

Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Topic Ideas
- 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 4. Appropriate Sources
- 5. Search Techniques
- 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 7. Evaluating Sources
- 8. Citations & Plagiarism
- 9. Writing Your Research Paper

About Thesis Statements
Qualities of a thesis statement.
Thesis statements:
- state the subject matter and main ideas of a paper.
- appear in the first paragraph and announces what you will discuss in your paper.
- define the scope and focus of your essay, and tells your reader what to expect.
- are not a simple factual statement. It is an assertion that states your claims and that you can prove with evidence.
- should be the product of research and your own critical thinking.
- can be very helpful in constructing an outline for your essay; for each point you make, ask yourself whether it is relevant to the thesis.
Steps you can use to create a thesis statement
1. Start out with the main topic and focus of your essay.
youth gangs + prevention and intervention programs
2. Make a claim or argument in one sentence. It can be helpful to start with a question which you then turn into an argument
Can prevention and intervention programs stop youth gang activities? How? ►►► "Prevention and intervention programs can stop youth gang activities by giving teens something else to do."
3. Revise the sentence by using specific terms.
"Early prevention programs in schools are the most effective way to prevent youth gang involvement by giving teens good activities that offer a path to success."
4. Further revise the sentence to cover the scope of your essay and make a strong statement.
"Among various prevention and intervention efforts that have been made to deal with the rapid growth of youth gangs, early school-based prevention programs are the most effective way to prevent youth gang involvement, which they do by giving teens meaningful activities that offer pathways to achievement and success."
5. Keep your thesis statement flexible and revise it as needed. In the process of researching and writing, you may find new information or refine your understanding of the topic.
You can view this short video for more tips on how to write a clear thesis statement.
An outline is the skeleton of your essay, in which you list the arguments and subtopics in a logical order. A good outline is an important element in writing a good paper. An outline helps to target your research areas, keep you within the scope without going off-track, and it can also help to keep your argument in good order when writing the essay. Once your outline is in good shape, it is much easier to write your paper; you've already done most of the thinking, so you just need to fill in the outline with a paragraph for each point.
To write an outline: The most common way to write an outline is the list format. List all the major topics and subtopics with the key points that support them. Put similar topics and points together and arrange them in a logical order. Include an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
A list outline should arrange the main points or arguments in a hierarchical structure indicated by Roman numerals for main ideas (I, II, III...), capital letters for subtopics (A, B, C...), Arabic numerals for details (1,2,3...), and lower-case letters for fine details if needed (a,b,c...). This helps keep things organized.
Here is a shortened example of an outline:
Introduction: background and thesis statement
I. First topic
1. Supporting evidence 2. Supporting evidence
II. Second Topic
III. Third Topic
I. Summarize the main points of your paper II. Restate your thesis in different words III. Make a strong final statement
You can see examples of a few different kinds of outlines and get more help at the Purdue OWL .
- << Previous: 2. Topic Ideas
- Next: 4. Appropriate Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 12:12 PM
- URL: https://butte.libguides.com/ResearchPaper
English for Academic and Professional Purposes Quarter 1 – Module 2: Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text
In this module, you will acquire knowledge of appropriate reading strategies for a better understanding of academic texts to be able to produce a detailed abstract of information gathered from the various academic texts read. Concepts like the structure, language used from various disciplines, ideas contained in various academic texts, knowledge of the text structure to glean information that is needed, various techniques,thesis statements, paraphrasing and outlining reading text in various disciplines are discussed in the following lessons:
- Lesson 1 – Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text
To accomplish the desired performance stated, please be guided with the following learning competencies as anchor:
- States the thesis statement of an academic text (CS_EN11/12A-EAPP-Ia-c-6)
- Outlines reading texts in various disciplines (CS_EN11/12A-EAPP-Ia-c-8)
Learning Objectives:
At the end of the lessons, you will be able to:
1. State the thesis statements of an academic text.
2. Create an outline reading texts in various disciplines.
Can't Find What You'RE Looking For?
We are here to help - please use the search box below.
1 thought on “English for Academic and Professional Purposes Quarter 1 – Module 2: Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text”
Good day ma’am/sir,
I would just like to ask where Module 5 for the First Quarter of “English for Academic and Professional Purposes” subject is? I have been trying to search it here but all I have been seeing is the modules 1 to 4 fin the first quarter, then the modules 6 to 8 for the second quarter, I can’t find the Module 5 for the first quarter.
Hoping you can help me po, thank you very much
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.2 Outlining
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in constructing an outline.
