, the impacts of the pandemic on the structure of higher education and the psychological impacts that COVID-19 is having on people involved in it are more organized and understandable.
– Physical Impacts –

First to be discussed are the physical impacts and how they have affected the structure of learning within the education system. To say that the pandemic has disrupted this structure of learning is an understatement. As of mid-April, according to UNESCO, 1.5 billion students and youth (roughly 87% of the world’s student population) were affected by school closures in 195 countries, from pre-primary to higher education ( Wolkoff ). The previously mentioned information is horrifying considering that almost 90% of students were affected by school closure.
On top of schools closing a cause and effect paradigm is also impacting higher education. The pandemic has caused schools to physically close. Those school closures, in turn, are causing the structure of teaching, which have been centered around the physical location of college campuses to collapse. When schools are physically closed the accessibility and reliability of their learning structure is reduced. A crumbling learning structure also affects students and teachers, the people entity of the college education system. Members of this system can’t attend school, give or receive lessons in their academic areas. This physical absence of a learning structure and a formal school setting is a perfect segway into the psychological impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on students and teachers.
– Psychological –

Everyone who has either heard of, attended, or sent their children off to be educated at college knows about the stress, anxiety, and responsibility that students at higher educational institutions have to deal with and learn to cope in order to excel in their learning. However, there is a limit to the amount of these three variables that an average student can handle. Once those levels are higher than they are supposed to be, they can cause students to do poorly in their school work, not get enough sleep, not eat, have a bad attitude, and not being the best person they can be, etc. A study by doctors and scientists from the Houston Methodist Hospital and the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Texas A&M University discovered that of the 195 students they tested,
“138 (71%) indicated increased stress and anxiety due to the COVID-19 outbreak. Multiple stressors were identified that contributed to the increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depressive thoughts among students. These included fear and worry about their own health and of their loved ones (177/195, 91% reported negative impacts of the pandemic), difficulty in concentrating (173/195, 89%), disruptions to sleeping patterns (168/195, 86%), decreased social interactions due to physical distancing (167/195, 86%), and increased concerns on academic performance (159/195, 82%). To cope with stress and anxiety, participants have sought support from others and helped themselves by adopting either negative or positive coping mechanisms” ( Son 21279).
From this study COVID-19 is having a massive psychological impact on students, the people entity of the college education system. Another study on the psychological effects that Coronavirus is having on student also noted, “Due to the long-lasting pandemic situation and onerous measures such as lockdown and stay-at-home orders, the COVID-19 pandemic brings negative impacts on higher education. The findings of our study highlight the urgent need to develop interventions and preventive strategies to address the mental health of college students” ( Bilecen ).
Adaptive Solutions (Short-Term & Long-Term)

What is being altered, changed, and inn ovated to combat the negative impacts that the pandemic is having on higher education must also be discussed. It is important to understand that the world, let alone the United States, has never experienced a natural crisis on such a widespread scale. This is mentioned throughout an interview conducted by the Harvard gazette on the former secretary of education for Massachusetts, Paul Reville. Reville, in response to a question about the similarities between today’s pandemic and other historical events, told the journalists, “There were substantial closings in many places during the 1918 Spanish Flu, some as long as four months, but not as widespread as those we’re seeing today. We’re in uncharted territory” ( Mineo ). However, Reville notes that there are solutions to the problems caused by COVID-19. When asked what can be learned and enacted in response to the pandemic crisis, Reveille points out that he had recently been talking to people in New Hampshire discovered that “because of all the snow days they have in the wintertime, they had already developed a backup online learning system. That made the transition, in this period of school closure, a relatively easy one for them to undertake. They moved seamlessly to online instruction” ( Mineo ).
New Hampshire’s example is something that the entire world, not just the U.S is trying to implement and take advantage of. This explains the massive amounts of video chat software (Zoom, Google hangouts, Microsoft meetings) that everybody is always hearing about in the news. Many schools have transferred to an online system of learning through these outlets to continue to educate students, offering them the ability to still go to class and learn while staying safe. One personal experience I have is the way Clemson has integrated online instruction into its learning structure. Clemson students can watch and listen to their professors’ lectures for each class through Zoom and other software and continue taking notes and asking questions like they did in their pre-pandemic college academics. Canvas, Clemson’s class work interface has also been a massive help during times where in-person questions and handouts cannot be applied. All the work for each of my classes appears in organized online spaces, where I can find recordings of teachers’ lectures, their lecture notes, and practice problems.
Other types of solutions to the impacts of the pandemic on the education system include correspondence schools, where the vast majority of interaction happening by email. Another solution is directing students to online tutoring and practice programs, and posting videos for them ( Harris ). The way that Clemson has responded to the pandemic, in my opinion, is superior to the other solutions mentioned. How higher education can better prepare for pandemics is a topic that is now widely being discussed. One example of this discussion is a realization that higher education institutions need to invest in high-quality educator preparation, with the inclusion of teacher and leader residencies in high-need communities. A research article by Darling-Hammond presents major suggestions on how contemporary pandemic societies can build stronger higher education. It notes that:
“High-quality programs begin with strong, research-aligned standards for teaching and school leadership, long-recognized as a foundation of high-achieving education systems and as a key feature for influencing preparation programs quality and supporting student learning. Policymakers can update and strengthen these standards to reflect the needs of today’s students – including new knowledge about social, emotional, and cognitive development; culturally responsive pedagogies; and trauma-informed practices and then ensure that these standards are reflected in licensure requirements, performance assessments for teacher and administrator candidates, and performance-based accreditation for programs ( Darling-Hammond & Hyler ).”
Relevance to STS Theory
Existing solutions are not perfect. A representative from the Brown Center on Education Policy explains that,
“Families will get more accustomed to online learning. However, this approach has the significant disadvantage that families have to play the role of hall monitor and teacher. Few families want or can afford that, given their work schedules and other responsibilities. Moreover, research consistently suggests that students learn less in fully virtual environments ( Harris ).
This is where STS, particularly its emphasis on understanding how new technology affects society comes into play. This emphasis can help create guidelines on which approach we should take to deal with the COVID-19 crisis. STS calls for us to question many of the innovations and solutions being provided during this troubling time, especially in education. This perspective is important in fixing the education system during the pandemic because the only way to escape the problems COVID-19 has caused is through technological and scientific learning. Integrating perspectives from STS with the development new technologies and strategies for dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic is important and helps us to come up with efficient, productive, and accessible solutions for the problems of today.
In terms of theory, changes to the physical education system brought about by COVID-19 and the psychological impact that it has had on those involved in the system reflect the STS paradigm of Path-Dependency. Put simply, Path-Dependency argues that future outcomes will shaped by what has happened in the past. For higher education the effects of the past are the psychological and physical changes it has experienced. By disrupting the higher education system that existed prior it, the pandemic will change our society in the future in unpredictable ways, possibly having economic or political impacts.
The structure of higher education between schools is different, and the psychological impact that COVID-19 is having may vary from one student to the next. However, it’s important to note that a majority of students and educational systems will experience a variety of everlasting effects that are similar, even if the impact of these effects might vary between schools. The COVID-19 pandemic and the public response to it will go down in history as a unique event because nothing like it has happened on such a global scale in the past. Neither has any previous event had such as an impact on higher education, if not all education as the Coronavirus. The pandemic in the short term has created chaos among many educational institutions. While solutions and patchwork fixes have been created to slow the massive implications caused by the pandemic, the permanent physical and psychological effects of COVID-19 on the educational systems is still unknown. Only with the passage of time will society fully understand the total disarray that the pandemic has left on education.
Bilecen, Basak. “Commentary: COVID‐19 Pandemic and Higher Education: International Mobility and Students’ Social Protection.” International Migration , vol. 58, no. 4, 2020, pp. 263–66, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/imig.12749 .
Darling-Hammond, Linda, and Maria E. Hyler. “Preparing Educators for the Time of COVID . and Beyond.” European Journal of Teacher Education , vol. 43, no. 4, 2020, pp. 457-465, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02619768.2020.1816961
Harris, D. N. “How will COVID-19 change our schools in the long run?” Brookings , 24 Apr. 2020, https://www.brookings.edu/brown-center-chalkboard/2020/04/24/how-will-covid-19-change-our-schools-in-the-long-run/ .
Mineo, Liz. “Time to fix American education with race-for-space resolve.” The Harvard Gazette , 10 Apr. 2020, https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2020/04/the-pandemics-impact-on-education/ .
Wolkoff, Melanie. “Education reinvented: How COVID-19 has changed how students learn.” ZDNet , 24 Jul. 2020, https://www.zdnet.com/article/education-reinvented-how-covid-19-has-changed-how-students-learn/ .
Son, Changwon et al. “Effects of COVID-19 on College Students’ Mental Health in the United States: Interview Survey Study.” Journal of Medical Internet Research, vol. 22, no. 9, 2020, pp. 21279, https://www.jmir.org/2020/9/e21279/ .
“ COVID-19 school closures ” by betseg is in the Public Domain
“School Closures – Covid” by Wikimedia Commons is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
“COVID Domino Effect” by Santima.Studio is in the Public Domain
“ Online, Education, E-learning ” by Needpix is in the Public Domain
COVID-19: Success Within Devastation Copyright © 2020 by Jack Klinge is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 27 September 2021
Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap
- Sébastien Goudeau ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7293-0977 1 ,
- Camille Sanrey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3158-1306 1 ,
- Arnaud Stanczak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2596-1516 2 ,
- Antony Manstead ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7540-2096 3 &
- Céline Darnon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2613-689X 2
Nature Human Behaviour volume 5 , pages 1273–1281 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
117k Accesses
159 Citations
128 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced teachers and parents to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers developed online academic material while parents taught the exercises and lessons provided by teachers to their children at home. Considering that the use of digital tools in education has dramatically increased during this crisis, and it is set to continue, there is a pressing need to understand the impact of distance learning. Taking a multidisciplinary view, we argue that by making the learning process rely more than ever on families, rather than on teachers, and by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities. To address this burning issue, we propose an agenda for future research and outline recommendations to help parents, teachers and policymakers to limit the impact of the lockdown on social-class-based academic inequality.
Similar content being viewed by others

Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures
Elementary school teachers’ perspectives about learning during the COVID-19 pandemic
Uncovering Covid-19, distance learning, and educational inequality in rural areas of Pakistan and China: a situational analysis method
The widespread effects of the COVID-19 pandemic that emerged in 2019–2020 have drastically increased health, social and economic inequalities 1 , 2 . For more than 900 million learners around the world, the pandemic led to the closure of schools and universities 3 . This exceptional situation forced teachers, parents and students to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers had to develop online academic materials that could be used at home to ensure educational continuity while ensuring the necessary physical distancing. Primary and secondary school students suddenly had to work with various kinds of support, which were usually provided online by their teachers. For college students, lockdown often entailed returning to their hometowns while staying connected with their teachers and classmates via video conferences, email and other digital tools. Despite the best efforts of educational institutions, parents and teachers to keep all children and students engaged in learning activities, ensuring educational continuity during school closure—something that is difficult for everyone—may pose unique material and psychological challenges for working-class families and students.
Not only did the pandemic lead to the closure of schools in many countries, often for several weeks, it also accelerated the digitalization of education and amplified the role of parental involvement in supporting the schoolwork of their children. Thus, beyond the specific circumstances of the COVID-19 lockdown, we believe that studying the effects of the pandemic on academic inequalities provides a way to more broadly examine the consequences of school closure and related effects (for example, digitalization of education) on social class inequalities. Indeed, bearing in mind that (1) the risk of further pandemics is higher than ever (that is, we are in a ‘pandemic era’ 4 , 5 ) and (2) beyond pandemics, the use of digital tools in education (and therefore the influence of parental involvement) has dramatically increased during this crisis, and is set to continue, there is a pressing need for an integrative and comprehensive model that examines the consequences of distance learning. Here, we propose such an integrative model that helps us to understand the extent to which the school closures associated with the pandemic amplify economic, digital and cultural divides that in turn affect the psychological functioning of parents, students and teachers in a way that amplifies academic inequalities. Bringing together research in social sciences, ranging from economics and sociology to social, cultural, cognitive and educational psychology, we argue that by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources rather than direct interactions with their teachers, and by making the learning process rely more than ever on families rather than teachers, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities.
First, we review research showing that social class is associated with unequal access to digital tools, unequal familiarity with digital skills and unequal uses of such tools for learning purposes 6 , 7 . We then review research documenting how unequal familiarity with school culture, knowledge and skills can also contribute to the accentuation of academic inequalities 8 , 9 . Next, we present the results of surveys conducted during the 2020 lockdown showing that the quality and quantity of pedagogical support received from schools varied according to the social class of families (for examples, see refs. 10 , 11 , 12 ). We then argue that these digital, cultural and structural divides represent barriers to the ability of parents to provide appropriate support for children during distance learning (Fig. 1 ). These divides also alter the levels of self-efficacy of parents and children, thereby affecting their engagement in learning activities 13 , 14 . In the final section, we review preliminary evidence for the hypothesis that distance learning widens the social class achievement gap and we propose an agenda for future research. In addition, we outline recommendations that should help parents, teachers and policymakers to use social science research to limit the impact of school closure and distance learning on the social class achievement gap.
Economic, structural, digital and cultural divides influence the psychological functioning of parents and students in a way that amplify inequalities.
The digital divide
Unequal access to digital resources.
Although the use of digital technologies is almost ubiquitous in developed nations, there is a digital divide such that some people are more likely than others to be numerically excluded 15 (Fig. 1 ). Social class is a strong predictor of digital disparities, including the quality of hardware, software and Internet access 16 , 17 , 18 . For example, in 2019, in France, around 1 in 5 working-class families did not have personal access to the Internet compared with less than 1 in 20 of the most privileged families 19 . Similarly, in 2020, in the United Kingdom, 20% of children who were eligible for free school meals did not have access to a computer at home compared with 7% of other children 20 . In 2021, in the United States, 41% of working-class families do not own a laptop or desktop computer and 43% do not have broadband compared with 8% and 7%, respectively, of upper/middle-class Americans 21 . A similar digital gap is also evident between lower-income and higher-income countries 22 .
Second, simply having access to a computer and an Internet connection does not ensure effective distance learning. For example, many of the educational resources sent by teachers need to be printed, thereby requiring access to printers. Moreover, distance learning is more difficult in households with only one shared computer compared with those where each family member has their own 23 . Furthermore, upper/middle-class families are more likely to be able to guarantee a suitable workspace for each child than their working-class counterparts 24 .
