Writing in Third Person – Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
The third-person narrative is often employed in narrative writing because it zooms in and out of character perspectives to describe actions, feelings, emotions, and thoughts. If you’re unsure how to use the 3rd person perspective in writing, here are some tips and examples.

What is Third Person Narrative?

The third person is one of three perspectives employed in speaking and writing. It’s used to describe the point of view of a third party and uses a variety of pronouns derived from he, her, and it. Books written in third person are often more popular, as well, for their ease of reading.
I often write in first-person narrative, but when I’m writing a complex story from the point of view of multiple characters, I use third person to make things more rounded and streamlined for the reader.
Using Third Person
Third person is a perspective used based on whoever the story or writing in question is about. The subject pronoun is outside of the narrator themself. Third-person texts do not include the perspective of the narrator/writer, nor does it address the reader directly. It also uses certain personal pronouns and possessive pronouns.
Example of a third person sentence:
Jeremy knew it was destined to be. He placed the dog in the backseat of his car and drove away. All he wanted at that time was to ensure the animal got the loving home he deserved.
Third Person Possessive Adjectives in Third Person
So, instead of using me, mine, ours, etc., you would use hers, his, theirs when writing in third person.
Does “You” Belong in 3rd Person Writing?
Third-person writing requires using third-person pronouns, including he, she, it, him, her, them, themselves, himself, herself, or a name. Using “you” means you’re switching to the second person.
How to Introduce Yourself in the Third Person
People typically use the first-person point of view when talking about themselves and their experiences. It would be odd to talk about oneself in the third person all the time, but you might use it occasionally for the sake of humorous effect or attract the attention of another person.
The third person introduces a third party to the person you’re speaking with. If you are a narrator, it’s best to introduce yourself in the first person and start narrating the events in the third person.
How to Start a Story in Third Person

In a story, narrators use the third person if they are not part of the story themselves. Third-person narratives show us a person’s actions, feelings, and thoughts.
Example of how to write in third person:
Nadia dreamt about being a gymnast her entire life. Ever since she can remember, she’s worked hard, sacrificed a lot, and hoped someone would notice all her efforts. She was never the smartest kid in school, but she believed in herself enough to never give up on that spot on the podium.
What Are the 3 Types of 3rd Person?
In writing, there are three ways to approach third-person writing.
Third-Person Omniscient
The story’s narrator is all-knowing and can see into the past, present, and future. This narrator can assume other people’s perspectives, jumping around in time and providing the reader with their thoughts and observations.
Third-Person Limited Omniscient
In this point of view, the author focuses on one persona and never switches to another. In a novel, the narrator may use this technique throughout the work or employ it in alternating chapters or sections.
The author can regulate the reader’s knowledge and experience by writing from a limited point of view. Used effectively, it can create a palpable sense of anticipation and excitement.
Third-Person Objective
The narrator of a story told from the third-person objective perspective is unbiased and does not share the viewpoint of the character’s emotional reactions. The story is told in an objective, third-person style.
How to Write In Third Person About Yourself
The easiest way to approach this problem is to create a character. You can also use your actual name to write from the third-person perspective.
Why Write in Third-Person?
Fiction writing uses third-person POV quite often. Here are some advantages of employing it as part of your narrative style.
Strong Character Growth Is Emphasized
More characters can be highlighted in a story told from the third-person perspective than in the first- or second-person. These varying perspectives give the reader a complete understanding of the story since they shed light on the plot in ways the other characters cannot.
It Employs Flexible Narrative Possibilities
The advantages of writing in the third person include greater freedom to move around, giving the reader a comprehensive view, and shifting perspectives among multiple characters. You can switch between being completely all-knowing and having only partial or first-person knowledge.
This latter technique allows the reader to experience the world through the eyes of a character, allowing for a more profound understanding of that person and their surroundings.
Makes the Author More Reliable
Third-person narration places the reader in a vantage point far above the action. With the author/narrator not part of the story, they can rise above it, having nothing to lose or gain from certain narrative developments. This makes the story more reliable and lends the story more authority and credibility.
First, Second, and Third Person Pronouns
If you’re confused about the types of pronouns used in each of the three main perspectives, here is a comprehensive list:
- First person pronouns: I, me, mine, myself, we, us, ourselves, ours.
- Second person pronouns: you, your, yours.
- Third person singular pronouns: he, him, his, she, her, it,
- Third person plural pronouns: its, itself, they, them, their, theirs, themselves.
Bottom Line on Third Person
Writing in 3rd person grants the author more credibility and offers a more objective perspective of the characters in the text. Often employed in fictional and academic writing, the third-person point of view makes the text seem more authentic and factually correct.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Editing and Style
How to Write in Third Person
Last Updated: May 10, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Alicia Cook . Alicia Cook is a Professional Writer based in Newark, New Jersey. With over 12 years of experience, Alicia specializes in poetry and uses her platform to advocate for families affected by addiction and to fight for breaking the stigma against addiction and mental illness. She holds a BA in English and Journalism from Georgian Court University and an MBA from Saint Peter’s University. Alicia is a bestselling poet with Andrews McMeel Publishing and her work has been featured in numerous media outlets including the NY Post, CNN, USA Today, the HuffPost, the LA Times, American Songwriter Magazine, and Bustle. She was named by Teen Vogue as one of the 10 social media poets to know and her poetry mixtape, “Stuff I’ve Been Feeling Lately” was a finalist in the 2016 Goodreads Choice Awards. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 19 testimonials and 86% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 1,152,927 times.
Writing in third person can be a simple task, with a little practice. For academic purposes, third person writing means that the writer must avoid using subjective pronouns like “I” or “you.” For creative writing purposes, there are differences between third person omniscient, limited, objective, and episodically limited points of view. Choose which one fits your writing project.
Writing Third Person Point of View
The third-person point of view discusses the person or people being talked about in academic or creative writing. In this perspective, you’d shift focus from subject to subject. Use pronouns like he/him, she/her, they/them, or it/itself.
Writing in Third Person Academically

- Third person helps the writing stay focused on facts and evidence instead of personal opinion.

- Third person pronouns include: he, she, it; his, her, its; him, her, it; himself, herself, itself; they; them; their; themselves.
- Names of other people are also considered appropriate for third person use.
- Example: “ Smith believes differently. According to his research, earlier claims on the subject are incorrect.”

- First person pronouns include: I, me, my, mine, myself, we, us, our, ours, ourselves. [3] X Research source
- The problem with first person is that, academically speaking, it sounds too personalized and too subjective. In other words, it may be difficult to convince the reader that the views and ideas being expressed are unbiased and untainted by personal feelings. Many times, when using first person in academic writing, people use phrases like "I think," "I believe," or "in my opinion."
- Incorrect example: “Even though Smith thinks this way, I think his argument is incorrect.”
- Correct example: “Even though Smith thinks this way, others in the field disagree.”

- Second person pronouns include: you, your, yours, yourself. [4] X Research source
- One main problem with second person is that it can sound accusatory. It runs to risk of placing too much responsibility on the shoulders of the reader specifically and presently reading the work.
- Incorrect example: “If you still disagree nowadays, then you must be ignorant of the facts.”
- Correct example: “Someone who still disagrees nowadays must be ignorant of the facts.”

- Indefinite third person nouns common to academic writing include: the writer, the reader, individuals, students, a student, an instructor, people, a person, a woman, a man, a child, researchers, scientists, writers, experts.
- Example: “In spite of the challenges involved, researchers still persist in their claims.”
- Indefinite third person pronouns include: one, anyone, everyone, someone, no one, another, any, each, either, everybody, neither, nobody, other, anybody, somebody, everything, someone.
- Incorrect example: "You might be tempted to agree without all the facts."
- Correct example: “ One might be tempted to agree without all the facts.”
- This is usually done in an attempt to avoid the gender-specific “he” and “she” pronouns. The mistake here would be to use the “they” pronoun with singular conjugation. [5] X Research source
- Incorrect example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. They was afraid of getting hurt if their name was spread.”
- Correct example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. They were afraid of getting hurt if their name was spread.”
Writing in Third Person Omniscient

- For instance, a story may include four major characters: William, Bob, Erika, and Samantha. At various points throughout the story, the thoughts and actions of each character should be portrayed. These thoughts can occur within the same chapter or block of narration.
- Writers of omniscient narratives should be conscious of “head-hopping” — that is, shifting character perspectives within a scene. While this does not technically break the rules of Third Person Omniscience, it is widely considered a hallmark of narrative laziness.
- In a sense, the writer of a third person omniscient story is somewhat like the “god” of that story. The writer can observe the external actions of any character at any time, but unlike a limited human observer, the writer can also peek into the inner workings of that character at will, as well.
- Know when to hold back. Even though a writer can reveal any information they choose to reveal, it may be more beneficial to reveal some things gradually. For instance, if one character is supposed to have a mysterious aura, it would be wise to limit access to that character's inner feelings for a while before revealing his or her true motives.

- Do not use first person and second person points of view in the narrative or descriptive portions of the text.
- Correct example: Bob said to Erika, “I think this is creepy. What do you think?”
- Incorrect example: I thought this was creepy, and Bob and Erika thought so, too. What do you think?
Writing in Third Person Limited

- The thoughts and feelings of other characters remain an unknown for the writer throughout the duration of the text. There should be no switching back and forth between characters for this specific type of narrative viewpoint.
- Unlike first person, where the narrator and protagonist are the same, third person limited puts a critical sliver of distance between protagonist and narrator. The writer has the choice to describe one main character’s nasty habit — something they wouldn’t readily reveal if the narration were left entirely to them.

- In other words, do not use first person pronouns like “I,” “me,” “my,” “we,” or “our” outside of dialog. The main character's thoughts and feelings are transparent to the writer, but that character should not double as a narrator.
- Correct example: “Tiffany felt awful after the argument with her boyfriend.”
- Correct example: “Tiffany thought, “I feel awful after that argument with my boyfriend.”
- Incorrect example: “I felt awful after the argument with my boyfriend.”

- Note that the writer can offer insight or guesses regarding the thoughts of other characters, but those guesses must be presented through the perspective of the main character.
- Correct example: “Tiffany felt awful, but judging by the expression on Carl's face, she imagined that he felt just as bad if not worse.”
- Incorrect example: “Tiffany felt awful. What she didn't know was that Carl felt even worse.”

- Correct example: “Tiffany watched from the window as Carl walked up to her house and rang the doorbell.”
- Incorrect example: “As soon as Tiffany left the room, Carl let out a sigh of relief.”
Writing in Episodically Limited Third Person

- Limit the amount of pov characters you include. You don't want to have too many characters that confuse your reader or serve no purpose. Each pov character should have a specific purpose for having a unique point of view. Ask yourself what each pov character contributes to the story.
- For instance, in a romance story following two main characters, Kevin and Felicia, the writer may opt to explain the inner workings of both characters at different moments in the story.
- One character may receive more attention than any other, but all main characters being followed should receive attention at some point in the story.

- Multiple perspectives should not appear within the same narrative space. When one character's perspective ends, another character's can begin. The two perspectives should not be intermixed within the same space.
- Incorrect example: “Kevin felt completely enamored of Felicia from the moment he met her. Felicia, on the other hand, had difficulty trusting Kevin.”

- In a novel-length work, a good time to switch perspective is at the start of a new chapter or at a chapter break.
- The writer should also identify the character whose perspective is being followed at the start of the section, preferably in the first sentence. Otherwise, the reader may waste too much energy guessing.
- Correct example: “Felicia hated to admit it, but the roses Kevin left on her doorstep were a pleasant surprise.”
- Incorrect example: “The roses left on the doorstep seemed like a nice touch.”

- For instance, if Kevin had a talk with Felicia's best friend about Felicia's feelings for him, Felicia herself would have no way of knowing what was said unless she witnessed the conversation or heard about it from either Kevin or her friend.
Writing in Third Person Objective

- There does not need to be a single main character to focus on. The writer can switch between characters, following different characters throughout the course of the narrative, as often as needed.
- Stay away from first person terms like “I” and second person terms like “you” in the narrative, though. Only use first and second person within dialog.

- Imagine that you are an invisible bystander observing the actions and dialog of the characters in your story. You are not omniscient, so you do not have access to any character's inner thoughts and feelings. You only have access to each character's actions.
- Correct example: “After class, Graham hurriedly left the room and rushed back to his dorm room.”
- Incorrect example: “After class, Graham raced from the room and rushed back to his dorm room. The lecture had made him so angry that he felt as though he might snap at the next person he met.”

- Correct example: “When no one else was watching her, Isabelle began to cry.”
- Incorrect example: “Isabelle was too prideful to cry in front of other people, but she felt completely broken-hearted and began crying once she was alone.”

- Let the reader draw his or her own conclusions. Present the actions of the character without analyzing them or explaining how those actions should be viewed.
- Correct example: “Yolanda looked over her shoulder three times before sitting down.”
- Incorrect example: “It might seem like a strange action, but Yolanda looked over her shoulder three times before sitting down. This compulsive habit is an indication of her paranoid state of mind.”
Examples of Third Person POV

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://stlcc.edu/student-support/academic-success-and-tutoring/writing-center/writing-resources/point-of-view-in-academic-writing.aspx
- ↑ http://studysupportresources.port.ac.uk/Writing%20in%20the%20third%20peson.pdf
- ↑ http://www.grammar-monster.com/glossary/third_person.htm
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/use-the-singular-they/
- ↑ Alicia Cook. Professional Writer. Expert Interview. 11 December 2020.
- ↑ https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/point-of-view-first-second-third-person-difference
- ↑ https://ojs.library.dal.ca/YAHS/article/viewFile/7236/6278
About This Article

To write in third person, refer to people or characters by name or use third person pronouns like he, she, it; his, her, its; him, her, it; himself, herself, itself; they; them; their; and themselves. Avoid first and second person pronouns completely. For academic writing, focus on a general viewpoint rather than a specific person's to keep things in third person. In other types of writing, you can write in third person by shifting your focus from character to character or by focusing on a single character. To learn more from our Literary Studies Ph.D., like the differences between third person omniscient and third person limited writing, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 31, 2016
Did this article help you?

Jean Scicluna
Jan 31, 2021
Nov 4, 2016
Karen Evans
Aug 5, 2016
Oct 20, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- [email protected]
- (650) 338-8226
Cupertino, CA

- Our Philosophy
- Our Results
- News, Media, and Press
- Common Application
- College Application Essay Editing
- Extracurricular Planning
- Academic Guidance
- Summer Programs
- Interview Preparation
Middle School
- Pre-High School Consultation
- Boarding School Admissions
College Admissions
- Academic and Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
- Senior Editor College Application Program
- Summer Program Applications
- Private Consulting Program
- Transfer Admissions
- UC Transfer Admissions
- Ivy League Transfer Admissions
Graduate Admissions
- Graduate School Admissions
- MBA Admissions
Private Tutoring
- SAT/ACT Tutoring
- AP Exam Tutoring
- Olympiad Training
Research Programs
- Science Research Program
- Humanities Competitions
- Passion Project Program
- Ad Hoc Consulting
- Athletic Recruitment
- National Universities Rankings
- Liberal Arts Colleges Rankings
- Public Schools Rankings
Acceptance Rates
- University Acceptance Rates
- Transfer Acceptance Rates
- Supplemental Essays
- College Admissions Data
- Chances Calculator
- GPA Calculator
National Universities
- College Acceptance Rates
- College Overall Acceptance Rates
- College Regular Acceptance Rates
- College Early Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Overall Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Regular Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Early Acceptance Rates
Public Schools
- Public Schools Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Overall Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Regular Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Early Acceptance Rates
Liberal Arts
- Liberal Arts Colleges Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Overall Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Regular Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Early Acceptance Rates

Third-Person Writing: A Guide for Effective Academic Writing

By Eric Eng

In this post, we will explore the concept of third-person writing and its importance for academic writing. We will discuss the benefits of using third-person language, provide examples of how it can be used in different types of academic writing, and offer practical tips for incorporating it into your writing. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of third-person writing and how to use it effectively in your academic work.
Academic writing is a fundamental part of any high school student’s education, and mastering the art of writing in a clear and concise manner is essential to academic success. One key aspect of effective academic writing is the use of third-person language, which can help writers create a more objective and authoritative tone.
What is third-person writing?
What is third-person writing? Third-person writing is a style of writing that involves using pronouns such as “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” or “one” to refer to individuals or objects instead of using first- or second-person pronouns like “I,” “me,” “we,” “us,” “you,” or “your.” Third-person language is commonly used in academic writing to create a more objective and authoritative tone.
For instance, instead of saying “I believe,” third-person writing would say, “It can be argued.” This writing style can be particularly effective when presenting research or making a persuasive argument, as it allows the writer to distance themselves from their ideas and present them as more balanced and objective.
Writing in the third person differs from first- and second-person writing in several key ways. First-person writing involves using pronouns like “I,” “me,” “we,” or “us” to refer to oneself or a group of individuals. This writing style is often used in personal narratives, memoirs, or opinion pieces, where the writer’s personal experiences or opinions are central to the piece.
Conversely, second-person writing involves using pronouns like “you” or “your” to address the reader directly.