- Construct a topic outline and a sentence outline.
Your prewriting activities and readings have helped you gather information for your assignment. The more you sort through the pieces of information you found, the more you will begin to see the connections between them. Patterns and gaps may begin to stand out. But only when you start to organize your ideas will you be able to translate your raw insights into a form that will communicate meaning to your audience.
Longer papers require more reading and planning than shorter papers do. Most writers discover that the more they know about a topic, the more they can write about it with intelligence and interest.
Organizing Ideas
When you write, you need to organize your ideas in an order that makes sense. The writing you complete in all your courses exposes how analytically and critically your mind works. In some courses, the only direct contact you may have with your instructor is through the assignments you write for the course. You can make a good impression by spending time ordering your ideas.
Order refers to your choice of what to present first, second, third, and so on in your writing. The order you pick closely relates to your purpose for writing that particular assignment. For example, when telling a story, it may be important to first describe the background for the action. Or you may need to first describe a 3-D movie projector or a television studio to help readers visualize the setting and scene. You may want to group your support effectively to convince readers that your point of view on an issue is well reasoned and worthy of belief.
In longer pieces of writing, you may organize different parts in different ways so that your purpose stands out clearly and all parts of the paper work together to consistently develop your main point.
Methods of Organizing Writing
The three common methods of organizing writing are chronological order , spatial order , and order of importance . You will learn more about these in Chapter 9 “Writing Essays: From Start to Finish” ; however, you need to keep these methods of organization in mind as you plan how to arrange the information you have gathered in an outline. An outline is a written plan that serves as a skeleton for the paragraphs you write. Later, when you draft paragraphs in the next stage of the writing process, you will add support to create “flesh” and “muscle” for your assignment.
When you write, your goal is not only to complete an assignment but also to write for a specific purpose—perhaps to inform, to explain, to persuade, or for a combination of these purposes. Your purpose for writing should always be in the back of your mind, because it will help you decide which pieces of information belong together and how you will order them. In other words, choose the order that will most effectively fit your purpose and support your main point.
Table 8.1 “Order versus Purpose” shows the connection between order and purpose.
Table 8.1 Order versus Purpose
| Order | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Chronological Order | To explain the history of an event or a topic |
| To tell a story or relate an experience | |
| To explain how to do or make something | |
| To explain the steps in a process | |
| Spatial Order | To help readers visualize something as you want them to see it |
| To create a main impression using the senses (sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound) | |
| Order of Importance | To persuade or convince |
| To rank items by their importance, benefit, or significance |
Writing a Thesis Statement
One legitimate question readers always ask about a piece of writing is “What is the big idea?” (You may even ask this question when you are the reader, critically reading an assignment or another document.) Every nonfiction writing task—from the short essay to the ten-page term paper to the lengthy senior thesis—needs a big idea, or a controlling idea, as the spine for the work. The controlling idea is the main idea that you want to present and develop.
For a longer piece of writing, the main idea should be broader than the main idea for a shorter piece of writing. Be sure to frame a main idea that is appropriate for the length of the assignment. Ask yourself, “How many pages will it take for me to explain and explore this main idea in detail?” Be reasonable with your estimate. Then expand or trim it to fit the required length.
The big idea, or controlling idea, you want to present in an essay is expressed in a thesis statement . A thesis statement is often one sentence long, and it states your point of view. The thesis statement is not the topic of the piece of writing but rather what you have to say about that topic and what is important to tell readers.
Table 8.2 “Topics and Thesis Statements” compares topics and thesis statements.
Table 8.2 Topics and Thesis Statements
| Topic | Thesis Statement |
|---|---|
| Music piracy | The recording industry fears that so-called music piracy will diminish profits and destroy markets, but it cannot be more wrong. |
| The number of consumer choices available in media gear | Everyone wants the newest and the best digital technology, but the choices are extensive, and the specifications are often confusing. |
| E-books and online newspapers increasing their share of the market | E-books and online newspapers will bring an end to print media as we know it. |
| Online education and the new media | Someday, students and teachers will send avatars to their online classrooms. |
The first thesis statement you write will be a preliminary thesis statement, or a working thesis statement . You will need it when you begin to outline your assignment as a way to organize it. As you continue to develop the arrangement, you can limit your working thesis statement if it is too broad or expand it if it proves too narrow for what you want to say.
Using the topic you selected in Section 8.1 “Apply Prewriting Models” , develop a working thesis statement that states your controlling idea for the piece of writing you are doing. On a sheet of paper, write your working thesis statement.
