

Telling the truth about SME life today
Home » Business » Nature of Business Meaning – Examples & Types
Nature of Business Meaning – Examples & Types

- June 4, 2023

Business success and a positive trajectory depend on many external factors. These include market dynamics, level of competition strength and internal strengths and weaknesses. All choices made by a business, big and small, will impact the type of company it will become and what it looks like. This leads us on to the nature of business.
Table of Contents
What is the Nature of a Business?
The nature of business defines the core identity of a company – what it does, how it operates, and its place in the market. Getting to grips with this concept provides valuable insight for entrepreneurs, investors and other stakeholders when evaluating a business.
Put simply, the nature of business refers to the fundamental characteristics that shape a company’s purpose, offerings and market approach. It encompasses aspects like:
- Legal structure – e.g partnership, private limited company
- Products and services – what the business sells or provides to customers
- Target market – the customer segments the business caters to
- Business model – how the company generates revenue and profit
So for example, an online retailer has a very different nature of business compared to a bricks-and-mortar supermarket, even though both sell groceries. Understanding these traits helps stakeholders make informed assessments about a company’s identity and potential value.
Business Nature Components
Purpose: Every business starts with a purpose. It’s the foundation, answering why the entity exists. For some it’s selling products, for others providing services, and many it’s solving market problems. This purpose becomes the guiding North Star for all activities and decisions.
Activities: Businesses have set operations like people have daily tasks. This could include designing products, sourcing materials, manufacturing, marketing and sales. These activities fulfil the business’s purpose.
Scale: Business scale varies. Some operate locally like mom-and-pop shops. Others are huge enterprises spanning countries and continents. Scale dictates reach, operations and complexities.
Stakeholders: Businesses involve stakeholders like owners, employees, customers, suppliers and communities. Each has a role, interest and expectation.
Economic Contribution: A business contributes via job creation, taxes, trade and innovation. It plays a key economic role.
Risks & Challenges: The landscape is dynamic with competition, trends, regulations and events posing risks. Recognizing and navigating challenges is vital.
Legal Structure: Businesses operate within legal frameworks. Structures like sole proprietorships, partnerships and corporations define responsibilities, benefits and limitations.
In summary, a business’s nature blends purpose, functions, size, relationships, economic contribution, challenges and legal standing. These interplaying components form the intricate mosaic of business.
Nature of Business Examples
| Transportation | Moves people and goods from one place to another |
| Manufacturing | Makes products |
| Agriculture | Cultivates crops and raises animals |
| Entertainment | Creates and distributes creative content |
| Construction | Erects buildings and infrastructure |
| Services | Provides intangible offerings |
| Freelancing | Provides services as an independent contractor |
| Real Estate | Buys, sells, and leases properties |
| Mining/Drilling | Extracts natural resources from the earth |
| Research & Development | Conducts research and develops new products/processes |
| Hospitality | Runs lodging, food/beverage, events and tourism |
| Retail | Sells to end consumers |
| Education | Provides teaching and training |
| Healthcare | Offers medical treatment and promotion of health |
| Wholesale | Sells in bulk to businesses |
| Utilities | Delivers essential services like power and water |
| Financial Services | Offers financial products like banking and insurance |
| Information Technology | Develops and provides IT products and services |
| E-Commerce | Sells goods and services online |
| Non-Profit | Operates to advance social, environmental or other causes |
What Impacts The Nature Of Business?
Legal structure.
A company’s legal structure has implications for ownership, financing, taxes and operational processes. Common structures include:
- Sole proprietorships – owned and run by one individual who has unlimited liability
- Partnerships – tow or more co-owners who share financing, profits and operational duties
- Private limited companies – separate legal entities that limit owners’ liability to their investment amount
- Public Limited companies – can trade shares publicly and often have access to great financing
- Non-profit organisations – focus on social impact rather than profits
Choosing an appropriate legal structure depends on the founders’ growth ambitions, target customers, financing needs and appetite fr personal liability. An eco-friendly startup might begin as a partnership before transitioning later toa private limited company structure to attract investor funding.
Products & Services
A company’s offering encompasses what it sells to customers – whether physical goods, services, digital technologies or even ideas. The specifics here characterise the business’ core purpose. For example, a bakery sells artisanal bread and cakes, a web design agency sells bespoke websites and a charity sells the idea of positive social change through donations.
Over time, businesses may adapt or expand their offerings to pursue new opportunities or reach to market changes but the original core products and services tend to shape ongoing business identity and purpose.
Target Market
The specific customer groups a company sells to dictate much of its branding, proposition development and communications tactics. Market segmentation by demographics, geography, behaviours and values allow organisations to match products/services to buyer preferences.
For example, a specialty pet food company that prides itself on using the finest ingredients may focus its marketing on targeting affluent urban dog owners who are more likely to pay a higher price for the knowledge that better ingredients are used.
Industry Sector
The industry sector that a business operates in directly impacts its competitive environment, distribution channels and regulatory obligations. Knowing that industry landscape is key to analysing a company’s market positioning and potential.
Business Model
Every company’s business model encompasses how it generates sales revenues and profits from its offerings. The main areas of a business model usually include:
- Value proposition – products/services offering value to customers
- Target market – the selected customer segments
- Distribution channels – how deliverables reach customers
- Revenue streams = where sales income is generated
- Cost structure – the expenses required to operate
- Margin model – how the profits are produced from revenue
The Internal & External Factors Influencing The Nature Of Business
Internal factors.
- Ownership Model – Group owned businesses rather than sole proprietorships often have wider financing options available to them but the downside is, having multiple people to run decisions past, can slow down decision making timelines.
- Management culture – Visionary leaders can create strong innovative work cultures whereas prudent leaders tend to create steadier, less risky operations.
- Company size – Large organisations benefit from economic scale but small operations tend to be more agile when it comes to customer interactions.
- Technology used – Digitally driven companies are fundamentally different from traditional manual operations. As digital revolutions continue to happen, back office processes transform to provide customers with better front end experiences and personalisation.
- Staff Skills – The skills available across employees will make or break your business. If you can’t get the talent required in house, then small firms may need to outsource specialist areas.
- Purpose Alignment – Workforce diversity, community development and social justice can also reshape business nature. Younger workers choose employers that can demonstrate genuine commitment to moral causes rather than simple virtue signalling.
External Factors
- Economic Landscape – Thriving economies provide more opportunities, whereas recessions force consolidation and cuts
- Geography – Rural businesses often focus on community values whereas city-based firms can afford to follow consumer trends
- Environmental Obligations – With climate change and ecological threats prominent, sustainability conscious customers will want to see greener practices in businesses they support. For example, petroleum companies investing in renewable energy sources would be an example of environmental obligations shaping the nature of business.
- Regulations – Plenty of industries have specific compliance rules to follow which can fundamentally shape operations
- Competitors – Start-ups in crowded marketplaces must be able to disturb, whereas monopolies control captive customer bases.
- Market Globalisation – Trading across borders requires adaptations to make in branding, trading partnership and supply chains.
- Investor demands – When investors are expecting results, companies may feel under pressure to scale up quickly
- Customer expectations – Customer focused businesses must continue to adapt to the needs and demands of consumers. Those who fail to continually increase the value they offer to their customers face displacement by others who will.
These internal and external factors are constantly evolving and changes here will inevitably impact the strategies and processes required within the business. In some cases, this may lead to a change in the overall nature of business.
Types Of Businesses and their Nature
Legal structures and ownership models have a big impact on the taxes, liabilities and grow strategies available to organisations. Here is an overview of the main types available in the UK:
Sole Proprietorships
A sole proprietorship is a business owned and run by a single individual. This is one of the easiest business structures to set up and manage, only requiring a unique business name. The owner then has complete control over strategy, operations and liability. This means that personal assets can be pursued to settle business debts as there is no distinction between the owner and the business.
This type of business tends to work well for solo entrepreneurs with specialist professional skillets such as photography, consultants or tradespeople. Many people love the simplicity, autonomy and low start up costs, but lack of work during slow periods, financial protections, and difficulty if operations come to a standstill reflect the downsides of this type of business.
Partnerships
Partnerships allow two or more co-owners to set up and operate a business. All parties will contribute financing, decision making and operational oversight whilst splitting any profits made. This type of business structure allows for owner-operator involvement whilst knowledge and resources are pooled to greater business impact.
Partnerships tend to open up wider funding opportunities, diverse skill sets and expansion opportunities across several locations. All costs, responsibilities and liabilities are shared too. For this to work, an excellent collaborative approach is required which involves communications and transparency over financials and performance.
Disagreements can quickly derail partnerships but this type of set up is common in professional services such as legal firms, medical practices and architecture firms. Overall, partnerships encourage contribution to the business whilst avoiding some of the limitations faced by sole proprietors.
Private Limited Companies
A private limited company creates a legal structure that is separate from its owners. This means the company is owned by shareholders in accordance with their initial investments but that their liability is also limited to the amount invested. The benefit of this set up is that personal assets cannot be pursued to settle company debts.
The independent legal entity of the business means company ownership can be transferred more easily through the buying and selling of shares, and limited companies are also able to access favourable tax efficiencies in several areas.
The downside of a limited company is the higher volume of administrative work required to operate. Including extensive financial reporting, annual government filings and statutory obligations; They must follow regulations around hiring, workforce policies and contracts.
Public Limited Companies
Public limited companies (PLCs) can raise funds by trading shares openly though stock exchanges. Doing this opens up the business for the biggest investment to fund projects and fuel growth. To do this, a business must meet strict reporting and operational standards.
The separation of ownership from management requires non-executive directors and structured leadership teams. PLCs operate with greater public scrutiny of salaries, diversity policies and carbon footprints and underperformers will face pressure to make changes to strategy or leadership.
Non-Profit Organisations
Rather than maximising profits for owners, non-profit organisations focus on social impact and community benefit. To do this, most require donations and public sector funding to fund and are also reliant on volunteers to make up a proportion of their workforce.
Any profits cannot be divided between owners, but must stay within the company. Examples of these kinds of businesses include wildlife conservation groups, universities, medical research charities and cultural institutions. Spending is constrained and should be purposeful to reassure donors that their money is being used wisely and for the good intentions of the operation rather than internal functions. Successful non-profit companies have strong community support who engage emotionally with their causes.
The Evolving Nature Of Business
Whilst most businesses will carry their original purpose and niche with them, the nature of business may evolve over time as the company grows or responds to external or internal forces impacting it.
The Role Of Stakeholders
Within business environments, internal and external stakeholders will always have an influence over an organisation’s direction.
Staff and unions that lobby for higher pay, improved working conditions and greater work-life balance can modify company behaviour over time.
Communities
Neighbouring communities affected by business operations advocate for social programs, environmental protections and local economic opportunities which will feed into corporate policies.
Business Partners
Suppliers will always request increased margins and better terms of trading while distributors request support in pushing products. The negotiations required for these relationships will inevitably shape operations.
Wrapping Up
The nature of business refers to the key characteristics of an organisation that shape its operations, identity and competitive landscape. Understanding these things ensures that entrepreneurs, inventors and other stakeholders make informed decisions about business potential, investment decisions and the timeframe that they might see a return on their investment.
The exact makeup of a business will depend on leadership, sector, strategic choices and where the company is in its cycle, but market focus, deliverables, capabilities and growth ambitions will all shape the way the business runs.

- August 8, 2024
UK Pension Reform Expected – What It Means For UK Workers

- August 5, 2024
Real-Time News Report – Life Insurance Costs and Payouts in the UK

- August 2, 2024
From Serial Entrepreneur To Philanthropist & Author, Real Business Meets Mike Greene, Founder Of Success Is A System

- July 30, 2024
How To Create An Effective Stakeholder Engagement Plan

Related Stories

Overpayment Of Wages – What To Do?

Can An Employer Change Working Hours?

How To Introduce A Working From Home Policy At Your Business

How To Create The Ultimate Garden Office & How It Can Benefit Your Mental Health In The Process

How Long Can Employees Be On Sick Leave Before Dismissal?

Why Businesses Need To Partner With Local Education Providers To Develop Relationships For Future Top Talent Recruitment

What Is A Limited Company Strike Off?

What is a Shareholders Agreement?

External v Internal Finance Sources

Advantages & Disadvantages Of Swot Analysis

The Ultimate Guide to Sole Trader Bookkeeping

What Is Conscious Business & How Can We Cultivate It?

What Is The Flat Rate Scheme And Its Percentages

Taking Holidays As A Freelancer

How to Start an Etsy Shop – Everything You Need to Know

What is Business Administration?

How to Write a Freelance Contract

10 Most Popular Ways to Promote Your Business

Qualities of a Good Team Leader

Funding Female-Led Businesses: The Way Forward

What Does Your Business Branding Say About You?

How Personalisation Can Improve the Employee Experience

Why Your Web Host Matters: Is It The Key To Improving SME Site Performance?

Three Tips for Success When Starting Your New Position as a Team Manager

How to Mold Top-Performing Employees

Smart1 Recruitment: Going the Extra Mile with Mike Harper

Why Personal Experience is the Key to Tech Launch Success

Investing in Well-being to Stem the Tides of the Great Resignation

Planning for the Future: 5 Tips for Building a Robust Financial Forecast

5 Types of Sales Enablement Content You Need for Your Business (and Tips on How to Create It)

How to Grow Your Business Organically
Drive to De-Risk and Crystallise Value Spurs Interest in ‘Cash-Out’ Opportunities

Work Perks: Why Your Business Should Say Goodbye to the Free Gym Membership

Celebrating British Excellence with Sarah Austin

Has Remote Working Changed B2B Purchasing Forever?

Out with the Old, In with the New: How Digital Agreements Redefine the Present of Work

Pitch Deck Design Trends and Top Tips for Making Your Pitch Deck Stand Out

Super Apps are the Way Forward for Modern Parents: Interviewing the Creator of Onoco

Financial and Funding Business Contingency Planning with Kevin Harfield – MD JamesField Executive Limited

Google Launches New Core Update: What This Means for Businesses

Why Firms Can See the Global Supply Chain Crisis as an Opportunity

Tackling Inflation As An SME: 5 Strategies For Corporate Success

How to find Inner Safety, Sleep Well and Increase Energy and Performance

Preventing a Wage Spiral: How to Balance Talent Retention and Recruitment Post-Pandemic

How To Beat Loneliness In The Workplace

How To Get Started In Property Investment

Conquering Dragons’ Den with cheesegeek Founder, Edward Hancock

How Small Businesses Can Capitalise on Demographic Changes
Lessons from the tv world: the link between developing tv shows and new businesses.

Branded Content Can Be Key To Protecting Your Reputation

Eskimoz Conquers the European SEO Market

“Inspire your team to excellence”: Interview with Marie Grove Walton

TikTok for Business: How to Market to Millions

How Has COP26 Affected The Corporate Sector Six Months Later?

It’s Time Businesses Reboot Their Employee Wellbeing Experience Tools

The Formula for High Fashion: How Sunglasses Deals Became Big Business for the F1 Industry

Should Employers Provide Workers Access to Mental Health Services?

The Best Tools for Creative Freelancers

Is Your Brand a Great Design Story in the Making?

Opening of GOV G-Cloud 13 Framework Means Huge Opportunities for SMEs

Lewis Hamilton: Lessons in Resilience and Determination

Adopting a People First Approach to Technology

Women-Led Businesses You Should Be Paying Attention To

Litalist: Building a Community Between Book Lovers and Booksellers

Breaking into the Publishing Industry? Start Your Own Crowdfunded Publisher

Marketing Strategies in a Technology-Driven Age

Business Leaders Are Under Unprecedented Pressure – But Have Unprecedented Opportunities

Productivity Wars: How Managers Can Re-Inspire Their Teams

Queer-owned Small Businesses: How To Celebrate LGBTQ+ History Month And People All Year Round

“Creators aren’t aspirational dreamers, they’re a critical part of the economy,” says Lotanna Ezeike, Founder and CEO, XPO

Why Parental Leave Isn’t the Issue for Young Professionals

With Love – Taking the Opportunity to Care for Your Staff on Valentine’s Day

Oldest Pair Breaks Record Rowing Talisker Whiskey Atlantic Challenge

Creating Skincare Brands for the TikTok Generation with Tiffany Salmon

How to Surmount Your Self-Doubt as an SME Entrepreneur

Social First, CV Second: How Gen Z is Changing the Hiring Process

Ocean Club Holidays: Vertically Integrated, Organically Grown

Private Capital Could Help Drive SMEs Forward on the Road to Recovery

Pioneering Adtech Company Keeps TV Advertisers Informed and Adaptable

The New Year: The New Loyalty and Rewards Strategy

What Business Owners Need to Know about Workplace Mental Health Support

Are Print Magazines Still Viable in our Increasingly Digital Lifestyles?

How to Make the Most Out of the New Year

Why Emotional Intelligence is Key to Successful Conscious Leadership

Ways to Avoid Burnout as a Freelancer

3 Easy Ways to Simplify Your Small Business For Streamlined Success

Elizabeth Holmes Found Guilty of Fraud in Theranos Case

There’s Bias in Burnout, and Things Need to Change

Is There a Correlation Between How You Sleep and How You Work?

Fashion’s Plagiarism Habit and The Impact on Small Brands

Living the Laptop Lifestyle with Social Cactus

The Competition to Create the Best Christmas TV Advert

Putting Cyber Security First: Why the Latest Trends make this Critical for SMEs

Finding the Perfect Gift: Interview with Louise Doyle and Steph Scholes

How Innovation is Driving New Sustainability Goals

How your SME can capitalise on the Festive Season

Narce Media: Video is the Ultimate Content Currency

A Chanel Christmas Story: How Important Are Customer Perceptions of Value for Money?

Starting Out in a New Market

Lush Exit: Can Brands Survive Without Social Media?

Introducing the Entrepreneur Who Has Banished Leathers for Making Timeless Sustainable Accessories

Increasing E-Commerce Sales with Website Analysis Insights

6 Tips for Selling your Business

Cybersecurity Business Leading the Charge Against Business Threats

“Diversity of thought” – Why it’s Crucial to Business Success

Did COP26 Inspire Business Sustainability Or Just Encourage A Future Of ‘Greenwashing’?

“The Entrepreneur Ship” Takes on the Talisker Rowing Challenge

Speaking your Mind as an Introvert in the Workplace

Wonsulting and TikTok Resumes: Revolutionising Recruitment for the Future

The Rising Wages Impact on Small Businesses

Black Friday Success: Ditch the Discounts and Get Creative

Don’t fall foul of disability discrimination

Finance directors have their say on what the most important economic issues are

Building a global business: Lessons from David Vermeulen, founder of The Inner Circle

Mubaloo sets down the road to disruption once more

The remarkable story of Tyrrells: From a small British farm to £300m acquisition

Influencer Marketing: From the Expert

The apparent solution to the small business “staff drain”

The gig economy: Is it time to change the law?

The tricky slope of modernising Britain’s broadband landscape

How brands can leverage the key #stayathome moments within their marketing strategy
More from business.

Choosing A Business Coaching Model To Achieve The Best Results

Inventory Management: From Just-in-Time To Just-in-Case & Implications On Your Cash Flow

How To Write The Ultimate Business Plan

How To Benefit From The 18-Year Property Cycle

What Are The Different Types Of Business Assets A Company Can Hold?

How to Create a LinkedIn Business Page

Advantages Of Proprietary Software For Businesses

What Is An EORI Number: The Ultimate Guide

Why Perfection is the Enemy of Progress for Entrepreneurs

Do employers have to pay shift allowance?

What it means to be a HR professional

Sole trader & unlimited liability – A professional answer

If you enjoyed this article, why not join our newsletter?
We promise only quality content, tailored to suit what our readers like to see!

