4 Steps for Preparing a Grant Proposal Presentation
If you have a lot of experience researching and writing grant applications, your nonprofit might turn to you as your team’s grant proposal writing wizard . But surprise—the next grant you’re applying for requires not just an application but a grant proposal presentation! The grant funder would like to speak with you in person to learn about your nonprofit and understand your request for support.
That means it’s time to put your public speaking hat on and prepare an engaging presentation that helps your organization win the grant. In this post, we’ll explain four steps to building an effective grant proposal presentation:
- Get to know your audience.
- Choose your presentation format deliberately.
- Build a streamlined presentation.
- Add engaging design elements.
You might already have some public speaking experience from presenting at nonprofit conferences and other events. Your grant presentation will require the same level of preparation and confidence even though you’ll be speaking to a much smaller audience. Keep this in mind as you move through these steps.

1. Get to know your audience.
One of the most important considerations for any presentation is knowing who your audience is. When you’re clear on whom you’re speaking to and why you can design your presentation to resonate with your target audience.
So, step one of your presentation planning process is to understand the grant funder’s perspective. What are their stated goals? What types of projects have they funded in the past? What aspects of their mission align with your nonprofit’s mission and goals? Consider contacting the funding organization’s program officer to gather this information.
After answering these questions, you can use your research to design your presentation to appeal to the grant funders. In addition to incorporating audience-specific information into your presentation, keep these other tips in mind:
- Make your presentation accessible to your unique audience. Accessibility means that all audience members can hear and understand your presentation. For example, if your audience members speak more than one language, offer your presentation in alternative language formats. If grant committee members have hearing impairments, provide live captions for your speech or recruit a sign language interpreter.
- Use your grant management software to track information about the funder. Grant management software is an online hub that tracks every aspect of the grant application process, from finding new opportunities to managing relationships with prospective funders. You can use this platform to create a workflow that helps your team research funders, coordinate proposal elements, and keep important files on hand. Grant management software can also help you organize and save the information you gather about funders in a central database where you and your colleagues can easily access it for future presentations to these funders or follow-up reports. These activities can help you create a well-researched presentation that speaks directly to your grant funders’ interests and objectives.
If this is your first time thinking about audience research strategically, you don’t have to do it alone. And, you don’t have to wade through heaps of advice articles on the internet, dodging public speaking cliches to find true guidance. According to Be Brilliant Presentation Group , a speaking coach can work with you to develop effective presentation skills and leverage your unique perspective and strengths. They can help streamline the presentation process and act as a sounding board to bounce ideas off.
Working with a public speaking coach can be worthwhile to ensure your presentation is as effective as possible before delivering it to potential grant funders.
2. Choose your presentation format deliberately.
After conducting audience research, you’ll be ready to start structuring your presentation. But don’t log into Google Slides or fire up PowerPoint just yet! Think deliberately about how you want to deliver your grant presentation for maximum impact.
Before choosing your presentation format, answer the following questions:
- Will you be able to use visual aids such as a slideshow, video, or handout? Or will you have to rely on your speech alone to make your case? You’ll have to structure your presentation differently depending on whether you can use visual aids.
- Will the presentation be in person or on a video meeting platform like Zoom? If you are presenting in person, you’ll have to determine whether there will be a screen you can use to display visual aids. If you’re presenting over video chat, you’ll have to practice with the video tools and prepare your background.
- Do you have any time constraints? If your presentation has a time limit, you’ll have to design it to fit within the restrictions. If the limit feels short to you, think strategically about including only the most critical information that will help you get your point across succinctly and effectively.
After answering these questions, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the types of presentation aids and tools you can use during the presentation. Then, you can craft a presentation that smoothly guides audience members from point to point and makes a strong case for why your organization deserves the grant.
3. Build a streamlined presentation.
If you’re required to submit both a grant application and an oral presentation, use your presentation time wisely. Don’t read your grant application word for word—just hit the highlights. Supplement the information in your application with stories, examples, and visual aids to build a well-rounded presentation.
Follow these steps to craft your streamlined grant presentation:
- Provide background information on your nonprofit. Make sure the grant committee understands your organization’s mission and how your nonprofit was started. Explain the day-to-day programs and projects you manage that help work toward your mission.
- Explain your need and how you plan to use the funding. Next, describe why you’re seeking grant funding and how you plan to put the funding to good use. The grant committee will need specifics here, so be very clear about your plans. Describe what the funding will go toward and why the project matters in the grand scheme of your mission. Learn more about Simple Steps to Write an Executive Summary .
- Use data and research to build credibility. Use data from your past projects and general research to make specific projections for what you can achieve with grant funding. For example, let’s say you’re hoping to earn grant funding to expand your community garden . In your presentation, you might reference studies that show how expanding community gardens reduces violent crime. You might also include evidence from your organization’s research and surveys that shows that your community garden increased community wellbeing.
- Wrap up with a compelling final appeal. Finishing with an appeal to emotion can make your presentation memorable and persuasive. For example, you might tell a story at the beginning of your presentation that you wrap up at the end. Or, you might leave the grant committee with one final look at an image of a community member who will be able to access help because of grant funding.
Make sure to follow any specific guidelines required by the grant committee as you build your presentation. Create a checklist based on the tips above and the grant funders’ requirements to ensure your presentation includes the content it needs to be effective and meet all guidelines.
4. Add engaging design elements.
Any visual presentation aids should support your argument, not distract from it. When you choose engaging, informative visuals, you can appeal to the visual learners in the audience and create a more interesting presentation overall.
Keep these tips in mind as you design your presentation :
- Brand the presentation to your organization. According to Getting Attention’s nonprofit branding guide, your brand affects how people view and engage with your organization, “impacting whether or not they’re willing to support your mission in any way.” When you brand your presentation to your organization, you can reinforce brand recognition and enhance the professionalism of your speech. This helps build trust with your audience, showing the grant committee that your nonprofit is well-established and can be relied on to use funding wisely.
- Include compelling images. Choose original images your organization owns (not stock photos) to bring your presentation to life. Include photos of your volunteers, staff, and individuals that your organization helped. Specifically, select visuals that illustrate your nonprofit’s mission in action. For example, if you’re a conservation organization, you might include a before and after picture of the forest that your organization has worked to restore.
- Consider incorporating audience engagement. Including interactive elements within your grant presentation can help it stand out. A few audience engagement ideas include asking for a volunteer to complete a demonstration, handing out a survey for the grant committee to fill out during your presentation, or taking polls throughout with a show of hands.
As you finalize your presentation, ensure your visual elements are uniform and cohesive. For example, double-check that your font sizes are consistent throughout, your logo use is identical across slides, and the colors you use on each slide are visually appealing. Perfecting even the most minor details of your presentation will make a difference by adding credibility to your grant request.
As your grant presentation date approaches, you may start growing anxious. You might think, “I need to deliver a flawless presentation, or we may lose out on important grant funding.” While these thoughts are natural and understandable, step back every so often and take a deep breath throughout your planning process.
Know that when you follow these tips (and work with a presentation coach as necessary), there’s no reason you shouldn’t be able to create a compelling presentation that makes a strong case for your organization. You’ll be well prepared with the tools and strategies you need to impress the grant committee and hopefully earn funding for your mission. Good luck!
This blog is an original work of the attributed author and is shared with permission via Foundant Technologies' website for informative purposes only as part of our educational content in the philanthropic sector. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text belong solely to the author and do not necessarily reflect Foundant's stance on this topic. If you have questions or comments, please reach out to our team.

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
04 Compelling Research Grant Proposal Presentation Tips
I. Preparation for Grant Proposal Presentation
Ii. structuring the grant proposal presentation, iii. creating visual aids for grant proposal presentation, iv. tips for delivering a successful grant proposal presentation, references and resources, introduction.
In today’s competitive funding landscape, grant proposal presentations are becoming increasingly important for researchers and organizations seeking to secure research grants. Whether you are presenting to a government agency, a private foundation, or an industry partner, a well-crafted grant proposal presentation can make all the difference in persuading funders to support your research project.
Grant proposal presentations are a crucial opportunity to make a compelling case for your research project, demonstrate your expertise and credibility, and show how your work aligns with the funder’s priorities and goals. A well-designed presentation can help you stand out from the competition and increase your chances of securing the funding you need to carry out your research.
In this post, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to make a research fund proposal presentation that effectively communicates the significance of your research, your research design and methodology, your preliminary results, and the potential impact of your work. We will also provide tips on creating effective visual aids, delivering a successful presentation, and addressing potential questions and concerns.
By the end of this post, you will have a clear roadmap for creating a winning grant proposal presentation that will impress funders and help you secure the funding you need for your research.
In case you are not familiar with writing research grant proposals, then please visit my post on Research Grants Uncovered: A Step-by-Step Guide to Funding Your Research Projects . This post will help you in writing powerful research grant proposals in minimal time.
- Identify the target audience: For example, if you are presenting to a funding agency that specializes in cybersecurity research, your target audience may consist of cybersecurity experts and policymakers who are interested in advancing the state of the art in this field. Understanding your target audience will help you tailor your presentation to their interests and priorities, and craft a message that resonates with them.
- Research the funder’s requirements and guidelines: For example, if you are applying for a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant in computer science , you will need to follow the NSF’s guidelines for proposal preparation, which include specific formatting requirements, page limits, and sections to include. You will also need to ensure that your proposed research aligns with the NSF’s mission and research priorities. Familiarizing yourself with the funder’s requirements and guidelines will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure that your proposal meets all the necessary criteria.
- Determine the key points to cover in the presentation: For example, if you are proposing a research project in computer security, some key points to cover in your presentation might include the significance of the problem you are addressing (e.g., the increasing threat of cyberattacks), the research questions you will be investigating (e.g., how to detect and prevent advanced persistent threats), your proposed research design and methodology (e.g., using machine learning to analyze network traffic), and the potential impact of your work (e.g., improving the security of critical infrastructure). Determining the key points you want to cover in your presentation will help you structure your message and ensure that you are communicating the most important aspects of your research to your audience.
- Start with a clear and concise introduction: Begin by introducing yourself and your research project. Explain the purpose of your presentation and provide an overview of what you will be covering. For example:
- “Good morning, my name is [name], and I am a computer science researcher at [institution]. Today, I am excited to present my research project on [project title], which focuses on [brief description of the project].”
- Provide background information: Explain the context and significance of your research project. Describe the current state of the art in your field, and highlight the gaps or limitations that your research aims to address. For example:
- “As you may know, cyber attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and difficult to detect. Current security systems rely on signature-based approaches, which are ineffective against advanced persistent threats. My research project aims to develop a machine learning-based system that can detect and prevent such attacks.”
- Outline your methodology: Describe your research design and methodology in detail, including any data sources, algorithms, or tools you will be using. Be clear and concise, and avoid technical jargon as much as possible. For example:
- “To achieve our research goals, we will be using a combination of supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms to analyze network traffic data. We will also be using feature selection and dimensionality reduction techniques to improve the accuracy and efficiency of our models.”
- Present your preliminary results: Share any preliminary results or findings you have obtained so far, highlighting their significance and potential impact. Be honest about any limitations or challenges you have encountered, and explain how you plan to address them. For example:
- “Our preliminary results show that our machine learning-based system is able to detect advanced persistent threats with a higher accuracy rate than existing signature-based systems. However, we have encountered some challenges with the size and complexity of the data, and we plan to explore additional feature engineering techniques to improve our models.”
- Discuss the potential impact of your research: Explain how your research project has the potential to advance the state of the art in your field, and how it aligns with the funder’s mission and research priorities. Use concrete examples to illustrate the real-world applications and benefits of your work. For example:
- “Our research has the potential to revolutionize the way we detect and prevent cyber attacks, and to improve the security of critical infrastructure such as power grids, transportation systems, and healthcare networks. By developing a more accurate and efficient machine learning-based system, we can help organizations stay one step ahead of sophisticated cyber threats.”
- Provide a clear budget: Explain how you plan to allocate the funds you are requesting, and provide a detailed budget that includes all the necessary expenses, such as equipment, personnel, and travel. Be realistic and transparent, and avoid over- or underestimating the costs. For example:
- “Our budget includes the cost of hiring two postdoctoral researchers, purchasing high-performance computing equipment, and attending relevant conferences and workshops. We have carefully calculated the costs of each item and ensured that our budget is realistic and reasonable.”
- Conclusion and next steps: Summarize the key points of your presentation, reiterate the significance and potential impact of your research project, and provide a clear call to action for your audience. For example:
- “In conclusion, our research project on [project title] has the potential to make significant contributions to the field of computer security, and to improve the security of critical infrastructure. We believe that our proposed methodology and research design are sound, and that we have the expertise and resources necessary to carry out this project successfully. We thank you for your attention and look
- The role of visual aids in grant proposal presentations: Visual aids are an important part of any grant proposal presentation, as they help to convey complex information in a clear and engaging way. They can also help to highlight key points, emphasize the significance of your research, and make your presentation more memorable. For example:
- “Visual aids such as graphs, charts, and images can help to illustrate our research findings and make our presentation more engaging for the audience. They can also help to convey complex information more clearly and concisely.”
- How to create effective visual aids: When creating visual aids for your grant proposal presentation, it is important to keep the following tips in mind:
- Keep it simple: Use clear and simple graphics that are easy to understand. Avoid cluttering your slides with too much information or too many images.
- Use relevant and accurate data: Use data that is relevant to your research project and accurately reflects your findings. Be sure to cite your sources if necessary.
- Emphasize key points: Use visual aids to highlight key points and draw attention to important findings or trends. Use contrasting colors or fonts to make important information stand out.
- Use appropriate visuals: Choose visuals that are appropriate for your research project and audience. For example, use flowcharts or diagrams to illustrate complex processes, and use graphs or charts to illustrate numerical data.
For example:
- “When creating visual aids for our grant proposal presentation, we made sure to use clear and simple graphics that accurately reflect our findings. We used graphs and charts to illustrate our numerical data, and flowcharts to illustrate our research methodology. We also used contrasting colors and fonts to highlight key points and draw attention to important information.”
- Practice, practice, practice: Practice your proposal presentation several times before the actual presentation date. This will help you to become more comfortable with the material, identify any areas that need improvement, and ensure that you stay within the allotted time frame. You can also practice in front of colleagues or friends to receive feedback.
- Speak clearly and confidently: Speak clearly and at an appropriate pace to ensure that your audience can understand you. Use pauses and emphasize key points to add emphasis to your presentation. Additionally, try to maintain eye contact with your audience to help build a connection.
- Engage with your audience: Engage with your audience by using storytelling, asking questions, or using humor to keep them engaged and interested. You can also provide examples and use case studies to illustrate your research findings.
- Address potential questions and concerns: Anticipate potential questions and concerns from your audience and be prepared to address them. This will help to build confidence and demonstrate your expertise in the subject matter. You can also provide handouts or additional materials to address any further questions or concerns.
- “When delivering our proposal presentation, we made sure to practice multiple times to ensure that we were comfortable with the material and stayed within the allotted time frame. We also spoke clearly and confidently, using pauses and emphasizing key points to keep our audience engaged. We provided examples and case studies to illustrate our research findings, and we anticipated potential questions and concerns to ensure that we were prepared to address them.”
In this post, we discussed how to create an effective research fund proposal presentation. We covered topics such as preparation, structuring the presentation, creating visual aids, and delivering a successful presentation.
Effective proposal presentations are critical to securing funding for research projects. A well-structured and engaging presentation can help to highlight the significance of your research, convey complex information clearly and concisely, and demonstrate your expertise in the subject matter.
By following the tips and best practices outlined in this post, you can create a successful grant proposal presentation that will increase your chances of securing funding for your research project. Remember to practice your presentation, speak clearly and confidently, engage with your audience, and address potential questions and concerns.
- National Science Foundation (NSF): The NSF provides funding for research in a variety of scientific and engineering fields. The NSF’s Grant Proposal Guide includes guidelines and tips for creating effective grant proposal presentations.
- Grant Writing Tips Sheets by NIH Office of Extramural Research: The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides grant writing tip sheets on various topics, including developing a budget, writing a cover letter, and creating effective visual aids for grant proposal presentations.
- American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) : The AAAS provides resources and webinars on grant writing and effective grant proposal presentations. Their website includes information on finding funding opportunities, preparing grant applications, and submitting proposals.
- Science Communication Lab: The Science Communication Lab provides resources and training for scientists and researchers to communicate their work effectively to a variety of audiences, including fund proposal presentations. They offer workshops, webinars, and online courses on topics such as storytelling, public speaking, and creating effective visuals.
- Online presentation tools: There are several online tools that can be helpful for creating effective fund proposals presentations, such as Prezi , Canva , and Slidebean . These tools offer a variety of templates, graphics, and design features that can help to make your presentation more engaging and professional-looking.
If you’re looking for additional resources and references to help you create an effective fund proposal presentation, here are some helpful options to consider.
- The National Science Foundation (NSF) provides a Grant Proposal Guide that includes tips and guidelines for creating effective grant proposal presentations.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) also provides grant writing tip sheets that cover a range of topics, including creating effective visual aids.
- The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) offers resources and webinars on grant writing and communication, and the Science Communication Lab provides training and resources on public speaking and storytelling.
- Additionally, online presentation tools such as Prezi, Canva, and Slidebean can be helpful for creating engaging and professional-looking visual aids.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Best 5 Journals for Quick Review and High Impact in August 2024
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

Grant Proposal Presentation Example
A grant proposal is an investment request for a nonprofit or a for-profit project. A successful grant proposal shows the grantee (the organization or individual investing) that the investment is worth their time and money.
To be successful, a grant proposal needs to define your organization’s goals, explain the impact of those goals, how you plan to achieve them, and how your grantee can make a difference with their funds. Using a grant proposal template can ensure that your presentation has everything it needs to wow your potential investors.
The most effective grant proposal presentation examples are used to:
- Convince grantees to invest in your project
- Raise funds for your nonprofit or business
- Explain to stakeholders how you’ll achieve specific objectives
A Grant Proposal Presentation Example
Each slide in your grant proposal plays an important role. Drive your point home by adding images, tables, charts, and video to your grant proposal. Each of these is available with your template and can be added with a single click. The slides used in our grant proposal presentation example are:

Pro Tips from our Grant Proposal Presentation Example
Here are a few ways you can customize a grant proposal presentation template:
Give your audience the basics up front: your organization, your mission, and why your proposed project fits that mission.
A grant letter is a shorter document, around a few pages, that’s less formal and more succinct. A full grant proposal is more detailed and can be as long as 20 to 25 pages.
Do your research on your grantees. Explain why funding your project will benefit their values and goals.
Stick to one topic or idea per slide. Your presentation will flow more smoothly and give your audience time to absorb what you’re saying.
More Popular Templates

Reddit Presentation Template
The popular site Reddit helps users engage with communities and conversations of varying topics so we’ve revamped their presentation deck to help them create more engagement with their presentations.

