- - worldnews
- - todayilearned
- - nottheonion
- - explainlikeimfive
- - mildlyinteresting
- - OldSchoolCool
- - TwoXChromosomes
- - LifeProTips
- - dataisbeautiful
- - Showerthoughts
- - askscience
- - Futurology
- - UpliftingNews
- - InternetIsBeautiful
- - GetMotivated
- - announcements
- - WritingPrompts
- - philosophy
- - Documentaries
- - EarthPorn
- - photoshopbattles
- - listentothis
use the following search parameters to narrow your results:
e.g. subreddit:aww site:imgur.com dog
see the search faq for details.
advanced search: by author, subreddit...
11 users here now
For sharing of academic works and discussion of issues and events relating to academia and the related political, economical, and social structures.
Commercial posts and endorsements of unethical services such as paper mills will be removed.
- message the mods

Welcome to Reddit,
the front page of the internet.
and join one of thousands of communities.
Is a PhD worth it? ( self.academia )
submitted 1 year ago by [deleted]
What are your thoughts and perspectives, I am considering to pursue a PhD in computational biology/neurogenetics but not sure it it worth it in long run (also for jobs after finishing PhD program)
- 14 comments
Want to add to the discussion?
Post a comment!
[–] DangerousBill 10 points 11 points 12 points 1 year ago * (2 children)
If you stop at a bachelor's or master's, your eventual boss might have a PhD. The advanced degree isn't for everyone, but it opens up depth and variety in your career options.
My PhD took me into six different specialties at five different employers ranging over government, industry, and academia.
A friend of mine worked on a single enzyme for his entire career, ending up as president of his university. Anything is possible.
[–] [deleted] 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (1 child)
True, thanks for the insight. Your career path is really amazing, in what field was your PhD?
[–] DangerousBill 1 point 2 points 3 points 1 year ago (0 children)
Biochemistry, but post docs in virus genetics and enzymology.
[–] [deleted] 4 points 5 points 6 points 1 year ago (2 children)
40-60% of graduate students don’t finish their PhDs. The only reason to do a PhD is if you are sufficiently passionate about a field that you want to devote 4-5 years to mastery of a highly specific component of it. If you don’t have that level of passion, you won’t finish. As for career prospects: it’s a crapshoot.
[–] _XtalDave_ -1 points 0 points 1 point 1 year ago (1 child)
Woah, where are you where the drop out rate is so high? Here in the UK the combination of failure and drop out rate is ~20%
[–] [deleted] 1 point 2 points 3 points 1 year ago (0 children)
[–] DeepSeaDarkness 5 points 6 points 7 points 1 year ago (1 child)
Do you want to do research as a career?
[–] [deleted] 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (0 children)
Yes, but doing research is also possible in companies for example so that’s why it seems difficult to decide
[–] FOXO1_IGMBC 1 point 2 points 3 points 1 year ago (0 children)
If you have to ask, you already know the answer. Once you start, you will continue to ask that question every year, and it will get harder and harder to justify the answer. Many will talk about the benefits after but you need to remember that you have to finish first, and if your asking this question as a graduate student the answer for just yourself is inevitably no.
[–] CptNemo55 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (2 children)
Well, it depends, what is the reason you want to get a PhD?
I want to get it as it allows for my research to have more societal impact, and the focus lies more on the research than just profit and money which can be the case in companies. And I enjoy going to conferences and am passionate about the topic
[–] CptNemo55 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (0 children)
Ok, all good reasons. What do you plan to do for a job after you have PhD?
[–] sbby31 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (0 children)
I think that, unfortunately, it is a personal decision. Your career aspects in that field are probably decent with or without a PhD. You can definitely get yourself into a role that supports research (research that greatly benefits society, if you are lucky) with a bachelors/masters degree, and many people are very happy in that kind of role.
I assume you are relatively young (20s-ish). Doing a PhD will rob you of the experience of having money pretty early in life, and that is a dealbreaker for some (no judgement, there is no right or wrong answer). The job market for PhDs is no longer a "sure thing" that guarantees you wealth/tenure later in life.
I got my PhD in a roughly comparable field- I did it mostly because I wanted the option to lead research efforts or teach afterwards. I do not think I would be happy in a bachelors level role working under PhDs who lead the research efforts, or in an industry role where I have very little autonomy, and I stand by that decision. I decided that was important to me and endured 5 years of BS getting another slip of paper. I am not far along enough in my career to know if a PhD was the right call, but so far it has worked out well for me and I am glad I did it.
[–] marcopoloman 0 points 1 point 2 points 1 year ago (0 children)
I did my PhD a few years ago. It did get me a much higher paying teaching position.
- advertising
- Reddit help center
- reddiquette
- mod guidelines
- apps & tools
- Reddit for iPhone
- Reddit for Android
- mobile website
- reddit premium
Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our User Agreement and Privacy Policy . © 2024 reddit inc. All rights reserved.
REDDIT and the ALIEN Logo are registered trademarks of reddit inc.
π Rendered by PID 60 on reddit-service-r2-loggedout-677b7fc8bf-52w6x at 2024-07-23 09:02:10.271193+00:00 running 570c7a4 country code: RU.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Applying for PhD with a 3.2 GPA - Do I even stand a chance? [duplicate]
I just read an incredibly disheartening post on reddit about Grad School admissions in the Biological sciences. The post basically makes it sound like I have no chance of getting into a good PhD program.
I graduated from UC Berkeley with a Degree in Biochemistry in 2012. While in school I worked as an undergraduate researcher for 3.5 years. Post graduation I've been working in Biotech Research for close to 3 years now.
I graduated Berkeley with somewhere in the range of a 3.2-3.3 GPA. The average GPA for my major at Cal is a 2.8 . Does the rigor of my undergraduate institution matter? Berkeley's grade deflation is pretty notorious but will that matter?
From what I read in the post it sounds like most schools won't even look at my application. I'm starting to wonder if its worth it for me to apply at all.
I've attached a link to the thread on reddit. Your honest opinions would be much appreciated.
https://www.reddit.com/r/GradSchool/comments/25gj24/a_somewhat_notgentle_guide_to_getting_into_grad/
- graduate-admissions
- I feel like this post you're flagging doesn't answer my question about how or if my undergraduate institution will play a role in my prospects. – Cole2790 Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 16:41
- Depends on what program you're applying for. If you're going for a program at Harvard, then you're probably competing against loads of other candidates from Stanford, MIT, etc. who have 4.0s. If you're applying to a lower tier university, then you might have a better chance. – Michael Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 16:55
- I see what you mean. I have a ton of research experience and I have industry experience so I think I'm a unique candidate who has proven that my GPA is not reflective of my ability to succeed in research. I just don't know if my application will get weeded out based off of GPA before anyone gets a chance to see that. – Cole2790 Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 18:14
- 1 From the accepted answer to henning's linked question: When admissions committees consider the GPA they are considering a number of factors including the grades, the strength of the school and major (emph mine). – Kimball Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 18:54
- 1 I honestly suspect the only true answer to your question is "no one can say for sure". If you apply and get rejected from everywhere, well then there you go, you've got your answer and you can continue on to Plan B. And if you get in, the probability is then 1 because you got in and it doesn't matter what your a priori odds were. I don't think anyone can say your chance is 0, so then effectively all that is left is: is it worth it to you to try to apply and see what happens? Apply broadly, to top R1 programs and those not so top (but that you'd still be honored to attend), and who knows! – BrianH Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 22:05
It depends. Different schools, programs, and faculty have different ways of looking at applicants. Based on my limited experience, a 3.30 GPA from an R1 will likely count for more than a 3.30 from a less reputable institution. However, if you are applying to top-tier programs, you may be competing with students who have higher GPAs, also from R1s.
The reddit link that you posted is from one single professor at one institution. Without knowing the specific institution, program, and/or faculty member you are applying to, it is impossible to say what will be weighed, as there are not standardized admission formulas.
Some faculty are looking for students who match their research agenda and have research experience (i.e., they are proficient enough at research so they won't suck the faculty member's time). Others may prioritize GPA, and some might place more emphasis on quantitative GRE scores.
The link that you posted and the link from @henning both have good advice for tailoring applications to fit the department, institution, or faculty member.
If you are uncertain about applying, it might not hurt to contact a faculty member you are interested in working with to ask if they would consider your application. Even better, you could find a common contact/reference (maybe your undergrad advisor/professor/? knows someone in the Ph.D. department you want to apply to?) who can introduce you.
You might also want to check out college/graduate school/institution GPA policies to see what the minimum GPA for doctoral study is at your prospective institutions. If you have to maintain a 3.0 as a doc student, some faculty may question your ability to succeed at a more rigorous level.
To summarize: Ask the faculty member you are interested in working with what they consider when selecting doctoral applicants.
- Thanks SB for you well thought out answer. Do you think I could get into an R1 institution at all? I know schools like MIT, Berkeley, and Harvard are a long shot for me but I would be equally happy at places like UW Madison, or University of Washington Seattle. Basically I know I want to go to graduate school the only thing that holds me back is fear that schools will look at me as a mediocre candidate due to my GPA and chuck my app in trash. – Cole2790 Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 18:02
- No chance at MIT, berkeley, harvard, etc. – Rüdiger Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 19:02
- 1 @Cole2790 I was a graduate student in a biological science at UW Madison. Your GPA would definitely be on the low side in my program and might bar you from consideration as an at-large candidate, though it isn't completely disqualifying. Note that at schools like UW, some specific programs are top 5 or top 3 and rank above those more famous names. A better path might be to take a research job in an academic lab (this will mean a big pay cut), letting your PI know that you are interested in grad school in the future. – Bryan Krause ♦ Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 19:21
- @Cole2790 I can't speak for Biology in particular, but I know people with lower GPAs who have been admitted to R1 PhD programs. – SB Ph.D. Commented Apr 7, 2017 at 23:14
- My husband had a shitty GPA and great letters. He applied to like 10 places for chemical/bio science/engineering and only got into the worst-ranked one and the best-ranked one. I think the explanation is that if you are an unusual candidate, you have to apply to a bunch of places and hope that at one you are the right kind of unusual! – Dawn Commented Apr 8, 2017 at 2:53
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged phd graduate-admissions grades .
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Tuesday, July 23rd 2024, 8 PM - Midnight EST (3 AM - 7 AM...
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- Spell slots of a Sorlock multiclass
- Three kilometers (~2 miles high) tsunamis go around the Earth - what kinds of ruins are left?
- Would auto-update policies have contained the Crowdstrike outage?
- Guess-the-number game in Python
- How do I distinguish between "e" the natural log base and a variable conventionally referred to as "e"?
- Vertical alignment of equations in column environment
- Does the "anti-dynasty" provision of the Philippines have parallels in other countries?
- Sobolev spaces are smooth? Their dual is strictly convex?
- Bosch 625Wh: How to Charge Spare Battery At Home?
- Why is 不 instead of 没 used to negate an action in the past in 过去三天为什么你不回我的电话?
- How to calculate FX Forward Rate to fit bloomberg
- Assign condition to variable
- Is a stiff chain after hot wax application a sign of a correct wax application?
- How to address past academic misconduct as a new faculty member?
- Prince Rupert's Drop Armor: How Expensive?
- ELI5: If SSL encrypts traffic, why does it expire?
- Event viewer showing 'logon' events, even when I'm currently using that PC
- Why do Bell states have all real coefficients?
- Density operator commutator in master equation
- FDA regulation of end user non-medical software
- Which word can be used to describe either the beat or the subdivision?
- Particles and fields
- Why is the future perfect used in "This latest setback will have done nothing to quell the growing doubts about the future of the club."?
- Does Event Viewer have any sensitive information like password, or such info?
Advertisement
Supported by
27 Facts About J.D. Vance, Trump’s Pick for V.P.
Mr. Vance spilled scores of details about his life in his coming-of-age memoir. We’ve collected the highlights.
- Share full article

By Shawn McCreesh
Follow the latest news from the Republican National Convention .
J.D. Vance, Donald J. Trump’s choice for vice president, has not lived an unexamined life. Here are 27 things to know about him, drawn from his best-selling 2016 memoir, “Hillbilly Elegy,” and the many other things he has said or written since.
1. His name was not always James David Vance. At birth, it was James Donald Bowman. It changed to James David Hamel after his mother remarried, and then it changed one more time.
2. He longed for a role model. His father left when he was 6. “It was the saddest I had ever felt,” he wrote in his memoir. “Of all the things I hated about my childhood,” he wrote, “nothing compared to the revolving door of father figures.”
3. He had a fraught relationship with his mother, who was married five times. One of the most harrowing scenes in the book occurs when he’s a young child, in a car with his mother, who often lapsed into cycles of abuse. She sped up to “what seemed like a hundred miles per hour and told me that she was going to crash the car and kill us both,” he writes. After she slowed down, so she could reach in the back of the car to beat him, he leaped out of the car and escaped to the house of a neighbor, who called the police.
4. He was raised by blue-dog Democrats. He spent much of his childhood with his grandfather and grandmother — papaw and mamaw, in his hillbilly patois. He described his mamaw’s “affinity for Bill Clinton” and wrote about how his papaw swayed from the Democrats only once, to vote for Ronald Reagan. “The people who raised me,” he said in one interview, “were classic blue-dog Democrats, union Democrats, right? They loved their country, they were socially conservative.”
5. As a teenager, he loved Black Sabbath, Eric Clapton and Led Zeppelin. But then his biological father, who was deeply religious, re-entered his life. “When we first reconnected, he made it clear that he didn’t care for my taste in classic rock, especially Led Zeppelin,” he wrote. “He just advised that I listened to Christian rock instead.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .


The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
Is a PhD Worth It? Should I Do a PhD?
It’s been almost a year since I was officially awarded my PhD. How time flies! I figure now is a good time to reflect on the PhD and answer some of life’s big questions. Is a PhD worth it? Does having a PhD help your future job prospects? Am I pleased that I did a PhD and would I recommend that you do a PhD?
In this post I’ll walk through some of the main points to consider. We’ll touch on some pros and cons, explore the influence it could have on your career and finally attempt to answer the ultimate question. Is a PhD worth it?
Before we get into the details, if you’re considering applying for a PhD you may also want to check out a few other posts I’ve written:
- How Hard is a PhD?
- How Much Work is a PhD?
- How Much Does a PhD Student Earn? Comparing a PhD Stipend to Grad Salaries
- Characteristics of a Researcher
Are you seated comfortably? Great! Then we’ll begin.
The Pros and Cons of PhDs
When I have a difficult decision to make I like to write a pros and cons list. So let’s start by breaking down the good and bad sides of getting a PhD. Although I’ve tried to stay objective, do take into account that I have completed a PhD and enjoyed my project a lot!
These lists certainly aren’t exhaustive, so be sure to let me know if you can think of any other points to add!
The Good Parts: Reasons to Do a PhD
Life as a phd student.
- You get to work on something really interesting . Very few people outside of academia get to dive so deep into topics they enjoy. Plus, by conducting cutting edge research you’re contributing knowledge to a field.
- It can be fun! For example: solving challenges, building things, setting up collaborations and going to conferences.
- Being a PhD student can be a fantastic opportunity for personal growth : from giving presentations and thinking critically through to making the most of being a student such as trying new sports.
- You are getting paid to be a student : I mean come on, that’s pretty good! Flexible hours, socialising and getting paid to learn can all be perks. Do make sure you consciously make the most of it!
Life As A PhD Graduate
- The main one: Having a PhD may open doors . For certain fields, such as academia itself, a PhD may be a necesity. Whilst in others having a PhD can help demonstrate expertise or competency, opening doors or helping you to leapfrog to higher positions. Your mileage may vary!
- You survived a PhD: this accomplishment can be a big confidence booster .
- You’ve got a doctorate and you can use the title Dr. Certainly not enough justification on it’s own to do a PhD, but for some people it helps!
The Bad Parts: Potential Reasons Not to Do a PhD
- It can be tough to complete a PhD! There are lots of challenges . Unless you’re careful and take good care of yourself it can take a mental and physical toll on your well being.
- A PhD can be lonely ( though doesn’t have to be ), and PhD supervisors aren’t always as supportive as you’d like them to be.
- Additionally, in particular now during the pandemic, you might not be able to get as much support from your supervisor, see your peers or even access the equipment and technical support as easily as in normal times.
- You might find that having a PhD may not bring the riches you were expecting . Have a certain career you’re looking to pursue? Consider trying to find out whether or not having a PhD actually helps.
- Getting a job with a PhD can still be tough . Let’s say you want to go for a career where having a PhD is required, even once you’ve got a PhD it might not be easy to find employment. Case in point are academic positions.
- Even though you’ve put in the work you may want to use your Dr title sparingly , it certain industries a PhD may be seen as pretencious. Also, use your title sparingly to avoid getting mistaken for a medic (unless of course you’re one of them too!)
Is a PhD Good For Your Career?
If you’re wondering “Should I do a PhD?”, part of your motivation for considering gaining a PhD may be your career prospects. Therefore I want to now dive deeper into whether or not a PhD could help with future employment.
It is difficult to give definitive answers because whether or not a PhD helps will ultimately depend a lot upon what kind of career you’re hoping to have. Anyway, let’s discuss a few specific questions.
Does a PhD Help You Get a Job?
For certain industries having a PhD may either be a requirement or a strong positive.
Some professions may require a PhD such as academia or research in certain industries like pharma. Others will see your qualification as evidence that you’re competent which could give you an edge. Of course if you’re aiming to go into a career using similar skills to your PhD then you’ll stand a better chance of your future employer appreciating the PhD.
In contrast, for other roles your PhD may not be much help in securing a job. Having a PhD may not be valued and instead your time may be better spent getting experience in a job. Even so, a PhD likely won’t have been completely useless.
When I worked at an engineering consultancy the recruitment team suggested that four years of a PhD would be considered comparable to two or three years of experience in industry. In those instances, the employer may actively prefer candidates who spent those years gaining experience on the job but still appreciates the value of a PhD.
Conclusion: Sometimes a PhD will help you get a job, othertimes it wont. Not all employers may appreciate your PhD though few employers will actively mark you down for having a PhD.
Does a PhD Increase Salary? Will it Allow You to Start at a Higher Level?
This question is very much relates to the previous one so my answer will sound slightly similar.
It’ll ultimately depend upon whether or not the industry and company value the skills or knowledge you’ve gained throughout your PhD.
I want to say from the start that none of us PhD-holders should feel entitled and above certain types of position in every profession just for having a PhD. Not all fields will appreciate your PhD and it may offer no advantage. It is better to realise this now.
Some professions will appreciate that with a PhD you’ll have developed a certain detail-orientated mindset, specialised knowledge or skills that are worth paying more for. Even if the position doesn’t really demand a PhD, it is sometimes the case that having someone with a PhD in that position is a useful badge for the company to wave at customers or competitors. Under these circumstances PhD-holders may by default be offered slightly higher starting positions than other new-starters will lower degree qualifications.
To play devil’s advocate, you could be spending those 3-4 (or more) years progressing in the job. Let’s look at a few concrete examples.
PhD Graduate Salaries in Academia
Let’s cut to the chase: currently as a postdoc at a decent university my salary is £33,787, which isn’t great. With a PhD there is potential to possibly climb the academic ladder but it’s certainly not easy. If I were still working in London I’d be earning more, and if I were speficially still working at Imperial in London I’d be earning a lot more. Browse Imperial’s pay scales here . But how much is it possible to earn with a PhD compared to not having one?
For comparison to research staff with and without PhDs:
As of 2023 research assistants (so a member of staff conducting research but with no PhD) at Imperial earn £38,194 – £ 4 1,388 and postdoctoral research associates earn £43,093 – £50,834 . Not only do you earn £5000 or more a year higher with a PhD, but without a PhD you simply can’t progress up the ladder to research fellow or tenure track positions.
Therefore in academia it pays to have a PhD, not just for the extra cash but for the potential to progress your career.
PhD Graduate Salaries in Industry
For jobs in industry, it is difficult to give a definitive answer since the variety of jobs are so wide ranging.
Certain industries will greatly reward PhD-holders with higher salaries than those without PhDs. Again it ultimately depends on how valuable your skills are. I’ve known PhD holders to do very well going into banking, science consultancy, technology and such forth.
You might not necessarily earn more money with a PhD in industry, but it might open more doors to switch industries or try new things. This doesn’t necessarily mean gaining a higher salary: I have known PhD-holders to go for graduate schemes which are open to grads with bachelors or masters degrees. Perhaps there is an argument that you’re more employable and therefore it encourages you to make more risky career moves which someone with fewer qualifications may make?
You can of course also use your PhD skills to start your own company. Compensation at a start-up varies wildly, especially if you’re a founder so it is hardly worth discussing. One example I can’t resist though is Magic Pony. The company was co-founded by a Imperial PhD graduate who applied expertise from his PhD to another domain. He sold the company two years later to Twitter for $150 million . Yes, including this example is of course taking cherry-picking to the extreme! The point stands though that you can potentially pick up some very lucrative skills during your PhD.
Conclusion: Like the previous question, not all industries will reward your PhD. Depending on what you want to go and do afterward your PhD, it isn’t always worth doing a PhD just for career progression. For professions that don’t specifically value a PhD (which is likely the majority of them!) don’t expect for your PhD to necessarily be your ticket to a higher position in the organisation.
Is a PhD Worth it?
What is “it”.
When we’re asking the question “is a PhD worth it?” it is a good idea to touch on what “it” actually is. What exactly are PhD students sacrificing in gaining a PhD? Here is my take:
- Time . 3-5 (more more) years of your life. For more see my post: how long a PhD takes .
- Energy. There is no doubt that a PhD can be mentally and physically draining, often more so than typical grad jobs. Not many of us PhD students often stick to normal office hours, though I do encourage you to !
- Money. Thankfully most of us, at least in STEM, are on funded PhD projects with tax free stipends. You can also earn some money on the side quite easily and without paying tax for a while. Even so, over the course of a PhD you are realistically likely to earn more in a grad job. For more details on how PhD stipends compare to grad salaries read my full analysis .
- Potential loss of opportunities . If you weren’t doing a PhD, what else could you be doing? As a side note, if you do go on to do a PhD, do make sure you to take advantage of the opportunities as a PhD student !
When a PhD Could Be Worth It
1. passion for a topic and sheer joy of research.
The contribution you make to progressing research is valuable in it’s own right. If you enjoy research, can get funding and are passionate about a subject by all means go and do the PhD and I doubt you’ll regret it.
2. Learning skills
If there is something really specific you want to spend three year or more years learning then a PhD can be a great opportunity. They’re also great for building soft skills such as independence, team work, presenting and making decisions.
Do be aware though that PhD projects can and do evolve so you can’t always guarantee your project will pan out as expected.
If there is the option to go into a career without a PhD I’d bet that in a lot of cases you’d learn more, faster, and with better support in industry. The speed of academic research can be painstakingly slow. There are upsides to learning skills in academia though, such as freedom and the low amount of responsibility for things outside your project and of course if you’re interested in something which hasn’t yet reached industry.
3. Helping with your career
See the section further up the page, this only applies for certain jobs. It is rare though that having a PhD would actively look bad on your CV.
When a PhD May Not Be Worth It
1. just because you can’t find another job.
Doing a PhD simply because you can’t find a job isn’t a great reason for starting one. In these circumstances having a PhD likely isn’t worth it.
2. Badge collecting
Tempted by a PhD simply to have a doctorate, or to out-do someone? Not only may you struggle with motivation but you likely won’t find the experience particularly satisfying. Sure, it can be the icing on the cake but I reckon you could lose interest pretty quickly if it is your only motivation for gaining a PhD.
Do I Feel That My Own PhD Was Worth It?
When I finished my undergrad I’d been tempted by a PhD but I wasn’t exactly sure about it. Largely I was worried about picking the wrong topic.
I spent a bit of time apprehensively applying, never being sure how I’d find the experience. Now that I’ve finished it I’m very pleased to have got my PhD!
Here are my main reasons:
- I enjoyed the research and felt relatively well fulfilled with the outcomes
- Having the opportunity to learn lots of some new things was great, and felt like time well spent
- I made new friends and generally enjoyed my time at the university
- Since I’d been interested in research and doing a PhD for so long, I feel like if I’d not done it I’d be left wondering about it and potentially end up regretting it.
In Summary, Is a PhD Worth It?
I’ve interviewed many PhD students and graduates and asked each one of them whether the PhD was worth it . The resounding answer is yes! Now of course there is some selection bias but even an interviewee who had dropped out of their PhD said that the experience had been valueable.

If you’ve got this far in the post and are still a little on the fence about whether or not a PhD is worth it, my advice is to look at the bigger picture. In comparison to your lifetime as a whole, a PhD doesn’t really take long:

People graduating now likely won’t retire until they’re in their 70s: what is 3-4 years out of a half century long career?
So Should I Do a PhD?
Whether a PhD is worth all the time and energy ultimately comes down to why you’re doing one in the first place.
There are many great reasons for wanting to do a PhD, from the sheer enjoyment of a subject through to wanting to open up new career opportunities.
Nevertheless, it is worth pointing out that practically every PhD student encounters difficult periods. Unsurprisingly, completing a PhD can be challenging and mentally draining. You’ll want to ensure you’re able to remind yourself of all the reasons why it is worth it to provide motivation to continue.
If you’re interested, here were my own reasons for wanting a PhD.
Why I decided to pursue a PhD
Saying that, if you’re interested in doing a PhD I think you should at least apply. I can’t think of any circumstances where having a PhD would be a hindrance.
It can take a while to find the right project (with funding ) so I suggest submitting some applications and see how they go. If you get interesting job offers in the meantime you don’t need to commit to the PhD. Even if you start the PhD and find you don’t enjoy it, there is no shame in leaving and you can often still walk away with a master’s degree.
My advice is that if you’re at all tempted by a PhD: go for it!
I hope this post helped you to understand if a PhD is worth it for you personally. If it is then best of luck with your application!
Considering doing a PhD? I have lots of other posts covering everything about funding , how much PhD students earn , choosing a project and the interview process through to many posts about what the life of a PhD student and graduate is like . Be sure to subscribe below!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

PhD Salary UK: How Much Do PhD Students Get Paid Compared to Graduates?
5th February 2024 4th July 2024

The Benefits of Having a PhD
7th September 2022 30th January 2024

My top PhD regrets: 10 lessons learned by a PhD grad
21st April 2022 25th September 2023
4 Comments on “Is a PhD Worth It? Should I Do a PhD?”
Hi Thanks for the post . I have been struggling to make a decision regarding doing a PhD or doing a second masters . I’m currently doing an msc civil engineering online (because of covid) so for my research I am not able to conduct lab experiments. Therefore my research is more of a literature review / inductive research. So I feel I’ll be at a disadvantage if I were to apply for a phd program especially at high ranking universities like oxford , imperial etc What are your thoughts?
Hey Esther,
I completely appreciate that it’s not an ideal situation at the moment so thanks for reaching out, it’s a great question. A few thoughts I have:
• If you are already tempted by a PhD and would do a second masters simply to gain lab experience, there is no harm in applying for the PhD now. At the very least I suggest considering reaching out to potential supervisors to discuss the situation with them. The universities realise that current applicants won’t have been able to gain as much research experience as normal over the last year. Practical lab experience has halted for so many people so don’t let it put you off applying!
• If you don’t get in on the first go, I don’t believe it looks bad to apply again with more experience. I applied for PhDs for three years, it doesn’t need to take this long but the point is that there’s not much reason to give it a go this year and stand a chance of getting accepted.
• Although we can be optimistic, even if you were to do a second masters it may not be guaranteed that you can gain as much lab experience as you’d like during it: even more reason to start the ball rolling now.
I hope that helps, let me know if you’d like any other further advice.
Best of luck. 🙂
Funny, every one i have talked to as well as myself when we asked ourselves and others whether the PhD was worth it is a resounding ‘No.’
I guess it comes down to a Blue or Red Pill, LoL.
Hi Joe, thanks for sharing this. I’ve spent enough time on the PhD subreddit to see many other people who haven’t had good experiences either! On the flipside many people do have positive experiences, myself included. There is perhaps an element of luck as to what your research environment turns out to be like which could somewhat dictate the PhD experience, but ultimately I do think that answering whether or not a PhD has been worth it really depends a lot on why someone is pursuing a PhD in the first place. I’m keen to make sure people don’t have unrealistic expectations for what it could bring them. I really welcome hearing about different experiences and if you’d fancy sharing your perspective for the PhD profiles series I’d love to hear from you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview

- 3 . 01 . 20
- Leaving Academia
Is a PhD Worth It? I Wish I’d Asked These 6 Questions First.
- Posted by: Chris
Updated Nov. 19, 2022
Is a PhD worth it?
Should I get a PhD?
A few people admit to regretting their PhD. Most—myself included — said that they don’t ( I wrote about why in this post ).
But we often say we don’t regret stupid things we’ve done or bad things that happen to us. This means we learned from them, not that we wanted them to happen.
So just because PhDs don’t regret it, doesn’t mean it was worth it.
But if you were to ask, Is a PhD worth it, it’s a different and more complicated question.
When potential PhD students ask me for advice, I hate giving it. I can’t possibly say whether it will be worth it for them. I only know from experience that for some PhDs the answer is no.
In this post, I’ll look at this question from five different directions, five different ways that a PhD could be worth it. Then I give my opinion on each one. You can tell me if I got the right ones of if I’m way off base. So here we go.
This is post contains affiliate links. Thanks for supporting Roostervane!
tl;dr It’s up to you to make it worth it. A PhD can hurt your finances, sink you in debt, and leave you with no clear path to success in some fields. But PhDs statistically earn more than their and have lower unemployment rates. A PhD also gives you a world-class mind, a global network, and a skill set that can go just about anywhere.
Should I Get a PhD?
tl;dr Don’t get a PhD by default. Think it through. Be clear about whether it’s going to help you reach career goals, and don’t expect to be a professor. A few rules of thumb- make sure you know where you want to go and whether a PhD is the ONLY way to get there, make sure it’s FUNDED (trust me), and make sure your program has strong ties into industry and a record of helping its students get there.
1. Is a PhD worth it for your finances?
My guess: Not usually
People waste a lot of their best years living on a grad stipend. To be honest, my money situation was pretty good in grad school. I won a large national grant, I got a ton of extra money in travel grants, and my Canadian province gave me grants for students with dependents. But even with a decent income, I was still in financial limbo–not really building wealth of any sort.
And many students scrape by on very small stipends while they study.
When it comes to entering the marketplace, research from Canada and the United States shows that PhD students eventually out-earn their counterparts with Master’s degrees. It takes PhDs a few years to find their stride, but most of us eventually do fine for earnings if we leave academia. Which is great, and perhaps surprising to many PhDs who think that a barista counter is the only non-academic future they have .
The challenge is not income–it’s time. If you as a PhD grad make marginally more than a Master’s graduate, but they entered the workforce a decade earlier, it takes a long time for even an extra $10,000 a year to catch up. The Master’s grad has had the time to build their net worth and network, perhaps buy a house, pay down debt, invest, and just generally get financially healthy.
While PhDs do fine in earnings in the long run, the opportunity cost of getting the PhD is significant.
The only real way to remedy this—if you’ve done a PhD and accumulating wealth is important to you, is to strategically maximize your earnings and your value in the marketplace to close the wealth gap. This takes education, self-discipline, and creativity, but it is possible.
I tried to calculate the opportunity cost of prolonging entry into the workforce in this post .
2. Is a PhD worth it for your career?
My guess: Impossible to tell
Most of my jobs have given me the perfect opportunity to see exactly where I could be if I’d stopped at a Master’s degree, often working alongside or for those who did and are further ahead. In terms of nuts and bolts of building career experience section on a resume, which is often the most important part, a PhD is rarely worth it. (Some STEM careers do require a PhD.)
However, at the start of my post-graduate educational journey, I was working part-time running teen programs and full time as a landscaper. I had an undergraduate degree. Despite my job and a half, I was still poor. My life had no direction, and had I not begun my Master’s to PhD journey I probably would have stayed there.
The PhD transformed me personally. It did this by developing my skills, or course. But even more so, it taught me that anything is possible. It took a poor kid from a mining town in northern Canada and gave me access to the world. It made my dreams of living abroad come true. I learned that anything is possible. And that will never go away.
It’s changed the course of my life and, subsequently, my career.
It’s impossible for you to know if it’s worth it for your career. But you can build a hell of a career with it.
So it wouldn’t be fair for me to say, “don’t get a PhD.” Because it worked out for me, and for some it does.
But there are a heck of a lot of people who haven’t figured out how to build a career with this thing. Which is one of the reasons Roostervane exists in the first place.
Psst! If you’re looking at doing a PhD because you don’t know where to go next with your career–I see you. Been there. Check out my free PDF guide– How to Build a Great Career with Any Degree.
3. Is a PhD worth it for your personal brand?
My guess: Probably
There’s some debate over whether to put a Dr. or PhD before or after your name. People argue over whether it helps in the non-academic marketplace. Some feel that it just doesn’t translate to whatever their new reality is. Some have been told by some manager somewhere that they’re overqualified and pulled themselves back, sometimes wiping the PhD off their resume altogether.
The truth is, if you have a PhD, the world often won’t know what to do with it. And that’s okay. Well-meaning people won’t understand how you fit into the landscape, and you may have to fight tooth and nail for your place in it. People may tell you they can’t use you, or they might go with what they know—which is someone less qualified and less-educated.
It happens.
But someone with a PhD at the end of their name represents an indomitable leader. So grow your possibilities bigger and keep fighting. And make your personal brand match those three little letters after your name. Do this so that the world around can’t help but see you as a leader. More importantly, do it so that you don’t forget you are.
Should I put “PhD” after my name on LinkedIn?
5 reasons you need to brand yourself
4. Is a PhD worth it for your sense of purpose?
Is getting a PhD worth it? For many people the answer is no.
PhDs are hurting.
If you’ve done one, you know. Remember the sense of meaning and purpose that drew you towards a PhD program? Was it still there at the end? If yours was, you’re lucky. I directed my purpose into getting hired in a tenure-track job, and got very hurt when it didn’t happen.
And people have vastly different experiences within programs.
Some people go through crap. But for them their research is everything and putting up with crap is worth it to feel like they have a sense of purpose. Many PhDs who are drawn into programs chasing a sense of purpose leave deeply wounded and disenchanted, ironically having less purpose when they started.
While new PhDs often talk about the PhD as a path do doing “something meaningful,” those of us who have been through entire programs have often seen too much. We’ve either seen or experienced tremendous loss of self. Some have friends who didn’t make it out the other end of the PhD program.
But there are some PhDs who have a great experience in their programs and feel tremendously fulfilled.
As I reflect on it, I don’t think a sense of purpose is inherently fulfilled or disappointed by a PhD program. There are too many variables.
However, if you’re counting on a PhD program to give you a sense of purpose, I’d be very careful. I’d be even more cautious if purpose for you means “tenure-track professor.” Think broadly about what success means to you and keep an open mind .
5. Is my discipline in demand?
Okay, so you need to know that different disciplines have different experiences. Silicon Valley has fallen in love with some PhDs, and we’re seeing “PhD required” or “PhD preferred” on more and more job postings. So if your PhD is in certain, in-demand subjects… It can be a good decision.
My humanities PhD, on the other hand, was a mistake. I’m 5 years out now, and I’ve learned how to use it and make money with it. That’s the great news. But I’d never recommend that anyone get a PhD in the humanities. Sorry. I really wish I could. It’s usually a waste of years of your life, and you’ll need to figure out how to get a totally unrelated job after anyway.
TBH, most of the skills I make money with these days I taught myself on Skillshare .
6. Is a PhD worth it for your potential?
My guess: Absolutely
Every human being has unlimited potential, of course. But here’s the thing that really can make your PhD worth it. The PhD can amplify your potential. It gives you a global reach, it gives you a recognizable brand, and it gives you a mind like no other.
One of my heroes is Brené Brown. She’s taken research and transformed the world with it, speaking to everyone from Wall-Street leaders to blue-collar workers about vulnerability, shame, and purpose. She took her PhD and did amazing things with it.
Your potential at the end of your PhD is greater than it has ever been.
The question is, what will you do with that potential?
Many PhD students are held back, not by their potential, but by the fact that they’ve learned to believe that they’re worthless. Your potential is unlimited, but when you are beaten and exhausted, dragging out of a PhD program with barely any self-worth left, it’s very hard to reach your potential. You first need to repair your confidence.
But if you can do that, if you can nurture your confidence and your greatness every day until you begin to believe in yourself again, you can take your potential and do anything you want with it.
So why get a PhD?
Because it symbolizes your limitless potential. If you think strategically about how to put it to work.
PhD Graduates Don’t Need Resumes. They Need a Freaking Vision

By the way… Did you know I wrote a book about building a career with a PhD? You can read the first chapter for free on Amazon.
So if you’re asking me, “should I do a PhD,” I hope this post helps you. Try your best to check your emotion, and weigh the pros and cons.
And at the end of the day, I don’t think that whether a PhD is worth it or not is some fixed-in-stone thing. In fact, it depends on what you do with it.
So why not make it worth it? Work hard on yourself to transform into a leader worthy of the letters after your name, and don’t be afraid to learn how to leverage every asset the PhD gave you.
One of the reasons I took my PhD and launched my own company is that I saw how much more impact I could have and money I could be making as a consultant (perhaps eventually with a few employees). As long as I worked for someone else, I could see that my income would likely be capped. Working for myself was a good way to maximize my output and take control of my income.
It’s up to you to make it worth it. Pick what’s important to you and how the degree helps you get there, and chase it. Keep an open mind about where life will take you, but always be asking yourself how you can make more of it.
Check out the related post- 15 Good, Bad, and Awful Reasons People Go to Grad School. — I Answer the Question, “Should I Go to Grad School?” )

Consulting Secrets 3 – Landing Clients
Photo by Christian Sterk on Unsplash There’s a new type of post buzzing around LinkedIn. I confess, I’ve even made a few. The post is

You’re Not Good Enough… Yet
Last year, I spent $7k on a business coach. She was fantastic. She helped me through sessions of crafting my ideas to become a “thought

$200/hr Expert? Here’s the Secret!
Photo by David Monje on Unsplash I was listening to Tony Robbins this week. He was talking about being the best. Tony asks the audience,
SHARE THIS:
EMAIL UPDATES
Weekly articles, tips, and career advice
Roostervane exists to help you launch a career, find your purpose, and grow your influence
- Write for Us
Terms of Use | Privacy | Affiliate Disclaimer
©2022 All rights reserved
Get the Reddit app
A place to post news and discuss the frontiers of biochemistry and biotechnology. Please refrain from posting home videos with songs and raps.
Was your PhD worth it?
Im strongly considering getting my PhD , and I most likely will attempt it. I'm just curious as to how other people who have achieved that major milestone in their life view it. It can range from profit to research or doing what you love. Anything.
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue

- Is Doing a PhD Worth It?
- Finding a PhD
Undertaking a PhD shouldn’t be a light decision. In fact, it’s one of the most challenging academic journeys you could embark on. This begs the question: Is a PhD worth it?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and extensive research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but can lead to improves job prospects, a higher salary on average, and sets you up for invaluable skills and traits. If you are a graduate student considering undertaking doctoral studies, read our guidance to help you make an informed decision.
Career Prospects
Although a full time PhD takes on average three to five years to complete, that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t have a long-term goal, especially with the possibilities that come with it. It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only open the door for educational based roles such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD does lend itself to an academic career, the opportunities extend far beyond the traditional academic job. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles. This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
Percentages aside, one of the most desirable post-doctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are incredibly lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on an R&D position. Completing an advanced degree programme demonstrates that you have developed a knowledge base in your research area which gives you a head start over other candidates who many only have an undergraduate degree or masters degree.
Pursuing your Interests
One factor to consider when asking ‘is a PhD worth it?’ is what your interests are. A doctoral degree is a fantastic opportunity to spend time learning about something that appeals to you. Having an interest in your research area as a PhD student is a massive advantage as you will always be motivated to push the boundaries of your research. Possessing an advanced degree in a field your are genuinely interested in can also help shape your career path and help you land your dream job.
Transferable Skills
PhD students are widely in demand for their wide range of skills they develop during their studies. Not only do these skills extend beyond that obtained by an undergraduate counterpart, but the transferability of the skills is what makes them stand out amongst employers.
Professional Networking
To successfully undertake a PhD, it’s paramount to have a good working relationship with your PhD supervisor and other students in your laboratory, workshop, or department. This relationship will also extend to undertaking short-term collaborative projects, delivering joint conferences and co-authoring research papers. The modern doctorate needs to demonstrate effective team working, collaboration and networking to be successful in their chosen field. This skill is highly sought by all employers, as open and effective communication is key to any project.
Publication
Although publishing isn’t a requirement of all PhD projects, all students will have the opportunity to produce technical or informative texts, regardless of whether it’s in the form of reports or academic journal articles.
The preparation, research, writing, and editing of such texts demonstrate your ability to amalgamate information and communicate complex ideas. Regardless of an employer’s field, the ability to record and summarise essential information is a fundamental skill they look for. Demonstrating you’re capable of delivering factual documents will help set you apart from colleagues, which will help make strides in your career.
Research Skills
One of the most valued skills you’ll gain during your PhD study is the ability to undertake original research. Not only does this demonstrate you are able to think independently, but also that you are prepared to take on responsibility and can contribute original ideas to the workplace. In undertaking a PhD, you will prove yourself as a professional expert in this area, making you a suitable candidate for research jobs.
Data analysis
A PhD programme, in particular a STEM PhD project, is likely to involve identifying, managing and analysing large amounts of complex information. In addition to this, you could be required to assimilate this information in an appropriate and understandable format. Because of this a data driven doctorate degree is highly desirable in numerical industries such as banking and engineering.
Public Speaking

