
10 Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A case study in academic research is a detailed and in-depth examination of a specific instance or event, generally conducted through a qualitative approach to data.
The most common case study definition that I come across is is Robert K. Yin’s (2003, p. 13) quote provided below:
“An empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident.”
Researchers conduct case studies for a number of reasons, such as to explore complex phenomena within their real-life context, to look at a particularly interesting instance of a situation, or to dig deeper into something of interest identified in a wider-scale project.
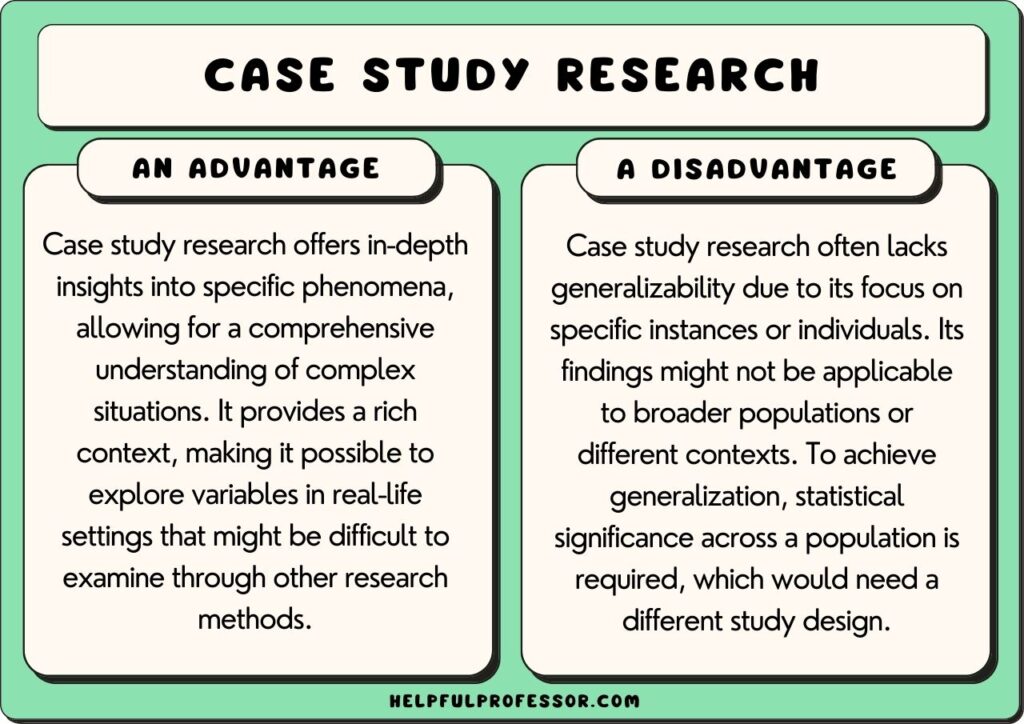
While case studies render extremely interesting data, they have many limitations and are not suitable for all studies. One key limitation is that a case study’s findings are not usually generalizable to broader populations because one instance cannot be used to infer trends across populations.
Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages
1. in-depth analysis of complex phenomena.
Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations.
By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue,
“It allows that particular event to be studies in detail so that its unique qualities may be identified.”
This depth of analysis can provide rich insights into the underlying factors and dynamics of the studied phenomenon.
2. Holistic Understanding
Building on the above point, case studies can help us to understand a topic holistically and from multiple angles.
This means the researcher isn’t restricted to just examining a topic by using a pre-determined set of questions, as with questionnaires. Instead, researchers can use qualitative methods to delve into the many different angles, perspectives, and contextual factors related to the case study.
We can turn to Lee and Saunders (2017) again, who notes that case study researchers “develop a deep, holistic understanding of a particular phenomenon” with the intent of deeply understanding the phenomenon.
3. Examination of rare and Unusual Phenomena
We need to use case study methods when we stumble upon “rare and unusual” (Lee & Saunders, 2017) phenomena that would tend to be seen as mere outliers in population studies.
Take, for example, a child genius. A population study of all children of that child’s age would merely see this child as an outlier in the dataset, and this child may even be removed in order to predict overall trends.
So, to truly come to an understanding of this child and get insights into the environmental conditions that led to this child’s remarkable cognitive development, we need to do an in-depth study of this child specifically – so, we’d use a case study.
4. Helps Reveal the Experiences of Marginalzied Groups
Just as rare and unsual cases can be overlooked in population studies, so too can the experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of marginalized groups.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue, “case studies are also extremely useful in helping the expression of the voices of people whose interests are often ignored.”
Take, for example, the experiences of minority populations as they navigate healthcare systems. This was for many years a “hidden” phenomenon, not examined by researchers. It took case study designs to truly reveal this phenomenon, which helped to raise practitioners’ awareness of the importance of cultural sensitivity in medicine.
5. Ideal in Situations where Researchers cannot Control the Variables
Experimental designs – where a study takes place in a lab or controlled environment – are excellent for determining cause and effect . But not all studies can take place in controlled environments (Tetnowski, 2015).
When we’re out in the field doing observational studies or similar fieldwork, we don’t have the freedom to isolate dependent and independent variables. We need to use alternate methods.
Case studies are ideal in such situations.
A case study design will allow researchers to deeply immerse themselves in a setting (potentially combining it with methods such as ethnography or researcher observation) in order to see how phenomena take place in real-life settings.
6. Supports the generation of new theories or hypotheses
While large-scale quantitative studies such as cross-sectional designs and population surveys are excellent at testing theories and hypotheses on a large scale, they need a hypothesis to start off with!
This is where case studies – in the form of grounded research – come in. Often, a case study doesn’t start with a hypothesis. Instead, it ends with a hypothesis based upon the findings within a singular setting.
The deep analysis allows for hypotheses to emerge, which can then be taken to larger-scale studies in order to conduct further, more generalizable, testing of the hypothesis or theory.
7. Reveals the Unexpected
When a largescale quantitative research project has a clear hypothesis that it will test, it often becomes very rigid and has tunnel-vision on just exploring the hypothesis.
Of course, a structured scientific examination of the effects of specific interventions targeted at specific variables is extermely valuable.
But narrowly-focused studies often fail to shine a spotlight on unexpected and emergent data. Here, case studies come in very useful. Oftentimes, researchers set their eyes on a phenomenon and, when examining it closely with case studies, identify data and come to conclusions that are unprecedented, unforeseen, and outright surprising.
As Lars Meier (2009, p. 975) marvels, “where else can we become a part of foreign social worlds and have the chance to become aware of the unexpected?”
Disadvantages
1. not usually generalizable.
Case studies are not generalizable because they tend not to look at a broad enough corpus of data to be able to infer that there is a trend across a population.
As Yang (2022) argues, “by definition, case studies can make no claims to be typical.”
Case studies focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. They explore the context, nuances, and situational factors that have come to bear on the case study. This is really useful for bringing to light important, new, and surprising information, as I’ve already covered.
But , it’s not often useful for generating data that has validity beyond the specific case study being examined.
2. Subjectivity in interpretation
Case studies usually (but not always) use qualitative data which helps to get deep into a topic and explain it in human terms, finding insights unattainable by quantitative data.
But qualitative data in case studies relies heavily on researcher interpretation. While researchers can be trained and work hard to focus on minimizing subjectivity (through methods like triangulation), it often emerges – some might argue it’s innevitable in qualitative studies.
So, a criticism of case studies could be that they’re more prone to subjectivity – and researchers need to take strides to address this in their studies.
3. Difficulty in replicating results
Case study research is often non-replicable because the study takes place in complex real-world settings where variables are not controlled.
So, when returning to a setting to re-do or attempt to replicate a study, we often find that the variables have changed to such an extent that replication is difficult. Furthermore, new researchers (with new subjective eyes) may catch things that the other readers overlooked.
Replication is even harder when researchers attempt to replicate a case study design in a new setting or with different participants.
Comprehension Quiz for Students
Question 1: What benefit do case studies offer when exploring the experiences of marginalized groups?
a) They provide generalizable data. b) They help express the voices of often-ignored individuals. c) They control all variables for the study. d) They always start with a clear hypothesis.
Question 2: Why might case studies be considered ideal for situations where researchers cannot control all variables?
a) They provide a structured scientific examination. b) They allow for generalizability across populations. c) They focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. d) They allow for deep immersion in real-life settings.
Question 3: What is a primary disadvantage of case studies in terms of data applicability?
a) They always focus on the unexpected. b) They are not usually generalizable. c) They support the generation of new theories. d) They provide a holistic understanding.
Question 4: Why might case studies be considered more prone to subjectivity?
a) They always use quantitative data. b) They heavily rely on researcher interpretation, especially with qualitative data. c) They are always replicable. d) They look at a broad corpus of data.
Question 5: In what situations are experimental designs, such as those conducted in labs, most valuable?
a) When there’s a need to study rare and unusual phenomena. b) When a holistic understanding is required. c) When determining cause-and-effect relationships. d) When the study focuses on marginalized groups.
Question 6: Why is replication challenging in case study research?
a) Because they always use qualitative data. b) Because they tend to focus on a broad corpus of data. c) Due to the changing variables in complex real-world settings. d) Because they always start with a hypothesis.
Lee, B., & Saunders, M. N. K. (2017). Conducting Case Study Research for Business and Management Students. SAGE Publications.
Meir, L. (2009). Feasting on the Benefits of Case Study Research. In Mills, A. J., Wiebe, E., & Durepos, G. (Eds.). Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (Vol. 2). London: SAGE Publications.
Tetnowski, J. (2015). Qualitative case study research design. Perspectives on fluency and fluency disorders , 25 (1), 39-45. ( Source )
Yang, S. L. (2022). The War on Corruption in China: Local Reform and Innovation . Taylor & Francis.
Yin, R. (2003). Case Study research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Number Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Word Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Outdoor Games for Kids
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 50 Incentives to Give to Students
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span eight subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Digital transformation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author

Case Study Method – 18 Advantages and Disadvantages
The case study method uses investigatory research as a way to collect data about specific demographics. This approach can apply to individuals, businesses, groups, or events. Each participant receives an equal amount of participation, offering information for collection that can then find new insights into specific trends, ideas, of hypotheses.
Interviews and research observation are the two standard methods of data collection used when following the case study method.
Researchers initially developed the case study method to develop and support hypotheses in clinical medicine. The benefits found in these efforts led the approach to transition to other industries, allowing for the examination of results through proposed decisions, processes, or outcomes. Its unique approach to information makes it possible for others to glean specific points of wisdom that encourage growth.
Several case study method advantages and disadvantages can appear when researchers take this approach.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. It requires an intensive study of a specific unit. Researchers must document verifiable data from direct observations when using the case study method. This work offers information about the input processes that go into the hypothesis under consideration. A casual approach to data-gathering work is not effective if a definitive outcome is desired. Each behavior, choice, or comment is a critical component that can verify or dispute the ideas being considered.
Intensive programs can require a significant amount of work for researchers, but it can also promote an improvement in the data collected. That means a hypothesis can receive immediate verification in some situations.
2. No sampling is required when following the case study method. This research method studies social units in their entire perspective instead of pulling individual data points out to analyze them. That means there is no sampling work required when using the case study method. The hypothesis under consideration receives support because it works to turn opinions into facts, verifying or denying the proposals that outside observers can use in the future.
Although researchers might pay attention to specific incidents or outcomes based on generalized behaviors or ideas, the study itself won’t sample those situations. It takes a look at the “bigger vision” instead.
3. This method offers a continuous analysis of the facts. The case study method will look at the facts continuously for the social group being studied by researchers. That means there aren’t interruptions in the process that could limit the validity of the data being collected through this work. This advantage reduces the need to use assumptions when drawing conclusions from the information, adding validity to the outcome of the study over time. That means the outcome becomes relevant to both sides of the equation as it can prove specific suppositions or invalidate a hypothesis under consideration.
This advantage can lead to inefficiencies because of the amount of data being studied by researchers. It is up to the individuals involved in the process to sort out what is useful and meaningful and what is not.
4. It is a useful approach to take when formulating a hypothesis. Researchers will use the case study method advantages to verify a hypothesis under consideration. It is not unusual for the collected data to lead people toward the formulation of new ideas after completing this work. This process encourages further study because it allows concepts to evolve as people do in social or physical environments. That means a complete data set can be gathered based on the skills of the researcher and the honesty of the individuals involved in the study itself.
Although this approach won’t develop a societal-level evaluation of a hypothesis, it can look at how specific groups will react in various circumstances. That information can lead to a better decision-making process in the future for everyone involved.
5. It provides an increase in knowledge. The case study method provides everyone with analytical power to increase knowledge. This advantage is possible because it uses a variety of methodologies to collect information while evaluating a hypothesis. Researchers prefer to use direct observation and interviews to complete their work, but it can also advantage through the use of questionnaires. Participants might need to fill out a journal or diary about their experiences that can be used to study behaviors or choices.
Some researchers incorporate memory tests and experimental tasks to determine how social groups will interact or respond in specific situations. All of this data then works to verify the possibilities that a hypothesis proposes.
6. The case study method allows for comparisons. The human experience is one that is built on individual observations from group situations. Specific demographics might think, act, or respond in particular ways to stimuli, but each person in that group will also contribute a small part to the whole. You could say that people are sponges that collect data from one another every day to create individual outcomes.
The case study method allows researchers to take the information from each demographic for comparison purposes. This information can then lead to proposals that support a hypothesis or lead to its disruption.
7. Data generalization is possible using the case study method. The case study method provides a foundation for data generalization, allowing researches to illustrate their statistical findings in meaningful ways. It puts the information into a usable format that almost anyone can use if they have the need to evaluate the hypothesis under consideration. This process makes it easier to discover unusual features, unique outcomes, or find conclusions that wouldn’t be available without this method. It does an excellent job of identifying specific concepts that relate to the proposed ideas that researchers were verifying through their work.
Generalization does not apply to a larger population group with the case study method. What researchers can do with this information is to suggest a predictable outcome when similar groups are placed in an equal situation.
8. It offers a comprehensive approach to research. Nothing gets ignored when using the case study method to collect information. Every person, place, or thing involved in the research receives the complete attention of those seeking data. The interactions are equal, which means the data is comprehensive and directly reflective of the group being observed.
This advantage means that there are fewer outliers to worry about when researching an idea, leading to a higher level of accuracy in the conclusions drawn by the researchers.
9. The identification of deviant cases is possible with this method. The case study method of research makes it easier to identify deviant cases that occur in each social group. These incidents are units (people) that behave in ways that go against the hypothesis under consideration. Instead of ignoring them like other options do when collecting data, this approach incorporates the “rogue” behavior to understand why it exists in the first place.
This advantage makes the eventual data and conclusions gathered more reliable because it incorporates the “alternative opinion” that exists. One might say that the case study method places as much emphasis on the yin as it does the yang so that the whole picture becomes available to the outside observer.
10. Questionnaire development is possible with the case study method. Interviews and direct observation are the preferred methods of implementing the case study method because it is cheap and done remotely. The information gathered by researchers can also lead to farming questionnaires that can farm additional data from those being studied. When all of the data resources come together, it is easier to formulate a conclusion that accurately reflects the demographics.
Some people in the case study method may try to manipulate the results for personal reasons, but this advantage makes it possible to identify this information readily. Then researchers can look into the thinking that goes into the dishonest behaviors observed.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. The case study method offers limited representation. The usefulness of the case study method is limited to a specific group of representatives. Researchers are looking at a specific demographic when using this option. That means it is impossible to create any generalization that applies to the rest of society, an organization, or a larger community with this work. The findings can only apply to other groups caught in similar circumstances with the same experiences.
It is useful to use the case study method when attempting to discover the specific reasons why some people behave in a specific way. If researchers need something more generalized, then a different method must be used.
2. No classification is possible with the case study method. This disadvantage is also due to the sample size in the case study method. No classification is possible because researchers are studying such a small unit, group, or demographic. It can be an inefficient process since the skills of the researcher help to determine the quality of the data being collected to verify the validity of a hypothesis. Some participants may be unwilling to answer or participate, while others might try to guess at the outcome to support it.
Researchers can get trapped in a place where they explore more tangents than the actual hypothesis with this option. Classification can occur within the units being studied, but this data cannot extrapolate to other demographics.
3. The case study method still offers the possibility of errors. Each person has an unconscious bias that influences their behaviors and choices. The case study method can find outliers that oppose a hypothesis fairly easily thanks to its emphasis on finding facts, but it is up to the researchers to determine what information qualifies for this designation. If the results from the case study method are surprising or go against the opinion of participating individuals, then there is still the possibility that the information will not be 100% accurate.
Researchers must have controls in place that dictate how data gathering work occurs. Without this limitation in place, the results of the study cannot be guaranteed because of the presence of bias.
4. It is a subjective method to use for research. Although the purpose of the case study method of research is to gather facts, the foundation of what gets gathered is still based on opinion. It uses the subjective method instead of the objective one when evaluating data, which means there can be another layer of errors in the information to consider.
Imagine that a researcher interprets someone’s response as “angry” when performing direct observation, but the individual was feeling “shame” because of a decision they made. The difference between those two emotions is profound, and it could lead to information disruptions that could be problematic to the eventual work of hypothesis verification.
5. The processes required by the case study method are not useful for everyone. The case study method uses a person’s memories, explanations, and records from photographs and diaries to identify interactions on influences on psychological processes. People are given the chance to describe what happens in the world around them as a way for researchers to gather data. This process can be an advantage in some industries, but it can also be a worthless approach to some groups.
If the social group under study doesn’t have the information, knowledge, or wisdom to provide meaningful data, then the processes are no longer useful. Researchers must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the case study method before starting their work to determine if the possibility of value exists. If it does not, then a different method may be necessary.
6. It is possible for bias to form in the data. It’s not just an unconscious bias that can form in the data when using the case study method. The narrow study approach can lead to outright discrimination in the data. Researchers can decide to ignore outliers or any other information that doesn’t support their hypothesis when using this method. The subjective nature of this approach makes it difficult to challenge the conclusions that get drawn from this work, and the limited pool of units (people) means that duplication is almost impossible.
That means unethical people can manipulate the results gathered by the case study method to their own advantage without much accountability in the process.
7. This method has no fixed limits to it. This method of research is highly dependent on situational circumstances rather than overarching societal or corporate truths. That means the researcher has no fixed limits of investigation. Even when controls are in place to limit bias or recommend specific activities, the case study method has enough flexibility built into its structures to allow for additional exploration. That means it is possible for this work to continue indefinitely, gathering data that never becomes useful.
Scientists began to track the health of 268 sophomores at Harvard in 1938. The Great Depression was in its final years at that point, so the study hoped to reveal clues that lead to happy and healthy lives. It continues still today, now incorporating the children of the original participants, providing over 80 years of information to sort through for conclusions.
8. The case study method is time-consuming and expensive. The case study method can be affordable in some situations, but the lack of fixed limits and the ability to pursue tangents can make it a costly process in most situations. It takes time to gather the data in the first place, and then researchers must interpret the information received so that they can use it for hypothesis evaluation. There are other methods of data collection that can be less expensive and provide results faster.
That doesn’t mean the case study method is useless. The individualization of results can help the decision-making process advance in a variety of industries successfully. It just takes more time to reach the appropriate conclusion, and that might be a resource that isn’t available.
The advantages and disadvantages of the case study method suggest that the helpfulness of this research option depends on the specific hypothesis under consideration. When researchers have the correct skills and mindset to gather data accurately, then it can lead to supportive data that can verify ideas with tremendous accuracy.
This research method can also be used unethically to produce specific results that can be difficult to challenge.
When bias enters into the structure of the case study method, the processes become inefficient, inaccurate, and harmful to the hypothesis. That’s why great care must be taken when designing a study with this approach. It might be a labor-intensive way to develop conclusions, but the outcomes are often worth the investments needed.
- Communication
- Recreational