This writing style is often used in instructional or self-help texts, where the writer gives advice or instructions to the reader. In contrast, writing in the third person avoids direct references to the writer or reader and instead focuses on the topic or subject. This writing style can be particularly effective in academic writing , where objectivity and a neutral tone are often valued.
The benefits of using third-person writing in academic writing
Using the third-person point of view in academic writing offers several benefits, including creating a more objective and authoritative tone. By using third-person pronouns instead of first-person pronouns, writers can present information more neutral and unbiased. This can be particularly important in academic writing, where presenting a balanced and objective perspective is often valued.
Writing in the third person can also help writers distance themselves from their arguments and present a more balanced perspective. By using third-person pronouns, writers can avoid appearing overly confident or biased. Instead, they can present their arguments in a more measured and thoughtful way, allowing readers to make their judgments about the validity of the arguments presented.
Moreover, it can be especially useful in academic writing that involves research. When presenting research findings or making a persuasive argument, writers may be tempted to rely heavily on first-person language to convince readers of the validity of their claims. However, this can undermine the persuasiveness of the argument.
Using third-person writing instead can help writers present their research findings and arguments in a more objective and authoritative way, ultimately making their work more convincing to readers.
In summary, using a third-person point of view in academic writing can help writers create a more objective and authoritative tone, distance themselves from their arguments, and present a more balanced perspective. By using third-person pronouns and language effectively, writers can make their writing more persuasive and ultimately more successful in communicating their ideas to their readers.
What are the words to avoid in third-person writing?
What are the words to avoid in third-person writing? When writing in the third person, it’s important to avoid using first- and second-person language, as these types can make the writing appear less objective and authoritative. Here are some examples of words and phrases to avoid when writing in the third person:
- First-person pronouns: This includes words like “I,” “me,” “my,” “we,” and “us.” Avoid using these pronouns in the third-person point of view.
- Second-person pronouns include words like “you” and “your.” Avoid using these pronouns, as they can make the writing feel more direct and less objective.
- Imperative verbs: Imperative verbs are those that give commands or instructions, such as “do,” “make,” or “take.” These verbs should generally be avoided as they can make the writing feel less objective and more directive.
- Personal opinions: It’s important to avoid including personal opinions or biases. Instead, focus on presenting the facts and allowing readers to draw their conclusions.
By avoiding these words and phrases, writers can create more effective and authoritative third-person writing better suited for academic and professional contexts.
Examples of third-person writing in academic writing
The third-person point of view is commonly used in various academic writing contexts, including research papers, literature reviews, and essays . Here are some examples of how third-person writing can be used effectively in these contexts:

- Research papers: In research papers, it can be used to present research findings and conclusions in a more objective and authoritative manner. For example, instead of saying, “I found that,” a third-person point of view would say, “It was found that.” This helps to create a more neutral tone and emphasizes the importance of the research itself rather than the researcher’s personal experience.
- Literature reviews: In literature reviews , it can be used to summarize and analyze existing research in an objective and authoritative way. For example, instead of saying, “I think that this study is important,” third-person writing would say, “This study has been found to be important by previous researchers.” This helps to emphasize the research’s importance and present it more objectively and neutrally.
- Essays: In essays, it can be used to present arguments and evidence in a more balanced and persuasive manner. For example, instead of saying, “I believe that,” a third-person point of view would say, “It can be argued that.” This helps to present the argument in a more objective and authoritative way, which can be particularly important in persuasive essays.
The potential benefits of using third-person writing in each of these contexts include the following:
- Creating a more objective and authoritative tone.
- Emphasizing the importance of the research or argument rather than the writer’s personal experience or opinion.
- Presenting information in a more balanced and neutral way.
By writing in the third person effectively, writers can make their academic writing more effective and persuasive, ultimately helping to communicate their ideas more effectively to their readers.
Tips for using third-person writing in academic writing
To effectively incorporate third-person writing into academic writing, consider the following tips:
- Use active voice: Using active voice can help to make the third-person point of view more engaging and direct. For example, instead of saying, “It was found that,” say, “Researchers found that.” This can make the writing feel engaging rather than passive and dull.
- Vary sentence structure: To avoid overusing third-person pronouns, try to vary sentence structure. For example, instead of repeatedly using “he” or “she,” try using more descriptive phrases or words, such as “the researcher” or “the author.”
- Avoid personal opinions: In third-person writing, it’s important to avoid personal opinions or biases. Instead, focus on presenting the facts and allowing readers to draw their own conclusions.
- Use reliable sources: In academic writing, it’s important to use reliable and trustworthy sources to support your arguments. Make sure to cite your sources properly and avoid using biased or unreliable sources.
- Proofread carefully: Finally, proofread your writing carefully to ensure you’ve used third-person language consistently and effectively. Look for instances of first- or second-person language and replace them with third-person language, as necessary.
Common mistakes to avoid when using third-person writing in academic writing include overusing third-person pronouns, failing to vary sentence structure, and using vague or ambiguous language. Additionally, it’s important to avoid using personal opinions or biases, as this can undermine the objectivity and authority of your writing.

By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively incorporate third-person pov into your academic writing and create more persuasive and authoritative pieces.
In conclusion, using third-person writing can be a powerful tool for high school students looking to improve their academic writing. Students can create a more objective, authoritative, and balanced tone in their writing by avoiding first- and second-person language and using third-person pronouns and another language.
The benefits of using third-person writing include presenting research findings and arguments in a more neutral and objective manner, emphasizing the importance of the research or argument rather than the writer’s personal experience or opinion, and presenting information in a more balanced and neutral way.
By incorporating these tips and avoiding common mistakes, students can make their academic writing more effective and persuasive.
Having all the necessary information is important before choosing any course of action. AdmissionSight is always here to assist you with any questions or concerns. We have more than ten years of expertise assisting students in successfully navigating the challenging admissions process.
Consult with AdmissionSight and find out what we can do to help you get into the school of your choice by ensuring that you are sufficiently aware and well-prepared for the application process.
Want to assess your chances of admission? Take our FREE chances calculator today!

Why College Admissions Isn’t Perfect

US News Rankings

The Personal Statement: The Holy Grail of College Admissions

The Modern Day 4.0 and 1600 SAT Score Student Is No Longer Impressive

The Competitive Nature of College Admissions for Asian Americans

The College Application

Our Comprehensive Approach

Ivy League Schools

How Early Should You Prepare for College?

Featured in US News & World Report Best Colleges Publication
Congratulations to AdmissionSight Students and their Acceptances!

College Rejection

College Rankings

College Consultants Could Make A Difference

College Admissions Scandal and Higher Education

Here Are the 7 Best Colleges for Sports

What is the Princeton Early Action Acceptance Rate for 2024?

Graduating with Honors in High School: A Complete Guide

Does Harvard Have Sororities? All You Need to Know

Discover the High School Classes That Ivies Require

What Exactly Is Dartmouth’s Mascot?

What Is the Columbia ED Acceptance Rate for 2024?

Everything You Need to Know About UCLA’s Campus Tour

Discover the Best Calculators for Calculus

Everything You Need to Know About Interact Club

Fun Facts About UCLA: A Deep Dive into One of America’s Top Universities

20 Fun Debate Topics for High School Students

Discover the Best Film Schools in California this 2024

Everything You Need to Know About an AB Degree

Why Brown University? 6 Reasons to Consider

How to Get a 1500+ on the SAT: Insights and Tips

Best High School Clubs for Ivy League Admissions
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Articles

Here Are the 7 Best...

What is the Princeton Early...

Graduating with Honors in High...

Does Harvard Have Sororities? All...

Discover the High School Classes...

What Is the Columbia ED...

Everything You Need to Know...

Discover the Best Calculators for...

Fun Facts About UCLA: A...

20 Fun Debate Topics for...
Sign up now to receive insights on how to navigate the college admissions process..

Admissions Counseling
- Academic & Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
Copyright © AdmissionSight 2024
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
7 Essential Tips for Writing in the Third Person

Table of contents

Alana Chase
Whether you’re a student, business professional, or writer, knowing how to write well in the third person is an essential skill.
But you may not be sure of all the rules or how to make your third-person writing shine.
As an editor and writing coach of 11 years, I’ve taught students and writers at all levels how to master the third-person point of view (POV). All you need to get started is a good understanding of third-person pronouns and a bit of practice for consistency.
By the end of this article, you’ll know when and how to use third-person perspective. You'll also find helpful tips for taking your third-person writing to the next level.
Key takeaways
- In the third-person perspective, the narrator is separate from the story.
- Third-person perspective uses he/him/his, she/her/hers, and they/them/their pronouns.
- Consistency is key: Don’t switch between perspectives in a single document.
- Practicing third-person writing and editing your work is vital to improving your skills.
What is third-person point of view (POV)?
In writing, there are three ways to tell a story: first-person, second-person, or third-person POV.
First-person POV is from the narrator’s perspective:
“ I saw the bird steal my sandwich, and I ran after it.”
Second-person POV is from the reader’s perspective:
“ You saw the bird steal your sandwich, and you ran after it.”
Third-person POV, however, separates the narrator from the story and uses third-person pronouns (like he/him, she/her, and they/them) to describe events, actions, thoughts, and emotions. Characters are referred to by name or one of these pronouns:
“ Alex saw the bird steal his/her/their sandwich, and he/she/they ran after it.”
Third-person POV is used in all kinds of writing — from novels to research papers, journalistic articles, copywriting materials, and more. Check out some examples below.
Examples of third-person perspective
- In a novel: “Robb and Jon sat tall and still on their horses, with Bran between them on his pony, trying to seem older than seven, trying to pretend that he’d seen all this before.” (From A Game of Thrones by George R. R. Martin)
- In a news article : “This weekend, Iceland experienced nearly 2,000 earthquakes within 48 hours. And they’ve kept coming since then – in swarms.” (From “Thousands of earthquakes have scientists watching for a volcanic eruption in Iceland” on NPR’s website )
- In copywriting : “Balm Dotcom’s formula has antioxidants and natural emollients to nourish dry lips.” (Website copy describing Glossier’s Balm Dotcom lip product )
7 tips for writing in the third person
Just like the first and second person, you’ve probably already written in the third person before. But to do it well , you’ll need some key tips and tricks in your writing toolkit.
Let’s dive into the seven essentials for third-person writing.
Tip 1: Use third-person determiners and pronouns
In grammar, determiners introduce and modify nouns. They’re used to specify what a noun refers to (like “ my laptop”) or the quantity of it (like “ many sandwiches”).
Meanwhile, pronouns are substitutes for nouns, referring to people, places, or things. For example, “Caroline [noun] is a skilled musician, and she [pronoun] especially loves playing the piano.”
When you write in the third person, use only third-person determiners and pronouns. Let’s take a look at the different types of pronouns.

Tip 2: Use names for clarity
In third-person writing, using names is crucial for clarity, especially when multiple people/characters share similar pronouns. Strategically incorporate names into your writing to help readers keep track of who’s who.
For example:
“She submitted the script draft to her, and she made suggestions for changes.”
“Mira submitted the script draft to Lynn, and Lynn made suggestions for changes.”
Tip: Use a character or person’s name when introducing them in your writing. Then, alternate between using pronouns and their name to prevent confusion.
Tip 3: Keep the narration neutral
When you write in the third person, your narrator is an uninvolved observer. They have no opinions on the people, places, things, or events they describe. Their words and tone should be neutral (but not boring).
To achieve this in your writing:
- Think of your narrator as a reporter. Their job is to detail what’s happening, when and why it’s occurring, who’s involved, and any background information that can give context. They don’t offer a personal interpretation of events. Instead, they provide facts and supporting details.
- Save the judgment for characters. Rather than having your narrator share their critique of events or individuals, have a character offer their opinion — either through dialogue, actions, or reactions. For instance, instead of writing, “Dr. Shaw was a courageous woman,” let a character convey admiration by telling Dr. Shaw, “I’ve always admired your fearlessness.”
- Be objective with your descriptions. Avoid subjective adjectives and focus on observable features. For example, instead of describing a landscape as “breathtaking,” write that it’s “marked with snow-capped mountains and patches of tall pine trees.”
Tip 4: Use descriptive language
Showing — and not just telling — is essential when writing in the third person. Instead of stating emotions and experiences outright, immerse your reader in your character’s reality. Create vivid descriptions of their thoughts, feelings, and surroundings. Use language that engages the senses: sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste.
For example:
“Aisha was nervous.”
“Aisha’s hands trembled, and her tongue felt dry against the roof of her mouth. The spotlight above the stage shone white-hot, causing beads of sweat to form along Aisha’s hairline.”
Tip 5: Be consistent
Once you establish a third-person POV, stick to it . Avoid switching from the third person to the first or second person. Otherwise, you’ll confuse the reader and disrupt the flow of your writing.
“Hannah felt a surge of excitement when her telephone rang, anticipating good news about her mortgage application. I felt my heart rate quicken as I answered.” (Switches from the third person to the first person)
“Hannah felt a surge of excitement when her telephone rang, anticipating good news about her mortgage application. She felt her heart rate quicken as she answered.” (Remains in the third person)
Tip 6: Practice
Writing in the third person might feel strange at first, especially if you’re used to using the first or second person. However, it’ll come more naturally to you with practice.
Here are two writing exercises you can try right now:
Writing Exercise #1
Take an excerpt from an article or book written in the first or second person and rewrite it in the third person. Below is an example using The Catcher in the Rye , whose main character is named Holden.
Before: “The other reason I wasn’t down at the game was because I was on my way to say good-by to old Spencer, my history teacher.”
After: “The other reason Holden wasn’t down at the game was because he was on his way to say good-by to old Spencer, his history teacher.”
Writing Exercise #2
Turn on a movie or television show, mute the sound, and closely observe two characters. Give them each a name. Using third-person pronouns and their names, describe the characters’ actions and what you believe they’re thinking and feeling.
Above all, write in the third person as often as possible , following the tips in this guide. Remember, your writing skills are like muscles: The more you exercise them, the stronger they become.
Tip 7: Carefully revise
After you’ve written something in the third person, carefully review and revise your work.
Check that your writing :
- Uses third-person determiners and pronouns accurately and consistently
- Incorporates names where pronouns may cause confusion
- Maintains a neutral tone, where your narrator doesn’t offer personal opinions or interpretations
- Doesn’t shift to the first or second person
Make changes where necessary, then read through your work a final time.
AI tip: Wordtune can help you self-edit and help improve your writing overall.
Paste your work into Wordtune’s Editor, or write in it directly, and use the features to shorten or expand your sentences, make your tone more casual or formal, and more. Wordtune will also automatically flag spelling and grammar errors and suggest ways to improve concision, clarity, and flow.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Bonus tip (advanced): Learn the different types of third-person POV
Did you know there are three types of third-person POV? Getting familiar with them can help you make your writing even more impactful.
- Third-person objective , where the narrator is “a fly on the wall”: They provide an objective account of events without exploring people/characters’ emotions or thoughts.
- Third-person omniscient , where the narrator has unlimited knowledge of all events and characters’ thoughts and feelings.
- Third-person limited , also called “close third,” where the narrator has access to just one character’s emotions, thoughts, and experiences.
With this knowledge, you can choose the right perspective for your writing depending on its purpose, tone, and goals.
For instance, use third-person omniscient to show readers what’s happening with everyone in your novel. Or, you could go for third-person objective in an academic paper where you must present facts without sharing your interpretation of them.
Writing well in the third person takes thought and effort. You must use third-person determiners and pronouns, weave in descriptive language, and keep your narration neutral. You also need to be consistent with your POV, ensuring you don’t accidentally switch to the first or second person. Finally, review and revise your work to make sure it’s clear and error-free.
Using this guide — and Wordtune’s tools to polish your writing — you’ll get the hang of the third-person perspective in no time.
To continue sharpening your writing skills, read our articles on mastering tone of voice and writing concisely (with help from AI). Then, check out our proofreading guide to keep your work flawless .
What is a third-person word example?
Third-person words are pronouns like “he,” “her,” “they,” “it,” “hers,” and “theirs.”
Should I write in the first or third person?
It depends on the closeness you want to create with your audience. The first person allows for a personal connection between the narrator and the reader, while the third person creates distance between the narrator and the audience.
What are the disadvantages of writing in the third person?
Third-person writing can lead to a lack of intimacy with the reader. This can be a disadvantage for some writers but an advantage for others, like those in academic and professional settings.
Share This Article:
%20(1).webp)
8 Tips for E-commerce Copywriting Success (with Examples!)
.webp)
The Brand Strategy Deck You Need to Drive Social Media Results + 5 Examples

