

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write an Introduction Paragraph in 3 Steps
General Education

It’s the roadmap to your essay, it’s the forecast for your argument, it’s...your introduction paragraph, and writing one can feel pretty intimidating. The introduction paragraph is a part of just about every kind of academic writing , from persuasive essays to research papers. But that doesn’t mean writing one is easy!
If trying to write an intro paragraph makes you feel like a Muggle trying to do magic, trust us: you aren’t alone. But there are some tips and tricks that can make the process easier—and that’s where we come in.
In this article, we’re going to explain how to write a captivating intro paragraph by covering the following info:
- A discussion of what an introduction paragraph is and its purpose in an essay
- An overview of the most effective introduction paragraph format, with explanations of the three main parts of an intro paragraph
- An analysis of real intro paragraph examples, with a discussion of what works and what doesn’t
- A list of four top tips on how to write an introduction paragraph
Are you ready? Let’s begin!

What Is an Introduction Paragraph?
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay , paper, or other type of academic writing. Argumentative essays , book reports, research papers, and even personal essays are common types of writing that require an introduction paragraph. Whether you’re writing a research paper for a science course or an argumentative essay for English class , you’re going to have to write an intro paragraph.
So what’s the purpose of an intro paragraph? As a reader’s first impression of your essay, the intro paragraph should introduce the topic of your paper.
Your introduction will also state any claims, questions, or issues that your paper will focus on. This is commonly known as your paper’s thesis . This condenses the overall point of your paper into one or two short sentences that your reader can come back and reference later.
But intro paragraphs need to do a bit more than just introduce your topic. An intro paragraph is also supposed to grab your reader’s attention. The intro paragraph is your chance to provide just enough info and intrigue to make your reader say, “Hey, this topic sounds interesting. I think I’ll keep reading this essay!” That can help your essay stand out from the crowd.
In most cases, an intro paragraph will be relatively short. A good intro will be clear, brief, purposeful, and focused. While there are some exceptions to this rule, it’s common for intro paragraphs to consist of three to five sentences .
Effectively introducing your essay’s topic, purpose, and getting your reader invested in your essay sounds like a lot to ask from one little paragraph, huh? In the next section, we’ll demystify the intro paragraph format by breaking it down into its core parts . When you learn how to approach each part of an intro, writing one won’t seem so scary!

Once you figure out the three parts of an intro paragraph, writing one will be a piece of cake!
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph
In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement . Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay.
Below, we’ll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an effective hook, providing context, and crafting a thesis statement. When you put these elements together, you’ll have an intro paragraph that does a great job of making a great first impression on your audience!
Intro Paragraph Part 1: The Hook
When it comes to how to start an introduction paragraph, o ne of the most common approaches is to start with something called a hook.
What does hook mean here, though? Think of it this way: it’s like when you start a new Netflix series: you look up a few hours (and a few episodes) later and you say, “Whoa. I guess I must be hooked on this show!”
That’s how the hook is supposed to work in an intro paragrap h: it should get your reader interested enough that they don’t want to press the proverbial “pause” button while they’re reading it . In other words, a hook is designed to grab your reader’s attention and keep them reading your essay!
This means that the hook comes first in the intro paragraph format—it’ll be the opening sentence of your intro.
It’s important to realize that there are many different ways to write a good hook. But generally speaking, hooks must include these two things: what your topic is, and the angle you’re taking on that topic in your essay.
One approach to writing a hook that works is starting with a general, but interesting, statement on your topic. In this type of hook, you’re trying to provide a broad introduction to your topic and your angle on the topic in an engaging way .
For example, if you’re writing an essay about the role of the government in the American healthcare system, your hook might look something like this:
There's a growing movement to require that the federal government provide affordable, effective healthcare for all Americans.
This hook introduces the essay topic in a broad way (government and healthcare) by presenting a general statement on the topic. But the assumption presented in the hook can also be seen as controversial, which gets readers interested in learning more about what the writer—and the essay—has to say.
In other words, the statement above fulfills the goals of a good hook: it’s intriguing and provides a general introduction to the essay topic.
Intro Paragraph Part 2: Context
Once you’ve provided an attention-grabbing hook, you’ll want to give more context about your essay topic. Context refers to additional details that reveal the specific focus of your paper. So, whereas the hook provides a general introduction to your topic, context starts helping readers understand what exactly you’re going to be writing about
You can include anywhere from one to several sentences of context in your intro, depending on your teacher’s expectations, the length of your paper, and complexity of your topic. In these context-providing sentences, you want to begin narrowing the focus of your intro. You can do this by describing a specific issue or question about your topic that you’ll address in your essay. It also helps readers start to understand why the topic you’re writing about matters and why they should read about it.
So, what counts as context for an intro paragraph? Context can be any important details or descriptions that provide background on existing perspectives, common cultural attitudes, or a specific situation or controversy relating to your essay topic. The context you include should acquaint your reader with the issues, questions, or events that motivated you to write an essay on your topic...and that your reader should know in order to understand your thesis.
For instance, if you’re writing an essay analyzing the consequences of sexism in Hollywood, the context you include after your hook might make reference to the #metoo and #timesup movements that have generated public support for victims of sexual harassment.
The key takeaway here is that context establishes why you’re addressing your topic and what makes it important. It also sets you up for success on the final piece of an intro paragraph: the thesis statement.
Elle Woods' statement offers a specific point of view on the topic of murder...which means it could serve as a pretty decent thesis statement!
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis
The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way . The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay. A good thesis statement will be clear, straightforward, and highlight the overall point you’re trying to make.
Some instructors also ask students to include an essay map as part of their thesis. An essay map is a section that outlines the major topics a paper will address. So for instance, say you’re writing a paper that argues for the importance of public transport in rural communities. Your thesis and essay map might look like this:
Having public transport in rural communities helps people improve their economic situation by giving them reliable transportation to their job, reducing the amount of money they spend on gas, and providing new and unionized work .
The underlined section is the essay map because it touches on the three big things the writer will talk about later. It literally maps out the rest of the essay!
So let’s review: Your thesis takes the idea you’ve introduced in your hook and context and wraps it up. Think of it like a television episode: the hook sets the scene by presenting a general statement and/or interesting idea that sucks you in. The context advances the plot by describing the topic in more detail and helping readers understand why the topic is important. And finally, the thesis statement provides the climax by telling the reader what you have to say about the topic.
The thesis statement is the most important part of the intro. Without it, your reader won’t know what the purpose of your essay is! And for a piece of writing to be effective, it needs to have a clear purpose. Your thesis statement conveys that purpose , so it’s important to put careful thought into writing a clear and compelling thesis statement.

How To Write an Introduction Paragraph: Example and Analysis
Now that we’ve provided an intro paragraph outline and have explained the three key parts of an intro paragraph, let’s take a look at an intro paragraph in action.
To show you how an intro paragraph works, we’ve included a sample introduction paragraph below, followed by an analysis of its strengths and weaknesses.
Example of Introduction Paragraph
While college students in the U.S. are struggling with how to pay for college, there is another surprising demographic that’s affected by the pressure to pay for college: families and parents. In the face of tuition price tags that total more than $100,000 (as a low estimate), families must make difficult decisions about how to save for their children’s college education. Charting a feasible path to saving for college is further complicated by the FAFSA’s estimates for an “Expected Family Contribution”—an amount of money that is rarely feasible for most American families. Due to these challenging financial circumstances and cultural pressure to give one’s children the best possible chance of success in adulthood, many families are going into serious debt to pay for their children’s college education. The U.S. government should move toward bearing more of the financial burden of college education.
Example of Introduction Paragraph: Analysis
Before we dive into analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of this example intro paragraph, let’s establish the essay topic. The sample intro indicates that t he essay topic will focus on one specific issue: who should cover the cost of college education in the U.S., and why. Both the hook and the context help us identify the topic, while the thesis in the last sentence tells us why this topic matters to the writer—they think the U.S. Government needs to help finance college education. This is also the writer’s argument, which they’ll cover in the body of their essay.
Now that we’ve identified the essay topic presented in the sample intro, let’s dig into some analysis. To pin down its strengths and weaknesses, we’re going to use the following three questions to guide our example of introduction paragraph analysis:
- Does this intro provide an attention-grabbing opening sentence that conveys the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide relevant, engaging context about the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide a thesis statement that establishes the writer’s point of view on the topic and what specific aspects of the issue the essay will address?
Now, let’s use the questions above to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of this sample intro paragraph.
Does the Intro Have a Good Hook?
First, the intro starts out with an attention-grabbing hook . The writer starts by presenting an assumption (that the U.S. federal government bears most of the financial burden of college education), which makes the topic relatable to a wide audience of readers. Also note that the hook relates to the general topic of the essay, which is the high cost of college education.
The hook then takes a surprising turn by presenting a counterclaim : that American families, rather than students, feel the true burden of paying for college. Some readers will have a strong emotional reaction to this provocative counterclaim, which will make them want to keep reading! As such, this intro provides an effective opening sentence that conveys the essay topic.
Does the Intro Give Context?
T he second, third, and fourth sentences of the intro provide contextual details that reveal the specific focus of the writer’s paper . Remember: the context helps readers start to zoom in on what the paper will focus on, and what aspect of the general topic (college costs) will be discussed later on.
The context in this intro reveals the intent and direction of the paper by explaining why the issue of families financing college is important. In other words, the context helps readers understand why this issue matters , and what aspects of this issue will be addressed in the paper.
To provide effective context, the writer refers to issues (the exorbitant cost of college and high levels of family debt) that have received a lot of recent scholarly and media attention. These sentences of context also elaborate on the interesting perspective included in the hook: that American families are most affected by college costs.
Does the Intro Have a Thesis?
Finally, this intro provides a thesis statement that conveys the writer’s point of view on the issue of financing college education. This writer believes that the U.S. government should do more to pay for students’ college educations.
However, the thesis statement doesn’t give us any details about why the writer has made this claim or why this will help American families . There isn’t an essay map that helps readers understand what points the writer will make in the essay.
To revise this thesis statement so that it establishes the specific aspects of the topic that the essay will address, the writer could add the following to the beginning of the thesis statement:
The U.S. government should take on more of the financial burden of college education because other countries have shown this can improve education rates while reducing levels of familial poverty.
Check out the new section in bold. Not only does it clarify that the writer is talking about the pressure put on families, it touches on the big topics the writer will address in the paper: improving education rates and reduction of poverty. So not only do we have a clearer argumentative statement in this thesis, we also have an essay map!
So, let’s recap our analysis. This sample intro paragraph does an effective job of providing an engaging hook and relatable, interesting context, but the thesis statement needs some work ! As you write your own intro paragraphs, you might consider using the questions above to evaluate and revise your work. Doing this will help ensure you’ve covered all of your bases and written an intro that your readers will find interesting!

