Home ➔ What's an Essay?

What Is an Essay and Its Features?
The are various definitions for “essay.” But here, we will focus on the meaning of this word, which has become a significant element of education in countries such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia.
If summarized in simple terms within the academic context, the essay’s definition would be the following:
An essay is a short, nonfictional piece of formal writing assigned to students to improve their writing skills or assess their knowledge of a given subject.

Alternative Essay Definitions
Here are some of the many definitions of an essay:
- According to Frederick Crews, professor of English at the University of California at Berkeley, an essay is “a fairly brief piece of nonfiction that tries to make a point in an interesting way.”
- A famous essayist, Aldous Huxley, notes that “the essay is a literary device for saying almost everything about almost anything” and divides essays into personal-biographical, objectively-factual, and abstract-universal.
- The Oxford Dictionary defines it as “a short piece of writing on a particular subject.”
Essays can be broadly categorized into formal essays and informal essays. Formal essays are characterized by their structured nature, employing a more formal language, and having a clearly defined purpose, contrasting with the more free-form and personal tone of informal essays.
Note: Apart from the secondary and tertiary education purpose, essays (also called papers reports) are often required when applying to colleges and universities to help them select the best applicants during the admissions.
If you study the word’s origin and history, you might better understand its purpose. The word “essay” comes from the Middle French word essayer, which in turn comes from Latin exigere, meaning “to test,” “examine,” and “drive out.”
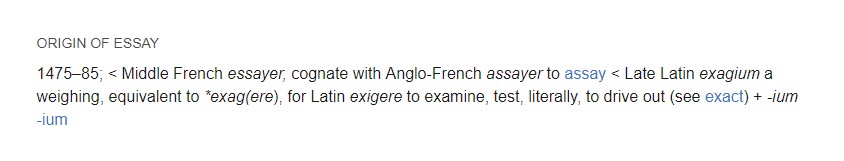
This “archaeological” linguistic journey reveals the idea behind essays, encouraging learners to examine their ideas concerning a particular topic in-depth and test them. By nature, essays are short and require a clearly defined purpose of writing that you must adhere to in your paper.
There’s a lot to be learned from essay writing: critical analysis, observation, interpretation, narration, persuasion, close reading, preparation, and time management. All these skills can be valuable even beyond the school walls.
Lastly, in the visual arts, creative works can also be called essays if they present a personal reflection on a particular matter. So, film essays or photo essays fall into the general category of essays.
What is an essay structure like?
An essay is generally composed of three parts and has the following structure :
- Introduction (hook, background information, and your thesis statement) – provides context for the reader and gives an argument in the form of a thesis statement.
- Body section (usually, one paragraph for each main idea) – the main section where evidence is presented to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s point of view or prove something.
- Conclusion – the last section that summarizes everything you have discussed in your essay and provides the final perspective on the subject.
Generally, an essay must focus on the author’s argument and supporting evidence. However, the variety of essay types involves many other forms and styles. Argumentative and expository essays are particularly common in university-level education, known for their structured approach to presenting information and making clear points.
Common Essay Types
Understanding the different types of essays is pretty important for your academic success. Each essay type serves its own purpose and requires a different approach, so here’s a brief look at some of the most common essay types you might encounter during your school times.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay demands you to present a viewpoint on a (usually) controversial issue. Your task would generally be to persuade the reader through some solid logical reasoning and credible evidence with relevant examples. All that will involve creating a very clear thesis statement, presenting well-researched evidence, and addressing opposing views and ideas, if there are such. Getting an argumentative essay as an assignment is common in subjects like politics, ethics, and social sciences, where there’s a lot of debate on different topics. An example of a common topic for this essay would be something like “Should the death penalty be abolished?”
Expository Essay
An expository essay focuses more on explaining a topic in a straightforward and logical manner. In such an essay, you will be presenting facts, statistics, and examples without any kind of your personal opinion. It’s usually built around a clear thesis statement and uses logical transitions to connect ideas from one paragraph to another. In general, expository essays are often used in academic settings to test students’ understanding of a subject or to explain complex ideas in a simple way. A common topic would be “The process of photosynthesis in plants.”, for example.
Narrative Essay
Narrative essays tell a story. These are often personal and can be both factual (based on a true story) and fictional. The key elements of this essay include a plot, characters, setting, and a climax. Unlike other essays, a narrative essay is much more creative and allows you to express your experiences or a story imaginatively and without some kind of rigid structure to follow. It’s often used in high school and college writing courses to develop storytelling skills. You would write about something like “A memorable trip to the mountains.”
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay aims to paint a picture but with words. This essay uses vivid descriptions and sensory details to engage the reader’s senses and emotions and is more focused on the details and nuances of the subject, whether it’s a person, place, object, or event. Descriptive essays are great for creative writing classes and help develop one’s ability to describe something in great detail. One of the possible topics here might be “The bustling atmosphere of a city market.”
Critical Essay
A critical essay evaluates a text, piece of art, or performance. It involves a thorough analysis and interpretation of the work, supported by credible evidence. The goal when writing this one is to provide a critical perspective, assessing the subject’s strengths and weaknesses. This type of essay is a common assignment in literature, film studies, and art history courses, where critical thinking and analytical skills are essential for the subject. A common topic here would be ‘An analysis of the themes in “To Kill a Mockingbird.”‘
History Essay
A history essay examines historical events and their impact. This type requires extensive research and a deep understanding of historical context. When writing it, you will be analyzing various historical sources, presenting a clear argument on the topic, and supporting it with historical evidence. History essays are obviously assigned in history courses and help develop research and analytical skills, as well as the ability to construct coherent historical narratives. Something like “The causes and effects of the French Revolution.” would be a common topic here.
10 Characteristics of a Good Essay
The structure and characteristics vary, but there are criteria you can apply to almost any academic essay. Below are ten characteristics that make a good essay.
You can find many works like Victor Segalen’s “Essay on Exoticism: An Aesthetics of Diversity” spanning many pages. But, as an academic assignment, essays are usually concise and range from 200 to 500 words.
Note: To learn more about essay length, check this article — How Long Should My Paper Be?
A narrowed-down topic
Because of the word count limit, your topic cannot be extensive and should focus on one aspect of the subject.
A subject is a broad concept: gun control, US history, WWII, Napoleonic Wars, business ethics, academic dishonesty, school dress code, etc. Those are not topics because you can write books on them.
Choose a more specific topic to cover. Ask yourself “Who? What? Where? When? Why? and How?” questions about the subject matter. That strategy will allow you to limit the number of choices and pick something you like.
For instance, let’s narrow down the gun control subject . Something like “Video games are not the problem, but poor gun control policies are” can be your topic.
Well-structured body paragraphs
In a nutshell, an essay’s body can be described as a series of paragraphs. But they all have a uniform structure you must maintain in the paper. It goes as follows:
1. Topic sentence
This is the first sentence, and it expresses the paragraph’s main idea. It acts like a mini-hook that attracts the reader’s attention.
Let’s say you’re working on a descriptive essay about your brother’s room.
Bad topic sentence:
My brother’s room is a mess.
Good topic sentence:
If they gave me one dollar every time I walked into my brother’s room and thought it was clean, I would be dead broke.
2. The main part
Here, you develop your topic sentence further, and there are many ways to do that:
- Provide facts or statistics
- Give reasons
- Illustrate with examples
- Use relevant quotes
- Present your opinion
- Share experiences
- Leverage human senses
Note: Make sure to cite your sources properly. Learn more here: How to Cite Sources (MLA and APA styles) .
3. Conclusion with a transition
If you had to write only one paragraph, this is where you would end the narrative. But, in academic essays, this last sentence transitions to the next idea — the next paragraph.
Clear thesis statement
A thesis is the main idea of your paper. It’s usually one sentence that shows the reader what your essay is about. The challenging part is to squeeze the purpose of your writing into one sentence and in such a way that would make the reader want to debate it.
To check if your thesis statement is correct, make sure:
- It’s not just an announcement of purpose that starts with “In this paper.”
- It’s not a question because thesis statements answer, not ask.
- It’s not a mere fact.
- It’s not a broad topic without a challenging opinion.
- It’s not a vague thought — make it more focused.
- It’s not disconnected from the main paragraphs.
Personal motivation
This one seems quite simple, but you won’t always find the answer to the “Why do I want to write about this topic” question easily. Even if the subject feels like the last thing you’d be interested in, there’s always something that can motivate you to write.
The reader would notice if you had zero motivation while writing the essay.
There’s no trick — just start writing . Once you are working on it, brainstorm all the ideas related to the subject. If you find it challenging to organize your thoughts right away, try freewriting — start writing everything that comes to your mind. Yes, there will be a lot of ideas not connected with one another, but you can choose the ones making sense and work with them further.
Evidence and examples support claims
Each of your topic sentences in the main paragraphs should be supported. You can:
- Explain what you meant by defining the main terms or phenomena.
- Provide more details about the topic sentence.
- Illustrate with examples, facts, or statistics.
- Cite field experts who support your opinion.
- Share your relevant experience, if any.
Use the method you believe is the most appropriate in your case.
Evidence is analyzed
Just facts, statistics, or quotations are not enough. You must analyze the proof and show how you can compare data and establish causal links.
Note: Use cohesive devices like transition words and conjunctions to hold your essay together as one unit.
No grammar mistakes
The last period is placed, and you think, “Finally, it’s done! Now, back to the fun stuff.” By doing so, you will hand in an essay riddled with mistakes.
Proofreading matters. After the first draft, double-check it for all possible mistakes: grammar, punctuation, word usage, logic flow, etc.
- Read it out loud.
- Ask your friend or family member to give their opinion.
- Put it away for some time to proofread it later.
The structure is consistent
Ensure your paper follows the structure described before. Check if your conclusion and introduction are about the same — the same applies to the body paragraphs.
Note: This article will give you valuable insights into the structure — How to Write an Essay .
It is coherent
Another criterion they use to grade your essay is its coherence (unity). To check this point, ask yourself:
- Are all ideas related to the essay’s topic and thesis statement?
- Are all my evidence, arguments, and conclusions connected to my thesis statement?
- Are all ideas arranged in a logical order?
- Are there enough linking words? Or is it too many of them?
- Are there enough pronouns and synonyms so that the essay isn’t repetitive?
The last tip on essay writing: always check your assignment sheet and clarify anything you don’t understand with your tutor or professor. Your college might have some special requirements regarding the content or style. So, make sure you studied all the instructions for the task thoroughly.
Why do we have to write essays in school?
Writing essays in school is a crucial component of academic writing, serving as a foundational practice for developing skills in various types of essays, such as argumentative, descriptive, narrative, expository, and more. Through the process of essay writing, students learn to articulate their ideas and thoughts more coherently, practice forming main and alternative arguments backed up by evidence, and enhance their ability to present clear explanations, craft creative descriptions, and structure narratives effectively. This practice not only helps build strong academic writing skills but also prepares students for writing research papers, submission essays, and contributing to academic journals, thereby playing a significant role in their academic and professional growth.
How are essays evaluated?
In schools, essays are typically evaluated based on a combination of criteria such as quality of your argument, evidence you presented, structure and organization, grammar and vocabulary accuracy, adherence to formatting requirements (if any), creativity, originality, critical thinking skills displayed, etc. The evaluator (usually your teacher or professor) will look at all these aspects to assess the essay’s overall quality.
How many paragraphs should there be in an essay?
The number of paragraphs in an essay will vary depending on its length and purpose. In general, a standard essay should have at least 3-4 paragraphs: an introduction paragraph to provide background information and set out your main argument; 2-3 body paragraphs where you flesh out your argument with evidence; and a conclusion paragraph summarizing your key points or drawing conclusions from your evidence.

