Fix "local variable referenced before assignment" in Python


Introduction
If you're a Python developer, you've probably come across a variety of errors, like the "local variable referenced before assignment" error. This error can be a bit puzzling, especially for beginners and when it involves local/global variables.
Today, we'll explain this error, understand why it occurs, and see how you can fix it.
The "local variable referenced before assignment" Error
The "local variable referenced before assignment" error in Python is a common error that occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. This error is a type of UnboundLocalError , which is raised when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned in the local scope.
Here's a simple example:
Running this code will throw the "local variable 'x' referenced before assignment" error. This is because the variable x is referenced in the print(x) statement before it is assigned a value in the local scope of the foo function.
Even more confusing is when it involves global variables. For example, the following code also produces the error:
But wait, why does this also produce the error? Isn't x assigned before it's used in the say_hello function? The problem here is that x is a global variable when assigned "Hello ". However, in the say_hello function, it's a different local variable, which has not yet been assigned.
We'll see later in this Byte how you can fix these cases as well.
Fixing the Error: Initialization
One way to fix this error is to initialize the variable before using it. This ensures that the variable exists in the local scope before it is referenced.
Let's correct the error from our first example:
In this revised code, we initialize x with a value of 1 before printing it. Now, when you run the function, it will print 1 without any errors.
Fixing the Error: Global Keyword
Another way to fix this error, depending on your specific scenario, is by using the global keyword. This is especially useful when you want to use a global variable inside a function.
No spam ever. Unsubscribe anytime. Read our Privacy Policy.
Here's how:
In this snippet, we declare x as a global variable inside the function foo . This tells Python to look for x in the global scope, not the local one . Now, when you run the function, it will increment the global x by 1 and print 1 .
Similar Error: NameError
An error that's similar to the "local variable referenced before assignment" error is the NameError . This is raised when you try to use a variable or a function name that has not been defined yet.
Running this code will result in a NameError :
In this case, we're trying to print the value of y , but y has not been defined anywhere in the code. Hence, Python raises a NameError . This is similar in that we are trying to use an uninitialized/undefined variable, but the main difference is that we didn't try to initialize y anywhere else in our code.
Variable Scope in Python
Understanding the concept of variable scope can help avoid many common errors in Python, including the main error of interest in this Byte. But what exactly is variable scope?
In Python, variables have two types of scope - global and local. A variable declared inside a function is known as a local variable, while a variable declared outside a function is a global variable.
Consider this example:
In this code, x is a global variable, and y is a local variable. x can be accessed anywhere in the code, but y can only be accessed within my_function . Confusion surrounding this is one of the most common causes for the "variable referenced before assignment" error.
In this Byte, we've taken a look at the "local variable referenced before assignment" error and another similar error, NameError . We also delved into the concept of variable scope in Python, which is an important concept to understand to avoid these errors. If you're seeing one of these errors, check the scope of your variables and make sure they're being assigned before they're being used.
Monitor with Ping Bot
Reliable monitoring for your app, databases, infrastructure, and the vendors they rely on. Ping Bot is a powerful uptime and performance monitoring tool that helps notify you and resolve issues before they affect your customers.
© 2013- 2024 Stack Abuse. All rights reserved.
[SOLVED] Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment

Python treats variables referenced only inside a function as global variables. Any variable assigned to a function’s body is assumed to be a local variable unless explicitly declared as global.
Why Does This Error Occur?
Unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when a variable is used before its created. Python does not have the concept of variable declarations. Hence it searches for the variable whenever used. When not found, it throws the error.
Before we hop into the solutions, let’s have a look at what is the global and local variables.
Local Variable Declarations vs. Global Variable Declarations
| Local Variables | Global Variables |
|---|---|
| A variable is declared primarily within a Python function. | Global variables are in the global scope, outside a function. |
| A local variable is created when the function is called and destroyed when the execution is finished. | A Variable is created upon execution and exists in memory till the program stops. |
| Local Variables can only be accessed within their own function. | All functions of the program can access global variables. |
| Local variables are immune to changes in the global scope. Thereby being more secure. | Global Variables are less safer from manipulation as they are accessible in the global scope. |
![python def local variable referenced before assignment [Fixed] typeerror can’t compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/typeerror-cant-compare-datetime.datetime-to-datetime.date_-300x157.webp)
Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment Error with Explanation
Try these examples yourself using our Online Compiler.
Let’s look at the following function:
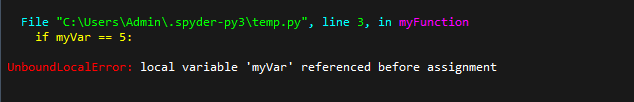
Explanation
The variable myVar has been assigned a value twice. Once before the declaration of myFunction and within myFunction itself.
Using Global Variables
Passing the variable as global allows the function to recognize the variable outside the function.
Create Functions that Take in Parameters
Instead of initializing myVar as a global or local variable, it can be passed to the function as a parameter. This removes the need to create a variable in memory.
UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘DISTRO_NAME’
This error may occur when trying to launch the Anaconda Navigator in Linux Systems.
Upon launching Anaconda Navigator, the opening screen freezes and doesn’t proceed to load.
Try and update your Anaconda Navigator with the following command.
If solution one doesn’t work, you have to edit a file located at
After finding and opening the Python file, make the following changes:
In the function on line 159, simply add the line:
DISTRO_NAME = None
Save the file and re-launch Anaconda Navigator.
DJANGO – Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment [Form]
The program takes information from a form filled out by a user. Accordingly, an email is sent using the information.
Upon running you get the following error:
We have created a class myForm that creates instances of Django forms. It extracts the user’s name, email, and message to be sent.
A function GetContact is created to use the information from the Django form and produce an email. It takes one request parameter. Prior to sending the email, the function verifies the validity of the form. Upon True , .get() function is passed to fetch the name, email, and message. Finally, the email sent via the send_mail function
Why does the error occur?
We are initializing form under the if request.method == “POST” condition statement. Using the GET request, our variable form doesn’t get defined.
Local variable Referenced before assignment but it is global
This is a common error that happens when we don’t provide a value to a variable and reference it. This can happen with local variables. Global variables can’t be assigned.
This error message is raised when a variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within the local scope of a function, even though it is a global variable.
Here’s an example to help illustrate the problem:
In this example, x is a global variable that is defined outside of the function my_func(). However, when we try to print the value of x inside the function, we get a UnboundLocalError with the message “local variable ‘x’ referenced before assignment”.
This is because the += operator implicitly creates a local variable within the function’s scope, which shadows the global variable of the same name. Since we’re trying to access the value of x before it’s been assigned a value within the local scope, the interpreter raises an error.
To fix this, you can use the global keyword to explicitly refer to the global variable within the function’s scope:
However, in the above example, the global keyword tells Python that we want to modify the value of the global variable x, rather than creating a new local variable. This allows us to access and modify the global variable within the function’s scope, without causing any errors.
Local variable ‘version’ referenced before assignment ubuntu-drivers
This error occurs with Ubuntu version drivers. To solve this error, you can re-specify the version information and give a split as 2 –
Here, p_name means package name.
With the help of the threading module, you can avoid using global variables in multi-threading. Make sure you lock and release your threads correctly to avoid the race condition.
When a variable that is created locally is called before assigning, it results in Unbound Local Error in Python. The interpreter can’t track the variable.
Therefore, we have examined the local variable referenced before the assignment Exception in Python. The differences between a local and global variable declaration have been explained, and multiple solutions regarding the issue have been provided.
Trending Python Articles
![python def local variable referenced before assignment [Fixed] nameerror: name Unicode is not defined](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Fixed-nameerror-name-Unicode-is-not-defined-300x157.webp)
Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min

# Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function.
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var .
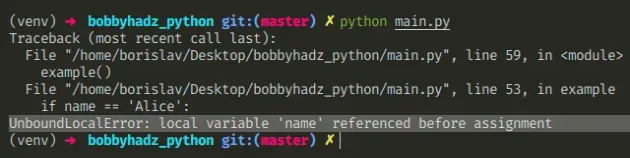
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We assign a value to the name variable in the function.
# Mark the variable as global to solve the error
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in your function definition.
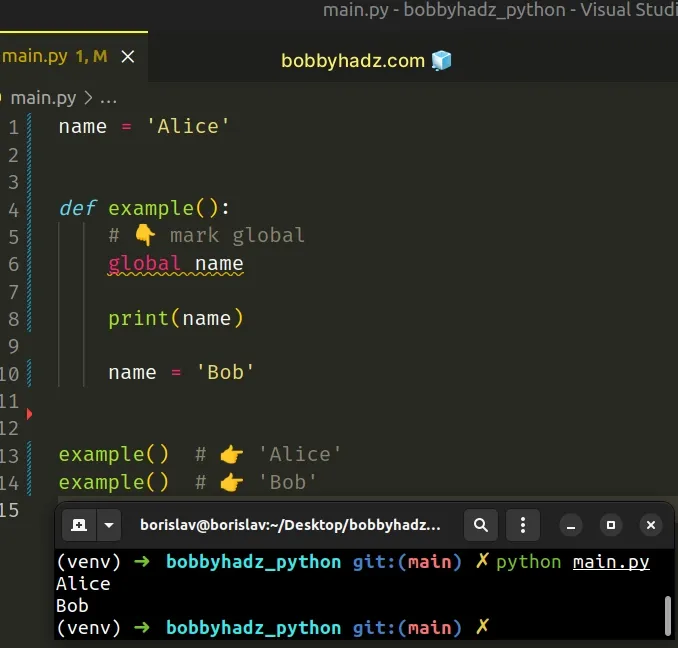
If a variable is assigned a value in a function's body, it is a local variable unless explicitly declared as global .
# Local variables shadow global ones with the same name
You could reference the global name variable from inside the function but if you assign a value to the variable in the function's body, the local variable shadows the global one.
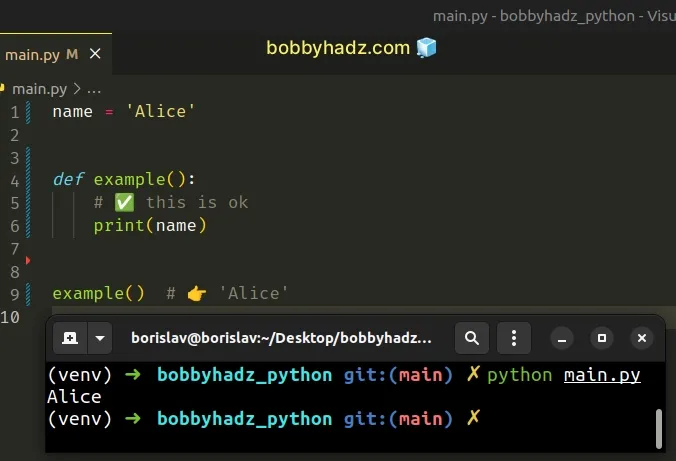
Accessing the name variable in the function is perfectly fine.
On the other hand, variables declared in a function cannot be accessed from the global scope.
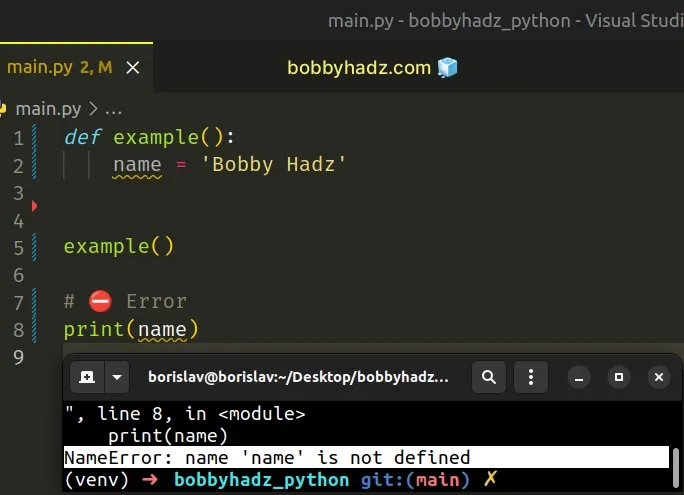
The name variable is declared in the function, so trying to access it from outside causes an error.
Make sure you don't try to access the variable before using the global keyword, otherwise, you'd get the SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration error.
# Returning a value from the function instead
An alternative solution to using the global keyword is to return a value from the function and use the value to reassign the global variable.
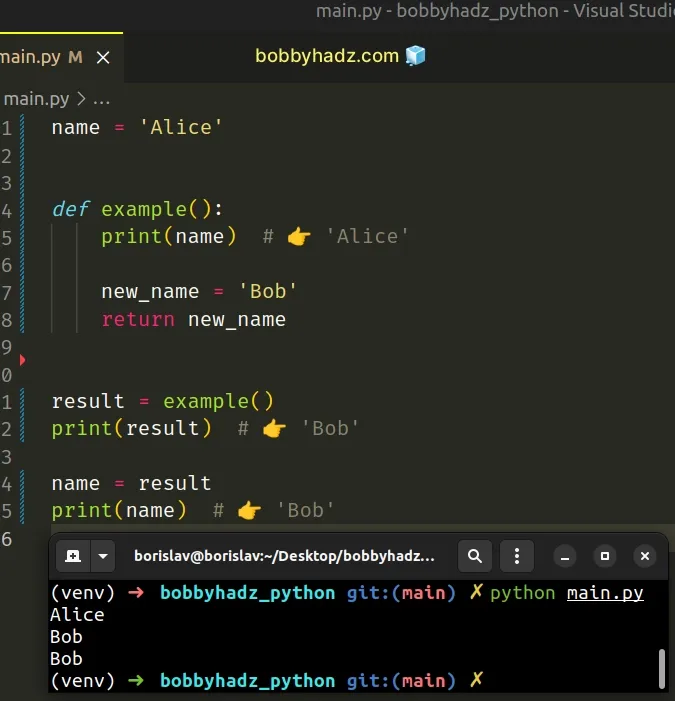
We simply return the value that we eventually use to assign to the name global variable.
# Passing the global variable as an argument to the function
You should also consider passing the global variable as an argument to the function.
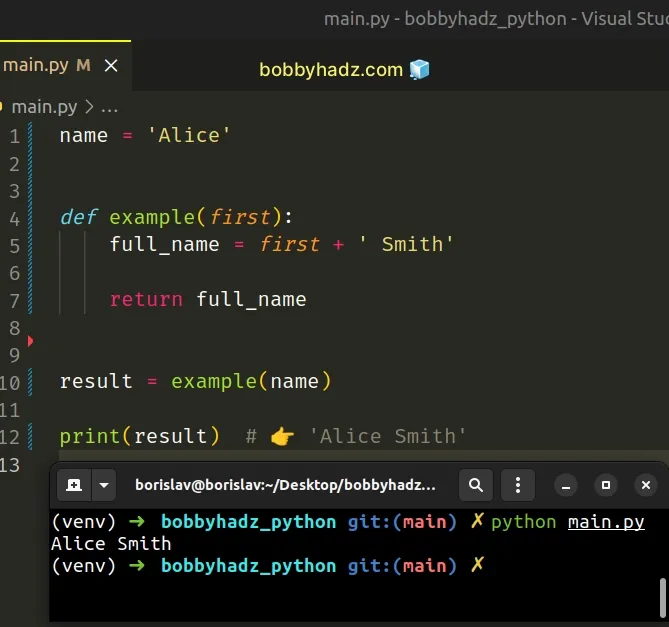
We passed the name global variable as an argument to the function.
If we assign a value to a variable in a function, the variable is assumed to be local unless explicitly declared as global .
# Assigning a value to a local variable from an outer scope
If you have a nested function and are trying to assign a value to the local variables from the outer function, use the nonlocal keyword.
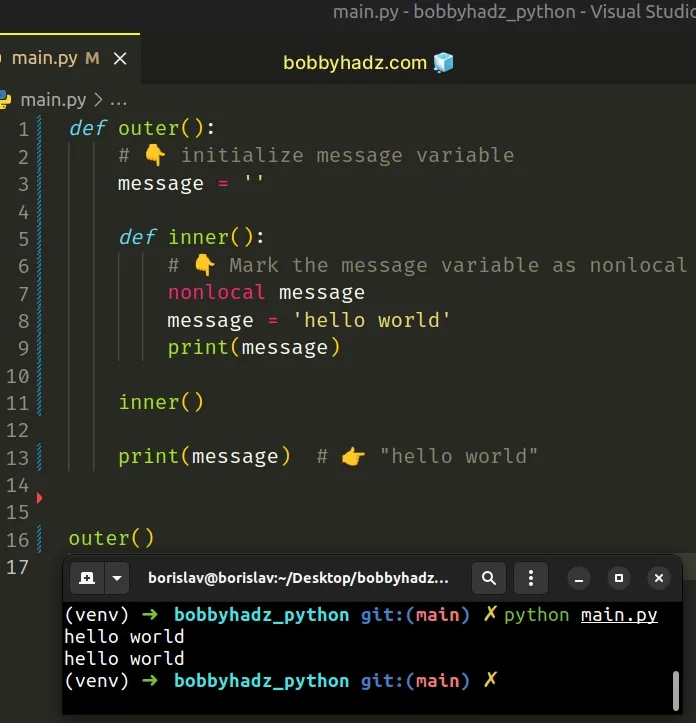
The nonlocal keyword allows us to work with the local variables of enclosing functions.
Had we not used the nonlocal statement, the call to the print() function would have returned an empty string.
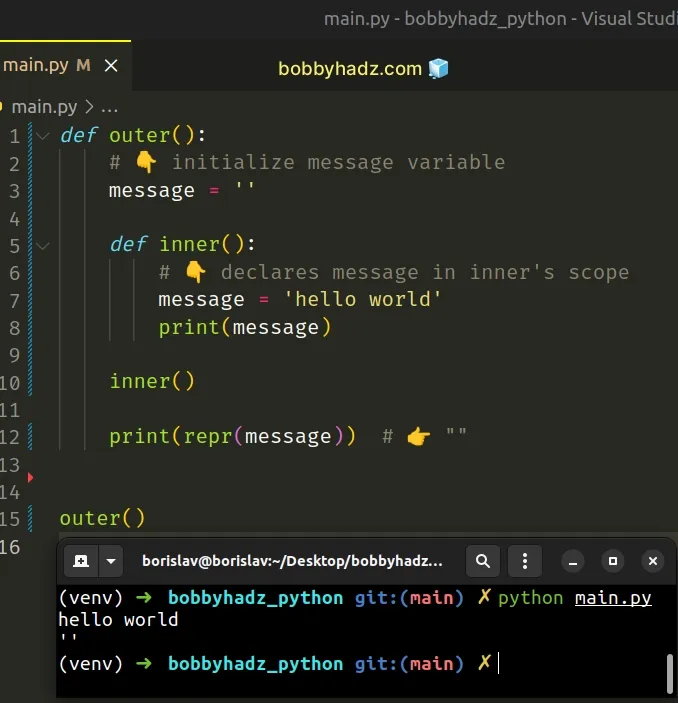
Printing the message variable on the last line of the function shows an empty string because the inner() function has its own scope.
Changing the value of the variable in the inner scope is not possible unless we use the nonlocal keyword.
Instead, the message variable in the inner function simply shadows the variable with the same name from the outer scope.
# Discussion
As shown in this section of the documentation, when you assign a value to a variable inside a function, the variable:
- Becomes local to the scope.
- Shadows any variables from the outer scope that have the same name.
The last line in the example function assigns a value to the name variable, marking it as a local variable and shadowing the name variable from the outer scope.
At the time the print(name) line runs, the name variable is not yet initialized, which causes the error.
The most intuitive way to solve the error is to use the global keyword.
The global keyword is used to indicate to Python that we are actually modifying the value of the name variable from the outer scope.
- If a variable is only referenced inside a function, it is implicitly global.
- If a variable is assigned a value inside a function's body, it is assumed to be local, unless explicitly marked as global .
If you want to read more about why this error occurs, check out [this section] ( this section ) of the docs.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
How to Fix Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment Error in Python