Published by Prosper 2 Media
Do you want to write for us click here to find out how.
Real Business has championed entrepreneurship in the UK since 1997. It is now the main source of inspiration, education, and collaboration for the owners of fast-growing businesses, from startups to mid-market companies. Real Business provides readers with high profile interviews, news, insight and industry benchmark reports, as well as a growing stable of events tailored to SME growth.
Privacy Policy
Privacy Overview
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
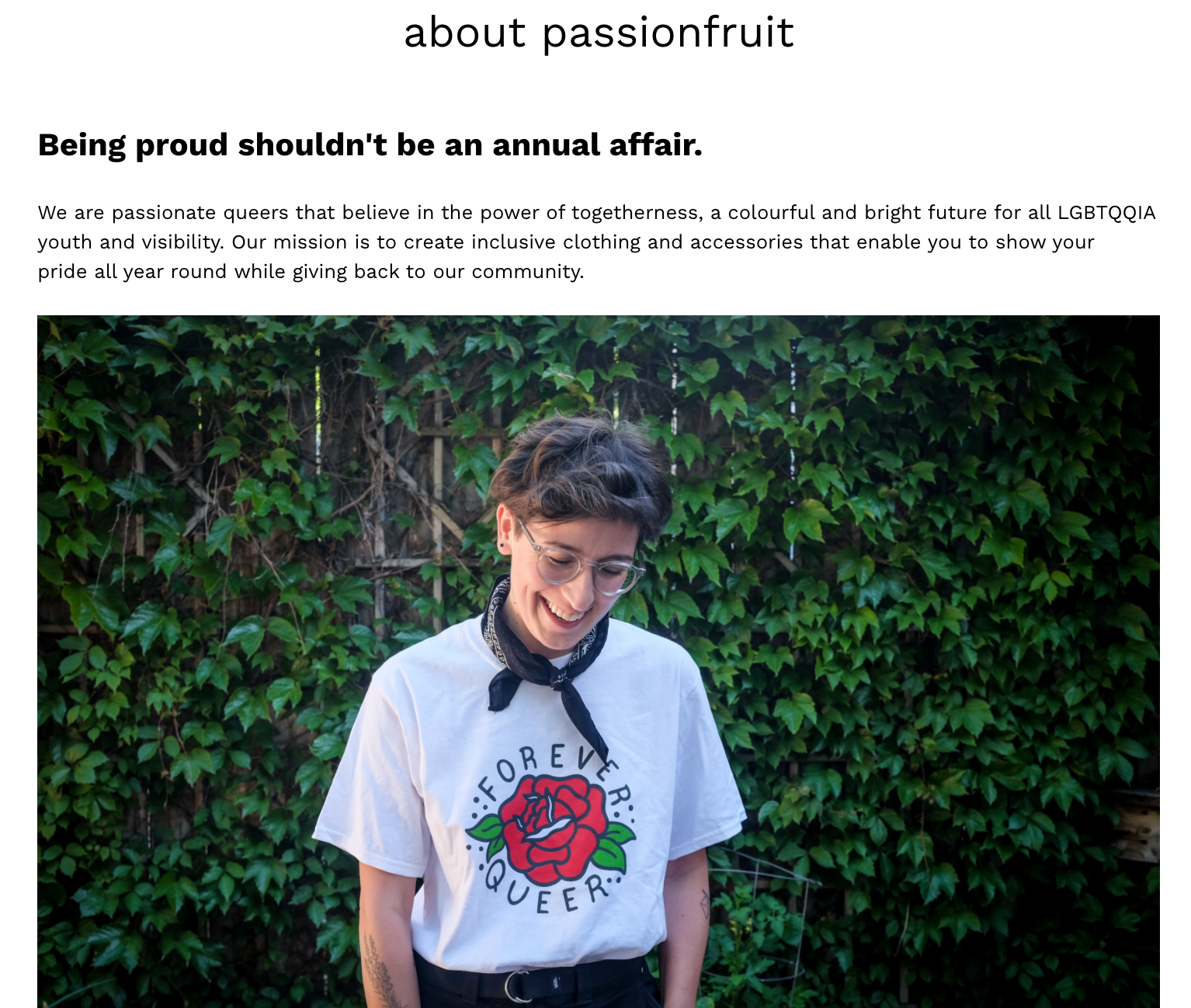
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
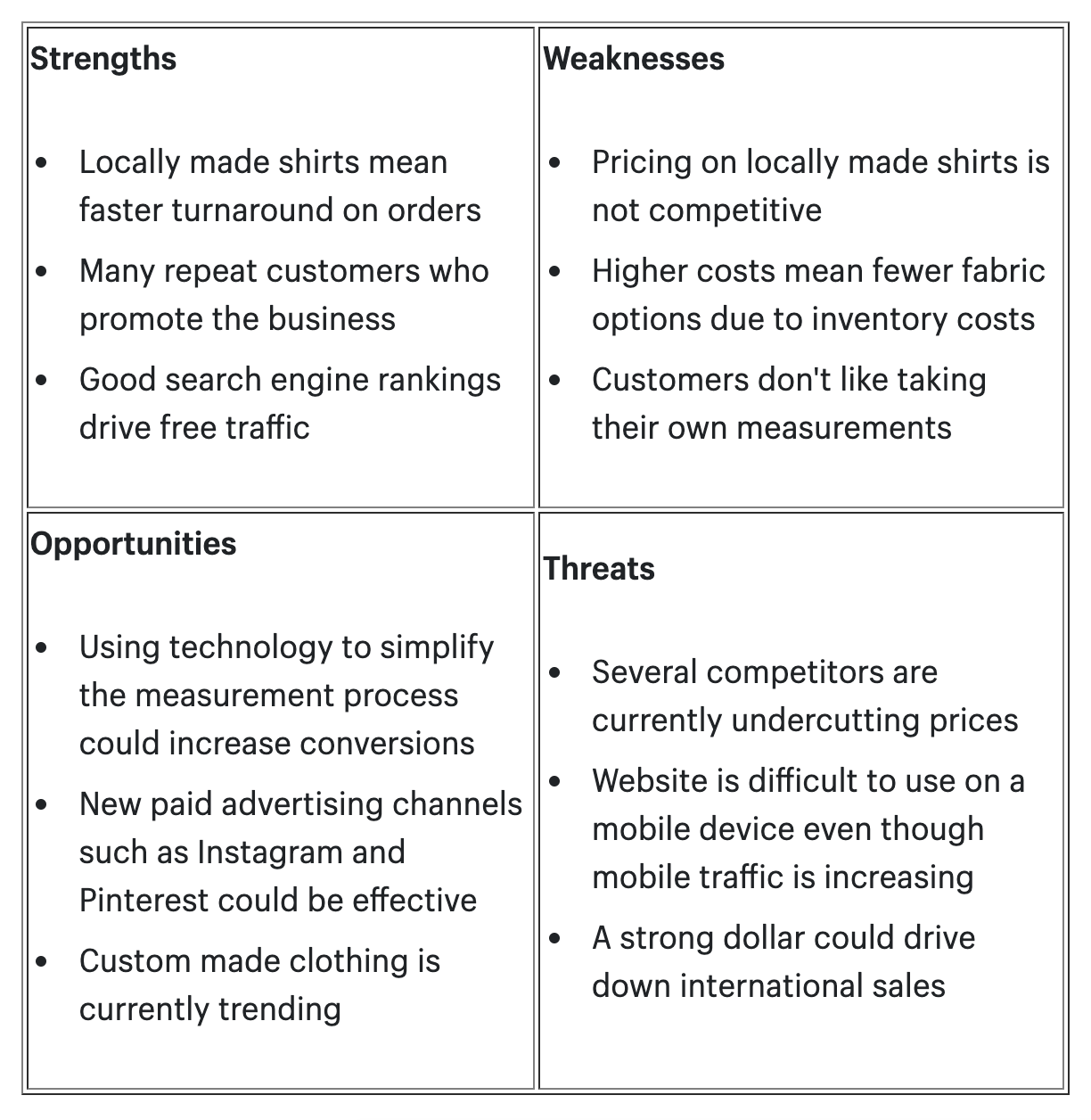
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
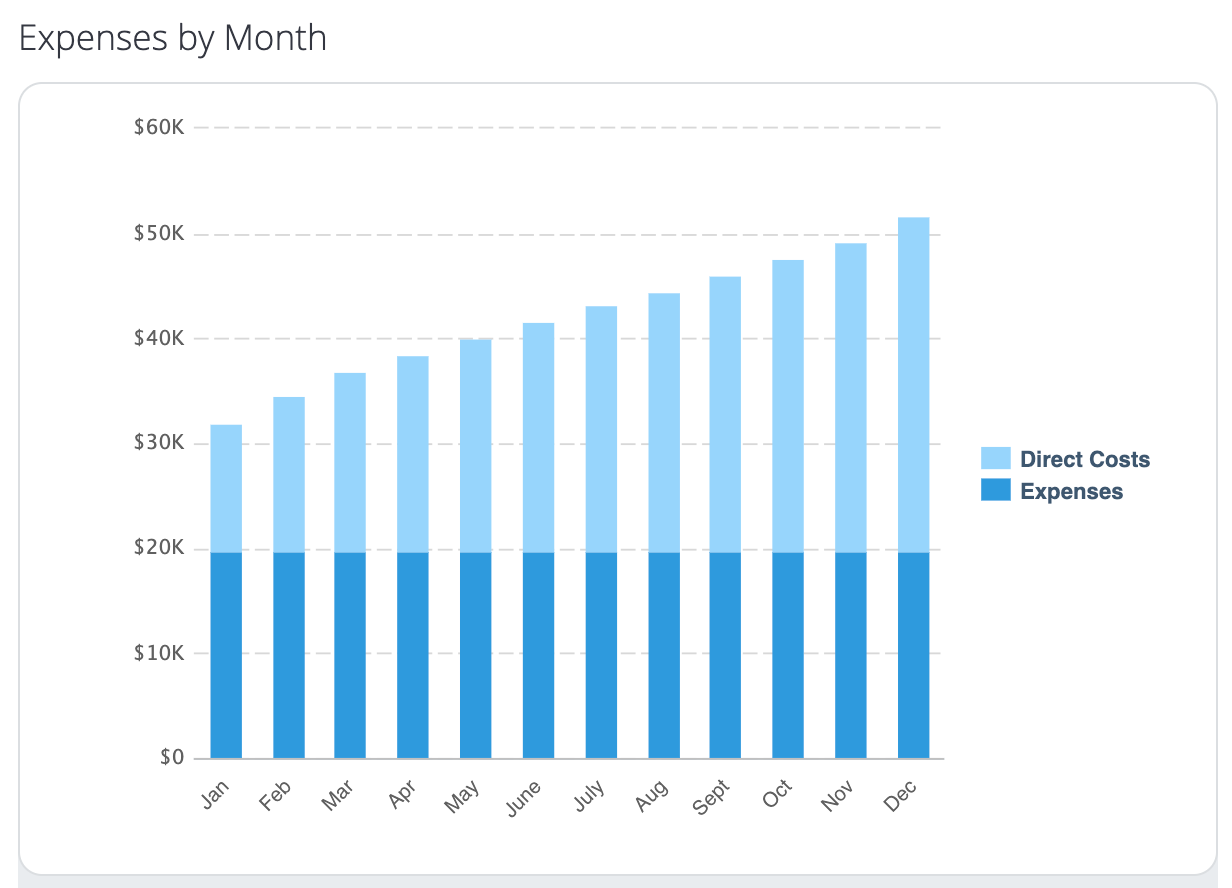
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 12, 2024
Aug 9, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Build your business
Business Tools
- Profit Margin Calculator
- Business Name Generator
- Slogan Generator
- Traffic Calculator
- Ecommerce Statistics
- Ecommerce Wiki
Free business tools
Start a business and design the life you want – all in one place.
- © 2015-2024 Oberlo

The 7 Best Business Plan Examples (2024)
As an aspiring entrepreneur gearing up to start your own business , you likely know the importance of drafting a business plan. However, you might not be entirely sure where to begin or what specific details to include. That’s where examining business plan examples can be beneficial. Sample business plans serve as real-world templates to help you craft your own plan with confidence. They also provide insight into the key sections that make up a business plan, as well as demonstrate how to structure and present your ideas effectively.
Example business plan
To understand how to write a business plan, let’s study an example structured using a seven-part template. Here’s a quick overview of those parts:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of your business and the contents of your business plan.
- Company description: More info about your company, its goals and mission, and why you started it in the first place.
- Market analysis: Research about the market and industry your business will operate in, including a competitive analysis about the companies you’ll be up against.
- Products and services: A detailed description of what you’ll be selling to your customers.
- Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market.
- Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background.
- Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even long-term) financial goals and the costs to run the business. If you’re looking for funding, this is the place to discuss your request and needs.
7 business plan examples (section by section)
In this section, you’ll find hypothetical and real-world examples of each aspect of a business plan to show you how the whole thing comes together.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary offers a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. You’ll want to include a brief description of your company, market research, competitor analysis, and financial information.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is three paragraphs and occupies nearly half the page:
- Company description
You might go more in-depth with your company description and include the following sections:
- Nature of the business. Mention the general category of business you fall under. Are you a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer of your products?
- Background information. Talk about your past experiences and skills, and how you’ve combined them to fill in the market.
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your company —as a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC, or other business type.
- Industry. Which business sector do you operate in? The answer might be technology, merchandising, or another industry.
- Team. Whether you’re the sole full-time employee of your business or you have contractors to support your daily workflow, this is your chance to put them under the spotlight.
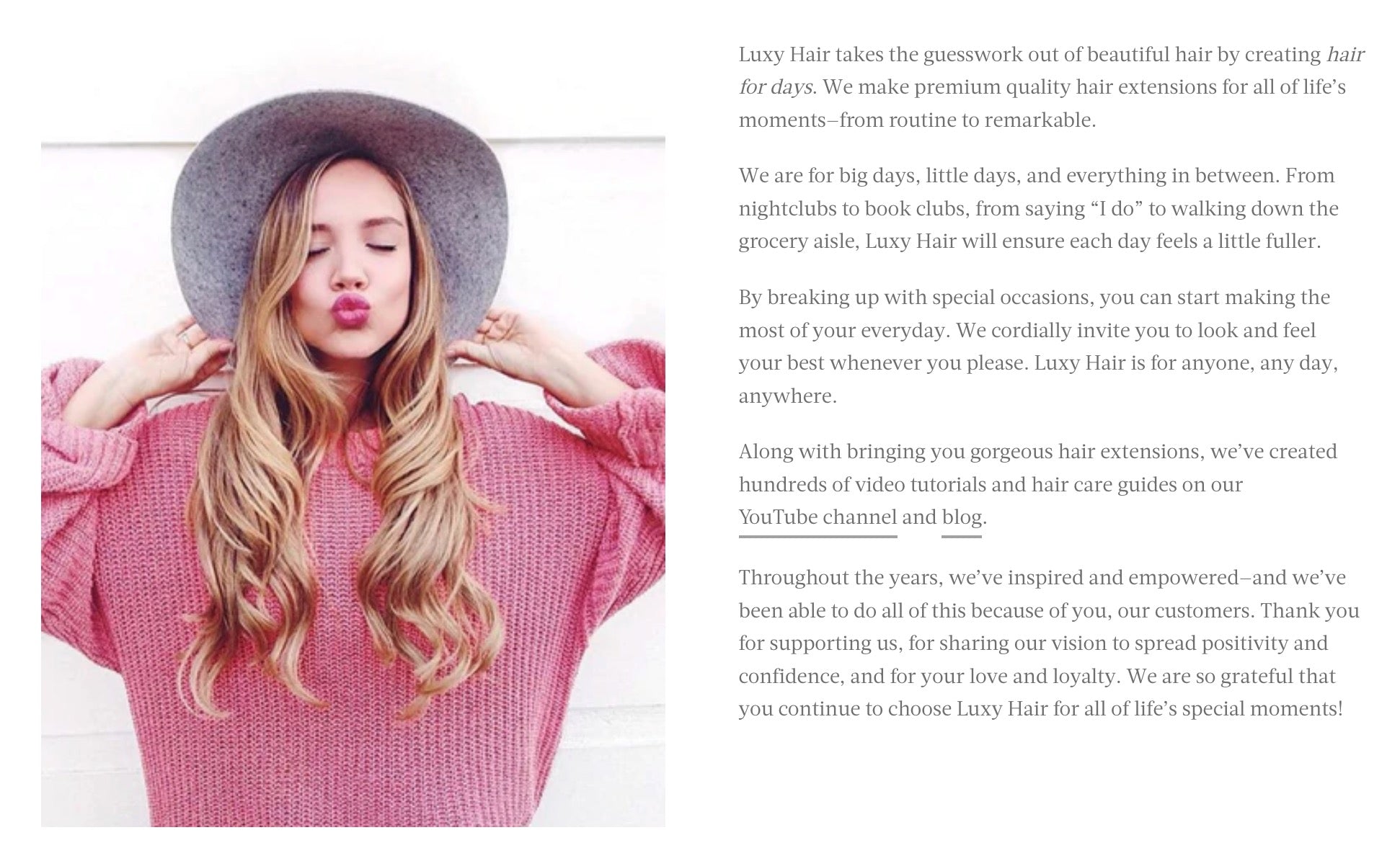
You can also repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business. Hair extensions brand Luxy Hair has a blurb on it’s About page that could easily be repurposed as a company description for its business plan.
- Market analysis
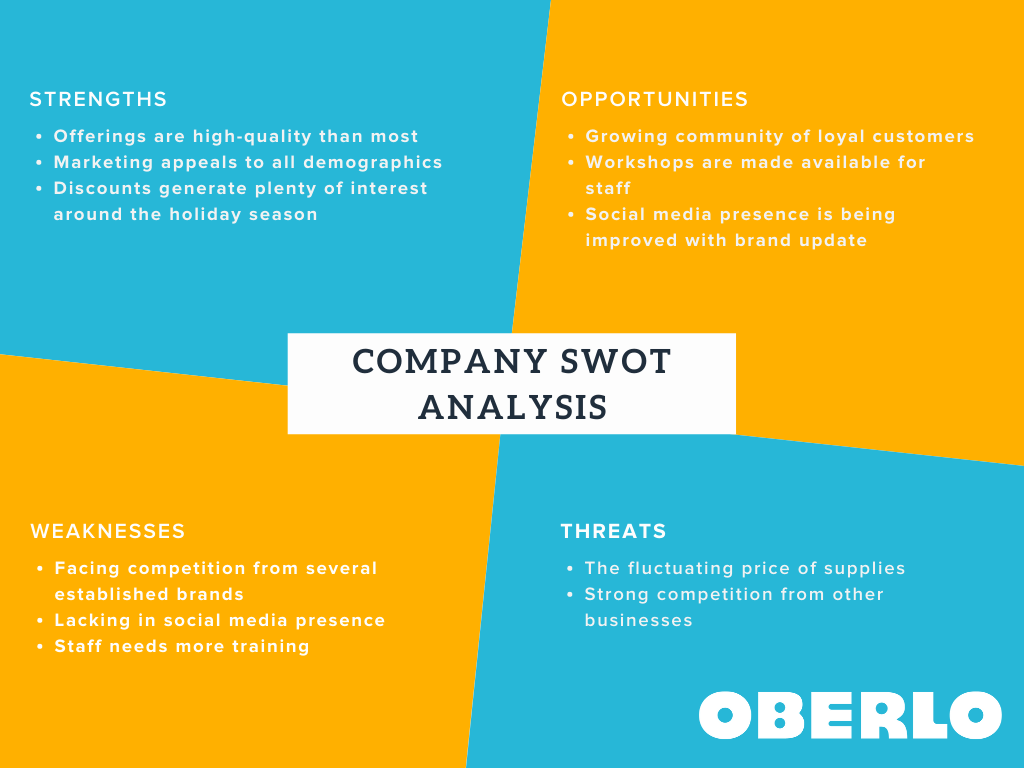
Market analysis comprises research on product supply and demand, your target market, the competitive landscape, and industry trends. You might do a SWOT analysis to learn where you stand and identify market gaps that you could exploit to establish your footing. Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical ecommerce business:
You’ll also want to run a competitive analysis as part of the market analysis component of your business plan. This will show you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to gain an edge over the competition.
- Products and services
This part of your business plan describes your product or service, how it will be priced, and the ways it will compete against similar offerings in the market. Don’t go into too much detail here—a few lines are enough to introduce your item to the reader.
- Marketing plan
Potential investors will want to know how you’ll get the word out about your business. So it’s essential to build a marketing plan that highlights the promotion and customer acquisition strategies you’re planning to adopt.
Most marketing plans focus on the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. However, it’s easier when you break it down by the different marketing channels . Mention how you intend to promote your business using blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth marketing.
Here’s an example of a hypothetical marketing plan for a real estate website:

