Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories


Renewable energy powerpoint presentation slides
Green energy is any energy produced from environmental resources such as sunshine, wind, or water. Check out our competently designed Green Energy template that provides an overview of the green energy power plant service provider firm, its mission, successful projects, and its scope of work. This Green Energy PowerPoint presentation covers the reasons to invest in green energy, introduces green energy by including its benefits, working and compares green, clear, and renewable energy. Additionally, this Clean Energy PPT talks about the various types of green energy such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, biomass, and biofuels. Furthermore, this Renewable Energy template includes a detailed overview of all the green energy type power plants by comprising their different types, working, components of power, and benefits. Also, this Green Energy PPT provides an estimated cost and maintenance expenses to implement the green energy plants. Lastly, this Clean Energy deck comprises a 30-60-90 days plan, a roadmap to implement a green energy power plant, and a dashboard. Book a free demo with our research team now.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
This complete presentation has PPT slides on wide range of topics highlighting the core areas of your business needs. It has professionally designed templates with relevant visuals and subject driven content. This presentation deck has total of seventy six slides. Get access to the customizable templates. Our designers have created editable templates for your convenience. You can edit the color, text and font size as per your need. You can add or delete the content if required. You are just a click to away to have this ready-made presentation. Click the download button now.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Complete Decks , All Decks , IT
- Overview Of Green Energy ,
- Solar Power ,
- Wind Power ,
- Geothermal Energy ,
- Biomass Energy ,
- Hydropower Station Project
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1 : This slide introduces Green Energy. State Your Company Name and begin. Slide 2 : This is an Agenda slide. State your agendas here. Slide 3 : This slide presents Table of Content for the presentation. Slide 4 : This is another slide continuing Table of Content for the presentation. Slide 5 : This is another slide continuing Table of Content for the presentation. Slide 6 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 7 : This slide represents the introduction of the green energy power firm. Slide 8 : This slide describes the mission to expand the green energy sector worldwide. Slide 9 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 10 : This slide represents the hydropower station project built by us by covering details such as cost, number of generators, area of the plant, used components, etc. Slide 11 : This slide depicts the offshore wind power project successfully set up by us. Slide 12 : This slide showcases the onshore wind power project established by the green energy power plant firm. Slide 13 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 14 : This slide illustrates why people, organizations, and governments should invest in green energy. Slide 15 : This slide depicts how green energy is economically viable and will become a better-suited option. Slide 16 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 17 : This slide represents what green energy is and how it is produced through natural resources. Slide 18 : This slide presents difference between green, clean and renewable energy. Slide 19 : This slide depicts how green energy works, derived from sun, wind, and water. Slide 20 : This slide represents the benefits of green energy, including reduced harmful emissions. Slide 21 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 22 : This slide illustrates the solar power type of green energy, how the sun's energy is used for multiple purposes. Slide 23 : This slide represents how solar energy works, can be used anywhere, reduces maintenance expenditure, etc. Slide 24 : This slide displays the solar panel components such as aluminum frame, tempered glass, encapsulant –EVA, etc. Slide 25 : This slide depicts the benefits of solar energy, including zero energy-production costs, versatile installation, etc. Slide 26 : This slide showcases utility-scale solar power panels that help to generate a massive amount of electricity. Slide 27 : This slide depicts the utility-scale solar power panels that help our future anticipation of generating electric. Slide 28 : This slide describes the residential solar power panels and their storing capacity of power. Slide 29 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 30 : This slide represents what wind power is, how the wind is caused, its less water usage, etc. Slide 31 : This slide depicts the types of wind turbines such as horizontal axis wind turbines and vertical axis wind turbines. Slide 32 : This slide describes how wind turbines work to generate electrical energy through wind energy. Slide 33 : This slide represents the components of wind turbines such as rotor, nacelle, control, etc. Slide 34 : This slide showcases benefits of wind energy by elaborating its advantages in cost-effectiveness. Slide 35 : This slide shows installation of wind turbines offered by green energy power plant firm. Slide 36 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 37 : This slide describes the hydropower type of green energy and how it is generated. Slide 38 : This slide depicts what is hydropower plants, on what principle it works, how it generates electric power, etc. Slide 39 : This slide presents the components of the hydropower plant such as dam, turbine, intake, etc. Slide 40 : This slide represents the working of hydropower plan and its various components. Slide 41 : This slide describes how the implementation of hydropower plants provides many benefits. Slide 42 : This slide showcases the diversion hydropower plant, the process of generating electricity by running water through penstocks. Slide 43 : This slide depicts the pumped-storage hydropower plant and how it generates electricity. Slide 44 : This slide represents the impoundment hydropower plant, how river water is stored in the large data lakes. Slide 45 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 46 : This slide showcases the geothermal energy type of green energy and how it is generated through the wells. Slide 47 : This slide represents the benefits of geothermal energy, such as being environmentally friendly. Slide 48 : This slide displays the dry steam geothermal power plant, its components such as injection well. Slide 49 : This slide presents the flash stream geothermal power plant, its working and components. Slide 50 : This slide depicts the binary cycle geothermal power plant, its working and components. Slide 51 : This slide represents the geothermal power plant method of geothermal energy and the process of power generation. Slide 52 : This slide depicts the geothermal heat pumps methods of geothermal energy and the process of energy production. Slide 53 : This slide showcases Components of Geothermal Power Plant. Slide 54 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 55 : This slide depicts the introduction of biomass energy, its usage, and its energy sources. Slide 56 : This slide represents the overview of biofuels that are produced from biomass energy. Slide 57 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 58 : This slide showcases the cost and maintenance of green energy plants by categorizing them. Slide 59 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 60 : This slide depicts the scope of work for the plant set up for customers. Slide 61 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 62 : This slide displays 30-60-90 Days Plan to Implement Green Energy Plant. Slide 63 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 64 : This slide represents the roadmap to set up the green energy plant by covering the steps involved. Slide 65 : This slide shows title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 66 : This slide depicts the dashboard for our green energy projects by covering details of total projects. Slide 67 : This slide displays Icons for Green Energy. Slide 68 : This slide is titled as Additional Slides for moving forward. Slide 69 : This slide presents Bar chart with two products comparison. Slide 70 : This slide describes Line chart with two products comparison. Slide 71 : This is a Comparison slide to state comparison between commodities, entities etc. Slide 72 : This slide depicts Venn diagram with text boxes. Slide 73 : This is a Timeline slide. Show data related to time intervals here. Slide 74 : This slide shows Post It Notes. Post your important notes here. Slide 75 : This slide contains Puzzle with related icons and text. Slide 76 : This is a Thank You slide with address, contact numbers and email address.
Renewable energy powerpoint presentation slides with all 81 slides:
Use our Renewable Energy Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