In the context of school closures, such disparities are likely to have important consequences for educational continuity. In line with this idea, a survey of approximately 4,000 parents in the United Kingdom confirmed that during lockdown, more than half of primary school children from the poorest families did not have access to their own study space and were less well equipped for distance learning than higher-income families 10 . Similarly, a survey of around 1,300 parents in the Netherlands found that during lockdown, children from working-class families had fewer computers at home and less room to study than upper/middle-class children 11 .
Data from non-Western countries highlight a more general digital divide, showing that developing countries have poorer access to digital equipment. For example, in India in 2018, only 10.7% of households possessed a digital device 25 , while in Pakistan in 2020, 31% of higher-education teachers did not have Internet access and 68.4% did not have a laptop 26 . In general, developing countries lack access to digital technologies 27 , 28 , and these difficulties of access are even greater in rural areas (for example, see ref. 29 ). Consequently, school closures have huge repercussions for the continuity of learning in these countries. For example, in India in 2018, only 11% of the rural and 40% of the urban population above 14 years old could use a computer and access the Internet 25 . Time spent on education during school closure decreased by 80% in Bangladesh 30 . A similar trend was observed in other countries 31 , with only 22% of children engaging in remote learning in Kenya 32 and 50% in Burkina Faso 33 . In Ghana, 26–32% of children spent no time at all on learning during the pandemic 34 . Beyond the overall digital divide, social class disparities are also evident in developing countries, with lower access to digital resources among households in which parental educational levels were low (versus households in which parental educational levels were high; for example, see ref. 35 for Nigeria and ref. 31 for Ecuador).
Unequal digital skills
In addition to unequal access to digital tools, there are also systematic variations in digital skills 36 , 37 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with digital tools and resources and are therefore more likely to have the digital skills needed for distance learning 38 , 39 , 40 . These digital skills are particularly useful during school closures, both for students and for parents, for organizing, retrieving and correctly using the resources provided by the teachers (for example, sending or receiving documents by email, printing documents or using word processors).
Social class disparities in digital skills can be explained in part by the fact that children from upper/middle-class families have the opportunity to develop digital skills earlier than working-class families 41 . In member countries of the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), only 23% of working-class children had started using a computer at the age of 6 years or earlier compared with 43% of upper/middle-class children 42 . Moreover, because working-class people tend to persist less than upper/middle-class people when confronted with digital difficulties 23 , the use of digital tools and resources for distance learning may interfere with the ability of parents to help children with their schoolwork.

Unequal use of digital tools
A third level of digital divide concerns variations in digital tool use 18 , 43 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more likely to use digital resources for work and education 6 , 41 , 44 , whereas working-class families are more likely to use these resources for entertainment, such as electronic games or social media 6 , 45 . This divide is also observed among students, whereby working-class students tend to use digital technologies for leisure activities, whereas their upper/middle-class peers are more likely to use them for academic activities 46 and to consider that computers and the Internet provide an opportunity for education and training 23 . Furthermore, working-class families appear to regulate the digital practices of their children less 47 and are more likely to allow screens in the bedrooms of children and teenagers without setting limits on times or practices 48 .
In sum, inequalities in terms of digital resources, skills and use have strong implications for distance learning. This is because they make working-class students and parents particularly vulnerable when learning relies on extensive use of digital devices rather than on face-to-face interaction with teachers.
The cultural divide
Even if all three levels of digital divide were closed, upper/middle-class families would still be better prepared than working-class families to ensure educational continuity for their children. Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with the academic knowledge and skills that are expected and valued in educational settings, as well as with the independent, autonomous way of learning that is valued in the school culture and becomes even more important during school closure (Fig. 1 ).
Unequal familiarity with academic knowledge and skills
According to classical social reproduction theory 8 , 49 , school is not a neutral place in which all forms of language and knowledge are equally valued. Academic contexts expect and value culture-specific and taken-for-granted forms of knowledge, skills and ways of being, thinking and speaking that are more in tune with those developed through upper/middle-class socialization (that is, ‘cultural capital’ 8 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ). For instance, academic contexts value interest in the arts, museums and literature 54 , 55 , a type of interest that is more likely to develop through socialization in upper/middle-class families than in working-class socialization 54 , 56 . Indeed, upper/middle-class parents are more likely than working-class parents to engage in activities that develop this cultural capital. For example, they possess more books and cultural objects at home, read more stories to their children and visit museums and libraries more often (for examples, see refs. 51 , 54 , 55 ). Upper/middle-class children are also more involved in extra-curricular activities (for example, playing a musical instrument) than working-class children 55 , 56 , 57 .
Beyond this implicit familiarization with the school curriculum, upper/middle-class parents more often organize educational activities that are explicitly designed to develop academic skills of their children 57 , 58 , 59 . For example, they are more likely to monitor and re-explain lessons or use games and textbooks to develop and reinforce academic skills (for example, labelling numbers, letters or colours 57 , 60 ). Upper/middle-class parents also provide higher levels of support and spend more time helping children with homework than working-class parents (for examples, see refs. 61 , 62 ). Thus, even if all parents are committed to the academic success of their children, working-class parents have fewer chances to provide the help that children need to complete homework 63 , and homework is more beneficial for children from upper-middle class families than for children from working-class families 64 , 65 .
School closures amplify the impact of cultural inequalities
The trends described above have been observed in ‘normal’ times when schools are open. School closures, by making learning rely more strongly on practices implemented at home (rather than at school), are likely to amplify the impact of these disparities. Consistent with this idea, research has shown that the social class achievement gap usually greatly widens during school breaks—a phenomenon described as ‘summer learning loss’ or ‘summer setback’ 66 , 67 , 68 . During holidays, the learning by children tends to decline, and this is particularly pronounced in children from working-class families. Consequently, the social class achievement gap grows more rapidly during the summer months than it does in the rest of the year. This phenomenon is partly explained by the fact that during the break from school, social class disparities in investment in activities that are beneficial for academic achievement (for example, reading, travelling to a foreign country or museum visits) are more pronounced.
Therefore, when they are out of school, children from upper/middle-class backgrounds may continue to develop academic skills unlike their working-class counterparts, who may stagnate or even regress. Research also indicates that learning loss during school breaks tends to be cumulative 66 . Thus, repeated episodes of school closure are likely to have profound consequences for the social class achievement gap. Consistent with the idea that school closures could lead to similar processes as those identified during summer breaks, a recent survey indicated that during the COVID-19 lockdown in the United Kingdom, children from upper/middle-class families spent more time on educational activities (5.8 h per day) than those from working-class families (4.5 h per day) 7 , 69 .
Unequal dispositions for autonomy and self-regulation
School closures have encouraged autonomous work among students. This ‘independent’ way of studying is compatible with the family socialization of upper/middle-class students, but does not match the interdependent norms more commonly associated with working-class contexts 9 . Upper/middle-class contexts tend to promote cultural norms of independence whereby individuals perceive themselves as autonomous actors, independent of other individuals and of the social context, able to pursue their own goals 70 . For example, upper/middle-class parents tend to invite children to express their interests, preferences and opinions during the various activities of everyday life 54 , 55 . Conversely, in working-class contexts characterized by low economic resources and where life is more uncertain, individuals tend to perceive themselves as interdependent, connected to others and members of social groups 53 , 70 , 71 . This interdependent self-construal fits less well with the independent culture of academic contexts. This cultural mismatch between interdependent self-construal common in working-class students and the independent norms of the educational institution has negative consequences for academic performance 9 .
Once again, the impact of these differences is likely to be amplified during school closures, when being able to work alone and autonomously is especially useful. The requirement to work alone is more likely to match the independent self-construal of upper/middle-class students than the interdependent self-construal of working-class students. In the case of working-class students, this mismatch is likely to increase their difficulties in working alone at home. Supporting our argument, recent research has shown that working-class students tend to underachieve in contexts where students work individually compared with contexts where students work with others 72 . Similarly, during school closures, high self-regulation skills (for example, setting goals, selecting appropriate learning strategies and maintaining motivation 73 ) are required to maintain study activities and are likely to be especially useful for using digital resources efficiently. Research has shown that students from working-class backgrounds typically develop their self-regulation skills to a lesser extent than those from upper/middle-class backgrounds 74 , 75 , 76 .
Interestingly, some authors have suggested that independent (versus interdependent) self-construal may also affect communication with teachers 77 . Indeed, in the context of distance learning, working-class families are less likely to respond to the communication of teachers because their ‘interdependent’ self leads them to respect hierarchies, and thus perceive teachers as an expert who ‘can be trusted to make the right decisions for learning’. Upper/middle class families, relying on ‘independent’ self-construal, are more inclined to seek individualized feedback, and therefore tend to participate to a greater extent in exchanges with teachers. Such cultural differences are important because they can also contribute to the difficulties encountered by working-class families.
The structural divide: unequal support from schools
The issues reviewed thus far all increase the vulnerability of children and students from underprivileged backgrounds when schools are closed. To offset these disadvantages, it might be expected that the school should increase its support by providing additional resources for working-class students. However, recent data suggest that differences in the material and human resources invested in providing educational support for children during periods of school closure were—paradoxically—in favour of upper/middle-class students (Fig. 1 ). In England, for example, upper/middle-class parents reported benefiting from online classes and video-conferencing with teachers more often than working-class parents 10 . Furthermore, active help from school (for example, online teaching, private tutoring or chats with teachers) occurred more frequently in the richest households (64% of the richest households declared having received help from school) than in the poorest households (47%). Another survey found that in the United Kingdom, upper/middle-class children were more likely to take online lessons every day (30%) than working-class students (16%) 12 . This substantial difference might be due, at least in part, to the fact that private schools are better equipped in terms of online platforms (60% of schools have at least one online platform) than state schools (37%, and 23% in the most deprived schools) and were more likely to organize daily online lessons. Similarly, in the United Kingdom, in schools with a high proportion of students eligible for free school meals, teachers were less inclined to broadcast an online lesson for their pupils 78 . Interestingly, 58% of teachers in the wealthiest areas reported having messaged their students or their students’ parents during lockdown compared with 47% in the most deprived schools. In addition, the probability of children receiving technical support from the school (for example, by providing pupils with laptops or other devices) is, surprisingly, higher in the most advantaged schools than in the most deprived 78 .
In addition to social class disparities, there has been less support from schools for African-American and Latinx students. During school closures in the United States, 40% of African-American students and 30% of Latinx students received no online teaching compared with 10% of white students 79 . Another source of inequality is that the probability of school closure was correlated with social class and race. In the United States, for example, school closures from September to December 2020 were more common in schools with a high proportion of racial/ethnic minority students, who experience homelessness and are eligible for free/discounted school meals 80 .
Similarly, access to educational resources and support was lower in poorer (compared with richer) countries 81 . In sub-Saharan Africa, during lockdown, 45% of children had no exposure at all to any type of remote learning. Of those who did, the medium was mostly radio, television or paper rather than digital. In African countries, at most 10% of children received some material through the Internet. In Latin America, 90% of children received some remote learning, but less than half of that was through the internet—the remainder being via radio and television 81 . In Ecuador, high-school students from the lowest wealth quartile had fewer remote-learning opportunities, such as Google class/Zoom, than students from the highest wealth quartile 31 .
Thus, the achievement gap and its accentuation during lockdown are due not only to the cultural and digital disadvantages of working-class families but also to unequal support from schools. This inequality in school support is not due to teachers being indifferent to or even supportive of social stratification. Rather, we believe that these effects are fundamentally structural. In many countries, schools located in upper/middle-class neighbourhoods have more money than those in the poorest neighbourhoods. Moreover, upper/middle-class parents invest more in the schools of their children than working-class parents (for example, see ref. 82 ), and schools have an interest in catering more for upper/middle-class families than for working-class families 83 . Additionally, the expectation of teachers may be lower for working-class children 84 . For example, they tend to estimate that working-class students invest less effort in learning than their upper/middle-class counterparts 85 . These differences in perception may have influenced the behaviour of teachers during school closure, such that teachers in privileged neighbourhoods provided more information to students because they expected more from them in term of effort and achievement. The fact that upper/middle-class parents are better able than working-class parents to comply with the expectations of teachers (for examples, see refs. 55 , 86 ) may have reinforced this phenomenon. These discrepancies echo data showing that working-class students tend to request less help in their schoolwork than upper/middle-class ones 87 , and they may even avoid asking for help because they believe that such requests could lead to reprimands 88 . During school closures, these students (and their families) may in consequence have been less likely to ask for help and resources. Jointly, these phenomena have resulted in upper/middle-class families receiving more support from schools during lockdown than their working-class counterparts.
Psychological effects of digital, cultural and structural divides
Despite being strongly influenced by social class, differences in academic achievement are often interpreted by parents, teachers and students as reflecting differences in ability 89 . As a result, upper/middle-class students are usually perceived—and perceive themselves—as smarter than working-class students, who are perceived—and perceive themselves—as less intelligent 90 , 91 , 92 or less able to succeed 93 . Working-class students also worry more about the fact that they might perform more poorly than upper/middle-class students 94 , 95 . These fears influence academic learning in important ways. In particular, they can consume cognitive resources when children and students work on academic tasks 96 , 97 . Self-efficacy also plays a key role in engaging in learning and perseverance in the face of difficulties 13 , 98 . In addition, working-class students are those for whom the fear of being outperformed by others is the most negatively related to academic performance 99 .
The fact that working-class children and students are less familiar with the tasks set by teachers, and less well equipped and supported, makes them more likely to experience feelings of incompetence (Fig. 1 ). Working-class parents are also more likely than their upper/middle-class counterparts to feel unable to help their children with schoolwork. Consistent with this, research has shown that both working-class students and parents have lower feelings of academic self-efficacy than their upper/middle-class counterparts 100 , 101 . These differences have been documented under ‘normal’ conditions but are likely to be exacerbated during distance learning. Recent surveys conducted during the school closures have confirmed that upper/middle-class families felt better able to support their children in distance learning than did working-class families 10 and that upper/middle-class parents helped their children more and felt more capable to do so 11 , 12 .
Pandemic disparity, future directions and recommendations
The research reviewed thus far suggests that children and their families are highly unequal with respect to digital access, skills and use. It also shows that upper/middle-class students are more likely to be supported in their homework (by their parents and teachers) than working-class students, and that upper/middle-class students and parents will probably feel better able than working-class ones to adapt to the context of distance learning. For all these reasons, we anticipate that as a result of school closures, the COVID-19 pandemic will substantially increase the social class achievement gap. Because school closures are a recent occurrence, it is too early to measure with precision their effects on the widening of the achievement gap. However, some recent data are consistent with this idea.