Investment Proposal Template
Inform and impress potential investors by using an investment proposal template to craft your story.

Agile Workflow Presentation Template
Learn how Beautiful.ai’s agile workflow template can help teams examine their current processes and look for ways to improve them.

Content Marketing Plan Template
Use a content marketing plan template to create, plan and organize a content strategy.

Agency Pitch Presentation Template
Beautiful.ai’s agency pitch presentation template showcases your team and what you do. Pitch your agency with an ai presentation template that matches your creativity and brand.

Total Addressable Market (TAM) Presentation Template
Learn how Beautiful.ai’s total addressable market (TAM) presentation template can help businesses identify the demand for their product or service.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write a Successful Research Grant Proposal: An Overview

Writing a research grant proposal can be a challenging task, especially for those who are new to the process. However, a well-written proposal can increase the chances of receiving the necessary funding for your research.
This guide discusses the key criteria to consider when writing a grant proposal and what to include in each section.
Table of Contents
Key criteria to consider
When writing a grant proposal, there are five main criteria that you need to consider. These are:
- Significance
- Innovation
- Investigators
- Environment
The funding body will look for these criteria throughout your statement, so it’s important to tailor what you say and how you say it accordingly.
1. Significance
Significance refers to the value of the research you are proposing. It should address an important research problem and be significant in your field or for society. Think about what you are hoping to find and how it could be valuable in the industry or area you are working in. What does success look like? What could follow-on work lead to?
2. Approach
Approach refers to the methods and techniques you plan to use. The funding body will be looking at how well-developed and integrated your framework, design, methods, and analysis are. They will also want to know if you have considered any problem areas and alternative approaches. Experimental design, data collection and processing, and ethical considerations all fall under this group.
3. Innovation
Innovation means that you are proposing something new and original. Your aims should be original and innovative, or your proposed methods and approaches should be new and novel . Ideally both would be true. Your project should also challenge existing paradigms or develop new methodologies or technologies.
4. Investigators
Investigators here refer to you and your team, or proposed team. The funding body will want to know if you are well-trained and have the right qualifications and experience to conduct the research . This is important as it shows you have the ability to undertake the research successfully. One part of this evaluation will be, have you been awarded grants in the past. This is one reason to start early in your career with grant applications to smaller funds to build up a track record.
5. Environment
Environment refers to the scientific environment in which the work will be done. The funding body will want to know if the scientific environment will contribute to the overall probability of success. This could include your institution, the building or lab you will be working in, and any collaborative arrangements you have in place. Any similar research work conducted in your institution in the past will show that your environment is likely to be appropriate.

Writing the grant proposal
It’s almost impossible to generalize across funders, since each has its own highly specific format for applications, but most applications have the following sections in common.
1. Abstract
The abstract is a summary of your research proposal. It should be around 150 to 200 words and summarize your aims, the gap in literature, the methods you plan to use, and how long you might take.
2. Literature Review
The literature review is a review of the literature related to your field. It should summarize the research within your field, speaking about the top research papers and review papers. You should mention any existing knowledge about your topic and any preliminary data you have. If you have any hypotheses, you can add them at the end of the literature review.
The aims section needs to be very clear about what your aims are for the project. You should have a couple of aims if you are looking for funding for two or three years. State your aims clearly using strong action words.
4. Significance
In this section, you should sell the significance of your research. Explain why your research is important and why you deserve the funding.
Defining Your Research Questions
It’s essential to identify the research questions you want to answer when writing a grant proposal. It’s also crucial to determine the potential impact of your research and narrow your focus.
1.Innovation and Originality
Innovation is critical in demonstrating that your research is original and has a unique approach compared to existing research. In this section, it’s essential to highlight the importance of the problem you’re addressing, any critical barriers to progress in the field, and how your project will improve scientific knowledge and technical capabilities. You should also demonstrate whether your methods, technologies, and approach are unique.
2. Research approach and methodology
Your research approach and methodology are crucial components of your grant proposal. In the approach section, you should outline your research methodology, starting with an overview that summarizes your aims and hypotheses. You should also introduce your research team and justify their involvement in the project, highlighting their academic background and experience. Additionally, you should describe their roles within the team. It’s also important to include a timeline that breaks down your research plan into different stages, each with specific goals.
In the methodology section, detail your research methods, anticipated results, and limitations. Be sure to consider the potential limitations that could occur and provide solutions to overcome them. Remember, never give a limitation without providing a solution.

Common reasons for grant failure
Knowing the common reasons why grant proposals fail can help you avoid making these mistakes. The five key reasons for grant failure are:
- Poor science – The quality of the research is not high enough.
- Poor organization – The proposal is not organized in a clear way.
- Poor integration – The proposal lacks clear integration between different sections.
- Contradiction – The proposal contradicts itself.
- Lack of qualifications or experienc e – The researcher lacks the necessary qualifications or experience to conduct the research.
By avoiding these pitfalls, you will increase your chances of receiving the funding you need to carry out your research successfully.
Tips for writing a strong grant proposal
Writing a successful grant proposal requires careful planning and execution. Here are some tips to help you create a strong grant proposal:
- Begin writing your proposal early. Grant proposals take time and effort to write. Start as early as possible to give yourself enough time to refine your ideas and address any issues that arise.
- Read the guidelines carefully . Make sure to read the guidelines thoroughly before you start writing. This will help you understand the requirements and expectations of the funding agency.
- Use clear, concise language . Avoid using technical jargon and complex language. Write in a way that is easy to understand and conveys your ideas clearly. It’s important to note that grant reviewers are not likely to be domain experts in your field.
- Show, don’t tell . Use specific examples and evidence to support your claims. This will help to make your grant proposal more convincing.
- Get feedback . Ask colleagues, mentors, or other experts to review your proposal and provide feedback. This will help you identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Writing a successful grant proposal is an important skill for any researcher. By following the key criteria and tips outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of securing funding for your research. Remember to be clear, concise, and innovative in your writing, and to address any potential weaknesses in your proposal. With a well-written grant proposal, you can make your research goals a reality.
If you are looking for help with your grant application, come talk to us at GrantDesk. We have grant experts who are ready to help you get the research funding you need.
Related Posts

Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Journal Turnaround Time: Researcher.Life and Scholarly Intelligence Join Hands to Empower Researchers with Publication Time Insights
- Product Catalog
- Services Overview
- Digital Assessment Tool
- Website Services
- Digital Marketing
- TechSoup Courses
- Consultant Connection
- Community Home
- Upcoming Events and Webinars
- Articles & How-Tos
- Events and Webinars Archive
- Impact Stories (495)
- Impact Stories Microsoft (352)
- Marketing and Communications (300)
- Tech Planning (194)
- Donor Management (141)
- Operations (140)
- IT Security (135)
- The Cloud (118)
- Web Development (118)
- TechSoup (114)
- Libraries (108)
- Social Media (101)
- Data Management (90)
- Education (75)
- Graphic Design (55)
- Hardware (49)
- Digital Divide (43)
- Grant Writing (40)
- Impact Stories Cisco (39)
- Accounting (35)
- The Future of Work (35)
- Impact Stories Intuit (34)
- Project Management (23)
- Impact Stories Symantec (22)
- Impact Stories Adobe (21)
- Event Planning (18)
- Disaster Preparedness (14)
- Impact Stories Veritas (13)
- E-Commerce (9)
- Impact Stories Autodesk (2)
- Impact Stories Box (2)
- Impact Stories ClickTime (2)
- Impact Stories NortonLifeLock (2)
- Impact Stories Shopify (2)
- Impact Stories Dell (1)
- Impact Stories Mailshell (1)
- Impact Stories ReadyTalk (1)
- Impact Stories Refurbished Computers (1)
- IT Security
- Donor Management
- Impact Stories
- Marketing and Communications
- Social Media
- Data Management
- The Future of Work
- Web Development
- Tech Planning
- Digital Divide
- Graphic Design
- Event Planning
- Grant Writing
- Project Management
- Disaster Preparedness
- Norton LifeLock

Getting the Grant: A Guide to Your First Grant Presentation

5 minute read
If you are new to grantmaking, preparing for a grant presentation can be a confusing and overwhelming task. Whether in person, over the phone, or on a video call, a presentation is an opportunity to convince a funder that you should be invited to apply for a grant. It doesn't take the place of a proposal, but rather gives the funder a taste of the work you are doing in order to decide whether they should invite your proposal. Read on for a guide on landing a grant presentation, what to include, and how to make the most of the opportunity.

Doing the Groundwork
Some grantmaking organizations do not accept unsolicited proposals or cold emails. This means that in order for a funder to read your proposal or listen to your presentation, you've got to build a relationship first. Utilize any preexisting relationships between people on your staff team or board and the staff at the foundation you're interested in. Once you've got a foot in the door, ask for an introduction to the relevant program manager, as this is ultimately who you'll want to build a relationship with. In the absence of any preexisting relationships, you can try to find a staff member's email on the website, or reach out on LinkedIn.
Preparing Well
So, you've opened a door with the organization and set up a meeting with the program officer. Great! As you prepare for your conversation, there are a few things you can do to ensure that you're as informed and prepared as you can be.
The first, vital step is to ensure that your project is within the parameters of what the foundation might fund. Look through their website and try to find guidelines on the types of projects they give grants to, as well as some organizations they've funded in the past. This will help you to evaluate whether your project fits with their goals. If it doesn't align, you may be wasting your time by chasing the grant. Most grantmaking organizations have tight guidelines on which kinds of projects they will fund. If your project sits outside those guidelines, you'll most likely be turned away, and you're better off finding a funder that aligns more closely with your project.
If your organization's work does sit within the parameters of the foundation's goals, use the website to gain a deeper understanding of the grantmaking process in this organization. Take note of the language they use when talking about the kind of work you do, and try to (subtly) reflect this in your presentation. You may also be able to find information on the timelines they operate on and the amounts they award. This way, you'll go into the presentation well informed about what you might ask from the funder.
Consider the format of your meeting as you prepare. If it's in person or on a video call, bring a slide deck with some high-level information about your organization and its work. If it's an in-person meeting, you can also bring some materials to leave with the program manager — perhaps a one-pager summarizing the project and your organization's background. You may also want to bring someone else with you. The person who made the initial introduction to the organization might be a good pick, or a subject matter expert if the project is particularly technical. If the meeting is over the phone, it may be more casual and conversational, and less in the style of a presentation.
Delivering the Presentation
During the presentation, remember that in most cases the aim is simply to have the program manager accept a grant proposal from you. For that to happen, they need to be convinced of the value of the work you are doing and that it fits within the grantmaker's funding goals. With that in mind, here are some guidelines for how to structure your presentation and curate the information you include.
History and Impact
Give the program officer an overview of how your organization came to be and your impact to date. Don't flood them with statistics, but explain the work you are currently doing and back it up with some compelling metrics that show its value. If your organization has been around for a while, a growth curve can be a helpful way of demonstrating the development in your work.
Once you've helped the program officer understand your organization as a whole, zoom in on what specifically you are fundraising for. This might be a project, an event, or perhaps general operational support for your organization. If you're running more than one project that you think they might fund, explain each one and give them options: you might be surprised at which project they are more interested in. Incorporate the research you did before the conversation, thinking about the language you use and how to best align it with the funder's theory of change.
A Conversational Approach
A grant presentation is both an opportunity for the grantmaker to learn about your organization and for you to learn more about them. Ask questions in order to better understand what they are looking for and pay attention to the language they use when talking about the issues you're working on. You may want to incorporate some of the language they use into your proposal, if the presentation goes well.
Give the program officer plenty of space to ask you questions, too. This is an opportunity to fill any gaps in your presentation, and possibly to dive deeper into certain elements of the project. Don't be afraid to get back to them later on if there's a question that requires some research or the help of a colleague.
Following Up
Make sure you don't leave the meeting without a specific, next-step request. Ask the program manager outright if they think this could be a good fit and if they would be willing to read a proposal. It's helpful to have them explain the next steps of the process to you, even if these details are on their website. If it's relevant and the funder is local, you could invite them to a site visit: some program officers do this anyway as part of their process. This can provide a more holistic view of what you do, as well as an opportunity to meet other members of your staff. By the end of the meeting, you should aim to have a clear yes or no answer about whether you will be moving forward with the proposal process. If the answer is no, ask the program officer if they have any suggestions on funders who might be more likely to support your effort.
Importantly, you should maintain a relationship with the program manager, even if you are unsuccessful in proceeding with the grantmaking process. Connect with them on LinkedIn and keep them on your mailing lists if you can, as you never know when this kind of relationship will be useful for a future grant or project.
Getting the Grant
Applying for grants is a delicate and sometimes frustrating process, and the first grants you win may well be the hardest. A grant presentation is a great way to build a relationship with an organization, and a way in with funders who do not accept unsolicited applications. Use a conversational and informative approach to showcase your brilliant work and get your project funded.
Additional Resources
- Sign up for TechSoup Courses' series on Grant Writing and Management .
- Have you Never Applied for a Grant? Here's What You Need to Know .
- Get a GrantStation 1-Year Membership at a huge savings.
- View a recorded Executive Directors Chat with TechSoup: Grant Writing Tips and More .
Top photo: Shutterstock
Related Content

More TechSoup
- Our Mission
- TechSoup Global Network
- Meet Our Donor Partners
- Meet Our Funders
- Anti-Discrimination Policy
Get in Touch
- Donate and Invest
- Partner with TechSoup
- Digital Resilience Program
- Returns and Refunds
- Media and Press
Subscribe to Our Newsletters
Get technology news and updates on exciting new offers from TechSoup.
Copyright © 2024, TechSoup Global. All Rights Reserved.
- Cookie Settings
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy

Home » Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide
Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide
Table of Contents

