The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

Introduction
Smart objectives, smart career goals.
SMART goal-setting was first introduced by Dr. Edwin Locke in the 1960s (Griffin, 2017). According to Locke, setting goals that fit into the SMART criteria provided motivation and empowerment to people, which was crucial to ensure that the goals are achieved (Griffin, 2017). Today, SMART criteria are applied to the goal-setting process in many organizations, regardless of their size and area of business. The rules are universal and can also be applied to personal goals, which makes them an excellent tool for developing a career plan.
The first criterion emphasizes that goals need to be specific and relevant to the desired outcome (Joseph, 2017). Setting general goals may reduce motivation, as the path to achieving them becomes unclear (Joseph, 2017).
In order to achieve success in pursuing a goal, there has to be a way to measure success, which is why the second point of SMART goals theory is that the goals need to be measurable (Joseph, 2017). By measuring success, it is possible to monitor the progress towards the goal, which ultimately improves motivation.
The third criterion to be applied to goals is attainability. A goal that is impossible to achieve becomes a burden rather than an opportunity, as all the efforts put in by the person will not help him or her to attain the goal. If the goal is achievable, on the other hand, it is possible to devise a clear strategy to ensure that it is reached.
The next criterion emphasizes the need for the goal to be realistic, which means that a goal has to be set with consideration of the current circumstances. If the goal is set too high comparing to the current career level, reaching it will be hardly possible.
The final stage of goal-setting is ensuring that the goals are time-bound. Setting a definite time limit by which the goal has to be achieved creates a sense of urgency, which may become a substantial motivating factor.
My ultimate aim is to become a Registered Nurse. However, there are three main stages that have to be completed before I can reach the desired position.
Stage One: Graduate from Regis Health Care Administration
The first step in my career plan is to graduate from Regis College with a degree in Health Care Administration. In order to do that, I need to complete all of the program requirements and courses, which is a specific objective. The goal can be easily measured, and the result of completing the goal will be receiving a Diploma that marks the successful ending of the course. I believe that this aim is also attainable, as I am working towards completing the course and so far my grades have been acceptable. Completing this stage of the plan is realistic, as the goal is set based on my current level of education and abilities. Finally, the expected time of completion is Summer 2018, which makes the goal time-bound.
Stage Two: Enroll in an Accelerated Nursing Program
After I receive my certificate in Health Care Administration, I will need to enroll in a nursing program to continue my nursing education. I plan on applying for an accelerated nursing program at Regis, Metro, or Denver School, which is a specific objective. Acceptance into the program will be the ultimate measure of success, which means that the goal is measurable. It is also attainable and realistic, as it is the next step after I graduate from my HCA program; I am aware of the requirements of these schools and believe that I can attain the results needed for acceptance. Finally, the anticipated start of the program is in Fall 2018, which sets a specific time limit for the goal.
Stage Three: Work as an RN in Sandalwood Rehabilitation Center
The ultimate goal of my career plan is to achieve an RN position at Sandalwood Rehabilitation Center, where I currently work as a CNA. This aim is specific, as it mentions the position and place of work. The goal is also measurable, as I will know when I receive this position. The goal is attainable, as I have been successful in my work here so far and I believe that upon completion of the nursing course, I will be accepted to work as an RN. The aim is also realistic as I understand the requirements of the position and the path to achieving certification. Finally, the time limit of the goal will be estimated as soon as I complete the second stage of the plan, as it depends on the length of the nursing program that I will complete. As soon as I receive the certification, I believe it will take me up to six months to gain an RN position.
Overall, I believe that separating my career plan into three SMART goals is a useful practice to gain more understanding of how to achieve the ultimate career aim. SMART goal-setting ensures that the goals are not unrealistic, which provides more motivation to work towards the goals. I feel that my current abilities and the chosen path of development will help me to reach my final goal and to receive an RN position at Sandalwood Rehabilitation Center.
Griffin, D. (2017). The SMART goal-setting process . Web.
Joseph, C. (2017). Elements of S.M.A.R.T. goal setting . Web.
- China and UAE: Management Analysis
- Integrated Emergency Management
- The Great Grandfather of the Sandalwood Mountains
- The "Kisses from Berlin" Photo by Regis Bossu
- Expectancy and Goal-Setting Theories in Healthcare
- The Balanced Scorecard Approach Implementation
- American Distribution and Manufacturing Company's Standards
- Balanced Score Card and Gamification for Performance
- "Competing on Analytics" by Davenport
- Wall Street Journal: The Work of Ford Company
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, September 13). The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-smart-goal-setting-process/
"The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment." IvyPanda , 13 Sept. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-smart-goal-setting-process/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment'. 13 September.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment." September 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-smart-goal-setting-process/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment." September 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-smart-goal-setting-process/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment." September 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-smart-goal-setting-process/.
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Goals — The Significance of SMART Goals
The Significance of Smart Goals
- Categories: Goals Personal Goals
About this sample

Words: 629 |
Published: Jan 31, 2024
Words: 629 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Definition and explanation of smart goals, setting specific goals, measuring progress and achievements, ensuring goals are achievable, relevance of goals, setting time-bound goals, references:.
- “Importance of Goal Setting: Why Set Goals?” Mind Tools, www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newHTE_87.htm.
- Locke, Edwin A., and Gary P. Latham. A Theory of Goal Setting & Task Performance. Prentice-Hall, 1990.
- Grant, Heid“SMART Goals: Definition and Examples.” The Balance Careers, 2021, www.thebalancecareers.com/smart-goals-4760192.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 546 words
7 pages / 2995 words
1 pages / 472 words
2 pages / 911 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Goals
Success is a multifaceted concept that varies from person to person, making it a subjective experience influenced by individual goals, values, and cultural backgrounds. At its core, success refers to achieving a desired outcome [...]
Having meaningful and fulfilling relationships is a fundamental aspect of a successful and well-rounded life. As a college student, I recognize the importance of setting clear relationship goals to guide me through this [...]
Goals give direction and meaning to life, and they keep individuals motivated. The acronym SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. SMART goals are the foundation of effective goal-setting and [...]
Apple Inc. is one of the most iconic and innovative companies in the world, known for its cutting-edge technology and sleek design. From the revolutionary iPhone to the game-changing iPad, Apple has consistently set the bar high [...]
In this essay I will be looking at a number of different sources from the Bible and Christian theory to understand what is Godʼs wider mission, how I can program my work towards the young people in my local community by using [...]
Leadership has always been the core value for founding an effective military organisation. Leadership can be defined as "a process of engaging others in concerted efforts to pursue a goal, in conditions of complexity and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
How to Write SMART Goals: Examples, Step-by-Step Guide, and Free Template
By Kate Eby | January 9, 2019 (updated August 6, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In order to be effective, your goals should be SMART: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. In this guide, we’ll show you how to write effective SMART goals for professional and personal scenarios. Included in this article, you’ll find the following:
- Step-by-step guide to writing SMART goals
- Free SMART goals worksheet to get started
- How to pick the right SMART goals for your project or organization
- How to track SMART goals
- Examples of professional and personal SMART goals
What Is a SMART Goal?
A SMART goal is a framework for defining objectives, where each goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Follow this method to establish clear, attainable goals that hold you accountable to a deadline. SMART goals are useful in all professional sectors and industries, as well as in personal life (see examples of personal and professional SMART goals below). Using this framework will help ensure that you are working toward clearly defined goals that you can execute by a deadline. Additionally, the SMART framework eliminates guesswork and back-and-forth among parties. It also helps individuals and teams track progress with pre-defined success metrics.

See how Smartsheet can help you deliver on SMART goals
Smartsheet is a cloud-based platform that allows teams and organizations to plan, manage, and report on work, helping you move faster and achieve your goals. See Smartsheet in action.
Watch a free demo
How to Create a SMART Goal
| Specific | What do you want to accomplish? What specific outcome do you want to achieve? | |
| Measurable | How will you measure your success? What type of data will you include? How will you evaluate it, and how frequently will you check? | |
| Attainable | Do you have all the necessary skills and resources to achieve this goal? If not, can you obtain them? | |
| Relevant | Is this goal aligned with your other goals, or the overarching goals of your team or organization? | |
| Time-Bound | What is the timeframe for achieving this goal? |
To create a SMART goal, decide what you want to accomplish, and then address each component of the SMART acronym. Make sure that your goal centers on an outcome, not a practice or set of behaviors. A SMART goal should, in the end, achieve something. Use the chart below to see if your goal meets the SMART criteria at a high level. For a more in-depth discussion of how to write SMART goals, see our step-by-step how-to below. Though it’s important that you clearly define your goal using the method above, remember that it’s still worthwhile to brainstorm all your various ideas. Once you see all the potential options, work with your team to refine the list and create SMART goals.

How to Write SMART Goals
To write a SMART goal, simply define each component in the SMART acronym. Go in order, and ensure that your proposed goal is specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. If it doesn’t meet each of these criteria, slowly refine it until it does. Follow the step-by-step how-to below for guidance on how to write and refine your goals to ensure that they are SMART. S: Ensure Your Goal Is Specific Think about this step as the mission statement for your goal. Focus on an outcome you want to achieve, not just a set of practices you want to implement. Be as specific as possible. To do this, answer the five W questions (who, what, when, where, and why):
- Who: Consider who needs to be involved to achieve the goal. Consider appointing roles and responsibilities.
- What: Dive into the details of what you want to accomplish.
- When: Envision a general sense of the timeline you anticipate you’ll need to achieve this goal. You’ll have to be much more specific about this in the “T” section of the how-to.
- Where: This question may not always apply, especially if you’re setting personal goals, but if there’s a location or relevant event your goal is tied to, identify it here.
- Why: What is the reason for the goal? When it comes to using this method for employees, the answer will likely be along the lines of company advancement or career development.
“Define the goal as clearly as possible. Avoid vagueness which can lead to misdirection,” says Munday. M: Decide How You Will Measure Your Goal In this step, decide which metrics you will use to track your progress and to define whether or not you are successful. Doing so makes a goal more tangible because it provides a way to concretely measure progress. If your goal will take several months to complete, set some milestones tied to specific subtasks. “Ensure that the goal can be quantified or a clear indicator of progress can be identified,” says Munday. If the goal can’t be quantified, you will need to adjust it. A: Ensure Your Goal Is Attainable “Your goal should be challenging yet attainable with the available resources,” continues Munday. Look at the resources available to you — people, capital, tools, etc. — and assess whether this goal is realistic with your current means. You might also look at data on past projects to determine whether this new goal is attainable. If not, that doesn’t mean you need to abandon your goal. Simply assess the costs of investing in additional resources, or consider extending your timeline in the time-bound section below. R: Ensure That Your Goal Is Relevant to Larger Objectives In this scenario, relevance refers to how well your goal aligns to larger team or organizational initiatives. Ideally, your goal will support the other work you’re doing and serve your long-term goals in some way. If nothing else, it should not detract or divert energy away from goals you’re already committed to. T: Give Yourself a Time Limit for Accomplishing Your Goal Setting a hard deadline will help you measure progress, even if you don’t accomplish your goal in the allotted time period. Anyone can set goals, but if it lacks realistic timing, chances are you’re not going to succeed. Commit to a target date for deliverables, and ask all stakeholders whether this goal is likely to be completed in the allotted time period. If the goal will take three months to complete, it’s useful to define what should be achieved halfway through the process. Providing time constraints also creates a sense of urgency.
Microsoft Word SMART Goals Worksheet

Download a SMART Goals Template for Microsoft Word | Google Docs
When to Use: Use this worksheet to brainstorm and refine your SMART goals. Start by making an extensive list of all possibilities, and then slowly edit and refine that list in order to draft your final SMART goal.
Notable Features: The template is broken out into sections for each letter in the acronym: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Each section includes prompts that will help you brainstorm all the variables that you need to take into account. Then, you can home in on your priorities and write your finalized SMART goals.
How to Pick the Right SMART Goals
The “right” SMART goals will be in line with larger team or organizational objectives. Don’t commit to any new goal that conflicts with or counteracts an existing goal. Instead, make sure all goals align and work together to achieve organizational success. “To choose the right SMART goals, I first assess the overall objectives of the project or initiative,” says Munday of Custom Neon. “Understanding the end game allows me to reverse engineer the steps needed to get there, which I then shape into specific SMART goals. It’s crucial that each goal directly contributes to the larger objective to maintain coherence and focus throughout the project.”

