

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers....
Essay writing: Introductions
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.” Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide
Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they should know if your essay is going to be a good one or not. An introduction has several components but the most important of these are the last two we give here. You need to show the reader what your position is and how you are going to argue the case to get there so that the essay becomes your answer to the question rather than just an answer.
What an introduction should include:
- A little basic background about the key subject area (just enough to put your essay into context, no more or you'll bore the reader).
- Explanation of how you are defining any key terms . Confusion on this could be your undoing.
- A road-map of how your essay will answer the question. What is your overall argument and how will you develop it?
- A confirmation of your position .
Background information
It is good to start with a statement that fixes your essay topic and focus in a wider context so that the reader is sure of where they are within the field. This is a very small part of the introduction though - do not fall into the trap of writing a whole paragraph that is nothing but background information.
Beware though, this only has to be a little bit wider, not completely universal. That is, do not start with something like "In the whole field of nursing...." or "Since man could write, he has always...". Instead, simply situate the area that you are writing about within a slightly bigger area. For example, you could start with a general statement about a topic, outlining some key issues but explain that your essay will focus on only one. Here is an example:
The ability to communicate effectively and compassionately is a key skill within nursing. Communication is about more than being able to speak confidently and clearly, it is about effective listening (Singh, 2019), the use of gesture, body language and tone (Adebe et al., 2016) and the ability to tailor language and messaging to particular situations (Smith & Jones, 2015). This essay will explore the importance of non-verbal communication ...
The example introduction at the bottom of this page also starts with similar, short background information.

Defining key terms
This does not mean quoting dictionary definitions - we all have access to dictionary.com with a click or two. There are many words we use in academic work that can have multiple or nuanced definitions. You have to write about how you are defining any potentially ambiguous terms in relation to your essay topic. This is really important for your reader, as it will inform them how you are using such words in the context of your essay and prevent confusion or misunderstanding.

Stating your case (road mapping)
The main thing an introduction will do is...introduce your essay! That means you need to tell the reader what your conclusion is and how you will get there.
There is no need to worry about *SPOILER ALERTS* - this is not a detective novel you can give away the ending! Sorry, but building up suspense is just going to irritate the reader rather than eventually satisfy. Simply outline how your main arguments (give them in order) lead to your conclusion. In American essay guides you will see something described as the ‘thesis statement’ - although we don't use this terminology in the UK, it is still necessary to state in your introduction what the over-arching argument of your essay will be. Think of it as the mega-argument , to distinguish it from the mini-arguments you make in each paragraph. Look at the example introduction at the bottom of this page which includes both of these elements.

Confirming your position
To some extent, this is covered in your roadmap (above), but it is so important, it deserves some additional attention here. Setting out your position is an essential component of all essays. Brick et al. (2016:143) even suggest
"The purpose of an essay is to present a clear position and defend it"
It is, however, very difficult to defend a position if you have not made it clear in the first place. This is where your introduction comes in. In stating your position, you are ultimately outlining the answer to the question. You can then make the rest of your essay about providing the evidence that supports your answer. As such, if you make your position clear, you will find all subsequent paragraphs in your essay easier to write and join together. As you have already told your reader where the essay is going, you can be explicit in how each paragraph contributes to your mega-argument.
In establishing your position and defending it, you are ultimately engaging in scholarly debate. This is because your positions are supported by academic evidence and analysis. It is in your analysis of the academic evidence that should lead your reader to understand your position. Once again - this is only possible if your introduction has explained your position in the first place.

An example introduction
(Essay title = Evaluate the role of stories as pedagogical tools in higher education)
Stories have been an essential communication technique for thousands of years and although teachers and parents still think they are important for educating younger children, they have been restricted to the role of entertainment for most of us since our teenage years. This essay will claim that stories make ideal pedagogical tools, whatever the age of the student, due to their unique position in cultural and cognitive development. To argue this, it will consider three main areas: firstly, the prevalence of stories across time and cultures and how the similarity of story structure suggests an inherent understanding of their form which could be of use to academics teaching multicultural cohorts when organising lecture material; secondly, the power of stories to enable listeners to personally relate to the content and how this increases the likelihood of changing thoughts, behaviours and decisions - a concept that has not gone unnoticed in some fields, both professional and academic; and finally, the way that different areas of the brain are activated when reading, listening to or watching a story unfold, which suggests that both understanding and ease of recall, two key components of learning, are both likely to be increased . Each of these alone could make a reasoned argument for including more stories within higher education teaching – taken together, this argument is even more compelling.
Key: Background information (scene setting) Stating the case (r oad map) Confirming a position (in two places). Note in this introduction there was no need to define key terms.
Brick, J., Herke, M., and Wong, D., (2016) Academic Culture, A students guide to studying at university, 3rd edition. Victoria, Australia: Palgrave Macmillan.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Main body >>
- Last Updated: Jul 4, 2024 10:15 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem


How to write an essay: Introduction
- What's in this guide
Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
The academic essay is a type of writing frequently used as an assessment task in university courses.
- An assignment essay is written over a number of weeks, as you research and read about the topic given. It is expected that you will develop your response to the essay question over an extended period of time, and include evidence from your research to support your ideas.
- You should be prepared to draft and rewrite several times before submitting your final essay for marking. This means you keep building on previous drafts to improve or add information to it. It does not mean starting from scratch for each draft.
- Your work must be correctly referenced and written in formal English.
Here are the steps to writing an academic essay:

Usually, the purpose of an essay is to answer a specific question within a given word limit.
An essay may be as short as 500 words or as long as 2000-3000 words.
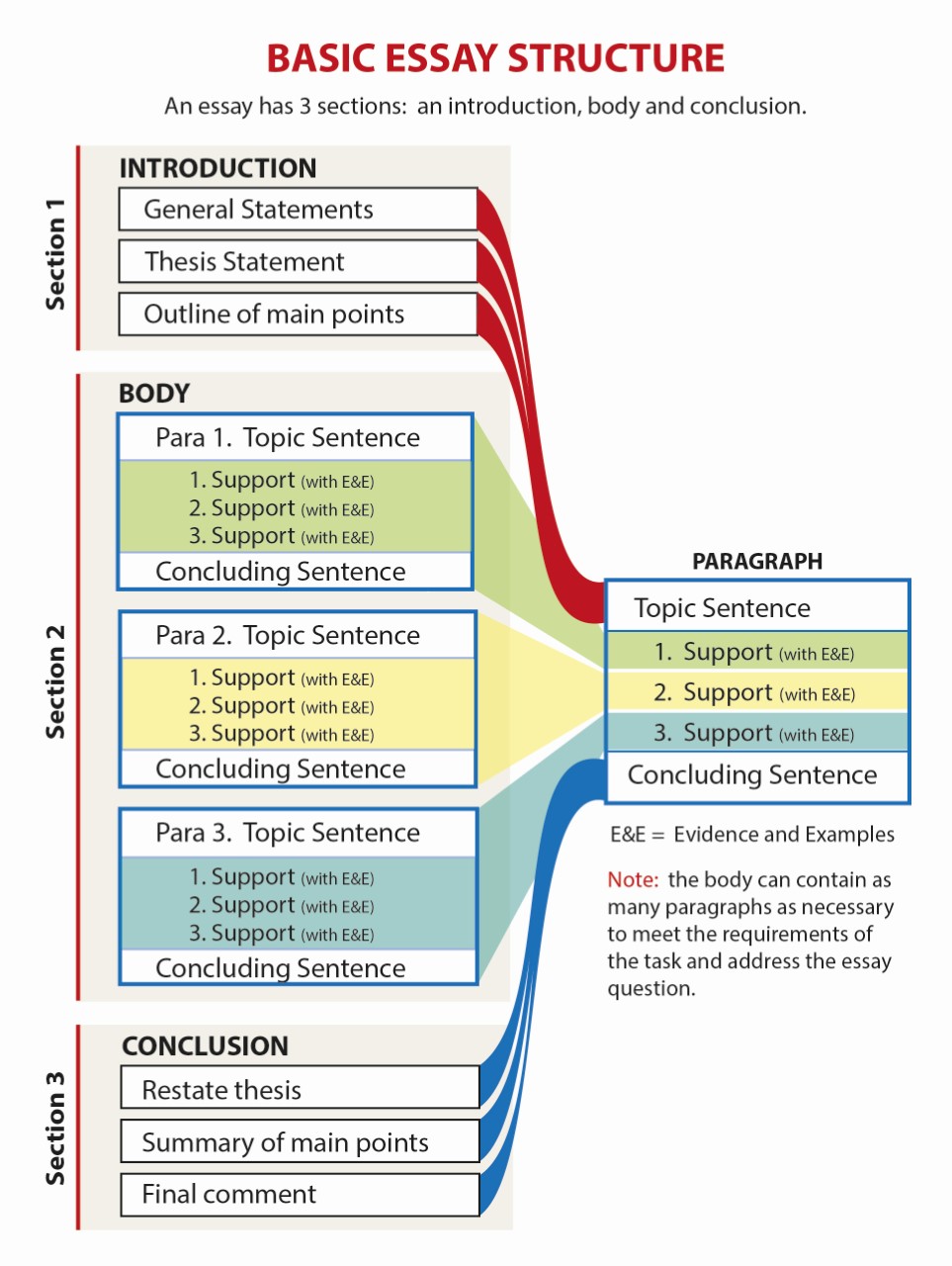
It has three main parts:
- the introduction
- and the conclusion, and is written in paragraphs with each paragraph dealing with one idea or part of the main topic. <
Watch the video below
- Transcript of "Essay structure" video
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: What's in this guide
- Next: Essay structure >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay

- Study and research support
- Academic skills
Structure your writing
The introduction.
Your introduction should tell the reader what to expect from your piece of writing.
What should be in an introduction?
There isn't one way to write an introduction. Your introduction should tell the reader what to expect from your assignment. It should present the main subject of the work so that your reader is clear what the writing will be about.
You should also explain why your topic is important and worthy of discussion. You may wish to highlight relevant publications to show how your argument fits into a wider context or conversation.
You might also provide definitions for any ambiguous terms or concepts; your reader needs to know what you mean or how you have interpreted them. For example, if you use "consumerism", are you discussing this as an ideology, economic policy or type of behaviour?
Your introduction should also give an indication of the structure of the rest of the assignment.
How long should an introduction be?
An introduction usually makes up 5–10% of your assignment, although there is no absolute rule.
The amount of detail that you can include in your introduction will depend on your word count.
Examples of introductions
Take a look at this detailed example of an introduction (PDF) , which is broken down to show the purpose of each sentence within the introductory paragraph.
There is also an example of an introductory paragraph in the Examples of paragraphs in academic writing resource.
Library Guides

Academic Support
- Code of Practice
- Get Academic Support
- Academic & Digital Skills Guides
What you are intending to do
Towards the end of the introduction you need to tell your reader exactly what you are going to cover. The way in which you do this will depend on the type of essay you are writing and what you have been asked to do. You may be required to give a point of view and often the stance ( point of view) of the essay is shown in the introduction. You may, for example, provide your argument and then reasons for it in a statement in your introduction. For example: This essay argues that television advertising plays a substantial part in teenage obesity as it targets young people and markets fast food. In some cases, you are not required to provide an opinion. It is still a good idea to explain what you intend to do in the essay.
The essay outline
It is often a good idea to explain briefly at the end of your introduction the stages of your essay. This is known as the outline . An outline doesn't have to say first this will be done and then this... but it can explain the different aspects you are going to be looking at within your writing. The good thing about an outline is it is like a road map for your reader. It shows how you are going to travel through your essay until you reach your conclusion .
Background information to your topic
In order to help your reader understand what you are going to be talking about, and get them interested, it is a good idea to give some sort of background to your essay topic. Background information could include some general information about your topic. You should aim to give enough information so that your reader understands what the topic is about. In an introduction you do not go in to much depth, you save your main points and the discussion of them for the main body of your essay.
The specific aspect you will be looking at
Once you have provided some background information to get your reader interested, you can say exactly what your essay is going to cover. This is known as the specific aspect or question that you will focus on. You have to show in this part of your essay why the topic you are writing about is important.
Your limitations
Another thing that is commonly found in an essay introduction is your limitations statement . If you are writing about a very large topic it will not be possible for you to discuss everything about that topic in your essay as you have a word count. With this in mind we often state the exact focus of what we are going to be writing about. This could include things like the period of time you are going to be discussing, the geographical area etc. For example if you were writing an essay in which the topic was obesity your limitations might include stating which element of obesity you were going to talk about, which type of people with obesity you would be discussing , the country you would focus on when looking at obese people and so on.. Limitations show that you have thought carefully about what you can and can't do in your essay and they make it easier for the reader to see what is going to be focused on.
When to write your introduction
Although the introduction is the first thing your reader will read, this does not mean you have to write it first. Many students find it is easier to put together the main body of their essay first and then their conclusion. When the whole of the main body and conclusion have been done this can make it easier for you to write a clear introduction. When you write the introduction is up to you.
Key points to remember
The length of your introduction will depend on your word count.
You should view your introduction like a satellite navigation system for your reader, they should be able to see the direction your essay is going in.
You should make things easier for your reader by explaining things they may not understand and include some general background information to engage them.
Make the purpose of your essay clear.
Don't be too general - provide some general information but also make it clear what aspect of the topic will be discussed in the essay.
Length of introduction
Many students think there is a set number of words to write in an introduction but this is not the case. The length of your introduction will depend on the length of your essay . It is common to write around two paragraphs for an introduction. You do not want your introduction to be too long otherwise it will be giving details that you should be including in the main body of your text. Lengthy introductions could also confuse your reader or bore them. You need to make sure you have provided some background, shown why the particular topic you are writing about is important , discussed any limitations , shown what exactly you are going to do in your essay and how you are going to do it and provide a basic outline. Once you have completed this information you can move on to the main body of your essay.
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 10:18 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gre.ac.uk/academicskills
Library policies | Library Code of Conduct | IT Service Status | Portal © University of Greenwich | FOI | Privacy and cookies | Legal | Terms & conditions