Grant Proposal
Grant Proposal is a written document that outlines a request for funding from a grant-making organization, such as a government agency, foundation, or private donor. The purpose of a grant proposal is to present a compelling case for why an individual, organization, or project deserves financial support.
Grant Proposal Outline
While the structure and specific sections of a grant proposal can vary depending on the funder’s requirements, here is a common outline that you can use as a starting point for developing your grant proposal:
- Brief overview of the project and its significance.
- Summary of the funding request and project goals.
- Key highlights and anticipated outcomes.
- Background information on the issue or problem being addressed.
- Explanation of the project’s relevance and importance.
- Clear statement of the project’s objectives.
- Detailed description of the problem or need to be addressed.
- Supporting evidence and data to demonstrate the extent and impact of the problem.
- Identification of the target population or beneficiaries.
- Broad goals that describe the desired outcomes of the project.
- Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that contribute to the goals.
- Description of the strategies, activities, and interventions to achieve the objectives.
- Explanation of the project’s implementation plan, timeline, and key milestones.
- Roles and responsibilities of project staff and partners.
- Plan for assessing the project’s effectiveness and measuring its impact.
- Description of the data collection methods, tools, and indicators used for evaluation.
- Explanation of how the results will be used to improve the project.
- Comprehensive breakdown of project expenses, including personnel, supplies, equipment, and other costs.
- Clear justification for each budget item.
- Information about any matching funds or in-kind contributions, if applicable.
- Explanation of how the project will be sustained beyond the grant period.
- Discussion of long-term funding strategies, partnerships, and community involvement.
- Description of how the project will continue to address the identified problem in the future.
- Overview of the organization’s mission, history , and track record.
- Description of the organization’s experience and qualifications related to the proposed project.
- Summary of key staff and their roles.
- Recap of the project’s goals, objectives, and anticipated outcomes.
- Appreciation for the funder’s consideration.
- Contact information for further inquiries.
Grant Proposal Template
Here is a template for a grant proposal that you can use as a starting point. Remember to customize and adapt it based on the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the funding organization.
Dear [Grant-making Organization Name],
Executive Summary:
I. Introduction:
II. Needs Assessment:
III. Goals and Objectives:
IV. Project Methods and Approach:
V. Evaluation and Monitoring:
VI. Budget:
VII. Sustainability:
VIII. Organizational Capacity and Expertise:
IX. Conclusion:
Thank you for considering our grant proposal. We believe that this project will make a significant impact and address an important need in our community. We look forward to the opportunity to discuss our proposal further.
Grant Proposal Example
Here is an example of a grant proposal to provide you with a better understanding of how it could be structured and written:
Executive Summary: We are pleased to submit this grant proposal on behalf of [Your Organization’s Name]. Our proposal seeks funding in the amount of [Requested Amount] to support our project titled [Project Title]. This project aims to address [Describe the problem or need being addressed] in [Target Location]. By implementing a comprehensive approach, we aim to achieve [State the project’s goals and anticipated outcomes].
I. Introduction: We express our gratitude for the opportunity to present this proposal to your esteemed organization. At [Your Organization’s Name], our mission is to [Describe your organization’s mission]. Through this project, we aim to make a significant impact on [Describe the issue or problem being addressed] by [Explain the significance and relevance of the project].
II. Needs Assessment: After conducting thorough research and needs assessments in [Target Location], we have identified a pressing need for [Describe the problem or need]. The lack of [Identify key issues or challenges] has resulted in [Explain the consequences and impact of the problem]. The [Describe the target population or beneficiaries] are particularly affected, and our project aims to address their specific needs.
III. Goals and Objectives: The primary goal of our project is to [State the broad goal]. To achieve this, we have outlined the following objectives:
- [Objective 1]
- [Objective 2]
- [Objective 3] [Include additional objectives as necessary]
IV. Project Methods and Approach: To address the identified needs and accomplish our objectives, we propose the following methods and approach:
- [Describe the activities and strategies to be implemented]
- [Explain the timeline and key milestones]
- [Outline the roles and responsibilities of project staff and partners]
V. Evaluation and Monitoring: We recognize the importance of assessing the effectiveness and impact of our project. Therefore, we have developed a comprehensive evaluation plan, which includes the following:
- [Describe the data collection methods and tools]
- [Identify the indicators and metrics to measure progress]
- [Explain how the results will be analyzed and utilized]
VI. Budget: We have prepared a detailed budget for the project, totaling [Total Project Budget]. The budget includes the following key components:
- Personnel: [Salary and benefits for project staff]
- Supplies and Materials: [List necessary supplies and materials]
- Equipment: [Include any required equipment]
- Training and Capacity Building: [Specify any training or workshops]
- Other Expenses: [Additional costs, such as travel, marketing, etc.]
VII. Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainability of our project beyond the grant period is of utmost importance to us. We have devised the following strategies to ensure its long-term impact:
- [Describe plans for securing future funding]
- [Explain partnerships and collaborations with other organizations]
- [Outline community engagement and support]
VIII. Organizational Capacity and Expertise: [Your Organization’s Name] has a proven track record in successfully implementing projects of a similar nature. Our experienced team possesses the necessary skills and expertise to carry out this project effectively. Key personnel involved in the project include [List key staff and their qualifications].
IX. Conclusion: Thank you for considering our grant proposal. We firmly believe that [Project Title] will address a critical need in [Target Location] and contribute to the well-being of the [Target Population]. We are available to provide any additional information or clarification as required. We look forward to the
opportunity to discuss our proposal further and demonstrate the potential impact of this project.
Please find attached the required supporting documents, including our detailed budget, organizational information, and any additional materials that may be helpful in evaluating our proposal.
Thank you once again for considering our grant proposal. We appreciate your dedication to supporting projects that create positive change in our community. We eagerly await your response and the possibility of partnering with your esteemed organization to make a meaningful difference.
- Detailed Budget
- Organizational Information
- Additional Supporting Documents]
Grant Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a grant proposal can be a complex process, but with careful planning and attention to detail, you can create a compelling proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the grant proposal writing process:
- Carefully review the grant guidelines and requirements provided by the funding organization.
- Take note of the eligibility criteria, funding priorities, submission deadlines, and any specific instructions for the proposal.
- Familiarize yourself with the funding organization’s mission, goals, and previous projects they have supported.
- Gather relevant data, statistics, and evidence to support the need for your proposed project.
- Clearly define the problem or need your project aims to address.
- Identify the specific goals and objectives of your project.
- Consider how your project aligns with the mission and priorities of the funding organization.
- Organize your proposal by creating an outline that includes all the required sections.
- Arrange the sections logically and ensure a clear flow of ideas.
- Start with a concise and engaging executive summary to capture the reader’s attention.
- Provide a brief overview of your organization and the project.
- Present a clear and compelling case for the problem or need your project addresses.
- Use relevant data, research findings, and real-life examples to demonstrate the significance of the issue.
- Clearly articulate the overarching goals of your project.
- Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that align with the goals.
- Explain the strategies and activities you will implement to achieve the project objectives.
- Describe the timeline, milestones, and resources required for each activity.
- Highlight the uniqueness and innovation of your approach, if applicable.
- Outline your plan for evaluating the project’s effectiveness and measuring its impact.
- Discuss how you will collect and analyze data to assess the outcomes.
- Explain how the project will be sustained beyond the grant period, including future funding strategies and partnerships.
- Prepare a comprehensive budget that includes all the anticipated expenses and revenue sources.
- Clearly justify each budget item and ensure it aligns with the project activities and goals.
- Include a budget narrative that explains any cost assumptions or calculations.
- Review your proposal multiple times for clarity, coherence, and grammatical accuracy.
- Ensure that the proposal follows the formatting and length requirements specified by the funder.
- Consider seeking feedback from colleagues or experts in the field to improve your proposal.
- Gather all the necessary supporting documents, such as your organization’s background information, financial statements, resumes of key staff, and letters of support or partnership.
- Follow the submission instructions provided by the funding organization.
- Submit the proposal before the specified deadline, keeping in mind any additional submission requirements, such as online forms or hard copies.
- If possible, send a thank-you note or email to the funding organization for considering your proposal.
- Keep track of the notification date for the funding decision.
- In case of rejection, politely ask for feedback to improve future proposals.
Importance of Grant Proposal
Grant proposals play a crucial role in securing funding for organizations and projects. Here are some key reasons why grant proposals are important:
- Access to Funding: Grant proposals provide organizations with an opportunity to access financial resources that can support the implementation of projects and initiatives. Grants can provide the necessary funds for research, program development, capacity building, infrastructure improvement, and more.
- Project Development: Writing a grant proposal requires organizations to carefully plan and develop their projects. This process involves setting clear goals and objectives, identifying target populations, designing activities and strategies, and establishing timelines and budgets. Through this comprehensive planning process, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and impact of their projects.
- Validation and Credibility: Successfully securing a grant can enhance an organization’s credibility and reputation. It demonstrates to funders, partners, and stakeholders that the organization has a well-thought-out plan, sound management practices, and the capacity to execute projects effectively. Grant funding can provide validation for an organization’s work and attract further support.
- Increased Impact and Sustainability: Grant funding enables organizations to expand their reach and increase their impact. With financial resources, organizations can implement projects on a larger scale, reach more beneficiaries, and make a more significant difference in their communities. Additionally, grants often require organizations to consider long-term sustainability, encouraging them to develop strategies for continued project success beyond the grant period.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Grant proposals often require organizations to form partnerships and collaborations with other entities, such as government agencies, nonprofit organizations, or community groups. These collaborations can lead to shared resources, expertise, and knowledge, fostering synergy and innovation in project implementation.
- Learning and Growth: The grant proposal writing process can be a valuable learning experience for organizations. It encourages them to conduct research, analyze data, and critically evaluate their programs and initiatives. Through this process, organizations can identify areas for improvement, refine their strategies, and strengthen their overall operations.
- Networking Opportunities: While preparing and submitting grant proposals, organizations have the opportunity to connect with funders, program officers, and other stakeholders. These connections can provide valuable networking opportunities, leading to future funding prospects, partnerships, and collaborations.
Purpose of Grant Proposal
The purpose of a grant proposal is to seek financial support from grant-making organizations or foundations for a specific project or initiative. Grant proposals serve several key purposes:
- Funding Acquisition: The primary purpose of a grant proposal is to secure funding for a project or program. Organizations rely on grants to obtain the financial resources necessary to implement and sustain their activities. Grant proposals outline the project’s goals, objectives, activities, and budget, making a compelling case for why the funding organization should invest in the proposed initiative.
- Project Planning and Development: Grant proposals require organizations to thoroughly plan and develop their projects before seeking funding. This includes clearly defining the problem or need the project aims to address, establishing measurable goals and objectives, and outlining the strategies and activities that will be implemented. Writing a grant proposal forces organizations to think critically about the project’s feasibility, anticipated outcomes, and impact.
- Communication and Persuasion: Grant proposals are persuasive documents designed to convince funding organizations that the proposed project is worthy of their investment. They must effectively communicate the organization’s mission, vision, and track record, as well as the specific problem being addressed and the potential benefits and impact of the project. Grant proposals use evidence, data, and compelling narratives to make a strong case for funding support.
- Relationship Building: Grant proposals serve as a platform for organizations to establish and strengthen relationships with funding organizations. Through the proposal, organizations introduce themselves, highlight their expertise, and demonstrate their alignment with the funding organization’s mission and priorities. A well-written grant proposal can lay the foundation for future collaborations and partnerships.
- Accountability and Evaluation: Grant proposals outline the expected outcomes, objectives, and evaluation methods for the proposed project. They establish a framework for accountability, as organizations are expected to report on their progress and outcomes if awarded the grant. Grant proposals often include plans for project evaluation and monitoring to assess the project’s effectiveness and ensure that the funding is being used appropriately.
- Sustainability and Long-Term Planning : Grant proposals often require organizations to consider the long-term sustainability of their projects beyond the grant period. This includes identifying strategies for continued funding, partnerships, and community involvement. By addressing sustainability in the proposal, organizations demonstrate their commitment to long-term impact and the responsible use of grant funds.
When to Write a Grant Proposal
Knowing when to write a grant proposal is crucial for maximizing your chances of success. Here are a few situations when it is appropriate to write a grant proposal:
- When There is a Funding Opportunity: Grants become available through various sources, including government agencies, foundations, corporations, and nonprofit organizations. Keep an eye out for grant announcements, requests for proposals (RFPs), or funding cycles that align with your organization’s mission and project goals. Once you identify a relevant funding opportunity, you can begin writing the grant proposal.
- When You Have a Well-Defined Project or Program: Before writing a grant proposal, it’s important to have a clearly defined project or program in mind. You should be able to articulate the problem or need you are addressing, the goals and objectives of your project, and the strategies and activities you plan to implement. Having a solid project plan in place will help you write a more compelling grant proposal.
- When You Have Conducted Research and Gathered Data: Grant proposals often require evidence and data to support the need for the project. Before writing the proposal, conduct thorough research to gather relevant statistics, studies, or community assessments that demonstrate the significance and urgency of the problem you aim to address. This data will strengthen your proposal and make it more persuasive.
- When You Have a Strong Organizational Profile: Funding organizations often consider the credibility and capacity of the applying organization. Before writing a grant proposal, ensure that your organization has a strong profile, including a clear mission statement, track record of accomplishments, capable staff or volunteers, and financial stability. These factors contribute to the overall credibility of your proposal.
- When You Have the Time and Resources to Dedicate to Proposal Writing: Writing a grant proposal requires time, effort, and resources. It involves conducting research, developing project plans, creating budgets, and crafting compelling narratives. Assess your organization’s capacity to commit to the grant proposal writing process. Consider the timeline, deadline, and any additional requirements specified by the funding organization before deciding to proceed.
- When You Have Identified Potential Partnerships or Collaborators: Some grant proposals may require or benefit from partnerships or collaborations with other organizations or stakeholders. If your project can be enhanced by partnering with other entities, it’s important to identify and secure these partnerships before writing the grant proposal. This demonstrates a collaborative approach and can strengthen your proposal.
- When You Are Committed to Project Evaluation and Accountability: Grant proposals often include requirements for project evaluation and reporting. If you are willing and able to commit to evaluating the project’s outcomes, tracking progress, and reporting on the use of funds, it is an appropriate time to write a grant proposal. This shows your dedication to transparency, accountability, and responsible use of grant funds.
Also see Proposal
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
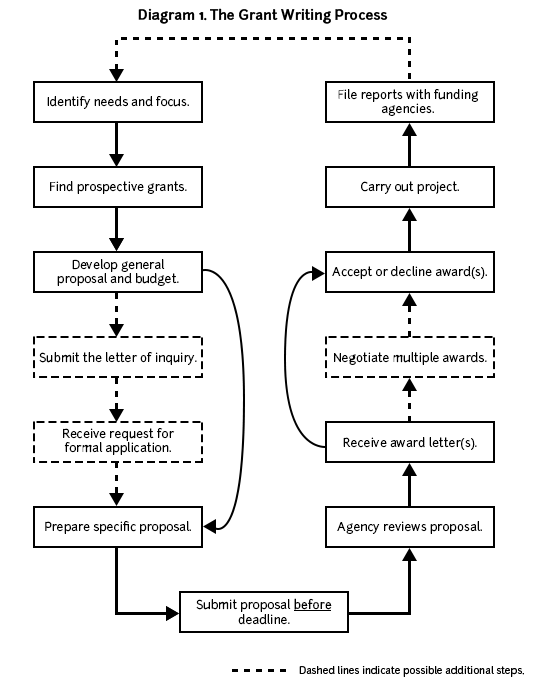
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
| Jet Travel | ||||
| RDU-Kigali (roundtrip) | 1 | $6,100 | $6,100 | |
| Maintenance Allowance | ||||
| Rwanda | 12 months | $1,899 | $22,788 | $22,788 |
| Project Allowance | ||||
| Research Assistant/Translator | 12 months | $400 | $4800 | |
| Transportation within country | ||||
| –Phase 1 | 4 months | $300 | $1,200 | |
| –Phase 2 | 8 months | $1,500 | $12,000 | |
| 12 months | $60 | $720 | ||
| Audio cassette tapes | 200 | $2 | $400 | |
| Photographic and slide film | 20 | $5 | $100 | |
| Laptop Computer | 1 | $2,895 | ||
| NUD*IST 4.0 Software | $373 | |||
| Etc. | ||||
| Total Project Allowance | $35,238 | |||
| Administrative Fee | $100 | |||
| Total | $65,690 | |||
| Sought from other sources | ($15,000) | |||
| Total Grant Request | $50,690 |
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
| Exploratory Research | Completed |
| Proposal Development | Completed |
| Ph.D. qualifying exams | Completed |
| Research Proposal Defense | Completed |
| Fieldwork in Rwanda | Oct. 1999-Dec. 2000 |
| Data Analysis and Transcription | Jan. 2001-March 2001 |
| Writing of Draft Chapters | March 2001 – Sept. 2001 |
| Revision | Oct. 2001-Feb. 2002 |
| Dissertation Defense | April 2002 |
| Final Approval and Completion | May 2002 |
Example #3: Project Timeline in Chart Format
Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to Write a Research Grant Proposal | Research Funding
5-tips-for-writing-a-successful-funding-application.
Helen Eassom, Copywriter, Wiley
January 27, 2022
How to Write a Research Grant Proposal
Most researchers in health and science come across grant proposals or applications at some point in their careers. In fact, many positions depend on them, whether they are doctoral students who require fellowships, postgraduates setting up relatively simple projects as they start employment, or more senior staff who need to have a steady stream of research projects. Although a significant amount of money is available from governmental bodies, charities and commercial organizations, there is a large pool of researchers, so competition can be very competitive. Developing a grant application can feel daunting at first, but with practice and good support, becomes easier with experience.
1. Get Visible – The Sooner, the Better!
It’s a good idea to start building up your profile within academia early on. Make use of all the resources available to you to showcase yourself, your research, and your achievements thus far. These include your page on your institution’s website, your personal website if you have one, and social media sites such as LinkedIn.
2. Collaboration Is Key
Try to build up your publication record as early as possible. This can obviously be tricky if you don’t have funding in the first place but think about collaborating with other academics who do have funding available to them. If you’re in the earlier stages of your career, you might consider applying for funding as a junior co-investigator with more senior academics. You might also want to think about making connections via social media, or through research networks, to establish relationships with potential collaborators.
3. Think Carefully About the Content
Your application will need to address some basics:
- Why is your research topic important?
- Why is further research needed in this area?
- Why am I the best person to carry out this research?
- What theories are you testing, or building upon, or contributing to?
- What would make funding your research worthwhile? What outputs will your research result in?
- What journals will you submit your research to, and what is the process to do it?
You’ll need to provide a clear justification for all costs, so think carefully about the time and resources needed to complete the research successfully within the specified period. Make sure you also devote enough space in your application to describing the research that you intend to carry out as well as the research design and methods that you will use.
If you’re unsure about what to include in your proposal, ask advice from senior or more experienced colleagues.
4. Review, Review, Review.
Make sure you leave plenty of time to review your application before submitting it. Begin drafting your application as soon as possible – don’t leave it until just before the deadline!
The more people you can get to review your draft application, the better, especially those from outside your specific area of research. Remember that most members of funding panels will have their own areas of subject expertise, so you’ll want to write your application so that it can be understood by a broader audience. Keep your language clear, simple, and free of any jargon.
Don’t forget to check your spelling, punctuation, and grammar – you may have written a brilliant application but if it’s full of spelling errors or grammatical mistakes it’s likely to be rejected.
5. Don’t give up!
Many good funding applications get rejected for a myriad of reasons, so don’t be discouraged by your first (or fifth) rejection. You do need to be in it to win it. Make sure that you address any feedback received and refine your proposal accordingly ready to try again.