Execute on SMART Goals with Project Management in Smartsheet
Once you’ve defined your SMART goals, it’s essential to put a plan in place to achieve them. To help with execution, you need a tool that enables you to plan, track, manage, automate, and report on your goals in real-time.
One such tool is Smartsheet, a work execution platform that enables enterprises and teams to get from idea to impact - fast. With a collaborative, real-time objectives tracker in Smartsheet, you can increase transparency and improve accountability across your initiatives.
Get the Team Objectives Tracker for Free
Plus, top project management leaders rely on Smartsheet to help align the right people, resources, and schedules to get work done. Use Smartsheet to create consistent project elements, increase speed, and improve collaboration with scalable options that fit individual work preferences. Hold yourself and your team accountable, improve visibility into team priorities, and ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Discover how Smartsheet can help maximize your project management efforts, today.
Try Smartsheet for Free
Examples of SMART Goals
You can write SMART goals for any professional setting or industry, as well as for your personal life. Below, you’ll find real-world examples of initiatives and how to format them as SMART goals.
Professional SMART Goal to Improve Employee Performance and Retention

Professional SMART Goal to Decrease Customer Churn Rate

Personal SMART Goal to Become a Better Leader
Jake Munday of Custom Neon wanted to improve his leadership skills and become a stronger CEO. However, he needed to focus his efforts on something tangible so the goal could be measured and the necessary actions wouldn’t be so vague. Here’s how he turned it into a SMART goal: I want to complete a leadership development course in three months, by dedicating two hours every week to study. “This goal was specific to professional growth, measurable by course completion, achievable within my weekly schedule, relevant to enhancing my leadership skills as a founder and CEO, and time-bound by a three-month period,” says Munday.
Personal SMART Goal to Increase My Business Knowledge
Lavergne of ReviewFlowz wanted to increase his business knowledge by reading more books but needed to concretize the goal. He followed the SMART formula and wrote the following SMART goal: I will increase my business knowledge by reading one business book per month for a year. “This goal was specific, measurable, achievable, relevant to my professional growth, and time-bound, helping me stay disciplined and informed,” says Lavergne. “It significantly broadened my knowledge and improved my business strategies, making me a more effective leader.” For dozens more examples of SMART goals, visit our roundup of SMART goals and examples . Additionally, check out this comprehensive guide to project management SMART goals and these examples of SMART goals for leadership .
How to Track SMART Goals
It is imperative to track SMART goals to measure your progress and assess whether or not you were successful. Because SMART goals require you to define the metrics and timeframe of each goal up front, they are relatively easy to track and report on. Below are some expert tips for tracking SMART goals:
- Ensure That the Goal Is Actually Measurable: “Make sure the goals you set out are actually measurable,” says Ugarte of London Office Space. “Have quantifiable criteria to track progress and determine when the goal has been achieved. For example, rather than aiming to ‘improve customer satisfaction,’ instead set a goal to ‘achieve a customer satisfaction score of 90 percent as measured by our end-of-service surveys.’"
- Stick to the Metrics You Defined Up Front: Part of defining a SMART goal is choosing how you will measure success. To effectively report on your performance, don’t change these metrics midway through.
- Set Up a Tracking System: Use project management software or another goal-tracking program to monitor your progress. This ensures that you have a single source of truth for all team members to refer to and will help keep you accountable to your goals. Visit our complete roundup of goal tracking templates to get started tracking your progress.
- Consistently Evaluate Your Progress: Decide how frequently you will track progress. Don’t refer to your metrics so often that it becomes its own source of stress (i.e. every day), but check often enough that you are looped into any unanticipated hangups. Consistently monitoring progress will allow you to communicate and collaborate early if things go off course.

- Reflect on and Learn from Each Round of Goals: Even if you fall short of a goal, it’s worth reflecting on it with the team. What went well, and what could have gone better? Bring those new insights to your next round of goals, and adjust criteria — such as time or resources — to hit your new goals.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Reassess and Edit Your SMART Goals: “I always make sure I've got a few sessions scheduled across a week or two to revisit my SMART goals before finalizing them,” says Mallory of Motivosity. “SMART goals are like any rough draft. The very first stab at it probably won't be the best or most elegant. Give yourself time to play around with the goals, revisiting their clarity and details and really leaving space for final tweaks.”
Establishing Clarity Around Success and Failure of Goals
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
The Ultimate Guide To S.M.A.R.T. Goals

Updated: Jul 9, 2024, 6:58am

Without concrete goals, you are essentially shooting in the dark trying to improve. S.M.A.R.T. goals are useful because they contain five aspects that help you focus and reevaluate goals as needed. This framework can be helpful for any team trying to practice effective project management . The five aspects of S.M.A.R.T. goals are that they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. We explore what S.M.A.R.T. goals are and how they can help your team.
Featured Partners
From $8 monthly per user
Zoom, LinkedIn, Adobe, Salesforce and more

On monday.com's Website
Yes, for one user and two editors
$9 per user per month
Google Drive, Slack, Tableau, Miro, Zapier and more

On Smartsheet's Website
Yes, for unlimited members
$7 per month
Slack, Microsoft Outlook, HubSpot, Salesforce, Timely, Google Drive and more

On ClickUp's Website
$9.80 per user per month
Salesforce, Adobe, Miro, Netsuite, Quickbooks, SAP

On Wrike's Website
S.M.A.R.T. Goals Defined
A S.M.A.R.T. goal is defined by its five key aspects or elements. Without all aspects, you might be goal setting but not effectively creating a plan for success. Let’s look at the five elements of S.M.A.R.T. goals.
Specific goals have a desired outcome that is clearly understood. This might be a sales number or a product rollout goal. No matter what it is, the goal should be clearly articulated so that everyone is on the same page with the objective. Define what will be accomplished and the actions to be taken to accomplish the goal.
These are the numbers used with the goal. You need to have a quantifiable objective so that you can track progress. Define what data will be used to measure the goal and set a method for collection.
Goals need to be realistic to maintain the enthusiasm to try to achieve them. Setting lofty goals is good, but you may want to break them down into smaller, bite-sized chunks. If the goal is not doable, you may need to first ramp up resources to give yourself a shot at success. Ramping up resources would likely be its own S.M.A.R.T. goal.
Goals should be aligned with the mission of the company. Don’t set goals just as an exercise for something to do. One way to determine if the goal is relevant is to define the key benefit to the organization.
Goals should have a deadline. A goal without a deadline doesn’t do much. How can you identify success or failure? This is why S.M.A.R.T. goals set a final date. This doesn’t mean that all the work is done, but it means that you can evaluate the success of the endeavor and set new goals.
Benefits of S.M.A.R.T. Goals
There are a lot of benefits to setting S.M.A.R.T. goals, which is why you should consider adding them to your business toolbox. First, a S.M.A.R.T. goal helps to give you an objective. In doing this, you can identify strengths and weaknesses. Second, a S.M.A.R.T. goal provides motivation to succeed. When you know where the goal line is, you’ll want to work to meet or beat it. Third, a good S.M.A.R.T. goal, while attainable, will also be challenging and force you out of your comfort zone. Ultimately, the S.M.A.R.T. goal is a useful tool to remain focused in attaining a goal.
Drawbacks of S.M.A.R.T. Goals
As with anything, there is a negative side to S.M.A.R.T. goals that you need to consider. By focusing on the S.MA.R.T. goal, you may overlook other areas of the business. There may be other tasks that command attention but the focus on the goal could overshadow them and leave other things undone. In addition to that, the S.M.A.R.T. goal can put a lot of pressure on people to succeed. You don’t want to set goals that people can’t achieve . It’s important to manage expectations and keep goals attainable to avoid burnout and morale issues.
Examples of S.M.A.R.T. Goals
Professional Goal: “I’m going to increase sales”
- Specific: “I am going to learn about social media marketing and invest in a social media management platform to start growing an online audience of potential customers.”
- Measurable: “The goal is to increase sales by 30% within the next quarter.”
- Achievable: “I can afford a subscription to Zoho Social, and I have a moderately successful business that can handle a large increase in customer demand.”
- Relevant: “I want to grow my sales volume so that I can buy a new vehicle for my business.”
- Time-bound: “I will subscribe to Zoho Social tomorrow and go through all of their instructional material to learn how the platform works. I will build a social media strategy and deploy it in two weeks.”
Personal Goal: “I’m going to get in shape.”
- Specific: “I am going to get at least 30 minutes of exercise three days a week and cut my caloric intake by 25%.”
- Measurable: “My goal is to lose 15 pounds within the next three months.”
- Achievable: “I already have a rowing machine and can afford to buy fresh, nutritious food for myself and my family.”
- Relevant: “I want to live a healthier lifestyle so that I feel better physically and mentally in my daily life”
- Time-bound: “I will go to the grocery store tomorrow after work and buy healthy food for the week. I will use my rowing machine for 30 minutes before cooking dinner. I will use the rower three times per week.”
How To Follow Through on Your Goals
What’s the use of having a goal if you aren’t going to follow through with it? Once you have the goals, there are a few things that you can do to ensure you stay on track and achieve them.
Write Goals Down
Take the time to write down your goals and post them somewhere that you can see them. For team goals, place them somewhere everyone can see them. If it’s just for yourself, post a note next to your computer screen with the goals. Writing goals down brings them to life and makes them real. It’s also a good reminder of what you are working on.
Share Goals With Relevant People
Sharing goals sets the tone of accountability. Share goals with your team, your supervisor or a mentor. A shared goal is a goal that comes with a commitment to work hard to achieve the goal. Make sure that you share goals with a supportive person who will encourage you to press on when things get hard.
Regularly Evaluate Progress
Check in and see how you’re doing toward your goal. If the goal is a monthly goal, you may want to have daily or weekly check-ins to see what progress has been made. This helps you redirect energy and change course if something you are doing isn’t working and you aren’t making progress. It’s better to see this sooner than later while you can still adapt with enough time to succeed.
Celebrate Wins
When you succeed, celebrate. But don’t think that you need to wait until the entire goal is achieved before you give yourself a pat on the back. If you find yourself making excellent progress during a check-in, celebrate that too. The little successes help you maintain the energy to work toward the bigger goal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is project management.
Project management uses processes, skills, tools and knowledge to complete a planned project and achieve its goals. It differs from general management because of the limited scope of a project, concrete deadlines and specific deliverables.
What does S.M.A.R.T. goal stand for?
Specific. Measurable. Achievable. Relevant. Time-Bound.
The acronym helps you remember the key aspects of a goal so that you have the best plan for success.
How do I write a goal plan?
Write a goal plan by starting with the specific goal to be measured. Establish a time frame or deadline in which you want to achieve the goal. Review what you write down to make sure it is both attainable and relevant to your overall objectives.
Why are S.M.A.R.T. goals used in performance reviews?
S.M.A.R.T. goals are a great way for managers and team members to get on the same page with expectations. Great managers work with team members to establish goals that fulfill the overall objective, but that the employee feels good about succeeding with.
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Construction Project Management Software
- Best Project Portfolio Management Software
- Best Gantt Chart Software
- Best Task Management Software
- Best Free Project Management Software
- Best Enterprise Project Management Software
- Best Kanban Software
- Best Scrum Software
- Asana Review
- Trello Review
- monday.com Review
- Smartsheet Review
- Wrike Review
- Todoist Review
- Basecamp Review
- Confluence Review
- Airtable Review
- ClickUp Review
- Monday vs. Asana
- Clickup vs. Asana
- Asana vs. Trello
- Asana vs. Jira
- Trello vs. Jira
- Monday vs. Trello
- Clickup vs. Trello
- Asana vs. Wrike
- What Is Project Management
- Project Management Methodologies
- 10 Essential Project Management Skills
- What is a Gantt Chart?
- What is a Kanban Board?
- What is a RACI Chart?
- What is Gap Analysis?
- Work Breakdown Structure Guide
- Agile vs. Waterfall Methodology
- What is a Stakeholder Analysis
- What Is An OKR?