Grammarly Alternatives: Which Writing Assistant is the Best Choice for You?
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
Examples of Writing in Third Person
Writing in third person is writing from the third-person point of view, or outsider looking in, and uses pronouns like he, she, it, or they. It differs from the first person , which uses pronouns such as I and me, and from the second person , which uses pronouns such as you and yours.
Writing in the third-person provides flexibility and objectivity. In fiction writing , it enables the narrator to be all-knowing. The personal pronouns used in third-person writing are he, she, it, they, him, her, them, his, her, hers, its, their, and theirs.
Third Person Writing in Literature
- "He is just what a young man ought to be," said she, "sensible, good humoured, lively; and I never saw such happy manners!-so much ease, with such perfect good breeding!" - Jane Austen, Pride and Prejudice
- "It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen." - George Orwell, 1984
- "Their commander was a middle-aged corporal-red-eyed, scrawny, tough as dried beef, sick of war. He had been wounded four times-and patched up, and sent back to war." - Kurt Vonnegut, Slaughterhouse-Five
- "It was a dark and stormy night; the rain fell in torrents, except at occasional intervals, when it was checked by a violent gust of wind which swept up the streets." - Edward George Bulwer-Lytton, Paul Clifford
- "He drank an Anis at the bar and looked at the people. They were all waiting reasonably for the train. He went out through the bead curtain. She was sitting at the table and smiled at him." - Ernest Hemingway, "Hills Like White Elephants"
- "She walks in beauty, like the night Of cloudless climes and starry skies; And all that's best of dark and bright Meet in her aspect and her eyes" - Lord Byron, "She Walks in Beauty"
Third Person Writing in Advertising
- Plop Plop Fizz Fizz. Oh, what a relief it is - Alka-Seltzer
- The King of Beers - Budweiser
- It's the real thing - Coca-Cola
- A diamond is forever - De Beers
- The happiest place on earth - Disneyland
- It keeps going and going and going - Energizer
- When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight - FedEx
- The Possibilities are Infinite - Fujitsu
- The best a man can get - Gillette
- It wouldn't be home without Hellmann's - Hellman's
- It's finger lickin' good - KFC
- Nobody can do it like McDonald's can - McDonald's
- Good to the last drop - Maxwell House
- Maybe she's born with it. Maybe it's Maybelline - Maybelline
- The greatest tragedy is indifference - Red Cross
- Takes a licking and keeps on ticking - Timex
Third Person Writing in Famous Quotes
- "A dreamer is one who can only find his way by moonlight, and his punishment is that he sees the dawn before the rest of the world." - Oscar Wilde
- "A pessimist sees the difficulty in every opportunity; an optimist sees the opportunity in every difficulty." - Winston Churchill
- "A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new." - Albert Einstein
- "Life is a succession of lessons which must be lived to be understood." - Helen Keller
- "Music expresses that which cannot be said and on which it is impossible to be silent." - Victor Hugo
- "Failure is simply the opportunity to begin again, this time more intelligently." - Henry Ford
- "Family is not an important thing. It's everything." - Michael J. Fox
- "It is not a lack of love, but a lack of friendship that makes unhappy marriages." - Friedrich Nietzsche
- "A bird doesn't sing because it has an answer, it sings because it has a song." - Lou Holtz
An Objective Point of View
These examples illustrate the different ways to write in the third person and which pronouns to use. The first person point of view might read "I never make mistakes so I never learn." The second person would read "You never make mistakes so you never learn." See how this differs from the third person, which would read "He never makes mistakes so he never learns" and is much more objective.
How to Write in Third Person Point of View: 12 Tips for Writing in Third-Person Point of View
- August 21, 2024
- Freelancing Tips
Table of Contents Hide
First-person, second-person, third-person, when to write in third-person point of view, third-person omniscient point of view:, third-person limited point of view:, third-person objective point of view:, how to use the third-person point of view, strong character development., narrative flexibility, an authoritative, trustworthy narrator, 1.choose the best type of third-person pov for your story, 2.use third-person pronouns, 3.understand your voice won’t always shine in your essays, 4.don’t focus on yourself or the reader — focus on the text, 5.coach yourself out of using first-person pronouns, 6.be as specific as possible, 7.write in the present tense when using third-person, 8.avoid adding your own thoughts, 9.in third-person objective, stay out of everyone’s heads., frequently asked questions about writing in third-person, we also recommend.
If your writing is for academic purposes, use third person point of view. Third person is pretty easy to master with a little practice.
If you’re new to it, we have a guide that will guide you in every step of the way
What does writing in the third person mean?
The third person point of view is one of three writing styles that can be used to explain a point of view. Even if you don’t realize it, you’ve most certainly used first, second, and third person in writing projects throughout your education.
It is a narrative in which you compose and examine the subject matter entirely on your initiative. You remain impartial. You do not attempt to change readers’ opinions. It’s a completely impartial, objective writing style that gets right to the heart of a subject or tells a story.
If you need to know how to differentiate between them three. Here’s a quick breakdown to understand the differences when you write your next paper:
See also: 10 Types of Creative Nonfiction Books and Genres and How to Write It
This is from the I/we perspective. This is where we talk about our beliefs, ourselves, and ourselves. When writing in the first person, you will use pronouns like I, me, myself, and mine.
This point of view belongs to the person you’re addressing; therefore, it is a ‘you’ perspective. You would use second-person pronouns in your work, such as you, your, and yourself.
The writing style used in stories is known as the third person point of view, and it is aimed at the person or people under discussion. In this perspective, the pronouns he, she, him, her, his, hers, himself, herself, it, them, their, and themselves are used. You may also use a name. But that tends to happen more in stories than research papers.
Can you now differentiate them?
The third-person point of view is quite common in academic writing since it tells the reader a story and is frequently used when taking an authoritative attitude in your work.
As a result, while writing academic materials such as essays and research papers, always use the third person.
The reason for this is that it will make your work less biased and more objective, thereby increasing your reputation. The third-person perspective allows you to focus on the facts and data rather than your personal opinion, which will eventually boost your grades.
You can break third-person perspectives into three other types, including omniscient, limited, and objective. Although they’re more associated with creative writing than academic work and essays, your writing is likely to fall under the third-person objective point of view.
See also: How to Write and Publish Your Poetry Book
The 3 Types of Third-Person Point of View
The omniscient narrator understands the plot and the characters. This narrator can travel freely across time, enter the minds of any character, and share with the reader both their own and the character’s thoughts and observations.
For example, Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice uses a third-person omniscient point of view, giving the reader complete access to the primary character, Elizabeth, and everyone around her.
Also known as a “close third,” this limited point of view happens when an author writes in the third person while focusing on a single character. The narrator can switch between characters in each chapter or portion of the book, or they can do so throughout.
With this point of view, the author can limit the reader’s perspective and control the information they are aware of. It is used to heighten tension and arouse curiosity.
In this type of narration, the narrator is objective and oblivious to any character’s emotions or ideas. The narrator tells the story with an observant approach.
Ernest Hemingway uses this third-person narrative voice in his short story “Hills Like White Elephants.” An unidentified narrator tells the story of a couple in Spain talking while waiting for a train. With this point of view, the reader becomes a voyeur, listening in on a scene or story.
See also: Do You Italicize Book Titles? Essay Secrets Revealed
Rule number one: never refer to yourself in the third person in an article. That’s not acceptable.
For example, if your essay is about virtual learning, here’s what not to include in the sentence.
“I feel like students perform better at home because they have more freedom and are more comfortable.”
It’s a simple sentence, but when addressing research papers and using a third-person narrative, there are various concerns. Why? You are making comments that sound like opinions because you are using first-person pronouns, and you are unable to back them up with facts or credible research.
Also, it isn’t very assertive. “I feel like” will not impress the person evaluating your work because it lacks authority and underlines that it originated just in your mind and is insignificant in any way.
However, if you alter the example to the third-person perspective, you can reference your sources, which is exactly what you should do to improve your essay and research paper marks.
Let’s rewrite the line in a more expansive third person point of view:
“A psychological study from Karrie Goodwin shows that students thrive in virtual classrooms as they offer flexibility. They can make their hours and take regular breaks. Another study from high school teacher, Ashlee Trip, highlighted that children enjoy freedom, the ability to work at their own pace and decide what their day will look like.”
With a third-person narrative, you can present evidence to the reader and back up the claims you make. As a result, it not only shows your knowledge but also your diligence in researching and backing up your work with credible sources and facts rather than simply your opinions.
Advantages and Reasons to Write in Third Person Point of View
When compared to the first and second person, the third person can highlight more characters and cover a longer narrative arc.
A reader can see the story from every perspective, and each one contributes elements that a character lacks in the other, resulting in a rich, complex narrative.
The third person allows for greater adaptability; you can help your reader see everything, be everywhere, and switch between different characters’ stories. You can go from complete omniscience to a limited or close third point of view.
This latter strategy allows readers to have a greater understanding of a character and scenario by entering the characters’ thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
See also: How to Write a Book With No Experience for Beginners in 12 Steps
Writing from the third person point of view places the narrator above the action, creating a bird’s-eye-view of the story.
Because the narrator has nothing at stake, this perspective, combined with knowledge of at least one character’s thoughts in both omniscient and limited third person, lends the story a more authoritative, trustworthy tone.
Tips for Writing in Third 3 rd person
Before you begin writing your story, think about whether a third person perspective—limited, omniscient, or objective—will work best for it. Each has an advantage when it comes to narrative. Do you want the reader to remain in suspense and only learn what the main character discovers?
Next, write your story in a limited third person. Consider writing an epic narrative in the third person omniscient viewpoint, allowing your narrator to be all-knowing and featuring a big cast of people.
When using third-person pronouns such as “he,” “she,” “it,” or “they” instead of referring to specific characters by name, make sure to be consistent.
Every written work has a voice or point of view that appears to be directed specifically at the reader. This is not always possible, however, because academic writing is more objective than, example, a book.
Your academic work does not require you to “fluff” up your writing to inject your personality into it.
The purpose of academic writing is to consistently maintain a formal tone. Your next paper should be written to write in mind, rather than the writer or reader.
If you’ve only ever written in the first or second person, this is easier said than done. If you find yourself writing in the first person when writing your next paper, go back and alter it to a third-person perspective.
This is the point at which things become a little unclear. The key to writing in the third person is to use pronouns like they, it, he, or she. However, using them at the beginning of sentences can appear confusing and potentially mislead the reader, which is the last thing you want in your paper or essay.
Instead, consider using nouns at the beginning of sentences as an alternative. For example, when beginning a statement, use the actual subject—the writer or the interviewer—rather than he, she, or they.
See also: 15 Best Personal Finance Books for Freelance Writers
All academic writing, including reports, essays, and research papers, must be written in the present tense, especially when introducing new themes or discoveries.
As a result, you should write “This report analyzes” as if you are analyzing right now, rather than “This paper analyzed,” which appears to be correct because it occurred in the past and the writing is in the present.
The difference is that you should use the past tense when describing your research approach. This implies, for example, that you would use the third person to refer to “the equipment that was used” or “the results were analyzed by.”
If the topic of your report is something you are deeply interested in, it can be very tempting to include some of your own thoughts. Although you must coach yourself out of it.
In academic writing, you aren’t a commentator. You’re a reporter. It is important to let readers draw their conclusions without over-analyzing them or making the reader lean one way or another.
If you want to write from an objective point of view, see your characters as complete outsiders, keep in mind that your narrator is blind to their thoughts. As an outside observer, you can only tell the reader what you observe.
Write in a detailed style to convey emotions. Describing a character’s eyes and facial emotions can help to emphasize character growth, conflict, and plot development.
The third person uses pronouns such he, she, him, her, his, hers, himself, herself, it, them, their, and themselves. You may also use a name.
You is used in second person and is therefore not used in third person. The second person is used for the person that is being addressed.
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you’d find in stories. When writing in third-person view, make sure to write in the present tense and avoid adding your own thoughts.
Writing in the third person in academic papers is easy to learn if you practice regularly and consistently. Examine and critique your work until it is regarded as the norm. Sure, it may be confusing at first, but you’ll rapidly learn the technique and be able to improve your papers and reports.
Keep in mind that the third-person narrator only knows what the character knows. Be aware of your characters’ limitations. Review your writing frequently to ensure that you haven’t given your characters information they shouldn’t have.
- Bibguru – how to write in 3rd person
- Masterclass – how to write in third 3rd person
- How To Write an Application Letter to Chicken Republic for a Job in Nigeria
- How To Write an Application Letter to Join a Church Choir in Nigeria
- How To Write an Application Letter For Daycare Teacher With No Experience in Nigeria
- How To Write an Application Letter for Public Relations Officer with no Experience in Nigeria
Related Posts
How to write a children’s picture book in 12 simple steps.
- August 29, 2024
How To Write A Montage In A Script In 5 Easy Steps
How to write a killer best man speech: free template, examples, & tips.
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write in third-person

Although there are three narratives you can use in any form of writing when it comes to your papers and anything academic you produce, it’s best to choose the third-person. It’s pretty simple with a bit of practice, but if you’re completely new to this writing style, here’s what you need to know about how to write in third-person.
What does writing in third-person mean?
Writing in third-person is one of the three styles you can use when describing a point of view. Even though you might not know it, chances are you’ve used first, second and third person in writing projects throughout your education.
It’s a narrative where you’re totally independent of the subject you’re analyzing and writing about. You don’t take sides. You don’t try to influence what readers feel. It’s a completely unbiased, objective way of writing that tells a story or dissects a topic right down the middle.
There’s a lot of information out there about how you can differentiate between the three in roundabout ways, making it unnecessarily complicated. Here’s a quick breakdown to understand the differences for when you write your following paper:
First-person
This is from the I/we perspective. It’s where we talk about us , ourselves, and our opinions. If we go down the first-person route, writing will include pronouns like I , me , myself, and mine .
Second-person
This point of view belongs to the person you’re addressing — so its a you perspective. In your writing, you’d use second-person pronouns such as you , your, and yourselves .
Third-person
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you’d find in stories. In this perspective, you’d use pronouns like he , she , him , her , his , hers , himself , herself , it , them , their, and themselves . Or, you’d use a name. But that tends to happen more in stories than research papers.
Notice the difference between the three?
When to write in third-person
The third-person point of view tells the reader a story and it’s often the go-to when you’re taking an authoritative stance in your papers, which is why it’s so common in academic writing.
So, always choose the third-person stance when writing academic copy, such as essays and research papers.
The reason for this is it’ll make your papers less personal and more objective, meaning the objectivity will make you come across as more credible and less biased. Ultimately, this will help your grades as the third-person view keeps you focused on evidence and facts instead of your opinion.
You can break third-person perspectives into three other types, including omniscient, limited, and objective. Although they’re more associated with creative writing than academic work and essays, your writing is likely to fall under the third-person objective point of view.
A third-person objective point of view is about being neutral and presenting your findings and research in an observational way, rather than influencing the reader with your opinions.
How to use the third-person point of view
Rule number one: Never refer to yourself in your essay in the third-person. That’s a no-no.
For instance, here’s how you shouldn’t write a sentence in your essay if you’re writing about virtual learning as an example.
“I feel like students perform better at home because they have more freedom and are more comfortable.”
It’s a simple sentence, but there’s a lot wrong with it when you’re talking about research papers and adopting a third-person narrative. Why? Because you’re using first-person pronouns and, as it sounds like an opinion, you can’t back up your claims with a stat or any credible research. There’s no substance to it whatsoever.
Also, it isn’t very assertive. The person marking your work won’t be impressed by “I feel like,” because it shows no authority and highlights that it came from your brain and not anywhere of note.
By including terms like “I think” or “I feel” like in the example above, you’re already off to a bad start.
But when you switch that example to the third-person point of view, you can cite your sources , which is precisely what you need to do in your essays and research papers to achieve higher grades.
Let’s switch that sentence up and expand it using the third-person point of view:
“A psychological study from Karrie Goodwin shows that students thrive in virtual classrooms as it offers flexibility. They can make their own hours and take regular breaks. Another study from high school teacher, Ashlee Trip, highlighted that children enjoy freedom, the ability to work at their own pace and decide what their day will look like.”
With a third-person narrative, you can present evidence to the reader and back up the claims you make. So, it not only shows what you know, but it also shows you took the time to research and strengthen your paper with credible resources and facts — not just opinions.
6 tips for writing in third-person
1. understand your voice won’t always shine in your essays.
Every single piece of writing tends to have a voice or point of view as if you’re speaking to the reader directly. However, that can’t always happen in academic writing as it’s objective compared to a novel, for example. Don’t try to ‘fluff’ up your piece to try and cram your personality in, as your academic work doesn’t need it.
2. Don’t focus on yourself or the reader — focus on the text
An academic piece of work always has a formal tone as it’s objective. When you write your next paper, focus on the writing itself rather than the writer or the reader.
3. Coach yourself out of using first-person pronouns
This is easier said than done if all you’ve ever done is first- or second-person writing. When you write your next paper, scan through it to see if you’ve written anything in first-person and replace it with the third-person narrative.
Here are a few regular offenders that pop up in academic papers — along with how you can switch the statements to third-person:
- I argue should be this essay argues
- I found that should be it was found that
- We researched should be the group researched
- I will also analyze should be topic X will also be analyzed
The same applies to second-person, as there are plenty of cases where it tends to slip through in academic writing. Again, it’s pretty straightforward to switch the more you practice. For instance:
- Your paper will be marked higher if you use a citation tool should be the use of a citation tool will improve one’s grades
4. Be as specific as possible
This is where things can get a little bit confusing. Writing in third-person is all about including pronouns like he, she, it, and they. However, using them towards the beginning of sentences can be pretty vague and might even confuse the reader — this is the last thing you want from your essay or paper.
Instead, try using nouns towards the beginning of sentences. For example, use the actual subject, such as the interviewer or the writer, rather than he, she, or they when you begin the sentence.
The same applies to terms like it. Start the sentence with the ‘it’ is that you’re describing. If it’s a citation tool, begin the sentence by referencing what you’re discussing, so you aren’t vague. Clarity is key.
5. Write in the present tense when using third-person
In any form of academic writing, you need to write your reports, essays, and research papers in the present tense, especially when introducing different subjects or findings.
So, rather than saying “This paper analyzed” (which does seem correct as technically that part was in the past and the writing is in the present), you should write “This report analyzes” — as if you’re analyzing right here and now.
However, the difference is when you highlight how you did the research, that should be in the past tense. This means you’d use third-person phrases like “The equipment that was used” or “The results were analyzed by”, for instance.
6. Avoid adding your own thoughts
If your report is on a subject that’s close to your heart, it can be super tempting to sprinkle in your own thoughts. It’s a challenge, but you need to coach yourself out of it.
In academic writing, you aren’t a commentator. You’re a reporter. You need to let readers draw their conclusions without over-analyzing them or making the reader lean one way or another.
The easiest way to get to grips with writing your academic papers in the third-person is to be consistent and practice often. Criticize your work and analyze it until it becomes the norm. Yes, it can be a little complex in the early days, but before you know it, you’d have mastered the technique, helping you take your papers and reports up a level.
Frequently Asked Questions about writing in third-person
In third-person, you’d use pronouns like he , she , him , her , his , hers , himself , herself , it , them , their, and themselves . Or, you’d use a name.
You is used in second person and is therefore not used in third person. The second person is used for the person that is being addressed.
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you’d find in stories. When writing in third-person view, make sure to write in the present tense and avoid adding your own thoughts.
When writing in third person, you should actually always write in the present tense since you are mostly presenting results in this view.
The second person point of view belongs to the person you’re addressing — so its a you perspective. In your writing, you’d use second-person pronouns such as you , your, and yourselves .