Watch our Webinar to help you get published
Please enter your Email Address
Please enter valid email address
Please Enter your First Name
Please enter your Last Name
Please enter your Questions or Comments.
Please enter the Privacy
Please enter the Terms & Conditions

Leveraging user research to improve author guidelines at the Council of Science Editors Annual Meeting

How research content supports academic integrity

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for Success

Software to Improve Reliability of Research Image Data: Wiley, Lumina, and Researchers at Harvard Medical School Work Together on Solutions

Driving Research Outcomes: Wiley Partners with CiteAb

ISBN, ISSN, DOI: what they are and how to find them

Image Collections for Medical Practitioners with TDS Health

How do you Discover Content?

Writing for Publication for Nurses (Mandarin Edition)

Get Published - Your How to Webinar
Related articles.
User Experience (UX) Research is the process of discovering and understanding user requirements, motivations, and behaviours
Learn how Wiley partners with plagiarism detection services to support academic integrity around the world
Medical student Nicole Foley shares her top tips for writing and getting your work published.
Wiley and Lumina are working together to support the efforts of researchers at Harvard Medical School to develop and test new machine learning tools and artificial intelligence (AI) software that can
Learn more about our relationship with a company that helps scientists identify the right products to use in their research
What is ISBN? ISSN? DOI? Learn about some of the unique identifiers for book and journal content.
Learn how medical practitioners can easily access and search visual assets from our article portfolio
Explore free-to-use services that can help you discover new content
Watch this webinar to help you learn how to get published.

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for success

How to Easily Access the Most Relevant Research: A Q&A With the Creator of Scitrus
Atypon launches Scitrus, a personalized web app that allows users to create a customized feed of the latest research.
FOR INDIVIDUALS
FOR INSTITUTIONS & BUSINESSES
WILEY NETWORK
ABOUT WILEY
Corporate Responsibility
Corporate Governance
Leadership Team
Cookie Preferences
Copyright @ 2000-2024 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., or related companies. All rights reserved, including rights for text and data mining and training of artificial technologies or similar technologies.
Rights & Permissions
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Research Grant Proposal Templates With Editable Samples and Examples

Nawsheen Muzamil
If Einstein wished to secure a grant for his next big research today, he would have had a tough time arranging funds. The reason being there are too many research enthusiasts today who could produce tangible proposals within the deadlines that would be more appreciated by the benefactors.
Similarly, if today's competition existed in the 1900s, many discoveries and research would never have seen the light of the day. The truth is stringent assessment kills the hopes of many researchers as they strive to secure their much-deserved grants. In fact, according to a report published by the National Science Foundation (NSF), in 2017, only 11,447 of the total received 49,415 research grant proposals acquired monetary support. That’s a staggering percentage of less than 25%!
What was so impressionable about those 25% grant proposals? Let's explore its answer.
How to increase the Odds of a Grant Getting Approved?
Many factors come into play that help in the conversion of a proposal into a grant, such as:
- Timely submission
- Benefits of research explained with reference to daily life
- Justifiable budget
- The proposal has to match the expectations of board members
We trust that all your research information is in-handy so let’s help you weave an effective proposal. Of course, one can take the help of formats that have won grants before and researchers will do well to focus on this aspect.
For starters, you need to get your research idea, expected timeline with a realistic budget, and the practical difference you will make, communicated properly. Conduct a thorough analysis of what the coming years of your undertaking are going to look like. Once that is done, proceed with the search for relevant research grant proposal templates. This much-needed aspect can make or break your chances of getting funds.
Like always, we are at hand to help. Our research grant proposal templates will provide the much-needed creative burst to your presentation. These PPT Designs are the most downloaded and used. Our templates are editable, easy to customize, and compatible with all popular presentation software. Scroll down to discover your ideal PPT Template(s) with editable samples and examples now!
Template 1: Psychology Research Proposal Template
Does your research revolve around a breakthrough in psychology? Then this 31-slide PPT Presentation is ideal for you to secure a grant. Address the project details in depth and answer the big question of why your project deserves the grant. Yellow is the color of this PPT Thematic, and psychology suggests it captures attention well! Why would you let this wonderful template pass? Download now!

Download this template
Template 2: Biology Research Proposal Template
Does the science of life and life processes fascinate you? And do you wish to make a breakthrough in it? Then this 29-slide-PPT Slideshow is all you need to keep your potential benefactors mesmerized. This ideal grant proposal template format is your best chance at securing the funding. Don’t wait any longer. This research grant proposal sample template is editable, shareable, and already compatible with your presentation software. Download now!

Template 3: Education Grant Proposal Template
Are you passionate about revolutionizing the education system? Then state your objectives and results you hope to achieve in a convincing manner with this collective of grant proposal templates. This 29-slide PPT design is your best shot at securing the much-needed grant. This template also gives you space to point out flaws in the existing learning system and provide a practical solution. Download right away!

Template 4: Study Stipend Proposal Example Document Report Doc PDF PPT
This is another intuitively designed PPT Presentation to seek an educational grant/ stipend. It comes with a creatively designed cover letter template, followed by a guided proposal to gain mass approval from your stakeholders. This 29-PPT Slideshow has impressive layouts that will justify your plea for seeking a stipend/ grant with ease. Without further ado, download it now!

Template 5: Sample Budget Proposal for Grant Example Document Report Doc PDF PPT
Here is an example of an editable research grant proposal budget template that will help you reveal in depth the exact distribution of the budget for your research. Use this 18-slide PowerPoint compilation to highlight the details of your meaningful expenses and convince your funding board about their importance in overall research. Download now.


Template 6: Annual Grant Report Sample PDF Document Report Template
To keep your sponsors associated with you for long, you must produce annual reports of how you used the grant. You can also include details of grants obtained by other organizations and showcase the expense distribution over the course of the year. This objective will be beautifully met with this PPT Layout that comes with 22 slides. Present your financial report vividly and comprehensively with these fantastic slides. Download now!

Template 7: One-Page Grant Proposal for Fund Request Presentation Report
Some organizations require researchers to be as concise as they can be when presenting their grant proposals. Here is a practical one-page template at your service. Specify the project purpose, your institution's background, and the problem statement that your research addresses. Then briefly state your major project goals, also specifying the budget and its distribution via this versatile collection of grant proposal templates.
Template 8: One-Page Grant Proposal Executive Summary Presentation Report
Here is another compact one-pager to share the executive summary of your grant proposal. Answer the primary questions of your stakeholders, such as project objective, expected outcome, and budget required via this template. Fill in this one-page template with your particulars, such as name and contact details, and make a bold attempt at impressing your stakeholders in the first go. Download now!

Template 9: Grant Proposal One-Page Application Presentation Report
Here is another concise yet impactful one-page proposal application designed to impress. Mention the highlights of your grant proposal to draw the attention of your stakeholders to the key aspects. Share your particulars, including the expected grant along with your project essentials in this comprehensive one-page proposal template. Download now!

Download this template
Template 10: Project Grant One-Page Proposal Presentation Report
Here is another PPT Template that is bound to get you that grant. Equip this powerful one-page template with the particulars of your project and the institution you represent. Mention the grant budget requirements in this editable PPT Template. You can even add your digital or electronic signature to this PPT Layout to sanctify the bond between you and the financiers. Hurry! Download this ready-made proposal layout now!

We hope this diversity served you well and you were able to find your requisite from this collection of grant proposal templates. Let us know in the comments how well we did in this regard.
PS: Tracing the research roadmap gets your team of workers and sponsors on the same page hence is the requirement for any project. Explore this supporting guide to find for yourself templates that are brimming with creativity and ease of use.
FAQs on Grant Proposals
How to write a research grant proposal.
When it comes to writing a research grant proposal, the ball is in your court. All you have to do is get your format right, and the facts and figures cross-checked. The standard components of a research grant proposal are:
- An impressive cover letter , that is a must.
- A short executive summary, also called a proposal summary.
- Introduction of your organization, specifying relevant information and facts about it.
- Highlighting the concern that your research offers solution to (the Needs Statement)
- Statement enlisting the practical goals and objectives of your research and its role in resolving the problem statement.
- Enumerating your research methodologies and strategies.
- Defining your metrics for tracking progress.
- An insight into your vision and research sustainability, along with any other financial collaborations.
- Finally, outlining your budget clearly, and comprehensively with all expenditure accounted for.
How to write a grant proposal for scientific research ?
Scientific research might include jargon, complex concepts, and calculations. Hence, it is vital to keep your proposal simple and understandable, especially for your benefactors who may not be as eloquent as you are in your field. Needless to say, the proposal should radiate both purpose and urgency to be able to seal the spot.
How to write a grant proposal for education?
An education grant proposal should, in addition to the standard elements, focus on the unique features of your vision to revamp the existing learning system. Talk about how your education project plans to improve the existing system of education and, in fact, add to it. For instance, your vision could be to ensure all schools are digitized. Yet, the sponsors may not be that accepting of the idea. In this case, you will need to focus more on the data that proves the effectiveness of digitization in education.
What is the budget portion of a grant proposal?
It enlists the feasible expenditures of research that would win funds from project stakeholders. Crosscheck the expenses with your team and record the realistic net total to present before your financial supporters. The budget part of any grant proposal shows the benefactor exactly where and how the money will be spent. So, keep your spending all accounted for.
Finally, how long should a research grant proposal be?
Typically, a grant should be 25 pages, but the number may vary according to the prescribed terms and conditions of the grant issuing institute or body. Kindly remember that, in all probability, the number of pages in a research grant proposal will be kept the same for everyone. The key to a good research proposal is the depth of your idea and the way you define its applications.
Related posts:
- [Updated 2023] 50 Best Company Presentation Templates To Ace The Corporate Ladder
- [Updated 2023] Top 10 Sales and Marketing Google Slides Templates for Sure Shot Business Success
- The Ultimate Guide to Project Management Lifecycle – 30+ Customizable Templates Included
- The Ultimate Guide To Brand Identity For Fostering Client Loyalty (Best Templates Included)
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Confidentiality Agreement Templates to Protect Your Ideas, Invention, and More [Free PDF Attached]

Top 12 Slides In Ultimate Practical Guide on Product Discovery Process
Top 14 pharmaceutical product development templates to document the discovery of effective drugs.

Top 10 Scientific Google Slides Templates For Science Geeks

Top 20 Research and Innovation PPT Templates To Get A Competitive Edge
![research grant proposal presentation Top 10 Research Roadmap Templates To Trace Your Journey of Innovations and Expeditions [Free PDF Attached]](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/1013x441no-button-20-1013x441.jpg)
Top 10 Research Roadmap Templates To Trace Your Journey of Innovations and Expeditions [Free PDF Attached]

The Ultimate Guide to Delivering an Outstanding Master's or PhD Thesis Dissertation Defense Presentation (Over 20 Templates Included)

Top 10 One-Page Thesis Outline Templates to Pave the Way to Academic Excellence
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format


- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Writing a Successful Research Grant Proposal
Published by Kelli Brockington Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Writing a Successful Research Grant Proposal"— Presentation transcript:

Computer English For Computer Major Master Candidates

DOs and DONTs Joan-Anton Carbonell Kingston University EC External Expert TEMPUS Modernising Higher Education TEMPUS INFORMATION DAY.

Analyzing Student Work

Dr Casey Wilson, 2009 Panels and Reviews. 1 st year Panels Dr C. Wilson, 2009 Format: (check details with your Dept) Chair, supervisor(s) and at least.

Creating Your Competitive Proposal Projects, Grants, Fellowships...

1.Project planning 2.Making applications Anne Pearson, Robertson Trust Jean Robertson, Scottish Borders Council Evelyn Boyd, Big Lottery Fund.

Careers In Academia – How to beat the competition! June Kay Careers Development Consultant.

Counting Down the Top Ten List for Proposal Writing Royal Roads University Office of Research February 26, 2010.

DR MACIEJ JUNKIERT PRACOWNIA BADAŃ NAD TRADYCJĄ EUROPEJSKĄ Guide for Applicants.

Grant Proposal Writing© Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid, CS5014, Fall CS5014 Research Methods in CS Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia.

Submission Writing Fundamentals – Part Webinar Series Leonie Bryen.

Copyright 2006 Theisen Consulting LLC Grant Writing & Grant Seeking: Advanced Level Healthcare Georgia Foundation Terri Theisen February 2006.

Page 1 Improving Research Grant Quality at GCU Professor John Marshall Director Academic Research Development.

1 Grant Process Proposal Preparation Proposal Writing Project Implementation Evaluation and Assessment Reporting.

Project Monitoring Evaluation and Assessment

Merit Review and Proposal Preparation Mark Courtney Division of Environmental Biology

Writing successful grant applications HEA Subject Centre Archaeology Student Conference, Birkbeck 30 June 2009 Mark Pearce.

E TENDERING MASTERCLASS ANN MCNICHOLL TENDERING MASTERCLASS ANN MCNICHOLL COMMISSIONING MASTER CLASS – LEWISHAM Date 24 th September Presenter Ann McNicholl.

© 2014 Public Health Institute PROPOSAL WRITING.

Jumping on the Funded Research Bandwagon Paul O’Reilly Dublin Institute of Technology Presentation to Faculty of Commerce and Centre for Innovation and.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