4 Tips for How To Write an Introduction Paragraph
Now that we’ve gone over an example of introduction paragraph analysis, let’s talk about how to write an introduction paragraph of your own. Keep reading for four tips for writing a successful intro paragraph for any essay.
Tip 1: Analyze Your Essay Prompt
If you’re having trouble with how to start an introduction paragraph, analyze your essay prompt! Most teachers give you some kind of assignment sheet, formal instructions, or prompt to set the expectations for an essay they’ve assigned, right? Those instructions can help guide you as you write your intro paragraph!
Because they’ll be reading and responding to your essay, you want to make sure you meet your teacher’s expectations for an intro paragraph . For instance, if they’ve provided specific instructions about how long the intro should be or where the thesis statement should be located, be sure to follow them!
The type of paper you’re writing can give you clues as to how to approach your intro as well. If you’re writing a research paper, your professor might expect you to provide a research question or state a hypothesis in your intro. If you’re writing an argumentative essay, you’ll need to make sure your intro overviews the context surrounding your argument and your thesis statement includes a clear, defensible claim.
Using the parameters set out by your instructor and assignment sheet can put some easy-to-follow boundaries in place for things like your intro’s length, structure, and content. Following these guidelines can free you up to focus on other aspects of your intro... like coming up with an exciting hook and conveying your point of view on your topic!
Tip 2: Narrow Your Topic
You can’t write an intro paragraph without first identifying your topic. To make your intro as effective as possible, you need to define the parameters of your topic clearly—and you need to be specific.
For example, let’s say you want to write about college football. “NCAA football” is too broad of a topic for a paper. There is a lot to talk about in terms of college football! It would be tough to write an intro paragraph that’s focused, purposeful, and engaging on this topic. In fact, if you did try to address this whole topic, you’d probably end up writing a book!
Instead, you should narrow broad topics to identify a specific question, claim, or issue pertaining to some aspect of NCAA football for your intro to be effective. So, for instance, you could frame your topic as, “How can college professors better support NCAA football players in academics?” This focused topic pertaining to NCAA football would give you a more manageable angle to discuss in your paper.
So before you think about writing your intro, ask yourself: Is my essay topic specific, focused, and logical? Does it convey an issue or question that I can explore over the course of several pages? Once you’ve established a good topic, you’ll have the foundation you need to write an effective intro paragraph .

Once you've figured out your topic, it's time to hit the books!
Tip 3: Do Your Research
This tip is tightly intertwined with the one above, and it’s crucial to writing a good intro: do your research! And, guess what? This tip applies to all papers—even ones that aren’t technically research papers.
Here’s why you need to do some research: getting the lay of the land on what others have said about your topic—whether that’s scholars and researchers or the mass media— will help you narrow your topic, write an engaging hook, and provide relatable context.
You don't want to sit down to write your intro without a solid understanding of the different perspectives on your topic. Whether those are the perspectives of experts or the general public, these points of view will help you write your intro in a way that is intriguing and compelling for your audience of readers.
Tip 4: Write Multiple Drafts
Some say to write your intro first; others say write it last. The truth is, there isn’t a right or wrong time to write your intro—but you do need to have enough time to write multiple drafts .
Oftentimes, your professor will ask you to write multiple drafts of your paper, which gives you a built-in way to make sure you revise your intro. Another approach you could take is to write out a rough draft of your intro before you begin writing your essay, then revise it multiple times as you draft out your paper.
Here’s why this approach can work: as you write your paper, you’ll probably come up with new insights on your topic that you didn’t have right from the start. You can use these “light bulb” moments to reevaluate your intro and make revisions that keep it in line with your developing essay draft.
Once you’ve written your entire essay, consider going back and revising your intro again . You can ask yourself these questions as you evaluate your intro:
- Is my hook still relevant to the way I’ve approached the topic in my essay?
- Do I provide enough appropriate context to introduce my essay?
- Now that my essay is written, does my thesis statement still accurately reflect the point of view that I present in my essay?
Using these questions as a guide and putting your intro through multiple revisions will help ensure that you’ve written the best intro for the final draft of your essay. Also, revising your writing is always a good thing to do—and this applies to your intro, too!

What's Next?
Your college essays also need great intro paragraphs. Here’s a guide that focuses on how to write the perfect intro for your admissions essays.
Of course, the intro is just one part of your college essay . This article will teach you how to write a college essay that makes admissions counselors sit up and take notice.
Are you trying to write an analytical essay? Our step-by-step guide can help you knock it out of the park.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Excellent Essay Introduction

- 3-minute read
- 27th September 2022
Love it or hate it, essay writing is a big part of student life. Writing a great essay might seem like a daunting task, especially when you’re staring at a blank document, but there are formulas you can follow to make sure your paper hits the mark.
When you plan your essays , don’t neglect your introduction! It might seem like a trivial part of the paper, but it can make it or break it. A badly written introduction can leave your reader feeling confused about the topic and what to expect from your essay.
To help your writing reach its full potential, we’ve put together a guide to writing an excellent essay introduction.
How to Write an Essay Introduction
An essay introduction has four main steps:
● Hook your reader
● Provide context
● Present your thesis statement
● Map your essay
Hook Your Reader
The first part of your introduction should be the hook. This is where you introduce the reader to the topic of the essay. A great hook should be clear, concise, and catchy. It doesn’t need to be long; a hook can be just one sentence.
Provide Context
In this section, introduce your reader to key definitions, ideas, and background information to help them understand your argument.
Present Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences.
Map Your Essay
Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your reader a sense of direction.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction:
Hook: Suspense is key for dramatic stories, and Shakespeare is well-known and celebrated for writing suspenseful plays.
Context: While there are many ways in which Shakespeare created suspension for his viewers, two techniques he used effectively were foreshadowing and dramatic irony. Foreshadowing is a literary device that hints at an event or situation that is yet to happen. Dramatic irony is a literary technique, originally used in Greek tragedy, by which the full significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience or reader, although it is unknown to the character.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Thesis statement: Foreshadowing and dramatic irony are two powerful techniques that Shakespeare used to create suspense in literature. These methods have been used to keep the reader intrigued, excited, or nervous about what is to come in many of his celebrated works.
Essay mapping: In this essay, I will be detailing how Shakespeare uses foreshadowing and dramatic irony to create suspense, with examples from Romeo and Juliet and Othello.
Pro tip: Essays take twists and turns. We recommend changing your introduction as necessary while you write the main text to make sure it fully aligns with your final draft.
Proofread and Editing
Proofreading is an essential part of delivering a great essay. We offer a proofreading and editing service for students and academics that will provide you with expert editors to check your work for any issues with:
● Grammar
● Spelling
● Formatting
● Tone
● Audience
● Consistency
● Accuracy
● Clarity
Want 500 words of your work proofread completely free of charge?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to Start an Essay: 13 Engaging Strategies
ThoughtCo / Hugo Lin
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
There are countless ways to start an essay effectively. A solid introductory paragraph both informs and motivates. It lets readers know what your piece is about and it encourages them to keep reading.
For folks new to learning how to start an essay, here are 13 introductory strategies accompanied by examples from a wide range of professional writers.
State Your Thesis Briefly and Directly
One straightforward way to begin is to get right to the point. But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...".
"It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving." The Camera Age: Essays on Television . Penguin, 1982)
Pose a Question Related to Your Subject
A thought-provoking way to start an essay is by asking a relevant question that needs to be unpacked. Follow up the question with an answer, or an invitation for your readers to answer the question.
"What is the charm of necklaces? Why would anyone put something extra around their neck and then invest it with special significance? A necklace doesn't afford warmth in cold weather, like a scarf, or protection in combat, like chain mail; it only decorates. We might say, it borrows meaning from what it surrounds and sets off, the head with its supremely important material contents, and the face, that register of the soul. When photographers discuss the way in which a photograph reduces the reality it represents, they mention not only the passage from three dimensions to two, but also the selection of a point de vue that favors the top of the body rather than the bottom, and the front rather than the back. The face is the jewel in the crown of the body, and so we give it a setting." (Emily R. Grosholz, "On Necklaces." Prairie Schooner , Summer 2007)
State an Interesting Fact About Your Subject
Leading with a fact that draws readers in immediately can grab their attention effectively.
" The peregrine falcon was brought back from the brink of extinction by a ban on DDT, but also by a peregrine falcon mating hat invented by an ornithologist at Cornell University. If you cannot buy this, Google it. Female falcons had grown dangerously scarce. A few wistful males nevertheless maintained a sort of sexual loitering ground. The hat was imagined, constructed, and then forthrightly worn by the ornithologist as he patrolled this loitering ground, singing, Chee-up! Chee-up! and bowing like an overpolite Japanese Buddhist trying to tell somebody goodbye...." (David James Duncan, "Cherish This Ecstasy." The Sun , July 2008)
Present Your Thesis as a Recent Discovery or Revelation
"I've finally figured out the difference between neat people and sloppy people. The distinction is, as always, moral. Neat people are lazier and meaner than sloppy people." (Suzanne Britt Jordan, "Neat People vs. Sloppy People." Show and Tell . Morning Owl Press, 1983)
Briefly Describe the Primary Setting of Your Essay
"It was in Burma, a sodden morning of the rains. A sickly light, like yellow tinfoil, was slanting over the high walls into the jail yard. We were waiting outside the condemned cells, a row of sheds fronted with double bars, like small animal cages. Each cell measured about ten feet by ten and was quite bare within except for a plank bed and a pot of drinking water. In some of them brown silent men were squatting at the inner bars, with their blankets draped round them. These were the condemned men, due to be hanged within the next week or two." (George Orwell, "A Hanging," 1931)
Recount an Incident That Dramatizes Your Subject
Sharing an incident from your life or history in general is an impactful way to start an essay.
"One October afternoon three years ago while I was visiting my parents, my mother made a request I dreaded and longed to fulfill. She had just poured me a cup of Earl Grey from her Japanese iron teapot, shaped like a little pumpkin; outside, two cardinals splashed in the birdbath in the weak Connecticut sunlight. Her white hair was gathered at the nape of her neck, and her voice was low. “Please help me get Jeff’s pacemaker turned off,” she said, using my father’s first name. I nodded, and my heart knocked." (Katy Butler, "What Broke My Father's Heart." The New York Times Magazine , June 18, 2010)
Use the Narrative Strategy of Delay
The narrative strategy of delay allows you to put off identifying your subject just long enough to pique your readers' interest without frustrating them.
"They woof. Though I have photographed them before, I have never heard them speak, for they are mostly silent birds. Lacking a syrinx, the avian equivalent of the human larynx, they are incapable of song. According to field guides the only sounds they make are grunts and hisses, though the Hawk Conservancy in the United Kingdom reports that adults may utter a croaking coo and that young black vultures, when annoyed, emit a kind of immature snarl...." (Lee Zacharias, "Buzzards." Southern Humanities Review , 2007)
Use the Historical Present Tense
An effective way to start an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now.
"Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother’s station wagon. We face glowing white headlights of cars following us, our sneakers pressed against the back hatch door. This is our joy—his and mine—to sit turned away from our moms and dads in this place that feels like a secret, as though they are not even in the car with us. They have just taken us out to dinner, and now we are driving home. Years from this evening, I won’t actually be sure that this boy sitting beside me is named Ben. But that doesn’t matter tonight. What I know for certain right now is that I love him, and I need to tell him this fact before we return to our separate houses, next door to each other. We are both five." (Ryan Van Meter, "First." The Gettysburg Review , Winter 2008)
Briefly Describe a Process That Leads Into Your Subject
"I like to take my time when I pronounce someone dead. The bare-minimum requirement is one minute with a stethoscope pressed to someone’s chest, listening for a sound that is not there; with my fingers bearing down on the side of someone’s neck, feeling for an absent pulse; with a flashlight beamed into someone’s fixed and dilated pupils, waiting for the constriction that will not come. If I’m in a hurry, I can do all of these in sixty seconds, but when I have the time, I like to take a minute with each task." (Jane Churchon, "The Dead Book." The Sun , February 2009)
Reveal a Secret or Make a Candid Observation
"I spy on my patients. Ought not a doctor to observe his patients by any means and from any stance, that he might the more fully assemble evidence? So I stand in doorways of hospital rooms and gaze. Oh, it is not all that furtive an act. Those in bed need only look up to discover me. But they never do." ( Richard Selzer , "The Discus Thrower." Confessions of a Knife . Simon & Schuster, 1979)
Open with a Riddle, Joke, or Humorous Quotation
A fun way to start an essay is to use a riddle , joke, or humorous quotation that reveals something about your subject.
" Q: What did Eve say to Adam on being expelled from the Garden of Eden? A: 'I think we're in a time of transition.' The irony of this joke is not lost as we begin a new century and anxieties about social change seem rife. The implication of this message, covering the first of many periods of transition, is that change is normal; there is, in fact, no era or society in which change is not a permanent feature of the social landscape...." (Betty G. Farrell, Family: The Making of an Idea, an Institution, and a Controversy in American Culture . Westview Press, 1999)
Offer a Contrast Between Past and Present
"As a child, I was made to look out the window of a moving car and appreciate the beautiful scenery, with the result that now I don't care much for nature. I prefer parks, ones with radios going chuckawaka chuckawaka and the delicious whiff of bratwurst and cigarette smoke." (Garrison Keillor, "Walking Down The Canyon." Time , July 31, 2000)
Offer a Contrast Between Image and Reality
A compelling way to start an essay is with a contrast between a common misconception and the opposing truth.
"They aren’t what most people think they are. Human eyes, touted as ethereal objects by poets and novelists throughout history, are nothing more than white spheres, somewhat larger than your average marble, covered by a leather-like tissue known as sclera and filled with nature’s facsimile of Jell-O. Your beloved’s eyes may pierce your heart, but in all likelihood they closely resemble the eyes of every other person on the planet. At least I hope they do, for otherwise he or she suffers from severe myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness), or worse...." (John Gamel, "The Elegant Eye." Alaska Quarterly Review , 2009)
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Essay Assignment: Descriptive and Informative Profile
- Practice in Supporting a Topic Sentence with Specific Details
- How to Start a Book Report
- What Is Expository Writing?
- An Essay Revision Checklist
- Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech (With Topic Ideas)
- Writing an Opinion Essay
Writing Help
Admission essays by, writing the essay: the first sentence.
For an introduction to writing the first sentence of an essay, see "The First Sentence" under Academic Essays . For an introduction to the different kinds of paths your essay might follow, see "Take Your Reader on a Trip" on the same page.
The first draft of your first sentence should be just enough to get you started as you begin to write. Later, after you have a good command of your topic and have a good sense of the overall tone of your essay--this may not be until after you have written several drafts--you can spend time focusing on the first sentence. This point in your writing is a good time to go back to sample essays to see what they accomplish in the first sentence. Does one of them provide a model for a sentence that would work well in your essay?
If you are having trouble structuring your essay, one good strategy is to look through everything you have written for the one best or most moving line. Try putting that sentence at the start and forming the rest of the essay around that primary idea. Note that this line might be the last point chronologically in your narrative--putting it first would give the whole essay an interesting "flashback" structure.
Here are some sample openings that might fit your essay.
1. Dialogue . Dialogue usually gets a reader's attention. This is because dialogue gives a sense of present action. Even one sentence in quotation marks can be enough. Example: "'I don't know where you get those ideas!' my mother said. I was drawing and explaining my latest, perhaps my craziest, back-of-the-placemat 'invention'..." This opening shows that the writer is thoughtful yet aware of the limitations of his ideas, friendly with his mom, and perhaps just the kind of person who can learn to focus his ideas with a good college education.
2. A short, striking sentence . Readers often appreciate writers who can pack a punch and then mellow out. You can be dramatic without being melodramatic. Example: "I held my gun firmly. The paintball field was covered in blue, yellow, and red splotches..."
3. A leisurely introduction . If the essay isn't action-packed but instead paints a beautiful picture for the reader, let the opening suggest a pleasant experience. Example: "Rowing out to the island on Lake Bled, dwarfed by the Slovenian Alps to the north and by an ancient castle high on the eastern hill, I was enjoying the best day of my summer vacation." Take the reader with you through this wonderful experience, using extra phrases and clauses beyond the simple subject and verb of the sentence.
4. A challenge . You can draw the reader into your argument if you advertise that you have learned something that goes against common knowledge. Perhaps you figured out that cats actually love to be petted the "wrong" way, back to front. Example: "Although my parents had warned me never to pet a cat from back to front, I recently discovered that Stitches can't get enough of my 'backward' attentions." This sentence suggests that the writer is willing to challenge cultural norms, which a lot of colleges want to see their students learn to do. Note that this kind of opening frequently starts out with the common knowledge but adds a challenging word such as although, but, while, or even though somewhere in the first clause, and then suggests the content of the challenge in the second clause.
5. A warning . A reader will pay attention when there is something to be concerned about. Examples: "I wish someone had told me two years ago that sometimes a pool of water on the road is really a mirage!" "When I worked for Representative Smith's political campaign last summer, I learned that pollution from factories in our state is far less of a danger to public health than runoff from farms." The second example shows that the writer knows something that readers should be aware of, that the writer did some interesting work, and that the writer learned something valuable from the experience.