Table of Contents
Fixing local variable referenced before assignment error.
In Python , when you try to reference a variable that hasn't yet been given a value (assigned), it will throw an error.
That error will look like this:
In this post, we'll see examples of what causes this and how to fix it.
Let's begin by looking at an example of this error:
If you run this code, you'll get
The issue is that in this line:
We are defining a local variable called value and then trying to use it before it has been assigned a value, instead of using the variable that we defined in the first line.
If we want to refer the variable that was defined in the first line, we can make use of the global keyword.
The global keyword is used to refer to a variable that is defined outside of a function.
Let's look at how using global can fix our issue here:
Global variables have global scope, so you can referenced them anywhere in your code, thus avoiding the error.
If you run this code, you'll get this output:
In this post, we learned at how to avoid the local variable referenced before assignment error in Python.
The error stems from trying to refer to a variable without an assigned value, so either make use of a global variable using the global keyword, or assign the variable a value before using it.
Thanks for reading!

- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
How to fix UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment in Python
You could also see this error when you forget to pass the variable as an argument to your function.
How to reproduce this error
How to fix this error.
I hope this tutorial is useful. See you in other tutorials.
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
- Python Course
- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries
UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Handling errors is an integral part of writing robust and reliable Python code. One common stumbling block that developers often encounter is the “UnboundLocalError” raised within a try-except block. This error can be perplexing for those unfamiliar with its nuances but fear not – in this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the UnboundLocalError and provide a comprehensive guide on how to effectively use try-except statements to resolve it.
What is UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python?
The UnboundLocalError occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within a function or method. This error typically surfaces when utilizing try-except blocks to handle exceptions, creating a puzzle for developers trying to comprehend its origins and find a solution.
Why does UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment Occur?
below, are the reasons of occurring “Unboundlocalerror: Try Except Statements” in Python :
Variable Assignment Inside Try Block
Reassigning a global variable inside except block.
- Accessing a Variable Defined Inside an If Block
In the below code, example_function attempts to execute some_operation within a try-except block. If an exception occurs, it prints an error message. However, if no exception occurs, it prints the value of the variable result outside the try block, leading to an UnboundLocalError since result might not be defined if an exception was caught.
In below code , modify_global function attempts to increment the global variable global_var within a try block, but it raises an UnboundLocalError. This error occurs because the function treats global_var as a local variable due to the assignment operation within the try block.
Solution for UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment
Below, are the approaches to solve “Unboundlocalerror: Try Except Statements”.
Initialize Variables Outside the Try Block
Avoid reassignment of global variables.
In modification to the example_function is correct. Initializing the variable result before the try block ensures that it exists even if an exception occurs within the try block. This helps prevent UnboundLocalError when trying to access result in the print statement outside the try block.
Below, code calculates a new value ( local_var ) based on the global variable and then prints both the local and global variables separately. It demonstrates that the global variable is accessed directly without being reassigned within the function.
In conclusion , To fix “UnboundLocalError” related to try-except statements, ensure that variables used within the try block are initialized before the try block starts. This can be achieved by declaring the variables with default values or assigning them None outside the try block. Additionally, when modifying global variables within a try block, use the `global` keyword to explicitly declare them.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Python Programs
- Python Errors
- How to Get a Free SSL Certificate
- Best SSL Certificates Provider in India
- Elon Musk's xAI releases Grok-2 AI assistant
- What is OpenAI SearchGPT? How it works and How to Get it?
- Content Improvement League 2024: From Good To A Great Article
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Python local variable referenced before assignment Solution
When you start introducing functions into your code, you’re bound to encounter an UnboundLocalError at some point. This error is raised when you try to use a variable before it has been assigned in the local context .
In this guide, we talk about what this error means and why it is raised. We walk through an example of this error in action to help you understand how you can solve it.
Find your bootcamp match
What is unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment.
Trying to assign a value to a variable that does not have local scope can result in this error:
Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable. If a variable is assigned in a function , that variable is local. This is because it is assumed that when you define a variable inside a function you only need to access it inside that function.
There are two variable scopes in Python: local and global. Global variables are accessible throughout an entire program; local variables are only accessible within the function in which they are originally defined.
Let’s take a look at how to solve this error.
An Example Scenario
We’re going to write a program that calculates the grade a student has earned in class.
We start by declaring two variables:
These variables store the numerical and letter grades a student has earned, respectively. By default, the value of “letter” is “F”. Next, we write a function that calculates a student’s letter grade based on their numerical grade using an “if” statement :
Finally, we call our function:
This line of code prints out the value returned by the calculate_grade() function to the console. We pass through one parameter into our function: numerical. This is the numerical value of the grade a student has earned.
Let’s run our code and see what happens:
An error has been raised.
The Solution
Our code returns an error because we reference “letter” before we assign it.
We have set the value of “numerical” to 42. Our if statement does not set a value for any grade over 50. This means that when we call our calculate_grade() function, our return statement does not know the value to which we are referring.
We do define “letter” at the start of our program. However, we define it in the global context. Python treats “return letter” as trying to return a local variable called “letter”, not a global variable.
We solve this problem in two ways. First, we can add an else statement to our code. This ensures we declare “letter” before we try to return it:
Let’s try to run our code again:
Our code successfully prints out the student’s grade.
If you are using an “if” statement where you declare a variable, you should make sure there is an “else” statement in place. This will make sure that even if none of your if statements evaluate to True, you can still set a value for the variable with which you are going to work.
Alternatively, we could use the “global” keyword to make our global keyword available in the local context in our calculate_grade() function. However, this approach is likely to lead to more confusing code and other issues. In general, variables should not be declared using “global” unless absolutely necessary . Your first, and main, port of call should always be to make sure that a variable is correctly defined.
In the example above, for instance, we did not check that the variable “letter” was defined in all use cases.
That’s it! We have fixed the local variable error in our code.
The UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment error is raised when you try to assign a value to a local variable before it has been declared. You can solve this error by ensuring that a local variable is declared before you assign it a value.
Now you’re ready to solve UnboundLocalError Python errors like a professional developer !
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Adventures in Machine Learning
4 ways to fix local variable referenced before assignment error in python, resolving the local variable referenced before assignment error in python.
Python is one of the world’s most popular programming languages due to its simplicity, readability, and versatility. Despite its many advantages, when coding in Python, one may encounter various errors, with the most common being the “local variable referenced before assignment” error.
