

ANA Nursing Resources Hub
Search Resources Hub

Leadership in Nursing: Qualities & Why It Matters
4 min read • May, 19 2023
Strong leaders in nursing are vital to help navigate the constant evolution of health care. Nurse leaders do more than balance costs, monitor productivity, and maintain patient and staff satisfaction. They serve as role models and influence health care organizations at all levels. A strong nurse leader motivates their colleagues, setting the tone for a safe, civil workplace with a culture of high morale and job retention.
What Is a Nurse Leader?
A nurse leader is defined by their actions, and not always by a position of authority. Leaders in nursing inspire and influence others to achieve their maximum potential. They use applied leadership in nursing by drawing upon critical thinking skills to manage a team.
Nurse leaders take a broad view of how daily tasks impact the overall goals of the health care organization. They communicate expectations to their team and motivate them to achieve predetermined goals. Nurses can lead from various organizational areas if they project the necessary leadership qualities to influence others.
Leadership Qualities in Nursing
A nurse leader role combines essential nursing, business, and leadership skills developed through ongoing learning . They must be flexible enough to adapt to technological changes, fluctuating payment methods, new treatment modalities, and regulatory and legislative environments. Critical skills for effective nursing leadership include:
- Communication and Collaboration : These skills can reduce miscommunication, encourage shared decision making, and provide a sense of working together toward common goals.
- Education and Quality of Practice : Continued professional development allows leaders in nursing to keep pace with the ever-changing health care environment while striving for excellence by supporting quality, evidence-based practice.
- Environmental Health and Resource Utilization : Leadership in nursing ensures that patient care can be provided effectively in a safe and healthy environment while promoting wellness among all health care staff.
- Ethics and Professional Practice Evaluation : Influential nurse leaders model ethical practices to guide decisions, display honesty by being accountable for their actions, and evaluate their adherence to professional practice standards. Learn more about the Code of Ethics for Nurses .
- Professionalism and Leadership : Leaders in nursing build vital relationships and collaborate with various health care teams on sensitive topics. Using critical thinking skills allows those in nursing leadership roles to analyze decisions impacting the organization. They then clearly explain the rationale in a manner that encourages staff support.
Other nursing leadership skills, such as displaying compassion and empathy, can assist the nurse leader in developing interpersonal relationships and gaining respect in their role.
7 Leadership Styles in Nursing
Nursing leadership styles can impact job satisfaction , nurse retention rates , quality of care, and patient outcomes . The nurse’s educational background, personality, and work environment may influence their nursing leadership style. Each type of nurse leader role can be valuable when utilized in the right setting.
- The Transformational nurse leader works to inspire nurses to achieve a greater vision by helping with strength development. This nursing leadership style works well with mentoring.
- The Autocratic nurse leader makes quick decisions with little input from employees and excels at task delegation. This nursing leadership style may be most effective in an emergency.
- A Laissez-faire leadership style puts faith in every facet of a well-oiled machine. This method may work well with experienced teams or self-directed nurses.
- The Democratic nurse leader is collaborative and focuses on team success. This nurse leader might excel in quality improvement roles but may not be effective in situations requiring independent decisions.
- The Servant nurse leadership style focuses on employee development and individual needs. This method works well with goal-driven environments or as a nurse educator.
- The Situational leadership style is the most adaptable since it analyzes the situation and determines the appropriate approach. This nurse leader is flexible enough to modify their approach based on the organization or individual’s needs. This style works well with nursing students but may divert from the organization’s long-term goals.
- The Transactional nurse leader does well with short-term goals by focusing on efficiency and performance. This task-oriented style reduces errors and works well with tight deadlines.

Examples of Leadership in Nursing
Projecting leadership skills in nursing that influences others can allow a nurse to lead without being assigned a specific leadership position. The aspiring nurse leader might:
- Seek out a mentor or become one
- Volunteer for committee roles
- Become involved in the community
- Take educational courses
- Stay current on the latest health care trends
- Get involved with public policy
A nurse aspiring for a nursing leadership role can get a certification or obtain additional degrees specific to nursing leadership to increase their knowledge base and expand upon professional development. But a title and the education aren’t enough to create an effective leader. Nurses and other health care staff need to believe their contributions make a difference in the organization.
Why Is Nurse Leadership Important?
Nurse leaders make a difference in workplace culture and drive positive changes in health care legislation. When a team admires the qualities of their leader, it boosts morale and promotes a psychologically safe workplace, which leads to higher job satisfaction and retention rates. Influential leaders in nursing ensure that the organization's vision is communicated to the nursing staff while mentoring the nursing leadership of tomorrow .
Explore courses, webinars, and other nursing leadership and excellence resources offered by ANA .
Images sourced from Getty Images
You May Also Like
Specialty Certifications
Nurse Executive Certification (NE-BC®)
Price From: $395.00
ANA Member Price: $295.00
Nurse Executive, Advanced Certification (NEA-BC®)
Related Resources

Item(s) added to cart
YOUR FINAL GRADE - GUARANTEED UK Essay Experts
Disclaimer: This essay is provided as an example of work produced by students studying towards a nursing degree, it is not illustrative of the work produced by our in-house experts. Click here for sample essays written by our professional writers.
Please refer to an authoritative source if you require up-to-date information on any health or medical issue.
The Importance of Leadership in Nursing
| ✅ Free Essay | ✅ Nursing |
| ✅ 2632 words | ✅ 1st Jun 2020 |
Reference this
What is leadership and culture?
Get Help With Your Essay
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help! Find out more about our Essay Writing Service
Nursing leadership
Factors which contribute to nursing leadership, collective leadership, cite this work.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services

Essay Writing Service

- Dissertation Writing Service

- Assignment Writing Service
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please:
Our academic writing and marking services can help you!
- Find out more about our Essay Writing Service
- Undergraduate 2:2
- 7 day delivery
- Marking Service
- Samples of our Service
- Full Service Portfolio
Related Lectures
Study for free with our range of university lecture notes!
- Nursing Lectures
- All Available Lectures

Freelance Writing Jobs
Looking for a flexible role? Do you have a 2:1 degree or higher?
Study Resources
Free resources to assist you with your university studies!
- More Nursing Resources at NursingAnswers.net
- Reflective Models at NursingAnswers.net
- How to Write an Essay
- Essay Buyers Guide
- Referencing Tools
- Essay Writing Guides
- Masters Writing Guides
leadership in nursing essay

Nursing Leadership In Nursing
A leader is a person who can motivate others to do work to achieve the goals of the organization. In a nursing organization, improving the quality of healthcare delivered by the department to be equal with the organizational performance is a key role of leadership(Marquis and Huston, 2015). Nursing leadership is essential in the clinical setting and plays an important role in the development of the nurse as an individual or as a professional. An effective leader often has persistence, initiative
Leadership in Nursing
management and leadership of the nursing and health care team. Appropriate management and leadership theories will be used to support the issues which would be discussed in this essay. A critical analyses of the event we be carried out. Confidentiality will be maintained. Name and places used in this essay will be changed to maintain confidentiality in accordance to the Nursing and Midwifery council (NMC, 2008). Database search was carried out MEDLINE, CINAHL, BRITISH NURSING INDEX
The Leadership Of The Nursing
Leadership in Nursing Florence Nightingale once said, “May we hope that when we are all dead and gone, leaders will arise who have been personally experienced in the hard, practical work, the difficulties and the joys of organizing nursing reforms, and who will lead far beyond anything we have done” (as cited in Hassmiller, 2010, p. 2). The development of leaders in nursing is one of the most important tasks the nursing community faces today. Nurses in all positions should possess the basic leadership
Nursing Leadership
Experience Of Nursing Leaders And Lesson Learned Nursing leaders are essential as they are the motivators and backbones of the profession. Every nurse is trained to be a leader, although the profession is autonomous there are cases where exemplary leadership skills would be exhibited either formally as a job description or informally. Therefore, it is essential that every nurse should strive to be the best leader they can be. There are nursing leaders in virtually every sector. Nursing leaders are
Leadership In Nursing
Healthcare organizations and nursing implications are constantly changing, is important Nurse Leaders to interpret implications in the delivery of healthcare system. Nursing Management and Nursing Leadership while both having similar attributes are two different concepts, with two different characteristics, roles, and responsibilities. There are multiple Management and Leadership qualities, in which ethical considerations must be addressed. As new changes are so frequent in health care the Institute
Nursing professionals are the principal embodiment amongst the healthcare team, indicating that nursing services play an integral part in the productivity of the clinical environment and predominately determines the satisfaction level of the patients being cared for (Gabi, Kontodimopoulos, & Niakas, 2013). More importantly, lack of productively by healthcare workers care can contribute towards the quality of care services provided if nursing staff are lacking support, poor
between leadership and PS in a clinical-setting.PS is a care requirement mandated to health professionals to deliver a safe healthcare system (Baid, 2016). PS promotes patient-centred-care, and creates systems and processes for healthcare professionals to promptly identify and correct errors before it causes patient harm, reduces the possibility of errors, and is developed on a culture of safety that comprises organisations, healthcare professionals and patients (Baid, 2016). Leadership is a social
Nursing Leadership And The Role Of Leadership In Nursing Care
For adequate nursing care, leadership must be applied at all levels of nursing practice. The nurses form the leaders in their patient care activities. The nurses form the players of implementing the interventions that are goal driven with the aim of making the health status of the patient better. The position that nurses serve as leaders in their practice as well as the dynamics that revolve around the nursing leadership. All nurses should be considered leaders because of the roles they play while
The Five Competesions Of Nursing Leadership And Leadership In Nursing
Leadership is defined by the Merriam-Webster dictionary as “the power or ability to lead other people” (Merriam-Webster, 2017). A leader may also be thought of as a guide or a director. Our sixth president, John Quincy Adams quoted that "If your actions inspire others to dream more, learn more, do more and become more, you are a leader" (GovLeaders.org, 2017). But what makes a nursing leader? In the book “Leadership & Nursing Care Management”, Huber defines a nursing leader “…as the ability to inspire
Nursing Leadership And Advocacy : Nursing
Nursing Leadership and Advocacy Nursing leaders promote individuals to reach their highest potential. They provide guidance and direction to reach goals and visions in healthcare. Advocacy means to support a cause as defined by Merriam-Webster (2015). An advocate supports the interest of a person or patient. A successful advocate uses skills which combine collaboration, influence, problem solving, and communication per the ANA (2015). Personal and Professional Accountability Personal growth
Popular Topics
- karl marx vs robert reich essay
- carol ann duffy valentine essay
- health psychology essay
- paper towns by john green essay
- kanthal essay
- why i choose nursing essay
- public humiliation essay
- museum visit essay
- unwanted pregnancy essay
- bruce dawe drifters essay
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
The essentials of nursing leadership: A systematic review of factors and educational interventions influencing nursing leadership
Affiliations.
- 1 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Department of Nutrition, Dietetics and Food, School of Clinical Sciences at Monash Health, Monash University, Level 1, 264 Ferntree Gully Rd, Notting Hill, VIC 3168, Australia.
- 3 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada.
- 4 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada; Technical High School of Campinas, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Barão Geraldo, Campinas - São Paulo 13083-970, Brazil.
- PMID: 33383271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103842
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
Objectives: To identify determining factors of nursing leadership, and the effectiveness of interventions to enhance leadership in nurses.
Design: We conducted a systematic review, including a total of nine electronic databases.
Data sources: Databases included: Medline, Academic Search Premier, Embase, PsychInfo, Sociological Abstracts, ABI, CINAHL, ERIC, and Cochrane.
Review methods: Studies were included if they quantitatively examined factors contributing to nursing leadership or educational interventions implemented with the intention of developing leadership practices in nurses. Two research team members independently reviewed each article to determine inclusion. All included studies underwent quality assessment, data extraction and content analysis.
Results: 49,502 titles/abstracts were screened resulting in 100 included manuscripts reporting on 93 studies (n=44 correlational studies and n=49 intervention studies). One hundred and five factors examined in correlational studies were categorized into 5 groups experience and education, individuals' traits and characteristics, relationship with work, role in the practice setting, and organizational context. Correlational studies revealed mixed results with some studies finding positive correlations and other non-significant relationships with leadership. Participation in leadership interventions had a positive impact on the development of a variety of leadership styles in 44 of 49 intervention studies, with relational leadership styles being the most common target of interventions.
Conclusions: The findings of this review make it clear that targeted educational interventions are an effective method of leadership development in nurses. However, due to equivocal results reported in many included studies and heterogeneity of leadership measurement tools, few conclusions can be drawn regarding which specific nurse characteristics and organizational factors most effectively contribute to the development of nursing leadership. Contextual and confounding factors that may mediate the relationships between nursing characteristics, development of leadership and enhancement of leadership development programs also require further examination. Targeted development of nursing leadership will help ensure that nurses of the future are well equipped to tackle the challenges of a burdened health-care system.
Keywords: Interventions; Leadership; Nursing workforce; Systematic Review.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
PubMed Disclaimer
- Targeting personalised leadership factors based on the organisational needs of nurses may cultivate and improve their nursing leadership. Singh S, Kapoor S. Singh S, et al. Evid Based Nurs. 2022 Apr;25(2):68. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103385. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Evid Based Nurs. 2022. PMID: 34407986 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Factors contributing to nursing leadership: a systematic review. Cummings G, Lee H, Macgregor T, Davey M, Wong C, Paul L, Stafford E. Cummings G, et al. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2008 Oct;13(4):240-8. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2008.007154. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2008. PMID: 18806183 Review.
- Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia. Osborne SR, Alston LV, Bolton KA, Whelan J, Reeve E, Wong Shee A, Browne J, Walker T, Versace VL, Allender S, Nichols M, Backholer K, Goodwin N, Lewis S, Dalton H, Prael G, Curtin M, Brooks R, Verdon S, Crockett J, Hodgins G, Walsh S, Lyle DM, Thompson SC, Browne LJ, Knight S, Pit SW, Jones M, Gillam MH, Leach MJ, Gonzalez-Chica DA, Muyambi K, Eshetie T, Tran K, May E, Lieschke G, Parker V, Smith A, Hayes C, Dunlop AJ, Rajappa H, White R, Oakley P, Holliday S. Osborne SR, et al. Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
- Faculty development initiatives designed to promote leadership in medical education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 19. Steinert Y, Naismith L, Mann K. Steinert Y, et al. Med Teach. 2012;34(6):483-503. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.680937. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22578043 Review.
- Leadership styles and outcome patterns for the nursing workforce and work environment: A systematic review. Cummings GG, Tate K, Lee S, Wong CA, Paananen T, Micaroni SPM, Chatterjee GE. Cummings GG, et al. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Sep;85:19-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 May 3. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 29807190
- Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter. Rees S, Williams A. Rees S, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
- Succession Planning and Leadership Development in Nursing: A Bibliometric Analysis (2000-2023). Al Hajri AK. Al Hajri AK. Nurs Res Pract. 2024 Aug 9;2024:6191008. doi: 10.1155/2024/6191008. eCollection 2024. Nurs Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39156228 Free PMC article. Review.
- Hit the ground running: Starting to manage personnel and budgets as a new nurse scholar. Fauer AJ, Wilson R. Fauer AJ, et al. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2024 Jun 12;11(8):100533. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2024.100533. eCollection 2024 Aug. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39040224 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Development of a training program prototype to enhance implementation leadership competencies and behaviours of Chinese unit nurse managers: a qualitative descriptive study. Chen W, Graham ID, Hu J, Lewis KB, Zhao J, Gifford W. Chen W, et al. BMC Nurs. 2024 May 30;23(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-01989-8. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38816867 Free PMC article.
- Nursing leaders' perceptions of the impact of the Strengths-Based Nursing and Healthcare Leadership program three months post training. Lavoie-Tremblay M, Boies K, Clausen C, Frechette J, Manning K, Gelsomini C, Cyr G, Lavigne G, Gottlieb B, Gottlieb LN. Lavoie-Tremblay M, et al. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024 Mar 12;6:100190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2024.100190. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024. PMID: 38746810 Free PMC article.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of a Strengths-Based Nursing and Healthcare Leadership program aimed at building leadership capacity: A concurrent mixed-methods study. Lavoie-Tremblay M, Boies K, Clausen C, Frechette J, Manning K, Gelsomini C, Cyr G, Lavigne G, Gottlieb B, Gottlieb LN. Lavoie-Tremblay M, et al. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024 Feb 6;6:100184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2024.100184. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2024. PMID: 38746801 Free PMC article.
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Elsevier Science
Other Literature Sources
- scite Smart Citations
- MedlinePlus Health Information
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