Pros and Cons of case studies
- Post author: admin
- Post published: March 27, 2020
- Post category: Education
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case studies are research methodologies that are used and analyzed in order to depict principles; they have been usually used in social sciences. They are research strategies and experiential inquiries that seek to examine various phenomena within a real-life context. Case studies seek to explain and give details in the analysis of people and events. There are several pros that back case studies and there are cons too that criticize them. The pros and cons are listed below.
1 . They show client observations- Since case studies are strategies that are used and analyzed in order to describe principles therefore it seeks to show indeed the client investigated and experienced a particular phenomenon.
2 . Makes practical improvements- Case studies present facts that categorically describe particular people or events in order to make some of the necessary improvements. Case studies data is what supports a particular belief.
3 . They are an influential way of portraying something- If a researcher wants to prove a particular principle to be true, he or she must back it by case studies in order to make the other people and the naysayers believe.
4 . They turn opinions into facts- Case studies present real data on a particular phenomenon. Since facts about various things are presented then it can be verified through this kind of data if the information presented is in the positive or negative development of opinion.
5 . It is relevant to all the parties that are involved- Case studies help the researchers in actively focusing on the data collection process and the participants’ knowledge is bettered. At the end of the process, everybody is able to defend his position through facts.
6 . A number of different research methodologies can be used in case the studies- Case study method goes beyond the interview and direct observations. Secondary data can be obtained from various historical sources that can be used to back the method.
7 . Case studies can be done remotely- It is not essential for a researcher to be present in the specific location of the study in order to effectively use the case study method. Other forms of communication come in to cover that gap for the researcher.
8 . It has a very high cost- If you put this research method in comparison to the others, this one seems more expensive because the cost of accessing data is very high.
9 . Readers can access data from this method very easily- The The format in which case studies present their data is very useful to the readers and easily note the outcomes of the same.
10 . Collects data that cannot be collected by another method- The type of data collected by case studies is much richer and greater in-depth than that of the other experimental methods.
1 . Data collected cannot be generalized- The data collected by the case study method was collected from a smaller population it cannot be generalized to the wider population.
2 . Some of the case studies are not scientific- The weakness of the data collected in some of the case studies that are not scientific is that it cannot be generalized.
3 . It is very difficult to draw a definite cause/effect from case studies- The the kind of data that case studies present cannot be used to draw a definite cause-effect relationship.
4 . Case studies concentrate on one experiment- The problem associated with concentrating on one experiment or a specific group of people is that the data presented might contain some kind of bias.
5 . It takes a lot of time to analyze the data- This process takes longer to analyze the data because there is a very large amount of data that must be collected. Participants might take a lot of time in giving answers or giving inaccurate information.
6 . Case studies can be inefficient processes- Sometimes the researchers are not present in the study areas which means they will not be able to notice whether the information provided is accurate or not terming the whole process inefficient.
7 . Case study method can only be effective with a small sample size- If a very large sample size is involved in the case study it is likely for it to become inefficient because the method requires a small sample size to get the data and analyze it.
8 . The method requires a lot of labor in data collection- The researcher is seriously needed in the data collection of this method. They have to be personally involved in order to be able to identify the quality of the data provided.
9 . There are factors that can influence the data- The method of data collection is meant to collect fact-based data but the power to determine what fact is and what is not is the person who is collecting the data.
10 . There is no right answer in case studies- Case studies do not present any specific answer that is right, the problem arises in the validation of solutions because there is more than one way of looking at things.
You Might Also Like

Pros and Cons of 360 Degree Feedback

Pros and Cons of Written Storytelling

Pros and Cons of Traditional Education System
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Home » Pros and Cons » 12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
A case study is an investigation into an individual circumstance. The investigation may be of a single person, business, event, or group. The investigation involves collecting in-depth data about the individual entity through the use of several collection methods. Interviews and observation are two of the most common forms of data collection used.
The case study method was originally developed in the field of clinical medicine. It has expanded since to other industries to examine key results, either positive or negative, that were received through a specific set of decisions. This allows for the topic to be researched with great detail, allowing others to glean knowledge from the information presented.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using the case study method.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. it turns client observations into useable data..
Case studies offer verifiable data from direct observations of the individual entity involved. These observations provide information about input processes. It can show the path taken which led to specific results being generated. Those observations make it possible for others, in similar circumstances, to potentially replicate the results discovered by the case study method.
2. It turns opinion into fact.
Case studies provide facts to study because you’re looking at data which was generated in real-time. It is a way for researchers to turn their opinions into information that can be verified as fact because there is a proven path of positive or negative development. Singling out a specific incident also provides in-depth details about the path of development, which gives it extra credibility to the outside observer.
3. It is relevant to all parties involved.
Case studies that are chosen well will be relevant to everyone who is participating in the process. Because there is such a high level of relevance involved, researchers are able to stay actively engaged in the data collection process. Participants are able to further their knowledge growth because there is interest in the outcome of the case study. Most importantly, the case study method essentially forces people to make a decision about the question being studied, then defend their position through the use of facts.
4. It uses a number of different research methodologies.
The case study method involves more than just interviews and direct observation. Case histories from a records database can be used with this method. Questionnaires can be distributed to participants in the entity being studies. Individuals who have kept diaries and journals about the entity being studied can be included. Even certain experimental tasks, such as a memory test, can be part of this research process.
5. It can be done remotely.
Researchers do not need to be present at a specific location or facility to utilize the case study method. Research can be obtained over the phone, through email, and other forms of remote communication. Even interviews can be conducted over the phone. That means this method is good for formative research that is exploratory in nature, even if it must be completed from a remote location.
6. It is inexpensive.
Compared to other methods of research, the case study method is rather inexpensive. The costs associated with this method involve accessing data, which can often be done for free. Even when there are in-person interviews or other on-site duties involved, the costs of reviewing the data are minimal.
7. It is very accessible to readers.
The case study method puts data into a usable format for those who read the data and note its outcome. Although there may be perspectives of the researcher included in the outcome, the goal of this method is to help the reader be able to identify specific concepts to which they also relate. That allows them to discover unusual features within the data, examine outliers that may be present, or draw conclusions from their own experiences.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. it can have influence factors within the data..
Every person has their own unconscious bias. Although the case study method is designed to limit the influence of this bias by collecting fact-based data, it is the collector of the data who gets to define what is a “fact” and what is not. That means the real-time data being collected may be based on the results the researcher wants to see from the entity instead. By controlling how facts are collected, a research can control the results this method generates.
2. It takes longer to analyze the data.
The information collection process through the case study method takes much longer to collect than other research options. That is because there is an enormous amount of data which must be sifted through. It’s not just the researchers who can influence the outcome in this type of research method. Participants can also influence outcomes by given inaccurate or incomplete answers to questions they are asked. Researchers must verify the information presented to ensure its accuracy, and that takes time to complete.
3. It can be an inefficient process.
Case study methods require the participation of the individuals or entities involved for it to be a successful process. That means the skills of the researcher will help to determine the quality of information that is being received. Some participants may be quiet, unwilling to answer even basic questions about what is being studied. Others may be overly talkative, exploring tangents which have nothing to do with the case study at all. If researchers are unsure of how to manage this process, then incomplete data is often collected.
4. It requires a small sample size to be effective.
The case study method requires a small sample size for it to yield an effective amount of data to be analyzed. If there are different demographics involved with the entity, or there are different needs which must be examined, then the case study method becomes very inefficient.
5. It is a labor-intensive method of data collection.
The case study method requires researchers to have a high level of language skills to be successful with data collection. Researchers must be personally involved in every aspect of collecting the data as well. From reviewing files or entries personally to conducting personal interviews, the concepts and themes of this process are heavily reliant on the amount of work each researcher is willing to put into things.
These case study method advantages and disadvantages offer a look at the effectiveness of this research option. With the right skill set, it can be used as an effective tool to gather rich, detailed information about specific entities. Without the right skill set, the case study method becomes inefficient and inaccurate.
Related Posts:
- 25 Best Ways to Overcome the Fear of Failure
- Monroe's Motivated Sequence Explained [with Examples]
- 21 Most Effective Bundle Pricing Strategies with Examples
- Force Field Analysis Explained with Examples
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. and Distinguished Service University Professor. He served as the 10th dean of Harvard Business School, from 2010 to 2020.
Partner Center
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved July 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study

- About This Site
- What is social theory?
- Habermas/Parsons
- Frankfurt School
- Inequalities
- Research Students
- Dirty Looks
- Latest Posts
- Pedagogy & Curriculum
- Contributors
- Publications
Select Page
What are the benefits and drawbacks of case study research?
Posted by Mark Murphy | May 24, 2014 | Method , Research Students | 0

There should be no doubt that with case studies what you gain in depth you lose in breadth – this is the unavoidable compromise that needs to be understood from the beginning of the research process. So this is neither an advantage nor a disadvantage as one aspect cancels out the benefits/drawbacks of the other – there are other benefits and drawbacks that need attention however …
- Their flexibility: case studies are popular for a number of reasons, one being that they can be conducted at various points in the research process. Researchers are known to favour them as a way to develop ideas for more extensive research in the future – pilot studies often take the form of case studies. They are also effective conduits for a broad range of research methods; in that sense they are non-prejudicial against any particular type of research – focus groups are just as welcome in case study research as are questionnaires or participant observation.
- Capturing reality: One of their key benefits is their ability to capture what Hodkinson and Hodkinson call ‘lived reality’ (2001: 3). As they put it, case studies have the potential, when applied successfully, to ‘retain more of the “noise” of real life than many other types of research’ (Hodkinson and Hodkinson, 2001: 3). The importance of ‘noise’ and its place in research is especially important in contexts such as education, for example in schools where background noise is unavoidable. Educational contexts are always complex, and as a result it is difficult to exclude other unwanted variables, ‘some of which may only have real significance for one of their students’ (Hodkinson and Hodkinson, 2001, 4).
- The challenge of generality: At the same time, given their specificity, care needs to be taken when attempting to generalise from the findings. While there’s no inherent flaw in case study design that precludes its broader application, it is preferable that researchers choose their case study sites carefully, while also basing their analysis within existing research findings that have been generated via other research designs. No design is infallible but so often has the claim against case studies been made, that some of the criticism (unwarranted and unfair in many cases) has stuck.
- Suspicion of amateurism: Less partisan researchers might wonder whether the case study offers the time and finance-strapped researcher a convenient and pragmatic source of data, providing findings and recommendations that, given the nature of case studies, can neither be confirmed nor denied, in terms of utility or veracity. Who is to say that case studies offer anything more than a story to tell, and nothing more than that?
- But alongside this suspicion is another more insiduous one – a notion that ‘stories’ are not what social science research is about. This can be a concern for those who favour case study research, as the political consequences can be hard to ignore. That said, so much research is based either on peoples’ lives or the impact of other issues (poverty, institutional policy) on their lives, so the stories of what actually occurs in their lives or in professional environments tend to be an invaluable source of evidence. The fact is that stories (individual, collective, institutional) have a vital role to play in the world of research. And to play the specific v. general card against case study design suggests a tendency towards forms of research fundamentalism as opposed to any kind of rational and objective take on case study’s strengths and limitations.
- Preciousness: Having said that, researchers should not fall into the trap (surprising how often this happens) of assuming that case study data speaks for itself – rarely is this ever the case, an assumption that is as patronising to research subjects as it is false. The role of the researcher is both to describe social phenomena and also to explain – i.e., interpret. Without interpretation the research findings lack meaningful presentation – they present themselves as fact when of course the reality of ‘facts’ is one of the reasons why such research is carried out.
- Conflation of political/research objectives: Another trap that case study researchers sometimes fall into is presenting research findings as if they were self-evidently true, as if the stories were beyond criticism. This is often accompanied by a vague attachment to the notion that research is a political process – one that is performed as a form of liberation against for example policies that seek to ignore the stories of those who ‘suffer’ at the hands of overbearing political or economic imperatives. Case study design should not be viewed as a mechanism for providing a ‘local’ bulwark against the ‘global’ – bur rather as a mechanism for checking the veracity of universalist claims (at least one of its objectives). The valorisation of particularism can only get you so far in social research.
[This post is adapted from material in ‘Research and Education’ (Curtis, Murphy and Shields , Routledge 2014), pp. 80-82].
Reference: Hodkinson, P. and H. Hodkinson (2001). The strengths and limitations of case study research. Paper presented to the Learning and Skills Development Agency conference, Making an impact on policy and practice , Cambridge, 5-7 December 2001, downloaded from h ttp://education.exeter.ac.uk/tlc/docs/publications/LE_PH_PUB_05.12.01.rtf.26.01.2013
About The Author
Mark Murphy
Mark Murphy is a Reader in Education and Public Policy at the University of Glasgow. He previously worked as an academic at King’s College, London, University of Chester, University of Stirling, National University of Ireland, Maynooth, University College Dublin and Northern Illinois University. Mark is an active researcher in the fields of education and public policy. His research interests include educational sociology, critical theory, accountability in higher education, and public sector reform.
Related Posts

Me, My PhD and my grumbles about Actor Network Theory
January 11, 2013

What comes first – the analytical framework or the data collection?
June 12, 2014

Foucault and the dyslexic subject
December 17, 2018

Interactive Grumbles: Bringing my BERA 2013 paper to life
October 21, 2013
Recent Posts

- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
What is a Case Study? Definition & Examples
By Jim Frost Leave a Comment
Case Study Definition
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a single person, group, event, or community. This research method involves intensively analyzing a subject to understand its complexity and context. The richness of a case study comes from its ability to capture detailed, qualitative data that can offer insights into a process or subject matter that other research methods might miss.