The two main types of wind turbines are horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) and vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT). HAWT works by using blades that rotate around a horizontal axis, whereas VAWT works by using blades that rotate around a vertical axis. Both types of wind turbines use the kinetic energy from wind to generate electrical energy through a generator.
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electrical energy through photovoltaic cells. These cells are made up of semiconducting materials that absorb the photons from the sun and release electrons, which generates electrical energy. The components of solar panels include an aluminum frame, tempered glass, encapsulant –EVA, solar cells, and a backing material.
Investing in green energy is beneficial for individuals, organizations, and governments. Green energy is eco-friendly and renewable, which helps reduce harmful emissions and protects the environment. It also reduces energy production costs in the long run, provides energy security, creates job opportunities, and contributes to economic growth.
Geothermal energy is a type of green energy that is generated by harnessing the heat from the earth's interior. It is generated through geothermal power plants and geothermal heat pumps. Geothermal power plants use wells to extract hot water or steam, which then powers a turbine that generates electricity. Geothermal heat pumps use the constant temperature of the earth to heat and cool buildings.
Green energy is a form of renewable energy that produces no or fewer harmful emissions than traditional energy sources. Clean energy refers to energy produced with minimal environmental impact, whereas renewable energy sources can be replenished naturally.
Ratings and Reviews
by Cruz Hayes
March 7, 2022
by Earl Contreras

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

free template
97 templates
digital footprint
17 templates

welcome back
88 templates
11 templates

38 templates

indigenous canada
39 templates
Renewable Energy Infographics
It seems that you like this template, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Renewable energies are the future. Clean energies with the potential to give us more than traditional sources of energy and without harming the planet. You may be preparing a presentation on this topic; do you need a set of infographics to express your data in a clear and original way? Here are your infographics! Graphs, maps, diagrams, and other infographic resources to talk about renewable energies are at your disposal.
Features of these infographics
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 31 different infographics to boost your presentations
- Include icons and Flaticon’s extension for further customization
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint and Keynote
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Include information about how to edit and customize your infographics
How can I use the infographics?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute the infographics?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?

Register for free and start downloading now
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

The Understand Energy Learning Hub is a cross-campus effort of the Precourt Institute for Energy .

Introduction to Renewable Energy
Exploring our content.
Fast Facts View our summary of key facts and information. ( Printable PDF, 270 KB )
Before You Watch Our Lecture Maximize your learning experience by reviewing these carefully curated readings we assign to our students.
Our Lecture Watch the Stanford course lecture.
Additional Resources Find out where to explore beyond our site.

Fast Facts About Renewable Energy
Principle Energy Uses: Electricity, Heat Forms of Energy: Kinetic, Thermal, Radiant, Chemical
The term “renewable” encompasses a wide diversity of energy resources with varying economics, technologies, end uses, scales, environmental impacts, availability, and depletability. For example, fully “renewable” resources are not depleted by human use, whereas “semi-renewable” resources must be properly managed to ensure long-term availability. The most renewable type of energy is energy efficiency, which reduces overall consumption while providing the same energy service. Most renewable energy resources have significantly lower environmental and climate impacts than their fossil fuel counterparts.
The data in these Fast Facts do not reflect two important renewable energy resources: traditional biomass, which is widespread but difficult to measure; and energy efficiency, a critical strategy for reducing energy consumption while maintaining the same energy services and quality of life. See the Biomass and Energy Efficiency pages to learn more.
Significance
14% of world 🌎 9% of US 🇺🇸
Electricity Generation
30% of world 🌎 21% of US 🇺🇸
Global Renewable Energy Uses
Electricity 65% Heat 26% Transportation 9%
Global Consumption of Renewable Electricity Change
Increase: ⬆ 33% (2017 to 2022)
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency measures such as LED light bulbs reduce the need for energy in the first place
Renewable Resources
Wind Solar Ocean
Semi-Renewable Resources
Hydro Geothermal Biomass
Renewable Energy Has Vast Potential to Meet Global Energy Demand
Solar >1,000x global demand Wind ~3x global demand
Share of Global Energy Demand Met by Renewable Resources
Hydropower 7% Wind 3% Solar 2% Biomass <2%
Share of Global Electricity Generation Met by Renewable Resources
Hydropower 15% Wind 7% Solar 5% Biomass & Geothermal <3%
Global Growth
Hydropower generation increase ⬆6% Wind generation increase ⬆84% Solar generation increase ⬆197% Biofuels consumption increase ⬆23% (2017-2022)
Largest Renewable Energy Producers
China 34% 🇨🇳 US 10% 🇺🇸 of global renewable energy
Highest Penetration of Renewable Energy
Norway 72% 🇳🇴 of the country’s primary energy is renewable
(China is at 16%, the US is at 11%)
Largest Renewable Electricity Producers
China 31% 🇨🇳 US 11% 🇺🇸 of global renewable electricity
Highest Penetration of Renewable Electricity
Albania, Bhutan, CAR, Lesotho, Nepal, & Iceland 100%
Iceland, Ethiopia, Paraguay, DRC, Norway, Costa Rica, Uganda, Namibia, Eswatini, Zambia, Tajikistan, & Sierra Leone > 90% of the country’s primary electricity is renewable
(China is at 31%, the US is at 22%)
Share of US Energy Demand Met by Renewable Resources
Biomass 5% Wind 2% Hydro 1% Solar 1%
Share of US Electricity Generation Met by Renewable Resources
Wind 10% Hydropower 6% Solar 3% Biomass 1%
US States That Produce the Most Renewable Electricity
Texas 21% California 11% of US renewable energy production
US States With Highest Penetration of Renewable Electricity
Vermont >99% South Dakota 84% Washington 76% Idaho 75% of state’s total generation comes from renewable fuels
Renewable Energy Expansion Policies
The Inflation Reduction Act continued tax credits for new renewable energy projects in the US.
Production Tax Credit (PTC)
Tax credit of $0.0275/kWh of electricity produced at qualifying renewable power generation sites
Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
Tax credit of 30% of the cost of a new qualifying renewable power generation site
To read more about the credit qualifications, visit this EPA site .
| Resource (Renewables) | Unsubsidized LCOE* | LCOE with ITC/PTC Tax Subsidy |
|---|---|---|
| Wind (Onshore) | $24 - $75 | $0 - $66 (PTC) |
| Solar PV (Utility Scale) | $24 - $96 | $16 - $80 (ITC) $0 - $77 (PTC) |
| Solar + Storage (Utility Scale) | $46 - $102 | $31 - $88 (ITC) |
| Geothermal | $61 - $102 | $37 - $87 |
| Wind (Offshore) | $72 - $140 | $56 - $114 (PTC) |
| Solar PV (Rooftop Residential) | $177 - $282 | $74 - $229 (ITC) |
| Wind + Storage (Onshore) | $24 - $75 | $0 - $66 (PTC) |
| Resource (Non-Renewables) | Unsubsidized LCOE* |
|---|---|
| Natural Gas (combined cycle) | $39 - $101 |
| Natural Gas Peaker Plants | $115 - $221 |
| Coal | $68 - $166 |
| Nuclear | $141 - $221 |
*LCOE (levelized cost of electricity) - price for which a unit of electricity must be sold for system to break even
Important Factors for Renewable Site Selection
- Resource availability
- Environmental constraints and sensitivities, including cultural and archeological sites
- Transmission infrastructure
- Power plant retirements
- Transmission congestion and prices
- Electricity markets
- Load growth driven by population and industry
- Policy support
- Land rights and permitting
- Competitive and declining costs of wind, solar, and energy storage
- Lower environmental and climate impacts (social costs) than fossil fuels
- Expansion of competitive wholesale electricity markets
- Governmental clean energy and climate targets and policies
- Corporate clean energy targets and procurement of renewable energy
- No fuel cost or fuel price volatility
- Retirements of old and/or expensive coal and nuclear power plants
- Most renewable resources are abundant, undepletable
- Permitting hurdles and NIMBY/BANANA* concerns
- Competition from subsidized fossil fuels and a lack of price for their social cost (e.g., price on carbon)
- Site-specific resources means greater need to transport energy/electricity to demand
- High initial capital expenditure requirements required to access fuel cost/operating savings
- Intermittent resources
- Inconsistent governmental incentives and subsidies
- Managing environmental impacts to the extent that they exist
*NIMBY - not in my backyard; BANANA - build absolutely nothing anywhere near anything
Climate Impact: Low to High