June 1, 2024 . By Kepher
Nursing Leadership Essay: Engaging Examples and Tips for Powerful Essays

Table of Contents
The world of nursing is a complex and demanding one. Beyond the technical skills required to care for patients, successful nurses possess a unique blend of compassion, resilience, and leadership qualities. These qualities become even more crucial as nurses ascend the ranks and take on leadership roles. Writing a nursing leadership essay is a valuable exercise that allows you to reflect on your own leadership journey and articulate your vision for the future.
This essay delves into the intricacies of crafting a compelling nursing leadership essay by providing insightful examples and practical tips. From understanding the core elements to crafting an engaging narrative, this guide will give you the tools to showcase your leadership potential and stand out in the competitive field of nursing.
Understanding the Essence: Core Elements of a Nursing Leadership Essay
A successful nursing leadership essay goes beyond merely outlining leadership skills. It dives deep into your personal experiences, showcasing how you embody specific leadership qualities and how these qualities translate into tangible impact. The foundation of a compelling essay rests on the following core elements:
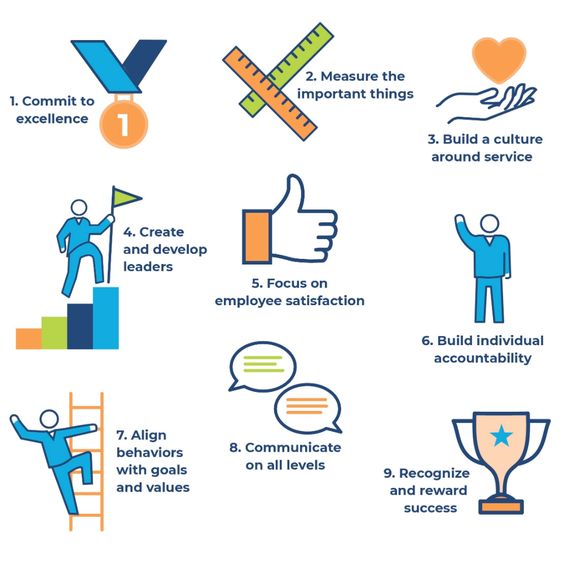
1. Defining Your Leadership Style:
Every leader possesses a unique approach. Identifying your leadership style is crucial for a compelling nursing leadership essay. Are you a transformational leader who inspires change and fosters a vision? Or perhaps a servant leader who prioritizes the needs of others and empowers team members?
- “My leadership style is rooted in collaboration and empathy. I believe in fostering a sense of shared purpose among my team members, empowering them to take ownership of their roles and contribute to a positive patient experience.”
2. Illustrating Your Leadership Journey:
This section is where you bring your leadership experiences to life. Choose impactful scenarios that demonstrate your abilities. Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to narrate these experiences effectively.
- Situation: “During a challenging shift with a surge in patient admissions, I noticed a sense of overwhelm among the staff.”
- Task: “I took the initiative to assess the situation and prioritize urgent tasks.”
- Action: “I delegated tasks strategically, ensuring efficient use of resources and maintaining patient safety.”
- Result: “Through effective communication and delegation, we were able to manage the influx of patients effectively, minimizing stress on the team and ensuring high-quality care.”
3. Demonstrating Impact:
Leadership is not just about skills; it’s about making a difference. Connect your leadership experiences to tangible outcomes.
- “By implementing a new protocol for patient education, I witnessed a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores and improved adherence to treatment plans.”
4. Reflecting on Your Growth:
Highlight your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. Mention specific courses, certifications, or mentorship experiences that have honed your leadership skills.
- “I am currently pursuing a Master’s degree in Nursing Administration to expand my knowledge base and develop advanced leadership skills.”
Crafting a Winning Narrative: Tips for a Standout Nursing Leadership Essay
Now that you understand the key elements, it’s time to craft a captivating narrative that showcases your leadership potential. Here are some valuable tips:
1. Start Strong with a Hook:
Grab the reader’s attention right from the start. Use a compelling anecdote, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful statement that sets the stage for your essay.

- “The call to nursing is not just about dispensing medication or monitoring vital signs; it’s about providing unwavering support and compassion to those in their most vulnerable moments.”
2. Weave a Consistent Theme:
Ensure your chosen examples and reflections all tie back to the central theme of your nursing leadership essay. A cohesive narrative will leave a lasting impression on the reader.
3. Stay Concise and Focused:
Avoid unnecessary details or tangents. Every sentence should contribute to your overall message.
4. Use Vivid Language:
Engage the reader with descriptive language that brings your experiences to life. Show, don’t tell, by using evocative imagery and specific examples.
5. Edit and Proofread Rigorously:
A well-written essay free from grammatical errors and typos demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail.
6. Seek Feedback from Mentors:
Before submitting your essay, ask trusted mentors or professors to review your work and offer constructive feedback.
Nursing Leadership Essay Examples: Inspiration from Leaders
To further inspire your own writing, here are some examples of how different leadership styles and experiences can be effectively conveyed in a nursing leadership essay:
Example 1: The Transformational Leader
- Theme: Empowering a team to achieve a shared vision.
- Experience: Implementing a new patient care model that prioritized patient-centered care and increased staff satisfaction.
- Impact: Improved patient outcomes and reduced staff burnout.
Example 2: The Servant Leader
- Theme: Prioritizing the needs of others and fostering a collaborative environment.
- Experience: Mentoring a new nurse during a challenging patient care situation.
- Impact: Enhanced the new nurse’s confidence and contributed to positive patient outcomes.
Example 3: The Visionary Leader
- Theme: Identifying future trends and implementing innovative solutions.
- Experience: Researching and implementing a new technology that streamlined patient care and improved efficiency.
- Impact: Enhanced patient safety and improved staff workflow.
Reputable academic writing websites like Nursing Papers provide well-articulated scholarly article samples that you can also refer to for more inspiration. The platform offers nursing essays, research papers and case studies that can be quite resourceful in writing your own papers.
Common Mistakes in Writing Nursing Leadership Essays
Writing a compelling nursing leadership essay can be challenging. It requires a strong understanding of leadership principles, clear communication, and a focused narrative. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Lack of a Clear Thesis Statement: A strong nursing leadership essay needs a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument. Avoid vague or generic statements and be specific about your leadership philosophy and its implications.
- Focusing Solely on Personal Experiences: While personal experiences can be valuable, relying solely on anecdotes without theoretical backing weakens the essay. Your nursing leadership essay should demonstrate your understanding of leadership theories and principles, using your experiences as illustrative examples.
- Ignoring the Audience: Remember your nursing leadership essay is for a specific audience, often an admissions committee. Tailor your language and content to address their expectations and the specific requirements of the essay prompt.
- Failing to Proofread Carefully: Typos, grammatical errors, and unclear writing can undermine the credibility of your nursing leadership essay. Take the time to proofread carefully and consider having a trusted friend or colleague review your work.
- Not Demonstrating Impact: A strong nursing leadership essay goes beyond simply describing leadership skills; it demonstrates how these skills have positively impacted others and contributed to the nursing profession.

By avoiding these common mistakes, you can craft a compelling nursing leadership essay that highlights your leadership potential and showcases your passion for the nursing profession. Remember, clarity, focus, and impactful storytelling are key to making your nursing leadership essay stand out.
Types of Nursing Leadership Essays
Nursing is a profession that demands strong leadership skills. From guiding patients and their families through challenging health journeys to leading teams of healthcare professionals, nurses are constantly demonstrating leadership in various ways. This diverse nature of nursing leadership lends itself to many types of essays, allowing students and professionals to explore different aspects of the field. Here are some common types of nursing leadership essays:
1. Personal Leadership Philosophy: These essays delve into an individual’s personal values, beliefs, and approaches to leadership. They often discuss the core principles that guide their actions and decision-making as a nurse leader.
2. Case Study Analysis: These essays involve analyzing a specific situation or case study related to nursing leadership. They can focus on a particular leadership challenge, a successful leadership initiative, or an ethical dilemma encountered by a nurse leader.
3. Leadership Theory Application: These essays explore how different leadership theories and models can be applied in real-world nursing practice. Students might analyze the strengths and weaknesses of various approaches and discuss their preferred leadership style based on specific contexts.
4. Transformational Leadership in Nursing: This type of essay focuses on the importance of transformational leadership in fostering positive change within the healthcare system. It might delve into strategies for motivating staff, promoting innovation, and improving patient care.

5. Ethical Dilemmas and Leadership: These essays examine ethical challenges faced by nurse leaders and explore how they can be addressed. They might discuss navigating conflict of interest, advocating for patient rights, or promoting ethical decision-making within a healthcare team.
6. Future of Nursing Leadership: This type of essay explores the evolving landscape of nursing leadership. It might discuss emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities for nurse leaders in the future. It can also consider the impact of technological advancements and changing healthcare systems on leadership practices.
7. The Role of Nurses in Advocacy: This essay explores how nurses can advocate for their patients, their profession, and the healthcare system as a whole. It highlights the importance of nurse leaders in advocating for policy changes, resource allocation, and improved patient outcomes.
These are just a few examples of the many types of nursing leadership essays that can be explored. Each type offers a unique opportunity to engage in critical thinking, reflection, and analysis of leadership principles in the context of nursing practice.
By exploring different aspects of nursing leadership essays, students and professionals can deepen their understanding of leadership concepts, hone their writing skills, and contribute valuable insights to the field. Regardless of the specific type, nursing leadership essays play a critical role in advancing the profession and fostering a more effective and compassionate healthcare system.
An engaging nursing leadership essay is a powerful tool for showcasing your commitment to professional development and your vision for the future of nursing. By understanding the core elements, crafting a compelling narrative, and seeking feedback, you can create an essay that leaves a lasting impression and helps you advance on your path to nursing leadership.
Remember, the essence of leadership lies in serving others and making a positive impact. Through your essay, let your passion for nursing shine through, demonstrating your ability to inspire, guide, and lead with compassion and integrity.
Get the Best Nursing Leadership Essay Writing Service
At phdnursewriter.com , we provide the best nursing leadership essay writing service to put you on the right path to academic success. Our service covers topic suggestion, paper writing, proof reading and editing, plagiarism check and removal. We guarantee an original and compelling nursing paper that will make you stand out from the rest.
- nursing leadership ,
- nursing leadership essay ,
- Article Reviews (2)
- Case Studies (9)
- Dissertations (13)
- Nursing essays (27)
- Nursing Thesis (6)
- Research papers (22)
- Uncategorized (28)
Recent News
Nursing Dissertation Outline: A Definitive Writing Guide
Dissertation writing pitfalls: the top 10 mistakes to avoid for success, nursing essay topic: top 20 topics for compelling nursing essays, struggling with your essay.
Top-class writers are here!