A case study strives for a holistic understanding of events or situations by examining all relevant variables. They are ideal for exploring ‘how’ or ‘why’ questions in contexts where the researcher has limited control over events in real-life settings. Unlike narrowly focused experiments, these projects seek a comprehensive understanding of events or situations.
In a case study, researchers gather data through various methods such as participant observation, interviews, tests, record examinations, and writing samples. Unlike statistically-based studies that seek only quantifiable data, a case study attempts to uncover new variables and pose questions for subsequent research.
A case study is particularly beneficial when your research:
- Requires a deep, contextual understanding of a specific case.
- Needs to explore or generate hypotheses rather than test them.
- Focuses on a contemporary phenomenon within a real-life context.
Learn more about Other Types of Experimental Design .
Case Study Examples
Various fields utilize case studies, including the following:
- Social sciences : For understanding complex social phenomena.
- Business : For analyzing corporate strategies and business decisions.
- Healthcare : For detailed patient studies and medical research.
- Education : For understanding educational methods and policies.
- Law : For in-depth analysis of legal cases.
For example, consider a case study in a business setting where a startup struggles to scale. Researchers might examine the startup’s strategies, market conditions, management decisions, and competition. Interviews with the CEO, employees, and customers, alongside an analysis of financial data, could offer insights into the challenges and potential solutions for the startup. This research could serve as a valuable lesson for other emerging businesses.
See below for other examples.
| What impact does urban green space have on mental health in high-density cities? | Assess a green space development in Tokyo and its effects on resident mental health. |
| How do small businesses adapt to rapid technological changes? | Examine a small business in Silicon Valley adapting to new tech trends. |
| What strategies are effective in reducing plastic waste in coastal cities? | Study plastic waste management initiatives in Barcelona. |
| How do educational approaches differ in addressing diverse learning needs? | Investigate a specialized school’s approach to inclusive education in Sweden. |
| How does community involvement influence the success of public health initiatives? | Evaluate a community-led health program in rural India. |
| What are the challenges and successes of renewable energy adoption in developing countries? | Assess solar power implementation in a Kenyan village. |
Types of Case Studies
Several standard types of case studies exist that vary based on the objectives and specific research needs.
Illustrative Case Study : Descriptive in nature, these studies use one or two instances to depict a situation, helping to familiarize the unfamiliar and establish a common understanding of the topic.
Exploratory Case Study : Conducted as precursors to large-scale investigations, they assist in raising relevant questions, choosing measurement types, and identifying hypotheses to test.
Cumulative Case Study : These studies compile information from various sources over time to enhance generalization without the need for costly, repetitive new studies.
Critical Instance Case Study : Focused on specific sites, they either explore unique situations with limited generalizability or challenge broad assertions, to identify potential cause-and-effect issues.
Pros and Cons
As with any research study, case studies have a set of benefits and drawbacks.
- Provides comprehensive and detailed data.
- Offers a real-life perspective.
- Flexible and can adapt to discoveries during the study.
- Enables investigation of scenarios that are hard to assess in laboratory settings.
- Facilitates studying rare or unique cases.
- Generates hypotheses for future experimental research.
- Time-consuming and may require a lot of resources.
- Hard to generalize findings to a broader context.
- Potential for researcher bias.
- Cannot establish causality .
- Lacks scientific rigor compared to more controlled research methods .
Crafting a Good Case Study: Methodology
While case studies emphasize specific details over broad theories, they should connect to theoretical frameworks in the field. This approach ensures that these projects contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the subject, rather than standing as an isolated entity.
The following are critical steps in developing a case study:
- Define the Research Questions : Clearly outline what you want to explore. Define specific, achievable objectives.
- Select the Case : Choose a case that best suits the research questions. Consider using a typical case for general understanding or an atypical subject for unique insights.
- Data Collection : Use a variety of data sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and archival records, to provide multiple perspectives on the issue.
- Data Analysis : Identify patterns and themes in the data.
- Report Findings : Present the findings in a structured and clear manner.
Analysts typically use thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes within the data and compare different cases.
- Qualitative Analysis : Such as coding and thematic analysis for narrative data.
- Quantitative Analysis : In cases where numerical data is involved.
- Triangulation : Combining multiple methods or data sources to enhance accuracy.
A good case study requires a balanced approach, often using both qualitative and quantitative methods.
The researcher should constantly reflect on their biases and how they might influence the research. Documenting personal reflections can provide transparency.
Avoid over-generalization. One common mistake is to overstate the implications of a case study. Remember that these studies provide an in-depth insights into a specific case and might not be widely applicable.
Don’t ignore contradictory data. All data, even that which contradicts your hypothesis, is valuable. Ignoring it can lead to skewed results.
Finally, in the report, researchers provide comprehensive insight for a case study through “thick description,” which entails a detailed portrayal of the subject, its usage context, the attributes of involved individuals, and the community environment. Thick description extends to interpreting various data, including demographic details, cultural norms, societal values, prevailing attitudes, and underlying motivations. This approach ensures a nuanced and in-depth comprehension of the case in question.
Learn more about Qualitative Research and Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data .
Morland, J. & Feagin, Joe & Orum, Anthony & Sjoberg, Gideon. (1992). A Case for the Case Study . Social Forces. 71(1):240.
Share this:

Reader Interactions
Comments and questions cancel reply.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
| Minority ethnic people experience considerably greater morbidity from asthma than the White majority population. Research has shown however that these minority ethnic populations are likely to be under-represented in research undertaken in the UK; there is comparatively less marginalisation in the US. |
| To investigate approaches to bolster recruitment of South Asians into UK asthma studies through qualitative research with US and UK researchers, and UK community leaders. |
| Single intrinsic case study |
| Centred on the issue of recruitment of South Asian people with asthma. |
| In-depth interviews were conducted with asthma researchers from the UK and US. A supplementary questionnaire was also provided to researchers. |
| Framework approach. |
| Barriers to ethnic minority recruitment were found to centre around: |
| 1. The attitudes of the researchers' towards inclusion: The majority of UK researchers interviewed were generally supportive of the idea of recruiting ethnically diverse participants but expressed major concerns about the practicalities of achieving this; in contrast, the US researchers appeared much more committed to the policy of inclusion. |
| 2. Stereotypes and prejudices: We found that some of the UK researchers' perceptions of ethnic minorities may have influenced their decisions on whether to approach individuals from particular ethnic groups. These stereotypes centred on issues to do with, amongst others, language barriers and lack of altruism. |
| 3. Demographic, political and socioeconomic contexts of the two countries: Researchers suggested that the demographic profile of ethnic minorities, their political engagement and the different configuration of the health services in the UK and the US may have contributed to differential rates. |
| 4. Above all, however, it appeared that the overriding importance of the US National Institute of Health's policy to mandate the inclusion of minority ethnic people (and women) had a major impact on shaping the attitudes and in turn the experiences of US researchers'; the absence of any similar mandate in the UK meant that UK-based researchers had not been forced to challenge their existing practices and they were hence unable to overcome any stereotypical/prejudicial attitudes through experiential learning. |
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
| Health work forces globally are needing to reorganise and reconfigure in order to meet the challenges posed by the increased numbers of people living with long-term conditions in an efficient and sustainable manner. Through studying the introduction of General Practitioners with a Special Interest in respiratory disorders, this study aimed to provide insights into this important issue by focusing on community respiratory service development. |
| To understand and compare the process of workforce change in respiratory services and the impact on patient experience (specifically in relation to the role of general practitioners with special interests) in a theoretically selected sample of Primary Care Organisations (PCOs), in order to derive models of good practice in planning and the implementation of a broad range of workforce issues. |
| Multiple-case design of respiratory services in health regions in England and Wales. |
| Four PCOs. |
| Face-to-face and telephone interviews, e-mail discussions, local documents, patient diaries, news items identified from local and national websites, national workshop. |
| Reading, coding and comparison progressed iteratively. |
| 1. In the screening phase of this study (which involved semi-structured telephone interviews with the person responsible for driving the reconfiguration of respiratory services in 30 PCOs), the barriers of financial deficit, organisational uncertainty, disengaged clinicians and contradictory policies proved insurmountable for many PCOs to developing sustainable services. A key rationale for PCO re-organisation in 2006 was to strengthen their commissioning function and those of clinicians through Practice-Based Commissioning. However, the turbulence, which surrounded reorganisation was found to have the opposite desired effect. |
| 2. Implementing workforce reconfiguration was strongly influenced by the negotiation and contest among local clinicians and managers about "ownership" of work and income. |
| 3. Despite the intention to make the commissioning system more transparent, personal relationships based on common professional interests, past work history, friendships and collegiality, remained as key drivers for sustainable innovation in service development. |
| It was only possible to undertake in-depth work in a selective number of PCOs and, even within these selected PCOs, it was not possible to interview all informants of potential interest and/or obtain all relevant documents. This work was conducted in the early stages of a major NHS reorganisation in England and Wales and thus, events are likely to have continued to evolve beyond the study period; we therefore cannot claim to have seen any of the stories through to their conclusion. |
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
| Healthcare systems globally are moving from paper-based record systems to electronic health record systems. In 2002, the NHS in England embarked on the most ambitious and expensive IT-based transformation in healthcare in history seeking to introduce electronic health records into all hospitals in England by 2010. |
| To describe and evaluate the implementation and adoption of detailed electronic health records in secondary care in England and thereby provide formative feedback for local and national rollout of the NHS Care Records Service. |
| A mixed methods, longitudinal, multi-site, socio-technical collective case study. |
| Five NHS acute hospital and mental health Trusts that have been the focus of early implementation efforts. |
| Semi-structured interviews, documentary data and field notes, observations and quantitative data. |
| Qualitative data were analysed thematically using a socio-technical coding matrix, combined with additional themes that emerged from the data. |
| 1. Hospital electronic health record systems have developed and been implemented far more slowly than was originally envisioned. |
| 2. The top-down, government-led standardised approach needed to evolve to admit more variation and greater local choice for hospitals in order to support local service delivery. |
| 3. A range of adverse consequences were associated with the centrally negotiated contracts, which excluded the hospitals in question. |
| 4. The unrealistic, politically driven, timeline (implementation over 10 years) was found to be a major source of frustration for developers, implementers and healthcare managers and professionals alike. |
| We were unable to access details of the contracts between government departments and the Local Service Providers responsible for delivering and implementing the software systems. This, in turn, made it difficult to develop a holistic understanding of some key issues impacting on the overall slow roll-out of the NHS Care Record Service. Early adopters may also have differed in important ways from NHS hospitals that planned to join the National Programme for Information Technology and implement the NHS Care Records Service at a later point in time. |
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
| There is a need to reduce the disease burden associated with iatrogenic harm and considering that healthcare education represents perhaps the most sustained patient safety initiative ever undertaken, it is important to develop a better appreciation of the ways in which undergraduate and newly qualified professionals receive and make sense of the education they receive. | |
|---|---|
| To investigate the formal and informal ways pre-registration students from a range of healthcare professions (medicine, nursing, physiotherapy and pharmacy) learn about patient safety in order to become safe practitioners. | |
| Multi-site, mixed method collective case study. | |
| : Eight case studies (two for each professional group) were carried out in educational provider sites considering different programmes, practice environments and models of teaching and learning. | |
| Structured in phases relevant to the three knowledge contexts: | |
| Documentary evidence (including undergraduate curricula, handbooks and module outlines), complemented with a range of views (from course leads, tutors and students) and observations in a range of academic settings. | |
| Policy and management views of patient safety and influences on patient safety education and practice. NHS policies included, for example, implementation of the National Patient Safety Agency's , which encourages organisations to develop an organisational safety culture in which staff members feel comfortable identifying dangers and reporting hazards. | |
| The cultures to which students are exposed i.e. patient safety in relation to day-to-day working. NHS initiatives included, for example, a hand washing initiative or introduction of infection control measures. | |
| 1. Practical, informal, learning opportunities were valued by students. On the whole, however, students were not exposed to nor engaged with important NHS initiatives such as risk management activities and incident reporting schemes. | |
| 2. NHS policy appeared to have been taken seriously by course leaders. Patient safety materials were incorporated into both formal and informal curricula, albeit largely implicit rather than explicit. | |
| 3. Resource issues and peer pressure were found to influence safe practice. Variations were also found to exist in students' experiences and the quality of the supervision available. | |
| The curriculum and organisational documents collected differed between sites, which possibly reflected gatekeeper influences at each site. The recruitment of participants for focus group discussions proved difficult, so interviews or paired discussions were used as a substitute. | |
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
| Author | Definition |
|---|---|
| Stake[ ] | (p.237) |
| Yin[ , , ] | (Yin 1999 p. 1211, Yin 1994 p. 13) |
| • | |
| • (Yin 2009 p18) | |
| Miles and Huberman[ ] | (p. 25) |
| Green and Thorogood[ ] | (p. 284) |
| George and Bennett[ ] | (p. 17)" |
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].

What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
| Approach | Characteristics | Criticisms | Key references |
|---|---|---|---|
| Involves questioning one's own assumptions taking into account the wider political and social environment. | It can possibly neglect other factors by focussing only on power relationships and may give the researcher a position that is too privileged. | Howcroft and Trauth[ ] Blakie[ ] Doolin[ , ] | |
| Interprets the limiting conditions in relation to power and control that are thought to influence behaviour. | Bloomfield and Best[ ] | ||
| Involves understanding meanings/contexts and processes as perceived from different perspectives, trying to understand individual and shared social meanings. Focus is on theory building. | Often difficult to explain unintended consequences and for neglecting surrounding historical contexts | Stake[ ] Doolin[ ] | |
| Involves establishing which variables one wishes to study in advance and seeing whether they fit in with the findings. Focus is often on testing and refining theory on the basis of case study findings. | It does not take into account the role of the researcher in influencing findings. | Yin[ , , ] Shanks and Parr[ ] |
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
| Clarity: Does the proposal read well? | |
| Integrity: Do its pieces fit together? | |
| Attractiveness: Does it pique the reader's interest? | |
| The case: Is the case adequately defined? | |
| The issues: Are major research questions identified? | |
| Data Resource: Are sufficient data sources identified? | |
| Case Selection: Is the selection plan reasonable? | |
| Data Gathering: Are data-gathering activities outlined? | |
| Validation: Is the need and opportunity for triangulation indicated? | |
| Access: Are arrangements for start-up anticipated? | |
| Confidentiality: Is there sensitivity to the protection of people? | |
| Cost: Are time and resource estimates reasonable? |
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
| Potential pitfall | Mitigating action |
|---|---|
| Selecting/conceptualising the wrong case(s) resulting in lack of theoretical generalisations | Developing in-depth knowledge of theoretical and empirical literature, justifying choices made |
| Collecting large volumes of data that are not relevant to the case or too little to be of any value | Focus data collection in line with research questions, whilst being flexible and allowing different paths to be explored |
| Defining/bounding the case | Focus on related components (either by time and/or space), be clear what is outside the scope of the case |
| Lack of rigour | Triangulation, respondent validation, the use of theoretical sampling, transparency throughout the research process |
| Ethical issues | Anonymise appropriately as cases are often easily identifiable to insiders, informed consent of participants |
| Integration with theoretical framework | Allow for unexpected issues to emerge and do not force fit, test out preliminary explanations, be clear about epistemological positions in advance |
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
| 1. Is this report easy to read? |
| 2. Does it fit together, each sentence contributing to the whole? |
| 3. Does this report have a conceptual structure (i.e. themes or issues)? |
| 4. Are its issues developed in a series and scholarly way? |
| 5. Is the case adequately defined? |
| 6. Is there a sense of story to the presentation? |
| 7. Is the reader provided some vicarious experience? |
| 8. Have quotations been used effectively? |
| 9. Are headings, figures, artefacts, appendices, indexes effectively used? |
| 10. Was it edited well, then again with a last minute polish? |
| 11. Has the writer made sound assertions, neither over- or under-interpreting? |
| 12. Has adequate attention been paid to various contexts? |
| 13. Were sufficient raw data presented? |
| 14. Were data sources well chosen and in sufficient number? |
| 15. Do observations and interpretations appear to have been triangulated? |
| 16. Is the role and point of view of the researcher nicely apparent? |
| 17. Is the nature of the intended audience apparent? |
| 18. Is empathy shown for all sides? |
| 19. Are personal intentions examined? |
| 20. Does it appear individuals were put at risk? |
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
EducationalWave
Pros and Cons of Case Studies Psychology