Evidence for a widening gap during the pandemic
Comparing academic achievement in 2020 with previous years provides an early indication of the effects of school closures during the pandemic. In France, for example, first and second graders take national evaluations at the beginning of the school year. Initial comparisons of the results for 2020 with those from previous years revealed that the gap between schools classified as ‘priority schools’ (those in low-income urban areas) and schools in higher-income neighbourhoods—a gap observed every year—was particularly pronounced in 2020 in both French and mathematics 102 .
Similarly, in the Netherlands, national assessments take place twice a year. In 2020, they took place both before and after school closures. A recent analysis compared progress during this period in 2020 in mathematics/arithmetic, spelling and reading comprehension for 7–11-year-old students within the same period in the three previous years 103 . Results indicated a general learning loss in 2020. More importantly, for the 8% of working-class children, the losses were 40% greater than they were for upper/middle-class children.
Similar results were observed in Belgium among students attending the final year of primary school. Compared with students from previous cohorts, students affected by school closures experienced a substantial decrease in their mathematics and language scores, with children from more disadvantaged backgrounds experiencing greater learning losses 104 . Likewise, oral reading assessments in more than 100 school districts in the United States showed that the development of this skill among children in second and third grade significantly slowed between Spring and Autumn 2020, but this slowdown was more pronounced in schools from lower-achieving districts 105 .
It is likely that school closures have also amplified racial disparities in learning and achievement. For example, in the United States, after the first lockdown, students of colour lost the equivalent of 3–5 months of learning, whereas white students were about 1–3 months behind. Moreover, in the Autumn, when some students started to return to classrooms, African-American and Latinx students were more likely to continue distance learning, despite being less likely to have access to the digital tools, Internet access and live contact with teachers 106 .
In some African countries (for example, Ethiopia, Kenya, Liberia, Tanzania and Uganda), the COVID-19 crisis has resulted in learning loss ranging from 6 months to more 1 year 107 , and this learning loss appears to be greater for working-class children (that is, those attending no-fee schools) than for upper/middle-class children 108 .
These findings show that school closures have exacerbated achievement gaps linked to social class and ethnicity. However, more research is needed to address the question of whether school closures differentially affect the learning of students from working- and upper/middle-class families.
Future directions
First, to assess the specific and unique impact of school closures on student learning, longitudinal research should compare student achievement at different times of the year, before, during and after school closures, as has been done to document the summer learning loss 66 , 109 . In the coming months, alternating periods of school closure and opening may occur, thereby presenting opportunities to do such research. This would also make it possible to examine whether the gap diminishes a few weeks after children return to in-school learning or whether, conversely, it increases with time because the foundations have not been sufficiently acquired to facilitate further learning 110 .
Second, the mechanisms underlying the increase in social class disparities during school closures should be examined. As discussed above, school closures result in situations for which students are unevenly prepared and supported. It would be appropriate to seek to quantify the contribution of each of the factors that might be responsible for accentuating the social class achievement gap. In particular, distinguishing between factors that are relatively ‘controllable’ (for example, resources made available to pupils) and those that are more difficult to control (for example, the self-efficacy of parents in supporting the schoolwork of their children) is essential to inform public policy and teaching practices.
Third, existing studies are based on general comparisons and very few provide insights into the actual practices that took place in families during school closure and how these practices affected the achievement gap. For example, research has documented that parents from working-class backgrounds are likely to find it more difficult to help their children to complete homework and to provide constructive feedback 63 , 111 , something that could in turn have a negative impact on the continuity of learning of their children. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that during lockdown, parents from upper/middle-class backgrounds encouraged their children to engage in practices that, even if not explicitly requested by teachers, would be beneficial to learning (for example, creative activities or reading). Identifying the practices that best predict the maintenance or decline of educational achievement during school closures would help identify levers for intervention.
Finally, it would be interesting to investigate teaching practices during school closures. The lockdown in the spring of 2020 was sudden and unexpected. Within a few days, teachers had to find a way to compensate for the school closure, which led to highly variable practices. Some teachers posted schoolwork on platforms, others sent it by email, some set work on a weekly basis while others set it day by day. Some teachers also set up live sessions in large or small groups, providing remote meetings for questions and support. There have also been variations in the type of feedback given to students, notably through the monitoring and correcting of work. Future studies should examine in more detail what practices schools and teachers used to compensate for the school closures and their effects on widening, maintaining or even reducing the gap, as has been done for certain specific literacy programmes 112 as well as specific instruction topics (for example, ecology and evolution 113 ).
Practical recommendations
We are aware of the debate about whether social science research on COVID-19 is suitable for making policy decisions 114 , and we draw attention to the fact that some of our recommendations (Table 1 ) are based on evidence from experiments or interventions carried out pre-COVID while others are more speculative. In any case, we emphasize that these suggestions should be viewed with caution and be tested in future research. Some of our recommendations could be implemented in the event of new school closures, others only when schools re-open. We also acknowledge that while these recommendations are intended for parents and teachers, their implementation largely depends on the adoption of structural policies. Importantly, given all the issues discussed above, we emphasize the importance of prioritizing, wherever possible, in-person learning over remote learning 115 and where this is not possible, of implementing strong policies to support distance learning, especially for disadvantaged families.
Where face-to face teaching is not possible and teachers are responsible for implementing distance learning, it will be important to make them aware of the factors that can exacerbate inequalities during lockdown and to provide them with guidance about practices that would reduce these inequalities. Thus, there is an urgent need for interventions aimed at making teachers aware of the impact of the social class of children and families on the following factors: (1) access to, familiarity with and use of digital devices; (2) familiarity with academic knowledge and skills; and (3) preparedness to work autonomously. Increasing awareness of the material, cultural and psychological barriers that working-class children and families face during lockdown should increase the quality and quantity of the support provided by teachers and thereby positively affect the achievements of working-class students.
In addition to increasing the awareness of teachers of these barriers, teachers should be encouraged to adjust the way they communicate with working-class families due to differences in self-construal compared with upper/middle-class families 77 . For example, questions about family (rather than personal) well-being would be congruent with interdependent self-construals. This should contribute to better communication and help keep a better track of the progress of students during distance learning.
It is also necessary to help teachers to engage in practices that have a chance of reducing inequalities 53 , 116 . Particularly important is that teachers and schools ensure that homework can be done by all children, for example, by setting up organizations that would help children whose parents are not in a position to monitor or assist with the homework of their children. Options include homework help groups and tutoring by teachers after class. When schools are open, the growing tendency to set homework through digital media should be resisted as far as possible given the evidence we have reviewed above. Moreover, previous research has underscored the importance of homework feedback provided by teachers, which is positively related to the amount of homework completed and predictive of academic performance 117 . Where homework is web-based, it has also been shown that feedback on web-based homework enhances the learning of students 118 . It therefore seems reasonable to predict that the social class achievement gap will increase more slowly (or even remain constant or be reversed) in schools that establish individualized monitoring of students, by means of regular calls and feedback on homework, compared with schools where the support provided to pupils is more generic.
Given that learning during lockdown has increasingly taken place in family settings, we believe that interventions involving the family are also likely to be effective 119 , 120 , 121 . Simply providing families with suitable material equipment may be insufficient. Families should be given training in the efficient use of digital technology and pedagogical support. This would increase the self-efficacy of parents and students, with positive consequences for achievement. Ideally, such training would be delivered in person to avoid problems arising from the digital divide. Where this is not possible, individualized online tutoring should be provided. For example, studies conducted during the lockdown in Botswana and Italy have shown that individual online tutoring directly targeting either parents or students in middle school has a positive impact on the achievement of students, particularly for working-class students 122 , 123 .
Interventions targeting families should also address the psychological barriers faced by working-class families and children. Some interventions have already been designed and been shown to be effective in reducing the social class achievement gap, particularly in mathematics and language 124 , 125 , 126 . For example, research showed that an intervention designed to train low-income parents in how to support the mathematical development of their pre-kindergarten children (including classes and access to a library of kits to use at home) increased the quality of support provided by the parents, with a corresponding impact on the development of mathematical knowledge of their children. Such interventions should be particularly beneficial in the context of school closure.
Beyond its impact on academic performance and inequalities, the COVID-19 crisis has shaken the economies of countries around the world, casting millions of families around the world into poverty 127 , 128 , 129 . As noted earlier, there has been a marked increase in economic inequalities, bringing with it all the psychological and social problems that such inequalities create 130 , 131 , especially for people who live in scarcity 132 . The increase in educational inequalities is just one facet of the many difficulties that working-class families will encounter in the coming years, but it is one that could seriously limit the chances of their children escaping from poverty by reducing their opportunities for upward mobility. In this context, it should be a priority to concentrate resources on the most deprived students. A large proportion of the poorest households do not own a computer and do not have personal access to the Internet, which has important consequences for distance learning. During school closures, it is therefore imperative to provide such families with adequate equipment and Internet service, as was done in some countries in spring 2020. Even if the provision of such equipment is not in itself sufficient, it is a necessary condition for ensuring pedagogical continuity during lockdown.
Finally, after prolonged periods of school closure, many students may not have acquired the skills needed to pursue their education. A possible consequence would be an increase in the number of students for whom teachers recommend class repetitions. Class repetitions are contentious. On the one hand, class repetition more frequently affects working-class children and is not efficient in terms of learning improvement 133 . On the other hand, accepting lower standards of academic achievement or even suspending the practice of repeating a class could lead to pupils pursuing their education without mastering the key abilities needed at higher grades. This could create difficulties in subsequent years and, in this sense, be counterproductive. We therefore believe that the most appropriate way to limit the damage of the pandemic would be to help children catch up rather than allowing them to continue without mastering the necessary skills. As is being done in some countries, systematic remedial courses (for example, summer learning programmes) should be organized and financially supported following periods of school closure, with priority given to pupils from working-class families. Such interventions have genuine potential in that research has shown that participation in remedial summer programmes is effective in reducing learning loss during the summer break 134 , 135 , 136 . For example, in one study 137 , 438 students from high-poverty schools were offered a multiyear summer school programme that included various pedagogical and enrichment activities (for example, science investigation and music) and were compared with a ‘no-treatment’ control group. Students who participated in the summer programme progressed more than students in the control group. A meta-analysis 138 of 41 summer learning programmes (that is, classroom- and home-based summer interventions) involving children from kindergarten to grade 8 showed that these programmes had significantly larger benefits for children from working-class families. Although such measures are costly, the cost is small compared to the price of failing to fulfil the academic potential of many students simply because they were not born into upper/middle-class families.
The unprecedented nature of the current pandemic means that we lack strong data on what the school closure period is likely to produce in terms of learning deficits and the reproduction of social inequalities. However, the research discussed in this article suggests that there are good reasons to predict that this period of school closures will accelerate the reproduction of social inequalities in educational achievement.
By making school learning less dependent on teachers and more dependent on families and digital tools and resources, school closures are likely to greatly amplify social class inequalities. At a time when many countries are experiencing second, third or fourth waves of the pandemic, resulting in fresh periods of local or general lockdowns, systematic efforts to test these predictions are urgently needed along with steps to reduce the impact of school closures on the social class achievement gap.
Bambra, C., Riordan, R., Ford, J. & Matthews, F. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 74 , 964–968 (2020).
Google Scholar
Johnson, P, Joyce, R & Platt, L. The IFS Deaton Review of Inequalities: A New Year’s Message (Institute for Fiscal Studies, 2021).
Education: from disruption to recovery. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse (UNESCO, 2020).
Daszak, P. We are entering an era of pandemics—it will end only when we protect the rainforest. The Guardian (28 July 2020); https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2020/jul/28/pandemic-era-rainforest-deforestation-exploitation-wildlife-disease
Dobson, A. P. et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 369 , 379–381 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Harris, C., Straker, L. & Pollock, C. A socioeconomic related ‘digital divide’ exists in how, not if, young people use computers. PLoS ONE 12 , e0175011 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhang, M. Internet use that reproduces educational inequalities: evidence from big data. Comput. Educ. 86 , 212–223 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Bourdieu, P. & Passeron, J. C. Reproduction in Education, Society and Culture (Sage, 1990).
Stephens, N. M., Fryberg, S. A., Markus, H. R., Johnson, C. S. & Covarrubias, R. Unseen disadvantage: how American universities’ focus on independence undermines the academic performance of first-generation college students. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 102 , 1178–1197 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Andrew, A. et al. Inequalities in children’s experiences of home learning during the COVID-19 lockdown in England. Fisc. Stud. 41 , 653–683 (2020).
Bol, T. Inequality in homeschooling during the Corona crisis in the Netherlands. First results from the LISS Panel. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/hf32q (2020).
Cullinane, C. & Montacute, R. COVID-19 and Social Mobility. Impact Brief #1: School Shutdown (The Sutton Trust, 2020).
Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 84 , 191–215 (1977).
Prior, D. D., Mazanov, J., Meacheam, D., Heaslip, G. & Hanson, J. Attitude, digital literacy and self efficacy: low-on effects for online learning behavior. Internet High. Educ. 29 , 91–97 (2016).
Robinson, L. et al. Digital inequalities 2.0: legacy inequalities in the information age. First Monday https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v25i7.10842 (2020).
Cruz-Jesus, F., Vicente, M. R., Bacao, F. & Oliveira, T. The education-related digital divide: an analysis for the EU-28. Comput. Hum. Behav. 56 , 72–82 (2016).
Rice, R. E. & Haythornthwaite, C. In The Handbook of New Media (eds Lievrouw, L. A. & Livingstone S. M.), 92–113 (Sage, 2006).
Yates, S., Kirby, J. & Lockley, E. Digital media use: differences and inequalities in relation to class and age. Sociol. Res. Online 20 , 71–91 (2015).
Legleye, S. & Rolland, A. Une personne sur six n’utilise pas Internet, plus d’un usager sur trois manques de compétences numériques de base [One in six people do not use the Internet, more than one in three users lack basic digital skills] (INSEE Première, 2019).
Green, F. Schoolwork in lockdown: new evidence on the epidemic of educational poverty (LLAKES Centre, 2020); https://www.llakes.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/RP-67-Francis-Green-Research-Paper-combined-file.pdf
Vogels, E. Digital divide persists even as americans with lower incomes make gains in tech adoption (Pew Research Center, 2021); https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/06/22/digital-divide-persists-even-as-americans-with-lower-incomes-make-gains-in-tech-adoption/
McBurnie, C., Adam, T. & Kaye, T. Is there learning continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic? A synthesis of the emerging evidence. J. Learn. Develop. http://dspace.col.org/handle/11599/3720 (2020).