Our Products/Tools
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Thesis statement generator
- Words to pages converter
- Free college GPA calculator
- Citation Generator
- Plagiarism Checker Reddit
Legal & Policies
- Terms & Conditions
- Refund policy
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
Customer Services
- Code of conduct
+1-917-810-5386
© 2024 PHD Nurse Writer. All rights reserved.
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Alban-Metcalfe J, Alimo-Metcalfe B. Reliability and validity of the ‘leadership competencies and engaging leadership scale’. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2013; 26:(1)56-73 https://doi.org/10.1108/09513551311294281
Avery GC. Understanding leadership: paradigms and cases.London: Sage; 2004
Avolio BJ, Waldman DA, Yammarino FJ. Leading in the 1990s: the four I's of transformational leadership. Journal of European Industrial Training. 1991; 15:(4) https://doi.org/10.1108/03090599110143366
Baker SD. Followership: the theoretical foundation of a contemporary construct. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies. 2007; 14:(1)50-60 https://doi.org/10.1177/0002831207304343
Binci D, Cerruti C, Braganza A. Do vertical and shared leadership need each other in change management?. Leadership and Organization Development Journal. 2016; 37:(5)558-578 https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-08-2014-0166
Braun S, Peus C, Weisweiler S, Frey D. Transformational leadership, job satisfaction, and team performance: a multilevel mediation model of trust. Leadership Quarterly. 2013; 24:(1)270-283 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2012.11.006
Carson JB, Tesluk PE, Marrone JA. Shared Leadership in teams: an investigation of antecedent conditions and performance. Academy of Management Journal. 2007; 50:(5)1217-1234
Summary of key research findings from the NHS staff survey. NHS Survey Coordination Centre. 2018. https://tinyurl.com/y4ofshoy (accessed 13 March 2019)
Deinert A, Homan AC, Boer D, Voelpel SC, Gutermann D. Transformational leadership sub-dimensions and their link to leaders' personality and performance. Leadership Quarterly. 2015; 26:(6)1095-1120 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2015.08.001
Report of the committee of inquiry into allegations of ill-treatment of patients and other irregularities at the Ely Hospital.Cardiff. London: HMSO; 1969
D'Innocenzo L, Mathieu JE, Kukenberger MR. A meta-analysis of different forms of shared leadership–team performance relations. Journal of Management. 2016; 42:(7)1964-1991 https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206314525205
Authentic leadership theory and practice: origins, effects and development. In: Gardner WL, Avolio BJ, Walumbwa FO (eds). Bingley: Emerald Press; 2005
Gillespie NA, Mann L. Transformational leadership and shared values: the building blocks of trust. Journal of Managerial Psychology. 2004; 19:(6)588-607 https://doi.org/10.1108/02683940410551507
Improving quality in the English NHS. A strategy for action. 2016. https://tinyurl.com/yxavguvr (accessed 13 March 2013)
Hamlin RG. A study and comparative analysis of managerial and leadership effectiveness in the National Health Service: an empirical factor analytic study within an NHS trust hospital. Health Serv Manage Res.. 2002; 15:(4)245-263 https://doi.org/10.1258/095148402320589046
Health Foundation. Transformational change in NHS providers. 2015. https://tinyurl.com/y5jryfgu (accessed 13 March 2013)
Jackson B, Parry K. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about studying leadership, 2nd edn. London: Sage; 2011
Investigating collaborative leadership for communities of practice in learning and skills. 2007. https://tinyurl.com/y5uuhly9 (accessed 13 March 2019)
The King's Fund. The future of management and leadership: no more heroes. 2011. https://tinyurl.com/yakyju8b (accessed 13 March 2019)
Merkens BJ., Spencer JS. A successful and necessary evolution to shared leadership: a hospital's story. Leadership in Health Services. 1998; 11:(1)1-4
NHS Leadership Academy. Healthcare leadership model: the nine dimensions of leadership behaviour. 2013. https://tinyurl.com/ybwfg7b7 (accessed 13 March 2019)
NHS Survey Coordination Centre. NHS staff survey 2017. National briefing. 2018. https://tinyurl.com/y6tla4bw (accessed 13 March 2019)
Nicolaides VC, LaPort KA, Chen TR The shared leadership of teams: a meta-analysis of proximal, distal, and moderating relationships. The Leadership Quarterly. 2014; 25:(5)923-942
Pearce CL, Sims HP. Shared leadership: toward a multi-level theory of leadership. Advances in Interdisciplinary Studies of Work Teams. 2000; 7:115-139
Robert LP, You S. Are you satisfied yet? Shared leadership, individual trust, autonomy, and satisfaction in virtual teams. Journal of the Association of Information Science and Technology. 2018; 69:(4)503-511
Saks AM. Antecedents and consequences of employee engagement. Journal of Managerial Psychology. 2006; 21:(7)600-619
Can we never learn? Abuse, complaints and inquiries in the NHS. History and Policy. 2015. https://tinyurl.com/yypm45ae (accessed 13 March 2019)
Tsai Y, Wu S-W. The relationships between organisational citizenship behaviour, job satisfaction and turnover intention. J Clin Nurs.. 2010; 19:(23–24)3564-3574 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03375.x
Tse H, Chiu W. Transformational leadership and job performance: a social identity perspective. Journal of Business Research. 2014; 67:(1)2827-2835 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2012.07.018
Uhl-Bien M, Riggio R, Lowe K, Carsten M. Followership theory: a review and research agenda. Leadership Quarterly. 2014; 25:(1)83-104 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2013.11.007
Wang XF., Howell JM. A multilevel study of transformational leadership, identification, and follower outcomes. Leadership Quarterly. 2012; 23:(5)775-790 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2012.02.001
It's not about the money: staff engagement comes first. 2018. https://tinyurl.com/yxnpqhj3 (accessed 13 March 2019)
Leadership and leadership development in health care: the evidence base. 2015. https://tinyurl.com/ybsmpmwn (accessed 13 March 2019)
Zhua W, Avolio BJ, Riggio RE, Sosik JJ. The effect of authentic transformational leadership on follower and group ethics. Leadership Quarterly. 2011; 22:(5)801-817
Models of leadership and their implications for nursing practice
S'thembile Thusini
MSc Student, Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery and Palliative Care, King's College London
View articles · Email S'thembile
Julia Mingay
Lecturer, Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery and Palliative Care, King's College London
View articles
Leadership in today's NHS, either as a leader or follower, is everybody's business. In this article, an MSc student undertaking the Developing Professional Leadership module at King's College London describes two leadership models and considers their application to two dimensions of the NHS Healthcare Leadership Model: ‘Engaging the team’ and ‘Leading with care’. The author demonstrates the value of this knowledge to all those involved in health care with a case scenario from clinical practice and key lessons to help frontline staff in their everyday work.
The Ely inquiry into the systematic brutal treatment of patients in a Cardiff mental institution was the first formal inquiry into NHS failings ( Department of Health and Social Security, 1969 ). Since that time there have been more than 100 inquiries with inadequate leadership persistently identified as a major concern ( Sheard, 2015 ). National responses have included the NHS Healthcare Leadership Model, delivered by the NHS Leadership Academy and its partners (2013) . A range of online and face-to-face programmes aim to increase an organisation's leadership capacity by developing leaders who pay close attention to their frontline staff, understand the contexts in which they work and the situations they face and empower them to lead continuous improvements that enhance patient outcomes and safety ( NHS Leadership Academy, 2013 ).
At King's College London, ‘Developing Professional Leadership’ is a core module of the Advanced Practice (Leadership) pathway. The module critically appraises theoretical and professional perspectives on leadership and supports participants to take up leadership roles with attention to ethical practice. Both national and college leadership activities promote an understanding of vertical transformational leadership (VTL) and shared leadership (SL).
Register now to continue reading
Thank you for visiting British Journal of Nursing and reading some of our peer-reviewed resources for nurses. To read more, please register today. You’ll enjoy the following great benefits:
What's included
Limited access to clinical or professional articles
Unlimited access to the latest news, blogs and video content
Signing in with your registered email address
Leadership in Nursing
This essay will discuss the concept and significance of leadership in nursing. It will explore the qualities and skills that make an effective nurse leader, such as communication, empathy, and decision-making. The piece will also examine the challenges nurse leaders face and the impact of good leadership on patient care, team dynamics, and healthcare systems. It will consider the evolving role of nurses in leadership positions within the healthcare sector. Moreover, at PapersOwl, there are additional free essay samples connected to Health Care.
How it works
Leadership is an art, skill or quality of an individual who can positively influence the people to achieve maximum in their life. A true leader is a person who can manage both success and failure with compassion. He or she tries to analyze what went wrong rather than blaming the team members. He has a vision and plan to accomplish the task. Along with the vision, he has a quality of conveying his vision in a way so that it can motivate his team members to work together in achieving a goal.
Fair leadership skills lead to success and happiness. After all, it’s not only the destination that matters but the journey too.
A good leader, positive work environment helps in the retention of the team employees. I am truly inspired by the legend “Dr APJ Abdul Kalam” who was the eleventh president of India. He was a great politician, a teacher, leader, space scientist and a humble person. He was the first scientist to chair the position of a president. (intext). He received many awards of honor such as Padma Bhusan(1981), Padma Vibhusan (1990), Bharat Ratna (1997). (intext). Not only he was an aerospace engineer but also a writer. He was a man with curiosity and passion to fly as high as he could in the sky. (intect) With his passion he ignited million of dreams of the people. One of the important qualities of a leader is to inspire others to believe in their dreams rather than making them believe in their own dreams.
APJ Abdul Kalam had such an amazing quality to let the people follow their dream instead of following what he say is right. He used to inspire everyone to follow their vision and transform them into actions. He always believed in having a clear vision, transparency, creativity, knowledge and integrity. I truly admire his qualities such as positive thinking, passion for work, integrity, hardworking, determination, accountability, punctuality and creativity. He was always transparent in his approach towards his team members. He always uses to listen to his colleagues before making any decision. He was humble and respectful towards his team, their viewpoint which is very important for an effective leadership. He always led the team from behind and put others in front specially at the time of success.
During the times of failure he always took front line approach and always was responsible and accountable for his actions. He was always appreciative towards his team members. (intext wagon). I personally believe in leading the team from back. Leadership does not mean that you give instructions to the team, but to encourage his or her team, listen to their viewpoint, analyze and assign tasks according to the strength and weakness of his team members. A leader should know his team well in order to succeed.
I also believe in accountability and compassion. As a nurse, it is very important that we should take responsibility of our actions as it affects patient’s safety and quality of life. Compassion, kindness and humanity are important for ever profession so as in nursing. At the end of the day, all that matters is how did the patient feel about the care. Communication technique is also very important quality a leader should have. The way you say certain things can have a great impact on others. It can build or destroy a relationship.
As nurses, we interact with other nurses, doctors, social worker, family members of the patient, patient etc.Good communication skills and qualities can enhance the workplace environment and patient’s satisfaction. I also believe in integrity. I am honest and passionate about my work. I follow the same rules and regulations what I expect from others. The workplace environment has a great psychological impact on our mind. A leader with good emotional intelligence and positive attitude can create a happy environment. Every team member feels valued and the staff builds a trustworthy and solid foundation. I always go to my clinical with a positive attitude. I always encourage my colleagues, help them, learn from them and appreciate them for their hard work. I am always empathetic because I know it feels great when someone understands your viewpoint without making judgments. I will be working in few months as a registered nurse. I have not accomplished a leadership status yet. But I believe everything takes time. I always take responsibility in what I do. I look at the whole situation before arriving to any statement and decision. I believe I can be a leader as well. Every journey has ups and downs.
A leader or a team also has to deal with many challenges during their way. I have a mindset that focusing on the ways of improving the situation rather than blaming or criticizing is the best approach at the time. As a leader, I will be respectful to my team members. I will strive for safe and quality care through effective teamwork and collaboration. I will respect my time and will try to be productive at work. Success of a team not only depends upon the hard work of the team members and leader but also upon the relationships amongst the team members. A toxic work environment and lack of communication can lead to error.
In my viewpoint, a favorable workplace is one where each member of the team feels respected and appreciated. I will always be grateful to my team members and will never consider someone superior or inferior. I will love to share my knowledge and learn new things from my team. I will be self aware and thoughtful in my actions. I will lead the team with an open mindset as I know people, situations and things change with time. As a team member I always expect that everyone is open to each other related to the work matter.
Coordination is very important to achieve a goal or accomplish a task. Team members should have a working agreement amongst them. I expect everyone in the team to be responsible of their actions. I want every team member to be sensitive and considerate to others. Leading a team is bringing best in the people even during difficult times. I want everyone to be honest and flexible to the people and situations. As a leader, I will give freedom to my team members so that our team can come up with new ideas and creativity. I will try to create a relaxing and positive work environment. My personal philosophy is that a great leader is the one who believes in shared vision, enables other to act and encourages everyone around him or her. As a leader, I will aim to open lines of communication and trust in order to attain the highest level of teamwork.
Cite this page
Leadership in Nursing. (2021, Jan 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/
"Leadership in Nursing." PapersOwl.com , 14 Jan 2021, https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/
PapersOwl.com. (2021). Leadership in Nursing . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/ [Accessed: 28 Aug. 2024]
"Leadership in Nursing." PapersOwl.com, Jan 14, 2021. Accessed August 28, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/
"Leadership in Nursing," PapersOwl.com , 14-Jan-2021. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/. [Accessed: 28-Aug-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2021). Leadership in Nursing . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/leadership-in-nursing/ [Accessed: 28-Aug-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Nurse — Importance of Leadership in Nursing: Styles and Impact
Importance of Leadership in Nursing: Styles and Impact
- Categories: Leader Nurse
About this sample

Words: 784 |
Published: Sep 12, 2023
Words: 784 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Leadership styles in nursing, adapting leadership styles, impact of effective nurse leadership, elevating nursing values.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 525 words
2 pages / 739 words
2 pages / 933 words
2 pages / 684 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled

Related Essays on Nurse
The topic of this essay is why I want to become a nurse. As just an only child from Canyon Lake, Texas, I have always been a helper. From taking out the trash to folding the laundry. This trait has followed me forever and I [...]
In a world filled with countless career paths and opportunities, the decision to become a nurse is one that requires a special kind of dedication, compassion, and resilience. From the bustling emergency room to the quiet halls [...]
International Journal of Nursing Practice, Nursing Prioritization of the Patient Need for care: A tact knowledge embedded in the clinical decision-making literature October 2009Nurses storied experiences of direction and [...]
I have always been drawn to the field of nursing because of its unique combination of scientific knowledge and compassionate care. The ability to make a positive impact on someone's life during their most vulnerable moments is a [...]
Bureau of Labor Statistics. ( 2019, September 4). Registered nurses. Retrieved from
Why do you want to become a nurse? When being asked such question I would respond that Nurse Practitioner is a great occupation for me because it satisfies my personality, interests, and values. I took two personality tests and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Academic Specialization
Marietta j. bell scriber’s mentorship, contribution.
In the field of nursing, mentors assist in critically advising and supporting students, they are our primary sources of valuable information on program operations, policies, and measures. In addition, they guide us on our career objectives and how to overcome obstacles and ensure success (Bell-Scriber & Morton 2009).
My mentor is Marietta J. Bell Scriber. Marietta holds a degree from Saginaw General Hospital School of Nursing. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) from Ferris State University, a Master’s of Science in Nursing from Grand Valley State University and a Ph.D. from Michigan State University.
Marietta specializes in the area of cardiovascular nursing. She also deals with nursing administration, family nursing, cultural diversity, and global consciousness.
Currently, she is an associate professor and she is still researching cultural diversity in relation to the nursing profession and practices. She holds a leadership position as the chairperson of Epsilon Eta chapter; this society assists in the advancement of nursing students through scholarships. I contacted her through the internet social media, read her various publications as well as attended her inspiring presentations.
Marietta’s personal interest in mentoring and genuine concern in student performance has contributed to her success as a mentor. This is evident in most of her inspirational books and various presentations. She also provides education to others as she will soon be teaching in the Republic of Cyprus as Fulbright scholar. She also offers guidance on time management, schedule benchmarks, and program concepts, which have assisted me in developing unique nursing skills and knowledge. In addition, she has helped me identify my strengths and weaknesses and overcome my weaknesses.
In her publications, she highlights the importance and ways of achieving quality and unique health care policies and good work ethics. These are essential for every nursing student worldwide. She emphasizes on the importance of consistency and proper protocol in nursing (American Psychological Association, 2010).
She also puts a lot of emphasis on interprofessional team building in nursing as a career as well as sharing of information. It does not only increase awareness but also reinforces student’s knowledge and helps in demonstrating one’s skills. By being a leader at Chair of Epsilon Eta Chapter, she has been able to assist many nursing students and contributed to a positive move in the nursing profession. She also helps nursing students in becoming effective leaders in future and in proper management in nursing. This includes stress management at work place since nursing is a very sensitive career (Sullivan, 2012).
The other common factors that she puts emphasis on are nurse coaching and discipline to assist future nurses maintain proper ethics and learn policies at work places about how to deal with problems as they arise and to improve problem solving skills. This includes the importance of professional behavior and proper communication. In her effort to support the nursing students, she highlights and discusses the importance of effective and efficient leadership in nursing and various ways of motivating and improving staff including career advancements. The importance of proper planning and reducing time wastage such as proper bookings are also essential and critical in nursing as they assist a nurse in setting and achieving departmental, professional, financial and social goals (Amer, 2013).
Amer, K. (2013). Quality and safety for transformational nursing: Core Competencies . Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson.
American Psychological Association. (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association . Washington, DC.
Bell-Scriber, M. & Morton, A. (2009). Clinical Instruction Institute: Train the trainer. Nurse Educator, Michigan, USA: Ferris State University.
Sullivan, J. (2012). Effective leadership and management in nursing (8th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson.
- Ethics in Nursing Profession and Its Importance
- Nurse Management: Finding the Most Useful Theory
- Female Philosophers Stands
- Quantitative Data in Social Sciences
- The Play "Tartuffe": Intro to Drama
- Nursing Students' Experiences With Incivility in Clinical Education
- Wisdom Teeth Removal Post-Effects, Diagnosis and Intervention
- Challenging Communication With an Angry Patient
- Increasing Participation in Medical Nursing
- "The Black Balloon" From a Psychological Perspective
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, April 23). Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing. https://ivypanda.com/essays/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/
"Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." IvyPanda , 23 Apr. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing'. 23 April.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." April 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
1. IvyPanda . "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." April 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." April 23, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
Inspiring Leadership in Nursing: Key Topics to Empower the Next Generation of Nurse Leaders

This article was written in collaboration with Christine T. and ChatGPT, our little helper developed by OpenAI.