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Start a College Essay to Hook Your Reader
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of the college essay introduction, tips for getting started on your essay, 6 effective techniques for starting your college essay.
- Cliche College Essay Introduction to Avoid
Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Have you sat down to write your essay and just hit a wall of writer’s block? Do you have too many ideas running around your head, or maybe no ideas at all?
Starting a college essay is potentially the hardest part of the application process. Once you start, it’s easy to keep writing, but that initial hurdle is just so difficult to overcome. We’ve put together a list of tips to help you jump that wall and make your essay the best it can be.
The introduction to a college essay should immediately hook the reader. You want to give admissions officers a reason to stay interested in your story and encourage them to continue reading your essay with an open mind. Remember that admissions officers are only able to spend a couple minutes per essay, so if you bore them or turn them off from the start, they may clock out for the rest of the essay.
As a whole, the college essay should aim to portray a part of your personality that hasn’t been covered by your GPA, extracurriculars, and test scores. This makes the introduction a crucial part of the essay. Think of it as the first glimpse, an intriguing lead on, into the read rest of your essay which also showcases your voice and personality.
Brainstorm Topics
Take the time to sit down and brainstorm some good topic ideas for your essay. You want your topic to be meaningful to you, while also displaying a part of you that isn’t apparent in other aspects of your application. The essay is an opportunity to show admissions officers the “real you.” If you have a topic in mind, do not feel pressured to start with the introduction. Sometimes the best essay openings are developed last, once you fully grasp the flow of your story.
Do a Freewrite
Give yourself permission to write without judgment for an allotted period of time. For each topic you generated in your brainstorm session, do a free-write session. Set a time for one minute and write down whatever comes to mind for that specific topic. This will help get the juices flowing and push you over that initial bit of writer’s block that’s so common when it comes time to write a college essay. Repeat this exercise if you’re feeling stuck at any point during the essay writing process. Freewriting is a great way to warm up your creative writing brain whilst seeing which topics are flowing more naturally onto the page.
Create an Outline
Once you’ve chosen your topic, write an outline for your whole essay. It’s easier to organize all your thoughts, write the body, and then go back to write the introduction. That way, you already know the direction you want your essay to go because you’ve actually written it out, and you can ensure that your introduction leads directly into the rest of the essay. Admissions officers are looking for the quality of your writing alongside the content of your essay. To be prepared for college-level writing, students should understand how to logically structure an essay. By creating an outline, you are setting yourself up to be judged favorably on the quality of your writing skills.
1. The Scriptwriter
“No! Make it stop! Get me out!” My 5-year-old self waved my arms frantically in front of my face in the darkened movie theater.
Starting your essay with dialogue instantly transports the reader into the story, while also introducing your personal voice. In the rest of the essay, the author proposes a class that introduces people to insects as a type of food. Typically, one would begin directly with the course proposal. However, the author’s inclusion of this flashback weaves in a personal narrative, further displaying her true self.
Read the full essay.
2. The Shocker
A chaotic sense of sickness and filth unfolds in an overcrowded border station in McAllen, Texas. Through soundproof windows, migrants motion that they have not showered in weeks, and children wear clothes caked in mucus and tears. The humanitarian crisis at the southern border exists not only in photographs published by mainstream media, but miles from my home in South Texas.
This essay opener is also a good example of “The Vivid Imaginer.” In this case, the detailed imagery only serves to heighten the shock factor. While people may be aware of the “humanitarian crisis at the southern border,” reading about it in such stark terms is bound to capture the reader’s attention. Through this hook, the reader learns a bit about the author’s home life; an aspect of the student that may not be detailed elsewhere in their application. The rest of the essay goes on to talk about the author’s passion for aiding refugees, and this initial paragraph immediately establishes the author’s personal connection to the refugee crisis.
3. The Vivid Imaginer
The air is crisp and cool, nipping at my ears as I walk under a curtain of darkness that drapes over the sky, starless. It is a Friday night in downtown Corpus Christi, a rare moment of peace in my home city filled with the laughter of strangers and colorful lights of street vendors. But I cannot focus.
Starting off with a bit of well-written imagery transports the reader to wherever you want to take them. By putting them in this context with you, you allow the reader to closely understand your thoughts and emotions in this situation. Additionally, this method showcases the author’s individual way of looking at the world, a personal touch that is the baseline of all college essays.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
4. The Instant Plunger
The flickering LED lights began to form into a face of a man when I focused my eyes. The man spoke of a ruthless serial killer of the decade who had been arrested in 2004, and my parents shivered at his reaccounting of the case. I curiously tuned in, wondering who he was to speak of such crimes with concrete composure and knowledge. Later, he introduced himself as a profiler named Pyo Chang Won, and I watched the rest of the program by myself without realizing that my parents had left the couch.
Plunging readers into the middle of a story (also known as in medias res ) is an effective hook because it captures attention by placing the reader directly into the action. The descriptive imagery in the first sentence also helps to immerse the reader, creating a satisfying hook while also showing (instead of telling) how the author became interested in criminology. With this technique, it is important to “zoom out,” so to speak, in such a way that the essay remains personal to you.
5. The Philosopher
Saved in the Notes app on my phone are three questions: What can I know? What must I do? What may I hope for? First asked by Immanuel Kant, these questions guide my pursuit of knowledge and organization of critical thought, both skills that are necessary to move our country and society forward in the right direction.
Posing philosophical questions helps present you as someone with deep ideas while also guiding the focus of your essay. In a way, it presents the reader with a roadmap; they know that these questions provide the theme for the rest of the essay. The more controversial the questions, the more gripping a hook you can create.
Providing an answer to these questions is not necessarily as important as making sure that the discussions they provoke really showcase you and your own values and beliefs.
6. The Storyteller
One Christmas morning, when I was nine, I opened a snap circuit set from my grandmother. Although I had always loved math and science, I didn’t realize my passion for engineering until I spent the rest of winter break creating different circuits to power various lights, alarms, and sensors. Even after I outgrew the toy, I kept the set in my bedroom at home and knew I wanted to study engineering.
Beginning with an anecdote is a strong way to establish a meaningful connection with the content itself. It also shows that the topic you write about has been a part of your life for a significant amount of time, and something that college admissions officers look for in activities is follow-through; they want to make sure that you are truly interested in something. A personal story such as the one above shows off just that.
Cliche College Essay Introductions to Avoid
Ambiguous introduction.
It’s best to avoid introductory sentences that don’t seem to really say anything at all, such as “Science plays a large role in today’s society,” or “X has existed since the beginning of time.” Statements like these, in addition to being extremely common, don’t demonstrate anything about you, the author. Without a personal connection to you right away, it’s easy for the admissions officer to write off the essay before getting past the first sentence.
Quoting Someone Famous
While having a quotation by a famous author, celebrity, or someone else you admire may seem like a good way to allow the reader to get to know you, these kinds of introductions are actually incredibly overused. You also risk making your essay all about the quotation and the famous person who said it; admissions officers want to get to know you, your beliefs, and your values, not someone who isn’t applying to their school. There are some cases where you may actually be asked to write about a quotation, and that’s fine, but you should avoid starting your essay with someone else’s words outside of this case. It is fine, however, to start with dialogue to plunge your readers into a specific moment.
Talking About Writing an Essay
This method is also very commonplace and is thus best avoided. It’s better to show, not tell, and all this method allows you to do is tell the reader how you were feeling at the time of writing the essay. If you do feel compelled to go this way, make sure to include vivid imagery and focus on grounding the essay in the five senses, which can help elevate your introduction and separate it from the many other meta essays.
Childhood Memories
Phrases like “Ever since I was young…” or “I’ve always wanted…” also lend more to telling rather than showing. If you want to talk about your childhood or past feelings in your essay, try using one of the techniques listed earlier (such as the Instant Plunger or the Vivid Imaginer) to elevate your writing.
CollegeVine has a peer essay review page where peers can tell you if your introduction was enough to hook them. Getting feedback from someone who hasn’t read your essay before, and thus doesn’t have any context which may bias them to be more forgiving to your introduction, is helpful because it mimics the same environment in which an admissions officer will be reading your essay.
Writing a college essay is hard, but with these tips hopefully starting it will be a little easier!


Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
| {{item.snippet}} |
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Essay Introduction
Last Updated: January 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,237,919 times.
The introduction of your essay serves two important purposes. First, it gets your reader interested in the topic and encourages them to read what you have to say about it. Second, it gives your reader a roadmap of what you're going to say and the overarching point you're going to make – your thesis statement. A powerful introduction grabs your reader's attention and keeps them reading.
Sample Essay Hooks & Introductions

Hooking Your Reader

- If you're writing a paper for a class, don't automatically assume your instructor is your audience. If you write directly to your instructor, you'll end up glossing over some information that is necessary to show that you properly understand the subject of your essay.
- It can be helpful to reverse-engineer your audience based on the subject matter of your essay. For example, if you're writing an essay about a women's health issue for a women's studies class, you might identify your audience as young women within the age range most affected by the issue.

- For this hook to be effective, your fact needs to be sufficiently surprising. If you're not sure, test it on a few friends. If they react by expressing shock or surprise, you know you've got something good.
- Use a fact or statistic that sets up your essay, not something you'll be using as evidence to prove your thesis statement. Facts or statistics that demonstrate why your topic is important (or should be important) to your audience typically make good hooks.

- For example, if you were writing an essay proposing a change to drunk driving laws, you might open with a story of how the life of a victim was changed forever after they were hit by a drunk driver.

- For example, if you're writing an essay about a public figure, you might include an anecdote about an odd personal habit that cleverly relates back to your thesis statement.
- Particularly with less formal papers or personal essays, humorous anecdotes can be particularly effective hooks.

- For example: "What would you do if you could play God for a day? That's exactly what the leaders of the tiny island nation of Guam tried to answer."
- If your essay prompt was a question, don't just repeat it in your paper. Make sure to come up with your own intriguing question.

- Broad, sweeping generalizations may ring false with some readers and alienate them from the start. For example, "everyone wants someone to love" would alienate someone who identified as aromantic or asexual.
Creating Your Context

- Use an appropriate transitional word or phrase, such as "however" or "similarly," to move from your specific anecdote back out to a broader scope.
- For example, if you related a story about one individual, but your essay isn't about them, you can relate the hook back to the larger topic with a sentence like "Tommy wasn't alone, however. There were more than 200,000 dockworkers affected by that union strike."

- For example, if your thesis relates to how blackface was used as a means of enforcing racial segregation, your introduction would describe what blackface performances were, and where and when they occurred.
- If you are writing an argumentative paper, make sure to explain both sides of the argument in a neutral or objective manner.

- Definitions would be particularly important if your essay is discussing a scientific topic, where some scientific terminology might not be understood by the average layperson.
- Definitions also come in handy in legal or political essays, where a term may have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used.

- If you're using 2 or 3 sentences to describe the context for your thesis, try to make each sentence a bit more specific than the one before it. Draw your reader in gradually.
- For example, if you're writing an essay about drunk driving fatalities, you might start with an anecdote about a particular victim. Then you could provide national statistics, then narrow it down further to statistics for a particular gender or age group.
Presenting Your Thesis

- For example, a thesis for an essay on blackface performance might be "Because of its humiliating and demoralizing effect on African American slaves, blackface was used less as a comedy routine and more as a way of enforcing racial segregation."
- Be assertive and confident in your writing. Avoid including fluff such as "In this essay, I will attempt to show...." Instead, dive right in and make your claim, bold and proud.
- Your outline should be specific, unique, and provable. Through your essay, you'll make points that will show that your thesis statement is true – or at least persuade your readers that it's most likely true.

- If you've created an outline for your essay, this sentence is essentially the main subjects of each paragraph of the body of your essay.
- For example, if you're writing an essay about the unification of Italy, you might list 3 obstacles to unification. In the body of your essay, you would discuss details about how each of those obstacles was addressed or overcome.
- Instead of just listing all of your supporting points, sum them up by stating "how" or "why" your thesis is true. For example, instead of saying, "Phones should be banned from classrooms because they distract students, promote cheating, and make too much noise," you might say "Phones should be banned from classrooms because they act as an obstacle to learning."

- To figure out if you need a transition sentence, read the introduction and the first paragraph out loud. If you find yourself pausing or stumbling between the paragraphs, work in a transition to make the move smoother.
- You can also have friends or family members read your easy. If they feel it's choppy or jumps from the introduction into the essay, see what you can do to smooth it out.
Bringing It All Together

- If you're writing your essay for a class assignment, ask your instructor for examples of well-written essays that you can look at. Take note of conventions that are commonly used by writers in that discipline.
- Make a brief outline of the essay based on the information presented in the introduction. Then look at that outline as you read the essay to see how the essay follows it to prove the writer's thesis statement.

- For shorter essays under 1,000 words, keep your introduction to 1 paragraph, between 100 and 200 words.
- Always follow your instructor's guidelines for length. These rules can vary at times based on genre or form of writing.

- As you write your essay, you may want to jot down things you want to include in your introduction. For example, you may realize that you're using a particular term that you need to define in your introduction.

- Delete any filler or unnecessary language. Given the shortness of the introduction, every sentence should be essential to your reader's understanding of your essay.

- The first sentence or two should be your hook, designed to grab your reader's attention and get them interested in reading your essay.
- The next couple of sentences create a bridge between your hook and the overall topic of the rest of your essay.
- End your introduction with your thesis statement and a list of the points you will make in your essay to support or prove your thesis statement.
Expert Q&A

- If you are answering or responding to an assigned question, make sure you've interpreted the question correctly. The quality of your writing is irrelevant if your essay doesn't answer the question. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 1
- Have friends or family members read your essay and provide you with feedback. If you're writing for a class, you might want to exchange essays with another classmate and give each other feedback on your work. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 1
Tips from our Readers
- Reread your intro after writing each section to make sure both the intro and section are relevant to each other and to the paper.
- A sharp, descriptive title is sometimes just as important as an intro!

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/audience/
- ↑ http://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/planning/intros-and-conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction/
- ↑ https://www.esu.edu/writing-studio/guides/hook.cfm
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/cliches/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185917
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/introductions-conclusions
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/planning/intros-and-conclusions/
About This Article

Start your introduction with a relevant story, fact, or quote that will engage readers. Then, add 2-3 sentences of background information to give your essay context, and include important dates, locations, or historical moments where applicable. Finally, include your thesis statement, which is a specific, arguable, and provable statement that answers a question about your essay topic. For example, your thesis might read: "In the modern age, online dating apps like Tinder provide a wider variety of romantic options than young people have ever had before." For more tips and examples on how to craft your thesis and put your introduction together, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 11, 2016
Did this article help you?
Jul 11, 2020
Teighan Vickrey
Mar 18, 2018
Apr 27, 2017
Arturo Rueda
Mar 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write an Essay Introduction?
16 January, 2021
8 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
You have been assigned to write an essay but you’re not quite sure how to get started. Don’t worry, after reading this introduction, you will have a better grasp on what you should do. The introduction of an essay is the first thing that a reader will see, so it can influence how your entire essay is received. Be sure to take your time to make it effective. Before you start, you should first identify the purpose of your introduction.