Case studies in psychology offer a detailed look at individual behaviors and experiences, revealing unique insights but posing challenges. They allow deep exploration of complex cases, providing rich understanding of rare phenomena . However, focusing on specific cases may limit generalizability and introduce potential for bias. Despite these limitations, case studies complement broader research methods and can generate hypotheses for further studies. Understanding the pros and cons of case studies in psychology can enhance research and therapeutic interventions.
Table of Contents
- Provide in-depth insights into individual behavior and experiences.
- Contribute to advancing psychological knowledge.
- Challenges in generalizing findings beyond specific cases.
- Potential for researcher and participant bias.
- Complement other research methods for holistic understanding.
Advantages of Case Studies
One of the primary advantages of case studies in psychology is their ability to provide in-depth, detailed insights into individual behavior and experiences. By focusing on a single individual or a small group, case studies allow researchers to deeply explore the unique circumstances and complexities of a particular case.
This level of detail is often not possible in larger-scale research methods, such as surveys or experiments, where individual variations may be overlooked.
Case studies also offer the opportunity to investigate rare or unusual phenomena that may not be easily studied through other research approaches. This can lead to the discovery of new theories or the validation of existing ones, contributing to the advancement of psychological knowledge.
Additionally, case studies can provide a more holistic understanding of complex behaviors or psychological disorders by considering multiple factors in a single case.
In-Depth Exploration of Individuals
The examination of individuals in psychology allows for a thorough analysis of their behaviors, thoughts, and emotions.
By conducting a detailed individual analysis, psychologists can gain rich personal insights that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of an individual's behavioral patterns.
This in-depth exploration provides a holistic view of the complexities that shape an individual's psychological makeup.
Detailed Individual Analysis
A thorough examination of the intricate layers of an individual's psyche reveals profound insights into their behaviors and thought processes. Through detailed individual analysis in psychology, researchers dive deep into the complexities of a person's mind to understand the underlying factors that drive their actions. This method involves thorough observation, interviews, and sometimes even psychological testing to gather extensive data about an individual's cognitive processes, emotions, and behaviors.
- Holistic Perspective: Provides a complete view of the individual's psychological makeup.
- Identification of Patterns: Helps in recognizing recurring themes or behaviors that may offer valuable insights.
- Understanding Triggers: Uncovers the specific stimuli or events that lead to certain reactions.
- Personalized Interventions: Enables the development of tailored psychological interventions based on the individual's unique characteristics.
Detailed individual analysis offers a rich source of information that contributes significantly to the field of psychology by offering a nuanced understanding of human behavior and cognition.
Rich Personal Insights
Through in-depth exploration of individuals, psychology uncovers rich personal insights that illuminate the intricacies of human behavior and cognition. By delving deeply into the lives, experiences, and thought processes of individuals, psychologists gain a profound understanding of the factors shaping behavior and mental processes.
Case studies offer a unique opportunity to observe and analyze the complexities of human nature in a real-world context, providing valuable insights that may not be captured through other research methods.
One of the key advantages of this approach is the ability to uncover unique patterns , motivations, and influences that contribute to an individual's behavior. These rich personal insights allow psychologists to develop a more nuanced understanding of how external and internal factors interact to shape an individual's thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Comprehensive Behavioral Understanding
By conducting in-depth exploration of individuals, psychologists aim to achieve a profound understanding of human behavior and cognition. This extensive behavioral understanding involves delving into the intricacies of an individual's thoughts, emotions, motivations, and actions to gain insight into the underlying factors that drive behavior.
Through in-depth case studies, psychologists can uncover patterns, triggers, and influences that contribute to a person's psychological makeup and decision-making processes.
- Identification of Root Causes : Case studies allow psychologists to identify the root causes of behaviors by examining the individual's past experiences, traumas, and environmental factors.
- Personalized Interventions : By understanding the unique aspects of an individual's behavior, psychologists can tailor interventions and treatments that are specifically suited to address their needs.
- Enhanced Empathy and Connection : Extensive behavioral understanding fosters empathy and connection between psychologists and their clients, promoting a more effective therapeutic relationship.
- Contribution to Psychological Knowledge : Through detailed case studies, psychologists contribute valuable insights to the broader field of psychology, advancing understanding of human behavior and cognition.
Limited Generalizability
Generalizability in case studies in psychology is often constrained by the unique and specific nature of individual cases . Unlike large-scale studies that aim for broad generalizability across populations, case studies explore deeply into the intricate details of a single individual or a small group .
This focused approach, while valuable for understanding the nuances of a particular case, limits the extent to which findings can be applied to a wider population. The idiosyncrasies of each case study subject, including their personal history, circumstances, and characteristics, make it challenging to extrapolate the results to the broader population.
This limitation is particularly evident in clinical psychology , where patients seeking treatment may have complex and individualized experiences that do not represent the typical response or behavior of the general population. While case studies offer rich insights into the complexities of human behavior and individual experiences, researchers and practitioners must exercise caution when attempting to generalize findings beyond the specific case under investigation.
Balancing the depth of understanding gained from case studies with the limited generalizability is a critical consideration in psychological research and practice.
Unique Insights Into Rare Phenomena
Exploring rare phenomena in psychology offers valuable opportunities to gain in-depth understanding that may not be possible through broader studies. By focusing on unique cases, researchers can uncover insights that provide a deeper understanding of complex psychological conditions or behaviors.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the limited generalizability of findings from these rare cases to the larger population.
Rare Phenomena Exploration
An examination of rare phenomena in psychology offers valuable and distinctive insights into the complexities of human behavior. These unique occurrences provide psychologists with a rare opportunity to explore further into understanding the intricacies of the human mind and its behavior.
When investigating rare phenomena, researchers can uncover hidden aspects of psychological processes that may not be observable in more common situations. This exploration can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in psychological knowledge.
- Uncover underlying mechanisms : Rare phenomena allow researchers to unveil the underlying mechanisms that govern human behavior, shedding light on the intricacies of cognitive processes.
- Challenge existing theories : Studying rare phenomena can challenge established psychological theories and offer new perspectives on human behavior.
- Inform therapeutic interventions : Insights gained from exploration of rare phenomena can inform the development of more effective therapeutic interventions for individuals facing similar challenges.
- Expand the boundaries of knowledge : Exploring rare phenomena pushes the limits of psychological knowledge, leading to a deeper understanding of human behavior and cognition.
In-depth Understanding Opportunities
Uncommon occurrences in psychology offer unparalleled opportunities for gaining in-depth understanding and unique insights into the complexities of human behavior. By focusing on rare cases or unusual events, researchers can delve deeply into the intricacies of individual experiences , behaviors, and mental processes that may not be easily observable in more common situations.
These unique cases offer a chance to explore the underlying factors contributing to specific behaviors or psychological conditions, providing a rich source of information that can inform theory development and therapeutic interventions.
Studying rare phenomena allows researchers to uncover hidden patterns , causal relationships , and potential mechanisms that may not be apparent in larger, more generalized studies. The detailed examination of these exceptional cases can lead to the discovery of novel perspectives and alternative explanations that challenge existing theories or shed light on previously unexplored aspects of human psychology.
Additionally, the insights gained from studying rare phenomena can have practical implications for clinical practice, offering new approaches to assessment, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for individuals with similar presentations.
Limited Generalizability Consideration
The examination of unique phenomena in psychology presents a challenge in considering the limited generalizability of findings to broader populations. When delving into rare occurrences, researchers must navigate the complexities of applying these insights to larger groups.
In the context of case studies, the following points highlight the considerations regarding limited generalizability:
- Small Sample Size: Case studies often involve a small number of participants, making it challenging to extend findings to the broader population.
- Unique Individual Factors: Each case study participant may possess unique characteristics or experiences that limit the applicability of findings to others.
- Context-Specific Dynamics: The specific circumstances surrounding a rare phenomenon may not be easily replicable or generalized to different settings.
- Potential Bias: Researchers and participants in case studies may introduce biases that affect the transferability of results to a wider population.
Navigating the tension between the richness of insights gained from unique cases and the limited generalizability to broader populations remains a critical consideration in psychological research.
Potential for Bias
In psychological case studies, the potential for bias must be carefully considered and managed to guarantee the integrity of the research findings. Bias can arise from various sources, such as researcher bias , participant bias , and even the inherent biases of the case study method itself.
Researcher bias occurs when the investigator's preconceived notions or beliefs influence the interpretation of data or the selection of information to include in the study. This can lead to skewed results that do not accurately reflect the reality of the case.
Participant bias is another significant concern, where participants may alter their behavior or responses based on what they believe the researcher wants to hear, impacting the validity of the findings.
Additionally, the qualitative nature of case studies can introduce inherent biases, as the interpretation of data is subjective and open to individual researcher perspectives.
To mitigate bias in case studies, researchers should employ rigorous methodologies, maintain transparency in data collection and analysis, consider alternative explanations for findings, and utilize triangulation by incorporating multiple data sources or researchers.
Complement to Other Research Methods
Given the potential for bias in psychological case studies, it is imperative to recognize how this research method can serve as a valuable complement to other research methods in the field. While case studies have their limitations, they offer unique advantages that can enhance the overall understanding of complex psychological phenomena when used in conjunction with other research methods.
Here are some ways in which case studies can complement other research approaches:
- In-depth exploration : Case studies allow for a detailed examination of individual cases, providing rich insights that may not be captured through quantitative methods alone.
- Hypothesis generation : They can help generate hypotheses for further research by highlighting patterns or relationships that warrant investigation on a larger scale.
- Real-world application : Case studies offer a bridge between theory and practical application, showcasing how psychological principles manifest in real-life settings.
- Thorough understanding : By incorporating varied sources of data, including interviews, observations, and archival records, case studies can offer a thorough understanding of complex phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can case studies be used to study large populations?.
Case studies are not typically used to study large populations due to their focus on in-depth examination of individual cases. They are more suited for exploring complex phenomena in detail rather than generalizing findings to broader populations.
Are There Ethical Concerns With Case Study Research?
Ethical concerns in case study research revolve around issues like informed consent, confidentiality, and potential harm to participants. Researchers must prioritize ethical guidelines to protect the rights and well-being of those involved in the study.
How Do Researchers Ensure the Objectivity of Case Studies?
Researchers guarantee objectivity in case studies by using rigorous data collection methods, maintaining transparency, employing multiple investigators for data analysis, and conducting member checks to verify findings. These practices help minimize bias and enhance the credibility of results.
What Are the Limitations of Using Case Studies in Psychology?
The limitations of utilizing case studies in psychology include issues related to generalizability, sample size, and potential researcher bias. While offering in-depth insights, they may not always be representative of broader populations or provide causal conclusions.
Can Findings From Case Studies Be Applied to Real-World Situations?
Findings from case studies can offer valuable insights into real-world situations. While individual cases provide in-depth understanding, generalizability may be limited. Applying findings cautiously, considering context and potential biases, can enhance their relevance in practical settings.
To sum up, case studies in psychology offer a valuable opportunity to explore individuals in depth and provide unique insights into rare phenomena. However, their limited generalizability and potential for bias must be carefully considered.
When used in conjunction with other research methods, case studies can complement and enhance our understanding of complex psychological phenomena.
Related Posts:
- Pros and Cons of Narrative Research
- Pros and Cons of Descriptive Research
- Pros and Cons of Evidence Based Practice in Psychology
- 20 Pros and Cons of Quantitative Research
- Pros and Cons of Meta Analysis
- Pros and Cons of Evolutionary Psychology
- Pros and Cons of Therapeutic Cloning
- Pros and Cons of Punishment Psychology
- Pros and Cons of Mixed Methods Research
Related posts:
- Pros and Cons of Positive Psychology
- Pros and Cons of Sports Psychology
- Pros and Cons of Stove Under Window
- Pros and Cons of Being a Case Manager
- Pros and Cons of Activity Theory
- Pros and Cons of Comparative Research
Educational Wave Team
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 21, Issue 1
- What is a case study?
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Roberta Heale 1 ,
- Alison Twycross 2
- 1 School of Nursing , Laurentian University , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- 2 School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Roberta Heale, School of Nursing, Laurentian University, Sudbury, ON P3E2C6, Canada; rheale{at}laurentian.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102845
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
What is it?
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research. 1 However, very simply… ‘a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units’. 1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a single individual, group, community or some other unit in which the researcher examines in-depth data relating to several variables. 2
Often there are several similar cases to consider such as educational or social service programmes that are delivered from a number of locations. Although similar, they are complex and have unique features. In these circumstances, the evaluation of several, similar cases will provide a better answer to a research question than if only one case is examined, hence the multiple-case study. Stake asserts that the cases are grouped and viewed as one entity, called the quintain . 6 ‘We study what is similar and different about the cases to understand the quintain better’. 6
The steps when using case study methodology are the same as for other types of research. 6 The first step is defining the single case or identifying a group of similar cases that can then be incorporated into a multiple-case study. A search to determine what is known about the case(s) is typically conducted. This may include a review of the literature, grey literature, media, reports and more, which serves to establish a basic understanding of the cases and informs the development of research questions. Data in case studies are often, but not exclusively, qualitative in nature. In multiple-case studies, analysis within cases and across cases is conducted. Themes arise from the analyses and assertions about the cases as a whole, or the quintain, emerge. 6
Benefits and limitations of case studies
If a researcher wants to study a specific phenomenon arising from a particular entity, then a single-case study is warranted and will allow for a in-depth understanding of the single phenomenon and, as discussed above, would involve collecting several different types of data. This is illustrated in example 1 below.
Using a multiple-case research study allows for a more in-depth understanding of the cases as a unit, through comparison of similarities and differences of the individual cases embedded within the quintain. Evidence arising from multiple-case studies is often stronger and more reliable than from single-case research. Multiple-case studies allow for more comprehensive exploration of research questions and theory development. 6
Despite the advantages of case studies, there are limitations. The sheer volume of data is difficult to organise and data analysis and integration strategies need to be carefully thought through. There is also sometimes a temptation to veer away from the research focus. 2 Reporting of findings from multiple-case research studies is also challenging at times, 1 particularly in relation to the word limits for some journal papers.
Examples of case studies
Example 1: nurses’ paediatric pain management practices.
One of the authors of this paper (AT) has used a case study approach to explore nurses’ paediatric pain management practices. This involved collecting several datasets:
Observational data to gain a picture about actual pain management practices.
Questionnaire data about nurses’ knowledge about paediatric pain management practices and how well they felt they managed pain in children.
Questionnaire data about how critical nurses perceived pain management tasks to be.
These datasets were analysed separately and then compared 7–9 and demonstrated that nurses’ level of theoretical did not impact on the quality of their pain management practices. 7 Nor did individual nurse’s perceptions of how critical a task was effect the likelihood of them carrying out this task in practice. 8 There was also a difference in self-reported and observed practices 9 ; actual (observed) practices did not confirm to best practice guidelines, whereas self-reported practices tended to.
Example 2: quality of care for complex patients at Nurse Practitioner-Led Clinics (NPLCs)
The other author of this paper (RH) has conducted a multiple-case study to determine the quality of care for patients with complex clinical presentations in NPLCs in Ontario, Canada. 10 Five NPLCs served as individual cases that, together, represented the quatrain. Three types of data were collected including:
Review of documentation related to the NPLC model (media, annual reports, research articles, grey literature and regulatory legislation).
Interviews with nurse practitioners (NPs) practising at the five NPLCs to determine their perceptions of the impact of the NPLC model on the quality of care provided to patients with multimorbidity.
Chart audits conducted at the five NPLCs to determine the extent to which evidence-based guidelines were followed for patients with diabetes and at least one other chronic condition.
The three sources of data collected from the five NPLCs were analysed and themes arose related to the quality of care for complex patients at NPLCs. The multiple-case study confirmed that nurse practitioners are the primary care providers at the NPLCs, and this positively impacts the quality of care for patients with multimorbidity. Healthcare policy, such as lack of an increase in salary for NPs for 10 years, has resulted in issues in recruitment and retention of NPs at NPLCs. This, along with insufficient resources in the communities where NPLCs are located and high patient vulnerability at NPLCs, have a negative impact on the quality of care. 10
These examples illustrate how collecting data about a single case or multiple cases helps us to better understand the phenomenon in question. Case study methodology serves to provide a framework for evaluation and analysis of complex issues. It shines a light on the holistic nature of nursing practice and offers a perspective that informs improved patient care.
- Gustafsson J
- Calanzaro M
- Sandelowski M
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples & Best Practices

Written by: Oghale Olori

Case studies are more than just success stories.
They are powerful tools that demonstrate the practical value of your product or service. Case studies help attract attention to your products, build trust with potential customers and ultimately drive sales.
It’s no wonder that 73% of successful content marketers utilize case studies as part of their content strategy. Plus, buyers spend 54% of their time reviewing case studies before they make a buying decision.
To ensure you’re making the most of your case studies, we’ve put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples span a variety of industries and formats. We’ve also included best practices, design tips and templates to inspire you.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a case study, 15 real-life case study examples, sales case study examples, saas case study examples, product case study examples, marketing case study examples, business case study examples, case study faqs.
- A case study is a compelling narrative that showcases how your product or service has positively impacted a real business or individual.
- Case studies delve into your customer's challenges, how your solution addressed them and the quantifiable results they achieved.
- Your case study should have an attention-grabbing headline, great visuals and a relevant call to action. Other key elements include an introduction, problems and result section.
- Visme provides easy-to-use tools, professionally designed templates and features for creating attractive and engaging case studies.
A case study is a real-life scenario where your company helped a person or business solve their unique challenges. It provides a detailed analysis of the positive outcomes achieved as a result of implementing your solution.
Case studies are an effective way to showcase the value of your product or service to potential customers without overt selling. By sharing how your company transformed a business, you can attract customers seeking similar solutions and results.
Case studies are not only about your company's capabilities; they are primarily about the benefits customers and clients have experienced from using your product.
Every great case study is made up of key elements. They are;
- Attention-grabbing headline: Write a compelling headline that grabs attention and tells your reader what the case study is about. For example, "How a CRM System Helped a B2B Company Increase Revenue by 225%.
- Introduction/Executive Summary: Include a brief overview of your case study, including your customer’s problem, the solution they implemented and the results they achieved.
- Problem/Challenge: Case studies with solutions offer a powerful way to connect with potential customers. In this section, explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Solution: Explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Results/Achievements : Give a detailed account of the positive impact of your product. Quantify the benefits achieved using metrics such as increased sales, improved efficiency, reduced costs or enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Graphics/Visuals: Include professional designs, high-quality photos and videos to make your case study more engaging and visually appealing.
- Quotes/Testimonials: Incorporate written or video quotes from your clients to boost your credibility.
- Relevant CTA: Insert a call to action (CTA) that encourages the reader to take action. For example, visiting your website or contacting you for more information. Your CTA can be a link to a landing page, a contact form or your social media handle and should be related to the product or service you highlighted in your case study.