Even the most experienced Python developers have encountered this error at some point in their programming career. In this article, we will look at four effective strategies for resolving the local variable referenced before assignment error in Python.
Strategy 1: Assigning a Value before Referencing
The first strategy is to assign a value to a variable before referencing it. The error occurs when the variable is referenced before it is assigned a value.
This problem can be avoided by initializing the variable before referencing it. For example, let us consider the snippet below:
In the snippet above, the variables x and y are not assigned values before they are referenced in the print statement. Therefore, we will get a local variable “referenced before assignment” error.
To resolve this error, we must initialize the variables before referencing them. We can avoid this error by assigning a value to x and y before they are referenced, as shown below:
Strategy 2: Using the Global Keyword
In Python, variables declared inside a function are considered local variables. Thus, they are separate from other variables declared outside of the function.
If we want to use a variable outside of the function, we must use the global keyword. Using the global keyword tells Python that you want to use the variable that was defined globally, not locally.
For example:
In the code snippet above, the global keyword tells Python to use the variable x defined outside of the function rather than a local variable named x . Thus, Python will output 30.
Strategy 3: Adding Input Parameters for Functions
Another way to avoid the local variable referenced before assignment error is by adding input parameters to functions.
In the code snippet above, x and y are variables that are passed into the add_numbers function as arguments.
This approach allows us to avoid the local variable referenced before assignment error because the variables are being passed into the function as input parameters.
Strategy 4: Initializing Variables before Loops or Conditionals
Finally, it’s also a good practice to initialize the variables before loops or conditionals.
If you are defining a variable within a loop, you must initialize it before the loop starts. This way, the variable already exists, and we can update the value inside the loop.
In the code snippet above, the variable sum has been initialized with the value of 0 before the loop runs. Thus, we can update and use the variable inside the loop.
In conclusion, the “local variable referenced before assignment” error is a common issue in Python. However, with the strategies discussed in this article, you can avoid the error and write clean Python code.
Remember to initialize your variables, use the global keyword, add input parameters in functions, and initialize variables before loops or conditionals. By following these techniques, your Python code will be error-free and much easier to manage.
In essence, this article has provided four key strategies for resolving the “local variable referenced before assignment” error that is common in Python. These strategies include initializing variables before referencing, using the global keyword, adding input parameters to functions, and initializing variables before loops or conditionals.
These techniques help to ensure clean code that is free from errors. By implementing these strategies, developers can improve their code quality and avoid time-wasting errors that can occur in their work.
Popular Posts
Analyzing numpy arrays: counting nan and non-nan elements, master data manipulation: extracting numbers from strings in pandas, mastering oracle: how to limit query results for efficient data retrieval.
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Python UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
If you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it within the body of a function, you will encounter the UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment.
The preferable way to solve this error is to pass parameters to your function, for example:
Alternatively, you can declare the variable as global to access it while inside a function. For example,
This tutorial will go through the error in detail and how to solve it with code examples .
Table of contents
What is scope in python, unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment, solution #1: passing parameters to the function, solution #2: use global keyword, solution #1: include else statement, solution #2: use global keyword.
Scope refers to a variable being only available inside the region where it was created. A variable created inside a function belongs to the local scope of that function, and we can only use that variable inside that function.
A variable created in the main body of the Python code is a global variable and belongs to the global scope. Global variables are available within any scope, global and local.
UnboundLocalError occurs when we try to modify a variable defined as local before creating it. If we only need to read a variable within a function, we can do so without using the global keyword. Consider the following example that demonstrates a variable var created with global scope and accessed from test_func :
If we try to assign a value to var within test_func , the Python interpreter will raise the UnboundLocalError:
This error occurs because when we make an assignment to a variable in a scope, that variable becomes local to that scope and overrides any variable with the same name in the global or outer scope.
var +=1 is similar to var = var + 1 , therefore the Python interpreter should first read var , perform the addition and assign the value back to var .
var is a variable local to test_func , so the variable is read or referenced before we have assigned it. As a result, the Python interpreter raises the UnboundLocalError.
Example #1: Accessing a Local Variable
Let’s look at an example where we define a global variable number. We will use the increment_func to increase the numerical value of number by 1.
Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we tried to read a local variable before assigning a value to it.
We can solve this error by passing a parameter to increment_func . This solution is the preferred approach. Typically Python developers avoid declaring global variables unless they are necessary. Let’s look at the revised code:
We have assigned a value to number and passed it to the increment_func , which will resolve the UnboundLocalError. Let’s run the code to see the result:
We successfully printed the value to the console.
We also can solve this error by using the global keyword. The global statement tells the Python interpreter that inside increment_func , the variable number is a global variable even if we assign to it in increment_func . Let’s look at the revised code:
Let’s run the code to see the result:
Example #2: Function with if-elif statements
Let’s look at an example where we collect a score from a player of a game to rank their level of expertise. The variable we will use is called score and the calculate_level function takes in score as a parameter and returns a string containing the player’s level .
In the above code, we have a series of if-elif statements for assigning a string to the level variable. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we input a score equal to 40 . The conditional statements in the function do not account for a value below 55 , therefore when we call the calculate_level function, Python will attempt to return level without any value assigned to it.
We can solve this error by completing the set of conditions with an else statement. The else statement will provide an assignment to level for all scores lower than 55 . Let’s look at the revised code:
In the above code, all scores below 55 are given the beginner level. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
We can also create a global variable level and then use the global keyword inside calculate_level . Using the global keyword will ensure that the variable is available in the local scope of the calculate_level function. Let’s look at the revised code.
In the above code, we put the global statement inside the function and at the beginning. Note that the “default” value of level is beginner and we do not include the else statement in the function. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! The UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it. Preferably, you can solve this error by passing parameters to your function. Alternatively, you can use the global keyword.
If you have if-elif statements in your code where you assign a value to a local variable and do not account for all outcomes, you may encounter this error. In which case, you must include an else statement to account for the missing outcome.
For further reading on Python code blocks and structure, go to the article: How to Solve Python IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level .
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
How to Solve Error - Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
- Python How-To's
- How to Solve Error - Local Variable …
Check the Variable Scope to Fix the local variable referenced before assignment Error in Python
Initialize the variable before use to fix the local variable referenced before assignment error in python, use conditional assignment to fix the local variable referenced before assignment error in python.