- Solar, wind, geothermal, and ocean have low climate impacts with near-zero emissions; hydro and biomass can have medium to high climate impact
- Hydro: Some locations have greenhouse gas emissions due to decomposing flooded vegetation
- Biomass: Some crops require significant energy inputs, land use change can release carbon dioxide and methane

Environmental Impact: Low to High
- Most renewable energy resources have low environmental impacts, particularly relative to fossil fuels; some, like biomass, can have more significant impacts
- No air pollution with the exception of biomass from certain feedstocks
- Can have land and habitat disruption for biomass production, solar, and hydro
- Potential wildlife impacts from wind turbines (birds and bats)
- Modest environmental impacts during manufacturing, transportation, and end of life
Updated January 2024
Before You Watch Our Lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy
We assign videos and readings to our Stanford students as pre-work for each lecture to help contextualize the lecture content. We strongly encourage you to review the Essential reading below before watching our lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy . Include the Optional and Useful readings based on your interests and available time.
- The Sustainable Energy in America 2024 Factbook (Executive Summary pp. 5-10) . Bloomberg New Energy Finance. 2024. (6 pages) Provides valuable year-over-year data and insights on the American energy transformation.
Optional and Useful
- Renewables 2024 Global Status Report (Global Overview pp. 10-39) . REN21. 2024. (30 pages) Documents the progress made in the renewable energy sector and highlights the opportunities afforded by a renewable-based economy and society.
Our Lecture on Introduction to Renewable Energy
This is our Stanford University Understand Energy course lecture that introduces renewable energy. We strongly encourage you to watch the full lecture to gain foundational knowledge about renewable energy and important context for learning more about specific renewable energy resources. For a complete learning experience, we also encourage you to review the Essential reading we assign to our students before watching the lecture.