Baillet, J., Croutte, P. & Prieur, V. Baromètre du numérique 2019 [Digital barometer 2019] (Sourcing Crédoc, 2019).
Giraud, F., Bertrand, J., Court, M. & Nicaise, S. In Enfances de Classes. De l’inégalité Parmi les Enfants (ed. Lahire, B.) 933–952 (Seuil, 2019).
Ahamed, S. & Siddiqui, Z. Disparity in access to quality education and the digital divide (Ideas for India, 2020); https://www.ideasforindia.in/topics/macroeconomics/disparity-in-access-to-quality-education-and-the-digital-divide.html
Soomro, K. A., Kale, U., Curtis, R., Akcaoglu, M. & Bernstein, M. Digital divide among higher education faculty. Int. J. Educ. Tech. High. Ed. 17 , 21 (2020).
Meng, Q. & Li, M. New economy and ICT development in China. Inf. Econ. Policy 14 , 275–295 (2002).
Chinn, M. D. & Fairlie, R. W. The determinants of the global digital divide: a cross-country analysis of computer and internet penetration. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 59 , 16–44 (2006).
Lembani, R., Gunter, A., Breines, M. & Dalu, M. T. B. The same course, different access: the digital divide between urban and rural distance education students in South Africa. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 44 , 70–84 (2020).
Asadullah, N., Bhattacharjee, A., Tasnim, M. & Mumtahena, F. COVID-19, schooling, and learning (BRAC Institute of Governance & Development, 2020); https://bigd.bracu.ac.bd/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/COVID-19-Schooling-and-Learning_June-25-2020.pdf
Asanov, I., Flores, F., McKenzie, D., Mensmann, M. & Schulte, M. Remote-learning, time-use, and mental health of Ecuadorian high-school students during the COVID-19 quarantine. World Dev. 138 , 105225 (2021).
Kihui, N. Kenya: 80% of students missing virtual learning amid school closures—study. AllAfrica (18 May 2020); https://allafrica.com/stories/202005180774.html
Debenedetti, L., Hirji, S., Chabi, M. O. & Swigart, T. Prioritizing evidence-based responses in Burkina Faso to mitigate the economic effects of COVID-19: lessons from RECOVR (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/prioritizing-evidence-based-responses-burkina-faso-mitigate-economic-effects-covid-19-lessons
Bosumtwi-Sam, C. & Kabay, S. Using data and evidence to inform school reopening in Ghana (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/using-data-and-evidence-inform-school-reopening-ghana
Azubuike, O. B., Adegboye, O. & Quadri, H. Who gets to learn in a pandemic? Exploring the digital divide in remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 2 , 100022 (2021).
Attewell, P. Comment: the first and second digital divides. Sociol. Educ. 74 , 252–259 (2001).
DiMaggio, P., Hargittai, E., Neuman, W. R. & Robinson, J. P. Social implications of the Internet. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 27 , 307–336 (2001).
Hargittai, E. Digital na(t)ives? Variation in Internet skills and uses among members of the ‘Net Generation’. Sociol. Inq. 80 , 92–113 (2010).
Iivari, N., Sharma, S. & Ventä-Olkkonen, L. Digital transformation of everyday life—how COVID-19 pandemic transformed the basic education of the young generation and why information management research should care? Int. J. Inform. Manag. 55 , 102183 (2020).
Wei, L. & Hindman, D. B. Does the digital divide matter more? Comparing the effects of new media and old media use on the education-based knowledge gap. Mass Commun. Soc. 14 , 216–235 (2011).
Octobre, S. & Berthomier, N. L’enfance des loisirs [The childhood of leisure]. Cult. Études 6 , 1–12 (2011).
Education at a glance 2015: OECD indicators (OECD, 2015); https://doi.org/10.1787/eag-2015-en
North, S., Snyder, I. & Bulfin, S. Digital tastes: social class and young people’s technology use. Inform. Commun. Soc. 11 , 895–911 (2008).
Robinson, L. & Schulz, J. Net time negotiations within the family. Inform. Commun. Soc. 16 , 542–560 (2013).
Bonfadelli, H. The Internet and knowledge gaps: a theoretical and empirical investigation. Eur. J. Commun. 17 , 65–84 (2002).
Drabowicz, T. Social theory of Internet use: corroboration or rejection among the digital natives? Correspondence analysis of adolescents in two societies. Comput. Educ. 105 , 57–67 (2017).
Nikken, P. & Jansz, J. Developing scales to measure parental mediation of young children’s Internet use. Learn. Media Technol. 39 , 250–266 (2014).
Danic, I., Fontar, B., Grimault-Leprince, A., Le Mentec, M. & David, O. Les espaces de construction des inégalités éducatives [The areas of construction of educational inequalities] (Presses Univ. de Rennes, 2019).
Goudeau, S. Comment l'école reproduit-elle les inégalités? [How does school reproduce inequalities?] (Univ. Grenoble Alpes Editions/Presses Univ. de Grenoble, 2020).
Bernstein, B. Class, Codes, and Control (Routledge, 1975).
Gaddis, S. M. The influence of habitus in the relationship between cultural capital and academic achievement. Soc. Sci. Res. 42 , 1–13 (2013).
Lamont, M. & Lareau, A. Cultural capital: allusions, gaps and glissandos in recent theoretical developments. Sociol. Theory 6 , 153–168 (1988).
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Phillips, L. T. Social class culture cycles: how three gateway contexts shape selves and fuel inequality. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 65 , 611–634 (2014).
Lahire, B. Enfances de classe. De l’inégalité parmi les enfants [Social class childhood. Inequality among children] (Le Seuil, 2019).
Lareau, A. Unequal Childhoods: Class, Race, and Family Life (Univ. of California Press, 2003).
Bourdieu, P. La distinction. Critique sociale du jugement [Distinction: a social critique of the judgement of taste] (Éditions de Minuit, 1979).
Bradley, R. H., Corwyn, R. F., McAdoo, H. P. & Garcia Coll, C. The home environments of children in the United States part I: variations by age, ethnicity, and poverty status. Child Dev. 72 , 1844–1867 (2001).
Blevins‐Knabe, B. & Musun‐Miller, L. Number use at home by children and their parents and its relationship to early mathematical performance. Early Dev. Parent. 5 , 35–45 (1996).
LeFevre, J. A. et al. Pathays to mathematics: longitudinal predictors of performance. Child Dev. 81 , 1753–1767 (2010).
Lareau, A. Home Advantage. Social Class and Parental Intervention in Elementary Education (Falmer Press, 1989).
Guryan, J., Hurst, E. & Kearney, M. Parental education and parental time with children. J. Econ. Perspect. 22 , 23–46 (2008).
Hill, C. R. & Stafford, F. P. Allocation of time to preschool children and educational opportunity. J. Hum. Resour. 9 , 323–341 (1974).
Calarco, J. M. A Field Guide to Grad School: Uncovering the Hidden Curriculum (Princeton Univ. Press, 2020).
Daw, J. Parental income and the fruits of labor: variability in homework efficacy in secondary school. Res. Soc. Strat. Mobil. 30 , 246–264 (2012).
Rønning, M. Who benefits from homework assignments? Econ. Educ. Rev. 30 , 55–64 (2011).
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R. & Olson, L. S. Lasting consequences of the summer learning gap. Am. Sociol. Rev. 72 , 167–180 (2007).
Cooper, H., Nye, B., Charlton, K., Lindsay, J. & Greathouse, S. The effects of summer vacation on achievement test scores: a narrative and meta-analytic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 66 , 227–268 (1996).
Stewart, H., Watson, N. & Campbell, M. The cost of school holidays for children from low income families. Childhood 25 , 516–529 (2018).
Pensiero, N., Kelly, A. & Bokhove, C. Learning inequalities during the Covid-19 pandemic: how families cope with home-schooling (University of Southampton, 2020); https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0025
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Townsend, S. S. Choice as an act of meaning: the case of social class. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 93 , 814–830 (2007).
Kraus, M. W., Piff, P. K. & Keltner, D. Social class, sense of control, and social explanation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 97 , 992–1004 (2009).
Dittmann, A. G., Stephens, N. M. & Townsend, S. S. Achievement is not class-neutral: working together benefits pople from working-class contexts. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 119 , 517–539 (2020).
Zimmerman, B. J. Investigating self-regulation and motivation: historical background, methodological developments, and future prospects. Am. Educ. Res. J. 45 , 166–183 (2008).
Backer-Grøndahl, A., Nærde, A., Ulleberg, P. & Janson, H. Measuring effortful control using the children’s behavior questionnaire–very short form: modeling matters. J. Pers. Assess. 98 , 100–109 (2016).
Johnson, S. E., Richeson, J. A. & Finkel, E. J. Middle class and marginal? Socioeconomic status, stigma, and self-regulation at an elite university. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 100 , 838–852 (2011).
Størksen, I., Ellingsen, I. T., Wanless, S. B. & McClelland, M. M. The influence of parental socioeconomic background and gender on self-regulation among 5-year-old children in Norway. Early Educ. Dev. 26 , 663–684 (2015).
Brady, L. et al. 7 ways for teachers to truly connect with parents. Education Week (31 December 2020); https://www.edweek.org/leadership/opinion-7-ways-for-teachers-to-truly-connect-with-parents/2020/12
Montacute, R. Social mobility and Covid-19: implications of the Covid-19 crisis for educational inequality (Sutton Trust, 2020); https://dera.ioe.ac.uk/35323/2/COVID-19-and-Social-Mobility-1.pdf
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and student learning in the United States: the hurt could last a lifetime (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-student-learning-in-the-united-states-the-hurt-could-last-a-lifetime
Parolin, Z. & Lee, E. K. Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 522–528 (2021).
Saavedra, J. A silent and unequal education crisis. And the seeds for its solution (World Bank, 2021); https://blogs.worldbank.org/education/silent-and-unequal-education-crisis-and-seeds-its-solution
Murray, B., Domina, T., Renzulli, L. & Boylan, R. Civil society goes to school: parent–teacher associations and the equality of educational opportunity. Russell Sage Found. J. Soc. Sci. 5 , 41–63 (2019).
Calarco, J. M. Avoiding us versus them: how schools’ dependence on privileged ‘helicopter’ parents influences enforcement of rules. Am. Sociol. Rev. 85 , 223–246 (2020).
Rist, R. Student social class and teacher expectations: the self-fulfilling prophecy in ghetto education. Harv. Educ. Rev. 40 , 411–451 (1970).
Tobisch, A. & Dresel, M. Negatively or positively biased? Dependencies of teachers’ judgments and expectations based on students’ ethnic and social backgrounds. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 20 , 731–752 (2017).
Brantlinger, E. Dividing Classes: How the Middle-class Negotiates and Rationalizes School Advantage (Routledge, 2003).
Calarco, J. M. ‘I need help!’ Social class and children’s help-seeking in elementary school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 76 , 862–882 (2011).
Calarco, J. M. The inconsistent curriculum: cultural tool kits and student interpretations of ambiguous expectations. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 77 , 185–209 (2014).
Goudeau, S. & Cimpian, A. How do young children explain differences in the classroom? Implications for achievement, motivation, and educational equity. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 16 , 533–552 (2021).
Croizet, J. C., Goudeau, S., Marot, M. & Millet, M. How do educational contexts contribute to the social class achievement gap: documenting symbolic violence from a social psychological point of view. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 18 , 105–110 (2017).
Goudeau, S. & Croizet, J.-C. Hidden advantages and disadvantages of social class: how classroom settings reproduce social inequality by staging unfair comparison. Psychol. Sci. 28 , 162–170 (2017).
Kudrna, L., Furnham, A. & Swami, V. The influence of social class salience on self-assessed intelligence. Soc. Behav. Personal. 38 , 859–864 (2010).
Wiederkehr, V., Darnon, C., Chazal, S., Guimond, S. & Martinot, D. From social class to self-efficacy: internalization of low social status pupils’ school performance. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 18 , 769–784 (2015).
Jury, M., Smeding, A., Court, M. & Darnon, C. When first-generation students succeed at university: on the link between social class, academic performance, and performance-avoidance goals. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 41 , 25–36 (2015).
Jury, M., Quiamzade, A., Darnon, C. & Mugny, G. Higher and lower status individuals’ performance goals: the role of hierarchy stability. Motiv. Sci. 5 , 52–65 (2019).
Autin, F. & Croizet, J.-C. Improving working memory efficiency by reframing metacognitive interpretation of task difficulty. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 141 , 610–618 (2012).
Schmader, T., Johns, M. & Forbes, C. An integrated process model of stereotype threat effects on performance. Psychol. Rev. 115 , 336–356 (2008).
Usher, E. L. & Pajares, F. Self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: a validation study. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68 , 443–463 (2008).
Bruno, A., Jury, M., Toczek-Capelle, M.-C. & Darnon, C. Are performance-avoidance goals always deleterious for academic achievement in college? The moderating role of social class. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 22 , 539–555 (2019).
Holloway, S. D. et al. Parenting self-efficacy and parental involvement: mediators or moderators between socioeconomic status and children’s academic competence in Japan and Korea? Res. Hum. Dev. 13 , 258–272 (2016).
Tazouti, Y. & Jarlégan, A. The mediating effects of parental self-efficacy and parental involvement on the link between family socioeconomic status and children’s academic achievement. J. Fam. Stud. 25 , 250–266 (2019).
Andreu, S. et al. Évaluations 2020, repères CP, CE1: premiers résultats [2020 assessments, first and second grades benchmarks: first results] (Ministère de l’Éducation nationale, de la Jeunesse et des Sports, 2020); https://www.education.gouv.fr/evaluations-2020-reperes-cp-ce1-premiers-resultats-307122
Engzell, P., Frey, A. & Verhagen, M. D. Learning loss due to school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , e2022376118 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Maldonado, J. E. & De Witte, K. The effect of school closures on standardized student test outcomes (KU Leuven—Faculty of Economics and Business, 2020); https://limo.libis.be/primo-explore/fulldisplay?docid=LIRIAS3189074&context=L&vid=Lirias&search_scope=Lirias&tab=default_tab&lang=en_US
Domingue, B., Hough, H. J., Lang, D. & Yeatman, J. Changing patterns of growth in oral reading fluency during the COVID-19 pandemic (PACE, 2021); https://edpolicyinca.org/publications/changing-patterns-growth-oral-reading-fluency-during-covid-19-pandemic
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and learning loss—disparities grow and students need help (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-learning-loss-disparities-grow-and-students-need-help
Angrist, N. et al. Building back better to avert a learning catastrophe: estimating learning loss from COVID-19 school shutdowns in Africa and facilitating short-term and long-term learning recovery. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 84 , 102397 (2021).