The list of references
- What is an essay? — Bow Valley College
- Overview of the Academic Essay — Harvard University
- Essay Writing — Purdue University
- Basic Essay and Paragraph Format — Utah Valley University
Was this article helpful?
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
Writing an effective and impactful essay is crucial to your academic or professional success. Whether it’s getting into the college of your dreams or scoring high on a major assignment, writing a well-structured essay will help you achieve it all. But before you learn how to write an essay , you need to know its basic components.
In this article, we will understand what an essay is, how long it should be, and its different parts and types. We will also take a detailed look at relevant examples to better understand the essay structure.
Get an A+ with our essay editing and proofreading services! Learn more
What is an essay?
An essay is a concise piece of nonfiction writing that aims to either inform the reader about a topic or argue a particular perspective. It can either be formal or informal in nature. Most academic essays are highly formal, whereas informal essays are commonly found in journal entries, social media, or even blog posts.
As we can see from this essay definition, the beauty of essays lies in their versatility. From the exploration of complex scientific concepts to the history and evolution of everyday objects, they can cover a vast range of topics.
How long is an essay?
The length of an essay can vary from a few hundred to several thousand words but typically falls between 500–5,000 words. However, there are exceptions to this norm, such as Joan Didion and David Sedaris who have written entire books of essays.
Let’s take a look at the different types of essays and their lengths with the help of the following table:
How many paragraphs are in an essay?
Typically, an essay has five paragraphs: an introduction, a conclusion, and three body paragraphs. However, there is no set rule about the number of paragraphs in an essay.
The number of paragraphs can vary depending on the type and scope of your essay. An expository or argumentative essay may require more body paragraphs to include all the necessary information, whereas a narrative essay may need fewer.
Structure of an essay
To enhance the coherence and readability of your essay, it’s important to follow certain rules regarding the structure. Take a look:
1. Arrange your information from the most simple to the most complex bits. You can start the body paragraph off with a general statement and then move on to specifics.
2. Provide the necessary background information at the beginning of your essay to give the reader the context behind your thesis statement.
3. Select topic statements that provide value, more information, or evidence for your thesis statement.
There are also various essay structures , such as the compare and contrast structure, chronological structure, problem method solution structure, and signposting structure that you can follow to create an organized and impactful essay.
Parts of an essay
An impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion.
1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader’s attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about.
2. The body is where you dive deeper into your topic and present your arguments and evidence. It usually consists of two paragraphs, but this can vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing.
3. The conclusion brings your essay to a close and is typically one paragraph long. It should summarize the main points of the essay and leave the reader with something to think about.
The length of your paragraphs can vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing. So, make sure you take the time to plan out your essay structure so each section flows smoothly into the next.
Introduction
When it comes to writing an essay, the introduction is a critical component that sets the tone for the entire piece. A well-crafted introduction not only grabs the reader’s attention but also provides them with a clear understanding of what the essay is all about. An essay editor can help you achieve this, but it’s best to know the brief yourself!
Let’s take a look at how to write an attractive and informative introductory paragraph.
1. Construct an attractive hook
To grab the reader’s attention, an opening statement or hook is crucial. This can be achieved by incorporating a surprising statistic, a shocking fact, or an interesting anecdote into the beginning of your piece.
For example, if you’re writing an essay about water conservation you can begin your essay with, “Clean drinking water, a fundamental human need, remains out of reach for more than one billion people worldwide. It deprives them of a basic human right and jeopardizes their health and wellbeing.”
2. Provide sufficient context or background information
An effective introduction should begin with a brief description or background of your topic. This will help provide context and set the stage for your discussion.
For example, if you’re writing an essay about climate change, you start by describing the current state of the planet and the impact that human activity is having on it.
3. Construct a well-rounded and comprehensive thesis statement
A good introduction should also include the main message or thesis statement of your essay. This is the central argument that you’ll be making throughout the piece. It should be clear, concise, and ideally placed toward the end of the introduction.
By including these elements in your introduction, you’ll be setting yourself up for success in the rest of your essay.
Let’s take a look at an example.
Essay introduction example
- Background information
- Thesis statement
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane in 1903 revolutionized the way humans travel and explore the world. Prior to this invention, transportation relied on trains, boats, and cars, which limited the distance and speed of travel. However, the airplane made air travel a reality, allowing people to reach far-off destinations in mere hours. This breakthrough paved the way for modern-day air travel, transforming the world into a smaller, more connected place. In this essay, we will explore the impact of the Wright Brothers’ invention on modern-day travel, including the growth of the aviation industry, increased accessibility of air travel to the general public, and the economic and cultural benefits of air travel.
Body paragraphs
You can persuade your readers and make your thesis statement compelling by providing evidence, examples, and logical reasoning. To write a fool-proof and authoritative essay, you need to provide multiple well-structured, substantial arguments.
Let’s take a look at how this can be done:
1. Write a topic sentence for each paragraph
The beginning of each of your body paragraphs should contain the main arguments that you’d like to address. They should provide ground for your thesis statement and make it well-rounded. You can arrange these arguments in several formats depending on the type of essay you’re writing.
2. Provide the supporting information
The next point of your body paragraph should provide supporting information to back up your main argument. Depending on the type of essay, you can elaborate on your main argument with the help of relevant statistics, key information, examples, or even personal anecdotes.
3. Analyze the supporting information
After providing relevant details and supporting information, it is important to analyze it and link it back to your main argument.
4. Create a smooth transition to the next paragraph
End one body paragraph with a smooth transition to the next. There are many ways in which this can be done, but the most common way is to give a gist of your main argument along with the supporting information with transitory words such as “however” “in addition to” “therefore”.
Here’s an example of a body paragraph.
Essay body paragraph example
- Topic sentence
- Supporting information
- Analysis of the information
- Smooth transition to the next paragraph
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane revolutionized air travel. They achieved the first-ever successful powered flight with the Wright Flyer in 1903, after years of conducting experiments and studying flight principles. Despite their first flight lasting only 12 seconds, it was a significant milestone that paved the way for modern aviation. The Wright Brothers’ success can be attributed to their systematic approach to problem-solving, which included numerous experiments with gliders, the development of a wind tunnel to test their designs, and meticulous analysis and recording of their results. Their dedication and ingenuity forever changed the way we travel, making modern aviation possible.
A powerful concluding statement separates a good essay from a brilliant one. To create a powerful conclusion, you need to start with a strong foundation.
Let’s take a look at how to construct an impactful concluding statement.
1. Restructure your thesis statement
To conclude your essay effectively, don’t just restate your thesis statement. Instead, use what you’ve learned throughout your essay and modify your thesis statement accordingly. This will help you create a conclusion that ties together all of the arguments you’ve presented.
2. Summarize the main points of your essay
The next point of your conclusion consists of a summary of the main arguments of your essay. It is crucial to effectively summarize the gist of your essay into one, well-structured paragraph.
3. Create a lasting impression with your concluding statement
Conclude your essay by including a key takeaway, or a powerful statement that creates a lasting impression on the reader. This can include the broader implications or consequences of your essay topic.
Here’s an example of a concluding paragraph.
Essay conclusion example
- Restated thesis statement
- Summary of the main points
- Broader implications of the thesis statement
The Wright Brothers’ invention of the airplane forever changed history by paving the way for modern aviation and countless aerospace advancements. Their persistence, innovation, and dedication to problem-solving led to the first successful powered flight in 1903, sparking a revolution in transportation that transformed the world. Today, air travel remains an integral part of our globalized society, highlighting the undeniable impact of the Wright Brothers’ contribution to human civilization.
Types of essays
Most essays are derived from the combination or variation of these four main types of essays . let’s take a closer look at these types.
1. Narrative essay
A narrative essay is a type of writing that involves telling a story, often based on personal experiences. It is a form of creative nonfiction that allows you to use storytelling techniques to convey a message or a theme.
2. Descriptive essay
A descriptive essay aims to provide an immersive experience for the reader by using sensory descriptors. Unlike a narrative essay, which tells a story, a descriptive essay has a narrower scope and focuses on one particular aspect of a story.
3. Argumentative essays
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that aims to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance based on factual evidence and is one of the most common forms of college essays.
4. Expository essays
An expository essay is a common format used in school and college exams to assess your understanding of a specific topic. The purpose of an expository essay is to present and explore a topic thoroughly without taking any particular stance or expressing personal opinions.
While this article demonstrates what is an essay and describes its types, you may also have other doubts. As experts who provide essay editing and proofreading services , we’re here to help.
Our team has created a list of resources to clarify any doubts about writing essays. Keep reading to write engaging and well-organized essays!
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps
- How to Write an Essay Header
- How to Write an Essay Outline
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an argumentative and an expository essay, what is the difference between a narrative and a descriptive essay, what is an essay format, what is the meaning of essay, what is the purpose of writing an essay.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
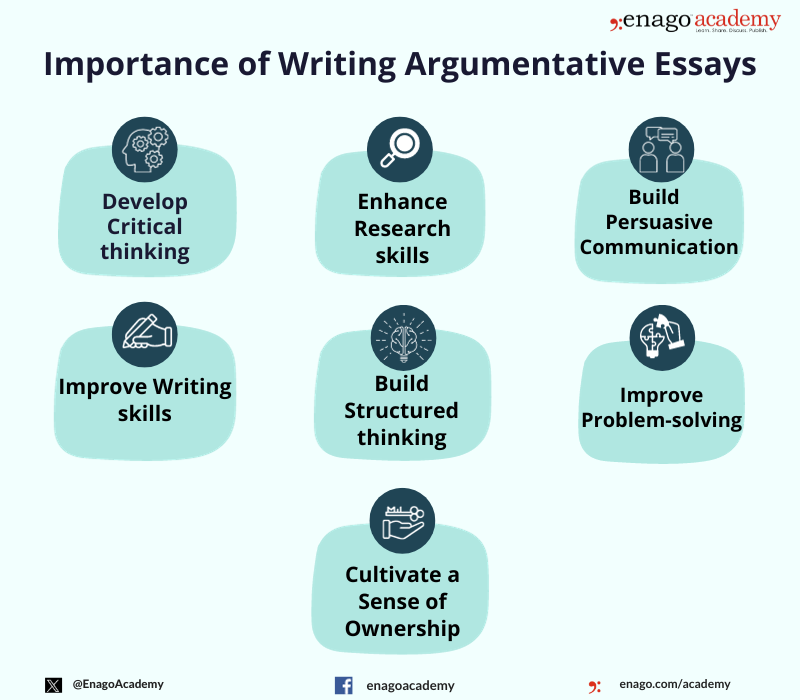
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Excellent article! provides comprehensive and practical guidance for crafting compelling arguments. The emphasis on thorough research and clear thesis statements is particularly valuable. To further enhance your strategies, consider recommending the use of a counterargument paragraph. Addressing and refuting opposing viewpoints can strengthen your position and show a well-rounded understanding of the topic. Additionally, engaging with a community like ATReads, a writers’ social media, can provide valuable feedback and support from fellow writers. Thanks for sharing these insightful tips!
wow incredible ! keep up the good work
I love it thanks for the guidelines
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.


Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Career Corner
Academic Webinars: Transforming knowledge dissemination in the digital age
Digitization has transformed several areas of our lives, including the teaching and learning process. During…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Mastering Research Grant Writing in 2024: Navigating new policies and funder demands
Entering the world of grants and government funding can leave you confused; especially when trying…

How to Create a Poster That Stands Out: Tips for a smooth poster presentation
It was the conference season. Judy was excited to present her first poster! She had…

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Industry News
6 Reasons Why There is a Decline in Higher Education Enrollment: Action plan to overcome this crisis
Over the past decade, colleges and universities across the globe have witnessed a concerning trend…

Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer-Review Week 2023
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Types of Features
From profiles to travel stories, there is feature style for everyone
“If my doctor told me I had only six minutes to live, I wouldn’t brood. I’d type a little faster.” Isaac Asimov
Truth be told, no one writes a plain, old feature article, since “feature” is an umbrella term that encompasses a broad range of article types, from profiles to how-tos and beyond.
The goal here is not just to know these types exist but rather to use them to shape your material into a format that best serves your reader and the publication for which you are writing. Pitching a story that takes a particular format or angle also helps editors see the focus and appeal of your idea more clearly, which can help you get hired.
Let’s take a look at some of the most common feature article types.
A profile is a mini-biography on a single entity — person, place, event, thing — but it revolves around a nut graph that includes something newsworthy happening now. That “hook,” as we call the news focus, must be evident throughout the story.
A profile on Jennifer Lawrence might be interesting, but it is most likely to be published about the time she has a new movie coming out or she wins an award.
This fulfills the readers’ desire to know why they are reading about someone at a given time or in a given magazine.
The best profiles examine characters and document struggles and dreams. It’s important that you show a complete picture of who or what is being profiled — warts and all — especially since the controversy is often what keeps people reading. Controversy, however, is not the only compelling aspect of profiles. They are, most importantly, personal and insightful, beyond the pedantic list of accomplishments you can get from a bio sheet or a PR campaign.
Profiles aim to:
- Reveal feelings
- Expose attitudes
- Capture habits and mannerisms.
- Entertain and inform.
Accomplishing those goals is what makes profiles challenging to write, but also makes them among the most compelling and fulfilling stories to create.
Delving deeply into your subject’s interests, career, education and family can bring out amazing anecdotes, as can reporting in an immersive style.
The goal is to watch your subject closely and document his or her habits, mannerisms, vocal tones, dress, interactions and word choice. Describing these elements for readers can contribute to a fuller and more accurate presentation of the interview subject.