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
How to Write in the Third Person
You may have heard someone talking about third person POV in an English class or on a writers’ panel. What does it mean? POV stands for point of view, and any piece of prose writing has one. The point of view helps anchor the reader, and it makes the text easier to understand. Even in a story that doesn’t appear to come from a particular character’s voice, we can still assign the narration a point of view. When the point of view isn’t yours (second person) or mine (first person), then we call it third person narration. In this article, we’ll give you some tips to help you learn to write this way.
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Avoid First Person
First person emphasizes the subjective point of view, and you can easily identify this writing style through the use of the pronouns “I” and “me”. Imagine an autobiography. The narrator explains his or her life by using phrases like this one: “I was born in a small town.” In a biography, written by another person, the text might read: “She was born in a small town.” That’s the difference between first person and third person. In first person, the narrator is the main character or, if not the main character, a character in the action. On the other hand, when a book is written in the third person, the story does not come from the point of view of a character. Instead, the writing describes things that happen to other people, characters besides the writer or the reader.
First person writing can be identified by the use of the following pronouns:

Avoid Second Person
Second person narration comes from the point of view of the reader. A second person point of view can often be found in the self-help or how-to genres, as well as in choice-based adventure books. “Choose Your Own Adventure® gamebooks began life in 1979 as the first publishing effort of a new division at Bantam Books focused on younger readers,” according to Chooseco LLC . Today, 265 million books have been published in this style. Let’s look at the summary of one of these books for a memorable example of second person narration:
“ You are a mountain climber, headed to the Himalayas to find proof that the mysterious yeti really exists. When your best friend Carlos goes missing from base camp, the fate of the expedition is in your hands.” — The Abominable Snowman
We added the bold font above to draw attention to some important pronouns. It’s easy to identify second person narration because it features second person pronouns:
What Is Third Person?
When a piece of writing does not assume the perspective of either the reader or the writer, it’s written in the third person point of view. Third person narratives have three distinct styles, known as third person objective, third person omniscient, and third person limited omniscient. You can recognize all three of these points of view through the use of third person pronouns, which include:
Third Person Objective
Imagine a history essay or a science article, written by a distant and neutral third party. The writer does not attempt to explain the perspective of any character; instead, he or she reports on the events with dispassion. If any opinions made their way into the text, they are properly attributed to the source.
Congressman Smith said, “X, Y, Z.” His constituent disagreed, arguing A.
The author of a third person objective article would never presume to speak for another person’s inner thoughts. Instead, the writer aims to present the facts and events in an orderly way, attributing the actions and dialogue to the proper characters.
This writing style is frequently used in academic writing and professional writing, but it can be used by fiction writers as well. As long as the author does not place thoughts inside the heads of characters, third person objective can work for any style of prose writing. If a writer wanted the reader to understand a character’s emotional state, he or she would have to make reference to body language, facial expression, and dialogue; otherwise, the character’s thoughts would remain opaque. The internal monologue of any character remains off limits from the objective point of view.
Third Person Omniscient
The third person omniscient point of view frequently appears in fiction writing. With this style, an all-knowing narrator has the ability to get inside any character’s head. That’s why an omniscient point of view can be thought of as “head-hopping.” The narrator has knowledge of everything. The characters have nowhere to hide—even their most intimate thoughts may be plumbed. Personal opinions and internal dialogue are all fair game, for any of the characters. In this style of writing, you can expect to see different points of view. As a reader, you can expect to know more about the different characters than the characters know about each other.
Third Person Limited Omniscient
Sometimes a writer engages a third person perspective, but they elevate one character above the rest. The writer may expound on that character’s thoughts, inner dialogue, and perspective. The focal character for the third person limited point of view is often called the viewpoint character. Typically, the viewpoint character is a main character in the story. The writer provides the reader with comprehensive access to this character’s thoughts, but all the other characters must be understood through actions, gestures, and dialogue. The reader must get by with limited information, since they rely on what the viewpoint character knows.
Still, the reader does not go “inside the head” of the viewpoint character completely. Rather than writing from the main character’s perspective in the first person point of view, the writer maintains a third person writing style. Without using first person pronouns, the author explores the thoughts of a single character. The narrator describes she and her, not I and me.
She worried that she would be late, but didn’t bother to tell her sister.
In the example above, the reader understands what the viewpoint character is thinking. On the other hand, the sister cannot read the viewpoint character’s thoughts. Likewise, the reader is not privy to the sister’s thoughts.
The omniscient limited and omniscient POV appear most commonly in creative writing. In general terms, third person objective or first person would be a more common choice for essays, articles, and nonfiction books.
Blending Perspectives
Now that you know the conventions for writing in first person, second person, third person objective, third person limited, and third person limited omniscient, you may want to revisit some of your favorite works of literature. Try to figure out their points of view, and think about why the author picked that perspective.
In your research, you may come across some books that defy categorization. Moby Dick by Herman Melville and Ulysses by James Joyce come to mind. Both books shift between third person and first person narration. Many fiction writers, especially modernist writers, flout convention by using a number of different narrative styles within the same work.
In creative writing, you should feel free to break the rules. Just be sure to understand the rules as you break them!
- https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-point-of-view.html
- https://www.britannica.com/art/novel/Narrative-method-and-point-of-view
- https://www.dictionary.com/e/1st-person-vs-2nd-person-vs-3rd-person-pov/
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/point-of-view-first-second-third-person-difference
- https://www.cyoa.com/

Kari Lisa Johnson
I’m an award-winning playwright with a penchant for wordplay. After earning a perfect score on the Writing SAT, I worked my way through Brown University by moonlighting as a Kaplan Test Prep tutor. I received a BA with honors in Literary Arts (Playwriting)—which gave me the opportunity to study under Pulitzer Prize-winner Paula Vogel. In my previous roles as new media producer with Rosetta Stone, director of marketing for global ventures with The Juilliard School, and vice president of digital strategy with Up & Coming Media, I helped develop the voice for international brands. From my home office in Maui, Hawaii, I currently work on freelance and ghostwriting projects.
Recent Posts

Dreams Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Chutzpah Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

White Roses Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It


7777 Angel Number Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How to Use It?
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Storyteller's Sale
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write in Third Person Point of View

By Sarah Oakley

Whether you’re going to write a short story, a novella, or a novel, one of the most important decisions you’ll need to make is which point of view (POV) to use.
Third person is the most popular POV for fiction writers to use. It gives the reader a chance to experience the narrative from a perspective above, or on the shoulder of, the characters.
In this article, we’ll learn what the third person POV is, how it compares to other points of view, and how to write in third person point of view.
What Is Third Person Point of View?
Third person pov meaning, how to write in third person, third person pov examples, conclusion on how to write in third person pov.
Third person POV is when the narrator exists outside of the story. This narrator relates the actions of the characters by using their name or third person pronouns such as “she,” “he,” and “they.”
There are three types of third person POV that you can choose from. Each POV provides a different reader experience as they reveal different amounts of information about the narrative, characters, and setting.
To decide on a POV, think about the type of story you are telling and whether your readers need to be aware of certain details at each point in the plot.

1. Third Person Objective Point of View
The third person objective POV is a way to tell your story by giving the reader all the details within the scenes without including what is going on in the characters’ minds.
To write in the third person objective POV, you will need to create an unbiased narrator who doesn’t tell the reader the thoughts and feelings of the characters. Instead, your narrator will simply relay the actions and dialogue of the story in an objective, impartial telling of the events.
This is great for keeping distance between the reader and the characters. It’s like looking through the window of a stranger’s house and trying to figure out why everything is happening.
2. Third Person Omniscient Point of View
When writing in the third person omniscient POV, you give your reader an all-access pass to the thoughts and feelings of any character in each scene of your story. You can give as much detail about the scene as you can in the third person objective POV, but this time you can also include information from the characters’ perspectives.
The narrator you create to speak in the third person omniscient POV will need to relay the thoughts and feelings of all the relevant characters in the scene. You can do this by switching perspectives. This is sometimes called “head hopping.”
You can use head hopping to show conflict in the story. For example, one paragraph is from the main character’s perspective, as they give some important information to another character. Then, the next paragraph is from the perspective of the person who received the information, which shows their reaction to what the main character just said.
Third person omniscient is perfect for sharing all the little details about the world you have created and allows the reader to pick up clues that some characters might not have noticed. Some writers refer to the third person omniscient POV as an all-seeing being who likes to give their thoughts on the plot.
3. Third Person Limited Point of View
This narrator sits on the shoulder of your main character and tells the story from their perspective. It’s close to being first person, but the reader isn’t solely within the character’s mind and this narrator still uses third person pronouns and verbs.
Sometimes, the third person limited POV narrator sticks to a different character each chapter instead of one character throughout the entire story. We refer to this as a viewpoint character, as we are seeing the world from their perspective.
You are controlling the amount of information given to the reader by focusing on one character’s awareness, rather than all characters’.
First Person vs Third Person
First person POV gives readers full access to the thoughts and feelings of the main character, as they are the one telling the story. There isn’t a narrator getting between the reader and the character.
Another key part of writing in the first person POV is that the character uses first person pronouns to tell the story. They use “I,” “me,” “my,” and “myself” as they are talking about actions and experiences.
Remember : not all main characters notice everything going on around them. It can break the reader’s immersion if they are wondering how the main character knew they were about to die, but there were no clues it was about to happen. Not all characters are psychic!

If you’re aiming to stick to one character’s thoughts and feelings, but you also want to add in some extra details that are in the character’s peripheral vision, try the third person limited perspective.
This POV can be used to great effect in thrillers where you want to stay close to the main character, so the reader connects with them.
Meanwhile, you can also give clues about things that are about to happen that the character is unaware of. Let us watch in horror as the character falls down a hole we all saw coming, but could do nothing to stop them.
Second Person vs Third Person
Second person POV puts you, the reader, in the driving seat as the main character. The narrator breaks the fourth wall and speaks to you directly.
This perspective uses second person pronouns such as “you,” “your,” and “yourself” to bring the reader into the narrative. The narrator uses third person pronouns to refer to other characters.
Second person works well in stories where you want full immersion for the reader. Some people love the feeling of being dropped onto the rollercoaster of drama in a good story. This is why second person is used in video games and Choose Your Own Adventure stories.
However, it is one of the least used POV types by fiction writers. One reason for this is that it takes a lot of skill to write about the reader in a way that feels natural to them while also giving away the right amount of information for the story. You don’t want your reader to lose interest because they don’t agree with something the narrator has said.

Third person objective would be a better option if you don’t want to write as though your story is about the person reading it. The third person POV allows the reader to focus more on the narrative and everything else that’s going on around the characters.
So far, we’ve discussed what the third person POV is, but what does the “third person” part of that mean?
Third person is a grammatical style of writing that uses pronouns such as “she,” “he,” “they,” and “it.” It also uses proper nouns and names when referring to specific individuals and objects.
1. Decide If Third Person Provides the Right Reader Experience
Do you want to tell the story from within the mind of your main character? Do you want to make the reader the main character of the story? If the answer is no to both questions, it’s time to look at your options for writing in the third person.
2. Pick the Type of Third Person Narrator
Go over the details of your story and your characters. You will need to establish whether third person limited, third person objective, or third person omniscient is the best POV for your story.
3. Read Examples of Writing in Third Person
It’s important to take the time to analyze what works and what doesn’t work in third person narration. The best way to do this is by reading other works that use third person points of view.
Focus on the information they are sharing. Did it work? Would you have used a different type of narrator for that story?
4. Use a Consistent POV
Switching POVs is a habit that a lot of writers do if they’re writing in a POV they’re not used to. Don’t worry, it happens. However, being aware that this is something to avoid before you get 200 pages into your novel and realize you switched POVs back on page 90 can help you be more observant of your writing habits.
5. Use the Correct Pronouns—ProWritingAid Can Help!
The third person POV means using third person pronouns when your narrator is speaking. Remembering this is one of the best ways to catch yourself from slipping into different points of view.

You can stop yourself from using the wrong pronouns by using ProWritingAid’s pronoun report. It’ll highlight all the examples of pronouns in your text, so you can easily work through your story and change them back into the third person if you’ve made any mistakes.
6. Create a Trustworthy Third Person Narrator
Your third person narrator is the voice of your narrative. How do they tell the story? Do we believe them?
Readers need to feel like your narrator has the authority to tell these events in a way that satisfies them. If you want to share the thoughts and feelings of the characters, the narrator needs to sound like they are confident in the details they are sharing.
Third Person Objective Example
If you’re wondering how to show conflict when writing in the third person objective POV, we would recommend reading Hills Like White Elephants by Ernest Hemingway.
Let’s look at an excerpt from the story:
The woman brought two glasses of beer and two felt pads. She put the felt pads and the beer glasses on the table and looked at the man and the girl. The girl was looking off at the line of hills. They were white in the sun and the country was brown and dry. “They look like white elephants,” she said. “I’ve never seen one.” The man drank his beer. “No, you wouldn’t have.” “I might have,” the man said. “Just because you say I wouldn’t have doesn’t prove anything.” The girl looked at the bead curtain. “They’ve painted something on it,” she said. “What does it say?” “Anis del Toro. It’s a drink.”
As you can see from this extract, the third person objective narrator is relaying the information about the scene without being biased to either of the characters. They do not quote the characters’ thoughts or feelings; they simply give details about their actions and words.
As a reader, you can still imagine what the characters are thinking and feeling, as the conflict is laid out bare for you to witness.
Third Person Omniscient Example
Readers of the third person omniscient POV expect the narrator to be all-seeing and all-knowing, so it makes sense that the narrator in Good Omens by Neil Gaiman and Terry Pratchett is “God” or the “Almighty.”
Here’s an extract from the novel:
“Er. Okay,” he said. “I’ll, er, be off then. Shall I? Get it over with. Not that I want to get it over with,” he added hurriedly, aware of the things that could happen if Hastur turned in an unfavourable report. “But you know me. Keen. So I’ll be popping along,” Cowley babbled. “See you guys... see you. Er. Great. Fine. Ciao.” As the Bentley skipped off into the darkness Ligur said, “Wossat mean?” “It’s Italian,” said Hastur. “I think it means food .” “Funny thing to say, then.” Ligur stared at the retreating tail-lights. “You trust him?” he said. “No,” said Hastur. “Right,” said Ligur. It’d be a funny old world, he reflected, if demons went round trusting one another.
This example shows how the third person omniscient narrator pops into the heads of several characters in one passage. At the beginning, we’re in Cowley’s mind, which is shown by the phrase “aware of things that could happen if Hastur turned in an unfavourable report.” However, within a few lines, we pop into Ligur’s mind, which is apparent in the sentence, “It’d be a funny old world, he reflected, if demons went round trusting one another.”
Third Person Limited Example
If you’re looking for examples of third person limited narrators that tell the story from one character’s perspective, we would recommend reading Happily Ever After by Harriet Evans.
Let’s check out a section of the novel:
She knew his face so well, knew him so well, how he drummed his fingers on any spare surface, how he looked vague when trying to get out of things, how his mouth curled to the side when he was making a joke. But she’d never sat this close to him before, because he was her boss. It didn’t feel like that tonight. It was as if they were different people. It was nice. Rory was nice, but then, she’d always known that.
Romance writers like writing first person POV, but third person limited also works well in this genre, like in this extract. The narrator is giving us a direct connection to the mind of the main character (Elle). They do this by describing everything Elle’s noticed about the man she’s attracted to.
Elle realizes her boss has always been nice and we get the impression she’s always secretly wanted to date him. The narrator shows us this by giving us Elle’s perspective on what’s happening in the scene. It’s as close as the narrator can be without Elle telling the story herself.
As you can see, writing in the third person isn’t hard when you follow the step-by-step process. It’s a lot of fun to experiment with the different types of third person POV. Which one do you prefer?
Don’t forget, if you’re worried about slipping into different POVs within your writing, you can always use the ProWritingAid pronoun report to keep you in check!
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Sarah Oakley
##About Sarah is a romance writer with a passion for studying human connections and psychology. She lives with her fiancé and two cats in Gloucester, UK. When she’s not writing, Sarah enjoys visiting theme parks, singing along to rock songs, and planning her next vacation. ##Writing Experience Sarah is an aspiring screenwriter who hopes to see her name in the credits of a romance film one day. She has also written short stories and has had many ideas for novels in a variety of genres. ##Education Sarah has been studying the art of writing and film from the age of 16 and she holds a BA in Creative Writing.
Get started with ProWritingAid

It's A Steal
Bring your story to life for less. Get 25% off yearly plans in our Storyteller's Sale. Grab the discount while it lasts.
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Third Person
What is third person.
- I am speaking to you about her .
- The policeman is speaking to the teacher about Anne .
Table of Contents
"Third Person" Explained
Third person in grammar, examples of third person pronouns in different cases, first, second, and third person pronouns, why the third person is important, video lesson.