How to Write a Successful Grant Proposal
You’re passionate about your research. Your work is crucial for scientific discovery and deserves to be carried out. We know that, and we love what you’re doing. So why can it be so challenging for academic researchers to obtain research funding? At Nicoya, we speak with researchers all over the world. We hear the same story about an amazing research project that can’t get funded. A worthy research proposal might not even get read by a reviewer if it lacks key elements stated in the grant requirements. Or, a well-structured grant proposal can fall short if the project isn’t a good fit for the grant that it was submitted to.
At Nicoya, we aim to improve human life by helping scientists succeed. We’re here to help you write a successful grant proposal to bring your next big idea to life. From grant prospecting to grant submission, we did our research to provide insight on each stage of the grant writing process. Let’s start at the beginning and choose the right grant for your project!
Choosing The Right Grant
If you’ve looked for academic funding before, you know that there is an alarming amount of publicly funded grants available. This overwhelming process is a lot easier when you know what you’re looking for. Before diving into open grants, take some time to identify the needs and focus of your research:
What will your research accomplish? Who directly benefits from the outcome of your research? This might sound like an obvious tip, but having a clear picture of the significance of your research will make it much easier to filter by the right research area. Choosing an appropriate audience from the beginning will also significantly increase your chances of success.
What are your credentials? If you’re a newer researcher, there are funding opportunities specifically tailored for you! These grants usually come with smaller budgets and timelines to help you get started. Alternatively, if you are a distinguished professor, you likely have a full team to support and a long project to carry out. This means that you will need a more competitive grant that offers significant funding and multiple years of support. Luckily, your previous experiences have set the stage for you to take on a larger project. Think about what size of budget and timeline fits well with your current career stage to help you be more selective of different grants.
So where should you look? If you’re based in the United States, here are some great places to start:
- grants.gov – A great general search engine that captures grant announcements from a number of different funding agencies.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – The largest funding body in the country. This page also includes important due dates associated with each grant.
If you are based in Canada, check out the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) . NSERC is the major funding source in Canada for natural science researchers – students and professors alike.
Writing The Research Funding Proposal
Now that you have selected some grants that fit your research and needs, it’s time to start working on the application. The next thing you should do – and I cannot stress this enough – is read through the grant application guidelines ( Grants.gov). These guidelines will cover the elements required in your proposal, the questions that the reviewers want answered, and how the application should be structured. We’ve summarized some tips for the most common elements of a proposal in a format that you can keep handy for later:
- Carefully follow your grant guidelines here for what information to include and how it should be formatted.
- In addition to a clear, explicit title, other elements such as your title, affiliations, and the funding agency are usually required as well.
- The most read section of your research funding proposal (The Writing Center, UNC).
- Be explicit, clear and concise. Make your project’s goals, significance (who does your research benefit?), and relation to the theme of the grant easy to find!
- Use future tense to summarize your plan to accomplish your goals.
Introduction
- Use this section to elaborate on everything you have stated in the abstract.
- Set the stage for your research: give a background on the research area, the knowledge gap you are addressing, and how your research is going to fill that gap. Start very general about the area of research and get increasingly more specific.
- Your introduction should sufficiently justify why your research is a good fit for this grant.
Project Narrative
- The main section of your proposal. There is a lot of information here so organize your information into subheadings as necessary.
- Elaborate on the problem you’re addressing and its significance again – this is why the funding agency is giving you money after all.
- Break down step by step how you’re planning to solve this problem and justify each step. The more thorough you can be here, the more confidence your reviewer will have in you.
- Focus on techniques that will provide quantitative data to back your claims. Using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to measure binding kinetics for any biomolecular interactions will significantly increase your credibility to a reviewer. Check out The Power of OpenSPR below to see how easily SPR can be included in your proposal.
- Finally, recheck your grant guidelines! Make sure that every question the reviewers had was answered sufficiently.
- The more specific you can be about how you plan to spend the money, the more credibility you will have.
- Include an itemized list of each anticipated expense. Think about instrument requirements, reagents, travel expenses, and personnel wages.
- Also, include a budget narrative explaining why each expense is crucial to your project and worth the funding agency’s money (The Writing Center, UNC).
- Follow the funding agency’s regulations closely here. Do your research to see what purchases they don’t cover and their limits around items such as air travel.
Timeline
- Justify the time frame of your project and set some approximate deadlines for the various stages of your project.
- Using an itemized list or a visual representation of your timeline will keep your reviewers happy here (The Writing Center, UNC).
Cover Letter
- The bonus section! A cover letter likely is not explicitly required but is highly recommended (The Balance; Kurzweil Educational Systems, 2002).
- Treat this like the cover letter on your resume; its purpose is to sell your project.
- Introduce your research group, highlight the significance of your project, and state the budget you are requesting.
These are just some of the elements that are normally required in a grant application. Each grant application will have its required elements and structure, so follow your grant guidelines meticulously.
Taking Your Research Funding Proposal To The Next Level
Congratulations! You now have a draft of your proposal completed. Stretch your legs, grab a cup of coffee and settle in as we highlight a few more tips to increase the chances of getting your project funded substantially.
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. While quality is better than quantity, applying for multiple grants will give you more opportunities to get funded. Since these proposals are incredibly time-consuming, write a general grant application for your project and then tailor it to each funding body.
Know your audience . It doesn’t matter how impactful your research is if it isn’t a good fit for the funding agency you’re applying to. The goals of your research should always circle back to the overall theme of the grant. This may require some rewording of your research outcomes to align better with the views of the funding agency. Check out our tips on publication writing for more advice on writing for your audience.
Use innovative techniques. As technology advances, so should your research techniques. For instance, using SPR to measure quantitative binding kinetics for your bio-molecular interactions will give you a huge advantage against your competitors. Since the OpenSPR is affordable and easy-to-use, we’ve had many researchers use the OpenSPR as leverage to get their grants approved. Check out The Power of OpenSPR below to see how easily SPR can be included in your proposal.
Review, review, review. Plenty of eyes should see your research funding proposal before the reviewers do. Consider getting your work reviewed by experts and non-experts in your field. It is also recommended to have a writing expert review your work for structure and style. If you let your proposal sit for a week and then pick it up again, you will be able to catch more mistakes with fresh eyes.
Read your grant requirements. Have we mentioned this already? A funding agency’s first screening of your proposal will be to see if you have followed their instructions. Just sticking to their guidelines will significantly increase your chances of success (Grants.gov; The Writing Center, UNC).
The Power of OpenSPR
With the finishing touches added to your award-winning grant proposal, we wanted to leave you with some closing thoughts on the difference SPR will make in your research. More and more reviewers (funding agencies and academic journals alike) are asking for quantitative binding kinetics data over simple yes/no binding confirmation for biomolecular interactions. SPR is a label-free technique that gets you this data in real-time and has never been more accessible with the OpenSPR . Your reviewers are going to love that you’ve chosen an instrument that provides the same quality of data of instruments over ten times its cost.
Let us help you take your grant proposal to the next level.
Request a quote today to see how easily the OpenSPR can be budgeted into your next project.
- The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!). Retrieved from https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/grant-proposals-or-give-me-the-money/
- Grants.gov. Grants 101 – Pre-Award Phase. Retrieved from https://www.grants.gov/web/grants/learn-grants/grants-101/pre-award-phase.html
- The Balance. How to Write a Winning Grant Proposal. Retrieved from https://www.thebalancesmb.com/how-to-write-a-grant-proposal-2501980
- Kurzweil Educational Systems (2002). Sample Grant Proposal. Retrieved from https://www.kurzweiledu.com/files/proof_resources_grant1.pdf
- Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools (RePORT). Funding Facts. Retrieved from https://report.nih.gov/fundingfacts/fundingfacts.aspx
Meet the world's first digital high‑throughput benchtop SPR system.
Accelerate your drug discovery with Alto.
Introduction to Digital SPR and its use in assessing the binding kinetics of DART (Drugs Acutely Restricted by Tethering)
" * " indicates required fields
Streamlining characterization of biomolecular binding kinetics with Alto™ and OpenSPR®
Rising investigators in spr, detecting emerging viral variants, laboratory automation, navigating the post-covid research landscape, covid-19 diagnostics using spr, binding techniques, enter the nicosystem, publish faster with binding kinetics & affinity data.
Over 600 researchers worldwide are using OpenSPR™ to get the data reviewers are looking for. Read our brochure to learn more!
The future of drug discovery is Alto.
Interested in learning more about how Alto can accelerate your drug discovery? Fill out the form below to download a product brochure.
Basics of scientific and technical writing: Grant proposals
- Career Central
- Published: 23 April 2021
- Volume 46 , pages 455–457, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Morteza Monavarian 1
5412 Accesses
145 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Grant proposals
A grant proposal is a formal document you submit to a funding agency or an investing organization to persuade them to provide the requested support by showing that (1) you have a plan to advance a certain valuable cause and (2) that the team is fully capable of reaching the proposed goals. The document may contain a description of the ideas and preliminary results relative to the state of the art, goals, as well as research and budget plans. This article provides an overview of some steps toward preparation of grant proposal applications, with a particular focus on proposals for research activities in academia, industry, and research institutes.
Different types of proposals
There are different types of grant proposals depending on the objectives, activity period, and funding organization source: (1) research proposals, (2) equipment proposals, and (3) industry-related proposals. Research proposals are those that seek funding to support research activities for a certain period of time, while equipment proposals aim for a certain equipment to be purchased. For equipment proposals to be granted, you need to carefully explain how its purchase could help advance research activities in different directions. Unlike research proposals, which are focused on a specific direction within a certain field of research, equipment proposals can have different directions within different areas of research, as long as the proposed equipment can be used in those areas.
There are also industry-related funding opportunities. For example, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has programs within its Division of Industrial Innovation and Partnerships, in which small businesses and industries can involve research funding opportunities. Examples of such programs include Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer programs. These opportunities are separate from any opportunities directly involving the companies funding your research, where the companies are the source of the funding.
Steps to submit a proposal
Figure 1 shows an overview of a standard process flow for a grant proposal application, from identifying the needs and focus to acceptance and starting the project. As shown, the process of writing grants is not linear, but rather a loop, indicating the need for consistent modifications and development of your ideas, depending on the input you receive from the funding agencies or the results you obtained from previously funded projects.
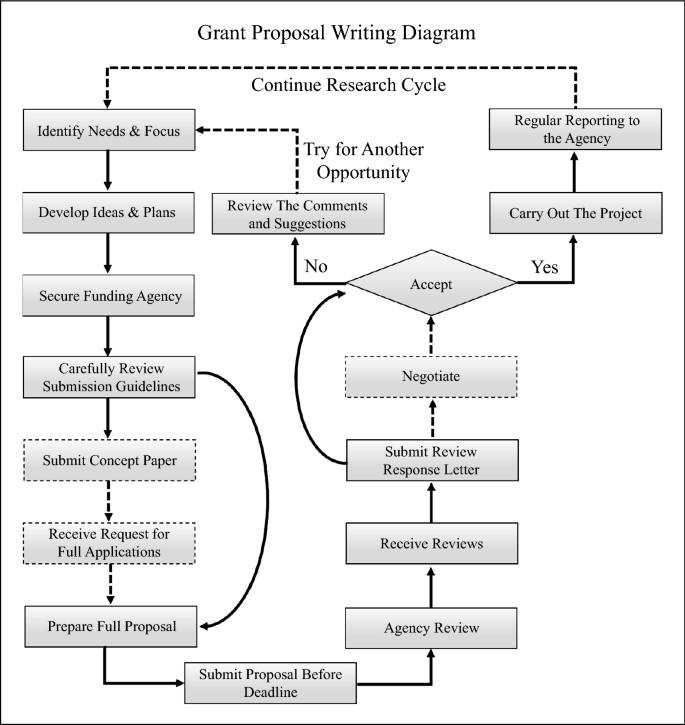
Diagram of grant proposal preparation.
Before starting, you need to define the ultimate purpose of the research you want to pursue and to convince others that the work is indeed worth pursuing. Think about your proposed research in the context of problems to solve, potential hypotheses, and research design. To start shaping the idea you are pursuing, ask yourself: (1) What knowledge do I gain from finishing this project? (2) What is the significance of the end goal of the project? (3) How would the completion of this project be useful in a broader sense? Having convincing answers to these questions would be extremely helpful in developing a good grant proposal.
After identifying the needs and focus and initially developing the ideas and plans, the next step is to secure a funding agency to which you would like to submit the grant proposal. It is a good practice to keep track of programs and corresponding funding opportunity announcements for different funding agencies relevant to your field of research. Once you secure a funding agency and find the deadline for submission, review the submission guidelines for the program carefully. The grant proposal document should be perfectly aligned with the structure and content proposed in the guidelines provided by the agency program to avoid any premature rejection of your application. Some programs only require a few documents, while others many more. Some agencies may require a concept paper: a short version of the proposal submitted before you are eligible for a full proposal submission.
After securing the agency/program and reviewing the guidelines, the next step is to write the full proposal document, according to the guidelines proposed by the funding agency. Before submission, review your documents multiple times to ensure the sections are well written and are consistent with one another and that they perfectly convey your messages. Some institutes have experts in reviewing proposal documents for potential linguistic and/or technical edits. Submit at least a day before the deadline to ensure that all documents safely go through. Some agencies have strict deadlines, which you do not want to miss, or you may have to wait upwards of a year to submit again. The agency then usually sends your documents to a few expert reviewers for their comments. The review may be graded or have written comments that require attention and response. A response letter has to be prepared and submitted (according to the agency guidelines) by a new deadline imposed by the agency for consideration by the program manager.
After reviewing the full response and revised documents, the agency will contact you with notification of their decision. If your proposal is accepted, the agency will provide details regarding funding and a start date. During the term of the project, agencies normally require a periodic (quarterly or annually) report in either a written or oral form. Different agencies may have rules for any publications or patents that could potentially result during the project term, when the work is complete or the idea is developed as a result of the awarded grant. As shown in the figure, even if the proposal is rejected, upon careful review, revision, and further development or adjustment of the proposal, you may try for another funding opportunity. After finishing a recently funded project, you can further develop an idea and submit another proposal for funding.
Structure of proposals (NSF example)
The structure of proposals differs with funding agencies. Included is an overview of an NSF proposal as a guide.
In addition to the technical volume (narrative) document, containing all the major descriptions of the project, other necessary documents include bio sketches, budget, justifications, management plan, and project summary. Bio sketches contain resumes of all the principal investigators (PIs), including any prior experience, relevant publications, and outreach activities. Budget and justifications are two separate documents relevant to a breakdown of the required budgets for the project, including salaries for the PIs and the team, travel, publication costs, equipment costs, materials and supplies, and any other relevant expenses. The budget document could be an Excel spreadsheet, indicating the exact dollar amounts, while the justification indicates the rationale for each charge. Depending on the agency and program, some expenses are allowed to be included in the budget list (carefully read related guidelines). Other potential requirements for submission may include a description of the project summary, management plans, and the facilities in which the work will be performed.
The technical volume is likely the one you will spend the most time preparing. It consists of several sections. Included is an example of a structure (read the Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide on the NSF website for details). The total technical volume should not exceed 15 pages, excluding the reference section, which will be submitted as a separate document. While there are different review criteria for an NSF proposal, the main two are intellectual merit (encompasses the potential to advance knowledge) and broader impacts (potential to benefit society). Your proposal should reflect that the work will be rich in these two criteria. NSF reviewers typically provide qualitative grades (ranging from poor to excellent) to the proposal and feedback in their review.
Introduction and overview
The first section of the technical volume may start with an introduction/motivation and overview of the proposed work. This section should be no longer than a page, but should give an overview of the background and state of the art in the research area, motivations, objectives of the proposed work (maybe in the context of intellectual merit and broader impacts), and a brief description of the work breakdown (tasks). The last couple of paragraphs of the introduction could summarize the education and outreach plans, as well as the PIs’ experience and expertise. Feel free to highlight any major statements in this section to serve as main takeaways for the reviewers. Also, making an overview figure for this section may help summarize the information.
Background and relationship to the state of the art
The second section gives more details of background and relationship to the state of the art. This section may be a few pages long and contain figures and relevant citations.
Technical methods and preliminary results
This section should describe the technical methods and preliminary results relevant to the proposed research from your prior work. It should contain illustrative figures and plots to back up the proposed work.
Research plan
After discussing the prior art and the technical methods and preliminary results (in previous sections), you should discuss the proposed research and plan. A good standard is to divide your work into two to three thrusts, with each thrust containing two to three tasks. You can also prepare a timetable (also called a Gantt chart) to indicate when the tasks will be completed with respect to the project term, which is usually between three to five years.
Integration of education and research
The last section should describe any plans for integration of education and research, including any K-12 programs or planned outreach activities.
Results from prior supports
Finally, describe results from all of your prior NSF supports. For each project, provide a paragraph describing the goal of the project, the outcomes, and any related publications. You can also write this section in the context of intellectual merit and broader impacts.
Things to remember when preparing grant proposals
Find the proper timing for any idea to explore. Sometimes the idea you think is worth pursuing is either too early or too late to explore, depending on the existing body of literature.
Begin early to avoid missing any deadlines. Give the process some time, as it could take a while.
Try to have sufficient preliminary results as seeds for the proposal.
Have a decent balance between the amount of ideas and preliminary results you put in the grant proposal. Too many ideas but too few results may make your proposal sound too ambitious, while too few ideas and too many results may make your proposed work seem complete, therefore no need for funding.
Try to attend funding agency panels. It will help you understand the review process, grading criteria, and mindsets of program managers. Learn about proposals that are funded.
Locate any related funding agency announcements to know the deadlines in advance.
Be mindful of deadlines. Last day submissions may jeopardize your funding opportunities.
Learn what is customary. One figure per page is ideal for the proposed technical volume. A wordy proposal with not enough figures will be boring and more difficult for the reviewers to follow.
Do not give up! You may need to submit several proposals (to different programs/agencies) to get one awarded.
Be cautious about self-plagiarism! Do not copy and paste texts/figures from your previously supported proposal or papers in your new submissions.
Be ambitious but practical when developing ideas.
Develop a solid research program. It is not all about hunting grants; it is also how to execute your funded projects. You may have periods (waves) of grant hunting followed by periods of delivering on the funded projects. Any successful prior research can help you gain more funding in the next wave.
Enjoy your research!
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Materials Department and Solid State Lighting & Energy Electronics Center, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA
Morteza Monavarian
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Additional information
This article is the third in a three-part series in MRS Bulletin that will focus on writing papers, patents, and proposals.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Monavarian, M. Basics of scientific and technical writing: Grant proposals. MRS Bulletin 46 , 455–457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00105-4
Download citation
Published : 23 April 2021
Issue Date : May 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00105-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
ANNOTATED SAMPLE GRANT PROPOSALS
How to Use Annotated Sample Grants
Are these real grants written by real students.
Yes! While each proposal represents a successfully funded application, there are two things to keep in mind: 1) The proposals below are final products; no student started out with a polished proposal. The proposal writing process requires stages of editing while a student formulates their project and works on best representing that project in writing. 2) The samples reflect a wide range of project types, but they are not exhaustive . URGs can be on any topic in any field, but all must make a successful argument for why their project should be done/can be done by the person proposing to do it. See our proposal writing guides for more advice. The best way to utilize these proposals is to pay attention to the proposal strengths and areas for improvement on each cover page to guide your reading.
How do I decide which sample grants to read?
When students first look through the database, they are usually compelled to read an example from their major (Therefore, we often hear complaints that there is not a sample proposal for every major). However, this is not the best approach because there can be many different kinds of methodologies within a single subject area, and similar research methods can be used across fields.
- Read through the Methodology Definitions and Proposal Features to identify which methodolog(ies) are most similar to your proposed project.
- Use the Annotated Sample Grant Database ( scroll below the definitions and features) filters or search for this methodology to identify relevant proposals and begin reading!
It does not matter whether the samples you read are summer grants (SURGs) or academic year grants (AYURGs). The main difference between the two grant types is that academic year proposals (AYURG) require a budget to explain how the $1,000 will be used towards research materials, while summer proposals (SURG) do not require a budget (the money is a living stipend that goes directly to the student awardee) and SURGs have a bigger project scope since they reflect a project that will take 8 weeks of full time research to complete. The overall format and style is the same across both grant cycles, so they are relevant examples for you to review, regardless of which grant cycle you are planning to apply.
How do I get my proposal to look like these sample grants?
Do not submit a first draft: These sample proposals went through multiple rounds of revisions with feedback from both Office of Undergraduate Research advisors and the student’s faculty mentor. First, it helps to learn about grant structure and proposal writing techniques before you get started. Then, when you begin drafting, it’s normal to make lots of changes as the grant evolves. You will learn a lot about your project during the editing and revision process, and you typically end up with a better project by working through several drafts of a proposal.
Work with an advisor: Students who work with an Office of Undergraduate Research Advisor have higher success rates than students who do not. We encourage students to meet with advisors well in advance of the deadline (and feel free to send us drafts of your proposal prior to our advising appointment, no matter how rough your draft is!), so we can help you polish and refine your proposal.
Review final proposal checklists prior to submission: the expectation is a two-page, single-spaced research grant proposal (1″ margins, Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11), and proposals that do not meet these formatting expectations will not be considered by the review committee. Your bibliography does not count towards this page limit.
Academic Year URG Submission Checklist
Summer URG Application Checklist
METHODOLOGY DEFINITIONS & PROPOSAL FEATURES
Research methodologies.
The proposed project involves collecting primary sources held in archives, a Special Collections library, or other repository. Archival sources might include manuscripts, documents, records, objects, sound and audiovisual materials, etc. If a student proposes a trip to collect such sources, the student should address a clear plan of what will be collected from which archives, and should address availability and access (ie these sources are not available online, and the student has permission to access the archive).
Computational/Mathematical Modeling
The proposed project involves developing models to numerically study the behavior of system(s), often through computer simulation. Students should specify what modeling tool they will be using (i.e., an off-the-shelf product, a lab-specific codebase), what experience they have with it, and what resources they have when they get stuck with the tool (especially if the advisor is not a modeler). Models often involve iterations of improvements, so much like a Design/Build project, the proposal should clearly define parameters for a “successful” model with indication of how the student will assess if the model meets these minimum qualifications.
Creative Output
The proposed project has a creative output such playwriting, play production, documentary, music composition, poetry, creative writing, or other art. Just like all other proposals, the project centers on an answerable question, and the student must show the question and method associated with the research and generation of that project. The artist also must justify their work and make an argument for why this art is needed and/or how it will add to important conversations .
Design/Build
The proposed project’s output centers around a final product or tool. The student clearly defines parameters for a “successful” project with indication of how they will assess if the product meets these minimum qualifications.
The project takes place in a lab or research group environment, though the methodology within the lab or research group vary widely by field. The project often fits within the larger goals/or project of the research group, but the proposal still has a clearly identified research question that the student is working independently to answer.
Literary/Composition Analysis
The project studies, evaluates, and interprets literature or composition. The methods are likely influenced by theory within the field of study. In the proposal, the student has clearly defined which pieces will be studied and will justify why these pieces were selected. Context will be given that provides a framework for how the pieces will be analyzed or interpreted.
Qualitative Data Analysis
The project proposes to analyze data from non-numeric information such as interview transcripts, notes, video and audio recordings, images, and text documents. The proposal clearly defines how the student will examine and interpret patterns and themes in the data and how this methodology will help to answer the defined research question.
Quantitative Data Analysis
The project proposes to analyze data from numeric sources. The proposal clearly defines variables to be compared and provides insight as to the kinds of statistical tests that will be used to evaluate the significance of the data.
The proposed project will collect data through survey(s). The proposal should clearly defined who will be asked to complete the survey, how these participants will be recruited, and/or proof of support from contacts. The proposal should include the survey(s) in an appendix. The proposal should articulate how the results from these survey(s) will be analyzed.
The proposed project will use theoretical frameworks within their proposed area of research to explain, predict, and/or challenge and extend existing knowledge. The conceptual framework serves as a lens through which the student will evaluate the research project and research question(s); it will likely contain a set of assumptions and concepts that form the basis of this lens.
Proposal Features
Group project.
A group project is proposed by two or more students; these proposals receive one additional page for each additional student beyond the two page maximum. Group projects must clearly articulate the unique role of each student researcher. While the uploaded grant proposal is the same, each student researcher must submit their own application into the system for the review.
International Travel