Consider this opening paragraph from one of my favorite profiles, Jeff Perlman’s look at one-time baseball bad boy John Rocker of the Atlanta Braves:
A MINIVAN is rolling slowly down Atlanta’s Route 400, and John Rocker, driving directly behind it in his blue Chevy Tahoe, is pissed. “Stupid bitch! Learn to f—ing drive!” he yells. Rocker honks his horn. Once. Twice. He swerves a lane to the left. There is a toll booth with a tariff of 50 cents. Rocker tosses in two quarters. The gate doesn’t rise. He tosses in another quarter. The gate still doesn’t rise. From behind, a horn blasts. “F— you!” Rocker yells, flashing his left middle finger out the window. Finally, after Rocker has thrown in two dimes and a nickel, the gate rises. Rocker brings up a thick wad of phlegm. Puuuh! He spits at the machine. “Hate this damn toll.”
Perlman does not have to tell us anything about Rocker; he has shown us and lets us make our own determinations as to the person we are getting to know through this article.
Research is key to any piece, but profiles provide the ultimate test of your interviewing skills. How well can you coax complete strangers into sharing details of their private lives? Your job is to get subjects to open up and share their true personalities, memories, experiences, opinions, feelings and reflections.
This comes from a true conversational style and a willingness to probe as deep as you need to get the material you need.
Interview your subject and as many people as you need to get clear perspectives of your profile subject.
Not everyone will make your article, but you can get background information and anecdotes that could be crucial to understanding your subject or asking key questions. (Now might be a good time to download “Always Get the Name of the Dog.”)
Take the time to watch your subject at work or play so you can really get to know them in a three-dimensional way.
The fewer sources and the less time you spend with your subject the less accurate or complex your profile will be.
The framework of a profile follows these guidelines:
Anecdotal lede
An engaging, revealing a little story to lure us into your article.
Nut graph/Theme
A paragraph that shows the reader what exactly this story is about and why does this entity matter now?
Observe our subject in action now using dialogue details and descriptions.
A recap of our subject’s past activities using facts, quotes and anecdotes as they relate to the theme.
Where Are We Now?
What is our subject doing now, as it relates to the theme?
What Lies Ahead?
Plans, dreams, goals and barriers to overcome.
Closing Quote
Bring the article home in a way that makes the reader feel the story is complete like they can sigh at the end of a good tale.
A Q&A article is just what it sounds like — an article structured in questions and answers.
Freelancers and editors both like them for several reasons:
- They’re easy to write.
- They’re easy to read.
- They can be used on a variety of subjects.
The catch is writers/interviewers must take even greater care with the questions asked and ensuring the quality of the answers received because they will provide both the skeleton and the meat of your piece.
This may seem obvious, but quality questions are vital, meaning we avoid closed-ended (yes or no, single-word answer) questions and instead ask questions that will inspire some thought, creativity and explanation or description.
Q&A articles start with an introduction into the subject — often as anecdotal as any other piece, but then transition into the fly-on-the-wall feeling of watching an interview take place. You are the interviewer.
The subject is the interviewee, and the reader is sitting alongside you both soaking in the experience and your relationship.
That means a Q&A has to stay conversational so it does not feel like a written interrogation.
The interview itself is much like we would use for an article, but you have to be more conscious of the order in which you ask questions, how they transition from one another and the quality of the answer so you are not tempted to move answers around.
You will be amazed at how many words get generated in an actual conversation or interview, so the Q&A is far from over when the interview concludes. Editing and cutting the interview transcript can take far longer than the interview itself.
You cannot change your subject’s words, but you take out redundancies and those verbal lubricants that keep conversations moving — “like,” “you know,” etc., Sentences and phrases can be edited out by using ellipses (…) to show you have removed something.
Grammar is a challenge with a lot of transcripts, and I will leave in that which represents the subject, but I will not let them come across badly by misusing words or phrases.
Instead, let’s take it out or ask them to clarify.
If you do an internet search on “round-up story,” you very often get a collection of information from various places on a central them.
Feature round-ups are written the same way.
These articles are like list blog posts, where you have a variety of suggestions from different sources that advance a common idea:
- 7 secrets to a happy baby
- 10 best vacation spots with a teenager
- 5 tips on how to pick the perfect roommate
You may notice that there is a numeric value on each of these ideas, and that is a key part of the roundup. You are offering a collection of suggestions, provided and supported by sources, on a specific topic.
The article begins, as most features do, with an anecdote that takes us to a theme, but instead of a uniform or chronological body style, we break it up into these sections outlined by each numbered suggestion.
Each section can be constructed like its own mini feature — complete with sources, facts, anecdote and quotes, or just the advice provided by a qualified source (not the author!).
There does not need to be a specific order to how each piece of the article is presented, rather their order is interchangeable.
It is important to have sources with some level of expertise and not merely opinions on the topic. Just because someone went to Club Med with their 5-year-old and had fun does not mean it’s the best vacation spot for kids.
We first need an idea of what makes a good vacation spot and then support with facts how this one fits the criteria.
Readers love to learn how to do new things, and there are few better ways to teach them than through how-to articles.
How-to articles provide a description of how something can be accomplished using information and advice, giving step-by-step directions, supplies and suggestions for success.
Unlike round-ups, these articles must be written sequentially and have to end with some sort of success.
Aim for something that most people don’t know how to do, or something that offers a new way of approaching a familiar task. Most importantly, make sure it is neither too simplistic, nor too complex for their attempt, and include provide definitions and anecdotes that show how things can go well or poorly in attempting this task.
Personal Experience
Most of us have had some experience that we think, “I would love to write about this so other people can learn or enjoy this with me.”
If you have a truly original and teachable moment and can find the right feature to which to pitch it, you may very well have a personal experience story on your hands.
Some guidelines for finding such a story include whether this is an experience readers would:
- Wish to share?
- Learn or benefit from?
- Wish to avoid?
- Help cope with a challenge?
Unlike a first-person lede, which might use your personal anecdote to get us into a broader story, in a personal experience article you are the story, and how we learn from your experience will help us navigate the same waters.
They can be emotional, like the New Yorker piece on women who share their abortion stories , but they can also be about amazing vacations that others might consider — “Bar Mitzvah trip to Israel” anyone? — or how about a man who quits a high-powered job to stay home with his kids?
No matter what your experience, you must be willing to tell your story with passion and objectivity, sharing the good, the bad and the uncomfortable, and making readers part of the experience.
It’s important that the experience is over before you pitch, so the reader can get a clear perspective of what happened and the resolution. Did it work or not?
As the author, you also need time to gain perspective on your issue so you can “report” it as objectively as possible.
Finally, make sure you are chronicling something attainable or achievable. We need to go through it and come out the other side with evidence that will make us smarter and better equipped to handle a similar situation that might come our way.
The Art of Covering Horse Racing
Melissa Hoppert is the racing writer from the New York Times, and despite covering the same events over and over she manages to find a unique story each time.
Belmont Park is called “Big Sandy,” because the track has so much sand on it. I rode the tractor and asked the trackman, “What makes it like that? What it’s like to race on it?”
It was my most-read story that year. You have to think outside the box.

When the horse Justify came along, it was like ”here we go again — another Triple Crown with the same trainer. What can I possibly write about Bob Baffert that has not written before?
We observed and thought outside the box. We didn’t do a Bob Baffert feature. We went to the barn and still talked to him every day, but we looked at things differently.
We focused more on the owners . They were in a partnership and that is a trend of the sport. Rich owners team up to share the risk. That made it more of a trend story. Is this where we are going.
Sometimes I like writing about the horse. American Pharoah was a really fun, quirky horse. My most favorite story was when I went to visit American Pharoah’s sire, Pioneer of the Nile , at the breeding shed. He has a weird breeding style. He needed the mood to be set. It was kind of random, but it helped tell a story of American Pharoah that had not yet been told.
True-Life Drama
Examples of these include:
- The couple on a sight-seeing plane ride that had to land the plane when their pilot died
- Aron Ralston frees himself by sawing off his own arm after getting trapped in the desert.
- Tornado survival stories
It is fitting that the first example I found to show you of true-life dramas came from Readers Digest because these types of stories are the bread and butter of that magazine.
They are the stories that are almost impossible to believe but are true, and they are driven by the characters who make them come to life.
Some “true-life dramas” become even more famous when they are adapted for the screen, like the Slate story of being rescued from Iran , you might know better as the film, “Argo.”
How about Capt. Richard Phillips’ dramatic struggle with Somali pirates, now a film starring Tom Hanks?
Steve Lopes of the Los Angeles Times found a violin-playing homeless man who became the subject of numerous columns and later the movie “The Soloist.”
These stories are, quite simply, dramatic experiences from real people, where they live through moments few of us can imagine.
Many of the feature versions of these stories start as newspaper coverage of the breaking event, and then a desire to go behind-the-scenes and chronicle exactly what happened over a much longer course of time — the lead-up, the culmination and the aftermath.
Being a consumer of news will help you come across these stories, and a desire to conduct really penetrating interviews to get the “real story” will make them come to life.
You might not be thinking about Christmas in May or back-to-school in February, but chances are editors will be scheduling those topics and looking for article ideas.
Seasonal stories are the ones that happen every year and need a fresh angle on an annual basis.
It goes beyond standbys like “Best side dishes for Thanksgiving,” and how to make a good Easter basket, to “ How to do the holidays in a newly divorced family ,” and “Back to school shopping for a home-schooled child.”
The key is that a timely observance is interwoven in the theme, and these stories are planned and often executed months in advance since we all know they are coming.
Seasonal can also relate to anniversaries — Sept. 11, Martin Luther King Jr. Day, Titanic sinking — and their marketability can escalate dramatically around an anniversary.
The angle is all about the audience, so think how you can spin one day or a milestone event to toddlers, teens, seniors, your local community, pets, business, food, travel and you may suddenly have 10 stories from one topic.
Remember, though, that your pitch has to come long before the event is even in the mind of most readers — at least six months and sometimes a year.
The perceived glamour division of freelance writing is the travel piece, which most people think comes with an all-expense-paid trip to swanky, exotic locations.
That can be true, but more likely writers make their own plans and accommodations and their pay reflects that a portion of their compensation comes from the good time they had traveling.
The good news is that with the rise of travel blogs and smaller travel publications there are more outlets than ever to pitch your ideas, provided they are original and unique to the audience.
That means, “Traveling to Paris,” probably won’t work, but “ Traveling to Paris on $50 a day ” just might.
That also does not mean that publications are looking for your personal essay on what you did for your summer vacation, or just because you visited Peru and loved it that it’s worthy of a feature article. You have to show the editor and the reader why you have a unique perspective and angle on a traveling experience.
Travel writing means looking for stories on about:
- How to travel
- When to travel
- Advice on traveling
The more specifically you can focus on a population of travelers — seniors, parents, honeymooners, first-time family vacation — the more likely you can come up with an idea that has not been overdone and pitch it to a niche magazine.
In a column on the Writer’s Digest website, Brian Klems writes the need to travel “deeply” as opposed to just widely, and I thought that was such an insightful term. He spelled out the need to really dig deep into whatever area you might cover and take copious, detailed notes, but I would add that you also have to really dig deep into what people want to know about travel and enough to go past the cliché or stereotypes.
The more descriptively you can present experiences, the more compelled readers may be to join you.
To separate yourself from the cacophony of travel voices out there, consider building up expertise in one subject or area. If you are from an interesting area, see how you can pitch stories to bring make outsiders insiders. Are you a big hockey fan? What about traveling to different hockey venues and making a weekend travel story out of what to see and do before and after the game?
The key to success is to become a curious and perceptive traveler from the minute you book a trip. Think about how your experience can be a travel story, as opposed to only looking to pitch stories that could become an experience.
Some other types to consider:
Essay or Opinion
First-person pieces, which usually revolve around an important or timely subject (if they’re to be published in a newspaper or “serious” magazine).
Historical Article
Focus on a single historical aspect of the subject but make a current connection.
Trend Story
Takes the pulse of a population right now, often in technology, fashion, arts and health.
No, we are not talking about trees.
Evergreen stories are ones that do not have an expiration date and can be pitched for creation at any time.
A profile on a new trend or profile-worthy person has to be pitched in relatively short order, or it will not really marketable anymore. But a story on how to build an exercise program around your pet does not really have to be published at a specific time.
Incorporating evergreen ideas into your repertoire of story ideas will open up even more publishing doors.
Writing Fabulous Features Copyright © 2020 by Nicole Kraft is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Argumentative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an argumentative essay?
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.
Please note : Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative essay differs from the expository essay in the amount of pre-writing (invention) and research involved. The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Argumentative essay assignments generally call for extensive research of literature or previously published material. Argumentative assignments may also require empirical research where the student collects data through interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Detailed research allows the student to learn about the topic and to understand different points of view regarding the topic so that she/he may choose a position and support it with the evidence collected during research. Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning.
The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
In the first paragraph of an argument essay, students should set the context by reviewing the topic in a general way. Next the author should explain why the topic is important ( exigence ) or why readers should care about the issue. Lastly, students should present the thesis statement. It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse. Transitions should wrap up the idea from the previous section and introduce the idea that is to follow in the next section.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the discussion of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. In addition, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph. Some paragraphs will directly support the thesis statement with evidence collected during research. It is also important to explain how and why the evidence supports the thesis ( warrant ).
However, argumentative essays should also consider and explain differing points of view regarding the topic. Depending on the length of the assignment, students should dedicate one or two paragraphs of an argumentative essay to discussing conflicting opinions on the topic. Rather than explaining how these differing opinions are wrong outright, students should note how opinions that do not align with their thesis might not be well informed or how they might be out of date.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence. As noted in the paragraph above, a successful and well-rounded argumentative essay will also discuss opinions not aligning with the thesis. It is unethical to exclude evidence that may not support the thesis. It is not the student’s job to point out how other positions are wrong outright, but rather to explain how other positions may not be well informed or up to date on the topic.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students may begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize the information presented in the body of the essay. Restate why the topic is important, review the main points, and review your thesis. You may also want to include a short discussion of more research that should be completed in light of your work.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of World War II and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the argument in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the conflict. Therefore, the argumentative essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph essay
A common method for writing an argumentative essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of (a) an introductory paragraph (b) three evidentiary body paragraphs that may include discussion of opposing views and (c) a conclusion.
Longer argumentative essays
Complex issues and detailed research call for complex and detailed essays. Argumentative essays discussing a number of research sources or empirical research will most certainly be longer than five paragraphs. Authors may have to discuss the context surrounding the topic, sources of information and their credibility, as well as a number of different opinions on the issue before concluding the essay. Many of these factors will be determined by the assignment.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay (With Features & Structure)
- Post author: Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka ACMC
- Post published: September 12, 2021
- Post category: Scholarly Articles
How To Write An Argumentative Essay : The Virtue’s English Dictionary (Encyclopaedic Edition) defines an Essay as a literary composition intended to prove some particular point or illustrate a particular subject. We all had at one time and the other written an essay. Did we ever consider the type and format of such writings? Of course there could be more than one type of essay writing incorporated or employed in a single writing.
Essays can be argumentative, expository, narrative and descriptive. These are the four main types of essay. There could be combination of two or more of these four types of essay employed in one essay. For instance, elements of descriptive essay can be found in an argumentative essay. This does not make it any less an argumentative essay.
Narrative Essay tells a story. There is usually a central point at which the writing is centered. The story could be from personal experience and of course can be figurative. Narrative essay gives an account of an event in a well-structured plot.
Descriptive Essay is a writing that attempts to describe an event, experience, object, person, place, idea or anything capable of being described. In other words, the essay attempts to characterize a given event, idea, person or place.
An expository essay attempts to explain, explicate, elucidate, illustrate, uncover and clarify a given concept or event.
This article is targeted at discussing how to write an argumentative essay.
Argumentative essay from the word “ Argument ”, according to Virtue’s English Dictionary (Encyclopaedia Edition) defines argument as a subject of a discourse or writing; a reason offered for or against something; a debate, controversy, discussion and a process of reasoning. Therefore argumentative essay can be defined as a debatable writing which upon choosing a stance, attempts to persuade and convince the mind of the readers into finding reasons with the points established by the writer.