In today’s industries, excellent oral communication skills are becoming more and more essential. Although many individuals struggle with this skill, as a PhD graduate, you’re more likely to excel in this area. This is because of the many public speaking opportunities you’ll be exposed to during your course. Through conference talks, presentations, and posters, you’ll learn to become confident and engaging when speaking to a broad audience. You’ll also showcase to future employers that you know how to present complex ideas and defend them.
Project management
Even if your career goal isn’t to become a project manager, all jobs require some project management. Fortunately, PhDs are a project management exercise. To complete your thesis, you must design a project, establish a realistic timetable, manage stakeholders and overcome failures. While attempting to achieve the long-term goal set out by the PhD, you must also set, manage, and achieve short-term goals to make progress.
This scenario accurately represents any modern workplace. You’ll be given the autonomy to manage your projects and workload and be expected to do so at a competent level. With this in mind, PhD holders can show they are more than capable of managing a team, and in doing so broaden their career options when entering the job market.
Critical Thinking
Every doctoral student will gain unparalleled skills in exercising critical thinking. This is due to having been trained to address problems, identify connections and analyse information to come to sensible conclusions. A critical thinker is exceptionally beneficial for any industry.
Co-operation
Nearly all careers place a strong emphasis on team working and interpersonal skills. Although producing a PhD thesis is an individual task, to complete your doctoral degree you’ll need to collaborate with others, whether it be to conduct experiments, collect data, operate as part of a larger research group or co-write manuscripts. To complete these tasks, you must know how to divide the task, share with others, communicate effectively, and resolve conflicts. All these skills carry over to any workplace, not just those in an academic position. By demonstrating that you can work as part of a team, you’ll significantly increase your desirability for any role.
Many prospective PhD students see a future in academia. Strong communication skills are essential in this line of work as in addition to giving lectures you may be involved in the supervision of graduate students during their final year projects.
As a graduate student you will have spent the last few years in university and likely have some student debt. A doctorate programme is a further large financial commitment, in particular if you self-fund your studies which can take 3-5 years to complete as a full time PhD student. Even if you secure a funded PhD, the available living stipend will comparatively be less than you would potentially earn if you had gone into employment instead. Part time PhD programmes also worth looking at for PhD candidates, as they allow researchers to work during their PhD course who can then spend their earnings towards their living costs and tuition fees.
In analysing the career prospects and transferable skills gained in undertaking a PhD degree, it is clear that pursuing a PhD is an extremely worthwhile venture.
You will develop deep knowledge in your research area which gives you an advantage when applying to academic jobs (for example a professor or research advisor/PostDoc). During your doctoral years you’ll also gain many skills valued in any career path, from problem solving, to managing tasks and communicating complex ideas. Possessing a PhD correlates to higher median salaries, and can aid career progression as a PhD holder can use their specialist skills to seek out unique opportunities in industry. These skills, combined with the new roles that open up for doctorate holders, such as working within innovative Research and Development teams, presents an exciting and prosperous future.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Jul 22, 2022
- 11 min read
Is a PhD Worth It? The Pros and Cons of Getting a Doctorate
To get a PhD or not to get a PhD? That is the question.
Valerie David
Lifestyle and Career Expert
Reviewed by Hayley Ramsey

Entering the job market for the first time can be a stressful experience, especially if you don't feel completely prepared. When deciding how to take those first steps toward your ultimate career , and how to give yourself a chance at the best jobs, you may find yourself asking: “Should I do a PhD?”.
While academics looking forward to a life of learning may consider this a no-brainer, there are important factors for everyone to consider. Finances, job prospects and quality of life issues can greatly affect the success of furthering your education.
To help you decide if the time and effort of a PhD is worth it, here are the major benefits and disadvantages of getting that doctorate.
After four or more years of intellectual pursuits, adding a PhD may seem like overkill. Before you make your choice, let's look at all the benefits that are exclusive to earning the most advanced degree.
1. You can contribute new knowledge to the world
Embarking on a PhD programme means delving into your preferred subject in a much deeper way than you have in any of your previous studies. The beauty of this advanced degree is that it allows you to sail in uncharted waters. Your goal is to find new information, draw new conclusions and, hopefully, make a significant contribution to your field.
Your intensive research, travel, collaboration and study will lead you on an unpredictable path to telling a story that no one has heard before. For some students, this pursuit of knowledge and discovery is enough to make all the hard work of earning a PhD worth it.
2. You'll have access to more prestigious jobs
One of the key benefits of a PhD is that it opens doors to careers at the highest levels. This can include leadership positions in science and engineering, government roles in economics and political science, and prestigious teaching posts for English and arts majors. Even if an advanced degree isn't required for the job you want, that PhD can give you an extra air of authority in your field and an edge over other candidates.
Another obvious upside to continuing your postgraduate studies is that landing these powerful positions can lead to large financial rewards. Some areas of study, like medicine and the law, tend to be more lucrative, but it can also depend on the type of job. For example, a university professor or researcher post can pay well for a wide variety of disciplines. Check out sites like the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the National Careers Service to investigate potential salaries.
3. Employers look for candidates with your superior writing skills
A study arranged by the National Commission on Writing discovered that blue-chip businesses (long-standing companies with stable stock growth) are spending more than $3 billion a year on remedial writing course for current employees. This includes staff with undergraduate degrees.
So, when a hiring manager peruses your résumé and sees that you've earned a PhD, they'll know immediately that you've spent years honing your skills at compiling research, organizing mountains of data and writing about your results in a cohesive and persuasive way. This will clearly set you apart from your competition, while landing your dream job will prove that pursuing that advanced degree was worth it.
4. You'll improve on all your soft skills
While pursuing your undergraduate degree, you likely noticed that you were learning more than just the subject matter taught in each class. Completing your studies also required time management skills , focus and problem solving .
Getting a doctorate degree requires even more of the soft skills that employers look for in applicants . Your intensive study and finished thesis should lead to improvements in your problem solving, critical thinking , patience and adaptability . These desirable skills won't just help you land a job but also excel in whatever career you choose to pursue .
5. You'll collect an extensive network of professional colleagues
When weighing the pros and cons of earning a PhD, consider all the professional contacts you'll make during the course of your studies. Working closely with professors, department heads, experts in your field, as well as fellow researchers, helps you develop an important resource. This network of colleagues can provide continual assistance with references, job leads, career advice and collaboration.
6. You can wait for a more favorable job market
Job prospects may not look that promising when you've completed your undergraduate degree, or even after you've been in the workforce for a few years. While there's no guarantee things will improve after a delay, some students may appreciate the benefit of a steady graduate assistant salary while they work on enhancing their résumé with a doctorate.
If you couldn't get a good internship during or after your undergrad studies, the PhD work also gives you the time to build that professional network . These contacts could prove to be the key to breaking into a specialized or highly competitive field.
You may still be thinking about all that time and commitment and wondering, “Is a PhD worth it?”. While there are always positive results from improving your education, there are some downsides to getting your doctorate.

1. It's expensive
This is a substantial factor for many students when weighing the merits of pursuing a PhD versus entering the job market right away. If you already have student loans , continuing your education will just increase your burden and add substantial pressure when you eventually begin your job search.
If cost is a concern, investigate graduate assistant jobs that help with expenses. Some programmes offer tuition assistance in return for teaching or research work. For those who already work full time and are hoping a PhD will help them advance in their career, consider keeping that job and pursuing your studies on a part-time basis.
2. Getting a PhD can be a lonely experience
Despite your interactions with professors and other students, pursuing a doctoral degree is ultimately a solitary pursuit. Your thesis topic is unique to you, and you'll spend a lot of time alone doing research and writing. Your social life can suffer, especially if you're also working in addition to your studies.
Career experts often talk about the necessity of work-life balance for physical and mental health, and this is just as important for PhD students as anyone else. It may take you a little longer to complete your degree, but it's worth taking the time to visit family and hang out with your friends. These positive interactions can help you stay motivated through the most tedious parts of your work.
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration
Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
A topic that seemed intriguing at first may not live up to years of scrutiny, causing boredom at best or requiring a complete thesis change at worst. Not all programmes are well-run, either, and you may have a supervisor who is too critical, offers poor advice or is just unavailable and unhelpful.
The difficulties of a PhD programme lead to rather substantial dropout rates. In the US alone, only 57% of PhD students obtained their degree within a decade of enrolling. If you want to be in the successful half of those stats, take extra time to review your choice of supervisor and topic focus. Ask every professor you have for advice on making the right decisions and talk with current graduate students to see what their experience has been.
4. There may be limited job openings
While getting a PhD can qualify you for better and higher-paying jobs , it can also put you in a position where you're competing for an extremely limited number of job openings. This is especially true of university jobs, where the number of advanced degree graduates far outpaces the need for full-time instructors, researchers and administrators.
Earning your PhD with a very obscure thesis in a niche speciality can also limit your options. When there are only a handful of jobs that suit your expertise, and they're already occupied, it can make you feel that your doctorate was a waste of time. Consider the job market before you make decisions about getting another degree. If you're determined to study in a niche area, think ahead of time about related fields or industries where your knowledge and skills will also prove useful to employers.
5. There may be little to no financial reward
While most studies concur that having a PhD increases your income potential substantially over the lifetime of your career, it's not a guarantee of job security or a financial windfall. A study by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) found that 5 years after earning their doctorates , 45% of grads in Germany were still on temporary contracts and 13% ended up in lowly occupations.
Other European countries, including Slovakia, Belgium and Spain, had similar results. In the US, in fields like engineering, the difference in pay scales between employees with a master's degree and a PhD was a mere 7%. When that small bump in salary is weighed against the amount of debt taken on in order to get your degree, you may decide it's not worth it.
6. You could lose out on valuable job experience
New forms of technology continue to change how organizations operate, and those changes can happen fast. If you've already spent several years in school, toiling away in solitary study of obscure subjects can cause you to fall further behind in learning the skills you'll actually need for a future career.
Before you invest in getting a PhD, research your chosen field and learn which type of degree will give you the most value. Many scientific, financial and computing careers rely more on skills acquired on the job, rather than in coursework that can quickly become outdated.
Questions to ask yourself
You’ve listed out the pros and cons, but that still may not be enough to help make your decision. When it comes to a life-altering change like getting a doctorate, it’s okay to take enough time to ask yourself specific questions to ensure you’re making the right move. Consider asking yourself the following:
- Why do I want to get a PhD?
- Do I have the pre-requisites to move forward to a PhD?
- What are my strengths and limitations?
- Am I financially prepared?
- Am I mentally prepared?
- How will this affect my relationship with my family or friends?
- Where will I study?
- What am I trying to achieve?
- What jobs will be available to me after I get my PhD?
- Are there other options or avenues to consider?
Unfortunately, you may not have the answer to every one of these questions, because let’s face it, you don’t know what you don’t know. You might not know how it will affect your relationship with family or friends, but why not ask them? Reach out to those closest to you and see how you pursuing this degree could trickle down to them and allow that to play into your decision. Evaluate the answers to these questions and use it to help you make an educated decision on your future moving forward.
The best PhD degrees
If you’ve weighed out the pros and cons, asked all the important questions, and now you’re set on getting your PhD, congratulations! To help you along the way, let’s look at a list of the most valuable PhD programs to start you on your way to this degree.
- Criminal Justice
- Engineering
- Cybersecurity
- Business Administration
These fields are rapidly growing and are among the highest-paying doctorate degrees in 2022 , so they might be worth considering as you start your journey.
Key takeaways
Pursuing your PhD requires an incredible amount of commitment, and it's important to take the necessary time to make the decision. As you’re evaluating a doctorate degree, remember the following:
- Evaluate the pros and cons list right from the beginning to ensure you’re weighing out both sides of the coin.
- Ask yourself the necessary questions. A doctorate degree commitment can affect more than just you, so be sure you’re factoring that into your decision.
- Review specifically which PhD would be best for you and your field progression.
- Research your chosen field carefully and evaluate the job market before you finalize your degree choice.
- Once you’ve selected your degree, stay focused and stay driven. It’s going to be a hard few years, but it will be worth the work!
Who knows, this may prompt you to move on to postgraduate study — never stop achieving!
Have you decided to pursue your PhD, or are you still considering your options? Join us in the comments below and let us know what’s stopping or encouraging you from getting a PhD.
Originally published on July 24, 2019. Updated by Shalie Reich.
Courses and Qualifications
Continuing Education

- Communities Pre-Med Medical Resident Audiology Dental Optometry Pharmacy Physical Therapy Podiatry Psychology Rehab Sci Veterinary
- What's new Trending New posts Latest activity
- Support Account Help Confidential Advising
- Vision, Values and Policies
- PreMed Communities
- Pre-Medical (MD)
My overly informative situation of MD vs PhD!
- Thread starter matthewsrr
- Start date May 15, 2012