Projects may take place internationally. If the proposed country is not the student’s place of permanent residence, the student can additionally apply for funding to cover half the cost of an international plane ticket. Proposals with international travel should likely include travel itineraries and/or proof of support from in-country contacts in the appendix.
Non-English Language Proficiency
Projects may be conducted in a non-English language. If you have proficiency in the proposed language, you should include context (such as bilingual, heritage speaker, or by referencing coursework etc.) If you are not proficient and the project requires language proficiency, you should include a plan for translation or proof of contacts in the country who can support your research in English.
DATABASE OF ANNOTATED SAMPLE GRANTS
| Subject Area | Methodology | Proposal Feature | Review Committee |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fieldwork; Interviews; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Computational/Mathematical Modeling | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Creative output; Survey | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Qualitative Data Analysis; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Computational/Mathematical Modeling; Design/Build | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Creative Output; Literary/Composition Analysis | Non-English Language Proficiency | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | |
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Surveys; Interviews; Fieldwork; Qualitative Data Analysis | International Travel | Social and Behavioral Sciences | |
| Qualitative Data Analysis; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Interviews; Qualitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Literary Analysis | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Literary/Composition Analysis; Theory | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Literary Analysis | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Archival; Literary/Compositional Analysis | International Travel; Non-English Language Competency | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | |
| Archival; Literary/Compositional Analysis | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Archival; Literary/Composition Analysis | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Indigenous Methods; Creative Output; Interviews; Archival | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Journalistic Output, Creative Output, Interviews | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Interviews; Creative Output; Journalistic Output | Group Project; International Travel; Non-English Language Proficiency | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | |
| Archival | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Theory | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Theory | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Design/Build | Group Project | Natural Sciences and Engineering | |
| Creative Output | Group Project; | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | |
| Creative Output | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Literary/Compositional Analysis; Theory | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Literary/Compositional Analysis; Theory | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Literary/Composition Analysis; Theory | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Fieldwork; Lab-based | Natural Sciences and Engineering | ||
| Fieldwork; Quantitative Data Analysis | Group Project | Natural Sciences and Engineering | |
| Quantitative Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Survey; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Survey; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Creative Output | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Interviews; Fieldwork | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Fieldwork; Quantitative Data Analysis | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Fieldwork; Interviews; Qualitative Data Analysis | International Travel | Social and Behavioral Sciences | |
| Design/Build; Quantitative Data Analysis; Lab-based | Social and Behavioral Sciences | ||
| Creative Output | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | ||
| Fieldwork; Interviews | International Travel | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism | |
| Creative Writing; Interviews; Creative Output | Arts, Humanities, and Journalism |
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Office of the Vice Provost for Research
Find Collaborators
Meaningful relationships are the foundation of successful, interdisciplinary research.
Faculty Profiles
Faculty Profiles is a search directory for Tufts faculty profiles which include bios, publications, research areas, and more.
Explore Tufts' scholarly activities using Dimensions, a research knowledge base.
Corporate Connections
Collaborations outside of academia are essential to Tufts success.
Tech Transfer and Industry Collaboration
Connect with Corporations or Foundations
Tufts Facilities & Technologies
Find research facilities and resources that are available at Tufts and connect with the experts who support them.
Search Core Facilities & Resources
Search Technologies for Licensing
Support Functions
Meet the teams that support research both within the OVPR and beyond.
Connect with Support Functions
Contact the OVPR
Tufts Centers & Institutes
Tufts University is home to more than 45 interdisciplinary centers and institutes with expertise on a broad range of topics.
Grant Proposal Checklists, Outlines, Tips and Templates
Research Development provides a curated list of resources related to general, NIH and NSF grant writing. Customized resources for other funding sources are available upon request.
General Grant Writing
Select external resources.
- NIH About Grants
- Rigor and Reproducibi lity Resources , Reproducibility Resource Chart , and How To Address Rigor and Reproducibility
- Sample Grant Applications from NIAID
- How To Determine Where Your Application Will Be Reviewed
- Know the Audience for Your Application
- Application Form Instructions
- NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) for proposals submitted or due on or after October 4, 2021
- New NSF Website
IACUC Resources
Research development services, additional federal funding agencies, talk to an expert.
Strategic Research Development experts can help you with targeted funding searches and proposal development.
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: Hi, my name is Shady Atia. I'm going to present today a presentation on writing a research proposal. This is a very important presentation for postgraduates in order to learn how to write a research proposal. My presentation will go through four main axes. I will present how to write a what is actually a research proposal, how to define your topic, how to organize your research proposal and finally how to write it technically and presented. Well, let's see the first question. What is a research proposal? A research proposal is a statement of intent where you describe your intentions and simply we can describe it into a motivational intention manuscript where you declare your intentions and show your motivations and it's very important in this sense that you define the scope of your topic, the subject enough it has to be specific enough and you have to have a specific aim and objective related to your topic and definitely it would reflect your interest and it should be your own research so therefore you should also explain why is this topic better than other topics and you have to show that this is the first time subject that will be innovative you not previously addressed in a way and that you will carry that responsibility and present it through the research proposal. Well, the next question comes to what are the types of research proposal that we have. Many people get confused about that. We have a research proposal that is mainly under a thesis. A thesis is mainly a manuscript that you write for a master degree and it answers a research question based on existing knowledge. And here we are looking to your capacity to critical think and analyze deep information and process that and presented as new knowledge. While there is another type of manuscript that is called dissertations, the dissertations that are mainly for PhD doctoral degrees and in this sense you have to create a significant new contribution to knowledge and you have to come up with a new solution for a problem or a cure for a certain contextual problem. Well there is a third type of research proposal that you could write for funding grants like the Belgian research institutes or you write it for national research organizations in order to go through a competition process to win a funding to cover research topic okay well these are the three type of proposal that you can write next I will move to the second important question how to define your topic this is a not an easy task because you are most probably not having large experience with doing research and sometimes it's very difficult to do that so in this sense you have to define your topic and the process should start by identifying a general idea or an area of research and then develop it and focus on a certain research question so you have to ask yourself the following question is the topic related to real life because we are looking to applied science we are looking applied research So you have to make sure that this is related to real life. When you answer this question, you have to come to the next question. Is your topic related to societal problem? Is it a real problem in the society that your research is addressing? Is your topic going to be useful and interesting or did someone before answer it? So you must make sure that the topic is useful and interesting. Is your topic focused and specific or is it very broad and large? The more the topic is large and generic, the more it's difficult to come up with something new, it's difficult to process the work. Can your idea fill a gap in research? Do we have a problem or a topic that was not addressed previously by another researcher? So you have also to make sure that your research topic is not a kind of common topic that has been processed by many people. Always you must look for a gap or something that is missing and make sure that your research will cover that area and definitely you should ask yourself will this study generate new knowledge and this is very important because when you generate new knowledge then you have a real contribution and your research is worthy and you should also ask would the benefit from it the architects the engineers the professional in your field is it going to advance the understanding or influence policy this is very important and definitely finally should ask yourself Will this study fill a gap in existing knowledge or resolve current controversies? So these kind of series of questions, you can use them as a kind of checklist, as a starting approach, after defining a general topic you are interested in, and go step by step trying to answer them until you can define and shape your research topic. Well, there are some golden rules you should keep in mind while defining your research topic. You must be passionate about the topic because it should come from you. It should be your interest that you are related. You might ask your supervisor or follow a previously developed idea or concept from your supervisor or your professor. But in the same time, you must have the passion related to this topic. So this is very important. The second Gordon rule is related to the discoveries. Could the topic lead to discoveries? you should not promise to guarantee a discovery, but you should have a kind of estimation this could topic lead to discoveries or not. And you have to make sure that this is catchy topic. It catch the attention. People will be interested in it. It's grabby. It's really related to society. People will really would like to listen to what you are going to present and read it through your manuscripts. And definitely you have to formulate very clearly your objectives and aims so that you are focused in your research and having a very specific topic. And finally, you should select a supervisor, he or she that can help you through this process and has the ability and the skills to guide you through the process. So these are kind of five golden rules I would like to highlight. You must follow them to make sure that you are on the right track. Now, after describing what is a research proposal and how to do it, I would start to talk about the content. The content is very important. Many people don't know how to write a proposal, what should be the order of the information. And here are kind of 10 major elements you should focus on in writing a research proposal. You should cover issues related to the title and the keywords related to your research topic, brief abstract describing your topic, a problem statement, aims and objectives, the significance and importance of your topic and the audience that your research is catering for, the state of the art, the methodologies, your expected results and definitely you should describe the project outline and the impact and the biography of your research. Well let's start with this and and I'm going to describe everyone into detail. Well, when I'm talking about title and keywords, this is very important. Why? Because a title and a keyword is not an easy task. A title in general should be catchy and should be precise. So these are some rules that you should follow to have a good title. It has to be a specific title, accurate, not too long, catchy, and it has to contain the main idea. I should read the title and figure out most probably what is this thesis about or what is this dissertation about. So you have to look at the title in a way and revise it and think about it and most of the time good titles start with an action verb let's say like simulation of comparison of assessment of these are all examples that you can look at and start with them your title. Once you have an action verb it shows already that you are trying to do something to cater or to address a certain problem and most of the time a researcher doing a master thesis or a PhD thesis or even a research for grant proposals he or she should look at these verbs as a starting to identify and formulate their title well once you are done with your title that's not enough you have to define next to the title keywords well you will ask what's the point I just defined the topic and I have a title now why should I use keywords well keywords are very important they should not exceed six to eight words and actually we use terminologies or we will use words that are not in the title in this sense you are helping the search engine to extend the topic so I let me let me give you an example. My topic of my research is called Dynamic Building Kit for Adaptable and Reusable Wall Solutions. That's the title. The title is talking about developing a building kit that could be adaptable, that could be assembled and disassembled for materials or building components that could be reused, okay, and specifically on walls. This is the title and I understand it like that? Well, I can add to that some keywords. These keywords can help me to describe more. I can say that I'm talking about design solutions. I'm talking specifically on post-war housing. I can add a context or a city to describe where I am, Liège in this case. I can add the keyword energy efficiency renovation like that I am extending my title and amending additional words that can help in the understanding of topic and once you do a research with these keywords the topic will pop up in the search engine much much easier so actually this is very important to define your keywords associated with your topic and in this sense they are very complementary well the next step is to move to the abstract well the abstract is one of the things you do at the end so you don't start with an abstract but let me tell you first what is an abstract an abstract simply is a text a piece of text that is not longer than 250 words and it describes simply your topic the research problem the objectives the methodology your results and the audience and the impact of your work so simply the abstract should be read by somebody in less than 3-4 minutes he or she can directly grasp the whole overview of your topic so you summarize the essence of your whole master thesis or PhD thesis in 250 words and therefore it should be really well thought well written and following this structure well let me give you an example here is a topic related to health the topic title is called the effect of exposure to natural environment on health inequalities and observational population study. As we can see those words are not exceeding 250 words, we have a background statement just two sentences, we have a methodology fully described where it has been done, what is the population, the population size, the sampling and finally we find the findings talking about this observational study results with some statistical analysis and the rates of the study that the rates of the study and finally we have to look at the final two sentences talking about interpretation in this sense this is an abstract it's compact but it's describing the whole study into a systematical approach so this is actually you do when you finish your thesis you write your abstract in order to communicate to people and actually when you publish your work on your abstract will be an open source and then after that when a researcher looking on internet they will be interested by your topic by title by keywords then when they will go through your abstract if they find the topic interesting they find interesting findings and interpretation they come up with the idea of investing in reading the whole manuscript or ordering the master thesis from another library or from another country okay so this is very important to start with after having defining the title and the keyword the third step is mainly related to the problem statement and here we are really starting the real work the serious work related to the research proposal well what is a problem statement you must start in your problem statement to contextualize your problem and you have to be concise you have to define exactly what's the what's the problem and most of the time it's good to link your background problem with authorities. So you start by saying the European Union has this objective, the national government has this objective, the region or the province or the city has these objectives. So you relate your background and the problem with political, governmental or non-governmental the United Nations, the World Health Organization, whatever authority that is stating something related to the topic. Also it's important to quantify this information and quantify the background. So it's advised here to define the problem into numbers, give some statistics, some figures related to the issue and you must also contain an overview of most relevant work. You should also try to cover others work saying in this context of this problem those stakeholders are doing that or doing that or covering this problem or addressing it from an angle or another. It's also important here to describe clearly your hypothesis that you have been done and how you are going to enter to propose the problem. Well, after describing this background and preparing the reader for the topic, you can directly now start to propose the problem and you have to show a really significant problem that is related to a a topic. So you should not make the reader get lost on the opposite. You should start to define a statement clearly and make sure that it's a societal problem in a certain context. Well this is an example. Just remember that at the end of the day a research proposal maybe in a master's thesis or a dissertation you will get funding or sometimes you don't get funding you do it work for free but at the end no one will fund a research proposal or find it reasonable as long as it's not solving a local or global problem. So my advice in writing a research proposal, make sure that your problem definition is by default solving a local or a global problem, trying to solve it in a way or another, linking to reality, linking to statistics, putting some figures, variables, and contextualizing the problem, describing it in a way that is viable, up-to-date, related to our current practice. Once you are done with that, you can start to define your aim and objectives. And you should take into account that an aim is not an objective. An aim is like a bullet. It's very important to define your aim. Once you define a good aim, you are sure that you will do a good research. So, aim well and you should hit your target cleanly. If you don't write a clear aim that is targeting a specific goal, you'll not succeed in doing your research. And simply you have to say what you want to simply and directly want to say. You have to explain what is this research going to do and who will benefit from it. I will give you some examples related to aims, but keep into account it has to be short, it has to be to the point, and it's like a bullet. you don't need to write a lot. It's the shorter the better. Well, what's the definition of an aim? An aim simply provides an answer to a general problem. So, so far we are not talking about the specific problem. This is the objective. In an aim I'm talking about the general problem. And the aim goes along with an adjective. It has to be concise. You should be aware that your grandmother can read the aim and understand it. And you should also keep in mind that it should be related to what's motivating you so this is very important and it should assist on improving the decision lead this is very important some examples of aims you can have a look lowering the dependency or the dependence on fossil fuel increasing the energy efficiency of improving the situation of increasing renovation rate dissemination knowledge sharing information general overall aims related to a serious problem and in this sense you don't need to write it more than one sentence maximum and then you are describing the topic in general in a sense in an aim that a non-technical person can understand it when I say here my aim of my research is to increase energy efficiency in the building sector this is a very broad generic aim anybody can understand and that's the purpose you should have this aim now once you define the aim you cannot be more specific and focus on the objective. But let me tell you what's the objective. The objective is more specific to your study, it's more accurate than the aim, and it's operational. So there is an action in it, you have to do something in it. In the aim, in the objective also it has to correspond to what you will try to produce and generate. So it has to be very precise in description, it has to focus on the central research question, and often contextualize it to a specific climate, context, country, region. Very important and these are some examples for objectives. So here I'm saying my objective to develop a software or a program to calculate turbulent nonlinear equation. Here the objective became very clear. Analyze the reason of low renovation rate identify barriers understand study the impact of assess compare so the objective has to be very clear very precise to the point talking about a specific aspect so in general it should be combined with the aim but let me give you an example with a good description of an aim with an objective well have a a look and read this sentence sorry just have a look I have a aim here the main aim of this research is this to disseminate technological knowledge on adaptive facade at a European level that's the overall aim very general I want to spread or share information related to a specific type of building facades in Europe and do it on a European level so this is a very broad aim and this is very successful one sentence like a bullet now how I'm going to do this aim I need to describe at least three four objectives to do this aim first of all I'm aiming to increase knowledge sharing secondly I'm looking to develop a new knowledge thirdly I'm starting new collaboration so in this sense I am precisely describing how I'm going to achieve this aim through operational tactical objectives. Another example could be interesting here, have a look at that. The project is aiming to improving building energy labeling schemes. So I would like to improve the labeling of buildings, so like you buy any food product you have a label telling what's the ingredients, I want to improve the labeling of buildings. But how I'm going to do that? These are the objectives that I'm going to do. I'm going to review different building labeling. I'm going to review different performance indicators. I will investigate possibilities for developing other labels. I will choose some case studies. I will examine the robustness of labeling schemes. I will evaluate their social acceptance. I will analyze the results. I will create a fair framework. Directly, you can see that we have here at least something around eight objectives serving one aim. So it's very important in your research proposal to keep this structure in your writing. You have an overall overarching aim with a very specific objectives that serves to achieve this aim and they as I told you it has to be operational with adjectives. Also a criteria to make sure that your objectives are well or right good written we call objective smart smart stands for specific measurable attainable realistic and time bound every reviewer reading your research proposal he or she will look at these objectives are the objectives specific are they measurable are they attainable realistic and time bound and this is very important you have to make sure that you have a pointed topic you are covering it you can measure the objective and measure what you are doing you must make sure that you can reach this objectives and that you have a realistic objective it's not a dream you have calculated the time and the effort and you can do it and definitely it should be time bound so you must put it in a frame of a deadline with a certain start and an end date once you make sure sure that your objectives are smart you can pass now and validate your topic and in this sense you can look to the topic and say I have smart objectives and you need some time to do it it's not easy to write it but you need just to take some time brainstorm your topic once you defined well the problem you can then define good the aim and from the aim you can break it down into specific objective. This is how it works. Another final advice for the aim and objective, don't forget to frame it. You need always to frame it. So these are the questions you should ask yourself at the end of writing your aim and objective. So first question, is it worth it answering your research question and the aim? What will benefit, am I going to benefit from it? Is the society, the community, the professional or the scientific community going to benefit from it? Is it specific, your aim and objective? Are they answerable? Can we answer them in this frame of thesis or dissertation? Is the topic original? Is it contribution to knowledge? Did somebody else do it or I'm really doing something new? What about the outcomes? Are they appropriate? Do they think ahead are the expected outcomes really achievable this is very important and finally you should ask yourself is this topic interesting to you there is many students who start a thesis and after a while they say I don't like this problem I don't like this topic they stop this means that you are not certain that you are motivated you are passionate and this topic is for your own personal interest is triggering you so these are some important advices to validate and to make sure that your aims and objectives are well written and this is a very fast example you can have a look for a winning proposal. This is simply an example showing the specific measurable and attainable realistic time-bound objectives. You can see here I have a precise problem. Agriculture is the backbone of Belgium's economy for example and it's central to the government development strategy but although the agricultural sector employs more than 75% of countries workforce and accounts both directly and indirectly for approximately 51% of countries Belgium's gross domestic product little is known about the scale of livestock farming livestock diversity distribution of livestock farms so here I have a problem very specific well described it's contextual there is a background on the national level I find some figures and statistics and the researcher simply wanted to say one thing we don't have information about the livestock farming in this country but instead of writing it directly he put a context he gives some numbers he put some figures he shows the importance of the topic and right after he will or she starts to write the objective. So the objective here is not a aim, he is directly talking about operational specific tasks. A team of eight researchers defining who will do that, eight researchers at the livestock research unit of Agricultural College for example at Liège University will research the types and extent of livestock farming in the country. A comprehensive report will be published and an online database and website will be created the project will be presented in its entirely four years after the start of the project at the sub-saharan agricultural summit in Botswana in November 2016 so you have here a very clear objective operational with steps following up and I can measure it it's specific it's attainable it's realistic it's time bound so this is the way how to write a good research aim and a research objective and this will be the start of your research proposal and just to remind you keep in mind that in the beginning of your search proposal you have to have a catchy and informative title the summary and the abstract leave it for the end you will not do it when you start this is after you finish write your six eight keywords that are not included in your title make sure that you have a good problem statement description with a problem related to contextual societal issues, define an overall aim and go for your operational step-by-step specific objectives. In this way if you keep this slide in mind while developing your first part of your proposal you are on the road to success. Well I'm done with the aims and objectives and I will move to the fifth component or element which is the significance and audience. It's very important in research to define why is this research important and who are the users of this research, who are the end users who should benefit from this study. Am I doing this study for myself, for fun? You should not do that in university. Even though that some people try to do explorational work, you can do it, but you should just succeed in translating your own interest into a common interest. Once you did it, you are on the track. So significance is meant the importance the importance here so you have to make sure and describe in your text what is the added value what is original about this work why is it important even if some people are not finding it important you have to defend the work and present it and write it in a way that is important something you should show that this is something never that was never did before and once you contextualize your topic you succeed to have a significance For example, if I'm talking about renovation using prefabricated units or if I'm talking about prefabricated housing. Once you open or would like to research the topic, you might get some feedback saying, yeah, but prefabricated construction, there is many countries who do it in the United States, in Canada, it's nothing new. But once you contextualize it, you can make it new. If you say studying prefabricated housing in Liège or in Wallonia or in Belgium or in the province X or in the region X or for residential housing or for a specific context, for a specific region. Once you contextualize a topic, you directly make it original. So there is many topics in your society, in our context here at Liège universities. Maybe there is advancement in Finland or in other European countries, but they are not contextualized. So you can also borrow ideas from abroad, from other researchers, and contextualizing and study how to implement them in our context here. Once you do that, your topic becomes significant and important and becomes unique because we don't have answers for that. Also, it's important that it does not mean that the question is new, but never approached like you. even some researchers they select a topic that has been selected or researched by many people before but you can show that how you will do it in a unique way