

How to Write a Nursing Case Study Paper (A Guide)

Most nursing students dread writing a nursing case study analysis paper, yet it is a mandatory assignment; call it a rite of passage in nursing school. This is because it is a somewhat tricky process that is often overwhelming for nursing students. Nevertheless, by reading this guide prepared by our best nursing students, you should be able to easily and quickly write a nursing case study that can get you an excellent grade.
How different is this guide from similar guides all over the internet? Very different!
This guide provides all the pieces of information that one would need to write an A-grade nursing case study. These include the format for a nursing case study, a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing case study, and all the important tips to follow when writing a nursing case study.
This comprehensive guide was developed by the top nursing essay writers at NurseMyGrade, so you can trust that the information herein is a gem that will catapult your grades to the next level. Expect updates as we unravel further information about writing a nursing case study.
Now that you know you've discovered a gold mine , let's get right into it.
What Is a Nursing Case Study?
A nursing case study is a natural or imagined patient scenario designed to test the knowledge and skills of student nurses. Nursing case study assignments usually focus on testing knowledge and skills in areas of nursing study related to daily nursing practice.
As a nursing student, you must expect a nursing case study assignment at some point in your academic life. The fact that you are reading this post means that point is now.
While there is no standard structure for writing a nursing case study assignment, some things or elements must be present in your nursing assignment for your professor to consider it complete.
In the next section, you will discover what your instructor n expects in your nursing case study analysis. Remember, these are assignments where you are given a case study and are expected to write a case analysis report explaining how to handle such scenarios in real-life settings.
The Nursing Case Study Template
The typical nursing case study has nine sections. These are:
- Introduction
- Case presentation (Patient info, history, and medical condition)
- Diagnosis/Nursing assessment
- Intervention/Nursing care plan
- Discussion and recommendations
The Structure of a Nursing Case Study Analysis
You now know what nursing professors expect in a nursing case study analysis. In this section, we will explain what to include in each section of your nursing case study analysis to make it an excellent one.
1. Title page
The title page is essential in all types of academic writing. You must include it in your nursing case study analysis or any other essay or paper. And you must include it in the format recommended by your college.
If your college has no specific title page format, use the title page format of the style requested in the assignment prompt. In nursing college, virtually all assignments should be written in Harvard or APA format .
So, check your assignment prompt and create your title page correctly. The typical title page should include the topic of your paper, your name, the name of your professor, the course name, the date you are submitting the paper, and the name of your college.
2. Abstract
Most nursing professors require you to include an abstract in your nursing case study analysis. And even when you are not explicitly required to write one, it is good to do so. Of course, you should consult with your professor before doing so.
When writing an abstract for your paper, make sure it is about 200 words long. The abstract should include a brief summary of the case study, including all the essential information in the patient presentation, such as the history, age, and current diagnosis.
The summary should also include the nursing assessment, the current interventions, and recommendations.
3. Introduction
After writing the title page and the abstract, start writing the introduction. The introduction of a nursing case study analysis must briefly include the patient's presentation, current diagnosis and medication, and recommendations. It must also include a strong thesis statement that shows what the paper is all about.
You shouldn't just write an introduction for the sake of it. If you do so, your introduction will be bland. You need to put in good effort when writing your introduction. The best way to do this is to use your introduction to show you understand the case study perfectly and that you will analyze it right.
You can always write your introduction last. Many students do this because they believe writing an introduction last makes it more precise and accurate.
4. Case Presentation (Status of the Patient)
After introducing your nursing case study analysis, you should present the case where you outline the patient's status. It is usually straightforward to present a case.
You must paraphrase the patient scenario in the assignment prompt or brief. Focus on the demographic data of the patient (who they are, age, race, height, skin tone, occupation, relationships, marital status, appearance, etc.), why they are in the case study or scenario, reasons they sought medical attention, chief complaint, and current diagnosis and treatment. You should also discuss the actions performed on the patient, such as admission to the ICU, taking vital signs, recommending tests, etc.
In short, everything necessary in the patient scenario should be in your case presentation. You only need to avoid copying the patient scenario or case study word-for-word when writing your case presentation.
5. Diagnosis and Assessment
After the case presentation, you should explain the diagnosis. In other words, you should explain the condition, disease, or medical situation highlighted in the case presentation. For example, if the patient is a heavy smoker and he has COPD, it is at this point that you explain how COPD is linked to heavy smoking.
This is the section where you thoroughly discuss the disease process (pathophysiology) by highlighting the causes, symptoms, observations, and treatment methods. You should relate these to the patient's status and give concrete evidence. You should describe the progression of the disease from when the client was admitted to a few hours or days after they were stabilized. Consider the first indication of the disease that prompted the patient to seek further medical assistance.
Your paper should also elucidate the diagnostic tests that should be conducted and the differential diagnosis. Ensure that each is given a well-founded rationale.
When explaining the condition, go deep into the pathophysiology. Focus specifically on the patient's risk factors. Ensure you get your explanation from recent nursing literature (peer-reviewed scholarly journals published in the last 5 years). And do not forget to cite all the literature you get your facts from.
In short, this section should explain the patient's condition or suffering.
6. Nursing Intervention
After the diagnosis and nursing assessment section, your nursing case study analysis should have an intervention section. This section is also known as the nursing care planning section. What you are supposed to do in this section is to present a nursing care plan for the patient presented in the patient scenario. You should describe the nursing care plan and goals for the patient. Record all the anticipated positive changes and assess whether the care plan addresses the patient's condition.
A good nursing care plan details the patient's chief complaints or critical problems. It then describes the causes of these problems using evidence from recent medical or nursing literature. It then details the potential intervention for each problem. Lastly, it includes goals and evaluation strategies for the measures. Most professors, predominantly Australian and UK professors, prefer if this section is in table format.
Some nursing professors regard the intervention section (or nursing care plan section) as the most critical part of a nursing case study. This is because this part details precisely how the student nurse will react to the patient scenario (which is what the nursing professors want to know). So, ensure you make a reasonable effort when developing this section to get an excellent grade.
7. Discussion and Recommendations
The intervention section in a nursing case study is followed by a discussion and recommendations section. In this section, you are supposed to expound on the patient scenario, the diagnosis, and the nursing care plan. You should also expound on the potential outcomes if the care plan is followed correctly. The discussion should also explain the rationale for the care plan or its significant bits.
Recommendations should follow the discussion. Recommendations usually involve everything necessary that can be done or changed to manage a patient's condition or prevent its reoccurrence. Anything that enhances the patient's well-being can be a recommendation. Just make sure your key recommendations are supported by evidence.
8. Conclusion
This is the second last section of a typical nursing case study. What you need here is to summarize the entire case study. Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations.
At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible.
9. References
This is the last section of a nursing case study. No nursing case study is complete without a references section. You should ensure your case study has in-text citations and a references page.
And you should make sure both are written as recommended in the assignment. The style section is usually Harvard or APA. Follow the recommended style to get a good grade on your essay.
Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Nursing Case Study
You know all the key sections you must include in a nursing case study. You also know what exactly you need to do in each section. It is time to learn how to write a nursing case study. The process detailed below should be easy to follow because you know the typical nursing case study structure.
1. Understand the Assignment
When given a nursing case study assignment, the first thing you need to do is to read. You need to read two pieces of information slowly and carefully.
First, you need to read the prompt itself slowly and carefully. This is important because the prompt will have essential bits of information you need to know, including the style, the format, the word count, and the number of references needed. All these bits of information are essential to ensure your writing is correct.
Second, you need to read the patient scenario slowly and carefully. You should do this to understand it clearly so that you do not make any mistakes in your analysis.
2. Create a Rough Outline
Failure to plan is a plan to fail. That is not what you are in it for anyway! In other words, do not fail to create an outline for your case study analysis. Use the template provided in this essay to create a rough outline for your nursing case study analysis.
Ensure your outline is as detailed as it can be at this stage. You can do light research to achieve this aim. However, this is not exactly necessary because this is just a rough outline.
3. Conduct thorough research
After creating a rough outline, you should conduct thorough research. Your research should especially focus on providing a credible and evidence-based nursing assessment of the patient problem(s). You should only use evidence from recent nursing or medical literature.
You must also conduct thorough research to develop an effective intervention or nursing care plan. So when researching the patient's problem and its diagnosis, you should also research the most suitable intervention or do it right after.
When conducting research, you should always note down your sources. So for every piece of information you find, and what to use, you should have its reference.
After conducting thorough research, you should enhance your rough outline using the new information you have discovered. Make sure it is as comprehensive as possible.
4. Write your nursing case study
You must follow your comprehensive outline to write your case study analysis at this stage. If you created a good outline, you should find it very easy to write your nursing case study analysis.
If you did not, writing your nursing case study will be challenging. Whenever you are stuck writing your case study analysis paper, you should re-read the part where we explain what to include in every section of your analysis. Doing so will help you know what to write to continue your essay. Writing a nursing case study analysis usually takes only a few hours.
5. Reference your case study
After writing your case study, ensure you add all in-text citations if you have not already. And when adding them, you should follow the style/format recommended in the assignment prompt (usually APA or Harvard style).
After adding in-text citations exactly where they need to be and in the correct format, add all the references you have used in a references page. And you should add them correctly as per the rules of the style you were asked to use.
Do not forget to organize your references alphabetically after creating your references page.
6. Thoroughly edit your case study
After STEP 5 above, you need to edit your case study. You should edit it slowly and carefully. Do this by proofreading it twice. Proofread it slowly each time to discover all the grammar, style, and punctuation errors. Remove all the errors you find.
After proofreading your essay twice, recheck it to ensure every sentence is straightforward. This will transform your ordinary case study into an A-grade one. Of course, it must also have all the standard sections expected in a case study.
Recheck your case study using a grammarly.com or a similar computer grammar checker to ensure it is perfect. Doing this will help you catch and eliminate all the remaining errors in your work.
7. Submit your case study analysis
After proofreading and editing your case study analysis, it will be 100% ready for submission. Just convert it into the format it is required in and submit it.
Nursing Case Study Tips and Tricks
The guide above and other information in this article should help you develop a good nursing case study analysis. Note that this guide focuses entirely on nursing case scenario-based papers, not research study-based nursing case studies. The tips and tricks in this section should help you ensure that the nursing case study analysis you create is excellent.
1. Begin early
The moment you see a nursing case study assignment prompt, identify a date to start writing it and create your own deadline to beat before the deadline stated in the prompt.
Do this and start writing your case study analysis early before your deadline. You will have plenty of time to do excellent research, develop an excellent paper, and edit your final paper as thoroughly as you want.
Most student nurses combine work and study. Therefore, if you decide to leave a nursing case study assignment until late to complete it, something could come up, and you could end up failing to submit it or submitting a rushed case study analysis.
2. Use the proper terminology
When writing an essay or any other academic paper, you are always encouraged to use the most straightforward language to make your work easy to understand. However, this is not true when writing a nursing case study analysis. While your work should certainly be easy to understand, you must use the right nursing terminology at every point where it is necessary. Failure to do this could damage your work or make it look less professional or convincing.
3. Avoid copying and pasting
If you are a serious nursing student, you know that copying and pasting are prohibited in assignments. However, sometimes copying and pasting can seem okay in nursing case studies. For example, it can seem okay to copy-paste the patient presentation. However, this is not okay. You are supposed to paraphrase the verbatim when presenting the patient presentation in your essay. You should also avoid copy-pasting information or texts directly. Every fact or evidence you research and find should be paraphrased to appear in your work. And it should be cited correctly.
4. Always ask for help if stuck
This is very important. Students are usually overwhelmed with academic work, especially a month or two to the end of the semester. If you are overwhelmed and think you will not have the time to complete your nursing case study analysis or submit a quality one, ask for help. Ask for help from a nursing assignment-help website like ours, and you will soon have a paper ready that you can use as you please. If you choose to get help from us, you will get a well-researched, well-planned, well-developed, and fully edited nursing case study.
5. Format your paper correctly
Many students forget to do proper formatting after writing their nursing case study analyses. Before you submit your paper, make sure you format it correctly. If you do not format your paper correctly, you will lose marks because of poor formatting. If you feel you are not very confident with your APA or Harvard formatting skills, send your paper to us to get it correctly formatted and ready for submission.
Now that you are all set up ...
Our company has been among the best-rated nursing homework help companies in the last few years. Thousands of students have benefitted from our many academic writing guides. Many more have benefitted from direct help given by our experts.
- How to write a nursing philosophy statement.
- Writing an abstract poster presentation.
We have experienced nursing experts available every day of the week to provide nursing assignment help. They can easily research and write virtually any nursing assignment, including a nursing case study. So, if the information provided in this article isn't making you feel any optimistic about writing an excellent nursing case study, get help from us.
Get help by ordering a custom nursing case study through this very website. If you do so, you will get a 100% original paper that is well-researched, well-written, well-formatted, and adequately referenced. Since the paper is original, you can use it anywhere without problems.
Thousands of students trust our company every week, month, and year. Be like them! Trust us for 100% confidentiality and speedy delivery.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Middle-Range Nursing Theories

Nursing Reflective Models - Guide
A Nursing Student Guide for SNAPPS in Assignments
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study [Examples, Format, & Tips]
✒️ case study topics for nursing students.
- 🩺️ The Basics
- 💉 Nursing Case Study: Writing Rules
📑 Nursing Case Study Format
📝 nursing case study examples.
- ⏱️ Tips on Quick Writing
🔗 References
A nursing case study is an in-depth analysis of the health situation of an individual patient.