Now that you understand what a case study is, let’s look at real-life case study examples. Among these, you'll find some simple case study examples that break down complex ideas into easily understandable solutions.
In this section, we’ll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
We’ve also included professionally designed case study templates to inspire you.
1. Georgia Tech Athletics Increase Season Ticket Sales by 80%

Georgia Tech Athletics, with its 8,000 football season ticket holders, sought for a way to increase efficiency and customer engagement.
Their initial sales process involved making multiple outbound phone calls per day with no real targeting or guidelines. Georgia Tech believed that targeting communications will enable them to reach more people in real time.
Salesloft improved Georgia Tech’s sales process with an inbound structure. This enabled sales reps to connect with their customers on a more targeted level. The use of dynamic fields and filters when importing lists ensured prospects received the right information, while communication with existing fans became faster with automation.
As a result, Georgia Tech Athletics recorded an 80% increase in season ticket sales as relationships with season ticket holders significantly improved. Employee engagement increased as employees became more energized to connect and communicate with fans.
Why Does This Case Study Work?
In this case study example , Salesloft utilized the key elements of a good case study. Their introduction gave an overview of their customers' challenges and the results they enjoyed after using them. After which they categorized the case study into three main sections: challenge, solution and result.
Salesloft utilized a case study video to increase engagement and invoke human connection.
Incorporating videos in your case study has a lot of benefits. Wyzol’s 2023 state of video marketing report showed a direct correlation between videos and an 87% increase in sales.
The beautiful thing is that creating videos for your case study doesn’t have to be daunting.
With an easy-to-use platform like Visme, you can create top-notch testimonial videos that will connect with your audience. Within the Visme editor, you can access over 1 million stock photos , video templates, animated graphics and more. These tools and resources will significantly improve the design and engagement of your case study.
Simplify content creation and brand management for your team
- Collaborate on designs , mockups and wireframes with your non-design colleagues
- Lock down your branding to maintain brand consistency throughout your designs
- Why start from scratch? Save time with 1000s of professional branded templates
Sign up. It’s free.

2. WeightWatchers Completely Revamped their Enterprise Sales Process with HubSpot

WeightWatchers, a 60-year-old wellness company, sought a CRM solution that increased the efficiency of their sales process. With their previous system, Weightwatchers had limited automation. They would copy-paste message templates from word documents or recreate one email for a batch of customers.
This required a huge effort from sales reps, account managers and leadership, as they were unable to track leads or pull customized reports for planning and growth.
WeightWatchers transformed their B2B sales strategy by leveraging HubSpot's robust marketing and sales workflows. They utilized HubSpot’s deal pipeline and automation features to streamline lead qualification. And the customized dashboard gave leadership valuable insights.
As a result, WeightWatchers generated seven figures in annual contract value and boosted recurring revenue. Hubspot’s impact resulted in 100% adoption across all sales, marketing, client success and operations teams.
Hubspot structured its case study into separate sections, demonstrating the specific benefits of their products to various aspects of the customer's business. Additionally, they integrated direct customer quotes in each section to boost credibility, resulting in a more compelling case study.
Getting insight from your customer about their challenges is one thing. But writing about their process and achievements in a concise and relatable way is another. If you find yourself constantly experiencing writer’s block, Visme’s AI writer is perfect for you.
Visme created this AI text generator tool to take your ideas and transform them into a great draft. So whether you need help writing your first draft or editing your final case study, Visme is ready for you.
3. Immi’s Ram Fam Helps to Drive Over $200k in Sales

Immi embarked on a mission to recreate healthier ramen recipes that were nutritious and delicious. After 2 years of tireless trials, Immi finally found the perfect ramen recipe. However, they envisioned a community of passionate ramen enthusiasts to fuel their business growth.
This vision propelled them to partner with Shopify Collabs. Shopify Collabs successfully cultivated and managed Immi’s Ramen community of ambassadors and creators.
As a result of their partnership, Immi’s community grew to more than 400 dedicated members, generating over $200,000 in total affiliate sales.
The power of data-driven headlines cannot be overemphasized. Chili Piper strategically incorporates quantifiable results in their headlines. This instantly sparks curiosity and interest in readers.
While not every customer success story may boast headline-grabbing figures, quantifying achievements in percentages is still effective. For example, you can highlight a 50% revenue increase with the implementation of your product.
Take a look at the beautiful case study template below. Just like in the example above, the figures in the headline instantly grab attention and entice your reader to click through.
Having a case study document is a key factor in boosting engagement. This makes it easy to promote your case study in multiple ways. With Visme, you can easily publish, download and share your case study with your customers in a variety of formats, including PDF, PPTX, JPG and more!

4. How WOW! is Saving Nearly 79% in Time and Cost With Visme
This case study discusses how Visme helped WOW! save time and money by providing user-friendly tools to create interactive and quality training materials for their employees. Find out what your team can do with Visme. Request a Demo
WOW!'s learning and development team creates high-quality training materials for new and existing employees. Previous tools and platforms they used had plain templates, little to no interactivity features, and limited flexibility—that is, until they discovered Visme.
Now, the learning and development team at WOW! use Visme to create engaging infographics, training videos, slide decks and other training materials.
This has directly reduced the company's turnover rate, saving them money spent on recruiting and training new employees. It has also saved them a significant amount of time, which they can now allocate to other important tasks.
Visme's customer testimonials spark an emotional connection with the reader, leaving a profound impact. Upon reading this case study, prospective customers will be blown away by the remarkable efficiency achieved by Visme's clients after switching from PowerPoint.
Visme’s interactivity feature was a game changer for WOW! and one of the primary reasons they chose Visme.
“Previously we were using PowerPoint, which is fine, but the interactivity you can get with Visme is so much more robust that we’ve all steered away from PowerPoint.” - Kendra, L&D team, Wow!
Visme’s interactive feature allowed them to animate their infographics, include clickable links on their PowerPoint designs and even embed polls and quizzes their employees could interact with.
By embedding the slide decks, infographics and other training materials WOW! created with Visme, potential customers get a taste of what they can create with the tool. This is much more effective than describing the features of Visme because it allows potential customers to see the tool in action.
To top it all off, this case study utilized relevant data and figures. For example, one part of the case study said, “In Visme, where Kendra’s team has access to hundreds of templates, a brand kit, and millions of design assets at their disposal, their team can create presentations in 80% less time.”
Who wouldn't want that?
Including relevant figures and graphics in your case study is a sure way to convince your potential customers why you’re a great fit for their brand. The case study template below is a great example of integrating relevant figures and data.
This colorful template begins with a captivating headline. But that is not the best part; this template extensively showcases the results their customer had using relevant figures.
The arrangement of the results makes it fun and attractive. Instead of just putting figures in a plain table, you can find interesting shapes in your Visme editor to take your case study to the next level.
5. Lyte Reduces Customer Churn To Just 3% With Hubspot CRM

While Lyte was redefining the ticketing industry, it had no definite CRM system . Lyte utilized 12–15 different SaaS solutions across various departments, which led to a lack of alignment between teams, duplication of work and overlapping tasks.
Customer data was spread across these platforms, making it difficult to effectively track their customer journey. As a result, their churn rate increased along with customer dissatisfaction.
Through Fuelius , Lyte founded and implemented Hubspot CRM. Lyte's productivity skyrocketed after incorporating Hubspot's all-in-one CRM tool. With improved efficiency, better teamwork and stronger client relationships, sales figures soared.
The case study title page and executive summary act as compelling entry points for both existing and potential customers. This overview provides a clear understanding of the case study and also strategically incorporates key details like the client's industry, location and relevant background information.
Having a good summary of your case study can prompt your readers to engage further. You can achieve this with a simple but effective case study one-pager that highlights your customer’s problems, process and achievements, just like this case study did in the beginning.
Moreover, you can easily distribute your case study one-pager and use it as a lead magnet to draw prospective customers to your company.
Take a look at this case study one-pager template below.

This template includes key aspects of your case study, such as the introduction, key findings, conclusion and more, without overcrowding the page. The use of multiple shades of blue gives it a clean and dynamic layout.
Our favorite part of this template is where the age group is visualized.
With Visme’s data visualization tool , you can present your data in tables, graphs, progress bars, maps and so much more. All you need to do is choose your preferred data visualization widget, input or import your data and click enter!
6. How Workato Converts 75% of Their Qualified Leads

Workato wanted to improve their inbound leads and increase their conversion rate, which ranged from 40-55%.
At first, Workato searched for a simple scheduling tool. They soon discovered that they needed a tool that provided advanced routing capabilities based on zip code and other criteria. Luckily, they found and implemented Chili Piper.
As a result of implementing Chili Piper, Workato achieved a remarkable 75–80% conversion rate and improved show rates. This led to a substantial revenue boost, with a 10-15% increase in revenue attributed to Chili Piper's impact on lead conversion.
This case study example utilizes the power of video testimonials to drive the impact of their product.
Chili Piper incorporates screenshots and clips of their tool in use. This is a great strategy because it helps your viewers become familiar with how your product works, making onboarding new customers much easier.
In this case study example, we see the importance of efficient Workflow Management Systems (WMS). Without a WMS, you manually assign tasks to your team members and engage in multiple emails for regular updates on progress.
However, when crafting and designing your case study, you should prioritize having a good WMS.
Visme has an outstanding Workflow Management System feature that keeps you on top of all your projects and designs. This feature makes it much easier to assign roles, ensure accuracy across documents, and track progress and deadlines.
Visme’s WMS feature allows you to limit access to your entire document by assigning specific slides or pages to individual members of your team. At the end of the day, your team members are not overwhelmed or distracted by the whole document but can focus on their tasks.
7. Rush Order Helps Vogmask Scale-Up During a Pandemic

Vomask's reliance on third-party fulfillment companies became a challenge as demand for their masks grew. Seeking a reliable fulfillment partner, they found Rush Order and entrusted them with their entire inventory.
Vomask's partnership with Rush Order proved to be a lifesaver during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rush Order's agility, efficiency and commitment to customer satisfaction helped Vogmask navigate the unprecedented demand and maintain its reputation for quality and service.
Rush Order’s comprehensive support enabled Vogmask to scale up its order processing by a staggering 900% while maintaining a remarkable customer satisfaction rate of 92%.
Rush Order chose one event where their impact mattered the most to their customer and shared that story.
While pandemics don't happen every day, you can look through your customer’s journey and highlight a specific time or scenario where your product or service saved their business.
The story of Vogmask and Rush Order is compelling, but it simply is not enough. The case study format and design attract readers' attention and make them want to know more. Rush Order uses consistent colors throughout the case study, starting with the logo, bold square blocks, pictures, and even headers.
Take a look at this product case study template below.
Just like our example, this case study template utilizes bold colors and large squares to attract and maintain the reader’s attention. It provides enough room for you to write about your customers' backgrounds/introductions, challenges, goals and results.
The right combination of shapes and colors adds a level of professionalism to this case study template.

8. AMR Hair & Beauty leverages B2B functionality to boost sales by 200%

With limits on website customization, slow page loading and multiple website crashes during peak events, it wasn't long before AMR Hair & Beauty began looking for a new e-commerce solution.
Their existing platform lacked effective search and filtering options, a seamless checkout process and the data analytics capabilities needed for informed decision-making. This led to a significant number of abandoned carts.
Upon switching to Shopify Plus, AMR immediately saw improvements in page loading speed and average session duration. They added better search and filtering options for their wholesale customers and customized their checkout process.
Due to this, AMR witnessed a 200% increase in sales and a 77% rise in B2B average order value. AMR Hair & Beauty is now poised for further expansion and growth.
This case study example showcases the power of a concise and impactful narrative.
To make their case analysis more effective, Shopify focused on the most relevant aspects of the customer's journey. While there may have been other challenges the customer faced, they only included those that directly related to their solutions.
Take a look at this case study template below. It is perfect if you want to create a concise but effective case study. Without including unnecessary details, you can outline the challenges, solutions and results your customers experienced from using your product.
Don’t forget to include a strong CTA within your case study. By incorporating a link, sidebar pop-up or an exit pop-up into your case study, you can prompt your readers and prospective clients to connect with you.

9. How a Marketing Agency Uses Visme to Create Engaging Content With Infographics

SmartBox Dental , a marketing agency specializing in dental practices, sought ways to make dental advice more interesting and easier to read. However, they lacked the design skills to do so effectively.
Visme's wide range of templates and features made it easy for the team to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently. SmartBox Dental enjoyed creating infographics in as little as 10-15 minutes, compared to one hour before Visme was implemented.
By leveraging Visme, SmartBox Dental successfully transformed dental content into a more enjoyable and informative experience for their clients' patients. Therefore enhancing its reputation as a marketing partner that goes the extra mile to deliver value to its clients.
Visme creatively incorporates testimonials In this case study example.
By showcasing infographics and designs created by their clients, they leverage the power of social proof in a visually compelling way. This way, potential customers gain immediate insight into the creative possibilities Visme offers as a design tool.
This example effectively showcases a product's versatility and impact, and we can learn a lot about writing a case study from it. Instead of focusing on one tool or feature per customer, Visme took a more comprehensive approach.
Within each section of their case study, Visme explained how a particular tool or feature played a key role in solving the customer's challenges.
For example, this case study highlighted Visme’s collaboration tool . With Visme’s tool, the SmartBox Dental content team fostered teamwork, accountability and effective supervision.
Visme also achieved a versatile case study by including relevant quotes to showcase each tool or feature. Take a look at some examples;
Visme’s collaboration tool: “We really like the collaboration tool. Being able to see what a co-worker is working on and borrow their ideas or collaborate on a project to make sure we get the best end result really helps us out.”
Visme’s library of stock photos and animated characters: “I really love the images and the look those give to an infographic. I also really like the animated little guys and the animated pictures. That’s added a lot of fun to our designs.”
Visme’s interactivity feature: “You can add URLs and phone number links directly into the infographic so they can just click and call or go to another page on the website and I really like adding those hyperlinks in.”
You can ask your customers to talk about the different products or features that helped them achieve their business success and draw quotes from each one.
10. Jasper Grows Blog Organic Sessions 810% and Blog-Attributed User Signups 400X
Jasper, an AI writing tool, lacked a scalable content strategy to drive organic traffic and user growth. They needed help creating content that converted visitors into users. Especially when a looming domain migration threatened organic traffic.
To address these challenges, Jasper partnered with Omniscient Digital. Their goal was to turn their content into a growth channel and drive organic growth. Omniscient Digital developed a full content strategy for Jasper AI, which included a content audit, competitive analysis, and keyword discovery.
Through their collaboration, Jasper’s organic blog sessions increased by 810%, despite the domain migration. They also witnessed a 400X increase in blog-attributed signups. And more importantly, the content program contributed to over $4 million in annual recurring revenue.
The combination of storytelling and video testimonials within the case study example makes this a real winner. But there’s a twist to it. Omniscient segmented the video testimonials and placed them in different sections of the case study.
Video marketing , especially in case studies, works wonders. Research shows us that 42% of people prefer video testimonials because they show real customers with real success stories. So if you haven't thought of it before, incorporate video testimonials into your case study.
Take a look at this stunning video testimonial template. With its simple design, you can input the picture, name and quote of your customer within your case study in a fun and engaging way.
Try it yourself! Customize this template with your customer’s testimonial and add it to your case study!

11. How Meliá Became One of the Most Influential Hotel Chains on Social Media

Meliá Hotels needed help managing their growing social media customer service needs. Despite having over 500 social accounts, they lacked a unified response protocol and detailed reporting. This largely hindered efficiency and brand consistency.
Meliá partnered with Hootsuite to build an in-house social customer care team. Implementing Hootsuite's tools enabled Meliá to decrease response times from 24 hours to 12.4 hours while also leveraging smart automation.
In addition to that, Meliá resolved over 133,000 conversations, booking 330 inquiries per week through Hootsuite Inbox. They significantly improved brand consistency, response time and customer satisfaction.
The need for a good case study design cannot be over-emphasized.
As soon as anyone lands on this case study example, they are mesmerized by a beautiful case study design. This alone raises the interest of readers and keeps them engaged till the end.
If you’re currently saying to yourself, “ I can write great case studies, but I don’t have the time or skill to turn it into a beautiful document.” Say no more.
Visme’s amazing AI document generator can take your text and transform it into a stunning and professional document in minutes! Not only do you save time, but you also get inspired by the design.
With Visme’s document generator, you can create PDFs, case study presentations , infographics and more!
Take a look at this case study template below. Just like our case study example, it captures readers' attention with its beautiful design. Its dynamic blend of colors and fonts helps to segment each element of the case study beautifully.