how you will go through personal endeavor that looks differently to process the topic so don't be afraid and saying yeah I when you look at the depository of previous master seasons if you find somebody else before you did the same topic that you are interested in, you should not stop. Take the topic, read it well and see how you can do it different. Once you define this difference and set it as a significant, as added value, you can guarantee that your research topic is significant and important. Also, your topic should lead to added value. At the end of the day, you should add value and make sure that you have important and significance has to take into account of the principal aim. It should be at the end related to your principal aim. Some other questions you could look at. Questions have to be open in general when you describe your topic. Here you can add a list of keywords not included in the title and the motivation is linked to the context. Well, defining the significance is important. Now you defined your problem, your title, your aim, your objective, why is this topic important, how is it significant. Now comes a very important topic people forget about and I think personally you might start by that. The audience. Why are you doing this study? Who is going to benefit from this study? Who you want to reach? Define your target audience very clearly and from the beginning. The easier the target audience is described, the easier you can do your research. Many people forget that it could be politicians your target, your target could be professional community, it could be the research community, it could be managers, it could be whoever, community or stakeholders. But leaving your research proposal without defining the audience, there is no meaning. Because many people do interesting studies, but then they don't contact their audience. If I'm doing a study, for example, about the green area spaces in Liège city, so I want to know how much green area per square meter per citizen is in the city of Liège. And I did a very beautiful analysis and I went through the neighborhoods of Liège and And I then identified through my analysis how much square meter of green spaces are available for the citizens of Liège. If at the end of this study I did not contact the community or the local authority of Liège city or the province and tell them here is my work, how can you benefit from them? If I didn't go and do an interview with them, if I didn't contact them to make sure that the municipality is benefiting from the study, then I failed to connect my research to the audience. So you must always to make sure what's the research and ask yourself, what's the relation between my research topic and the audience? And did I allow the audience to intervene in my study? In this sense, I should have maybe went to the municipality and asked the urbanism sector or unit and tell them, I'm doing a study about Liège. Can you help me with this information? Is this information for you helpful? How can this information, can I modify it to meet a kind of certain requirement from your side? So it's very important to define the audience and not to define it theoretically on paper. No, you have to go engage with those people, contact them before starting your study, during your study, and after your study. You can even invite them to your defense. If you don't do this step, our research will have no impact. It will be just theoretical research hidden in research university without having any impact on society. So therefore, make sure always what is the audience of your research. Get in contact with these people. And as I told, why you have to reach those people? Because you have to consider your motives and why you feel this group should be targeted. You have to know why you want to reach a particular group. And you should provide insight that will help develop effective study. and you should say also why should they be interested in my research this is very important once you define that you can start now your research I'm moving now to the step number six but I would say that this is the first chunk of your research proposal it does not need to be more than one or two pages defining clearly from the title going to the keywords talking about your problem statement and the background defining the aim and objective the significance of your work and finally the audience once you define this one or two pages i can guarantee you that you have a good topic well defined and make sure that you revise it with your supervisor well you are now ready to embark and start your topic more clearly but you have to describe another additional component in your proposal? The state of the art or the literature review. What is the state of the art? Why do we do a research related to state of the art? Why do we review literature for a research proposal? Number one, you have to improve your own understanding. You have to understand, you have to become an expert because now you are talking about a topic, you don't know enough information about it. So you have to understand what has been done before and you have to read literature so number one why we do a literature review to improve the understanding number two you have to build your expertise in the specific domain number three you have to demonstrate knowledge and show that you understand a specific knowledge related to the topic and you have to update the reader with the state of the art because at the end of the of the end of the day the master thesis or the phd you will submit it to a jury or a reader or you will set it online and you would like the community to read it. Once they read it, they must make sure that they are up to date to the latest information related to this topic and therefore we should do a literature review. To do a good literature review, you must guarantee that you have good resources. You should look at major published work, you should look at a narrow specific topic and you should start your review. The review should cover the major concepts, snapshots relationships classifications and extractions so the literature review actually is like an essence you go through different publications different sources and you extract the most important information and you provide me with a snapshot with a pattern image describing what has been done before what are the major publication related to this topic and like that you can put me up-to-date related to the topic. Does one of the criteria that anybody would like a professor will look at a research proposal will ask does the proposal advance the state of the art? Does it introduce innovative approaches? This is very important and the more you go into this a PhD or a grant proposal the more the answer for these questions is very important. If the proposal shows it does it show a good understanding of the major work? Does it identify the gaps of existing knowledge and so on so this is very important and you should also say what is currently available in Liège in Belgium in Europe and worldwide so this is the aim of the literature review to make sure what is done also in the North America what's done in Asia to make sure that I am up-to-date related to this topic well you should also capture the major concept and ideas related to research and finally you should ask yourself how is your research you are doing compared with similar research in other contexts so you should not only describe your research topic and forget that others maybe did the same idea 90% of ideas are not new we are processing others ideas so 90% of ideas are not new So you should keep in mind, put an assumption in your mind, that maybe somebody else, someone, somewhere else, tried to address the same problem. What about looking, exploring, how did those other people do my work? So this is the aim of literature review, to make sure that I cover the literature, I am up to date, I am covering the major concepts and publications that describe the topic, and also similar studies related to my research topic. once you did that you can move to the methodology and the methodology should describe how you are going to do your research in the proposal and this could not should not be a long text it could be a couple of paragraphs or maybe maximum three paragraphs describing how we are going to do your research there is in general different methodologies you can do strategic research you can do applied research you can do experimental research and these are all examples of researchers that you can do if you like to do lab work and monitoring then it's experimental work if you would like to do applied then it's more like simulation case studies system analysis comparison analysis if you are looking to develop concepts model standards prototypes solutions you are more into strategical basic research and definitely if you are looking for developing things beyond applied research, pure basic research, a theory, an equation, a philosophy, then you are looking at basic research. So you should define clearly what is your methodology and these are all examples for different methodologies as you can see and every researcher and every specialization, every group of specialization has its own collection of methodologies they use. People in social sciences, we know that they use a lot interview and they use surveying techniques. This is their methodology they come up with. People working in engineering, for example, they go more for experimentation and so on and so forth. So you must make sure your domain, your expertise, your field of expertise, what are the common methodology. In the field of architecture or buildings in general, we use analysis research, development research, we do a lot of case studies research, evidence-based design, parametric research, optimization, also participatory or action research, operational research, post-occupancy evaluation, lab research, and system analysis research. So just you must be familiar with these types of methodology and describe them in your research proposals and now I will move to another thing which is called a method which means that like in the aims and objective there is an aim and there is an objective here there is something called methodology and method. A method is a small action of research done to achieve a methodology for example I can have a case study as a methodology but in order to achieve this methodology, I have several methods that I can do. I can do some drawings, photography, videotaping, visualization, sketching, mapping, process analysis, technology review, history review. These are all methods that I can use in my research to achieve my methodology. So it's very important in your research proposal that you define in the beginning your research methodological on this level. Is it basic research, is it strategical, is it applied, is it experimental. Then you pick up a methodology and don't hesitate, you can have several methodology in a research. You can combine evidence-based design with case studies, there is no problem at all. But once you define your methodology, you have to pick up a collection of methods. A systematic review is a method, data analysis is a method, GIS or simulation, visualizing, classification and categorization, These are all methods. So your research proposal should address these methods and simply your methodology in general should describe how are you going to approach your work. So as I said you start with a literature review and from the literature review you see what has been done by previous researchers. You have to outline the instrument, fix boundaries of diseases and we should look at different methodology, describe them well, make sure that you have qualitative and quantitative approaches for your methodology, and make sure how you will collect the information, how this information will be robust. I give you a very important example here you should keep into account. When we talk about methodology, one of the big problems we see today in research, the methodology should be replicable, which means that any independent researcher is going to do the same research you have been doing, he or she should be able to repeat the same methodology and come up with the same research. One of the problems we find today in research, very common, that researchers, they do the research without describing it well, without a clear methodology, and as a consequence, the results are fake, because they didn't have a methodology. And once you describe your methodology, keep into account that it should be replicable and repeatable by others. So this is very important. And how to present a methodology, this is how to do it. You have to come up with a study design. A study design is simply a specific plan or a protocol for conducting the study. and it allows you to investigate and translate the conceptual hypothesis into operational research. So actually in this section of methodology I should see this overview design. I'm saying that my methodology is based on quantitative and qualitative research methods. I have here case studies and so on and so forth and I here have my own other quantitative approaches and you draw it into a sort of diagram and this is another representation I have descriptive analysis I have analytical here I'm going to do a survey here I'm going to do experiment here I'm going to do a cross-sectional analysis once you think about your methodology and represented in a graph like that and describe it into a couple of paragraphs you are done with the methodology it's accessible and I have a very interesting document you can ask me for it it describes the different research methodologies in architecture. So you can go from theoretical research, interpretative research, experimental, survey, simulation, qualitative, even action research, and for each of these methodologies there are different ontological assumptions, epistemological assumptions also, methodologies, how you validate, how you have examples for each of those so this is very important very helpful you might use it and I would like to ask you to start your methodology by sketching drawing thinking about picking up some methods making sure how you will address it you have to define your method your sample your case studies what are the target users are you going to use equipment analysis this is very important and you can draw a study design scheme for that and the study design scheme like I showed you based on this analysis using this Excel or this table I provided previously. Make sure that you draw a study design scheme and integrate it in your proposal, discuss it with your supervisor, explain why it is the most appropriate to effectively answer your research question and you have also to explain what alternatives have been considered when and why these have been disregarded. So these are the golden rules for the methodology. Don't forget you have to come up with a study design scheme, describe your methodology on the level of what is the strategical level of your research, what is the methodologies you are using, what are the methods and summarize it into a scheme and present it and describe it. Well now I would like to move to the expected results even in a research proposal before doing your research you should describe your expected results this is very important and how are you going to do that it's mainly based on your literature review if you are going to read some major publication related to your topic you can be able to expect what will be the results of your work you may fragment you may grab fragments from other studies but you can predict possible outcomes and that's all what you are expected to report in this sense. You have to be based on the literature review, linked to the aims and objectives, explain what you will be producing, something concrete, evidence-based with numbers, you have to define how is it going to be usable, is it some rules of thumb, is it findings, is it guidelines, is it advice, is it a strategy, what it is and for example you can say I'm going to come up with a prototype, with a design concept, with a solution. These are all important to define in the expected results. So it's not here meant that you will say exactly what will come out from the study but you will define what parameters, what outcomes you are looking at and these are examples of outcomes you must keep into account that you answer this question very important in your research proposal because if you are just putting facts they are called data if you are classifying them they can become information they will become only knowledge if you are adding an analysis and interpretation kind of working the information into a useful information and once you have knowledge you can help in decisions and actually that's the cycle of knowledge so your thesis is mainly looking to collect the data and information and process them to generate knowledge so that this knowledge can help the community and the decision makers to take decision and become more informed, more knowledgeable. Well, what could be examples of outcomes? This is a series of outcomes. It could be a product, rules of thumb, guidelines, a manual, a website, an application, even an app. Don't hesitate to develop an app for your master's thesis. This could be interesting, a map, a tool, a website, a program, a book, an infographic, a cartographic guide, equation, model, benchmark, simulation, a checklist, sometimes some students come up with their master outcome, a checklist, a policy, a strategy, a theory. You must be sure that you come up with a concrete outcome that you will present at the end of your thesis and you link this outcome to the audience as described previously. So this is very important and to validate that you have good expected result describe how the work will be validated. You must make sure that your outcomes and what you are going to present will be compared with results published and other works. Are you going to use a user group or a case study to test this outcome because it's not enough to tell me I will come up with a map or a tool and then it was not used by anyone or it was not tested by anyone. Make sure that you have a validation process and in the validation process you have some groups or users who make sure that your outcome that you use was developed for them in a useful way and you should look for internal and external validity of your result. If this research is repeated by someone else, would they get the same results you did or not? Is your work accurate enough? Do you have a systematic approach? Can the result be generalized in another similar context? These are interesting discussion questions that you can use to develop your final conclusion later in the thesis, but also you could address them in your proposal writing to make sure that you are not only looking to produce an information and through it without making sure that it works that it function that will have an effect and impact well by that I am approaching almost the end now you are described you have described those major topics from the keywords until the research results and outcomes now it's time to talk about outline and talk in the language of professional language professional language this is not a research topic this is more related to professionalism and any institution should talk about it. Once you go through any professional document you must develop an organizational chart. Organizational chart it's a chart that tells me what are the parts and the component of your research or your research thesis. In this sense you should have a description of your chapters maybe you can put your chapters you can put the topics you are talking about and it should represent your work and it should predict the possible progress of your work. So here I'm drawing all the component of my research in one diagram. In French we call it Organigramme, in English it's called the organizational chart and any research proposal must include an organizational chart to describe the components of the work and the main work packages that you will do and in every work packages I have associated activities. This is very important to clarify the topic. I have many master students, they come up at the end of their master thesis and they are not able even to write a structure or a table of content of their own thesis. Why? Because they didn't do an organizational chart. Once you do it early enough, you know that you will start with an introduction chapter, you will have something about a methodology, what are your case studies, your results, what would be the validation part, what would be your conclusion part, the discussion. So therefore it's very important it's also important to be added you can add it in the annex of your research proposal don't hesitate to do that and you should do use it also to discuss with your supervisor in the beginning how are you going to proceed with your master's thesis or your PhD dissertation very important to include it another important organizational chart related to the professional work the Gantt chart. Any master student graduating from Liège University he or she must know what is a Gantt chart because without that you are not going to be able to process tasks on long term. A Gantt chart is a professional diagram it is a methodology used to define milestones and work packages and activities and in this sense you describe your work in sufficient details and you set up deliverables, steps, deadlines. Very important. More detail than the organizational chart. So if you look at the organization chart, it's mainly chunky. It's looking at big scale component of your research. While here you are going more into detail and it's very important to be also placed in the annex of your research proposal. As you can see, here's a list of activities. Here is the master thesis. It takes an average in Liège four months I can define every month in two weeks and define with these dark bars when I'm going to do the literature review, the interviews, the case study analysis, the simulation work, when I'm going to start to write my thesis. Very important to do that as early as possible to make sure that you go psychologically through the process of your thesis writing. Because if you leave everything till the end you will be improvising and improvising you can never become professional with improvisation as long you have a lot of time and in fact you don't have time you must try your thesis to graduate so this is the best way to do it as early as possible and try to explore previous master's thesis of older students who graduated and see how they did it to make sure that what could be the tasks and activities that you must come up and how much time they will take Some people would say, I will do a literature review in two months. In reality, it might need three months. Maybe it will need eight weeks. You never know. Six weeks. You never know. So it's very important to have this translation into deliverable steps and time. And it's very important once you finish this, that you have a section in your research proposal called project outline. The project outline. You link it to the organizational chart and you link it to your Gantt chart and your proposal must describe where are you going to start. You say when are you going to start, what steps are you going to do and where are you heading to, where will you get to, how you will get there. Very important. If you don't do this in the project outline, the certainty that you will do successful work is very weak. So make sure that you have defined the step of your research, you say where are you starting, describe what's the problem, the literature view where are you heading and make sure that you will describe that accurately and what are the final aim to go for well the last step that you should look at before leaving that I have just forgot to say that you should describe every milestone into activity description and evidence of progress the last thing you should look at is the impact and biography this This is the last part of your proposal and the last element that you should address in your proposal. And first I will start with the impact. It's very important to identify, does the proposal clarify clearly how it is relevant and realistic on the short-term and long-term. By definition, impact is the effect or influence on short-term to long-term scientific, technological or socio-economical changes produced by a research, directly or indirectly, intended or unintended. And you should ask yourself, are the impacts identified by the proposal relevant to the society at large? Can the impact be listed and realistically achieved? And let me give some examples. The impact should be able to be explained. is different from the objective and it's the only way to do an impact is to publish your work because if I'm going to spend maybe six months of my life on a manuscript for a thesis or maybe four years for my PhD work if this document is going to be in the depository of the library of Liège University no one on earth will access it even it's not on Google so forget about it the only way make sure that your work has an impact and other researchers and other professionals and the society in large is going to access it, read it, benefit from it is to publish the work and study or look at the impact of your work. Here is an example of a work I will read you I will read you this very fast energy certification labels increases the awareness of energy consumption and enables consumers to compare buildings therefore providing builders with an incentive to improve energy efficiency in buildings? Improving energy efficiency in buildings is one of the most cost-effective ways across all sectors to reduce energy consumption and hence green gas house emissions. Energy efficiency is the most cost-effective method to improve energy security. From the household perspective, energy efficiency seems to be profitable. you are telling how energy efficiency or the labels are you how is this impact of this topic energy efficient lighting and appliances can save about 465 euro per year per household in energy bills much more savings can be easily insured when the whole building is energy efficient the energy efficiency of buildings can only be guaranteed by creditable building energy label so here you are describing what is the impact of your research you are saying that while studying the labeling of buildings already I can promise to have a cost-effective savings and I can guarantee a security and independence from fossil fuels and you try to quantify it with some example saying that for example a building that has energy label a for example can save up to 465 euro per year so we give an example so this is a very important aspect that you should include what would be the impact of your study and this is difficult you have to brainstorm you have to think if I come up with my research and I publish it could it be useful examples for dissemination activities also to spread dissemination means spreading your research findings is there a clear or attainable plan for dissemination for results this is a question. Is the dissemination plan targeted, clear and attainable? Is it relevant and you have a clear exploitation of the results? These are all important topics and you can disseminate your work by publishing it, by having internal seminars, regular reporting, publication, conferences, exhibition or reaching out communicating with the community. If you go to an NGO and tell them I would like to present my master's thesis to you, I would like to share with you my document. These are all important activities you must guarantee to make sure that you are disseminating your knowledge. In a PhD it's very important to do a lot of effort to disseminate the information. In a master thesis it would be enough to publish in a conference or publish in a journal, your results, and this is the only way to validate and make sure that your information now is available to the public, it's accessible, and it could be shared and become beneficial to the society. Last part is the biography. In your research proposal, you should include a bibliographical sector. You should have references cited in a specific format. In my lab, I prefer the APA standard, and I have a presentation on that. But you should make sure that many reviewers, they go at the end of your research proposal and read the biography. And based on the quality of biography they find, they start to say this is a good research or not. This means that the more you are describing the key publication-related topic, it means that you did your homework, you read, and you should pay attention how you write it, because there are rules in citation. You should write, for example, the family name, and then the year, and then the title, and then the city, and so on. There are different styles. Make sure that you are using the right style. You just ask your supervisor for that. You can show your motivation on the subject also based on that. Use a reference management system. There are many softwares. Previously, there was a software called EndNote. Today, the most commonly used is Zotero, and I advise you to use Zotero. Well, I'm going to the end. This is it. This is the research proposal. It sounds maybe dense, very informative, but keep in mind that a research proposal does not need to be more than five, six pages. Sometimes the research proposal, a large European project, can be something like 25 pages. I'm talking about funding of millions. So in your case, all you need to have five pages, six pages, describing and covering these issues and just start to write and go through it I give you some golden final tips structure your text make sure you have headings address every topic into a heading structure section and write under it write short sentences this is a very important thing many I figured out that in the French speaking word many students seems to write long sentences chop your sentence keep it short and follow your ideas and don't make it complex just write you can write down first in a sketch what ideas you want to communicate and start to make them short sentences in a row use bullets bullets are very important because readers get bored when they find a full block of text try to make bullets to highlight important topics provide images charts i already told you that you need a gun chart an organizational chart a study research design for the methodology try as maximum to have a kind of visual component don't make it exceed 30 40 percent of the proposal so that the proposal is readable and accessible and the keys are access to success are important that you should assure that all relevant chapters of the proposal have been addressed accurately the ten themes that I described are addressed in detail be brief and concise as possible you should support your information with empirical and proof try to have always statistics numbers references to cite your work right don't hesitate don't leave it till the end if you have time write a part of the proposal later on write another part so just keep writing it's very easy it's not a difficult thing it's just that you have to get used to answer these kind of questions and do it and improvise it ask for peers you can send it to colleagues to a teaching assistant to your supervisor don't hesitate to do that to review the proposal and improve it you can make draft 1 draft 2 until you are satisfied and willing to submit it you can get expert help you can talk to the audience people you can talk to somebody who knows about the problem go consult a professor or any person who is professional you should be well organized synthesized and don't forget that we are looking for a master student a master student who has a critical appraisal who can criticize who can build up a case with new information and this is very important by describing any controversies that you find in the objectives include the evidence as possible whether it's against or with your proposition these are the key rules of success I would like to go back just to remind you that this is very important to respect this structure cover it go step by step until you have a good proposal one thing I can promise you if you developed and invested as much as possible time in writing your research proposal your master thesis process will go as smooth as possible because you thought ahead about what you are going to do so instead of going reactive and just reacting on everyday crisis the simulation is not working the interviews is not doing you have here something that protects you it makes you more certain stable and you see what are you going to do and already you are certain that you can achieve the goal easier so this is very important I would like to thank you for your presentation here are my reference and those don't hesitate to contact me I'm looking forward for your proposals thank you very much