Full Member
- May 15, 2012
You sound like an old guy so I don't know if this would be good for you but why not MD/PhD?
Nah I'm actually only 23 years old. I've thought about it but worry about the time commitment of doing MD/PhD,and I've actually heard some say that MD is fine, and then just do research. But, I also heard an MD doing research compared to a PhD doing it is vastly different. Basically I love learning and can't make a decision! Sometimes I kinda wish I could just get paid to learn for the rest of my life haha.
matthewsrr said: Nah I'm actually only 23 years old. I've thought about it but worry about the time commitment of doing MD/PhD,and I've actually heard some say that MD is fine, and then just do research. But, I also heard an MD doing research compared to a PhD doing it is vastly different. Basically I love learning and can't make a decision! Sometimes I kinda wish I could just get paid to learn for the rest of my life haha. Click to expand...
huskydock said: And again, MD/PhD programs are typically 5 years, which still totally beats the PhD route which could, again, be up to 8 years. Click to expand...
notbobtrustme
Crux terminatus.
MD >>>>>>>>>>>> PhD.
If you want to work less than 40 hours a week and spend a lot of time with your family, then I wouldn't recommend becoming a physician or scientist. There are very few medical specialties that work so few hours. Although emergency physicians do work about 35-40 hrs/wk as attendings, after 7-8 years of 60-80 hour weeks in med school and residency, that's still a misleading number. Since we work 24/7 in EM, there is a lot of time spent recovering from night shifts, and we work many nights, weekends and holidays. Our free time doesn't coincide with the free time of family members who have normal work or school schedules. If you're concerned about lack of variety in emergency medicine, I don't know how to help you as we probably have a wider variety of almost everything than any other specialty. So far I find it a very stimulating and rewarding field (granted, only ten months into my intern year). Although there may be a small fraction of patients who shouldn't be in the ED, this isn't as much of an issue as you seem to think. I have yet to see anyone return three times in a day. Others have touched on some issues with the PhD route. The average length of a PhD in biology is around 7 years these days, although it can be 5 or 6, followed by years of postdoc work. The funding environment is terrible and likely to get worse due to Republican antipathy toward science and the poor economy. Again, it's hard to be successful without working long hours. I would really urge you to spend a lot more time exploring your options rather than rushing into something that's going to eat your soul for a decade.
Algophiliac
pseudoknot said: Others have touched on some issues with the PhD route. The average length of a PhD in biology is around 7 years these days, although it can be 5 or 6, followed by years of postdoc work. The funding environment is terrible and likely to get worse due to Republican antipathy toward science and the poor economy. Again, it's hard to be successful without working long hours. I would really urge you to spend a lot more time exploring your options rather than rushing into something that's going to eat your soul for a decade. Click to expand...
xXIDaShizIXx
notbobtrustme said: MD >>>>>>>>>>>> PhD. Click to expand...
the evil queen of numbers
Have you considered engineering? Regular hours. Entertaining: http://www.slashgear.com/university-of-pennsylvania-makes-robots-to-play-james-bond-theme-02216575/ Help millions of people. If you are reading this, you can thank an engineer! I think that medicine or academic-based research are bad ideas if you want a 40 hour/wk schedule.
Has an MD in Horribleness
LizzyM said: I think that medicine or academic-based research are bad ideas if you want a 40 hour/wk schedule. Click to expand...
Ebola4Breakfast
pseudoknot said: ... Others have touched on some issues with the PhD route. The average length of a PhD in biology is around 7 years these days, although it can be 5 or 6, followed by years of postdoc work. The funding environment is terrible and likely to get worse due to Republican antipathy toward science and the poor economy. Again, it's hard to be successful without working long hours. I would really urge you to spend a lot more time exploring your options rather than rushing into something that's going to eat your soul for a decade. Click to expand...
Algophiliac said: Is it really so bad to become a PhD? I've heard all of these stories about how it would be difficult to find a decent-paying teaching or research position as a post-PhD student, but I still see so many well-employed, tenured professors. Numerous PhD students graduate from the universities in my area and still get into fantastic programs afterward, but obviously these are all just useless and random statistics. Click to expand...
pseudoknot said: Others have touched on some issues with the PhD route. The average length of a PhD in biology is around 7 years these days, although it can be 5 or 6, followed by years of postdoc work. The funding environment is terrible and likely to get worse due to Republican antipathy toward science and the poor economy. Again, it's hard to be successful without working long hours. Click to expand...
Ebola4Breakfast said: The problem is that we educate more PhDs than the available number of tenure track positions. The bottleneck isn't immediately after graduation. Postdoc positions are a dime a dozen, especially if you have good communication skills. The problem comes in trying to find a position with upward mobility AFTER a postdoc. It's not easy. Click to expand...
huskydock said: http://100rsns.blogspot.com/ http://www.economist.com/node/17723223?story_id=17723223&CFID=157679668&CFTOKEN=82403941 Click to expand...
Perrotfish said: And let us not forget the incredibly unhealthy system of tying your entire career to a single professor who has the ability to completely f- over your career and who also has every professional motivation to keep you around as indentured labor rather than letting you actually graduate. Say what you will about medical school, but it does try its best to be objective and you do know how long its going to last. Click to expand...
TheMightySmiter
It will be very tough to have a 40 hour workweek in either career path.
Membership Revoked
LizzyM said: Have you considered engineering? Regular hours. Entertaining: http://www.slashgear.com/university-of-pennsylvania-makes-robots-to-play-james-bond-theme-02216575/ Help millions of people. If you are reading this, you can thank an engineer! I think that medicine or academic-based research are bad ideas if you want a 40 hour/wk schedule. Click to expand...
Perrotfish said: Not nearly as bad as all the interesting kinds of engineering. Or law. Or business. I think medicine is actually one of the best alternatives for a 40 hour week. It's 7 years of terrible hours while you're in training, but when you get to the end of it there actually is a very robust market for shift work, and a lot of people do work 40 hours worth of shifts a week. Engineers don't work shifts, and neither do researchers, lawyers, or businessmen: they stay until the project is done. Click to expand...
LizzyM said: Engineers don't work shifts which means they are at the table for every holiday meal, every celebratory event in their extended familiy. Engineers work until the project gets done but projects get done over weeks, months or years. I shared a house with an employed mechanical engineer for 2 academic years and I don't think he missed being home in time for dinner more than twice. Electrical/electronics engineers do their work and have every weekend free to go to their kids' games. Civil engineers, out in the field Monday through Friday and home all weekend. Click to expand...
Ebola4Breakfast said: And then there's graduation. The departmental average may be X number of years, but that's in no way a guarantee that you'll be able to graduate in that many years. There are so many factors involved, both controllable and uncontrollable. The biggest uncontrollable factor is your committee. If they don't feel you are "ready to graduate"... then it won't happen. After all, your committee has to sign off on your defense. How many years you've been in the program doesn't mean a whole lot. People are asked to leave. Sometimes with a terminal Masters... sometimes not. I honestly didn't "know" I was going to attempt my defense until about six months prior. Click to expand...
YMMV as they say. My family's experiences are with Raytheon, Texas Instruments, Sikorsky Aircraft, local government (civil engineering), and self-employment (civil engineering and mechanical engineering/computer engineering of factory systems).
K31 said: Come again? Click to expand...
- May 16, 2012
matthewsrr said: So the big question is how do MDs keep themselves intrigued with their profession and prevent themselves from developing a poor attitude? Click to expand...
matthewsrr said: I just love medicine AND science so I can't decide if I should still go to medical school or go to grad school for biochemistry, physics, biomedical engineering, or something similar. Click to expand...
Gut Shot said: 1. PhD: 5-7+ years living on dirt wages. 2. PostDoc: 3-9+ years living on double dirt wages. 3. Assistant professorship. After 1-2 years your salary is dependent on getting grants funded, which are each 100+ pages and have about a 5-15% chance of success. 4. Oops, your money ran out and nothing got funded. Time to move to a new institution and get fresh startup funds. 5. Go back to 3. The halcyon days of stable, predictable funding for medical sciences is over. The image of a career in science that we grew up with is now a caricature from a bygone era. Click to expand...
- May 17, 2012
Yes, very few postdocs go on to become independent investigators. Science is a pyramid scheme.
Perrotfish said: I remember at my undergrad we had one materials science professor who gave his PhDs 5 years to graduate, which is lightning fast even by the already fast standards of engineering doctorates. No one worked for him longer than that, almost everyone finished in 5 years and the rest got ****canned. One day in class, someone asked him why and he did that. He said that when he was in his doctoral program he had a classmate that had been stuck in a PhD for 10 years. He wasn't incompetent, he published regularly, taught well, and was well liked. However he was the only one in his lab who knew how to do a number of fairly involved technical procedures, and his 'mentor' refused to sign off on his thesis defense because he wanted to keep him around for the labor. Everyone knew about the situation and thought it was appalling but the way doctoral programs there is basically no appeal for this kind of thing. On his 10th anniversary of the program the student went to his professor, one last time, and asked him if he could finally graduate. The professor said at least one more year. That's when the student shot him in the head. That apparently made an impression on my prof. He decided that everyone was getting out of his lab within 5 years, one way or another. Click to expand...
Alakazam123
- Aug 16, 2019
I think it's important to consider that there are other career options after PhD as well. Academia is just one option, and there are many people who go into industry. Currently there is a high demand for Data Scientists and AI/ML trained PhDs in the industry. However there is sort of a glut in the wet-lab PhD industry. Companies are outsourcing research to Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and getting a job there often doesn't require a PhD due to the fact that the assay development happens in-house at the pharmaceutical company. So, it really depends on what you get your PhD in. The following fields are good: 1. Applied Mathematics 2. Statistics 3. Computer Science (w/ AI and ML focus) 4. Data Science (though there's only a handful of Data Science exclusive PhD programs) 5. Bioinformatics/Biostatistics
Alakazam123 said: I think it's important to consider that there are other career options after PhD as well. Academia is just one option, and there are many people who go into industry. Currently there is a high demand for Data Scientists and AI/ML trained PhDs in the industry. However there is sort of a glut in the wet-lab PhD industry. Companies are outsourcing research to Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and getting a job there often doesn't require a PhD due to the fact that the assay development happens in-house at the pharmaceutical company. So, it really depends on what you get your PhD in. The following fields are good: 1. Applied Mathematics 2. Statistics 3. Computer Science (w/ AI and ML focus) 4. Data Science (though there's only a handful of Data Science exclusive PhD programs) 5. Bioinformatics/Biostatistics Click to expand...
Alta California
Closing a really old thread.
Similar threads
- always_hungry
- Jan 18, 2024
- Jun 4, 2024
- Mar 24, 2024
- Help Me Decide: X vs Y Medical School
- rivertalon123
- Dec 31, 2022
- SolarPistachio
- Aug 27, 2023
- This site uses cookies to help personalize content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies and terms of service . Accept Learn more…
The Grad Student Way
Your One Stop Grad School and PhD Resource
- Second Income Ebook
- Twitter GradStudentWay
- LinkedIn GradStudentWay
- Facebook Page
- RSS Feed GradStudentWay
- Networking Guide
- Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
Some may look back 5 years or even 10 years post-PhD and say it was definitely worth it. Others may be fresh out of graduate school and have a different view/opinion or may only feel frustration.
It may be defined by the job you ended up with (or ultimately want), the opportunities that your PhD led to, or how you define success . Others may say the PhD gave them more credibility, upwards mobility, and technical expertise needed for their job. Others may have pursued a different field apart from their PhD training and claim the PhD served a much different purpose (such as self-discovery).
The skills learned during a PhD are also invaluable in many ways, but the reality is that these transferable skills still don’t seem to be enough by themselves to land your first job in many cases (although very job and company dependent). But whether a PhD program ‘fully’ trains or prepares you for the job market or not, still doesn’t define its worth. The point is that a PhD-even if it doesn’t pay off now-certainly can (or will) later. But one very important point to make is this :
How you define the value of a PhD or if it was worth 5-7 years of your life (and time out of the workforce)-is entirely individualistic .
With that said, let’s go into this article-which is written by Michelle Capes, along with 2 other PhD’s who offer their perspective. Please keep an open mind as you read through the comments, as each PhD will have their own experiences which may be different from your own.
Is A PhD Really Worth It? – Michelle Capes
I am often asked whether my PhD was worth it. Would I do it again?
PhD programs are almost universally trial-by-fire experiences. When they’re completed, many new PhDs find out that they’re underprepared for finding jobs in anything but academia .
This should come as no surprise to any PhD . But the real question is what are you doing about it ? With the flood of articles that are heightening awareness and pitching the idea of careers outside of academia as the norm, it all becomes diluted unless you actually put it into action .
As they begin their job hunt, they run up against the “ overqualified, inexperienced ” wall with a resounding thud. They are often turned away from entry-level positions in favor of bachelors and master’s level candidates, and become disillusioned about having earned their PhD at all.
I decided to ask couple of my colleagues about their thoughts on this question before weighing in with comments of my own. This article will give you three different answers and perspectives on the question “Is A PhD Worth It?” From there, you decide (it is very individualistic).
Debbie completed her PhD in 2012 and is currently on her second postdoc . Although she had funding for another year, she realized that complacency was not an option. She got a head start on her job search by participating in frequent networking events, serving on a committee to organize biotech events in the community, and building up leadership cred by acting as president of her university’s postdoctoral association.
She is no stranger to the frustrations of the job hunt, having weathered some truly frustrating situations: being told, for example, during an informational interview with an industry scientist that she should complete a third postdoc in order to broaden her skill set, and losing out as #2 on the short list after several exhausting interviews.
At the time of this writing, Debbie has accepted a position as Associate Medical Writer at a large contract research organization.
Debbie’s response to “Was your PhD worth it?” was this:
The answer is no longer the obvious ‘yes’ that it would have been in the past. With a tough job market and increasingly high [hiring] standards, having a PhD doesn’t seem to mean as much as it did in the past. However, there is more to the picture as well. Getting my PhD ensured that I was trained to think as a scientist. It altered my whole thought process for the better and that shouldn’t be taken for granted.
Debbie also spoke about her sense of accomplishment:
I kept working through some tough times and finished my degree. I’m proud of that. I eventually realized that the job market is going to be tough at any level – it is what it is. No matter what level you are at, what job you are trying to get, if you apply yourself to networking and distinguishing yourself from the herd, eventually you will earn yourself a good job.
I knew Holly while I was in graduate school, when she was completing a postdoc in a neighboring lab. After the postdoc, Holly became assistant scientist in a clinical research lab , then left for a position with a global leader in the medical device industry . Her pathway toward deciding to pursue a career outside of academia sounds (unsurprisingly) familiar.
Here’s Holly’s response:
Yes, my PhD was completely worth it, although for surprising reasons. Following my decision to pursue a career in the industry, I was unsure of what to expect since I had previously been pursuing an academic track. The decision was largely due to frustration with: (1) the grant landscape (2) the lengthy amount of time to impact patient’s lives pursuing academic research (I was interested in bench-to-bedside science). The benefit of having a PhD was realized as early as my interview. I had pursued a clinical research position and discovered that while PhD’s in the bench-science arena are very common, if not required, in clinical research, it is not necessarily expected. My PhD, along with some experience in clinical research, and the ability to communicate effectively, landed me the job . The most surprising element of my training which has given me the best advantage? My post-doctoral years. These years have set me apart from other colleagues who have a PhD. Having 1 or more post-doctoral years has shown my ability to expand my knowledge into another area , and also the ability to manage my own research ideas and projects . In my experience, research in the industry is not only about what you know – it’s also about project management and the ability to communicate across groups of people .”
Holly continues:
Another benefit of the PhD is the characterization that you are a learner . ‘Learner’ personalities love to expand and grow, which is encouraged in the industry. If [they are] going into industry, someone with a PhD should understand their value is not necessarily the knowledge they bring to the company (although that is important), but the characteristics that are needed to finish a PhD which include: (1) persistence , (2) resilience , (3) idea generation , (4) project management , and, (5) dedication . This list is not comprehensive, but gives a view into the dimensions [that] a PhD has to offer. Potential PhD students, current students and post-graduates should reflect on what their PhD experience will or has taught them, not just about the science, but the soft skills that help to set them apart – I wish it hadn’t taken me so long to figure it out; it might have paid off even sooner .
And I’m back (Michelle Capes).
For my part, I am very happy to have earned my PhD and I would do it again , although not for the original reason I had in mind when I began my program. Sure, I gained a lot of expertise in a niche area of science, and that was all very interesting. But I knew it wouldn’t sustain me for my entire professional career.
When I made the decision to leave academia, I had to capitalize on the other things I learned during grad school and my postdoc, beginning with marketing myself effectively during my job search .
I attained a position as a scientific recruiter precisely because I had a PhD. The agency prided itself on “scientists recruiting scientists,” and having that credential after my name lent credibility to their selling point. (In fact, when my first set of business cards arrived without my credentials, they were immediately re-ordered at the supervisor’s request.)
Now that I have launched my own business venture, I realize that the network I built during graduate school and my postdoc is priceless . I have numerous contacts, both in academia and industry, who know me well and are willing to vouch for my abilities, refer potential clients, and put me in touch with additional colleagues.
It was during the PhD program that I got my first experience doing many of the things that I now offer as services through my business, including grant writing and editing, writing articles, and mentoring . When I pitch these services to prospective clients, having a PhD imparts a high degree of clout. It’s also helpful to be able to point to the successful grant applications I prepared during grad school and my postdoc.
Let’s re-visit the original question: “Is a PhD Worth It?”
I’ve related three positive responses about the value of a PhD. However, a simple Google search will turn up a plethora of negative responses, along with doom-and-gloom articles relating the poor job prospects for PhDs .
If you’re asking this question and you already have your PhD, it probably means that you’re not planning to stay in academia. It likely also means that you’ve made the realization that your training didn’t include the part about looking for jobs, writing resumes, interviewing, etc .
You’re in good company: many other PhDs are waking up to the hard reality that there simply are not enough academic positions for the 64,000-odd PhDs awarded every year in the U.S. alone. Some would make the case that this imbalance is a good thing, because more students are given the chance to succeed and to benefit from one-on-one advice from professors during their education (Source: The Wire ).
Regardless, the realization that too many PhDs were being cranked out for the number of tenured academic positions available set in as early as the 1990’s . Way back then , PhDs were forced to search for employment in other sectors, belatedly realizing that they were woefully unprepared to transition into such careers.
That the situation has not been remediated almost twenty-five years later is reprehensible , especially now that funding crunches are forcing not only new PhDs and postdocs into the non-academic career path, but also established professors .
I recently read an article on The New York Times titled “ When Education Brings Depression .” The comments (which admittedly got off-topic) about the article ranged from personal experiences of depression in grad school to questioning the point of going through graduate school at all, with one reader (we’ll identify her as Suzanne) complaining, “If I had it to do over again, I would never have devoted all those years to a doctorate. Graduate school is definitely a total scam .”
To which “lxp19” replied the following (emphasis added):
It [grad school] is only a scam if you only went into it to get a job…if you went into it thinking it was the ticket to a job…or if you were misled by the department, who sold it as a ticket to a job. Education is about a lot more than getting a particular job. I agree that grad schools need to promote and prepare students for a broader spectrum of professional opportunities. But learning to understand the world in more depth, to develop our own ideas in more depth is not a scam. But it may be an expensive proposition that does not quickly turn into a lucrative career .
One article I came across recently provides a colorful narrative explaining that the only PhD worth getting is in economics , and pointing out the drawbacks of pursuing a PhD in other fields. The author suggests that those who pursue a PhD in the life sciences are either “suicidal fool[s]” or “incomprehensible sociopath[s].”
Further, he cautions, “if you are considering getting a lab science PhD, please immediately hit yourself in the face with a brick. Now you know what it’s like.”
However, the author brings up several caveats, among which was my major bugaboo with the article: “if enough people read and believe this blog post, it will cease to be true. There’s a piece of economics for you: as soon as people become aware that a thing is overvalued, they will start bidding up its price.” Every time there’s a mention of a shortage in X sector, you can be reasonably sure that there will be an excess in 10 years’ time.
(Side thought: You don’t get a PhD for money. If you are-it is for the wrong reasons)
A great example of this is the purported STEM shortage touted by the Obama administration. Though the debate continues to this day as to whether that shortage actually exists, one piece of evidence stands out to me. The National Institutes of Health recently trotted out a program to help new biomedical PhDs find alternative careers in the face of “unattractive” job prospects in the field.
Regardless of the situation across STEM fields as a whole, the situation at the top seems clear: there are too many biomedical PhDs . The overwhelming numbers of resumes that flood in for nearly every industry position posted further bolsters this conclusion .
As a recruiter, I was frequently contacted by PhDs wanting to apply for positions advertized for bachelor’s-level candidates.
The conversations would go something like this: Candidate X calls to inquire about a position with Y Biotech Company. “I’m familiar with that position,” I might say, “and it’s honestly too entry-level for someone with your credentials.” I say this based on the fact that I’ve spoken personally with the hiring manager for the position to see what points they might be flexible on. Hiring a PhD to do menial tasks is not one of them.
Candidate X protests, “but I’m willing to do any kind of [grunt work] and I’m okay with the [horrible] salary. I just want to get my foot in the door in industry.” There it is. Candidate X has told me a whole lot of things about him-/herself that are not conducive to getting a job at Y Biotech .
At this point in the conversation I’m already put off. And then it happens. Candidate X drops the bomb. “Would it help to leave the PhD off my resume?”
This question has sparked numerous, sometimes heated debates—one of which has been raging on LinkedIn since 2011, with almost 400 comments (see http://ow.ly/CkDPq ). This seems like a no-brainer to me: it’s completely unethical. Starting a new position under false pretenses is never a good thing. And nobody —not even the PhDs themselves —really believes that a PhD will be happy with an entry-level industry position involving, say, calibrating lab equipment .
Employers are savvy to this strategy: candidate X will exploit valuable company resources and training to get the critical “1-2 years of industry experience” that every job description seems to require, and then pursue a better opportunity elsewhere. Trying to convince them otherwise simply will not work.
Let’s recap again. Despite my earlier positive reflections on whether getting a PhD is worthwhile, I believe (and I’m sure I’m not alone here) that there should be far, far fewer students entering PhD programs. The job market, be it in academia or industry, just can’t support such a top-heavy pool of candidates, and there are plenty of embittered, unemployed, or underemployed PhDs to prove it .
If you do decide to pursue a PhD, you should know exactly what you want to get out of it. Choose your advisor carefully : if yours is the old-school, 24/7/365 in-the-lab type of person , you will have very little opportunity to do anything other than lab work, let alone career development . When you finish, you’ll be well prepared to be a postdoc. If you decide to pursue a career outside of academia, you will have a very hard time.
Realize that you need MORE than just a PhD . You have to squeeze as many transferable/soft skills as you possibly can out of your degree program . THESE are the skills that will allow you to make a successful transition .
EDUCATE YOURSELF about other sectors and career paths where your skills apply . A lot of PhDs I’ve spoken to have a very narrow view of career opportunities for PhDs in STEM. They are accustomed to doing research in academia, so the default answer for industry seems to be R&D Scientist.
There are so many more opportunities out there that capitalize on your PhD training ! You are severely limiting your chances of finding a job if “R&D Scientist” is the only avenue you pursue. I highly recommend checking out Toby Freedman’s book, “Careers in Biotechnology and Drug Development” to investigate the diverse career paths that are available.
Make a list of possible careers, and write down the value proposition you bring to each one. What I mean is this: just about anyone can do a Western blot or run a PCR. But do you have the sort of dynamism it takes to head up a lab, lead a project, or be effective in a customer-facing role? Did you organize seminars or conferences? Serve in a leadership role? Manage the lab? Mentor people?
Believe me : if you are up against 30 other PhD-level molecular biologists, there have to be extra qualities that differentiate you from the herd.
“Was your PhD worth it?”
If you’re asking yourself this question, here’s my advice: It doesn’t matter. You got your PhD. Be proud of your accomplishment and move on: a defeatist attitude will not get you a job. Remember that YOU get to create the lens that potential employers view you through, and that starts with crafting a positive narrative to explain who you are and what you want to achieve.
Further Reading
The culture of non-responsibility must be changed
Point of view: How postdocs benefit from building a union
Hit the Ground Running: Life After Academia (The PostDocWay)
PhD as a training of the mind
Why won’t anyone respect me for the years of work I’ve done (instead of getting ‘work experience’) and give me a job?
Enough doom and gloom Part 3: Standing upon the great infrastructure of science
About the Author:
Search The Grad Student Way
Most recent posts.
- PhD Career Series: Finding and Developing Your Inner Leader
- Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- PhD Myth Busters: Making the Transition From Academia to Industry
- How A Rock Band Helped Save My PhD
- Dealing With PhD Stress The Right Way: Advice From 3 PhD Graduates
- Write Your PhD Thesis In One Month Or Less
- PhD Career Series: Product Management
- 5 Ways to Gain Valuable Skills Outside of Your Academic Training
- A PhD Student’s Race Against Time – How To Win/Graduate Faster
- Going Freelance Out of Graduate School
- 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Considering Grad School? Important Things You Should Know Before, During, and After Applying
- Short and Sweet: Five Job Hunting Mistakes PhD Graduates Should Avoid
- Welcome To The ‘Academic Fight Club’
Second Income
- Career Development
- Cool Research
- Entrepreneurship
- Grad School Finance
- Grad School Hardships
- Grad School Humor
- Grad School Insights
- Grad School Poetry
- Grad Student Advice Series
- Grad Student Way Background
- Guest Posts
- PhD Careers In-Depth
- Popular Posts
- Post-Doctoral Related
- Professional Development
- Scientific Discoveries
- Transition From Academia Into Industry
- What's The Worst That Can Happen?
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||
Recent Comments
- Andrew Martin on Top 11 Alternative Entry Level PhD Science Careers To Skip the PostDoc
- Ryan Raver on Is A PhD Really Worth It? Or A Waste of Time?
- Ya-Huei Huang on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Krutika I on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- HABIB ULLAH SIDDIQUI on Grad Student Advice Series: 10 Ways To Be A Successful PhD Student
- sgo on 10 Ways To Successfully Defend Your PhD
- Tuscon Peter on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
- Jim on 7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Recent Posts
- October 2018
- November 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Grad School Networking
Featured Posts
Grad Student Advice Series: What to do with your PhD: Post Doc or Real Job?
6 Ways To Survive Grad School and Achieve Work-Life Balance
7 Easy Ways For Graduate Or College Students To Earn Alternative Income Or Make Money Online
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · eleven40 Child Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Who is the director of the Secret Service? Kimberly Cheatle has led agency since 2022
A House Republican leader is planning for an oversight hearing with the U.S. Secret Service after President Donald Trump was shot in the ear at a campaign rally in Pennsylvania on Saturday evening.
Sunday morning the FBI identified Thomas Matthew Crooks as the gunman who opened fire at Trump's rally . The Secret Service reported that the shooter and one rally attendee are dead. Two spectators are critically injured following the shooting.
House Committee on Oversight and Accountability Chairman James Comer, R-Kentucky, made the request for a briefing with the Secret Service and said he would call Kimberly Cheatle, the agency's director, to testify at a hearing.
"My prayers are with President Trump and the victims of the assassination attempt at today’s rally in Pennsylvania. I thank the brave Secret Service members who put their lives at risk to protect President Trump and for the American patriots in the audience who helped innocent victims," Comer said in a news release Saturday. "Political violence in all forms is unamerican and unacceptable. There are many questions and Americans demand answers. I have already contacted the Secret Service for a briefing and am also calling on Secret Service Director Kimberly Cheatle to appear for a hearing. The Oversight Committee will send a formal invitation soon.”
So who is Kimberly Cheatle?
Who is in charge of the Secret Service?
Kimberly Cheatle was sworn in as the 27th director of the U.S. Secret Service in September 2022. She was selected by President Joe Biden in August 2022.
Cheatle has served more than 25 years with distinction for the United States Secret Service across a number of leadership roles. She worked on the Vice Presidential Protective Division, and in 2021, Biden awarded Cheatle with a Presidential Rank Award.
What does the director of the Secret Service do?
In Cheatle's role as director of the U.S. Secret Service, she is in charge of executing protection and investigations for the agency.
The workforce is composed of multiple divisions within the Secret Service including Special Agents, Uniformed Division Officers, Technical Law Enforcement Officers and Administrative, Professional and Technical personnel, according to the Secret Service's website .
What did Kimberly Cheatle do before the Secret Service?
Prior to becoming the Secret Service director, Cheatle worked for PepsiCo as the senior director in Global Security, according to her biography with the Secret Service . There, Cheatle oversaw and directed security protocols for the company's facilities in North America.
Cheatle was the agency's assistant director of the Office of Protective Details, prior to joining PepsiCo. She also served as the Special Agent in Charge of the Secret Service's Atlanta Field Office. In that position, she provided oversight for all missions related to investigation, protective intelligence and protective visits in the state of Georgia.
When will the director of the Secret Service testify?
🚨BREAKING🚨 @RepJamesComer has invited U.S. Secret Service Director Kimberly Cheatle to testify at a hearing on Monday, July 22. Americans demand answers about the assassination attempt of President Trump. pic.twitter.com/zKia2oIxCf — Oversight Committee (@GOPoversight) July 14, 2024
The hearing is expected to take place July 22, 2024, according to a letter from the Committee on Oversight and Accountability.
When was the Secret Service created?
Established in 1865, the U.S. Secret Service is one of the country's oldest federal law enforcement agencies. The U.S. Secret Service Uniformed Division protects the White House Complex and Naval Observatory, according to the Secret Service's website .
One of the newest expansions of the Secret Service's protective missions includes the issuance of Presidential Decision Directives. This established the agency as the lead for coordinating the development and implementation of security plans for National Special Security Events. This covers presidential inaugurations, State of the Union Addresses and other events of national significance.
Kate Kealey is a general assignment reporter for the Des Moines Register. Reach her at [email protected] or follow her on Twitter at @ Kkealey17 .
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Is it worth doing a PhD when an academic career is not the goal?
To read this article for free register now.
Once registered, you can:
- Read free articles
- Get our Editor's Digest and other newsletters
- Follow topics and set up personalised events
- Access Alphaville: our popular markets and finance blog
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.