Nursing leadership plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, influencing the quality of patient care and the overall performance of healthcare organizations. As the nursing profession continues to evolve, aspiring nurse leaders must stay informed about the latest developments and best practices in nursing leadership. This comprehensive guide explores essential nursing leadership topics, offering valuable insights and strategies for success.
The Importance of Nursing Leadership
Impact on patient care.
Effective nursing leadership directly impacts patient care, ensuring that nurses provide safe, high-quality, and evidence-based care. Nurse leaders play a critical role in developing and implementing policies, protocols, and standards of practice that promote positive patient outcomes.
Topic Examples
- The role of nurse leaders in reducing hospital-acquired infections
- How nurse leaders can improve patient satisfaction
- The effect of nursing leadership on patient safety initiatives
- Combating health care-associated infections: a community-based approach
- Nurse leaders’ impact on the reduction of medication errors
- Promoting patient-centered care through nursing leadership
- The role of nurse leaders in implementing evidence-based practices to improve patient outcomes
- How transformational leadership can positively impact patient satisfaction
- The impact of nurse leaders on patient safety and error reduction initiatives
Medical Studies Overwhelming?
Delegate Your Nursing Papers to the Pros!
Get 15% Discount
+ Plagiarism Report for FREE
Influence on Organizational Performance
Nurse leaders contribute to the overall performance of healthcare organizations by guiding and supporting nursing teams, managing resources, and participating in decision-making processes. Their leadership helps create a positive work environment, reduce staff turnover, and improve patient satisfaction.
- How nurse leaders can contribute to reducing staff turnover
- The role of nurse leaders in improving the hospital’s financial performance
- Nurse leaders as drivers of organizational culture
- The integral role of nurses in healthcare systems: the importance of education and experience
- The relationship between nurse leadership and hospital readmission rates
- How nurse leaders can contribute to reducing healthcare costs
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting interprofessional collaboration to improve organizational performance
- Strategies for nurse leaders to foster a positive work environment
- The impact of nursing leadership on employee engagement and satisfaction
Advancement of the Nursing Profession
Nurse leaders advocate for nursing, promoting professional development, innovation, and research. They also work to elevate the nursing profession’s status, fostering collaboration and interdisciplinary partnerships.
- The role of nurse leaders in shaping the future of nursing education
- How nurse leaders can advocate for the nursing profession
- The impact of nurse leaders on the development of nursing standards and policies
- Encouraging research and evidence-based practice among nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting interprofessional collaboration
- Encouraging the pursuit of advanced nursing degrees and certifications among nursing staff
- The impact of nurse leaders on shaping healthcare policies and regulations
- How nurse leaders can advocate for improved working conditions and fair compensation for nursing staff
Essential Nursing Leadership Skills
Communication and interpersonal skills.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are crucial for nursing leaders. They must listen actively, express themselves clearly, and demonstrate empathy and understanding when interacting with colleagues, patients, and families.
- Active listening skills for nurse leaders
- Developing emotional intelligence in nursing leadership
- The role of nonverbal communication in nursing leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to improve communication with their teams
- How nurse leaders can facilitate open and honest feedback
- The importance of emotional intelligence in nurse leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to improve their communication skills with diverse populations
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering effective communication within interdisciplinary healthcare teams
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Abilities
Nurse leaders must be skilled in making informed decisions and solving complex problems. They should be able to analyze situations, weigh the pros and cons of various options, and choose the best course of action.
- Critical thinking skills for nurse leaders
- Ethical decision-making in nursing leadership
- The role of evidence-based practice in nursing leadership decisions
- Strategies for nurse leaders to develop effective problem-solving skills
- The importance of collaboration and teamwork in decision-making for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in crisis management and emergency preparedness
- How nurse leaders can develop effective problem-solving strategies to address complex healthcare challenges
Time Management and Organization
Managing time and resources effectively is essential for nurse leaders. They must be able to prioritize tasks, delegate responsibilities, and balance competing demands to ensure the smooth operation of their teams and organizations.
- Prioritization techniques for nurse leaders
- The role of delegation in effective time management for nursing managers
- Strategies for nurse leaders to manage workload and reduce stress
- Balancing clinical and administrative responsibilities as a nurse leader
- Time management tools and techniques for nurse leaders
- The importance of delegation in nurse leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to effectively manage their workload and prioritize tasks
- The role of nurse leaders in creating efficient workflows and processes within nursing teams
Embracing Diversity and Inclusivity in Nursing Leadership
The value of a diverse nursing workforce.
A diverse nursing workforce brings unique perspectives, experiences, and skills to the healthcare environment, benefiting patient care. By embracing diversity, nurse leaders can foster a more inclusive and supportive work environment that encourages collaboration and innovation.
- The benefits of diverse nursing teams for patient care
- The role of nurse leaders in recruiting and retaining diverse nursing staff
- Addressing health disparities through a diverse nursing workforce
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice and leadership
- Encouraging diverse perspectives and experiences in nursing teams
- Global health learning in nursing and health care disparities
- The benefits of having a diverse nursing workforce on patient outcomes and satisfaction
- Addressing health disparities through culturally competent nursing leadership
Strategies for Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
Nurse leaders can promote diversity and inclusion by implementing hiring and promotion practices that support equal opportunities, offering cultural competency training, and actively addressing discrimination and bias within their organizations.
- Overcoming unconscious bias in nursing leadership
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering an inclusive work environment
- Strategies for promoting diversity and inclusion in nursing education
- The impact of diversity and inclusion on nursing team performance
- Encouraging cultural competence and sensitivity among nursing staff
- Implementing diversity and inclusion training programs for nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a culture of respect and inclusivity within nursing teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address unconscious bias and promote equity in the workplace
Developing and Mentoring Future Nurse Leaders
Identifying and nurturing leadership potential.
Nurse leaders play an essential role in identifying and nurturing the leadership potential of their staff. By offering guidance, encouragement, and opportunities for growth, they can help prepare the next generation of nurse leaders.
- Recognizing leadership potential in nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to develop their team’s leadership skills
- The importance of succession planning in nursing leadership
- Encouraging a growth mindset among nursing teams
- The role of mentorship and coaching in nurturing future nurse leaders
- Strategies for nurse leaders to identify and develop emerging nurse leaders within their teams
- The role of nurse leaders in creating leadership development programs for nursing staff
Mentorship and Coaching
Mentorship and coaching are invaluable for aspiring nurse leaders. By sharing their knowledge, experience, and insights, experienced nurse leaders can help guide and support those looking to advance in nursing.
- The benefits of mentorship for both mentors and mentees in nursing
- Developing effective mentoring relationships in nursing
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a mentoring culture
- Strategies for providing constructive feedback and coaching to nursing staff
- Encouraging professional growth and development through mentorship
- The benefits of mentorship relationships for both mentors and mentees in nursing
- Strategies for nurse leaders to establish effective mentorship programs within their organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in providing coaching and feedback to nursing staff for professional growth
Promoting Teamwork and Collaboration in Nursing
The importance of teamwork in healthcare.
Teamwork is crucial for delivering safe, high-quality patient care. Nurse leaders must foster a culture of collaboration, encouraging open communication, mutual support, and shared decision-making among their teams.
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting effective teamwork
- Strategies for building trust and collaboration among nursing teams
- The impact of teamwork on patient care and safety
- The benefits of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a positive team culture
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting collaboration and teamwork among nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address and resolve conflicts within nursing teams
- The impact of effective teamwork on patient outcomes and staff satisfaction in healthcare settings
Strategies for Building Effective Nursing Teams
Nurse leaders can build effective nursing teams by promoting shared goals and values, providing clear expectations and feedback, and recognizing and celebrating team achievements. Additionally, they should facilitate team-building activities and opportunities for professional development, which can strengthen team cohesion and performance.
- The importance of clear communication and expectations in nursing teams
- Strategies for addressing and resolving conflicts within nursing teams
- The role of team-building activities in fostering collaboration and trust among nursing staff
- The impact of shared decision-making on nursing team performance
- Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and learning within nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in selecting and retaining top nursing talent
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create a positive work environment that fosters teamwork and collaboration
- The importance of team-building activities and exercises for nursing staff
Advocating for Nursing and Improving Patient Care
Policy and advocacy.
Nurse leaders are responsible for advocating for policies and initiatives that support the nursing profession and improve patient care. They should be informed about healthcare legislation, engage in advocacy efforts, and encourage their teams to participate in policy-making.
- The role of nurse leaders in shaping healthcare policy
- Strategies for nurse leaders to advocate for the nursing profession at the local, state, and national levels
- The impact of nursing leadership on the development and implementation of healthcare policies and regulations
- Engaging nursing staff in policy discussions and advocacy efforts
- The importance of staying informed about current healthcare policy issues for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in advocating for policies that improve patient care and support the nursing profession
- Strategies for nurse leaders to effectively engage with policymakers and stakeholders
- The impact of nurse leaders on shaping healthcare policies at the local, state, and national levels
Driving Quality Improvement and Innovation
Nurse leaders must be committed to continuous quality improvement and innovation in patient care. By staying informed about evidence-based practices and encouraging their teams to adopt innovative approaches, they can drive positive change within their organizations and the healthcare industry.
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting a culture of continuous quality improvement
- Strategies for nurse leaders to identify and address areas for improvement in patient care
- The impact of nursing leadership on the implementation of evidence-based practices and innovations
- Encouraging a culture of creativity and innovation among nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in driving change and improvement in healthcare organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in leading quality improvement initiatives within their organizations
- Strategies for nurse leaders to foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation among nursing staff
- The impact of nurse-led quality improvement projects on patient care and organizational performance
Fostering a Positive Work Environment
Creating a supportive and respectful culture.
A positive work environment is essential for nursing staff satisfaction, retention, and performance. Nurse leaders should foster a culture of support and respect where staff feels valued, empowered, and motivated to provide the best possible care.
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a positive work environment
- Strategies for nurse leaders to promote a culture of support and respect among nursing staff
- The importance of addressing and preventing workplace bullying and incivility in nursing
- Encouraging open and honest communication within nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting work-life balance and well-being among nursing staff
Addressing Workplace Challenges and Conflicts
Nurse leaders must be proactive in addressing workplace challenges and conflicts. They can maintain a healthy and productive work environment by developing and implementing strategies to manage issues such as workload, burnout, and interpersonal conflicts.
- The role of nurse leaders in conflict resolution within nursing teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address common workplace challenges, such as staffing shortages and burnout
- The importance of developing a proactive approach to addressing conflicts and challenges in nursing
- Promoting a culture of accountability and responsibility among nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in providing support and resources for nursing staff facing challenges and conflicts
- Conflict resolution strategies for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in mediating and resolving interprofessional conflicts within healthcare teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to prevent and address workplace burnout among nursing staff
Lifelong Learning and Professional Development
Commitment to continuing education.
Lifelong learning is essential for nurse leaders to stay current with healthcare and nursing practice advances. They should pursue continuing education opportunities, research, and stay informed about industry trends and best practices.
- The importance of lifelong learning for nurse leaders and nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to promote a culture of continuous education and professional development within their teams
- The impact of continuing education on nursing practice and leadership
- Encouraging nursing staff to engage in professional development opportunities
- Transforming advanced nursing practice: embracing IOM recommendations and higher education
- The role of nurse leaders in staying informed about current nursing research and best practices
- The impact of continuing education on nursing practice and patient outcomes
- Strategies for nurse leaders to support and encourage continuing education among their nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in staying up-to-date with the latest nursing research, guidelines, and best practices
Encouraging Professional Development in Nursing Teams
Nurse leaders should support and encourage the professional development of their nursing teams. By providing resources, opportunities, and encouragement, they can help their staff grow professionally and contribute to advancing the nursing profession.
- The role of nurse leaders in identifying professional development opportunities for nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create individualized professional development plans for their team members
- The importance of fostering a growth mindset among nursing staff
- Encouraging nursing staff to participate in conferences, workshops, and other professional development activities
- The role of nurse leaders in providing mentorship and guidance for nursing staff seeking career advancement
- The benefits of ongoing professional development for nursing staff and healthcare organizations
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create professional development opportunities within their organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in developing and implementing career advancement pathways for nursing staff
The Power of Inspiring Leadership in Nursing
Nursing leadership is a critical component of the healthcare industry, impacting patient care, organizational performance, and the advancement of the nursing profession. By mastering essential leadership skills, embracing diversity, promoting teamwork, and fostering a positive work environment, aspiring nurse leaders can make a meaningful difference in the lives of their patients, colleagues, and organizations. Committing to lifelong learning and professional development will ensure that nurse leaders remain at the forefront of their field, inspiring and empowering the next generation of nursing professionals.
Table of content
Crafted with Care:
Nursing Essays!
Precision, Passion, & Professionalism in Every Page.
Leadership in Nursing
Leadership plays a crucial role in effectively developing and implementing healthcare policies, and nurse leaders face unique challenges. When creating and implementing policy, a particular type of leadership stands out as best suited for the task. Transformational leadership is widely regarded as the most effective approach for driving policy changes in healthcare settings (Specchia et al., 2021). This leadership style empowers individuals, fosters innovation, and inspires a shared vision, all essential for navigating healthcare policy’s complex and dynamic landscape.
Transformational leadership is characterized by its ability to inspire and motivate followers to achieve extraordinary outcomes. Nurse leaders who adopt this approach empower their team members by encouraging autonomy, creativity, and critical thinking (Ferreira et al., 2020). In healthcare policy, this involves stakeholders at every level, including frontline nurses, administrators, patients, and other relevant parties, in the policy development process. By giving them a voice and a sense of ownership, transformational leaders create an environment that encourages the generation of innovative ideas and solutions.
Transformational leaders excel at creating a shared vision and aligning the efforts of diverse individuals towards a common goal. This is especially crucial in healthcare policy, as policy changes often require collaboration among various stakeholders with different perspectives and interests. Nurse leaders who adopt a transformational approach can articulate a compelling vision of improved healthcare outcomes and engage others in working towards it (Collins et al., 2020). By fostering a shared understanding of the desired policy objectives and the potential benefits, these leaders can rally support and build momentum for policy implementation.
The dynamic and ever-changing nature of healthcare policy necessitates a leadership style that can adapt to new challenges and foster continuous improvement. Transformational leaders are known for embracing change and inspiring others to do the same (Ferreira et al., 2020). Policy development and implementation means being responsive to emerging evidence, technological advancements, and evolving healthcare needs. By encouraging a culture of learning and adaptation, transformational leaders can guide their teams through the complexities and uncertainties inherent in healthcare policy, ensuring that policies remain relevant, effective, and responsive to the population’s needs.
Transformational leadership also promotes a culture of trust and collaboration. These elements are essential for successful policy development and implementation in healthcare. Trust enables open communication, facilitates sharing of ideas and concerns, and encourages constructive feedback (Collins et al., 2020). In policy, nurse leaders can foster an environment where stakeholders feel safe to voice their opinions and participate actively in policy-making. Collaboration, on the other hand, ensures that diverse perspectives are taken into account and that decisions are made with the input and consensus of relevant parties. Nurse leaders can create an environment conducive to effective policy development and implementation by prioritising trust and collaboration.
While transformational leadership is the most suitable style for healthcare policy creation and implementation, nurse leaders may encounter challenges. These challenges often stem from the complex nature of the healthcare system, which involves multiple stakeholders, competing interests, and a rapidly changing landscape (Ferreira et al., 2020). Nurse leaders may face resistance to change, limited resources, and bureaucratic hurdles that can impede policy progress. However, nurse leaders can navigate these challenges more effectively by adopting a transformational leadership approach. Transformational leadership’s empowering and inspirational nature can help overcome resistance to change by fostering a culture of engagement and collaboration. Nurse leaders can find creative solutions to resource constraints and bureaucratic obstacles by encouraging innovation and creativity, ultimately driving policy changes forward.
One notable example of policy development that exemplifies transformational leadership is the implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) in an extensive hospital system. The nurse leader responsible for this initiative demonstrated transformational leadership by inspiring and engaging the nursing staff (Collins et al., 2020). Through regular communication and active involvement, the leader created a shared vision of the benefits and importance of EHRs, addressing potential concerns and resistance among the nurses. This leadership style fostered a sense of trust and commitment among the nursing staff, resulting in their active participation and cooperation throughout the implementation process.
The success of this initiative can be attributed to the transformational leadership approach employed. The nurse leader provided clear guidance and encouraged the nursing staff to contribute their ideas and suggestions. By valuing their input, the leader empowered the nurses to take ownership of the project, which enhanced their motivation and commitment (Kiwanuka et al., 2021). The transformational leader also facilitated the necessary training and support, ensuring the nurses were adequately prepared for the EHR implementation. As a result, the hospital system successfully transitioned to electronic health records, improving efficiency, patient safety, and overall quality of care.
Another example of policy change that illustrates transformational leadership is implementing a new pain management protocol in a healthcare organization. The nurse leader leading this initiative adopted a transformational leadership style by involving multidisciplinary teams of nurses, physicians, and pharmacists. Through open and transparent communication, the leader created an environment where ideas and perspectives were valued, developing a comprehensive pain management protocol that incorporated best practices and evidence-based guidelines.
The success of this policy change can be attributed to the transformational leadership style employed by the nurse leader. The leader promoted a shared commitment to improving pain management practices by fostering collaboration and teamwork among the various stakeholders. The transformational leader provided mentorship and support to the nursing staff, encouraging them to embrace and implement the new protocol consistently (Collins et al., 2020). Through ongoing education and training, the leader ensured that all healthcare providers were well-informed and equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to implement the new pain management protocol effectively.
Effective leadership is crucial in the development and implementation of healthcare policies. Transformational leadership, in particular, has shown to be successful in driving policy development and change. Through the examples of implementing electronic health records and a new pain management protocol, we have seen how transformational leaders inspire, motivate, and empower their teams. By fostering collaboration, trust, and innovation, transformational leaders create an environment supporting healthcare policy implementation. These examples highlight the importance of leadership in navigating challenges and achieving positive outcomes in policy development and change within healthcare organizations.
Collins, E., Owen, P., Digan, J., & Dunn, F. (2020). Applying transformational leadership in nursing practice. Nurs Stand , 35 (5), 59-66.
Ferreira, V. B., Amestoy, S. C., Silva, G. T. R. D., Trindade, L. D. L., Santos, I. A. R. D., & Varanda, P. A. G. (2020). Transformational leadership in nursing practice: Challenges and strategies. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem , 73 .
Kiwanuka, F., Nanyonga, R. C., Sak‐Dankosky, N., Muwanguzi, P. A., & Kvist, T. (2021). Nursing leadership styles and their impact on intensive care unit quality measures: An integrative review. Journal of Nursing Management , 29 (2), 133-142.
Specchia, M. L., Cozzolino, M. R., Carini, E., Di Pilla, A., Galletti, C., Ricciardi, W., & Damiani, G. (2021). Leadership styles and nurses’ job satisfaction. Results of a systematic review. International journal of environmental research and public health , 18 (4), 1552.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Related Essays
Fuel costs and air travel dynamics, ethics and power, investigating factors that contribute to increased rate of unemployment in the u.s., venture development project-analysis and recommendations for saltbox company, saudi aramco company analysis, real estate industry study – chapters 1 and 2, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
School of Nursing
Triple alumna shares leadership lessons and insights from a distinguished nursing career.
August 27, 2024
Author: Moira Neve
Jeniece Roane, Ph.D., vice president of operations for the Children's Hospital of Richmond at VCU offers a glimpse into the experiences that have shaped her journey in and beyond the classroom.