RECOMMENDED: How to write a perfect affidavit with examples
Table of Contents
How to write an argumentative essay step by step
The goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the mind of the readers that your position is preferable and should be considered. In order to produce a logical and sound argumentative essay, it is important that the writer be well abreast with the features of an argumentative essay. This guides the writer not to derogate from the argumentative genre of essay intended, and also to render a logically structured and sound essay.
For a writing to be considered argumentative, it has to conform to a particular format and fulfil certain requirement, otherwise one may be writing any other type of essay in the thought of an argumentative one. This would lead us to discussing the features of an argumentative essay together with the structure.
Also see: How to introduce yourself in a debate
Features of Argumentative Essay
The main five features of an argumentative essay are:
a. Introduction and Thesis
b. Opposing and Qualifying Ideas
c. Evidence in Support of Claim
d. Style and Tone of Language
e. Compelling Conclusion
a. Introduction and Thesis: An argumentative essay must begin with introduction. This is simply to give the general introduction of the topic to be discussed. The introduction shall then include the thesis which is the writer’s point of view.
b. Opposing and Qualifying Ideas: While writing an argumentative essay, the writer has to state and acknowledge the possible points and ideas of the opposing side which are certainly not in his favour. Acknowledging those points and ideas enable lay a grounded foundation of his own points by juxtaposing the sides. This also has a way of arousing the interest of the readers to finding reasoning with your points.
c. Evidence in Support of Claim : A good argumentative essay should has a strong evidence to support the claims asserted. Evidence in the context of an argumentative essay is simply the information sourced for and logically analyzed for the purpose of justifying a stated claim. A writer is expected to source for articulated, logical and statistical points to support the claims asserted.
d. Style and Tone of Language : The language and tone of an argumentative essay must be persuasive and convincing. The tone must be confident enough to lure or compel the mind of the readers into finding reasons with the argument of the writer.
An argumentative essay should be well paragraphed. Paragraphing contributes to the logicality of the structure as well as suggest the appropriate intended tone of the writer.
Style is the manner of expression and choice of words employed by the writer, whereas tone is the attitude of the writer towards the topic and the audience.
e. Compelling Conclusion : An argumentative essay should have a compelling conclusion. Compelling here means that it has to be sound and convincing. The conclusive point should resolve the thriving issues implicated in the course of the argument.

There are basically four parts of an argument. They include:
b. Counterclaims
d. Evidence
RECOMMENDED: How to improve your emotional intelligence
a. Claims: Claim is simply as assertion stated as a fact and backed up with evidence. It is also known as thesis. It fact includes the writer’s position in an argumentative essay. Assertion of claim directs the readers mind to the writer’s position, purpose and line of argument. Typical example of claim – “ Gold Values More That Silver”
b. Counterclaim: Counterclaim is also known as counterargument. It is the point of view of the opposing side of an argument which is capable of weakening the argument of the writer. The writer is however expected to raise these points and discredit them in his own favour by marshaling out points which is capable of rendering them wrong, inapplicable or invalid.
The writer is advised not to avoid those points which seem to be against his line of argument as this can leave doubts in the mind of the readers or audience. The writer is expected to acknowledge them and criticize them to his or her own advantage.
Also see: How to become a successful lawyer: 10 Qualities you need
c. Reasons: An argumentative essay should incorporate points and facts which are the suggested reasons why the writer’s line of argument should be considered. Therefore, a reason is a kind of justification for the writer’s claims.
d. Evidence: Evidence includes objectively verifiable facts which demonstrates and strengthens the writer’s claim. They are those verifiable facts which the writer can show in order to establish his point of view for the purpose of tilting the mind of the audience into affirming the claims asserted, and finding reasons with the writer’s line of argument.
Evidence can be factual, logistical and or statistical but in all, it has to be verifiable.
RECOMMENDED: Causes, Effects and Solutions to Low Self-esteem
Writing a Compelling Argument
On writing a compelling argument, the writer must be meticulous in considering the points on which his or her argument should base, otherwise one may end up antagonizing his or her own point of view. Employment of fallacies should be avoided as much as possible. The writer should be careful not to make hasty generalization. Understanding the opposing point of view is a key element because this goes a long way guiding the writer in preparing the evidence and defence. For an argument to be compelling, the writer must clarify and resolve every point raised in order that questions would not be created in the minds of the audience. The writer’s point must be realistic, practicable and obtainable.
Recommended: Advantages and Disadvantages of a written constitution
It is advised that the conclusion be as explicit as possible and at the same time, concise and precise. In other words, conclusion should be straight to the point and exhume confidence.
In all, an argumentative essay must be suggestive and convincing, otherwise the purpose of the essay would be entirely defeated.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.
9 Essential Features of the Personal Essay Format