Presented by: Kirsten Stasio , Adjunct Lecturer, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Stanford University; CEO, Nevada Clean Energy Fund (NCEF) Recorded on: May 15, 2024 Duration: 68 minutes
Table of Contents
(Clicking on a timestamp will take you to YouTube.) 00:00 Introduction 02:06 What Does “Renewable” Mean? 15:29 What Role Do Renewables Play in Our Energy Use? 27:12 What Factors Affect Renewable Energy Project Development?
Lecture slides available upon request .
Additional Resources About Renewable Energy
Stanford university.
- Precourt Institute for Energy Renewable Energy , Energy Efficiency
- Stanford Energy Club
- Energy Modeling Forum
- Sustainable Stanford
- Sustainable Finance Initiative
- Mark Jacobson - Renewable energy
- Michael Lepech - Life-cycle analysis
- Leonard Ortolano - Environmental and water resource planning
- Chris Field - Climate change, land use, bioenergy, solar energy
- David Lobell - Climate change, agriculture, biofuels, land use
- Sally Benson - Climate change, energy, carbon capture and storage
Government and International Organizations
- International Energy Agency (IEA) Renewables Renewables 2022 Repor .
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
- US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy (EERE)
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Renewable Energy Explained
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Energy Kids Renewable Energy
- US Energy Information Administration (EIA) Today in Energy Renewables
Other Organizations and Resources
- REN21: Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century
- REN21 Renewables 2023 Global Status Report Renewables in Energy Supply
- BloombergNEF (BNEF)
- Carnegie Institution for Science Biosphere Sciences and Engineering
- The Solutions Project
- Renewable Energy World
- World of Renewables
- Energy Upgrade California
- Windustry Community Wind Toolbox
Next Topic: Energy Efficiency Other Energy Topics to Explore
Fast Facts Sources
- Energy Mix (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Energy Mix (US 2022): US Energy Information Agency (EIA). Total Energy: Energy Overview, Table 1.3 .
- Electricity Mix (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Electricity Mix (US 2022): US Energy Information Agency (EIA). Total Energy: Electricity, Table 7.2a.
- Global Solar Use (2022): REN21. Renewables 2023 Global Status Report: Renewables in Energy Supply , page 42. 2023
- Global Consumption of Renewable Electricity Change (2017-2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Renewable Energy Potential: Perez & Perez. A Fundamental Look at Energy Reserves for the Planet . 2009
- Share of Global Energy Demand (2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Share of Global Electricity Demand (2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Global Growth (2017-2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Largest Renewable Energy Producers (World 2022): International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Renewable Capacity Statistics 2023 . 2023.
- Highest Penetration Renewable Energy (World 2022): Our World in Data. Renewable Energy . 2023.
- Largest Renewable Electricity Producers (World 2022): Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy . 2023.
- Highest Penetration Renewable Electricity (World 2022): Our World in Data. Renewable Energy . 2023.
- Share of US Energy Demand (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- Share of Electricity Generation (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- States with Highest Generation (2022): Energy Information Administration (EIA). Electric Power Monthly. 2023.
- States with Highest Penetration (2021): Energy Information Administration (EIA). State Profile and Energy Estimates. 2023.
- LCOE of US Renewable Resources: Lazard. LCOE. April 2023.
- LCOE of US Non Renewable Resources: Lazard. LCOE. April 2023.
More details available on request . Back to Fast Facts
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker
Design Services
Business PPTs
Business Plan
Introduction PPT
Self Introduction
Startup Business Plan
Cyber Security
Digital Marketing
Project Management
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Target Market
Communication
Supply Chain
Google Slides
Research Services
All Categories
Renewable Resources And Energy PowerPoint Presentation Templates and Google Slides
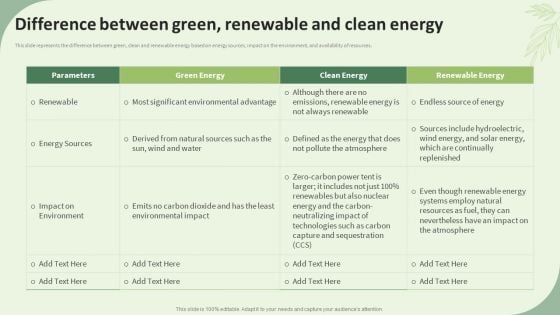
Sustainable Energy Resources Difference Between Green Renewable And Clean Energy Diagrams PDF
This slide represents the difference between green, clean and renewable energy based on energy sources, impact on the environment, and availability of resources. Deliver an awe inspiring pitch with this creative Sustainable Energy Resources Difference Between Green Renewable And Clean Energy Diagrams PDF bundle. Topics like Green Energy, Clean Energy, Renewable Energy can be discussed with this completely editable template. It is available for immediate download depending on the needs and requirements of the user.
Ratings and Reviews
Most relevant reviews, by tarun saini.
November 25, 2022
by Uus Sutisna
- Collections
Renewable Energy
- Sustainable Energy
Editable Sustainable Energy PowerPoint And Google Slides

Sustainable Energy PowerPoint Slides
Discover Sustainable Energy, referring to renewable, non-polluting energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy, which meet current needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet theirs. This energy promotes energy independence, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and supports economic growth through innovation and job creation in renewable energy sectors. Embrace sustainable energy to mitigate climate change, enhance energy security, and promote environmental stewardship for a sustainable future.
Environmental advocates, policymakers, energy consultants, and educators can effectively utilize this PowerPoint template to promote sustainable energy solutions. The template provides a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format for presenting key concepts, data, and case studies related to sustainable energy sources and technologies. Each slide is fully editable, allowing customization to fit specific educational or advocacy needs. Using this template saves time and effort in creating professional presentations that clearly convey the importance and benefits of sustainable energy. Encourage your audience to use the template to advocate for policy changes, promote renewable energy projects, and educate communities about sustainable energy sources. Elevate your presentations to inspire action toward a cleaner, more sustainable energy future, supporting global efforts for a healthier planet.
Feature of this templates
- 100% customizable slides and easy to download.
- The slide contains 16:9 and 4:3 formats.
- Easy to change the colors of the slide quickly.
- Highly compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides.
- Green Energy
- Renewable Energy Sources
- Energy Types
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Hydro Energy
- Google Slides