Not every nurse gets to build a hospital as part of their career, but Jeniece Roane, Ph.D., RN, NE-BC, (B.S. ‘93, M.S. ‘07, Ph.D. ‘24), has done just that. The three-time alumna has made a mark on improving health care for children, perhaps most visibly in the child-centered design of the Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU (CHoR) where she is the vice president of operations.
Recently honored by the school with the Paul A. and Veronica H. Gross Achievement in Nursing Award, Roane, who began her career in a pediatric intensive care unit, has been a dedicated member of the VCU healthcare community since 1997. In reflecting on this pivotal phase of her career, she shared valuable insights into the leadership lessons and academic accomplishments in nursing.
How did your experiences as a pediatric nurse inspire you to advocate for improvements in healthcare environments for children?
I'm a triple alumna of the VCU School of Nursing, but I actually started out as a pharmacy major before choosing to become a nurse due to my passion for directly engaging with patients and making a meaningful impactful difference in their care experience. Additionally, as long as I have been able to remember I have had a love for children, and so being able to marry this care with then specializing in pediatrics very early on in my career really was the impetus for becoming a nurse practitioner.
I earned my bachelor's, master’s and then most recently my Ph.D. from the VCU School of Nursing. Every step with every degree that I've gone on to pursue, my goal has been to help me develop new skills that will help me improve the health outcomes for children. I think that those experiences as a pediatric ICU nurse, if I were to really hone in and reflect are the experiences that led me down this path, led me to pursue both my masters and my Ph.D. As a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) nurse, you are put in these positions where you're working with families that many times right didn't even know that an ICU existed let alone finding themselves needing the services of the ICU. So, my experiences as a PICU nurse and then later as their nurse manager really helped shape my advocacy skills. On the one hand, you have to advocate as a part of the medical team. Also, as a PICU nurse you build relationships with family members at a very critical juncture in their child's life, and find yourself stepping in frequently to serve as a parental advocate and support. It's those experiences in the ICU that really shaped me and changed me as a nurse.
Your dissertation focused on "Nurse-Led Home Visitation and Parental Reasoning About Child Discipline." Could you share what initially sparked your interest in this topic and how it influences your work at the Children's Hospital?
As a PICU nurse, I saw, and frankly had the misfortune of having to care for, children who were abused. My Ph.D. work focuses on trying to understand what interventions might be most effective at reducing the incidence of child maltreatment. Those PICU years were formative not only in who I became as a bedside nurse, but in creating the foundation for who I am today and what I hoped that I would accomplish by pursuing my Ph.D.
What was it like to transition in your career from being in nursing school, to working as a pediatric nurse, to finishing the Ph.D. program, and now to step into such an important leadership role within the VCU Health System?
When I started the program, I was the nursing director for Women’s and Children’s Health. As I moved through the program, along the way I was promoted to associate VP for Women’s and Children’s Health. Then, during COVID, I was asked to step up to an interim position while I was still in the program as the Chief Nursing Officer (CNO) for the medical center. Once we found a permanent CNO, I went back to my role as vice president of operations for the Children’s Hospital.
The support I received from the faculty of the School of Nursing has just been incredible. Honestly, reflecting on navigating the undergraduate program, the graduate program and then my Ph.D. program, I have had incredible support from my advisors and the faculty, and from the dean at the time. Dean Jean Giddens served as dean for most of my Ph.D. program, and provided amazing support throughout the time of my entire academic pursuits.
One way was that they were incredibly flexible: my dissertation topic was not a typical subject area that a nursing student might pursue, but my committee and advisors worked very closely with me to ensure that I was able to focus on an area that I wanted, while still meeting expectations, completing the rigorous coursework required of me, moving into the dissertation phase, and completing my dissertation. Without a doubt, I feel that I was very supported by the VCU Nursing school community.
What advice would you give to current students in the VCU Nursing School?
It took me eight years to complete my Ph.D. I think this is important for other students who are in this program to understand and know because it is easy to watch other people who are on this journey. Some people move pretty quickly and others move slowly.
What I tried to remember and encourage everyone to remember is, your journey is your journey. Your work is your work. If you're going to make a meaningful impact, you have to embrace whatever the timeline is so that you can produce a quality research project. I took my time.
What was it like stepping up into your role during COVID-19?
It was definitely challenging, but that's really where I think the support, particularly from my advisor Terry Jones , Ph.D., was pivotal for me. As I was contemplating whether or not I was going to accept this interim appointment, she and I met to talk about what it would mean for my Ph.D. journey. Together we crafted a plan for how I could still progress, while taking on this demanding role right at the height of COVID. This was before[the] Delta [variant], this was before [the] Omicron [variant], this was before we even had vaccines. Stepping up to this interim role was challenging, but I think with the support of Dr. Jones as well as my colleagues I really felt like they gave me the space to be able to fulfill my role, but also carve out time to continue to progress within the program. I would also add, having a really special husband and supportive friends and family goes a long way as well, because without that support and grace, I don’t know if I would've been able to do it all.
Yes, are there challenges everyday? Sure there are. But for me, when you are working for a group of people that share a common mission–and for us that is being organized and focused around providing care for children–I don’t think there is anything better than that. It is an honor to get to come in and do this work everyday. Jeniece Roane, Ph.D.
What drew you to your current role?
Well I think that for us for those of us who have really dedicated our careers to caring for children, particularly if you've been here in the City of Richmond (I've been at VCU at the medical center since 1997), we have always felt like we needed a place that was dedicated to a space dedicated to caring for children. To now have an entire tower that is dedicated to the care and enhancing the well-being of children has been a game-changer: not only for the children and their families in the region, but also for our teams. We have always provided exceptional care, and now we have the environment that reflects the exceptional care that they have always provided.
What is your favorite thing about your role at CHoR?
For me, serving in this role as vice president of operations, the greatest joy that I have is getting to see and support our team members, and helping to remove barriers for them that might impede their ability to deliver their very best care everyday. It is being able to see the joy my team gets from working in a place that is dedicated to the delivery of care for children. Yes, are there challenges everyday? Sure there are. But for me, when you are working for a group of people that share a common mission–and for us that is being organized and focused around providing care for children–I don’t think there is anything better than that. It is an honor to get to come in and do this work everyday.
How does it feel to have the new CHoR Tower?
It feels like a dream that has come true. Not every story is a happy story, but to see children and families in this environment where every detail was thought about, debated, fine tuned, with a child and a family in mind, that brings me so much joy that it is difficult to articulate. When you’ve dedicated your career to children, and come from an environment where you had [only] one level dedicated to children’s in-patient services within the adult hospital, to now three in-patient units, plus an emergency department, growing child-life programs, spaces that have been crafted so we can carry out high and specialty care like bone-marrow transplants, a dedicated trauma bay, and all our personnel that help us deliver on that promise to take care of children, it really is something special to be a part of. I am grateful to have played a small role in this work. There are people that never get to build a new hospital as part of their career, so to be able to influence the decisions that are made and knowing that the decisions have an impact on how care is delivered today is really special.
What is your favorite space in the tower?
That’s a hard question, but I think it's probably going to be a space that hasn't come online yet, but is in the works. The new Child Life Zone is expected to open in late summer 2024, and this zone will be one of 15 child life zones across the country that is supported through a partnership with Garth Brooks Foundation, called Teammates for Kids. We are able to bring the space to fruition through a philanthropy. We've got a donor from the community that has pledged two million dollars to help bring the space online. This Child Life Zone helps us try to “normalize” the experience of a child that is in the hospital. There's nothing normal about that, but spaces like these help us distract the child and the family from what they are going through. These Child Life Zones are filled with all kinds of places for children to be engaged, to be creative, and to step away from the stressors of the bedside in order to just be a child, even just for a few short minutes. The work that our Child Life team has done to think through all the details, and work to make this zone unique and special to VCU and to CHoR has brought this space to life.
I am grateful to have played a small role in this work. There are people that never get to build a new hospital as part of their career, so to be able to influence the decisions that are made and knowing that the decisions have an impact on how care is delivered today is really special. Jeniece Roane, Ph.D.
The other space is the Ronald McDonald House Charity Space. We have the first house in a hospital, the first of its kind in the Commonwealth of Virginia. We have partnered with Ronald McDonald Charities to build out a four bed suite where parents can come down and find some time to lay down, step away from the bedside, and get some rest. There is also a kitchenette that enables parents to get some food, there's an outdoor terrace on it so there's space for parents to step outside without having to physically leaving the building, there’s laundry for parents to utilize, and the house is staffed and manned by a Ronald McDonald House Charities staff. That level of support and care our families can receive with a trusted partner like the team at Ronald McDonald House Charities makes this one of my favorite aspects of the space. This space also sets our building and the care that we're delivering apart from what we were able to do previously, and sets us apart from other places that deliver children’s care.
Looking ahead, what are your goals and vision for the future of the Children's Hospital of Richmond, and how do you plan to achieve them?
We are actually preparing to expand services here, so I would say that is what I'm most excited about. We have seen double digit growth in almost every service–our emergency department visits, acute pediatric care volume, pediatric intensive care volume, our operating room volume–since we built the tower. We knew that we were going to likely need some additional space to build out over time, and so there's plenty of shell space here in the tower. We're in the discussion and design phase right now for adding 18-20 additional beds for our neonatal intensive care unit. Next, we are going to be building out a second floor of acute care pediatric services. It is very busy within the children’s space, so I am very excited that I will be working together with our teams to build those spaces out.
Academic Support for Nursing Students
No notifications.
Disclaimer: This essay has been written by a student and not our expert nursing writers. View professional sample essays here.
View full disclaimer
Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this essay are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of NursingAnswers.net. This essay should not be treated as an authoritative source of information when forming medical opinions as information may be inaccurate or out-of-date.
The Importance of Leadership in Nursing
Info: 2632 words (11 pages) Nursing Essay Published: 11th Feb 2020
Reference this
If you need assistance with writing your nursing essay, our professional nursing essay writing service is here to help!
What is leadership and culture?
Nursing leadership, factors which contribute to nursing leadership, collective leadership, cite this work.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services

- Nursing Essay Writing Service

- Nursing Dissertation Service

- Reflective Writing Service
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on the NursingAnswers.net website then please:
Our academic writing and marking services can help you!
- Marking Service
- Samples of our Work
- Full Service Portfolio
Related Lectures
Study for free with our range of nursing lectures!
- Drug Classification
- Emergency Care
- Health Observation
- Palliative Care
- Professional Values

Write for Us
Do you have a 2:1 degree or higher in nursing or healthcare?
Study Resources
Free resources to assist you with your nursing studies!
- APA Citation Tool
- Example Nursing Essays
- Example Nursing Assignments
- Example Nursing Case Studies
- Reflective Nursing Essays
- Nursing Literature Reviews
- Free Resources
- Reflective Model Guides
- Nursing and Healthcare Pay 2021
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Management and Professional Concepts [Internet]. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2022.