What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Kimberlee Leonard has 22 years of experience as a freelance writer. Her work has been featured on US News and World Report, Business.com and Fit Small Business. She brings practical experience as a business owner and insurance agent to her role as a small business writer.
With over a decade of editorial experience, Rob Watts breaks down complex topics for small businesses that want to grow and succeed. His work has been featured in outlets such as Keypoint Intelligence, FitSmallBusiness and PCMag.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
SMART Goals and Objectives: Definition, Characteristics, and Examples

Setting SMART objectives and goals is an important step toward success in both personal and professional life. However, merely stating goals or purpose is insufficient; it must be SMART goal. SMART objectives and goals assist you in developing objectives that are clear, specified, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
In this article, we’ll define SMART objectives and goals, describe their qualities, and present examples to help you understand how to use them.
Content Index
What are SMART goals and objectives?
What does s.m.a.r.t. stand for, why should you clearly define smart goals and objectives, management by objectives (mbo).
- Principles in setting up SMART Goals and Objectives
- What is the Difference between Smart Goals and Objectives?
- Importance of SMART Goals and Objectives
- Advantages and disadvantage of SMART goals and objectives
- SMART Objectives and Goals Examples
SMART goals and objectives are a method for establishing Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound aims. The SMART framework defines goals and objectives clearly and practically, making them more actionable and increasing the likelihood of success. SMART is an acronym that stands for SMART goal and is used to help in goal setting.
In this modern, technology-driven world, one of the most widely used words is “SMART.”
This word is utilized in many industries due to its efficiency and objectivity. The SMART technique is also a practical tool that can save relevant professionals in competitive industries like marketing, sales, advertising, market research, etc.
Smartphones, smart TVs, and other everyday items have this word prefixed to their names. We now realize that term refers to something intelligent due to its operation and technological progress.
More than just Theory: 300+ Ready-Made Survey Templates to evaluate your SMART goal and objective.
Take a few minutes to clear your head; let us analyze the SMART method to achieve SMART objectives and goals. With constant practice, it will be easier to apply this method. However, for starters, let us understand what each alphabet in the word “SMART” mean.
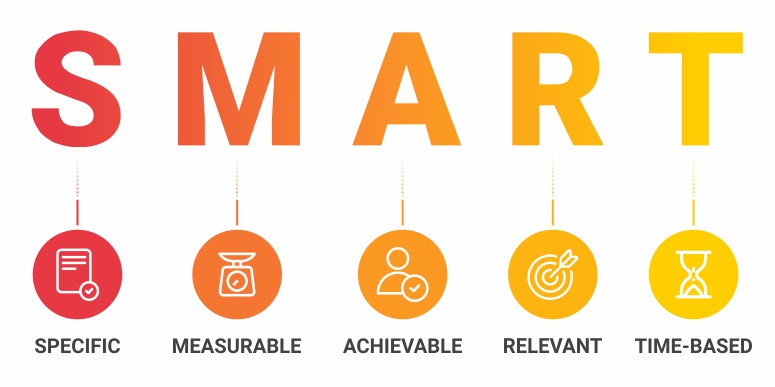
M-MEASURABLE
A-achievable, t-time-based.
Do you know what the importance of clearly defining objectives and goals is?
- Time doesn’t pass in vain for anyone, more importantly, not for organizations or businesses. Every minute, every second, a new idea is conceptualized, and with these ideas growing, there is a growing competition out there.
- Every day there is a new organization or business ready to give tough competition to its counterparts and competitors. In this competitive atmosphere, it is also essential to win customers and also understand customer satisfaction levels. Not only this, you have to constantly monitor to verify that every department in your business or organization is working efficiently, just like perfect machinery.
- It may sound like a tedious process in which one question leads you to more questions , and then it seems like a never-ending story because only some know how to land their thoughts. Remember, putting down your goals and objectives on paper will help you put your thoughts and your imagination to work in reality.
To summarize it in a concise and very significant sentence: walking without objectives is like navigating without a compass.
Imagine the immensity of the open sea and you in the middle of it, it is a moment in which you do not know what to do, nor do you know the resources you can count on and much less know which side of the ocean or sea will be better to go.
The best thing is to start making some kind of effort to move forward, right? You cannot stay there; however, it is difficult to know at that stage if everything you do will have optimal results and bring you closer to the right path.
The most likely thing is that these efforts might exhaust you, and you do not know if everything you did will be worthwhile for something. On the contrary, if you know the goal you should reach, it will be easier to use your energy to achieve it once and for all.
People, groups, and systems need clear, structured, and well-defined objectives from the particular to the general. setting a goal is stated to gain a clear understanding of what needs to be delivered, and the person assessing may then judge the outcome based on defined smart criteria.
The same happens with the objectives of a company. We all have an end to this life, and we cannot get up every day thinking about facing when we are approaching the end because, in this way, there will come a time when we feel that we are not doing enough to sustain ourselves in this world.
Learn more: Demographic Segmentation .
SMART objectives are a primary way to collect feedback and communicate within the organization. SMART goal and objective is directly derived from management by objectives (M.B.O.). It was an effective way of completing tasks by prioritizing objectives.
Feedback is important because it showcases the room for improvement and is an insight into the company. Feedback includes periodic checks to measure current results vs. expected and current results vs. end objectives. The progress can be recorded by asking basic questions like:
- Is the plan being executed in the right manner?
- Are the efforts tangible that they are aiding the progress of the project?
- Are changes required to be made to the current plan?
The SMART objective helps break down these questions and goals even further, where the scope of every milestone is measured. The SMART objective help set goals and track progress to meet the end objective.
A SMART goal helps in following through on goals and prevents getting distracted. Through these goals, different objective goals can be set up, namely:
Long term goals
Intermediate-term goals, short term goals, principles in setting up smart goals and objectives.
It is an essential task to write SMART goals and objectives and setting up them. The smart goal criteria or the principles of goal-setting theory are:

Task complexity
What is the difference between smart goals and smart objectives.
“SMART goals” and “SMART objectives” are frequently used interchangeably, although their meanings might vary depending on the context. However, in some circumstances, a difference can be made between the two. Let us analyze the distinction:
- Goals are broad, all-encompassing statements that describe the desired outcome or result. They are frequently long-term and give a general framework for your activities.
- These goals are clear, measurable, doable, important, and have deadlines. They use the SMART goal framework to ensure their goals are clear and improve their chances of success.
- Goals concentrate on the “what” you want to accomplish and provide a precise aim to work toward.
SMART Objective
- Objectives are more defined, short-term milestones that help to reach the overall aim. They are actionable steps that explain the actions and activities needed to achieve the intended result.
- SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They are intended to be more specific and to provide a clear roadmap for attaining the goal.
- SMART Objectives concentrate on the “how” and “when” of achieving a goal, breaking it into achievable steps.
Importance of SMART goals and objectives
SMART goals and objectives are highly important for individuals and organizations alike. Here are several reasons why they are crucial:
Clarifies end objective
Effective time management, reminds you of priorities, obliges to take action, advantages and disadvantages of smart goals and objectives.
SMART goals and objectives offer several advantages, but they also have some potential disadvantages. Let’s explore both sides:
Advantages of SMART goals and objectives
SMART goals and objectives have several advantages that make them effective. Some of the primary advantages are as follows:
They are not vague: Since SMART goals and objectives are extremely procedural, each milestone and feedback is planned and monitored in complete detail. It mitigates the factor of uncertainty.
Missed work is easy to track: Each person is given a specific responsibility; hence, when work is not completed, it is very easy to troubleshoot the gaps in delivery. It makes everyone extremely accountable, and any loss of work is easy to track.
Goals are divided into small achievable objectives: SMART goals have an end, but SMART objectives are further divided into bite-sized milestones. Hence, no matter the scale of the end goal, it is very easily achievable.
Disadvantages of SMART goals and objectives
SMART goals and objectives have several disadvantages that make them effective. Some of the primary disadvantages are as follows:
No importance to other tasks: All other work gets ignored due to the system’s rigidity. Also, there is lesser scope for innovation or trying to complete work differently because the work is milestone based.
Lots of pressure: There is immense pressure to complete work in a given time frame, making the environment extremely stressful and challenging.
Different interpretations by different people: The pressure to complete goals and objectives is open to interpretation by different people. The urgency or rigidity of the process is construed differently by different people.
LEARN ABOUT: Theoretical Research
SMART objectives and goals examples
Here are a few examples to help you strategize and define your organization’s SMART objectives and Goals :
- Defining objectives requires time, patience, and the complete know-how of how an organization functions, but it needs clarity above anything else. For example, many organizations need to define clear objectives, which reflects in many ways. But with SMART objectives and methods, it is possible to define goals clearly.
- To clearly define objectives, one may need to sit down and ask questions, for example, “What is that I would like my organization or business to achieve? Why do I want to achieve these targets? Do I have the necessary resources to achieve these objectives?”, among many other questions that you need to ask yourself, let’s accept it feel like this is boring and absolutely unnecessary.
- Take a step back and think, do you even know how many companies have suffered bankruptcy because they didn’t feel the need to define their objectives? You might even be tempted to think that the process is a complete waste of your time. Instead of wasting your valuable time speculating and penning down your thoughts, it is advisable to get down to do some real work and start with the action plan.
- While you may have decided to start functioning without a plan, there are hundreds of companies that take the target date to do it step by step and then achieve goals in a faster way, winning customers, reducing customer churn , taking away place, and even unseat everything you have already achieved. Taking action concretely and clearly understanding facts and figures will not take you anywhere. On the contrary, this will waste your time, effort, work, quality, and even your reputation in the market.
- To avoid all the tragedies previously reported, do you still think this is a waste of time? Do you still believe that it is better to postpone it? If your answer is NO, congratulations! The SMART method is easier than you imagined it to be.
Learn more: Customer Satisfaction Surveys
Let us take an example to understand how SMART objectives and SMART goals help save time. Image an organization that works to remove plastic bags and similar waste from the entire city has objectives and goals defined as:
“Our goal is to make the entire city clean and free of any plastic and plastic waste.”
This goal is a little vague. However, if the objective and goal were rewritten as, “As an organization, we aim to clean the city and make it free from any plastic waste in the next two years with the help and support of our volunteers.”
The second time the goal and objective were rewritten, it had a particular timeline, the specific activity was mentioned, who would be helping the organization was clear, and what they wanted to achieve was certain.
In this manner, people who are associated with the organization know what their tasks are and what the time-bound in which they need to achieve them. This helps avoid any confusion, and activities go on smoothly without hesitation.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
SMART objectives and Goals are an important part of a company’s growth. The Managers and Directors of Marketing, Sales, Human Resources, and many other areas must be fully involved in defining these goals.
For all, the growth of the company also implies personal growth. The only way to achieve this is by having order and structure clearly defining the objectives.
Do not waste more time doing actions that won’t yield the desired results. Start defining your SMART objectives and give your team enough reasons why they should get down to work as soon as possible.
Giving them a good goal is part of the motivation everyone in the organization needs. Remember increasing team productivity is always favorable and does wonders for achieving the organization’s overall growth.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer Experience Lessons from 13,000 Feet — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Aug 20, 2024

Insight: Definition & meaning, types and examples
Aug 19, 2024

Employee Loyalty: Strategies for Long-Term Business Success
Jotform vs SurveyMonkey: Which Is Best in 2024
Aug 15, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
SMART Goals
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely
What are SMART Goals?
Goals are part of every aspect of business/life and provide a sense of direction, motivation , a clear focus , and clarify importance. By setting goals, you are providing yourself with a target to aim for. A SMART goal is used to help guide goal setting. SMART is an acronym that stands for S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R ealistic, and T imely. Therefore, a SMART goal incorporates all of these criteria to help focus your efforts and increase the chances of achieving your goal.

SMART goals are:
- S pecific: Well defined, clear, and unambiguous
- M easurable: With specific criteria that measure your progress toward the accomplishment of the goal
- A chievable: Attainable and not impossible to achieve
- R ealistic: Within reach, realistic, and relevant to your life purpose
- T imely: With a clearly defined timeline, including a starting date and a target date. The purpose is to create urgency.
Specific SMART Goals
Goals that are specific have a significantly greater chance of being accomplished. To make a goal specific, the five “W” questions must be considered:
- Who: Who is involved in this goal?
- What: What do I want to accomplish?
- Where: Where is this goal to be achieved?
- When: When do I want to achieve this goal?
- Why: Why do I want to achieve this goal?
For example, a general goal would be “I want to get in shape.” A more specific goal would be “I want to obtain a gym membership at my local community center and work out four days a week to be healthier.”
Measurable SMART Goals
A SMART goal must have criteria for measuring progress. If there are no criteria, you will not be able to determine your progress and if you are on track to reach your goal. To make a goal measurable, ask yourself:
- How many/much?
- How do I know if I have reached my goal?
- What is my indicator of progress?
For example, building on the specific goal above: I want to obtain a gym membership at my local community center and work out four days a week to be healthier. Every week, I will aim to lose one pound of body fat.
Achievable SMART Goals
A SMART goal must be achievable and attainable. This will help you figure out ways you can realize that goal and work towards it. The achievability of the goal should be stretched to make you feel challenged, but defined well enough that you can actually achieve it. Ask yourself:
- Do I have the resources and capabilities to achieve the goal? If not, what am I missing?
- Have others done it successfully before?
Realistic SMART Goals
A SMART goal must be realistic in that the goal can be realistically achieved given the available resources and time. A SMART goal is likely realistic if you believe that it can be accomplished. Ask yourself:
- Is the goal realistic and within reach?
- Is the goal reachable, given the time and resources?
- Are you able to commit to achieving the goal?
Timely SMART Goals
A SMART goal must be time-bound in that it has a start and finish date. If the goal is not time-constrained, there will be no sense of urgency and, therefore, less motivation to achieve the goal. Ask yourself:
- Does my goal have a deadline?
- By when do you want to achieve your goal?
For example, building on the goal above: On August 1, I will obtain a gym membership at my local community center. In order to be healthier, I will work out four days a week. Every week, I will aim to lose one pound of body fat. By the end of August, I will have realized my goal if I lose four pounds of fat over the course of the month.
The Importance of SMART Goal Setting
Often, individuals or businesses will set themselves up for failure by setting general and unrealistic goals such as “I want to be the best at X.” This goal is vague, with no sense of direction.
SMART goals set you up for success by making goals specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and timely. The SMART method helps push you further, gives you a sense of direction, and helps you organize and reach your goals.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading this guide to SMART Goal-setting in business. Below are additional free resources from CFI, the global provider of financial analyst certification courses.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Time Management
- Leadership Traits
- Eisenhower Matrix
- See all management & strategy resources

- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
SMART Goals in Education: Importance, Benefits, Limitations

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
The SMART Goals framework is an acronym-based framework used in education to help students set clear and structured goals related to their learning.
The framework stands for:
- Specific – The goal is clear and has a closed-ended statement of exactly what will be achieved.
- Measurable – The goal can be measured either quantitatively (e.g. earning 80% in an exam) or qualitatively (e.g. receiving positive feedback from a teacher).
- Achievable – The goal is not too hard and can reasonably be met with some effort and within the set timeframe.
- Relevant – The goal is relevant to the student’s learning and development.
- Time-Based – A clear timeframe is set to keep you on task.
(If you’re a teacher, you might prefer to read my article on goals for teachers ).
The SMART Goals Framework in Education

The framework has had multiple variations over time. However, the most common framework is in the format: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based.
1. Specific
Your goal needs to be specific. This means that you need to note a clear target to aspire toward rather than something that is vague.
For students, this is important to clarify exactly what it is you’re aiming for.
Some strategies for making sure your goal is specific include:
- State what, when, where, why, and how your goals will be achieved
- State what the goal will look like when it is achieved
- Focus on the “vital few” [1] things that you want to see done to have your goal achieved
Sometimes, this may also be stated as “strategic” rather than “specific”.
| Improve my English Speaking Skills | |
| Reach C1 Level in English Speaking on the IELTS test by May next year. |
See our in-depth article on examples of specific goals for students to get more ideas!
2. Measurable
Your goal needs to be measurable. This ensures that you can identify improvements from the baseline as well as know when the goal has been met.
Your objectives can be formative, summative, or a mix of both.
A formative assessment is an assessment that takes place part-way through the project. It assesses where you’re at and how much more you need to do. Formative assessments allow you to pivot and make small adjustments to your action to make sure you meet the final goal.
A summative assessment is an assessment at the end of the project to see if you met your goal. This is the final measure of success or failure.
A measurable goal may also be qualitative or quantitative.
A quantitative goal will have a grade or numerative evaluation, such as 80% on a test.
A qualitative goal will be based on a subjective evaluation, such as getting a positive report card from a mentor, or, attaining the confidence to do a public speech.
| Become a good academic writer. | |
| Gain an A grade on a college paper by the end of next semester. |
See our in-depth article on examples of measurable goals for students to get more ideas!
3. Attainable
Your goal needs to be attainable. This means that it can’t be something that’s impossible to achieve. You need to know you’ll be able to reach your goals in order to sustain motivation.
This could be compared to the goldilocks principle . Goldilocks didn’t like porridge that was too cold or too hot. It had to be just right.
In education, we use the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) to explain how to promote student development and motivation. The ZPD refers to learnable content that is not too easy and not too hard.
In this zone, students can do tasks with the support of teachers and have the motivation to work because they know the content is attainable with some effort.
| To learn the Spanish language in 7 days. | |
| To be able to recite the top 10 Spanish verbs from memory within 7 days. |