25+ Templates

268+ Templates

128+ Templates

Agriculture
61+ Templates

53+ Templates

13+ Templates

67+ Templates

70+ Templates

56+ Templates

31+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates

- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer
- Immigration
- Criminal Justice
- Silicon Valley
- The California Report
Renewable and Non-renewable Energy Resources Explained
by Kevin Stark
There are two major categories of energy: renewable and non-renewable.
Non-renewable energy resources are available in limited supplies, usually because they take a long time to replenish. The advantage of these non-renewable resources is that power plants that use them are able to produce more power on demand. The non-renewable energy resources are:
- Natural gas
Renewable resources, on the other hand, replenish themselves. The five major renewable energy resources are:
- Water, also called hydro
- Biomass, or organic material from plants and animals
- Geothermal, which is naturally occurring heat from the earth
While renewable energy resources have the advantage of unlimited supply over the long haul, they are limited in their availability at any given moment.
For example, the sun rises each day, but its ability to generate power is limited when its cloudy . Another disadvantage is that power plant operators can’t crank up renewable energy production when people are consuming more power, such as on a hot day when many people are running air conditioners at the same time.
States like California are trying to solve this problem by using energy storage, like large batteries, to collect electricity from renewable sources when demand is low in order to use it later when demand goes up.
Non-renewable Energy and Climate Change
When coal, natural gas and oil are burned to produce energy, they emit heat-trapping gases such as carbon dioxide. This process of trapping heat is what drives climate change, and the failure to address this problem is what's catalyzing the current climate crisis.
Fossil fuels are hydrocarbon-containing materials like coal or gas that are found in the Earth’s crust and formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms. These energy sources account for the majority of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions .
If emissions continue unrestrained, the atmosphere could warm by as much as 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit above preindustrial levels by the year 2040, according to the latest report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a group of international scientists empowered by the United Nations to advise world leaders.
Scientists say this increase in the temperature would threaten life on the planet in a myriad of ways, including severe water shortages; more air pollution; rising sea levels, habitat loss; heat waves; melting ice sheets in West Antarctica and Greenland; and destruction of the world’s coral reefs.
Over the last 150 years, humans are responsible for the vast majority of the increase of these gases in the atmosphere, and the burning of fossil fuels through activities like driving a car is the largest source of these emissions.
There is a vocal group of environmentalists and researchers —Stanford’s Mark Jacobson, who developed a state-by-state 100% renewable plan for one — who argue that the power grid should be supported only by renewable resources.
Policy makers who invest in renewable energy often do so with the goal of generating power without emitting these planet-warming gases.
The Nuclear Debate
Experts debate whether nuclear energy should be considered a renewable or non-renewable energy resource.
Nuclear energy is considered clean energy, as it doesn’t create any air pollution or emit carbon dioxide, but generates energy through nuclear fission, the process of atoms splitting apart.
For this reason, supporters of nuclear energy argue it should be considered renewable.
Those who are in favor of more nuclear energy hold that that even with investment in wind, solar and other renewable resources, nuclear power is necessary, because without it we can’t reduce emissions quickly enough to stave off the worst impacts of climate change. Without contributions from nuclear energy “the cost of achieving deep decarbonization targets increases significantly,” wrote MIT researchers in a 2018 paper examining the issue.
Detractors of this approach say that both the mining and refining of uranium and the building of nuclear power plants is energy-intensive. Other downsides to nuclear energy are the finite amount of uranium deposits on the planet and the production of harmful waste from nuclear reactors.
For these reasons, the U.S. Energy Information Administration considers it a non-renewable energy resource.
Links to Learn More
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Change A body of the United Nations, the IPCC regularly assesses the science of climate change and issues annual reports on the impacts and risks of warming, as well as guidance for adaptation and mitigation.
U.S. Energy Administration This U.S. Department of Energy website includes detailed information, analysis and graphics about energy production and use in the U.S.
The United States of Energy A series of infographics provides insight on our country’s energy production and consumption of both renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
PBS LearningMedia Find hundreds of digital media resources about renewable energy for use in the classroom from public media stations across the country.
Andrea Aust contributed to this post.
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Environmental science
Course: ap®︎/college environmental science > unit 5, renewable and nonrenewable energy resources.
- Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources
- Global energy use
- Intro to energy resources and consumption
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Video transcript
16,132 English ESL powerpoints

According to the DOE’s most recent liftoff report regarding offshore wind deployment , the market is currently a critical inflection point. Offshore wind presents a very promising source of renewable energy for the country, especially in light of the urgency to restructure our energy portfolio to meet the 2050 net-zero emission targets. Investing in wind complements other clean energy sources, supporting grid reliability and resource diversity, making this source a promising area of investment and a powerful resource to tap into for clean energy.
One of the primary concerns for the future of offshore wind is its cost. Though wind has proven to be a highly effective source of clean energy, costs have risen over the past several years, raising questions about the source’s competitiveness. The liftoff report outlines several paths to cost reduction and scalability, but significant technological advancements will also be needed to accelerate this process.
In this regard, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has performed an impressive body of research to help offshore wind scale as needed. This blog post will discuss some of NREL’s most promising technologies and recent research efforts that are paving the way for the future of offshore wind.
Learn more about NREL and its experts here.
Autonomous Roaming Turbine
Traditional wind turbines often face limitations regarding mobility. Turbines are placed in arrays at fixed locations, limiting the areas they can cover for perpetual energy generation. NREL’s autonomous turbines can extract wind energy without this limitation. Using a floating hull and propellers, the autonomous turbine can be deployed into the ocean, where it can move in an eight-figure pattern. By covering a larger area, the turbine can capitalize on more wind sources while adapting to weather conditions in the process.
Learn more about Autonomous Roaming Turbines here.
Universal Joints Floating Substructure
One of NREL’s most promising cost-cutting innovations involves a new and efficient way to build offshore turbines. Using this innovative substructure, wind turbines can be quickly and easily mounted for ocean water deployment. A series of joints in the design help manage weight and load while simultaneously minimizing disturbances to the turbines themselves.
Discover how the Universal Joints Floating Substructure works here.
Inflatable Blades
The larger the wind turbine, the more efficient it is at capturing and converting wind into energy. However, transporting these larger blades is often difficult, facing additional installation constraints. NREL’s inflatable blades provide a unique solution to this problem. These blades have a fabric aerodynamic shell that protects them while they are deflated, allowing for easy transportation. Once inflated, the blades can be easily mounted and installed, allowing for large amounts of wind-generated energy while improving practicality and cost-efficiency.
Learn about NREL’s Inflatable Blades Technology here.
By focusing on these innovations, NREL is helping to lower costs and improve the scalability of offshore wind energy, making it a more viable option for the future. For more detailed information on these and other technologies, visit the Lab Partnering Service website.
Watch CBS News
Battery storage is key to scaling up solar and wind power. Here's why.
By Ben Tracy
July 10, 2024 / 7:49 PM EDT / CBS News
Rachel Harper used to work in the oil and gas industry in Texas and never thought she'd be working next to solar panels all day.
"It's a much more peaceful environment," Harper said. "I like this way better."
She's now at a startup in California called B2U that takes the still-usable batteries out of older electric vehicles, slides them into large racks and then plugs them into solar panels so they can store solar power.
"We're basically a retirement home for these EV batteries," Harper said.
Battery storage allows renewable energy to provide power even when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing. It's key to making the electrical grid reliable as the U.S. transitions away from coal and gas and their planet-warming emissions. Batteries also help keep the lights on when heat waves put a strain on the power grids .
As director of energy storage and systems at the University of California, San Diego, Mike Ferry is at the forefront of the next generation of battery technology.
He says batteries are getting better and costs are dropping. That has allowed California to install more than 10,000 megawatts of battery storage, which is equivalent to the output of about five nuclear power plants, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
California and Texas account for 85% of the battery storage in the nation, according to Ferry. The two states combined have more than any other country except China, which has 31,400 megawatts of battery storage, according to the China National Energy Administration.
"This year, 81% of all new capacity on our national grid is going to be solar and storage. And these two technologies go hand in hand, sort of like chocolate and peanut butter," Ferry said.
Nationwide, solar power is the fastest growing form of renewable energy, but it still accounts for only about 5% of electricity generated. In California, it's nearly 30%, thanks to massive new projects like one in the Mojave Desert, where an array of 2 million solar panels near Edwards Air Force Base can be seen from space.
The 4,000-acre site is the largest solar storage facility in the country and has enough energy to power about a quarter million homes.
"Without this, I think renewable energy would hit a limit fairly quickly," said Gus Luna, the chief development officer for Terra-Gen, the company that built the site.
California, the fifth largest economy in the world, aims to run on 100% renewable energy by 2045.
"You'll probably need something like another 20, maybe 30, more of these projects to be able to reach that," Luna said.
That's because to truly make all those panels and turbines work, you need batteries included.
- Renewable Energy
- Climate Change
- Environment
- Solar Power