12. Tea’s Me Cafe: Tamika Catchings is Brewing Glory

Tamika's journey began when she purchased Tea's Me Cafe in 2017, saving it from closure. She recognized the potential of the cafe as a community hub and hosted regular events centered on social issues and youth empowerment.
One of Tamika’s business goals was to automate her business. She sought to streamline business processes across various aspects of her business. One of the ways she achieves this goal is through Constant Contact.
Constant Contact became an integral part of Tamika's marketing strategy. They provided an automated and centralized platform for managing email newsletters, event registrations, social media scheduling and more.
This allowed Tamika and her team to collaborate efficiently and focus on engaging with their audience. They effectively utilized features like WooCommerce integration, text-to-join and the survey builder to grow their email list, segment their audience and gather valuable feedback.
The case study example utilizes the power of storytelling to form a connection with readers. Constant Contact takes a humble approach in this case study. They spotlight their customers' efforts as the reason for their achievements and growth, establishing trust and credibility.
This case study is also visually appealing, filled with high-quality photos of their customer. While this is a great way to foster originality, it can prove challenging if your customer sends you blurry or low-quality photos.
If you find yourself in that dilemma, you can use Visme’s AI image edit tool to touch up your photos. With Visme’s AI tool, you can remove unwanted backgrounds, erase unwanted objects, unblur low-quality pictures and upscale any photo without losing the quality.
Constant Contact offers its readers various formats to engage with their case study. Including an audio podcast and PDF.
In its PDF version, Constant Contact utilized its brand colors to create a stunning case study design. With this, they increase brand awareness and, in turn, brand recognition with anyone who comes across their case study.
With Visme’s brand wizard tool , you can seamlessly incorporate your brand assets into any design or document you create. By inputting your URL, Visme’s AI integration will take note of your brand colors, brand fonts and more and create branded templates for you automatically.
You don't need to worry about spending hours customizing templates to fit your brand anymore. You can focus on writing amazing case studies that promote your company.
13. How Breakwater Kitchens Achieved a 7% Growth in Sales With Thryv

Breakwater Kitchens struggled with managing their business operations efficiently. They spent a lot of time on manual tasks, such as scheduling appointments and managing client communication. This made it difficult for them to grow their business and provide the best possible service to their customers.
David, the owner, discovered Thryv. With Thryv, Breakwater Kitchens was able to automate many of their manual tasks. Additionally, Thryv integrated social media management. This enabled Breakwater Kitchens to deliver a consistent brand message, captivate its audience and foster online growth.
As a result, Breakwater Kitchens achieved increased efficiency, reduced missed appointments and a 7% growth in sales.
This case study example uses a concise format and strong verbs, which make it easy for readers to absorb the information.
At the top of the case study, Thryv immediately builds trust by presenting their customer's complete profile, including their name, company details and website. This allows potential customers to verify the case study's legitimacy, making them more likely to believe in Thryv's services.
However, manually copying and pasting customer information across multiple pages of your case study can be time-consuming.
To save time and effort, you can utilize Visme's dynamic field feature . Dynamic fields automatically insert reusable information into your designs. So you don’t have to type it out multiple times.
14. Zoom’s Creative Team Saves Over 4,000 Hours With Brandfolder

Zoom experienced rapid growth with the advent of remote work and the rise of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such growth called for agility and resilience to scale through.
At the time, Zoom’s assets were disorganized which made retrieving brand information a burden. Zoom’s creative manager spent no less than 10 hours per week finding and retrieving brand assets for internal teams.
Zoom needed a more sustainable approach to organizing and retrieving brand information and came across Brandfolder. Brandfolder simplified and accelerated Zoom’s email localization and webpage development. It also enhanced the creation and storage of Zoom virtual backgrounds.
With Brandfolder, Zoom now saves 4,000+ hours every year. The company also centralized its assets in Brandfolder, which allowed 6,800+ employees and 20-30 vendors to quickly access them.
Brandfolder infused its case study with compelling data and backed it up with verifiable sources. This data-driven approach boosts credibility and increases the impact of their story.
Bradfolder's case study goes the extra mile by providing a downloadable PDF version, making it convenient for readers to access the information on their own time. Their dedication to crafting stunning visuals is evident in every aspect of the project.
From the vibrant colors to the seamless navigation, everything has been meticulously designed to leave a lasting impression on the viewer. And with clickable links that make exploring the content a breeze, the user experience is guaranteed to be nothing short of exceptional.
The thing is, your case study presentation won’t always sit on your website. There are instances where you may need to do a case study presentation for clients, partners or potential investors.
Visme has a rich library of templates you can tap into. But if you’re racing against the clock, Visme’s AI presentation maker is your best ally.

15. How Cents of Style Made $1.7M+ in Affiliate Sales with LeadDyno

Cents of Style had a successful affiliate and influencer marketing strategy. However, their existing affiliate marketing platform was not intuitive, customizable or transparent enough to meet the needs of their influencers.
Cents of Styles needed an easy-to-use affiliate marketing platform that gave them more freedom to customize their program and implement a multi-tier commission program.
After exploring their options, Cents of Style decided on LeadDyno.
LeadDyno provided more flexibility, allowing them to customize commission rates and implement their multi-tier commission structure, switching from monthly to weekly payouts.
Also, integrations with PayPal made payments smoother And features like newsletters and leaderboards added to the platform's success by keeping things transparent and engaging.
As a result, Cents of Style witnessed an impressive $1.7 million in revenue from affiliate sales with a substantial increase in web sales by 80%.
LeadDyno strategically placed a compelling CTA in the middle of their case study layout, maximizing its impact. At this point, readers are already invested in the customer's story and may be considering implementing similar strategies.
A well-placed CTA offers them a direct path to learn more and take action.
LeadDyno also utilized the power of quotes to strengthen their case study. They didn't just embed these quotes seamlessly into the text; instead, they emphasized each one with distinct blocks.
Are you looking for an easier and quicker solution to create a case study and other business documents? Try Visme's AI designer ! This powerful tool allows you to generate complete documents, such as case studies, reports, whitepapers and more, just by providing text prompts. Simply explain your requirements to the tool, and it will produce the document for you, complete with text, images, design assets and more.
Still have more questions about case studies? Let's look at some frequently asked questions.
How to Write a Case Study?
- Choose a compelling story: Not all case studies are created equal. Pick one that is relevant to your target audience and demonstrates the specific benefits of your product or service.
- Outline your case study: Create a case study outline and highlight how you will structure your case study to include the introduction, problem, solution and achievements of your customer.
- Choose a case study template: After you outline your case study, choose a case study template . Visme has stunning templates that can inspire your case study design.
- Craft a compelling headline: Include figures or percentages that draw attention to your case study.
- Work on the first draft: Your case study should be easy to read and understand. Use clear and concise language and avoid jargon.
- Include high-quality visual aids: Visuals can help to make your case study more engaging and easier to read. Consider adding high-quality photos, screenshots or videos.
- Include a relevant CTA: Tell prospective customers how to reach you for questions or sign-ups.
What Are the Stages of a Case Study?
The stages of a case study are;
- Planning & Preparation: Highlight your goals for writing the case study. Plan the case study format, length and audience you wish to target.
- Interview the Client: Reach out to the company you want to showcase and ask relevant questions about their journey and achievements.
- Revision & Editing: Review your case study and ask for feedback. Include relevant quotes and CTAs to your case study.
- Publication & Distribution: Publish and share your case study on your website, social media channels and email list!
- Marketing & Repurposing: Turn your case study into a podcast, PDF, case study presentation and more. Share these materials with your sales and marketing team.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Case Study?
Advantages of a case study:
- Case studies showcase a specific solution and outcome for specific customer challenges.
- It attracts potential customers with similar challenges.
- It builds trust and credibility with potential customers.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of your company’s problem-solving process.
Disadvantages of a case study:
- Limited applicability. Case studies are tailored to specific cases and may not apply to other businesses.
- It relies heavily on customer cooperation and willingness to share information.
- It stands a risk of becoming outdated as industries and customer needs evolve.
What Are the Types of Case Studies?
There are 7 main types of case studies. They include;
- Illustrative case study.
- Instrumental case study.
- Intrinsic case study.
- Descriptive case study.
- Explanatory case study.
- Exploratory case study.
- Collective case study.
How Long Should a Case Study Be?
The ideal length of your case study is between 500 - 1500 words or 1-3 pages. Certain factors like your target audience, goal or the amount of detail you want to share may influence the length of your case study. This infographic has powerful tips for designing winning case studies
What Is the Difference Between a Case Study and an Example?
Case studies provide a detailed narrative of how your product or service was used to solve a problem. Examples are general illustrations and are not necessarily real-life scenarios.
Case studies are often used for marketing purposes, attracting potential customers and building trust. Examples, on the other hand, are primarily used to simplify or clarify complex concepts.
Where Can I Find Case Study Examples?
You can easily find many case study examples online and in industry publications. Many companies, including Visme, share case studies on their websites to showcase how their products or services have helped clients achieve success. You can also search online libraries and professional organizations for case studies related to your specific industry or field.
If you need professionally-designed, customizable case study templates to create your own, Visme's template library is one of the best places to look. These templates include all the essential sections of a case study and high-quality content to help you create case studies that position your business as an industry leader.
Get More Out Of Your Case Studies With Visme
Case studies are an essential tool for converting potential customers into paying customers. By following the tips in this article, you can create compelling case studies that will help you build trust, establish credibility and drive sales.
Visme can help you create stunning case studies and other relevant marketing materials. With our easy-to-use platform, interactive features and analytics tools , you can increase your content creation game in no time.
There is no limit to what you can achieve with Visme. Connect with Sales to discover how Visme can boost your business goals.
Easily create beautiful case studies and more with Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Shots - Health News
Mammograms have pros and cons. women can handle the nuance, study argues.
Ronnie Cohen

The most recent recommendation of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force is that all women 40 to 74 get mammograms every other year. A previous recommendation said screening should start at 50. One doctor suggests that people "test smarter, not test more." Heather Charles/Tribune News Service via Getty Images hide caption
New research makes the case for educating women in their 40s — who've been caught in the crossfire of a decades-long debate about whether to be screened for breast cancer with mammograms — about the harms as well as the benefits of the exam.
After a nationally representative sample of U.S. women between the ages of 39 and 49 learned about the pros and cons of mammography, more than twice as many elected to wait until they turn 50 to get screened, a study released Monday in the Annals of Internal Medicine found.
Most women have absorbed the widely broadcast message that screening mammography saves lives by the time they enter middle age. But many remain unaware of the costs of routine screening in their 40s — in false-positive results, unnecessary biopsies, anxiety and debilitating treatment for tumors that left alone would do no harm.
"In an ideal world, all women would get this information and then get to have their further questions answered by their doctor and come up with a screening plan that is right for them given their preferences, their values and their risk level," said social psychologist Laura Scherer , the study's lead author and an associate professor of research at the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
Of 495 women surveyed, only 8% initially said they wanted to wait until they turned 50 to get a mammogram. After researchers informed the women of the benefits and the harms, 18% said they would wait until 50.
"We're not being honest"
Learning about the downsides of mammograms did not discourage women from wanting to get the test at some point, the study showed.
The benefits and the harms of mammography came as a surprise to nearly half the study's participants. More than one-quarter said what they learned from the study about overdiagnosis differed from what their doctors told them.
"We're not being honest with people," said breast cancer surgeon Laura Esserman , director of the University of California San Francisco Breast Care Center, who was not involved with the research.
"I think most people are completely unaware of the risks associated with screening because we've had 30, 40 years of a public health messaging campaign: Go out and get your mammogram, and everything will be fine," she said in an NPR interview.

What is the breast cancer calculator actor Olivia Munn suggested after her mastectomy?
Esserman sees women who are diagnosed with slow-growing tumors that she believes in all likelihood would never harm them. In addition, mammography can give women a false sense of security, she said, like it did for Olivia Munn .
The 44-year-old actress had a clean mammogram and a negative test for cancer genes shortly before her doctor calculated her score for lifetime breast cancer risk, setting off an alarm that led to her being treated for fast-moving, aggressive breast cancer in both breasts.
Toward a personalized plan for screening
Esserman advocates for a personalized approach to breast cancer screening like the one that led to Munn's diagnosis. In 2016, she launched the WISDOM study , which aims to tailor screening to a woman's risk and, in her words, "to test smarter, not test more."
The National Cancer Institute estimates that more than 300,000 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer and 42,250 will die in the U.S. this year. Incidence rates have been creeping up about 1% a year, while death rates have been falling a little more than 1% a year.