Logistics and operations
This section of your business plan provides information about your production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan (a.k.a. financial statement) offers a breakdown of your sales, revenue, expenses, profit, and other financial metrics. You’ll want to include all the numbers and concrete data to project your current and projected financial state.
In this business plan example, the financial statement for ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy includes forecasted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
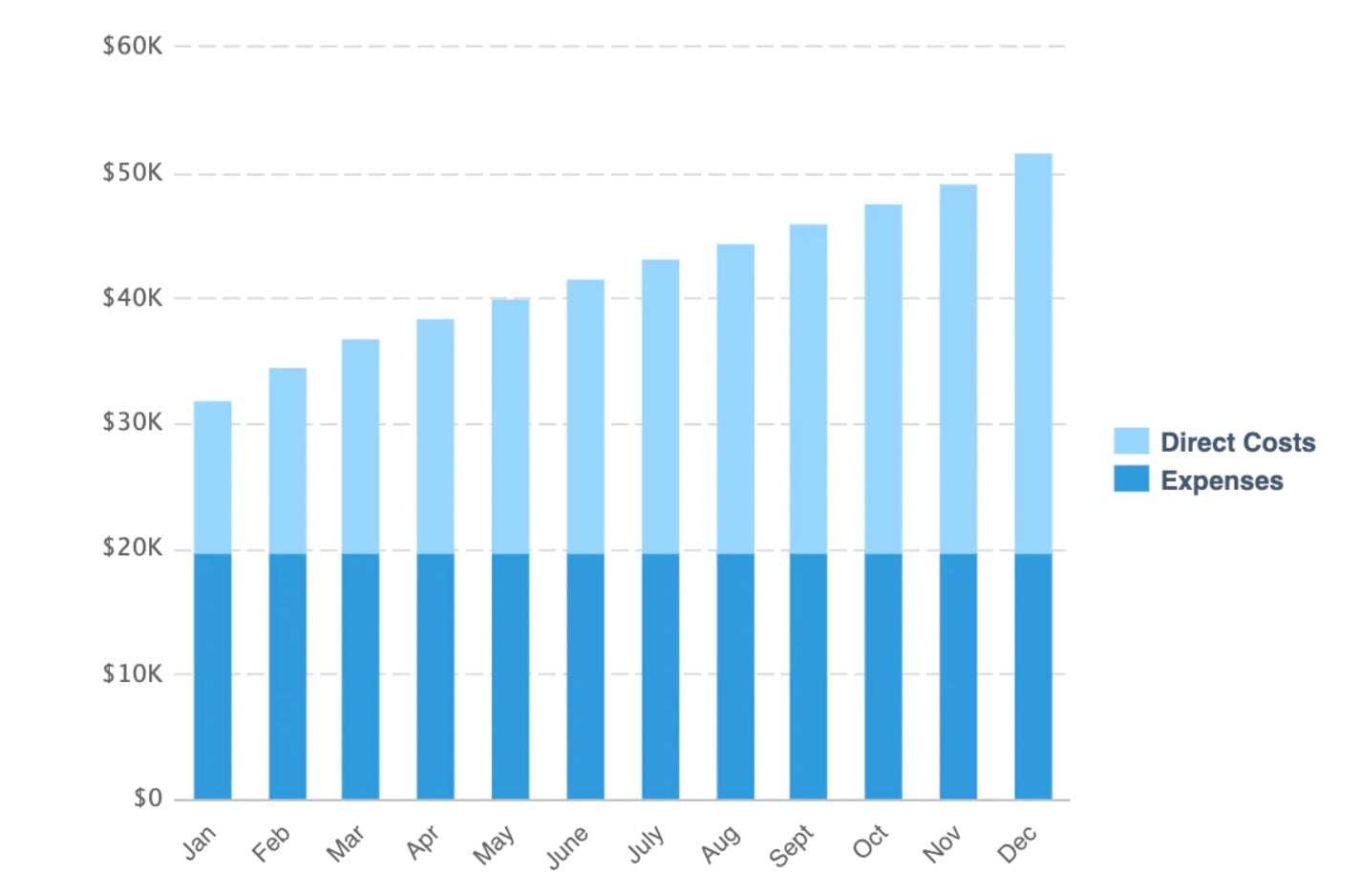
It then goes deeper into the financials, citing:
- Funding needs
- Project cash-flow statement
- Project profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
You can use Shopify’s financial plan template to create your own income statement, cash-flow statement, and balance sheet.
Types of business plans (and what to write for each)
A one-page business plan is a pared down version of a standard business plan that’s easy for potential investors and partners to understand. You’ll want to include all of these sections, but make sure they’re abbreviated and summarized:
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there’s a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example. Shopify has a great business plan template for startups that include all the below points:
- Market research: in depth
- Financials: in depth
Your internal business plan acts as the enforcer of your company’s vision. It reminds your team of the long-term objective and keeps them strategically aligned toward the same goal. Be sure to include:
- Market research
Feasibility
A feasibility business plan is essentially a feasibility study that helps you evaluate whether your product or idea is worthy of a full business plan. Include the following sections:
A strategic (or growth) business plan lays out your long-term vision and goals. This means your predictions stretch further into the future, and you aim for greater growth and revenue. While crafting this document, you use all the parts of a usual business plan but add more to each one:
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Market analysis: detailed analysis
- Marketing plan: detailed strategy
- Logistics and operations plan: detailed plan
- Financials: detailed projections
Free business plan templates
Now that you’re familiar with what’s included and how to format a business plan, let’s go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from.
Bplans’ free business plan template

Bplans’ free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business. It has many pages just for your financial plan and statements. Once you fill it out, you’ll see exactly where your business stands financially and what you need to do to keep it on track or make it better.
PandaDoc’s free business plan template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is detailed and guides you through every section, so you don’t have to figure everything out on your own. Filling it out, you’ll grasp the ins and outs of your business and how each part fits together. It’s also handy because it connects to PandaDoc’s e-signature for easy signing, ideal for businesses with partners or a board.
Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template

Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template helps you map out the essentials of your business, like partnerships, core activities, and what makes you different. It’s a collaborative tool for you and your team to learn how everything in your business is linked.
Better business planning equals better business outcomes
Building a business plan is key to establishing a clear direction and strategy for your venture. With a solid plan in hand, you’ll know what steps to take for achieving each of your business goals. Kickstart your business planning and set yourself up for success with a defined roadmap—utilizing the sample business plans above to inform your approach.
Business plan FAQ
What are the 3 main points of a business plan.
- Concept. Explain what your business does and the main idea behind it. This is where you tell people what you plan to achieve with your business.
- Contents. Explain what you’re selling or offering. Point out who you’re selling to and who else is selling something similar. This part concerns your products or services, who will buy them, and who you’re up against.
- Cash flow. Explain how money will move in and out of your business. Discuss the money you need to start and keep the business going, the costs of running your business, and how much money you expect to make.
How do I write a simple business plan?
To create a simple business plan, start with an executive summary that details your business vision and objectives. Follow this with a concise description of your company’s structure, your market analysis, and information about your products or services. Conclude your plan with financial projections that outline your expected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The optimal format for a business plan arranges your plan in a clear and structured way, helping potential investors get a quick grasp of what your business is about and what you aim to achieve. Always start with a summary of your plan and finish with the financial details or any extra information at the end.
Want to learn more?
- Question: Are You a Business Owner or an Entrepreneur?
- Bootstrapping a Business: 10 Tips to Help You Succeed
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: 20 Ways to Think Like an Entrepreneur
- 101+ Best Small Business Software Programs
Reference.com
What's Your Question?
- History & Geography
- Science & Technology
- Business & Finance
- Pets & Animals
What is a Nature of Business Statement? Meaning and Examples

Running a business generally isn’t a “set it and forget it” proposition. It takes careful planning, nurturing and dedication to even get a new business started — and that’s not to mention all the work that goes into actually operating it once it’s up and running or solving problems that crop up along the way. One of those important tasks is determining your nature of business.
Operating a business carries a certain level of risk. However, new business owners can tip the odds in their favor with careful business planning and by understanding the wide variety of activities — along with the focus of those activities — involved in each aspect of running a company. Learning more about the nature of business is key in accomplishing this goal.
What Is the Nature of Business?
The nature of business is a structured method of describing a company. This concept is a synthesis of what type of business it is and what the business does. The nature of business also highlights the specific problems a given business solves. It encompasses everything a business does to reach its goals and describes the main focus of the company’s offerings.

A discussion of the nature of business of a company usually appears in a business plan that describes how the company will operate. Entrepreneurs, investors and lenders use nature of business statements to ensure that a company is viable before offering to fund it. They want to know about the potential success of the company before deciding whether it’ll likely be a profitable investment. Grant applications are another area where nature of business statements can be necessary because this paperwork also involves funding.
A nature of business statement should thoroughly address the following elements of the business:
Regular process : This separates businesses from hobbies. Businesses have processes that repeat over and over again to produce the same result. That result is a product or service for consumers and income for the business owner.
Economic activity : All businesses have the core goal of generating income.
Utility creation – To be useful to customers, the product or service must be delivered at the right time and place, and it should solve a problem or meet a need. Goods that are not accessible to consumers, for one reason or another, serve no use.
Capital requirement : In simple terms, it takes money to make money. Every business requires employees, equipment and other goods that cost money. These are necessary for producing the product or delivering the service that leads to income.
Goods and services : All businesses deliver something to the public. Some businesses produce tangible goods, such as clothes or cars. Others produce intangible services, such as computer repairs.
Anticipated risk : All businesses require some level of investment of time and money. Sometimes a business owner makes money, and sometimes a business owner loses money. There’s always a risk of losing money when doing business, and some risks are more common in certain industries than others.
Profit-earning motive : The central motive for starting a business is to make a profit.
Satisfaction of consumers’ needs : Businesses operate on supply and demand. When consumers express a want or need, wise businesses answer the call by supplying something to meet that demand.
Involvement from the buyer and seller : In every business transaction, the customer buys something and the business sells something.
Social obligations : Businesses have an impact on their communities at large. They hire people, form relationships with other businesses and help communities by offering a needed product or service. They may also give back to the community through philanthropic efforts or enrichment programs.
A statement about the nature of a business should also explain what problem the business will solve and what type of business the company is.
The Biggest Business Goal: Products Solving Problems
A successful business must solve a problem. Making a concerted effort to discover and fix a problem builds the business’s reputation over the long term and increases its success. It’s important to perform research about consumer preferences and geographic area before starting a company to ensure that there’s a true need for the product.
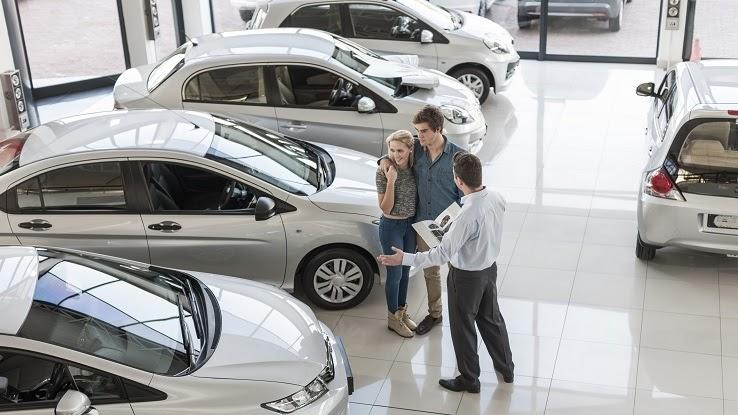

For example, say you’re thinking about opening a sushi restaurant in a nearby town. However, during your research you find that there are already five sushi restaurants open there, and one recently closed. You find out that the town is lacking a good Korean barbecue place, and people are posting on social media about how they wish this type of restaurant existed nearby. Without having done this research, you might’ve moved forward with the sushi restaurant — only to see it fail.
Although every business’ product or service won’t be totally unique, the business should try to address a specific need. For example, many larger cities have at least one street that’s lined with car dealerships. Each dealership sells cars, but they specialize in different brands to solve the problem of consumers not having enough choices. One dealership may sell used luxury cars, while another specializes in Ford vehicles. One dealership has the lowest prices, while another offers in-house financing. Each of these offerings is the solution to a problem that a different group of customers has.
The Business’ Type Matters, Too
Although there’s a vast variety of businesses in the world, there are relatively few types of businesses. Wholesale and manufacturing businesses often sell products to other businesses, but they can be consumer-facing as well. Retail and service businesses often sell directly to customers.

Manufacturers are businesses that start the chain by building a product. Wholesale businesses then sell these products in bulk to retail businesses. Retail businesses sell smaller quantities of products directly to customers. Service-based businesses offer non-tangible services.
In today’s world, however, new forms of business are emerging. Projec-development businesses help other businesses gather the necessary people and capital to complete a specific major project. Hybrid businesses mix a variety of business types. For example, a used car dealership (retail) may also repair cars (service) and auction off excess inventory (wholesale). Understanding what type of business yours would be can better guide you in developing a plan for it.
Common Types of Small Businesses

Here are some of the most popular and profitable business enterprises today and the specific considerations you should make for each when it comes time to draft your nature of business statement.
Retailers earn a livelihood by selling products and services. Many items and services were only available at brick-and-mortar locations in the past. Now, it is possible to order products and services online, after which the retailer delivers them.
Retail businesses include stores that sell clothing, pharmaceuticals, food, and machine parts, among other things. For retail businesses, a nature of business statement should contain the company structure, legal name, location, and—most significantly—the products sold.
2. Hospitality
At its core, hospitality refers to making another person feel at home in one’s presence by providing entertainment and comfort. It may have a variety of definitions depending on the context. There are several sub-sectors within the hospitality business. The top four hospitality industries are food and beverage, lodging, travel and tourism, and entertainment and recreation.
The nature of the business statement will define the hospitality sub-industry in which the business operates. It should also address factors such as location, cost, facilities, and services offered.
Instead of making products, service businesses focus on providing maintenance and repair, training, and consulting services. In other words, they provide intangible value. Those who work in a service business are individuals or groups of individuals who use specialized knowledge and skills to provide value to others.
For this industry, the nature of business statement has to include the kinds of activities that the business performs daily to boost the value of operations and raise profits.
4. Real Estate
Land and buildings are the focus of a real estate business, including everything from purchasing and selling to managing and operating properties. Despite the many hurdles to starting a business in the industry, it is vibrant and incredibly appealing.
Real estate businesses must establish a specific niche, market location, and possible rivals as part of their business plan, and detail these in their nature of business statement. This is an addition to the other components typical to service or hospitality businesses.
Business Operations Guide Companies to Success
Business operations should be tied to the problem the business solves. Operations involve every aspect of managing a business, from the hours a store is open to the number of employees to hire. If the company has a brick-and-mortar presence, the location and hours of operation should serve the people who have the problem the business solves. Marketing must also be geared towards reaching the target audience — the ideal customers for the product or service who most likely have the problem the business’ product or service solves. Beyond running the business, a new business owner must decide how to handle necessary functions like accounting and inventory management.

After careful planning, the final step before starting a business is to make it official and legal by forming the business entity properly. The most common business structures to choose from include sole proprietorship, LLC, LLP, S Corp and C Corp. It’s important to consult with a legal professional who’s familiar with business law to get help in deciding what type of structure will best fit your business. Choosing the wrong entity can have serious liability and tax consequences. But, armed with a strong nature of business statement and some outside assistance where necessary, you’ll be primed for success.
MORE FROM REFERENCE.COM

Nature of a Business Plan: Everything You Need to Know
The nature of a business plan discusses what the future of the business is. It should list how you plan to run the company and what you plan to do with it. 3 min read updated on September 19, 2022
What Are the Parts of a Business Plan?
Even if you just write on an envelope a few ideas about your business strategy, you've started a business plan. Business plans can be helpful, as they list all the tasks necessary to run a company. Entrepreneurs use them to explain their vision to possible investors. These plans can be used by firms that want to attract important employees, find potential business prospects, handle suppliers, and understand how to better manage their companies.
Items to include are the industry, the business concept, the business structure, what the service or product is, and what your marketing plan is in order for the company to be successful.
The marketplace section will talk about defining and analyzing possible customers. This includes where and who they are, what drives them to buy, and so on. The financial section includes your cash flow and income statement, a balance sheet, and additional financial ratios, including break-even analyses. You may want to invest in an accountant and a spreadsheet software program for this. There are seven main components in a business plan, including:
- Market strategies
- Business description
- Executive summary
- Development and design plan
- Competitive analysis
- Financial factors
- Management and operations plan
How Long Should Your Business Plan Be?
A helpful business plan can be short or long, depending on the reason you're creating it. It can be anything from a scrawl on a piece of paper to a detailed plan that's over 100 pages long. The average business plan runs between 15 and 20 pages, but there's room for variation. If your concept is simple, you might be able to define it with only a few words. If you're talking about a new business or industry, you'll need a much lengthier explanation to describe what your idea is.
What your purpose is will also define how long your business plan is. If you want to get millions of dollars to start a venture that's risky, you'll need to do plenty of convincing and explaining. On the other hand, if you use your plan internally to govern ongoing business, you can easily have a more abbreviated version of the plan.
Why Do Startups Need a Business Plan?
A traditional business plan writer is someone who considers themselves an entrepreneur and is looking for funds to start a new venture. Many successful companies originally started their plan on paper to convince investors they should put up capital to help them get started. There are many books on business planning that are aimed at the owners of startup businesses. This is because they're the least experienced and are likely the most appreciative of any help. However, small startups aren't the only companies that need a business plan.
Why Do Established Firms Need a Business Plan?
Not every business plan is written by an excited entrepreneur who is just starting their company. Many are written for and by companies that are well past the startup phase. For example, WalkerGroup/Designs was considered a well-established designer for large retailers. The founder thought of the idea of licensing and trademarking to apparel makers with the symbols 01-01-00. This was aimed at targeting the approaching millennium. Before the costly and difficult task of trademarking this around the world, the founder had a business plan that included sales forecasts. This was to convince larger retailers that it'd be smart to carry their 01-01-00 products.
Enterprises that are middle-stage might draft plans that help them get funding to grow their company similar to startups. However, they may be after larger amounts and looking for investors who will spend more. These enterprises feel it's necessary to have a written plan to manage their business that's already growing. This plan can be a helpful tool to get across their mission to potential suppliers, customers, and more.
If you need help with the nature of a business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Creating a Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- Do I Need a Business Plan
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- Startup Business Plan Presentation Template
- Business Plan for Existing Company
- Purpose of Business Plan Sample: Everything You Need To Know
- Details of a Business Plan
- Business Plan for New Company
18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: July 01, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
So what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing? I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Types
Business plan format, sample business plan: section by section, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ultimately, the format of your business plan will vary based on your goals for that plan. I’ve added this quick review of different business plan types that achieve differing goals.
For a more detailed exploration of business plan types, you can check out this post .
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas. If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
A strategic business plan is another business plan that's often shared internally. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
I’m going to focus on a startup business plan that needs to be detailed and research-backed as well as compelling enough to convince investors to offer funding. In my experience, the most comprehensive and convincing business plans contain the following sections.
Executive Summary
This all-important introduction to your business plan sets the tone and includes the company description as well as what you will be exchanging for money — whether that’s product lines, services, or product-service hybrids.
Market Opportunity
Information about gaps in your industry’s market and how you plan to fill them, focused on demand and potential for growth.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
An overview of your competitors that includes consideration of their strengths and how you’ll manage them, their weaknesses and how you’ll capitalize on them, and how you can differentiate your offerings in the industry.
Target Audience
Descriptions of your ideal customers, their various problems that you can solve, and your customer acquisition strategy.
Marketing Strategy
This section details how you will market your brand to achieve specific goals, the channels and tactics you’ll utilize to reach those goals, and the metrics you’ll be using to measure your progress.
Key Features and Benefits
This is where you’ll use plain language to emphasize the value of your product/service, how it solves the problems of your target audiences, and how you’ll scale up over time.
Pricing and Revenue
This section describes your pricing strategy and plans for building revenue streams that fit your audiences while achieving your business goals.
This is the final section, communicating with investors that your business idea is worth investing in via profit/loss statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets to prove viability.
Okay, so now that we have a format established, I’ll give you more specific details about each section along with examples. Truthfully, I wish I’d had this resource to help me flesh out those first business plans long ago.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan. It is essentially an overview of and introduction to your entire project.
Write this in such a way that it grabs your readers' attention and guides them through the rest of the business plan. This is important because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary: your company description and your products and services.
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front. This is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up your business goals? I’d recommend HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set meaningful goals that matter most for your business.
Products and Services
Here, you will incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive, as it is just a chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business. I recommend including snippets of information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here as well.
Keep in mind that you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. The executive summary should be clear and brief, only including the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template . What makes this executive summary good is that it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
Our Mission
Maria’s Gluten Free Bagels offers gluten-free bagels, along with various toppings, other gluten-free breakfast sandwich items, and coffee. The facility is entirely gluten free. Our team expects to catch the interest of gluten-free, celiac, or health-conscious community members who are seeking an enjoyable cafe to socialize. Due to a lack of gluten-free bagel products in the food industry currently, we expect mild competition and are confident we will be able to build a strong market position.
The Company and Management
Maria’s Gluten Free Bagels was founded in 2010 by Maria Jones, who first began selling her gluten-free bagels online from her home, using social media to spread the word. In 2012 she bought a retail location in Hamilton, MA, which now employs four full-time employees and six part-time employees. Prior to her bagel shop, Maria was a chef in New York and has extensive experience in the food industry.
Along with Maria Jones, Gluten Free Bagel Shop has a board of advisors. The advisors are:
- Jeni King, partner at Winding Communications, Ltd.
- Henry Wilson, president of Blue Robin, LLP.
Our Product
We offer gluten-free products ranging from bagels and cream cheese to blueberry muffins, coffee, and pastries. Our customers are health-conscious, community-oriented people who enjoy gluten-free products. We will create a welcoming, warm environment with opportunities for open mic nights, poetry readings, and other community functions. We will focus on creating an environment in which someone feels comfortable meeting a friend for lunch, or working remotely.
Our Competitive Advantages
While there are other coffee shops and cafes in the North Shore region, there are none that offer purely gluten-free options. This restricts those suffering from gluten-free illnesses or simply those with a gluten-free preference. This will be our primary selling point. Additionally, our market research [see Section 3] has shown a demand for a community-oriented coffee and bagel shop in the town of Hamilton, MA.
Financial Considerations
Our sales projections for the first year are $400,000. We project a 15% growth rate over the next two years. By year three, we project 61% gross margins.
We will have four full-time employees. The salary for each employee will be $50,000.
Start-up Financing Requirements
We are seeking to raise $125,000 in startup to finance year one. The owner has invested $50,000 to meet working capital requirements, and will use a loan of $100,000 to supplement the rest.
Example 2 :
Marianne and Keith Bean have been involved with the food industry for several years. They opened their first restaurant in Antlers, Oklahoma in 1981, and their second in Hugo in 1988. Although praised for the quality of many of the items on their menu, they have attained a special notoriety for their desserts. After years of requests for their flavored whipped cream toppings, they have decided to pursue marketing these products separately from the restaurants.
Marianne and Keith Bean have developed several recipes for flavored whipped cream topping. They include chocolate, raspberry, cinnamon almond, and strawberry. These flavored dessert toppings have been used in the setting of their two restaurants over the past 18 years, and have been produced in large quantities. The estimated shelf life of the product is 21 days at refrigeration temperatures and up to six months when frozen. The Beans intend to market this product in its frozen state in 8 and 12-ounce plastic tubs. They also intend to have the products available in six ounce pressurized cans. Special attention has been given to developing an attractive label that will stress the gourmet/specialty nature of the products.
Distribution of Fancy's Foods Whipped Dream product will begin in the local southeastern Oklahoma area. The Beans have an established name and reputation in this area, and product introduction should encounter little resistance.
Financial analyses show that the company will have both a positive cash flow and profit in the first year. The expected return on equity in the first year is 10.88%
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company that showcases your mission and impact, then outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, you might emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists, whereas you might emphasize community benefits and minimal environmental impact for progressive nonprofits.
For more guidance, check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary .
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market. Ask and answer: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, SOM analysis , a SWOT analysis , and perform market research on your industry to get some insights for this section. More specifically, here’s what I’d include.
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.
Example: The market for Doggie Pause is all of the dog owners in the metropolitan area and surrounding areas of the city. We believe that this is going to be 2/3 of the population, and we have a goal of gaining a 50% market share. We have a target of a 20% yearly profit increase as the business continues.
Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape Analysis
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you‘ll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are. After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you’ll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover the following:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing.
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle.
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points.
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers.
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are. It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location. This demonstrates useful experience in the industry, helping to build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Competitive Environment
Currently, there are four primary competitors in the Greater Omaha Area: Pinot’s Palette Lakeside (franchise partner), Village Canvas and Cabernet, The Corky Canvas, and Twisted Vine Collective. The first three competitors are in Omaha and the fourth is located in Papillion.
Despite the competition, all locations have both public and private events. Each location has a few sold-out painting events each month. The Omaha locations are in new, popular retail locations, while the existing Papillion location is in a downtown business district.
There is an opportunity to take advantage of the environment and open a studio in a well-traveled or growing area. Pinot’s Palette La Vista will differentiate itself from its competitors by offering a premium experience in a high-growth, influential location.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience? I’d recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear about why you're targeting them. Here are some questions I’d ask myself:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
The Audience
Recognize that audiences are often already aware of important issues. Outreach materials should:
- Emphasize a pollution-prevention practice
- Tell audience a little about how to prevent pollution
- Tell audience where they can obtain information about prevention.
Message Content
- Focus the content for outreach materials on cost savings, such as when and where pollution prevention is as cheap as or cheaper than traditional techniques. Include facts and figures.
- Emphasize how easy it is to do the right thing and the impacts of not engaging in pollution prevention.
- Stress benefits such as efficiency or better relations with government, for businesses not primarily concerned with public image.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you‘ll discuss how you’ll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier. I’d suggest including these details:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it.
- The goal targets you aim to achieve.
- The metrics you'll use to measure success.
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler. In my opinion, it works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
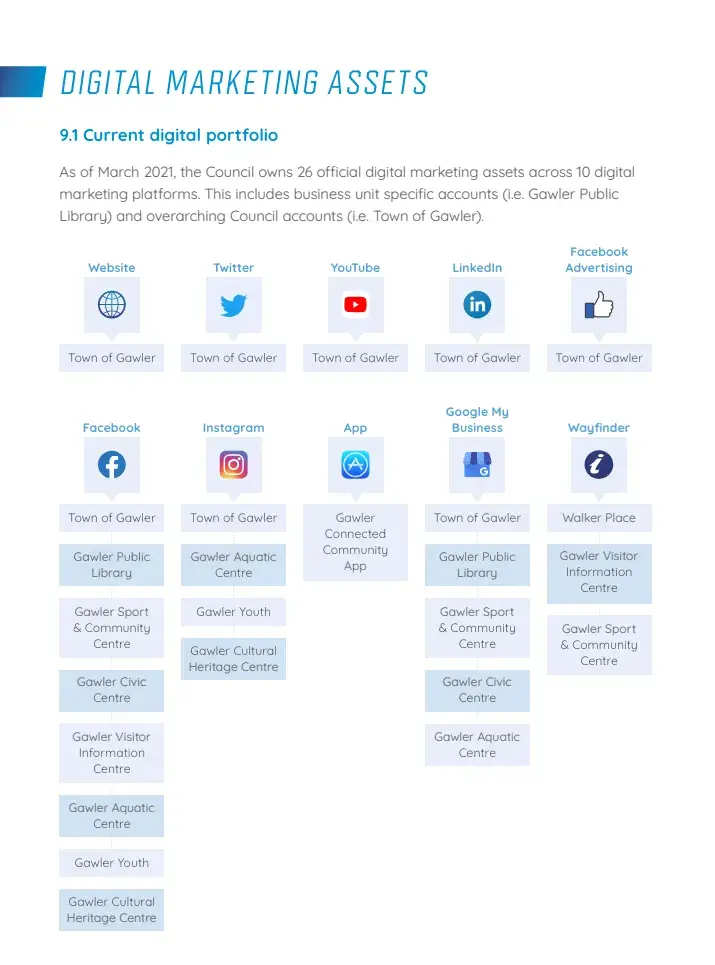
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business