Should You Get a Master’s or a PhD in Biotechnology?
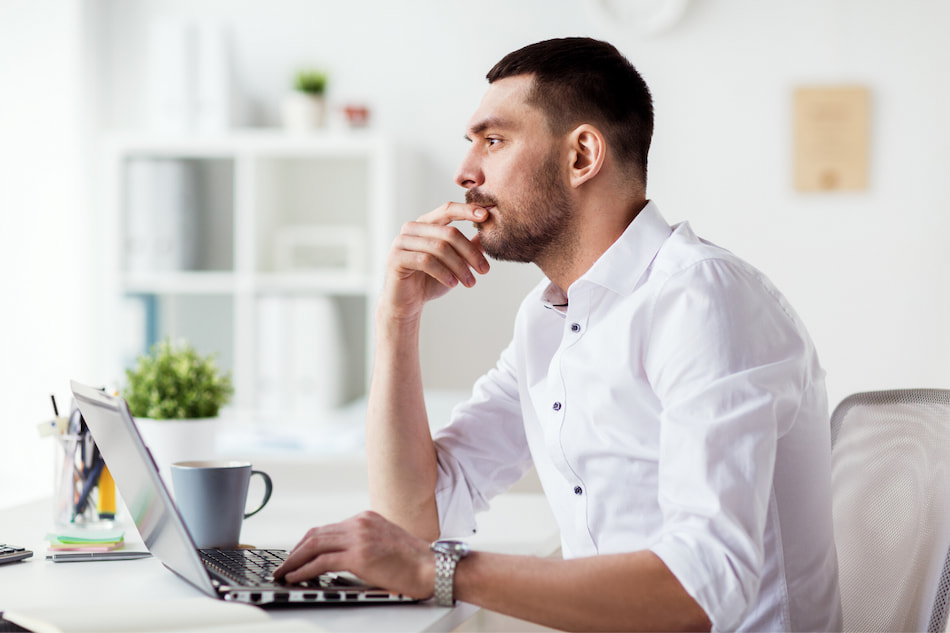