We're not dying of metastatic breast cancer. We're living with it
For the past 28 years, the influential U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has been flip-flopping in its recommendations about when women should begin mammography screening.
From 1996 until 2002, the independent panel of volunteer medical experts who help guide physicians, insurers and policymakers said women should begin screening at 50. In 2002, the task force said women in their 40s should be screened every year or two. In 2009, it said that 40-something women should decide whether to get mammograms based on their health history and individual preferences.
The new study was conducted in 2022, when the task force guidelines called for women in their 40s to make individual decisions.
New guidelines
In 2024, the panel returned to saying that all women between the ages of 40 and 74 should be screened with mammograms every other year. Rising breast cancer rates in younger women, as well as models showing the number of lives that screening might save, especially among Black women, drove the push for earlier screening.
An editorial accompanying the new study stresses the need for education about mammography and the value of shared decision-making between clinicians and patients.
"For an informed decision to be made," states the editorial written by Dr. Victoria Mintsopoulos and Dr. Michelle B. Nadler, both of the University of Toronto in Ontario, "the harms of overdiagnosis — defined as diagnosis of asymptomatic cancer that would not harm the patient in the future — must be communicated."
- breast cancer
- mammography
The power of peer recognition points: does it really boost employee engagement?
Strategic HR Review
ISSN : 1475-4398
Article publication date: 8 July 2024
This paper aims to explore the impact of peer recognition points (PRP) on employee engagement and motivation within organizations. It investigates whether PRP systems genuinely satisfy employees’ need for appreciation and how they can be effectively implemented to enhance employee performance and retention.
Design/methodology/approach
This study uses a comprehensive literature review and analysis of existing peer recognition platforms alongside case studies of organizations implementing PRP systems. Surveys and qualitative interviews with employees and HR professionals provide additional insights into the practical application and effectiveness of PRP.
The research indicates that PRP systems significantly boost employee engagement and motivation by fulfilling the psychological need for recognition. Organizations with robust PRP programs experience lower voluntary turnover rates and higher employee satisfaction. The study also identifies and addresses potential challenges, such as lack of interest or shy employees, for implementing PRP systems effectively.
Research limitations/implications
While the study offers substantial insights into PRP's benefits, it acknowledges the limitations of generalizability due to the primary focus on IT companies. Future research should examine a more diverse range of industries and consider long-term effects. Additionally, the study emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring and adjustment of PRP systems to sustain their effectiveness.
Practical implications
The most important value of the paper is the actionable strategies provided for managers and organizations to integrate PRP into various work cultures and systems. These strategies focus on enhancing team morale and productivity, ensuring adaptability across different industries and organizational structures. The findings serve as a practical guide for fostering a more appreciative and motivated workplace culture.
Social implications
By promoting a culture of recognition and appreciation, PRP systems contribute to a more positive and supportive work environment. This, in turn, can lead to improved employee well-being, job satisfaction and a sense of belonging, ultimately enhancing the overall social dynamics within the workplace.
Originality/value
This paper contributes to the understanding of nonmonetary recognition strategies in HR management. It highlights the psychological benefits of peer recognition and provides practical recommendations for organizations seeking to improve their employee engagement through PRP systems. The findings offer valuable insights for HR practitioners aiming to foster a more appreciative and motivated workplace culture.
- Employee engagement
- Organizational behavior
- Employee retention
- Workplace culture
- HR management
- Peer recognition
- Non-monetary rewards
Rusin, N. and Szandała, T. (2024), "The power of peer recognition points: does it really boost employee engagement?", Strategic HR Review , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/SHR-06-2024-0040
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2024, Natalia Rusin and Tomasz Szandała.
Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial & non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
Organizations worldwide strive to build an environment where employees feel appreciated. An adequate salary or social benefits may be the keys; however, the answer may be even more straightforward. It turns out that 84% of people think it is essential to receive rewards for their efforts ( Reward Gateway, 2022 ). While rewards themselves are important, recognition is what really drives employee engagement and productivity. Even 78% of employees looking to leave their job said they would stay if the company offered more recognition and reward ( Reward Gateway, 2022 ). Employees who feel appreciated and valued are more likely to stay engaged and motivated to contribute their best work.
Unsurprisingly, positive affirmation from line managers or higher management undeniably validates one’s efforts, enhancing the prospects of job security, promotions or salary increments. However, according to a survey by QuantumWorkplace, 41% of employees value acknowledgment from their peers or even those lower on the organizational chart just as much as they do from their superiors. It means that the source of praise does not diminish its impact, as the joy of being recognized transcends organizational structure and is fulfilling regardless of who delivers it. The challenge is to provide all the employees with an equal and efficient possibility to freely recognize each other's contributions, help and hard work. Organizations can fulfill this need by introducing a peer recognition system, such as peer recognition points (PRP). Popular peer recognition platforms include Kudos or Applauz, which allow staff members to praise their peers by giving each other points or virtual tokens that can be later spent on chosen awards. Are these PRP another superficial answer to the need for appreciation, or are they genuinely satisfying for the employees?
This study will answer this question by discussing the impact of recognition, the concept of PRP and how self-motivation is connected with PRP. Most importantly, we will indicate how organizations can use it to boost employee engagement effectively.
The impact of peer recognition
Adrian Gostick and Chester Elton, authors of Leading with Gratitude, found that 67% of managers think they are above average in offering praise and recognition to their employees. However, only 23% of their subordinates agree. The discrepancy is significant, indicating that the need for recognition is much higher than the managers expect. Increasing the frequency of acknowledging employees’ efforts can positively impact engagement and productivity. Bersin and associates found that companies with a strong culture of recognition have a 31% lower voluntary turnover rate. Peer recognition can be a powerful tool to fulfill employees’ need for appreciation without introducing complex processes. However, how much impact can it have?
According to a study by Globoforce, companies that use peer recognition have a 14% higher employee engagement rate than those that do not. Additionally, a survey by Achievers found that 92% of employees surveyed felt more engaged with their work when they received recognition from their peers. Peer recognition has been successfully applied in many institutions and organizations. For instance, Keck Medicine of (University of Southern California) USC provides staff with opportunities for on-the-spot, peer-to-peer recognition with Trojan Bucks and Trojan Points. As a result, employee engagement was boosted by 16% ( Ryan, 2016 ). The University of British Columbia saw an even more significant increase after implementing a peer-to-peer recognition program called “Applause”, where employees awarded contributions with digital badges. The initiative positively impacted engagement ( Figure 1 ), with a 23% increase and a 26% gain in recognition messages sent ( Gallup, 2019 ).
The concept of peer recognition points
One of the ways of including peer recognition in daily work is by introducing the idea of PRP. The general concept is to give employees some points each period which can be given to co-workers to show appreciation for their hard work on a project, help or various initiatives. For instance, regardless of experience or seniority, every employee gets 2,000 points each quarter; however, they cannot use them for themselves. The only possible operation is to award peers by transferring a selected number of points and a note of appreciation. They can be donated either publicly or privately, and they can also be given anonymously.
Moreover, some platforms allow users to make a quick, additional donation for those employees that received public recognition if they feel it is worth further appreciation. The time when employees can transfer their points to other peers is limited. If not all points are donated within a given timeframe, they expire. The points an employee has collected from peers can be exchanged for awards such as vouchers, electronics and virtual goods, and there is no time limit for collecting the awards. Sometimes an employee can collect the gift even after finishing their job at a company.
In some cases, the managers might give additional points outside their personal pool for outstanding contributions to the company or participation in a contest or hackathon. The admin can usually access statistics of PRP. Many platforms implement the idea of PRP, such as Kudos, Motivosity, Reward Gateway, Applauz and Bonusly. They may differ slightly, but the general concept remains the same, regardless of the system the company is using.
Psychological aspects of intrinsic motivation and peer recognition points
Understanding the psychological factors behind motivation is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of PRP. At its core, peer recognition taps into employees’ intrinsic motivation by aligning with their desire for autonomy and empowerment. Longing for a sense of achievement or personal growth are key drivers of intrinsic motivation. By recognizing peers, employees feel more connected to their work and team, boosting their self-motivation.
The principles of autonomy, mastery and relatedness, as proposed by self-determination theory, align with the practice of peer recognition. Autonomy is fostered as employees have control over whom they recognize and why. Mastery is encouraged by promoting the recognition of skills and growth within the workplace. Relatedness is built through the strengthening of interpersonal connections and the cultivation of a positive team environment. The connection between self-motivation and PRP reveals an exciting path toward employee satisfaction, engagement and overall well-being. By understanding these psychological factors, organizations can design and implement peer recognition programs that resonate with their employees’ innate desires and drive them to excel in their roles.
Show, do not tell : Actions, through awarding points, resonate more than mere words, demonstrating genuine appreciation.
Catalyze the movement : Giving and receiving points can inspire emulation of positive behaviors, spotlighting valued actions.
Celebrate progress : Recognize small wins and growth, not just significant achievements, fostering an environment of continuous encouragement.
Change the narrative : Recognitions can emphasize collaboration and connection over mere business outcomes, transforming workplace conversations.
Anchor through artifacts : Visual representations of points, like leaderboards or awards, serve as reminders of the value of human connections.
Demonstrate the value : The data from these recognition points can tangibly showcase the economic and cultural merits of close-knit workplace relationships.
Incorporating PRP amplifies the principles of “Elevating the Human Experience” but also addresses core psychological aspects of motivation, creating an environment of intrinsic drive and deepened connections. In summary, from a psychological point of view with PRP organizations can craft a workspace where individuals feel seen, appreciated and invigorated to contribute their best.
The pros of peer recognition points
There are several advantages to introducing PRP, as they benefit employees and organizations simultaneously.
The most prominent asset of PRP lies in the root of their idea. It aims to encourage employees to take notice of their colleagues’ contributions and accomplishments. By recognizing mutual work, employees are more likely to feel a sense of belonging and camaraderie, strengthening the team’s bounds. Moreover, in this situation, the principle of hope for favor return comes into play as employees will recognize their peers, hoping that somebody could acknowledge their efforts back.
Furthermore, PRP are an effective tool that helps organizations fulfill employees’ need for recognition. They provide instant feedback and gratification, boosting morale and motivation. The cycle of donating and receiving points repeats; therefore positive impact can be sustained in the long term. There are no negative points, so the possibility of discouragement is limited. Notably, the risk of conflict or jealousy is low as the points are donated by all peers, not just the managers.
PRP are a low-cost and easily scalable way to recognize employees’ contributions and initiatives ( Figure 2 ). The system only requires a little attention from HR departments or managers, apart from monitoring possible pathologies, which are discussed later. In many organizations, the efforts are recognized only periodically, e.g. annually or during special events or competitions. This way decreases significantly the number of awarded people and gratitude to only a small group of top performers. With PRP, it is possible to show appreciation for all contributions daily, which makes recognition more accessible to everyone.
Another benefit is spending the points according to the employee’s desire. This approach can accidentally train people to accumulate assets, as some rewards may require more points. At the same time, the need to collect more expensive awards can mean the employee will keep working in the organization.
In the context of the article “How to Create Belonging for Remote Workers” ( Fosslien and West-Duffy, 2019 ), addressing the challenge of fostering a sense of belonging among remote employees is essential. In the post-COVID era, as remote work happens daily and face-to-face interactions are minimized, the PRP system encourages employees to take more exposed and noteworthy actions, ensuring their work does not go unnoticed in a virtual environment. The pursuit of recognition is a reason to facilitate teamwork and collaboration, strengthening bonds among remote colleagues. The PRP system becomes a strategic tool for maintaining cohesion and community in an increasingly dispersed work world, effectively responding to the challenges and opportunities of the new normal.
Finally, points can be an additional factor for motivating people to perform their duties on time, like doing mandatory training or submitting reviews and documents required by company’s policy ( Black, 2023 ). Finally, it can act later during an employee’s salary or annual incentive review evaluation as a measurable factor. It can be considered from multiple angles: is this person recognized only from inside their team or from others? Are donors the same people each period or different? The statistics provided by PRP systems can be helpful for managers to observe how the teams interact internally and as a whole organization.
Understanding resistance and overcoming the challenges of adoption
Despite having many benefits, there are also potential drawbacks and reasons why only some companies embrace PRP. We have surveyed people ( Figure 3 ): why is your company not using PRP to engage employees? Respondents had to specify their role: ordinary employee, manager or director and HR specialist and could give several reasons. Furthermore, they were able to justify the shared concern.
Over one-third of employees and almost two-thirds of managers were unaware of such systems. This implies the importance of PRP popularization efforts like this article.
The big concern, mainly for HR departments, is the cost for the company. While the value of a single point can be freely adjusted by the company individually, it is worth mentioning that PRP generates costs when they can be exchanged for rewards. This is also tied to the complexity of tax payments, especially nowadays, as many companies hire internationally, so different policies apply. We can address this by simplifying awards, for instance by limiting them only to vouchers that do not require an individual approach. Furthermore, management raised concerns regarding complexity of such systems as they fear that PRP might be included in periodic reviews of employees. Organizations would have to carefully adjust the value of the points in comparison to other factors to minimize this issue. Still, PRP systems provided by third-party companies come with built-in tracking systems that can facilitate the process rather than be an obstacle, as they could provide insight into employees’ cooperation and activity inside the company.
Other concerns focus on the pathologies of PRP. The first one, mainly raised by employees, is the quantity over quality of recognition. This leads to the “gaming” mentality, where employees are more concerned with earning points than recognizing meaningful contributions. Another related issue is the risk of creating the custom of points swapping, noticed by HR specialists, especially near the end of the period. Because the unused points expire, some employees might agree to donate them to one another without any significant reason. This aspect can be addressed effectively by limiting the maximum number of points an employee can transfer to a particular person within a period. Finally, people who are shy or introverted might have a more challenging time getting recognized for their valuable work. It may be a setback in the case of peer recognition, as a genuinely deserving person might be omitted due to not being prominent. On the other hand, this issue is not specific to only PRP, as research suggests that introverted individuals can face difficulties in recognition and promotion in the workplace even when they perform well (The Hidden Advantages of Quiet Bosses, HBR 2013). A suggested approach to counter this issue is to allow for rewarding the whole team working on a particular project, not just an individual.
Our study also confirms other studies that demonstrate people acknowledge the recognition, regardless of its source, as less than one in ten respondents valued only managers’ recognition as an essential factor against introducing PRP.
On the other hand, there is the lack of interest of employees in PRP. All three groups of respondents notice it as a severe obstacle. Some employees may feel uncomfortable giving or receiving recognition from their peers. Among the reasons for this behavior, we can list personality traits or simply a lack of interest in participation in the program. A reluctant approach might also be caused by cultural differences or a solid attachment to a company's hierarchical structure. To minimize negative responses to PRP, a behavioral prediction analysis should be performed to evaluate potential risks, e.g. a summary of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis. No matter how well the system is designed and easy to maintain, it is up to the employees to fully embrace its potential and benefits. Most importantly, the PRP may not effectively address deeper employee engagement and motivation issues, such as workload, job design or leadership. If all the mentioned aspects are lacking, PRP will not be a satisfactory solution to an organization’s problems. The crucial thing is constant monitoring, reviewing and adjusting rules of PRP to satisfy all employees, management and HR in having a healthy working environment.
Making the most of peer recognition points
There are several good practices that organizations should follow to make the most of PRP.
Align peer recognition with company values : Peer recognition should become a custom tied to the organization’s core values and goals. Additionally, the acknowledged effort should be linked to a particular company value so that employees can understand how their actions align with the company’s principles. A green-energy investment bank dedicated to financing environmentally sustainable projects can recognize the importance of aligning internal practices with its mission of ecological responsibility. Employees should be encouraged to identify peers who demonstrated exemplary eco-friendly behaviors, such as organizing carpooling, reducing paper usage and proposing or participating in community green initiatives, by giving them a certain amount of points. By doing so, they become a way to strengthen the company’s mission and culture without overwhelming the employee. A good example can be Salesforce’s Ohana program, where employees are encouraged to perform peer-supportive actions like carsharing during work commuting. Each trip can be recognized with e-Thanks redeemable for small vouchers to Amazon.
Encourage frequent appreciation : Peer recognition should be encouraged regularly. Organizations can achieve it through regular reminders, prompts and by integrating peer recognition into daily workflows. PRP can help foster frequent appreciation as they often expire after a certain period. For instance, employees of MultiMedia LLC are granted hundred points per month to be spent within that period. By doing so, employees can freely recognize each other’s efforts without worrying about the lack of points to give. As the points expire after a month, frequent reminders are shared on the company’s social channels like Slack or Gmail.
Recognize all efforts : The concept should be inclusive and recognize all contributions, big or small. It aids in creating a culture of appreciation and recognition, which is essential for building a positive workplace and boosting engagement. PRP are an efficient tool to help achieve this as they can easily be implemented into daily workflows like code review in IT companies. Pink Identity proposed such a solution in their product PinkDataGovernance. If a code review had been accepted, all employees who contributed to this process would have been automatically given points.
Measure and track : Organizations should monitor PRP to understand their impact on employee engagement and productivity. A multitude of third-party SaaS tools provides a visible recognition dashboard. Such a solution was used in a company Vonage, wherein the tool Applauze employees could browse the list of recent recognitions and the number of points granted in each donation. To minimize the risk of rivalry, the total amount of points each employee collected was not available publicly. However, this tool provided detailed statistics to HR departments to help make improvements and adjust the program to ensure it is relevant and timely.
Be precise : When introducing the recognition system, emphasize the need for specific details about acknowledged actions. It is crucial to tailor the note of appreciation to the person and avoid a generic message that has been used numerous times. Nokia encourages such an approach in their Everyday Excellence program, where providing a custom comment is obligatory when sending e-thanks for recognizing employees’ efforts with points. Giving explicit recognition has a positive impact, making employees 2.5 times more likely to repeat their behavior ( Globoforce, 2018 Employee Recognition Report).
The success of PRP relies heavily on the organization’s culture. If introduced properly, the system can boost employee engagement, but the positive impact might be limited without proper care, supervision and encouragement.
Numerous pieces of research prove that employees must be recognized for their efforts and contributions. PRP are an efficient and scalable solution that, when introduced correctly, can effectively boost employee engagement while fulfilling the need for acknowledgment ( Figure 4 ). Aligning the recognition process with the company’s values can increase awareness of an organization’s mission. It can be a great tool to spark employee creativity while looking for new ways to be recognized. Furthermore, it teaches the importance of valuing all kinds of efforts, not only the big ones. By including this concept in daily workflows, organizations can encourage employees to appreciate each other’s contributions and strengthen workplace culture. PRP differ from traditional recognition methods. At the same time, they fulfill the natural desire for connection and growth, making them a unique and valuable approach to maintaining a positive and engaged workplace.
Statistics about peer recognition impact on organization
Balance between peer recognition investments and return
Survey results among employees, managers and HR specialists
Summary of benefits from peer recognition points
Black , P.W. ( 2023 ), “ The effect of peer-to-peer recognition systems on helping behavior: the influence of rewards and group affiliation ”, Accounting, Organizations and Society , Vol. 109 .
Fosslien , L. and West-Duffy , M. ( 2019 ), “ How to create belonging for remote workers ”, MIT Sloan Management Review .
Gallup ( 2019 ), “ Why peer-to-Peer recognition Is powerful ”, available at: www.gallup.com/workplace/242230/why-peer-peer-recognition-powerful.aspx
Globoforce ( 2018 ), “ SHRM/globoforce employee recognition report ”, available at: www.shrm.org/hr-today/trends-and-forecasting/research-and-surveys/pages
Reward Gateway ( 2022 ), “ 2022 Reward gateway summit ”, available at: www.rewardgateway.com/uk/resource/summit-digital-experience-2022
Ryan , C. ( 2017 ), “ Sustaining and growing a winning culture ”, Journal of Healthcare Management , Vol. 62 No. 6 , pp. 361 - 365 .
Further reading
Achievers ( 2020 ), “ The state of employee recognition ”, available at: www.achievers.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/2020-State-of-Employee-Recognition-Report.pdf
QuantumWorkplace ( 2023 ), “ The importance of employee recognition: statistics and research ”, available at: www.quantumworkplace.com/future-of-work/importance-of-employee-recognition
Bersin & Associate ( 2013 ), “ The state of employee recognition in 2012 ”.
Gostick , A. and Elton , C. ( 2020 ), Leading with Gratitude: Eight Leadership Practices for Extraordinary Business Results , HarperCollins .
Grant , A.M. , Gino , F. and Hofmann , D.A. ( 2010 ), “ The hidden advantages of quiet bosses ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 88 No. 12 , p. 28 .
Wang , P. ( 2023 ), “ When peer recognition backfires: the impact of peer information on subsequent helping behavior ”, Accounting Perspectives – May 2023 .
Corresponding author
About the authors.
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
- Data Science
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI ML DS Interview Series
- AI ML DS Projects series
- Data Engineering
- Web Scrapping
Roles of Generative AI in Drug is Discovery: Advantages, Case Studies and Examples
Drug discovery is a complex and costly process, often taking years and billions of dollars to bring a new drug to market. Traditional methods involve extensive experimentation and testing, which can be both time-consuming and inefficient. Enter generative AI—a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform the landscape of drug discovery.
This article explores the Roles of Generative AI in drug discovery, highlighting its advantages, presenting case studies, and providing examples of its successful application.
Table of Content
What is Generative AI?
Role of generative ai in drug discovery, advantages of generative ai in drug discovery, case studies and examples of gen ai in drug discovery, challenges and limitations of using gen ai in drug discovery.
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence systems that can generate new content, ideas, or data that resemble the patterns observed in their training data. Unlike traditional AI, which primarily focuses on recognition, classification, and prediction, Generative AI is designed to create new outputs. This can include generating text, images, music, or even designing new molecules.
Generative AI plays a transformative role in drug discovery by enhancing the efficiency, speed, and creativity of the process. Here’s a breakdown of its key roles:
1. Molecular Generation and Optimization
- Novel Molecule Design : Generative AI algorithms can design new molecules with desired properties by learning from vast chemical datasets. This is crucial for identifying potential drug candidates that may not have been considered using traditional methods.
- Property Optimization : AI can optimize the chemical structure of molecules to improve their efficacy, reduce toxicity, and enhance other desirable properties, such as solubility and stability.
2. Target Identification and Validation
- Identifying Biological Targets : Generative AI can help identify new biological targets (e.g., proteins, genes) that are associated with specific diseases. This is done by analyzing biological data and predicting interactions between molecules and targets.
- Validating Targets : AI models can simulate and predict how potential drug candidates interact with biological targets, aiding in the validation of these targets as viable for drug development.
3. De Novo Drug Design
- Designing Drugs from Scratch : Generative AI can create entirely new drug-like molecules (de novo design) that have not been seen before. This is particularly useful for developing treatments for diseases with few existing therapeutic options.
- Generating Drug Candidates : AI systems can rapidly generate a diverse set of potential drug candidates, which can then be tested and refined in laboratory and clinical settings.
4. Predicting Drug-Drug Interactions and Side Effects
- Interaction Prediction : Generative AI can predict how new drug candidates might interact with other medications, which is crucial for avoiding adverse effects in patients.
- Side Effect Profiling : By analyzing patterns in data, AI can predict potential side effects of new drugs, helping to mitigate risks early in the drug development process.
5. Accelerating the Drug Discovery Pipeline
- Data-Driven Insights : Generative AI can analyze vast amounts of biomedical data to provide insights that guide researchers in drug discovery, such as identifying biomarkers or suggesting potential drug combinations.
- Reducing Time and Cost : By automating parts of the discovery process and generating a large number of candidates, AI can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional drug development.
6. Personalized Medicine
- Customized Treatments : Generative AI can aid in the development of personalized medicines tailored to individual genetic profiles, improving treatment efficacy and reducing adverse reactions.
7. Case Studies and Success Stories
- Real-world examples include AI-driven discoveries of new antibiotics, treatments for rare diseases, and optimization of existing drugs for new therapeutic uses.
Generative AI offers several advantages in the field of drug discovery, significantly enhancing the process by making it more efficient, cost-effective, and innovative. Here are some key advantages:
1. Accelerated Drug Discovery Process
- Rapid Molecule Generation : Generative AI can quickly generate a vast number of potential drug candidates, drastically reducing the time needed to identify promising compounds.
- Faster Screening : AI can automate and speed up the screening of these candidates for desirable properties, such as potency, selectivity, and safety.
2. Cost Reduction
- Lower Research Costs : By automating the initial phases of drug discovery, AI reduces the need for expensive laboratory work and manual experimentation.
- Efficient Resource Utilization : AI-driven predictions help focus resources on the most promising candidates, minimizing the costs associated with pursuing less viable options.
3. Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
- Novel Compound Discovery : Generative AI can explore chemical space in ways that human researchers may not, leading to the discovery of novel compounds that could be missed by traditional methods.
- Design of Unconventional Molecules : AI can design unconventional molecules with unique structures, expanding the possibilities for new types of drugs.
4. Improved Success Rates
- Better Prediction of Efficacy and Safety : AI models can predict the biological activity and potential side effects of compounds, helping to weed out less promising candidates early on.
- Reduced Failure Rates : By focusing on more promising candidates, AI reduces the likelihood of failures in later stages of development, which are often costly and time-consuming.
5. Precision and Personalization
- Tailored Treatments : Generative AI can design drugs tailored to specific genetic profiles or disease states, enabling more personalized medicine approaches.
- Biomarker Identification : AI can help identify biomarkers that predict how different patients will respond to a particular drug, guiding personalized treatment plans.
6. Data-Driven Insights
- Utilization of Big Data : Generative AI can analyze and integrate vast amounts of biological and chemical data, uncovering patterns and insights that may not be evident to human researchers.
- Informed Decision-Making : These insights enable more informed decision-making throughout the drug discovery process, from initial research to clinical trials.
7. Scalability and Reproducibility
- High Throughput : AI systems can handle large-scale data and processes, enabling high-throughput screening and analysis.
- Consistent Results : AI models provide consistent and reproducible results, reducing the variability and subjectivity that can arise in manual research.
Generative AI has made significant contributions to drug discovery, with several notable case studies and examples showcasing its potential. Here are a few prominent examples:
1. BenevolentAI and Baricitinib for COVID-19
- Context : During the COVID-19 pandemic, the urgent need for effective treatments led to the repurposing of existing drugs. BenevolentAI, a company specializing in AI-driven drug discovery, used its platform to identify potential treatments.
- AI Role : The AI system analyzed vast amounts of biomedical data to identify existing drugs that could potentially inhibit the virus’s ability to enter and infect human cells.
- Outcome : The AI identified baricitinib, a drug originally used for rheumatoid arthritis, as a potential treatment. Clinical trials confirmed its efficacy in reducing the severity of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients.
2. Insilico Medicine and New Drug Candidates
- Context : Insilico Medicine, a biotechnology company, uses AI to accelerate drug discovery and development. They focus on generating novel molecules for various diseases.
- AI Role : Using generative adversarial networks (GANs) and reinforcement learning , Insilico Medicine designed a new molecule targeting a protein associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- Outcome : The AI-designed drug candidate was synthesized and tested, showing promising results. This process took less than 50 days, significantly faster than traditional drug discovery timelines.
3. Exscientia and DSP-1181
- Context : Exscientia, an AI-driven pharmaceutical company, collaborated with Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma to develop new drug candidates.
- AI Role : Their AI platform, Centaur Chemist, designed DSP-1181, a drug candidate for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
- Outcome : The drug was successfully advanced to clinical trials, marking it as one of the first AI-designed drugs to reach this stage. The AI system reduced the typical timeline from initial compound design to clinical trials from years to just a few months.
4. Atomwise and Malaria Drug Discovery
- Context : Atomwise, known for its AI platform AtomNet, partnered with various organizations to discover new drugs for diseases like malaria.
- AI Role : AtomNet used deep learning to predict the binding affinity of small molecules to protein targets, screening millions of compounds in silico.
- Outcome : The platform identified potential compounds that could act against drug-resistant strains of malaria, leading to further research and development efforts.
5. EQRx and AI-Driven Drug Pricing
- Context : EQRx aims to develop affordable new medicines using AI. The company focuses on reducing drug costs by leveraging AI in the drug discovery and development process.
- AI Role : EQRx uses AI to streamline the discovery process, from target identification to molecule design, aiming to cut costs and pass the savings onto patients.
- Outcome : The company has initiated multiple drug programs, demonstrating the potential of AI to reduce the overall cost of drug development and make treatments more accessible.
6. Gero and Anti-Aging Research
- Context : Gero, a biotech company, uses AI to discover drugs that target aging and age-related diseases.
- AI Role : The AI analyzes biological data to understand the mechanisms of aging and identify potential therapeutic targets.
- Outcome : Gero’s AI platform has identified several promising compounds that could potentially extend lifespan and improve healthspan, which are under preclinical investigation.
While Generative AI offers many benefits in drug discovery, it also comes with several challenges and limitations. Addressing these is crucial for realizing the full potential of AI in this field. Here are some key challenges and limitations:
1. Data Quality and Availability
- Limited and Biased Data : The effectiveness of Generative AI relies heavily on high-quality data. However, the available datasets may be limited, biased, or incomplete, affecting the AI models’ accuracy and generalizability.
- Data Privacy and Security : Accessing and utilizing sensitive patient data or proprietary information involves significant privacy and security concerns. Ensuring data protection while training AI models is a complex challenge.
2. Complexity of Biological Systems
- Biological Complexity : The human body is highly complex, and accurately modeling biological processes, interactions, and disease mechanisms is challenging. Generative AI models may oversimplify these systems, leading to inaccurate predictions.
- Unanticipated Side Effects : AI-generated compounds may exhibit unexpected interactions or side effects that are not predicted during the computational phase, necessitating extensive laboratory and clinical validation.
3. Computational Limitations
- High Computational Costs : Training advanced AI models, especially those involving deep learning and large-scale simulations, requires significant computational resources, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Scalability Issues : Scaling AI models for practical use in drug discovery, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex simulations, poses technical and logistical challenges.
4. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
- Regulatory Approval : Drugs developed or identified using AI need to go through rigorous regulatory processes to ensure safety and efficacy. Regulatory agencies may lack the frameworks or expertise to evaluate AI-derived drugs, potentially slowing down approval processes.
- Ethical Concerns : The use of AI in drug discovery raises ethical questions, including the potential for AI bias, the transparency of AI decision-making processes, and the implications of AI-generated intellectual property.
5. Interpretability and Transparency
- Black Box Nature : Many AI models, particularly deep learning systems, are often described as “black boxes” because they lack interpretability. Understanding how the model arrives at specific predictions is crucial for gaining trust and ensuring safety in drug discovery.
- Lack of Explainability : Without explainable AI models, it can be challenging to identify why a particular molecule or target was selected, making it difficult for researchers to validate and trust the results.
Generative AI is revolutionizing the field of drug discovery, offering unprecedented speed, cost efficiency, and innovation. By leveraging advanced algorithms and vast datasets, AI can generate novel drug candidates, predict drug-target interactions, optimize drug properties, and perform virtual screening. Case studies from companies like Insilico Medicine, Atomwise, Exscientia, BenevolentAI, and Schrödinger demonstrate the transformative potential of generative AI in bringing new drugs to market more quickly and efficiently.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- AI-ML-DS Blogs
- Artificial Intelligence AI Blogs
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
More From Forbes
New study finds that a guaranteed income does not guarantee benefits.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
A man in a gray T-shirt holds dollars in his hands. Bank. Casino. Salary. Rates.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, the idea of a guaranteed income (or universal basic income (UBI)) took off. Cities from Philadelphia to Compton partnered with philanthropists to conduct several experiments to examine the health and economic impacts of giving people money with no strings attached. The results of these and other programs have been mixed, providing support for both critics and fans.
A recent, comprehensive study that uses a randomized controlled trial provides new evidence that largely supports the critics who worry that a guaranteed income will undermine work and investment while doing little to promote healthy behaviors.
The study gave 1,000 people, chosen randomly from select counties in Illinois and Texas, $1,000 per month for three years. A control group of 2,000 people received $50 per month for three years. The $1,000 per month payment was approximately a 40% increase in total household income for the average participant. This substantial increase in income combined with the three-year time frame should have been enough to improve various outcomes, but that is not what happened.
The authors examined several health outcomes , including stress, mental health, and physical health, the latter measured via both self-reporting and clinical blood tests. Initially, the treated group reported improvements in stress and mental health relative to the control group, but by the second year the gap closed. Similarly, there was an initial decline in food insecurity for the treated group, but that effect also disappeared by year two.
The cash payments had no impact on physical health, nor did they induce better health behaviors such as more sleep or exercise. People in the treated group made more hospital and emergency room visits relative to those in the control group and used more dental care, but greater use of these services did not translate to better health outcomes.
‘Say It To My Face’: Harris Issues New Trump Debate Challenge At Raucous Atlanta Rally
Nyt ‘strands’ hints, spangram and answers for wednesday, july 31st, today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for wednesday, july 31.
What about the economic impacts? One prediction from economic models of cash transfers is that recipients will work less and spend more time on non-work activities. Sure enough , the people in the treated group worked less than those in the control group and increased the time they spent on leisure activities. The decline in work hours led to smaller paychecks, which offset some of the cash transfer. For every $1 received from the program, total household income only rose by around $0.80.
One argument proponents of guaranteed income programs often make is that people receiving the cash can use it and their newfound free time to train for or find a better job that provides more benefits or greater flexibility. While possible in theory, the authors find no evidence that job quality increased in the treated group and only weak evidence that more people enrolled in post-secondary education.
No single study is definitive, but the scale of this study, its methodology, and its findings strongly suggest that guaranteed income programs are unlikely to dramatically improve people’s health. The findings also refute the notion that by providing a financial cushion, a guaranteed income encourages people to find better jobs. Instead, it appears most people respond by working less and spending more time doing other non-work things.
Despite these findings, I remain convinced that cash benefits are superior to in-kind assistance for mitigating poverty and improving people’s lives. In-kind assistance invites too much meddling from government officials, with different political factions arguing for or against different bans, such as a “junk food” ban in SNAP or the smoking ban in public housing. Cash empowers individuals to make decisions about what they need. Mistakes will be made, but mistakes are learning opportunities that help people improve their decision making over time.
Cash benefit programs should be means tested, however, to avoid the excessive taxation that is necessary to fund a $4 trillion nationwide universal income program. Targeting assistance to those who need it most is the fiscally responsible thing to do, even though phasing out benefits as income increases modestly discourages work. Ideally, there would be one means-tested cash benefit program to avoid the benefits cliff that arises when multiple programs with different eligibility rules and phase out schedules overlap.
This new study weakens the case for a nationwide guaranteed income program, but the case was never very strong to begin with. Such a program would be expensive, inefficient , and largely duplicative if layered on top of other programs. Even worse, it implicitly signals that as a society we think a significant portion of our fellow Americans are incapable of supporting themselves. A competently administered cash benefit program that targets those most in need is superior, and that should be our focus.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Koopman Analytical Modeling of Position and Attitude Dynamics: a Case Study for Quadrotor Control
- Martini, Simone
- Valavanis, Kimon P.
- Stefanovic, Margareta
This research presents a novel, analytical, Koopman Operator based formulation for position and attitude dynamics which can be used to derive control strategies for underactuated systems. Compared to data driven Koopman based techniques, the analytical approach presented in this work is model based and allows for an exact linear representation of the original nonlinear position and attitude dynamics. In fact, the resulting infinite dimensional model, defined in the lifted state space, is linear in the autonomous component and state dependent in the control. A boundary study is carried on to define the range of validity of the finite truncation of the Koopman based model followed by a controllability and stabilizability analysis to show the feasibility of employing the derived model for control system design. Compared to existing literature formulation, the presented model results in a better approximation of the original dyanmics using a more compact truncation of the lifted state space. Moreover, the model is derived using the Koopman approach on the entirety of the dynamics and does not require the need of angular velocity dynamic compensation. A case study involving an underactuated quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is provided to show that, for practical use, a truncated subset of the infinite dimensional model, embeds most of the original nonlinear dynamics and can be used to design linear control strategies in the lifted space which results in nonlinear controllers in the original state space. The main advantages of the presented approach reside in the effective use of linear control strategies for nonlinear plats and the solution of the underactuation problem employing a single control loop.
- Electrical Engineering and Systems Science - Systems and Control
Energy & Environmental Science
Pros and cons of hole-selective self-assembled monolayers in inverted pscs and tscs: extensive case studies and data analysis.