Nursing Management and Professional Concepts [Internet].
- About Open RN
Chapter 2 - Prioritization
2.1. prioritization introduction, learning objectives.
• Prioritize nursing care based on patient acuity
• Use principles of time management to organize work
• Analyze effectiveness of time management strategies
• Use critical thinking to prioritize nursing care for patients
• Apply a framework for prioritization (e.g., Maslow, ABCs)
“So much to do, so little time.” This is a common mantra of today’s practicing nurse in various health care settings. Whether practicing in acute inpatient care, long-term care, clinics, home care, or other agencies, nurses may feel there is “not enough of them to go around.”
The health care system faces a significant challenge in balancing the ever-expanding task of meeting patient care needs with scarce nursing resources that has even worsened as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. With a limited supply of registered nurses, nurse managers are often challenged to implement creative staffing practices such as sending staff to units where they do not normally work (i.e., floating), implementing mandatory staffing and/or overtime, utilizing travel nurses, or using other practices to meet patient care demands.[ 1 ] Staffing strategies can result in nurses experiencing increased patient assignments and workloads, extended shifts, or temporary suspension of paid time off. Nurses may receive a barrage of calls and text messages offering “extra shifts” and bonus pay, and although the extra pay may be welcomed, they often eventually feel burnt out trying to meet the ever-expanding demands of the patient-care environment.
A novice nurse who is still learning how to navigate the complex health care environment and provide optimal patient care may feel overwhelmed by these conditions. Novice nurses frequently report increased levels of stress and disillusionment as they transition to the reality of the nursing role.[ 2 ] How can we address this professional dilemma and enhance the novice nurse’s successful role transition to practice? The novice nurse must enter the profession with purposeful tools and strategies to help prioritize tasks and manage time so they can confidently address patient care needs, balance role demands, and manage day-to-day nursing activities.
Let’s take a closer look at the foundational concepts related to prioritization and time management in the nursing profession.
2.2. TENETS OF PRIORITIZATION
Prioritization.
As new nurses begin their career, they look forward to caring for others, promoting health, and saving lives. However, when entering the health care environment, they often discover there are numerous and competing demands for their time and attention. Patient care is often interrupted by call lights, rounding physicians, and phone calls from the laboratory department or other interprofessional team members. Even individuals who are strategic and energized in their planning can feel frustrated as their task lists and planned patient-care activities build into a long collection of “to dos.”
Without utilization of appropriate prioritization strategies, nurses can experience time scarcity , a feeling of racing against a clock that is continually working against them. Functioning under the burden of time scarcity can cause feelings of frustration, inadequacy, and eventually burnout. Time scarcity can also impact patient safety, resulting in adverse events and increased mortality.[ 1 ] Additionally, missed or rushed nursing activities can negatively impact patient satisfaction scores that ultimately affect an institution’s reimbursement levels.
It is vital for nurses to plan patient care and implement their task lists while ensuring that critical interventions are safely implemented first. Identifying priority patient problems and implementing priority interventions are skills that require ongoing cultivation as one gains experience in the practice environment.[ 2 ] To develop these skills, students must develop an understanding of organizing frameworks and prioritization processes for delineating care needs. These frameworks provide structure and guidance for meeting the multiple and ever-changing demands in the complex health care environment.
Let’s consider a clinical scenario in the following box to better understand the implications of prioritization and outcomes.
Imagine you are beginning your shift on a busy medical-surgical unit. You receive a handoff report on four medical-surgical patients from the night shift nurse:
• Patient A is a 34-year-old total knee replacement patient, post-op Day 1, who had an uneventful night. It is anticipated that she will be discharged today and needs patient education for self-care at home.
• Patient B is a 67-year-old male admitted with weakness, confusion, and a suspected urinary tract infection. He has been restless and attempting to get out of bed throughout the night. He has a bed alarm in place.
• Patient C is a 49-year-old male, post-op Day 1 for a total hip replacement. He has been frequently using his patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump and last rated his pain as a “6.”
• Patient D is a 73-year-old male admitted for pneumonia. He has been hospitalized for three days and receiving intravenous (IV) antibiotics. His next dose is due in an hour. His oxygen requirements have decreased from 4 L/minute of oxygen by nasal cannula to 2 L/minute by nasal cannula.
Based on the handoff report you received, you ask the nursing assistant to check on Patient B while you do an initial assessment on Patient D. As you are assessing Patient D’s oxygenation status, you receive a phone call from the laboratory department relating a critical lab value on Patient C, indicating his hemoglobin is low. The provider calls and orders a STAT blood transfusion for Patient C. Patient A rings the call light and states she and her husband have questions about her discharge and are ready to go home. The nursing assistant finds you and reports that Patient B got out of bed and experienced a fall during the handoff reports.
It is common for nurses to manage multiple and ever-changing tasks and activities like this scenario, illustrating the importance of self-organization and priority setting. This chapter will further discuss the tools nurses can use for prioritization.
2.3. TOOLS FOR PRIORITIZING
Prioritization of care for multiple patients while also performing daily nursing tasks can feel overwhelming in today’s fast-paced health care system. Because of the rapid and ever-changing conditions of patients and the structure of one’s workday, nurses must use organizational frameworks to prioritize actions and interventions. These frameworks can help ease anxiety, enhance personal organization and confidence, and ensure patient safety.
Acuity and intensity are foundational concepts for prioritizing nursing care and interventions. Acuity refers to the level of patient care that is required based on the severity of a patient’s illness or condition. For example, acuity may include characteristics such as unstable vital signs, oxygenation therapy, high-risk IV medications, multiple drainage devices, or uncontrolled pain. A “high-acuity” patient requires several nursing interventions and frequent nursing assessments.
Intensity addresses the time needed to complete nursing care and interventions such as providing assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs), performing wound care, or administering several medication passes. For example, a “high-intensity” patient generally requires frequent or long periods of psychosocial, educational, or hygiene care from nursing staff members. High-intensity patients may also have increased needs for safety monitoring, familial support, or other needs.[ 1 ]
Many health care organizations structure their staffing assignments based on acuity and intensity ratings to help provide equity in staff assignments. Acuity helps to ensure that nursing care is strategically divided among nursing staff. An equitable assignment of patients benefits both the nurse and patient by helping to ensure that patient care needs do not overwhelm individual staff and safe care is provided.
Organizations use a variety of systems when determining patient acuity with rating scales based on nursing care delivery, patient stability, and care needs. See an example of a patient acuity tool published in the American Nurse in Table 2.3 .[ 2 ] In this example, ratings range from 1 to 4, with a rating of 1 indicating a relatively stable patient requiring minimal individualized nursing care and intervention. A rating of 2 reflects a patient with a moderate risk who may require more frequent intervention or assessment. A rating of 3 is attributed to a complex patient who requires frequent intervention and assessment. This patient might also be a new admission or someone who is confused and requires more direct observation. A rating of 4 reflects a high-risk patient. For example, this individual may be experiencing frequent changes in vital signs, may require complex interventions such as the administration of blood transfusions, or may be experiencing significant uncontrolled pain. An individual with a rating of 4 requires more direct nursing care and intervention than a patient with a rating of 1 or 2. [3]
Example of a Patient Acuity Tool [ 4 ]
View in own window
| Q8h VS A & O X 4 | Q4h VS CIWA < 8 | Q2h VS Delirium CIWA > 8 | Unstable VS | |
| Stable on RA | O2 < 2L NC | O2 > 2L NC | O2 via mask | |
| VS | Temp < 98.7 F Pacemaker/AICD HR > 130 | Change in BP Temp > 100.3 F | Unstable rhythm Afib | |
| PO/IVPB | TPN, heparin infusion, blood glucose, PICC for blood draws | CBI 1 unit blood transfusion Fluid bolus | > 1 unit blood transfusion Chemotherapy | |
| < 2 JP, hemovac, neph tube | Chest to water seal NG tube | Chest tube to suction Drain measured Q2 hrs | Drain measured Q1 hr CT > 100 mL/2 hrs | |
| Pain well- managed with PO or IV meds Q4 hrs | PCA, nerve block Nausea/Vomiting | Q2h pain management | Uncontrolled pain with multiple pain devices | |
| Stable transfer, routine discharge | Discharge to outside facility | New admission, discharge to hospice | Complicated post-op | |
| Independent | Assist with ADLs Two-person assist out of bed Isolation | Turns Q2h Bedrest Respiratory isolation | Paraplegic Total care | |
Read more about using a patient acuity tool on a medical-surgical unit.
Rating scales may vary among institutions, but the principles of the rating system remain the same. Organizations include various patient care elements when constructing their staffing plans for each unit. Read more information about staffing models and acuity in the following box.
Staffing Models and Acuity
Organizations that base staffing on acuity systems attempt to evenly staff patient assignments according to their acuity ratings. This means that when comparing patient assignments across nurses on a unit, similar acuity team scores should be seen with the goal of achieving equitable and safe division of workload across the nursing team. For example, one nurse should not have a total acuity score of 6 for their patient assignments while another nurse has a score of 15. If this situation occurred, the variation in scoring reflects a discrepancy in workload balance and would likely be perceived by nursing peers as unfair. Using acuity-rating staffing models is helpful to reflect the individualized nursing care required by different patients.
Alternatively, nurse staffing models may be determined by staffing ratio. Ratio-based staffing models are more straightforward in nature, where each nurse is assigned care for a set number of patients during their shift. Ratio-based staffing models may be useful for administrators creating budget requests based on the number of staff required for patient care, but can lead to an inequitable division of work across the nursing team when patient acuity is not considered. Increasingly complex patients require more time and interventions than others, so a blend of both ratio and acuity-based staffing is helpful when determining staffing assignments.[ 5 ]
As a practicing nurse, you will be oriented to the elements of acuity ratings within your health care organization, but it is also important to understand how you can use these acuity ratings for your own prioritization and task delineation. Let’s consider the Scenario B in the following box to better understand how acuity ratings can be useful for prioritizing nursing care.
You report to work at 6 a.m. for your nursing shift on a busy medical-surgical unit. Prior to receiving the handoff report from your night shift nursing colleagues, you review the unit staffing grid and see that you have been assigned to four patients to start your day. The patients have the following acuity ratings:
Patient A: 45-year-old patient with paraplegia admitted for an infected sacral wound, with an acuity rating of 4.
Patient B: 87-year-old patient with pneumonia with a low grade fever of 99.7 F and receiving oxygen at 2 L/minute via nasal cannula, with an acuity rating of 2.
Patient C: 63-year-old patient who is postoperative Day 1 from a right total hip replacement and is receiving pain management via a PCA pump, with an acuity rating of 2.
Patient D: 83-year-old patient admitted with a UTI who is finishing an IV antibiotic cycle and will be discharged home today, with an acuity rating of 1.
Based on the acuity rating system, your patient assignment load receives an overall acuity score of 9. Consider how you might use their acuity ratings to help you prioritize your care. Based on what is known about the patients related to their acuity rating, whom might you identify as your care priority? Although this can feel like a challenging question to answer because of the many unknown elements in the situation using acuity numbers alone, Patient A with an acuity rating of 4 would be identified as the care priority requiring assessment early in your shift.
Although acuity can a useful tool for determining care priorities, it is important to recognize the limitations of this tool and consider how other patient needs impact prioritization.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
When thinking back to your first nursing or psychology course, you may recall a historical theory of human motivation based on various levels of human needs called Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs reflects foundational human needs with progressive steps moving towards higher levels of achievement. This hierarchy of needs is traditionally represented as a pyramid with the base of the pyramid serving as essential needs that must be addressed before one can progress to another area of need.[ 6 ] See Figure 2.1 [ 7 ] for an illustration of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs places physiological needs as the foundational base of the pyramid.[ 8 ] Physiological needs include oxygen, food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, and excretion. The second level of Maslow’s hierarchy reflects safety needs. Safety needs include elements that keep individuals safe from harm. Examples of safety needs in health care include fall precautions. The third level of Maslow’s hierarchy reflects emotional needs such as love and a sense of belonging. These needs are often reflected in an individual’s relationships with family members and friends. The top two levels of Maslow’s hierarchy include esteem and self-actualization. An example of addressing these needs in a health care setting is helping an individual build self-confidence in performing blood glucose checks that leads to improved self-management of their diabetes.
So how does Maslow’s theory impact prioritization? To better understand the application of Maslow’s theory to prioritization, consider Scenario C in the following box.
You are an emergency response nurse working at a local shelter in a community that has suffered a devastating hurricane. Many individuals have relocated to the shelter for safety in the aftermath of the hurricane. Much of the community is still without electricity and clean water, and many homes have been destroyed. You approach a young woman who has a laceration on her scalp that is bleeding through her gauze dressing. The woman is weeping as she describes the loss of her home stating, “I have lost everything! I just don’t know what I am going to do now. It has been a day since I have had water or anything to drink. I don’t know where my sister is, and I can’t reach any of my family to find out if they are okay!”
Despite this relatively brief interaction, this woman has shared with you a variety of needs. She has demonstrated a need for food, water, shelter, homeostasis, and family. As the nurse caring for her, it might be challenging to think about where to begin her care. These thoughts could be racing through your mind:
Should I begin to make phone calls to try and find her family? Maybe then she would be able to calm down.
Should I get her on the list for the homeless shelter so she wouldn’t have to worry about where she will sleep tonight?
She hasn’t eaten in awhile; I should probably find her something to eat.
All of these needs are important and should be addressed at some point, but Maslow’s hierarchy provides guidance on what needs must be addressed first. Use the foundational level of Maslow’s pyramid of physiological needs as the top priority for care. The woman is bleeding heavily from a head wound and has had limited fluid intake. As the nurse caring for this patient, it is important to immediately intervene to stop the bleeding and restore fluid volume. Stabilizing the patient by addressing her physiological needs is required before undertaking additional measures such as contacting her family. Imagine if instead you made phone calls to find the patient’s family and didn’t address the bleeding or dehydration – you might return to a severely hypovolemic patient who has deteriorated and may be near death. In this example, prioritizing emotional needs above physiological needs can lead to significant harm to the patient.
Although this is a relatively straightforward example, the principles behind the application of Maslow’s hierarchy are essential. Addressing physiological needs before progressing toward additional need categories concentrates efforts on the most vital elements to enhance patient well-being. Maslow’s hierarchy provides the nurse with a helpful framework for identifying and prioritizing critical patient care needs.
Airway, breathing, and circulation, otherwise known by the mnemonic “ABCs,” are another foundational element to assist the nurse in prioritization. Like Maslow’s hierarchy, using the ABCs to guide decision-making concentrates on the most critical needs for preserving human life. If a patient does not have a patent airway, is unable to breathe, or has inadequate circulation, very little of what else we do matters. The patient’s ABCs are reflected in Maslow’s foundational level of physiological needs and direct critical nursing actions and timely interventions. Let’s consider Scenario D in the following box regarding prioritization using the ABCs and the physiological base of Maslow’s hierarchy.
You are a nurse on a busy cardiac floor charting your morning assessments on a computer at the nurses’ station. Down the hall from where you are charting, two of your assigned patients are resting comfortably in Room 504 and Room 506. Suddenly, both call lights ring from the rooms, and you answer them via the intercom at the nurses’ station.
Room 504 has an 87-year-old male who has been admitted with heart failure, weakness, and confusion. He has a bed alarm for safety and has been ringing his call bell for assistance appropriately throughout the shift. He requires assistance to get out of bed to use the bathroom. He received his morning medications, which included a diuretic about 30 minutes previously, and now reports significant urge to void and needs assistance to the bathroom.
Room 506 has a 47-year-old woman who was hospitalized with new onset atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. The patient underwent a cardioversion procedure yesterday that resulted in successful conversion of her heart back into normal sinus rhythm. She is reporting via the intercom that her “heart feels like it is doing that fluttering thing again” and she is having chest pain with breathlessness.
Based upon these two patient scenarios, it might be difficult to determine whom you should see first. Both patients are demonstrating needs in the foundational physiological level of Maslow’s hierarchy and require assistance. To prioritize between these patients’ physiological needs, the nurse can apply the principles of the ABCs to determine intervention. The patient in Room 506 reports both breathing and circulation issues, warning indicators that action is needed immediately. Although the patient in Room 504 also has an urgent physiological elimination need, it does not overtake the critical one experienced by the patient in Room 506. The nurse should immediately assess the patient in Room 506 while also calling for assistance from a team member to assist the patient in Room 504.
Prioritizing what should be done and when it can be done can be a challenging task when several patients all have physiological needs. Recently, there has been professional acknowledgement of the cognitive challenge for novice nurses in differentiating physiological needs. To expand on the principles of prioritizing using the ABCs, the CURE hierarchy has been introduced to help novice nurses better understand how to manage competing patient needs. The CURE hierarchy uses the acronym “CURE” to guide prioritization based on identifying the differences among Critical needs, Urgent needs, Routine needs, and Extras.[ 9 ]
“Critical” patient needs require immediate action. Examples of critical needs align with the ABCs and Maslow’s physiological needs, such as symptoms of respiratory distress, chest pain, and airway compromise. No matter the complexity of their shift, nurses can be assured that addressing patients’ critical needs is the correct prioritization of their time and energies.
After critical patient care needs have been addressed, nurses can then address “urgent” needs. Urgent needs are characterized as needs that cause patient discomfort or place the patient at a significant safety risk.[ 10 ]
The third part of the CURE hierarchy reflects “routine” patient needs. Routine patient needs can also be characterized as “typical daily nursing care” because the majority of a standard nursing shift is spent addressing routine patient needs. Examples of routine daily nursing care include actions such as administering medication and performing physical assessments.[ 11 ] Although a nurse’s typical shift in a hospital setting includes these routine patient needs, they do not supersede critical or urgent patient needs.
The final component of the CURE hierarchy is known as “extras.” Extras refer to activities performed in the care setting to facilitate patient comfort but are not essential.[ 12 ] Examples of extra activities include providing a massage for comfort or washing a patient’s hair. If a nurse has sufficient time to perform extra activities, they contribute to a patient’s feeling of satisfaction regarding their care, but these activities are not essential to achieve patient outcomes.
Let’s apply the CURE mnemonic to patient care in the following box.