Ben Tracy is CBS News' senior national and environmental correspondent based in Los Angeles. He reports for all CBS News platforms, including the "CBS Evening News with Norah O'Donnell," "CBS Mornings" and "CBS Sunday Morning."
More from CBS News

Sheryl Lee Ralph earns 3rd Emmy nomination before new movie release

Climate protesters steer clear of Republican National Convention

Here's what some Olympic athletes get instead of cash prizes

Best wireless outdoor security cameras 2024
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Amazon Says It Reached a Climate Goal Seven Years Early
The company said it effectively got all of the electricity it used last year from sources that did not produce greenhouse gas emissions. Some experts have faulted the company’s calculations.

By Ivan Penn and Eli Tan
Amazon announced on Wednesday that effectively all of the electricity its operations used last year came from sources that did not produce greenhouse gas emissions. But some experts have criticized the method the company uses to make that determination as being too lenient.
In its announcement, Amazon said it had reached its goal of 100 percent clean energy seven years ahead of schedule. The company said it invested billions of dollars in more than 500 solar and wind projects to achieve its target. The energy generated by those projects is equivalent to the electricity consumed by the company’s data centers, corporate buildings, grocery stores and fulfillment centers in 27 countries.
But because the solar and wind farms do not all directly power Amazon’s operations — most of that energy is sent to electricity grids that serve many businesses and homes — some critics say that the company’s calculations can create a misleading impression of its effect on the climate.
The clean energy projects Amazon has invested in can produce enough electricity to power the equivalent of 7.6 million U.S. homes, the company said. Amazon aims to reach net-zero carbon emissions from all of its operations, including its delivery vans, planes and other means of transportation, by 2040.
“We’re really excited about, obviously, the goal that we set five years ago and reaching it seven years early,” said Kara Hurst, vice president of worldwide sustainability at Amazon. “That’s quite an achievement for us.”
Amazon and other tech companies have said for years that they aim to eliminate the planet-warming effect of their operations. But those promises have been called into question recently by the industry’s decisions to invest heavily in artificial intelligence, which consumes vast amounts of electricity through its use of data centers .
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
China is installing the wind and solar equivalent of five large nuclear power stations per week
Science China is installing the wind and solar equivalent of five large nuclear power stations per week
China is installing record amounts of solar and wind, while scaling back once-ambitious plans for nuclear.
While Australia is falling behind its renewables installation targets, China may meet its end-of-2030 target by the end of this month, according to a report.
What's next?
Energy experts are looking to China, the world's largest emitter and once a climate villain, for lessons on how to rapidly decarbonise.
While Australia debates the merits of going nuclear and frustration grows over the slower-than-needed rollout of solar and wind power, China is going all in on renewables.
New figures show the pace of its clean energy transition is roughly the equivalent of installing five large-scale nuclear power plants worth of renewables every week.
A report by Sydney-based think tank Climate Energy Finance (CEF) said China was installing renewables so rapidly it would meet its end-of-2030 target by the end of this month — or 6.5 years early.
It's installing at least 10 gigawatts of wind and solar generation capacity every fortnight.
By comparison, experts have said the Coalition's plan to build seven nuclear power plants would add fewer than 10GW of generation capacity to the grid sometime after 2035.
Energy experts are looking to China, the world's largest emitter, once seen as a climate villain, for lessons on how to go green, fast.
"We've seen America under President Biden throw a trillion dollars on the table [for clean energy]," CEF director Tim Buckley said.
"China's response to that has been to double down and go twice as fast."
Smart Energy Council CEO John Grimes, who recently returned from a Shanghai energy conference, said China has decarbonised its grid almost as quickly as Australia, despite having a much harder task due to the scale of its energy demand.
"They have clear targets and every part of their government is harnessed to deliver the plan," he said.
China accounts for about a third of the world's greenhouse gas emissions. A recent drop in emissions (the first since relaxing COVID-19 restrictions), combined with the decarbonisation of the power grid, may mean the country's emissions have peaked.
"With the power sector going green, emissions are set to plateau and then progressively fall towards 2030 and beyond," CEF China energy policy analyst Xuyang Dong said.
So how is China building and connecting panels so fast, and what's the role of nuclear in its transition?
Like building solar farms near Perth to power Sydney
Because its large cities of the eastern seaboard are dominated by apartment buildings, China hasn't seen an uptake of rooftop solar like in Australia.
To find space for all the solar panels and wind turbines required for the nation's energy needs, the planners of China's energy transition have looked west, to areas like the Gobi Desert.
The world's largest solar and wind farms are being built on the western edge of the country and connected to the east via the world's longest high-voltage transmission lines.
These lines are so long they could span the length of our continent.
In Australian terms, it's the equivalent of using solar panels near Perth to power homes in Sydney.
Mr Buckley said China's approach was similar to the Australian one of developing regional "renewable energy zones" for large-scale electricity generation.
"They're doing what Australia is doing with renewable energy zones but they're doing it on steroids," he said.
What about 'firming' the grid?
One of the issues with switching a grid to intermittent renewables is ensuring a steady supply of power.
In technical terms, this is the difference between generation capacity (measured in gigawatts) and actual energy output (measured in gigawatt-hours, or generation over time).
Renewables have a "capacity factor" (the ratio of actual output to maximum potential generation) of about 25 per cent, whereas nuclear's is as high as 90 per cent.
So although China is installing solar and wind generation equivalent to five large nuclear power plants per week, their output is closer to one nuclear plant per week.
Renewables account for more than half of installed capacity in China, but only amount to about one-fifth of actual energy output over a year, the CEF's Tim Buckley said.
To "firm" or stabilise the supply of power from its renewable energy zones, China is using a mix of pumped hydro and battery storage, similar to Australia.
"They're installing 1GW per month of pumped hydro storage," Mr Buckley said.
"We're struggling to build the 2GW Snowy 2.0 in 10 years."
There are some major differences between Australia's and China's approaches, though.
Somewhat counterintuitively, China has built dozens of coal-fired power stations alongside its renewable energy zones, to maintain the pace of its clean energy transition.