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principal tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question

English for Uni
Essay Writing
Ms parrot: essay chef.
View the video, then try the essay exercises to test your knowledge! Watch the whole story, or see sections of the story below. All the videos have captions that you can view on YouTube.
View the video on the Chinese site youku .
View the individual video chapters
To view the individual chapters of the above video, you can either click the 'PLAYLIST' menu item in the above YouTube video and select the chapter from there, or, you can click one of the links below and view the individual video on YouTube.
- Essay Chef - Introduction
- Essay Chef - The cooking show
- Essay Chef - Teaching
- Exercise 1: Introductions
- Exercise 2: Conclusions
- Exercise 3: Voice
- Exercise 4: Paraphrasing
- Exercise 5: Referencing
- Exercise 6: Academic Integrity
Download the transcript of the video or download the exercises in PDF format or as a Word document .
Essays in different academic cultures Teachers' notes
Essay structure
Essays help you discover more about a topic and write a reasoned analysis of the issues in question, using a range of external sources to support your position.
An essay is a highly structured piece of writing with follow a typical pattern:
| Section | Explanation of section contents |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | ackground statement — where you set the context for your essay ssue(s) — where you outline the specific issues that are relevant to your essay. hesis — where you state your position in relation to the issues. cope — where you outline what exactly is going to be covered in relation to your argument. |
| 2. Main body | Each paragraph should focus on one idea only. The idea can then be developed in a number of ways, such as through explanation, evaluation, exemplification or incorporation of research data. Your paragraphs should be balanced — keep to the rule of no less than 3 sentences per paragraph. Your paragraphs should link together — use connective words, both within and between paragraphs, to keep a sense of cohesion and linkage. |
| 3. Conclusion | Begin with a link to the preceding paragraph. Restate your thesis and summarise your principal points. End with a broad statement relating to the significance of your argument. |
Writing a good essay can be compared to baking a cake—if you do not mix the right ingredients in the right quantities or order, and do not follow the required processes, then the end result will not be what you hoped for! There is no set model for an essay, but the English for Uni website presents one popular way to do it. The following example is based around a 1000 word discussion essay. To read about essays in greater detail, download this PDF or Word document .
Topic/title
It is important for you to analyse your topic and title very carefully in order to understand the specific aim of the question. To do this, you need to break down the question. Most essay questions will contain these three elements:
Content/Topic words give the subject of the essay. Limiting/Focus words provide a narrower scope for the essay. Directive or Instructional words tell you how to approach the essay. Look at these sample essay titles from A) Economics and B) Nutrition:
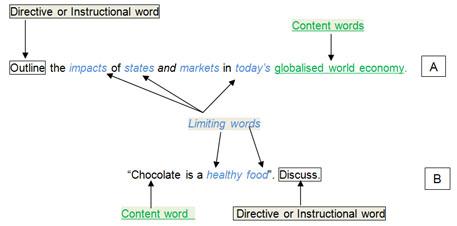
In example B, answering the question fully involves looking closely at the directive word Discuss and analysing its exact meaning.
Discuss: Present various points and consider the different sides. A discussion is usually longer than an explanation, as you need to present evidence and state which argument is more persuasive.
So, in your essay entitled:
“Chocolate is a healthy food”. Discuss.”
you would need to:
- consider a number of points in relation to the title
- balance your points between supporting and opposing positions
- consider which of the positions is the most persuasive and explain why
You also need to consider the length of your essay. In a 2000 word essay you can cover more points than in a 1000 word one! This example is based on a 1000 word essay.
In relation to Content words your focus is clear: chocolate!
In relation to Limiting words, you need to consider what healthy food actually means. A good way to expand your vocabulary is to look at the Academic Word List (developed by Averil Coxhead at Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand). The uefap website also has very useful lists of words found in particular subjects, such as mathematics, business and health science.
Directive or Instructional words
There are a number of directive words, or instructional words as they are sometimes called, which tell you what to do in your essay. Some common directive words include:
| Look at something in depth, examining the details. | |
| Give reasons for why you agree or disagree with something and show that you understand different points of view. | |
| Compare different points and see if the argument or information is true or persuasive. | |
| Show the similarities between two sets of information or arguments. ‘Compare’ often appears with ‘contrast’ in essay questions. | |
| Show the differences between two sets of information or arguments. ‘Contrast’ often appears with ‘compare’ in essay questions. | |
| Evaluate an argument or a text to see if it is good. ‘Criticise’ does not mean you have to be negative. | |
| Evaluate an argument or a text to see if it is good. ‘Critique’ does not mean you have to be negative. | |
| Explain the meaning of a word or a term, especially in the context of your essay. You can use a dictionary definition if it’s helpful, but remember that the word might be used in a particular way in the subject you are studying. | |
| Give details about something. | |
| Look at the different sides of an argument and say which is more convincing. Help your reader to understand more about something by giving relevant details. | |
| Look at the strengths and weaknesses of the material and give your final opinion of it. | |
| Look at the strengths and weaknesses of the material and give your final opinion of it. | |
| Help your reader to understand more about something by giving relevant details. | |
| Give examples to make something clearer. | |
| Help your reader to understand more about something and provide your own perspective if necessary. | |
| Give reasons to explain what you think about a subject. | |
| Give a broad explanation of something without too many details. | |
| Show if something is true and demonstrate how you reached that conclusion. | |
| Look at something in detail and give your perspective on it. | |
| Put your ideas or arguments clearly. | |
| Pull everything together and present it clearly without using too much detail. |
Brainstorming
Brainstorming means producing ideas related to a theme. You can write the ideas down in any order.
Here is a possible brainstorm for the chocolate essay, done in the form of a mind map:
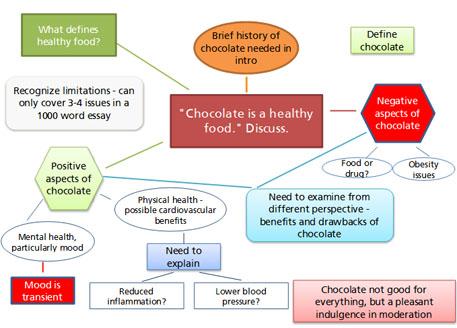
Text description of the above image.
Note that the central focus (the essay question) has several boxes linked to it which represent the writer’s first ideas. Other boxes area then added. A brainstorm like this is organic; it does not necessarily stop growing. You can add, remove or reorganise it as you wish. If you like to put more system into your brainstorm, use a step-based model such as the following:
Step 1 Time yourself for the first draft of your mind map Set a fixed time for this drafting from your base topic/question and stick to it.
Step 2 Look critically at your draft Which ideas could you develop or remove? Is there a balance of ideas?
Step 3 Think about ordering Which issues might you tackle first in your essay and why?
Step 4 Anticipate readers’ needs Are there any words and/or phrases that might need explaining? If so, when is the best time in the essay to do this?
Step 5 Move Reflect upon your brainstorming. Once you are happy with your brainstorm you can use it to plan your essay.
Researching for your essay
Once you have done some brainstorming, it’s time to get researching!
Remember that an academic essay requires academic sources.
Finding what you want takes time and effort. The best place to start (assuming you haven’t already been given a prescribed reading list!) is by using an academic database. If you are not sure how to use a database, then book an appointment with your subject librarian at your institution.
Another option is to use an internet academic search engine such as Google Scholar. N.B. Make sure you are logged in to the library at your educational institution, so that you can use the full database capacities linked to Google Scholar.
You need to enter keywords to begin with. For the chocolate essay, one of the first associations we thought of was chocolate and mood. If we enter these words into Google Scholar it will look like this:

This will take you to a webpage which lists a number of relevant articles, like this:
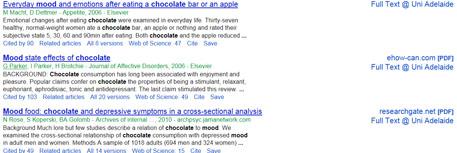
The first two articles have been cited 90 times and 103 times respectively, suggesting that they might be good sources for your essay. The links to the right indicate that you can access the articles through your university website.
If you think an article looks promising, click on the link and look at the abstract:
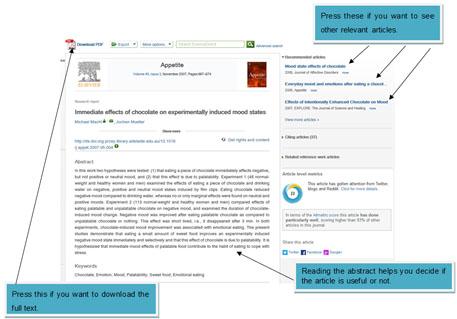
Read the abstract and ask yourself if the content of the article is likely to be relevant to your essay.
a) If yes, click on the PDF. This will take you to the full article which you can then skim read quickly to decide if it is relevant. b) If no, then you have a choice. Either click on the links to other related articles or go back to Google Scholar and then choose another article to skim read.
If you do not find what you are looking for, then you need to change your keywords search.
When you have found what you think might be useful, make a note in your plan at the appropriate place.
Do the same thing for all the points that need academic references to support them.
Remember that during your research you might discover new issues and perspectives that you hadn’t considered before, so your original plan might be quite different from the final one!
Planning your essay
Once you have brainstormed your ideas and done some initial research, start putting them into a logical order as part of the essay planning process. Brainstorming helps you to see what you know about the topic. Researching will give you more depth. Brainstorming, researching and planning are cyclical, which means that each process helps the other processes and you might want to do each process more than once.
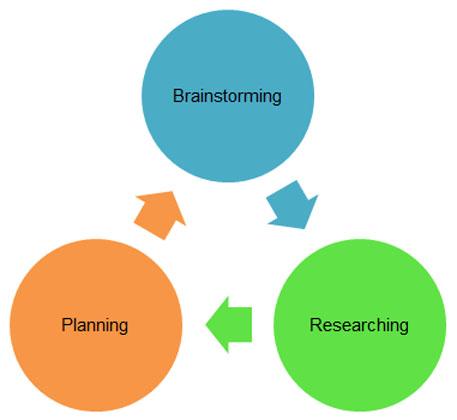
Here is the brainstorm for the chocolate essay again, which you can use to develop the planning process:
Read the text version of the brainstorming mind map .
Planning or a plan?
In the first instance, it is important to distinguish between planning and a plan . Planning is an ongoing process, from when you receive the essay title to when you submit your final draft. A plan is a physical outline of the way you intend to conceptualise, structure and present your ideas.
Plans can be structured/restructured at any time during the planning process.
At this point it is time to write your first plan. However, do not stop doing research yet. Why not?
| A plan helps you to put your ideas into a form which gives you a for your . | Once you have written your ideas up into a plan, you are beginning to in . | You might surprise yourself by discovering . This can help . |