If we return to Scenario D regarding patients in Room 504 and 506, we can see the patient in Room 504 is having urgent needs. He is experiencing a physiological need to urgently use the restroom and may also have safety concerns if he does not receive assistance and attempts to get up on his own because of weakness. He is on a bed alarm, which reflects safety considerations related to his potential to get out of bed without assistance. Despite these urgent indicators, the patient in Room 506 is experiencing a critical need and takes priority. Recall that critical needs require immediate nursing action to prevent patient deterioration. The patient in Room 506 with a rapid, fluttering heartbeat and shortness of breath has a critical need because without prompt assessment and intervention, their condition could rapidly decline and become fatal.
In addition to using the identified frameworks and tools to assist with priority setting, nurses must also look at their patients’ data cues to help them identify care priorities. Data cues are pieces of significant clinical information that direct the nurse toward a potential clinical concern or a change in condition. For example, have the patient’s vital signs worsened over the last few hours? Is there a new laboratory result that is concerning? Data cues are used in conjunction with prioritization frameworks to help the nurse holistically understand the patient’s current status and where nursing interventions should be directed. Common categories of data clues include acute versus chronic conditions, actual versus potential problems, unexpected versus expected conditions, information obtained from the review of a patient’s chart, and diagnostic information.
Acute Versus Chronic Conditions
A common data cue that nurses use to prioritize care is considering if a condition or symptom is acute or chronic. Acute conditions have a sudden and severe onset. These conditions occur due to a sudden illness or injury, and the body often has a significant response as it attempts to adapt. Chronic conditions have a slow onset and may gradually worsen over time. The difference between an acute versus a chronic condition relates to the body’s adaptation response. Individuals with chronic conditions often experience less symptom exacerbation because their body has had time to adjust to the illness or injury. Let’s consider an example of two patients admitted to the medical-surgical unit complaining of pain in Scenario E in the following box.
As part of your patient assignment on a medical-surgical unit, you are caring for two patients who both ring the call light and report pain at the start of the shift. Patient A was recently admitted with acute appendicitis, and Patient B was admitted for observation due to weakness. Not knowing any additional details about the patients’ conditions or current symptoms, which patient would receive priority in your assessment? Based on using the data cue of acute versus chronic conditions, Patient A with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis would receive top priority for assessment over a patient with chronic pain due to osteoarthritis. Patients experiencing acute pain require immediate nursing assessment and intervention because it can indicate a change in condition. Acute pain also elicits physiological effects related to the stress response, such as elevated heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, and should be addressed quickly.
Actual Versus Potential Problems
Nursing diagnoses and the nursing care plan have significant roles in directing prioritization when interpreting assessment data cues. Actual problems refer to a clinical problem that is actively occurring with the patient. A risk problem indicates the patient may potentially experience a problem but they do not have current signs or symptoms of the problem actively occurring.
Consider an example of prioritizing actual and potential problems in Scenario F in the following box.
A 74-year-old woman with a previous history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. She has generalized weakness, a weak cough, and crackles in the bases of her lungs. She is receiving IV antibiotics, fluids, and oxygen therapy. The patient can sit at the side of the bed and ambulate with the assistance of staff, although she requires significant encouragement to ambulate.
Nursing diagnoses are established for this patient as part of the care planning process. One nursing diagnosis for this patient is Ineffective Airway Clearance . This nursing diagnosis is an actual problem because the patient is currently exhibiting signs of poor airway clearance with an ineffective cough and crackles in the lungs. Nursing interventions related to this diagnosis include coughing and deep breathing, administering nebulizer treatment, and evaluating the effectiveness of oxygen therapy. The patient also has the nursing diagnosis Risk for Skin Breakdown based on her weakness and lack of motivation to ambulate. Nursing interventions related to this diagnosis include repositioning every two hours and assisting with ambulation twice daily.
The established nursing diagnoses provide cues for prioritizing care. For example, if the nurse enters the patient’s room and discovers the patient is experiencing increased shortness of breath, nursing interventions to improve the patient’s respiratory status receive top priority before attempting to get the patient to ambulate.
Although there may be times when risk problems may supersede actual problems, looking to the “actual” nursing problems can provide clues to assist with prioritization.
Unexpected Versus Expected Conditions
In a similar manner to using acute versus chronic conditions as a cue for prioritization, it is also important to consider if a client’s signs and symptoms are “expected” or “unexpected” based on their overall condition. Unexpected conditions are findings that are not likely to occur in the normal progression of an illness, disease, or injury. Expected conditions are findings that are likely to occur or are anticipated in the course of an illness, disease, or injury. Unexpected findings often require immediate action by the nurse.
Let’s apply this tool to the two patients previously discussed in Scenario E. As you recall, both Patient A (with acute appendicitis) and Patient B (with weakness and diagnosed with osteoarthritis) are reporting pain. Acute pain typically receives priority over chronic pain. But what if both patients are also reporting nausea and have an elevated temperature? Although these symptoms must be addressed in both patients, they are “expected” symptoms with acute appendicitis (and typically addressed in the treatment plan) but are “unexpected” for the patient with osteoarthritis. Critical thinking alerts you to the unexpected nature of these symptoms in Patient B, so they receive priority for assessment and nursing interventions.
Handoff Report/Chart Review
Additional data cues that are helpful in guiding prioritization come from information obtained during a handoff nursing report and review of the patient chart. These data cues can be used to establish a patient’s baseline status and prioritize new clinical concerns based on abnormal assessment findings. Let’s consider Scenario G in the following box based on cues from a handoff report and how it might be used to help prioritize nursing care.
Imagine you are receiving the following handoff report from the night shift nurse for a patient admitted to the medical-surgical unit with pneumonia:
At the beginning of my shift, the patient was on room air with an oxygen saturation of 93%. She had slight crackles in both bases of her posterior lungs. At 0530, the patient rang the call light to go to the bathroom. As I escorted her to the bathroom, she appeared slightly short of breath. Upon returning the patient to bed, I rechecked her vital signs and found her oxygen saturation at 88% on room air and respiratory rate of 20. I listened to her lung sounds and noticed more persistent crackles and coarseness than at bedtime. I placed the patient on 2 L/minute of oxygen via nasal cannula. Within 5 minutes, her oxygen saturation increased to 92%, and she reported increased ease in respiration.
Based on the handoff report, the night shift nurse provided substantial clinical evidence that the patient may be experiencing a change in condition. Although these changes could be attributed to lack of lung expansion that occurred while the patient was sleeping, there is enough information to indicate to the oncoming nurse that follow-up assessment and interventions should be prioritized for this patient because of potentially worsening respiratory status. In this manner, identifying data cues from a handoff report can assist with prioritization.
Now imagine the night shift nurse had not reported this information during the handoff report. Is there another method for identifying potential changes in patient condition? Many nurses develop a habit of reviewing their patients’ charts at the start of every shift to identify trends and “baselines” in patient condition. For example, a chart review reveals a patient’s heart rate on admission was 105 beats per minute. If the patient continues to have a heart rate in the low 100s, the nurse is not likely to be concerned if today’s vital signs reveal a heart rate in the low 100s. Conversely, if a patient’s heart rate on admission was in the 60s and has remained in the 60s throughout their hospitalization, but it is now in the 100s, this finding is an important cue requiring prioritized assessment and intervention.
Diagnostic Information
Diagnostic results are also important when prioritizing care. In fact, the National Patient Safety Goals from The Joint Commission include prompt reporting of important test results. New abnormal laboratory results are typically flagged in a patient’s chart or are reported directly by phone to the nurse by the laboratory as they become available. Newly reported abnormal results, such as elevated blood levels or changes on a chest X-ray, may indicate a patient’s change in condition and require additional interventions. For example, consider Scenario H in which you are the nurse providing care for five medical-surgical patients.
You completed morning assessments on your assigned five patients. Patient A previously underwent a total right knee replacement and will be discharged home today. You are about to enter Patient A’s room to begin discharge teaching when you receive a phone call from the laboratory department, reporting a critical hemoglobin of 6.9 gm/dL on Patient B. Rather than enter Patient A’s room to perform discharge teaching, you immediately reprioritize your care. You call the primary provider to report Patient B’s critical hemoglobin level and determine if additional intervention, such as a blood transfusion, is required.
2.4. CRITICAL THINKING AND CLINICAL REASONING
Prioritization of patient care should be grounded in critical thinking rather than just a checklist of items to be done. Critical thinking is a broad term used in nursing that includes “reasoning about clinical issues such as teamwork, collaboration, and streamlining workflow.”[ 1 ] Certainly, there are many actions that nurses must complete during their shift, but nursing requires adaptation and flexibility to meet emerging patient needs. It can be challenging for a novice nurse to change their mindset regarding their established “plan” for the day, but the sooner a nurse recognizes prioritization is dictated by their patients’ needs, the less frustration the nurse might experience. Prioritization strategies include collection of information and utilization of clinical reasoning to determine the best course of action. Clinical reasoning is defined as, “A complex cognitive process that uses formal and informal thinking strategies to gather and analyze patient information, evaluate the significance of this information, and weigh alternative actions.” [2]
When nurses use critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills, they set forth on a purposeful course of intervention to best meet patient-care needs. Rather than focusing on one’s own priorities, nurses utilizing critical thinking and reasoning skills recognize their actions must be responsive to their patients. For example, a nurse using critical thinking skills understands that scheduled morning medications for their patients may be late if one of the patients on their care team suddenly develops chest pain. Many actions may be added or removed from planned activities throughout the shift based on what is occurring holistically on the patient-care team.
Additionally, in today’s complex health care environment, it is important for the novice nurse to recognize the realities of the current health care environment. Patients have become increasingly complex in their health care needs, and organizations are often challenged to meet these care needs with limited staffing resources. It can become easy to slip into the mindset of disenchantment with the nursing profession when first assuming the reality of patient-care assignments as a novice nurse. The workload of a nurse in practice often looks and feels quite different than that experienced as a nursing student. As a nursing student, there may have been time for lengthy conversations with patients and their family members, ample time to chart, and opportunities to offer personal cares, such as a massage or hair wash. Unfortunately, in the time-constrained realities of today’s health care environment, novice nurses should recognize that even though these “extra” tasks are not always possible, they can still provide quality, safe patient care using the “CURE” prioritization framework. Rather than feeling frustrated about “extras” that cannot be accomplished in time-constrained environments, it is vital to use prioritization strategies to ensure appropriate actions are taken to complete what must be done. With increased clinical experience, a novice nurse typically becomes more comfortable with prioritizing and reprioritizing care.
Prioritization of patient care should be grounded in critical thinking rather than just a checklist of items to be done. Critical thinking is a broad term used in nursing that includes “reasoning about clinical issues such as teamwork, collaboration, and streamlining workflow.”[ 1 ] Certainly, there are many actions that nurses must complete during their shift, but nursing requires adaptation and flexibility to meet emerging patient needs. It can be challenging for a novice nurse to change their mindset regarding their established “plan” for the day, but the sooner a nurse recognizes prioritization is dictated by their patients’ needs, the less frustration the nurse might experience. Prioritization strategies include collection of information and utilization of clinical reasoning to determine the best course of action. Clinical reasoning is defined as, “A complex cognitive process that uses formal and informal thinking strategies to gather and analyze patient information, evaluate the significance of this information, and weigh alternative actions.”[ 2 ]
2.7. LEARNING ACTIVITIES
Learning activities.
(Answers to “Learning Activities” can be found in the “Answer Key” at the end of the book. Answers to interactive activities are provided as immediate feedback.)
| Temperature | 98.9 °F (37.2°C) |
|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 182 beats/min |
| Respirations | 36 breaths/min |
| Blood Pressure | 152/90 mm Hg |
| Oxygen Saturation | 88% on room air |
| Capillary Refill Time | >3 |
| Pain | 9/10 chest discomfort |
| Physical Assessment Findings | |
|---|---|
| Glasgow Coma Scale Score | 14 |
| Level of Consciousness | Alert |
| Heart Sounds | Irregularly regular |
| Lung Sounds | Clear bilaterally anterior/posterior |
| Pulses-Radial | Rapid/bounding |
| Pulses-Pedal | Weak |
| Bowel Sounds | Present and active x 4 |
| Edema | Trace bilateral lower extremities |
| Skin | Cool, clammy |
| Nursing Action | Indicated | Contraindicated | Nonessential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apply oxygen at 2 liters per nasal cannula. | |||
| Call imaging for a STAT lung CT. | |||
| Perform the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Stroke Scale Neurologic Exam. | |||
| Obtain a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP). | |||
| Obtain a STAT EKG. | |||
| Raise the head-of-bed to less than 10 degrees. | |||
| Establish patent IV access. | |||
| Administer potassium 20 mEq IV push STAT. |
The CURE hierarchy has been introduced to help novice nurses better understand how to manage competing patient needs. The CURE hierarchy uses the acronym “CURE” to help guide prioritization based on identifying the differences among C ritical needs, U rgent needs, R outine needs, and E xtras.
You are the nurse caring for the patients in the following table. For each patient, indicate if this is a “critical,” “urgent,” “routine,” or “extra” need.
| Critical | Urgent | Routine | Extra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient exhibits new left-sided facial droop | ||||
| Patient reports 9/10 acute pain and requests PRN pain medication | ||||
| Patient with BP 120/80 and regular heart rate of 68 has scheduled dose of oral amlodipine | ||||
| Patient with insomnia requests a back rub before bedtime | ||||
| Patient has a scheduled dressing change for a pressure ulcer on their coccyx | ||||
| Patient is exhibiting new shortness of breath and altered mental status | ||||
| Patient with fall risk precautions ringing call light for assistance to the restroom for a bowel movement |
II. GLOSSARY
Airway, breathing, and circulation.
Nursing problems currently occurring with the patient.
The level of patient care that is required based on the severity of a patient’s illness or condition.
A staffing model used to make patient assignments that reflects the individualized nursing care required for different types of patients.
Conditions having a sudden onset.
Conditions that have a slow onset and may gradually worsen over time.
A complex cognitive process that uses formal and informal thinking strategies to gather and analyze patient information, evaluate the significance of this information, and weigh alternative actions.”[ 1 ]
A broad term used in nursing that includes “reasoning about clinical issues such as teamwork, collaboration, and streamlining workflow.”[ 2 ]
A strategy for prioritization based on identifying “critical” needs, “urgent” needs, “routine” needs, and “extras.”
Pieces of significant clinical information that direct the nurse toward a potential clinical concern or a change in condition.
Conditions that are likely to occur or anticipated in the course of an illness, disease, or injury.
Prioritization strategies often reflect the foundational elements of physiological needs and safety and progr ess toward higher levels.
A staffing model used to make patient assignments in terms of one nurse caring for a set number of patients.
A nursing problem that reflects that a patient may experience a problem but does not currently have signs reflecting the problem is actively occurring.
A prioritization strategy including the review of planned tasks and allocation of time believed to be required to complete each task.
A feeling of racing against a clock that is continually working against you.
Conditions that are not likely to occur in the normal progression of an illness, disease, or injury.
Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
- Cite this Page Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Management and Professional Concepts [Internet]. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2022. Chapter 2 - Prioritization.
- PDF version of this title (18M)
In this Page
- PRIORITIZATION INTRODUCTION
- TENETS OF PRIORITIZATION
- TOOLS FOR PRIORITIZING
- CRITICAL THINKING AND CLINICAL REASONING
- LEARNING ACTIVITIES
Other titles in this collection
- Open RN OER Textbooks
Related Items in Bookshelf
- All Textbooks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 2 - Prioritization - Nursing Management and Professional Concepts Chapter 2 - Prioritization - Nursing Management and Professional Concepts
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Admission office: +7 969 2834820 [email protected]
Department of Nursing
MBBS in Russia | MBBS in Moscow | Study Nursing in Russia | Study Nursing in Moscow | Nursing Education in Russia | Nursing Education in Moscow | MBBS Admission in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | MBBS Fee in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | Apply for MBBS Admission in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | How to Get Direct Admission in MBBS in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | Study Nursing in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | Nursing Fee in I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University | About Nursing
The Department of Nursing was opened in accordance with the order of the Rector and the decision of the Academic Council of the I. Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy (now the First Moscow State Medical University named after I. Sechenov) in February 2004.
The Department of Nursing is the first department of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov (Sechenov University), created to provide clinical training for students of the Faculty of Higher Nursing Education and Psychological Social Work (FVSO and SDP) in the direction of training 34.03.01 “Nursing” ( Bachelor’s degree) and the ACT in the specialty 34.02.01 “Nursing”. Since 2011, the department taught the discipline “Nursing” and the practice of obtaining the primary professional skills “Care of the sick” at the medical faculty in the specialty 31.05.01 “General Medicine”. Since 2014, the department also teaches the discipline “First Aid and Nursing” and the practice of obtaining professional skills and professional experience “Sister” in the specialty 31.05.03 “Dentistry”.
The department is located on the basis of the Clinical Center of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov (Sechenov University) in UKB number 3 at ul. Rossolimo house 11, page 5, students of the medical faculty, the dental faculty and the faculty of the MPF are engaged in this base. In 2017, the department allocated educational premises at the address: ul. 1st Borodino, house 2.
Since January 31, 2018, the Department of Nursing Year is part of the Medical and Preventive Faculty (MPF).
Scientific work of the department: Complex scientific theme of the department “Psychovegetative correlations in patients with coronary heart disease.”
The department has postgraduate study and a competition in scientific specialties: cardiology and internal diseases.
The department has a scientific student circle, research work is devoted to topical issues of clinical medicine.
Employees of the department conduct advisory and medical work in medical institutions in Moscow.
Admission is open
- Admission process
- Admission requirements
- Application form
- Admission 2021-2022
- Tuition fee
- Apply online
- Visa requirements
- Our representatives
- Russian embassies
- Airport pickup
Admission 2021-2022 is open now. Join to thousands of happy students in First Moscow State Medical University
Admission Office
Admission office for international students.
Adfress: 119991, Moscow, Trubetskaya street, house 8, building 2, Russia
Phone: +7 (969) 283-48-20
Email: [email protected]