The analysis is based on:
- medical history,
- other relevant criteria.
In most cases, you will be asked to diagnose to suggest the first aid measures. Alternatively, nurses can be asked to describe a patient in their practice and analyze the correctness of their actions. The purpose is to recreate a realistic hospital setting in the classroom and make students reflect on the treatment process from diagnosis to treatment.
- Anaphylactic shock in a teenager with peanut allergy.
- Non-compliant patient with diabetes: ways to improve adherence.
- Telehealth intervention for managing chronic disease.
- Communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy in a rural community.
- Postpartum hemorrhage in a new mother: risk factors and interventions.
- Ways to improve recognition of dehydration in aging adults.
- The effective ways of maintaining work-life balance for nurses.
- Cultural competency in providing care to migrants and refugees.
- Why should every patient’s medical history remain confidential?
- The use of massage therapy in relieving pain.
- The challenges facing medicine in 2024.
- How does modern technology impact nursing?
- The significance of regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider.
- What are the primary treatments for postpartum depression?
- The use of steroids in cancer treatment.
🩺️ Nursing Case Study: What Is It About?
As a nursing student, you should understand that no two patients are the same. Each has a unique clinical record and condition. And although most nursing case study tasks will ask you to suggest a diagnosis or treatment, your focus should rest on the patient.
Busy nurses can sometimes see their patients in the framework of an illness to be treated or a procedure to be fulfilled. But you should do your best to remember that each patient is a living person with a complex set of needs, emotions, and preferences. A ready-made textbook answer is rarely the best solution for them. Moreover, it rarely helps to analyze a condition in isolation from the patient.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don’t do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types.
Once again:
A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient’s condition. Meanwhile, a nursing essay will explore the disease, prevention methods, treatment, or possible consequences of the disease.
Even if the case is hypothetical, it should focus on the suggested reality. On the other hand, essays are usually literature-based. You are expected to do some reading for a case study too, but you should research and present the information within the context of the patient. In simple terms, a case study uses information in the actual application, and an essay uses it for the sake of generalized suggestions.
💉 How to Write a Nursing Case Study: 3 Key Rules
- Do the fieldwork. Before setting your hands to writing, you should collect all of the available materials: clinical notes, results of medical tests, x-rays, sickness records, etc. Use this information to draw a clear picture of the story. It is always helpful to ask yourself, “What is interesting or unusual about this patient’s condition?” In the course of writing, recall your answer from time to time not to get lost in words. It will help you to convey a definite and appropriate message.
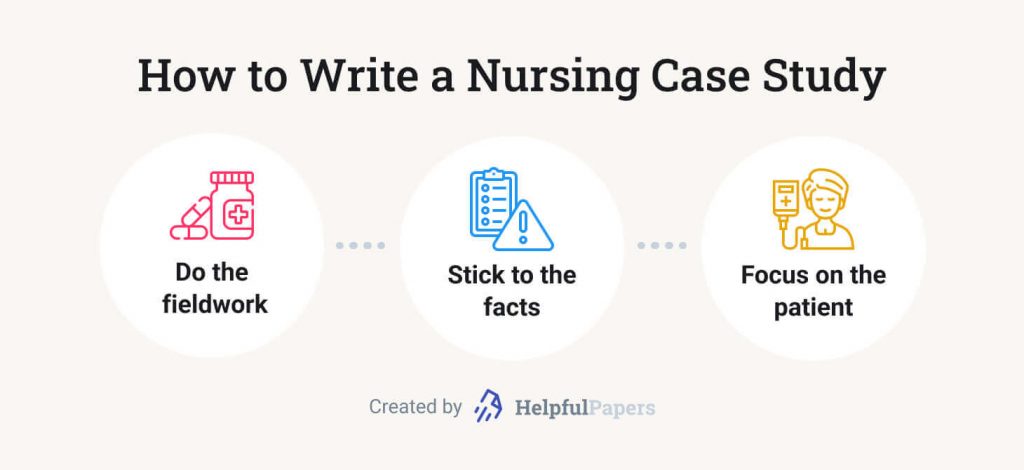
- Stick to the facts. A nursing case study should be an accurate description of the actual situation. Restrain from speculating about the inherent mechanisms of the illness or the general treatment methodology. In fact, students are rarely prepared enough to discuss pathology and physiology. Leave this to reputable experts. The best result you can provide in a case study is an honest account of clinical events.
- Concentrate on the patients and their progress. Remember that a nursing case study is a story of a patient’s progress and not a narrative about their nurse. No matter how efficiently the medical specialist acted, it would be incorrect to add any praiseful remarks. The optimal way is to tell the story in its logical and time order and outline the result of treatment. In this case, the outcome will speak for itself.
Introduction
It is where you should tell the reader why this case is interesting . Place your study in a social or historical context. If, during your preliminary research, you found some similar cases, describe them briefly. If you had a hard time diagnosing the patient or your proposed treatment is complicated, mention it here. Don’t forget to cite the references to each of them!
The introduction should not exceed several paragraphs. The purpose is to explain why the reader will benefit from reading about the case.

Case Presentation
- Why did the patient seek medical help? (Describe the symptoms.)
- What is known about the patient? (Mention only the information that influenced your diagnosis. Otherwise, explain why some information is irrelevant to the diagnosis.)
- Stick to the narrative form. (Make it a story!)
- What are the variants for diagnosis? (Make a shortlist of possible disorders that fall under the patient’s symptoms. But make it specific: not just “pneumonia” but “bilateral pneumonia,” for example. Besides, this point is optional.)
- What were the results of your clinical examination? (If you saw the patient in person.)
- Explain the results of lab tests. (The words “positive” or “negative” are not always clear.)
Actions and Their Results
This section describes the care that has been provided and/or is planned. You can answer the following questions in narrative form . If some information is missing, skip the point:
- What preliminary actions have been taken? (Be specific: not just “wound care,” but “wound cleaning and dressing.”)
- How long has the patient been under care?
- Has the previous treatment given any visible result?
- Why was it suspended or finished?
- Why did the patient withdraw from treatment (if applicable)?
- How could you improve the patient’s condition if the result was negative?
- If the disease is incurable (like in the case of diabetes), which activities would stabilize the patient’s condition?
- If possible, include the patient’s reports of their own physical and mental health.
In this section, you should identify your questions about the case. It is impossible to answer all of them in one case study. Likewise, it is unreal to suggest all the relevant hypotheses explaining the patient’s condition. Your purpose is to show your critical thinking and observation skills. Finalize your conclusion by summarizing the lessons you learned from the nursing case study.
Whenever you directly or indirectly cite other sources or use data from them, add these books and documents to the references list. Follow the citation style assigned by your professor. Besides, 15 items are already too much. Try to make a list of up to 10. Using textbooks as references can be viewed as bad manners.
Include all the tables, photographs, x-rays, figures, and the journal of medication usage in this section. Unless required otherwise in the assignment, start each item from a new page, naming them “Appendix A,” “Appendix B…”.
Below you will find case study samples for various topics. Using them as a reference will improve your writing. If you need more ideas, you are welcome to use our free title-generating tool .
- Case study: healing and autonomy.
- Sara’s case study: maternal and child nursing.
- COPD medical diagnostics: case study.
- Care standards in healthcare institutions: case study.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis: case study analysis.
- Alzheimer disease: the patient case study.
- The treatment of foot ulcers in diabetic patients: case study.
- Hypertension: C.D’s case study.
- Myocardial infarction: cardiovascular case study.
- Major depressive disorder case.
- Case study of the patient with metabolic syndrome .
- Pulmonary analysis case study .
- Older adults isolation: Case study .
- The holistic care: Case study .
- Obesity in the Elderly: The Case Study.
- Medical ethics: Case study .
- Patient diagnoses and treatment: Case study .
- Obesity case study: Mr. C .
- Nurse Joserine: Case study problems .
- Chronic stable angina: Case study .
- Fetal abnormality: Case study .
- Researching SOAP: Case study .
- Case study for a patient with hormonal disorders .
- “Walking the Tightrope”: A case study analysis .
- ARNP approach: Case study analysis .
- Case study on biomedical ethics in the Christian narrative .
- Thermal injury: Case study .
- Ethical dilemma in nursing: Case study .
- Asthma: A case study of the patient .
- Asthma discharge plan: Mini case study .
- Case study: An ethics of euthanasia .
- Case study: Head-to-toe assessment steps .
- Pain management strategies: Case study .
- Case study: Inflammatory bowel disease .
- Sleep deprivation and insomnia: The case study .
- The case study of a heart failure .
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: Disease case study .
- Case study: Hardy Hospital case summary .
- Obesity and its complications: Case study .
- Angina disease case study .
- Nursing ethics case study .
- Case study of a patient: Assessment and treatment plan .
- Cecile case study: Mrs. J .
- Nursing power in the emergency department: Case study .
- Heart failure case study: Mrs. J .
- Application of ethics in nursing: Case study .
- Sudden visual impairment: Case study .
- Epidemiology case study: Outbreak at Watersedge — Public health discovery game .
- Wellness of senior citizens: Case study .
- Healthcare organization evaluation: Case study of Banner Health .
⏱️ Bonus: Tips on Writing a Case Study in Record Time
Need to prepare a case study on nursing or in another field? Below you’ll find a collection fo tips that will help you do it as quickly as possible!
3 Shortcuts for a Quick Start
If you’re about to start writing a case study, you should check yourself if you’re not doing any of the following:
- spending too much time on selecting a topic;
- reading too much before selecting a topic;
- making conclusions too early – creating bias.
Instead of killing time doing the three useless things discussed above, consider these:
- Choose approach. Note that there are 2 major approaches to case studies: the analytical approach (investigating possible reasons without making any conclusions) and problem-oriented approach (focusing on a particular problem and investigating it).
- Skim some sources (DON’T READ THEM). Select several sources. Simply skim abstracts and conclusions.
- Start making notes early. Simply reading is ineffective unless you’re lucky to have a phenomenal memory. Always make notes of any useful arguments.
4 Shortcuts Not to Get Stuck in the Middle
Even if you kick started your case study, it’s too early to celebrate it. Consider the following traps in the middle of the project:
- Watch the structure. The classic logical structure is your formula of success. It will help you move from one point to another without the unnecessary procrastination:
- Respect the logic. Make your case study flow – make logical transitions between the different parts and make it consistent. Avoid changing your position throughout the paper.
- Be detail-oriented. Any trifle deserves attention when you write a case study.
- Avoid bias. Be sure that all your opinions are based on the specific arguments form the case study. Avoid pouring your biased views into the project.
3 Shortcuts for a Happy Ending
- Offer a realistic solution. College case study is a rehearsal of real-life situations. Take the responsibility for your suggestions.
- Keep your conclusion short. Avoid repeating the details and don’t include any new information.
- Consider creating a Power Point. If your task is not only writing a case study, but also presenting it – why not create PowerPoint slides to help you?
As the last step on your way to a perfect nursing case study, prepare the title page. Its format usually depends on the professor’s requirements. But if you know the citation style, our Title Page Maker is a perfect tool to apply the right formatting and accelerate the process. And if you have any know-how on how to write a medical case study, you are very welcome to share it with other students in the comments below.
❓ Nursing Case Study: FAQ
What is a case study in nursing.
A nursing case study explores the condition of a patient. It is based on previous clinical records, lab reports, and other medical and personal information. A case study focuses on the patient and describes the treatment that was (or should be) applied and its (expected) outcome.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study?
- Collect the bulk of data available about the patient.
- Read literature about the diagnosed condition.
- Focus on the individual patient and their symptoms.
- Describe the situation and outline its development in time.
- Analyze the actions of the medical personnel that have been done.
- Plan further treatment of the patient.
Why Are Case Studies Good for Nursing Students?
Nursing case studies offer you a priceless opportunity to gain experience of different patient conditions and cure methods without visiting the clinic. You can think about whether the proposed treatment was appropriate or wrong and suggest a better solution. And the best thing, your teacher will indicate your mistakes (and no patient will be hurt in the process).
Why Are Case Studies Important in Nursing?
- You learn to distinguish the relevant data and analyze it.
- You learn to ask the right questions.
- You learn to evaluate the severity of symptoms.
- You learn to make better diagnoses.
- You train your critical thinking in terms of treatment methods
- Case studies are in-class simulators of authentic atmosphere in a clinical ward.
- What is a case study? | Evidence-Based Nursing
- Case Studies – Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Case Study Research Design in Nursing
- Case study report for Nursing | Learning Lab – RMIT University
- Case Study or Nursing Care Study? – jstor
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.
Registered Nurse RN
Registered Nurse, Free Care Plans, Free NCLEX Review, Nurse Salary, and much more. Join the nursing revolution.
Next Generation NCLEX Case Study Sample Questions
One of the big changes on the Next Generation NCLEX exam is a shift toward case studies. Case studies often require a deeper level of critical thinking, and understanding diseases on a more in-depth level (especially the pathophysiology) will make these types of questions easier to answer.
In this article, you’ll be able to watch a free video to help you prepare for the new Next Generation NCLEX case study format. Nurse Sarah will walk you step-by-step through each scenario and help you understand how to use critical thinking and nursing knowledge to answer these types of questions.
Next Generation NCLEX Case Study Review Questions Video
NGN Case Study Sample Questions and Answers
First, let’s take a look at our case study summary below:
Case Study Summary:
A 68-year-old male is admitted with shortness of breath. He reports difficulty breathing with activity, lying down, or while sleeping. He states that in order to “breathe easier,” he has had to sleep in a recliner for the past week. The patient has a history of hypertension, myocardial infarction (2 years ago), and cholecystectomy (10 years ago). The patient is being transferred to a cardiac progressive care unit for further evaluation and treatment.
Question 1 of 6: The nurse receives the patient admitted with shortness of breath. What findings are significant and require follow-up? The options are listed below. Select all that apply.
To answer this first question in the NGN case study, let’s look at the information provided in the nursing notes and vital signs tabs provided:

This question is asking us to identify findings that are significant and require the nurse to follow-up. In other words, what is presenting that we can’t ignore but need to investigate further.
Therefore, let’s comb through the nursing notes and vital signs to see what is abnormal and requires follow-up.
First, the patient arrived to the room via stretcher. That’s fine and doesn’t necessarily require follow-up.
Next, the patient is alert and oriented x 4 (person, place, time, event). This tells us that the patient’s neuro status is intact so far. Therefore, the shortness of breath isn’t affecting the patient’s mental function yet (we have enough oxygen on board right now for brain activity).
However, the nurse has noticed the shortness of breath with activity and talking, which should not normally happen. This tells us something is wrong and is significant enough to require follow-up. We want to know why is this happening, is it going to get worse, etc.
The patient’s weight and vital signs were collected (this is good). Weight is 155 lbs. and BMI is within a healthy range (doesn’t tell us too much but may be useful later). The patient is also connected to a bedside monitor, so they need to be monitored constantly like on a progressive care unit.
The monitor shows sinus tachycardia . This is significant because it seems the patient’s shortness of breath is causing the heart to compensate by increasing the heart rate to provide more oxygen (hence the lungs may be compromised).
Then we find out that the lungs are indeed compromised because crackles are heard in both lungs , and this may be why our patient is short of breath. This is significant (could the patient have pulmonary edema?)
Then we find out the nurse has noted an S3. This is an extra heart sound noted after S2. And what jumps out to me about this is that it is usually associated with volume overload in the heart like in cases of heart failure . However, S3 may be normal in some people under 40 or during pregnancy, but that’s not the case with our patient based on what we read in the case summary.
Therefore, based on everything I’m reading in this case study, I’m thinking this patient may have heart failure, but we need those test results back (especially the echo and chest x-ray, and hopefully a BNP will be in there too).
We are also told that the patient has an 18 gauge IV inserted (which is good thing to have so we can give medications if required), orders have been received, labs drawn, and testing results are pending.