Why do I Need an Introduction Paragraph?
You’re writing an introduction to your essay for two reasons. First, its purpose is to hook your readers so that they will read on and see what you have to say. Second, it will provide a guideline for your topic and main argument, known as the thesis statement. Your first sentences should pull the readers in – this is the hook that tells your readers something they didn’t know before. It can be an interesting fact, a surprising statistic, or a quote from a well-known person. Basically, it can be anything that has the ability to catch your readers’ attention. Choose the right hook based on your topic and style. Your readers need enough information to understand the background of your essay. Make sure, however, to keep it short, too, not to lose their interest. Your thesis statement, on the other hand, should provide an answer to the main problem of your essay.

How Long Should an Essay Introduction Be?
This depends on the overall length of your essay. There is no set rule for how long an introduction should be. For a 2- to a 3-page essay, the appropriate length is usually one paragraph. But in case the overall length of your essay is more, for example, 4−5 pages, two paragraphs is considered more appropriate. A general rule is that your introduction should be between 5 and 10 percent of the overall length of your essay.
How to Write a Good Essay Introduction?
Being able to write a good essay is an essential skill for your future. As many as 80 percents of corporations with employment growth potential assess their applicants’ writing skills during the hiring process.
To write a good introduction paragraph, you need to first identify your audience. You want your essay to evoke emotions and to keep your readers interested from start to finish. Before you can do that, you need to know who your readers are. If you’re writing an essay as a class assignment, you don’t necessarily have to write for your instructor. Choose your audience based on the subject matter of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about career paths, you may want to identify students and young professionals as your target audience. Your target audience determines what information you should include and what you can leave out.
To make the introduction of your essay effective, you can appeal to your readers’ emotions. This is a good strategy, especially when writing a persuasive essay introduction about a personal topic. It will help you get your audience emotionally involved in the topic. For example, if you’re writing an essay about foreign aid, you can describe the tragedy of undernourished children to evoke some emotions in your readers. Another strategy is to ask thought-provoking questions. This way, you will draw your readers in by making them think about your subject matter. As long as these questions are intriguing enough, your readers will want to find out the answers.

Move From the General to the Specific
Perhaps you have heard of the upside-down pyramid. Place your hook at the top, and use 2 to 3 sentences to describe the wider context of your thesis. You should try to make each sentence more specific than the one before it. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the crimes committed by refugees, you could start with an anecdote about a victim of these crimes. Then you could provide statistics about the problem in a specific country, and finally narrow it down to a particular age group or social group.
Make a Smooth Transition to the Body
In many cases, you can move straight from your introduction to the first paragraph of your body. Sometimes, however, you may need a transition sentence to move naturally to the rest of your essay. You can test whether you need this transition sentence by reading your introduction and the first paragraph of your body out loud. If you find yourself pausing between the two paragraphs, it’s better to write a transition sentence.
Pay Attention to Your Structure
Keep in mind that it’s not necessary to write the introduction first. In fact, it’s often easier to write it after writing the body and conclusion. On the other hand, others find it convenient to write the introduction first and use it as an outline for the rest of the essay.
While your introduction needs to be short, it should also convey a lot of information. The first sentence is your hook that catches your readers’ attention. The next sentences build a bridge between your hook and the general topic of your essay. The ending sentence of your introduction should include your thesis statement or points that you will discuss in more detail in the body and which support the main argument of your essay.
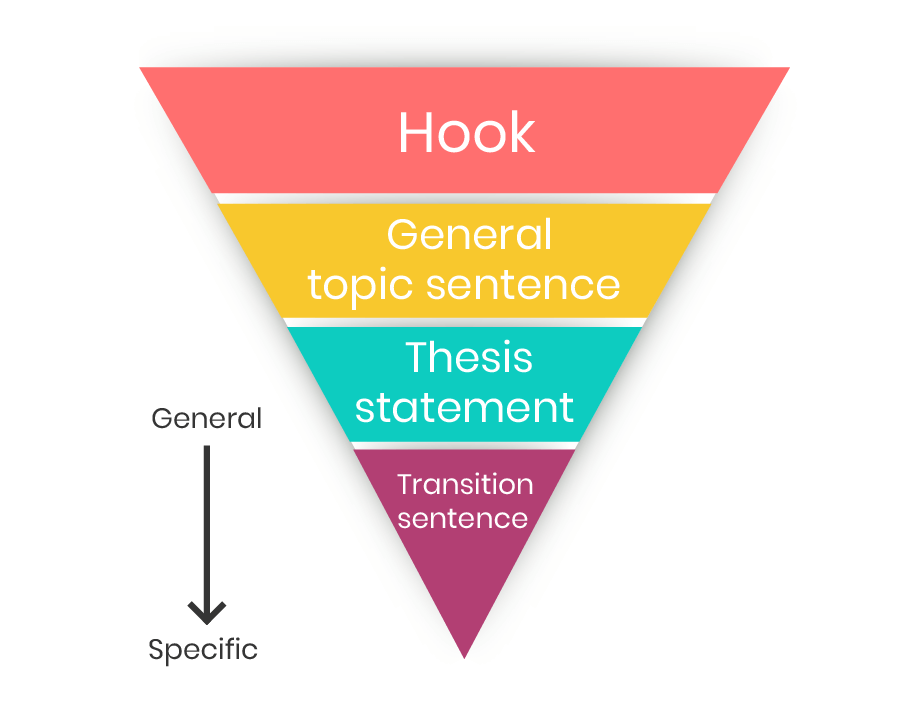
Remember to Revise
This is important for those who prefer to write their introduction first. Since it’s not uncommon to deviate from your outline, make sure that your introduction is in line with your completed essay. Make every sentence count and remove any unnecessary parts.
In case you’re struggling to find the time for your essay, you can always contact our essay writer . We have been in the business long enough to know the ins and outs of a perfect essay. Save your time and let us ease your burden.
Check Some Essay Introduction Examples
Now that you know the theory behind writing an effective essay introduction, it’s time to see things in practice. Samples are useful for learning how to put all the information into action. Check the samples below to figure out what your introduction should look like.
Argumentative Essay Introduction
In an argumentative essay introduction, you should present your own personal opinion on the topic based on your evaluation which you will present in the body.

You can also check this argumentative essay sample.
Persuasive Essay Introduction
Persuasive essay introduction also should attempt to convince readers to believe in an idea or opinion. It needs to showcase some personal attitude to the topic.

You can also check more in-depth instructions for writing a persuasive essay.
Compare and Contrast Essay Introduction
A compare and contrast essay introduction should describe two sides of a problem. It’s easier to consider two very different things. You can start with a brief description of the problem and then move on to talk about the two things.

You can also check topic ideas for your compare and contrast essay.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
How To Write An Essay
How To Start An Essay

Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Published on: Mar 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jul 23, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
Are you feeling overwhelmed at the prospect of writing an essay ? Are you struggling to come up with a clear focus, introduction, and structure for your work?
Don't worry—you are not alone! Writing can be challenging but there are ways to make it easier.
In this blog post, we will discuss proven strategies on how to start an essay that will help jumpstart your creativity and enhance your overall writing process.
From figuring out which topic is best for you to create a persuasive main argument, these tips are essential tools that any student can use to write powerful essays.
Let's get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
How To Start an Essay Introduction
The introduction of your essay is the first opportunity to capture your reader's attention and make a lasting impression. By following these five steps, you can create an introduction that stands out from the start.
1. Hook your reader
To engage your reader from the beginning, consider using an interesting story or anecdote that relates to your topic.
For instance, if you are writing an essay about the importance of environmental conservation, you could begin with a compelling story. The story can be about a community coming together to save a local endangered species.
This not only grabs the reader's attention but also provides a glimpse of what your essay will discuss and why it matters.
Check out these hook examples that you may use!
2. Provide background information
After hooking your reader, it's essential to provide some background information on the topic. This helps your readers understand the context and significance of your essay.
You can offer relevant facts, statistics, or historical context to set the stage for the discussion that follows.
3. Present your thesis statement
A well-crafted thesis statement is the backbone of your essay. It conveys the main point or argument you will make throughout the paper. Your thesis statement should be clear, concise, and impactful, providing a roadmap for the reader to follow.
4. Outline your essay's structure
To enhance the organization and coherence of your essay, it's helpful to create an outline of the main points you will be discussing. This not only assists you in structuring your thoughts but also helps the reader anticipate the flow and content of your essay.
Read our detailed guide to learning to create a perfect essay outline !
5. Check and revise
Once you have drafted your introduction, it is crucial to carefully review it for any grammar or spelling errors that may have been missed.
Take the time to refine your language, ensure clarity, and confirm that your introduction effectively sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
By following these steps, you can create an engaging and well-structured introduction that sets the tone for your essay and captivates your
How To Start an Essay Writing - 8 Best Ways
Writing an essay can be a daunting task, but here are the 8 best ways to start your essay that will help you create a strong introduction and body.
Introduce your topic
Start your essay by introducing your topic and giving the reader some context. Make sure to include relevant background information so that readers understand how the topic relates to their own lives.
For example, if you are writing about the effects of social media on modern society, you could introduce your topic with something like:
âSocial media has drastically transformed our lives over the past decade. From connecting us with friends and family to influencing political views, it is undeniable that social media has had an immense effect on our day-to-day lives.â |
Start Your Essay With a Quote
Begin your essay with a thought-provoking quote that relates to the topic of your essay. This will engage the reader and give them an idea of what to expect in your essay.
For example, if you are writing about the importance of education, you could start with a quote such as:
| âEducation is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.â ? Nelson Mandela |
Set Up a Mystery
Start your essay with a mysterious scenario that will draw the reader in. You can create a sense of intrigue by leaving out important details so that readers are curious to learn more.
For example, if you are writing about the effects of climate change, you could start with something like:
| âThe sun rose slowly over the horizon, casting a mysterious orange glow across the sky. It was hard to ignore the feeling that something ominous was about to happen.â |
Use Rhetorical Questions
Start your essay with a rhetorical question that will leave readers thinking and wondering what will come next.
This can be an effective way to draw readers in and make them want to find out more.
For example, if you are writing about the importance of standing up for your beliefs, you could start with a rhetorical question such as:
| âWhat would you do if someone told you that you couldnât believe in something? Would you stay quiet, or would you stand up for what you believe in?â |