Kate Sliunkova
AdmitYogi, Stanford MBA & MA in Education

1. Writing Quality
Because personal essays hold a mirror up to the author and are also compositions, they allow for and demand some elements of originality and creativity.
The key is to craft an essay that is uniquely yours, impactful, succinct, and authentic. You’ll want to make every word count, strive to “show not tell,” and excel at improving word choice during the revision process to give full expression to your experiences and insights.
You, and someone not you (with good written communication skills), should review for final editing and to ensure the essay is carefully proofread.
2. Personal Point of View and Voice
Unlike expository essays or news writing, personal essays are subjective, and use first-person speech and perspective. Everything in the essay projects your unique personality, emotions, imunication style, making your college essay both “personal” and distinctive.
3. Authenticity and Vulnerability
Personal essays often explore sensitive or vulnerable topics, allowing readers to connect with YOU, the speaker. At the same time you’ll want to leave out overly personal or private details that don’t really fit the purpose or goal of the essay! Your essay is personal but it’s also shared publicly. You present an authentic self, without coming across boastful or artificial, and without being overly familiar…
PRO TIP: Respect your boundaries when it comes to what you feel okay sharing or not sharing. > Get input from an outside reader who knows you well for more input on what you’re sharing about > yourself and your life experiences before you press “submit.”
4. An Individual Value System
A great GPA and great letters of recommendation carry weight, but your personal essay is a way to present consequential character traits admissions officers are unlikely to find elsewhere in your application packet. A strong essay will communicate your values AND anchor them in lived experiences and reflections — making these personal beliefs more vivid, memorable, and also persuasive. Finally, look for opportunities to share how your values inform your passion for learning, your vocational interests, and your potential to contribute positively to campus life.
Personal essays aren’t just lists of experiences or lists of personality traits…Personal essays are a great format for highlighting your own level of self awareness. In an essay this often involves showing pivotal experiences or influences in your life and how you actively learn from them. Don’t feel valuable experiences need to be exceptional or fit any mold, we all learn from big and small experiences in our lives, and both successes and challenges can offer equally valuable insights!
6. Storytelling
Some personal essays are structured as narratives or “stories.” In fact, sometimes personal essay and personal narrative are terms used to describe the same essay format. We’ll talk more about narrative elements under “structure” below.
7. Emotional Connection
Successful personal essays evoke emotions in the reader. They use concrete details, imagery, or emphatic language to help the reader connect on a more personal and intimate level with the writer’s individual circumstances, experiences, joys, hardships, or challenges…
8. Universality
Although subjective, the personal essay is a format that lets the writer share personal insights and reflections that touch on more universal themes about life. These larger themes make the piece more memorable for the reader and allow the reader to compare their own insights and experiences with those of the writer.
Personal essays, and admissions essays in particular, are usually concise and to the point. Although you’ll likely want to add color and realism with some descriptive details, dialogue, or other vivid elements, you’ll typically want to maintain a strong focus on your formative experiences and most meaningful reflections.
Since the College Admissions essay is part of the Personal Essay family, the principles we’ve just listed go a long way in helping you understand how to format a winning college essay!
PRO TIP: When you’re ready for some additional feedback on your essay try checking with an academic advisor at your school. It is also very helpful to seek feedback from someone who knows you well - a parent, sibling, or friend would do great, even better if they have recently gone through the admissions process themselves.
Get ahead of the pack by using more sophisticated AI tools designed specifically for evaluating college application essays, such as Admit Yogi AI Essay Reviewer . Our essay reviewer is designed specifically for college admissions essays with input from experienced admissions consultants and former admissions officers, offers prompts in an intuitive format, and is keyed to read for high-impact essay components such as writing quality, personal voice, authenticity, values, and insights…
Now that you’ve got some quick insights into the essential features of a powerful personal essay, let’s go on to talk about the kinds of content, themes, and structures that work best in a college essay format.
Read applications
Read the essays, activities, and awards that got them in. Read one for free !

Benjamin Sanchez Pla
Yale (+ 31 colleges)
Harvard Student
Harvard (+ 11 colleges)
Jaden Botros
Stanford (+ 22 colleges)
Related articles
Demystifying College Admissions Essays
This guide provides insights into college admissions essays, discussing their vital role in showcasing your unique personality and passions. It navigates through different essay types, their objectives, and examples of potential prompts to help streamline your college application process.

Guide to Admit Yogi AI Essays Reviewer Methodology
Learn how Admit Yogi AI Essays Reviewer functions and how to use it to craft compelling college admission essays that stand out in the competitive application landscape.


The Essential List of Language Features You Should Know for English

In any of your English subjects, there are always so many language features that are important to learn!
Understanding how a text is constructed will unlock key points for analysis and discussion, boosting your English marks. Even better — understanding language features can enrich your skills in other subjects too. You might find yourself analysing primary and secondary sources in history better, or delving deeper into a scientific report.
Whatever it is, understanding language features is a great skill to have. If you want to know more, you’re totally in the right place — keep reading for a comprehensive list! Our HSC English tutors can help you identify the perfect language features for your essay, so get in touch if you’re looking for guidance!
Persuasive Devices Language Techniques Modality Grammatical and Story Structures
Download our list of English Language Features here!