Reddy, V., Soudien, C. & Winnaar, L. Disrupted learning during COVID-19: the impact of school closures on education outcomes in South Africa (The Conversation, 2020); https://theconversation.com/impact-of-school-closures-on-education-outcomes-in-south-africa-136889
Entwisle, D. R. & Alexander, K. L. Summer setback: race, poverty, school composition, and mathematics achievement in the first two years of school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 57 , 72–84 (1992).
Kieffer, M. J. Catching up or falling behind? Initial English proficiency, concentrated poverty, and the reading growth of language minority learners in the United States. J. Educ. Psychol. 100 , 851–868 (2008).
Calarco, J. M., Horn, I. & Chen, G. A. ‘You need to be more responsible’: how math homework operates as a status-reinforcing process in school. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/xf96q (2020).
Kaiper-Marquez, A. et al. On the fly: adapting quickly to emergency remote instruction in a family literacy program. Int. Rev. Educ. 66 , 1–23 (2020).
Barton, D. C. Impacts of the COVID‐19 pandemic on field instruction and remote teaching alternatives: results from a survey of instructors. Ecol. Evol. 10 , 12499–12507 (2020).
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
IJzerman, H. et al. Use caution when applying behavioural science to policy. Nat. Hum. Behav. 4 , 1092–1094 (2020).
Taylor, J. & Mallery, J. In person and online learning go together (Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research, 2020); https://siepr.stanford.edu/research/publications/person-and-online-learning-go-together
Dietrichson, J., Bøg, M., Filges, T. & Klint Jørgensen, A. M. Academic interventions for elementary and middle school students with low socioeconomic status: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 87 , 243–282 (2017).
Núñez, J. C. et al. Teachers’ feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors, and academic achievement. J. Educ. Res. 108 , 204–216 (2015).
Singh, R. et al. In Artificial Intelligence in Education (eds Biswas, G.et al.) 328–336 (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011).
Harackiewicz, J. M., Rozek, C. S., Hulleman, C. S. & Hyde, J. S. Helping parents to motivate adolescents in mathematics and science: an experimental test of a utility-value intervention. Psychol. Sci. 23 , 899–906 (2012).
Jeynes, W. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of different types of parental involvement programs for urban students. Urban Educ. 47 , 706–742 (2012).
Mol, S. E., Bus, A. G., De Jong, M. T. & Smeets, D. J. Added value of dialogic parent–child book readings: a meta-analysis. Early Educ. Dev. 19 , 7–26 (2008).
Angrist, N., Bergman, P. & Matsheng, M. School’s out: experimental evidence on limiting learning loss using “low-tech” in a pandemic (National Bureau of Economic Research, 2021); https://www.nber.org/papers/w28205
Carlana, M. & La Ferrara, E. Apart but connected: online tutoring and student outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic (Institute of Labor Economics, 2021); http://hdl.handle.net/10419/232846
Pagan, S. & Sénéchal, M. Involving parents in a summer book reading program to promote reading comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary in grade 3 and grade 5 children. Can. J. Educ. 37 , 1–31 (2014).
Sénéchal, M. & LeFevre, J. A. Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: a five‐year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 73 , 445–460 (2002).
Starkey, P. & Klein, A. Fostering parental support for children’s mathematical development: an intervention with Head Start families. Early Educ. Dev. 11 , 659–680 (2000).
Buheji, M. et al. The extent of Covid-19 pandemic socio-economic impact on global poverty: a global integrative multidisciplinary review. Am. J. Econ. 10 , 213–224 (2020).
The world economy on a tightrope (OECD, 2020); http://www.oecd.org/economic-outlook/june-2020/
Martin, A., Markhvida, M., Hallegatte, S. & Walsh, B. Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Econ. Disasters Clim. Change 4 , 453–479 (2020).
Jetten, J., Mols, F. & Selvanathan, H. P. How economic inequality fuels the rise and persistence of the Yellow Vest movement. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 33 , 2 (2020).
Wilkinson, R. G. & Pickett, K. E. Income inequality and social dysfunction. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 35 , 493–511 (2009).
Sommet, N., Morselli, D. & Spini, D. Income inequality affects the psychological health of only the people facing scarcity. Psychol. Sci. 29 , 1911–1921 (2018).
Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-analyses Relating to Achievement (Routledge, 2008).
Cooper, H., Charlton, K., Valentine, J. C., Muhlenbruck, L. & Borman, G. D. Making the most of summer school: a meta-analytic and narrative review. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child 65 , 1–127 (2000).
Heyns, B. Schooling and cognitive development: is there a season for learning? Child Dev. 58 , 1151–1160 (1987).
McCombs, J. S., Augustine, C. H. & Schwartz, H. L. Making Summer Count: How Summer Programs can Boost Children’s Learning (Rand Education, 2011).
Borman, G. D. & Dowling, N. M. Longitudinal achievement effects of multiyear summer school: evidence from the teach Baltimore randomized field trial. Educ. Eval. Policy 28 , 25–48 (2006).
Kim, J. S. & Quinn, D. M. The effects of summer reading on low-income children’s literacy achievement from kindergarten to grade 8: a meta-analysis of classroom and home interventions. Rev. Educ. Res. 83 , 386–431 (2013).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Reis for editing the figure. The writing of this manuscript was supported by grant ANR-19-CE28-0007–PRESCHOOL from the French National Research Agency (S.G.).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Université de Poitiers, CNRS, CeRCA, Centre de Recherches sur la Cognition et l’Apprentissage, Poitiers, France
Sébastien Goudeau & Camille Sanrey
Université Clermont Auvergne, CNRS, LAPSCO, Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale et Cognitive, Clermont-Ferrand, France
Arnaud Stanczak & Céline Darnon
School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK
Antony Manstead
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sébastien Goudeau .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Human Behaviour thanks Daniele Checchi and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Goudeau, S., Sanrey, C., Stanczak, A. et al. Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap. Nat Hum Behav 5 , 1273–1281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Download citation
Received : 15 March 2021
Accepted : 06 September 2021
Published : 27 September 2021
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
It’s a problem, but not mine: exploring bias-related message acceptance among teachers.
- Lewis Doyle
- Matthew J. Easterbrook
- Peter R. Harris
Social Psychology of Education (2024)
Socioeconomic inequalities in psychosocial well-being among adolescents under the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-regional comparative analysis in Hong Kong, mainland China, and the Netherlands
- Gary Ka-Ki Chung
- Xiaoting Liu
- Roger Yat-Nork Chung
Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology (2024)
Developmental Losses of Preschool Children Three Years into the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Alejandro Vásquez-Echeverría
- Meliza Gónzalez
- Sylvana M Côté
Prevention Science (2024)
Digital gender gaps in Students’ knowledge, attitudes and skills: an integrative data analysis across 32 Countries
- Diego G. Campos
- Ronny Scherer
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Online learning problems, academic worries, social interaction, and psychological well-being among secondary school students in Hong Kong during the COVID-19 pandemic: the socioeconomic and gender differences
- Siu-Ming Chan
- Esther Sui-Chu Ho
European Journal of Psychology of Education (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Search the United Nations
- Policy and Funding
- Recover Better
- Disability Inclusion
- Secretary-General
- Financing for Development
- ACT-Accelerator
- Member States
- Health and Wellbeing
- Policy and Guidance
- Vaccination
- COVID-19 Medevac
- i-Seek (requires login)
- Awake at Night podcast

"The future of education is here"
About the author, antónio guterres.
António Guterres is the ninth Secretary-General of the United Nations, who took office on 1st January 2017.
Education is the key to personal development and the future of societies.
It unlocks opportunities and narrows inequalities.
It is the bedrock of informed, tolerant societies, and a primary driver of sustainable development.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the largest disruption of education ever.
In mid-July, schools were closed in more than 160 countries, affecting over 1 billion students.
At least 40 million children worldwide have missed out on education in their critical pre-school year.
And parents, especially women, have been forced to assume heavy care burdens in the home.
Despite the delivery of lessons by radio, television and online, and the best efforts of teachers and parents, many students remain out of reach.
Learners with disabilities, those in minority or disadvantaged communities, displaced and refugee students and those in remote areas are at highest risk of being left behind.
And even for those who can access distance learning, success depends on their living conditions, including the fair distribution of domestic duties.
We are at a defining moment for the world’s children and young people.
We already faced a learning crisis before the pandemic.
More than 250 million school-age children were out of school.
And only a quarter of secondary school children in developing countries were leaving school with basic skills.
Now we face a generational catastrophe that could waste untold human potential, undermine decades of progress, and exacerbate entrenched inequalities.
The knock-on effects on child nutrition, child marriage and gender equality, among others, are deeply concerning.
This is the backdrop to the Policy Brief I am launching today, together with a new campaign with education partners and United Nations agencies called ‘Save our Future’.
The decisions that governments and partners take now will have lasting impact on hundreds of millions of young people, and on the development prospects of countries for decades to come.
This Policy Brief calls for action in four key areas:
First, reopening schools.
Once local transmission of COVID-19 is under control, getting students back into schools and learning institutions as safely as possible must be a top priority.
We have issued guidance to help governments in this complex endeavour.
It will be essential to balance health risks against risks to children’s education and protection, and to factor in the impact on women’s labour force participation.
Consultation with parents, carers, teachers and young people is fundamental.
Second, prioritizing education in financing decisions.
Before the crisis hit, low and middle-income countries already faced an education funding gap of $1.5 trillion dollars a year.
This gap has now grown.
Education budgets need to be protected and increased.
And it is critical that education is at the heart of international solidarity efforts, from debt management and stimulus packages to global humanitarian appeals and official development assistance.
Third, targeting the hardest to reach.
Education initiatives must seek to reach those at greatest risk of being left behind -- people in emergencies and crises; minority groups of all kinds; displaced people and those with disabilities.
They should be sensitive to the specific challenges faced by girls, boys, women and men, and should urgently seek to bridge the digital divide.
Fourth, the future of education is here.
We have a generational opportunity to reimagine education.
We can take a leap towards forward-looking systems that deliver quality education for all as a springboard for the Sustainable Development Goals.
To achieve this, we need investment in digital literacy and infrastructure, an evolution towards learning how to learn, a rejuvenation of life-long learning and strengthened links between formal and non-formal education.
And we need to draw on flexible delivery methods, digital technologies and modernized curricula while ensuring sustained support for teachers and communities.
As the world faces unsustainable levels of inequality, we need education – the great equalizer – more than ever.
We must take bold steps now, to create inclusive, resilient, quality education systems fit for the future.
- Policy Brief: Education during COVID-19 and beyond

S7-Episode 2: Bringing Health to the World
“You see, we're not doing this work to make ourselves feel better. That sort of conventional notion of what a do-gooder is. We're doing this work because we are totally convinced that it's not necessary in today's wealthy world for so many people to be experiencing discomfort, for so many people to be experiencing hardship, for so many people to have their lives and their livelihoods imperiled.”
Dr. David Nabarro has dedicated his life to global health. After a long career that’s taken him from the horrors of war torn Iraq, to the devastating aftermath of the Indian Ocean tsunami, he is still spurred to action by the tremendous inequalities in global access to medical care.
“The thing that keeps me awake most at night is the rampant inequities in our world…We see an awful lot of needless suffering.”
:: David Nabarro interviewed by Melissa Fleming

Brazilian ballet pirouettes during pandemic
Ballet Manguinhos, named for its favela in Rio de Janeiro, returns to the stage after a long absence during the COVID-19 pandemic. It counts 250 children and teenagers from the favela as its performers. The ballet group provides social support in a community where poverty, hunger and teen pregnancy are constant issues.

Radio journalist gives the facts on COVID-19 in Uzbekistan
The pandemic has put many people to the test, and journalists are no exception. Coronavirus has waged war not only against people's lives and well-being but has also spawned countless hoaxes and scientific falsehoods.
The Role of Online University Teaching and Learning during COVID-19 Pandemic
Proceedings of the International Conference on Best Innovative Teaching Strategies (ICON-BITS 2021)
4 Pages Posted: 6 Aug 2024
Monali Chatterjee
Nirma University, Ahmedabad
Date Written: August 06, 2024
Amidst the worldwide prevalence of the COVID-19 pandemic since March 2020, there has been an abrupt transition to online teaching and learning. Among students of various age groups, students pursuing university education have been one of the most drastically affected by this sudden change. Responding to this critical predicament adapting completely and rapidly to online education that ensures effective learning, has been the need of the hour. It is imperative to also investigate the ways in which Information and Communication Technologies affect the learners, teachers and supporting staff members during the lockdown of COVID-19. This paper proposes to evaluate the challenges faced by instructors across universities in India. Through this exploratory research, an attempt will be made to understand through an exhaustive literature review, the measures that have been deployed to overcome the challenges that hamper effective learning among university students and online pedagogies. The paper concludes with insights to focus on students' experiences of learning online. As a part of this prescriptive research, it also aims to propose effective best practices of teaching and learning as well as pedagogical innovations that can improve distance education.
Keywords: online university teaching, COVID-19, pedagogy, learning, ICT, higher education
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Monali Chatterjee (Contact Author)
Nirma university, ahmedabad ( email ).
Ahmedabad India
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, humanities education ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Life Sciences Education eJournal
Educational impact & evaluation research ejournal.
Subscribe to this free journal for more curated articles on this topic
Communication Education eJournal

Air Quality Alert from 7 a.m. through 8 p.m. Wednesday. High levels of ozone pollution are expected in the El Paso area
- Weather Section
- Interactive Maps
- Upload weather pics/video
Fact Check Team: Exploring the uneven recovery in student learning post-COVID
by EMMA WITHROW and JANAE BOWENS | Fact Check Team

WASHINGTON (TND) — As students across the nation head back to school, the long-lasting impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education still lingers. Recent data from the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWAE) found many students are still grappling with the academic setbacks caused by a prolonged period of disrupted learning.