2. Lula Body

23 of My Favorite Free Marketing Newsletters
![nature of the business example business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-flowchart-template-1-20240716-6679104-1.webp)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
![nature of the business example business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![nature of the business example business plan How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Nature of Business: Definitions and Examples
Welcome to the exciting world of business! In this journey, we’re going to explore what business really means.
It’s not just about profits and offices; it’s a vibrant landscape where ideas take shape, needs are met, and dreams are realized.
At its core, the nature of business is to provide value, whether through products, services, or both, to a group of people or other businesses.
This exchange is the heartbeat of economies worldwide, large and small.
But what exactly constitutes the nature of business? It’s a rich tapestry woven with various elements – innovation, market strategies, economic impact, and so much more.
The nature of a business defines how it operates, competes, and serves its purpose in the vast economic ecosystem. Whether it’s a small local bakery or a global tech giant, each business has a unique DNA that sets it apart.
Throughout this article, we’ll dive into different business types, from startups to multinational corporations, explore various business models, and examine how external factors like technology and globalization shape the business landscape.
So, whether you’re a budding entrepreneur, a business student, or just curious about the business world, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the nature of business.
Table of Contents
Defining Business in Today’s World
Now, let’s delve into what defines a business in today’s dynamic world. The nature of business is not static; it evolves with time, technology, and consumer behavior.
Today, a business can be defined as an entity that creates and sells goods or services for profit. But it’s more than just transactions and trade. The nature of business is about identifying needs and fulfilling them, creating value not just for the owners but also for customers, employees, and society at large.
In the modern context, a business operates in an incredibly interconnected environment. Technology, for instance, has transformed how businesses function, enabling them to reach a global audience and operate 24/7.
The digital era has given rise to new business models and strategies, shifting the focus from mere transactions to relationships and experiences.
Another defining aspect of today’s businesses is their adaptability. In a rapidly changing world, businesses must be agile, ready to pivot in response to market trends, consumer preferences, and economic shifts. This adaptability is crucial for survival and growth.
Additionally, the nature of businesses in society has expanded. Beyond profit-making, businesses today are increasingly held accountable for their social and environmental impact. This has led to a rise in sustainable practices and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
In summary, a business today is not just an economic entity; it’s a versatile, dynamic organism that plays a critical role in shaping the world we live in. It’s about creating meaningful experiences, fostering innovation, and making a positive impact on society.
The Core Elements of a Business
The product or service: heart of business.
At the center of every business is its product or service—the primary offering that meets the customer’s needs. This could be a tangible item, like a smartphone, or an intangible one, like software services.
The success of a business hinges on how well this core offering aligns with market needs and expectations. It’s about finding that sweet spot where your product or service solves a problem or fulfills a desire more effectively than anyone else.
Understanding Market Demand
Understanding market demand is like reading a road map; it guides businesses to where they should go. It involves researching and analyzing who the customers are, what they want, and how much they’re willing to pay.
A business that keenly understands its market can adapt and thrive, even in changing conditions. This understanding helps in tailoring products or services to suit customer needs, creating targeted marketing strategies, and finding new market opportunities.
The Role of Innovation in Business
Innovation in business is not just about coming up with new products; it’s a mindset, a way of thinking. It’s about constantly questioning the status quo and seeking better, more efficient ways to meet customer needs.
Innovation can be in product design, business models, customer service, or even in the way a company approaches its internal processes. Businesses that prioritize innovation tend to stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changes faster, and enjoy long-term success.
Types of Businesses: A Broad Overview
Small and medium enterprises (smes).
SMEs are the backbone of many economies. They are characterized by their smaller size, but don’t let that fool you—they pack a punch in innovation and flexibility.
These businesses often cater to niche markets or local communities and are known for their personalized customer service. They are also critical in generating employment and driving economic growth at the local level.
Large Corporations and Multinationals
Large corporations and multinationals operate on a vast scale, often with a significant presence in multiple countries. They wield considerable economic power and resources, allowing them to undertake extensive research and development, influence market trends, and access a global customer base.
These entities face different challenges, like managing complex operations and navigating diverse market regulations.
Non-Profits and Social Enterprises
Non-profits and social enterprises are unique in the business world. Their primary goal is not profit, but social good. They operate by providing services or products that address societal issues—be it in health, education, or environmental conservation.
These organizations often rely on donations, grants, and other funding sources and are increasingly adopting business strategies to sustain and increase their impact.
Sector-Specific Business Nature
Businesses differ vastly depending on the sector they operate in and the target market they are focused on. Each sector has unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities, shaped by different market demands and regulations.
Manufacturing Sector Insights
The manufacturing sector is the powerhouse of tangible products, from cars to canned food. A manufacturing business is characterized by its focus on efficiency, production processes, and quality control.
With a manufacturing company, the balance between cost, speed, and quality is crucial. Advances in technology, like automation and robotics, are transforming the manufacturing landscape, leading to increased productivity and new ways of production.
A manufacturing business often enters the international sector and often needs a unique legal structure to offer services across the globe. For example, a hybrid business could have manufacturing operations in Asia but mainly sell goods and services in the Americas – requiring a more intricate structure.
The Service Industry Explored
The service industry is all about delivering intangible value, be it through hospitality, banking, or education. Here, customer experience and service quality are paramount.
A service business relies heavily on human skills and interaction, although technology is playing a growing role in enhancing service delivery and customer engagement.
Service businesses need to provide customer-centered strategies for success – whether it be a small business owner or a large-scale established business.
Digital and Tech Businesses
In the digital and technological sector, innovation is the name of the game. This sector encompasses businesses that are at the forefront of technological advancements – think software companies, e-commerce platforms, and tech startups.
The pace of change here is rapid, with businesses continuously evolving to stay ahead in a highly competitive market. Success in this sector often hinges on the ability to anticipate and quickly adapt to technological shifts.
Agricultural and Resource-Based Industries
These industries are foundational, dealing with the production of raw materials like food, wood, and minerals.
They are crucial for sustaining life and other industries but are heavily dependent on natural factors like climate and geography. Sustainability and environmental impact are increasingly significant concerns in these sectors.
It encompasses a wide array of businesses that are owned, operated, and managed by individual private owners or corporations, rather than by the government or public entities. The private sector is known for its diversity, innovation, and contribution to economic growth.
Private Sector Industries
The private sector, comprising a diverse range of businesses owned and operated by individual entrepreneurs or corporations, stands in contrast to government-run entities.
This sector is a powerhouse of innovation and economic growth, driven by private ownership and management.
Integral to the economy, it spans multiple industries, each uniquely contributing to financial stability and job creation. These businesses are often for-profit organisations, influencing their agility, efficiency, and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Characterized by market-driven operations, the private sector adjusts swiftly to consumer demands and trends, shaping the landscape of goods and services available. Financial sustenance is primarily derived from private investments and revenue generation, emphasizing the importance of sound financial strategies and growth orientation.
Employment opportunities are abundant within this sector, covering a spectrum from manufacturing to tech-based services. Innovation and competition are at the heart of its ethos, spurred by the continuous quest to meet evolving customer needs and to stay ahead in the market race.
Yet, the private sector faces its own set of challenges, including market volatility, regulatory shifts, and the imperative for constant innovation. Just like with the public sector, its fortunes are often closely tied to the broader economic climate, making it sensitive to global economic shifts and trends.
Types of Business Entities: Understanding LLC, Limited Liability Partnership, and Sole Proprietorship
In the diverse world of business, the choice of business entity significantly impacts taxation, liability, and management structures. Three common types are Limited Liability Companies (LLC), Limited Liability Partnerships (LLP), and Sole Proprietorships. Each has distinct characteristics suited for different business needs.
Which business entity is right for you?
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is a popular business structure that offers flexibility and protection. It combines the liability protection of a corporation with the tax efficiencies and operational flexibility of a partnership.
- Liability Protection : Owners of a limited liability company, known as members, are typically not personally liable for the business’s debts or liabilities. This protection is akin to that of a corporation, safeguarding personal assets like homes and savings.
- Taxation : A limited liability company can benefit from pass-through taxation, where the business income is not taxed at the company level but passed through to members’ personal income tax returns, avoiding the double taxation often seen in corporations.
- Management Flexibility : A limited liability company can offer flexibility in management. They can be managed by members (owner-managed) or by appointed managers (manager-managed), allowing for adaptability in operations and decision-making.
- Formation and Maintenance : Forming an LLC involves filing articles of organization with the state and drafting an operating agreement. While simpler than a corporation, it requires more formalities than a sole proprietorship.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP is ideal for professional groups like lawyers, accountants, or consultants, offering a combination of partnership benefits with liability protection.
- Liability Protection : In an LLP, partners are not responsible for the malpractice of other partners, offering protection from joint liability. This does not cover personal negligence or misconduct.
- Taxation : Similar to LLCs, LLPs enjoy pass-through taxation, where income is reported on each partner’s personal tax returns, eliminating the corporate tax layer.
- Management Structure : In LLPs, partners have equal rights in management decisions, though roles can be defined differently in the partnership agreement.
- Suitability : LLPs are often restricted to certain professional services and may have varied regulations depending on the jurisdiction.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common structure, owned and operated by one person. This type of business involves a single individual and this person is personally responsible for any debts occured.
- Ease of Setup and Low Cost : This form of business is straightforward to establish, often requiring no formal action other than necessary permits and licenses. It’s a low-cost option with minimal regulatory requirements.
- Personal Liability : The owner has unlimited personal liability for debts and obligations, as there is no legal separation between the owner and the business.
- Taxation : Earnings are reported on the owner’s personal income tax returns. This simplicity in taxation is one of the key attractions of this business model.
- Control and Decision-Making : The owner has complete control over decision-making processes but also bears all the responsibility for the business’s success or failure.
Choosing the Right Type
The choice between an LLC, LLP, and Sole Proprietorship depends on various factors, including the level of liability protection desired, tax implications, the nature of the business, capital needs, and the number of owners involved.
Businesses often start as sole proprietorships or partnerships and evolve into LLCs as they grow and seek more protection and structure. Consulting with legal and gaining professional advice can provide insights tailored to specific business needs and goals, ensuring the right structure for successful operations.
The Business Environment
The environment in which a business operates is a complex web of factors that can significantly impact its operations and strategies.
Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is key for any business. It involves analyzing competitors, market position, and industry trends. Staying competitive means continuously improving products or services, innovating, and understanding customer preferences.
Economic Influences
Economic factors like inflation, interest rates, and economic growth can greatly affect a business. These elements influence consumer spending, investment decisions, and overall business health.
A solid business plan must account for these economic variables and be flexible enough to adapt to changes.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Businesses must navigate a web of legal requirements, from employment laws to environmental regulations. Moreover, ethical considerations are increasingly at the forefront of business operations.
Practices like fair trade, sustainable sourcing, and corporate social responsibility are not just legal requirements but also essential for building trust and maintaining a positive brand image.
Business Models and Strategies
In the landscape of business, the concepts of business models and strategies are like the blueprint and roadmap guiding a company’s journey. Understanding and innovating in these areas is key to business success.
Traditional vs. Modern Business Models
Traditional business models have long focused on brick-and-mortar operations, with value creation coming from physical goods or in-person services. But the modern business arena has expanded dramatically, embracing digital and online models.
This shift includes e-commerce platforms, subscription services, and freemium models, where basic services are provided free with premium features available at a cost. The transformation from traditional to modern models is not just about going digital; it’s a complete rethink of how value is delivered to customers.
Innovation in Business Strategy
Innovation in business strategy goes beyond new products or technologies; it’s about reimagining how a business operates and engages with its market. This includes exploring new marketing techniques, adopting sustainable practices, or even overhauling the supply chain for greater efficiency.
The digital age has opened new avenues for strategy, where data analytics and customer feedback loops can drastically improve business decisions and customer experiences.
Globalization and Business Nature
The reach of businesses today transcends local and national boundaries, stepping into the global arena. This shift has profound implications for how businesses operate and compete.
Navigating International Markets
Expanding into international markets is more than just selling products or services globally. It involves understanding diverse cultural nuances, complying with different legal environments, and adapting to varied economic conditions.
Businesses must be nimble and culturally aware to succeed in this global marketplace, often requiring a localized approach to marketing and operations to resonate with different audiences.
Cultural Impact on Business Practices
Culture deeply influences business practices. From decision-making processes to marketing campaigns, understanding and respecting cultural differences is vital.
This cultural awareness affects everything from negotiation styles to the design of products and services. As businesses go global, embracing and celebrating this diversity can become a significant strength, helping to forge deeper connections with customers and partners worldwide.
9. Technology’s Role in Shaping Business
The influence of technology on the business world is a tale of revolution and transformation. It’s about how tech has redefined not just the way businesses operate, but also how they think and strategize.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is a buzzword that captures the essence of technology’s impact on business. It’s not merely about adopting new tech tools; it’s a radical shift in business operations, culture, and customer engagement.
Businesses are leveraging cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and create personalized customer experiences. This transformation is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental change in how businesses exist and thrive in the digital age.
The Future of Business in the Tech Age
Looking ahead, the interplay between technology and business will continue to evolve. Technologies like blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and quantum computing are poised to further revolutionize various sectors.
The future of business lies in embracing these technologies, adapting to their disruptions, and innovating continuously. This evolution isn’t just about survival; it’s about thriving in a tech-driven world.
Entrepreneurship and Start-up Culture
In the contemporary business landscape, entrepreneurship and start-up culture have become the heartbeats of innovation and economic growth.
From Idea to Execution
The journey from a spark of an idea to a successful business is a thrilling yet challenging path. It involves market research, business planning, securing funding, and relentless execution.
This process demands not just a great idea, but also the grit, adaptability, and resilience to navigate the ups and downs of start-up life. Entrepreneurship is about turning challenges into opportunities and ideas into realities.
Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Every successful start-up has a story, often filled with obstacles overcome and lessons learned. These narratives are rich with insights on perseverance, innovative thinking, and strategic pivoting.
By examining these stories, budding entrepreneurs can gain valuable knowledge and inspiration. These tales are not just about financial success; they’re about the passion, hard work, and creativity that drive the business world forward.
Challenges Facing Businesses Today
In today’s ever-changing business landscape, companies face a multitude of challenges that test their resilience, adaptability, and foresight.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
The growing urgency of environmental sustainability has put businesses in a critical position. They are increasingly expected to adopt eco-friendly practices, reduce carbon footprints, and contribute to sustainable development goals.
This shift not only involves rethinking operational processes but also aligning corporate values with environmental stewardship. Embracing these changes is not just a moral imperative but a business necessity, as consumers and stakeholders increasingly favor environmentally conscious companies.
Navigating Market Uncertainties
The business world is fraught with uncertainties arising from various factors like economic fluctuations, geopolitical tensions, and technological disruptions. These uncertainties can impact market trends, consumer behavior, and overall business stability.
Companies must develop robust risk management strategies and maintain agility to adapt to these unpredictable changes. Staying ahead in this volatile environment requires keen market insights, flexible business models, and an innovative mindset.
Real-World Examples of Diverse Businesses
Examining real-world examples offers invaluable insights into the practical application of business concepts and strategies.
Case Studies Across Industries
Exploring case studies from different industries sheds light on varied business models, strategies, and challenges. For instance, tech giants like Apple and Amazon demonstrate how innovation and customer-centric approaches drive success.
On the other hand, companies like Patagonia in the apparel industry show how commitment to sustainability can be a unique selling proposition. These case studies not only provide a learning platform but also inspire new ways of thinking and operating in business.
Lessons from Successful Enterprises
Analyzing the journeys of successful businesses reveals common threads of resilience, adaptability, and vision. Whether it’s a small start-up that scaled up or a legacy company that reinvented itself, there are lessons to be learned about navigating challenges, seizing opportunities, and staying true to core values.
These narratives are a rich source of knowledge and motivation for anyone looking to understand the intricacies of running a successful business in today’s dynamic world.
Conclusion: The Evolving Nature of Business
As we reach the conclusion of our exploration into the nature of business, it’s evident that the business landscape is not static but in a state of constant evolution. This dynamic environment is shaped by myriad factors, from technological advances and globalization to shifting market demands and environmental concerns.
The rise of digital technologies has revolutionized the way businesses operate, communicate, and market themselves. Globalization has expanded market reach but also introduced complex challenges such as cultural differences and international competition. Today’s businesses must navigate these waters with agility and foresight.
The modern business is no longer just a commercial entity; it’s a part of a larger societal and environmental system. With this comes the responsibility to operate ethically, sustainably, and with a greater focus on social impact. This shift in perspective is not just driven by regulatory demands but also by a growing awareness among consumers who seek to support businesses that align with their values.
Entrepreneurship and start-ups have added new dimensions to the business world, bringing innovation and fresh approaches to traditional industries. They remind us that at the heart of every successful business lies the courage to take risks, the vision to see opportunities where others see obstacles, and the tenacity to turn ideas into realities.
As we’ve seen through various examples across industries, successful businesses are those that can adapt to changes, foresee trends, and continuously evolve. Whether it’s a small local business or a multinational corporation, the ability to innovate and adapt is key.
In conclusion, the nature of business is multifaceted and ever-changing. It’s shaped by external forces and internal decisions. Businesses that understand and embrace this dynamic nature are better equipped to thrive in the unpredictable yet exciting world of commerce. As we move forward, the future of business looks both challenging and promising, filled with opportunities for those willing to innovate, adapt, and lead with purpose.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Is Your Business Being Found Online?