Now let’s look at the “Vital Signs” tab above, and ask yourself what is normal vs. abnormal for this patient (adult male).
- The heart rate is high at 112 (tachycardia), and should normally be 60-100 bpm (see heart rhythms ).
- Blood pressure is higher than normal (normal is 120/80), which indicates hypertension.
- Oxygen saturation is 94% (this is on the low side as we’d normally want around 95% or higher, and the patient is on 4 L nasal cannula, which tells us the lungs are not okay).
- Respiratory rate is increased (26 breaths per minute)…normal is 12-20 breaths per minute.
Based on the information we were provided, I’ve selected the answers below. These findings are significant and definitely require follow-up by the nurse.

When answering these NGN case study questions, it’s helpful to think of the ABCDE (airway, breathing, circulation, etc.) as all of these fall into that category. If we don’t follow-up on the shortness of breath, crackles, respiratory rate, o2 saturation (94% on 4 L nasal cannula), the respiratory system can further decline.
In addition, the sinus tachycardia, S3 gallop, and hypertension could indicate fluid overload in the heart. This may cause the heart to tire out and lead the lethal rhythm. On the other hand, temperature, pain, weight, and BMI are not abnormal and do not require follow-up.
See the Complete Next Generation NCLEX Case Study Review
Each question in the case study builds on the previous question. To see how these questions evolve based on the patient’s condition and labs, watch the entire Next Generation NCLEX Case Study Review video on our YouTube Channel (RegisteredNurseRN).
NCLEX Practice Quizzes
We’ve developed many free NCLEX review quizzes to test your knowledge on nursing topics and to help you prepare for the Next Generation NCLEX exam.
Nurse Sarah’s Notes and Merch

Just released is “ Fluid and Electrolytes Notes, Mnemonics, and Quizzes by Nurse Sarah “. These notes contain 84 pages of Nurse Sarah’s illustrated, fun notes with mnemonics, worksheets, and 130 test questions with rationales.
You can get an eBook version here or a physical copy of the book here.
Please Share:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Disclosure and Privacy Policy
Important links, follow us on social media.
- Facebook Nursing
- Instagram Nursing
- TikTok Nurse
- Twitter Nursing
- YouTube Nursing
Copyright Notice
📕 Studying HQ
10 Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples [Format + Structure]
Bob cardens.
- August 6, 2022
If you are a nursing student, you may be asked to write a case study analysis. This can be a daunting task, but it is possible to do if you follow some simple steps. Here we include Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples to help you get started.
First, read the case study and make sure you understand the situation. Next, identify the key players involved and their role in the case. Finally, analyze the data presented and draw your own conclusions.
Writing a case study analysis can be challenging, but it is also an excellent way to learn more about nursing care. By taking the time to understand the situation and identify the key players, you will be able to gain valuable insights that can be applied to future cases.
What You'll Learn
10 Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
| Title | Description | Purpose |
| The case analysis explores some of the ways in which the curriculum development leader can adopt measures that enhance faculty support and development in the task of curriculum development | Problem-solving case analysis | |
| The case analysis explores the issues that the Dean of a nursing school should do to ensure a new curriculum is developed | Problem-solving case analysis | |
| This post includes benchmark patient’s spiritual needs: case analysis benchmark, how would a spiritual needs assessment help the physician, how would a spiritual needs assessment help the physician assistant mike, definition of spiritual care and ethical decision-making and intervention in the event of a difficult situation. | Explores the spiritual needs of patients and how to address them. | |
| The post includes a case study: fetal abnormality gcu, and discussions on the Christian concept of the imago Dei, and what value does a human person have? How does your position affect your stance on controversial bioethical issues, such as abortion, designer babies, and stem cell research. | Explores ethical and spiritual influences to decision making | |
| Utilizes systematic problem-solving method, nurses can determine the health care needs of an individual and provide personalized care. | Improve care planning and decision-making. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples | |
| The post includes Case Study: Healing and Autonomy Case Study, applying the four principles: case study, answers questions about a patient’s spiritual needs in light of the Christian worldview, describes how principalism would be applied according to the Christian worldview, the importance of each of the four principles, and What do the four parts of the Christian biblical narrative (i.e., creation, fall, redemption, and restoration) say about the nature of God and of reality in relation to the reality of sickness and disease? | Helps nurses learn how to ethically analyze a case. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples | |
| Evaluates the Health History and Medical Information for Mr. C. and expects the nurse to demonstrate an enhanced understanding of the pathophysiological processes of disease, the clinical manifestations and treatment protocols, and how they affect clients across the life span. | Improves the decision making of nurses. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples | |
| The paper proposes a change project at ABC Medical Center (ABC-MC) in response to the prevailing forces, identifies the need for change before developing a vision that inspires the change and provides a rationale for the change. | Case analysis example of a change project | |
| The nursing case study example on Death and Dying and answers questions on Suffering and the Fallenness of the World, Suffering and the Hope of Resurrection, Value of Life, Euthanasia, and Morally Justified Options, also offers an analysis of the sin of suicide. | Explores Ethical end of life decision making. | |
| Case analysis of a scenario | Improves the decision making of nurses |
Nursing Case study Analysis Format and Structure
When it comes to writing a case study analysis, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there is a general format and structure that you can follow to ensure your analysis is well-organized and flows smoothly. Here are the basics:
A nursing case study is a detailed study of a patient that is encountered by a nurse. The purpose of the case study is to provide a comprehensive view of the patient’s health condition and history. Nurse practitioners use case studies to enhance their ability to care for patients by providing them with a more complete picture of the patient’s health. Nurse practitioners may use different formats for their nursing case studies. However, all case studies should include certain key elements. These key elements include:
As a nursing practitioner, you will be responsible for analyzing patient cases and providing care based on your findings. There are key elements that you must take into account when performing a case analysis in order to ensure that you are providing the best possible care for your patients.
- The first element is the patient’s history. You will need to obtain a complete medical history in order to understand the background of the case and identify any potential risk factors.
- Next, you will need to perform a physical examination of the patient. This will help you to identify any physical signs or symptoms that may be related to the case.
- You will also need to order and review any laboratory tests or imaging studies that have been performed on the patient. These results can provide valuable information about the patient’s condition.
- Once you have gathered all of this information, you will need to start piecing together the puzzle to form a diagnosis. This process will involve synthesizing all of the information you have gathered and making a determination about what is causing the patient’s symptoms.
- Once you have made a diagnosis, you can start developing a treatment plan. This plan should be tailored specifically to the needs of the individual patient.
When writing a nursing case study, nurse practitioners should use a clear and concise format. The format should be easy to follow and understand. Nurse practitioners should also include all of the key elements in their nursing case studies. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
How to write a case study assignment
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a real-life situation or incident, as a way to illustrate content and theory to students. It is usually presented as a written report, but can also be done in the form of a presentation, video, or multimedia production.
Case studies are used in many different disciplines, including business, law, psychology, nursing, social work, and medical sciences.
A case study assignment is a type of paper that requires you to analyze a real-life or fictional situation and offer possible solutions. This can be a challenging task, but if you follow some basic guidelines, you can write a successful case study assignment.
Here are some tips on how to write a case study assignment:
- Read the case study carefully. Make sure you understand the situation and the problem that needs to be solved.
- Research the subject matter. You will need to have a good understanding of the relevant theories and concepts in order to offer possible solutions.
- Read the case study carefully. This may seem obvious, but it is important to get a clear understanding of the situation before you start writing. Make sure you have all the relevant facts and figures to hand before you start.
- Identify the key issues. Once you have read and understood the case study, you need to identify the key issues that it raises. These will form the basis of your analysis.
- Research the law/theory applicable to the key issues. Once you have identified the key issues, you need to research the law or theory that applies to them. This will help you to form your arguments and conclusions.
- Write your paper. Be sure to present your analysis in a clear and concise manner. Your paper should be well-organized and well-written
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter.
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

How to Present a Nursing Case Study

What Is a Case Study in Nursing?
A nursing case study is an in-depth examination of a situation that a nurse encounters in her daily practice. The case study offers a safe way for the nurse to apply theoretical and actual knowledge to an actual or potential patient scenario. She can employ her decision-making skills, use critical thinking to analyze the situation, and develop cognitive reasoning abilities without harming a patient. Nursing case studies are commonly used in undergraduate nursing programs, graduate schools offering a master’s of science degree in nursing (MSN), and orientation programs for new graduate nurses. They may be presented in written form, online, or live in a classroom setting.
Choose a topic. According to Sigma Theta Tau International, the topic should be focused, based in reality, and relevant. It should demonstrate current best practices that are supported by nursing research. The nurse may choose to discuss a situation from his past experience, or delve into something in his current job.
Write objectives. There should be at least three learning objectives, or outcomes, that identify what the learner will gain from completing the case study. Learning objectives are written as clear, measurable behaviors, such as “Identify five risk factors for falls in older adults.”
Write an introduction. This should be a one- or two-paragraph overview that describes the patient, the situation, and circumstances relevant to that situation. The introduction can also include a little about the patient’s history leading up to the situation.
Integrate more history and background. The next 1 to 2 paragraphs provide the learner with in-depth information to analyze the situation, such as lab values, diagnostic study results, findings from the nurse’s assessment of the patient, and a more detailed patient history.
Formulate questions. Nursing case studies are interactive scenarios that stimulate analysis and critical thinking. The questions typically require the learner to use the nursing process (assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation) and to anticipate what will happen next in the situation.
Give feedback. According to Sigma Theta Tau, the nursing case study provides the learner with two types of feedback: informational and reinforcing. Informational feedback lets the learner know if she has answered questions correctly, and gives her an idea of how she is progressing through the patient scenario. Reinforcing feedback gives the learner additional information about her responses to the questions. If she answers the question correctly, she’ll be given the rationale behind her right answer. If she gives the wrong answer, reinforcing feedback lets her know why that answer is wrong.
Provide references. It’s important to point the learner toward additional learning opportunities in print or on the web.
Related Articles
How to become a continuing education provider for nurses, how to study for fundamentals of nursing.

How to Apply Havelocks Theory of Change in Nursing

The Structure of the NCLEX

How to Apply Critical Thinking to Concept Map for Nursing

How to Write Nursing Theory Proposition Statements

Peer Counseling Techniques

What Classes in College Must You Take to Become a Nurse?
- Sigma Theta Tau International
Sandy Keefe, M.S.N., R.N., has been a freelance writer for over five years. Her articles have appeared in numerous health-related magazines, including "Advance for Nurses" and "Advance for Long-Term Care Management." She has written short stories in anthologies such as "A Cup of Comfort for Parents of Children with Special Needs."
- General Nursing
- Nursing Specialties
- Nursing Students
- United States Nursing
- World Nursing
- Boards of Nursing
- Breakroom / Clubs
- Nurse Q&A
- Student Q&A
- Fastest BSN
- Most Affordable BSN
- Fastest MSN
- Most Affordable MSN
- Best RN to BSN
- Fastest RN to BSN
- Most Affordable RN to BSN
- Best LPN/LVN
- Fastest LPN/LVN
- Most Affordable LPN/LVN
- Fastest DNP
- Most Affordable DNP
- Medical Assistant
- Best Online Medical Assistant
- Best Accelerated Medical Assistant
- Most Affordable Medical Assistant
- Nurse Practitioner
- Pediatric NP
- Neonatal NP
- Oncology NP
- Acute Care NP
- Aesthetic NP
- Women's Health NP
- Adult-Gerontology NP
- Emergency NP
- Best RN to NP
- Psychiatric-Mental Health NP
- RN Specialties
- Best RN Jobs and Salaries
- Aesthetic Nurse
- Nursing Informatics
- Nurse Case Manager
- Forensic Nurse
- Labor and Delivery Nurse
- Psychiatric Nurse
- Pediatric Nurse
- Travel Nurse
- Telemetry Nurse
- Dermatology Nurse
- Best NP Jobs and Salaries
- Family NP (FNP)
- Orthopedic NP
- Psychiatric-Mental Health NP (PMHNP)
- Nurse Educator
- Nurse Administrator
- Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS)
- Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)
- Best Free Online NCLEX-RN Study Guide
- The Nursing Process
- Question Leveling
- NCLEX-RN Question Identification
- Expert NCLEX-RN Test-Taking Strategies
- Best Scrubs for Nurses
- Best Shoes for Nurses
- Best Stethoscopes for Nurses
- Best Gifts for Nurses
- Undergraduate
- How to Become an LPN/LVN
- How to Earn an ADN
- Differences Between ADN, ASN, AAS
- How to Earn a BSN
- Best MSN Concentrations
- Is an MSN Worth It?
- How to Earn a DNP
- MSN vs. DNP
Nursing Case Studies: Diagnosis, Rationales, Fundamentals
Test your knowledge and clinical investigative skills in trying to diagnose what is going on with the patients presented in each of the Case Study Investigations. Can you come up with the right diagnosis? Case Studies Articles

Case Study: Child With Altered Mental Status
In this Case Study, an 11-year-old child with autism presents by ambulance to the children's hospital with altered mental status, bizarre behavior and fever....

Four Days of Nausea, Vomiting and Fever
What is most important in this case study in which an older Vietnamese woman presents to the ER with fever, nausea and vomiting?

I'm Dizzy, Tired and Can't Remember What I Ate for Lunch
A 74-year-old white male presents to the ED with confusion, fatigue, dizziness, headache and distal right arm paresthesia. Experienced nurses, model your...

Agonizing Pelvic Pain: What's Going On with this 17-year-old? | Ca…
A new case study in which the patient, a 17-yr-old African American female, is having ongoing, excruciating pelvic pain. This case study is based upon the very...

A Fracture from a Fall: What's Going on Here?
A new case study in which a 77 yo white female arrives to the emergency room by taxi with a suspected skull fracture. This topic was suggested by a reader –...

Breathless, Coughing and Run-down: What's Going On? | Case Study
A new case study in which the patient, a 32-yr-old white male presents to a local free clinic with fatigue, moderate dyspnea, and a persistent and...

Suicidal Ideation and Muscle Twitches | Case Study
A new case study in which the patient, a 40 yr-old mixed-race woman presents to her primary care physician with concerns about suicidal ideation. She has some...

Unexplained Diarrhea and Weight Loss: What's going on? | Case Stud…
A new case study in which the patient, a 28 y/o white female presents to a primary care clinic complaining of recurrent diarrhea. She first experienced diarrhea...

Repeat After Me... What's the problem here? | Case Study
A homeless man is brought to the ER by the local police after he is found sitting at a bus stop with a bloody rag pressed to his left knee. The temperature...

Wild Mood Swings and Outbursts of Anger: What's Wrong with this M…
A new case study in which the patient, a 50-yr-old male of mixed race visits his primary care physician with concerns about wild mood swings and outbursts of...


Case Study: Does this Cherokee Woman Have Dementia?
An 85-yr-old Cherokee woman living in a skilled nursing facility has lost weight since admission and won’t socialize or join in activities. She won't...

Case Study: It's a Lump, but is it Breast Cancer?
I am so excited about this Case Study because I feel it will be useful to so many of you! Welcome to a new Case Study in which the patient, a 45-yr-old, white,...