Remember that a plan is just that—a plan. It can be modified after you do more research; you might discover some different perspectives or issues you hadn’t previously anticipated.
Example: Developing an essay plan after research (linear style)
Title: “Chocolate is a healthy food.” Discuss.
Introduction Context for paper – popularity of chocolate. Issue – whether chocolate is a healthy food is questionable. Thesis – chocolate may be enjoyable but not healthy. Scope – (only 4 aspects are covered here to keep the example short)
| Positive: | Can positively impact on mood |
|---|---|
| Positive: | Possible health benefits for cardiovascular system |
| Negative: | Chocolate can be seen as a drug rather than a food |
| Negative: | Potential correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity |
Main body Paragraph 1 with possible sources Ways in which chocolate can impact positively on mood. ‘Feel good effect’ - Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006), Scholey and Owen (2013), Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007).
Is the chocolate and improved mood scenario measurable/transient? Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006) – chocolate mood effects do not last. Macht and Dettmer (2006) – anticipation effect and more studies needed.
Paragraph 2 Possible benefits of chocolate on cardiovascular health – how much/what type(s) of chocolate have benefit? (Sources needed to help answer these questions.) Problems with measuring correlation between chocolate consumption and cardiovascular health. (Sources needed to help answer this.)
Paragraph 3 Chocolate best viewed as a food or a drug? Indulgence or addiction – are the boundaries unclear? (See what external sources have to say on this) Medication elements of chocolate? (Readings needed around this issue.)
Paragraph 4 The correlation between chocolate and obesity. (Definition of obesity needed.) What does the literature say in relation to other causal factors?
Conclusion Summary of four arguments presented. Chocolate is not a healthy food, but it is enjoyable nevertheless.
Example: Developed essay plan (linear style)
Main body Paragraph 1 Ways in which chocolate can impact positively on mood. ‘Feel good effect’-Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006), Scholey and Owen (2013), Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007)
Is the chocolate and improved mood scenario measurable/transient? Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006) chocolate mood effects do not last. Macht and Dettmer (2006) – anticipation effect and more studies needed.
Paragraph 2 Possible benefits of chocolate on cardiovascular health – how much/what type(s) of chocolate have benefit? Can provide heart-friendly flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002) – helps with blood clotting and is anti-inflammatory (Schramm et al., 2001) Maximising benefits of chocolate lies in minimising fat levels (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). Current processes destroy flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). Note the change of focus from the original idea (correlation between chocolate consumption and cardiovascular health) due to the lack of research data available.
Paragraph 3 Chocolate best viewed as a food or a drug? Indulgence or addiction – are the boundaries unclear? Chocolate contains some biologically active ingredients, but in small amounts (Bruinsma & Taren, 1999). ‘Chocolate addicts’ – negative correlation: chocolate consumption and mood (Macdiramid & Hetherington, 1995) but chocolate cravings sensory rather than addictive (Bruinsma & Taren,1999). Medication elements of chocolate? Used in relation to magnesium deficiency in women (Pennington, 2000 in Steinberg et al., 2003). Findings concur with Abraham and Lubran (1981) who found a correlation between magnesium deficiency and nervous tension in women. Note the narrow focus of medical benefits (i.e. only considering magnesium) due to the short length of the essay.
Paragraph 4 The correlation between chocolate and obesity. No specific correlation found in literature (Beckett, 2008; Lambert, 2009). Note the findings show that there is no clear relationship between chocolate and obesity – an issue flagged in the introduction. Typified by Mellor’s (2013) findings – adults showed no weight increase after chocolate controlled diet. Lambert (2009) exemplified that chocolate consumption alone unlikely to precipitate obesity. ‘Chocoholic’ more likely to consume other sweet foods and less likely to exercise as much as others. Chocolate consumption thus marginal in causes of obesity.
Conclusion Summary of four arguments presented Chocolate is not a healthy food, but it is enjoyable nevertheless.
Writing your conclusion
It might seem strange to think about writing your conclusion before you write the body of your essay, but unless you know where you are going you can easily lose direction. Also, the conclusion is the last thing the reader actually reads, so it needs to be memorable.
There are a number of questions you should ask yourself, such as:
How will everything finish? What are you aiming for? What final impression do you want your readers to have?
Your conclusion ties your essay together. It should normally:
- Begin with a link to the preceding paragraph.
- Restate your thesis and summarise your principal points.
- End with a broad statement relating to the significance of your argument.
So, our chocolate essay conclusion should mirror this pattern.
The conclusion should not just repeat the ideas from the introduction. The introduction includes the background to the essay, the important issues and a thesis statement. The introduction leads your reader into the essay. The conclusion reminds your reader of the main points made in your essay and leaves your reader with a final impression and ideas to think about later.
Chocolate essay conclusion
The following conclusion has three parts.
(A) The first sentence links the conclusion to the discussion in the previous paragraph. (B) The following sentences restate the main points and reaffirm the thesis. (C) The last sentence is a broad statement relating to the significance of the argument.
(A) Obesity and chocolate consumption seemingly have no proven correlations. (B) Yet, in this essay, many chocolate focused arguments have been presented, including the transient effect of chocolate on mood and evidence that it is as likely to create feelings of guilt as of well-being. Another possible positive dimension to chocolate is a correlation with cardiovascular health. Yet the potential benefits of flavanols in chocolate are currently offset by the high fat/carbohydrate content of most forms of chocolate. Whether chocolate is a food or a drug is also unclear. The literature outlines the chemical properties of chocolate which could help explain some addictive type behaviour, particularly in regards to nervous tension in women, but also there is a strong research focus on chocolate as a sensory-based indulgence. (C) It can therefore be said that chocolate is not a healthy food, but can be enjoyed as part of a healthy and balanced diet and lifestyle.
Writing the body paragraphs
At the heart of your essay lie your body paragraphs. Typically, a body paragraph will follow the format below.
| The topic sentence can function as a sentence of transition from the previous paragraph. The Topic Sentence should unambiguously express the topic of the paragraph and be linked with the overall thesis of the essay. | |
| Elaboration of the main point should add more detailed information in relation to the topic sentence. Examples and Evidence should support your main point using paraphrases, summaries or direct quotations, all of which need to be appropriately referenced. | |
| The Concluding Sentence should echo the main point of the paragraph and function as a bridge to the next paragraph. |
N.B. Paragraphs should be balanced – keep to the ‘no less than 3 sentences per paragraph’ rule.
Remember to link all the points in your paragraph to the idea in the topic sentence. One way to check if you have done this is to write keywords in the margin for each sentence. If your keywords are related to the topic sentence, your paragraph is good. If there are ideas that are not related, you should remove them.
In the following example, the unrelated ideas are highlighted in red:
| Paragraph | Sentence keywords |
|---|---|
| It has been claimed that chocolate is a healthy food, but in fact it contains a lot of sugar, which can be unhealthy. For example, sugar can cause tooth decay, which can lead to dental problems in later life. Too much sugar can also lead to obesity, which is a serious health risk. In addition, sugar contains a high amount of fructose, which is bad for the liver. The amount of sugar contained in chocolate means, therefore, that chocolate, particularly milk and white chocolate, may not be healthy. | Topic sentence – sugar and health sugar and tooth decay (health)
obesity (health)
|
These unrelated ideas can be removed to make a more coherent paragraph:
It has been claimed that chocolate is a healthy food, but in fact it contains a lot of sugar, which can be unhealthy. For example, sugar can cause tooth decay, which can lead to dental problems in later life. Too much sugar can also lead to obesity, which is a serious health risk. In addition, sugar contains a high amount of fructose, which is bad for the liver. The amount of sugar contained in chocolate means, therefore, that chocolate, particularly milk and white chocolate, may not be healthy.
You can then add examples and references to make your paragraph stronger.
Here is an example:
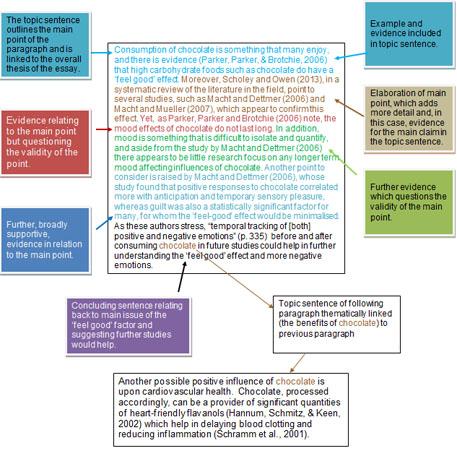
View the text description of the above body paragraph example .
Writing your introduction
Once you have drafted your main body paragraphs and your conclusion, it is time to draft your introduction.
Writing your introduction last means you are more likely to have a tighter fit between the introduction, main body and conclusion because you already know what your essay will be about.
Let us have another look at the functions of an introduction:
B ackground statement — where you set the context for your essay I ssue(s) — where you outline the specific issues that are relevant to your essay. T hesis — where you state your position in relation to the issues. S cope — where you outline what exactly is going to be covered in relation to your argument.
The thesis and scope are sometimes combined to form one or more sentences known as a thesis statement . The thesis statement often comes at the end of the introduction, although it can be written earlier.
Sometimes an essay will begin with a direct quote to draw readers into the essay.
Sometimes, particularly in very short essays, the essay will begin with an issue rather than a background statement.
Essays also sometimes begin with an issue, outline the scope and then move on to end the introduction with the thesis statement.
It is important to remember that there is not a fixed ordering for the introduction, though the BITS/BIST patterning is a very common one, which is why it is modelled for you as an example.
Example introduction
“Chocolate is a healthy food”. Discuss.
| Explanation | Sentence(s) in order |
|---|---|
| Background statement which draws the reader into the issue | Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. |
| Additional information to the background statement | At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. |
| The issue that is suggested by the title | However, chocolate's inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. |
| Scope of the essay | The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. |
| Thesis statement | Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate's positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity. |
Writing references for your essay
When you are writing an essay you will need to include references to external academic sources.
Why do you need to reference?
- To show respect for other people's ideas and work
- To clearly identify information coming from another source
- To distinguish an external source from your interpretation or your own findings
- To support your own arguments, thus giving you more credibility
- To show evidence of wide (and understood) reading
- To avoid being accused of plagiarism, which includes copying another’s work, paraphrasing or summarising without acknowledgement, colluding with others and presenting either identical or very similar essays
What does referencing include?
A. In-text citations, which can take three forms:
- Paraphrasing, where you keep the original author’s ideas intact, but just change the wording
- Summarising, where you summarise the whole of the author’s work, rather than one particular aspect
- Direct quoting, where you take a word-for-word copy of a short extract from the original author’s work, and include it in your essay, making use of quotation marks and page number
- All of these need a reference in the text.
B. A reference list at the end of your essay, which includes details such as:
- Date of publication
- Publisher and place of publication (for books)
- Journal name, volume and issue (for journals)
- Internet address or doi (digital object identifier) for electronic sources
Referencing is integral to academic essay writing and shouldn’t be viewed as an ‘add-on’. When you are referencing, always use a referencing guide to help you ensure 100% accuracy.
Normally, when writing an essay at university you will be expected to use only academic sources. The following learning guide on source credibility will help you to determine whether an external source is academic or not.
The chocolate essay uses the American Psychological Association (APA) style of referencing, which is easy to distinguish from the Harvard Author-Date System, as the format is different:
| Harvard | APA |
|---|---|
When you are writing an essay and including external sources, more often than not you want the reader to focus on what is said rather than who is saying it. In that case the information comes before the author. For example:
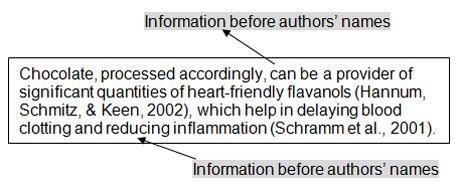
Such citations are called information-centred citations.
When the focus is more on who is saying it then the citation is written like this:

Such citations are called author-centred citations.
Try and achieve a balance between both types of in text-references in your essay writing.
Reference list
In the APA style of referencing, the reference list has certain conventions that you must also follow. Here are some examples from the chocolate essay:

Text description of the APA style of referencing example above.
Don’t make referencing something you do just as an editing or proofreading activity. Include your in-text citations and reference list as part of your first draft.
An excellent website to help with your APA referencing is the APA Interactive tool at Massey University.
Redrafting your essay
Leave yourself enough time to look at your essay more than once. For a 1000 word essay you need at least three days to redraft your essay.
Always save each draft as a separate file; then you can see how your essay develops and improves.
Here are the sorts of questions you should ask yourself:
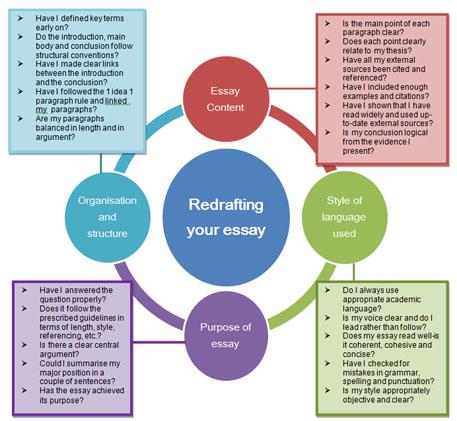
View a text version of the redrafting your essay diagram above.
You can also look at other checklists such as this one on editing your own work .
Let’s see how the writer of the chocolate essay redrafted their original introduction:

View the text version of the redrafted essay .
Now compare the above with the final draft:
Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. However, chocolate’s inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate’s positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity.
Take your time and be careful when redrafting—it will be worth it!
Incorporating your own voice
How do you write in an academic way?
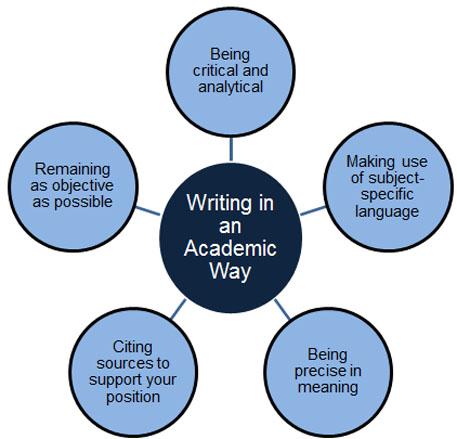
Your lecturers will want to hear your ‘voice’ as they read your essay.
Imagine your essay as a kind of story. You are the principal storyteller, the internal voice of the writer, leading the reader through to your conclusion.
During the story, there are different voices that appear from time to time. These are the external voices (citations) that add substance to your story, providing detail and support for what you are saying and sometimes even giving an alternative perspective. The external voices can be divided into two categories in your essay: the direct external voice of an author (through a direct quote) and the indirect external voice of an author (through a paraphrase).
The reader needs to know at all times whose voice they are hearing. Is it your internal voice or the external voice of other authors?
You might wonder how you can include your own voice and still sound academic when you are writing about a subject area in which you have little (or no) knowledge. Including your voice does not mean that you should say ‘I think’ or ‘in my opinion’.
Here are some examples of the critical/analytical language that you can use as your own internal voice when you present other people’s ideas:
| Phrase | How your voice is included |
|---|---|
| It has been argued (Smith & Jones, 2010) that… | Pointing out what has been said by an external source |
| As Smith and Jones (2010) note… | Showing your agreement with the external source |
| However, Smith and Jones (2010) fail to address… | Showing that you recognise the limitations of the source |
| Seemingly, Smith and Jones (2010) have… | Showing you have tentative support for the external source |
| On the other hand, Smith and Jones (2010) argue that… | Showing that there is a contrast with a previous argument you have included |
| Smith and Jones (2010) assert that… | Showing that the position of the external source is strong but you are likely to have doubts about it |
| It has been suggested that… (Smith & Jones, 2010; Brown & Culbertson, 2005; Lloyd & Giggs, 2004) | Showing that you recognise a number of authors have reached a similar conclusion, and you might/might not agree with it |
| One advantage of the work of Smith and Jones (2010)… | Showing that you are positively engaging with an external source |
Let’s look at one of the paragraphs from the chocolate essay to see how the text is an interplay of the internal voice of the writer and the external voices of other authors. The internal voice of the writer is colour-coded in yellow; the indirect external voices of other authors (i.e. paraphrases) are coded in grey; and the direct external voices of other authors (i.e. quotations) are coded in blue.

View a text version of the voice explanation above.
This is a balanced paragraph. The writer sets the scene at the beginning of the topic sentence and also links together all of the sentences, using their own voice to lead into content which is provided by the external voices.
Look at the same paragraph re-written, with the amount of the writer’s voice substantially reduced:
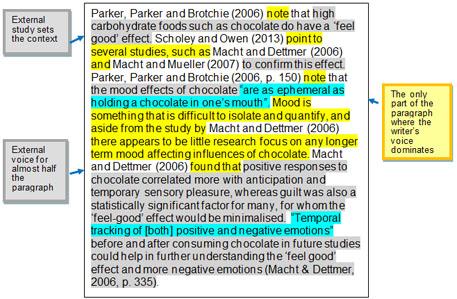
View a text version of the above re-written paragraph .
Here the writer is not ‘in charge’ of the paragraph, and it reads a little like a list. That is something your lecturers do not want to see.
When you are drafting your paragraphs, use a colour-coding system like the one used here. It will help you ensure your academic voice is clear!
When you get more confident in using external sources, you will gradually expand the language of your critical internal voice. The Phrasebank website at Manchester University provides examples of some more expressions to use when assessing external sources.
Proofreading and editing your essay
Editing focuses on the big picture elements such as overall structure, appropriate paragraphing and whether the question has been answered.
Proofreading has a micro-focus on the details of your essay, such as formatting, grammar and punctuation.
Everybody has their own personal style of editing and proofreading. You need to focus on the types of errors you commonly make by looking at the marker’s comments on your previous work.
Some people proofread alone; some get other people involved. Having others involved is a really good idea.
Fresh eyes can help you find things you might not otherwise have seen.
Here are some things to consider when proofreading and editing:
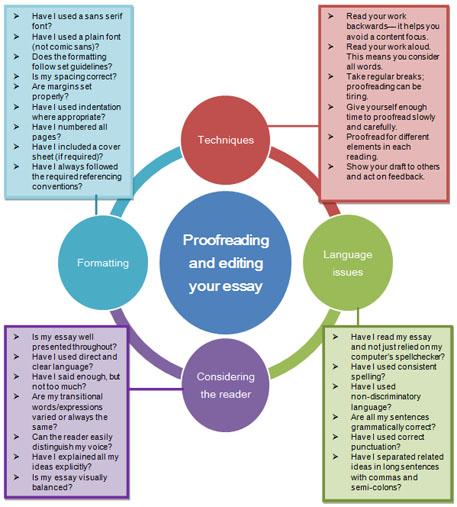
View a text version of the above proofreading and editing your essay considerations.
The Purdue OWL website has even more detail on the proofreading process.
Submitting on time
Students regularly underestimate the time it takes to write an essay, in particular the planning and researching stages.
Before you begin your essay, have a look at the Massey University assignment planning calculator . You might be surprised how long the whole process takes!
As you can see from the assignment planning calculator, if you only start your essay a few days before the due date, you will have to do things too quickly.
If you think of the essay/cake analogy, you need time to mix all the ingredients properly, or the end result will not be what you want to share with others!
To write a 1000 word essay, ideally you should allow yourself about 3 weeks.
Let’s have a look at how an essay time management ‘cake’ could be divided into slices:

View a text description of the writing an essay time management 'cake' .
You can see that the biggest part of your time is spent on the planning/research elements and redrafting/editing/proofreading elements, which together should comprise around 60% of your time.
Have a look at another model to see what you also need to consider:
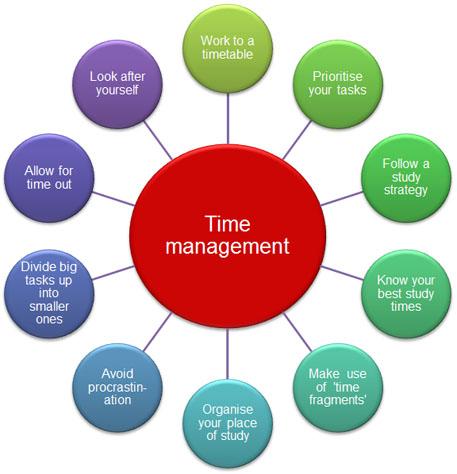
Essay example
Here is the final version of the chocolate essay. You can also download a PDF version of the chocolate essay .
“Chocolate is a healthy food.” Discuss.
Since Spanish explorers brought back chocolate from the new world, chocolate consumption has become a worldwide phenomenon. At first, chocolate, a derivative of the cacao bean, was consumed as a drink, only later achieving mass popularity in tablet or bar form. However, chocolate’s inherent popularity does not equate to it possessing healthy properties, as suggested by the title. The realities of chocolate are more down to earth; a number of these realities will be addressed in this essay. Chocolate has chemical properties that can influence mood and there is possible evidence for some positive impacts of chocolate on cardiovascular health. Yet, such positive attributes are counterbalanced somewhat by the argument that, in some instances, chocolate can be viewed as a drug rather than a food. Moreover, there is the possibility of some correlation between over-consumption of chocolate and obesity. Thus, it will be argued that despite chocolate’s positive effect in some cases on mood and the cardiovascular system it has also been linked to addiction and obesity.
Consumption of chocolate is something that many enjoy, and there is evidence (Parker, Parker, & Brotchie, 2006) that high carbohydrate foods such as chocolate do have a ‘feel good’ effect. Moreover, Scholey and Owen (2013) in a systematic review of the literature in the field point to several studies, such as Macht and Dettmer (2006) and Macht and Mueller (2007), which appear to confirm this effect. Yet, as Parker, Parker and Brotchie (2006, p. 150) note, the mood effects of chocolate "are as ephemeral as holding a chocolate in one’s mouth". In addition, mood is something that is difficult to isolate and quantify, and aside from the study by Macht and Dettmer (2006) there appears to be little research on any longer term mood affecting influences of chocolate. Another point is raised by Macht and Dettmer (2006), whose study found that positive responses to chocolate correlated more with anticipation and temporary sensory pleasure, whereas guilt was also a statistically significant factor for many, for whom the ‘feel-good’ effect would be minimalised. As these authors stress, “temporal tracking of [both] positive and negative emotions” (p.335) before and after consuming chocolate in future studies could help in further understanding the ‘feel good’ effect and more negative emotions.
Another possible positive influence of chocolate is upon cardiovascular health. Chocolate, processed accordingly, can be a provider of significant quantities of heart-friendly flavanols (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002) which help in delaying blood clotting and reducing inflammation (Schramm et al., 2001). Such attributes of flavanols in chocolate need to be considered in the context of chocolate’s other components – approximately 30% fat, 61% carbohydrate, 6% protein and 3% liquid and minerals (Hannum, Schmitz, & Keen, 2002). The key to maximising the benefits of flavanols in chocolate appears to lie in the level of fats present. Cocoa, which is simply chocolate minus the fat, is the most obvious candidate for maximising heart health, but as Hannum, Schmitz and Keen (2002) note, most cocoa products are made through an alkali process which destroys many flavanols. Optimal maximisation of the flavanols involves such compounds being present in cocoa and chocolate products at levels where they are biologically active (Ariefdjohan & Savaiano, 2005).
The biological makeup of chocolate is also relevant in determining whether chocolate is better viewed as a food or a drug, but the boundaries between indulgence and addictive behaviour are unclear. Chocolate contains some biologically active elements including methylxanthines, and cannabinoid-like unsaturated fatty acids (Bruinsma & Taren, 1999) which could represent a neurochemical dependency potential for chocolate, yet are present in exceedingly small amounts. Interestingly, and linked to chocolate and mood, Macdiarmid and Hetherington (1995) claim their study found that “self-identified chocolate ‘addicts’” reported a negative correlation between chocolate consumption and mood. This is perhaps indicative of addictive or compulsive type behaviour. However, as Bruinsma and Taren (1999) note, eating chocolate can represent a sensory reward based, luxurious indulgence, based around texture, aroma and flavour anticipation, rather than a neurochemically induced craving. Yet, it has been argued that chocolate is sometimes used as a form of self-medication, particularly in relation to magnesium deficiency. A study by Pennington (2000 in Steinberg, Bearden, & Keen 2003) noted that women do not generally meet US guidelines for trace elements, including magnesium. This correlates with earlier studies by Abraham and Lubran (1981), who found a high correlation between magnesium deficiency and nervous tension in women. Thus, tension-related chocolate cravings could be a biological entity fuelled by magnesium deficiency. Overall, however, it would appear that the proportion of people using chocolate as a drug rather than a food based sensory indulgence is small, though further research might prove enlightening.
A final point to consider in relation to chocolate is the perception that chocolate is linked to obesity. A person is defined as being obese when their Body Mass Index is greater than 30. The literature on chocolate and obesity has clearly demonstrated that there are no specific correlations between the two variables (Beckett, 2008; Lambert, 2009). This is typified by the findings of Mellor (2013), who found that, over a period of eight weeks of eating 45 grams of chocolate per day, a group of adults demonstrated no significant weight increase. As Lambert (2009) notes, chocolate consumption alone is not likely to cause obesity, unless large amounts of other calorie dense foods are consumed and this calorie dense intake is greater than needed for bodily function, bearing in mind levels of activity. The stereotypical ‘chocoholic’ seems more likely to consume many other sweet foods and be less likely to take exercise than other people, so chocolate consumption is only one possible variable when considering the causes of obesity.
Obesity and chocolate consumption seemingly have no proven correlations. Yet, in this essay, many chocolate focused arguments have been presented, including the transient effect of chocolate on mood and the fact that it is as likely to create feelings of guilt as of well-being. Another possible positive dimension to chocolate is a correlation with cardiovascular health. Yet the potential benefits of flavanols in chocolate are currently offset by the high fat/carbohydrate content of most forms of chocolate. Whether chocolate is a food or a drug is also unclear. The literature outlines the chemical properties of chocolate which could help explain some addictive type behaviour, particularly in regards to nervous tension in women, but there is also a strong research focus on chocolate as a sensory-based indulgence. It can therefore be said that chocolate is not a healthy food, but can be enjoyed as part of a healthy and balanced diet and lifestyle.
(Word count: 1087. This is within 10% of the word limit, which is usually acceptable. Check this with your lecturer if you are in any doubt.)
Abraham, G. E., & Lubran, M. M. (1981). Serum and red cell magnesium levels in patients with premenstrual tension. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , 34 (11), 2364-2366. Retrieved from http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/34/11/2364.short
Ariefdjohan, M. W., & Savaiano, D. A. (2005). Chocolate and cardiovascular health: Is it too good to be true? Nutrition Reviews , 63 (12), 427-430. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2005.tb00118.x
Beckett, S. T. (2000). The science of chocolate . Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Bruinsma, K., & Taren, D. L. (1999). Chocolate: Food or drug? Journal of the American Dietetic Association , 99 (10), 1249-12. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(99)00307-7
Hannum, S. M., Schmitz, H. H., & Keen, C. L. (2002). Chocolate: A heart-healthy food? Show me the science! Nutrition Today , 37 (3), 103-109. Retrieved from http://journals.lww.com/nutritiontodayonline/Abstract/2002/05000/Chocol…
Lambert, J. P. (2009). Nutrition and health aspects of chocolate. In S. Beckett (Ed.), Industrial chocolate manufacture and use , (4th ed., pp. 623-635). London: Wiley Blackwell. Retrieved from http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781444301588.ch27/pdf
Macht, M., & Dettmer, D. (2006). Everyday mood and emotions after eating a chocolate bar or an apple. Appetite , 46 (3), 332-336. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2006.01.014
Macht, M., & Mueller, J. (2007). Immediate effects of chocolate on experimentally induced mood states. Appetite , 49 (3), 667-674. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2007.05.004
Macdiarmid, J. I., & Hetherington, M. M. (1995). Mood modulation by food: An exploration of affect and cravings in ‘chocolate addicts’. British Journal of Clinical Psychology , 34 (1), 129-138. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1995.tb01445.x
Mellor, D. D. (2013). The effects of polyphenol rich chocolate on cardiovascular risk and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (Doctoral dissertation, University of Hull, UK). Retrieved from https://hydra.hull.ac.uk/resources/hull:7109
Parker, G., Parker, I., & Brotchie, H. (2006). Mood state effects of chocolate. Journal of Affective Disorders , 92 (2), 149-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.02.007
Scholey, A., & Owen, L. (2013). Effects of chocolate on cognitive function and mood: a systematic review. Nutrition reviews , 71 (10), 665-681. doi:10.1111/nure.12065
Schramm, D. D., Wang, J. F., Holt, R. R., Ensunsa, J. L., Gonsalves, J. L., Lazarus, S. A., Schmitz, H. H., German, J. Bruce, & Keen, C. L. (2001). Chocolate procyanidins decrease the leukotriene-prostacyclin ratio in humans and human aortic endothelial cells. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , 73 (1), 36-40. Retrieved from http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/73/1/36.full
Steinberg, F. M., Bearden, M. M., & Keen, C. L. (2003). Cocoa and chocolate flavonoids: Implications for cardiovascular health. Journal of the American Dietetic Association , 103 (2), 215-223. doi: 10.1053/jada.2003.50028
Academic integrity and plagiarism
‘Integrity’ relates to ‘honesty’, and academic integrity involves writing in an honest way, so that no one will think you are claiming that words or ideas from someone else are your own. This is very important in academic writing in western countries, and if you do not do this you might be accused of plagiarism, which is a serious offence at university.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words, ideas or diagrams without acknowledgement.
Of course, when we write an essay we need to refer to other people’s ideas. We gave some of the reasons for this before:
Being a good writer involves using other people’s ideas to support your work. However, you should never forget to say where these ideas come from, even if you don’t quote the person’s exact words.
Include a reference in the text, where the words or ideas appear, and in a reference list at the end of the essay.
All the references in the text must appear in the reference list, and all the references in the list must also appear in the text.
There is a short video clip on plagiarism here and a wonderful Plagiarism Carol video here (click on ‘captions’ to get subtitles in English).
Another word connected to academic integrity is collusion .
Collusion means that you work with someone else and submit the same or very similar assignments without your lecturer’s permission.
For example, if you and a friend work together on an essay and then submit identical or very similar versions of the essay, one under your name and one under your friend’s name, that is collusion . However, if you are doing a group work assignment and your lecturer has asked you to work together and submit the assignment jointly, that is not collusion . Collusion, like plagiarism, has an element of dishonesty in it. People who collude do so secretly, as they know that the lecturer would not be happy.
People make genuine mistakes, so lecturers are usually very happy to advise you if you ask them.

Successful University Writing
- Before You Start Writing...
Structuring an essay
- Report writing
- Annotated bibliography
- Literature review
- Reflective writing
- Using Ideas from sources in your writing
- Writing concisely and editing your work
- Student Success study support

Thesis statements
Most academic writing at university will require you to argue a position. This means including a thesis statement upfront in the first paragraph that concisely states the central argument and purpose of the essay. This video addresses the key features of a thesis statement.
- Parts of an essay
- Writing introductions and conclusions
- Writing paragraphs
- Making your writing flow
Academic writing structures may vary, but the main sections are the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Here is an overview of what these sections contain:
Introduction
- The introduction tells the reader what your writing is about.
- Start by defining the topic and any terms which will be crucial for your discussion.
- The introduction should also state what position you will argue and how you will do it. This is the thesis statement .
- Use words and phrases which are in the assignment question to help the reader see that you are directly addressing the main issues.
- It can help to write the introduction last. This is particularly helpful if you have not yet fully determined what your document is going to say and what your arguments will be.
- This is the most important part of your writing. Begin each sentence with a "topic sentence" which is then discussed and explained.
- Each paragraph must discuss a different point. Each paragraph should be a discussion on the point you have made in the first sentence.
- Paraphrase or summarise the sources you have read in your research. If using direct quotes, ensure they are relevant and impactful. Evaluate what is being said. Never assume the reader knows what you are talking about.
- Always reference any ideas you have used in your writing.
- Paragraphs should flow in an organised and logical sequence. One way to do this is by introducing the next paragraph (topic) in the last sentence of the previous paragraph.
- Avoid repetition and rewriting another version of what you have already said.
- Transition or linking words , such as however, therefore, and although tell the reader about the direction you are arguing or when there is a change of direction.
- Avoid using first person point of view.
- Avoid slang or jargon (use academic language).
- Avoid using long and complicated sentences. Make your point obvious and easy to read.
- The work should read as one organised discussion, not a mix of unrelated information. Make sure each sentence in the paragraphs has a role in the discussion and contributes to the overall argument and topic you are addressing.
- Restate what you planned to do in your introduction and discuss how you have done it. You should tell the reader that your discussion led to the conclusion that your thesis (argument/position) supported.
- No new information should be included in the conclusion.
An essay introduction usually:
- clearly states the topic that will be the focus of the essay;
- offers a preview of main aspects that will addressed, or the particular angle that will be taken in; and
- clearly articulates the position that will be argued. This is known as the thesis statement.
Consider this introduction:
Leadership has been defined as “the process of influencing the activities of an organized group toward goal achievement” (Block & Tackle, 2019 , p. 46). This essay compares and contrasts two approaches to leadership from Western and Eastern traditions. The first is Fayol’s Administrative Principles approach, considered to be one of the foundations of the study of Management. The second approach is Confucianism, which is said to continue to guide leadership and management across China and much of South-East Asia (Shih, Wong, Han, Zheng, & Xin, 2004). It will be argued that these two approaches share certain core values, and a critical understanding of both approaches can support management decision-making.
The first sentence clearly states the topic. Leadership has been defined as “the process of influencing the activities of an organized group toward goal achievement” (Block & Tackle, 2019 , p. 46).
The middle sentences preview the aspects that will be addressed and hints at the approach (compare and contrast). This essay compares and contrasts two approaches to leadership from Western and Eastern traditions. The first is Fayol’s Administrative Principles approach, considered to be one of the foundations of the study of Management. The second approach is Confucianism, which is said to continue to guide leadership and management across China and much of South-East Asia (Shih, Wong, Han, Zheng, & Xin, 2004).
The final sentence clearly states the thesis, or position that will be argued. This is essentially a succinct version of the response to the essay question. It will be argued that these two approaches share certain core values, and a critical understanding of both approaches can support management decision-making.
In any academic essay, the paragraphs should follow the key points that have been outlined in the introduction. Each paragraph then contextualises and expands upon these points in relation the thesis statement of the essay. Having a paragraph plan is an effective way to map out your essay and ensure that you address the key points of the essay in detail – especially for longer forms of essays and academic writing that students engage with at university.
An basic paragraph plan would generally contain:
- The thesis statement (for an essay)
- A topic heading for each paragraph
- The claim of argument to be made in each paragraph (this will be, or will inform, your topic sentence)
- The evidence that will be presented to support the claim
- Summary of the conclusion paragraph
Consider this example of a paragraph plan:
| What are the benefits and risks of cryptocurrencies? Would you recommend a fellow student to invest in them? Cryptocurrencies The cryptocurrency boom presents novel investment and return options but also present associated exposure to inherent risk vulnerabilities. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| To be recommended in very limited circumstances |
Paragraph plans provide an overview of your essay and provide an effective starting point for structured writing. The next step is using this plan to expand on the points as you write your essay.
Getting your writing to flow.
In almost all cases, written assignments call for students to explore complex topics or aspects of an area of study. Any academic writing task is an opportunity to show how well you understand a particular topic, theme or area. Usually this means demonstrating how various ideas, knowledge, information or ways of thinking are connected within the context of the task or area of focus.
This means that successful academic writing presents ideas logically, and that there is high connectivity within the writing. In other words, the aim should be for writing to have high flow to help make the connections clear.
Three ways to achieve this include:
- ensuring that there is good connection from one paragraph to another;
- ensuring that there is good connection from one sentence to another; and
- using transition words effectively to make the logical connections between ideas clear.
Flow from one paragraph to another
Topic sentences, or the leading sentences of a paragraph, play a key role in connecting the ideas of an essay. High-flow topic sentences should look to include three key elements:
- An explicit reference to the topic of the essay.
- A reference to the main aspect of the previous paragraph
- An introduction to the topic of the new paragraph
Consider the following examples of topic sentences in response to an essay question about Virtue Ethics.
A low-flow topic sentence : Aristotle defined phronesis as practical wisdom.
This sentence does not reference the topic (virtue ethics), nor does it link to an idea from a previous paragraph. It does however, introduce the sub-topic of the paragraph (phronesis).
A high-flow topic sentence: Another fundamental concept in Virtue Ethics is phronesis.
This sentence refers to the essay topic (virtue ethics), acknowledges that this is an additional concept that build on the previous paragraph, and introduces the topic of this paragraph (phronesis).
Flow from one sentence to another
Well-constructed paragraphs have high connections between sentences. In general sentences that promote flow should:
- reference the topic of the previous sentence;
- add new information in the second half; and
- use topic words.
The following paragraph example can be considered high-flow. It includes sentences that reference the previous sentence ( underlined ), add new information ( maroon ) and use topic words ( green ).
Another fundamental concept in Virtue Ethics is phronesis. According to Aristotle, phronesis is a form of practical wisdom through which individuals make principled decisions in line with virtues such as courage and honesty (reference). Its practical nature means that phronesis can only be developed over a lifetime of carefully considered actions and sober reflection . This practice builds a person’s moral character, allowing them to make morally-defensible choices even in unfamiliar and complex situations (reference). In other words, it is a kind of social and professional skill, which at first requires conscious effort and can still result in mistakes. However, through discipline and persistence, it becomes second nature. As a result, practitioners consistently act wisely and in accordance with the virtues they uphold . Their wise actions further strengthen their own character and contribute to human fulfilment at both individual and community levels (reference).