Free Digital Marketing Report ($150 Value)
How to Write an Effective Press Release: Tips from the Pros
Considerations for starting up your recycling firm, boost your marketing efforts with interactive digital business cards , maximizing roi with innovative digital content, eeat breakdown – let’s enhance the signals for high-quality content and higher search engine ranking, what is the lorem ipsum meaning and translation, sending large attachments here are 3 easy email methods, dominating the digital landscape: a comprehensive guide to law firm digital marketing, read more articles about business..
Increased environmental consciousness and government regulations have caused unparalleled growth in the recycling industry, presenting a good chance for businesspeople to make profits while bringing about positive change. Nevertheless, setting up a recycling company...
The Complete Guide to Managed IT Services: Unlocking Growth and Efficiency for Your Business
As companies increasingly rely on complex technology frameworks bolstering operations, dedicating scarce budget and focus to simultaneously optimizing infrastructure while pushing strategic initiatives becomes untenable. Managed IT services help bridge...

Exploring the Benefits of a Singapore Dedicated Server
In the world of digital infrastructure, businesses are continually seeking reliable and efficient solutions to meet their growing needs. One of the most robust options available today is the use of a dedicated server. Specifically, this hosting can offer...

How Professional IT Support and Service Propel Small Businesses Forward
Business without tech in the 21st century? That's very unlikely. Matter of fact, studies show that about 93% of small businesses today use some form of tech to keep their daily grind going. But tech, while helpful, comes with issues. Sometimes it fails....

VAT in Ireland
Value added tax (VAT) is a common sales tax applicable in most European Union countries, including Ireland. This is a tax charged at every stage of the supply chain, from production to retail. The purpose of VAT is to tax added value at every stage of the production...

Enhancing Corporate Events With Innovative Photo Booth Experiences
When aiming to elevate your corporate event, the inclusion of photo booths has become a crucial element, providing attendees with a delightful and interactive experience. With various options available, ranging from virtual photo booths to green screen setups, the...
- Corporations
- Definitions

Nature of Business (What It Is And What You Must Know)
What is the Nature of Business ?
How do you legally define it?
What are the essential elements you should know!
In this article, we will break down the Nature of Business meaning so you know all there is to know about it!
Keep reading as we have gathered exactly the information that you need!
Let’s dig into our business terms knowledge!
Are you ready?
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is Nature of Business
The nature of business is a phrase referring to the overall purpose and existence of a company within a market sector or industry.
When we say nature of a business, we are alluding to:
- What type of products and services are sold by a company
- The industry in which the company operations
- Its overall mission and purpose
- Other distinctive characteristics of the business
For example, to understand the nature of business, we can classify the “nature” into different categories:
- By product or service
- By organizational setup
- By organizational structure
- By business type
Nature of Business Definition
How do you define nature of business?
The definition of “nature of business” can vary from one person to another.
The nature of business is a statement about a company’s offering to its clients, its industry, legal structure, or any other distinctive qualities of the business.
For example, if you say a company in the “private sector”, you evaluate the nature of the company based on its nature to earn profits.
If you say that a company is the “manufacturing sector”, you refer to a company primarily concerned with manufacturing operations.
If you refer to a company as a “corporation”, you are qualifying the nature of the company by assessing its legal structure.
Let’s look at different categories in which you can classify the nature of different businesses.
Nature of Business Categories
To better illustrate the concept, we have put together a list of different ways you can view or consider the nature of your business.
Nature of business types
The nature of business can be considered as business types.
A business type refers to the market sector in which the company operations, such as:
- Government sector
- Military sector
- International sector
- Private sector
- Technology sector
- Merchandising sector
- Service sector
- Manufacturing sector
- Non-profit sector
- Public sector
Within each of these sectors, you may have subcategories.
Organization Type
Within our nature of business list, the nature of company can be viewed as the manner the company has been structured.
A company’s organizational setup can be:
- A corporation
- A partnership
- A sole proprietorship
- A limited liability company
- A limited liability partnership
The legal manner of how the business entity formed is an angle to describe the nature of your business.
Business Classification
You can consider the “nature” of a business based on its industry classification.
The government classifies all companies into different categories.
This is useful for research and statistical purposes allowing the government to track how a specific industry or business category is doing in the economy.
There are two business classifications commonly used:
- The Standard Industrial Classification (SIC)
- The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS)
SIC is a classification used by the U.S. Department of Labor whereas the NAICS is a classification system jointly used by Canada, Mexico, and the United States.
Nature of Business Examples
Let’s look at a nature of business example by type of business to complete our illustration of this notion.
Service Business
A service business is a type of business that provides intangible products to its clients.
For example, the service business can be subdivided into:
- Accounting firms
- Public relations firms
- Medical practitioners
- Software consultants
- Marketing consultants
- Banks
- Repair shops
Merchandising Business
A merchandising business is a type of business that buys products wholesale and sells them at the retail price.
Their overall objective is to sell products at a price point higher than what it cost them.
Examples of merchandising companies can be:
- Grocery stores
- Convenience stores
- Distributors
- Resellers
Manufacturing Business
A manufacturing business is a type of business that purchases products to combine them into something new.
They transform existing products (such as raw material or other material), into manufactured goods sold to customers.
For example, a manufacturing company may purchase nuts or grains as raw commodities and produce consumer-friendly goods.
Takeaways
So what is the legal definition of Nature of Business ?
Let’s look at a summary of our findings.
Nature of Business
If you enjoyed this article on Nature of Business , we recommend you look into the following legal terms and concepts. Enjoy!
Related legal terms
Business definition Characteristics of business Cooperative Financial independence Knowledge workers Limited liability company Market expansion Nature of management Partnership Revenue generation Sole proprietorship Types of businesses Author
- Business Classification
RELATED ARTICLES
What is contract manufacturing (all you need to know), types of business strategy (all you need to know), is it cc’d or cc’ed (explained: all you need to know), most popular, what is a special purpose entity (all you need to know), what is corporate raiding (explained: all you need to know), what are golden shares (explained: all you need to know), what is a targeted repurchase (explained: all you need to know), what is a friendly takeover (explained: all you need to know), editor's picks, llc vs corporation (key differences you must know), how to start a business in massachusetts [step-by-step ultimate guide], business license california (explained: all you need to know), ltd company (what is a limited company: overview), how to start a business in illinois [step-by-step ultimate guide].
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
Purposes of a Business Plan
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.
What are the essential components of a business plan?