This article delves into various strategies to resolve the common local variable referenced before assignment error. By exploring methods such as checking variable scope, initializing variables before use, conditional assignments, and more, we aim to equip both novice and seasoned programmers with practical solutions.
Each method is dissected with examples, demonstrating how subtle changes in code can prevent this frequent error, enhancing the robustness and readability of your Python projects.
The local variable referenced before assignment occurs when some variable is referenced before assignment within a function’s body. The error usually occurs when the code is trying to access the global variable.
The primary purpose of managing variable scope is to ensure that variables are accessible where they are needed while maintaining code modularity and preventing unexpected modifications to global variables.
We can declare the variable as global using the global keyword in Python. Once the variable is declared global, the program can access the variable within a function, and no error will occur.
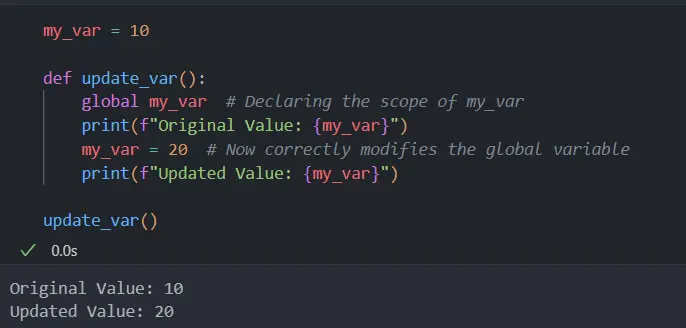
The below example code demonstrates the code scenario where the program will end up with the local variable referenced before assignment error.
In this example, my_var is a global variable. Inside update_var , we attempt to modify it without declaring its scope, leading to the Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error.
We need to declare the my_var variable as global using the global keyword to resolve this error. The below example code demonstrates how the error can be resolved using the global keyword in the above code scenario.
In the corrected code, we use the global keyword to inform Python that my_var references the global variable.
When we first print my_var , it displays the original value from the global scope.
After assigning a new value to my_var , it updates the global variable, not a local one. This way, we effectively tell Python the scope of our variable, thus avoiding any conflicts between local and global variables with the same name.
Ensure that the variable is initialized with some value before using it. This can be done by assigning a default value to the variable at the beginning of the function or code block.
The main purpose of initializing variables before use is to ensure that they have a defined state before any operations are performed on them. This practice is not only crucial for avoiding the aforementioned error but also promotes writing clear and predictable code, which is essential in both simple scripts and complex applications.
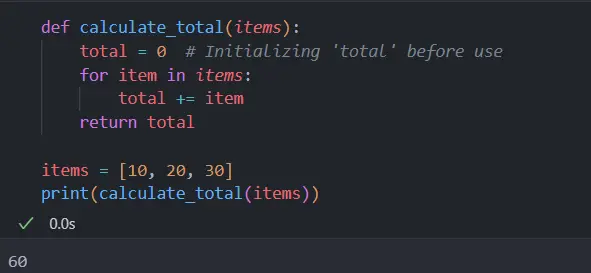
In this example, the variable total is used in the function calculate_total without prior initialization, leading to the Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error. The below example code demonstrates how the error can be resolved in the above code scenario.
In our corrected code, we initialize the variable total with 0 before using it in the loop. This ensures that when we start adding item values to total , it already has a defined state (in this case, 0).
This initialization is crucial because it provides a starting point for accumulation within the loop. Without this step, Python does not know the initial state of total , leading to the error.
Conditional assignment allows variables to be assigned values based on certain conditions or logical expressions. This method is particularly useful when a variable’s value depends on certain prerequisites or states, ensuring that a variable is always initialized before it’s used, thereby avoiding the common error.
In this example, message is only assigned within the if and elif blocks. If neither condition is met (as with guest ), the variable message remains uninitialized, leading to the Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error when trying to print it.
The below example code demonstrates how the error can be resolved in the above code scenario.
In the revised code, we’ve included an else statement as part of our conditional logic. This guarantees that no matter what value user_type holds, the variable message will be assigned some value before it is used in the print function.
This conditional assignment ensures that the message is always initialized, thereby eliminating the possibility of encountering the Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error.
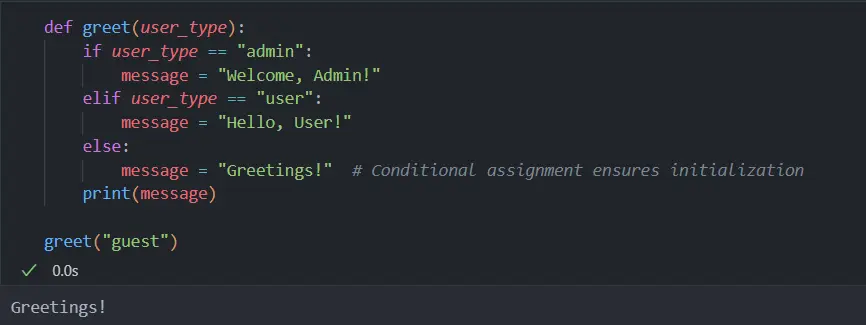
Throughout this article, we have explored multiple approaches to address the Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error in Python. From the nuances of variable scope to the effectiveness of initializations and conditional assignments, these strategies are instrumental in developing error-free code.
The key takeaway is the importance of understanding variable scope and initialization in Python. By applying these methods appropriately, programmers can not only resolve this specific error but also enhance the overall quality and maintainability of their code, making their programming journey smoother and more rewarding.
Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
The “local variable referenced before assignment” error occurs when you try to use a local variable before it has been assigned a value. This is a general programming concept describing the situation typically arises in situations where you declare a variable within a function but then try to access or modify it before actually assigning a value to it.
In Python, the compiler might throw the exact error: “UnboundLocalError: cannot access local variable ‘x’ where it is not associated with a value”
Here’s an example to illustrate this error:
In this example, you would encounter the above error because you’re trying to print the value of x before it has been assigned a value. To fix this, you should assign a value to x before attempting to access it:
In the corrected version, the local variable x is assigned a value before it’s used, preventing the error.
Keep in mind that Python treats variables inside functions as local unless explicitly stated otherwise using the global keyword (for global variables) or the nonlocal keyword (for variables in nested functions).
If you encounter this error and you’re sure that the variable should have been assigned a value before its use, double-check your code for any logical errors or typos that might be causing the variable to not be assigned properly.
Using the global keyword
If you have a global variable named letter and you try to modify it inside a function without declaring it as global, you will get error.
This is because Python assumes that any variable that is assigned a value inside a function is a local variable, unless you explicitly tell it otherwise.
To fix this error, you can use the global keyword to indicate that you want to use the global variable:

Using nonlocal keyword
The nonlocal keyword is used to work with variables inside nested functions, where the variable should not belong to the inner function. It allows you to modify the value of a non-local variable in the outer scope.
For example, if you have a function outer that defines a variable x , and another function inner inside outer that tries to change the value of x , you need to use the nonlocal keyword to tell Python that you are referring to the x defined in outer , not a new local variable in inner .
Here is an example of how to use the nonlocal keyword:
If you don’t use the nonlocal keyword, Python will create a new local variable x in inner , and the value of x in outer will not be changed:
You might also like
Consultancy
- Technology Consulting
- Customer Experience Consulting
- Solution Architect Consulting
Software Development Services
- Ecommerce Development
- Web App Development
- Mobile App Development
- SAAS Product Development
- Content Management System
- System Integration & Data Migration
- Cloud Computing
- Computer Vision
Dedicated Development Team
- Full Stack Developers For Hire
- Offshore Development Center
Marketing & Creative Design
- UX/UI Design
- Customer Experience Optimization
- Digital Marketing
- Devops Services
- Service Level Management
- Security Services
- Odoo gold partner
By Industry
- Retail & Ecommerce
- Manufacturing
- Import & Distribution
- Financical & Banking
- Technology For Startups
Business Model
- MARKETPLACE ECOMMERCE
Our realized projects