Case Study: Newborn with Vomiting and Diarrhea
A three-day old male infant is brought to the ER by his 22-yr-old mother with vomiting and diarrhea. Diagnostic results will be released upon request, with the...

Case Study: Joint Pain, Rash, Hair Loss - What's Going On?
A new case study in which R.W. presents to her PCP with a cough, mild fever, joint stiffness and pain and a history of rashes, anemia and hair loss.

Case Study: An OB Catastrophe
The following is a case simulation involving a patient initially encountered in Labor and Delivery. While the initial encounter occurred in a specific setting,...

Differential Case Study: Lyme Disease or Covid-19?
Lakeith, a 35-year-old black man living in New York State, presents with a fever of 101 degrees F. He is concerned he might have contracted Covid-19. Based upon...

Case Study: Sudden Severe Pain
A new case study in which the patient, D.C., a 52-year-old, white, married college professor wakes up to severe and intensifying pain. Though the coronavirus...

Case Study: Unexplained Bruises
Karen brings her daughter, Ann into the pediatric clinic stating, "She's just been so tired lately. All she wants to do is sleep and she’s got no appetite....

Case Study: What's Causing This Cough?
A new case study in which the patient, H.T. an 82-year-old Hispanic man presents to his primary care clinic with cough, malaise and confusion. How well do you...

Case Study(CSI): Stomach flu? Anxiety? What's Going on Here?
A new case study in which the patient, A.W. a 65-year-old African American woman presents to her primary care clinic with unspecified complaints. She told the...

Case Study: I'm too tired to walk the dog...
A new case study in which the patient, T.K. a 51-year-old woman who has finally taken a staycation, doesn’t have enough energy to walk her dog. You’re the...

Case Study: My Stomach Hurts
It's late in the day on a beautiful Saturday in late summer. You are finishing up your shift at a local urgent care clinic when a 28-year-old, white male comes...

Case Study: Trust Your Gut? A Fecal Transplant Could Change Your L…
Fecal Microbial Transplant (FMT) is a well-accepted practice for the treatment of C. diff, however in the U.S. it is still typically used only after multiple...

Case Study: Magic Mushrooms as Medicine? Mind-Body Connection Pt. …
Can "tripping" cure depression? Can LSD reduce chronic anxiety? This article explores the use of psychedelics to treat mental illness. Read on to find links for...

Case Study: Does Childhood Abuse Prevent Weight Loss? Pt. 2
This is an important topic for nurses. We need to understand the connection between childhood trauma and mind/body issues to build trust with patients and...

Nursing Case Study Examples and Solutions
- Premium Academia
- August 17, 2023
- Nursing Essay Examples
NursingStudy.org is your ultimate resource for nursing case study examples and solutions. Whether you’re a nursing student, a seasoned nurse looking to enhance your skills, or a healthcare professional seeking in-depth case studies, our comprehensive collection has got you covered. Explore our extensive category of nursing case study examples and solutions to gain valuable insights, improve your critical thinking abilities, and enhance your overall clinical knowledge.
Comprehensive Nursing Case Studies
Discover a wide range of comprehensive nursing case study examples and solutions that cover various medical specialties and scenarios. These meticulously crafted case studies offer real-life patient scenarios, providing you with a deeper understanding of nursing practices and clinical decision-making processes. Each case study presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for learning, making them an invaluable resource for nursing education and professional development.
- Nursing Case Study Analysis [10 Examples & How-To Guides] What is a case study analysis? A case study analysis is a detailed examination of a specific real-world situation or event. It is typically used in business or nursing school to help students learn how to analyze complex problems and make decisions based on limited information.
- State three nursing diagnoses using taxonomy of North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) that are appropriate, formatted correctly, prioritized, and are based on the case study. NUR 403 Week 2 Individual Assignment Case Study comprises: Resources: The case study found on p. 131 in Nursing Theory and the Case Study Grid on the Materials page of the student website Complete the Case Study Grid. List five factors of patient history that demonstrates nursing needs.
- Neuro Case Study
- Endocrine Case Study
- Anxiety & Depression Case Study
- Ethical dilemma
- A Puerto Rican Woman With Comorbid Addiction
- Tina Jones Comprehensive SOAP Note
- Insomnia 31 year old Male
- Chest Pain Assessment
Pediatric Nursing Case Studies

In this section, delve into the world of pediatric nursing through our engaging and informative case studies. Gain valuable insights into caring for infants, children, and adolescents, as you explore the complexities of pediatric healthcare. Our pediatric nursing case studies highlight common pediatric conditions, ethical dilemmas, and evidence-based interventions, enabling you to enhance your pediatric nursing skills and deliver optimal care to young patients.
- Case on Pediatrics : Part 1& 2 Solutions
- Pediatric Infant Reflux : History and Physical – Assignment 1 Solution
- Otitis Media Pediatrics Toddler – NSG 5441 Reflection Assignment/Discussion – Solution
- Pediatric Patient With Strep – NSG 5441 Reflection Assignment/Discussion
- Pediatric Urinary Tract infections (UTI) -NSG 5441 Reflection Assignment/Discussion – Solution
- Week 3 discussion-Practical Application in critical care/pediatrics
- Cough Assessmen t
Mental Health Nursing Case Study Examples
Mental health nursing plays a crucial role in promoting emotional well-being and providing care for individuals with mental health conditions. Immerse yourself in our mental health nursing case studies, which encompass a wide range of psychiatric disorders, therapeutic approaches, and psychosocial interventions. These case studies offer a holistic view of mental health nursing, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to support individuals on their journey to recovery.
- Psychiatric Nursing: Roles and Importance in Providing Mental Health Care
- Mental Health Access and Gun Violence Prevention
- Fundamentals of neurotransmission as it relates to prescribing psychotropic medications for clients with acute and chronic mental health conditions – Unit 8 Discussion – Reflection
- Unit 7 Discussion- Complementary and Alternative Medicine in Mental Health Care – Solution
- Ethical and Legal Foundations of PMHNP Care Across the Lifespan Assignment – Analyze salient ethical and legal issues in psychiatric-mental health practice | Solution
- Pathways Mental Health Case Study – Review evaluation and management documentation for a patient and perform a crosswalk of codes – Solution
- Analyze salient ethical and legal issues in psychiatric-mental health practice
- SOAP notes for Mental Health Examples
- compare and contrast two mental health theories
- Environmental Factors and Health Promotion Presentation: Accident Prevention and Safety Promotion for Parents and Caregivers of Infants
Geriatric Nursing Case Studies
As the population ages, the demand for geriatric nursing expertise continues to rise. Our geriatric nursing case studies focus on the unique challenges faced by older adults, such as chronic illnesses, cognitive impairments, and end-of-life care. By exploring these case studies, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of geriatric nursing principles, evidence-based gerontological interventions, and strategies for promoting optimal health and well-being in older adults.
- M5 Assignment: Elderly Driver
- HE003: Delivery of Services – Emmanuel is 55-year-old man Case – With Solution The Extent of Evidence-Based Data for Proposed Interventions – Sample Assignment 1 Solution
- Planning Model for Population Health Management Veterans Diagnosed with Non cancerous chronic pain – Part 1 & 2 Solutions
- PHI 413 Case Study Fetal Abnormality Essay
- Insomnia Response and Insomnia
- Analysis of a Pertinent Healthcare Issue: Short Staffing
- Paraphrenia as a Side of the Schizophrenia – Week 4 Solution
- Module 6 Pharm Assignment: Special Populations
- Public Health Nursing Roles and Responsibilities in Disaster Response – Assignment 2 Solution
- Theory Guided Practice – Assignment 2 Solution
- How can healthcare facilities establish a culture of safety – Solution
- Discuss the types of consideration a nurse must be mindful of while performing a health assessment on a geriatric patient as compared to a middle-aged adult – Solution
- Promoting And Protecting Vulnerable Populations – Describe what is meant by vulnerable populations and explain strategies you, as the public health nurse, could use to best facilitate the achievement of healthful outcomes in this population?
Community Health Nursing Case Studies
Community health nursing plays a vital role in promoting health, preventing diseases, and advocating for underserved populations. Dive into our collection of community health nursing case studies, which explore diverse community settings, public health issues, and population-specific challenges. Through these case studies, you’ll gain insights into the role of community health nurses, interdisciplinary collaboration, health promotion strategies, and disease prevention initiatives.
- Community and Target Aggregate: Residents of the community health center, particularly those aged 65 and above Topic: Secondary Prevention/Screenings for a Vulnerable Population
- Tools For Community Health Nursing Practice2
- 5 Theories in Community Health Nursing: A Complete Guide
- Role of community health nursing and community partnerships as they apply to the participating family’s community – Assignment 1 Solution
- Community/Public Health Nursing DQ2
- CSU-Community healthcare Presentation – Assignment 1 Solution
- Community Healthcare Presentation – Domestic Violence And Level Of Prevention – Solution
Critical Care Nursing Case Study Examples
Critical care nursing demands swift decision-making, advanced technical skills, and the ability to provide intensive care to acutely ill patients. Our critical care nursing case studies encompass a range of high-acuity scenarios, including trauma, cardiac emergencies, and respiratory distress. These case studies simulate the fast-paced critical care environment, enabling you to sharpen your critical thinking skills, enhance your clinical judgment, and deliver exceptional care to critically ill patients.
- Nursing Case Study Parkinsons Disease
- Nursing Case Study: Patient with Drug and Alcohol Induced Paranoid Schizophrenia
- Neonatal Hypothermia and Neonatal Sepsis: Nursing Case Study
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Nursing Case Study
Maternal and Child Health Nursing Case Study Examples
The field of maternal and child health nursing requires specialized knowledge and skills to support the health and well-being of women and children throughout their lifespan. Explore our collection of maternal and child health nursing case studies, which encompass prenatal care, labor and delivery, postpartum care, and pediatric nursing. These case studies provide a comprehensive view of maternal and child health, allowing you to develop expertise in this essential area of nursing practice.
You can also check out Patient Safety in High-Tech Settings PICOT Questions Examples
Surgical Nursing Case Studies
Surgical nursing involves caring for patients before, during, and after surgical procedures. Our surgical nursing case studies cover a wide range of surgical specialties, including orthopedics, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal surgeries. Delve into these case studies to gain insights into preoperative assessment, perioperative management, and postoperative care. By examining real-life surgical scenarios, you’ll develop a comprehensive understanding of surgical nursing principles and refine your skills in providing exceptional care to surgical patients.
- Discuss DI in relation to a postoperative neurosurgical patient – Week 2, 3, 4 Solution
- DISCUSSION WK 3
- Career Planning & Professional Identity Paper
- N ursing Case Analysis
- Ethical Dilemma on Robotic Surgery and ACS Codes of Ethics – Post 2
- NURS – 6521C Advanced Pharmacology
- Essay on Alterations in Neurological and Endocrine Functions
- Clinical Preparation Tool – Child and Adolescent Symptom Inventory – Unit
- Initial Psychiatric Interview/SOAP Note – Assignment 1 Solution
- Current Trends in Nursing Practice: Electronic Prescriptions for Opioids – Week 4 Solution
- Nurse-Sensitive Indicators -Week 3 Solution
- Theory–Practice Gap in Jean Watson Theory of Human Caring – Assignment 1 Solution
- Bowel Obstruction Case Video Presentation – Week 4 Solution
- Appendicitis SOAP Note – Sample SOAP Solution 1
- Week 4: GERD SOAP Note Assignment Solution
Obstetric Nursing Case Study
Obstetric nursing focuses on providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Our obstetric nursing case studies explore various aspects of prenatal care, labor and delivery, and postpartum recovery. Gain valuable knowledge about common obstetric complications, evidence-based interventions, and strategies for promoting maternal and fetal well-being. These case studies will enhance your obstetric nursing skills and prepare you to deliver compassionate and competent care to expectant mothers.
- Capstone Proposal: Postpartum Hemorrhage Education To Nursing Students
- Progress Evaluation Telecommunication: Teleconference on Post-Partum Hemorrhage
- Case Study 5.2 the Moral and Ethical Questions of Aborting an Anencephalic Baby
- Holistic intervention plan design to improve the quality of outcomes – Problem Statement (PICOT)
- ADV HEALTH ASSESSMENT: TJ a 32-year-old pregnant lesbian, is being seen for an annual physical exam and has been having vaginal discharge – Solution
- Facilitative Communication and Helping Skills in Nursing & Decision Making Assignment Solution
- Benchmark – Evidence-Based Practice Proposal Paper Example
- Three nursing diagnoses for this client based on the health history and screening (one actual nursing diagnosis, one wellness nursing diagnosis, and one “risk for” nursing diagnosis)
- Identify two or more issues with the existing system
- Differences between inpatient and outpatient coding
Nursing Ethics Case Study
Ethical dilemmas are an inherent part of nursing practice. Our nursing ethics case studies shed light on complex ethical issues that nurses encounter in their daily work. Explore thought-provoking scenarios involving patient autonomy, confidentiality, end-of-life decisions, and resource allocation. By examining these case studies, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of ethical principles, ethical decision-making frameworks, and strategies for navigating ethical challenges in nursing practice.
- Ethics in Complementary Therapies
- Ethics Case Study Analysis
- Ethics in Practice
- Ethical Dilemma on Robotic Surgery and ACS Codes of Ethics – Post 1
- Case Study on Biomedical Ethics in the Christian Narrative
- Academic Success and Professional Development Plan Part 2: Strategies to Promote Academic Integrity and Professional Ethics
- Week 9 Assignment 9.1: Mercy Killing Ethics – Using one theory that you have studied that you agree with and one theory that you disagree with, describe how Officer Jones would act in each case – Solution
- Deliverable 4 – Code of Ethics Intake Packet
- Ethics in the Workplace
- code of ethics for nurses
- Applying the ANA Code of Ethics
Health Promotion Case Study
Community health promotion plays a crucial role in improving the health and well-being of populations. Our community health promotion case studies highlight successful initiatives aimed at preventing diseases, promoting healthy lifestyles, and addressing social determinants of health. Explore strategies for community engagement, health education, and collaborative interventions that make a positive impact on the well-being of individuals and communities.
- Health Promotion in Minority Populations
- Environmental Factors and Health Promotion Presentation: Accident Prevention and Safety Promotion for Parents and Caregivers of Infants
- Health Education And Current Challenges For Family-Centered Health Promotion
- Cultural Competence And Nutrition In Health Promotion
- Why is the concept of family health important? Consider the various strategies for health promotion.
- levels of health promotion
- Integrate evidence from research and theory into discussions of practice competencies, health promotion and disease prevention strategies, quality improvement, and safety standards.
- Discuss various theories of health promotion, including Pender’s Health Promotion Model, the Health Belief Model, the Transtheoretical Theory, and the Theory of Reasoned Action.
- What strategies, besides the use of learning styles, can a nurse educator consider when developing tailored individual care plans, or for educational programs in health promotion?
- Describe health promotion for Pregnant women
- Identify a health problem or need for health promotion for a particular stage in the life span of a population from a specific culture in your area. Choose one of the Leading Health Indicators (LHI) priorities from Healthy People 2020: https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/Leading-Health-Indicators
- A description of a borrowed theory (expectancy-value theory and social cognitive theory) that could be applied to improve health promotion patient education in primary care clinic. Is this borrowed theory appropriate?
- How has health promotion changed over time
- Primary Prevention/Health Promotion
- Health Risk Assessment and Health Promotion Contract
Nursing Leadership Case Studies
Nursing leadership is essential for driving positive change and ensuring high-quality patient care. Our nursing leadership case studies examine effective leadership strategies, change management initiatives, and interprofessional collaboration in healthcare settings. Gain insights into the qualities of successful nurse leaders, explore innovative approaches to leadership, and learn how to inspire and motivate your team to achieve excellence in nursing practice.
- Part 3: Nursing Leadership – Childbearing after menopause – Assignment Solution
- Capstone Project Ideas for Nursing Leadership
- The purpose of this assignment is to examine the impact of contemporary challenges in care delivery facing nursing leadership. Select and research a major issue in the delivery of care facing nurse leaders today and write a 1,250-1,500 word paper addressing the following:
- One nursing theory will be presented as a framework to resolve a problem occurring within one of the professional areas of leadership, education, informatics, healthcare policy or advance clinical practice. The same nursing theory selected in Assignment One may be used to resolve the identified problem.
- Module 6: Change and Leadership in Nursing Education – Professional Development
- Module 6: Change and Leadership in Nursing Education – Critical Thinking
- Module 6: Change and Leadership in Nursing Education – Discussion
- Analyze one of the following concepts: “Advanced Practice Nursing,” “Leadership in Nursing Practice” or “Holistic Nursing Practice”
- Nursing Administration Function: A Comprehensive Guide for Nursing Students
- Theory and Leadership
- NUR-514: Organizational Leadership and Informatics
- Leadership: Workplace Environment Assessment
- Professional Development in Nursing – Topic 3 Assignment Solution
- Leadership Change Framework – Week 8 Assignment Solution
At NursingStudy.org, we strive to provide you with a comprehensive collection of nursing case study examples and solutions that align with the best practices recommended by YOAST and RankMath. By exploring these diverse case studies, you’ll enhance your clinical knowledge, critical thinking abilities, and overall understanding of nursing practice. Take advantage of this valuable resource and elevate your nursing skills to new heights.
Remember, success in nursing begins with knowledge and continues with lifelong learning. Explore our nursing case study examples and solutions today and embark on a journey of professional growth and excellence.
Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, what you'll learn.
- Nursing Paper Examples
Related Posts
- Personal Philosophy Statement Example for a PMHNP
- Leadership Strategies for Success-Nursing Paper Examples
- Applying the Scientific Method-Nursing Paper Examples
Important Links
Knowledge base, paper examples, nursing writing services.
Nursingstudy.org helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Phone: +1 628 261 0844
Mail: [email protected]