4. Relevant
Often also written as ‘realistic’, a relevant goal is one that makes sense to your situation. If you are setting goals in your class, your teacher would expect that the goal was about your education and not something irrelevant to class.
Your goal should also be one that is consistent with your life plan and will help you get to where you need to be. This will help you to sustain motivation and ensure the goal makes sense in the long term.
While having personal goals unrelated to your coursework is great, it’s not relevant to the lesson that you’re doing within the class on the day, so remember to set your goal so it’s related to your learning.
| To beat Level 7 of my video game on the weekend. | |
| To get an A+ on my Geography paper so I can sustain a GPA above 3.0. |
5. Time-Based
Setting a time by which you want to meet your goals helps to keep you on track and accountable to yourself. Without time-based end goals, you may delay your goals and lose momentum.
You can also set intermittent milestones to help keep yourself on track. This can ensure you don’t let other shorter-term and more pressing tasks get in the way and get you off track.
| To graduate from university. | |
| To complete 4 courses per semester and graduate from the university by November next year. |
SMARTER Goals Add-On
Some scholars have provided additional steps to the framework. One common one is to add ‘ER’ [2] :
6. Exciting
You are more likely to achieve a goal if you make it exciting. This will motivate you to carry out your plan.
An example of excitement added to a goal would be to create some self-rewards if it is completed, like “If I complete the goal I will take myself out for dinner.”
The ‘E’ is also often added when the goals are for teachers or leaders who are setting goals for their students or staff. By making the goal exciting, they’ll be able to get buy-in from students and staff.
7. Recorded
The ‘R’ often stands for ‘Recorded’ and asks you to show how you are going to record progress.
This one is somewhat similar to ‘Measurable’ but expands on it by asking not only how you’re going to measure success, but how are you going to record progress. Keeping a journal, for example, can help you record progress and reflect on the process of chasing your coals.
The Importance of SMART Goals in Education
Goal setting helps students and teachers to develop a vision for self-improvement . Without clear goals, there is no clear and agreed-upon direction for learning.
For this reason, goals have been used extensively in education. Examples include:
- Curriculum outcomes
- Developmental milestones
- Standardized testing
- Summative and formative assessments
The SMART framework, however, tends to be a student-led way of setting goals. It enables students to reflect on what they want to achieve and plan how to achieve these goals.
As a result, the framework doesn’t just help students articulate what they want out of their education. It also provides a range of soft skills for students such as:
- Motivation for growth
- Reflective practice
- Self Evaluation
- Structured analytical thinking
Read Also: Examples of SMART Goals for Students
SMART Goals Advantages and Disadvantages
Benefits of smart goals.
The SMART framework is widely used because it helps students to clarify their goals and how they are going to go about achieving them. Often, students start with a vague statement of intention, but by the end of the session, they have fleshed out their goals using the SMART template.
Some benefits of the template include:
| Students are given a framework to flesh out their goals and clarify them in their own minds. | |
| When using the framework, students can identify problems they may face, such as whether their timeframe is realistic or whether they have been specific enough. | |
| The framework can be understood and implemented within a single lesson. | |
| The framework isn’t only used for students but also in a wide range of other fields such as business, teaching, and leadership. | |
| There are many different iterations of the SMART framework (such as SMARTER) which can be used if the most common framework isn’t quite right in your situation. |
Limitations of SMART Goals
While the framework is easy to use and implement, it does face a few limitations. One major downside is that it doesn’t account for the importance of incrementalism in self-improvement. Students need to break down their goals into a series of milestones.
Some limitations of the template include:
| There is no clear consensus over what the ‘correct’ S.M.A.R.T acronym is. For example, sometimes the ‘R’ is realistic and other times it is relevant. Sometimes the ‘A’ is attainable and other times it is assignable. | |
| Goal setting should involve a series of short, medium, and that build upon one another. | |
| Other self-development frameworks such as the SWOT Analysis provide a stronger focus on barriers to success (both internal and external – see our list of ). By looking at barriers to success, you can predict them and work to mitigate their effects. |
SMART Goals Template
Get the Google Docs Template Here
SMART goals help students to reflect on what they want from their education and how to achieve it. They provide a template and framework for students to go into more depth about their goals so they are not simply vague statements, but rather actionable statements of intent.
A lesson where you get your students to set out their goals will often have students leaving the class with a much deeper understanding of what they want out of their education and how they might go about getting it.
Read Also: A List of Long-Term Goals for Students and A List of Short-Term Goals for Students
[1] O’Neil, J. and Conzemius, A. (2006). The Power of SMART Goals: Using Goals to Improve Student Learning . London: Solution Tree Press.
[2] Yemm, G. (2013). Essential Guide to Leading Your Team: How to Set Goals, Measure Performance and Reward Talent . Melbourne: Pearson Education. pp. 37–39.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Green Flags in a Relationship
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Signs you're Burnt Out, Not Lazy
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Toxic Things Parents Say to their Children
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Red Flags Early in a Relationship
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- eLearning Platform
- eLearning Content
- Access 800 Courses on our Platform
- Bespoke eLearning
- Our Pricing
- Request a Demo
- Content Partnerships
- Whitepapers
- Most Popular Blogs
- Personal Learning Journeys
- Training Feedback Form
- Training Needs Analysis Template
- Personal Development Plan Template
- Learning and Development Strategy
- Talent Management Strategy
- Kirkpatrick Evaluation Model
- Microlearning
- Informal Learning
- 70 20 10 Learning
Home » Blog » How To Write SMART Learning Objectives & Outcomes
How To Write SMART Learning Objectives & Outcomes

As a methodology first created for business management, SMART has since been adapted across numerous fields, including education. SMART objectives offer a structured framework to help educators design effective learning goals that are clear, focused, and reachable. They ensure that learners can understand what is expected from them, fostering a more efficient and meaningful learning experience.

What are SMART Learning Objectives?
The SMART framework breaks down learning objectives into five key characteristics: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Each characteristic plays a pivotal role in creating a comprehensive learning goal that is practical, attainable, and aligned with overall educational targets.
George T. Doran first proposed the SMART framework in the November 1981 issue of Management Review . In his initial formulation, Doran’s A stood for “assignable,” meaning a task that can meaningfully be given to a specified individual. His R stood for “realistic,” a concept now captured by the latter-day “achievable” component.
In its current form, the framework offers a set of criteria that can be applied to any learning methodology to ensure that its content and assessment systems are fit for purpose.

The learning objective should be well-defined, clear, and unambiguous. Instead of setting a broad or generic goal, educators should aim to specify what the learner will achieve upon successful completion of the course or lesson.
Another way to think of this is to consider what the learner will be able to do or understand, having completed the course, that they couldn’t have done or understood beforehand. How will it change their work life, skillset, or understanding?

The objective must include criteria for measuring progress and outcome. This ensures that the learner’s progress can be tracked, and the effectiveness of the learning process can be evaluated.
With eLearning content , there are numerous ways to measure progress and comprehension, including completion percentages, internal quizzes, and final assessments. Various interactive tools allow for gamifying the process of measurement with puzzles and challenges that can be inserted into the course material to maintain interest and gauge understanding.

The learning objective should be realistic and attainable. While ambitious goals can be motivational, they should not be so challenging as to be unattainable, which might lead to frustration or discouragement.
Stepped courses with modules for complete beginners, intermediate-level learners and experts can help ensure that the student completes a course at a level they can manage. Courses should avoid being too lengthy or complicated, or the end goal can begin to seem unreachable.
Break down your course materials into slides, lessons, and modules to motivate students to persist, and reward completion stages with badges, congratulations, or other markers of success.

The objective should align with the learner’s broader educational or professional goals, ensuring the learning process is meaningful and applicable to their overall development. This is particularly important in mandatory training courses such as fire and safety training, first aid or DEI courses.
By tailoring courses to the day-to-day situations your students and employees will face, you will increase engagement.
If a course has an in-person element, make sure it incorporates time for students to discuss how each lesson relates to their own life or work. Lively discussions will follow, and the relevance of the topic will hit home.

Each objective should have a defined timeline, offering a clear deadline for when the learning goal should be achieved. This enhances motivation and allows progress tracking over time.
Run many trials of your courses and time how long it takes the average student to complete the various modules, then tweak the content and design accordingly. Experience has shown that an individual module should take no longer than 15 minutes to complete.
Another good idea is to give students a realistic notion of how long each part of the course will take to finish. This will allow them to allocate sufficient time for completion, without having to interrupt their flow.

Step-by-Step Guide to Writing SMART Learning Objectives
Creating SMART learning objectives involves six critical steps – an initial definitional stage and then one step for each concept in the SMART framework. By following these steps methodically, you’ll ensure your courses are well-designed and fit for purpose.
Step 1: Identify Desired Outcome(s)
Before setting an objective, identify the desired learning outcomes of the lesson or course. What should learners know or be able to do by the end? It’s a good idea to specify this up front to set expectations.
When you’ve devised the course, you can run tests and examine the achieved outcomes. Do they match your intentions when designing the course? If not, a rethink may be required.
Step 2: Be Specific
Use action verbs to precisely define what the learner will achieve. Clearly state the scope of the objective to eliminate ambiguity.
Here’s an example of a poorly written course objective:
“Students will gain an understanding of the basics of social media marketing.”
And here’s that objective written with more specificity (with action verbs in bold):
“Students will appreciate the different audiences of Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and TikTok, understand the marketing objectives that can be achieved using each one, and will practise using some marketing techniques to make best use of each medium.”
Step 3: Ensure Objectives are Measurable
Define clear, quantifiable criteria to evaluate progress and success. You might establish various methods of assessment, including quizzes, projects, or discussions.
Be very transparent upfront about what constitutes an excellent, good, or acceptable “pass mark.” While some courses pass or fail only (driver’s tests, for example), others have gradations of achievement.
It can be difficult to quantify comprehension of a complex topic with multiple choice questions, so if it is vital that students gain an in-depth knowledge of a complex subject, then it is better to include a project, in-person assessment or written essay.
Without some sort of measurable outcome, there’s a danger students can complete courses as “lip service” to the notion of education, without really learning anything.
Step 4: Ensure Objectives are Achievable
Consider the resources available and the learners’ current capabilities when setting objectives. This ensures that the goals are challenging but within reach.
It can be helpful to run a “pre-assessment” test or questionnaire to gauge current comprehension level. If you do so, make sure you stress that there is no good or bad level of achievement; you are simply trying to identify a place to begin.
Match your course materials to the age, reading level and/or educational level of your students. Don’t use overly complicated language when simpler terms will do.
Step 5: Ensure Objectives are Relevant/Personalised
Align the learning objectives with the overall goals of the course and the individual learner’s needs. This ensures the learning process is valuable and beneficial for the learner.
Online systems allow for a high degree of learning personalisation of courses, including offering modules in a range of languages or including various optional extras.
As well as making the course content fit students’ needs, you need to make sure the outcomes match what they’ll be able to use in their employment or day-to-day lives.
For instance, if you were teaching a course in beer-making in a microbrewery setting, but most of your students were likely to work in commercial breweries, it would be wise to tailor the outcomes to include those very different environments.
Step 6: Establish Deadlines/Timeframes
Set clear deadlines for each objective. Balance the time constraints with the scope of the objective to ensure it’s feasible within the given timeframe. This may involve a degree of trial and error as you’re designing the course.
There’s little more frustrating than being told a course must be completed in one hour, only to find that its quizzes are so lengthy and challenging that it takes twice as long to finish.

Examples of SMART Learning Objectives
Here are examples of SMART objectives in different settings:
Classroom Setting
“In this semester, students will improve their writing skills by composing and revising at least three essays, with each essay receiving a score of 70% or higher.”
Note that there is room for variation in this objective – some students may complete three essays while others may do more. 70% is an ambitious but not unrealistic goal if your student intake has been pre-selected for basic literacy.
Online Courses
“By the end of this 20-hour online photography course, participants will produce a portfolio of ten high-quality photographs demonstrating mastery of advanced lighting techniques.”
This course may use advanced photo analytics to judge whether specific lessons about dynamic range, composition, colour, focus and subject choice have been adhered to and demonstrated.
What’s especially good about this objective is that it specifies the completion time (20 hours) and work volume (ten photos) very precisely.
Professional Development
“Within six months, team members will complete an advanced project management course, implement new strategies in their work, and show a 20% decrease in project overruns.”
Although the 20% overrun reduction may prove ambitious, it’s likely that the course organisers have researched the difference between the effect on deadlines of trained versus untrained teams.
“Within six months” is time-bound, but allows some wriggle room, for learners who can complete their coursework more quickly. The objective promises real professional and personal development.
Each of the above examples is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.