- Third Person Narrative . A third-person narrative is a story told using the pronouns "he," "she," "it," or "they" or using nouns. In other words, the story is not told from a personal perspective. A third-person narrative contrasts with a first-person narrative, which is a story told from a personal perspective using the pronoun "I" (and sometimes "we").
- To Write in the Third Person . "To write in the third person" means to use nouns or the pronouns "he," "she," "it," or "they." It is common in business writing.
- Third Party Insurance . Third-party insurance protects against the claims of others. Look at the following sentence: I (the first party) am ensured by you, the insurer (the second party), to protect me against them (the third party).
- First person : "I" and "we"
- Second person : "you"
- Third person: "He/She/It" and "They"

| Person | | Possessive Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third Person Singular | he / she / it Example: is not happy. | him / her / it Example: We saw . | his / her / its Example: We were support. | his / hers / its These were . |
| Third Person Plural | they Example: are leaving. | them Example: We like . | their Example: We were allies. | theirs These are . |
- Masculine gender : He, him, his
- Feminine gender : She, her, hers
- Neuter gender : It, its
| Person | | Possessive Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person Singular | I | me | my | mine |
| Second Person Singular | you | you | your | yours |
| Third Person Singular | he/she/it | him/her/it | his/her/its | his/hers/its |
| First Person Plural | we | us | our | ours |
| Second Person Plural | you | you | your | yours |
| Third Person Plural | they | them | their | theirs |
(Reason 1) Understanding the person categories is useful for learning a foreign language.
| Person | English | German | French | Spanish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person Singular | I play | ich spiele | je joue | yo juego |
| Second Person Singular | you play | du spielst | tu joues | tu juegas |
| Third Person Singular | he/she/it plays | er/sie/es spielt | il/elle joue | el/ella/usted juega |
| First Person Plural | we play | wir spielen | nous jouons | nosotros jugamos |
| Second Person Plural | you play | ihr spielt | vous jouez | vosotros jagais |
| Third Person Plural | they play | Sie spielen | ils/ells jouent | ellos/ellas/ustedes juegan |
(Reason 2) Using the third person presents a formal air.
- Avro Corps will handle your complaint within 48 hours.
- We will handle your complaint within 48 hours.
(Reason 3) Using the third person for storytelling can make you seem all-knowing.
- In business, write in the first person for a personal touch.
- When writing fiction, write in the first person to engage your audience quickly.
- Don't say or write "between you and I"...ever.
(Reason 4) The third-person possessive determiner "its" not "it's."
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code

First, Second, and Third Person: Definition and Examples
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » First, Second, and Third Person: Definition and Examples
Point of view definition: First, second, and third person are categories of grammar to classify pronouns and verb forms.
- First person definition: first person indicates the speaker.
- Second person definition: second person indicates the addressee .
- Third person definition: third person indicates a third party individual other than the speaker.
What is the difference Between First Person, Second Person, and Third Person?
First, second, and third person refer to pronouns and their verb forms.
What is First Person?

First Person Example:
- I prefer coffee to hot cocoa.
In this example, “I” am the speaker. This is first person.
What is Second Person?
Second person point of view: Second person refers to the addressee. It uses the subject pronoun “you.”
Second Person Example:
- You prefer coffee to hot cocoa.
In this example “you” is the addressee. The speaker is addressing “you.” This is second person.
What is Third Person?

Third Person Example:
- He prefers coffee to hot cocoa.
In this example “he” is the third party. The speaker is referring to him as the addressee. He prefers coffee to hot cocoa.
When using the different points of view, verbs need to be conjugated appropriately to fit the pronoun use.
Note: Pronouns are only used in English when an antecedent has been clearly identified.
What Are First Person Pronouns?
First person pronouns always refer to the speaker himself. These pronouns are only used when the speaker is making a statement about himself or herself.
First Person Pronoun List:
Here is a list with examples of the first person words we use in writing and speech.
- I prefer coffee to hot cocoa. (First person singular)
- We prefer burgers to pasta. (First person plural)
- Jacob embarrassed me.
- Jacob embarrassed us.
- The hat is mine.
- The hat is ours.
- That is my hat.
- That is our hat.
What Are Second Person Pronouns?

When you are writing, a good way to think about the second person’s point of view is that it addresses the reader (as I just did in that sentence).
Second person pronouns are only used when the speaker is making a statement to the addressee, i.e., to someone.
Second Person Pronoun List:
Here is a list with examples of the second person words we use in writing and speech.
- Jacob embarrassed you.
- The hat is yours.
- That is your hat.
Note: In each of these examples, “you” can be an individual (singular) or multiple people (plural).
What Are Third Person Pronouns?
Third person pronouns always refer to a third party. These pronouns are used when the speaker is making a statement about a third party.
Third Person Pronoun List:
Here is a list with examples of the third person words we use in writing and speech.
- He prefers coffee to hot cocoa. (Third person singular)
- They prefer tea to coffee. (Third person plural)
- Jacob embarrassed her.
- The hat is theirs.
- That is their hat.
First, Second, and Third Person in Writing

Writing in first person: Literature in the first person point of view is written from the speaker’s perspective. This point of view uses first person pronouns to identify the speaker/narrator. First person point of view is generally limited in that the audience only experiences what the speaker/narrator himself experiences.
Writing in third person: Literature in third person point of view is written from an “outside” perspective. This point of view uses third person pronouns to identify characters. In third person writing, the narrator is not a character in the text. Because of this, he can usually “see” what happens to all of the characters.
Writing in second person: In non-fiction writing, a speaker will often switch between pronouns. Writers do this only for effect. For example, if a speaker wants to be clear and “get through” to the audience, he might say “you” (second person) throughout the text even if the text is mostly in third person. Again, this is strictly for rhetorical effect. Experienced writers use this as a literary tool.
Common Questions and First, Second, and Third Person
Here, I want to go quickly through a few questions I get about first, second, and third person pronouns.
Questions About the First Person
Is our first person? Yes, our is one of the first person pronouns.
- Are you coming to our wedding?
Is you first person? No, you is a second person pronoun.
- You are a great friend.
Is we first person? Yes, we is a first person pronoun.
- We are great friends.
- We polled this group of political observers and activists each week prior to the Iowa caucuses to produce the USA TODAY GOP Power Rankings and went back to them this week to ask who is the best choice for Trump’s running mate. – USA Today
Is my first person? Yes, my is a first person pronoun.
- My glasses are broken.
Is they first person? No, they is a third person pronoun.
- They can’t find parking.
- For frugal travelers, there are some smart alternatives if they are willing to do a bit of homework. – The New York Times
Is us first person? Yes, us is one of the first person pronouns.
- The president congratulated us.
Questions About the Second Person

- You are causing a scene.
Is they second person? No, they is a one of the third person pronouns.
- They are our neighbors.
Is we second person? No, we is one of the first person pronouns.
- We are going to get groceries.
Questions About the Third Person
Is their third person? Yes, their is a third person pronoun.
- Their hat is over there.
Is we third person? No, we is a first person pronoun.
- We are going to the beach.
Is our third person? No, our is a first person pronoun.
- This is our cake.
Is you third person? No, you is a second person pronoun.
- You are a nice person.
Is they third person? Yes, they is a third person pronoun.
- They are nice people.
Is he third person? Yes, he is one of the third person pronouns.
- He is a great man.
- Last week, he restated that he believes he deserves a maximum contract. – The Washington Post
Trick to Remember the Difference

Here are a few helpful memory tricks that always help me.
In the first person writing, I am talking about myself.
- I enjoy singing.
In the second person writing, I am talking to someone.
- You enjoy singing.
In the third person writing, I am talking about someone.
- He enjoys singing.
Summary: What is the First, Second, and Third Person Perspective?
Define first person: The definition of first person is the grammatical category of forms that designate a speaker referring to himself or herself. First person pronouns are I, we, me, us, etc.
Define second person: The definition of second person is the grammatical category of forms that designates the person being addressed. Second person pronouns are you, your, and yours.
Define third person: The definition of third person is the grammatical category of forms designating someone other than the speaker. The pronouns used are he, she, it, they, them, etc.
If this article helped you understand the differences between the three main English points of view, you might find our other article on English grammar terms helpful.
You can see our full list of English grammar terms on our grammar dictionary .
Learn English
Abbreviations, absolute possessive pronouns, abstract noun, accusative case, active sentence, active voice, adjective clause, adjective for kids, adjective phrase, adverb for kids, adverbial clauses, adverbial phrases, alliteration for kids, antecedents, auxiliary verb, collective noun, collocation, colloquialism, common noun, comparative, complex sentence, compound nouns, compound predicate, compound sentences, compound subject, compound verb, compound words, concrete noun, conditional sentence, conjugation, conjunction, conjunctions for kids, conjunctive adverbs, connotation, contraction, coordinate conjunctions, copular verb, correlative conjunctions, countable noun, dangling modifier, dative case, declarative sentence, definite article, demonstrative adjectives, demonstrative pronoun, dependent clause, direct object, emotive language, emphatic pronoun, feminine noun, figurative language, figures of speech, finite verb, first person, flat adverb, free morpheme, frequentative, future continuous tense, future perfect progressive tense, future present tense, future tense, gender specific noun, gradable adjectives, helping verbs, imperative mood, imperative sentence, indefinite adjective, indefinite article, indefinite aspect, indefinite pronoun, indefinite tense, independent clause, indicative mood, indirect object, indirect questions, infinitive form, infinitive phrase, intensifier, intensive pronoun, interjection, interrogative adjective, interrogative adverb, interrogative pronoun, interrogative sentence, intransitive verb, irregular verb, labile verb, lexical item, lexical verb, limiting modifier, linking verb, main clause, misplaced modifier, mnemonic devices, nominal relative clause, nominative case, non-countable nouns, non-finite verbs, non-restrictive clause, noun for kids, noun phrase, object complement, object of a preposition, objective case, objective personal pronoun, onomatopoeia, parallel lists, parentheses, passive sentence, passive voice, past continuous tense, past perfect continuous tense, past perfect tense, perfect aspect, perfect continuous tense, perfect progressive aspect, perfect tense, period full stop, periodic sentence, personal pronoun, personification, phrasal verb, positive degree, possessive adjectives, possessive noun, possessive pronoun, predicate adjectives, predicate nominative, preposition, prepositional phrase, present continuous tense, present participle, present perfect continuous, present perfect tense, present tense, progressive aspect, progressive tense, proper nouns, punctuation, question mark, quotation marks, reciprocal pronoun, reflexive pronouns, regular verb, rhetorical question, run-on sentence, second person, simple future tense, simple present tense, simple sentence, simple subject, split infinitive, squinting modifier, staccato sentences, stative verbs, subject complement, subject-verb agreement, subjective case, subjective personal pronoun, subjunctive mood, subordinate clause, subordinating conjunctions, superlative, transitive verb, verb phrase, verbs for kids.
Home » English » Third Person
Third Person
θɜːd ˈpɜːsn
Pronunciation:
Edulyte 24x7 English Class
Learn English anytime, anywhere
Beyond 'Me' and 'You': The Third Person Odyssey
Comprehensive Definition, Description, Examples & Rules
Among the three ‘persons’ used in English grammar to refer to nouns, pronouns and verbs in a sentence, the ‘third person’ is used to talk about someone or something that is not a part of the conversation and is being discussed by keeping it outside the conversation. When you want to tell someone about something that happened to you or about someone that did something to you, you use third-person pronouns.
What is the third person?
Third person pronoun, or simply the third person is a set of pronouns used for entities apart from the sender and the receiver of any conversation. The third-person pronoun can be most appropriately defined as something or someone that is being talked about. Some common third-person pronouns are he, she, it, they, and them. While the first person is used by the speaker f the conversation (i, we, us) and the second person is used for the receiver of the conversation (you), the third person is used for the topic of the conversation.
Significance of the third person in communication and writing:
- The third person can be useful in formal and academic writing as it provides a sense of impartiality to the tone of the conversation by making the subject the centre of focus and not the speaker or the listener.
- Third person pronoun can come in handy when writing fiction as it allows the writer to write from an outsider’s point of view, lending a broader perspective to events, characters and settings.
- The third person can lend clarity to a text, especially when multiple entities are involved by dismissing confusion about who or what is being talked about in a conversation.
Understanding Third person pronouns
Third-person pronouns are used to refer to entities outside of a conversation. They provide spontaneity and smoothness to a conversation by allowing people n the conversation to refer to people, places, animals or things without having to explicitly use their names repeatedly. Here are some examples of how you can use third-person pronouns in sentences:
- I met Rita yesterday. She looked a bit pale.
- Kenny invited me to his house party but I told him I couldn’t attend.
- Have you seen my purse? I think I kept it over here.
- I think they are going to stay the night.
- Didn’t you tell them that the party is over?
Exploring Third person language
The third person pronoun is specifically used for referring to people outside the scope of a conversation and differs from the first and second person in unique ways. For example:
- First Person: Using first-person pronouns, the speaker refers to themselves or the group they belong to. The first-person perspective puts the limelight on the speaker of the conversation and their experiences and attitudes. Common first-person pronouns: I, we, us.
- Second Person: Using second-person pronouns, the speaker refers to the person or group they’re talking to. It addresses the reader or the listener directly and can be used in giving instructions, advice and suggestions. Common second person pronoun: you.
- Third person: Using third-person pronouns, the speaker refers to things and entities that are not a part of the conversation. Third-person pronouns provide an objective view of looking at things and are commonly found in academic and formal writings and fictional stories. Common third-person pronouns: He, she, it, they, them.
Advantages and purposes of using the third person in various contexts:
The third person can provide many advantages to your writing. For example:
- The third person allows the writer to keep an objective and impartial tone in academic and official writings.
- The third-person pronoun helps avoid confusion and provides clarity when there is more than one entity present outside the conversation.
- A third-person pronoun is used in storytelling to enable readers to view characters from an outsider’s point of view.
Some other purposes of third-person pronouns besides referring to people outside the conversation include:
- In certain official contexts, the third person is also used to extend respect and formality to higher authorities.
- The third person can be used to hide the identity of entities where confidentiality is needed.
Writing in the third person: Style and Perspective
Writing in the third person requires you to remember certain guidelines to use the third person correctly and efficiently. Such guidelines are explained below:
How to write in the third person perspective:
- Decide on a narrative mood and choose whether you want to write in the third person omniscient (which knows and sees everything happening in a story and knows about the inner thoughts of all the characters) or third person limited (which knows the in-depth thoughts of only one character in the story and tells the story from his point of view).
- Use third-person pronouns consistently throughout your piece of writing to provide an outsider’s perspective.
- Maintain an impartial and objective tone and avoid including personal opinions and perspectives.
- Use vivid language and descriptive imagery to show what’s happening in the story rather than just plainly stating it.
Techniques for maintaining consistency and clarity in third-person writing:
- If you choose to write in the third person limited, stick to that particular character’s point of view and avoid jumping or ‘head-hopping’ to other characters’ minds to avoid confusion.
- Avoid certain shifts in tone and voice and maintain a particular narrative voice throughout the text.
- Introduce character names early on in the text and use them consistently throughout the text to make sure that the third-person pronouns have clear antecedents they’re referring to.
How to write in the third person: Tips and Guidelines
Writing in the third person can be a useful tool in storytelling as well as formal writing. Here’s how to use them effectively:
Step-by-step guide on writing effectively in the third person:
- Choose the type of third-person narrator (omniscient or limited) and stick to it throughout the text.
- Be objective and impartial.
- Substitute first and second-person pronouns with third-person pronouns.
- Use descriptive language and dialogues creatively.
- Maintain consistent tense throughout the text.
Common challenges and how to overcome them:
Here is a list of common mistakes that you should avoid while writing in third person pronouns and tips on avoiding them:
- Provide clarity about what nouns the third-person pronouns are referring to. Use character names to avoid confusion.
- Writing in the third person can sometimes create emotional distances between the characters and readers. Overcome this by showing characters’ emotions through actions, dialogues, expressions, etc.
- To avoid confusion and ambiguity, give each character a distinctive voice and pattern of behaviour.
Crafting a third-person narrative
The third-person narrative is a writing technique where the story is told from a character’s point of view or an all-knowing point of view of an invisible narrator. Understanding the third-person narrative is crucial to effective storytelling.
Understanding third person narrative and its role in storytelling:
- The third-person narrative provides an objective and impartial viewpoint.
- The third-person narrative allows multiple perspectives into the story.
- The third-person narrative allows the author to move between characters and scenes smoothly.
Examples of well-known literary works that use the third-person narrative:
- ‘To Kill a Mockingbird’ by Harper Lee: This classic American novel is a story seen through the third person limited point of view of Scout Finch.
- ‘Pride and Prejudice’ by Jane Austen: The novel is told from the third person omniscient point of view about the Bennet sister.
‘Harry Potter series by J. K. Rowling uses a third-person limited point of view, focussing on Harry.