Transition words that improve flow
Transition words help make the relationships and connections between ideas clear. Some examples of helpful transition words and phrases for various types of connections include:
| Like X, Y is... Unlike X, Y is... In other words, This means that... For example, For instance, | Moreover, Furthermore, Additionally, Likewise, Similarly, | However, On the other hand, Therefore, As a result, Consequently, Hence, Thus, |
Success Now! workshops and consultations
Success Now! workshops are available live online or on campus. Register here for workshops on research and writing . You can also organise an individual consultation here to talk to a learning advisor about planning your assignments.
- << Previous: Types of university academic writing
- Next: Report writing >>
- Last Updated: Jul 17, 2024 11:40 AM
- URL: https://library.nd.edu.au/writing
How to Start an Essay: 7 Tips for a Knockout Essay Introduction

Sometimes, the most difficult part of writing an essay is getting started. You might have an outline already and know what you want to write, but struggle to find the right words to get it going. Don’t worry; you aren’t the first person to grapple with starting an essay, and you certainly won’t be the last.
Writing an essay isn’t the same as writing a book. Or writing a poem. Or writing a scientific research paper. Essay writing is a unique process that involves clear sequencing, backing up your positions with quality sources, and engaging language. But it’s also got one important thing in common with every other type of writing: You need to hook your reader’s attention within the first few sentences.
Give your essays extra polish Grammarly helps you write with confidence Write with Grammarly
Intriguing ways to start an essay
There are many different ways to write an essay introduction. Each has its benefits and potential drawbacks, and each is best suited for certain kinds of essays . Although these essay introductions use different rhetorical devices and prime the reader in different ways, they all achieve the same goal: hooking the reader and enticing them to keep reading.
To “hook” a reader simply means to capture their attention and make them want to continue reading your work. An essay introduction that successfully hooks readers in one essay won’t necessarily hook readers in another essay, which is why it’s so important for you to understand why different types of essay openings are effective.
Take a look at these common ways to start an essay:
Share a shocking or amusing fact
One way to start your essay is with a shocking, unexpected, or amusing fact about the topic you’re covering. This grabs the reader’s attention and makes them want to read further, expecting explanation, context, and/or elaboration on the fact you presented.
Check out these essay introduction examples that use relevant, engaging facts to capture the reader’s attention:
“More than half of Iceland’s population believe that elves exist or that they possibly can exist. Although this might sound strange to foreigners, many of us have similar beliefs that would sound just as strange to those outside our cultures.”
“Undergraduate students involved in federal work-study programs earn an average of just $1,794 per year. That’s just slightly more than the average rent for a one-bedroom apartment in our city.”
Relevance is key here. Make sure the fact you choose directly relates to the topic you’re covering in your essay. Otherwise, it will feel random, confusing, or at best, shoehorned into the essay. In any case, it will undermine your essay as a whole by making it seem like you don’t have a full grasp on your topic.
If you’re writing an expository or persuasive essay , including a shocking or amusing fact in your introduction can be a great way to pique your reader’s curiosity. The fact you present can be one that supports the position you argue in the essay or it can be part of the body of data your expository essay explains.
Ask a question
By asking a question in your essay opening, you’re directly inviting the reader to interact with your work. They don’t get to be a passive consumer; they’re now part of the conversation. This can be a very engaging way to start an essay.
Take a look at these examples of essay openings that use questions to hook readers:
“How many times have you been late to class because you couldn’t find parking? You’re not alone—our campus is in desperate need of a new parking deck.”
“How frequently do you shop at fast fashion retailers? These retailers include H&M, Zara, Uniqlo and other brands that specialize in inexpensive clothing meant for short-term use.”
Asking a question is an effective choice for a persuasive essay because it asks the reader to insert themselves into the topic or even pick a side. While it can also work in other kinds of essays, it really shines in any essay that directly addresses the reader and puts them in a position to reflect on what you’re asking.
Dramatize a scene
Another effective way to write an essay introduction is to dramatize a scene related to your essay. Generally, this approach is best used with creative essays, like personal statements and literary essays. Here are a few examples of essay introductions that immerse readers in the action through dramatized scenes:
“The rain pounded against the roof, loudly drowning out any conversations we attempted to have. I’d promised them I’d play the latest song I wrote for guitar, but Mother Earth prevented any concert from happening that night.”
“Imagine you’ve just gotten off an airplane. You’re hot, you’re tired, you’re uncomfortable, and suddenly, you’re under arrest.”
Beyond creative essays, this kind of opening can work when you’re using emotional appeal to underscore your position in a persuasive essay. It’s also a great tool for a dramatic essay, and could be just the first of multiple dramatized scenes throughout the piece.
Kick it off with a quote
When you’re wondering how to write an essay introduction, remember that you can always borrow wisdom from other writers. This is a powerful way to kick off any kind of essay. Take a look at these examples:
“‘The past is never dead. It’s not even past.’ —William Faulkner. In his novel Requiem for a Nun , our changing perspective of the past is a primary theme.”
“‘It always seems impossible until it’s done.’ —Nelson Mandela. Before I joined the military, boot camp seemed impossible. But now, it’s done.”
Just as in choosing a fact or statistic to open your essay, any quote you choose needs to be relevant to your essay’s topic . If your reader has to perform a web search for your quote to figure out how it relates to the rest of your essay, it’s not relevant enough to use. Go with another quote that your text can easily explain.
State your thesis directly
The most straightforward kind of essay introduction is one where you simply state your thesis. Take a look at these examples:
“Fraternity culture is dangerous and contrary to campus values. Banning it is in the campus community’s best interest.”
“We can’t afford to ignore the evidence any longer; we need climate action now.”
How to write an essay introduction
Pick the right tone for your essay.
You probably shouldn’t use a funny quote to start a persuasive essay on a serious subject. Similarly, a statistic that can evoke strong emotions in the reader might not be the right choice for an expository essay because it could potentially be construed as your attempt to argue for a certain viewpoint, rather than state facts.
Read your essay’s first paragraph aloud and listen to your writing’s tone. Does the opening line’s tone match the rest of the paragraph, or is there a noticeable tone shift from the first line or two to the rest? In many cases, you can hear whether your tone is appropriate for your essay. Beyond listening for the right tone, use Grammarly’s tone detector to ensure that your essay introduction—as well as the rest of your essay—maintains the right tone for the subject you’re covering.
When you’re stuck, work backwards
Starting an essay can be difficult. If you find yourself so caught up on how to write an essay introduction that you’re staring at a blank screen as the clock ticks closer to your deadline, skip the introduction and move onto your essay’s body paragraphs . Once you have some text on the page, it can be easier to go back and write an introduction that leads into that content.
You may even want to start from the very end of your essay. If you know where your essay is going, but not necessarily how it will get there, write your conclusion first. Then, write the paragraph that comes right before your conclusion. Next, write the paragraph before that, working your way backwards until you’re in your introduction paragraph. By then, writing an effective essay introduction should be easy because you already have the content you need to introduce.
Polish your essays until they shine
Got a draft of a great essay? Awesome! But don’t hit “submit” just yet—you’re only halfway to the finish line. Make sure you’re always submitting your best work by using Grammarly to catch misspelled words, grammar mistakes, and places where you can swap in different words to improve your writing’s clarity.

- Current students
- New students
- Returning students
- Support for students
- Semester and term dates
- Policies and regulations
- Online learning tools
- Your feedback
- Studying off campus
- Results and graduation
- Student Portal
- Student handbook
- Student news

Writing an introduction & conclusion
About these study tips.
Improve your essays by following these tips on writing a good introduction and conclusion. This guide includes key information your introduction and conclusion should contain and examples of what this means in practice.
Introduction
Your introduction is important as it sets the tone of your essay. It should break down what the essay is about and summarise what the main body of the essay will cover. One method that you can use to write your introduction is the What, Why and How approach.
What is the essay about? This is where you explain what the purpose and focus of the essay is. Often you will be able to find this information in your assignment brief or in the essay question.
Why is the topic of the essay being discussed? This is where you should consider why the topic is of relevance and importance within your field. This could also be classed as a rationale for your essay.
How will you approach the essay? This is where you should outline the main points that you would discuss within the essay.
When using this approach, you do not necessarily have to present it in this order. It depends on what makes the most sense for the topic that you are exploring.

Example of an introduction

Examine the impact of physical inactivity on mental health (1000 words)
What: This essay will review the relationship between physical inactivity and mental health.
Why: The UK government recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity per week and two days of strengthening activities (Public Health England, 2019). However, 39% of adults are failing to meet the recommendations for physical activity (British Heart Foundation, 2017). A lack of physical activity increases the risk of individuals being affected by mental health and physical health conditions, with one in six UK deaths being attributed to physical inactivity (Public Health England, 2019).
How: This essay will critically discuss the impact of physical inactivity on depression, anxiety, self-esteem and stress. The essay will then go on to provide recommendations to promote and increase physical activity.
Your conclusion gives the reader a summary of the ideas you covered in your assignment. At this point, you should not be introducing any new ideas or information.
In your conclusion, you should:
- Summarise each of your points from the main body of your essay.
- Summarise the main conclusions based upon the evidence you used.
- Link your conclusions back to the title of your essay – if you were asked a question, make sure that you have shown how you have answered it.
You might be asked to:
- Offer recommendations and/or solutions.
- Comment on broader implications for this area of study or research.

Example of a conclusion

Summary of the essay: This essay has critically examined the relationship between physical inactivity on mental health. The impact of physical inactivity on depression, stress, self-esteem and anxiety has been discussed.
Main conclusion: Through the review of literature, it has been determined that a lack of physical activity can negatively affect mental health and in some cases, worsen symptoms.
Further research and recommendations: It is suggested that health education should be advertised to individuals susceptible to physical and mental health conditions. It is also recommended that healthy living programmes are integrated into workplaces and other high stress environments.
Tips for writing your introduction and conclusion
Use it as a signposting opportunity If your introduction and conclusion are clear enough, it should direct the reader through the main body easily.
Avoid being repetitive Whilst an introduction and conclusion cover similar areas, they are not the same. They both serve different purposes; therefore, they require their own attention.
10% of your word count Unless you have been given a specific word count for your introduction or conclusion, each section should only be 10% of your word count (20% in total). The remaining 80% of the word count should be for your main body.
Avoid going into too much detail You do not want to take anything away from your main body, where you will get the majority of your marks.
Make sure that you are only mentioning relevant points If you are writing five hundred words in your introduction and your essay is 1000 words, then you may be going into too much detail and including irrelevant information.
British Heart Foundation (2017) Physical Inactivity and Sedentary Behaviour. Available via the British Heart Foundation website (Accessed: 13 December 2019).
Public Health England (2019) Everybody active, every day: An evidence-based approach to physical activity. Available via the government website (Accessed: 13 December 2019).
You might be interested in
Planning your assignment.

Writing an introduction and conclusion

Reflective writing

Critical writing

Writing critical paragraphs

Studying mathematics - advice

You can also access our study support community on BlackBoard. We have developed a guide that will instruct you on how to join the study support community on BlackBoard. Here you can access our online resources and workshops.