Benefits of Using SMART Learning Objectives
Enhanced focus and clarity.
SMART objectives provide clear and concise goals, aiding learners in understanding exactly what is expected. They ensure that a higher percentage of learners engage with course materials and see courses through to completion.
Improved Measurement and Assessment
Because they’re measurable, SMART objectives make progress tracking and outcome assessment easier and more effective. It becomes easier to demonstrate the efficacy of a course, and to identify places where materials can be improved in future iterations.
Increased Motivation and Engagement
Achievable and time-bound objectives motivate and engage learners by providing clear goals and a sense of urgency. They can foster a spirit of friendly rivalry too, as team members compete with one another to gain the best completion scores.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing SMART Objectives
Here are some of the frequent pitfalls course creators face:
- Avoid vague or overly broad objectives that fail to clearly state what is expected from the learner. These will not inspire excitement and may lead to students feeling adrift as they work through the course materials.
- Avoid objectives without measurable criteria that offer no way to evaluate success. Neither the course creator nor the student is well-served by a course with no objective measure of achievement.
- Avoid irrelevant content that students won’t be able to incorporate within their lives or working environment. If elements add to completion time but don’t contribute to course objectives, the content should be left out.
- Lastly, steer clear of unattainable or unrealistic goals that may frustrate or discourage learners. This will reduce engagement and can cause you to receive poor reviews of your courses.

Strategies for Implementing and Monitoring SMART Objectives
Methods for effective implementation include:
- Incorporating objectives into lesson planning and making sure they are at the forefront when designing a course.
- Tracking progress and adjusting as necessary. Run numerous trials of your courses in the design stage, including participants at various levels of prior subject knowledge.
- Providing regular feedback and support to learners. Take stock at various points during your course, either with recaps (for an online course) or in-person discussions of “what we’ve learned so far.” This helps learners feel they’re keeping up.
SMART is Objectively Better
Creating SMART learning objectives plays an important role in enhancing educational effectiveness. It enables learners to understand expectations, focus their efforts, and measure their progress.
As an eLearning company , Skillshub is committed to creating efficient and impactful learning experiences.
We incorporate these principles into our learning modules, providing a well-rounded eLearning platform and approach that caters to each learner’s unique needs and abilities.
Join us today to elevate your learning experience!

Sean McPheat
Sean is the CEO of Skillshub. He’s a published author and has been featured on CNN, BBC and ITV as a leading authority in the learning and development industry. Sean is responsible for the vision and strategy at Skillshub, helping to ensure innovation within the company.
Learn How To Create Personal Learning Journeys For FREE!
Updated on: 6 September, 2023
Would your connections like this too? Please share.

You might also be interested in…

How To Transform Existing Content into Engaging eLearning

The Impact of Return To Work on UK Employees

10 Essential Elements for a Winning L&D Strategy

Refining Healthcare Through Health eLearning

13 Strategies for Enhancing Training & Development in Your Organisation

Pedagogy vs Andragogy: What’s the Difference for Learning Strategies?
- elearning Content
- Virtual Training
- Get In Touch

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer

How to write SMART goals
It’s easier to succeed when you have clearly defined objectives that are based in reality.
Get stories about tech and teams in your inbox
5-second summary
- Teams often fall short of meeting their goals due to a lack of consensus on the definition of success.
- SMART goals use a specific set of criteria to help ensure that objectives are clearly defined and attainable within a certain timeframe.
- Working through each step of creating a SMART goal can reveal instances where priorities and resources are out of alignment.
Meet Jane. She’s a product manager at a mid-sized tech company – let’s call it Techfirm, Inc. Jane has been tasked with increasing usage of Techfirm’s mobile app.
She knows she’ll need all hands on deck to make this happen, but when Jane has set team-wide goals in the past, they’ve quickly fallen off track. Nobody seemed to have a clear understanding of what success should look like; progress wasn’t monitored closely enough, and inevitably, that important objective slipped to the back burner (before toppling off the stove entirely).
That’s why, this time around, Jane plans to leverage SMART goals for setting an action plan and staying the course.
Want to get started right now?
Use our template to define the different components of your SMART goal.
What are SMART goals?
The SMART in SMART goals stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound.
Defining these parameters as they pertain to your goal helps ensure that your objectives are attainable within a certain time frame. This approach eliminates generalities and guesswork, sets a clear timeline, and makes it easier to track progress and identify missed milestones.
An example of a SMART-goal statement might look like this: Our goal is to [quantifiable objective] by [timeframe or deadline]. [Key players or teams] will accomplish this goal by [what steps you’ll take to achieve the goal]. Accomplishing this goal will [result or benefit].
Let’s use Jane’s objective to work through each component.
S: Specific
In order for a goal to be effective, it needs to be specific. A specific goal answers questions like:
- What needs to be accomplished?
- Who’s responsible for it?
- What steps need to be taken to achieve it?
Thinking through these questions helps get to the heart of what you’re aiming for. Here’s an example of a specific goal Jane might come up with:
Grow the number of monthly users of Techfirm’s mobile app by optimizing our app-store listing and creating targeted social media campaigns.
M: Measurable

Don’t underestimate the outsized impact of short-term goals
Specificity is a solid start, but quantifying your goals (that is, making sure they’re measurable) makes it easier to track progress and know when you’ve reached the finish line.
Jane and her product team want to grow the number of their mobile app users – but by how much? If they get even one new signup, that’s technically positive growth – so does that mean they’re done? Same goes for their strategy – how many platforms will they advertise on?
To make this SMART objective more impactful, Jane should incorporate measurable, trackable benchmarks.
Increase the number of monthly users of Techfirm’s mobile app by 1,000 by optimizing our app-store listing and creating targeted social media campaigns for four social media platforms: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
A: Achievable
This is the point in the process when you give yourself a serious reality check. Goals should be realistic – not pedestals from which you inevitably tumble. Ask yourself: is your objective something your team can reasonably accomplish?
Jane might look at her goal and realize that, given her small team and their heavy workload, creating ad campaigns for four social platforms might be biting off more than they can chew. She decides to scale back to the three social networks where she’s most likely to find new clients.
Increase the number of monthly users of Techfirm’s mobile app by 1,000 by optimizing our app-store listing and creating targeted social media campaigns for three social media platforms: Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Safeguarding the achievability of your goal is much easier when you’re the one setting it. However, that’s not always the case. When goals are handed down from elsewhere, make sure to communicate any restraints you may be working under. Even if you can’t shift the end goal, at least you can make your position (and any potential roadblocks) known up-front.
R: Relevant
Here’s where you need to think about the big picture. Why are you setting the goal that you’re setting? Jane knows that the app is a huge driver of customer loyalty, and that an uptick in their app usage could mean big things for the company’s bottom-line revenue goals. Now she revises her statement to reflect that context.
Grow the number of monthly users of Techfirm’s mobile app by 1,000 by optimizing our app-store listing and creating targeted social media campaigns for three social media platforms: Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Because mobile users tend to use our product longer, growing our app usage will ultimately increase profitability.
T: Time-bound
To properly measure success, you and your team need to be on the same page about when a goal has been reached. What’s your time horizon? When will the team start creating and implementing the tasks they’ve identified? When will they finish?
SMART goals should have time-related parameters built in, so everybody knows how to stay on track within a designated time frame.
When Jane incorporates those dates, her SMART goal is complete.
Grow the number of monthly users of Techfirm’s mobile app by 1,000 within Q1 of 2022. This will be accomplished by optimizing our app-store listing and creating targeted social media campaigns, which will begin running in February 2022, on three social media platforms: Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Since mobile is our primary point of conversion for paid-customer signups, growing our app usage will ultimately increase sales.
Knowing how to set goals using the SMART framework can help you succeed in setting and attaining goals, no matter how large or small.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.

Intelligence
What smart really is, do you think of yourself as exceptionally smart.
Posted December 22, 2017

In today's society, being smart is usually associated with measures such as IQ ( Intelligence quotient ), EQ ( emotional intelligence quotient) or some similar way of calculating how smart you are. However, the world is becoming increasingly aware of the absurdity of IQ scores and how do they do not correlate with intelligence or job performance . And a high EQ too, though sometimes helpful, has been shown to have negative effects on health, academic and job outcomes. Given these paradoxical findings, how should we be thinking of our own smartness, as well as the smartness of people we teach, partner with, marry, hire, or lead?
What about the immeasurable qualities of intelligence? There are things about you that are measurable, like how well you do at math tests, and how well you perform in a particular sport. But there is a large part of your intelligence that is immeasurable, yet very impactful. Called qualia , these are private conscious experiences that you cannot describe to others. Your brain is wired to transmit these intangible messages. You feel them, yet you cannot explain them. That's what might make one designer make a red tie that stands out from the rest. Their understanding of the redness of red is different.
So what? Don't always assume that what you see is what others see. There are many of your own subtleties that you may bring to the table. For example, you might want to start a T-shirt business, and people may say there are too many others to compete with. Yet, your qualia may guide you to a unique T-shirt business that allows you to be profitable.
Does curiosity count? You may be a deeply curious person, yet you may not think of this as your intelligence. It's notable that we ignore curiosity, yet this is one of the key ingredients of intelligence. Curiosity rewards your brain , and it even helps you remember more because it stimulates memory circuits in the brain. It also influences how we make decisions . We may choose to go down one path versus another simply because we are curious.
We routinely underestimate curiosity, yet it can produce some amazing results. Take the " One Laptop Per Child " project, where children in rural Ethiopia who had never seen technology before found the on/off switch within minutes. Within five days they were using 47 apps per day per child, and they also were able to sing ABC songs within 2 weeks. Within five months, they had hacked Android without a degree in Computer Science.
So what? Qualifications can only get you so far. Often, it's a genuine curiosity that matters. Genuine curiosity can stimulate memory and help your brain make connections. Rather than be imprisoned by your qualifications, ask yourself, "What am I truly curious about?" Then pursue that further. Qualifications can open doors, but in so doing, they may inadvertently make you close the door to yourself.
You don't have to be systematic: I resisted writing my latest book in a totally systematic way because I wanted people to face the reality that my systems may be satisfying to understand, but they do not correlate with the systems in your head. Those are the systems that matter, and they may not correlate with the systems of others.
Take Kary Banks Mullis, for example, a Nobel laureate who refined our understanding of the polymerase chain reaction so that we can make synthetic DNA . Many people ignored him at first. He was the consummate explorer, and even said , "I never tired of tinkering in labs." Yet, his discovery did not come from hours of systematic work in a laboratory. It came to him while he was on a drive from Berkeley to Mendocino. He rarely consulted experts, and he was not a slave to feedback. In fact, his colleagues thought he was rather disorderly. Yet, somehow, his disorderliness led to a discovery.
So what? You may feel like you are all over the place, but like Mullis, you may actually be truly alive and in the line with a real discovery. While prescribed "methods," "feedback," and "controlled experiments" are meant to guide you, they also imprison your mind. Free thinking is every bit as valid as controlled experiments. And oftentimes, this is what allows you to make the leaps that you want. So, from time to time, face your fears about what others think of you, and ask yourself, "What do I truly want to do?" You'll be surprised by how far you have strayed from the path of your actual intelligence when you see how conformity has stopped you from being yourself. This is no harm to this if you don't hurt others in the process.