We Accept:

@2015-2024, Nursingstudy.org

How to Write a Case Study Paper for Nursing
A well-written case study paper for a nursing program requires some planning and consideration. All too often, students begin writing before they complete appropriate, preliminary steps. Ideally, before you start a paper, you should already have determined the focus and format of it. You will then follow this up with a fact-gathering step in which you will gather and collate the content of your paper. Finally, there is the construction/execution step in which you will write the paper in a standard format (such as the APA style) and edit it.
A nursing case study paper contains several sections that fall into three categories:
1. The status of the patient
- Demographic data
- Medical History
- Current diagnosis and treatment
2. The nursing assessment of the patient
- Vital signs and test results
- Nursing observations (i.e., range of motion, mental state)
3. Current Care Plan and Recommendations
- Details of the nursing care plan (including nursing goals and interventions)
- Evaluation of the current care plan
- Recommendations for changes in the current care plan
Patient Status
The first portion of the case study paper will talk about the patient — who they are, why they are being included in the study, their demographic data (i.e., age, race), the reason(s) they sought medical attention and the subsequent diagnosis. It will also discuss the role that nursing plays in the care of this patient.
Next, thoroughly discuss any disease process. Make sure you outline causes, symptoms, observations, and how preferred treatments can affect nursing care. Also, describe the history and progression of the disease. Some important questions for you to answer are: 1) What were the first indications that there was something wrong, and 2) What symptoms convinced the patient to seek help?
Nursing Assessment
When you are discussing the nursing assessment of the patient, describe the patientΓÇÖs problems in terms of nursing diagnoses. Be specific as to why you have identified a particular diagnosis. For example, is frequent urination causing an alteration in the patientΓÇÖs sleep patterns? The nursing diagnoses you identify in your assessment will help form the nursing care plan.
Current Care Plan and Recommendations for Improvement
Describe the nursing care plan and goals, and explain how the nursing care plan improves the quality of the patientΓÇÖs life. What positive changes does the nursing care plan hope to achieve in the patientΓÇÖs life? How will the care plan be executed? Who will be responsible for the delivery of the care plan? What measurable goals will they track to determine the success of the plan?
The final discussion should be your personal recommendations. Based on the current status of the patient, the diagnosis, prognosis, and the nursing care plan, what other actions do you recommend can be taken to improve the patientΓÇÖs chances of recovery? You must support your recommendations with authoritative sources and cite appropriately per APA style guidelines.
Creating a well-written nursing case study paper doesnΓÇÖt need to be a grueling challenge. It can be gratifying, and itΓÇÖs good practice for assessing patients while out in the field, too. Keep in mind that your instructor will not only grade you on the quality of the content of your paper but by how you apply the APA style, as well. If you find that you are spending too much time formatting your paper, consider using formatting software as a helpful tool to ensure accuracy, so you donΓÇÖt lose points on a well-written paper because of some formatting errors.
For more information about APA or MLA formats, contact us today.
David Plaut
David Plaut is the founder of Reference Point Software (RPS). RPS offers a complete suite of easy-to-use formatting template products featuring MLA and APA style templates, freeing up time to focus on substance while ensuring formatting accuracy. 
Reference Point Software is not associated with, endorsed by, or affiliated with the American Psychological Association (APA) or with the Modern Language Association (MLA).
Tags: medical writing tips , nurse writing tips , reference point software
Comments are closed.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Nursing Case Study

For accessible versions of these activities, please refer to our document Step 1: Ask – Accessible Case Studies .
Evidence-Based Practice Copyright © by Various Authors - See Each Chapter Attribution is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