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Get to know your audience. One of the most important considerations for any presentation is knowing who your audience is. When you're clear on whom you're speaking to and why you can design your presentation to resonate with your target audience. So, step one of your presentation planning process is to understand the grant funder's ...
Grant proposal presentations are a crucial opportunity to make a compelling case for your research project, demonstrate your expertise and credibility, and show how your work aligns with the funder's priorities and goals. A well-designed presentation can help you stand out from the competition and increase your chances of securing the funding ...
A grant proposal is an investment request for a nonprofit or a for-profit project. A successful grant proposal shows the grantee (the organization or individual investing) that the investment is worth their time and money. To be successful, a grant proposal needs to define your organization's goals, explain the impact of those goals, how you ...
1. Abstract. The abstract is a summary of your research proposal. It should be around 150 to 200 words and summarize your aims, the gap in literature, the methods you plan to use, and how long you might take. 2. Literature Review. The literature review is a review of the literature related to your field.
Getting the Grant. Applying for grants is a delicate and sometimes frustrating process, and the first grants you win may well be the hardest. A grant presentation is a great way to build a relationship with an organization, and a way in with funders who do not accept unsolicited applications. Use a conversational and informative approach to ...
Purpose of A Proposal. To show you have a worthwhile research project to undertake. To demonstrate that YOU have the competence to complete it. To discuss all relevant aspects of the research process. To enable others to evaluate whether enough information exists to want to support the proposed study. As a supervisor (e.g. a thesis)
Grant Proposal. Grant Proposal is a written document that outlines a request for funding from a grant-making organization, such as a government agency, foundation, or private donor. The purpose of a grant proposal is to present a compelling case for why an individual, organization, or project deserves financial support.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It's targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
Writing a grant proposal is not something to be undertaken alone. Even the most seasoned of researchers will need advice, guidance and constructive criticism from trusted and experienced colleagues when developing new grant proposals. For many junior researchers, a supervisor will be the appropriate person to provide this support.
Developing a grant application can feel daunting at first, but with practice and good support, becomes easier with experience. 1. Get Visible - The Sooner, the Better! It's a good idea to start building up your profile within academia early on. Make use of all the resources available to you to showcase yourself, your research, and your ...
Template 10: Project Grant One-Page Proposal Presentation Report. Here is another PPT Template that is bound to get you that grant. Equip this powerful one-page template with the particulars of your project and the institution you represent. Mention the grant budget requirements in this editable PPT Template.
Download ppt "Writing a Successful Research Grant Proposal". Research Experience Dr. S. Arunachalam: Research grants - £0.5 million Publications - over 200 articles PhD supervision- 7 PhD examination - 42 (UK: UEL, CU, UH; India Anna University, MKU, MSU, NITT) UK industrial consultancy in manufacturing (Ford Motors and SMEs) Prof. S. J ...
As any GradFund advisor would surely caution, the exact structure of your grant proposal will depend on the grant for which you are applying and your discipline. However, many successful dissertation research grant proposals will contain similar components: an introduction; a background, methodology, and/or literature review; your previous ...
Step by step guide to writing a research grant proposal Introduction Step 1: Announce the topic and the area Step 2: State your focus Step 3: Place the proposed research in context and explain the need for this research. Is the research timely? Why? Step 4: State the broad aims of the study ...
responsibilities. 9. Be prepared as time from call for proposal to last date may only be 1 2 weeks. 10. Have a maximum of three to four research objectives in the grant application. 11. Detail the ...
Introduce your research group, highlight the significance of your project, and state the budget you are requesting. These are just some of the elements that are normally required in a grant application. Each grant application will have its required elements and structure, so follow your grant guidelines meticulously.
Grant proposals. A grant proposal is a formal document you submit to a funding agency or an investing organization to persuade them to provide the requested support by showing that (1) you have a plan to advance a certain valuable cause and (2) that the team is fully capable of reaching the proposed goals. The document may contain a description ...
These sample proposals went through multiple rounds of revisions with feedback from both Office of Undergraduate Research advisors and the student's faculty mentor. First, it helps to learn about before you get started. Then, when you begin drafting, it's normal to make lots of changes as the grant evolves.
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
Plan: Overarching principles. Be specific- even if it might change - instructions for person who will do this research on your behalf. Be chronological, orderly, logical- "best manual you've ever read". Timeline covers background research through final product; most of airtime to data collection.
Research Development provides a curated list of resources related to general, NIH and NSF grant writing. Customized resources for other funding sources are available upon request. Grant Proposal Checklists, Outlines, Tips and Templates | Tufts Office of the Vice Provost for Research
What is a research proposal? •Outlines (in narrative form) the plans for your research project ... •To apply for funding for your research •To request approval for your research from an IRB. Basic Elements of a Research Proposal Abbreviated versions of: •Introduction •Literature review •Methodology •Theoretical framework ...
This is a very important presentation for postgraduates in order to learn how to write a research proposal. My presentation will go through four main axes. ... cater or to address a certain problem and most of the time a researcher doing a master thesis or a PhD thesis or even a research for grant proposals he or she should look at these verbs ...