You will make several attempts before you devise a working thesis statement that you think is effective. Each draft of the thesis statement will bring you closer to the wording that expresses your meaning exactly.
Writing an Outline
For an essay question on a test or a brief oral presentation in class, all you may need to prepare is a short, informal outline in which you jot down key ideas in the order you will present them. This kind of outline reminds you to stay focused in a stressful situation and to include all the good ideas that help you explain or prove your point.
For a longer assignment, like an essay or a research paper, many college instructors require students to submit a formal outline before writing a major paper as a way to be sure you are on the right track and are working in an organized manner. A formal outline is a detailed guide that shows how all your supporting ideas relate to each other. It helps you distinguish between ideas that are of equal importance and ones that are of lesser importance. You build your paper based on the framework created by the outline.
Instructors may also require you to submit an outline with your final draft to check the direction of the assignment and the logic of your final draft. If you are required to submit an outline with the final draft of a paper, remember to revise the outline to reflect any changes you made while writing the paper.
There are two types of formal outlines: the topic outline and the sentence outline. You format both types of formal outlines in the same way.
- Place your introduction and thesis statement at the beginning, under roman numeral I.
- Use roman numerals (II, III, IV, V, etc.) to identify main points that develop the thesis statement.
- Use capital letters (A, B, C, D, etc.) to divide your main points into parts.
- Use arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) if you need to subdivide any As, Bs, or Cs into smaller parts.
- End with the final roman numeral expressing your idea for your conclusion.
Here is what the skeleton of a traditional formal outline looks like. The indention helps clarify how the ideas are related.
Introduction
Thesis statement
Main point 1 → becomes the topic sentence of body paragraph 1
Main point 2 → becomes the topic sentence of body paragraph 2
Main point 3 → becomes the topic sentence of body paragraph 3
In an outline, any supporting detail can be developed with subpoints. For simplicity, the model shows them only under the first main point.
Formal outlines are often quite rigid in their organization. As many instructors will specify, you cannot subdivide one point if it is only one part. For example, for every roman numeral I, there must be a For every A, there must be a B. For every arabic numeral 1, there must be a 2. See for yourself on the sample outlines that follow.

Constructing Topic Outlines
A topic outline is the same as a sentence outline except you use words or phrases instead of complete sentences. Words and phrases keep the outline short and easier to comprehend. All the headings, however, must be written in parallel structure. (For more information on parallel structure, see Chapter 7 “Refining Your Writing: How Do I Improve My Writing Technique?” .)
Here is the topic outline that Mariah constructed for the essay she is developing. Her purpose is to inform, and her audience is a general audience of her fellow college students. Notice how Mariah begins with her thesis statement. She then arranges her main points and supporting details in outline form using short phrases in parallel grammatical structure.

Writing an Effective Topic Outline
This checklist can help you write an effective topic outline for your assignment. It will also help you discover where you may need to do additional reading or prewriting.
- Do I have a controlling idea that guides the development of the entire piece of writing?
- Do I have three or more main points that I want to make in this piece of writing? Does each main point connect to my controlling idea?
- Is my outline in the best order—chronological order, spatial order, or order of importance—for me to present my main points? Will this order help me get my main point across?
- Do I have supporting details that will help me inform, explain, or prove my main points?
- Do I need to add more support? If so, where?
- Do I need to make any adjustments in my working thesis statement before I consider it the final version?
Writing at Work
Word processing programs generally have an automatic numbering feature that can be used to prepare outlines. This feature automatically sets indents and lets you use the tab key to arrange information just as you would in an outline. Although in business this style might be acceptable, in college your instructor might have different requirements. Teach yourself how to customize the levels of outline numbering in your word-processing program to fit your instructor’s preferences.
Using the working thesis statement you wrote in Note 8.32 “Exercise 1” and the reading you did in Section 8.1 “Apply Prewriting Models” , construct a topic outline for your essay. Be sure to observe correct outline form, including correct indentions and the use of Roman and arabic numerals and capital letters.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your outline. Point out areas of interest from their outline and what you would like to learn more about.
Constructing Sentence Outlines
A sentence outline is the same as a topic outline except you use complete sentences instead of words or phrases. Complete sentences create clarity and can advance you one step closer to a draft in the writing process.
Here is the sentence outline that Mariah constructed for the essay she is developing.

The information compiled under each roman numeral will become a paragraph in your final paper. In the previous example, the outline follows the standard five-paragraph essay arrangement, but longer essays will require more paragraphs and thus more roman numerals. If you think that a paragraph might become too long or stringy, add an additional paragraph to your outline, renumbering the main points appropriately.