If you have any questions or need study support please email [email protected] .
If you are after more general student support on issues such as welfare, money and health advice, please visit the support for students page or contact Student Services on:
- 020 8231 2345
- [email protected]
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
Writing a great essay
This resource covers key considerations when writing an essay.
While reading a student’s essay, markers will ask themselves questions such as:
- Does this essay directly address the set task?
- Does it present a strong, supported position?
- Does it use relevant sources appropriately?
- Is the expression clear, and the style appropriate?
- Is the essay organised coherently? Is there a clear introduction, body and conclusion?
You can use these questions to reflect on your own writing. Here are six top tips to help you address these criteria.
1. Analyse the question
Student essays are responses to specific questions. As an essay must address the question directly, your first step should be to analyse the question. Make sure you know exactly what is being asked of you.
Generally, essay questions contain three component parts:
- Content terms: Key concepts that are specific to the task
- Limiting terms: The scope that the topic focuses on
- Directive terms: What you need to do in relation to the content, e.g. discuss, analyse, define, compare, evaluate.
Look at the following essay question:
Discuss the importance of light in Gothic architecture.
- Content terms: Gothic architecture
- Limiting terms: the importance of light. If you discussed some other feature of Gothic architecture, for example spires or arches, you would be deviating from what is required. This essay question is limited to a discussion of light. Likewise, it asks you to write about the importance of light – not, for example, to discuss how light enters Gothic churches.
- Directive term: discuss. This term asks you to take a broad approach to the variety of ways in which light may be important for Gothic architecture. You should introduce and consider different ideas and opinions that you have met in academic literature on this topic, citing them appropriately .
For a more complex question, you can highlight the key words and break it down into a series of sub-questions to make sure you answer all parts of the task. Consider the following question (from Arts):
To what extent can the American Revolution be understood as a revolution ‘from below’? Why did working people become involved and with what aims in mind?
The key words here are American Revolution and revolution ‘from below’. This is a view that you would need to respond to in this essay. This response must focus on the aims and motivations of working people in the revolution, as stated in the second question.
2. Define your argument
As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument.
Consider these two argument statements:
The architectural use of light in Gothic cathedrals physically embodied the significance of light in medieval theology.
In the Gothic cathedral of Cologne, light served to accentuate the authority and ritual centrality of the priest.
Statements like these define an essay’s argument. They give coherence by providing an overarching theme and position towards which the entire essay is directed.
3. Use evidence, reasoning and scholarship
To convince your audience of your argument, you must use evidence and reasoning, which involves referring to and evaluating relevant scholarship.
- Evidence provides concrete information to support your claim. It typically consists of specific examples, facts, quotations, statistics and illustrations.
- Reasoning connects the evidence to your argument. Rather than citing evidence like a shopping list, you need to evaluate the evidence and show how it supports your argument.
- Scholarship is used to show how your argument relates to what has been written on the topic (citing specific works). Scholarship can be used as part of your evidence and reasoning to support your argument.
4. Organise a coherent essay
An essay has three basic components - introduction, body and conclusion.
The purpose of an introduction is to introduce your essay. It typically presents information in the following order:
- A general statement about the topic that provides context for your argument
- A thesis statement showing your argument. You can use explicit lead-ins, such as ‘This essay argues that...’
- A ‘road map’ of the essay, telling the reader how it is going to present and develop your argument.
Example introduction
"To what extent can the American Revolution be understood as a revolution ‘from below’? Why did working people become involved and with what aims in mind?"
Introduction*
Historians generally concentrate on the twenty-year period between 1763 and 1783 as the period which constitutes the American Revolution [This sentence sets the general context of the period] . However, when considering the involvement of working people, or people from below, in the revolution it is important to make a distinction between the pre-revolutionary period 1763-1774 and the revolutionary period 1774-1788, marked by the establishment of the continental Congress(1) [This sentence defines the key term from below and gives more context to the argument that follows] . This paper will argue that the nature and aims of the actions of working people are difficult to assess as it changed according to each phase [This is the thesis statement] . The pre-revolutionary period was characterised by opposition to Britain’s authority. During this period the aims and actions of the working people were more conservative as they responded to grievances related to taxes and scarce land, issues which directly affected them. However, examination of activities such as the organisation of crowd action and town meetings, pamphlet writing, formal communications to Britain of American grievances and physical action in the streets, demonstrates that their aims and actions became more revolutionary after 1775 [These sentences give the ‘road map’ or overview of the content of the essay] .
The body of the essay develops and elaborates your argument. It does this by presenting a reasoned case supported by evidence from relevant scholarship. Its shape corresponds to the overview that you provided in your introduction.
The body of your essay should be written in paragraphs. Each body paragraph should develop one main idea that supports your argument. To learn how to structure a paragraph, look at the page developing clarity and focus in academic writing .
Your conclusion should not offer any new material. Your evidence and argumentation should have been made clear to the reader in the body of the essay.
Use the conclusion to briefly restate the main argumentative position and provide a short summary of the themes discussed. In addition, also consider telling your reader:
- What the significance of your findings, or the implications of your conclusion, might be
- Whether there are other factors which need to be looked at, but which were outside the scope of the essay
- How your topic links to the wider context (‘bigger picture’) in your discipline.
Do not simply repeat yourself in this section. A conclusion which merely summarises is repetitive and reduces the impact of your paper.
Example conclusion
Conclusion*.
Although, to a large extent, the working class were mainly those in the forefront of crowd action and they also led the revolts against wealthy plantation farmers, the American Revolution was not a class struggle [This is a statement of the concluding position of the essay]. Working people participated because the issues directly affected them – the threat posed by powerful landowners and the tyranny Britain represented. Whereas the aims and actions of the working classes were more concerned with resistance to British rule during the pre-revolutionary period, they became more revolutionary in nature after 1775 when the tension with Britain escalated [These sentences restate the key argument]. With this shift, a change in ideas occurred. In terms of considering the Revolution as a whole range of activities such as organising riots, communicating to Britain, attendance at town hall meetings and pamphlet writing, a difficulty emerges in that all classes were involved. Therefore, it is impossible to assess the extent to which a single group such as working people contributed to the American Revolution [These sentences give final thoughts on the topic].
5. Write clearly
An essay that makes good, evidence-supported points will only receive a high grade if it is written clearly. Clarity is produced through careful revision and editing, which can turn a good essay into an excellent one.
When you edit your essay, try to view it with fresh eyes – almost as if someone else had written it.
Ask yourself the following questions:
Overall structure
- Have you clearly stated your argument in your introduction?
- Does the actual structure correspond to the ‘road map’ set out in your introduction?
- Have you clearly indicated how your main points support your argument?
- Have you clearly signposted the transitions between each of your main points for your reader?
- Does each paragraph introduce one main idea?
- Does every sentence in the paragraph support that main idea?
- Does each paragraph display relevant evidence and reasoning?
- Does each paragraph logically follow on from the one before it?
- Is each sentence grammatically complete?
- Is the spelling correct?
- Is the link between sentences clear to your readers?
- Have you avoided redundancy and repetition?
See more about editing on our editing your writing page.
6. Cite sources and evidence
Finally, check your citations to make sure that they are accurate and complete. Some faculties require you to use a specific citation style (e.g. APA) while others may allow you to choose a preferred one. Whatever style you use, you must follow its guidelines correctly and consistently. You can use Recite, the University of Melbourne style guide, to check your citations.
Further resources
- Germov, J. (2011). Get great marks for your essays, reports and presentations (3rd ed.). NSW: Allen and Unwin.
- Using English for Academic Purposes: A guide for students in Higher Education [online]. Retrieved January 2020 from http://www.uefap.com
- Williams, J.M. & Colomb, G. G. (2010) Style: Lessons in clarity and grace. 10th ed. New York: Longman.
* Example introduction and conclusion adapted from a student paper.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
Essay Introduction Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Always have a road map for an essay introduction . Having a strong essay introduction structure is critical to a successful paper. It sets the tone for the reader and interests them in your work. It also tells them what the essay is about and why they should read it at all.
It shouldn't leave the reader confused with a cliffhanger at the end. Instead, it should generate interest and guide the reader to Chapter One. Using the right parts of an essay introduction can help with this.
Check out an effective essay introduction structure below. It’s a road map for writing an essay—just like the parts of essay introductions are road maps for readers.
Essay Introduction Structure
Attention-grabbing start
Outline of argument
Thesis statement
Some academics find the beginning the most difficult part of writing an essay , so our editors have created some examples of good essay introductions to guide you. Let's take a look at the samples below to see how the essay introduction structures come together.
If you are unsure about your paper, our essay editors would love to give you some feedback on how to write an essay introduction.
[1] According to Paul Ratsmith, the tenuous but nonetheless important relationship between pumpkins and rats is little understood: "While I've always been fascinated by this natural kinship, the connection between pumpkins and rats has been the subject of few, if any, other studies" (2008). [2] Ratsmith has been studying this connection, something he coined "pumpkinology," since the early 1990s. He is most well known for documenting the three years he spent living in the wild among pumpkins and rats. [3] Though it is a topic of little recent interest, the relationship has been noted in several ancient texts and seems to have been well understood by the Romans. Critics of Ratsmith have cited poor science and questionable methodology when dismissing his results, going so far as to call pumpkinology "rubbish" (de Vil, 2009), "stupid" (Claw, 2010), and "quite possibly made up" (Igthorn, 2009). [4] Despite these criticisms, there does appear to be a strong correlation between pumpkin patches and rat populations, with Ratsmith documenting numerous pumpkin–rat colonies across North America, leading to the conclusion that pumpkins and rats are indeed "nature's best friends" (2008).
Let's break down this example of a good essay introduction structure. The beginning hooks our attention from the get-go in section one. This is because it piques our curiosity. What is this strange relationship? Why has no one studied it? Then, section two gives us context for the topic. Ratsmith is an expert in a controversial field: pumpkinology. It's the study of the connection between pumpkins and rats.
The second half of the paragraph also demonstrates why this is a good essay introduction example. Section three gives us the main argument: the topic is rarely studied because critics think Ratsmith's work is "rubbish," but the relationship between pumpkins and rats has ancient roots. Then section four gives us the thesis statement: Ratsmith's work has some merit.
The parts of an essay introduction help us chart a course through the topic. We know the paper will take us on a journey. It's all because the author practiced how to write an essay introduction.
Let’s take a look at another example of a good essay introduction.
[1] Societies have long believed that if a black cat crosses one's path, one might have bad luck—but it wasn't until King Charles I's black cat died that the ruler's bad luck began (Pemberton, 2018). [2] Indeed, for centuries, black cats have been seen as the familiars of witches—as demonic associates of Satan who disrespect authority (Yuko, 2021). Yet, they have also been associated with good luck, from England's rulers to long-distance sailors (Cole, 2021). [3] This essay shows how outdated the bad luck superstition really is. It provides a comprehensive history of the belief and then provides proof that this superstition has no place in today's modern society. [4] It argues that despite the prevailing belief that animals cause bad luck, black cats often bring what seems to be "good luck" and deserve a new reputation.
This example of a good essay introduction pulls us in right away. This is because section one provides an interesting fact about King Charles I. What is the story there, and what bad luck did he experience after his cat passed away? Then, section two provides us with general information about the current status of black cats. We understand the context of the essay and why the topic is controversial.
Section three then gives us a road map that leads us through the main arguments. Finally, section four gives us the essay's thesis: "black cats often bring what seems to be 'good luck' and deserve a new reputation."
Still feeling unsure about how to write an essay introduction? Here's another example using the essay introduction structure we discussed earlier.
[1] When the Lutz family moved into a new house in Amityville, New York, they found themselves terrorized by a vengeful ghost (Labianca, 2021). Since then, their famous tale has been debunked by scientists and the family themselves (Smith, 2005). [2] Yet ghost stories have gripped human consciousness for centuries (History, 2009). Scientists, researchers, and theorists alike have argued whether ghosts are simply figments of the imagination or real things that go bump in the night. In considering this question, many scientists have stated that ghosts may actually exist. [3] Lindley (2017) believes the answer may be in the quantum world, which "just doesn’t work the way the world around us works," but "we don’t really have the concepts to deal with it." Scientific studies on the existence of ghosts date back hundreds of years (History, 2009), and technology has undergone a vast evolution since then (Lamey, 2018). State-of-the-art tools and concepts can now reveal more about ghosts than we've ever known (Kane, 2015). [4] This essay uses these tools to provide definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm.
This example of a good essay introduction uses a slightly different strategy than the others. To hook the reader, it begins with an interesting anecdote related to the topic. That pulls us in, making us wonder what really happened to the Lutzs. Then, section two provides us with some background information about the topic to help us understand. Many people believe ghosts aren't real, but some scientists think they are.