Transform Your English Skills
Free sign-up for a personalised dashboard, learning tools, and unlimited possibilities!

PTE Tutorials: Fast-Track to Your Top Score!
Master PTE: Dive in for success!

Key Takeaways
- Third-person pronouns such as ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’, ‘they’, and ‘them’ refer to people outside the scope of the conversation.
- The third-person narrative provides impartiality to the text.
- A third-person perspective is used to tell a story from one character’s point of view or an all-knowing point of view.
Question comes here
- Answer Option
Frequently Asked Questions
Some examples of sentences in the third person are: He kicked the ball; She ate her food; They will be coming early; It is kept on the table.
To write in the third person perspective, choose a type of third-person narrator and then stick to it throughout and avoid confusion by introducing the names of the characters beforehand and consistently throughout the text.
To write a third-person narrative, remain consistent with your chosen point of view, use creative dialogues and vivid action to describe the characters’ emotions.
Yes, the third person is used in academic writing to sound objective and impartial and focus on the subject of the text.
Third-person pronouns add a touch of impartiality to the text end also extend a sense of respect and reverence.
Some common mistakes to avoid while writing in the third person are pronoun confusion, inconsistent point of view and lack of character depth.

PTE Tutorials: Customised Packages for Every Learner
- Valid for 60 Days
- 10 AI Scored Exam-like Mock Tests
- 20 Scored Section-wise Tests
- 4500+ Practice Questions
- Unlimited Practice
- All Question Types
- Email & Chat Support

- Valid for 90 Days
- All Benefits of Standard Plus
- Exclusive PTE strategy Videos
- Latest Templates
- 1 Live Class Per Week
- Valid for 180 Days
- All Benefits of Premium Plus
- 15 AI Scored Exam-like Mock Tests
- 3 Live Classes with PTE Experts Per Week
- 1 Post-test Session with Expert Teacher
- 3 One-on-one Expert Teacher Tutorial (30 mins)
- Premium Support
Everything You Need to Know to Write & Speak In Third Person
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

The third person is frequently used in formal writing, such as research and argumentative papers. When you write in the third person, things become more impersonal and impartial. This impartiality makes the writer appear less prejudiced and, thus, more believable in academic and professional writing. The usage of the third person aids in keeping the text objective and away from subjective opinion.
Why should you write in Third-Person?
In third-person narration, the narrator lives outside of the story’s events and describes the activities of the characters by using their names or the third-person pronouns “he,” “she,” or “them.” The story is not recounted from the author’s point of view. A third-person narrative differs from a first-person story, a personal account told using the pronoun “I.”
Flexibility : Third-person narration can be more flexible since you can flip between the stories of different people while still being everywhere and allowing your audience to see everything. You can switch between total omniscience and a distant or constrained third point of view. The latter method will enable you to experience a character’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences firsthand, which can help the audience have a more in-depth understanding of the narrative.
Trust : When writing in the third person, the narrator is placed above the action. This gives the reader a bird’s-eye view of the narrative. Since the narrator has no stake in the outcome, this perspective, together with the knowledge of at least one character’s thoughts gives the speech a more authoritative, trustworthy voice.
Types of Third Person Point of View
Third-person objective : The facts of a narrative are presented by an observer or recorder who seems dispassionate and impartial. The narrative is told in a detached and observant manner by the narrator.
Third-person omniscient : The narrator is fully aware of both the plot and the characters. This narrator may easily travel across time, enter anyone’s head, and provide the reader with both their own thoughts and views as well as those of the characters.
Third-person limited : The story is told from the viewpoint of a single character who recounts the facts and evaluates the occurrences. It is frequently known as a closed third.
Learning to Write in Third-Person
Using the correct pronouns .
Apply the appropriate pronouns. People “on the outside” are referred to in the third person. Either use third-person pronouns when referring to someone or use their name. He, his, himself, she, her, herself, they, and them are examples of third-person pronouns. The third person is also employed by using other people’s names.
Avoiding First and Second Person Perspectives
First-person indicates the point of view when the author expresses ideas from a purely individual viewpoint. This viewpoint is excessively subjective and judgmental. In a formal essay, stay away from the first person. Pronouns in the first person are I, me, we, and us.
The term “second person” describes a point of view that addresses the reader directly. Speaking directly to the reader as though the author personally knows them, this point of view displays an excessive level of reader familiarity. In academic writing, never use the second person. Words like you or yours are examples of this point of view.
Indefinite terminology is often used to refer to people in writing. In other words, they could have to refer to or talk generically about a person. The desire to use the second-person pronoun “you” generally arises at this point. It is permissible to use a noun or third person pronoun in this sentence. One, someone, another, any, neither, nobody, other, somebody, and everything are examples of indefinite third-person pronouns.
Incorrect example: “You need to read this thesis to understand the study better.”
Correct example: “Reading this thesis will help one understand the research better.”
Understand how to use Plural pronouns in Third Person
It is important to know when and where to use plural pronouns. When we write in the third person, the usage of they/them/theirs, is not just for when referring to a group, but also for singular individuals when we are unaware of their gender. People may use alternative pronouns. Employing “they” helps prevent misunderstanding that could arise from using “he,” “she,” or the “he/she” terminology.
When writing in the third person, one error that writers frequently make is conjugating a plural pronoun as a single. Saying “They was the driver,” for instance, would be incorrect. The proper phrase would be “They were the driver.”
Being Objective
When you write in the third person, use the objective perspective if you are simply presenting facts to your listeners without any mention of feelings. When speaking from an objective point of view, the tone is frequently matter-of-fact and uninfluenced by any commentary or opinions or by any prior knowledge of events occurring elsewhere. You are just listing the facts and making inferences based on them without attempting to manipulate anyone’s emotions. Describe situations that could be moving while being factual.
Adding descriptions
We can use key details to improve characterisation and clarity. Mention it in more detail if the audience needs to know how difficult your labour was or how delicious the cuisine was. This is because while you speak or write in the third person, it is simple for the listener to become confused about what is being discussed. Therefore, it is helpful to reaffirm the situational circumstances.
For example: “The team received thunderous cheers.”
Updated Example: “The entire stadium thunderously cheered the squad.”
Use character evaluations
The perspective becomes clearer when you provide evaluations and insights from your character. Remember that adverbs have a strong role to play when you write in the third person. Words like surprisingly, definitely, oddly, and disastrously can convey the wants, concerns, presumptions, and confidence of the POV character. They also reveal who is performing the observations and evaluations.
For instance, we can say “the experimenter was presumably tired” rather than “The experimenter was tired.”
This demonstrates how we maintained the third person while avoiding adopting the experimenter’s viewpoint.
Using Third Person for Business
Writing in the third person offers the author more power while narrating a narrative since it enables them to be outside of the story and omnipresent. When creating a business proposal or report, the same rule applies. Now, the majority of corporate and professional writing rules advise the applicant to write in the third person . Compared to the first or second person, it is more formal.
Avoid switching between the third and the first person. It is quite simple to unintentionally use the first-person narrative while drafting a business report. Check your work frequently to make sure you are not drifting into your own first-person perspective to avoid that. Pronouns like my, our, us, and I should be avoided. This is fixed during revising the work.
The first-person voice is typically employed in professional communications like business emails, letters, memoranda, and most other types of correspondence. This is why using the third person in your company papers is a risky move . One significant benefit, especially when it’s a delicate subject, is that you don’t come out as accusing. Instead of sa ying “You did not reach the yearly target goal,” use “The staff did not meet the annual target goal.”
The third-person account, which may be found in newsletters, adopts an authoritative and impartial tone. When one writes in the third person, they come out as being more detached, especially when writing about poor attendance at the office. It doesn’t sound like they are blaming the reader.
Understanding the importance of the first and third person is essential in effective workplace communication. Here is an article to learn more about how to use effective communication.
Should you use the Third-Person for your CV or Resume?
Never write in the third person on your CV. The key to producing a superb CV is to avoid pronouns completely; since their use is assumed, applicants don’t need to mention “I,” “he,” or “she.” If you’re an executive assistant, for instance, you should simply state “Organized accommodation for staff” rather than “I coordinated accommodations for the staff.”
Use an action verb at the start of each bullet point in your list of duties to organise them into bullet points. Say “Generated reports” in place of, for instance, “I ran reports.”
First-person pronouns are frequently preferred by job applicants when writing their profiles. This is okay, but to preserve consistency and professionalism, the rest of the CV must utilise first-person pronouns as well.
We suggest using the absent first-person perspective and eliminating all first- and third-person pronouns from every section of your CV to make it stand out. It will help keep your resume professional (and not too personal) and could provide you with a little more room to discuss the talents that matter most.
Be mindful of whether you are using the present or past tense while writing your resume. To describe your current situation, use the present tense; to describe earlier ones, use the past tense.
Using the Third-Person in Academic Writing and Essays
You must use the third person pronoun when writing anything official, such as research articles or argumentative essays. That’s because it paints an objective rather than a subjective view of your work. By being objective in this way, your work will appear more credible and unprejudiced.
First-person pronouns are never appropriate in academic writing. This is because it will force you to look at your work subjectively . First-person pronouns make it challenging to persuade readers that your work is fact-based because it will appear to be your personal ideas. Avoid using your own words and instead cite sources. Words like “I feel” need to be dropped. Additionally, using “I feel” or “I believe” while writing an essay is useless because these words are not very assertive.
When you write in the third person, you concentrate on the facts at hand rather than your own ideas. You may provide your reader with proof by writing in the third person. Show whatever you know and provide support for your claims while writing in the third person. As opposed to stating “I think” or “I feel,” it won’t be as repetitive. If you have a piece by the Washington Post, for instance, you may remark “According to the Washington Post…”
As for the second-person point of view, this is a point of view that speaks directly to the readers. The issue with this point of view is that it gives the impression that you know the readers well. It is advisable to avoid this since it may quickly become direct or accusing .
Converting First and Second Person to Third Person
Using the first and the second person in writing is something that comes more naturally to us since these are the voices used in daily life. Follow these procedures to remove the first and second person and write in the third person:
1. As you read the article, keep an eye out for first- or second-person pronouns . Keep an eye out for any personal anecdotes that could demand the usage of first-person. Use a highlighter or a pen to highlight these words.
2. Go back to any words you marked. Drop expressions like “I think” or “I believe”.
Example: I believe counselling to be quite beneficial.
Updated Example: Counseling is really beneficial.
3 . Could any of the remaining words be changed to third-person terms ?
Example: You need to ensure that all of your students have stationery.
Updated Example: A teacher is responsible for ensuring that all of their students have stationery.
4. Can personal stories be altered into hypothetical ones if they are still present and cannot be amended or removed?
Example: As a person who goes to the gym, I know some people who could buy this product.
Updated example: Many gym-goers could be interested in purchasing this item.
By revising phrases or even altering words, it is simple to get rid of most instances of first- and second-person use. It is well worth the work to change and write in a third person paper since it produces a better, more objective argument.
Should you speak in third person?
Illeism is when we speak, think or write in the third person perspective about ourself. A common internal monologue that appears when we’re trying to decide what to do, thinking back on the past, or directing ourselves through ordinary situations is shared by many people. So is it weird to talk about yourself in the third person? Yes, in a way; it’s not typical for most individuals. However, it seems that using the third person while talking about oneself has helped certain people, according to psychologists.
Third-person speaking has previously been extensively researched and has been demonstrated to momentarily enhance decision-making. Currently, a PsyArxiv article reveals that it can also improve cognitive and emotional management over the long run. This, according to the researchers, is “the first indication of how wisdom-related cognitive and emotional processes may be taught in daily life.”
The fact that using detached self-talk to regulate emotions seems to require minimal effort is one of its most fascinating features. Along with reducing emotional overwhelm, third-person inner monologue also prevented cognitive control brain regions from going into overdrive( Moser et. al., 2017 ).
Consider the scenario when you and your partner are bickering. Taking on a third-person viewpoint may assist you in understanding their perspective or in accepting the limitations of your own comprehension of the issue at hand. Or assume that you are thinking about changing careers. You might be able to analyse the advantages and hazards of the shift with more objectivity if you adopt a detached approach.
First and Second Person
I had to leave my home for the first time ever and relocate to the campus of the university. I had to choose between living in an apartment and a dorm. Although both have advantages, I believe the dormitories are superior. While we are transitioning to college, we have more opportunities for social engagement in the dorms. Food is also readily available to us . Also, throughout your first year of college, a resident assistant serves as your mentor and adviser. Dorms are a better match for me because of the social possibilities, endless food, and mentorship, even if apartments would provide me with more independence.
Third Person
Many students have to leave their homes for the first time ever and relocate to the campus of the university. They have to choose between living in an apartment and a dorm. Although both have advantages, it is usually believed that the dormitories are superior. While the students are transitioning to college, they have more opportunities for social engagement in the dorms. Food is also readily available to them . Also, throughout their first year of college, a resident assistant serves as their mentor and adviser. Dorms are a better match for the students because of the social possibilities, endless food, and mentorship, even if apartments would provide them with more independence.
One of the three writing styles you may employ when presenting a point of view is third-person writing. Although you may not be aware of it, chances are you have utilised all three when writing or speaking throughout your life.
Consistency and frequent practice are the keys to mastering the art of writing speeches and papers in the third person. Analyze and critique your work until it becomes the standard. In the beginning, it could seem a little complicated, but before you know it, you’ll have mastered the method. This will undoubtedly enable you to elevate your papers and presentations to a new level.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Writing in Third Person: How to, When to, and Why
When it comes to writing, the third person is one of the most commonly used points of view. This point of view allows readers to get inside the heads of multiple characters and can make stories more immersive and engaging.
What Is Writing In Third Person?
Please enable JavaScript
Writing in the third person point of view is when the writer tells the story using third-person pronouns like "he" or "she".
It gives the story a more objective perspective and can be less confusing for the reader.
However, some people struggle to write in the third person, as they have to keep track of the thoughts and actions of all the different characters in the story.
How to Write in Third Person About Yourself
It can be helpful to think of yourself as if you're someone else observing yourself from the outside. This will help you stay in the third person when describing your own actions and thoughts.
When Should You Write In Third Person?
Now that you know how to write in third person point of view, when should you use third person?
The third person point of view is most commonly used in fiction writing, but it can also be used when writing non-fiction or even when writing about yourself.
- Who is your audience?
If you're writing a more personal piece, such as a memoir, you might want to consider writing in a first-person point of view. This will allow you to share your personal thoughts and experiences more directly with the reader.
On the other hand, using third-person pronouns like "he," "she," and "him" can make your writing sound more personal.
Ultimately, the best point of view for your story will be the one that allows you to tell your story most effectively.
How to Write in Third Person Omniscient
The narrator can only know what each individual character knows. This is important to remember when writing dialogue and internal thoughts for each character. What one character knows will be different from what another character knows.
Why Do Authors Write in Third Person?
Finally, some authors simply find it easier to write in third person point of view because it allows them to distance themselves from their characters.
Are Biographies Written in Third Person?
An autobiography, on the other hand, is usually written from a first-person point of view. This is because an autobiography is typically more personal and intimate than a biography.
About The Author
Arielle phoenix, related posts, what is the average time it takes to write a book, should i write a book or a screenplay, how to write a zombie book: 8 easy steps, pdf template for writing a book.

How to Use Third Person in a Paragraph Essay

How to Identify Figurative Language
Writing in the third person is more formally known as using the third-person objective point of view. The third person point of view in an essay is characterized by the use of personal pronouns such as he, she, they or one rather than I, we or you. Formal essays as well as some types of informal essays are typically written in the third person. The third person can apply to single-paragraph essays as well as more common, longer essay formats.
Use the words he, she, it and they for your personal pronouns in the nominative case, meaning when they're the subject of a sentence or clause. Eliminate any references to I, we, or you. "A man's clothing affects how he looks," for example, is written in the third person. "Your clothing affects how you look" is written in the second person. "My clothing affects how I look" is first person.
Use the words him, her, it and them for your personal pronouns in the objective case. Eliminate any references to me, us or you in this case. "Clothes are important to them," for example, is written in the third person. "Clothes are important to you" is in the second person, while "Clothes are important to me" is written in the first person.
Use the words his, her, hers, it, their and theirs for your personal pronouns in the possessive case. Eliminate any references to my, mine, our, ours, your or yours in this case. "The clothes are theirs," for example, is written in the third person. "The clothes are yours" is written in the second person. "The clothes are mine" is first person.
Use indefinite pronouns such as anybody, anyone, both, each, everybody, somebody, someone and several. "Anybody can state an opinion," for example, is written in the third person. "I can state an opinion" is written in the first person.
Review your essay to ensure it remains in the third person throughout. "Unless someone trains harder, your fitness level will hit a plateau," for example, mixes third person with second person. Instead, write: "Unless someone trains harder, his fitness level will hit a plateau."
Related Articles

Purpose of a Pronoun

Difference Between Nominative & Objective Pronouns

How to Use Adverbs in Writing

The Difference Between Participles & Verbs

What Is the Relationship Between a Noun or Pronoun and the Rest of ...