Executive summary
The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
Business description or overview
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
Product and price
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Competitive analysis
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Target market
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
Financial plan
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Funding requirements
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Types of business plan.
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
How often should a business plan be reviewed and revised?
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
What are the key elements of a lean startup business plan?
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
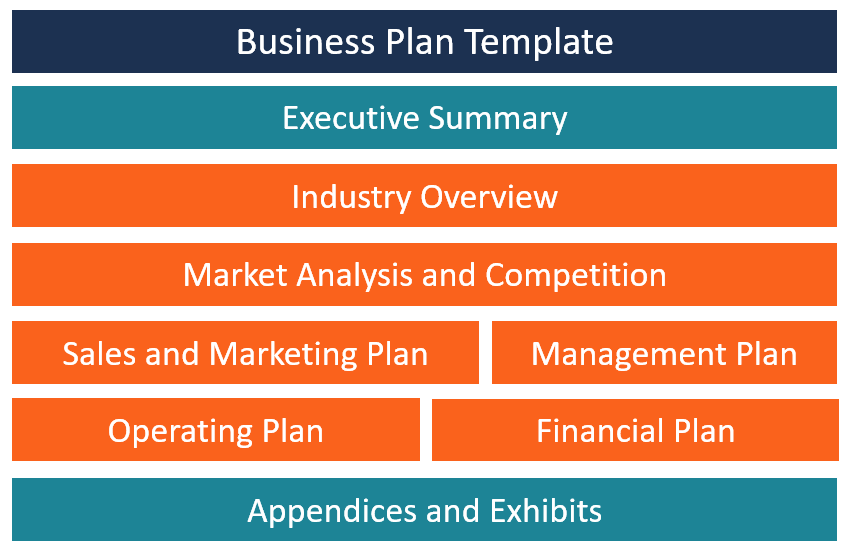
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1222648303-e00f14f235ba4c63aa222a87f430e345.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Products For
- Help Guides
- Billing FAQs
- Business Plan
Anatomy of a Business Plan: 15 Tips for Writing a Plan That Leads to Success
If you are starting a new business or restructuring a business you already own, then one of your most important tasks is writing a business plan.
Table of Contents
Remember the reasons why you need a business plan, make the company description your elevator pitch, know your numbers, do a thorough market analysis, be clear about your business organization, create an organizational chart, use graphs and charts to make the plan come alive, create a private business plan, make it actionable, establish a page limit, ask others to review and proofread your plan, show them the money, be realistic, tell a human story.
Before you write a business plan, consider the function of a business plan document to a new business or company changing direction.
Investopedia defines a business plan as “[a] written document that describes in detail how a new business is going to achieve its goals.”
A comprehensive legal business plan includes sections about the company's budget, financing, projected revenue, marketing strategies, market analysis, expenses, costs, and operational objectives.
Many people think a business plan document is just a report that is created to attract potential investors or to secure a loan. While a business plan is definitely valuable for investors, it is also a tool to help the business owner understand how his or her business will operate.
The act of writing a business plan forces owners to examine their assumptions and identify areas that may have been overlooked. In addition, business plan documents will identify goals and milestones that the company can use as targets during the official launch and beyond.
Before you sit down to write your business plan, make sure you understand what areas are usually included in a business plan template.
The plan is a document that should guide your business for the first years of its operation, so plan to revisit your plan periodically to update your progress.
One of the common mistakes people make when drafting a business plan is opening with a dry description of the company and its objectives. Instead, your business plan should open with an attention-grabbing hook that describes why your business is an incredible idea.
An elevator pitch is a brief speech that you use to generate interest in what your company does. The reason it is called an elevator pitch is because it should be a statement you can deliver in the time it would take to ride down in an elevator.
When you make the company description section of your business plan read like an elevator pitch, you are defining the company in a succinct, memorable, and persuasive way.
Assume your audience is someone who has no experience in your industry. Use a three-step process:
- First, begin by identifying the problem that your business will solve.
- Second, give a brief explanation of how your company solves the problem and why your solution is unique.
- Third, include a call to action that makes the reader want to connect with the business in the future.
Limit your pitch to no more than three quarters of a page. Once you have an engaging description of your company, you can move on to the next phase of your business plan.
If you've ever watched ABC's investor reality show Shark Tank , you know that one of the death knells for entrepreneurs is a failure to know their numbers. This is a common problem, but one that can easily be resolved by putting time into market analysis and financial projections in your business plan.
The market analysis section should always come before the financial projections section of your business plan document. Some business owners skip this step, going straight to financial projections without laying the foundation for where the data comes from.
These companies may struggle because they did not do their due diligence and do not have a thorough understanding what the numbers are based on.
A common mistake in business plans is relying on projections or guesses about what will happen in the future. Since investors can take six months or more to make decisions, make sure you can easily update your business plan documents to include the latest numbers.
There are many factors that should be analyzed when considering the market for your business. According to the Small Business Administration , the most important factors include understanding your target market and performing a competitive analysis.
Figure out what your target market is and narrow it down to a realistic size. Consider the following questions about your target market:
- Characteristics – What are the group's demographics, where can you find them, and what problem can you solve?
- Market share – What is the market share percentage and/or number of customers you think you can attain in your area?
- Pricing – Define your pricing structure and set your gross margins.
Identify your competitors in the market and consider their characteristics:
- Market share – Define the size of the market and what share your competitors hold.
- Strengths/weaknesses – Where are your competitors strong? Where are they vulnerable?
- Barriers to entry – Identify any barriers that will prevent you from entering the market, such as government regulations, secondary competitors, new technology, or high investment costs.
In order to run a business, you need to decide how your business will be legally organized. The first task is selecting the right legal structure for your business. Is it a sole proprietorship or a limited liability company (LLC)? Is it a general partnership or a corporation?
Be familiar with the legal business plan documents and requirements that apply in your state and consult a lawyer if you have questions. Wherever possible, use business plan templates that provide legally sound language to ensure that you have not overlooked any detail in corporate formation.
Once your legal structure has been completed, draft an organizational chart showing the complete hierarchy of the company. A good chart will:
- help identify any gaps or redundancy in your management structure;
- show ownership, management, and employees; and
- define job responsibilities.
Since some job functions will change and become more detailed after your company launches, remember to update your plan to reflect actual practice.
Use hard data to back up assertions you make in your business plan. Consider putting your data in easily readable form by using charts, graphs, and other visual formats to make your business plan more readable and easier to understand.
A line chart, for example, is an excellent way to demonstrate your company's projected growth.
Use software that imports data from QuickBooks directly into tables and charts so investors can see how actual sales, profits, and expenses compare to your projections.
For some business owners, having two business plans may be even more helpful, especially if this is the person's first business.
A public business plan is for lenders or investors. A private business plan document is closer to a personal road map on what should be done week by week and month to month. This is a good way to ensure you do not overlook important details.
When you are writing your private business plan, it is important to make your goals actionable.
It is fine to have a goal of achieving a 5% conversion rate after six months in business, for example, but you also need actionable steps to help you get there.
Using this example, make a list of actions you will take to achieve your goals, which in this case is to increase your conversions.
- Do A/B testing – A/B or split testing is comparing two versions of a website to see which performs better.
- Set up a sales funnel – A sales funnel refers to the buying process that companies lead customers through when buying products. In this example, a sales funnel could be as simple as awareness/interest/sale, or it could be more complex and include things like offering free trials. Make sure you include a date for when this item should be done.
- Collect testimonials – Once you have satisfied customers, you could collect testimonials. These are useful as references for other customers, as calls to action on social media, and as examples for your website. Once again, establish deadlines for completing this action.
Writing a business plan can be a daunting task. Seeking out examples from other businesses or using a business plan template removes the guesswork and saves you time.
Speak to people you admire and seek out people in your network who have successful businesses. They are usually willing to offer you advice.
Ask them what part of the business plan was most helpful to their business, and what parts of the business plan they wished they had approached differently.
Business plan templates give your plan structure, but there is no generally accepted length for business plans.
Impose a page limit on your business plan documents, such as 20 pages, and stick to it. This will force you to use clear and concise language.
Include only the details that are most essential, which means you will avoid turning your plan into an endless to-do list.
There are other productivity apps you can use to manage your day-to-day tasks, so leave the minutia out of your finished plan.
To help you stick to your page limit, come up with creative ways to present information. As explained in tips 9 and 10, graphs and charts are an excellent way to convey data. The mark of a true professional is making the proposal easy for other busy professionals to digest.
A business plan is not a school test where you must do your own work and then turn it in to your teacher. Friends, family, employees, other business owners—all of them can provide important feedback about what you've written.
Your social network is the best test of your document's readability, clarity, and ability to generate interest. Take the opportunity to see what others think after they read your plan.
You also want to ensure that there are no errors in your document. A single spelling, numerical, or grammatical error can be devastating in a professional environment. Trust others to proofread your work.
If lenders and investors are an important audience for your business plan, then you need to explain how they will make money by investing with you .
Don't forget to investigate the people you are pitching to: What kinds of businesses have they funded? What things do they avoid? Why are they a good fit for your company?
The following is a non-exhaustive list of what investors want to see when they are reviewing a proposal.
- State how much money you will need and how that money will be spent
- Identify when the business will start making a profit
- State when investors can expect to make a return on their investment
- Explain the projected growth of the company over time
- State how much control of the company you are willing to give up
- Identify the risks that investors will face in this particular market
- Explain whether you will run your business full-time and whether you will take a salary
After you've addressed these questions, then go back and write your executive summary.
It's important to have goals and dreams, but be wary of including your fantasies of world domination in your business plan.
For instance, assume you have started a company that is creating eco-friendly baby bottles and cups. Some first-time entrepreneurs will define their target market as all parents who have children under four years old.
Since there were about 22 million children under the age of two in the United States in 2014, a hopeful business owner may say that the market encompasses all 22 million kids and their parents.
If you have included calculations that look like this, then go back and re-do your market analysis because you have totally overestimated the market.
Determining the real available market is a necessity.
This process starts by creating a profile of your ideal customer. Figure out who is most likely to have the problem that your company wants to solve. Determine where this customer lives and works and where they are likely to buy products or services. Consider your ideal customer's purchasing strategies.
- Do they use coupons?
- Are they on a tight budget?
- How much money do they allocate to your kind of product or service?
Once you have narrowed down the ideal customer, include a brief profile of this person in your business plan documents.
Take a look at the number of people that fit your demographic who live in a geographic area that is reachable by your company.
For example, do you have the capacity to create and ship products from New York to California? Does it make financial sense for you to focus on customers on the other side of the country?
Don't act on a hunch; always get numbers to back up your claims. Decide whether you can meet the needs of people in the area you are targeting.
Your business structure may be sound and your numbers all add up, but at the center of every business is a human story.
Lenders and investors are constantly receiving strong pitches. Your personal history can make you stand out. The same is true of your customers—telling your story and explaining why it enables you to solve their problems is the essence of sales.
Passion and excitement are infectious. A compelling story will explain why you are the one who deserves their attention and purchasing power.
Use the process of writing a business plan as an exercise to immerse yourself in what will make your company successful.
Begin with business plan templates that will give your report structure and then start your research.
Knowing your numbers, analyzing the market, and presenting your information in a compelling way will help create a business plan that makes sure your business is a hit with investors, employees and customers.
Ready to get started? Create a business plan right now.
1.1 The Nature of Business
- How do businesses and not-for-profit organizations help create our standard of living?
Take a moment to think about the many different types of businesses you come into contact with on a typical day. As you drive to class, you may stop at a gas station that is part of a major national oil company and grab lunch from a fast food chain such as Taco Bell or McDonald’s or the neighborhood pizza place. Need more cash? You can do your banking on a smartphone or other device via mobile apps. You don’t even have to visit the store anymore: online shopping brings the stores to you, offering everything from clothes to food, furniture, and concert tickets.
A business is an organization that strives for a profit by providing goods and services desired by its customers. Businesses meet the needs of consumers by providing medical care, autos, and countless other goods and services. Goods are tangible items manufactured by businesses, such as laptops. Services are intangible offerings of businesses that can’t be held, touched, or stored. Physicians, lawyers, hairstylists, car washes, and airlines all provide services. Businesses also serve other organizations, such as hospitals, retailers, and governments, by providing machinery, goods for resale, computers, and thousands of other items.
Thus, businesses create the goods and services that are the basis of our standard of living. The standard of living of any country is measured by the output of goods and services people can buy with the money they have. The United States has one of the highest standards of living in the world. Although several countries, such as Switzerland and Germany, have higher average wages than the United States, their standards of living aren’t higher, because prices are so much higher. As a result, the same amount of money buys less in those countries. For example, in the United States, we can buy an Extra Value Meal at McDonald’s for less than $5, while in another country, a similar meal might cost as much as $10.
Businesses play a key role in determining our quality of life by providing jobs and goods and services to society. Quality of life refers to the general level of human happiness based on such things as life expectancy, educational standards, health, sanitation, and leisure time. Building a high quality of life is a combined effort of businesses, government, and not-for-profit organizations. In 2017, Vienna, Austria, ranked highest in quality of life, followed by Zurich, Switzerland; Auckland, New Zealand; and Munich, Germany. It may come as a surprise that not one of the world’s top cities is in the United States: seven of the top 10 locations are in western Europe, two are in Australia/New Zealand, and one is in Canada. At the other end of the scale, Baghdad, Iraq, is the city scoring the lowest on the annual survey. 1 Creating a quality of life is not without risks, however. Risk is the potential to lose time and money or otherwise not be able to accomplish an organization’s goals. Without enough blood donors, for example, the American Red Cross faces the risk of not meeting the demand for blood by victims of disaster. Businesses such as Microsoft face the risk of falling short of their revenue and profit goals. Revenue is the money a company receives by providing services or selling goods to customers. Costs are expenses for rent, salaries, supplies, transportation, and many other items that a company incurs from creating and selling goods and services. For example, some of the costs incurred by Microsoft in developing its software include expenses for salaries, facilities, and advertising. If Microsoft has money left over after it pays all costs, it has a profit . A company whose costs are greater than revenues shows a loss.
When a company such as Microsoft uses its resources intelligently, it can often increase sales, hold costs down, and earn a profit. Not all companies earn profits, but that is the risk of being in business. In U.S. business today, there is generally a direct relationship between risks and profit: the greater the risks, the greater the potential for profit (or loss). Companies that take too conservative a stance may lose out to more nimble competitors who react quickly to the changing business environment.
Take Sony , for example. The Japanese electronics giant, once a leader with its Walkman music player and Trinitron televisions, steadily lost ground—and profits—over the past two decades to other companies by not embracing new technologies such as the digital music format and flat-panel TV screens. Sony misjudged what the market wanted and stayed with proprietary technologies rather than create cross-platform options for consumers. Apple , at the time an upstart in personal music devices, quickly grabbed the lion’s share of the digital music market with its iPods and iTunes music streaming service. By 2016, Sony restructured its business portfolio and has experienced substantial success with its PlayStation 4 gaming console and original gaming content. 2
Not-for-Profit Organizations
Not all organizations strive to make a profit. A not-for-profit organization is an organization that exists to achieve some goal other than the usual business goal of profit. Charities such as Habitat for Humanity , the United Way , the American Cancer Society , and the World Wildlife Fund are not-for-profit organizations, as are most hospitals, zoos, arts organizations, civic groups, and religious organizations. Over the last 20 years, the number of nonprofit organizations—and the employees and volunteers who work for them—has increased considerably. Government is our largest and most pervasive not-for-profit group. In addition, more than 1.5 million nongovernmental not-for-profit entities operate in the United States today and contribute more than $900 billion annually to the U.S. economy. 3
Like their for-profit counterparts, these groups set goals and require resources to meet those goals. However, their goals are not focused on profits. For example, a not-for-profit organization’s goal might be feeding the poor, preserving the environment, increasing attendance at the ballet, or preventing drunk driving. Not-for-profit organizations do not compete directly with one another in the same manner as, for example, Ford and Honda , but they do compete for talented employees, people’s limited volunteer time, and donations.
The boundaries that formerly separated not-for-profit and for-profit organizations have blurred, leading to a greater exchange of ideas between the sectors. As discussed in detail in the ethics chapter, for-profit businesses are now addressing social issues. Successful not-for-profits apply business principles to operate more effectively. Not-for-profit managers are concerned with the same concepts as their colleagues in for-profit companies: developing strategy, budgeting carefully, measuring performance, encouraging innovation, improving productivity, demonstrating accountability, and fostering an ethical workplace environment.
In addition to pursuing a museum’s artistic goals, for example, top executives manage the administrative and business side of the organization: human resources, finance, and legal concerns. Ticket revenues cover a fraction of the museum’s operating costs, so the director spends a great deal of time seeking major donations and memberships. Today’s museum boards of directors include both art patrons and business executives who want to see sound fiscal decision-making in a not-for-profit setting. Therefore, a museum director must walk a fine line between the institution’s artistic mission and financial policies. According to a survey by The Economist , over the next several years, major art museums will be looking for new directors, as more than a third of the current ones are approaching retirement. 4
Factors of Production: The Building Blocks of Business
To provide goods and services, regardless of whether they operate in the for-profit or not-for-profit sector, organizations require inputs in the form of resources called factors of production . Four traditional factors of production are common to all productive activity: natural resources , labor (human resources) , capital , and entrepreneurship . Many experts now include knowledge as a fifth factor, acknowledging its key role in business success. By using the factors of production efficiently, a company can produce more goods and services with the same resources.
Commodities that are useful inputs in their natural state are known as natural resources. They include farmland, forests, mineral and oil deposits, and water. Sometimes natural resources are simply called land, although, as you can see, the term means more than just land. Companies use natural resources in different ways. International Paper Company uses wood pulp to make paper, and Pacific Gas & Electric Company may use water, oil, or coal to produce electricity. Today urban sprawl, pollution, and limited resources have raised questions about resource use. Conservationists, environmentalists, and government bodies are proposing laws to require land-use planning and resource conservation.
Labor, or human resources, refers to the economic contributions of people working with their minds and muscles. This input includes the talents of everyone—from a restaurant cook to a nuclear physicist—who performs the many tasks of manufacturing and selling goods and services.
The tools, machinery, equipment, and buildings used to produce goods and services and get them to the consumer are known as capital . Sometimes the term capital is also used to mean the money that buys machinery, factories, and other production and distribution facilities. However, because money itself produces nothing, it is not one of the basic inputs. Instead, it is a means of acquiring the inputs. Therefore, in this context, capital does not include money.
Entrepreneurs are the people who combine the inputs of natural resources, labor, and capital to produce goods or services with the intention of making a profit or accomplishing a not-for-profit goal. These people make the decisions that set the course for their businesses; they create products and production processes or develop services. Because they are not guaranteed a profit in return for their time and effort, they must be risk-takers. Of course, if their companies succeed, the rewards may be great.
Today, many individuals want to start their own businesses. They are attracted by the opportunity to be their own boss and reap the financial rewards of a successful firm. Many start their first business from their dorm rooms, such as Mark Zuckerberg of Facebook , or while living at home, so their cost is almost zero. Entrepreneurs include people such as Microsoft cofounder Bill Gates , who was named the richest person in the world in 2017, as well as Google founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page . 5 Many thousands of individuals have started companies that, while remaining small, make a major contribution to the U.S. economy.
Catching the Entrepreneurial Spirit
Stickergiant embraces change.
Entrepreneurs typically are not afraid to take risks or change the way they do business if it means there is a better path to success. John Fischer of Longmont, Colorado, fits the profile.
The drawn-out U.S. presidential election in 2000 between Bush and Gore inspired Fischer to create a bumper sticker that claimed, “He’s Not My President,” which became a top seller. As a result of this venture, Fischer started an online retail sticker store, which he viewed as possibly the “ Amazon of Stickers.” Designing and making stickers in his basement, Fischer’s start-up would eventually become a multimillion-dollar company, recognized in 2017 by Forbes as one of its top 25 small businesses.
The StickerGiant online store was successful, supplying everything from sports stickers to ones commemorating rock and roll bands and breweries. By 2011, the business was going strong; however, the entrepreneur decided to do away with the retail store, instead focusing the business on custom orders, which became StickerGiant ’s main product.
As the company became more successful and added more employees, Fischer once again looked to make some changes. In 2012 he decided to introduce a concept called open-book management, in which he shares the company’s financials with employees at a weekly meeting. Other topics discussed at the meeting include customer comments and feedback, employee concerns, and colleague appreciation for one another. Fischer believes sharing information about the company’s performance (good or bad) not only allows employees to feel part of the operation, but also empowers them to embrace change or suggest ideas that could help the business expand and flourish.
Innovation is also visible in the technology StickerGiant uses to create miles and miles of custom stickers (nearly 800 miles of stickers in 2016). The manufacturing process involves digital printing and laser-finishing equipment. Fischer says only five other companies worldwide have the laser-finishing equipment StickerGiant uses as part of its operations. Because of the investment in this high-tech equipment, the company can make custom stickers in large quantities overnight and ship them to customers the next day.
This small business continues to evolve with an entrepreneur at the helm who is not afraid of making changes or having fun. In 2016, StickerGiant put together Saul the Sticker Ball, a Guinness World Records winner that weighed in at a whopping 232 pounds. Fischer and his employees created Saul when they collected more than 170,000 stickers that had been lying around the office and decided to put them to good use. With $10 million in annual sales and nearly 40 employees, StickerGiant continues to be a successful endeavor for John Fischer and his employees almost two decades after Fischer created his first sticker.
- How does being a risk-taker help Fischer in his business activities?
- If you were a small business owner, would you consider sharing the company’s financial data with employees? Explain your reasoning.
Sources: “All About StickerGiant,” https://www.stickergiant.com, accessed May 29, 2017; Bo Burlingham, “Forbes Small Giants 2017: America’s Best Small Companies,” Forbes, http://www.forbes.com, May 9, 2017; Karsten Strauss, “Making Money and Breaking Records in the Sticker Business,” Forbes, http://www.forbes.com, January 26, 2016; Emilie Rusch, “StickerGiant Does Big Business in Tiny Town of Hygiene,” Denver Post, April 19, 2016, http://www.denverpost.com; Eric Peterson, “StickerGiant,” Company Week, https://companyweek.com, September 5, 2016.
A number of outstanding managers and noted academics are beginning to emphasize a fifth factor of production—knowledge. Knowledge refers to the combined talents and skills of the workforce and has become a primary driver of economic growth. Today’s competitive environment places a premium on knowledge and learning over physical resources. Recent statistics suggest that the number of U.S. knowledge workers has doubled over the last 30 years, with an estimated 2 million knowledge job openings annually. Despite the fact that many “routine” jobs have been replaced by automation over the last decade or outsourced to other countries, technology has actually created more jobs that require knowledge and cognitive skills. 6
Concept Check
- Explain the concepts of revenue, costs, and profit.
- What are the five factors of production?
- What is the role of an entrepreneur in society?
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lawrence J. Gitman, Carl McDaniel, Amit Shah, Monique Reece, Linda Koffel, Bethann Talsma, James C. Hyatt
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Business
- Publication date: Sep 19, 2018
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-1-the-nature-of-business
© Apr 5, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Simple Business Plan Template for Entrepreneurs
Follow This Business Plan Outline to Write Your Own
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Pros and Cons of Using a Business Plan Template
Do i need a simple or detailed business plan, how to use this business plan template, table of contents, section 1: executive summary, section 2: business/industry overview.
- Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
Section 5: ownership and management plan, section 6: operating plan, section 7: financial plan.
- Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
Ariel Skelley / Getty Images
Think you have a great idea for a business? The best way to find out whether your idea is feasible is to create a business plan .
A solid, well-researched business plan provides a practical overview of your vision. It can be used to ground your ideas into workable actions and to help pitch your idea to financial institutions or potential investors when looking for funding.
The standard business plan consists of a single document divided into several sections for distinct elements, such as a description of the organization, market research, competitive analysis, sales strategies, capital and labor requirements, and financial data. Your plan may include more or fewer sections to best represent your business.
The template presented here will get you well on your way toward your simple business plan.
Ready-made layouts
Free downloads
Generic, not customized
No financial guidance
Additional skills needed
- Ready-made layouts : Templates offer general guidance about what information is needed and how to organize it, so you’re not stuck looking at a blank page when getting started. Especially detailed templates may offer instructions or helpful text prompts along the way.
- Variations : If you know what type of business plan you need—traditional, lean, industry-specific—chances are you can find a specialized template.
- Free downloads : There are many free business plan templates available online, which can be useful for comparing formats and features, or refining your own.
- Generic, not customized : Templates typically contain just the basics, and there will still be a lot of work involved to tailor the template to your business. For instance, you'll have to reformat, refine copy, and populate tables.
- No financial guidance : You’ll need enough industry knowledge to apply financial models to your specific business, and the math skills to generate formulas and calculate figures.
- Additional skills needed : Some degree of tech savvy is required to integrate charts and graphs, merge data from spreadsheets, and keep it all up-to-date.
A corporate business plan for a large organization can be hundreds of pages long. However, for a small business, it's best to keep the plan short and concise, especially if you're submitting it to bankers or investors . Around 35 to 50 pages should be sufficient, and more allowed for extras, such as photos of products, equipment, logos, or business premises or site plans. Your audience will likely prefer solid research and analysis over long, wordy descriptions.
An entrepreneur who creates a business plan is nearly twice as likely to secure financing and grow their business compared with those who do not have a plan.
The business plan template below is divided into sections as described in the table of contents. Each section can be copied into a document of your own; you may need to add or delete sections or make adjustments to fit your specific needs.
Once complete, be sure to format it attractively and get it professionally printed and bound. You want your business plan to convey the best possible impression. Make it engaging, something people will to want to pick up and peruse.
Enter your business information, including the legal name and address. If you already have a business logo, you can add it at the top or bottom of the title page.
- Business Plan for "Business Name"
- Business address
- Website URL
If you're addressing it to a company or individual, include:
- Presented to "Name"
- At "Company"
- Executive Summary................................................Page #
- Business/Industry Overview.................................Page #
- Market Analysis and Competition.........................Page #
- Sales and Marketing Plan.......................................Page #
- Ownership and Management Plan.......................Page #
- Operating Plan..........................................................Page #
- Financial Plan............................................................Page #
- Appendices and Exhibits........................................Page #
The executive summary introduces the plan, but it is written last. It provides a concise and optimistic overview of your business and should capture the reader's attention and create a desire to learn more. The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, with highlights or brief summaries of other sections of the plan.
- Describe your mission —what is the need for your new business? Sell your vision.
- Introduce your company briefly, sticking to vital details such as size, location, management, and ownership.
- Describe your main product(s) and/or service(s).
- Identify the customer base you plan to target and how your business will serve those customers.
- Summarize the competition and how you will get market share. What is your competitive advantage?
- Outline your financial projections for the first few years of operation.
- State your startup financing requirements.
This section provides an overview of the industry and explains in detail what makes your business stand out.
- Describe the overall nature of the industry, including sales and other statistics. Note trends and demographics, as well as economic, cultural, and governmental influences.
- Explain your business and how it fits into the industry.
- Mention the existing competition, which you'll expand upon in the following section.
- Identify what area(s) of the market you will target and what unique, improved, or lower-cost products and/or services you will offer.
Many business plans cover their products/services in a standalone section to add more detail or emphasize unique aspects.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
This section focuses on the competitive factor of your business and justifies it with financial models and statistics. You need to demonstrate that you have thoroughly analyzed the target market, assessed the competition, and concluded that there is enough demand for your products/services to make your business viable.
- Define the target market(s) for your products/services in your geographic locale.
- Explain the need for your products/services.
- Estimate the overall size of the market and the units of your products/services that the target market might buy. Include forecasts of potential repeat-purchase volume and how the market might be affected by economic or demographic changes.
- Estimate the volume and value of your sales in comparison with any existing competitors. Highlight any key strengths over the competition in easily digestible charts and tables.
- Describe any helpful barriers to entry that may protect your business from competition, such as access to capital, technology, regulations, employee skill sets, or location.
You may opt to split the target market description and competitive analysis into two separate sections, if either (or both) portray your business especially favorably.
Here's where you dive into profits, giving detailed strategic view of how you intend to entice customers to buy your products and/or services, including advertising or promotion, pricing, sales, distribution, and post-sales support.
Product or Service Offerings
If your products and/or services don't take up a standalone section earlier in the plan, here is where you can answer the question: What is your unique selling proposition? Describe your products and/or services, how they benefit the customer and what sets them apart from competitor offerings.
Pricing Strategy
How will you price your products/services? Pricing must be low enough to attract customers, yet high enough to cover costs and generate a profit. You can base pricing decisions on a number of financial models, such as markup from cost or value to the buyer, or in comparison with similar products and/or services in the marketplace.
Sales and Distribution
For products, describe how you plan to distribute to the customer. Will you be selling wholesale or retail? What type of packaging will be required? How will products be shipped? If you offer a service, how will it be delivered to the customer? What methods will be used for payment?
Advertising and Promotion
List the various forms of media you will use to get your message to customers (e.g., website, email, social media, or newspapers). Will you use sales promotional methods such as free samples and product demonstrations? What about product launches and trade shows? Don't forget more everyday marketing materials such as business cards, flyers, or brochures. Include an approximate budget.
This section describes the legal structure, ownership, and (if applicable) management and staffing requirements of your business.
- Ownership structure : Describe the legal structure of your company (e.g., corporation, partnership, LLC, or sole proprietorship ). List ownership percentages, if applicable. If the business is a sole proprietorship, this is the only section required.
- Management team : Describe managers and their roles, key employee positions, and how each will be compensated. Include brief résumés.
- External resources and services : List any external professional resources required, such as accountants, lawyers, or consultants.
- Human resources : List the type and number of employees or contractors you will need, and estimate the salary and benefit costs of each.
- Advisory board : Include an advisory board as a supplemental management resource, if applicable.
The operating plan outlines the physical requirements of your business, such as office, warehouse, or retail space; equipment; supplies; or labor. This section will vary greatly by industry; a large manufacturer, for instance, should provide full details about supply chain or specialty equipment, while a therapist's office can get by with a much shorter list.
If your business is a small operation (like a one-person, home-based consulting firm), you might choose to eliminate the operating plan section altogether and include the operating essentials in the business overview.
- Development : Explain what you have done to date to identify possible locations, sources of equipment, supply chains, and other relevant relationships. Describe your production workflow.
- Production : For manufacturing, explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be ready to start production. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and how you'll deal with potential problems, such as rush orders.
- Facilities : Describe the physical location of the business. Include geographical or building requirements; square footage estimates (with room for expansion if expected); mortgage or leasing costs; and estimates of maintenance, utilities, and related overhead costs . Include zoning approvals and other permissions that are necessary in order to operate.
- Staffing : Outline expected staffing needs and the main duties of staff members, especially the key employees. Describe how the employees will be sourced and the employment relationship (i.e., contract, full-time, part-time) as well as any training needs and how these will be provided.
- Equipment : Include a list of any specialized equipment needed, along with cost, whether it will be leased or purchased, and sources.
- Supplies : If your business is, for example, manufacturing, retail, or food services, include a description of the materials needed, reliable sources, major suppliers, and how you will manage inventory.
The financial plan is the most important section for lenders or investors. The goal is to demonstrate that your business will grow and be profitable. To do this, you will need to create realistic predictions or forecasts.
To avoid inflated expectations, a prudent financial plan underestimates revenues and overestimates expenses.
- Income statements : The income statement displays projected revenues, expenses, and profit. Do this on a monthly basis for at least the first year for a startup business.
- Cash-flow projections : The cash-flow projection shows your monthly anticipated cash revenues and disbursements for expenses. To be considered a good credit risk, it is important to demonstrate that you can manage your cash flow.
- Balance sheet : The balance sheet is a snapshot summary of the assets, liabilities, and equity of your business at a particular point in time. For a startup, this would be on the day the business opens.
- Breakeven analysis : Including a breakeven analysis will demonstrate to lenders or investors what level of sales you need to achieve to make a profit.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits section contains any detailed information needed to support other sections of the plan.
Possible Appendix or Exhibit items include:
- Credit histories for the business owners
- Detailed market research and analysis of competitors
- Résumés of the owners and key employees
- Diagrams and/or research about your products and/or services
- Site, building, or office plans
- Copies of mortgage documents or equipment leases (or quotes)
- Marketing brochures and other materials
- References from business colleagues
- Links to your business website
- Any other material that may impress potential lenders or investors
SCORE. " Business Plan Template for a Startup Business ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write your business plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " SBA Recommended Business Plans and Length ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Bplans. " Why Plan Your Business? Look at This Data ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Marketing MO. " Pricing Strategy ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Incorporate.com. " Write a Business Plan, a Step-by-Step Guide ." Accessed April 29, 2021.
Startup Nation. " The Five Costs You're Most Likely to Underestimate in Your Business Plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.

Simple Business Plan

To reach your goals in business , you need to have strategies in mind. There must be somewhere you can list down all the variables to your success; all the necessary factors to get to where you want to be. If you know how to create a business plan , then you’re a step closer to what you want. Allow this article to shed some light on its complexity. Learn about its purpose, its formats, and browse through an amazing list of sample business plans . Without further ado, here are some of the most useful templates and examples that you can ever find online!
46+ Simple Business Plan Examples
1. simple business plan template.