NWAE's assessment found that students, particularly those in middle school, are still far behind in math and reading. According to their report , 8th graders are trailing by an entire school year in both subjects. On average, students need approximately four extra months of instruction to catch up in these core areas.
The learning loss isn't the same for all students though. According to the data, students in 7th and 8th grades require the most academic support. Disparities among ethnic groups have also widened, with Hispanic students emerging as the group most in need of additional resources to catch up.
Achievement disparities that predate the pandemic have been starkly exacerbated over the last four years, and marginalized students remain the furthest from recovery. By failing to close gaps for these students, we prevent them from achieving their full potential as they progress through the education system.
The gap between pre-COVID and current test scores has widened across nearly all grades, with a 36% increase in the reading gap and an 18% increase in the math gap.
Despite the challenges, there are signs of significant recovery. A new study conducted by researchers at Stanford University and Harvard University reveals that during the 2022-23 school year, students made historic strides in regaining lost ground. The report analyzed data from school districts across 30 states and found that students recovered about one-third of their lost progress in math and one-quarter in reading.
Alabama stood out as the only state where students exceeded their pre-pandemic achievement levels in math. However, this level of recovery is not seen across the board, with most students in other states still lagging by more than a third of a grade level in math and reading.
While the pandemic posed unprecedented challenges for students, it also brought some needed advancements in K-12 education. Education experts say the use of technology and the expansion of online and hybrid learning models are among the most significant shifts. These options have been beneficial for certain students, particularly those who struggled in traditional classroom settings due to shyness, bullying, or health issues.
Graphics explain: How has college enrollment changed in the past decade?
Rising college tuition costs, the COVID-19 pandemic, and a bungled FASFA rollout have impacted the financial circumstances of many prospective college students. After several years of declining enrollment, the numbers spiked up about 1.2% in the 2023-2024 academic year, the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center reported. Enrollment numbers remained below pre-pandemic levels of 16 million.
While it's too early to track the impact tuition costs will have on enrollment numbers for the upcoming semester, some students have already said they're opting out of college due to the financial aid fiasco .
USA TODAY identified undergraduate enrollment trends from the past decade to see who is attending college, the most common fields of study and how the pandemic impacted enrollment.
Here's what you need to know about changes in college enrollment:
College enrollment upticks in 2023
Undergraduate enrollment increased by about 176,000 students in fall 2023, according to a report published earlier this year by the National Student Clearinghouse. That’s a spike of about 1.2% from the previous fall.
About 15.2 million undergraduate students enrolled in college for the 2023-2024 academic year. The biggest growth came at community colleges, which gained 118,000 students this fall. Private, for-profit colleges also experienced an uptick in enrollments.
The Department of Education has not yet published their data on total undergraduate enrollment for Fall 2023.
Four-year universities and two-year colleges experienced dramatic declines in enrollment since the COVID-19 pandemic hit in March of 2020. Undergraduate numbers fell by 15% between 2010 and 2021 , according to the National Center for Education Statistics.
Who is most likely to enroll in college?
Women made up nearly 60% of all college students enrolling in Fall of 2022, the Education Department found, up from 56.6% eight years earlier. For several decades women have outnumbered men as college enrollees and attendees, but the gender gap has only widened.
FASFA fiasco: For low-income students, FAFSA can be a lifeline. When it didn't work, they were hardest hit.
College enrollment by major
For students graduating with an associate degree or bachelor's degree, business and health professions and related programs were the top three most common fields of study, the Education Department said.
For the past decade, business has been the most common degree granted to graduating students.
In the 2021-2022 academic year, these were the top five most common bachelor degrees granted by field of study:
- 18.2% in business
- 12.9% in health professions and related studies
- 7.7% in social sciences and history
- 6.1% in psychology
- 6.3% in biological and biomedical sciences
Graphics explain: How are college costs adding up these days and how much has tuition risen?
Why is college enrollment declining?
College tuition has become unaffordable for many prospective students. For those who do pursue higher education, many will be paying nearly two-fold what their parents paid for an undergraduate education 20 years earlier.
According to the Education Data Initiative, the average cost of college tuition and fees at public four-year institutions has risen 179.2% over the last two decades.
At the same time, difficulty applying for financial aid upended the college decision-making process, and disrupted the lives of many students. USA TODAY previously reported that delays and technical problems with the FASFA form left many economically disadvantaged students scrambling for financial aid, jeopardizing their college aspirations.
Contributing: Zachary Schermele, USA TODAY
Texas schools got billions in federal pandemic relief. It is coming to an end as the school year starts.
Educators say they’ll struggle to keep the programs they created with those funds, highlighting their precarious situation without more state help.
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/files/3629b869e1496093cdfe86c392ec10ca/0723%20SEISD%20JH%2038.jpg)
Sign up for The Brief , The Texas Tribune’s daily newsletter that keeps readers up to speed on the most essential Texas news.
The $43 million infusion the Port Arthur Independent School District received in federal COVID-19 pandemic relief funds accomplished more than Phyllis Geans could have ever imagined.
The money allowed the district to upgrade antiquated heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. Teachers earned retention stipends at a time when many were leaving the profession. Students received new band instruments. An ambitious summer program taught them about photography, robots and skydiving.
“We were excited, really excited, because we started thinking about things that we knew were almost impossible,” said Geans, Port Arthur ISD’s assistant superintendent of operations. “It was unreal.”
Districts like Port Arthur ISD , where roughly 85% of students are economically disadvantaged, received a level of financial support they likely wouldn’t have received otherwise — and they took advantage of it by investing in community health, learning, infrastructure and safety.
But the more than $19 billion Texas schools received in Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief funds over the last four years will expire on Sept. 30, with a few exceptions .
The money will go away at a time when Texas schools are already struggling to keep the lights on. A number of districts are planning to enter the next school year with multimillion-dollar holes in their budgets as inflation has sent costs soaring. The Texas Legislature failed last year to approve a significant boost to the base amount of money every school receives per student — an amount that hasn’t changed since 2019 — as lawmakers fought over whether to fund private education with taxpayer dollars.
School administrators say losing the pandemic relief funds not only threatens the programs they paid for but also highlights how precarious their districts’ situation has become after years of clamoring for more state funding.
“It's not about making up ESSER, because we all knew that was one-time funding,” said La Joya ISD Superintendent Marcey Sorensen. “I just would ask, without getting political whatsoever, that everybody just look in the mirror and say, OK, if we really haven't provided additional funding since 2019, maybe it's time that we just give school districts a little bit more of what they need, knowing that kids have different needs now.”
Congress established the ESSER program in 2020 to help schools address the devastating impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. In Texas, districts experienced significant enrollment declines and the number of burnt-out teachers exiting the profession skyrocketed. Years of educational gains unraveled as kids, parents and teachers struggled with school closures and the hurried transition to online learning.
District leaders say the federal pandemic relief funds helped them address learning disruptions and provide additional academic support for students.
“They helped us ride out the five years of no new funding from the state,” said Ronald Wilson, Hearne ISD’s chief financial officer.
Recent studies show the relief funds helped schools across the country improve test scores . For districts where most students come from low-income households, the funds were particularly meaningful, and not just for academics.
In Port Arthur ISD, where most students are Black and Hispanic and the four-year graduation rate is well below the state average, the Brilliance Academy summer program took students on an indoor skydiving trip , where they learned about wind resistance, speed and velocity. The district created a program that paid high school seniors to provide supplemental classroom instruction to elementary kids. Geans said some of the students who participated in the program later expressed interest in pursuing a career in teaching.
Meanwhile, Paris ISD established income incentives for teachers to mentor students. Hearne ISD hired behavioral specialists and social workers to assist students and their families during the pandemic. San Elizario ISD built spaces for recreational activities like playing the piano and hosted family fitness, literacy and math events.
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/files/7360eb436b7ca1f3718af87126feffe9/0723%20SEISD%20JH%2008.jpg)
“I think we were more successful in growing the whole child, on the part where we're growing young ladies and young men,” said Jerrica Liggins, Paris ISD’s secondary education director and college transition coordinator. “We gave them things that they need to be successful in the next grade level or whether they were graduating and going out into the workforce. We gave them things that helped make them a better person.”
Schools across the country have faced questions about how they’ve spent federal relief funds. District officials who used them for things like hiring more staff for their central offices, purchasing pool passes or renovating sports stadiums have received the harshest criticism .
Texas schools will likely face similar spending questions next year. Lt. Gov. Dan Patrick , who presides over the Texas Senate, recently directed that chamber’s education committee to review how public schools spent the massive influx of federal COVID-19 relief money. The review will likely focus on how districts used the funds to improve student outcomes.
Standardized test scores are one of the main ways in which student achievement and growth are measured in the state, and the same is true for how the use of pandemic relief funds has been evaluated in national studies .
In Texas, the pandemic caused a dramatic decline in learning, with reading and math scores hit particularly hard. The effects were even more profound for students who participated in online classes. Math scores have yet to rebound to pre-pandemic levels.
How to hold schools accountable for Texas students’ academic performance has also been a contentious issue in recent years. School districts have fought with the Texas Education Agency over its letter grade accountability system, claiming recent changes would hurt their ratings. School officials have argued that testing scores alone are not enough to measure school systems’ effectiveness.
What ESSER spending evaluations sometimes miss is the extent to which the relief funds helped school districts stay alive, said Amanda Brownson, deputy executive director of the Texas Association of School Business Officials.
The funds “helped them keep the doors open, helped them make sure staff were in classrooms ready to greet kids when they came back; it helped them not … collapse,” Brownson said. “What we don't have is the counterfactual: What shape would school districts be in right now if they had to manage the pandemic and had not had ESSER funding available?”
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/files/577034f8e6c88e1e758f5cc2e4539951/0723%20SEISD%20JH%2018.jpg)
Maintaining the programs Texas schools created with federal relief funds will likely be difficult without them.
A recent survey conducted by the TASBO found that out of 313 school districts across the state, nearly 80% reported deficit budgets or a lack of resources as one of their top challenges. Ninety percent of respondents said they have less than a quarter of pandemic relief funds remaining.
Gov. Greg Abbott has faced sharp criticism from public school advocates for his unwillingness to support standalone legislation to significantly boost school funding.
Since last year, Abbott has pushed for education savings accounts, which would allow families to use tax dollars to pay for their children’s private education and other school-related expenses. Opponents in the Texas House, citing worries that such a program would siphon funds away from public schools, successfully blocked the measure. But it meant public schools wouldn’t get the funding boost they wanted: Abbott had said he would veto any school funding proposal that did not include an education savings accounts program.
The governor has vowed to make a similar push when the Legislature reconvenes next year.
The uncertainty around state funding for public schools has created a situation where school districts are spending more time worrying about their financial sustainability and less about what’s best for students, said Monty Exter, governmental relations director of the Association of Texas Professional Educators.
But for low-income districts, money difficulties are not unfamiliar. And they plan to do what they’ve always done: find ways to provide for students and families with their limited resources.
Some school districts are encouraging their staff to be on the lookout for local grant opportunities. Others are thinking of asking voters to increase the tax revenue going to schools or support school bonds. Few say they are looking to the Legislature for solutions.
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/files/3db1cc009f8da76a42de3ad50326b38a/0723%20SEISD%20JH%2034.jpg)
”We're taking as much of the funding issues on ourselves and moving forward,” said Hearne ISD Superintendent Adrian Johnson, adding that he is still hopeful that legislators will do more to fund public schools.
“But we're not waiting on that to happen,” he said.
Disclosure: Association of Texas Professional Educators and Texas Association of School Business Officials (TASBO) have been financial supporters of The Texas Tribune, a nonprofit, nonpartisan news organization that is funded in part by donations from members, foundations and corporate sponsors. Financial supporters play no role in the Tribune's journalism. Find a complete list of them here .
The full program is now LIVE for the 2024 Texas Tribune Festival , happening Sept. 5–7 in downtown Austin. Explore the program featuring more than 100 unforgettable conversations on topics covering education, the economy, Texas and national politics, criminal justice, the border, the 2024 elections and so much more. See the full program.
Texans need truth. Help us report it.
Independent Texas reporting needs your support. The Texas Tribune delivers fact-based journalism for Texans, by Texans — and our community of members, the readers who donate, make our work possible. Help us bring you and millions of others in-depth news and information. Will you support our nonprofit newsroom with a donation of any amount?
Support independent Texas news
Become a member. Join today.
Choose an amount or learn more about membership .
Information about the authors
/https://static.texastribune.org/media/profiles/Jaden-Edison_headshot.jpeg)
Jaden Edison
Public education reporter.
@edisonjaden
Learn about The Texas Tribune’s policies , including our partnership with The Trust Project to increase transparency in news.
Explore related story topics
Public education School finance
How To Tackle The Weirdest Supplemental Essay Prompts For This Application Cycle
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Writing the college essay
How do you write a letter to a friend that shows you’re a good candidate for the University of Pennsylvania? What reading list will help the Columbia University admissions committee understand your interdisciplinary interests? How can you convey your desire to attend Yale by inventing a course description for a topic you’re interested in studying?
These are the challenges students must overcome when writing their supplemental essays . Supplemental essays are a critical component of college applications—like the personal statement, they provide students with the opportunity to showcase their authentic voice and perspective beyond the quantitative elements of their applications. However, unlike the personal essay, supplemental essays allow colleges to read students’ responses to targeted prompts and evaluate their candidacy for their specific institution. For this reason, supplemental essay prompts are often abstract, requiring students to get creative, read between the lines, and ditch the traditional essay-writing format when crafting their responses.
While many schools simply want to know “why do you want to attend our school?” others break the mold, inviting students to think outside of the box and answer prompts that are original, head-scratching, or downright weird. This year, the following five colleges pushed students to get creative—if you’re struggling to rise to the challenge, here are some tips for tackling their unique prompts:
University of Chicago
Prompt: We’re all familiar with green-eyed envy or feeling blue, but what about being “caught purple-handed”? Or “tickled orange”? Give an old color-infused expression a new hue and tell us what it represents. – Inspired by Ramsey Bottorff, Class of 2026
What Makes it Unique: No discussion of unique supplemental essay prompts would be complete without mentioning the University of Chicago, a school notorious for its puzzling and original prompts (perhaps the most well-known of these has been the recurring prompt “Find x”). This prompt challenges you to invent a new color-based expression, encouraging both linguistic creativity and a deep dive into the emotional or cultural connotations of color. It’s a prompt that allows you to play with language, think abstractly, and show off your ability to forge connections between concepts that aren’t typically linked—all qualities that likewise demonstrate your preparedness for UChicago’s unique academic environment.