China was responsible for 95 per cent of the world's new coal power construction activity last year.
The new plants are partly needed to meet demand for electricity, which has gone up as more energy-hungry sectors of the economy, like transport, are electrified.
The coal-fired plants are also being used, like the batteries and pumped hydro, to provide a stable supply of power down the transmission lines from renewable energy zones, balancing out the intermittent solar and wind.
Despite these new coal plants, coal's share of total electricity generation in the country is falling.
The China Energy Council estimated renewables generation would overtake coal by the end of this year.
The CEF's Xuyang Dong said despite the country's reliance on coal, "having China go green at this speed and scale provides the world with a textbook to do the same".
"China is installing every week the equivalent of what we're doing every year."
Despite this speed, China wasn't installing renewables fast enough to meet its 2060 carbon neutrality target, she added.
"According to our analysis, [the current rate of installation] is not ambitious enough for China."
What about nuclear?
China is building new nuclear plants, although nowhere near as fast as it once intended.
In 2011, Chinese authorities announced fission reactors would become the foundation of the country's electricity generation system in the next "10 to 20 years".
But Japan's 2011 Fukushima disaster prompted a moratorium on inland nuclear plants, which have to use river water for cooling and are more vulnerable to frequent flooding.
Meanwhile, over the following decade, solar became the cheapest electricity in the world.
From 2010 to 2020, the installed cost of utility-scale solar PV declined by 81 per cent on a global average basis.
As well as cheap, it was safe, which made solar farms quicker to build than nuclear reactors.
Instead of nuclear, solar is now intended to be the foundation of China's new electricity generation system.
Authorities have steadily downgraded plans for nuclear to dominate China's energy generation. At present, the goal is 18 per cent of generation by 2060.
China installed 1GW of nuclear last year, compared to 300GW of solar and wind, Mr Buckley said.
"That says they're all in on renewables.
"They had grand plans for nuclear to be massive but they're behind on nuclear by a decade and five years ahead of schedule on solar and wind."
How is China transitioning so fast?
In June of this year, on the eve of the Coalition's nuclear policy announcement, former Queensland Premier Annastacia Palaszczuk, who's now a Smart Energy Council "international ambassador", led a delegation of Australians to the world's largest clean energy conference in Shanghai.
The annual Smart Energy Conference hosts more than 600,000 delegates across three days.
Its scale underlines China's increasing dominance of the global clean energy economy and, for some attendees, prompted unenviable comparisons with Australia's progress.
Mr Buckley, who was part of the delegation, said he was "blown away".
"China is winning this race."
John Grimes, the Smart Energy Council CEO who also attended, said Australia could learn from the Chinese government's ability to execute a long-term, difficult and costly transition plan, rather than relying on market forces to find a solution.
"Australia's transition is going too slow, there was a lost decade of action," he said.
"The world today spends about $7 trillion a year on coal, gas and oil and that money is going to find a new home.
"Who is going to be the economic winner in that global economic transition? It's going to be China."
He and other energy experts are frustrated with the progress of Australia's transition, including the discussion of nuclear power and the "weaponisation of dissent" from community groups over new wind farms and transmission lines .
Stephanie Bashir, CEO of the Nexa energy advisory, said Australia's transition was tangled in red tape.
"The key hold-up for a lot of projects is the slow planning approvals," Ms Bashir, who also attended the conference, said.
"In China they decide they're going to do something and then they go and do it."
The Australian Energy Market Operator's (AEMO) plan to decarbonise the grid and ensure the lights stay on when the coal-fired power stations close requires thousands of kilometres of new transmission lines and large-scale solar and wind farms.
Australia is installing about half the amount of renewables per year required under the plan.
Due to this shortfall, many experts say it's unlikely to meet its 2030 target of 82 per cent renewables in the grid and 43 per cent emissions reduction.
"We need to build 6GW each year from now until each power station closes, and so far we're only bringing online 3GW," Ms Bashir said.
"If we identify some projects are nation-building … and we need them for transition, we just have to get on with it."
Mr Buckley predicted China would accelerate its deployment of renewables.
"My forecast is it will lift 20 per cent per annum on current levels."
Science in your inbox
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Dutton reveals seven sites for proposed nuclear power plants.
On New Year's Eve, all of South Australia's power was coming from rooftop solar panels
Analysts say mounting problems mean Australia will fall well short of 2030 renewable energy target
- Climate Change
- Nuclear Energy
- Science and Technology
- Solar Energy
- United States
- Wind Energy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Green energy is any energy produced from environmental resources such as sunshine, wind, or water. Check out our competently designed Green Energy template that provides an overview of the green energy power plant service provider firm, its mission, successful projects, and its scope of work. This Green Energy PowerPoint presentation covers the reasons to invest in green energy, introduces ...
Free Renewable Energy Presentation Templates. Turn up the eco-volume on your presentations with free renewable energy PowerPoint templates and Google Slides. Explain the benefits of solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power with captivating visuals. Impress your audience with clear diagrams, informative infographics, and inspiring quotes.
The sooner we're aware of this, the better! Teach about renewable and non-renewable energy in school, and who's a better ally in education than Slidesgo? We've prepared this template, with real content by educators, some photos and colorful gradients, to make things much easier for you. This template is available in different languages, so enjoy!
Renewable energies are the future. Clean energies with the potential to give us more than traditional sources of energy and without harming the planet. You may be preparing a presentation on this topic; do you need a set of infographics to express your data in a clear and original way? Here are your infographics!
The term "renewable" encompasses a wide diversity of energy resources with varying economics, technologies, end uses, scales, environmental impacts, availability, and depletability. For example, fully "renewable" resources are not depleted by human use, whereas "semi-renewable" resources must be properly managed to ensure long-term ...
This slide represents the difference between green, clean and renewable energy based on energy sources, impact on the environment, and availability of resources. Deliver an awe inspiring pitch with this creative Sustainable Energy Resources Difference Between Green Renewable And Clean Energy Diagrams PDF bundle.