How to Use Unfolding Case Studies as a Clinical Replacement Activity

Keith Rischer – Ph.D., RN, CCRN, CEN
As a nurse with over 35 years of experience who remained in practice as an educator, I’ve witnessed the gap between how nursing is taught and how it is practiced, and I decided to do something about it! Read more…
The Ultimate Solution to Develop Clinical Judgment Skills
KeithRN’s Think Like a Nurse Membership
Access exclusive active learning resources for faculty and students, including KeithRN Case Studies, making it your go-to resource.
Sign up to receive a free KeithRN NextGen Case Study!
Develop clinical judgment skills with this innovative new case study on asthma to prepare your students for nextgen nclex and practice.
" * " indicates required fields
Keith Rischer
A practical strategy to address incivility in nursing education, recommended for you.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.10(9); 2023 Sep
- PMC10415993
A mixed methods study using case studies prepared by nursing students as a clinical practice evaluation tool
Ana maría palmar‐santos.
1 Nursing Department, Faculty of Medicine, Autonomous University of Madrid, Madrid Spain
2 Member of the Nursing and Health Care Research Group of the Health Research Institute “Puerta de Hierro‐Segovia de Arana” (IDIPHISA), Majadahonda Spain
Cristina Oter‐Quintana
Ricardo olmos.
3 Social Psychology and Methodology Department, Faculty of Psychology, Autonomous University of Madrid, Madrid Spain
Azucena Pedraz‐Marcos
4 Health Care Research Unit, Institute of Health Carlos III; Nursing Department, Faculty of Medicine, Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain
Juana Robledo‐Martin
5 Member of the Gregorio Marañon Health Research Institute, IiSGM, Madrid Spain
Associated Data
Data available on request from the authors: The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
To identify the presence of variability in the evaluation of case studies prepared by nursing students during their primary care rotations based on the existing evaluation rubric. To explore the difficulties experienced by link lecturers and students in preparing and evaluating case studies.
A mixed methods study.
The scores for the rubric items and the final grades for the case studies were collected from a sample of 132 cases. Qualitative information was collected by conducting open‐ended interviews with lecturers and a focus group session with students.
Statistically significant differences were identified between the lecturers' mean final grades [ F (5.136) = 3.984, p = 0.002] and a variety of items in the evaluation rubric ( p < 0.05). In addition, effect sizes [ η 2 (≈0.14)] of considerable magnitude were found.
Two themes emerged from the qualitative data: (1). the challenge of preparing the case studies and (2). the variable nature of the evaluations.
1. INTRODUCTION
Clinical training of nursing students is an essential part of the nursing degree curriculum. In the European context, this training is determined by a European Union directive and accounts for ‘at least one half of the minimum duration of the training’. The same directive states that ‘this training shall take place in hospitals and other health institutions and the community, under the responsibility of nursing teachers, in cooperation with and assisted by other qualified nurses’ (Directive 2005/36/EC of the European Parliament, 2005 ). Evaluating skills in a real‐life environment with a multitude of different professionals accompanying the students' learning process poses a challenge for institutions training future nursing professionals (Almalkawi et al., 2018 ; Pramila‐Savukoski et al., 2020 ).
Evaluating the acquisition of clinical practice skills is an ongoing task for clinical mentors that poses a constant challenge (Tuomikoski et al., 2020 ). Although clinical mentors have improved the evaluation procedures and rubrics at their disposal (Stanley et al., 2020 ), they continue to call for greater communication with universities (Bos et al., 2015 ). At most institutions, this continuous evaluation process is supplemented by reflective evaluation in an attempt to measure not only performance but also the thought processes leading to that performance, that is, critical thinking and decision‐making. Various methods and tools have been used for this purpose, including portfolios (Buckley et al., 2009 ), reflective journals (Hwang et al., 2018 ), case scenarios and 360‐degree evaluations (González‐Gil et al., 2020 ) and performance checklist and assessment tests, like in the Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) (Sabzi et al., 2018 ). These methods have all proven effective in evaluating nursing students' clinical practice and are considered not only evaluation tools but also learning tools (Driessen, 2017 ).
2. BACKGROUND
Case studies have been widely used in nursing theory training because they help students to build on the basic knowledge taught and to collect information and analyse it to make diagnoses and support interventions (O'Rourke & Zerwic, 2016 ). In addition, there is considerable research on the use of case studies in simulation settings, which are practical environments where students gain confidence before moving on to clinical practice (Wong & Kowitlawakul, 2020 ). Case studies have been included in OSCEs as part of the final evaluation of skills acquired through clinical practice (Kelly et al., 2016 ) and as tools for learning critical thinking and decision‐making skills in healthcare institutions (Englund, 2020 ). At our university, the students study the nursing process and the standardised nursing languages (North American Nursing Diagnosis Classification (NANDA), Nursing Outcomes Classification (NOC) and Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC)) in the first year. In the second and third years, the students are asked to prepare a clinical case consisting in designing a care plan for a person or a family in their clinical practice unit. The students must develop the different phases of the nursing process: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation and evaluation of their care plan. They must use the standardised nursing languages too. To guide this process, the student is supervised by a link lecturer, who can be an academic lecturer (full lecturer) or a clinical lecturer (assistant lecturer), who combines their teaching work at the university with clinical activity. The grade obtained in the clinical case is part of the overall evaluation of the clinical practice module, which also includes other components such as being assessed by the clinical nurse responsible for mentoring them at the clinical placement and a self‐evaluation component. This kind of summative assessment with several tools used in direct patient care and simulated practice, which are marked using a multi‐level observational rubric, supplemented by self‐evaluation of clinical performance, is in line with the findings of Clemett and Raleigh ( 2021 ) in their systematic review.
Despite the wide use and positive outcomes gained from cases studies, students still feel that the evaluation of their clinical practice varies depending on the clinical nurse mentor, who decides what is relevant in ‘the real world’ and the link lecturer, who, despite being relatively invisible to students during their clinical practice, has a major influence on their final grade (Foster et al., 2015 ; Helminen et al., 2016 ).
3. THE STUDY
The aim of this study is twofold. On the one hand, to identify the presence of variability in the evaluation of case studies prepared by nursing students during their primary care rotations based on a module's existing evaluation rubric. On the other hand, to explore the difficulties experienced by link lecturers and students in preparing and evaluating case studies.
4.1. Design
A mixed methods design was used, analysing the scores given to the case studies during the evaluation and qualitative information on link lecturers' and students' assessments of the evaluation process.
4.2. Population and sample
The study was carried out during the 7‐week rotation of third‐year students on primary care clinical placements during the 2018–2019 academic year. The study population included 132 students, who prepared a case study during their rotation in primary care, and 6 link lecturers, who assessed their case studies. Each case study was evaluated by the link lecturer responsible for monitoring that student during the clinical practices in that period. During the 2018–2019 academic year, evaluation of the primary care case studies was undertaken by six link lecturers.
4.3. Data collection
Data were collected in the following ways: the scores awarded to the 132 case studies by the various link lecturers, a focus group session with the participating students and in‐depth interviews with the lecturers involved in their evaluation.
Data were collected on the following variables: the link lecturer responsible for evaluating each student, the final grade for each student's case and the grades awarded to each of the items in the evaluation rubric. This rubric (see Annex 1 ) is the tool usually used by link lecturers to correct clinical cases. This evaluation tool was developed by a group of nursing professors with extensive experience in the preparation of clinical cases but has not been subjected to a formal validation process.
Four of the six link lecturers were interviewed since two of the link lecturers had participated in the development of the research project and their participation in the interviews was not considered appropriate. Of the four link lecturers interviewed: one was an academic lecturer (full lecturer) and three were clinical lecturers (who combine clinical care with teaching). An interview script covering the following topics was used: experience in evaluating case studies; the influence of the aspects they value most and least on the grades they award; difficulties in using the rubric and recommendations for improvement (see Annex 2 ). The interviews lasted between 40 and 60 min and took place in a space chosen by each participant. They were audio‐recorded and then transcribed for analysis.
Students with the highest and lowest grades in the case study were invited to participate in a focus group session. To ensure the heterogeneity of the group, students evaluated by different link lecturers were represented. For the focus group session, a thematic script was created, addressing aspects relating to the preparation of students' case studies during their clinical placements and recommendations for improvement (see Annex 3 ). Five students participated in the focus group, which was led by a moderator accompanied by an observer who took notes during the development of the session. All students actively participated in the discussion. The focus group session lasted 90 min and was audio‐recorded and transcribed for subsequent analysis, after obtaining informed consent from all participants.
4.4. Data analysis
The data from the case study evaluation were statistically analysed to assess any differences between link lecturers in the final grade they awarded to each case study and the grades they awarded to each of the items in the evaluation rubric. To analyse the data, a between‐subjects one‐factor ANOVA model was used (one lecturer representing one factor) using the total score given by the lecturer (the sum of all the rubric items) and each rubric item separately as the dependent variable. This was used to assess whether the average scores differed. Pairwise comparisons of lecturers were performed to establish whether lecturers differed in the average scores awarded using Tukey's method (controlling for the type I error rate). The statistical significance threshold for all analyses was set at 0.05. In addition, the assumptions of normality and homoscedasticity were fulfilled for the dependent variables. Normality was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The assumption of homoscedasticity was assessed using Levene's test. When the assumption of the equality of variances was not met, Welch's corrected F ‐statistic was used. The non‐parametric Kruskal–Wallis test was also used to analyse whether the results were sensitive to the statistical model. The data were analysed using SPSS (version 25) software from IBM.
The qualitative data from the interviews and focus group sessions were analysed thematically using Braun and Clarke method ( 2006 ). All authors read and underlined the interview and focus group transcripts to familiarise themselves with the data and to identify the first emerging codes. At a series of analytical meetings, the authors identified potential themes by clustering the codes and created a relationship map to refine and link the themes found. This refinement of the themes led to the final report, which included quotes from participants and analytical notes on each theme.
4.5. Ethical considerations
This study is part of a teaching innovation project entitled ‘Strategies for harmonising clinical practice evaluation standards’, approved by the Autonomous University of Madrid Teaching Innovation Ethical Committee, involving internal and external evaluators, with reference number M_015.18_INN.
All individuals involved in the study participated voluntarily, were informed about the study objectives and signed an informed consent form. Students were assured that their participation would have no impact on their grades. To this end, double anonymisation was carried out at the time of recruitment and during transcription.
A total of 132 case study evaluations were collected from 6 lecturers, with the number of cases evaluated by each lecturer ranging between 18 and 26 (see Table 1 ).
Means, standard deviations and number of students ( N ) per lecturer based on final grades and rubric items.
| Lecturer | N | Final grade | Structure selection | Information analysis | Planning | Follow‐up | Final assessment | Literature review | Written communication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 | 7.52 (1.35) | 2.16 (0.63) | 1.34 (0.46) | 1.27 (0.51) | 0.88 (0.27) | 0.89 (0.25) | 0.35 (0.31) | 0.33 (0.18) |
| 2 | 23 | 7.87 (0.92) | 2.30 (0.43) | 1.32 (0.36) | 1.71 (0.32) | 0.87 (0.21) | 0.75 (0.31) | 0.44 (0.11) | 0.50 (0.00) |
| 3 | 26 | 7.83 (1.23) | 2.35 (0.36) | 1.65 (0.30) | 1.52 (0.33) | 0.76 (0.16) | 0.75 (0.14) | 0.40 (0.07) | 0.41 (0.06) |
| 4 | 22 | 7.21 (1.24) | 2.34 (0.61) | 1.31 (0.31) | 1.57 (1.48) | 0.71 (0.23) | 0.72 (0.19) | 0.29 (0.19) | 0.45 (0.06) |
| 5 | 18 | 7.90 (1.07) | 2.45 (0.36) | 1.56 (0.21) | 1.58 (0.21) | 0.79 (0.13) | 0.74 (0.22) | 0.38 (0.06) | 0.40 (0.06) |
| 6 | 22 | 8.66 (0.95) | 2.48 (0.37) | 1.74 (0.26) | 1.75 (0.25) | 0.95 (0.10) | 0.85(0.16) | 0.45 (0.11) | 0.45 (0.08) |
| Total | 132 | 7.83 (1.23) | 2.34 (0.48) | 1.49 (0.36) | 1.57 (0.69) | 0.83 (0.21) | 0.78 (0.22) | 0.39 (0.14) | 0.43 (0.10) |
Table 2 shows the results comparing the means of the six lecturers. The results of the parametric ANOVA model and the non‐parametric Kruskal–Wallis model are also provided, with a sensitivity analysis performed in consideration of the fact that the assumptions required by the ANOVA are not always met. The results suggest that the two statistical models are robust and consistent with one another. In virtually all items of the rubric (in addition to the final grade), there are statistically significant differences in the mean grades awarded between the lecturers. The items in which significant differences were identified between the lecturers using both statistical models were information analysis, planning, follow‐up of the individual's progress and written communication. In the final assessment and literature review, differences were detected only in the non‐parametric test. Furthermore, in the final grade, the effect size measure, η 2 , exhibited a considerable magnitude according to Cohen's criteria ( 1988 , ps. 280–287), where 0.01, 0.07 and 0.14 are set as criteria for weak, moderate and strong effect sizes respectively. Table 2 shows that in four of the eight items evaluated, the effect size was high.
Significance of ANOVA tests based on final grades and rubric items.
| Final grade | Structure selection | Information analysis | Planning | Follow‐up | Final assessment | Literature review | Written communication | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One‐way ANOVA (lecturer) | |||||||||
| (5.136) = 3.984 = 0.002 = 0.137 | (5.126) = 1.392 = 0.232 = 0.052 | (5.58) = 7.914 < 0.001 = 0.228 | (5.58) = 3.791 = 0.005 = 0.039 | (5.57) = 7.968 < 0.001 = 0.155 | (5.126) = 2.325 = 0.055 = 0.078 | (5.54) = 1.801 = 0.128 = 0.073 | (5.126) = 9.186 < 0.001 = 0.267 | ||
| Kruskal–Wallis test | |||||||||
| (5) = 17.069 = 0.004 | (5) = 7.083 = 0.215 | (5) = 29.969 < 0.001 | (5) = 23.925 < 0.001 | (5) = 34.480 0.001 | (5) = 20.289 = 0.001 | (5) = 14.983 = 0.010 | (5) = 44.271 < 0.001 |
Note: Bold values indicate the statistical significance of p < 0.05.
Pairwise comparisons between all lecturers were also assessed and one lecturer was found to differ significantly from two other lecturers ( p < 0.05). Lecturer 6, in particular, awarded significantly higher averages than lecturers 1 and 4 (see Table 1 ). Finally, the six lecturers were grouped into two categories according to their job category (academic lecturer or clinical lecturer) in order to analyse whether academic and clinical lecturers used the rubric differently. The T ‐test for independent samples was used to compare the averages. The results showed no significant differences in any of the items analysed or in the total, except for written communication. In this item, the group of academic lecturers ( M = 0.38, SD = 0.12) awarded significantly lower average scores than the group of clinical lecturers ( M = 0.47, SD = 0.06): T (93) = 5.281, p < 0.001.
Regarding the qualitative phase of the study, the thematic analysis of the discourses from the interviews with the link lecturers and the focus group with the students generated two core categories:
- The challenge of preparing the case study
- The variable nature of the evaluations
5.1. The challenge of preparing the case study
The link lecturers participating in the study viewed case studies as an opportunity to integrate theory and practice. However, they highlighted students' difficulties in incorporating theory into the case they are working on. They also pointed out that students tended to focus their attention on the physical problems of the people they care for. They stressed that a reductionist, superficial nursing assessment will not lead to a deep understanding of the social and emotional problems of the individual under their care.
The link lecturers participating in the study explained that the limitations of the case study were due, on the one hand, to the incorporation of the nursing process into the computer system, which simplifies the approach of a comprehensive vision of said process, and on the other hand, to the internalisation of care models that fail to take a holistic view of the individual by nursing students during their placements.
So, I think that this may be influencing a lot […] that they are influenced a lot by the computer systems, which, in some way, shape how you think, or your own mentalization. But, sometimes, what I am seeing is that there are students who do not go further. (E1)
(They are preparing) a case with a mentor, who almost always has a hospital background, who is not teaching them a holistic approach to patients. (E4)
During the focus group, the students stated that the clinical nurse mentors helped them in choosing a patient and support them in preparing their case. However, they pointed out that sometimes the clinical nurse mentors failed to fully understand the work they must carry out, even questioning the practicality of this type of exercise for their future professional practice.
I've even heard that. They [clinical nurse mentors] say “but this is a waste of time, you're never going to do this…” If the person who is above you, so to speak, comes to you and says: “don't do that, it's nonsense” or “it's no use”, they're not exactly going to be of much help. (FG)
In the focus group, the students identified the lack of precise, uniform instructions from all link lecturers as to the structure and basic contents of the case study as one of the main difficulties involved in the process. This prompts them to prioritise the creation of their own case study, ‘the model case study’, for which they resort to the following: 1. reviewing learning materials from previous modules in their academic training; 2. using available bibliographic resources; and 3. compiling case studies carried out by colleagues or by themselves that have already been corrected. The students expressed that they felt that some of the instructions provided by link lecturers were contradictory and wondered whether those instructions reflect personal inclinations rather than academic criteria.
The link lecturers who participated in the study also pointed to the lack of a precise, standardised structure and content as particularly problematic when it came to helping them guide the student in the development of the clinical case. They considered that the fact that the students could receive different indications from each link lecturer contributed to generating confusion among them.
Yes, I see the fact that you can have a tutor every year as an inconvenience, […]each tutor asks you really one thing. Maybe it's not worth it, even if it's well done, it's not worth it, because they wants… "No, I don't want this, I want you to develop this pattern more for me", "I don't like this, remove it" , and then, suddenly, the following year, or in the following practice, you get another one, and it's the other way around, they likes what you had done at the beginning better. (FG)
I really don't think the problem is that students aren't trying hard enough, it's that they're quite disoriented. We're giving them different instructions if you like. (E2)
During the focus group, the students complained that case studies were expected to meet certain requirements without considering the reality in which they carry out their clinical placements, such as requiring the case study to be carried out in a home environment or demanding that the care plan designed to be put into practice. This last point is also noted by the interviewed link lecturers.
The students and link lecturers mentioned that they sometimes resorted to ‘embellishing’ the real case study with fictitious content as a way of fulfilling the requirements, or to taking more simplistic approaches enabling them to obtain results in the short term.
I understand that the student may have difficulty understanding that we propose a care plan, and an evaluation, above all […], but the evaluation is very difficult, an evaluation in three weeks [the duration of the internship], in primary care. It is that sometimes not even in three weeks is a wound managed, nor is a therapeutic eating plan managed, nor is a grieving coping plan managed, nor do you manage… it is that practically very little. (E4)
But to comply with all the requirements, I think that I personally, in some cases, and I think other people too, end up having to make something up in the end. And just for that, for a good grade, when in reality it's not entirely true. (FG)
5.2. The variable nature of the evaluations
Despite the evaluation rubric, the students participating in the focus group perceived differences in the demands made by different link lecturers. They believed that there was variability in the grading of the cases that was intrinsic to the lecturers themselves and did not reflect the quality of their work. Students felt evaluation discrepancies as ‘unfair’, indicating the need to establish common, precise standards in line with the level of skills to be acquired.
Really, I've had classmates whose cases would have been graded a 9 (by the mentors that I've had), but if I'd handed over my case to their mentor, my case would've got a 5 instead of an 8. That's unacceptable. (FG)
Link lecturers participating in the study viewed the rubric as an instrument that could sometimes ‘constrict’ the evaluation process by requiring a separate grade for each item, overlooking the fact that the final grade was based on the overall quality of the student's work rather than on the sum of the individual parts of the rubric.
The rubric (…) was a bit constricting, I mean, it didn't allow me (…) to be consistent with my impressions after evaluating the student and after adjusting the items to the main dimensions of the rubric. (E2)
The link lecturers reported that the tool displays a central tendency in grades, causing difficulties in the evaluation of the case studies when it comes to minimum and maximum grades. They also believed that there were items in the rubric that needed to be changed and that, in order to reduce variability, certain adjectives should be more specific, for example, ‘complete’, ‘consistent’ and ‘appropriate’. They argued that the fact that not all link lecturers were experts in nursing methodology, and evaluation strategies resulted in the rubric not being used properly or in each link lecturer using it ‘in their own way’ in the evaluation process.
Each of us evaluators evaluate in a different way, from a different perspective. I think we try to do it in the same way, but we end up doing it in a different way. We all have different professional experience, or different academic experience (…). Each one of us might add a different nuance to it. (E3)
Link lecturers also mentioned that students failed to take on board their recommendations for improvement, partly due to discrepancies as to what was considered relevant in each case study.
6. DISCUSSION
The results of our study suggest that, despite the availability of a rubric for evaluating case studies, there are statistically significant differences in the mean grades given by the sample of lecturers. This echoes the findings of previous studies suggesting that, although the availability of rubrics reduces between‐lecturer variability, rubrics fail to eliminate all differences attributable to lecturer idiosyncrasies (Bearman & Ajjawi, 2021 ).
The benefits of using rubrics include the possibility of directing students' efforts towards core aspects of learning. When teachers' expectations are made explicit to students, they are more likely to be met (Panadero & Jonsson, 2013 ). No mention was made of the utility of the rubric as a ‘guide’ for the learning process by the participating students. Rubrics have been justified in academia as a way of ensuring transparency in evaluation. However, without student participation in their development and use, they provide little support for student learning and evaluation (Bearman & Ajjawi, 2021 ; Kilgour et al., 2020 ).
Case studies have been incorporated into nursing degrees as a tool for learning to apply critical reasoning to nursing diagnoses, outcomes and interventions. Most of the experiences reported refer to the use of case studies designed by teachers and incorporated into clinical practice by students (Popil, 2011 ) or in comparison with other methods, such as simulated patients (Karadag et al., 2016 ). Several studies analysing the development of care plans by students based on real patients highlight the importance of nursing taxonomies (NANDA, NIC and NOC) in incorporating evaluation criteria into the case study objectives and improving nursing interventions of a less technical nature (Palese et al., 2009 ). However, as in our study, students report that nurses working at the healthcare facilities where they are carrying out their clinical placements make marginal use of the nursing methodology. Link lecturers also highlight the biological approach occasionally permeating case studies. Echoing these findings, Türk et al. ( 2013 ) explain the significant presence of physiological diagnoses in care plans made by students based on Benner's Novice to Expert Model. To these authors, the fact that ‘novices’ tend to identify problems of a biological nature results from their limited capacity to understand the situation of the individual being cared for as a whole, to apply critical thinking and to take a holistic approach. It is expected that novices will develop these skills with experience as they become experts. At the same time, identification of psychosocial problems requires a level of communication skill that is not available to students in the early stages of their training.
In our study, students and link lecturers both said that the case study script lacked clarity and specificity. In this sense, students and mentors said that having a follow‐up structure, with specific tasks relating to the preparation of the case study, could be a viable avenue for improvement. This is consistent with a study by Brugnolli et al. ( 2011 ), where students reported that gradual, experiential and guided learning was the most appropriate mentoring tool for their learning process. Palese et al. ( 2008 ) found that students who had received more intensive mentoring in the development of critical thinking skills made fewer errors in the initial formulation of hypotheses in case studies.
Furthermore, in a review by Flott and Linden ( 2016 ), the interaction between mentors and students in clinical practice learning, along with the physical space where learning takes place and the organisational culture, were considered essential components of the clinical learning environment (CLE). Student ‘exposure’ to clinical practice conditions echoes existing findings in the literature regarding the gap between theory and practice. Solutions include greater involvement of link lecturers in the acquisition of clinical skills and experimentation with the realities of practice, as well as a greater presence of clinical mentors in theory training, allowing them to build more meaningful bonds with students (Masterson et al., 2020 ). This is especially relevant in primary care, where the gap between the hospital setting and the academic environment has been highlighted by various authors (Peters et al., 2015 ; Valaitis et al., 2020 ).
Finally, in our study, students and link lecturers feel that they are expected to produce work in accordance with requirements that are far removed from the reality of care. The theory taught at educational institutions aims to provide general practice guidelines that may be meaningless when they materialise in the dynamic, changing world of clinical care, causing feelings of frustration and futility (Salifu et al., 2019 ).
6.1. Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, for the exploration of the difficulties expressed by the students, only one focus group was conducted with nursing students. This affects the possibility that different student profiles could be represented within the group. Nevertheless, an attempt was made to ensure a certain heterogeneity of the attendees in terms of experiential characteristics considered relevant to the phenomenon under study, such as grades obtained in the clinical case and specific primary health centre of clinical practice. Another limitation of the study is the number of cases evaluated by each teacher, which made it necessary to use non‐parametric tests. It should also be noted that the participants were recruited from a single university institution. This limits transferability to other academic contexts. On the other hand, it should be noted that the rubric used in the elaboration of the clinical cases was developed by a group of expert teachers in this teaching methodology, and has not been subjected to a formal validation process. This prevents knowing the reliability and validity of the instrument to evaluate the clinical cases prepared by the student.
7. CONCLUSION
The use of case studies based on real individuals cared for by students during their practical training as an evaluation tool poses several challenges. Students and link lecturers point out the complexity of the process of preparing a case study and consider that having uniform, clear criteria in line with the reality of clinical settings is essential to facilitate this task. The use of case studies as an evaluation tool requires the availability of rubrics that concisely reflect lecturers' expectations as to the work to be carried out, which can be used by students as a roadmap in preparing their case study.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Acknowledgements.
This study is part of a teaching innovation project entitled ‘Strategies for harmonising clinical practice evaluation standards’, approved by the Autonomous University of Madrid Teaching Innovation Ethical Committee, involving internal and external evaluators, with reference number M_015.18_INN. We would like to thank the students and link lecturers for their collaboration in the study.
Rubric for evaluating case studies.
| Case study | Inadequate <5 | Adequate 5–6 | Good 7–8 | Excellent 9–10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection and structure of the individual's data (3 points) | Selects incomplete information and does not structure it on the basis of a theoretical model or functional health patterns (FHPs) | Selects incomplete information and structures it on the basis of a theoretical nursing model or FHP in a disorganised way | Selects sufficient information and structures it on the basis of a theoretical nursing model or FHP | Selects complete and relevant information, structuring it on the basis of a theoretical nursing model or FHP |
| Data analysis: problem identification and formulation (2 points) | Only 25% of the problems identified are based on the data provided and/or are well described | 50% of the problems identified are based on the data provided and/or are well described | 75% of the problems identified are based on the data provided and are well described | All problems are well identified, analysed and described. |
| Planning (2 points) | Does not set priorities. Selects outcomes and interventions that are not relevant to the patient's problems. Plans inappropriate activities | Does not set priorities. Selects outcomes and interventions that are 50% relevant to the patient's problems Incomplete planning of activities | Sets priorities. Selects outcomes, interventions and activities that are 75% relevant to the patient's problems. Plans an adequate number of activities. | The care plan is comprehensive, consistent and relevant to the patient |
| Follow‐up of the individual's progress (1 point) | Does not make notes on the individual's progress | Incomplete monitoring of the individual's progress | Monitors the individual's progress but fails to propose changes to the care plan | Monitors the individual's progress and proposes changes to the care plan |
| Final assessment (1 point) | Fails to carry out a final assessment | Makes an incomplete assessment of the expected outcomes for the individual | Describes the current status of the outcomes correctly but fails to consider making any changes to the care plan | Analyses the outcomes and makes proposals for improving the care plan |
| Literature review (0.5 points) | Fails to provide references or selects non‐technical references. References do not conform to international standards | Provides references relevant to solving the case but these are insufficient and/or poorly referenced | References are relevant, appropriate and sufficient. Not all of them are well referenced | Includes articles and guidelines supporting evidence‐based practice. References conform to international standards |
| Writing skills (0.5 points) | Disorganised structure. Grammatical errors. Incorrect use of technical language | Organised structure. Makes no grammatical errors, although writing is not very sophisticated. Difficulty in using technical language | Organised structure. Writes and uses technical language correctly | Excellent structure, writing skills and use of professional language. Employs typographical resources that facilitate the understanding of the text |
Interview guide for link lecturers.
| Thematic fields | Questions |
|---|---|
| General experience in evaluating clinical cases | How has your experience been in the assessment of clinical cases in this academic year? |
| Aspects considered in the evaluation of clinical cases | What aspects do you value most in a clinical case? How do these positive aspects influence the marks? What aspects do you value most negatively in a clinical case? How do these negative aspects influence the marking? |
| Tools used in the evaluation of the clinical cases. | What tools do you use to correct the clinical case? What difficulties do you encounter in using the rubric to correct the clinical case? What do you do in those situations? How do you think the available rubric could be improved? |
Focus group guide.
| Thematic fields | Questions |
|---|---|
| Elaboration of the clinical case | Could you talk about how is the process that you follow for the elaboration of the clinical case? What resources do you use to make it? What difficulties do you encounter when making it? How do you think they could be fixed? How do the clinical tutors participate in the elaboration of the clinical case? |
| Evaluation of the clinical case | What has been your experience in relation to the evaluation of your clinical case? What do you think about the clinical case evaluation rubric? Have you had discrepancies with the evaluation report of your clinical case? What have these been? How were they resolved? How do you think the difficulties encountered could be better overcome? What do you think is positive about the evaluation process? |
Palmar‐Santos, A. M. , Oter‐Quintana, C. , Olmos, R. , Pedraz‐Marcos, A. , & Robledo‐Martin, J. (2023). A mixed methods study using case studies prepared by nursing students as a clinical practice evaluation tool . Nursing Open , 10 , 6592–6601. 10.1002/nop2.1919 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
- Almalkawi, I. , Jester, R. , & Terry, L. (2018). Exploring mentors' interpretation of terminology and levels of competence when assessing nursing students: An integrative review . Nurse Education Today , 69 , 95–103. 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.07.003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bearman, M. , & Ajjawi, R. (2021). Can a rubric do more than be transparent? Invitation as a new metaphor for assessment criteria . Studies in Higher Education , 46 , 359–368. 10.1080/03075079.2019.1637842 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bos, E. , Silén, C. , & Kaila, P. (2015). Clinical supervision in primary health care; experiences of district nurses as clinical supervisors – a qualitative study . BMC Nursing , 14 , 39. 10.1186/s12912-015-0089-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braun, V. , & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 ( 2 ), 77–101. 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brugnolli, A. , Perli, S. , Viviani, D. , & Saiani, L. (2011). Nursing students' perceptions of tutorial strategies during clinical learning instruction: A descriptive study . Nurse Education Today , 31 ( 2 ), 152–156. 10.1016/j.nedt.2010.05.008 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buckley, S. , Coleman, J. , Davison, I. , Khan, K. S. , Zamora, J. , Malick, S. , Morley, D. , Pollard, D. , Ashcroft, T. , Popovic, C. , & Sayers, J. (2009). The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: A best evidence medical education (BEME) systematic review. BEME guide No. 11 . Medical Teacher , 31 ( 4 ), 282–298. 10.1080/0142159090288989 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clemett, V. J. , & Raleigh, M. (2021). The validity and reliability of clinical judgement and decision‐making skills assessment in nursing: A systematic literature review . Nurse Education Today , 102 , 104885. 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104885 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2 nd ed.). LEA. [ Google Scholar ]
- Directive 2005/36/EC of the European Parliament . (2005). And of the Council of 7 September . On the recognition of professional qualifications. Official Journal of the European Union, 22–142.
- Driessen, G. (2017). The validity of educational disadvantage policy indicators . Educational Policy Analysis and Strategic Research , 12 ( 2 ), 93–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Englund, H. (2020). Using unfolding case studies to develop critical thinking skills in baccalaureate nursing students: A pilot study . Nurse Education Today , 93 , 104542. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104542 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flott, E. A. , & Linden, L. (2016). The clinical learning environment in nursing education: A concept analysis . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 72 ( 3 ), 501–513. 10.1111/jan.12861 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foster, H. , Ooms, A. , & Marks‐Maran, D. (2015). Nursing students' expectations and experiences of mentorship . Nurse Education Today , 35 ( 1 ), 18–24. 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.04.019 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- González‐Gil, M. T. , Parro‐Moreno, A. I. , Oter‐Quintana, C. , González‐Blázquez, C. , Martínez‐Marcos, M. , Casillas‐Santana, M. , Arlandis‐Casanova, A. , & Canalejas‐Pérez, C. (2020). 360‐degree evaluation: Towards a comprehensive, integrated assessment of performance on clinical placement in nursing degrees: A descriptive observational study . Nurse Education Today , 95 , 104594. 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104594 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Helminen, K. , Coco, K. , Johnson, M. , Turunen, H. , & Tossavainen, K. (2016). Summative assessment of clinical practice of student nurses: A review of the literature . International Journal of Nursing Studies , 53 , 308–319. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2015.09.014 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hwang, B. , Choi, H. , Kim, S. , Kim, S. , Ko, H. , & Kim, J. (2018). Facilitating student learning with critical reflective journaling in psychiatric mental health nursing clinical education: A qualitative study . Nurse Education Today , 69 , 159–164. 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.07.015 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karadag, M. , Calıskan, N. , & Iseri, O. (2016). Effects of case studies and simulated patients on Students' nursing care plan . International Journal of Nursing Knowledge , 27 ( 2 ), 87–94. 10.1111/2047-3095.12080 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kelly, M. A. , Mitchell, M. L. , Henderson, A. , Jeffrey, C. A. , Groves, M. , Nulty, D. D. , Glover, P. , & Knight, S. (2016). OSCE best practice guidelines‐applicability for nursing simulations . Advances in Simulation (London, England) , 1 , 10. doi: 10.1186/s41077-016-0014-1 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kilgour, P. , Northcote, M. , Williams, A. , & Kilgour, A. (2020). A plan for the co‐construction and collaborative use of rubrics for student learning . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 45 ( 1 ), 140–153. 10.1080/02602938.2019.1614523 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Masterson, A. , Lee, G. , Khan, E. , Titchener, K. , Doyle‐Blunden, J. , Metcalfe, A. , Tee, S. , & Bliss, J. (2020). Redefining the role of the nurse academic in practice: A pilot study . Nurse Education in Practice , 44 , 102750. 10.1016/j.nepr.2020.102750 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O'Rourke, J. , & Zerwic, J. (2016). Measure of clinical decision‐making abilities of nurse practitioner students . The Journal of Nursing Education , 55 ( 1 ), 18–23. 10.3928/01484834-20151214-06 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palese, A. , De Silvestre, D. , Valoppi, G. , & Tomietto, M. (2009). A 10‐year retrospective study of teaching nursing diagnosis to baccalaureate students in Italy . International Journal of Nursing Terminologies and Classifications : The Official Journal of NANDA International , 20 ( 2 ), 64–75. 10.1111/j.1744-618X.2009.01117.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palese, A. , Saiani, L. , Brugnolli, A. , & Regattin, L. (2008). The impact of tutorial strategies on student nurses' accuracy in diagnostic reasoning in different educational settings: A double pragmatic trial in Italy . International Journal of Nursing Studies , 45 ( 9 ), 1285–1298. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2007.10.003 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panadero, E. , & Jonsson, A. (2013). The use of scoring rubrics for formative assessment purposes revisited: A review . Educational Research Review , 9 , 129–144. 10.1016/j.edurev.2013.01.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peters, K. , McInnes, S. , & Halcomb, E. (2015). Nursing students' experiences of clinical placement in community settings: A qualitative study . Collegian (Royal College of Nursing, Australia) , 22 ( 2 ), 175–181. doi: 10.1016/j.colegn.2015.03.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method . Nurse Education Today , 31 , 204–207. 10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pramila‐Savukoski, S. , Juntunen, J. , Tuomikoski, A. M. , Kääriäinen, M. , Tomietto, M. , Kaučič, B. M. , Filej, B. , Riklikiene, O. , Vizcaya‐Moreno, M. F. , Perez‐Cañaveras, R. M. , De Raeve, P. , & Mikkonen, K. (2020). Mentors' self‐assessed competence in mentoring nursing students in clinical practice: A systematic review of quantitative studies . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 29 ( 5–6 ), 684–705. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15127 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabzi, Z. , Modanloo, M. , Yazdi, K. , Kolagari, S. , & Aryaie, M. (2018). The validity and reliability of the objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) in pre‐internship nursing students . Journal of Research Development in Nursing and Midwifery , 15 ( 1 ), 1–9. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salifu, D. A. , Gross, J. , Salifu, M. A. , & Ninnoni, J. P. K. (2019). Experiences and perceptions of the theory‐practice gap in nursing in a resource‐constrained setting: A qualitative description study . Nursing Open , 6 , 72–83. 10.1002/nop2.188 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanley, D. , Coman, S. , Murdoch, D. , & Stanley, K. (2020). Writing exceptional (specific, student and criterion‐focused) rubrics for nursing studies . Nurse Education in Practice , 49 , 102851. 10.1016/j.nepr.2020.10285 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tuomikoski, A. M. , Ruotsalainen, H. , Mikkonen, K. , & Kääriäinen, M. (2020). Nurses' experiences of their competence at mentoring nursing students during clinical practice: A systematic review of qualitative studies . Nurse Education Today , 85 , 104258. 10.1016/j.nedt.2019.104258 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Türk, G. , Tuğrul, E. , & Sahbaz, M. (2013). Determination of nursing diagnoses used by students in the first clinical practice . International Journal of Nursing Knowledge , 24 ( 3 ), 129–133. 10.1111/j.2047-3095.2013.01243.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valaitis, R. , Gaber, J. , Waters, H. , Lamarche, L. , Oliver, D. , Parascandalo, F. , Schofield, R. , & Dolovich, L. (2020). Health TAPESTRY: Exploring the potential of a nursing student placement within a primary care intervention for community‐dwelling older adults . SAGE Open Nursing , 6 , 2377960820909672. 10.1177/2377960820909672 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong, S. H. V. , & Kowitlawakul, Y. (2020). Exploring perceptions and barriers in developing critical thinking and clinical reasoning of nursing students: A qualitative study . Nurse Education Today , 95 , 104600. 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104600 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