* Corresponding authors
a State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou 350002, China E-mail: [email protected]
b Laboratory for Advanced Functional Materials, Xiamen Institute of Rare Earth Materials, Haixi Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xiamen 361021, China
c University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Inverted perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered increased attention, achieving a notable power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 26.1%, surpassing that of the n–i–p configuration. This significant progress within the perovskite community owes much to the advancement and application of hole-selective self-assembled monolayers (HSSAMs). Representing a novel category of hole-selective layers (HSLs), HSSAMs offer several advantages. They are cost-effective, enable easy modulation of the substrate's work function, facilitate effortless interface modification, demonstrate minimal optical and electrical losses, and are compatible with conformal coatings and tandem solar cells (TSCs), thereby accelerating the advancement of inverted PSCs. This review systematically categorizes and evaluates the multifaceted roles of HSSAMs with diverse structures in inverted PSCs and TSCs, encompassing various anchoring and functional groups. Furthermore, an extensive analysis of literature data was conducted to summarize the deposition methods of hole-selective molecules with alternative structures and explore their relationship with device photovoltaic parameters and stability. Concurrently, an overview of the current status of HSSAMs is provided. This timely review offers a distinct perspective on the perovskite photovoltaic community and valuable insights into the ongoing development of these promising materials.

Article information
Download citation, permissions.
C. Li, Y. Chen, Z. Zhang, C. Liu, F. Guo, W. Ahmad and P. Gao, Energy Environ. Sci. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4EE02492C
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Advantages. 1. In-depth analysis of complex phenomena. Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations. By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
Through the case method, you can "try on" roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career. 5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and ...
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method. 1. It requires an intensive study of a specific unit. Researchers must document verifiable data from direct observations when using the case study method. This work offers information about the input processes that go into the hypothesis under consideration.
The pros and cons are listed below. Pros: 1. They show client observations-Since case studies are strategies that are used and analyzed in order to describe principles therefore it seeks to show indeed the client investigated and experienced a particular phenomenon. 2.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using the case study method. List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method 1. It turns client observations into useable data. Case studies offer verifiable data from direct observations of the individual entity involved. These observations provide information about input processes.
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches. Summary. It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case Study Defined. Case study research involves an in-depth investigation of a contemporary, real-life phenomenon in its context. A case study can focus on one person, a group, an organization ...
Advantages of Case Study Research. There are several advantages of case study research, including: In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may ...
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
Benefits. Their flexibility: case studies are popular for a number of reasons, one being that they can be conducted at various points in the research process. Researchers are known to favour them as a way to develop ideas for more extensive research in the future - pilot studies often take the form of case studies.
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a single person, group, event, or community. This research method involves intensively analyzing a subject to understand its complexity and context. The richness of a case study comes from its ability to capture detailed, qualitative data that can offer insights into a process or subject matter that ...
Advantages of Case Studies. Intensive Study. Case study method is responsible for intensive study of a unit. It is the investigation and exploration of an event thoroughly and deeply. You get a very detailed and in-depth study of a person or event. This is especially the case with subjects that cannot be physically or ethically recreated.
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5),5 ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Case studies in psychology offer a detailed look at individual behaviors and experiences, revealing unique insights but posing challenges. They allow deep exploration of complex cases, providing rich understanding of rare phenomena. However, focusing on specific cases may limit generalizability and introduce potential for bias.
Advantages of case studies Case studies provide researchers with several unique advantages, including: They allow researchers to observe and record information about rare, impractical, or unethical conditions and behaviours. They provide researchers with new evidence to support psychological theories.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
Advantages of a case study: Case studies showcase a specific solution and outcome for specific customer challenges. It attracts potential customers with similar challenges. It builds trust and credibility with potential customers. It provides an in-depth analysis of your company's problem-solving process.
Guidelines for when women should start getting mammograms have been changing. A new study makes the case for explaining to women the risks and benefits of screening for breast cancer.
This study uses a comprehensive literature review and analysis of existing peer recognition platforms alongside case studies of organizations implementing PRP systems. Surveys and qualitative interviews with employees and HR professionals provide additional insights into the practical application and effectiveness of PRP. ... The pros of peer ...
This article explores the Roles of Generative AI in drug discovery, highlighting its advantages, presenting case studies, and providing examples of its successful application. Table of Content. ... Case Studies and Success Stories. Real-world examples include AI-driven discoveries of new antibiotics, treatments for rare diseases, and ...
A new study weakens the case for a nationwide guaranteed income program, but the case was never very strong to begin with. A new study weakens the case for a nationwide guaranteed income program ...
A case study involving an underactuated quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is provided to show that, for practical use, a truncated subset of the infinite dimensional model, embeds most of the original nonlinear dynamics and can be used to design linear control strategies in the lifted space which results in nonlinear controllers in the ...
Pros and Cons of Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayers in Inverted PSCs and TSCs: Extensive Case Studies and Data Analysis ... (HSL), HSSAMs offer several advantages. They are cost-effective, enable easy modulation of substrate work function, facilitate effortless interface modification, demonstrate minimal optical and electrical loss, and ...