- Apple Pages
- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
2. Spa Business Plan Template

3. Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Size: 39 KB
4. Trucking Business Plan Template

Size: 31 KB
5. Business Plan Template

Size: 35 KB
6. Business Plan Table of Contents Template

- MS Publisher
Size: 57 KB
7. Sports Bar Business Plan Template

8. Saas Business Plan Template

Size: A4 & US
9. Startup Business Plan Template

Size: 33 KB
10. Rental Property Business Plan Template

11. Construction Business Plan Template

Size: 34 KB
12. Sample Construction Business Plan Template

Size: 58 KB
13. Restaurant Business Plan Template

Size: 36 KB
14. Generic Business Plan Template

15. Freight Trucking Business Plan Template

Size: 40 KB
16. Mortgage Broker Business Plan Template

17. Boutique Business Plan Template

Size: 42 KB
18. Recruitment/Staffing Agency Business Plan Template

Size: 45 KB
19. Modern Business Plan Template

20. Travel Business Plan Template

21. Veterinary Business Plan Template

22. Renovation Business Plan Template

23. Sample Business Plan Template

24. Simple Business Plan Template

25. Business Plan Outline Template

26. Sample Marketing Business Plan Template

27. Business Operational Plan Template

Free Download
28. 30 60 90 Day Business Plan Template

29. Business Plan Presentation Template

30. Business Plan Outline

Size: 79 kB
31. Small Business Sample
Size: 199 kB
32. Cafe Business Plan

Size: 151 kB
33. Restaurant Business Example

34. Mini Business Plan

35. Farm Business Plan

Size: 32 kB
36. Social Business Sample

37. Presentation Business Plan

Size: 774 kB
38. Start-up Business Example

39. Bakery Business Plan

40. Car Wash Business Sample

Size: 125 kB
41. Cleaning Business Plan

Size: 140 kB
42. Daycare Business Example

Size: 171 kB
43. Insurance Business Sample

Size: 324 kB
44. Lawn Care Business Plan

Size: 397 kB
45. Personal Business Plan

Size: 237 kB
46. Real Estate Business Sample

47. Retail Business Plan

48. Student Business Plan

What Is the Purpose of a Business Plan?
A business plan has one true purpose and that is to help determine the success of a company. No organization makes it to the top of their industry on sheer luck and hard work alone. Writing a business plan becomes essential so that a company can have as much direction as it needs as it claws its way towards the point of success. Such is the role of a quality plan for business and is defined by the following:
- To explain the business model – A good business plan clarifies what the business is about and what is needed to be done to attain success.
- Set goals – Business plans, like work plans , are made to ascertain specific goals detailed in strategic plans directed towards the profitability and success of a company or business
- Detect potential problems – A sure way of finding out problems within a business is the inclusion of an evaluation as a result of actions being done in a business plan.
- Measure development – Having a budget plan for business provides the owner or decision-maker a guide of sorts in determining where the current business is and the next step of the management plan to take in progressing towards the success set by the business plan.
Tips on How to Pick the Right Business Plan Format
Remember that there’s no such thing as right or wrong when you want to learn how to write a business plan. Instead, adjust your thinking towards what is more effective or appropriate for your needs. Keep in mind that formatting is always an important consideration. You can stay up all night working on your simple analysis plan or spend hours browsing for the right business plan template, but if the formatting is wrong, then you still won’t be able to guarantee your document’s efficacy. Nowadays, there are two major formats that you can select. One is the traditional business plan format while the other is the lean start-up format . To help you decide between either of these, here are some important tips to consider:
1. Determine Your Specific Need for the Business Plan
As stated in the previous section, the main purpose of a business plan is to serve as a guide. What hasn’t been said yet is that it doesn’t necessarily have to be your guide alone. Those who want to attract investors or lenders will want the traditional business plan format for reasons that will become apparent soon. Otherwise, the lean start-up format may be more suitable.
2. Look into the Characteristics of Each Type
After you’ve determined why there’s a need for a business plan, now it’s time to tackle the elements of the formats. The traditional format, for example, is much longer and more detailed. Its precise nature is what makes this format attractive to investors or lenders—people who normally require a lot of information. On the other hand, the lean start-up format focuses only on the significant bits of info, such as the company’s organizational infrastructure, finances, and value proposal.
3. Determine Whether or Not Time is on Your Side
The lengthy and specific nature of traditional business plans requires a lot of time and effort to do. If you only have a longer time to prepare, then perhaps that is the best choice for you. Yet those who only have a few hours or days to prepare one may have to go for the lean start-up format instead.
4. Look into Which Type is Better for You
Both of these business plan outline formats have their weaknesses and strengths. It is up to you to choose which of these will you apply in composing your business plan. Remember, consider not your wants but your needs. If you need to obtain a simple, less hassle and faster yet more likely to be ambiguous, you may utilize the lean start-up format. Conversely, if you need to have a precise and detailed business plan which is paired with challenging and time-consuming composition then use the traditional one.
General FAQs
1. what is a business plan.
A business plan is a formal and comprehensive document that is prepared by a business to outline the goals of the business and how it can be attained. It states the time frame within which these goals should be achieved, along with the product details, manpower, and financial estimates.
2. What are the main components of a business plan?
Each business plan examples share common components such as the executive summary , company description, marketing plan, operational plan , and so much more. However, how these components are expressed or explained will differ according to the needs and designs of the business owner.
3. What is the purpose of a business plan?
The purpose of a business plan is to define the goals of a business along with the steps needed to reach them. It also helps in maintaining the focus of your business and securing long-term financing .
If you weren’t so sure before about how to make a business plan, well you are now. Whether it is a simple one-page version, a non-profit business plan , or even a business continuity plan , you now have the skills and knowledge necessary to make a highly effective document. Should that be something you aren’t too keen on yet, then there are always templates like the ones above. Stop hesitating and get started on your plan today!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Press ESC to close

Cloud Kitchen Business Model: Examples, Benefits, Business Plan, and Investment Ideas
- Cloud Kitchen
- August 9, 2024

Cloud kitchens are shaking up the food industry in the USA. They’re growing fast, at a rate of 11.8% each year, and big brands are jumping on this trend. In 2021, the real estate company CBRE predicted that ghost kitchens would make up 21% of the U.S. restaurant industry by 2025 .
This blog contains the ins and outs of various cloud kitchen models. Ever wondered how a restaurant without tables or chairs works? You’ll learn about single-brand cloud kitchens like Wow Bao, which focuses only on delivery. Discover multi-brand cloud kitchens like Rebel Foods, offering many cuisines in one place. Explore the pros and cons of delivery app-owned kitchens, shared commissaries, and franchises. Finally, see how hybrid models blend different services. Find out which model suits your business best and how to succeed in this exciting food trend.
1. Single Brand Cloud Kitchen

Ever heard of a restaurant without tables or chairs? That’s a single-brand cloud kitchen model! A single-brand cloud kitchen is like your secret kitchen, focusing on just one type of food—maybe your favorite pizzas or awesome burgers. It is a delivery-only restaurant, a concept that’s becoming increasingly popular in the restaurant industry. Unlike a traditional brick and mortar restaurant, these kitchens are set up specifically for delivery, allowing restaurant owners to streamline operations and reduce overhead costs. This innovative approach to dining is reshaping how we think about the cloud kitchen business models and offering new opportunities in the food delivery market.
Famous Cloud Kitchen Example: Wow Bao’s cloud kitchen in the United States represents a single-brand cloud kitchen; it is a brand-owned cloud kitchen that specializes in Asian-inspired foods such as steamed buns, potstickers, and rice bowls, only accepts delivery and takeaway orders, removing the need for a permanent eating location. This focus allows them to refine their menu and manage costs effectively. Their locations in cities like Chicago and New York are in cost-effective industrial areas. Advanced technology helps them streamline operations, manage orders, and maintain quality, ensuring that every dish is fresh and well-prepared.
Concept: The idea of a single-brand Cloud Kitchen is an online-only restaurant that doesn’t have an actual location. Customers use apps or websites to order their favorite meals and give delivery information. The cloud kitchen’s special tablet or system gets these orders and tells the cooks to start making the food. It’s like a virtual restaurant where you can order tasty food and deliver it to your door.
Cost Savings: No dining area means you can set up your kitchen in cheaper spots and need fewer staff since there’s no need for waiters.
Focus on Quality: A smaller, specialized menu ensures that every dish is perfect. Less distractions also allow the chefs to maintain high standards for every order.
Flexibility: You can set up your kitchen in various places, even less expensive areas, and it’s easier to open new cloud kitchens to reach more customers.
Efficiency: By focusing on delivery, you can streamline operations and get food out quickly. Advanced software helps manage orders and track deliveries.
Wider Reach: By focusing on delivery, your restaurant business can serve a larger area, reaching more people who prefer eating at home.
Limited Customer Interaction: Without face-to-face contact, getting immediate feedback is harder, which helps improve service and menu items. Also, customers miss out on the atmosphere and experience of a traditional restaurant.
Underutilization During Off-Peak Times: Walk-in traffic is necessary for the kitchen to avoid slow periods, affecting overall profits.
Marketing and Brand Awareness: Building your brand can be tougher without a physical location. You should invest more in online marketing to attract and keep customers coming back for more.
2. Multi-Brand Cloud Kitchen

A Multi-Brand Cloud Kitchen is a cloud kitchen model in which several restaurant brands operate out of a single kitchen facility. This arrangement enables different brands, usually under the same parent company, to share resources and infrastructure. Each brand can offer a range of cuisines from the same location, maximizing efficiency and reducing costs.
Famous Examples : All Day Kitchens is a standout example of a multi-brand cloud kitchen in the USA. They operate a network of small, distributed kitchens close to residential areas, allowing quick and efficient delivery. Each kitchen serves food from numerous local restaurants, enabling customers to order from multiple eateries in a single delivery. This model helps local restaurants scale without traditional setups’ overhead costs, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. All Day Kitchens has rapidly grown, boasting impressive delivery times and profitability.
Concept: A multi-brand cloud kitchen operates from a single building, sharing resources such as equipment, supplies, and workers. This configuration lowers expenses and increases efficiency. Customers can place orders via numerous delivery apps or straight on brand websites. The kitchen can handle many cuisines simultaneously, and the chefs are educated to maintain good quality across all menu options. Advanced software organizes orders, maintains inventories, and optimizes delivery routes. Once cooked, the food is wrapped and given to delivery drivers, ensuring rapid and efficient service.
Cost Efficiency: Sharing kitchen resources reduces costs on rent, utilities, and equipment. Purchasing ingredients in bulk lowers food expenses across brands.
Flexibility and Scalability: By adding new brands or entering new markets, multi-brand cloud kitchens readily grow without requiring additional physical sites, enabling easy testing and rollout of new menu items.
Resource Optimization: Using the same kitchen staff, equipment, and space for multiple brands increases resource efficiency and minimizes downtime.
Market Reach: The more the cuisine is equal, the wider the market reach. Offering a range of cuisines from one location attracts a larger customer base and boosts revenue. Cross-promotion between brands increases overall visibility.
Risk Mitigation: Operating multiple brands reduces financial risk enables testing new concepts, and avoids chances of failure.
Operational Complexity: Running multiple brands from one kitchen can be quite challenging, especially during busy times. It requires precise coordination to keep quality consistent across different menus and dishes.
Brand Identity: When several brands share a single space, their unique identities might become blurred, reducing their appeal. Creating distinct and compelling marketing strategies for each brand can also be a tough and time-consuming.
Resource Allocation: Sharing kitchen staff and equipment among different brands can strain resources, leading to slower service and possible mistakes. Managing inventory for multiple brands demands careful oversight to avoid waste and ensure everything is in stock.
Customer Experience: With a physical restaurant, connecting personally with customers is easier, which can impact their loyalty. Relying on third-party delivery services introduces risks like high fees and inconsistent service.
Technological Dependence: A heavy reliance on technology means that any system issues can significantly disrupt operations. Managing large amounts of customer data also increases the risk of breaches, requiring strong security measures.
3. Delivery App-Owned Cloud Kitchen

A Delivery App-Owned Cloud Kitchen is a cloud kitchen operated by food delivery platforms. These kitchens prepare food exclusively for delivery without a dine-in option. The delivery app owns and manages the kitchen space, providing infrastructure and technology for various restaurant brands to cook and fulfill online orders efficiently.
Famous Examples : Uber Eats runs virtual restaurants that only prepare food for delivery, using their extensive network to reach customers quickly. DoorDash also operates cloud kitchens where multiple brands cook exclusively for delivery, with locations chosen to speed up service. Meanwhile, Deliveroo’s Deliveroo Editions features a network of cloud kitchens hosting various brands, helping them expand delivery without opening new physical spots. These examples highlight how cloud kitchens are evolving to meet today’s delivery needs.
Concept : Delivery app-owned cloud kitchens (such as Uber Eats) are a strategic combination of food preparation and delivery services. These kitchens are run directly by online food delivery platforms that concentrate only on cooking meals for delivery via their applications. Unlike typical restaurants, they do not serve clients on-site and instead rely on their parent company’s extensive delivery network to complete orders. This concept simplifies operations since the kitchens are designed for speed and efficiency while preparing and delivering orders. These solutions can maintain constant service quality while reducing delivery time by regulating the kitchen and the delivery process. Using innovative technology to manage orders, maintain inventory, and coordinate delivery improves operational efficiency and customer happiness.
Cost Savings : By sharing kitchen space, restaurants save money on rent, utilities, and upkeep. They do not need a physical store, so their costs are lower.
Wider Reach : The kitchen’s visibility on popular delivery apps increases its reachability. It can attract more customers without having a physical restaurant. These kitchens can also open in different locations quickly, helping restaurants grow their business faster.
Efficient Operations : Delivery apps provide advanced technology to manage orders and track inventory, making kitchen operations smoother and faster.
Flexible and Scalable : The expansion of cloud kitchens is easy. It can be done by opening new locations or adding new brands without much investment. They can also quickly try out new menu items or concepts to keep up with changing customer tastes.
Data Insights : Delivery apps gather important information about what customers like and how they order. This data helps restaurants improve their menus and make better business decisions. Performance metrics from the app also help restaurants see where they can improve.
Better Customer Experience : Customers enjoy the convenience of ordering from many brands through one app. The reliable delivery service ensures their food arrives on time and as ordered. Plus, having many brands in one kitchen means more choices for different tastes.
Limited Control : Restaurants may not have much say in how their brand appears on the app, which can affect its image. Also, the app controls customer data, making it hard for restaurants to connect directly with customers.
High Dependence : Big commission fees paid to the app can cut profits, and any changes the app makes can hurt visibility and earnings. Restaurants have little control over these changes.
Operational Challenges : Managing multiple brands from one kitchen is complex, with different menus and ingredients. Keeping quality consistent across brands is also difficult.
Financial Risks : Setting up a cloud kitchen needs a lot of money for tech, equipment, and training, which can be tough for small businesses. Fluctuating demand can lead to wasted resources and unpredictable revenue.
Customer Experience : Without a physical store, building a personal connection with customers is harder, which might affect loyalty. Relying on delivery services can also lead to high fees, delays, and inconsistent service.
Tech Dependence : Heavy reliance on technology means any tech issues can disrupt operations. Plus, handling lots of customer data increases the risk of data breaches, needing strong security.
4. Commissary/Shared Kitchen Model

Originally designed for food truck operators’ requirements, the Commissary/Shared Kitchen Model is a commercial-grade kitchen leased by many restaurants. It offers necessary cooking, cleaning, food storage tools, and equipment. This approach lets foodies run without having to pay for a full kitchen.
Famous Examples : The Commissary or Shared Kitchen Model has been instrumental in expanding many famous food brands. For example, the Vancouver, Canada-based Kozu Sushi Pizza serves a unique combination of sushi and pizza out of the Coho Commissary Kitchens. Famous American gyros and platter makers The Halal Guys eliminate the need for additional storefronts by using shared kitchens across many US sites to increase delivery reach.
Concept : Shared kitchens are spaces with pre-installed arrangements of kitchen gear. The commercial kitchen spaces have different chefs, first-timers, food truck owners, and stall owners who can find breakthroughs. They can rent the kitchen by the hour, day, or month. This way, they can cook and sell food without spending too much money.
Cost-Effective Option : Renting a shared kitchen is much cheaper than building your own, perfect for new food businesses and startups.
Shared Resources : You can use high-quality, commercial-grade kitchen gear without a big upfront cost.
Potential Collaboration : Working alongside other food entrepreneurs can lead to valuable networking and partnerships.
Scalability : Easily rent more kitchen time or space as your business grows without a huge investment.
Compliance and Safety : Shared kitchens meet health and safety regulations, ensuring you operate legally.
Less Kitchen Control : Customization of the kitchen is not possible in shared spaces as the brand does not fully own the place.
Access and Scheduling : The most negative aspect of shared kitchens is that they can get crowded during busy times, making it hard to find a spot to cook.
Increased Costs : While renting a full kitchen is cheaper than owning one, rental fees can still be significant, especially for small businesses.
Brand Recognition and Customer Proximity : Operating from a shared kitchen can limit your ability to build a strong brand identity.
Operational Challenges : Managing operations in a shared space requires careful planning to avoid disruptions and conflicts with other businesses.
5. Franchise Model

The franchise model for cloud kitchens allows you to run your branch of a well-known food brand without needing a full-service restaurant. You pay an initial fee to use their name, logo, and business plan, plus ongoing royalties. In return, the brand provides training, marketing, and support, making succeeding easier. This model is popular because it combines the stability of an established brand with the entrepreneurial spirit of owning your own business.
Famous Examples : Wayback Burgers is a great example of a successful franchise. Launched in 1991, it now has over 170 locations. While most of its outlets are full-service restaurants, it also offers ghost kitchens. Their menu includes burgers, chicken meals, salads, sandwiches, and milkshakes. By opting for a Wayback Burgers cloud kitchen, you save on business costs, enter new markets, and delight customers with premium burgers and other delicious foods without the overhead of a full-service restaurant.
Concept : A franchise model lets you run your branch of a famous brand. You pay an initial fee to use their name, logo, and business plan, plus ongoing royalties. In return, the brand gives you training, marketing, and support, making success easier than starting from scratch. It’s a win-win: the brand expands with less risk, and you get their reputation and customer base.
Faster Brand Recognition: Customers will recognize and trust new cloud kitchens faster using a well-known food brand.
Built-In Customer Base: Franchisees take advantage of customer trust and brand recognition, speeding up market entry and boosting initial sales.
Operational help: The owner provides franchisees with thorough training, operational rules, and ongoing help, which lowers the chance that the business will fail.
Standardized Processes: The staff and the owner follow pre-defined processes and systems for consistent service and food quality.
Marketing and advertising: The brand’s marketing keeps the customer aware of new offers.
Initial Fees: You’ll need to pay a significant upfront license fee, which adds to your startup costs.
Ongoing Royalties: Regular royalty payments to the company can reduce your overall profits.
Strict Compliance: You have to follow the franchisor’s rules, limiting your ability to make independent decisions.
Limited Customization: To maintain brand consistency, you can’t change much about the menus, marketing tactics, or operations.
Operational Constraints: There are limits on where you can source goods, pricing, and the kinds of promotions you can run.
Innovation Limitations: Sticking to the franchisor’s model can restrict your creativity and make adapting to local market trends tough.
Corporate Cloud Kitchens

Think of it as a big, shared kitchen where several restaurants cook their meals. These kitchens, also called ghost kitchens, don’t have dining areas. These ghost kitchen models instead focus on online orders and delivery through apps like Uber Eats or DoorDash. This setup helps keep costs low and reach more customers without needing a physical restaurant.
Conclusion
After researching the numerous restaurant models, their advantages, and drawbacks, it’s time to choose which one best meets your company’s objectives. Whether you opt for pop up locations, a delivery only business model, or a virtual kitchen, the choice depends on your target market and resources. Some may find dark kitchens or a central kitchen appealing for their low overhead and efficient production. Whichever model you decide on, choosing the right tech partner is important to control costs and streamline operations. An integrated kitchen display system can be crucial for managing the entire business operation, from order taking to food preparation. Additionally, leveraging the right marketing channels will help you reach your audience effectively and maximize your restaurant’s visibility and success.
That’s where Restroworks can help— Restroworks Cloud Kitchen Software .
Frequently Asked Questions
Cloud kitchens can make substantial income due to lower overhead costs and high demand for delivery services. Successful ones often surpass traditional restaurants in profitability. However, exact earnings depend on location, market demand, and operational efficiency.
Cloud kitchens can be both B2B and B2C. They enable restaurants and brands to operate delivery and takeout locations without a storefront (B2B), while also facilitating direct sales to consumers (B2C) through online platforms.
Cloud kitchens are quite successful due to low overhead costs and high profit margins. They are popular among food entrepreneurs and established restaurants for expanding delivery services. Success, however, depends on factors like location, market demand, and operational efficiency.
CloudKitchens, founded by Travis Kalanick, provides shared kitchen spaces for multiple food brands. They enable delivery-only food services by offering necessary infrastructure and technology.
Kitchen United in the USA provides shared kitchen spaces for multiple food brands to operate delivery-only services. They partner with various restaurants and virtual brands, offering a streamlined solution for food preparation and delivery.
In the USA, cloud kitchens, also known as ghost kitchens, are commercial food preparation facilities for delivery-only brands. They rely on online ordering platforms without having physical dining areas.
Cloud kitchens offer lower startup and operational costs, flexibility, and the ability to reach a wider audience through delivery platforms. They allow businesses to focus on food preparation and marketing without managing a physical restaurant.
Yes, cloud kitchens are worth it due to their cost-effectiveness and potential for high profit margins. They are ideal for startups and small businesses looking to enter the food industry with minimal risk.
A cloud kitchen is a commercial kitchen used solely for preparing food for delivery. They do not offer dine-in or take-out options, focusing exclusively on delivering fresh, made-to-order meals.
Yes, you can operate a cloud kitchen from home, primarily taking orders from online platforms or phone calls. This setup doesn’t require a dine-in area and can be a cost-effective way to start a food business.
CloudKitchens continues to expand, providing infrastructure for delivery-focused food businesses. They have grown significantly, helping numerous brands operate efficiently in the food delivery market.
Manasi Sharma
Manasi Sharma is the Product Marketing Manager at Restroworks. With a dynamic role in product and marketing teams and experience in the F&B industry, she drives product visibility on our website by aligning with customer needs. Her focus on understanding user requirements ensures that Restroworks delivers solutions tailored to meet customer expectations effectively

Restroworks is a leading platform that specializes in providing technological solutions to the restaurant industry. It stands out for its ability to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and enable scalability for global restaurant chains.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay ahead of the curve with Restroworks industry insights.
Explore Topics
- Digital Ordering
- Editor's Pick
- Management Software

Recent Blogs

Restroworks: Unveiling a Unified Restaurant Technology Platform
- 09 April 2024

5 Restaurant Pricing Strategies to Build a Profitable Menu
- 19 December 2023

Implementing the 4 P of Marketing for a Restaurant
- 09 May 2024

Restaurant Supply Chain Strategy with 7 Best Practices
- 06 December 2023

Restaurant Sales Forecast: A Comprehensive Guide
- 27 May 2024

NASA admits it's been working with SpaceX on a backup plan to retrieve Boeing's 2 stuck astronauts. It doesn't sound ideal.
- Two astronauts are stuck on the International Space Station due to issues with Boeing's spaceship.
- NASA officials admitted Wednesday that they ordered SpaceX to make a backup plan.
- If Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams return to Earth on SpaceX's Crew Dragon, it won't be until February.