How to Study with CASE STUDIES in Nursing School
Instructors LOVE to use case studies in nursing school, but they can be SUPER tricky to figure out!
They’ll also show up a lot on your nursing exams, where they’ll give you a case scenario question and you’ll have to choose the best answer based on the info they give you.
So I’m going to give you the BEST strategies to help you rock your case studies in nursing school.
HERE’S A BREAKDOWN OF WHAT WE’LL TALK ABOUT:
9 critical thinking questions (0:58)
The nursing process (3:30)
Prioritizing patient needs – ABCs (6:07)
Prioritizing patient needs – Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (7:26)
RELATED VIDEOS
How to CRITICALLY THINK in Nursing School (Your COMPLETE Step-By-Step Guide)
How to Critically Think (Nursing)
Master the Nursing Process (Top Tips)
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (Nursing)
ABC Nursing (Airway Breathing Circulation)
VIDEO TRANSCRIPT
In this video, we’re diving into how to study using CASE STUDIES . Instructors LOVE to use case studies in nursing school. They’ll also show up a lot on your nursing exams, where they’ll give you a case scenario question and you’ll have to choose the best answer based on the info they give you. But they can be SUPER tricky to figure out sometimes! So I’m going to give you the BEST strategies to help you rock your case studies in nursing school. So hit that subscribe button and click the notification bell and let’s dive in.
So the first thing you need to know about case studies in nursing school is that they’re meant to test your critical thinking.
But don’t freak out, critical thinking is a LOT easier than you’re thinking right now. There’s only 2 parts to it:
- Planning ahead
- Connecting the dots
That’s it.
If you want a deep dive into those 2 things, be sure to check out this video here .
Now, I have a list of critical thinking questions that will really help as you’re working on answering your case study questions in nursing school. They will help get you in the mindset of figuring out what’s going on with the patient, and what you need to do about it.
I’ll go through them with you here, but don’t worry, I’ve listed them all out on a free cheat sheet for you that you can print off and use as your work on your homework and case studies in nursing school. The link is in the description below for you to download it.
So these 9 key questions are:
- What do I need to assess and look for with this disorder? (Which includes lab values and signs and symptoms)
- How does this disorder impact a patient without comorbidities? (meaning, this is the ONLY health concern, disorder or disease they have)
- How does this disorder impact a patient WITH comorbidities? (which means, they have ANOTHER health concern, disease or disorder at the same time)
- What interventions are most likely to be ordered by the doctor? What would you expect to see ordered for this patient, including medications and lab draws?
- What interventions are within my scope of practice as a nurse to do without an order? So what can you do as the nurse to help this patient get better, things like position changes and patient education, things like that?
- How do these interventions impact a patient without comorbidities? So how would that medication or position change or other intervention impact the patient and their condition?
- How do these interventions impact a patient with co-morbidities? So ask yourself how that medication or position change or other intervention impact the other illnesses the patient has.
- What patient and family education needs to occur?
- And what other disorders or problems are commonly associated with this disorder?
These critical thinking questions will help guide your critical thinking as you go through your case studies. So be thinking about each of these questions as you answer your case study questions in nursing school.
So now that you’ve elevated your critical thinking skills by using those 9 key critical thinking questions, the next step is to answer your case study questions correctly. Of course, we want to get them all correct, right?
And there are 2 things you should focus your attention on:
- Walking through the nursing process
- Prioritizing patient needs
Let’s start with the nursing process and how to apply it to a case study question.
Often times, your case studies will ask you a series of questions, like:
- What would you do to help the patient improve?
- What would you look for and assess with a particular patient?
These are all questions that relate to the nursing process:
- Implementation
They’ll ask you what you should look for (meaning the nursing assessment), what you should do about it (meaning what interventions and implementation should be done), or what nursing diagnosis or goals you would make for the patient.
The nursing process is EVERYTHING in nursing school; you’re walking through it all the time. And answering case study questions is no different. Even though the questions may use different language, like “what would you look for” or ” “what’s the best course of action,” you should always be thinking about how it fits into the nursing process, and that will make it a whole lot simpler for you!
Now another HUGE thing you should focus on is prioritizing patient needs, and there are 2 ways to do this that we’ll talk about here.
But before we get to that, I want to give a shout out to Nurse Z for our YouTube comment of the week, which says
“This video came right on time. I start my 3rd semester today! Woohoo! Thanks hun, super helpful.”
YAY ! Congrats on starting your 3rd semester that’s so exciting!! I hope it goes super well for you!
Thank you so much for all your sweet comments and your constant support. I feel so blessed that you’re here right now and I get super pumped each week to help you through nursing school! So keep your comments coming, friend!
Alright, so the 2 big strategies you should use to prioritize patient care and answer your case scenario questions correctly are:
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
I’m going to walk you through how to use these 2 strategies to answer case scenario questions right. But if you’re a NursingSOS Member, be sure to log-into your dashboard and check out the Fundamentals Course, where we have a whole video training for you on patient prioritization. I also walk you through some practice case scenario questions in there as well, which will help it all click and come together for you. So be sure to check that out.
So ABC stands for airway, breathing and circulation.
These are your top 3 priorities when doing patient care, and when you’re answering case scenario questions. You need to make sure your patient has a clear airway, you need to make sure they are breathing adequately, and you need to make sure their blood is flowing and circulating.
If one of these isn’t happening, it’s game over, right? So that’s why the ABCs should be your top priority.
So often times when you’re faced with a case scenario question, it might ask you what your “priority” nursing action would be, or what your “initial” or “immediate” action would be.
When you see this on your exam, the first thing you should think about is the ABCs. Look at each answer to the question and ask yourself if any of them relate to the ABCs: anything that that keeps the patient’s airway clear, keeps them breathing, or keeps their blood circulating.
So if you identify an answer like that, go back, re-read the question to make sure that answer makes sense. And if it does, PERFECT ! That’s the answer I would choose.
The same thing goes for Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Here is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in order of priority:
- Physiological needs
- Safety and security needs
- Love and belonging
- Self-esteem
- Self-actualization
It makes it really easy to follow, because they are already listed in order of priority. This hierarchy means that you will need to solve a patient’s physiological needs FIRST before you focus on their other needs, like love and belonging and self-esteem needs.
Physiological needs include things like making sure they can breathe and that their blood is circulating properly.
Safety and security needs include things like making sure their IV tubing is out of the way and they can’t trip on it, and making sure their bed is in the lowest position and they have their call light. This also refers to things like being financially secure and having secure relationships. Those are all safety and security things.
Love and belonging needs refer to the patient’s connectedness with others, and if they feel like they have people who care about them.
The self-esteem tier is the need to have confidence in themselves and their abilities and that they believe in themselves and have a sense of accomplishment.
And self-actualization means that they are achieving their full potential and striving to always become better.
Looking at this hierarchy, it makes sense how they are prioritized, because if a patient can’t breathe (which is a physiological problem), we want to fix that problem first before we help them feel loved and connected with people.
So as you’re answering your case scenario questions, figure out how Maslow’s Hierarchy fits into it. Where is the patient in this hierarchy, and how can you help them move up the hierarchy.
These are all the critical thinking aspects that your nursing instructors are testing you on when they give you a case scenario question. They’re looking at how you take all the information they give you, and draw conclusions and make decisions with it.
Now, the biggest KEY to remember when answering case scenario questions is patient safety. Patient safety is ALWAYS your number 1 priority. So if there is something you can do to keep the patient safer, that’s most likely the answer your instructors are looking for.
In a few weeks, I’m going to be releasing a video all about why med-surg is so hard! I know case scenario questions play into that, but there’s a lot of other factors too. We’ll talk about why it’s hard, and I’ll also give you my BEST TIPS to overcome it and rock med-surg, even though it’s super tough.
So don’t forget to hit the notification bell to get notified when that video is available. It’s one you DO NOT want to miss!
Now make sure to like, comment, and share this video with a friend.
And click on one of these videos here so you can keep rocking nursing school, and go become the nurse that God created only YOU to be. And I’ll catch you in the next video.
NursingSOS Membership Community
Enrollment open until friday, get better grades and have more free time, pass nursing school or get your money back.
Recent Posts
- Dose Calc Practice Problems Walkthrough | Tablets and PO Meds
- The MUST-KNOW Dose Calc Conversions For Your Exam | Dosage Calculations For Nursing Students
- Hyperthyroid Disease Practice Questions
- Hyperthyroid Pathophysiology (Visual Breakdown!)
- How to Pass the HESI Exit Exam
- Degree of Burns (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th Degree Burn Breakdown)
- Osteoporosis Pathophysiology in 3 Simple Steps
- What is Hemoglobin? (Lab Values Series)
- Furosemide Mechanism of Action And How It Impacts Electrolytes (VISUAL WALKTHROUGH)
- What is Hematocrit? (Lab Values Series)
Anatomy & Physiology Assessment Cardiac Care Plans Clinical Critical Care Nursing Dosage Calculations Endocrine Fluid and Electrolytes GI Inspire Me Med Surg Member Exclusive Membership Community Membership Promo Nursing Labs OB and Pediatrics Pathophysiology Pharmacology Renal Respiratory Rest and Relaxation Skills Study Tips and Getting Organized Test Taking Tips Uncategorized