Persuasive Devices
A persuasive device is a type of language feature that expresses and supports an opinion, making it stand out. The following are some specific techniques.
Looking for tips on writing a persuasive text? Check out our guide here!
A situation or statement where two opposing things are presented, often to create favour for one or highlight their differences. Example: In Despicable Me, Gru’s house is black and angular, contrasted with the more rounded and lightly coloured houses of the neighbours.
Like contrast, analogies are not always a persuasive device, but they can be used powerfully as one. The device contrasts two ideas to create an otherwise unstated relationship between them. It’s often used to prove an already established argument. Example: In Luka Lesson’s poetry, he compares a sword and spoken word, implying the power of language.
Language Techniques
This means a subtle reference to an event, person, text, place, you name it that readers may infer. Allusions are often made in passing, but reveal deeper meaning in the text. Example: In Sylvia Plath’s ‘Daddy’, Plath uses allusions to Hitler to emphasise the foul character of her father.
Often in texts, the ending of a story or line is left for the reader to determine. This is particularly common in postmodern texts. Authors who use ambiguity do not explicitly state what has happened to a character or plot. They may offer some clue for the reader to decipher, or they may keep it completely open-ended. This encourages readers to think critically and engage more deeply with the text. Example: At the end of Inception (Christopher Nolan), we do not know whether the main character is in reality or dreaming. This is shown through a camera cut just as audiences feel they are about to find out.
A technique that you probably know, but don’t realise it! Assonance is like alliteration but emphasises vowel sounds being repeated. This is often at the start of words, but it can include repetition of vowels within words, too. Example: “See ya later skater” repeats the ‘e’ and ‘a’ vowels, in this case creating a rhyming sequence. “‘Zooper Dooper’ (every Aussie kid’s favourite ice block) repeats the ‘o’.
Connotation
Some words or phrases evoke certain feelings for a reader. This can be because of how they sound or feel, historical context or pop culture. Example: ‘Beautiful’ and ‘cute’, while both describing how something is visually appealing, have different connotations. ‘Beautiful’ creates a sense of grace, elegance and maturity, while ‘cute’ is typically associated with youth and innocence.
Lost or confused already? Let us help you with a tailored approach to your studies with English Tutoring across Sydney.
Diction refers to the author’s choice and use of words in a literary work. It includes the specific words chosen, their connotations, and the style in which they are used. Diction can have a powerful effect on the tone and meaning of a piece of writing. For example, the word “frustrated” has a different connotation than the word “angry.” A writer may choose one over the other based on the desired effect on the reader. Additionally, the style of diction can be formal or informal, and can help convey the tone of the writing. Example: From George Orwell’s “1984” : “The hallway smelt of boiled cabbage and old rag mats. At one end of it a coloured poster, too large for indoor display, had been tacked to the wall. It depicted simply an enormous face, more than a metre wide: the face of a man of about forty-five, with a heavy black moustache and ruggedly handsome features.” In this passage, Orwell’s diction is clear and descriptive, with words like “boiled,” “old,” and “coloured” creating a specific and vivid image of the hallway. The choice of words “enormous face,” “ruggedly handsome features” and “heavy black moustache” gives the reader a clear image of the poster, and its size and characteristics. The use of specific and descriptive words can help the reader create a more detailed mental image of the setting, characters, and objects within the narrative.
When a mild or “polite” expression is used instead of a vulgar or blunt term, it is a euphemism. Example: We often say “passed away” instead of referring to death directly.
Figurative Language
A little like connotation or euphemism, figurative language is a type of language feature used when certain words have meanings behind what is really being said. You can think of this like an extended metaphor. This type of language is particularly common in poetry. Example: “A handsome manor house grew out of darkness at the end of the straight drive.” (JK Rowling, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows)
The deliberate exaggeration of a topic for emphasis or humour. Often, hyperbole is used in already emotional situations to gain greater reaction. Example: “I was so exhausted that I slept for ten days.”
Language that creates a mental picture of the topic it talks about, often to enhance the mood behind a text. Example: “The leaves created a blanket on the ground, with all kinds of red and gold hues to match my boots.”
When language is used to express somebody’s meaning or situation, that generally means the opposite. Irony is often a tip-of-the-tongue kind of humour that points out awkward or funny situations. Example: Saying “isn’t this great weather?” right before storm hits.
Often, two things are compared to one another by describing one thing as being ‘like’ the other. This can create contrast or offer more power to a concept. Usually similes are phrased with the words ‘like’ or ‘as’. Example: “He roared like a lion.”
Juxtaposition
When two things that are generally very opposite are placed next to each other, creating a stark contrast. Example: A brand new building standing next to an old, historical one.
Stating that something ‘is’ another thing to draw comparison or deeper understanding to a text. Often, figurative meanings can give the reader a greater appreciation of what is written. Some metaphors appear continually throughout a text and help to shape the narrative arc. These are known as extended metaphors. Example: “She had once been a great fortress, keeping secrets closely hidden.
Onomatopoeia
A word that sounds exactly like what it represents, allowing the reader to ‘hear’ the text. Example: Pop, snap, simmer, bubble, slop.
An oxymoron is a type of language feature where two words or concepts that contradict each other are used to create a complex idea, while maintaining some sense. Example: “The dinner was awfully good.”
Personification
Personification is a literary device that involves giving human qualities, attributes, or emotions to non-human things or inanimate objects. The purpose of personification is to make the object or thing more relatable or understandable to the reader, by imbuing it with human-like qualities. Personification is often used in poetry, prose, and other forms of creative writing to create a vivid and engaging image or scene. Example: In the sentence “The wind whispered through the trees,” the wind is given a human-like quality of being able to whisper. This makes it easier for the reader to imagine and empathise with the wind.
Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated in a text to create emphasis, create a specific rhythm, or reinforce a specific idea or theme. It is a common technique used in poetry and prose, and can be used in various ways to achieve different effects. Example: Consider the following passage from Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous “I Have a Dream” speech: “I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.'” In this passage, the phrase “I have a dream” is repeated several times to create a powerful and memorable rhythm. The repetition of this phrase emphasises King’s central message of hope and optimism and draws the listener’s attention to the idea of a better future. Additionally, the repetition of the phrase “We hold these truths to be self-evident” emphasises the importance of these words and their connection to the American Creed of freedom and equality.
Rhetorical Question
A question that has a very obvious answer, which the author does not expect to receive. Often rhetorical questions are used to make the audience think deeply about a topic. They can also provide humour and sarcasm. Example: “Did you know that thousands of plastic bags wash up on beaches each year?”
Sibilance sort of sounds like what it is! This technique is like alliteration, but when all ‘s’ sounds are used. It can add an air of mystery or danger to a character, or it can be soft and flowing. Example: When the snake talks in The Jungle King movie, she often uses several ‘s’ words in a row to highlight her hissing and sound more dangerous.
Sound Devices
This is a blanket term for techniques often used within a text to focus on the sounds words produce and how they relate to each other. This can be important for rhyming schemes and tempo. You’ll find many examples of this in poetry or songs. Example: Rhythm, rhyme, resonance, etc.
The strength or force of a word, with low modality words being passive while high modality words are forceful.
Characters giving speeches or rallying crowds would use high modality words, as they raise the intensity and strength of the language and scene.
Exclamation
This is one form of showing modality within a text. Exclamation marks generally suggest high modality, or shock, excitement and anger. This can express the tone of dialogue being written. Example: “This is the best day of my life!” elicits a response of elation.
Tone and Mood
Like the atmosphere, tone or mood is about creating certain feelings within a text. This time, it focusses more on the emotions the author has towards very specific subjects, rather than the scene as a whole. Example: The enemy? His sense of duty was no less that yours, I deem. You wonder what his name was, where he came from. And if he was really evil at heart. […] War will make corpses of us all.” (J. R. R. Tolkien, Lord of the Rings) This dialogue expresses a mood of distaste for war and that it only leads to death, reflecting Tolkien’s own views. Learn more about emotive language here!
Syntax is all about specific sentence structure and how the construction of words into a sentence creates meaning. This is a huge topic (in fact, people do entire degrees on it). In a simple sense, syntax affects the readability and tone of a certain text. Short sentences create urgency, while compound sentences can create a more passive flow. Example: “I could hear him behind me. Just one step off. I ran. I ran.”
Grammatical and Story Structures
This type of language feature is used when a story or narrative has two meanings that are presented. One is overt, or obvious. The other may be metaphoric and hidden. Often, this second meaning forms commentary around social or political aspects of the narrative. Example: Narnia is often viewed as an allegory for the Bible, with Aslan as a symbol of Jesus. This creates religious understanding that runs alongside the main plot.
Putting two sentences, people or situations that are entirely different next to each other or in immediate succession. This technique can increase tension, help audiences weigh up different scenarios or allow characters to balance one another out. Example: “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail.”
Archetypes are incredibly important in shaping stories. These characters or objects have recognisable tropes, often progressed across different texts by various authors. This technique can add an element of predictability or certainty to a piece, but it can also be subverted to create great plot twists. Example: Cady in Mean Girls and Mia in The Princess Diaries fit the archetype of a nerdy girl who is transformed.
Atmosphere, or mood, is vital in creating a compelling story. It refers to the feeling created by a scene, situation or text. It’s often driven by careful word choice. You might think of it a little like mise en scène in a movie, but in written form. Example: “It was a cruel day, the bright orange blaze ripped through the treetops as I stood and watched it ravage homes, helpless.”
Characterisation
Characters are first introduced in a certain light, then formed through the arc of the story, often by their own actions or the actions of those around them. You know the characterisation of a person is strong if you can imagine how they would react in a situation they are not already in. Example: Sybil in Downton Abbey is characterised as being forthright and rebellious. Through her relationships, her empathetic side is drawn out.
Overused expressions that create instant meaning. Sometimes cliches can be annoying, but when used effectively, they create humour and momentum. Example: “He ran like the wind.”
The time, place and social setting in which a text was written or set. Often, this determines the values and perspectives within a certain text. It’s important to understand three kinds of contexts within text. First, we have literary (what was being written and created at the time of writing), historical (what was going on in the border world when the text was written), and personal (who the author was and what they had experienced). On top of this, there’s also the internal context of where the text is set, which may be different from the context of when it was written. Example: Picasso’s painting ‘Guernica’ was informed by the context of pre-WW2 Europe, so Picasso used blue and red in the work to symbolise anti-war sentiment.
A flashback is a literary device in which the narrative of a story shifts to a previous time period or event. Flashbacks are often used to provide additional context or backstory for a character, setting, or plot, and can be used to reveal important information or character development. Example: Consider the following passage from F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby”: “He smiled understandingly-much more than understandingly. It was one of those rare smiles with a quality of eternal reassurance in it, that you may come across four or five times in life. It faced–or seemed to face–the whole external world for an instant, and then concentrated on you with an irresistible prejudice in your favor. It understood you just so far as you wanted to be understood, believed in you as you would like to believe in yourself, and assured you that it had precisely the impression of you that, at your best, you hoped to convey.” In this passage, the narrator describes a smile that he had seen in the past. The description of the smile is a flashback, as it shifts the narrative to a previous time period. The purpose of the flashback is to provide context for the relationship between the narrator and the person who smiled, and to suggest that the relationship was a significant and memorable one.
Linear and Non-linear Narrative
Narratives in this context are about how a text is structured to create meaning. Linear narratives follow the same time sequence as our usual days — always moving forward, in sequential order. A non-linear narrative jumps around in time to draw the audience’s attention to different elements. You will notice that it’s quite rare for a novel or movie to be purely linear, as some non-linear elements break up pacing. Example: The Age of Adeline is a film that follows a non-linear narrative.
Frame Narrative
Sometimes, texts present a ‘story within a story’, where the main narrative is being told by someone outside of the narrative itself. This can add suspense of an extra layer of context. Example: In Little Women, Jo tells the story through her book by the same name.
Intertextuality
When a text references another text, it’s known as intertextuality. This can be very overt, or it can be an allusion designed only for those who know both texts to pick up on it. Example: Ten Things I Hate About You is based on and makes references to Shakespeare’s The Taming Of The Shrew.
Foreshadowing
When a situation is hinted at before it actually occurs. This is usually done by drawing audience attention to a particular subject or item that drops hints. Example: In Juno, the main character by the same name starts displaying pregnancy symptoms before she actually takes a test.
The location that a narrative is placed in, like an internal context. This often affects the arc of the story. Example: Abandoned castles and stormy moors are classic settings used in Gothic texts, while teen dramas are typically set in high schools and suburban towns.
The structure of a text that comes from the text type, broader context and stylistic choices of the author. This may include the way language is structured or different sentence choices. Example: Divergent and The Hunger Games are both survival young adult novels, yet the authors’ choices and context of writing create differing themes.
An object or subject that symbolises a much larger element of the story. Hero characters often have a symbol attached as a way to enhance meaning and importance. Example: Superman is symbolised by his cape, Katniss by a Mockingjay, etc.
Sometimes elements are intentionally left out of a text by the author. This is called omission, and it leaves a level of ambiguity for audiences to ‘fill in the blank’. Sometimes, an ending scenario can be implied but this is not always the case. Example: At the end of the book, The Great Gatsby , the audience isn’t told explicitly what happens to each character, but they are given enough information to infer an ending.
Like so many language features, parallels create a contrast between two characters or plot points, allowing links to be formed between them. This is often seen if two plots run next to each other, or two characters with similar features but differing stories are introduced. Example: In the film, Fantastic Mr Fox, Ash follows his father and lives a younger version of his life. However, he makes different decisions that reveal Mr Fox’s mistakes to himself.
Pathetic Fallacy
When you give a non-human object feelings or senses, you are using pathetic fallacy. This is most commonly associated with weather. Example: “The wind was angry as it ran through the trees.”
Point of View
Point of view refers to the perspective from which a story or narrative is told. It is the way that the author chooses to present the events of a story to the reader. There are three main points of view: first-person, second-person, and third-person. First-person point of view is when the story is told from the perspective of a character within the story, using “I” or “we”. For example, in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby,” the narrator is Nick Carraway, who tells the story from his own perspective. He says, “In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I’ve been turning over in my mind ever since.” The reader experiences the events of the story through Nick’s eyes, and only knows what he knows. Second-person point of view is less common in literature and is when the story is told directly to the reader, using “you.” An example of second-person point of view is Jay McInerney’s “Bright Lights, Big City,” in which the author speaks directly to the protagonist, saying, “You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning.” Third-person point of view is when the story is told by a narrator outside of the story, using “he,” “she,” or “they.” The narrator may be omniscient (knowing everything about the characters and their thoughts), limited omniscient (knowing some, but not all, of the characters’ thoughts and feelings), or objective (reporting only the facts). An example of third-person point of view is Harper Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird,” in which the story is told by an omniscient narrator who is not a character in the story. The narrator says, “Maycomb was a tired old town, even in 1932 when I first knew it.” The choice of point of view can greatly impact the way a story is received by the reader, and different points of view can create different effects and meanings in a story.
In literature, a theme is a central idea or message that the author wants to convey to the reader. Themes can be expressed in various ways, such as through the characters, setting, plot, or symbolism of a work. A theme is often universal and can be applied to the human experience in general, rather than specific to a particular story or character. Example: In William Shakespeare’s play “Romeo and Juliet”, one of the main themes is the destructive power of hatred and the consequences of feuding. Throughout the play, the hatred between the Capulet and Montague families drives the actions of the characters, ultimately leading to the tragic deaths of Romeo and Juliet. The theme of hatred and feuding is expressed through the actions of the characters, such as the street brawls, the harsh words exchanged between the families, and the way the characters treat each other. The theme is also reflected in the setting, which is a city torn apart by conflict and violence.
Dramatic Irony
When a story is structured to provide the audience with an ‘inside scoop’ that characters do not know about. This is often shown through different phrasing to create tension. Example: In Hamlet , revolving scenes allow the audience to see who is plotting to kill, without it being given away to characters. This creates suspense and betrayals of trust.
There you have it!
Now you have a complete guide to English language features, it’s time to put them into practice! Refer back to this list as you keep progressing in your studies.
On the hunt for other English resources, aside from language features?
Check out some of our other articles and guides below:
Did you know that the English Syllabus has recently changed for Years 7-10 in NSW? Check out the major details here!
- How to Write a TEEL Paragraph for Your English Essay
- The Ultimate Guide to Crafting your English Feature Article
- How to Elevate Your Essays in English Using the Thesis + 3 Technique
- How to Make Your Essay Stand Out in HSC English with a Strong Thesis Statement
- The Complete Guide to Writing an Analytical Essay for QCE English
- QCE English: The Ultimate Guide to Achieving an A
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Recount in Primary School
- How to Write an Extended Response in High School
- Band 6 Guide to Year 11 Advanced English Module B: Critical Study of Literature
- Your Kickass Guide to Analysing Visual Texts for HSC English
Are you looking for some extra help with studying English and understanding language features?
We have an incredible team of english tutors and mentors.
We can help you master your analysis of your English text by taking you through its summary, key characters, language features and themes. We’ll also help you ace your upcoming English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational English tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Lucinda Garbutt-Young hopes to one day be writing for a big-shot newspaper… or maybe just for a friendly magazine in the arts sector. Right now, she is enjoying studying a Bachelor of Public Communication (Public Relations and Journalism) at UTS while she writes on the side. She also loves making coffees for people in her job as a barista, and loves nothing more than a sun shower.
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
The ultimate hsc english literary techniques cheat sheet, the complete hsc english visual techniques cheat sheet, 3 hacks to read your prescribed english text quickly and effectively, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in
Essay Ai 17+
Creative essay writer ai, syed abdullah arif, designed for ipad, screenshots, description.
Unlock the power of AI to craft compelling essays effortlessly with EssayAI! Whether you're a student, writer, or just someone in need of a well-written essay, EssayAI is your go-to tool for generating high-quality essays on any topic in seconds. Key Features: Instant Essay Generation: Simply enter a topic, and let our advanced AI model create a detailed and coherent essay for you. Easy to Use: Designed with simplicity in mind, EssayAI offers a clean and minimalistic interface that makes essay generation quick and straightforward. Versatile Output: Generate essays on a wide range of topics, from technology and science to arts and humanities. Tailor the output to your needs. Powered by OpenAI: Our app leverages the power of GPT-3.5-turbo, one of the most advanced language models, ensuring that the essays are well-written and relevant. Time-Saving: Skip the writer’s block and get started on your writing tasks instantly. Perfect for brainstorming, study aids, or simply getting inspired. Safe and Secure: Your data is private and secure with us. We do not store any of your personal information. Why Choose EssayAI? Efficient: Save time and effort by letting AI handle the heavy lifting. Inspiration on Demand: Get creative ideas and structured content in moments. Accessible: No need for complex tools or software—just your phone and a topic. How It Works: Enter Your Topic: Type in the subject or theme you want the essay to cover. Generate: Tap the "Generate Essay" button and let the AI do the work. Read & Use: Instantly view the generated essay, perfect for your needs. Whether you need help starting an essay, want to explore new ideas, or need a full essay on short notice, EssayAI is here to help. Download now and experience the future of writing!
App Privacy
The developer, Syed Abdullah Arif , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Not Collected
The developer does not collect any data from this app.
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
Quantum ChatAi
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an expository essay
How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples
Published on July 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
“Expository” means “intended to explain or describe something.” An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a particular topic, process, or set of ideas. It doesn’t set out to prove a point, just to give a balanced view of its subject matter.
Expository essays are usually short assignments intended to test your composition skills or your understanding of a subject. They tend to involve less research and original arguments than argumentative essays .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should you write an expository essay, how to approach an expository essay, introducing your essay, writing the body paragraphs, concluding your essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
In school and university, you might have to write expository essays as in-class exercises, exam questions, or coursework assignments.
Sometimes it won’t be directly stated that the assignment is an expository essay, but there are certain keywords that imply expository writing is required. Consider the prompts below.
The word “explain” here is the clue: An essay responding to this prompt should provide an explanation of this historical process—not necessarily an original argument about it.
Sometimes you’ll be asked to define a particular term or concept. This means more than just copying down the dictionary definition; you’ll be expected to explore different ideas surrounding the term, as this prompt emphasizes.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn’t about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person (“I” or “you”).
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It’s worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline .
A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Like all essays, an expository essay begins with an introduction . This serves to hook the reader’s interest, briefly introduce your topic, and provide a thesis statement summarizing what you’re going to say about it.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
The body of your essay is where you cover your topic in depth. It often consists of three paragraphs, but may be more for a longer essay. This is where you present the details of the process, idea or topic you’re explaining.
It’s important to make sure each paragraph covers its own clearly defined topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Different topics (all related to the overall subject matter of the essay) should be presented in a logical order, with clear transitions between paragraphs.
Hover over different parts of the example paragraph below to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion of an expository essay serves to summarize the topic under discussion. It should not present any new information or evidence, but should instead focus on reinforcing the points made so far. Essentially, your conclusion is there to round off the essay in an engaging way.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a conclusion works.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 19, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/expository-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