Industry Advice Science & Mathematics
The job outlook for biotechnology professionals is very positive, with 2020 salaries averaging between $80,000 and $90,00 per year. As a result, many individuals are pursuing advanced degrees in biotechnology in hopes of acquiring the training and experience needed to land a role in this lucrative field.
Luckily, those with an undergraduate degree have the benefit of tailoring their graduate education by choosing to enroll in either a biotech master’s or a PhD program. Read on to explore how these two programs differ and what the five key aspects you should consider when deciding which is the right fit for you.
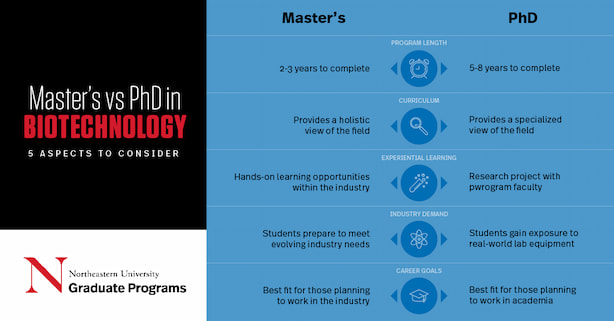
Choosing a Master’s vs. a PhD in Biotechnology: What to Consider
1. your career goals.
Perhaps the most significant question you can ask yourself when picking between a master’s and a PhD is, “What do I intend to do with my degree?”
For example, because PhDs require an extensive time commitment and provide students the chance to explore the academic side of the field, individuals who want to pursue research are best suited for this degree.
“If you want to be an academic, you absolutely have to get a PhD,” says Jared Auclair, director of the biotechnology and bioinformatics programs at Northeastern. Conversely, he explains, “if you want to go work the industry, a master’s is the way to go.”
A master’s degree is designed to transition students seamlessly from the classroom into the workforce. These programs tend to be shorter, and they provide chances for hands-on learning within real-world organizations. In short, they are developed in a way that allows students to begin shaping their careers in biotech before they even graduate.
“Because a master’s degree takes less time schooling-wise, you can go out and work in the industry sooner, get hands-on experience, and then move up in the chain of command,” Auclair says.
Learn More: Industry vs. Academia: Which is Right for You?
PhD candidates considering work in industry (versus academia) are not as easily set up for success. This is because, while a PhD candidate is spending years in a classroom, professionals with master’s degrees are already out in the field collecting valuable real-world experiences that will help prepare them to advance within an organization.
And while there are still some companies that might value a PhD applicant’s extensive study over a master’s degree applicant’s time in the workforce, Auclair explains that, in most cases, a master’s is really all a hiring manager is looking for among applicants.
“In most of the job postings I see…companies are looking for those with master’s [degrees], not PhDs,” he says, noting that there are only a few situations where, in C-level leadership roles specifically, a PhD candidate might have an edge.
2. Curriculum
“A master’s program and a PhD program in biotechnology will have similar coursework,” Auclair says. Both are designed to provide students with an expansive understanding of the field, including the tools, practices, and trends that define it today.
In a PhD program, however, students will have the opportunity to specialize in a specific area of practice within the larger biotechnology field. “A master’s offers a broader depth of training…[whereas] PhDs are trained to do something very specific,” he continues.
As a result, master’s students may end up taking more classes and leaving with a much broader and holistic understanding of the field than their PhD counterparts.
3. Program Length
A master’s program is designed to be completed quickly so that students can explore opportunities within the industry earlier in their careers. At Northeastern, for example, the master’s in biotechnology program can take anywhere from two to three years to complete, depending on whether a student pursues it in a full-time or part-time capacity.
A PhD, on the other hand, requires a much longer time commitment. After completing core classes, PhD students complete a three- to five-year research project with the faculty of their program, effectively delaying their release into the workforce.
4. Experiential Learning Opportunities
The experiential component of a student’s education is perhaps the biggest differentiator in the structures of PhD and master’s programs.
Students who pursue their master’s at Northeastern, for example, have unparalleled opportunities to practice their skills hands-on at organizations in the industry before ever entering the workforce.
“Our master program has a mandatory co-op , which is 12 weeks to six months of experience in the industry,” Auclair says. This paid and credited work provides students with the chance to explore the trends of the industry first-hand, network with leaders in the field, and begin to develop working relationships with organizations they may hope to be employed by after they graduate.
Just as industry experience prepares master’s students to thrive in the field, many PhD programs provide experiential learning opportunities for their students that expose them to the types of research and academia they can expect to pursue post-graduation.
“After you do your mandatory coursework for your PhD, you’re going to do a research project with a faculty,” Auclair says. “And that’s not industry experience, it’s academic research experience, which is completely different.”
This academic research gives students a chance to become comfortable in a lab or research setting, gain exposure to some of the technology and tools they will use in practice, and begin developing working relationships with professors and other university faculty.
5. Demands of the Industry
Some professionals considering an advanced degree do so knowing exactly what they want to do with their careers. For these individuals, the process of deciding between a master’s and a PhD may stop after consideration of their career goals.
However, some individuals embark on advanced education not to fulfill a specific career objective, but to simply pursue their passion for biotechnology. These individuals should think about not only what career opportunities each program might lead to, but which degree will best set them up to meet the current demands of the industry.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic has created a plethora of lucrative possibilities for those in the biotechnology sector. Between a need for expedited vaccine development, a rethinking of telemedicine, and much more, Auclair notes there will be many new and exciting opportunities for those hoping to get involved.
“With COVID…sciences and new technologies are going to evolve rapidly,” he says. “The master’s degree sets you up to be more nimble and flexible [in order] to adapt to those [changes] and to really have a broader impact.”
Though there are opportunities for PhD holders to carve out a place for themselves in the industry, Auclair explains that the depth and type of training required at their level don’t as easily translate.
“Traditionally a person with a PhD is very specialized in one specific technique or aspect of the sciences, whereas somebody with a master’s is [better] able to adapt to the evolution of where the science is going to go. I’m not saying that PhDs can’t do that, but it’s typically not as easy for them.”
Weighing Your Options
If you’re considering a career in biotechnology, an advanced degree provides a perfect opportunity to gain the training and hands-on experience necessary to thrive within this ever-evolving field.
The Master of Science in Biotechnology at Northeastern, for example, has been designed with the input of industry experts and is constantly evolving to best prepare its students to meet the changing needs of the field.
“Part of my mission is to develop all of our programs in collaboration with industry,” Auclair says. “[We] monitor the trends and evolve and adapt as the trends evolve and adapt so that we’re producing people who are ready to work in the business of today or tomorrow, and not of yesterday.”
Northeastern has also taken steps to create opportunities for students who want both the industry exposure of a master’s degree with the cumulative title of a PhD.
The Experiential PhD is a unique program that allows students to work toward their PhD while simultaneously holding a full-time position within the industry. While this degree can be applied to any field, it’s particularly relevant to master’s degree holders who later realize they want to specialize their knowledge or to pivot their career toward research.
Northeastern’s master’s in biotechnology is designed to effectively complement this degree, as well. The Experiential PhD allows students to build off the holistic understanding of the industry obtained at the master’s level, preventing them from repeating much of the same coursework over again as they would in pursuit of a different science-based PhD.
The way it works, Auclair explains, is that “when you have your master’s…and you’re working at a company, you find a mentor in that company and a mentor at the university, and you [choose and then] work on a project that’s interesting to all three of you.”
This type of industry-applicable PhD is ideal for those who have already spent time working within organizations in the field. It allows you to advance your education while still continuing to function as an employee at your company. “You get all the benefits and the money and the salary and everything, but you’re still getting your PhD and it [only takes] three years,” Auclair says.
Take the Next Step
No matter which program you choose, pursuing an advanced degree in biotechnology is sure to be a positive step toward success in this field. If you’re still struggling to determine which path is right for you, consult with an expert in the field. Whether that person is someone in your network that works in biotech or an enrollment coach at Northeastern, (who are well-versed in Northeastern’s variety of programs), gaining some outside perspective can help you make this important career choice.
Explore the master’s in biotechnology at Northeastern on our program page then download our free e-Book to learn more about how you can advance your career in biotechnology.

Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Compliance Specialists: Who They Are and What They Earn
Science or science fiction the future of personalized medicine.

In-Demand Biotechnology Careers Shaping Our Future
Did you know.
The average U.S. bioscience worker earned nearly $99,000 in 2016, 85% greater than the average for the overall private sector. (BIO, 2018)
Master of Science in Biotechnology
An innovative degree for a dynamic industry.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

Healthcare Leadership: What Is It and Why Is It Important?

How To Develop a Project Scope Statement in 8 Steps

What Do Pharmacists Do? Roles and Responsibilities

Should I Go to Grad School: 4 Questions To Consider
College Reality Check
Are PhDs Worth It Anymore? Should You Do It?
A bachelor’s degree can make you earn more money than someone whose highest educational attainment is a high school diploma or an associate degree.
On the other hand, a master’s degree can make you make even more. And if that’s not enough, you can consider getting a PhD, although it’s something that you will have to work hard for.
PhDs are worth it for individuals willing to devote resources to the attainment of the degree that can make them experts in specific fields and open doors to more career opportunities and higher salary potential. This is especially true for those who want to pursue a career in academia or research.
Continue reading if you are thinking about enrolling in a Ph.D. program.
Below, I will try to answer as many pressing questions as you probably have in your mind about getting a PhD, thus allowing you to determine whether you should give it a go or go get employed instead.
Why Should You Do a PhD?
Getting a PhD allows one to enjoy broader career opportunities where having the highest academic degree is an advantage. Naturally, a PhD paves the way to greater earning potential. Typically, individuals who do a PhD wish to reach their full capabilities, become experts in their chosen fields and make a difference.

Let’s get one thing clear: a PhD is an academic degree that takes a lot of time and money to get.
Individuals who are PhD holders, because of this, are quite rare . As a matter of fact, in the US, only around 1.2% of the entire population has a PhD — and this is why they are considered valuable.
While it’s true that completing a PhD program requires a lot of money and hard work as well as can cause stress, anxiety and many sleepless nights, it’s not uncommon for some students to still dedicate much of their resources to earning a PhD. It’s because the returns in terms of career opportunities, earnings and prestige are all worth the commitment.
What are Reasons Not to Do a PhD?
Expensive, time-consuming, requires lots of work, can cause psychological distress — these are some of the disadvantages of getting a PhD. Individuals who are not financially stable, don’t like working for several hours a week and are not fully invested in a discipline should think twice before working on a PhD.
Although there are lots of reasons for you to get your hands on a PhD, there are also some that may keep you from considering applying to a PhD program.
Leading the list is the exorbitant cost — in a few, I will talk about just how expensive a PhD is, so don’t stop reading now. And then there’s also the fact that it can take twice as long to earn a PhD than a bachelor’s degree. Typically, a PhD program can take anywhere from 4 to 5 years to complete. But for many, it can take up to 8 long years!
How long it will take for you to earn a PhD all depends on the program’s curriculum rigor and requirements.
When deciding whether or not you should push through with your plan on getting a PhD, carefully weigh the pros and cons. Dropping out somewhere in the middle of your studies can result in the wastage of both time and money.
How Many Hours Do PhD Students Study?
The vast majority of Ph.D. students spend anywhere from 35 to 40 hours per week studying and completing coursework tasks. In many instances, around 20 hours per week go to lab time or assistantship. As a result of this, enrolling in a Ph.D. program is said to be similar to having a full-time 9-to-5 job.
Undergraduate students are typically encouraged to devote 15 to 20 hours of their time per week studying in order to get good grades — for a final exam, 20 to 30 hours per week is recommended.
Since a PhD is harder, students should study twice as long (or longer) as when they were undergraduates.
During some of the busiest periods in a PhD program, such as when one is writing a dissertation, working substantially longer hours may be warranted. While a timely completion of the coursework and other tasks is obligated, however, students are free to manage their time in a way that goes with their preferences and lifestyles.
Part-time PhD students, by the way, usually work around 17.5 hours per week.
Can Students Work While Earning Their PhDs?
Although challenging, it’s possible for students to work while enrolled in a PhD program. Many working PhD students teach undergraduates at their respective universities. Some are full-time PhD students with part-time work, while others are part-time PhD students with full-time work.
First things first: earning a PhD can be hard and working on a PhD while employed can be harder. But it’s completely doable, particularly with excellent planning and time management.
As mentioned, teaching at a university is one of the most common jobs among working PhD students. But there are many other jobs available for them on and outside of the campus. Some of them are part-time jobs, while others are full-time jobs. Some have contractual work, while others take on more permanent workforce roles.
You can be a full-time employee and a part-time PhD student for better juggling of roles. But just make sure that you will be able to complete your studies within a certain period if such is a requirement at your university.
Do PhD Students Have a Social Life?
PhD students, despite all the rigorous academic and research activities they do, can have a social life. They can socialize with the members of their research group and meet new people during departmental parties and public engagement events. PhD students also have the freedom to manage their own schedule.