Conclusion : IQ and EQ reflect domains of intelligence, but they are not the be-all and end-all of it. Rather, your uniqueness, curiosity and freedom from authority also contribute to your intelligence. All of these dimensions of intelligence may help or hurt you. So, seek ways in which they help you. Express them. And ignore the naysayers who want to define you by conventional metrics. You can learn from others, but they should not own you or your mind simply because they have decided what intelligent is. Through your own self-discovery, you can redefine what intelligence is.

Srini Pillay, M.D. , is the author of Tinker Dabble Doodle Try: Unlock the Power of the Unfocused Mind . He is also a former Assistant Clinical Professor at Harvard Medical School and current chief medical officer and co-founder of Reulay.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Military & Veterans
- Transfer Students
- Education Partnerships
- COVID-19 Info
- 844-PURDUE-G
- Student Login
- Request Info
- Bachelor of Science
- Master of Science
- Associate of Applied Science
- Graduate Certificate
- Master of Business Administration
- ExcelTrack Master of Business Administration
- ExcelTrack Bachelor of Science
- Postbaccalaureate Certificate
- Certificate
- Associate of Applied Science (For Military Students)
- Programs and Courses
- Master of Public Administration
- Doctor of Education
- Postgraduate Certificate
- Bachelor of Science in Psychology
- Master of Health Care Administration
- Master of Health Informatics
- Doctor of Health Science
- Associate of Applied of Science (For Military Students)
- Associate of Science (For Military Students)
- Master of Public Health
- Executive Juris Doctor
- Juris Doctor
- Dual Master's Degrees
- ExcelTrack Master of Science
- Master of Science (DNP Path)
- Bachelor of Science (RN-to-BSN)
- ExcelTrack Bachelor of Science (RN-to-BSN)
- Associate of Science
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Master of Professional Studies
The average Purdue Global military student is awarded 54% of the credits needed for an associate's and 45% of the credits needed for a bachelor's.
- General Education Mobile (GEM) Program
- AAS in Health Science
- AS in Health Science
- BS in Organizational Management
- BS in Professional Studies
- AAS in Criminal Justice
- AAS in Small Group Management
- AAS Small Group Management
- Master's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Associate's Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Continuous Learning Courses
- Tuition and Financial Aid Overview
- Financial Aid Process
- Financial Aid Awards
- Financial Aid Resources
- Financial Aid Frequently Asked Questions
- Financial Aid Information Guide
- Tuition and Savings
- Aviation Degree Tuition and Fees
- Professional Studies Tuition and Fees
- Single Courses and Micro-Credentials
- Time and Tuition Calculator
- Net Price Calculator
- Military Benefits and Tuition Assistance
- Military Educational Resources
- Military Tuition Reductions
- Military Spouses
- Student Loans
- Student Grants
- Outside Scholarships
- Loan Management
- Financial Literacy Tools
- Academic Calendar
- General Requirements
- Technology Requirements
- Returning Students
- Work and Life Experience Credit
- DREAMers Education Initiative
- Student Identity
- Student Experience
- Online Experience
- Student Life
- Alumni Engagement
- International Students
- Academic Support
- Career Services
- COVID-19 FAQs
- Faculty Highlights
- Student Accessibility Services
- Student Resources
- Transcript Request
- About Purdue Global
- Accreditation
- Approach to Learning
- Career Opportunities
- Diversity Initiatives
- Purdue Global Commitment
- Cybersecurity Center
- Chancellor's Corner
- Purdue Global Moves
- Leadership and Board
- Facts and Statistics
- Researcher Request Intake Form
Most Commonly Searched:
- All Degree Programs
- Communication
- Criminal Justice
- Fire Science
- Health Sciences
- Human Services
- Information Technology
- Legal Studies
- Professional Studies
- Psychology and ABA
- Public Policy
- Military and Veterans
- Tuition and Fee Finder
- Financial Aid FAQs
- Military Benefits and Aid
- Admissions Overview
- Student Experience Overview
- Academic Support Overview
- SMART Goals for Students

The Student's Guide to SMART Goals
Goal setting is an important aspect of preparing to be successful, both academically and professionally. College students may use goals to help meet deadlines. In the workplace, you will often be asked to set formal goals as part of your performance review.
In this guide, we’ll explain what SMART goals are and provide tips and examples for college students looking to develop their own SMART goals.
What Are SMART Goals?
The SMART acronym is a commonly used guideline for goal setting. SMART stands for s pecific, m easurable, a chievable, r elevant, and t ime-bound. These criteria can be used as a guide when writing down your goals.
- S pecific: Adding specificity to your goal makes it easier to achieve. Detail what you want to accomplish, when you would like to accomplish it, and what actions you will need to take to meet the goal.
- M easurable: Your goal should be something that can be tracked. If your goal is too vague, it can be difficult to assess how close you are to achieving it.
- A ttainable: College students have a lot on their plate. Make sure your goal is something you can realistically accomplish within the given time frame.
- R elevant: SMART goals for students should relate back to academic or professional growth. When creating a new goal, ask yourself how this accomplishment could benefit your academic performance or set you up for success in your desired career.
- T ime-bound: It’s easier to stick with a goal when it has a specific deadline associated with it. Determine when you would like to meet your goal, and consider setting target dates for each step involved in meeting the goal.
>> Read: 4 Goal Setting Strategies and Resources to Get You Motivated for the New Year
Examples of SMART Goals for College Students
Students can use SMART goals to keep themselves motivated while pursuing their degree. Goals may relate to specific coursework, career planning, or even health and wellness . Below are a few examples of SMART goals for college students. Each of them includes specific deadlines and actionable next steps.
Earn my degree by the end of the year by completing required courses over the summer and during the fall semester.
By the end of the month, I'll create a list of at least five internship opportunities in my field, and meet with a career advisor to discuss next steps for applying to these internships.
Complete this semester with a GPA of 3.0 or higher.
By the end of the month, I'll join a student club or organization. After joining an organization, I will attend at least one meeting every month.
Improve my time management skills by dedicating 1 hour each weekday to uninterrupted studying. At the end of the month, I will reflect on my focus levels and adjust this study routine as needed.
For the duration of the semester, I'll maintain an up-to-date digital planner that lists assignment due dates for each of my classes.
I’ll meet with each of my professors at least once during the course of the semester.
Over the course of the next month, I will spend at least 1 hour each week reading a nonfiction book related to my major or catching up on industry news. Books that are assigned as part of a course will not count toward this goal.
By the end of the week, I will update my LinkedIn profile with completed coursework relevant to my desired career path.
>> Read: Time Management Tips for Busy College Students
How to Measure Your Progress Toward SMART Goals
According to the American Psychological Association , monitoring your progress can increase your chances of meeting your goals. Here are some of our top tips for college students looking to track their SMART goals.
1. Share Your Goal With Others
Many people find that they are more motivated to achieve their goals when they have a support system in place. After setting your goal, find a trusted person who can hold you accountable. This may be a friend, family member, classmate, or coworker. In return for providing support, you can offer to help them track progress for any of their own goals.
2. Set Check-In Reminders
Frequently checking in with your progress ensures that your goal remains top of mind. Consider adding check-in reminders to your calendar for the duration of your goal, keeping in mind that the time frame of your goal will affect how often you want to check in. For example, progress on a semester-long goal may only need to be measured once a month, but if your goal is something you want to achieve more quickly, you may want to check in weekly or even multiple times per week.
3. Put It Into Writing
Monitoring your goal is particularly effective when you physically record your progress. Each time you check in with your goal, write down the progress you’ve made and outline the next steps you need to take. You can send these updates to a trusted friend or even share your progress on social media. Either way, putting your progress into writing can help make sure you follow through on your goal.
4. Adjust Deadlines as Needed
As you make progress toward your goal, you may find that you need more time than you originally thought. If the original date you set no longer seems achievable, don’t be afraid to adjust your goal as needed. You may also consider breaking up the goal into smaller, more manageable steps, each with their own deadline. Pushing your completion date out by a few weeks or months is better than getting overwhelmed and giving up on the goal altogether.
Achieve Your Goals With Purdue Global
Since SMART goals are so commonly used by employers, it’s a good idea for college students to become comfortable with setting and tracking these types of goals. Whether you’re looking to improve your grades or explore potential career paths, SMART goals can help you get there.
For help meeting your academic goals, be sure to take advantage of any support that may be offered by your school. For example, Purdue Global offers online Academic Success Centers focused on writing, math, technology, and more. In addition, our Center for Career Advancement can assist with creating measurable and attainable career goals.
We offer more than 175 online programs for students looking to enter a new field or advance within their current career. Request more information today to learn more.
About the Author
Purdue Global
Earn a degree you're proud of and employers respect at Purdue Global, Purdue's online university for working adults. Accredited and online, Purdue Global gives you the flexibility and support you need to come back and move your career forward. Choose from 175+ programs, all backed by the power of Purdue.
- Alumni & Student Stories
- General Education
- Legal Studies & Public Policy
- Online Learning
Your Path to Success Begins Here
Learn more about online programs at Purdue Global and download our program guide.
Connect with an Advisor to explore program requirements, curriculum, credit for prior learning process, and financial aid options.
Employment and Career Advancement: Purdue Global does not guarantee employment placement or career advancement. Actual outcomes vary by geographic area, previous work experience and opportunities for employment.
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of smart
(Entry 1 of 4)
Definition of smart (Entry 2 of 4)
intransitive verb
Definition of smart (Entry 3 of 4)
Definition of smart (Entry 4 of 4)
Examples of smart in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'smart.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle English smert causing pain, from Old English smeart ; akin to Old English smeortan
Middle English smerten , from Old English smeortan ; akin to Old High German smerzan to pain
before the 12th century, in the meaning defined at sense 7
13th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
13th century, in the meaning defined above
Phrases Containing smart
- as smart as a whip
- get smart with
- play (it) smart
- smart aleck
- smart - arse
- smart as a whip
- smart - ass
- smart cookie
- smart money
- smart - mouthed
- smart phone
- street - smart
- the smart set
Articles Related to smart

Read This to Get 'Smart'
Are you smart enough to juggle the word's multiple meanings?
Dictionary Entries Near smart
Cite this entry.
“Smart.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/smart. Accessed 22 Aug. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of smart.
Kids Definition of smart (Entry 2 of 4)
Kids Definition of smart (Entry 3 of 4)
Kids Definition of smart (Entry 4 of 4)
Medical Definition
Medical definition of smart, more from merriam-webster on smart.
Nglish: Translation of smart for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of smart for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Definition Essay
Last Updated: January 27, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 454,538 times.
A definition essay requires you to write your own definition of a word. The definition must be thorough and well supported by research and evidence. You may have to write a definition essay for a class or try it as a writing challenge to help improve your English skills. Start by selecting and defining the word. Then, create a draft that presents a detailed definition using references and sources. Polish the essay when you are done so it flows well and does not contain any grammatical errors.
Selecting the Word

- You can also pick a concept like “Success,” “Friendship,” or “Faith.”
- Concepts like “Pain,” “Loss,” or “Death” are also good options.