Sustainable Energy PowerPoint Slides. Discover Sustainable Energy, referring to renewable, non-polluting energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy, which meet current needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet theirs. This energy promotes energy independence, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and supports ...
inexhaustible. Examples of renewable resources include wind power, solar power, geothermal energy, tidal power and hydroelectric power. The most important features of renewable energy is that it can be harnessed without the release of harmful pollutants. • Non-renewable energy is the conventional fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas, which ...
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass fuels. These energy sources are sustainable and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels. Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources. Clockwise from top left: a solar power station, a wind farm, a hydroelectric power plant, and a coal-fired ...
In 2022, annual U.S. renewable energy generation surpassed coal for the first time in history. By 2025, domestic solar energy generation is expected to increase by 75%, and wind by 11%. The United States is a resource-rich country with enough renewable energy resources to generate more than 100 times the amount of electricity Americans use each ...
There are two major categories of energy: renewable and non-renewable. Non-renewable energy resources are available in limited supplies, usually because they take a long time to replenish. The advantage of these non-renewable resources is that power plants that use them are able to produce more power on demand.
device that converts electrochemical energy into dc directly by using a constant flow of fuel (usually hydrogen) from an outside source. portion of a fuel cell system that converts the input fuel into a form useable by the fuel cell. part of the fuel cell that processes the excess heat for another use such as hot water or steam.
Transcript. Energy sources are categorized into renewable and nonrenewable types. Nonrenewable energy sources are those that exist in a fixed amount and involve energy transformation that cannot be easily replaced. Renewable energy sources are those that can be replenished naturally, at or near the rate of consumption, and reused.
Renewable energy sources play a role in providing energy services in a sustainable manner and, in particu-lar, in mitigating climate change. This Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation explores the current contribution and potential of renewable energy (RE) sources to provide energy services for a sus-
These resources help practitioners to deliver the renewable energy components of engineering and manufacturing-related qualifications at levels 2 and 3. They introduce the topic and stimulate learners to explore and reflect on key concepts and are designed to complement and enhance practitioners' own lesson materials and schemes of work.
* Shifting entirely to renewable energy would require massive investment in new infrastructure to replace the current fossil fuel infrastructure. But the overall land requirement is not a high proportion of global land area, and in many cases can be combined with agricultural uses. * The potential of increased energy efficiency is about 50% of ...
Application of Renewable Energy resources Hydropower energy •Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production. •Since ancient times, hydropower from watermills has been used as a renewable energy source for irrigation and the operation of mechanical devices, such as gristmills, sawmills,
What is Solar Energy? One of the alternative energy sourse that comes from the sun. It is converted into thermal or electrical energy. Five Types of Alternative Renewable Energy. Solar energy Geothermal energy Biomass Wind energy Tidal power Pros and Cons of Solar Energy
An easy Power Point Presentation about renewable and non-renewable energy sources. It could be used to introduce the topic of energy sources or to revise them... 981 uses. A selection of English ESL renewable energy ppt slides.
According to the DOE's most recent liftoff report regarding Offshore Wind deployment, the market currently finds itself at a critical inflection point. Offshore wind presents a very promising source of renewable energy for the country, especially in light of the urgency to restructure our energy portfolio to meet the 2050 net-zero emission targets. Investing in wind complements other clean ...
This helpful PowerPoint provides definitions of renewable and non-renewable energy, with illustrated examples of each and how they work. Perfect for whole-class teaching, this renewable and nonrenewable resources ppt is suitable for a range of abilities in KS2 lessons.Learn what we use energy for and why we can't use renewable energy all the time. This could be a great accompaniment to ...
BOSTON (AP) — The Massachusetts House on Wednesday approved a bill that would help boost the state's reliance on renewable energy, in part by streamlining the state and local permitting process for projects that shift the state away from using fossil fuels. ... The House proposal also calls for procuring additional clean energy resources ...
Nationwide, solar power is the fastest growing form of renewable energy, but it still accounts for only about 5% of electricity generated. In California, it's nearly 30%, thanks to massive new ...
On a smaller scale, system operators at the Electric Reliability Council of Texas recently used the model in a project showing that grid-forming technology can better support the connection of renewable sources in "weak" power grids, which typically refer to remote rural areas far away from energy generators.. A renewable power plant in eastern Oregon plans to demonstrate the grid-forming ...
As a result, to achieve 100 percent clean energy — at least on paper — companies often buy what are known as renewable energy certificates, or RECs, from a solar or wind farm owner.
To "firm" or stabilise the supply of power from its renewable energy zones, China is using a mix of pumped hydro and battery storage, similar to Australia. "They're installing 1GW per month of ...
Plural Energy, an on-chain investing platform, announced its launch at the Ethereum Community Conference in Brussels, and the first asset to raise capital on the platform, The Ace Portfolio, is live and available to those interested in renewable energy investing. "The launch of our platform is the ...
What is this Renewable vs Nonrenewable Resources PowerPoint? Our Renewable vs Nonrenewable Resources PowerPoint is a fun and engaging way to teach 5th-grade students about different types of energy resources. With colorful illustrations throughout, this 15-slide presentation covers the basics of renewable and nonrenewable resources, perfect for Earth Day lessons.
Project 2025, a controversial conservative roadmap that aims to guide the next Republican administration, calls for the elimination of multiple energy- and environment-related offices and rules.
He's a Russian gentleman working in Saudi Arabia on The Line, a 105-mile-long indoor city running on renewable energy, described as a "giga-project" that will revolutionize the way residents will live their lives. There will be no cars, no emissions, and the people living there will spend most of their time "indoors."