Everyone knows that a PhD is the highest level of degree that students can obtain. And it’s also no secret that earning a PhD is associated with a lot of time, stress and anxiety.
It’s a good thing that it’s still very much possible for you to have a social life while working on a PhD.
One of the reasons for such is that PhD students are usually allowed to follow their own schedule for as long as they get the work done. Paired with great time-management skills, you can have room to go out with friends and make new ones. Besides, there are plenty of activities PhD students attend where they can mingle with others.
However, there’s no denying that enjoying a social life can be challenging for PhD students who have to work, too. And, in some instances, one of the two tasks may fail to get ample focus and attention.
Do I Need a Bachelor’s and a Master’s to Get a PhD?
Many PhD programs require a master’s degree. However, there are some where a previously earned master’s degree is not a prerequisite. So, in other words, one may apply straight from a bachelor’s program. In some cases, however, completing a master’s program even if not a requirement can come with benefits.
Saving both time and money — arguably, this is the biggest benefit to have for completing a PhD without a master’s. And then there’s also the fact that you can flex your degree and earn money ASAP.
While there are perks that come with earning a PhD without a master’s, there are some downsides, too.
In some industries, for instance, candidates with both a master’s and a PhD may enjoy an advantage in both employability and salary potential, too. In addition, a prior master’s degree can help you decide much better on the path of your PhD studies and research for a more satisfying and fulfilling outcome.
But keep in mind that while a university may admit applicants to a PhD program without a master’s degree, it may require top-notch and impressive performance in an undergraduate program in exchange for an acceptance letter.
What are Integrated PhDs?
An integrated PhD is a combination of the taught study of a master’s program and the research element of a PhD program. It can take anywhere from 4 to 5 years to complete, depending on the program. At some universities, an integrated PhD degree is commonly referred to as an integrated master’s degree.
Earlier, we talked about the fact that you can work on a PhD without a prior master’s degree.
If the PhD requires a master’s degree or you want to earn one before applying to a PhD program, you may consider what’s referred to as an integrated PhD. As the name suggests, it’s a PhD with a master’s degree integrated into it.
Typically, a traditional PhD takes anywhere from 4 to 6 years to complete. On the other hand, an integrated PhD can take 4 to 5 years to complete — the first 1 to 2 years are for studying the master’s course and the remaining ones are for the completion of the PhD course.
But since an integrated PhD is relatively new, not too many universities offer it.
What are the Easiest PhDs to Get?
Although all PhDs require a lot of time and hard work, some are easier to obtain than the rest because of either lighter coursework and other program requirements or a shorter completion time or both. Many of the easiest PhDs to earn are available online, but only for students with the appropriate learning style.

Naturally, some of the easiest PhDs are those without dissertations, which can take 1 to 2 years to write, not to mention that most PhD students spend a couple of years conducting research and reviewing literature.
The following are some examples of Ph.D. programs minus any dissertation:
- Adult and career education
- Business administration
- Criminal justice
- Educational administration
- Grief counseling
- Human resources
- Information technology
- Nursing practice
- Public administration
- Social work
But keep in mind that different universities may have different PhD completion requirements.
Of all the easiest PhD programs, the general consensus is that most can be found online. But if you are like some students who find online learning more difficult than traditional learning, earning one can still be hard.
What are the Hardest PhDs to Get?
Some PhD programs are longer to complete and involve a lot of complex coursework and other completion requirements, thus making them some of the hardest to earn. Just like among various bachelor’s degrees, some of the most challenging PhDs to earn include those in the STEM- and healthcare-related fields.
In most instances and for most students, a PhD is harder to earn than a master’s degree. And, needless to say, it’s so much harder to obtain than a bachelor’s degree.
But some PhDs are simply more challenging to get than other PhDs.
Just like what’s mentioned earlier, STEM PhD programs are some of the hardest. Many agree that the likes of pure mathematics, theoretical physics, aerospace engineering, chemical engineering and computer science can prove to be so taxing. The same is true for healthcare PhD programs such as pharmacy, nursing and optometry.
Are PhDs Expensive?
The cost of enrolling in a PhD program amounts to $28,000 to $40,000 per year. So, in other words, a full PhD can cost anywhere from $112,000 to $200,000 or up to $320,000 (8 years). Tuition and living expenses are the primary costs of a PhD. There are ways PhD students can get funding for their studies.
Other than time, a PhD can also take up lots of money. Certain factors can impact just how much you will have to spend to get your hands on a PhD, and some of them include the university, program and length of completion.
But did you know that many PhD students don’t have to pay full price?
Because of the steep cost, it’s not uncommon for those who are enrolled in PhD programs to fund their studies through things such as studentships, research council grants, postgraduate loans and employer funding. As a matter of fact, some of them do not pay for their PhD programs — they are, instead, paid to take them.
And just like what we talked about earlier, it’s very much possible for you to be a PhD student and an employee, whether part-time or full-time, at the same time in order to earn money and fund your postgraduate studies.
Is a PhD Worth It Financially?
Without careful planning, completing a PhD program can hurt one’s finances. And if the return on investment (ROI) isn’t that substantial, it can be a waste of resources, too. For many, however, earning a PhD to secure their dream jobs or follow their true callings makes all the financial and time investments worth it.
After discussing just how much a PhD costs, it’s time to talk about if investing in it financially is a good idea.
It’s no secret that, generally speaking, the higher the educational attainment, the higher the earnings. True enough, the median weekly earning of a PhD holder is $1,909.
Doing the math, that’s equivalent to about $99,268 per year. On the other hand, the median weekly earning of a master’s degree holder is $1,574 or $81,848 per year — that’s a difference of $17,420 per year. Please keep in mind that it’s not uncommon for some master’s degree holders to make more than PhD holders.
The difference, however, becomes substantial when the average salary of bachelor’s degree holders is taken into account: $1,334 per week or $69,368 per year, which is $29,882 lower than the annual salary of those with PhDs.
Let’s take a look at the estimated annual median earnings of some PhD holders in some disciplines:
- Engineering: $107,000
- Mathematics: $104,000
- Healthcare: $98,000
- Business: $94,000
- Social science: $90,000
- Physical science: $89,000
- Public policy: $84,000
- Agriculture: $83,000
- Social work: $78,000
- Architecture: $73,000
- Communications: $72,000
Are PhDs in Demand?
PhDs are especially in demand in areas where highly specialized and very high-level research skills are important. Some of the most sought-after PhDs are those in STEM- and healthcare-related fields such as information systems, environmental engineering, chemistry, nursing and physical therapy.
As a general rule of thumb, some of the hardest PhDs to earn tend to be the most in-demand, too.
Simply put, PhDs in disciplines required for a better understanding of currently existing knowledge and challenges, development of modern-day technologies and discovery of new life-changing stuff are highly employable.
And this is why industries such as scientific research and development, manufacturing, health and social work are on the lookout all the time for promising PhD holders. Areas where PhDs are also commonly required include the education sector as well as various segments of the business industry.
Numerous transferable skills learned and developed by students, many of which are appreciated by employers across various industries, also help those with PhDs have increased job market value.
Just Before You Get a PhD
Does getting a PhD still sound great after everything you have read above? Then the smartest step for you to take next is to find the right PhD program for you and apply to it.
But keep in mind that while there are many perks that come with being a PhD holder, there are some sacrifices you will have to make before you get your hands on the prestigious academic degree. But by working hard and staying committed, it won’t take long before you are one of the country’s highest-paid and most satisfied professionals!

I graduated with BA in Nursing and $36,000 in student loan debt from the UCF. After a decade in the workforce, I went back to school to obtain my MBA from UMGC.
Similar Posts

What is a Doctorate Degree?

VIDEO
COMMENTS
I know for a fact that in the consulting industry, fresh PhD grads start at the same lateral level as MBA grads with 3-5 years of prior experience. You'd work 60-80 hours a week, but make 30-40% more than a 9-5 bench scientist in industry. 2.
And a PhD is not a marriage, you can always step down and go back to industry if it becomes a hurdle for you. I would say yes if your goal is to be a PI equivalent / mid to high level management in biotech on the R&D side. Otherwise not really. 5 to 6 years, not 2 to 4.
A general rule of thumb is that without a PhD, you will almost never be able to move up from a bench/hands on work only job. Then do the math on average salary with and without PhD and determine the opportunity cost of doing a PhD in terms of salary loss (and any other personal factors), and whether it is worth it for you. 2.
If OP goes into industry, the last six years could be well worth it! - Sam. Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 19:45. 1 @Sam That's nice, but I never said getting a PhD is a bad idea. I was only correcting the previous poster. ... In some countries DSc is just what a PhD in biology/physics is called, while in other countries DSc is just honorary, while ...
In fact, from a simple employment perspective those with Ph.D.s in science, engineering, and health are doing much better than the general population. In February 2013, the unemployment rate for the general U.S. population was at 6.3% while that of U.S. science, engineering, and health Ph.D.s was way down at 2.1% (7).
Is a PhD worth it? ( self.academia) submitted 1 year ago by [deleted] What are your thoughts and perspectives, I am considering to pursue a PhD in computational biology/neurogenetics but not sure it it worth it in long run (also for jobs after finishing PhD program) 14 comments. share.
I've actually often heard that a computational biology MD/PhD is faster than a wet-lab one. Anecdotally, from the handful of students I've known, 7-year MD/PhDs are more common for computational projects. Like for anyone else, though, at the end of the day it depends on the whims of one's thesis committee! 1 user. T.
I just read an incredibly disheartening post on reddit about Grad School admissions in the Biological sciences. The post basically makes it sound like I have no chance of getting into a good PhD program. I graduated from UC Berkeley with a Degree in Biochemistry in 2012. While in school I worked as an undergraduate researcher for 3.5 years.
Here are nine careers that you can pursue after earning a Ph.D. in biology. For the most up-to-date Indeed salaries, please click on the links below: 1. Postsecondary biological sciences teacher. National average salary: $53,712 per year Primary duties: Postsecondary biological sciences teachers lecture biology students on various related ...
Often in bio Ph.D. programs this takes the form of a unified Molecular Biology department with divisions like genetics, biophysics, computational, biochemistry, etc. It makes sense, if you think about it. An immunology program might only have 2 or 3 slots, but an umbrella biology program would have 10-15 or 20-30 slots to fill.
Mr. Vance spilled scores of details about his life in his coming-of-age memoir. We've collected the highlights. By Shawn McCreesh Follow the latest news from the Republican National Convention ...
In the United States, about 12,500 students obtained a PhD degree in 2014. 2 While in the 1970s more than 50% of PhDs in biology successfully transitioned to a faculty position, this number currently is less than 15%. Just because we are graduating more PhD students each year does not mean that universities will grow their departments and ...
When a PhD Could Be Worth It. 1. Passion for a topic and sheer joy of research. The contribution you make to progressing research is valuable in it's own right. If you enjoy research, can get funding and are passionate about a subject by all means go and do the PhD and I doubt you'll regret it. 2.
In terms of nuts and bolts of building career experience section on a resume, which is often the most important part, a PhD is rarely worth it. (Some STEM careers do require a PhD.) However, at the start of my post-graduate educational journey, I was working part-time running teen programs and full time as a landscaper.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
BoBeard27. • 9 yr. ago. I have my PhD in biochemistry and instead of relaying my personal experience a great book to read before considering graduate school of any kind is "Getting What You Came For" by Robert L. Peters. The only thing I would say is that when interviewing for graduate school positions be sure to ask how the program prepares ...
A doctoral degree is a fantastic opportunity to spend time learning about something that appeals to you. Having an interest in your research area as a PhD student is a massive advantage as you will always be motivated to push the boundaries of your research. Possessing an advanced degree in a field your are genuinely interested in can also help ...
PhD graduates do at least earn more than those with a bachelor's degree. A study in the Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management by Bernard Casey shows that British men with a bachelor's degree earn 14% more than those who could have gone to university but chose not to. The earnings premium for a PhD is 26%. But the premium for a master's degree, which can be accomplished in as ...
3. You'll experience extreme stress and frustration. Pursuing a PhD may seem like a noble and interesting endeavor, and extended life as a student can appear more attractive than wading into the job market. You must be aware, however, that getting a doctorate can be a very stressful and frustrating experience.
The average length of a PhD in biology is around 7 years these days, although it can be 5 or 6, followed by years of postdoc work. The funding environment is terrible and likely to get worse due to Republican antipathy toward science and the poor economy. Again, it's hard to be successful without working long hours.
Here's Holly's response: Yes, my PhD was completely worth it, although for surprising reasons. Following my decision to pursue a career in the industry, I was unsure of what to expect since I had previously been pursuing an academic track. The decision was largely due to frustration with: (1) the grant landscape.
A House Republican leader is planning for an oversight hearing with the U.S. Secret Service after President Donald Trump was shot in the ear at a campaign rally in Pennsylvania on Saturday evening ...
Measuring worth in a purely financial and employment point of view, PhDs have better outcomes than masters or first-degree graduates. Across the UK, 95 per cent of PhDs 15 months after leaving ...
2. Curriculum. "A master's program and a PhD program in biotechnology will have similar coursework," Auclair says. Both are designed to provide students with an expansive understanding of the field, including the tools, practices, and trends that define it today. In a PhD program, however, students will have the opportunity to specialize ...
True enough, the median weekly earning of a PhD holder is $1,909. Doing the math, that's equivalent to about $99,268 per year. On the other hand, the median weekly earning of a master's degree holder is $1,574 or $81,848 per year — that's a difference of $17,420 per year.