MB Securities - A Premier Brokerage

iONAH - A Pioneer in Consumer Electronics Industry

Emers Group - An Official Nike Distributing Agent

Academy Xi - An Australian-based EdTech Startup
- Market insight

- Ohio Digital
- Onnet Consoulting
What is UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment?
Trying to assign a value to a variable that does not have local scope can result in this error:
Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable. To clarify, a variable is assigned in a function, that variable is local. Because it is assumed that when you define a variable inside a function, you only need to access it inside that function.
There are two variable scopes in Python: local and global. Global variables are accessible throughout an entire program. Whereas, local variables are only accessible within the function in which they are originally defined.
An example of Local variable referenced before assignment
We’re going to write a program that calculates the grade a student has earned in class.
Firstly, we start by declaring two variables:
These variables store the numerical and letter grades a student has earned, respectively. By default, the value of “letter” is “F”. Then, we write a function that calculates a student’s letter grade based on their numerical grade using an “if” statement:
Finally, we call our function:
This line of code prints out the value returned by the calculate_grade() function to the console. We pass through one parameter into our function: numerical. This is the numerical value of the grade a student has earned.
Let’s run our code of Local variable referenced before assignment and see what happens:
Here is an error!
The Solution of Local variable referenced before assignment
The code returns an error: Unboundlocalerror local variable referenced before assignment because we reference “letter” before we assign it.
We have set the value of “numerical” to 42. Our if statement does not set a value for any grade over 50. This means that when we call our calculate_grade() function, our return statement does not know the value to which we are referring.
Moreover, we do define “letter” at the start of our program. However, we define it in the global context. Because Python treats “return letter” as trying to return a local variable called “letter”, not a global variable.
Therefore, this problem of variable referenced before assignment could be solved in two ways. Firstly, we can add an else statement to our code. This ensures we declare “letter” before we try to return it:
Let’s try to run our code again:
Our code successfully prints out the student’s grade. This approach is good because it lets us keep “letter” in the local context. To clarify, we could even remove the “letter = “F”” statement from the top of our code because we do not use it in the global context.
Alternatively, we could use the “global” keyword to make our global keyword available in the local context in our calculate_grade() function:
We use the “global” keyword at the start of our function.
This keyword changes the scope of our variable to a global variable. This means the “return” statement will no longer treat “letter” like a local variable. Let’s run our code. Our code returns: F.
The code works successfully! Let’s try it using a different grade number by setting the value of “numerical” to a new number:
Our code returns: B.
Finally, we have fixed the local variable referenced before assignment error in the code.
To sum up, as you can see, the UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment error is raised when you try to assign a value to a local variable before it has been declared. Then, you can solve this error by ensuring that a local variable is declared before you assign it a value. Moreover, if a variable is declared globally that you want to access in a function, you can use the “global” keyword to change its value. In case you have any inquiry, let’s CONTACT US . With a lot of experience in Mobile app development services , we will surely solve it for you instantly.
>>> Read more
- Average python length: How to find it with examples
- List assignment index out of range: Python indexerror solution you should know
- Spyder vs Pycharm: The detailed comparison to get best option for Python programming
- fix python error , Local variable referenced before assignment , python , python dictionary , python error , python learning , UnboundLocalError , UnboundLocalError in Python
Our Other Services
- E-commerce Development
- Web Apps Development
- Web CMS Development
- Mobile Apps Development
- Software Consultant & Development
- System Integration & Data Migration
- Dedicated Developers & Testers For Hire
- Remote Working Team
- Saas Products Development
- Web/Mobile App Development
- Outsourcing
- Hiring Developers
- Digital Transformation
- Advanced SEO Tips

Lastest News

Challenges and Advices When Using AWS Cloud Managed Services
Comprehensive Guide about AWS Well Architected Framework
AWS Cloud Migration: Guide-to-Guide from A to Z

Uncover The Treasures Of Cloud Computing For Healthcare

A Synopsis of Cloud Computing in Financial Services

Discover Cutting-Edge Cloud Computing Applications To Optimize Business Resources
Tailor your experience
- Success Stories
Copyright ©2007 – 2021 by AHT TECH JSC. All Rights Reserved.
Thank you for your message. It has been sent.
Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Python, as a programming language, is lauded for its simplicity and readability, which makes it an excellent choice for both beginners and seasoned developers. However, even in the most straightforward languages, certain errors can perplex programmers. One such common error in Python is when a local variable is referenced before assignment. This article aims to dissect this error, understand its origins, and provide practical solutions to avoid it in your coding journey.
Understanding Local Variables and Scope in Python
Before diving into the error itself, it’s crucial to understand the concept of local variables and scope in Python. Variables in Python are names that are mapped to objects in memory. The scope of a variable determines the region of the program where that variable is accessible.
What is a Local Variable?
A local variable is a variable that is declared inside a function or block and is only accessible within that function or block. It cannot be accessed from outside its local scope.
Python’s Variable Scope Hierarchy
The ‘local variable referenced before assignment’ error, common causes of the error, examples of the error.
Let’s look at some code snippets that result in the ‘local variable referenced before assignment’ error.
Resolving the Error
To fix the ‘local variable referenced before assignment’ error, we need to ensure that variables are correctly initialized and declared within their respective scopes.
Initializing Local Variables
Always initialize local variables before using them. Here’s a corrected version of the previous example:
Using the Global Statement
Understanding variable namespaces.
Be aware of the namespace in which your variables exist. Avoid using the same name for local and global variables to prevent confusion.
Best Practices to Avoid the Error
Here are some best practices to prevent the ‘local variable referenced before assignment’ error:
Advanced Insights
Faq section, what is a variable’s scope.
A variable’s scope is the region of a program where the variable is recognized and can be accessed.
Can I use a global variable inside a function without declaring it as global?
What is the legb rule in python.
The LEGB rule is the order in which Python looks for a variable’s scope: Local, Enclosing, Global, and Built-in.
How can I modify a variable in an enclosing scope?
Use the nonlocal statement to modify a variable in an enclosing scope.
How to Comment All Lines in Python
How to remove items from a list python, how to use sublime text for python.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Password Generator
- HTML Editor
- HTML Encoder
- JSON Beautifier
- CSS Beautifier
- Markdown Convertor
- Find the Closest Tailwind CSS Color
- Phrase encrypt / decrypt
- Browser Feature Detection
- Number convertor
- CSS Maker text shadow
- CSS Maker Text Rotation
- CSS Maker Out Line
- CSS Maker RGB Shadow
- CSS Maker Transform
- CSS Maker Font Face
- Color Picker
- Colors CMYK
- Color mixer
- Color Converter
- Color Contrast Analyzer
- Color Gradient
- String Length Calculator
- MD5 Hash Generator
- Sha256 Hash Generator
- String Reverse
- URL Encoder
- URL Decoder
- Base 64 Encoder
- Base 64 Decoder
- Extra Spaces Remover
- String to Lowercase
- String to Uppercase
- Word Count Calculator
- Empty Lines Remover
- HTML Tags Remover
- Binary to Hex
- Hex to Binary
- Rot13 Transform on a String
- String to Binary
- Duplicate Lines Remover
Python 3: UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
This error occurs when you are trying to access a variable before it has been assigned a value. Here is an example of a code snippet that would raise this error:
Watch a video course Python - The Practical Guide
The error message will be:
In this example, the variable x is being accessed before it is assigned a value, which is causing the error. To fix this, you can either move the assignment of the variable x before the print statement, or give it an initial value before the print statement.
Both will work without any error.
Related Resources
- Using global variables in a function
- "Least Astonishment" and the Mutable Default Argument
- Why is "1000000000000000 in range(1000000000000001)" so fast in Python 3?
- HTML Basics
- Javascript Basics
- TypeScript Basics
- React Basics
- Angular Basics
- Sass Basics
- Vue.js Basics
- Python Basics
- Java Basics
- NodeJS Basics