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Provoke Emotion
Start your essay with a vivid description that will evoke emotions in the reader. This is an effective way to grab their attention and set the tone for your essay.
For example, if you are writing about the effects of poverty, you could start with something like:
| âThe streets were filled with an eerie silence as I walked by rows of dilapidated buildings. Everywhere I looked, I saw people struggling to make a better life for themselves.â |
Use An Anecdote
Start your essay with an anecdotal story that will give readers a glimpse into the topic.
This can be an effective way to capture their attention and make them more interested in learning more about your topic.
Check out this video to learn more about using anecdotes in your essays!
For example, if you are writing about the impact of technology on our lives, you could start with something like:
| âI remember when I was first introduced to computers. I was amazed at how quickly they could do calculations and complex tasks. Little did I know, this technology would shape my life in so many ways over the years.â |
Stamp Of Authority
Start your essay with a statement of authority that will give readers a sense of legitimacy.
This can be an effective way to establish yourself as an expert on the topic and make readers trust you more.
For example, if you are writing about the history of human rights, you could start with something like:
| âSince the dawn of civilization, the struggle for human rights has been a defining aspect of our species. From ancient societies to modern democracies, this fight has shaped the world as we know it today.â |
Start Your Essay With A âContrary Toâ Or âFill The Gapâ Sentence
Start your essay with a sentence that introduces an idea contrary to popular opinion, or one that âfills the gapâ between two competing theories.
This can be an effective way to make readers think more deeply about the topic and challenge their preconceived notions.
For example, if you are writing about the importance of diversity, you could start with something like:
| âContrary to popular belief, diversity isnât just about superficial differences. Itâs also about embracing different perspectives and ideas which can lead to greater understanding and progress.â |
Interesting Essay Starting Examples for Students
These examples of how to open your essay are designed to help students craft interesting and attention-grabbing introductions.
With a few tweaks, these ideas can be adapted to any type of essay topic or style.
Use them as inspiration when writing your own introduction and youâll be sure to capture readersâ interest right away.
how to start an essay about yourself
how to start an essay sample
how to start an essay about yourself examples
how to start an essay about a person
In conclusion, crafting an effective essay introduction is essential for grabbing your reader's attention and setting the tone for your essay.
We are sure that with the tips outlined, you can create a bold and compelling opening that will leave a lasting impression. Also, you can take help from an AI writing tool to get ideas.
And if you're still struggling, don't hesitate to seek professional help from our top essay writing service .
With our expert assistance, you can be sure that your essay introduction will be the best it can possibly be. Whether you are writing a college essay, an expository essay, or an argumentative essay, we can help you always!
So what are you waiting for? Order now and make your essay stand out from the crowd!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction.
A good introduction should include a few key components:
- Identifying the topic
- Providing context
- Thesis statement
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Anne R. Allen's Blog... with Ruth Harris
Writing about writing. Mostly.
April 28, 2018 By Anne R. Allen 53 Comments
How to Write a Great First Sentence—with 22 Inspiring Examples

First sentences from classic and contemporary literature analyzed.
by Ruth Harris
No matter what genre you write, your first sentence is a seduction. It can be in the form of an invitation. A declaration. A tease. A promise. A jolt. A shock.
You must be shameless and your first sentence must be irresistible. It must induce curiosity and promise the answer to an urgent question.
You must do whatever you can to lure your reader into the web you’ve woven by writing a sentence so provocative and so powerful that s/he is compelled to continue.
You’re the master of ceremonies and in your first sentence you must present yourself and your book with confidence and authority. If you’ve written a thriller, your first sentence must promise thrills. If you’ve written a romance, your first sentence must promise romance.
Just like a nothingburger cover or a meh blurb, a clunky or poorly-conceived first sentence that’s inconsistent with your genre, will turn readers off and cause them to skip your book.
Whether you’re writing fiction or non-fiction, romance or sci fi, a thriller or a mystery, the first sentence of your book must achieve one goal: compel the reader to read on.
Stephen King has said that he spends “months and years” creating that first line. He goes on to say: “An opening line should invite the reader to begin the story. It should say: Listen. Come in here. You want to know about this.”
The question is, how do we accomplish all this in one sentence? From Moby Dick ’s “ Call me Ishmael” to Charles Dickens’ “ It was the best of times, it was the worst of times ,” some first sentences have become famous classics. So, too, Jane Austen’s “ It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune must be in want of a wife.”
A deeper look into the breadth of masterful first sentences offers a wide array of the ways writers draw readers into their stories and inspiring examples of how much information can be conveyed in a single sentence.
The First Person Introduction.
In a memoir or a novel written in the first person, the author puts himself in the mind of the central character and, in one way or another, tells us that we are about to get the real deal. No BS here, the sentence promises, just the honest, unvarnished truth about someone we want to know more about.
Sylvia Plath uses the first sentence of The Bell Jar , to establish the nervous, dark mood that hovers over the character and the story. Her story begins—
“It was a queer, sultry summer, the summer they electrocuted the Rosenbergs, and I didn’t know what I was doing in New York.”
Plath’s use of the word electrocuted provides an unexpected jolt and mention of the Rosenbergs sets a time (June 1953). Sultry summer sets an uncomfortable season, New York establishes a place, and the final phrase conveys the uncertainty of a young woman struggling to find an identity and a place in life.
Vladimir Nabokov uses the first nine words of Lolita to convey the note of obsessive erotic desire that pulses through the entire novel.
“Lolita, light of my life, fire of my loins.”
Nabokov begins by naming the object of his passion, the word light expresses her transformative influence on the narrator, the word loins promises that we will be reading a story about sex, and the repetition of the letter l creates the feeling of an incantation.
In Ghostwriters In The Sky , Book 1 of The Camilla Randall Mysteries, Anne uses her first sentence to introduce the MC, locate the place (the subway can only mean NYC), and refer to the season (sweaty indicates hot, most likely summer).
“The subway car was so crowded I couldn’t tell which one of the sweaty men pressing against me was attached to the hand now creeping up my thigh.”
The phrase “creeping up my thigh” indicates a level of unwanted personal attention which places the character in an uncomfortable, if rather ludicrous situation—a theme that will be repeated in different variations throughout the novel.
In Catcher In the Rye , J.D. Salinger uses an effective but contradictory combination of bravado and vulnerability to establish a unique voice as he introduces us to preppy Holden Caulfield.
“If you really want to hear about it, the first thing you’ll probably want to know is where I was born, and what my lousy childhood was like, and how my parents were occupied and all before they had me, and all that David Copperfield kind of crap, but I don’t feel like going into it, if you want to know the truth.
We read on because Salinger’s confessional tone makes us want to know more about his lousy childhood and find out why he doesn’t feel like going into it.
The Third Person Introduction.
In Goldfinger , Ian Fleming introduces 007 in the first sentence.
“James Bond, with two double bourbons inside him, sat in the final departure lounge of Miami airport and thought about life and death.”
Fleming has told us in only a few words that his MC is a drinking man, one who travels, and one who contemplates the larger questions of existence. Where, we wonder, is Bond going, what is he going to do once he gets there, and why does he need to down two double bourbons before he boards his flight?
In The Hobbit , JRR Tolkien simply tells us where his MC lives, but in such a startling way that we feel compelled to read on.
“In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit.”
A hobbit? A story about a creature who lives in a hole? Who or what is this hobbit and why does he live in a hole. Curious, we read on.
I introduce DeeDee Dahlen, the MC in Love And Money , Book 1 of the Park Avenue Series with a brief, declarative sentence.
“Her name was DeeDee Dahlen and she was famous from the day she was born.”
How can a newly-born infant be famous?, the reader wonders. What rewards—and penalties—does unasked-for celebrity impose? What secrets and scandal will shadow her future?—urgent questions that will reverberate throughout the entire novel.
Graham Greene, in Brighton Rock , compels us to want to know more.
“Hale knew, before he had been in Brighton three hours, that they meant to murder him.”
Who are the ‘they?’ we wonder. And what has Hale done? Why do ‘they’ want to kill him?
Gabriel Garcia Marquez begins One Hundred Years of Solitude with this famous sentence—
“Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendia was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.”
The author uses a shocking situation—a man facing a firing squad—plus a long-ago memory to pique our curiosity. Who is the Colonel and what had he done that he ends up facing a firing squad? What was there about the discovery of ice that it has lodged so forcefully in his memory? Compelling questions to which we must find the answer and, thus, we continue to read.
Whether classic literature, hard-boiled pulp fiction, or cyberpunk scifi, the first sentence establishes a theme that will continue throughout the story. If the book does not follow through on the promise of that first sentence, the disappointed reader will feel cheated.
In his first sentence, Leo Tolstoy in Anna Karenina tells us that we are about to read a story about an unhappy family.
“All happy families are alike; each unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”
Why, we ask ourselves, are they unhappy? What has happened to them and what will they do? Powerful questions the reader wants answered.
James Matthew Barrie establishes the theme of Peter Pan with a brief, declarative statement.
“All children, except one, grow up.”
Which child, we wonder. Why not? And what will happen to a child who doesn’t grow up?
A far different theme is set by Franz Kafka in his posthumously published 1925 novel, The Trial.
Someone must have slandered Josef K., for one morning, without having done anything truly wrong, he was arrested.
Kafka’s first sentence thrusts us immediately into the MC’s waking nightmare of terror and paranoia that will be sustained throughout the story.
William Gibson’s Neuromancer was the first novel to win the Nebula Award, the Philip K. Dick Award, and the Hugo Award. The chilling first sentence, said to have been written at the last minute, sets the novel’s theme of a burnt-out computer hacker adrift in a dystopian near future governed by artificial intelligence.
“The sky above the port was the color of television, tuned to a dead channel.”
Hunter S Thompson, starts his novel, Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas , by establishing a place, a mood, and a theme (a disenchanted retrospective look at the 1960s) in the first sentence.
“We were somewhere around Barstow on the edge of the desert when the drugs began to take hold.”
A Tease, a Shock, a Jolt.
A skillfully written first sentence containing a tease, a shock or a jolt can introduce a character, establish a tone or a setting, and dare the reader not to continue.
The first sentence of Nineteen Eighty-Four, George Orwell’s dystopian novel, often considered one of the best one hundred books of the 20 th Century, tells us immediately that something—time itself—is awry in a future world of Big Brother, doublethink and government surveillance.
“It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.”
Joe Konrath pulls us right into the action in the first sentence of his mystery thriller, Dirty Martini , Book 4 of the Jacqueline “Jack” Daniels Mystery series.
“No security cameras this time, but he still has to be careful.”
What is he doing, we wonder? In his first sentence, Konrath lets us know that whatever it is, it’s something he’s done before. Something risky, perhaps dangerous, and, even though experienced, he still has to be careful. Of what? Of whom?
In his legal thriller, The Firm , John Grisham uses his first sentence to tell us that this unnamed and mysterious senior partner will indeed find something to dislike about Mitchell Y. McDeere who, the word résumé indicates, is being considered for a job.
“The senior partner studied the résumé for the hundredth time and again found nothing he disliked about Mitchell Y. McDeere, at least not on paper.”
What kind of job, we wonder, and what will the senior partner find to dislike? Grisham’s tease promises evil doings and the reader is lured on.
In L.A. Confidential, James Ellroy’s first sentence introduces a main character, sets a theme, and tells us exactly what we are about to read. Ellroy uses a knowledgable tone and vernacular language to let us know that he knows what he’s talking about.
“An abandoned auto court in the San Berdoo foothills; Buzz Meeks checked in with ninety-four thousand dollars, eighteen pounds of high-grade heroin, a 10-gauge pump, a .38 special, a .45 automatic, and a switchblade he’d bought off a pachuco at the border—right before he spotted the car parked across the line: Mickey Cohen goons in an LAPD unmarked, Tijuana cops standing by to bootsack his goodies, dump his body in the San Ysidro River.”
Dennis Lehane, in his short story, Until Gwen pulls us in with the use of the second person combined with the promise of drugs and sex.
“Your father picks you up from prison in a stolen Dodge Neon, with an 8-ball of coke in the glove compartment and a hooker named Mandy in the back seat.”
The Rule Breakers.
Although writers are often cautioned about starting a book with a character’s dream, that rule was effectively broken in the classic first sentence of Daphne DuMaurier’s famous gothic mystery, Rebecca .
“Last night I dreamt I went to Manderley again.”
Marie Force begins her Gansett Island romance, Meant For Love , with a reference to a dream.
“The dream was always the same, the last perfect moment before life as Jenny Wilks knew it changed forever.”
Both dreams refer to emotionally significant aspects of the characters’ pasts. The reader wonders why the unidentified first-person narrator of Rebecca dreams of a place and Jenny Wilks of a “perfect” life now gone forever. The authors use dreams to provoke interest in their characters and in the events of the story to come.
The passive tense is usually considered to be another no-no. Charles McCarry, in TheTears Of Autumn, considered to be one of the best espionage thrillers of the 20 th Century, uses the passive tense to introduce American intelligence officer, Paul Christopher, who is investigating the assassination of John F. Kennedy.
“Paul Christopher had been loved by two women who could not understand why he had stopped writing poetry.”
McCarry’s elegant use of the passive tense to introduce his MC sets the theme of the book: an exploration of glittering promise that results in the wreckage of unintended consequences—the end of poetry and the end of Camelot.
Your first sentence is your opportunity to let your creativity shine. Whether you decide to go for a tease or a jolt, a theme or a rule breaker, a first person or third person introduction, remember what Mom always said: You never have a second chance to make a first impression.
For more info on beginnings, Anne and I have both opined about first chapters. For Anne’s take . For Ruth’s take .
by Ruth Harris (@RuthHarrisBooks) April 29, 2018
What about you, scriveners? Do you have a favorite first line? Do you find your first line hard to write? (I usually write mine last.) Do you have a dynamite first line for a book you haven’t written yet?
This week Anne is Poisoning People for Fun and Profit again. This time she’s talking about Gelsemium , a pretty plant that may be growing in your own backyard. And is so deadly it’s the drug of choice of many professional assassins. It also nearly killed Arthur Conan Doyle.
BOOK OF THE WEEK