- You can try taking a concrete object and using a similar word to make it more open-ended. For example, the word “house” is concrete and obvious. But the word “home” is more open-ended and allows you to create your own definition of the word.

- For example, you may choose a word like “success” because you are familiar with the word and feel you may have a lot to say about what it means to be successful or to feel success in your life.

- For example, you may choose a word like “pain” because you feel there are a variety of meanings for the word based on who you talk to and how they experience “pain” in their lives.
Defining the Word

- For example, if you look up the word “justice” in the dictionary, you may get this definition: “noun, the quality of being just; righteousness, equitableness, or moral rightness.”
- You can then determine that “justice” is a noun and can be compared to other terms like “righteousness” and “moral rightness.”

- For example, you may look up the word “justice” in an online encyclopedia that focuses on philosophy or law. You may then find information on Western theories of justice and how it became an important concept in Western history and the legal system.

- Look on academic search engines like Google Scholar, JSTOR, and ProQuest for scholarly articles.
- You can also look for educational videos that have been made about the word on YouTube and other video websites.

- “What comes to mind when you think of the word?”
- “How do you feel about the word on a personal level?”
- “How do you interact or deal with the word?”
- “What does the word mean to you?”
- Take notes or record the interviews so you can use them as sources in your essay.

- For example, you may write: “Justice, a quality or trait where you act in a morally right way.” Or you may write: “Justice, a concept in the legal system where the fair or equitable thing is done, as in ‘justice has been served.’”
- It's important to have tact and tread carefully here. It's important to preface your own definition of the word, making it clear that's a personal opinion. Make sure not to create the misconception that your own definition is the accepted or official one.
- At the end of the day, your objective should be to write the actual definition, and not an opinion essay.
Creating an Essay Draft

- Your thesis statement should appear in the introduction and conclusion section of your essay.

- For example, you may write, “According to the Oxford Dictionary, justice is a noun, and it means: the quality of being just; righteousness, equitableness, or moral rightness.”

- For example, you may have a thesis statement like, “According to my research and my personal experiences, justice is a quality or trait where you act in a morally correct way.”

- For example, you may write, “Justice comes from the Latin jus , which means right or law. It is a commonly used concept in politics, in the legal system, and in philosophy.”

- For example, you may discuss how justice works as a noun or an idea in politics, the legal system, and in philosophy. You may also discuss what the “quality of being just” means in our society.

- For example, you may talk about how justice is similar and also not quite the same as words like “righteousness” and “equitableness.”
- You can also discuss words that mean the opposite of the term you are defining. For example, you may contrast the word “justice” with the word “injustice” or “inequality.”

- For example, you may write, “On a personal level, I view justice as an essential concept” or “Based on my own experiences, I think justice is blind and often does not serve those who need it the most.”
- You can also include personal experiences of the word based on interviews you conducted with others.

- Make sure you follow your instructor’s preferred citation style, such as MLA , APA , or Chicago Style .

- Look at the first sentence in each section of the paragraph to help you gather your main points.
- Include a last sentence that has a strong image or that describes a key phrase in your essay.
Polishing the Essay

- You should also check for any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors in the essay.

- Be open to constructive criticism from others and take their feedback to heart. It will only make your essay better.

- If there is a word count or a page count for the definition essay, make sure you meet it.
- Include a reference page at the end of the essay and a cover page at the beginning of the essay, if required.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about writing essays, check out our in-depth interview with Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. .
- ↑ https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/definition-essay/
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/10-6-definition/
- ↑ https://quillbot.com/courses/introduction-to-college-level-academic-writing/chapter/how-to-write-a-definition-essay/
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/definition-essay-examples-and-topic-ideas.html
- ↑ https://owlcation.com/humanities/How-to-Write-a-Definition-Essay-from-Multiple-Sources
- ↑ https://academichelp.net/academic-assignments/essay/write-definition-essay.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/definitions.html
- ↑ https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/definition-essay/definition-essay-techniques/
- ↑ https://quillbot.com/courses/rhetorical-methods-based-essay-writing/chapter/how-to-write-a-definition-essay/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/using-evidence.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
About This Article

To write a definition essay, choose a word that describes a concept or idea. Look up the dictionary definition, the origin of the word, and any scholarly essays or articles that discuss the word in detail, then use this information to create your own definition. When you write your paper, introduce the term and the standard dictionary definition of the word, followed by a thesis stating your own definition. Use the body of the paper to include historical information and explain what the word means to you, then conclude by restating your thesis. For tips on picking your word, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ron Fortney
Sep 27, 2016
Did this article help you?

Apr 26, 2018
Apr 24, 2017
Mar 6, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

IMAGES
COMMENTS
SMART goal-setting was first introduced by Dr. Edwin Locke in the 1960s (Griffin, 2017). According to Locke, setting goals that fit into the SMART criteria provided motivation and empowerment to people, which was crucial to ensure that the goals are achieved (Griffin, 2017). Today, SMART criteria are applied to the goal-setting process in many ...
The SMART Goals image shows the acronym SMART down the left side of the image. Next to each letter is the word that correlates to each letter and the definition of each part. On the right side of the image are simple icons of a target, a sheet of paper and an arrow, a mountain scene with a flag, a pencil with a checkmark and squiggles, and a ...
SMART Goal ExamplesOngoing Provide high quality customer service resulting in a 90% customer satisfaction rating from external customers on accuracy, timeliness and courtesy m. asures on an ongoing basis. On an ongoing basis, reconcile the department financial reports by the 15th of every month with no increa.
Definition and Explanation of SMART Goals. SMART goals are goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Specific goals are clear and well-defined, measurable goals track progress, achievable goals are realistic, relevant goals align with one's values and aspirations, and time-bound goals have a set deadline for ...
A SMART goal is a framework for defining objectives, where each goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Follow this method to establish clear, attainable goals that hold you accountable to a deadline. SMART goals are useful in all professional sectors and industries, as well as in personal life (see examples of personal and professional SMART goals below).
There are a lot of benefits to setting S.M.A.R.T. goals, which is why you should consider adding them to your business toolbox. First, a S.M.A.R.T. goal helps to give you an objective. In doing ...
The SMART framework defines goals and objectives clearly and practically, making them more actionable and increasing the likelihood of success. SMART is an acronym that stands for SMART goal and is used to help in goal setting. In this modern, technology-driven world, one of the most widely used words is "SMART.".
A SMART goal is used to help guide goal setting. SMART is an acronym that stands for S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R ealistic, and T imely. Therefore, a SMART goal incorporates all of these criteria to help focus your efforts and increase the chances of achieving your goal. SMART goals are: S pecific: Well defined, clear, and unambiguous.
A Guide to Using SMART Goals. SMART goals (standing for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-bound) help you outline action plans to achieve your short-term or long-term goals. It has origins in the business world, but it can be applied to anything you aspire to bring to life. SMART goals (standing for specific, measurable ...
SMART Goals Advantages and Disadvantages Benefits of SMART Goals. The SMART framework is widely used because it helps students to clarify their goals and how they are going to go about achieving them. Often, students start with a vague statement of intention, but by the end of the session, they have fleshed out their goals using the SMART template.
The SMART framework breaks down learning objectives into five key characteristics: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Each characteristic plays a pivotal role in creating a comprehensive learning goal that is practical, attainable, and aligned with overall educational targets.
Patrick Lencioni's central thesis in this book is that an ideal team player possesses a potent combination of three virtues — they are humble, hungry, and smart. Further, Lencioni states, when ...
An example of a SMART-goal statement might look like this: Our goal is to [quantifiable objective] by [timeframe or deadline]. [Key players or teams] will accomplish this goal by [what steps you'll take to achieve the goal]. Accomplishing this goal will [result or benefit].
Essay On Being Smart. 833 Words4 Pages. Being smart is more than being intelligent. Smart people are those who are self-aware, mentally prepared, clever, prompt, neat in appearance, shrewd, up on current events, charismatic, and socially adept. The totality of your personality, character, and behavior is the core of being smart.
To refrain from using "smart" is to embrace a certain humility, a certain distance from our own evaluations. A similar point applies to those who aspire to ask "smart" questions or to pursue ...
The question is not whether you'll change; you will. Research clearly shows that everyone's personality traits shift over the years, often for the better.
The SMART acronym is a commonly used guideline for goal setting. SMART stands for s pecific, m easurable, a chievable, r elevant, and t ime-bound. These criteria can be used as a guide when writing down your goals. S pecific: Adding specificity to your goal makes it easier to achieve. Detail what you want to accomplish, when you would like to ...
The acronym SMART, mentioned earlier in this chapter, is helpful in identifying goals and steps: Specific: The more specific the goal, the easier it is to attain. For example, if the client's goal is to be more social, the specific goal of having coffee with one friend each week is easier to check off as an accomplished goal.
Definition Essay On Being Smart. 571 Words3 Pages. What does it actually mean to be "smart?". According to the dictionary, smart is defined as, "having or showing a quick-witted intelligence.". There are many factors that go into being smart such as, getting good grades in school, or having common sense. Getting good grades is great but ...
How to use smart in a sentence. having or showing a high degree of mental ability : intelligent, bright; witty, clever; rude or impolite in a bold and disrespectful way… See the full definition
5. Create your own definition of the word. Use your research and your own experiences to write the definition. You may focus on how the word works in society or the world at large. You can also compare it to other similar terms. Format the definition by stating the word, followed by a one-sentence definition. [8]
Smart work is optimal for industries, such as technology, that seek to create innovative products constantly. Consider working hard first so that you can learn a process and gain a full understanding that allows you to analyse the tasks and work smart. Often you can integrate methods of hard work with smart work and achieve the best results.
According to Merriam-Webster's Dictionary, the literal definition of being smart is showing intelligence and being mentally alert or knowledgeable. Looking at this, it appears as if we have been looking at the word 'smart' in only one very dim light. There are so many things that could be derived from this definition, one being that there ...