How to Write a Retreat Letter

Properties of a Pronoun

How to Punctuate Song Titles
Steven Wilkens has been a professional editor and writer since 1994. His work has appeared in national newspapers and magazines, including "The Honolulu Advertiser" and "USA Today." Wilkens received a Bachelor of Arts in English from Saint Joseph's University.
Why Third-Person Writing Is Critical to a Great Essay
In the past, you might have had problems getting that polished, professional feel to your essays, but you couldn’t quite figure out why. Are your ideas too underdeveloped? Is your thesis statement not good enough? Do you not have enough support for your arguments?
Sometimes the problem with your essay is simply the point of view you choose to write in. Using third-person writing can make a world of difference in giving your essay the right tone.
Three Different Points of View

If you’re not sure what the different points of view are, I’ll give you a run-down and some examples to help you see more clearly. And for an added bonus, I’ll give you a couple clips from the king of narration himself, Morgan Freeman.
First-Person Writing
When you write in first person , you use I and me . Think of yourself as the “first person”–any pronoun that indicates something you do or think is going to be first person. You see this a lot when you’re reading books from the main character’s perspective.
Typically, however, first-person writing is not very effective in writing essays. (We’ll get to why that is in a second.)
Example: I believe that third-person writing is the best point of view when writing an essay.
First-person writing or narration also uses us and we , as you’ll see in this example:
Second-Person Writing
Second-person point of view uses the pronoun you . Second-person writing is the equivalent to a choose-your-own-adventure novel or a self-help book. It speaks directly to the audience.
However, the conversational tone of writing in second-person is not usually ideal for academic writing.
Example: You would do better on your essays if you wrote in third person .
It is important to note that when you aren’t writing strictly in third person, the point of view can shift from sentence to sentence.
In the next example, you’ll notice that both first-person and second-person points of view are present. The lyrics Freeman reads shift between using “you/your” and first-person singular pronouns throughout the clip.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NRKZh-2j4PY
Third-Person Writing
Third-person writing uses the pronouns they, him, her, and it , as well as proper nouns. This is the type of writing you would see in a novel with an outside narrator.
Example: Teachers and students agree that third-person writing makes essays sound better.
Here’s one last video example, this one using third-person perspective, from the man with the golden voice:
Why Third-Person Writing is Important
Third-Person Writing Makes Your Essay Sound More Assertive.
If you write your essay in first person, you risk the chance of statements like “I think” or “I believe.” These kinds of statements sound more passive than just stating your facts. Notice the difference between the following sentences:
The second sentence–the one that uses third-person–sets a more definite tone. You are presenting the sentence as a statement of fact instead of a personal belief.
Third-Person Writing Makes Your Support Sound More Credible.
On a related note, first-person writing makes your support sound like it’s coming from a non-credible source. Presenting facts or opinions with “I think” or “I believe” in front doesn’t give any validity to the statement.
Third-person writing encourages you to use other sources to validate your claims. The following two sentences will illustrate this further:
The second sentence pulls an authoritative source to support the claim instead of you, the writer. This makes the claim more credible to the reader.
Third-Person Writing Sounds Less Conversational and More Professional.
As I mentioned before, writing in the first or second person leads to a more conversational tone. While this may be good for some forms of writing (this blog post, for example), you want your academic writing to take on a more formal tone. Consider the following examples:
The first sentence creates a more intimate and conversational tone with the reader, but the second sentence tells the reader what kind of person (authors) would benefit from reading the sentence.
It is more specific and, therefore, creates a more formal tone.
Exceptions to the Third-Person Writing Rule
I won’t ever tell you that it’s always a good idea to write one specific way. Third-person writing is usually a good idea in academic writing, but there are cases where first-person writing is a better call.
When You’re Writing A Personal Narrative.
Personal narrative essays are designed to tell the reader something that has happened in your life, so first-person writing would be the preferred choice here. Whether it be something that embarrassed you, angered you, or made you proud or happy, narrative essays are all about real-world life experiences.
When You’re Talking About Your Own Opinions.
Like narrative essays, using your own opinions in essays may sometimes require the use of the first person, especially if you are drawing on personal experiences. Usually, this will happen in persuasive essays.
It is important to note that you should still try to use third-person writing for your persuasive essays because, as I mentioned earlier, it will give a more formal tone and more credibility to your argument. However, if some personal experience is especially relevant, it would be okay to use the first person (unless your teacher says otherwise, of course).
When You’re Doing Other Informal Types of Writing.
Essays are not the only types of writing assignments you’re likely to receive. Short stories and poetry pop up in classes from time to time, and these can be written any number of ways. Short stories can take the first- or third-person perspective–they rarely use second person. Poetry can use any of the three points of view.
(For more, read When to Use First-Person Writing in Your Essays )
When you are concentrating strictly on academic essays, third-person writing is (usually) crucial. And it’s not hard to do. Just look at any references to yourself or the reader and change around the sentence to eliminate the I, me, you, we, and us pronouns. Doing so will make your writing stronger, clearer, and more professional.
If you still can’t quite get the hang of third-person writing, there’s no need to stress out over it. Just send your essay to one of the Kibin editors to help you out.
Now… go try your hand at third-person writing!
Psst... 98% of Kibin users report better grades! Get inspiration from over 500,000 example essays .

About the Author
Eden Meirow is a full-time copywriter and part-time freelance writer. Along with her BS in marketing from Florida State University and MA in museum studies from Johns Hopkins University, she has spent the past 7 years learning how best to reach and teach people using the power of words. When she's not working, she's constantly trying to expand her creativity through music, writing, art, and animation.
- third-person
- writing strategies
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Nouns and pronouns
- Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation
Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation
Published on December 1, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on February 24, 2023.
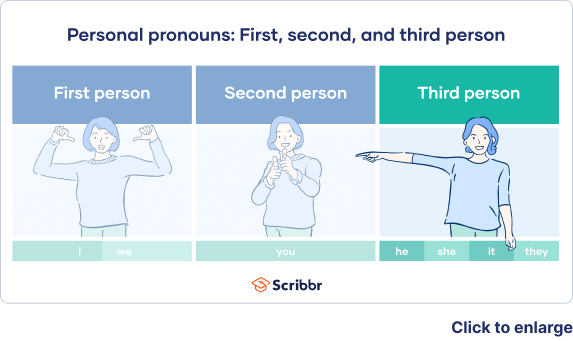
Third-person pronouns are words such as “she,” “it,” and “they” that are used to refer to other people and things that are not being directly addressed, without naming them specifically with a noun . Like first- and second-person pronouns , they are a type of personal pronoun .
There are quite a lot of third-person pronouns, since they differ based on the gender (or lack thereof) and number of who or what is being referred to. They also change based on whether they are used based on case: subject , object , possessive , or reflexive / intensive . The table below shows all the third-person pronouns.
| Subject | Object | Possessive | Reflexive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| he | him | his | himself | |
| she | her | hers | herself | |
| it | its | itself | ||
| they | them | theirs | themself | |
| they | them | theirs | themselves | |
Table of contents
Masculine singular pronouns (“he”), feminine singular pronouns (“she”), neuter singular pronouns (“it”), third-person plural pronouns (“they”), the singular “they”, frequently asked questions.
The masculine singular pronouns are he , him , his , and himself . The masculine singular possessive determiner (used to modify a noun instead of replacing it) is also his .
These words are used to refer to individual men and boys—and sometimes to male animals.
| Subject | Ahmad is good at math, but doesn’t particularly enjoy it. |
|---|---|
| Object | After Jim started a fight with another attendee, event security kicked out. |
| Possessive | This isn’t my jacket, but Dolf was sitting here earlier. I think it’s . |
| Reflexive | Eric introduced already. We had a nice chat! |
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
The feminine singular pronouns are she , her , hers , and herself . The feminine singular possessive determiner is also her .
These words are used to refer to individual women and girls—and sometimes to female animals.
| Subject | Laura says can’t make it to the party. |
|---|---|
| Object | It’s not Ida’s fault. Leave alone! |
| Possessive | gift do you like better, mine or ? |
| Reflexive | Mei ought to realize she can just be around us, but she always tries to act tough. |
The neuter singular pronouns (also called inanimate singular pronouns) are it (used in both the subject and object position), its , and itself . The neuter singular possessive determiner is also its .
These words refer to something other than a person: a concept, object, place, or animal (although gendered pronouns are sometimes used instead for animals). It’s considered very rude to refer to a person as “it”; to refer to someone without specifying gender, use the singular “they” instead.
| Subject | wasn’t a great concert, but I’ve seen worse. |
|---|---|
| Object | Don’t say ! I know what you’re thinking. |
| Possessive | The flashing light on the side of the device indicates remaining battery life. |
| Reflexive | The average cat spends a lot of time washing . |
The third-person plural pronouns are they , them , theirs , and themselves . The third-person plural possessive determiner is their .
These words are used to refer to more than one of anything: people, things, concepts, places, animals, and so on. No distinction is made between people and things or between male and female in this case; the plural pronouns are always the same.
| Subject | are important, but can develop and change over time. |
|---|---|
| Object | I can’t decide whether to go to Paris or Berlin; I’d love to visit both. |
| Possessive | My flight home is on Sunday morning, and is in the afternoon. |
| Reflexive | Teaching can be stressful when the kids won’t behave . |
The third-person plural pronouns and possessive determiner— they , them , theirs , themselves , and their —are now commonly used as gender-neutral singular pronouns (also called epicene pronouns) to refer to people. This usage is often called the singular “they.”
The singular “they” has existed for a long time, but it was typically viewed as an error in the past. However, most style guides now endorse it, recognizing the need for a way to refer to individuals in a gender-neutral way.
These words are used (instead of “he or she”) when referring to a generic individual whose gender is unspecified or to an individual who identifies as neither male nor female.
| Subject | When someone signs up to participate in the trial, are given a preliminary questionnaire. |
|---|---|
| Object | It’s important to show the customer that you are listening to . |
| Possessive | Max is really smart. are always the best ideas. |
| Reflexive | Sacha will have the place all to . |
In grammar, person is how we distinguish between the speaker or writer (first person), the person being addressed (second person), and any other people, objects, ideas, etc. referred to (third person).
Person is expressed through the different personal pronouns , such as “I” ( first-person pronoun ), “you” ( second-person pronoun ), and “they” (third-person pronoun). It also affects how verbs are conjugated, due to subject-verb agreement (e.g., “I am” vs. “you are”).
In fiction, a first-person narrative is one written directly from the perspective of the protagonist . A third-person narrative describes the protagonist from the perspective of a separate narrator. A second-person narrative (very rare) addresses the reader as if they were the protagonist.
The term preferred pronouns is used to mean the (third-person) personal pronouns a person identifies with and would like to be referred to by. People usually state the subject and object pronoun (e.g., “she/her”) but may also include the possessive (e.g., “she/her/hers”).
Most people go by the masculine “he/him,” the feminine “she/her,” the gender-neutral singular “they/them,” or some combination of these. There are also neopronouns used to express nonbinary gender identity, such as “xe/xem.” These are less common than the singular “they.”
The practice of stating one’s preferred pronouns (e.g., in a professional context or on a social media profile) is meant to promote inclusion for transgender and gender-nonconforming people. The first- and second-person pronouns (“I” and “you”) are not included, since they’re the same for everyone.
In most contexts, you should use first-person pronouns (e.g., “I,” “me”) to refer to yourself. In some academic writing, the use of the first person is discouraged, and writers are advised to instead refer to themselves in the third person (e.g., as “the researcher”).
This convention is mainly restricted to the sciences, where it’s used to maintain an objective, impersonal tone. But many style guides (such as APA Style ) now advise you to simply use the first person, arguing that this style of writing is misleading and unnatural.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Caulfield, J. (2023, February 24). Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/nouns-and-pronouns/third-person-pronouns/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, first-person pronouns | list, examples & explanation, second-person pronouns | list, examples & explanation, what is a pronoun | definition, types & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

We Vs. They: Using the First & Third Person in Research Papers
Writing in the first , second , or third person is referred to as the author’s point of view . When we write, our tendency is to personalize the text by writing in the first person . That is, we use pronouns such as “I” and “we”. This is acceptable when writing personal information, a journal, or a book. However, it is not common in academic writing.
Some writers find the use of first , second , or third person point of view a bit confusing while writing research papers. Since second person is avoided while writing in academic or scientific papers, the main confusion remains within first or third person.
In the following sections, we will discuss the usage and examples of the first , second , and third person point of view.
First Person Pronouns
The first person point of view simply means that we use the pronouns that refer to ourselves in the text. These are as follows:
Can we use I or We In the Scientific Paper?
Using these, we present the information based on what “we” found. In science and mathematics, this point of view is rarely used. It is often considered to be somewhat self-serving and arrogant . It is important to remember that when writing your research results, the focus of the communication is the research and not the persons who conducted the research. When you want to persuade the reader, it is best to avoid personal pronouns in academic writing even when it is personal opinion from the authors of the study. In addition to sounding somewhat arrogant, the strength of your findings might be underestimated.
For example:
Based on my results, I concluded that A and B did not equal to C.
In this example, the entire meaning of the research could be misconstrued. The results discussed are not those of the author ; they are generated from the experiment. To refer to the results in this context is incorrect and should be avoided. To make it more appropriate, the above sentence can be revised as follows:
Based on the results of the assay, A and B did not equal to C.
Second Person Pronouns
The second person point of view uses pronouns that refer to the reader. These are as follows:
This point of view is usually used in the context of providing instructions or advice , such as in “how to” manuals or recipe books. The reason behind using the second person is to engage the reader.
You will want to buy a turkey that is large enough to feed your extended family. Before cooking it, you must wash it first thoroughly with cold water.
Although this is a good technique for giving instructions, it is not appropriate in academic or scientific writing.
Third Person Pronouns
The third person point of view uses both proper nouns, such as a person’s name, and pronouns that refer to individuals or groups (e.g., doctors, researchers) but not directly to the reader. The ones that refer to individuals are as follows:
- Hers (possessive form)
- His (possessive form)
- Its (possessive form)
- One’s (possessive form)
The third person point of view that refers to groups include the following:
- Their (possessive form)
- Theirs (plural possessive form)
Everyone at the convention was interested in what Dr. Johnson presented. The instructors decided that the students should help pay for lab supplies. The researchers determined that there was not enough sample material to conduct the assay.
The third person point of view is generally used in scientific papers but, at times, the format can be difficult. We use indefinite pronouns to refer back to the subject but must avoid using masculine or feminine terminology. For example:
A researcher must ensure that he has enough material for his experiment. The nurse must ensure that she has a large enough blood sample for her assay.
Many authors attempt to resolve this issue by using “he or she” or “him or her,” but this gets cumbersome and too many of these can distract the reader. For example:
A researcher must ensure that he or she has enough material for his or her experiment. The nurse must ensure that he or she has a large enough blood sample for his or her assay.
These issues can easily be resolved by making the subjects plural as follows:
Researchers must ensure that they have enough material for their experiment. Nurses must ensure that they have large enough blood samples for their assay.
Exceptions to the Rules
As mentioned earlier, the third person is generally used in scientific writing, but the rules are not quite as stringent anymore. It is now acceptable to use both the first and third person pronouns in some contexts, but this is still under controversy.
In a February 2011 blog on Eloquent Science , Professor David M. Schultz presented several opinions on whether the author viewpoints differed. However, there appeared to be no consensus. Some believed that the old rules should stand to avoid subjectivity, while others believed that if the facts were valid, it didn’t matter which point of view was used.
First or Third Person: What Do The Journals Say
In general, it is acceptable in to use the first person point of view in abstracts, introductions, discussions, and conclusions, in some journals. Even then, avoid using “I” in these sections. Instead, use “we” to refer to the group of researchers that were part of the study. The third person point of view is used for writing methods and results sections. Consistency is the key and switching from one point of view to another within sections of a manuscript can be distracting and is discouraged. It is best to always check your author guidelines for that particular journal. Once that is done, make sure your manuscript is free from the above-mentioned or any other grammatical error.
You are the only researcher involved in your thesis project. You want to avoid using the first person point of view throughout, but there are no other researchers on the project so the pronoun “we” would not be appropriate. What do you do and why? Please let us know your thoughts in the comments section below.
I am writing the history of an engineering company for which I worked. How do I relate a significant incident that involved me?