OPPORTUNITY ALERTS
Central Coasters: Don’t miss the “Writers in Action: From Idea to Publication” Workshop on May 19th! 1-day workshop by Sisters in Crime, Central Coast at the PG&E Energy Center in San Luis Obispo. Should be a lot of fun. Here’s a link to the application form and lunch menu.
Red Hen Press annual Nonfiction Contest. $25 entry FEE. $1,000 prize and publication by the prestigious Red Hen Press. They’re looking for an essay collection, memoir, or book of narrative nonfiction. Florencia Ramirez will judge. Using the online submission system, submit a manuscript of at least 150 pages. Deadline April 30
CRAFT Literary Short Story contest. $20 FEE . Short fiction up to 6000 words. $2000 first prize; the two runners-up will receive $500 and $300, respectively. plus publication in CRAFT Literary Magazine. Deadline April 30th.
Mad Scientist Journal: Battling in All Her Finery. Genre : Speculative fiction stories about women leaders in any field. Payment : 2 cents/word. Deadline: April 30, 2018.
13 Imprints of Big 5 publishers who take unagented submissions. From the good people at Authors Publish Magazine.
Supernatural Fiction Award : $1000 prize + publication in The Ghost Story magazine. Not just ghost stories. Any paranormal story welcome. 1500-10,000 words $20 entry fee. Deadline April 30 th .
Prophecy Creek Book Award for Speculative Fiction . Prize $1,000 and publication by Hidden River Publishing. Any length novel that includes elements of science fiction, supernatural fiction, or fantasy. $22 fee. Deadline May 15.
Smokelong Quarterly Flash Fiction contest. $13 Fee. Under 1000 words. Nominates for Pushcart. Must never have been published (including on blogs.) $1500 prize plus publication. Runner-up prizes, too. Deadline May 20th.
Nowhere Spring Travel Writing Contest $10 Fee. 800-5000 words showing a powerful sense of place: Fiction or nonfiction. Previous publication okay. $1000 prize plus publication in Nowhere magazine. Deadline May 31st
Share this:
Blog archives, search anne & ruth’s blog.
About Anne R. Allen
Anne writes funny mysteries and how-to-books for writers. She also writes poetry and short stories on occasion. Oh, yes, and she blogs. She's a contributor to Writer's Digest and the Novel and Short Story Writer's Market.
Her bestselling Camilla Randall Mystery RomCom Series features perennially down-on-her-luck former socialite Camilla Randall—who is a magnet for murder, mayhem and Mr. Wrong, but always solves the mystery in her quirky, but oh-so-polite way.
Anne lives on the Central Coast of California, near San Luis Obispo, the town Oprah called "The Happiest City in America."
April 29, 2018 at 10:27 am
I didn’t fully appreciate the importance of the first line until after my first book. I am proud of the first lines of the next three books, especially the two that say so much about the character. Those are excellent examples and a good breakdown as to why they work. Knowing that is half the struggle.
April 29, 2018 at 12:54 pm
Alex—Thanks! Congratulations on your quality first lines….knowing what and where the target is makes it so much easier to score!
April 29, 2018 at 11:10 am
Couldn’t agree more Ruth, and it’s one of my favorite topics to cover with aspiring authors on the library-circuit. It’s one of those things a newish writer hasn’t truly considered, but they light up when you show examples like these gems (we overlap with several!). I would suggest there’s also the out-and-out lunatic opening to consider, like Ian Banks who set the bar pretty high with his opening to “The Crow Road” (1992):
“It was the day my grandmother exploded.”
Tell me who’s going to put that one back on the rack!
April 29, 2018 at 12:56 pm
Will—Love the Ian Banks first line. Thanks for the great addition!
April 29, 2018 at 11:28 am
Excellent! I particularly like the constellation of 1st person examples: Plath, Nabokov, Salinger, & Allen! Well-chosen, indeed. And, as I am big-idea person more than an analytical person, I love seeing these split into categories — I simply wouldn’t think to do that to these fine examples, but it helps me conceptualize it all. Thanks again.
April 29, 2018 at 12:59 pm
CS—Thanks and happy to hear my category breakdown helped. There are infinite ways to write a great first sentence!
April 29, 2018 at 1:39 pm
I love the topic you chose for today, Ruth, and the way you take a close, illuminating look at each one. Thanks so much for the insight.
I think you had one or two short story first lines in the mix, and I’m glad for that.(I write short stories.) I think an awesome first line is every bit as important in short stories. (Last line too.)
Tolstoy’s Anna Kerenina first line is also an example of what I think has the potential to be powerful: A truism, or a simple philosophical (sort of) statement. He certainly nails it with this one!
An article on great last lines would be a fascinating complement to this one.
April 29, 2018 at 4:32 pm
Tricia—thanks! Yes, the Dennis Lehane first sentence was from a short story. First sentences matter!
April 29, 2018 at 2:35 pm
My favourite opening line is from J.G. Ballard’s ‘High-Rise’:
“Later, as he sat on his balcony eating the dog, Dr Robert Laing reflected on the unusual events that had taken place within this huge apartment building during the previous three months.”
It sets tone, character, place…and the opportunity to decline an invitation to proceed.
April 29, 2018 at 4:34 pm
Patricia—that’s just great! Thanks!
April 29, 2018 at 3:44 pm
I used my favorite first line in an email signature that earned me a visit from the President of the college; he never made me take it down, but I knew somebody had asked about it nonetheless. From James Crumley’s Last Good Kiss: “When I finally caught up with Abraham Trahearne, he was drinking beer with an alcoholic bulldog named Fireball Roberts in a ramshackle joint just outside of Sonoma, California, drinking the heart right out of a fine spring afternoon.” I can smell that wasted, lost afternoon, I know the likes of Abraham Trahearne right up front, and one day I’m going to name my new bulldog Fireball Roberts.
April 29, 2018 at 4:38 pm
Ruthie—thanks for another fabulous first line! Wonder if anyone would name a kitten Fireball Roberts? Nah, don’t think so. 😉
April 29, 2018 at 4:35 pm
Sorry to be picky, but there are two typos in this article…which, by the way, is great. This a wonderful collection of first lines, some of which I’ve never seen before. ‘auto court’, I think, rather than ‘auto cout’ – although maybe this is a type of area I’ve not come across before! And Mr Grisham gets spelt as Grosham at one point….
April 29, 2018 at 4:47 pm
Mcrow—Thanks for your eagle eye! I wondered about “cout” but that’s how it came up in my research so I decided to go with it. Maybe a regionalism? Grissom is just a plain vanilla typo. (As I type this, tho, autocorrect turns it into Grissom.) lol
April 30, 2018 at 8:53 am
This is such a great post. I love to look at the first line of a book. It really does either pull you in … or not. I really liked ““All children, except one, grow up.” I’ve never read the book. Maybe now I will. I always try to write a first line or at least the first few lines in a way that the reader will wonder what’s going to happen next and what’s going on. Thanks for this.
April 30, 2018 at 11:24 am
Patricia—thanks for the kind words. First lines are well worth the effort.:)
April 30, 2018 at 10:01 am
First lines are tough and hard to make appealing to a large group of people–even within our own genres.
One I like is: This is the way the world ends – not with a band or a whimper, but with zombies breaking down the back door. – Hollowland by Amanda Hocking
I love the call back to Eliot with a fantasy twist.
April 30, 2018 at 11:27 am
HR—thanks for another good example and fine analysis!
April 30, 2018 at 5:48 pm
Thanks so much for this insightful look into first lines, Ruth. A good reminder to go over some of my old favs and revisit first lines in particular. 🙂
May 1, 2018 at 6:11 am
Dg—appreciate your kind words. Have fun with your old faves!
April 30, 2018 at 6:41 pm
Thanks for this article! I was inspired to re-check out some first lines. I’m pretty happy with the first lines of my two fantasy novels…the second one took a long time. The whole first chapter and especially the first paragraph went through a dozen false starts before I managed to like one I tried. But the first line of Stephen King’s “The Gunslinger” is wonderful–and it must be, as it begins not only a novel, but an epic seven-book series. The line: “The man in black fled across the desert, and the gunslinger followed.”
May 1, 2018 at 6:15 am
Fred—*only* a dozen tries? Wow! Speedy. ;-). Thanks for the excellent Stephen King addition. Much appreciated!
May 6, 2018 at 4:32 pm
Not really speedy. I had it published about twenty-two years after I finished the first draft. I’m finishing a paranormal romance and beginning a fantasy series. Thanks to your article I re-examined, and changed, the first sentence of each one. And of course I may do so again before I’m finished. My thanks to you and Anne both for all these great helpful blogs.
May 1, 2018 at 6:47 am
Wow, those are some great first lines. I’ve always found first lines hard to write and this post has really motivated me to make sure the promise I’m making to my audience is there inside it.
One of my favorite first lines is from the manga Fullmetal Alchemist (English Translation):
“Teachings that do not speak of pain have no meaning…for humankind cannot gain anything without first giving something in return.”
May 1, 2018 at 7:25 am
Amy—happy to hear the post helped. 🙂 thanks,too, for the excellent addition to our first lines!
May 1, 2018 at 7:30 am
I often write my first lines after the first draft. Rather, I should say, I “rewrite” my first line a gazillion times after the first draft. Great post, Ruth. Thanks for the inspiration!
May 1, 2018 at 11:06 am
Sue—yes! It’s not the writing. It’s the rewriting. + the revisions. Facts of life! 😉
May 1, 2018 at 10:17 pm
I love, love, love first sentences. I’ve written hundreds of them! If only I had completed stories to go with all with my first lines….heavy sigh. Enjoyed the post.
May 2, 2018 at 4:13 am
Tammy—ditto and thanks. Maybe find the love for second sentences? 😉
May 6, 2018 at 8:26 am
A great article, Anne.
May 6, 2018 at 12:20 pm
Robbie–The thanks go entirely to Ruth. Not only did she write the piece. but she chose the image this time too. I thought it was perfect!
May 6, 2018 at 4:52 pm
Robbie—glad to learn you enjoyed the post!
May 6, 2018 at 10:31 am
3 greatest are from Moby Dick, Old Man and Sea and Tale of 2 Cities. Oh, and that “In the beginning…” one is pretty famous too.
May 6, 2018 at 1:10 pm
Carl—thanks for the suggestions. We should also add “once upon a time.” 🙂
May 7, 2018 at 3:55 am
Yes, of course !
May 6, 2018 at 4:50 pm
Fredwaiss—22 years? Definitely not speedy! I stand corrected. 🙂 Pleased to learn the post encouraged you to go back and review your first lines. Anne and I work with the goal of helping writers avoid the mistakes we made!
May 8, 2018 at 12:23 pm
Great post, thanks! It was a dark and stormy night…?????
May 8, 2018 at 12:52 pm
M. L.—Perfecto! A truly worthy addition! 🙂
May 8, 2018 at 1:08 pm
Great article Ruth! I have a harder time with LAST lines but reading this reminded me of an unread book I peeked at while unpacking last week that made me want to sit in the pile boxes to keep reading:
“Even before I push the fucking door open I know.” First line of IN SIGHT OF THE STARS by Gae Polisner.
I’m a little envious of that opening…
May 8, 2018 at 2:06 pm
Eldonna—Thanks. 🙂 Thanks, too, for adding another great first sentence!
May 10, 2018 at 3:17 pm
What a fun post – and great comments with more first lines – love it! Thanks for this.
My favorite for description is from IN COLD BLOOD by Truman Capote because of the contrast with the title:
“The village of Holcomb stands on the high wheat plains of western Kansas, a lonesome area that other Kansans call ‘out there.’ ”
and my favorite for ‘you had me at the first line’ (technically, 3 sentences, they could have been separated by commas… but it would change the rhythm) still, it got me and I read this one, then pretty much all his other books in a 2-month binge. It’s in STRAIGHT by Dick Francis:
“I inherited my brother’s life. Inherited his desk, his business, his gadgets, his enemies, his horses and his mistress. I inherited my brother’s life, and it nearly killed me.”
May 10, 2018 at 5:58 pm
Msmartha—Thanks for the kind words—and for two great suggestions! I recall a lengthy dick Francis binge, too. 🙂
June 3, 2018 at 3:09 pm
I don’t have a favorite first line, sorry! I opened an email from you and saw this as title as one of your previous posts and was intrigued. Fantastic post! I’m starting my new WIP today and you’ve inspired me to nail down that first line of my WIP. Thanks!
June 3, 2018 at 4:16 pm
Fiona—Ruth Harris here. Glad you enjoyed the post! Even happier to learn it was inspiring. Good luck with your great first sentence!
October 7, 2018 at 3:21 pm
“If there were a way, if I could, I would write this book in sign language.” Ruth Sidranski’s first line in her memoir entitled In Silence.
October 7, 2018 at 4:48 pm
Katherine—excellent! Thank you.
October 28, 2019 at 8:58 am
I read and try to write romance. This is my favorite opening line from a romance novel, The Best Man by Kristan Higgins:
“On a beautiful day in June, in front of literally half the town, wearing a wedding dress that made her look like Cinderella and holding a bouquet of perfect pink roses, Faith Elizabeth Holland was left at the altar.”
It was my first book by Kristan Higgins, but I can assure you it wasn’t my last!
October 28, 2019 at 10:24 am
Dena Jo—Wonderful! Thanks for a great addition to the list of compelling first lines. Appreciated! 🙂
November 21, 2019 at 6:54 am
First lines–yes! I waffled when I started to write my first book. (A fantasy novel based on a D&D scenario I wrote.) I decided to self-publish it after an agent who had taken me on tried to get me to publish with a publisher who asked for a lot of money. At least it was a lot to me. I was proud of that book, but it took far too long to get to the story proper. I wrote part 2 of the series and published it. Then I found a publisher for my next book, who wanted to take on my previously published books, so I took the opportunity of rewriting the beginning. I cut at least the first 4 chapters and began where the protagonist and his friends were given their quest. A much better beginning,I think.
November 21, 2019 at 1:34 pm
V.M.—Thanks for the great comment! Sounds like you’re on the right track by cutting your early chapters and starting with the quest. And yes, indeed, sometimes getting a book right does take “too long.” Frustrating but worth it!
June 19, 2020 at 5:30 am
so I wrote a first paragraph and I was hoping that someone might help me with critiquing it “You know that every time I peek my head through this window and see the tower, my heart fills with uneasiness, how it pokes into the sky here in Paris and is quite the centerpiece in the culture. Of course, I was talking about the Eiffel tower, the looming feeling I get measures to about the amount you get when you see the corpse of a person next to a puddle of blood with a 15mm Occitane Pistol floating along slowly to a sewer pipe. When you know whatever caused it can just peek out and get you too, slide its fingers along the side of the trigger, and in seconds your years of life have come to an end. ” by the way, Occitane is a region in France, in the book I am writing it also holds a secret underground gun producing factory.
June 19, 2020 at 6:26 am
Noah—Thanks for taking the time to comment. Anne and I do not offer critique services, but wish you the best of luck with your book.
August 15, 2021 at 4:10 pm
Here’s the first sentence of my second novel, plus the short one that follows:
“Who was that,” Greg asked as he and Josie drove home from the folk dance, “the fiddler, singing, at the end? You know him?” Jealousy tainted his question.
It seems to set up the emotional tension that permeates the book.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Anne r allen’s blog with ruth harris.
- Blog Vacation Time! This Blog is Taking a Hiatus. July 14, 2024 Anne R. Allen
- Books by Anne R. Allen
- Books by Ruth Harris
- Shirley S. Allen
- Guest Bloggers
- HOW TO GET YOUR BOOK PUBLISHED