- View Active Threads
- View Today's Posts
- View New Posts
- My Discussions
- Unanswered Posts
- Unread Posts
- Active Threads
- Mark all forums read
- Member List
- Interpreter
UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
- Python Forum
- Python Coding
- General Coding Help
- 0 Vote(s) - 0 Average
| Unladen Swallow Dec-27-2019, 05:23 AM https://docs.python.org/3/faq/programming.html#why-am-i-getting-an-unboundlocalerror-when-the-variable-has-a-value I used both global , nonlocal but both throws different error throws this error nonlocal test_var ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax throws this error ^ NameError: global name 'test_var' is not defined Any suggestions ? I have gone through top 10 search results , all suggest to use nonlocal or global... Dec-27-2019, 09:08 AM I think that this boils down to this: You should also understand difference between reference and assignment: When you reference a variable in an expression, the Python interpreter will traverse the scope to resolve the reference in following order: - current function’s scope - any enclosing scopes (like containing functions) - scope of the module that contains the code (global scope) - built-in scope (that contains functions like int and abs) If Python doesn't find defined variable with the referenced name, then a NameError exception is raised. Assigning a value to a variable works differently. If the variable is already defined in the current scope, then it will just take on the new value. If the variable doesn’t exist in the current scope, then Python treats the assignment as a variable definition. The scope of the newly defined variable is the function that contains the assignment. Bucky Katt, Get Fuzzy : There's a dead bishop on the landing. I don't know who keeps bringing them in here. ....but society is to blame. |
| 225 | Yesterday, 03:19 PM : | ||||
| 694 | Jun-15-2024, 07:15 PM : | ||||
| 1,711 | Oct-02-2023, 12:57 AM : | ||||
| 1,996 | Jan-10-2023, 10:58 PM : | ||||
| 1,948 | Feb-25-2022, 01:21 AM : | ||||
| 2,251 | Feb-10-2022, 07:36 PM : | ||||
| 3,623 | Mar-02-2021, 08:11 PM : | ||||
| 3,943 | Feb-04-2021, 06:27 AM : | ||||
| 4,779 | Jul-13-2020, 03:53 PM : | ||||
| 2,525 | Jun-11-2020, 12:45 PM : | ||||
- View a Printable Version
User Panel Messages
Announcements.

Login to Python Forum
- 1. Introduction
- 3. Errors and Complexity
- 4. Floating Point Representation
- 5. Rounding
- 6. Taylor Series
- 7. Random Number Generators and Monte Carlo Method
- 8. Vectors, Matrices, and Norms
- 9. LU Decomposition for Solving Linear Equations
- 10. Sparse Matrices
- 11. Condition Numbers
- 12. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- 13. Markov chains
- 14. Finite Difference Methods
- 15. Solving Nonlinear Equations
- 16. Optimization
- 17. Least Squares Fitting
- 18. Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
- 19. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- 1. Session 1
If you cannot see the PDF here, click here to download the PDF.
Learning Objectives
- Get familiar with the Python 3 syntax
- Understand the difference between mutable and immutable objects
- Understand the purpose of NumPy and learn about common operations with NumPy datatypes.
Remember, the most efficient way to learn a programming language is to practice!
Google is a great resource for any programming language.
Just like any other language, variables can store data of different types in Python, such as int , float , or str . We can use the type() function to find the type of an expression.
What are the correct types for variables c and d ?
Names and Values
Consider the following example:
In this case, a and b are not separate entities, even though they are different variables. The list [1, 2, 3] is an object, and both variable names a and b are bounded to the same list.
Modifying an Object
Now let's consider another example:
b.append(4) modifies the object list, such that the list is now [1, 2, 3, 4] . We know that b is now [1, 2, 3, 4] , but what happens to the variable name a?
Get the "id" for an object
Let's see how we can use a built-in Python function to see whether a and b point to the same object or not.
Memory Management
To review the way Python manages memory, let's look at the following examples:
Mutable and Immutable Objects
In Python, objects are divided into mutable and immutable . Mutable objects can be modified after they are first created, including lists, dictionaries, NumPy arrays, etc. Immutable objects cannot be modified once they are created, including tuples, strings, floats, etc.
For example,
A list is an example of a mutable object. Let's take a look at how it behaves in different situations:
Which of the following code snippets result in print(a==c) -> True :
A is incorrect because c ends up having two "hey" elements in its list. B is incorrect because a += b adds each character of "hey" as its own element. Hence, C must be the correct choice.
Objects and Naming
Advanced naming.
Let's make some objects and see what happens in this next snippet of code:
What is the correct output for the following code snippet?
A: computer_science, math ['electrical', 'physics']
B: computer_science, math ['electrical']
C: computer_science ['electrical', 'physics']
D: computer_science ['electrical']
In the above code snippet, John and Tim refer to separate objects since strings are immutable in Python, and so the variable John is equal to 'computer_science' . Lists are mutable, so Julie and Anna are equal to the same list: ['electrical', 'physics'] . Hence, C is the correct choice.
Indexing is important to iterate through for loops in a variety of ways in Python. Given a list a , the formatting for indexing follows this standard: a[i:j:k] . Here, i is the starting index of the iteration, j is the stopping index (exclusive) of the iteration, and k is the step size.
What is the output for the command line above?
Control Flow
Control flow includes iterating over list-like objects with for/while loops, using if/else blocks to perform logic for certain conditions, and using break and continue statements to control when you exit a for loop or move onto the next iteration of a loop, respectively. Let's see a simple example of this:
Defining Functions
Sometimes it's useful to define a function. This is done by using the keyword "def" followed by a list of parameters. Here is a basic example of a function definition:
Here is the official documentation for function definition.
Function Scope
It's important to understand the idea of scope. A variable created inside a function can only be used inside that function, because it has local scope . A variable created in the main body of the Python code is a global variable and hence has global scope . This variable has no restrictions and can be used/accessed anywhere. Again, the best way to learn this is by looking at an example:
Which code snippet does not modify the variables?
B is the correct answer because ints in Python are immutable. This means that incrementing a by 1 and b by 2 inside the function just creates new objects for both a and b. These new objects will be restricted to the scope of this function, and as a result the variables will not be modified. However, lists are mutable objects, and appending values to them does not create new objects. The function simply updates the variables that already have global scope, and so these variables are modified.
A dictionary is an important and useful structure in Python. A dictionary is made up of key-value pairs, where the value is extracted using the key. You will be using dictionaries a lot in this class for later chapters. Here are some examples on how to use a dictionary:
Here is the official documentation for dictionaries and some other useful data structures.
Type Annotations
Python is a dynamically typed language, meaning that the variable type is determined at runtime. As you've likely noticed, this is why we have the luxury to declare and initialize variables without assigning a type to the variable. This wouldn't be allowed in languages like C++ or Java.
Type Annotations , however, provide a way for developers to specify the type of a variable, function parameter, or function result. While it doesn't really improve performance, it helps developers get a better understanding of the type of data they're dealing with, whether that be in the form of variables or inputs and outputs of a function call. Here's an example of what a type-annotated variable/function definition might look like:
NumPy is a Python library used for numerical computing. Developed almost entirely in C and C++, it is highly performant and can easily support operations on large amounts of data. This section will serve as a brief intro to some common NumPy tools you'll be expected to use throughout the class. While this section will explain some of these common tools, the NumPy documentation goes into much greater detail and is always the go-to resource whenever unsure how to use a specific function.
NumPy Arrays
NumPy arrays are generally preferred over lists because you can conduct highly performant operations on them to accomplish any task. This is specifically important in a class like Numerical Methods. The following are ways you can initialize different types of NumPy arrays:
We can find out additional information about the NumPy array and do more with them with the following functions:
Indexing and Slicing
We can use indexing and slicing on NumPy arrays in order to extract specific information from arrays/matrices. This will be a constant part of the class, so it's better to get used to indexing/slicing now! Note that this section is similar to the above indexing section. A NumPy array a will follow the standard: a[i:j:k] , where i is the starting index of the iteration, j is the stopping index (exclusive) of the iteration, and k is the step size.
Array Manipulation
Array manipulation is particularly useful when certain formulas in later chapters require building matrices or perform certain operations on matrices (for instance, transposing a matrix). Below are some examples:
Array Mathematics
NumPy provides several math functions that can be performed on each element in the array. Rather than iterating through each element, these functions will do the operation over the entire array and are hence extremely convenient. Which math functions might be relevant in Numerical Methods? Let's take a look:
Linear Algebra
This class will often ask you to perform linear algebra operations on vectors/matrices. This is when the numpy.linalg library and the following functions it provides will be useful:
Random Numbers
Random numbers are always an integral part of Numerical Methods. NumPy has provided several functions that makes it super easy to use random numbers, and this will be key during chapters like Monte Carlo. Let's dive into what NumPy has to offer for random numbers:
Python also has a random module that is separate from NumPy but can be used to do a lot of similar operations as the ones introduced above.
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is a powerful technique in Python that allows us to perform arithmetic between two differently-shaped arrays.
Say we have a smaller array A (with a shape of 1 x 5) and a larger array B (with a shape of 4 x 5), and we want to add these arrays together.
Without broadcasting, only the first row in B would be modified by A . With broadcasting, however, A 's values are added to each row of B . Hence, A is broadcasted onto B . The dimension sizes need to cooperate as they did in this example, or we'll receive some error when performing this arithmetic.
Here is an example illustrating the concept:
This result demonstrates how the values from array A were added to each row of array B, thanks to broadcasting. The dimension of A (1 x 5) was compatible with B (4 x 5), allowing A to be "stretched" across B to perform the element-wise addition.
External Links
Here is some documentation for other packages we will be using in CS 357.
SciPy, a scientific computing package used to solve mathematical problems.
MatPlotLib, a visualizaion and graphing package.
- March 17th, 2024: Dev Singh (dsingh14) — modified notes content for clarity
- March 16th, 2024: Arnav Aggarwal (arnava4) — aligned notes with slides and added additional examples
- View Remaining Entries
- CS 357 Course Staff
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Local variable referenced before assignment
hi guys i am new to data structures and i have been trying to solve a maze using left hand rule algorithm. However, i have been facing difficulty in trying to print out the number of steps to take to solve the maze as i keep facing this error :
i tried to initialize a step variable to no avail.
the error in the code happened in this few lines
- steps can be referenced but not changed unless you declare it global – Rolf of Saxony Commented Nov 16, 2020 at 11:58
Insert global steps as the first line of every function that assigns a new value to steps . This lets Python know that you mean to modify the global variable, and not set a local variable that just happens to have the same name.
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged python or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Where does Postgres fit in a world of GenAI and vector databases?
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- What does a new user need in a homepage experience on Stack Overflow?
- Feedback requested: How do you use tag hover descriptions for curating and do...
- Staging Ground Reviewer Motivation
Hot Network Questions
- What is the significance of bringing the door to Nippur in the Epic of Gilgamesh?
- Do metal objects attract lightning?
- Equations for dual cubic curves
- Topology on a module over a topological ring
- Story where character has "boomerdisc"
- How would increasing atomic bond strength affect nuclear physics?
- How do you determine what order to process chained events/interactions?
- DATEDIFF Rounding
- Does the Greek used in 1 Peter 3:7 properly translate as “weaker” and in what way might that be applied?
- Recovering data from a phone that won't boot
- `Drop` for list of elements of different dimensions
- Optimal Bath Fan Location
- Can you solve this median geometry problem?
- 3 Aspects of Voltage that contradict each other
- Is it possible to create a board position where White must make the move that leads to stalemating Black to avoid Black stalemating White?
- Meaning of “ ’thwart” in a 19th century poem
- My colleagues and I are travelling to UK as delegates in an event and the company is paying for all our travel expenses. what documents are required
- What is the difference between using a resistor or a capacitor as current limiter?
- Why do National Geographic and Discovery Channel broadcast fake or pseudoscientific programs?
- How can these humans cross the ocean(s) at the first possible chance?
- How could Bangladesh protect itself from Indian dams and barrages?
- What would the appropriate cost be for a magical set of full plate with a Cast On and Cast Off property?
- How to total time duration for an arbitrary number of tracked tasks in Excel?
- wp_verify_nonce is always false even when the nonces are identical