If Boeing and NASA can't get their spaceship together, SpaceX may have to come to two astronauts' rescue . The downside is the duo will be stuck on the International Space Station for about eight months longer than planned.
Astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams launched into orbit aboard Boeing's Starliner vehicle on June 5. They were the spaceship's first crew, and their test flight was supposed to last about a week.
Two months later, though, they're still on the International Space Station . That's because Starliner suffered thruster issues and a helium leak, causing NASA to postpone the astronauts' return while engineers examined the issue.
NASA and Boeing are still working to ensure Starliner is safe for the journey home.
But NASA has been keeping options open.
On Wednesday, the space agency finally admitted it has SpaceX actively working on a backup plan using its Crew Dragon spaceship .
A SpaceX save would leave the astronauts in space until February
The SpaceX spaceship has been reliably flying astronauts to and from the ISS since 2020, making it an obvious plan B.
But NASA officials have avoided talking about the Crew Dragon backup, until now.
Earlier, in a late July press conference about Williams' and Wilmore's predicament, NASA official Steve Stich said it was an option they could turn to if needed, but it was unclear if NASA was actively looking into it.
"I would rather not go into all those details until we get to that time, if we ever get to that time," he said in the July briefing.
Related stories
Well, that time came this week, when NASA announced it was postponing SpaceX's next astronaut launch to September 24 at the earliest — a delay of over a month.
"We have tried to buy ourselves a little bit of time to work various options for return," Stich said in a briefing on Wednesday.
The move preserves the option of leaving the four-person Crew Dragon spaceship with two empty seats for Williams and Wilmore.
The pair would essentially become members of that SpaceX mission, called Crew-9, and return aboard the Crew Dragon around February 2025 — about 8 months later than when Williams and Wilmore were scheduled to return.
If that happens, Boeing's Starliner ship would undock from the ISS and fall to an ocean splashdown autonomously, with nobody on board.
NASA is weighing risks
Stich said NASA had been working out the details of this backup plan with SpaceX since early July.
They've set up the Crew Dragon to be able to fly to the space station with just two astronauts if needed, he said, and they've identified spacesuits that Williams and Wilmore could wear on the Dragon.
What's left is configuring the vehicle and training the crew for the two-person option. Stich declined to say which of the four Crew-9 astronauts would be taken off the mission to make room.
"Our prime option is to return Butch and Suni on Starliner. However, we have done the requisite planning to make sure we have other options open," Stich said.
The agency isn't ready to decide yet, as engineers are still working to fully understand the "physics" behind Starliner's problems, Stich said. However, he added, they'll likely need to make the call by mid-August.
"Reasonable people could pick either path," Ken Bowersox, the associate administrator of NASA's Space Operations Mission Directorate, said in the Wednesday call.
"When we started this mission, it was a test mission. We knew that it potentially had a higher risk," he added later in the briefing.
Now, with Starliner's mid-flight technical issues, Bowersox said, NASA sees "additional risk" with "fairly broad" uncertainty. But taking the backup option with SpaceX has its own risks.
"We have to compare all those risks and we'll weigh all that as we make our final decision," he said.
2 astronauts caught in the middle
Starliner and Crew Dragon were developed on a similar timeline through the same NASA-funded initiative, called the Commercial Crew Program , which Stich oversees.
NASA has always insisted that the program wasn't a competition. But if it was, SpaceX won by a landslide. Crew Dragon completed its first crewed test flight — the very test Boeing is struggling with now — four years ago, in 2020. SpaceX also did it for cheaper, costing NASA just $2.6 billion compared to Boeing's $4.2 billion contract for Starliner.
Since overstaying their planned mission, Williams and Wilmore have only appeared in one brief press call in early July. The pair put on happy faces, said they were "absolutely confident" in Starliner , and did a couple flips in the station's microgravity.
Stich said that Williams and Wilmore get daily or weekly updates on NASA's testing and risk assessments.
"I think Butch and Suni are ready to do whatever we need them to do," he said.
Watch: Boeing's problems reach new heights with stranded astronauts
- Main content
- Patient advocacy

alotofpeople - stock.adobe.com
What is corporate social responsibility in healthcare?
Corporate social responsibility in healthcare can include sdoh work and investing in community benefits..

- Sara Heath, Executive Editor
As businesses across the country continue to assess the impacts they have on the environment and society around them, corporate social responsibility in healthcare is likewise becoming prominent.
Indeed, corporate social responsibility ( CSR ) is not a concept unique to healthcare. Rather, it can apply to all businesses and corporations, and since most hospitals and health systems are corporations, it applies to healthcare, too.
As more business sectors embrace principles of ethics and CSR, so too are healthcare organizations. Those trends, plus obligations for claiming tax-exempt nonprofit status and pushes for more social determinants of health (SDOH) work, are pushing more hospitals and health systems to assess their CSR strategies.
Defining corporate social responsibility in healthcare
According to the Harvard Business School, corporate social responsibility is "the idea that a business has a responsibility to the society that exists around it."
IBM says that corporate social responsibility means companies prioritize not just profit but also the impact they have on the environment and society around them.
"Through CSR, companies make decisions driven by financial gain and profitability, and the impact of their actions on their communities and the world at large," IBM says on its website . "CSR goes beyond legal obligations: by voluntarily adopting ethical, sustainable and responsible business practices, companies seek to deliver benefits to consumers, shareholders, employees and society."
Like other industries, many healthcare organizations have embraced their social responsibility. According to Charity Miles, an organization that facilitates corporate walks and runs for charitable causes, healthcare social responsibility is closely linked to SDOH.
"Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in healthcare involves healthcare organizations ethically contributing to community health and well-being through sustainable practices, enhanced healthcare access, and initiatives tackling social health determinants like poverty and education to better health outcomes," Charity Miles says .
According to the American College of Healthcare Executives (ACHE), which counts CSR among its chief commitments, social responsibility can be exemplified in six pillars:
- Responsible advocacy.
- Environmental and economic stability.
- Public protection through ethical practices, self-regulation and support of human rights.
- Philanthropy and community service.
- Socially responsible leadership.
The benefits of CSR are manifold. Of course, CSR can support the community a hospital or health system serves, but most experts agree the practice can also support the healthcare organization itself.
Hospitals and health systems that practice CSR might improve their public image, boosting consumer trust and patient loyalty . On the flip side, they might also help close health disparities by supporting SDOH.
Notably, CSR is voluntary for nearly every corporation, including hospitals and health systems. However, for hospitals and health systems with nonprofit and tax-exempt status, CSR might seem like a de facto requirement.
Corporate social responsibility and nonprofit status
Nonprofit 501(c)(3) hospitals receive tax-exempt status from the IRS in exchange for practices related to charity care and social responsibility. Those requirements, mandated as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), include the following:
- Completion of a community health needs assessment.
- Operating an emergency department open to everyone, regardless of ability to pay.
- Financial assistance policy.
- Limitations on charges for individuals who qualify.
- Compliance with certain billing and collections policies.
To be clear, the IRS does not mandate CSR for nonprofit hospitals. However, the community benefits that nonprofit hospitals do have to provide, which can include charity care and other charitable programs to benefit the community, often align with a strong CSR strategy.
In essence, nonprofit hospitals are required to design their operations to support the communities they serve rather than funneling all profits to shareholders. This means operating under a CSR structure.
However, murky requirements make it difficult to measure a hospital or health system's social responsibility. There is no minimum amount nonprofit hospitals need to spend on community benefits, meaning some hospitals spend as little as $.01 on the dollar in community benefits, according to one 2018 Health Affairs study .
Oversight might also be lacking. A 2020 Government Accountability Office (GAO) report showed as many as 30 hospitals did not spend anything on community benefits.
This has led to some discrepancies regarding how much nonprofit hospitals and health systems put toward community services and whether that is enough.
According to a 2023 American Hospital Association (AHA) report, nonprofit hospitals gave more than $20 billion in community benefits in 2020, accounting for 15.5% of total expenses.
That conflicts with a 2024 report from the Lown Institute showing that nonprofit hospitals spent 3.87% of their budgets on community benefits , making the tax breaks they see as 501(c)(3) organizations exceed their total community benefit spend.
There is little evidence explaining the discrepancy between community benefit and social responsibility giving. Factors like variable definitions and standards, accounting practices, reporting requirements and data sources could be at play.
Regardless, nonprofit hospitals and health systems looking to improve their community benefit practices or public image and patient loyalty might turn to common CST practices.
Examples of CSR in healthcare
There is no one-size-fits-all approach for CSR in healthcare. Social responsibility in one community might look different than it does in another.
For example, a hospital prioritizing CSR in a community with many food deserts might invest in food delivery modalities and fund community food banks or farmer's markets.
Meanwhile, a different health system's CSR might manifest as financially backing affordable housing complexes because it treats a larger unhoused population .
CSR does not need to be informed by community needs assessments, but it does help to know what types of resources would support the community a hospital serves. From there, health systems can assess their own resources and community partnerships to identify high-yield intervention areas.
Some leading examples of CSR in healthcare include the following:
- Mobile health clinics to support free or subsidized patient care access.
- Workforce development.
- Environmental conservation.
- Donating of medical supplies.
- Investments in affordable housing.
- Social determinants of health interventions.
As noted above, CSR work can be closely linked to a nonprofit hospital's community benefits. Offering charity care is considered CSR work, as is reviewing financial assistance programs.
Practicing CSR is part of a key cultural shift focusing on social responsibility and business ethics. As key anchor institutions, healthcare organizations might consider different CSR strategies as they work not just to improve the health of communities but also their own public image and consumer loyalty.
Sara Heath has covered news related to patient engagement and health equity since 2015.
Dig Deeper on Patient advocacy

What is corporate social responsibility (CSR)?

ESG vs. CSR vs. sustainability: What's the difference?

What Is a Community Health Needs Assessment?

Nonprofit Hospitals Offer Less Charity Care Despite Rising Profits

The proposed rule, which is available for public comment until October 8, 2024, would require HHS contractors to use certified ...
Generative AI in clinical documentation can ease EHR burdens and enhance patient communication, but issues with accuracy ...
LOINC release 2.78 includes nearly 3,000 terminology updates across various domains, including social determinants of health (...

- Biodiversity
- Cities & society
- Land & water
- All research news
- All research topics
- Learning experiences
- Programs & partnerships
- All school news
- All school news topics
- In the media
- For journalists
New climate and sustainability research efforts will focus on eight ‘Solution Areas’
The Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability will establish new research initiatives under topics including climate, water, energy, food, nature, and cities.
The Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability has selected eight interconnected Solution Areas to focus its research efforts over the next decade. This new research plan amplifies the school’s ability to translate Stanford research into large-scale solutions and inform key decision makers in policy and business.
Selected based on extensive faculty input and assessment of where Stanford can make the most meaningful impact, the eight areas are: climate; water; energy; food; risk, resilience, and adaptation; nature; cities; and platforms and tools for monitoring and decision making.
“Solution Areas identify and leverage the critical junctions between the most pressing global sustainability challenges and the areas where Stanford has the talent and expertise to find solutions,” said Dean Arun Majumdar. “This collaborative all-campus approach expands and strengthens our commitment to using all the power we have – the knowledge, the education, the talent, the innovation, the resources, the influence – to build a thriving planet for future generations.”
‘Integrative Projects’ and ‘Flagship Destinations’
In each Solution Area, the school plans to build two types of research initiatives. One type, called Integrative Projects, will be managed by the school’s institutes, including the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment , the Precourt Institute for Energy , and a planned Sustainable Societies Institute.
Integrative Projects will be organized around decade-long research themes and dedicated to creating solutions through interdisciplinary collaboration, engagement with partners beyond Stanford, identifying significant knowledge gaps, and understanding systems.
According to Chris Field , the Perry L. McCarty Director of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and a professor in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability and the School of Humanities and Sciences , the new commitment to these areas “will provide both resources and coordination that expand Stanford faculty’s capacity to deliver sustainability solutions at scale.”
A second type of research initiative, called Flagship Destinations, is managed by Stanford’s Sustainability Accelerator . Flagship Destinations are targets for the pace and scale of work to address challenges facing Earth, climate, and society. For example, the school’s first Flagship Destination, announced in 2023 , calls for enabling the removal of billions of tons of planet-warming gases annually from Earth’s atmosphere by the middle of this century. By working backward from sustainability targets in consultation with faculty and external experts, this initiative seeks to rapidly translate Stanford research into policy and technology solutions. Additional Flagship Destinations will be announced later this week.
Whereas Integrative Projects are designed to produce knowledge and evidence that can eventually lead to solutions, Flagship Destination projects are intended to help verify and demonstrate that well-studied solutions can succeed at large scale so they can be launched out of Stanford and implemented for the benefit of humanity and our planet. Scalable solutions nurtured and launched through these projects could take the form of policy frameworks, open-source platforms, nonprofit organizations, new for-profit companies, and ongoing collaborations all committed to addressing pressing sustainability challenges.
“By working together in these Solution Areas across disciplines and with collaborators beyond the university, we maximize our ability to have positive impacts on the timeframe and scale needed for the planet and humanity,” said Scott Fendorf , senior associate dean for integrative initiatives and the Terry Huffington Professor in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability.
Workshops will be held with faculty and external experts to develop research strategies for each Solution Area on a rolling basis. Strategy workshops, opportunities to provide input on future Integrative Projects, and requests for proposals (open to all Stanford faculty) will be announced in the coming months.
Related message from leadership: Read a letter to faculty about the new Solution Areas from Dean Majumdar with Precourt Institute for Energy director William Chueh; Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment director Chris Field; Accelerator faculty director Yi Cui and executive director Charlotte Pera; and Integrative Initiatives associate dean Jenna Davis and senior associate dean Scott Fendorf.
Media Contacts
Josie garthwaite, explore more.

Stanford’s Sustainability Accelerator adds new targets
The Sustainability Accelerator in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability will support work in new areas including energy, climate adaptation, industry, and more.
- School planning

Solution Areas and research funding
A message from school leadership announcing solutions-oriented and scale-focused research funding opportunities to address pressing sustainability challenges.

Forecasting climate’s impact on a debilitating disease
In Brazil, climate and other human-made environmental changes threaten efforts to fight schistosomiasis, a widespread and debilitating parasitic disease. Stanford and Brazilian researchers have now developed models that can predict how disease risk will shift in response to environmental changes.
- Health and wellbeing
- Share full article

Swindled Savings
How One Man Lost $740,000 to Scammers Targeting His Retirement Savings
Criminals on the internet are increasingly going after Americans over the age of 60 because they are viewed as having the largest piles of savings.
Barry Heitin, a 76-year-old retired lawyer, in Arlington, Virginia. Mr. Heitin was the victim of a sophisticated online scam. Credit... Hailey Sadler for The New York Times
Supported by

By Tara Siegel Bernard
Tara Siegel Bernard spoke to people who’ve fallen victim to scams that target savings of Americans, particularly older adults. This article is the first in a series.
- July 29, 2024
For nearly three months, Barry Heitin, a 76-year-old retired lawyer, thought he was part of a government investigation that felt like something out of the movies. He was actually assisting criminals in stealing hundreds of thousands of dollars — of his own money.
Last fall, he spent just about every weekday doing the legwork and making withdrawals from his bank accounts as part of an intricate scam: He believed he was helping the feds safeguard his money and catch thieves who were after it.
“They kept telling me, ‘This is a big case and we are going to stop a whole ring of people,’” Mr. Heitin said. “It was like a rabbit hole. I was going down the hole with them.”
It cost him almost all of his retirement savings: roughly $740,000.
Americans spend a lot of energy saving for retirement and worrying about losing money to the gyrations of the stock market. But these days, sophisticated criminals — on dating sites, on social media, in messaging apps or using malicious software — present an ever-growing risk to people and their savings.
The nature of these schemes makes it nearly impossible to recover the money, leaving victims with little recourse. The stolen funds are often whisked to overseas accounts or laundered through cryptocurrency wallets, which are quickly emptied.
Mr. Heitin was one of many people interviewed by The New York Times who were ensnared in scams that could be so elaborate it’s as if they were created in a writer’s room testing different plot devices. Scammers can impersonate government officials, tech support staff or love interests. They coach victims on how to sidestep fraud prevention measures at financial institutions, and they use manipulative psychological tactics — isolation, a sense of urgency or preying on people’s willingness to trust or connect — to keep the scam going.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Legal structure - e.g partnership, private limited company. Products and services - what the business sells or provides to customers. Target market - the customer segments the business caters to. Business model - how the company generates revenue and profit. So for example, an online retailer has a very different nature of business ...
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market. Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background. Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even ...
This structure defines legal responsibilities, benefits, and limitations a business has. To sum it up, the nature of business is a blend of its purpose, daily functions, size, interconnected relationships, contribution to the economy, potential challenges, and legal standing. Each component interplays with the other, forming the intricate ...
The nature of business is a structured method of describing a company. This concept is a synthesis of what type of business it is and what the business does. The nature of business also highlights the specific problems a given business solves. It encompasses everything a business does to reach its goals and describes the main focus of the ...
A helpful business plan can be short or long, depending on the reason you're creating it. It can be anything from a scrawl on a piece of paper to a detailed plan that's over 100 pages long. The average business plan runs between 15 and 20 pages, but there's room for variation. If your concept is simple, you might be able to define it with only ...
1. Startups. Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas. If you're planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business. You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration. 2.
Today, a business can be defined as an entity that creates and sells goods or services for profit. But it's more than just transactions and trade. The nature of business is about identifying needs and fulfilling them, creating value not just for the owners but also for customers, employees, and society at large.
EB-5 Business Plan. Acquisition Business Plan. Private Placement Memorandum. L-1 Visa Business Plan. EB2-NIW Visa Business Plan. EB-5 Regional Center. Exit Business Plan. Franchise Business Plans. As an entrepreneur, effectively pitching your idea to attract investors and secure funding can be a challenge.
The nature of business is a statement about a company's offering to its clients, its industry, legal structure, or any other distinctive qualities of the business. For example, if you say a company in the "private sector", you evaluate the nature of the company based on its nature to earn profits. If you say that a company is the ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Nature of Business Plan. Business Description: Detailed information about the business, including its products or services, target market, and unique value proposition. Market Analysis: Research on the industry, market trends, target audience, and competitive landscape. This section shows an understanding of the market environment.
Follow the steps below to start drafting a business overview to include in your business plan: 1. Start with your pitch. The first sentence of your business overview should serve as a sort of elevator pitch for your company—a quick summary that defines who you are and what you do. In your pitch, you may include your offerings as a company and ...
Before you write a business plan, consider the function of a business plan document to a new business or company changing direction. Investopedia defines a business plan as "[a] written document that describes in detail how a new business is going to achieve its goals.". A comprehensive legal business plan includes sections about the company's budget, financing, projected revenue ...
A traditional business plan should include an executive summary, a business description, market research, a business structure, a products and services overview, a marketing plan, your financial ...
Target market (who will buy your product or services) Competitive advantage (what sets you apart in the marketplace to allow you to succeed) Objectives and goals (plans for growth) Company's history, such as a family business that's been in operation for multiple generations. Business objectives, including short-term and long-term goals.
A business plan is a document that thoroughly outlines the nature of your business, the direction or ... Example of Business Plan Executive Summary. Business Concept: Green Innovations Ltd. is dedicated to developing eco-friendly technologies that reduce environmental impact. Our flagship product is a biodegradable packaging solution designed ...
In addition to pursuing a museum's artistic goals, for example, top executives manage the administrative and business side of the organization: human resources, finance, and legal concerns. Ticket revenues cover a fraction of the museum's operating costs, so the director spends a great deal of time seeking major donations and memberships.
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the ... For example, a business plan for a non-profit might discuss the fit between the business plan ...
The business plan template below is divided into sections as described in the table of contents. Each section can be copied into a document of your own; you may need to add or delete sections or make adjustments to fit your specific needs. ... Describe the overall nature of the industry, including sales and other statistics. Note trends and ...
Each business plan examples share common components such as the executive summary, company description, marketing plan, operational plan, and so much more. However, how these components are expressed or explained will differ according to the needs and designs of the business owner. 3.
A comprehensive business plan includes t-shirt market analysis, operational strategies, and financial projections. Regular updates and expert feedback can refine your business plan, making sure it stays relevant and effective. Starting with Printify simplifies setting up a t-shirt company, making it accessible to entrepreneurs with various budgets.
Famous Cloud Kitchen Example: Wow Bao's cloud kitchen in the United States represents a single-brand cloud kitchen; it is a brand-owned cloud kitchen that specializes in Asian-inspired foods such as steamed buns, potstickers, and rice bowls, only accepts delivery and takeaway orders, removing the need for a permanent eating location. This focus allows them to refine their menu and manage ...
NASA officials admitted Wednesday that they ordered SpaceX to make a backup plan. If Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams return to Earth on SpaceX's Crew Dragon, it won't be until February.
Examples of CSR in healthcare. There is no one-size-fits-all approach for CSR in healthcare. Social responsibility in one community might look different than it does in another. For example, a hospital prioritizing CSR in a community with many food deserts might invest in food delivery modalities and fund community food banks or farmer's markets.
This new research plan amplifies the school's ability to translate Stanford research into large-scale solutions and inform key decision makers in policy and business. ... and society. For example, the school's first Flagship Destination, announced in 2023, calls for enabling the removal of billions of tons of planet-warming gases annually ...
Riots have swept Britain over recent days, and more outbreaks of anti-immigrant violence are feared this week, leaving the new UK government scrambling to control the worst disorder in more than a ...
Criminals on the internet are increasingly going after Americans over the age of 60 because they are viewed as having the largest piles of savings.