This immediately flows into section three, which charts a course through the main arguments the essay will make. Finally, it ends with the essay's thesis: there is definitive proof of the existence of ghosts in the quantum realm. It all works because the author used the parts of an essay introduction well.
For attention-grabbing introductions, an understanding of essay introduction structure and how to write an essay introduction is required.
Our essay introduction examples showing the parts of an essay introduction will help you craft the beginning paragraph you need to start your writing journey on the right foot.
If you'd like more personalized attention to your essay, consider sending it for Essay Editing by Scribendi. We can help you ensure that your essay starts off strong.
Image source: Prostock-studio/Elements.envato.com
Let’s Get Your Essay Ready to Wow an Audience
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Essay Introductions
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
Contact The Effective Writing Center
E-mail: writingcenter@umgc.edu
Write an introduction that interests the reader and effectively outlines your arguments.
Every essay or assignment you write must begin with an introduction. It might be helpful to think of the introduction as an inverted pyramid. In such a pyramid, you begin by presenting a broad introduction to the topic and end by making a more focused point about that topic in your thesis statement. The introduction has three essential parts, each of which serves a particular purpose.
The first part is the "attention-grabber." You need to interest your reader in your topic so that they will want to continue reading. You also want to do that in a way that is fresh and original. For example, although it may be tempting to begin your essay with a dictionary definition, this technique is stale because it has been widely overused. Instead, you might try one of the following techniques:
Offer a surprising statistic that conveys something about the problem to be addressed in the paper.
Perhaps you can find an interesting quote that nicely sums up your argument.
Use rhetorical questions that place your readers in a different situation in order to get them thinking about your topic in a new way.
If you have a personal connection to the topic, you might use an anecdote or story to get your readers emotionally involved.
For example, if you were writing a paper about drunk drivers, you might begin with a compelling story about someone whose life was forever altered by a drunk driver: "At eighteen, Michelle had a lifetime of promise in front of her. Attending college on a track scholarship, she was earning good grades and making lots of friends. Then one night her life was forever altered…"
From this attention grabbing opener, you would need to move to the next part of the introduction, in which you offer some relevant background on the specific purpose of the essay. This section helps the reader see why you are focusing on this topic and makes the transition to the main point of your paper. For this reason, this is sometimes called the "transitional" part of the introduction.
In the example above, the anecdote about Michelle might capture the reader's attention, but the essay is not really about Michelle. The attention grabber might get the reader thinking about how drunk driving can destroy people's lives, but it doesn't introduce the topic of the need for stricter drunk driving penalties (or whatever the real focus of the paper might be).
Therefore, you need to bridge the gap between your attention-grabber and your thesis with some transitional discussion. In this part of your introduction, you narrow your focus of the topic and explain why the attention-grabber is relevant to the specific area you will be discussing. You should introduce your specific topic and provide any necessary background information that the reader would need in order to understand the problem that you are presenting in the paper. You can also define any key terms the reader might not know.
Continuing with the example above, we might move from the narrative about Michelle to a short discussion of the scope of the problem of drunk drivers. We might say, for example: "Michelle's story is not isolated. Each year XX (number) of lives are lost due to drunk-driving accidents." You could follow this with a short discussion of how serious the problem is and why the reader should care about this problem. This effectively moves the reader from the story about Michelle to your real topic, which might be the need for stricter penalties for drinking and driving.
Finally, the introduction must conclude with a clear statement of the overall point you want to make in the paper. This is called your "thesis statement." It is the narrowest part of your inverted pyramid, and it states exactly what your essay will be arguing.
In this scenario, your thesis would be the point you are trying to make about drunk driving. You might be arguing for better enforcement of existing laws, enactment of stricter penalties, or funding for education about drinking and driving. Whatever the case, your thesis would clearly state the main point your paper is trying to make. Here's an example: "Drunk driving laws need to include stricter penalties for those convicted of drinking under the influence of alcohol." Your essay would then go on to support this thesis with the reasons why stricter penalties are needed.
In addition to your thesis, your introduction can often include a "road map" that explains how you will defend your thesis. This gives the reader a general sense of how you will organize the different points that follow throughout the essay. Sometimes the "map" is incorporated right into the thesis statement, and sometimes it is a separate sentence. Below is an example of a thesis with a "map."
"Because drunk driving can result in unnecessary and premature deaths, permanent injury for survivors, and billions of dollars spent on medical expenses, drunk drivers should face stricter penalties for driving under the influence." The underlined words here are the "map" that show your reader the main points of support you will present in the essay. They also serve to set up the paper's arrangement because they tell the order in which you will present these topics.
In constructing an introduction, make sure the introduction clearly reflects the goal or purpose of the assignment and that the thesis presents not only the topic to be discussed but also states a clear position about that topic that you will support and develop throughout the paper. In shorter papers, the introduction is usually only one or two paragraphs, but it can be several paragraphs in a longer paper.
For Longer Papers
Although for short essays the introduction is usually just one paragraph, longer argument or research papers may require a more substantial introduction. The first paragraph might consist of just the attention grabber and some narrative about the problem. Then you might have one or more paragraphs that provide background on the main topics of the paper and present the overall argument, concluding with your thesis statement.
Below is a sample of an introduction that is less effective because it doesn't apply the principles discussed above.
An Ineffective Introduction
Everyone uses math during their entire lives. Some people use math on the job as adults, and others used math when they were kids. The topic I have chosen to write about for this paper is how I use math in my life both as a child and as an adult. I use math to balance my checkbook and to budget my monthly expenses as an adult. When I was a child, I used math to run a lemonade stand. I will be talking more about these things in my paper.
In the introduction above, the opening line does not serve to grab the reader's attention. Instead, it is a statement of an obvious and mundane fact. The second sentence is also not very specific. A more effective attention grabber may point out a specific, and perhaps surprising, instance when adults use math in their daily lives, in order to show the reader why this is such as important topic to consider.
Next the writer "announces" her topic by stating, "The topic I have chosen to write about…" Although it is necessary to introduce your specific topic, you want to avoid making generic announcements that reference your assignment. What you have chosen to write about will be evident as your reader moves through the writing. Instead, you might try to make the reader see why this is such an important topic to discuss.
Finally, this sample introduction is lacking a clear thesis statement. The writer concludes with a vague statement: "I will be talking more about these things in my paper." This kind of statement may be referred to as a "purpose statement," in which the writer states the topics that will be discussed. However, it is not yet working as a thesis statement because it fails to make an argument or claim about those topics. A thesis statement for this essay would clearly tell the reader what "things" you will be discussing and what point you will make about them.
Now let's look at how the above principles can be incorporated more effectively into an introduction.
A More Effective Introduction
"A penny saved is a penny earned," the well-known quote by Ben Franklin, is an expression I have never quite understood, because to me it seems that any penny—whether saved or spent—is still earned no matter what is done with it. My earliest memories of earning and spending money are when I was ten years old when I would sell Dixie cups of too-sweet lemonade and bags of salty popcorn to the neighborhood kids. From that early age, I learned the importance of money management and the math skills involved. I learned that there were four quarters in a dollar, and if I bought a non-food item—like a handful of balloons—that I was going to need to come up with six cents for every dollar I spent. I also knew that Kool-Aid packets were 25 cents each or that I could save money and get five of them for a dollar. Today, however, money management involves knowing more than which combinations of 10-cent, five-cent, and one-penny candies I can get for a dollar. Proper money management today involves knowing interest rates, balancing checkbooks, paying taxes, estimating my paycheck, and budgeting to make ends meet from month-to-month.
In the first line the writer uses a well-known quotation to introduce her topic.
The writer follows this "attention-grabber" with specific examples of earning and spending money. Compare how the specific details of the second example paint a better picture for the reader about what the writer learned about money as a child, rather than this general statement: "As a child, I used math to run a lemonade stand." In the first introduction, this statement leaves the reader to guess how the writer used math, but in the second introduction we can actually see what the child did and what she learned.
Notice, too, how the reader makes the transition from the lessons of childhood to the real focus of her paper in this sentence: "Today, however, money management involves knowing…."
This transition sentence effectively connects the opening narrative to the main point of the essay, her thesis: "Proper money management today involves knowing interest rates, balancing checkbooks, paying taxes, estimating my paycheck, and budgeting to make ends meet from month-to-month ." This thesis also maps out for the reader the main points (underlined here) that will be discussed in the essay.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
| Part | Content |
|---|---|
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
An introduction generally does three things. The first part is usually a general comment that shows the reader why the topic is important, gets their interest, and leads them into the topic. It isn't actually part of your argument. The next part of the introduction is the thesis statement. This is your response to the question; your final answer.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Essay writing: Introductions. "A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.". Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide. Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: Orienting Information. When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis.
It does not mean starting from scratch for each draft. Your work must be correctly referenced and written in formal English. Here are the steps to writing an academic essay: Usually, the purpose of an essay is to answer a specific question within a given word limit. An essay may be as short as 500 words or as long as 2000-3000 words.
The writer of the academic essay aims to persuade readers of an idea based on evidence. The beginning of the essay is a crucial first step in this process. In order to engage readers and establish your authority, the beginning of your essay has to accomplish certain business. Your beginning should introduce the essay, focus it, and orient ...
Unoriginal essay introductions are easily forgotten and don't demonstrate a high level of creative thinking. A college essay is intended to give insight into the personality and background of an applicant, so a standard, one-size-fits-all introduction may lead admissions officers to think they are dealing with a standard, unremarkable applicant.
Your introduction should tell the reader what to expect from your assignment. It should present the main subject of the work so that your reader is clear what the writing will be about. You should also explain why your topic is important and worthy of discussion. You may wish to highlight relevant publications to show how your argument fits ...
The way in which you do this will depend on the type of essay you are writing and what you have been asked to do. You may be required to give a point of view and often the stance ( point of view) of the essay is shown in the introduction. You may, for example, provide your argument and then reasons for it in a statement in your introduction.
The process involves. 1. Preparing a schedule. Use a yearly or monthly time planner to draw up a schedule that allows time to consider the question, research, write and proof-read your answer. Inevitably, the research and writing stages will account for up to 80% of the schedule, but you must allocate enough time to proof-read your work ...
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
Section Explanation of section contents; 1. Introduction: Background statement — where you set the context for your essay Issue(s) — where you outline the specific issues that are relevant to your essay. Thesis — where you state your position in relation to the issues. Scope — where you outline what exactly is going to be covered in relation to your argument.
Introduction. An essay introduction usually: clearly states the topic that will be the focus of the essay;; offers a preview of main aspects that will addressed, or the particular angle that will be taken in; and; clearly articulates the position that will be argued. This is known as the thesis statement.; Consider this introduction:
Intriguing ways to start an essay. There are many different ways to write an essay introduction. Each has its benefits and potential drawbacks, and each is best suited for certain kinds of essays.Although these essay introductions use different rhetorical devices and prime the reader in different ways, they all achieve the same goal: hooking the reader and enticing them to keep reading.
Whilst an introduction and conclusion cover similar areas, they are not the same. They both serve different purposes; therefore, they require their own attention. 10% of your word count. Unless you have been given a specific word count for your introduction or conclusion, each section should only be 10% of your word count (20% in total). The ...
2. Define your argument. As you plan and prepare to write the essay, you must consider what your argument is going to be. This means taking an informed position or point of view on the topic presented in the question, then defining and presenting a specific argument. Consider these two argument statements:
The introduction to an academic essay will generally present an analytical question or problem and then offer an answer to that question (the thesis). Your introduction is also your opportunity to explain to your readers what your essay is about and why they should be interested in reading it. You don't have to "hook" your
Example 3. [1] When the Lutz family moved into a new house in Amityville, New York, they found themselves terrorized by a vengeful ghost (Labianca, 2021). Since then, their famous tale has been debunked by scientists and the family themselves (Smith, 2005). [2]
Every essay or assignment you write must begin with an introduction. It might be helpful to think of the introduction as an inverted pyramid. In such a pyramid, you begin by presenting a broad introduction to the topic and end by making a more focused point about that topic in your thesis statement. The introduction has three essential parts ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
A good essay introduction catches the reader's attention immediately, sets up your argument, and tells the reader what to expect. This video will walk you th...