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Clues And Answers For Thursday, August 15
The backlash against blake lively, explained, wwe releases roman reigns’ new entrance song, hits 61k views in 3 hours.
How to Answer it: While it may be easy to get distracted by the open-ended nature of the prompt, remember that both the substance and structure of your response should give some insight into your personality, perspective, and characteristics. With this in mind, begin by considering the emotions, experiences, or ideas that most resonate with you. Then, use your imagination to consider how a specific color could represent that feeling or concept. Remember that the prompt is ultimately an opportunity to showcase your creativity and original way of looking at the world, so your explanation does not need to be unnecessarily deep or complex—if you have a playful personality, convey your playfulness in your response; if you are known for your sarcasm, consider how you can weave in your biting wit; if you are an amateur poet, consider how you might take inspiration from poetry as you write, or offer a response in the form of a poem.
The goal is to take a familiar concept and turn it into something new and meaningful through a creative lens. Use this essay to showcase your ability to think inventively and to draw surprising connections between language and life.
Harvard University
Prompt: Top 3 things your roommates might like to know about you.
What Makes it Unique: This prompt is unique in both form and substance—first, you only have 150 words to write about all 3 things. Consider using a form other than a traditional essay or short answer response, such as a bullet list or short letter. Additionally, note that the things your roommate might like to learn about you do not necessarily overlap with the things you would traditionally share with an admissions committee. The aim of the prompt is to get to know your quirks and foibles—who are you as a person and a friend? What distinguishes you outside of academics and accolades?
How to Answer it: First and foremost, feel free to get creative with your response to this prompt. While you are producing a supplemental essay and thus a professional piece of writing, the prompt invites you to share more personal qualities, and you should aim to demonstrate your unique characteristics in your own voice. Consider things such as: How would your friends describe you? What funny stories do your parents and siblings share that encapsulate your personality? Or, consider what someone might want to know about living with you: do you snore? Do you have a collection of vintage posters? Are you particularly fastidious? While these may seem like trivial things to mention, the true creativity is in how you connect these qualities to deeper truths about yourself—perhaps your sleepwalking is consistent with your reputation for being the first to raise your hand in class or speak up about a cause you’re passionate about. Perhaps your living conditions are a metaphor for how your brain works—though it looks like a mess to everyone else, you have a place for everything and know exactly where to find it. Whatever qualities you choose, embrace the opportunity to think outside of the box and showcase something that admissions officers won’t learn about anywhere else on your application.
University of Pennsylvania
Prompt: Write a short thank-you note to someone you have not yet thanked and would like to acknowledge.
What Makes it Unique: Breaking from the traditional essay format, this supplement invites you to write directly to a third party in the form of a 150-200 word long letter. The challenge in answering this distinct prompt is to remember that your letter should say as much about you, your unique qualities and what you value as it does about the recipient—all while not seeming overly boastful or contrived.
How to Answer it: As you select a recipient, consider the relationships that have been most formative in your high school experience—writing to someone who has played a large part in your story will allow the admissions committee some insight into your development and the meaningful relationships that guided you on your journey. Once you’ve identified the person, craft a thank-you note that is specific and heartfelt—unlike other essays, this prompt invites you to be sentimental and emotional, as long as doing so would authentically convey your feelings of gratitude. Describe the impact they’ve had on you, what you’ve learned from them, and how their influence has shaped your path. For example, if you’re thanking a teacher, don’t just say they helped you become a better student—explain how their encouragement gave you the confidence to pursue your passions. Keep the tone sincere and personal, avoid clichés and focus on the unique role this person has played in your life.
University of Notre Dame
Prompt: What compliment are you most proud of receiving, and why does it mean so much to you?
What Makes it Unique: This prompt is unique in that it invites students to share something about themselves by reflecting on someone else’s words in 50-100 words.
How to Answer it: The key to answering this prompt is to avoid focusing too much on the complement itself and instead focus on your response to receiving it and why it was so important to you. Note that this prompt is not an opportunity to brag about your achievements, but instead to showcase what truly matters to you. Select a compliment that truly speaks to who you are and what you value. It could be related to your character, work ethic, kindness, creativity, or any other quality that you hold in high regard. The compliment doesn’t have to be grand or come from someone with authority—it could be something small but significant that left a lasting impression on you, or it could have particular meaning for you because it came from someone you didn’t expect it to come from. Be brief in setting the stage and explaining the context of the compliment—what is most important is your reflection on its significance and how it shaped your understanding of yourself.
Stanford University
Prompt: List five things that are important to you.
What Makes it Unique: This prompt’s simplicity is what makes it so challenging. Stanford asks for a list, not an essay, which means you have very limited space (50 words) to convey something meaningful about yourself. Additionally, the prompt does not specify what these “things” must be—they could be a physical item, an idea, a concept, or even a pastime. Whatever you choose, these five items should add depth to your identity, values, and priorities.
How to Answer it: Start by brainstorming what matters most to you—these could be values, activities, people, places, or even abstract concepts. The key is to choose items or concepts that, when considered together, provide a comprehensive snapshot of who you are. For example, you might select something tangible and specific such as “an antique telescope gifted by my grandfather” alongside something conceptual such as “the willingness to admit when you’re wrong.” The beauty of this prompt is that it doesn’t require complex sentences or elaborate explanations—just a clear and honest reflection of what you hold dear. Be thoughtful in your selections, and use this prompt to showcase your creativity and core values.
While the supplemental essays should convey something meaningful about you, your values, and your unique qualifications for the university to which you are applying, the best essays are those that are playful, original, and unexpected. By starting early and taking the time to draft and revise their ideas, students can showcase their authentic personalities and distinguish themselves from other applicants through their supplemental essays.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education: Critical Reflections
Lingnan University, Tuen Mun, Hong Kong, China
This Special Issue has chosen the major focus to examine how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected higher education development and governance. The collection of articles in this Special Issue is organized with three key sub-themes, namely, student mobility, teaching and student learning, and university governance. Papers selected in this Issue were presented at different international conferences examining how the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in late 2019 has affected higher education development from international and comparative perspectives. During the international research events, authors contributing their papers to this Special Issue indeed benefitted from the exchanges and dialogues from international peers. Drawing insights from the papers collected in this Special Issue, this introductory article concludes by drawing the implications for future development of international education.
Teaching and Student Learning
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed higher education systems across different parts of the globe to adopt online platforms for conducting teaching and learning activities. Angela Hou and colleagues , in her article, ask a very important and reflective question: How would COVID-19 drive digitalization, innovations, and crisis management of higher education? More importantly, they also raise the issue of quality assurance when most higher education teaching and learning had been operating through online platforms. Based upon a case study of the INQAAHE Virtual Review, they critically examine issues related to quality assurance when higher education teaching and learning of had been digitalized. Their article does not only offer a case study of Taiwan, showing how one of the East Asian economies responded to the outbreak of the COVID-19 crisis through digitalizing higher education. This case studies also shows relevance to other parts of the world, especially when those countries/regions encounter difficulties in realizing the digitalization of teaching and student learning. International research reports educational inequality and disparity being intensified after the widespread the COVID-19 pandemic (UNESCO, 2020 , 2021 ). International and comparative research report higher education systems from relatively low-income countries/regions have suffered tremendously simply because of the lack of resources/infrastructural support for online teaching/learning, let alone diverse differences in educational cultures/management and practices across different parts of the globe (Vegas, 2020 ; Mok, et al., 2021 ).
The second article contributed by Mok , Xiong, and Ke critically examines how Chinese students evaluate overseas studies during and in the post-COVID-19 crisis, showing the growing interest of Chinese students in making Asia their future destination for studying abroad, especially when becoming more concerned about public health conditions in traditional destinations based in Europe, the UK and the USA (QS, 2020 ). The motivations and desires of Chinese students choosing overseas learning would have been affected by the new geopolitics and different kinds of “cultural shocks”, particularly when Asian students were reportedly being discriminated/stigmatized after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic when studying abroad (Mbous, et al2022; Mok and Zhang, 2021 ).
Institutional Response and University Governance
Moving beyond management of teaching and student learning, Susan Robertson, critically reflecting upon the future of higher education governance set against the COVID-19 context, presented a paper at the Conference for Higher Education Research (CHER) 2020. Based upon recent works on temporality and higher education, Robertson considers such works have made important contributions to work on time, though time-future continues to be under-developed. In her presentation, she attempted to explore anticipatory governance in the contemporary university. Exploring a range of anticipatory practices and their logic in the contemporary academy, from goals to planning, predictions, forecasts, indicators, specialised knowledge, and agreements, Robertson believed we should think beyond our own box of how the future presents potential opportunities for academic development. Adopting the time-future lens in conceiving future university governance, Robertson’s paper shows the anticipatory practices mobilise different kinds of socio-temporal and political sensibilities and expectations, practices, and institutional arrangements, that constitute timescapes in the contemporary academy (Robertson, 2020 ).
Whereas Robertson discusses temporality in general, Tilak critically examines the impact of the pandemic on Indian higher education. In his article, he presents the major challenges confronting higher education development in India against the COVID-19 crisis, discussing major strategies/policy measures adopted by the Indian government in managing challenges for higher education. As India is committed to further increasing its higher education enrolments in order to produce sufficient young talents for the changing economic needs of the country, the current COVID-19 crisis would considerably disrupt its plans for higher education development. To which extent the Indian government and university leaders make use of innovative measures through the technology-enabled platforms to achieve its development goals depends not only on resources but also on careful policy coordination.
Moving away from Asia, the article contributed by O’Shea, Mou, Xu, and Aikins critically examine how higher education institutions (HEIs) in three countries, namely, Canada, China, and the USA, responded to the challenges of COVID-19 over a six-month period at the outbreak of the global pandemic. Employing document analysis, they analyze 732 publicly available communications from 27 HEIs in Canada, China, and the United States. Through the theoretical framework of Situational Critical Communications Theory (SCCT), O’Shea et al ., explore how HEIs respond to the crisis and communicate their response to the crisis to campus stakeholders. While there are important country-level distinctions among HEIs in how they communicate and respond to crisis, this research finds there are common themes across the three countries, including (1) emphasizing social responsibilities of serving the community, (2) referencing public health guidelines, and (3) offering different kinds of financial support to students. The findings shed light on strengths and weaknesses of the SCCT model in analyzing HEI responses to COVID-19 and may be helpful for HEIs to prepare for the next crisis.
Future of International Education
After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, international students are considered to be more adversely affected by COVID-19 restrictions than other student and population groups (e.g., local students) in the world (Dodd, et al., 2021 ). According to research conducted by Amoah and Mok in 2020, international students find themselves living in foreign countries/regions with limited social and economic support and in a context of rising discrimination (Amoah and Mok, 2020 ). With special attention to international student well-being, the article contributed by Amoah and Esther Mok examines the effects that COVID-19 restrictions have had and are having on the lives of international students. Such effects include direct consequences of the disease itself and its disruptive effect on this group of students and the effectiveness of the support offered by universities for the well-being of international students. The study analyzed data from a global survey conducted among international students in April 2020. They found that the well-being of international students is negatively associated with being worried about COVID-19 itself ( B = − 0.218, p = .027); with perceived COVID-19 disruption of academic activities ( B = − 0.162, p = .016); and with feelings of loneliness ( B = − 0.317, p = .000). Notably, COVID-19 information support provided by universities was positively associated with the students’ well-being ( B = 0.224, p = 0.003). These findings are discussed in the context of education policy and practical changes introduced by the COVID-19 pandemic. The discussion also considers the influence of the changing geopolitical and social environment (e.g., racism) on higher education internationalisation, critically reflecting upon management and governance issues faced by universities worldwide when promoting the well-being of international students (Mok, 2022 ).
A critical reflection of how the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the Australian university system, Anthony Welch shows the impact of COVID as a stark reminder that international students are so much more than cash cows for universities. Not merely do they add immeasurably to the vibrant cultural diversity of universities, they “are vital parts of communities. Indeed, many international students are future Australian citizens. It is estimated that between 20,000 and 30,000 international students move from student visas to permanent residency visas every year” a figure that is likely to be an underestimate, since students often gain another form of temporary visa, before attaining permanent residence. During the COVID-19 crisis, we have witnessed how academic cooperation and research collaboration have become highly politicized, especially when the new geopolitics has emerged as an influential force shaping international education and research.
In view of the worsening diplomatic relationship between China and Australia, Welch highlights the potential for COVID to curtail staff and student mobility, restricting research collaboration between colleagues in Australia and China. The growing anti-Chinese and anti-Asian sentiments commonly found not only in Australia but also in other major university systems in Europe and North America would create disincentives for inter-university and cross-border collaboration, which would be detrimental to future development of international education and research. According to Welch, what is urgently needed is a dialogue of civilizations, rather than a clash of civilizations, with the associated rancorous and rivalrous international relations that threaten international academic mobility and collaboration.
This Special Issue brings together thought-provocative pieces, critically reflecting upon the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on higher education development. The challenges confronting contemporary universities are partly caused by the pandemic, disrupting the “normal operation” of universities. Nonetheless, the present global health crisis has also opened new opportunities for university teachers and leaders for exploring innovative modes of teaching and student learning, moving beyond the conventional models in developing new forms of inter-university collaborations. However, part of the problems facing universities globally is the unfavorable influences of new geopolitics creating mistrust across countries/regions. Perhaps world leaders as well as university leaders should be humbled to learn from the global health crisis resulting from the outbreak of COVID-19, seeking appropriate ways for closer and deeper collaboration for the betterment of the humanity.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Amoah, P.A. and Mok, K.H. (2020) ‘The Covid-19 pandemic and internationalisation of higher education: International students knowledge, experiences and well-being’, Higher Education Policy Institute's blog , 13 June. Available on https://www.hepi.ac.uk/2020/06/13/weekend-reading-the-covid-19-pandemic-and-internationalisation-of-higher-education-international-students-knowledge-experiences-and-wellbeing/ , accessed 18 June 2020.