IMAGES
COMMENTS
File "weird.py", line 5, in main. print f(3) UnboundLocalError: local variable 'f' referenced before assignment. Python sees the f is used as a local variable in [f for f in [1, 2, 3]], and decides that it is also a local variable in f(3). You could add a global f statement: def f(x): return x. def main():
x = "Hello "def say_hello (name): x = x + name print (x) say_hello("Billy") # UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment But wait, why does this also produce the error? Isn't x assigned before it's used in the say_hello function?
Output. Hangup (SIGHUP) Traceback (most recent call last): File "Solution.py", line 7, in <module> example_function() File "Solution.py", line 4, in example_function x += 1 # Trying to modify global variable 'x' without declaring it as global UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment Solution for Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Therefore, we have examined the local variable referenced before the assignment Exception in Python. The differences between a local and global variable declaration have been explained, and multiple solutions regarding the issue have been provided.
The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function. To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var .
If you run this code, you'll get. BASH. UnboundLocalError: local variable 'value' referenced before assignment. The issue is that in this line: PYTHON. value = value + 1. We are defining a local variable called value and then trying to use it before it has been assigned a value, instead of using the variable that we defined in the first line.
The UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment occurs when you reference a variable inside a function before declaring that variable. To resolve this error, you need to use a different variable name when referencing the existing variable, or you can also specify a parameter for the function. I hope this tutorial is useful.
Avoid Reassignment of Global Variables. Below, code calculates a new value (local_var) based on the global variable and then prints both the local and global variables separately.It demonstrates that the global variable is accessed directly without being reassigned within the function.
Trying to assign a value to a variable that does not have local scope can result in this error: UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment. Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable. If a variable is assigned in a function, that variable is local. This is because it is assumed that when you define a ...
Strategy 2: Using the Global Keyword. In Python, variables declared inside a function are considered local variables. Thus, they are separate from other variables declared outside of the function.
UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment. Example #1: Accessing a Local Variable. Solution #1: Passing Parameters to the Function. Solution #2: Use Global Keyword. Example #2: Function with if-elif statements. Solution #1: Include else statement. Solution #2: Use global keyword. Summary.
This tutorial explains the reason and solution of the python error local variable referenced before assignment
@HoKy22: Are you asking why dct[key] = val does not raise a "local variable referenced before assignment" error? The reason is that this is not a bare name assignment. Instead, it causes Python to make the function call dct.__setitem__ ... As the Python interpreter reads the definition of a function (or, I think, ...
Using nonlocal keyword. The nonlocal keyword is used to work with variables inside nested functions, where the variable should not belong to the inner function. It allows you to modify the value of a non-local variable in the outer scope. For example, if you have a function outer that defines a variable x, and another function inner inside outer that tries to change the value of x, you need to ...
1 UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment. Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable. To clarify, a variable is assigned in a function, that variable is local. Because it is assumed that when you define a variable inside a function, you only need to access it inside that function.
What is a Local Variable? A local variable is a variable that is declared inside a function or block and is only accessible within that function or block. It cannot be accessed from outside its local scope. Python's Variable Scope Hierarchy. Python follows the LEGB rule for scopes: Local (L): Defined inside a function.
To fix this, you can either move the assignment of the variable x before the print statement, or give it an initial value before the print statement. def example (): x = 5 print (x) example()
6. When Python sees that you are assigning to x it forces it to be a local variable name. Now it becomes impossible to see the global x in that function (unless you use the global keyword) So. Case 1) Since there is no local x, you get the global. Case 2) You are assigning to a local x so all references to x in the function will be the local one.
The official dedicated python forum. This is topic with lot of subtlety. Some of the scenarios are discussed in this thread: Namespace and scope difference I think that this boils down to this: Quote:You should also understand difference between reference and assignment: When you reference a variable in an expression, the Python interpreter will traverse the scope to resolve the reference in ...
Here is the official documentation for function definition. Function Scope. It's important to understand the idea of scope. A variable created inside a function can only be used inside that function, because it has local scope. A variable created in the main body of the Python code is a global variable and hence has global scope. This variable ...
Notice the two spaces before print in the snippet with the if, elif, else statements. These spaces are called indentation and they are important as they tell python when the condition starts and stops. ... < and > are the strict less and greater than operators, while == is the equality operator (not to be confused with =, the variable ...
1. The variables wins, money and losses were declared outside the scope of the fiftyfifty() function, so you cannot update them from inside the function unless you explicitly declare them as global variables like this: def fiftyfifty(bet): global wins, money, losses. chance = random.randint(0,100)
hi guys i am new to data structures and i have been trying to solve a maze using left hand rule algorithm. However, i have been facing difficulty in trying to print out the number of steps to take to