PowerPoint presentations, used both in schools and in the workplace, are organized in a way very similar to formal outlines. PowerPoint presentations often contain information in the form of talking points that the presenter develops with more details and examples than are contained on the PowerPoint slide.
Expand the topic outline you prepared in Note 8.41 “Exercise 2” to make it a sentence outline. In this outline, be sure to include multiple supporting points for your main topic even if your topic outline does not contain them. Be sure to observe correct outline form, including correct indentions and the use of Roman and arabic numerals and capital letters.
Key Takeaways
- Writers must put their ideas in order so the assignment makes sense. The most common orders are chronological order, spatial order, and order of importance.
- After gathering and evaluating the information you found for your essay, the next step is to write a working, or preliminary, thesis statement.
- The working thesis statement expresses the main idea that you want to develop in the entire piece of writing. It can be modified as you continue the writing process.
- Effective writers prepare a formal outline to organize their main ideas and supporting details in the order they will be presented.
- A topic outline uses words and phrases to express the ideas.
- A sentence outline uses complete sentences to express the ideas.
- The writer’s thesis statement begins the outline, and the outline ends with suggestions for the concluding paragraph.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Related Resources
- —Reading Academic Texts
Self-Learning Module- Quarter 1-English for Academic Professional Purposes: Grade 11 Modules 1-5 View Download
Self Learning Module | ZIP
Curriculum Information
| Education Type | K to 12 |
| Grade Level | Grade 11 |
| Learning Area | |
| Content/Topic | Reading Academic Texts Writing the Reaction Paper/Review/ Critique Writing Concept Paper |
| Intended Users | Educators, Learners |
| Competencies | Determines the structure of a specific academic text Differentiates language used in academic texts from various disciplines Explains the specific ideas contained in various academic texts Uses knowledge of text structure to glean the information he/she needs Uses various techniques in summarizing a variety of academic texts States the thesis statement of an academic text Paraphrases/ explains a text using one’s own words Outlines reading texts in various disciplines Summarizes the content of an academic text Writes a précis/abstract/summary of texts in the various disciplines Defines what a concept paper is Determines the ways a writer can elucidate on a concept by definition, explication and clarification Comprehends various kinds of concept papers |
Copyright Information
| Copyright | Yes |
| Copyright Owner | Department of Education |
| Conditions of Use | Use, Copy, Print |
Technical Information
| File Size | 5.14 MB |
| File Type | application/x-zip-compressed |
Module 2: Critical Reading
Identifying thesis statements, introduction, learning objectives.
- identify explicit thesis statements in texts
- identify implicit thesis statements in texts
- identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you’re reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice.
One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you’re reading is to make a visual “map” of the ideas. Mind maps, whether hand-drawn or done through computer programs, can be fun to make, and help put all the ideas of an essay you’re reading in one easy-to-read format.
Your understanding of what the “central” element of the mind map is might change as you read and re-read. Developing the central idea of your mind map is a great way to help you determine the reading’s thesis.

Hand-drawn Mind Map
Locating Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit.
Topic Sentences
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
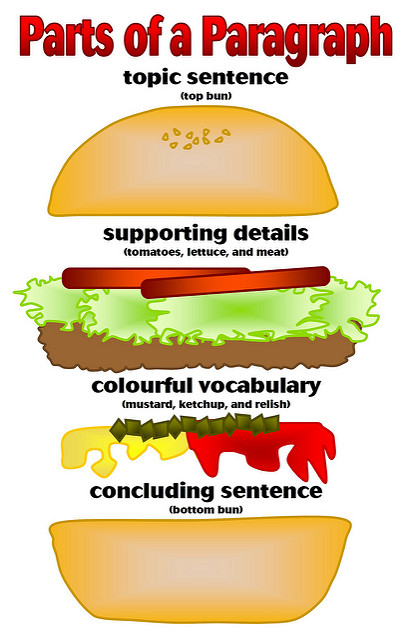
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The topic sentence is often, though not always, the first sentence of a paragraph.