Hi Roger, Thank you for your question. If you are narrating the history for the company that you worked at, you would have to refer to it from an employee’s perspective (third person). If you are writing the history as an account of your experiences with the company (including the significant incident), you could refer to yourself as ”I” or ”My.” (first person) You could go through other articles related to language and grammar on Enago Academy’s website https://enago.com/academy/ to help you with your document drafting. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter: https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
Good day , i am writing a research paper and m y setting is a company . is it ethical to put the name of the company in the research paper . i the management has allowed me to conduct my research in thir company .
thanks docarlene diaz
Generally authors do not mention the names of the organization separately within the research paper. The name of the educational institution the researcher or the PhD student is working in needs to be mentioned along with the name in the list of authors. However, if the research has been carried out in a company, it might not be mandatory to mention the name after the name in the list of authors. You can check with the author guidelines of your target journal and if needed confirm with the editor of the journal. Also check with the mangement of the company whether they want the name of the company to be mentioned in the research paper.
Finishing up my dissertation the information is clear and concise.
How to write the right first person pronoun if there is a single researcher? Thanks
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Reporting Research
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
- Essay Editor
How to Use Transition Words for Essays + Examples

Transition words play a key role in essay writing. They connect ideas, sentences, and paragraphs, helping readers follow your text easily. These words do many jobs, from comparing things to showing cause and effect. They turn scattered thoughts into a clear story.
Learning to use transition words for essays isn't just about making your writing sound better. It's about making your ideas clearer and easier for readers to understand. Let's look at transition words and how to use them well in your essays.
Understanding Transition Words for Essays
Transition words for essays are like road signs. They guide readers through your ideas. They help show how your thoughts connect, making your writing easier to follow.
The Purpose and Placement of Transition Sentences
Transition sentences do several important things:
- They make your ideas flow better
- They help readers grasp your main point
- They link sentences and paragraphs
- They show how ideas relate to each other
- They make your writing easier to read
Where you put transitions matters. They're often used:
- Between parts of an essay to sum up or introduce new ideas
- Between paragraphs to show connections or changes in focus
- Within paragraphs to link related thoughts
Here's an example:
"The Industrial Revolution brought many new technologies. On the other hand, it also caused social problems."
In this case, "On the other hand" shows a contrast between the good and bad effects of the Industrial Revolution.
Putting transitions in the right places helps your ideas flow smoothly. For instance, transition words to start a paragraph in an essay can signal a new point or a shift in focus, preparing the reader for what's next.
Types of Transitions Words
There are different types of transition words for essays, each with its own job. Knowing these types can help you pick the right words for different parts of your writing.
- Adding information: "Also," "In addition," "Furthermore"
- Showing contrast: "But," "However," "On the other hand"
- Showing cause and effect: "So," "As a result," "Therefore"
- Showing order: "First," "Second," "Finally"
- Giving examples: "For example," "Such as," "To illustrate"
Using different transition words can make your essay flow better and be more coherent. Aithor can suggest good transition words based on what your essay is about, helping you improve your writing.
Creating Smooth Transitions in Your Writing
To make your transitions smooth:
- Use your essay's structure to find logical connections between sections.
- Put transitions where they best show how ideas relate.
- Don't use too many transition words, or your writing might sound forced.
- Try not to use the same few transitions over and over.
Remember, sometimes less is better. Using too many transition words can make your writing sound unnatural. Writing tools like Aithor can help you find places where transitions might make your essay flow better, suggesting good transition words based on your essay's content.
List of Transitions
Let's look at different types of transition words and phrases you can use in your essays:
1. Addition
Transition words to start a paragraph in an essay that add information include:
- Furthermore
- Additionally
- In addition
Example: "The new policy aims to cut down on carbon emissions. Also, it encourages the use of energy from renewable sources."
2. Contradiction
To show contrast, you can use:
- Nevertheless
- On the other hand
- In contrast
- Despite this
Example: "Many people thought the project would fail. On the other hand, it did better than anyone expected."
3. Condition
Conditional transitions include:
- Provided that
- In the event that
Example: "The company will grow bigger if the market stays good."
4. Emphasis
To highlight important points, use:
- Undoubtedly
Example: "The experiment gave surprising results. In fact, it made people question many old theories in the field."
5. Similarity
Transition words for the second body paragraph showing similarity include:
- In the same way
Example: "The novel explores themes of love and loss. In the same way, the author's previous work dealt with complex human emotions."
To show outcomes or consequences, use:
- As a result
- Consequently
Example: "The team worked very hard on the project. As a result, they finished it early."
7. Conclusion Transitions
Transition words for the conclusion paragraph include:
- In conclusion
- To summarize
Example: "In conclusion, the study shows that social media greatly affects how consumers behave."
8. Sequence
To show order or progression, use:
- First, Second, and Third
- Subsequently
Example: "First, we'll look at the data. Then, we'll explain what it means. Finally, we'll make conclusions based on what we found."
9. Location
Spatial transitions include:
- Adjacent to
- In the vicinity of
Example: "The rare plant was found growing nearby the river bank."
As you start writing, remember this important tip: use transition words carefully. While these words help make your writing easy to read, using too many can confuse your reader. Think of transition words like spices in food — they make it taste better, but too much can ruin the dish.
Your goal is to help your reader easily follow your ideas, not to create a maze of connecting words. So, when you write your next essay, remember: when it comes to transitions, often using fewer is better. Use them thoughtfully to make your argument clear, and your writing will be easy to understand and follow.
If you want to get even better at writing essays, Aithor has special features that can help you choose the best transitions for what you're writing about, making sure your essays flow smoothly from start to finish.
Happy writing!
Related articles
Paraphrasing vs plagiarism: do they really differ.
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
Can Plagiarism Be Detected on PDF?
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Resume and Cover Letter
- How to Write a Short Bio?...
How to Write a Short Bio? (With Examples)
7 min read · Updated on August 28, 2024

A short professional biography is a great tool to have in your career marketing toolkit.
As you progress through your career, there will likely come a time when someone wants you to provide them with a professional biography. It could be that your boss wants to include something on the team page of the company website or perhaps you need to write a blurb about your biggest achievements for a social media page.
Regardless of the reason, you should always have one ready to go. Many people have quite a few questions about writing short professional bios, though, including
What is a bio?
How to write a short bio?
What voice to use in a short bio – first person or third person?
What is the format of a short biography?
What is a good bio example?
Let's just say that you're in the right place to find out.
What is a short bio?
Have you ever heard the phrase “elevator pitch?” Well, that's what a bio is. It's about 200 words that define who you are, what you do, what you've accomplished, and what your goals are. If that seems like a lot to put into a couple hundred words, you're right.
This isn't the time to go on and on about everything you've ever done. Since the purpose of a short professional bio is to introduce you to whoever is reading it, it's best to worry about only hitting the high notes.
Think about what you say when someone asks you the following:
What do you do?
How long have you done it?
What do you like most about it?
Have you ever won an award ?
Why do you want to keep doing what you do?
Your answers to those questions will help you craft your biography, though you'll probably have to pare down the wording to keep it within the requisite word count. Always remember KISS – Keep it Short and Simple.
How to write a short professional bio?
Just like with your resume, a short professional bio should contain key details. Those details should also appear in a predictable order.
Your name and current job title
Your professional philosophy
Some of your best skills
Career achievements
What you have your sights set on for the future
You could also include things like links to online portfolios or your contact information, depending on where the bio is going to be used. For example, if you're adding the short professional bio to a web page that already has your contact info, then you don't need to add it to the bio itself.
First-person vs third-person for your short professional bio
Before you start writing, you have to decide which voice you're going to use for your biography. Meaning, are you going to write it using first-person or third-person?
First-person writing involves using pronouns like “I,” “me,” and “my”
Third-person writing is when you avoid using personal pronouns and stick to possessive pronouns or possessive adjectives like "he," "she," "his," and "her"
It all depends on your audience. You'd choose to write your short professional bio in the first person if you're using it for personal websites, social media profiles , and networking events. It's better to use the third person when you're writing for company websites, professional directories, or other formal settings.
Short professional bio examples: Your name and current job title
This may seem like a given, but because it's such a simple thing, a lot of people try to overdo it. You literally only need to write something like this
Third-person: Janet Plunder is the Head of Marketing for We Are Creatives, Inc.
First-person: My name is Jeff Safeport, and I am the Network Manager for BitBytes.
Short professional bio examples: Your professional philosophy
Have you ever thought about the values and ethics you possess and how those shape your work and interaction with others? That is the basis of your professional philosophy. Prospective employers and future clients want to know how you distinguish yourself from others. The way you come up with your professional philosophy is through a little self-assessment. Ask yourself
What do I believe in?
What am I committed to?
What values are most important in my professional life?
How do I approach challenges?
Have I made any type of impact in my field?
This is what the philosophy statement could look like in your short bio:
- Third-person: She is known for leading with integrity, fostering collaborative environments, and continuously seeking innovative solutions that drive success.
- First-person: I am committed to prioritizing client satisfaction. Also, by embracing the idea of lifelong learning, I consistently strive for excellence in everything all projects I undertake.
Short professional bio examples: Your skills and qualifications
Going back to the concept of KISS, you want to avoid trying to include a laundry list of every skill you possess. The idea here is to focus on the abilities that set you apart in your field. You need to be specific not only about what you excel at but also how the particular skills you choose for your short professional bio have helped you be successful.
For example:
- Third-person: Jane is known for creating digital marketing strategies, with a particular focus on SEO and content marketing. She has a proven track record of increasing online visibility, brand awareness, and consumer engagement for countless globally branded companies.
- First-person : One of my strong suits is the ability to streamline processes in a way that improves productivity across international teams. I do this through full lifecycle project management and deep-dive data analysis.
Short professional bio examples: Your career achievements
Back when you were writing your resume, you probably heard over and over again how important career achievements are. There are millions of articles out there that tell you how to quantify the things you've accomplished in past jobs because that's how prospective employers know you'll be a benefit to their team.
The same holds true for your short professional bio. Your readers will be able to tell how you can help them by getting a glimpse into your career wins. Focus on notable awards and major projects that point to you achieving milestones.
Here's what that could look like:
- Third-person: Recently, she led a rebranding project that increased revenue by more than 20%, earning her the Innovator of the Year award.
- First-person : In my last position, I ascended to the prestigious President's Club after overhauling project processes and saving the company $10M.
Short professional bio examples: Your professional goals
The one thing that distinguishes a short professional bio from your other career marketing documents is that it not only showcases your history but it's also future-facing. This gives you a great opportunity to talk about your aspirations and which direction you are heading in your career.
You can show prospective employers and future clients that you're going to be around a while by talking about things like being “forward-thinking” and emphasizing your “commitment to growth,” as examples.
Here are a couple of short professional bio examples you can use as inspiration for your own professional goals :
- Third-person: Jane is looking forward to developing leadership skills to transition into an executive management role so that she can foster innovation at the corporate level.
- First-person : Since the beginning of my career, I've focused on expanding my expertise in cybersecurity and am poised to move into a Chief Information Officer position.
Leave a lasting impression
No matter what type of document you're writing for your career, the object is always to leave a lasting impression. That holds true even for a short professional bio. It may only be a couple hundred words, but they're very important words. Keep it concise, relevant, and engaging, and the right doors will open to propel you along your career journey.
The best way to get the right details into your short professional bio is to use information from your resume. Does your resume say what you need it to say about your skills, qualifications, and achievements? Upload it for a free review and find out.
Recommended reading:
20 Funny and Awkward Zoom Fails: Meetings Gone Wrong
10 Things Every Job Seeker Should Know Before Starting Their Search
Why the Handshake May Go Away — and Options to Replace It
Related Articles:
7 Best Personal Skills for Your Resume (With Examples)
Great Jobs for Teens: Top Picks for 16-Year-Olds
Functional Resume: Writing Guide, Examples, & Template
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Tiny Memoir Contest for Students: Write a 100-Word Personal Narrative
We invite teenagers to tell a true story about a meaningful life experience in just 100 words. Contest dates: Nov. 6 to Dec. 4, 2024.

By The Learning Network
Illustrations from Modern Love’s Tiny Love Stories , the inspiration for this contest.
Can you tell a meaningful and interesting true story from your life in just 100 words? That’s the challenge we pose to teenagers with our 100-Word Personal Narrative Contest, a storytelling form popularized by Modern Love’s Tiny Love Stories series .
After running this contest for two years, receiving a total of more than 25,000 entries, and honoring dozens of excellent miniature teen-written memoirs, we have discovered the answer is a resounding yes .
So, we challenge you to try it yourself.
We’re not asking you to write to a particular theme or to use a specific structure or style, but we are looking for short, powerful stories about a particular moment or event in your life. We want to hear your story, told in your unique voice, and we hope you’ll experiment with style and form to tell a tale that matters to you, in a way you enjoy telling it.
And, yes, it’s possible to do all that in only 100 words. For proof, just look at last year’s 15 winning entries . We also have a step-by-step guide full of advice that is grounded in 25 excellent 100-word mentor texts, as well as a rehearsal space , published for our first year’s contest, that has over 1,000 student-written mini memoirs. Because that space was so successful, we’re keeping it open for this year’s contest. We hope students will use it to get inspiration, experiment and encourage each other.
Take a look at the full guidelines and related resources below. Please post any questions you have in the comments and we’ll answer you there, or write to us at [email protected]. And, consider hanging this PDF one-page announcement on your class bulletin board.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Resources for Teachers and Students
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Submission Form
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The third-person narrative is often employed in narrative writing because it zooms in and out of character perspectives to describe actions, feelings, emotions, and thoughts. If you're unsure how to use the 3rd person perspective in writing, here are some tips and examples.
Writing in third person can be a simple task, with a little practice. For academic purposes, third person writing means that the writer must avoid using subjective pronouns like "I" or "you." For creative writing purposes, there are differences between third person omniscient, limited, objective, and episodically limited points of view. Choose which one fits your writing project.
By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of third-person writing and how to use it effectively in your academic work.
Learn how to write in the third person with this essential guide, featuring practical tips and examples.
Writing in third person can give your reader the unique perspective of an outsider looking. Explore these notable examples of writing in third person.
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you'd find in stories. When writing in third-person view, make sure to write in the present tense and avoid adding your own thoughts.
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you'd find in stories. In this perspective, you'd use pronouns like he, she, him, her, his, hers, himself, herself, it, them, their, and themselves. Or, you'd use a name. But that tends to happen more in stories than research ...
When a piece of writing does not assume the perspective of either the reader or the writer, it's written in the third person point of view. Third person narratives have three distinct styles, known as third person objective, third person omniscient, and third person limited omniscient. You can recognize all three of these points of view ...
Want to know how to write in third person? You'll need the third person pronouns and one of three types of narrators. Learn more in this article.
In literature, third-person point of view follows multiple characters and narrative arcs, zooming in and out of a story the way a camera does in a movie. A third-person narrator can be all-knowing (aware of every character's thoughts and feelings) or limited (focused on a single character, or aware only what certain characters say and do).
As the author of a novel, you get to decide who tells your story. Writing in the third-person point of view is like hearing an announcer call a sporting event—a narrator gives a play-by-play of the plot from an outside perspective.
"Third Person" Explained "Third person" most commonly appears in the phrases "third-person narrative," "to write in the third person," and "third-party (or -person) insurance." Third Person Narrative. A third-person narrative is a story told using the pronouns "he," "she," "it," or "they" or using nouns. In other words, the story is not told from a personal perspective. A third-person ...
Define First, Second, & Third Person: Learn the definition of the three points of view in writing with examples. When do you use the first person narrative?
Discover how to write in the third person, understand third person pronouns, and master the art of third person narrative with helpful tips and examples.
What is third-person POV? In academic writing, the use of the third-person pronouns (he/she/it and they/them) neither refer to the writer or the person being addressed. For example, in academic writing one may say "the study from the University of Pennsylvania states that 1 in 5 people have blue eyes.". On the other hand, first-person ...
The third person is frequently used in formal writing, such as research and argumentative papers. When you write in the third person, things become more impersonal and impartial. This impartiality makes the writer appear less prejudiced and, thus, more believable in academic and professional writing. The usage of the third person aids in keeping the text objective and away from subjective opinion.
When it comes to writing, the third person is one of the most commonly used points of view. This point of view allows readers to get inside the heads of multiple characters and can make stories more immersive and engaging.
Third-person writing is not only easy to learn, but highly versatile across genres. Here are tips on how to use it in fiction and nonfiction, with examples.
The third person point of view in an essay is characterized by the use of personal pronouns such as he, she, they or one rather than I, we or you. Formal essays as well as some types of informal essays are typically written in the third person. The third person can apply to single-paragraph essays as well as more common, longer essay formats.
Using third-person writing can make a world of difference in giving your essay the right tone.
First vs. Third Person First and third person are points of view. They are the perspectives from which a piece of writing is told. Different writing assignments and types use different points of view.
Third-person pronouns are words such as "she," "it," and "they" that are used to refer to other people and things that are not being directly addressed, without naming them specifically with a noun. Like first- and second-person pronouns, they are a type of personal pronoun.
Some writers find the use of first, second, or third person point of view a bit confusing while writing research papers. Since second person is avoided while writing in academic or scientific papers, the main confusion remains within first or third person.
Transition words play a key role in essay writing. They connect ideas, sentences, and paragraphs, helping readers follow your text easily. These words do many jobs, from comparing things to showing cause and effect. They turn scattered thoughts into a clear story. Learning to use transition words for essays isn't just about making your writing sound better. It's about making your ideas clearer ...
Third-person writing is when you avoid using personal pronouns and stick to possessive pronouns or possessive adjectives like "he," "she," "his," and "her" It all depends on your audience. You'd choose to write your short professional bio in the first person if you're using it for personal websites, social media profiles , and networking events.
It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group's efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone ...
We invite teenagers to tell a true story about a meaningful life experience in just 100 words. Contest dates: Nov. 6 to Dec. 4, 2024.