Season’s Greetings from Sechenov University
University News | Student life in Russia | Student life in Moscow | News and events in Russia | News and events in Moscow | Study in Russia | Study in Moscow | Education in Russia | Education in Moscow | Study abroad in Russia | International students life abroad | Study abroad in Russia…

Sechenov University Maintained its Position in the 5-100 Project
- Faculties and Departments
- University Leadership
- FMSMU Worldwide
- Clinics of FMSMU
Copyright © 2020-2023 First Moscow State Medical University. All Rights Reserved.

Leadership Moscow
Leadership Moscow is a leadership development program designed to cultivate the next generation of community leaders in Moscow and Latah County. This program offers a concentrated, hands-on learning experience to enhance and build leadership qualities. Leadership Moscow develops advocates for Moscow and its surrounding rural communities who will serve as a voice for Moscow and Latah County for generations to come. The program consists of ten monthly sessions over a nine-month period.
Participants will develop knowledge and understanding of our community, its complexities, and its potential. During this time there will be opportunities for participants to meet and exchange ideas with current elected officials, community/area leaders, and business owners. Our hope is that this experience will encourage participants to pursue leadership roles within their organizations and the community.
Change Location
Find awesome listings near you.

COMMENTS
A clinical nursing leader is one who is involved in direct patient care and who continuously improves the care that is afforded to such persons by influencing the treatment provision delivered by others (Cook, 2001). Leadership is not merely a series of skills or tasks; rather, it is an attitude that informs behaviour (Cook, 2001).
Professionalism and Leadership: Leaders in nursing build vital relationships and collaborate with various health care teams on sensitive topics. Using critical thinking skills allows those in nursing leadership roles to analyze decisions impacting the organization. They then clearly explain the rationale in a manner that encourages staff support.
The importance of leadership is now widely recognised as a key part of overall effective healthcare, and nursing leadership is a crucial part of this as nurses are now the single largest healthcare discipline (Swearingen, 2009). The findings of the Francis Report (2013) raised major questions into the leadership and organisational culture which allowed hundreds of patients to die or come to ...
Nursing leadership is critical in facilitating and improving nurse performance, which is essential for providing quality care and ensuring patient safety. The aim of this study is to explore the relationship between nursing leadership and nurse performance by understanding the leadership behaviors and factors that motivate nurses to perform ...
Over the past 27 years as a nurse and nurse leader, I have reflected many times on the importance of nursing leadership. Nursing leadership creates a safe workplace environment where nurses can be and perform at their best to provide for an excellent patient experience of care. I have been blessed with great mentors along my journey as a nursing leader.
In a nursing organization, improving the quality of healthcare delivered by the department to be equal with the organizational performance is a key role of leadership (Marquis and Huston, 2015). Nursing leadership is essential in the clinical setting and plays an important role in the development of the nurse as an individual or as a professional.
By using the transformational leadership style, nursing supervisors offer support, inspiration, individual-focused attention, and act as a role model for nurses, that fosters psychological empowerment and well-being. Nurses will have more independence and will be mentally satisfied while performing their job duties. In high-stress environments ...
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
Leadership in health care is recognized as a necessity to ensure high-quality care, embody support for staff, and establish working environments that prioritize people over rules, regulations, and hierarchies (West et al., 2015).It is argued that compassionate leadership has a positive impact on "patient experience, staff engagement and organisational performance" (Bolden et al., 2019, p. 2).
Leadership Theory Application: These essays explore how different leadership theories and models can be applied in real-world nursing practice. Students might analyze the strengths and weaknesses of various approaches and discuss their preferred leadership style based on specific contexts.
VTL is a hierarchical leadership model that describes an individual leader who, through various influences and mechanisms, elevates himself or herself and followers towards self-actualisation (Pearce and Sims, 2000). VTL values collaboration and consensus, integrity and justice, empowerment and optimism, accountability and equality, and honesty ...
Essay Example: Leadership is an art, skill or quality of an individual who can positively influence the people to achieve maximum in their life. ... This essay will discuss the concept and significance of leadership in nursing. It will explore the qualities and skills that make an effective nurse leader, such as communication, empathy, and ...
Leadership in nursing is a critical component of healthcare delivery, influencing patient outcomes, nurse performance, job satisfaction, and the overall quality of care. ... This essay explores the significance of leadership in nursing by examining various leadership styles, including transformational, democratic, autocratic, and servant ...
There are several formal leadership theories, including transformational, democratic, laissez-faire, autocratic, and servant. Targeted leadership development in nursing will ensure that future health workers will be well prepared to meet the challenges of an overburdened health care system (den Breejen-de Hooge et al., 2021).
1. Introduction. 1.1 This report looks at my existing leadership skills and how they have developed when implementing a postnatal group within my practice. Through developing this group, I will look at how the team responds to my leadership and how I approach situations. As part of my continuing professional development, I will identify changes ...
Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing Essay. In the field of nursing, mentors assist in critically advising and supporting students, they are our primary sources of valuable information on program operations, policies, and measures. In addition, they guide us on our career objectives and how to overcome obstacles and ensure success ...
Nursing leadership is a critical component of the healthcare industry, impacting patient care, organizational performance, and the advancement of the nursing profession. By mastering essential leadership skills, embracing diversity, promoting teamwork, and fostering a positive work environment, aspiring nurse leaders can make a meaningful ...
These examples highlight the importance of leadership in navigating challenges and achieving positive outcomes in policy development and change within healthcare organizations. References. Collins, E., Owen, P., Digan, J., & Dunn, F. (2020). Applying transformational leadership in nursing practice. Nurs Stand, 35(5), 59-66.
What was it like to transition in your career from being in nursing school, to working as a pediatric nurse, to finishing the Ph.D. program, and now to step into such an important leadership role within the VCU Health System? When I started the program, I was the nursing director for Women's and Children's Health.
The importance of leadership is now widely recognised as a key part of overall effective healthcare, and nursing leadership is a crucial part of this as nurses are now the single largest healthcare discipline (Swearingen, 2009). The findings of the Francis Report (2013) raised major questions into the leadership and organisational culture which allowed hundreds of patients to die or come to ...
The health care system faces a significant challenge in balancing the ever-expanding task of meeting patient care needs with scarce nursing resources that has even worsened as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. With a limited supply of registered nurses, nurse managers are often challenged to implement creative staffing practices such as sending staff to units where they do not normally work ...
In 2017, the department allocated educational premises at the address: ul. 1st Borodino, house 2. Since January 31, 2018, the Department of Nursing Year is part of the Medical and Preventive Faculty (MPF). Scientific work of the department: Complex scientific theme of the department "Psychovegetative correlations in patients with coronary ...
in the governance of universities. Citizenship is also part of the university core functions. f teaching, learning and research. Citizenship happens when students are willing to act beyond their self-interests, even if personal an. communal interests often overlap. Citizenship happens when students engage with peers and the teachers, in ...
Leadership Moscow is a leadership development program designed to cultivate the next generation of community leaders in Moscow and Latah County. This program offers a concentrated, hands-on learning experience to enhance and build leadership qualities. Leadership Moscow develops advocates for Moscow and its surrounding rural communities who ...