- Outcome: Thesis. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and Adaptation of Topic Sentences. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of hand-drawn mind map. Authored by : Aranya. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Guru_Mindmap.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Topic Sentences. Authored by : Ms. Beardslee. Located at : http://msbeardslee.wikispaces.com/Topic+Sentences?showComments=1 . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Parts of a Paragraph. Authored by : Enokson. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/ak9H3v . License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Introduction to Academic Reading and Writing: Outline
- Concept Map
- Select a Topic
- Develop a Research Question
- Identify Sources
- Thesis Statements
- Effective Paragraphs
- Introductions and Conclusions
- Quote, Paraphrase, Summarize
- Synthesize Sources
- MLA and APA
- Transitions
- Eliminate Wordiness
- Grammar and Style
- Resource Videos
Use an outline to organize and order your ideas, using main and subheadings to indicate the logical relationships between ideas.
Place your thesis statement at the top
List your major supporting points. Writing them as complete sentences gives you topic sentences around which you can build your paragraphs in your draft. Label these using Roman numerals (I, II, III, …).
Order your major supporting points in logical order or in order of importance (least to most important is generally suggested)
List supporting ideas for each major point, labeling them in capital letters (A, B, C, …).
Continue to sub-divide each supporting idea to fully develop each major supporting point. Use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3 ...) and lower-case letters (a, b, c, ...).
Include bibliographic information for research material with each major or supporting idea.
© 2010-2019 The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
- Steps to outlining with a template from EasyBib
- Sample outline for argumentative paper by BridgePoint Education
- More outlining resources from Walden University
- << Previous: Thesis Statements
- Next: Effective Paragraphs >>
- Last Updated: Jul 11, 2024 10:58 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lbc.edu/Introtoacademicreadingandwriting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quarter 1 - Module 2: Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for
State the thesis statements of an academic text. Create an outline reading texts in various disciplines. CO_Q1_SHS English for Academic and Professional Purposes _ Module. 3. Summarizing Technique Use: Lesson 1 Identifying Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text What's In. Activity 1.
Here is a shortened example of an outline: Introduction: background and thesis statement. Body. I. First topic. A. Point A. 1. Supporting evidence 2. Supporting evidence. a. Detail. II. Second Topic. III. Third Topic. Conclusion. I. Summarize the main points of your paper II. Restate your thesis in different words III. Make a strong final statement
States the thesis statement of an academic text (CS_EN11/12A-EAPP-Ia-c-6) Outlines reading texts in various disciplines (CS_EN11/12A-EAPP-Ia-c-8) Learning Objectives: At the end of the lessons, you will be able to: 1. State the thesis statements of an academic text. 2. Create an outline reading texts in various disciplines.
Using the working thesis statement you wrote in Note 8.32 "Exercise 1" and the reading you did in Section 8.1 "Apply Prewriting Models", construct a topic outline for your essay. Be sure to observe correct outline form, including correct indentions and the use of Roman and arabic numerals and capital letters.
thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you'll make in the rest of your paper. What is a thesis statement? A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of ...
Developing a Thesis Statement and Outline Review instructions and restate the prompt in your own words Brainstorm topic and main ideas Identify the type of thesis you will need dependent on the type of paper you are writing Adapt your thesis idea to suit the needs of the paper, this can include gathering resources…
Description. Contents: 1. English 11 Quarter 1- Module 1: Reading Academic Texts. 2. English 11 Quarter 1- Module 2: Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text. 3. English 11 Quarter 1- Module 3: Approaches in Literary Criticism. 4. English 11 Quarter 1- Module 4: Writing the Reaction Paper/ Review/ Critique.
identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts. Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you're reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice. One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you're reading is to make a visual "map" of the ideas.
Outline. Place your thesis statement at the top. List your major supporting points. Writing them as complete sentences gives you topic sentences around which you can build your paragraphs in your draft. Label these using Roman numerals (I, II, III, …). Order your major supporting points in logical order or in order of importance (least to ...
Reading Text. CO_Q1_SHS English for Academic and. English for Academic and Professional Purposes - Grade 11 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 - Module 2: Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text First Edition, 2020. Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines.
Capitalize the first letter of each item. The terms Introduction, Body, and Conclusion do not have to be included in the outline. They are not topics; they are merely organizational units in the writer's mind. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The topic or subject of your paper.
Identifying the Thesis Statement. In the first three modules of this quarter, you have been exposed to various academic texts, and in every text you read and/or write, it should have a main point, a main idea, or central message. ... Quarter 3-Module 5: Outlining Reading Texts in Various Disciplines. ... This type of outline is useful for ...
State the thesis statements of an academic text. Create an outline reading texts in various disciplines. CO_QProfessional Purposes1_SHS English for Academic and _ Module 2 ##### 5. Lesson 1 Identifying Thesis Statement and Outline Reading Text What's In Activity 1. Direction: Summarize the following excerpt below from Understanding. Calories.