- Dodd RH, Dadaczynski K, Okan O, McCaffery KJ, Pickles K. Psychological Wellbeing and Academic Experience of University Students in Australia during COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18 (3):866. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18030866. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mbous, Y.P.V., Mohamed, R., Rudisill, T.M. (2022) ‘International Students Challenges during the COVID-19 Pandemic in a university in the USA: A focus group study’, Current Psychology . Published online 4 February. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-02776-x. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mok KH. COVID-19 Pandemic and International Higher Education Major Challenges and Implications for East Asia. In: Marginson S, Xu X, editors. Higher Education in East Asia Internationalization Strategy and National Agendas. London: Bloomsbury; 2022. pp. 225–246. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mok KH, Xiong WY, Bin Aedy Rahman HN. COVID-‘19 pandemic’s disruption on university teaching and learning and competence cultivation: Student evaluation of online learning experiences in Hong Kong’ International Journal of Chinese Education. 2021; 10 (1):1–20. doi: 10.1177/22125868211007011. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mok, K.H. and Zhang, Y.L. (2021) ‘Remaking International Higher Education for an Unequal World’, Higher Education Quarterly . Published online 13 November. doi.org/10.1111/hequ.12366.
- QS (2020) International Student Survey: Global Opportunities in the New Higher Education Paradigm. QS Report, London: QS. Available on https://unibuddy.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/QS_ISS2020_GLOBAL_FINAL.pdf , accessed 21 February 2022.
- Robertson, S. (2020) Radical Uncertainty and Anticipatory Practices in the Pandemic University. Keynote speech presented at the Conference for Higher Education Research (CHER) 2020, Lingnan University, Hong Kong, 13-14 November 2020.
- UNESCO (2020) Education: From Disruption to Recovery . https://www.unesco.org/en/covid-19/education-response , accessed 6 March 2022.
- UNESCO (2021) About Virtual Student Mobility in Higher Education . https://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/2021/01/20/about-virtual-student-mobility-in-higher-education/#_ftn1 .
- Vegas, E. (2020) ‘School closures, government responses, and learning inequality around the world during COVID-19’ , Brookings, 14 April. Available on https://www.brookings.edu/research/school-closures-government-responses-and-learning-inequality-around-the-world-during-covid-19/ .
How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
I've heard about antibody testing for covid-19. what is antibody testing is it the same as testing to diagnose covid-19.
Antibody testing shows whether you have antibodies to the virus that causes COVID-19, also called coronavirus disease 2019.
Having antibodies suggests you've either had an infection with the virus in the past or you've had the COVID-19 vaccine. Antibody testing is not used to diagnose COVID-19.
What are antibodies and why are antibody tests done?
Antibodies are proteins. The body makes antibodies when there are things in the body that shouldn't be there, such as viruses. The antibodies help clear out the virus. Having antibodies to a virus may give some protection from the disease caused by the virus for a time.
A blood test can show whether you have antibodies to the COVID-19 virus within days to weeks of having the infection or the vaccine. But antibody testing, also called serology testing, is not done routinely.
A healthcare professional might use an antibody test to diagnose complications of COVID-19. These include multisystem inflammatory syndrome, a rare condition linked to COVID-19.
If you've gotten over COVID-19, you might be able to help others who have COVID-19. If testing shows that you have a high level of antibodies, you might donate part of your blood called plasma. This is called convalescent plasma. It may help others with severe disease who have a weakened immune system.
What tests are used to diagnose COVID-19?
Two types of tests can help diagnose COVID-19.
Molecular tests. These tests look for genetic material from the COVID-19 virus.
Polymerase chain reaction tests, shortened to PCR tests, are molecular tests. You may also hear this type of test called an NAAT test, short for nucleic acid amplification test.
PCR tests are more accurate than the other type of COVID-19 test, called an antigen test. You can do PCR tests at home. But they are more likely to be done by a healthcare professional and processed in a lab.
Antigen tests. These tests look for viral proteins called antigens.
Antigen tests also may be called rapid COVID-19 tests or at-home COVID-19 tests. These tests are useful if you need quick results.
Antigen tests are accurate. But they're less accurate than PCR tests. If you have symptoms and an antigen test is negative for COVID-19, take another antigen test after 48 hours to get the best result.
If you don't have symptoms and get a negative result, test again after 48 hours. If the result is still negative and you think you have COVID-19, you can test a third time after another 48 hours. Or you can get a molecular test or call your healthcare professional.
How do I get a COVID-19 diagnostic test?
In the United States, at-home COVID-19 tests are available from several sources. Free tests can be mailed to U.S. addresses, or you can buy tests in stores and pharmacies or online. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves the tests. On the FDA website, you can find a list of the tests that are validated and when they expire.
Daniel C. DeSimone, M.D.
- COVID-19 variant
- COVID-19 drugs: Are there any that work?
- AskMayoExpert. Serological antibody testing. Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- Interim guidelines for COVID-19 antibody testing. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/testing/antibody-tests-guidelines.html. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- Antibody (serology) testing for COVID-19: Information for patients and consumers. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/antibody-serology-testing-covid-19-information-patients-and-consumers. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Drug regimens and other treatment options. Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- COVID-19 testing: What you need to know. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/testing.html. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- At-home COVID-19 antigen tests: Take steps to reduce your risk of false negative results: FDA safety communication. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/home-covid-19-antigen-tests-take-steps-reduce-your-risk-false-negative-results-fda-safety. Accessed March 6, 2024.
- AT-home OTC COVID diagnostic tests. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/home-otc-covid-19-diagnostic-tests. Accessed March 6, 2024.
- Zhang Y et al. Molecular and antigen tests, and sample types for diagnosis of COVID-19: A review. Future Virology. 2022; doi:10.2217/fvl-2021-0256.
Products and Services
- A Book: Endemic - A Post-Pandemic Playbook
- Begin Exploring Women's Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
- A Book: Future Care
- Antibiotics: Are you misusing them?
- COVID-19 and vitamin D
- Convalescent plasma therapy
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- COVID-19: How can I protect myself?
- Herd immunity and respiratory illness
- COVID-19 and pets
- COVID-19 and your mental health
- COVID-19 antibody testing
- COVID-19, cold, allergies and the flu
- Long-term effects of COVID-19
- COVID-19 tests
- COVID-19 in babies and children
- Coronavirus infection by race
- COVID-19 travel advice
- COVID-19 vaccine: Should I reschedule my mammogram?
- COVID-19 vaccines for kids: What you need to know
- COVID-19 vaccines
- COVID-19 vs. flu: Similarities and differences
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
- Debunking coronavirus myths
- Different COVID-19 vaccines
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Fever: First aid
- Fever treatment: Quick guide to treating a fever
- Fight coronavirus (COVID-19) transmission at home
- Honey: An effective cough remedy?
- How to measure your respiratory rate
- How to take your pulse
- How to take your temperature
- How well do face masks protect against COVID-19?
- Is hydroxychloroquine a treatment for COVID-19?
- Loss of smell
- Mayo Clinic Minute: You're washing your hands all wrong
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How dirty are common surfaces?
- Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pregnancy and COVID-19
- Safe outdoor activities during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Safety tips for attending school during COVID-19
- Sex and COVID-19
- Shortness of breath
- Thermometers: Understand the options
- Treating COVID-19 at home
- Unusual symptoms of coronavirus
- Vaccine guidance from Mayo Clinic
- Watery eyes
Related information
- COVID-19 diagnostic testing - Related information COVID-19 diagnostic testing
- COVID-19 antibody testing - Related information COVID-19 antibody testing
- How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests
Help transform healthcare
Your donation can make a difference in the future of healthcare. Give now to support Mayo Clinic's research.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How China Built Tech Prowess: Chemistry Classes and Research Labs
Stressing science education, China is outpacing other countries in research fields like battery chemistry, crucial to its lead in electric vehicles.

By Keith Bradsher
Reporting from Changsha, Beijing and Fuzhou, China
China’s domination of electric cars, which is threatening to start a trade war, was born decades ago in university laboratories in Texas, when researchers discovered how to make batteries with minerals that were abundant and cheap.
Companies from China have recently built on those early discoveries, figuring out how to make the batteries hold a powerful charge and endure more than a decade of daily recharges. They are inexpensively and reliably manufacturing vast numbers of these batteries, producing most of the world’s electric cars and many other clean energy systems.
Batteries are just one example of how China is catching up with — or passing — advanced industrial democracies in its technological and manufacturing sophistication. It is achieving many breakthroughs in a long list of sectors, from pharmaceuticals to drones to high-efficiency solar panels.
Beijing’s challenge to the technological leadership that the United States has held since World War II is evidenced in China’s classrooms and corporate budgets, as well as in directives from the highest levels of the Communist Party.
A considerably larger share of Chinese students major in science, math and engineering than students in other big countries do. That share is rising further, even as overall higher education enrollment has increased more than tenfold since 2000.
Spending on research and development has surged, tripling in the past decade and moving China into second place after the United States. Researchers in China lead the world in publishing widely cited papers in 52 of 64 critical technologies, recent calculations by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute reveal.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The reactions of students varied, with 75.8% admitting to agreeing with the decision, 34.7% feeling guilty, and 27.0% feeling relieved.39In the same survey, 74.7% of students felt that their medical education had been disrupted, 84.1% said they felt increased anxiety, and 83.4% would accept the risk of COVID-19 infection if they were able to ...
The descriptive and content analysis yielded two major strands of studies: (1) online education and (2) COVID-19 and education, business, economics, and management. The online education strand focused on the issue of technological anxiety caused by online classes, the feeling of belonging to an academic community, and feedback.
COVID-19 has had a huge impact on children and their education. Image: UNICEF. Out-of-school children are among the most vulnerable and marginalized children in society, says UNICEF. They are the least likely to be able to read, write or do basic maths, and when not in school they are at risk of exploitation and a lifetime of poverty and ...
Education The impact of COVID-19 on student achievement and what it may mean for educators Jim Soland, Megan Kuhfeld, Beth Tarasawa, Angela Johnson, Erik Ruzek, Jing Liu May 27, 2020 ...
A student wearing a protective mask, attends class on the first day of school, amid the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, at St. Lawrence Catholic School in North Miami Beach, Florida, U.S ...
experienced an average decrease of 11.5 hours of work per week and a 21% decrease in weekly earnings, arnings for 52% of the sample, which again re ects s. variation in the e ects of COVID-19 across students. In terms of labor market expectations, on average, students foresee a 13 percentage points decrease in.
The COVID-19 pandemic has created the largest disruption of education systems in human history, affecting nearly 1.6 billion learners in more than 200 countries. ... to provide a comprehensive report on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on online teaching and learning of various papers and indicate the way forward. ... Education during COVID ...
The rapid and unexpected onset of the COVID-19 global pandemic has generated a great degree of uncertainty about the future of education and has required teachers and students alike to adapt to a new normal to survive in the new educational ecology. Through this experience of the new educational ecology, educators have learned many lessons, including how to navigate through uncertainty by ...
The aim of this survey study is to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the education, health, and lifestyle of students from different age-groups. 2.2. Statistical analysis. In this study, we conducted a cross-sectional survey with a sample size of 1182 students from different educational institutions.
UNESCO. COVID-19 Recovery. Education: From COVID-19 school closures to recovery. After the historic disruption of the COVID-19 pandemic, most schools are back open worldwide but education is still in recovery assessing the damage done and lessons learned. Education: The pandemic affected more than 1.6 billion students and youth globally, with ...
COVID-19 has fuelled a global 'learning poverty' crisis. This article was originally published on the World Bank 's website. The pandemic saw empty classrooms all across the world. Before the pandemic, the world was already facing an education crisis. Last year, 53% of 10-year-old children in low- and middle-income countries either had ...
As this most disrupted of school years draws to a close, it is time to take stock of the impact of the pandemic on student learning and well-being. Although the 2020-21 academic year ended on a high note—with rising vaccination rates, outdoor in-person graduations, and access to at least some in-person learning for 98 percent of students—it was as a whole perhaps one of the most ...
March 12, 2021. 11 min read. One year ago, the World Health Organization declared the spread of COVID-19 a worldwide pandemic. Reacting to the virus, schools at every level were sent scrambling ...
This image shows the severity of higher education school closures throughout the world. Red being worse off, yellow being best off. This image puts into perspective the length of the pandemic's impacts on college education. Since the beginning of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, the global population has been going through a whirlpool of side effects.
An update to the Education Recovery Scorecard, including data from 12 additional states whose 2022 scores were not available in October. The project now includes a district-level view of the pandemic's effects in 40 states (plus D.C.). ... New research finds achievement gaps in math and reading, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, remain ...
The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom. As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms. Research suggests that online learning has been shown to ...
The COVID-19 pandemic led to school closures and distance learning that are likely to exacerbate social class academic disparities. This Review presents an agenda for future research and outlines ...
Introduction. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education is both unprecedented and widespread in education history, impacting nearly every student in the world (UNICEF 2020; United Nations 2020).The unexpected arrival of the pandemic and subsequent school closures saw massive effort to adapt and innovate by educators and education systems around the world.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the largest disruption of education ever. In mid-July, schools were closed in more than 160 countries, affecting over 1 billion students.
Responding to this critical predicament adapting completely and rapidly to online education that ensures effective learning, has been the need of the hour. It is imperative to also investigate the ways in which Information and Communication Technologies affect the learners, teachers and supporting staff members during the lockdown of COVID-19.
WASHINGTON (TND) — As students across the nation head back to school, the long-lasting impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education still lingers. Recent data from the Northwest Evaluation ...
Rising college tuition costs, the COVID-19 pandemic, and a bungled FASFA rollout have impacted the financial circumstances of many prospective college students. After several years of declining ...
Congress established the ESSER program in 2020 to help schools address the devastating impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. ... conversations on topics covering education, the economy, Texas and ...
How to Answer it: While it may be easy to get distracted by the open-ended nature of the prompt, remember that both the substance and structure of your response should give some insight into your ...
Future of International Education. After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, international students are considered to be more adversely affected by COVID-19 restrictions than other student and population groups (e.g., local students) in the world (Dodd, et al., 2021).According to research conducted by Amoah and Mok in 2020, international students find themselves living in foreign countries ...
Antigen tests also may be called rapid COVID-19 tests or at-home COVID-19 tests. These tests are useful if you need quick results. Antigen tests are accurate. But they're less accurate than PCR tests. If you have symptoms and an antigen test is negative for COVID-19, take another antigen test after 48 hours to get the best result.
A Texas judge once again blocked the release of A-F accountability grades for public schools that were to be published Thursday. The order comes in response to a lawsuit from a handful of ...
Republicans have leveled inaccurate or misleading attacks on Mr. Walz's response to protests in the summer of 2020, his positions on immigration and his role in the redesign of Minnesota's flag.
Stressing science education, China is outpacing other countries in research fields like battery chemistry, crucial to its lead in electric vehicles. By Keith Bradsher Reporting from Changsha ...