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Good sentence starters to establish cause and effect. It's common to use two different sentences to discuss a cause-and-effect relationship, as in something making something else happen. Sentence starters can make this relationship clear and show which sentence is the cause and which is the effect. As a result . . .
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
For many, getting started is the hardest part of anything. And that's understandable. First, because it turns whatever you're doing into a reality, which raises the stakes. Second, because where you start can easily dictate the quality of where you end up. College essays have their own special brand of DTDT.
If you know where your essay is going, but not necessarily how it will get there, write your conclusion first. Then, write the paragraph that comes right before your conclusion. Next, write the paragraph before that, working your way backwards until you're in your introduction paragraph. By then, writing an effective essay introduction should ...
Step 4: Preview the Main Points. Don't go into too much detail here: just quickly—in a few words—list your reasons that support your thesis. For example, "Hamlet is a tragic hero according to Aristotle's definition, because he is good (virtuous), realistic (flawed), and experiences a fall.".
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
Begin with a great first sentence. The introductory paragraph of any paper, long or short, should start with a sentence that piques the interest of your readers . In a well-constructed first paragraph, that first sentence leads into three or four sentences that provide details about the subject you address in the body of your essay.
The Bottom Line: How to Start a College Essay. The college essay introduction should hook your reader and make her want to know more and read more. Good personal statement introductions will contain the following features: A killer first line. A detailed description of an experience from your life.
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph. In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement. Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay. Below, we'll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an ...
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences. Map Your Essay. Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your reader a sense of direction. Here's an example of an essay introduction:
One straightforward way to begin is to get right to the point. But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...". "It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving."
You can do this by establishing the current state of the field, or by presenting an assumption in the field which you will either support or argue against. You should feel free to "jump right in" to your paper in your first sentence. You can also enter into your paper more subtly, either by using a relevant and artistic first sentence (as ...
Admission Essays by Writing the Essay: The First Sentence. For an introduction to writing the first sentence of an essay, see "The First Sentence" under Academic Essays. For an introduction to the different kinds of paths your essay might follow, see "Take Your Reader on a Trip" on the same page. The first draft of your first sentence should be ...
Starting your essay with dialogue instantly transports the reader into the story, while also introducing your personal voice. In the rest of the essay, the author proposes a class that introduces people to insects as a type of food. ... The descriptive imagery in the first sentence also helps to immerse the reader, creating a satisfying hook ...
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
How to start a body paragraph. Often the hardest sentence to write, the first sentence of your body paragraph should act as the topic sentence, introducing the main point of the entire paragraph. Also known as the "paragraph leader," the topic sentence opens the discussion with an underlying claim (or sometimes a question).
Make a brief outline of the essay based on the information presented in the introduction. Then look at that outline as you read the essay to see how the essay follows it to prove the writer's thesis statement. 2. Keep your introduction short and simple.
Place your hook at the top, and use 2 to 3 sentences to describe the wider context of your thesis. You should try to make each sentence more specific than the one before it. For example, if you're writing an essay about the crimes committed by refugees, you could start with an anecdote about a victim of these crimes.
By following these five steps, you can create an introduction that stands out from the start. 1. Hook your reader. To engage your reader from the beginning, consider using an interesting story or anecdote that relates to your topic. For instance, if you are writing an essay about the importance of environmental conservation, you could begin ...
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay. General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body. The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
It can be in the form of an invitation. A declaration. A tease. A promise. A jolt. A shock. You must be shameless and your first sentence must be irresistible. It must induce curiosity and promise the answer to an urgent question. You must do whatever you can to lure your reader into the web you've woven by writing a sentence so provocative ...