COMMENTS
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Here are some of the many definitions of an essay: According to Frederick Crews, professor of English at the University of California at Berkeley, an essay is "a fairly brief piece of nonfiction that tries to make a point in an interesting way.". A famous essayist, Aldous Huxley, notes that "the essay is a literary device for saying ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
Parts of an essay. An impactful, well-structured essay comes down to three important parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. 1. The introduction sets the stage for your essay and is typically a paragraph long. It should grab the reader's attention and give them a clear idea of what your essay will be about.
3 Drafting: Write a rough draft of your essay. It helps to include any data and direct quotes as early as possible, especially with argumentative essays that often cite outside sources. 4 Revising: Polish your rough draft, optimize word choice, and restructure your arguments if necessary. Make sure your language is clear and appropriate for the ...
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
4. Types of Features. From profiles to travel stories, there is feature style for everyone. "If my doctor told me I had only six minutes to live, I wouldn't brood. I'd type a little faster.". Isaac Asimov. Truth be told, no one writes a plain, old feature article, since "feature" is an umbrella term that encompasses a broad range of ...
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence.
Argumentative essay from the word "Argument", according to Virtue's English Dictionary (Encyclopaedia Edition) defines argument as a subject of a discourse or writing; a reason offered for or against something; a debate, controversy, discussion and a process of reasoning.Therefore argumentative essay can be defined as a debatable writing which upon choosing a stance, attempts to persuade ...
A good essay features a clear and concise thesis, coherent structure, strong argumentation, and substantial evidence. It should have an engaging introduction, well-organized body paragraphs, and a ...
Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks. Published on February 9, 2015 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes. This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction, focused paragraphs, clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion.
The six basic parts of an essay are: Outline (optional) Thesis statement; Introduction (contains Thesis) Body (methods, quotes) Conclusion; Bibliography (citations and sources)
What is an example of informative writing? There are four types of informative essay. One example would be a definition essay about gothic architecture. Another is a compare and contrast essay ...
An essay (ES-ey) is a nonfiction composition that explores a concept, argument, idea, or opinion from the personal perspective of the writer. Essays are usually a few pages, but they can also be book-length. Unlike other forms of nonfiction writing, like textbooks or biographies, an essay doesn't inherently require research. Literary essayists are conveying ideas in a more informal way.
4 Create an outline. All it takes to understand the importance of an outline is listening to someone who struggled to tell a personal story. Often, the story will seem to have no real point. The switchbacks where the teller says "But wait, I have to tell you about this part, first!" are maddening and disruptive.
8. Universality. Although subjective, the personal essay is a format that lets the writer share personal insights and reflections that touch on more universal themes about life. These larger themes make the piece more memorable for the reader and allow the reader to compare their own insights and experiences with those of the writer. 9. Brevity.
Whatever it is, understanding language features is a great skill to have. If you want to know more, you're totally in the right place — keep reading for a comprehensive list! Our HSC English tutors can help you identify the perfect language features for your essay, so get in touch if you're looking for guidance! Persuasive Devices
An example of a short descriptive essay, written in response to the prompt "Describe a place you love to spend time in," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how a descriptive essay works. On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green ...
such features as style and tone (e.g. familiar or formal); the presence or absence of specialized language and knowledge; the amount of time spent orienting a gen-eral, non-expert reader; the use of scholarly conven-tions of form and style. Your stance should be estab-lished within the first few paragraphs of your essay, and
Your AI Writing Partner for EveryStage of Essay Writing. Brainstorm and outline with generative AI prompts. Get real-time, strategic writing feedback on tone, clarity, conciseness, and more. Check for plagiarism and generate citations. Review, rewrite, and revise in a few clicks, not a few hours.
Key Features: Instant Essay Generation: Simply enter a topic, and let our advanced AI model create a detailed and coherent essay for you. Easy to Use: Designed with simplicity in mind, EssayAI offers a clean and minimalistic interface that makes essay generation quick and straightforward.
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
We are adding AI detection to our existing academic integrity features, such as the ability to cite generative AI use, to further empower our users. We want to encourage them to make informed decisions about the content they create and incorporate into their writing, cite sources appropriately, and use AI responsibly.