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations. At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible. 9.
To write a case study analysis in nursing, follow these steps: Introduction: Begin with a brief overview of the patient, the diagnosis, and the purpose of the case study. Patient History: Present the patient's background, including age, gender, medical history, and any relevant social or family history.
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
A nursing case study can be described as a student-learning activity that tells a story about a patient/family (clinical scenario) and requires thinking to translate knowledge into nursing practice through the use of questions related to the story (Oermann & Gaberson, 2017; Ignatavicius, 2019). Billings and Halstead (2020) state that completing ...
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don't do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types. Once again: A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient's condition.
In summary, the best way to prepare for the case studies on the Next Generation NCLEX is to actually understand the disease holistically, which means digging into the pathophysiology first, and then allowing that to flow to the signs and symptoms, medications, patient education, and so forth. By taking the time to absorb the material, and ...
NGN Case Study Sample Questions and Answers. First, let's take a look at our case study summary below: Case Study Summary: A 68-year-old male is admitted with shortness of breath. He reports difficulty breathing with activity, lying down, or while sleeping. He states that in order to "breathe easier," he has had to sleep in a recliner for ...
This video introduces the concept of the case study in a nursing context, but concepts are applicable to other areas. It identifies how case studies differ ...
The nursing case study example on Death and Dying and answers questions on Suffering and the Fallenness of the World, Suffering and the Hope of Resurrection, Value of Life, Euthanasia, and Morally Justified Options, also offers an analysis of the sin of suicide. Explores Ethical end of life decision making.
Write an introduction. This should be a one- or two-paragraph overview that describes the patient, the situation, and circumstances relevant to that situation. The introduction can also include a little about the patient's history leading up to the situation. Integrate more history and background. The next 1 to 2 paragraphs provide the ...
Case Study: Joint Pain, Rash, Hair Loss - What's Going On? by SafetyNurse1968, BSN, MSN, PhD. A new case study in which R.W. presents to her PCP with a cough, mild fever, joint stiffness and pain and a history of rashes, anemia and hair loss. Critical.
6 Steps to Replace Clinical Using Case Studies. 1. Watch the intro video as a group. Gather the entire class together and view the intro video. This video lays out the scenario for the given case study and helps them begin to consider the disease process. 2.
A nursing case study is an in-depth investigation and accompanying explanation of a patient or a group of patients suffering from a specific illness or disor...
Patricia Benner (1982) identified that recognizing relevance and nursing priorities are a weakness and work in progress for inexperienced novice nursing students. By addressing these weaknesses, nurse educators can help develop this weakness by the time they graduate! Plan B: Use Case Studies to Construct Knowledge.
Critical Care Nursing Case Study Examples . Critical care nursing demands swift decision-making, advanced technical skills, and the ability to provide intensive care to acutely ill patients. Our critical care nursing case studies encompass a range of high-acuity scenarios, including trauma, cardiac emergencies, and respiratory distress.
A nursing case study paper contains several sections that fall into three categories: 1. The status of the patient. Demographic data. Medical History. Current diagnosis and treatment. 2. The nursing assessment of the patient. Vital signs and test results.
Nursing Case Study Your patient is a 48-year-old premenopausal, multiparous female suffering from urinary stress incontinence. She has been doing pelvic floor exercises on her own, following instructions on a patient education handout she got from her doctor, to improve the symptoms, but she is not happy with the results and isn't sure if she is doing the exercises correctly.
By using unfolding case studies that integrate all three paradigm shifts, you will accomplish two essential objectives: You are providing a meaningful learning activity that practices the essence of clinical reasoning that leads to correct clinical judgments in practice. Just like high fidelity simulation provides a replication of the clinical ...
Nursing Case Study: Baby S - Respiratory distress and hypoxemia Background of baby's respiratory distress and hypoxemia. Baby S is a 10-day-old infant who was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) due to respiratory distress and hypoxemia. Baby S was born prematurely at 34 weeks gestation via emergency cesarean section due to ...
2. BACKGROUND. Case studies have been widely used in nursing theory training because they help students to build on the basic knowledge taught and to collect information and analyse it to make diagnoses and support interventions (O'Rourke & Zerwic, 2016).In addition, there is considerable research on the use of case studies in simulation settings, which are practical environments where ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply... 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described ...
In this video, we're diving into how to study using CASE STUDIES. Instructors LOVE to use case studies in nursing school. They'll also show up a lot on your nursing exams, where they'll give you a case scenario question and you'll have to choose the best answer based on the info they give you. But they can be SUPER tricky to figure out ...
How to Study with CASE STUDIES in Nursing SchoolInstructors LOVE to use case studies in nursing school, but they can be SUPER tricky to figure out!They'll al...
Answering questions well is critical for any nursing interview, but that is only part of the equation. Asking insightful questions during your interview shows a prospective employer your interest in the role, while also helping you determine whether the organization is the right fit for you.Sit down and prepare questions that demonstrate that you are enthusiastic and curious about the position.
The most shocking case remains that of Aruna Shanbaug, a nurse at a prominent Mumbai hospital, who was left in a persistent vegetative state after being raped and strangled by a ward attendant in ...